Burkholderia gladioli strain and method for producing alkaline lipase through strain fermentation
The technology of Holder bacteria and lipase is applied in the field of Burkholderia strain and its fermentation to produce alkaline lipase, which can solve the problems of lipase activity and stability limitation, and achieve low production cost and good production potential. , the effect of a wide range of application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1: Screening and identification of alkaline lipase-producing strains
[0033] 1. Preparation of Oriented Screening Plates
[0034] According to the characteristics that Burkholderia can use special metabolites and resistance to antibiotics, an improved TB-T plate is designed for directional screening, and the positive rate of screening Burkholderia can be as high as 100%. The detailed formula is as follows: 1L modified TB-T directional screening plate contains 2g of glucose, 0.5g of L-asparagine, NaHCO 3 0.5g, KH 2 PO 4 0.25g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.05g, trypan blue 0.05g, tetracycline 0.01g, ampicillin 0.15g, agar powder 15g.
[0035] 2. Preparation of Identification Plates
[0036] The 1 L rhodamine B identification plate contains 5 g of peptone, 3 g of yeast extract, 8 g of NaCl, 4 mL of rhodamine B solution (0.1%, W / V), and 10 mL of soybean oil emulsion.
[0037] The preparation method of the soybean oil emulsion is as follows: 3mL soybean oil and 9mL polyvi...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: Utilize BPS-1 bacterial strain and optimize medium fermentation to produce lipase
[0050] (1) Seed culture: After the BPS-1 strain is activated, it is inoculated in liquid LB medium, and cultivated at 30-35°C for 12-18 hours to obtain a seed culture solution;
[0051] (2) Fermentation culture: inoculate the seed liquid into the initial fermentation medium (as described in Example 1) by the amount of 1-1.5% (V / V), after continuous cultivation for 72 hours, 8000r / mim, centrifugal 10min, measure lipase activity.
[0052] The carbon source (glucose, sucrose, molasses, dextrin, maltose, malt extract, starch) and nitrogen source (peptone, yeast extract, corn steep liquor, urea, NaNO) of the fermentation medium were studied by single factor replacement method. 3 , NH 4 SO 4 ) and inducers (olive oil, palm oil, corn oil, soybean oil, rice bran oil, castor oil, rapeseed oil) on the production of enzymes, the optimized components were molasses 1.0% (v / v), Palm ...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Embodiment 3: the purification of alkaline lipase
[0054] 1. The optimized fermentation broth described in Example 2 is precipitated with ethanol with a final concentration of 60% (v / v), centrifuged at 8000r / mim for 10min to remove foreign proteins, and then the final concentration is 95% (v / v) The target protein was precipitated with ethanol, and the obtained precipitate was collected after centrifugation at 8000 r / mim for 10 min, and dissolved in 0.05 mol / L piperazine buffer solution with a pH value of 9.7 to obtain a preliminary purified enzyme solution.
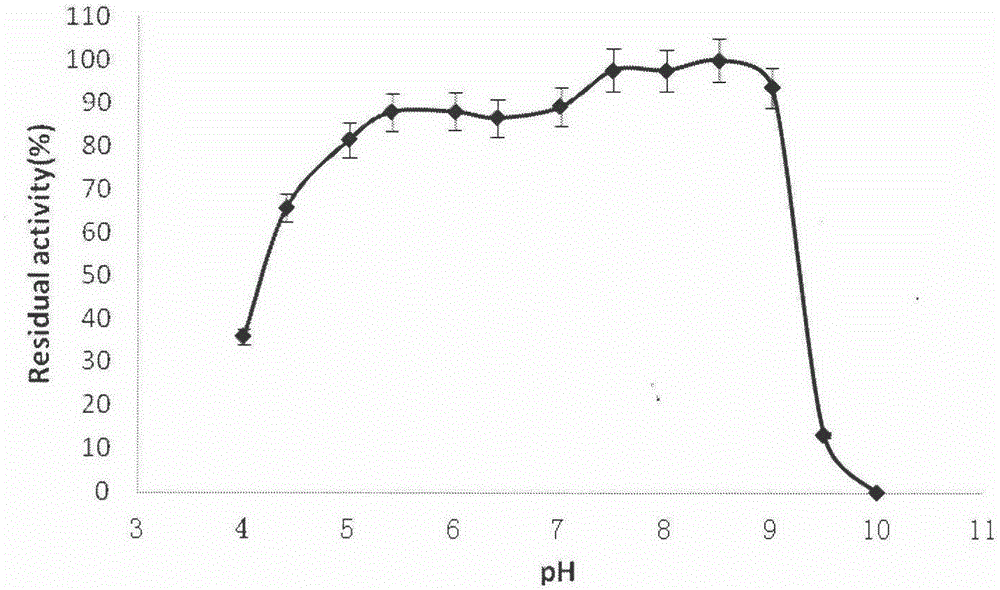
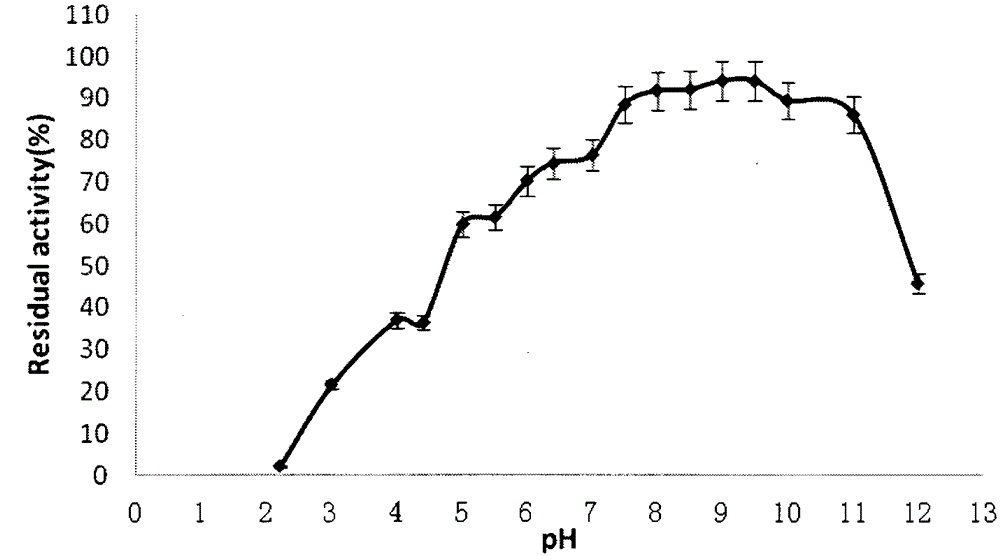
[0055] 2. The initially purified enzyme solution is subjected to HiTrapQ ion exchange chromatography and superdex75 gel filtration chromatography, and further purified to obtain electrophoretic pure lipase protein (such as figure 1 Shown), the molecular weight of this lipase is about 35kDa, and the lipase specific activity after purification is 443904.8U / mg.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com