Phosphinothricin dehydrogenase mutant, genetically engineered bacteria and one-pot multi-enzyme synchronous directed evolution method
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria, glufosinate-ammonium, applied in genetic engineering, microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem that the conversion rate cannot reach 100%, the raw material PPO cannot be completely converted, and the aspartic acid can not be fully converted. L-PPT separation is troublesome and other problems, to achieve the effect of high synergy efficiency, high space-time yield, and high total conversion number
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
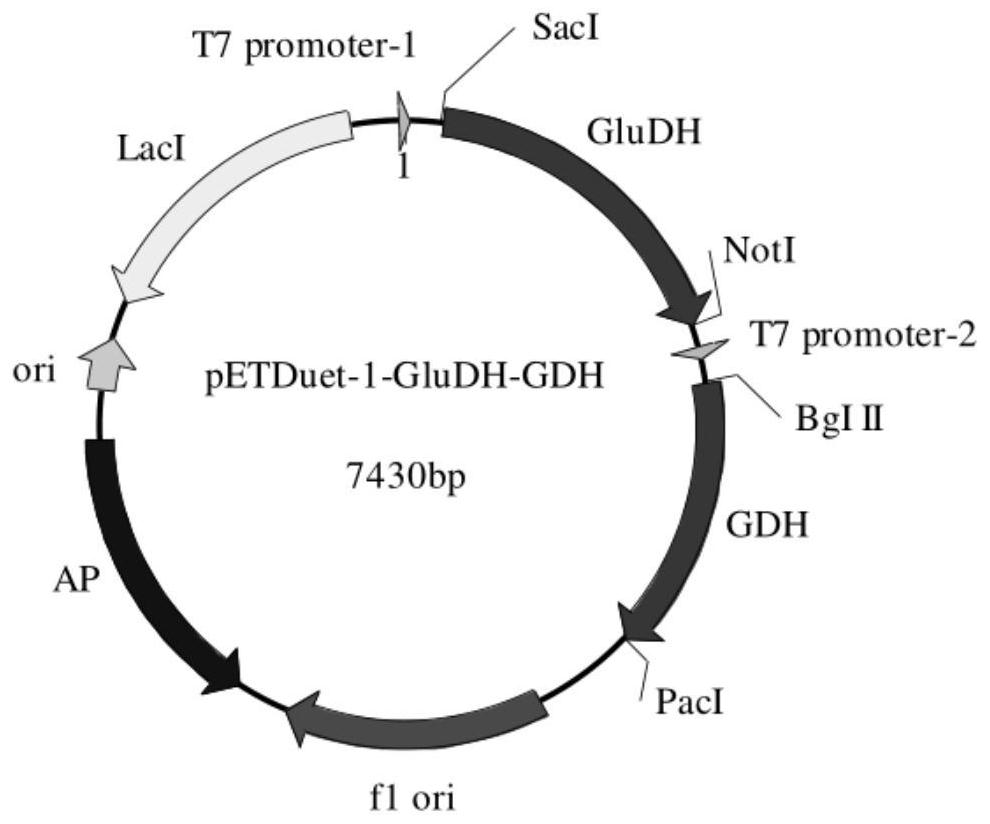
[0049] Construction of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase and glucose dehydrogenase or formate dehydrogenase coupling expression vector and engineering bacteria.
[0050] Construction of expression vectors: The gene synthesis of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase, glucose dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase described below was completed by Hangzhou Qingke Zixi Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase gene (NCBI accession number WP_150701510.1) derived from Pseudomonas fluorescens was seamlessly cloned into SacI and NotI of the first multiple cloning site of pETDuet-1 vector by PCR In between, the glucose dehydrogenase gene (NCBI accession number: KM817194.1) derived from Exiguobacterium sibiricum or the formate dehydrogenase derived from Lactobacillus buchneri (NCBI accession number: WP_013726924.1) were seamlessly cloned into pETDuet- Between Bg1II and PacI of the second multiple cloning site of the 1 vector, obtain the expression vector pETDuet-PPTD...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Construction and screening of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase and glucose dehydrogenase / formate dehydrogenase dual-enzyme coupled gene libraries.
[0055] 1) Establishment of high-throughput screening method
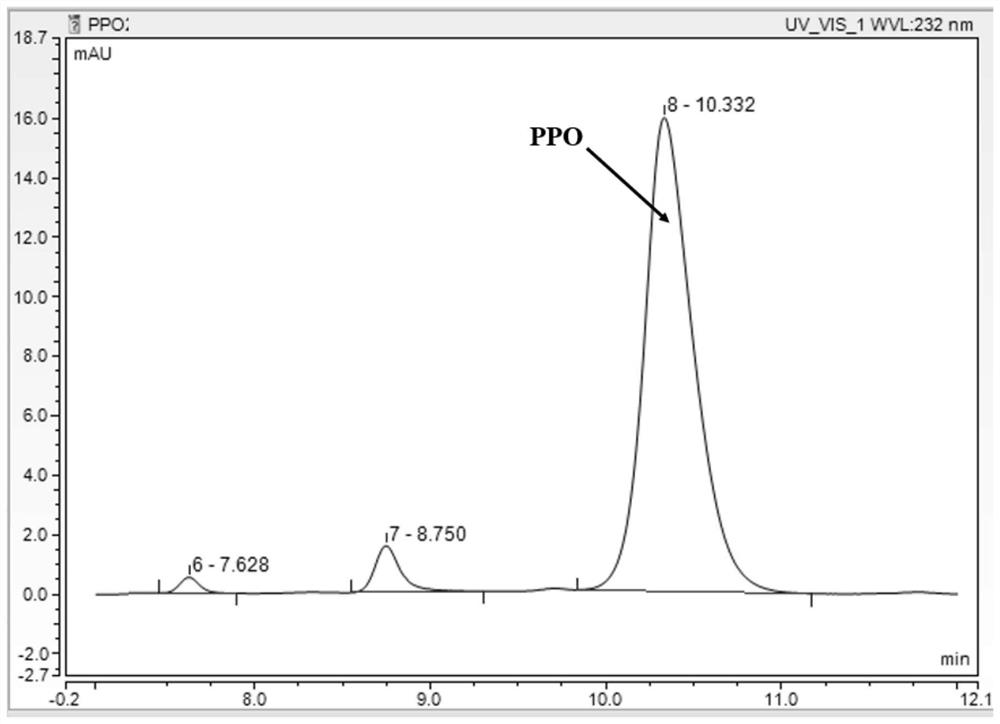
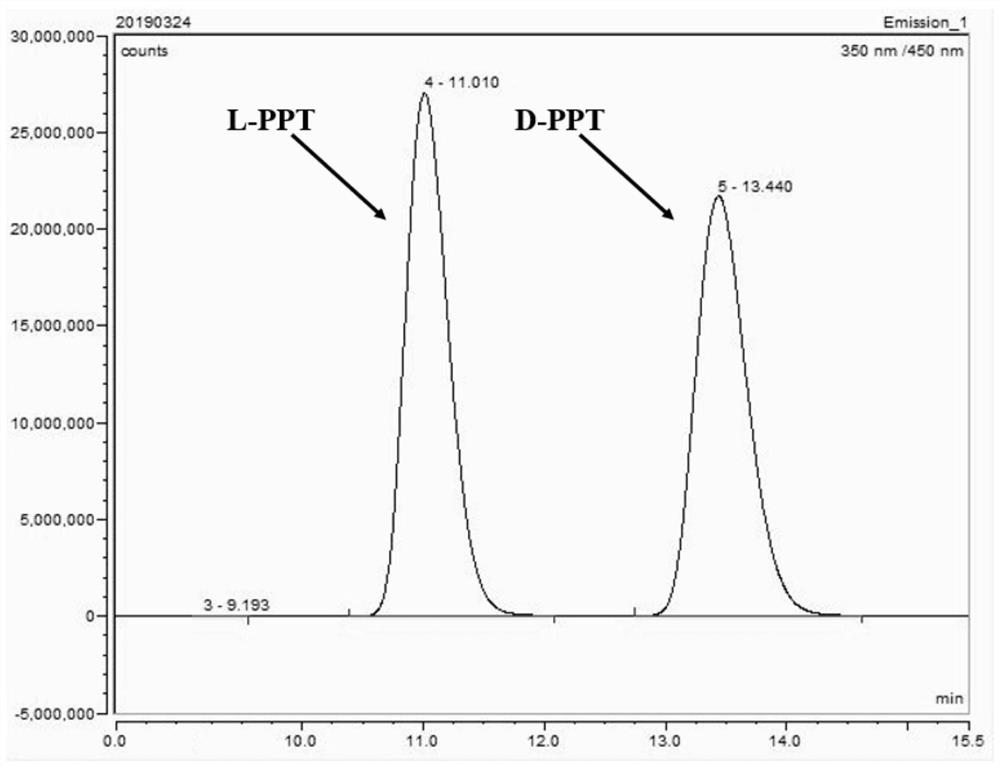
[0056]Prepare 50mL working solution (derivatization reagent): o-phthalaldehyde 0.013g, N-acetyl-L-cysteine 0.032g, dissolve with pH=9.8 boric acid buffer to 50mL, shake to fully dissolve, 4 Store in the refrigerator at ℃ for later use (no more than 4 days), as a high-throughput working solution, also known as a derivatization reagent. Draw 50 μL sample reaction solution and add 50 μL working solution to shake and react for 30 seconds, then add 100 μL ddH2O, at λ ex =340nm,λ em Fluorescence value was measured under the condition of =455nm.
[0057] 2) One-pot multi-enzyme simultaneous directed evolution
Embodiment 3
[0065] Site-directed saturation mutation of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase in multi-enzyme coupling reaction system.
[0066] In order to further screen potential activity-promoting bacterial strains, two beneficial mutation sites of A164 and R205 of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase obtained in Example 2 were first subjected to site-directed saturation mutation for further screening, and the PCR primers were designed as shown in Table 1 , PCR system (50 μL): 2*Phanta Max buffer 25 μL, dNTPs 1 μL, mutation primers 1 μL each, template (starting strain) 1 μL, Pfu DNA polymerase 0.5 μL, add ddH2O to 50 μL. The PCR conditions were: 95°C pre-denaturation for 3 minutes: 95°C denaturation for 15 s, 60°C annealing for 15 s, 72°C extension for 7 min 20 s, 30 cycles; 72°C final extension for 10 min. The PCR product was verified by DNA agarose gel electrophoresis, and after the template was digested by DpnI, the PCR product was transformed into Escherichia coli E.coli BL21 (DE3) com...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com