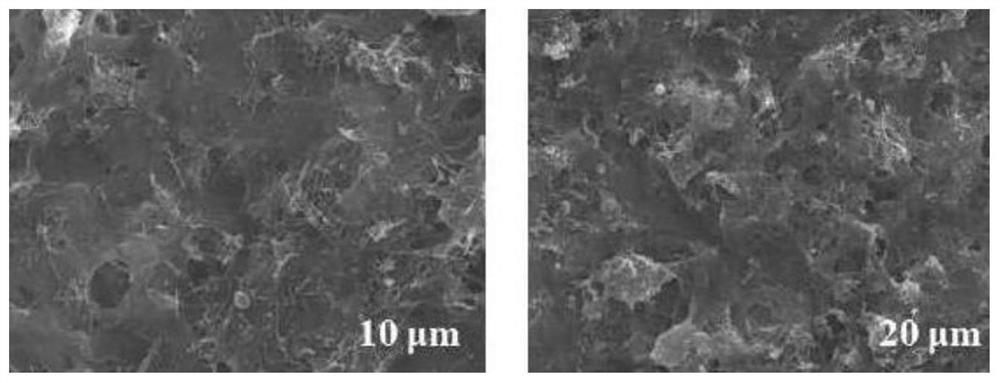
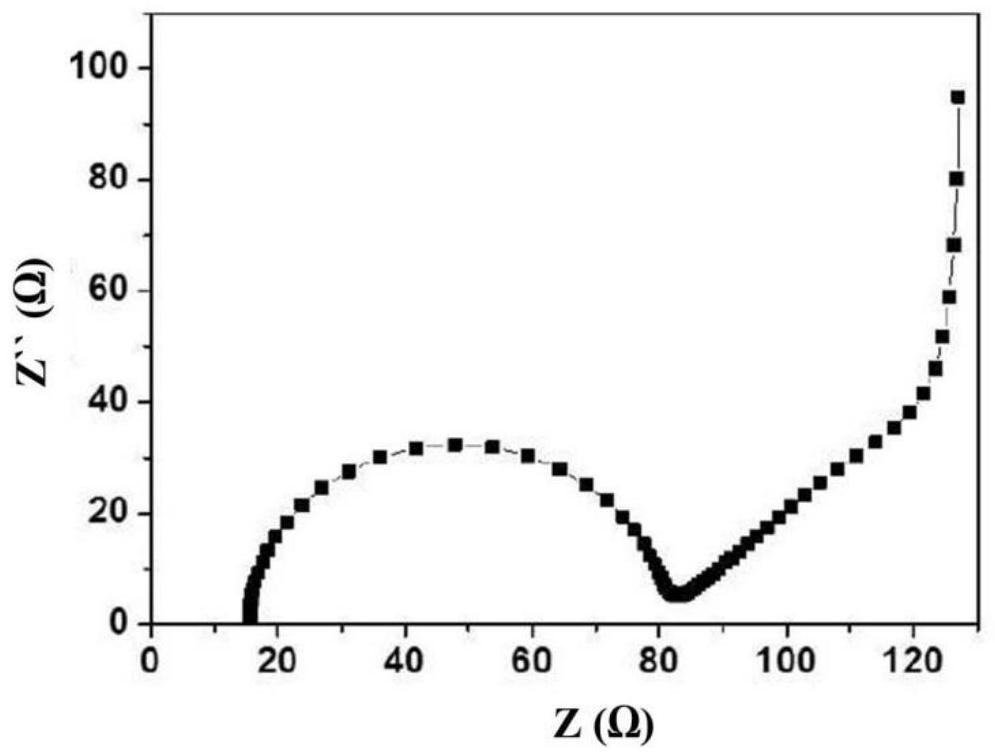
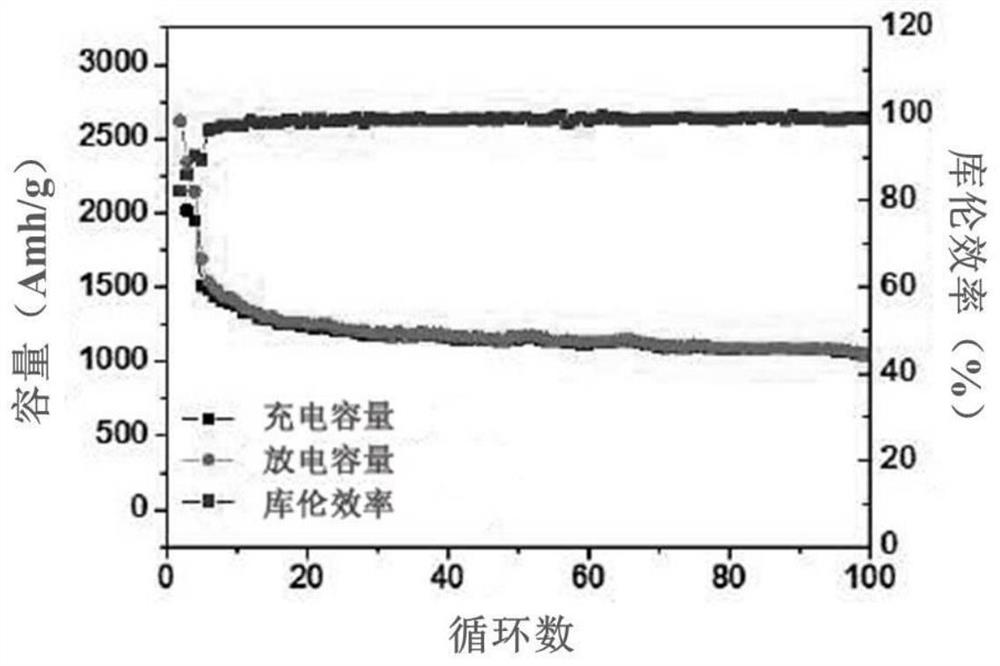
Preparation method of lithium ion battery negative electrode material
A technology for lithium-ion batteries and negative electrode materials, applied in electrode manufacturing, battery electrodes, lithium batteries, etc., can solve problems such as capacity decay, volume expansion, and poor cycle stability, and achieve the effect of preventing sudden drop in capacity and preventing shedding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] A preparation method for a negative electrode material of a lithium ion battery, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0026] S1: Add graphene oxide into DMAc solvent, stir well, then add 2,2-bis[4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl]hexafluoropropane monomer and 3,3,4,4 -Biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride, stirred and reacted at -3°C for 10h to obtain a polyamic acid / graphene oxide mixture (PAA / GO), in which 2,2-bis[4-(4-aminophenoxy ) phenyl]hexafluoropropane monomer and the mass ratio of 3,3,4,4-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride is 1:1.
[0027] S2: Dissolve acetic anhydride and triethylamine in DMAc solvent, wherein the mass ratio of acetic anhydride and triethylamine is 1:1, then slowly add the PAA / GO mixed solution in step S1, speed up the stirring speed, at 65°C Under reaction for 8h, the concentrated solution was obtained.
[0028] S3: put the concentrated solution obtained in step S2 into a tube furnace under a nitrogen atmosphere, bake at 150°C for 30min, the...
Embodiment 2
[0032] A preparation method for a negative electrode material of a lithium ion battery, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0033] S1: Add graphene oxide into DMAc solvent, stir well, then add 2,2-bis[4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl]hexafluoropropane monomer and 3,3,4,4 -Biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride, stirred and reacted at 0°C for 14h to obtain a polyamic acid / graphene oxide mixture (PAA / GO), in which 2,2-bis[4-(4-aminophenoxy) The mass ratio of phenyl]hexafluoropropane monomer to 3,3,4,4-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride is 1:1.
[0034] S2: Dissolve acetic anhydride and triethylamine in DMAc solvent, wherein the mass ratio of acetic anhydride and triethylamine is 1:1, then slowly add the mixed solution of PAA / GO in step S1, speed up the stirring, at 100°C The reaction was carried out for 10h to obtain a concentrated solution.
[0035] S3: put the concentrated solution obtained in step S2 into a tube furnace under a nitrogen atmosphere, burn at 250°C for 30min,...
Embodiment 3
[0039] A preparation method for a negative electrode material of a lithium ion battery, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0040] S1: Add graphene oxide into DMAc solvent, stir well, then add 2,2-bis[4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl]hexafluoropropane monomer and 3,3,4,4 -Biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride, stirred and reacted at -2°C for 11h to obtain a polyamic acid / graphene oxide mixture (PAA / GO), in which 2,2-bis[4-(4-aminophenoxy ) phenyl]hexafluoropropane monomer and the mass ratio of 3,3,4,4-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride is 1:1.
[0041] S2: Dissolve acetic anhydride and triethylamine in DMAc solvent, wherein the mass ratio of acetic anhydride and triethylamine is 1:1, then slowly add the PAA / GO mixed solution in step S1, speed up the stirring speed, at 70°C The reaction was carried out for 8-10 hours to obtain a concentrated solution.
[0042] S3: put the concentrated solution obtained in step S2 into a tube furnace under a nitrogen atmosphere, burn at 200°...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com