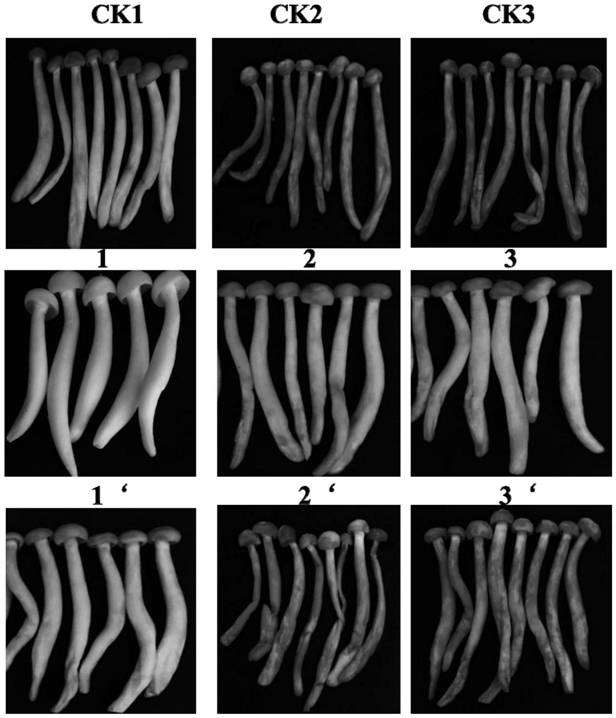
Bacillus subtilis, preharvest preparation of edible fungus and its application
A Bacillus subtilis and preharvest treatment technology is applied to improve the postharvest storage quality of edible fungi, and in the field of preharvest preparations for Bacillus subtilis and edible fungi, and can solve the problem of Pseudomonas or Trichoderma contamination and postharvest quality deterioration. It can achieve the effect of maintaining relative stability, reducing the level of membrane lipid peroxidation, and inhibiting postharvest fungal diseases and bacterial diseases.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1 strain screening
[0047] 1.1 Screening method:
[0048] (1) Preliminary screening: the above-mentioned soil samples or mushroom samples were gradiently diluted with sterile physiological saline to the soil bacterial suspension, and 10 -2 、10 -3 Dilution The dilution is spread on the beef extract peptone medium plate, cultured upside down at 37°C for 1-2 days, and the growth of the bacteria is observed every 12 hours. After the colony on the beef extract peptone plate grows, select the appropriate colony, use a sterilized toothpick to spot the selected colony on the primary screening medium plate, mark it, and place it at 37 ° C for 1-2 days.
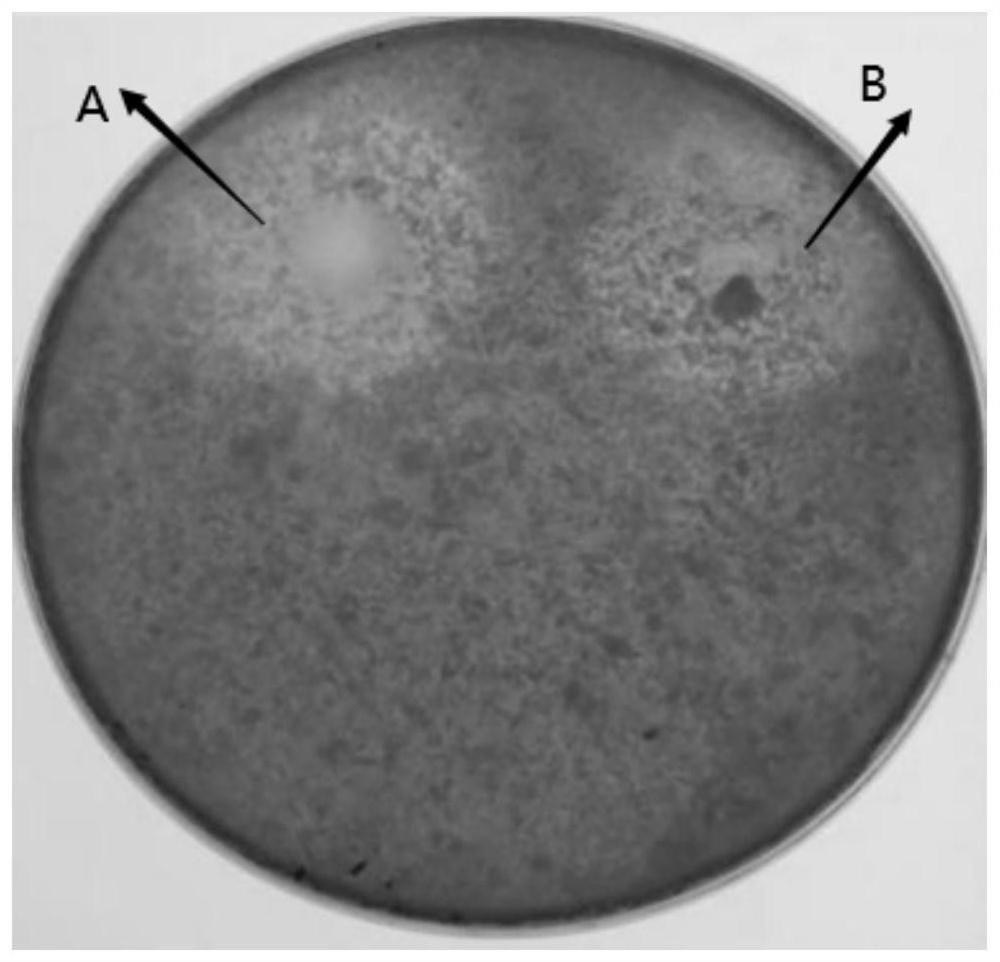
[0049] (2) Re-screening: Use the plate confrontation method to judge whether the screened bacterial strains have inhibitory effect on the pathogenic fungus Trichoderma harzianum and white jade mushroom hyphae: pick the bacteria that are screened and place them in a dotted manner with the pathogenic fungus or white jad...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Identification of Example 2 bacterial strain B.subtilis NYB169
[0053] 2.1 Morphological identification results
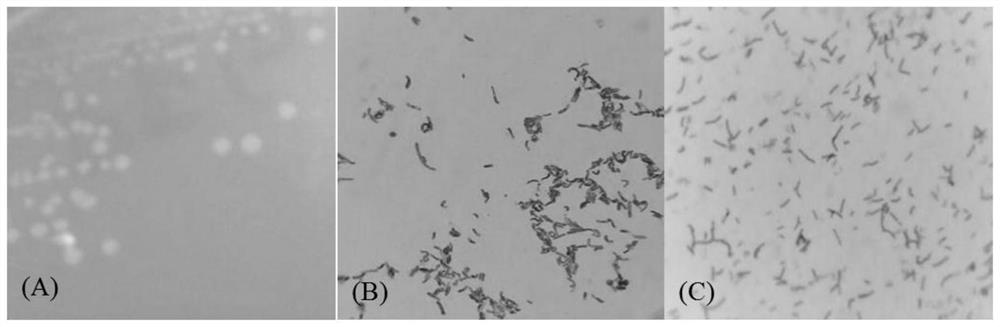
[0054] Such as figure 1 As shown, the colonies grown by the strain B.subtilis NYB169 on the primary screening plate are about 3mm in diameter, roughly round, off-white, opaque, with a little wrinkle and rough edges. The strain showed blue-purple after staining, so it can be determined that the strain belongs to Gram-positive bacteria.
[0055] 2.2 Physiological and biochemical identification results
[0056] Physiological and biochemical experiments were carried out on B. subtilis NYB169, and the results are shown in Table 1. The strain can hydrolyze tyrosine and starch, and tyrosine crystals can be completely hydrolyzed to become transparent; methyl red (MR) test, peroxidation Hydrogenase test and indole test were both positive.
[0057] Table 1 Physiological and biochemical experiment results
[0058]
[0059] Note: "+" means positive, "-" means n...
Embodiment 3
[0067] The preparation of embodiment 3 edible fungi preharvest treatment preparation
[0068] 1. Cultivation and fermentation of strains
[0069] Fermentation medium: 0.06% potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH 2 PO 4 ), 0.14% dipotassium hydrogen phosphate (K 2 HPO 4 ), 0.1% magnesium sulfate (MgSO 4 ), 0.06% yeast powder, 0.06% peptone, pH 7.0. Use water as solvent. The above-mentioned percentage content is a mass percentage.
[0070] Insert the strain B. subtilis NYB169 into the seed culture solution, cultivate overnight at 37°C and 150 r / min, and then inoculate the seed solution with the above-mentioned fermentation medium at an inoculation amount of 1% (v / v). In the Erlenmeyer flask, cultivate under the conditions of 37° C. and 150 r / min for 12 to 30 hours to obtain a fermentation broth. Separation of fermentation broth and bacteria by centrifugation or filtration.
[0071] 2. Preparation of preharvest preparations for edible fungi
[0072] After dissolving methyl ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com