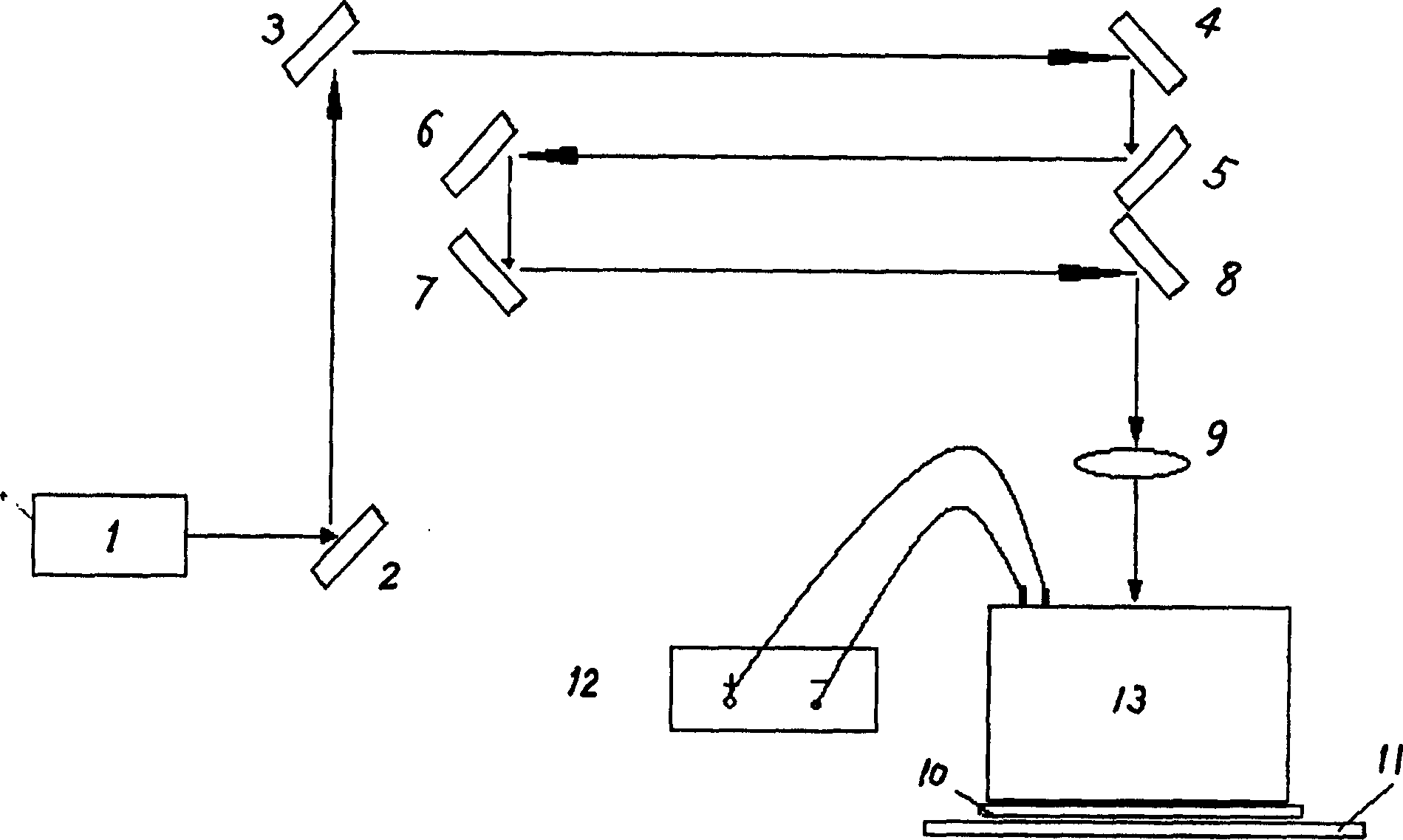
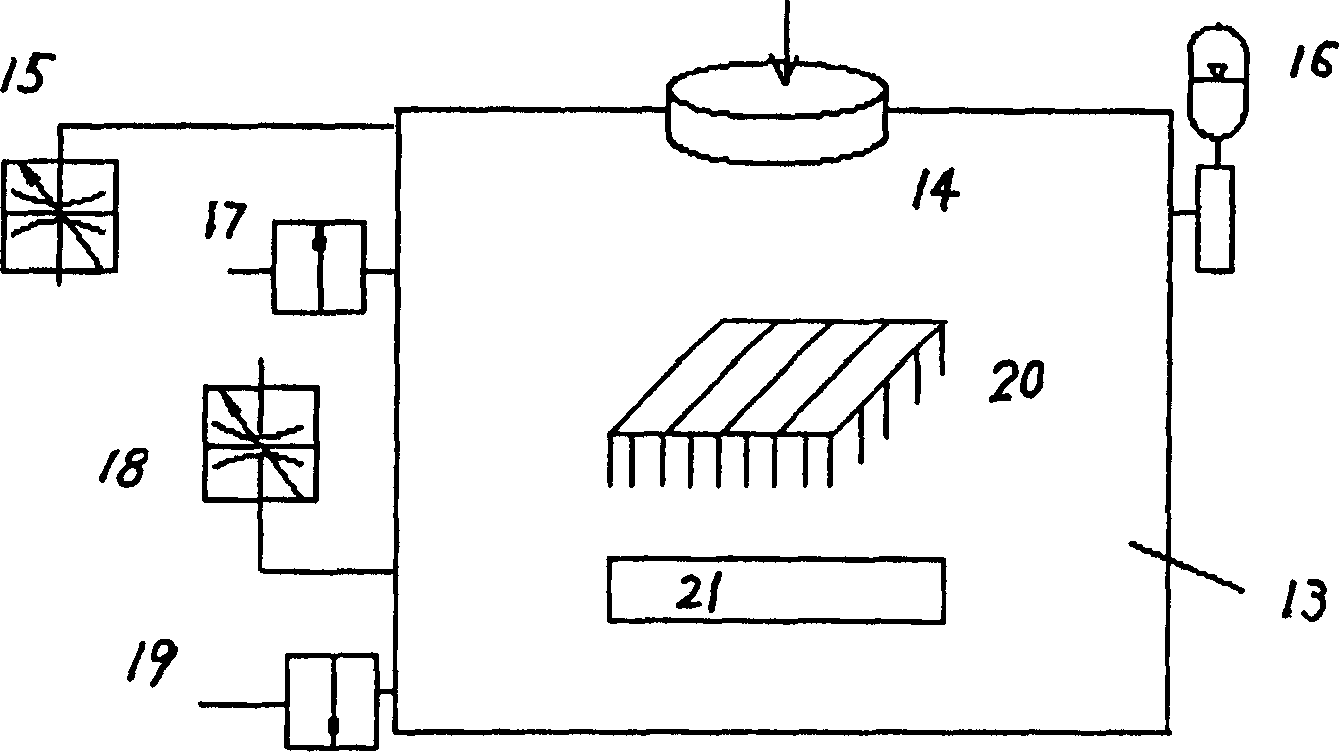
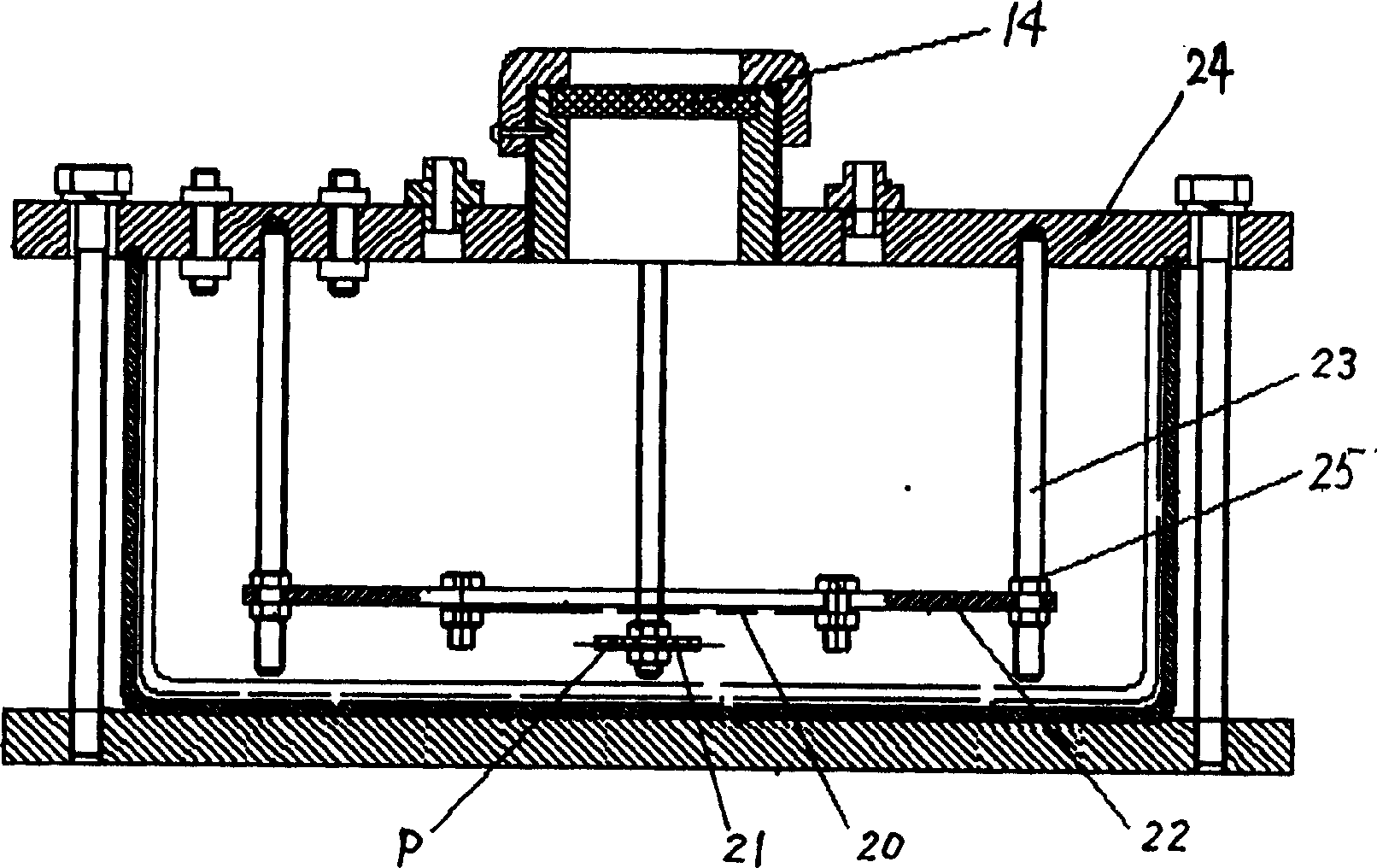
Quasi-molecule laser electrochemical microstructure manufacturing method and equipment
A technology of excimer laser and manufacturing method, which can be used in photoplate-making process exposure devices, optics, optomechanical equipment, etc., and can solve the problems of low power, long laser wavelength, and limited application range.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1: the processing of metal microhole array
[0029] First, a layer of copper conductive layer is formed on the glass surface by chemical deposition, then, photoresist is coated on the copper conductive layer, and then the pattern is transferred to the photoresist by photolithography technology, and then it is dried. Etch and remove the photoresist, and then install the glass plate with copper conductive layer constituting the microprobe array at the cathode position in the laser electrochemical reaction chamber, so that the copper layer faces down, and connect with the cathode in it The post is connected, and the metal copper substrate to be processed is placed at the anode position, and connected to the anode terminal through the flat electrode. The distance between the electrodes is 0.2mm, the electrolyte is 5% NaCl solution, the liquid surface submerges the workpiece by 1mm, the power supply voltage is 12V, the wavelength of the excimer laser is 248nm, the...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2: the processing of metal microhole array
[0031] The fabrication and installation of the microprobe array are the same as the above example. The electrode spacing is 2mm, the electrolyte is 30% NaCl solution, the liquid surface submerges the workpiece by 2.5mm, the power supply voltage is 3V, the wavelength of the excimer laser is 248nm, the pulse energy is 100mJ, and the pulse number is 1000. After 1 minute, a microhole array with a pitch of 15 microns and a diameter of 5 microns is etched on the metal copper substrate with a thickness of about 0.5 mm.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Embodiment 3: the processing of metal microhole array
[0033] The fabrication and installation of the microprobe array are the same as the above example. The electrode spacing is 2mm, the electrolyte is 10% NaCl solution, the liquid surface submerges the workpiece by 2.5mm, the power supply voltage is 6V, the wavelength of the excimer laser is 248nm, the pulse energy is 250mJ, and the pulse number is 500. After 1 minute, a microhole array with a pitch of 50 microns and a diameter of 50 microns is etched on the stainless steel substrate with a thickness of about 0.5 mm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com