Patents
Literature
54 results about "Banding Artifact" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An artifact often associated with cardiac imaging where the algorithm which provides the best temporal resolution for each slice can provides suboptimal image quality for the entire volume since the cardiac temporal resolution changes from slice to slice.
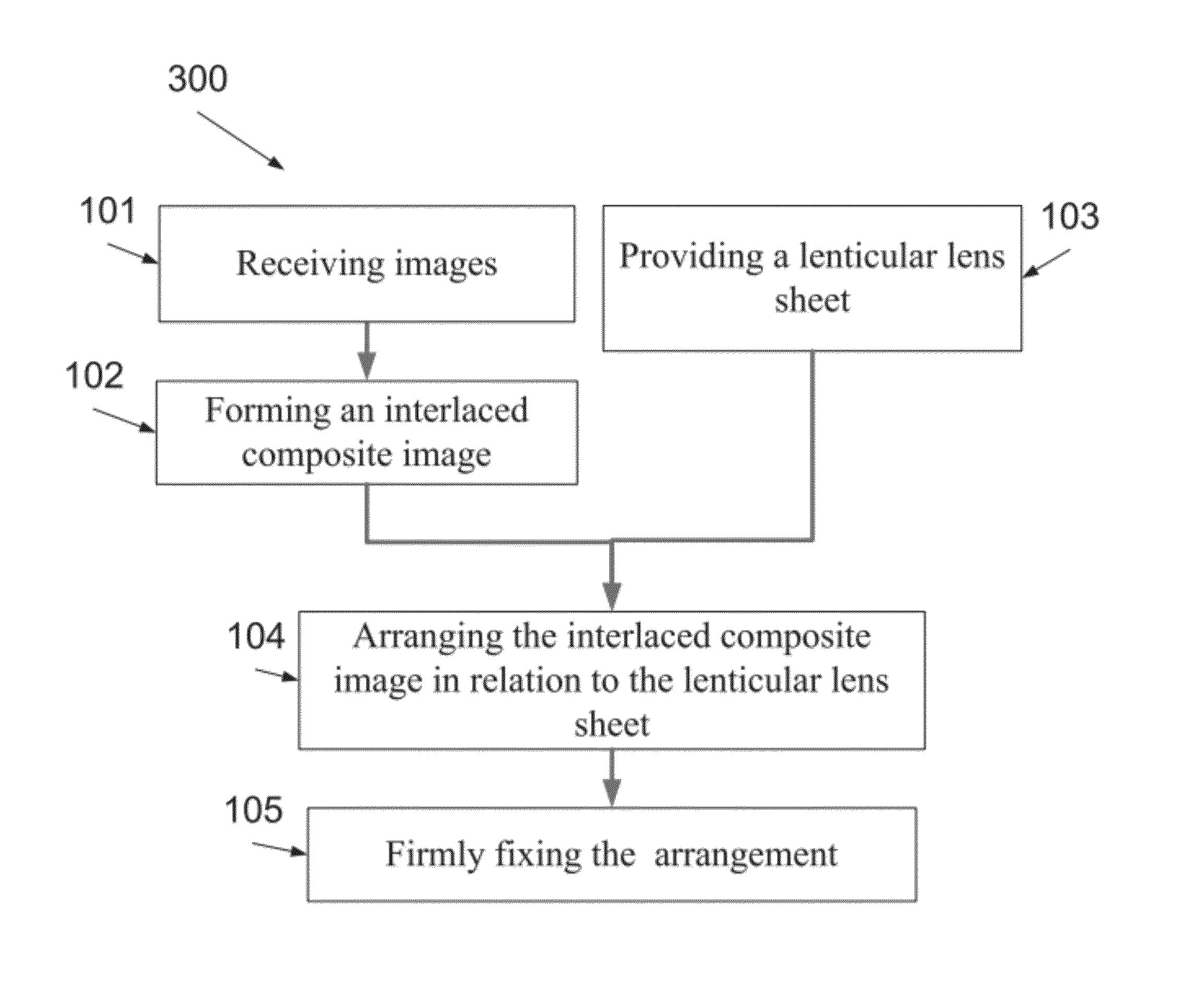
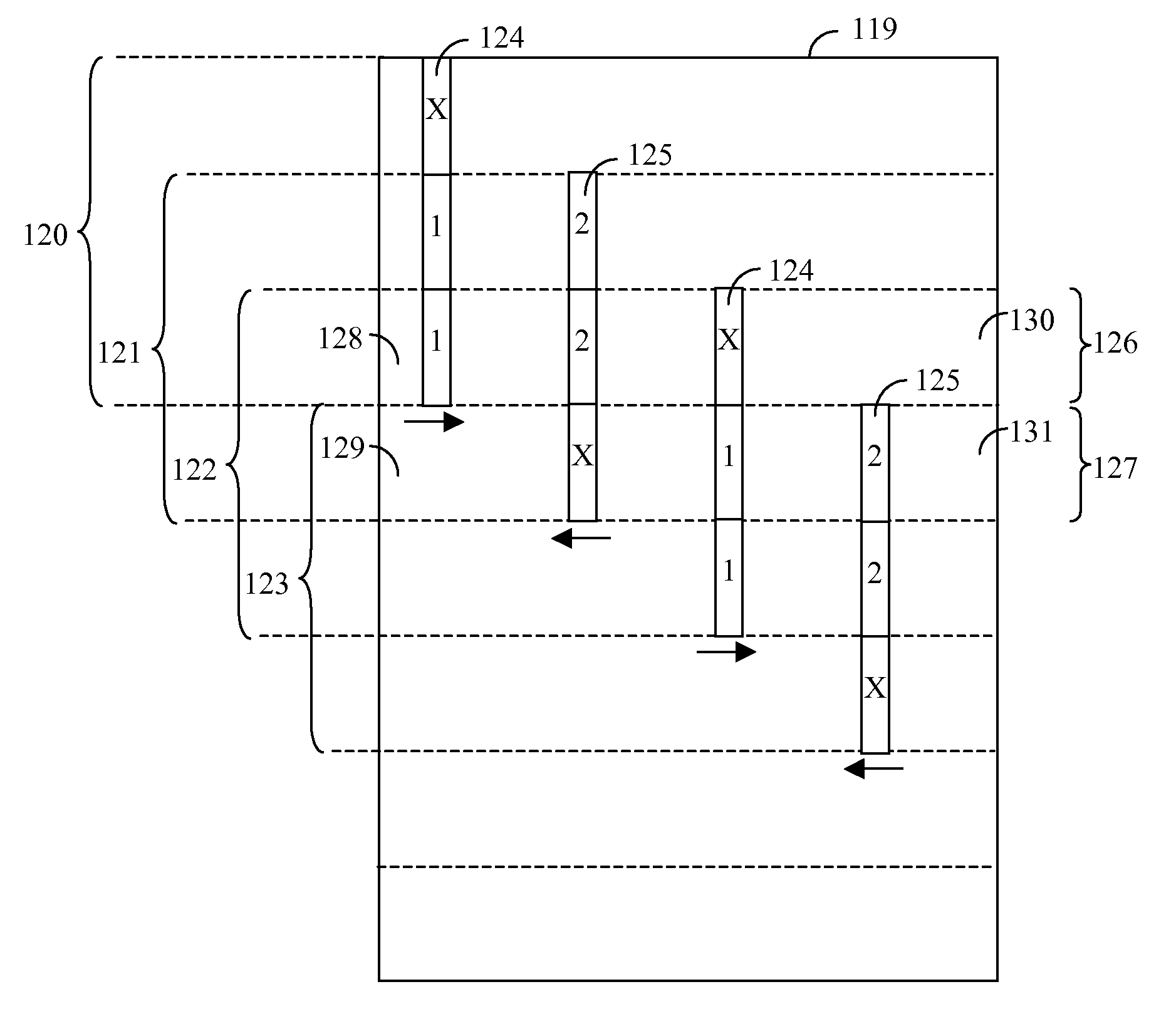
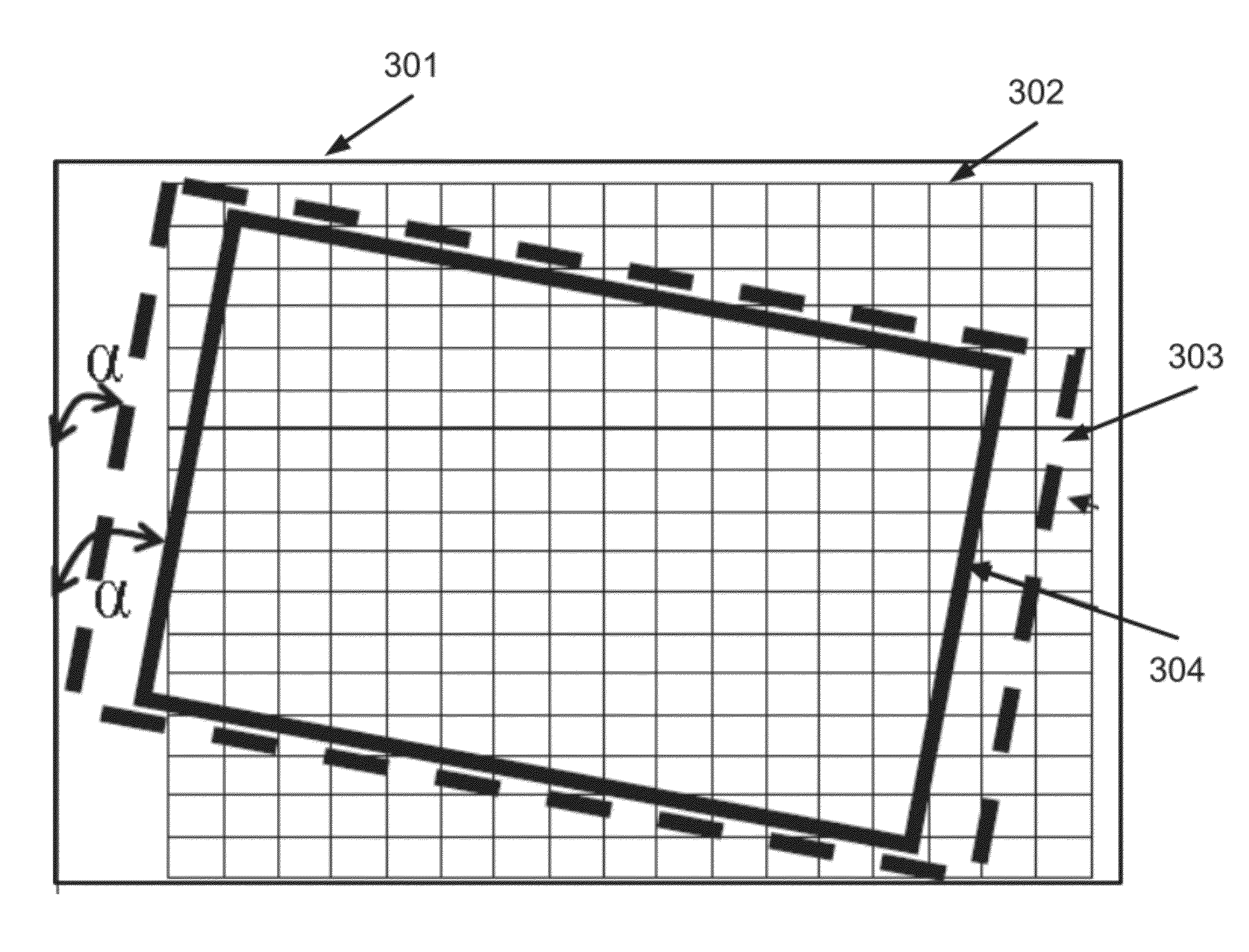
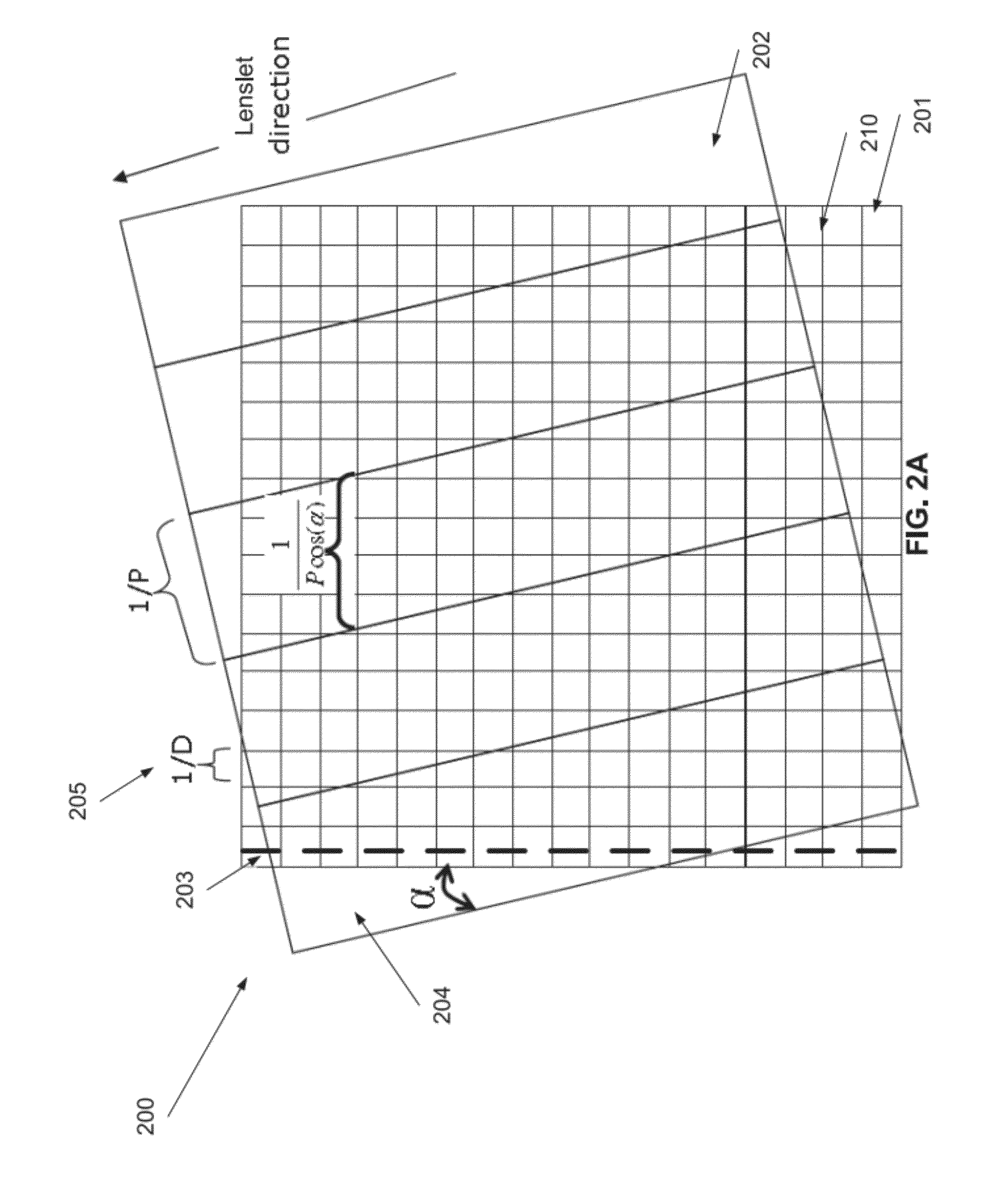
Lenticular image articles and method and apparatus of reducing banding artifacts in lenticular image articles
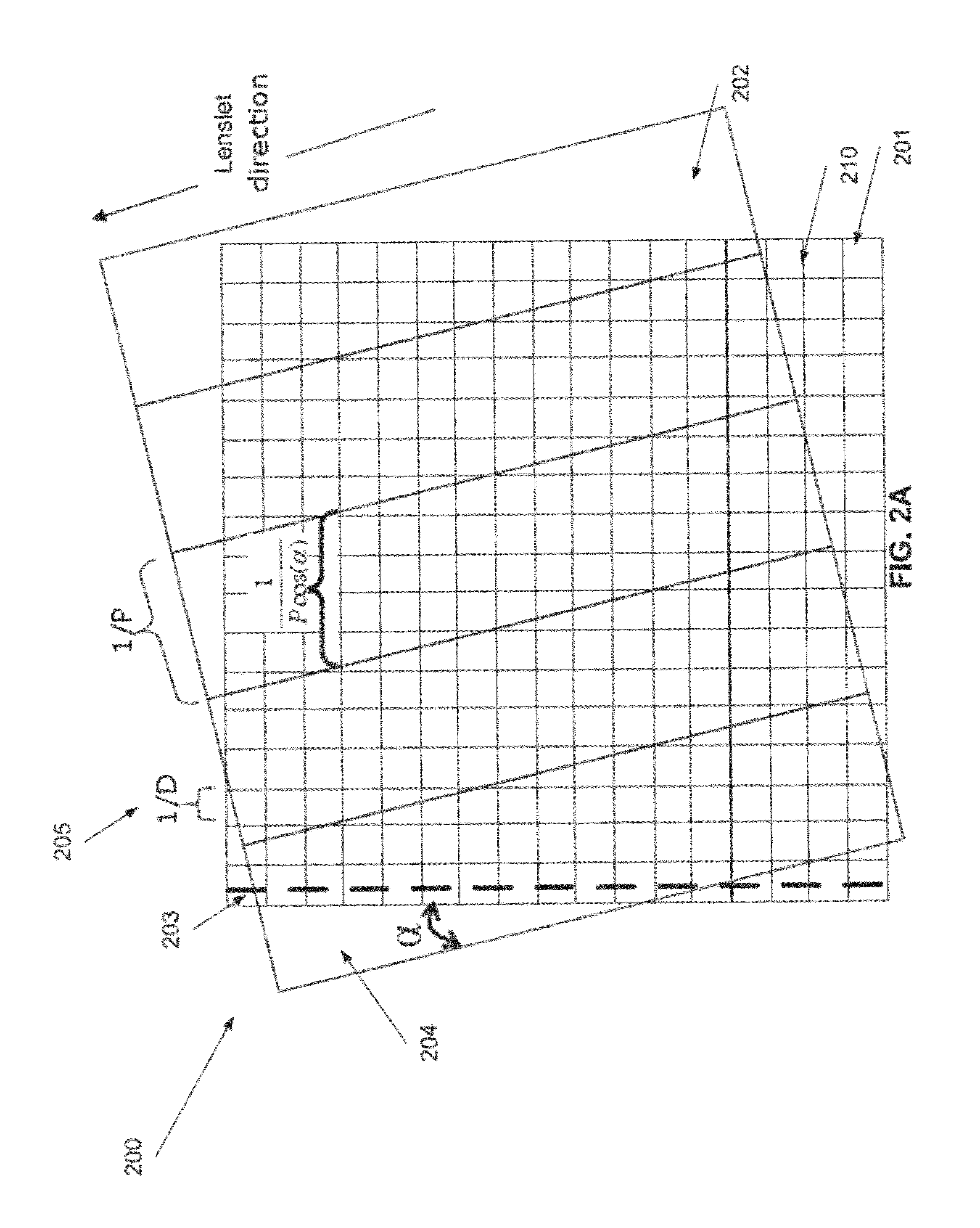
A method of creating a lenticular imaging article. The method comprises printing an interlaced composite image according to a reference grid of a printer, providing a lenticular lens sheet having a plurality of parallel lenticular lines between a plurality of lenslets, selecting an acute angle for an intersection between the first and second axes according to a function of a resolution of the interlaced composite image and a pitch of the lenticular lens sheet, and positioning the lenticular lens sheet so that the intersection forms the acute angle.
Owner:HUMANEYES TECH
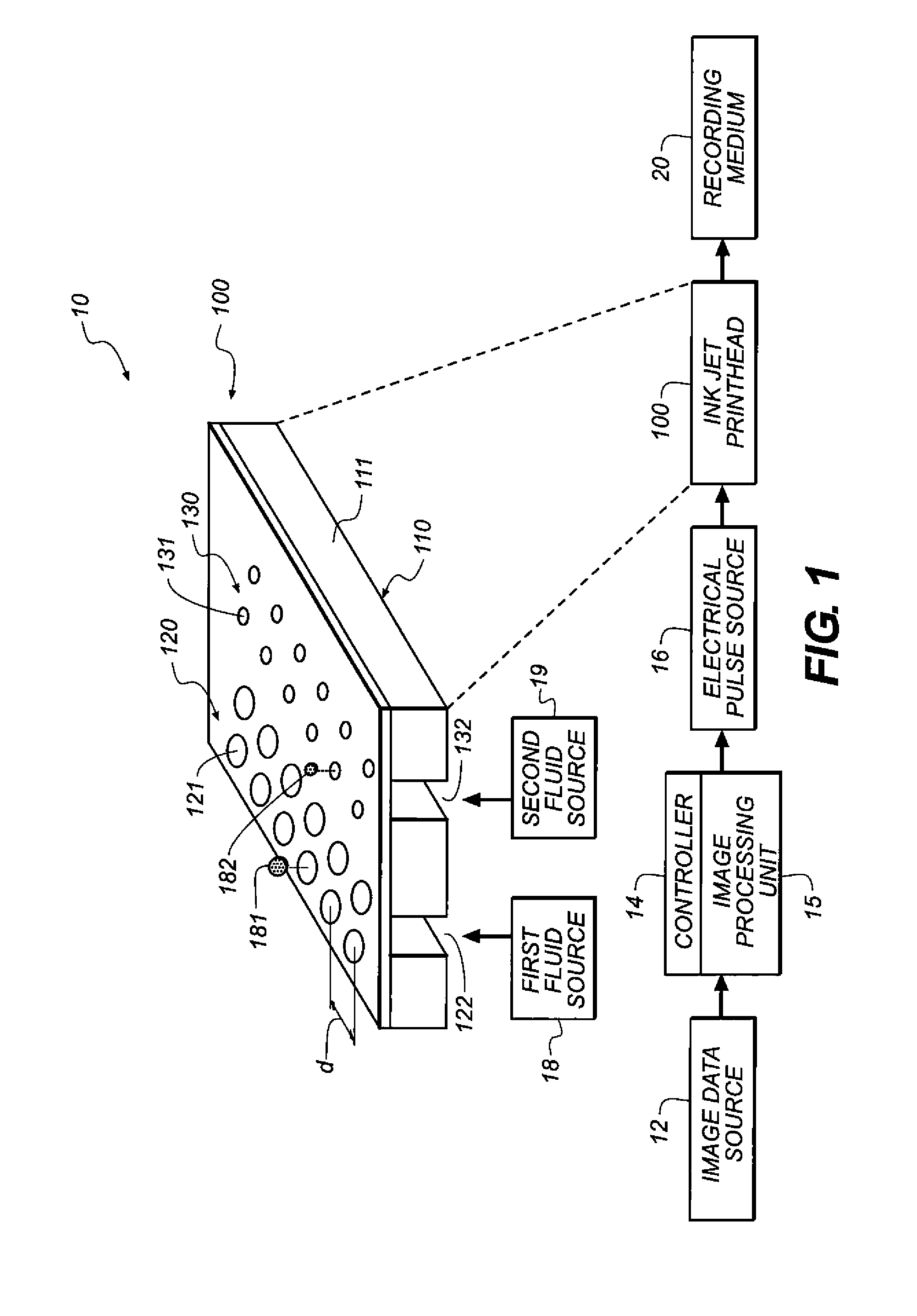
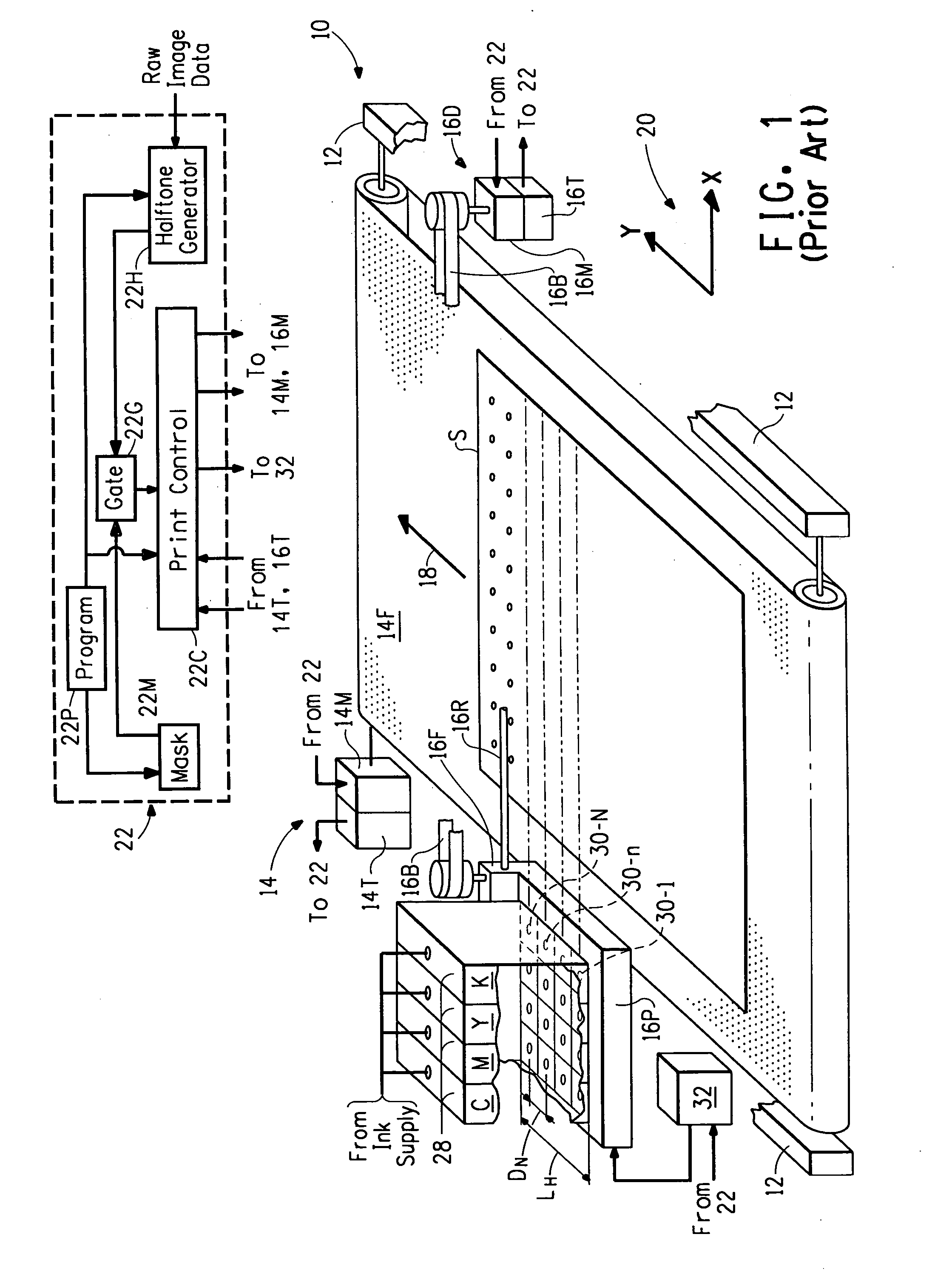
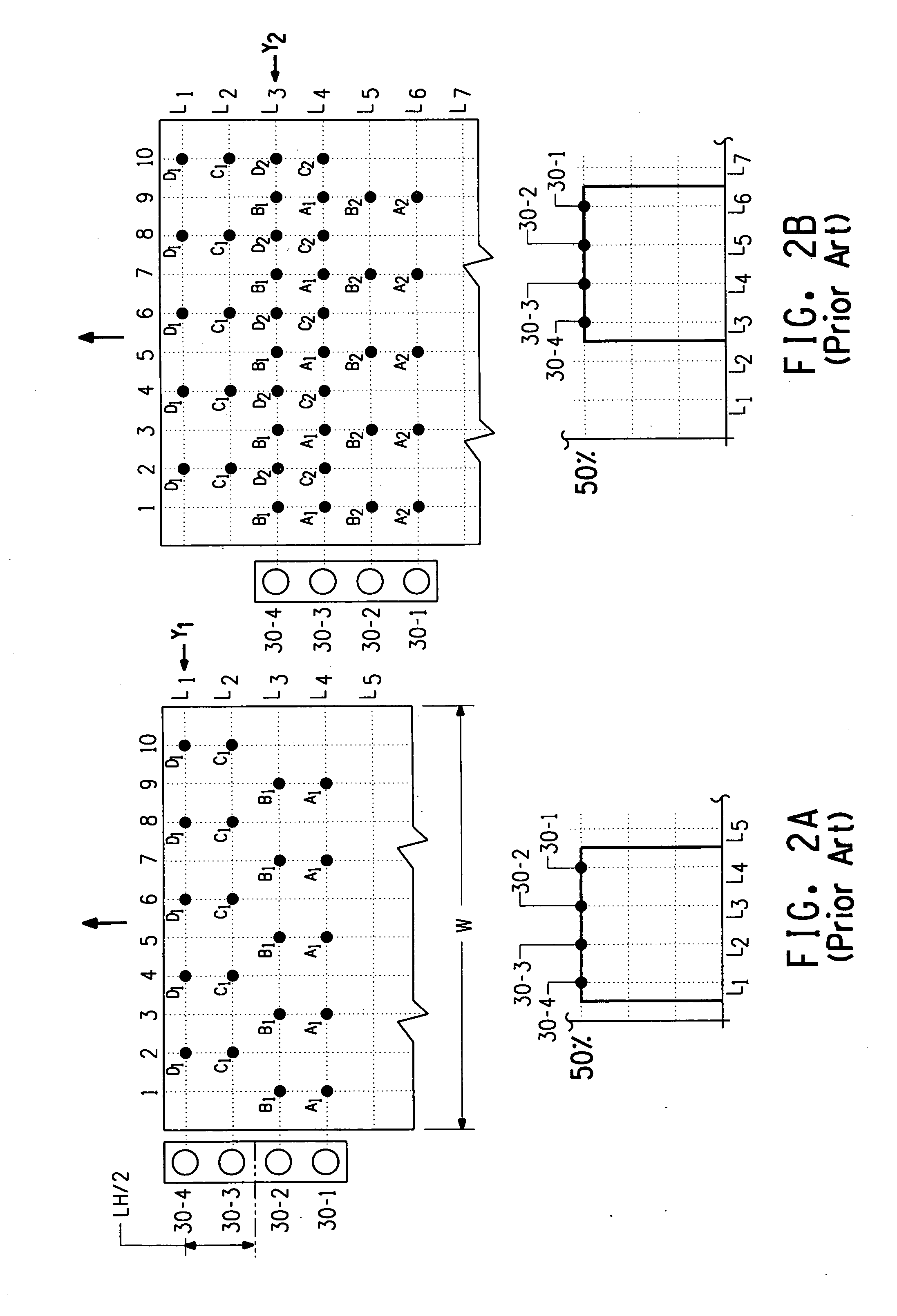
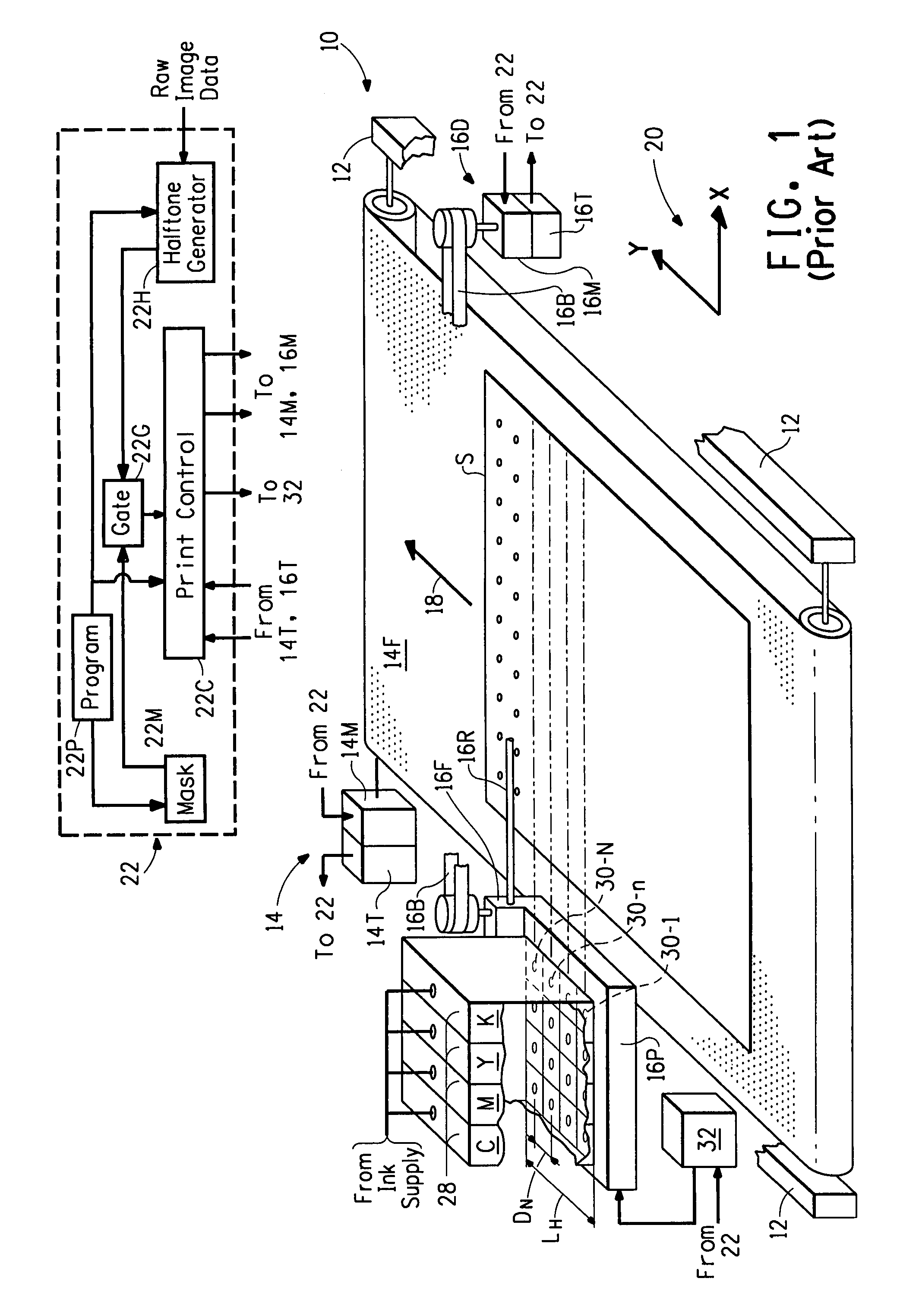
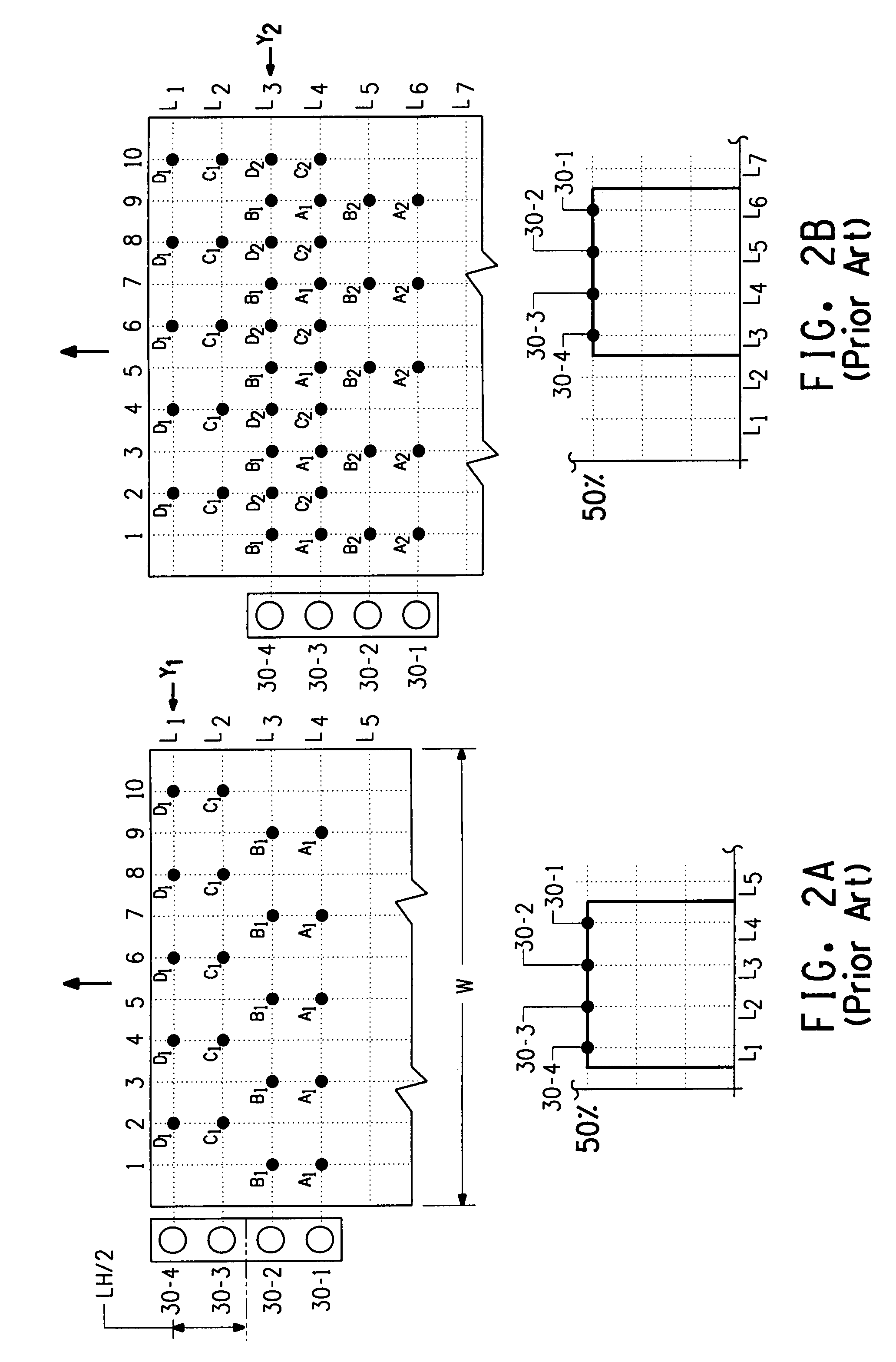
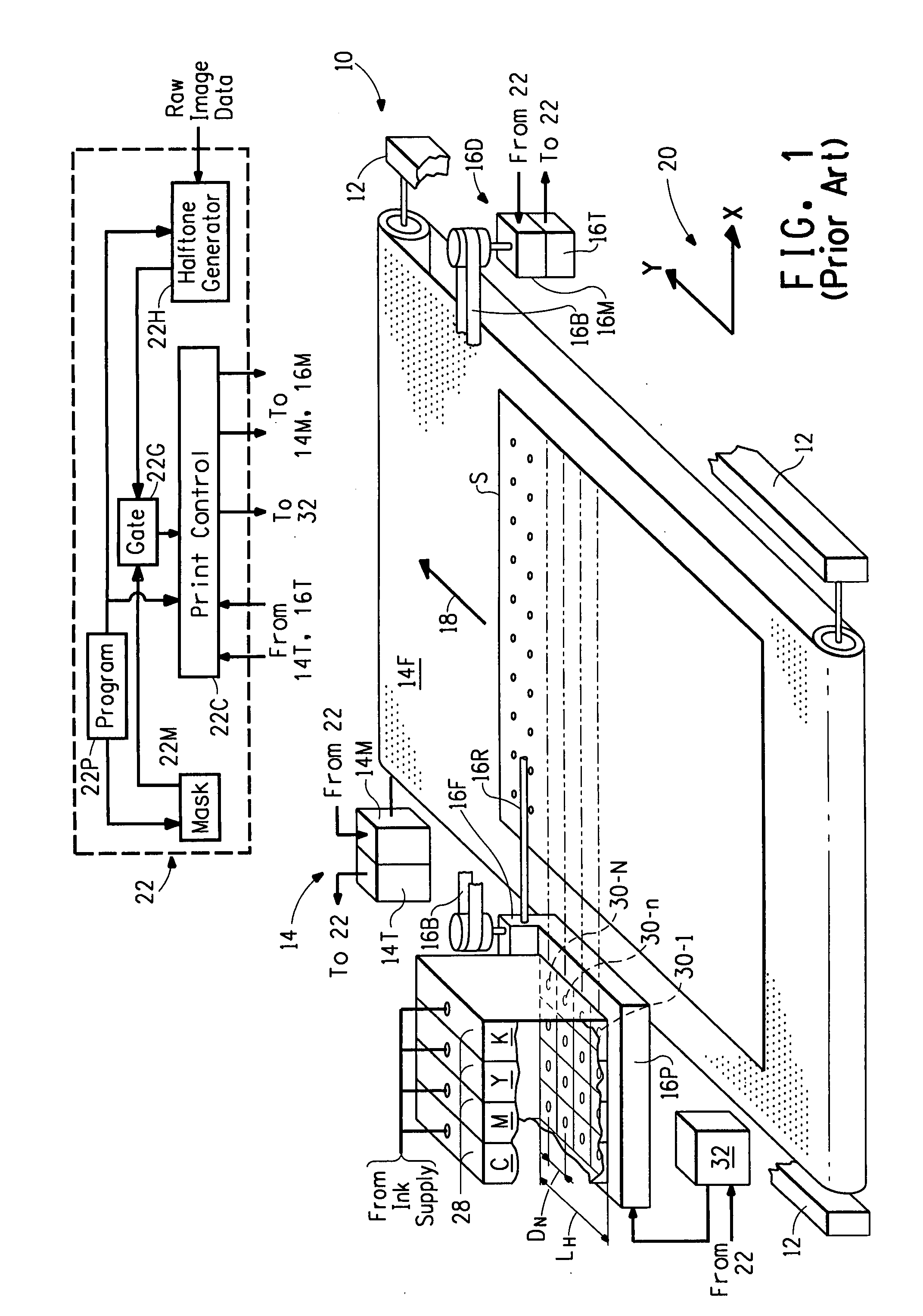
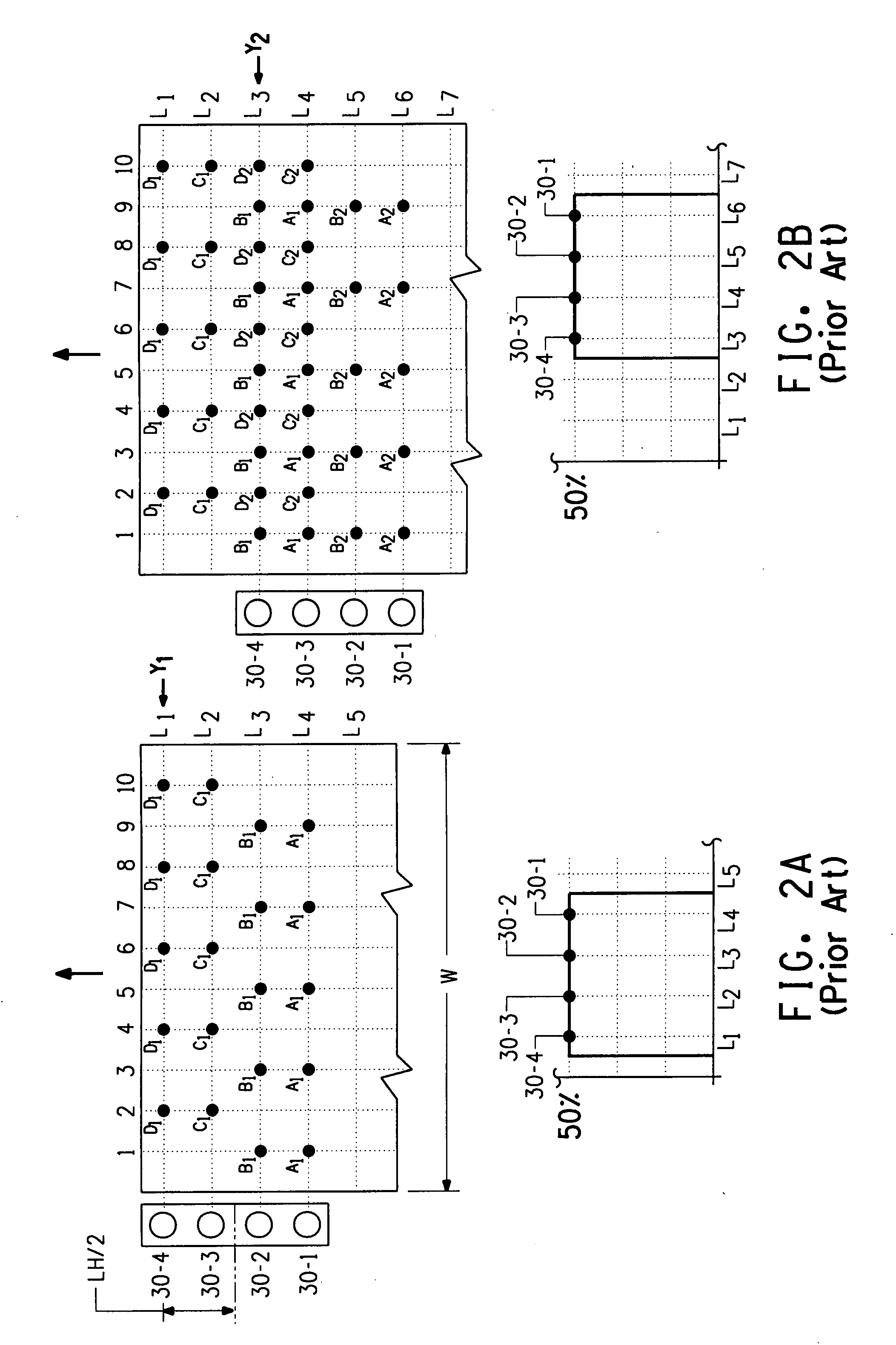
Bi-directional print masking
ActiveUS20100013878A1Reduced bidirectional banding artifactReduce bidirectional banding artifactSpacing mechanismsVisual presentationSpray nozzleEngineering
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
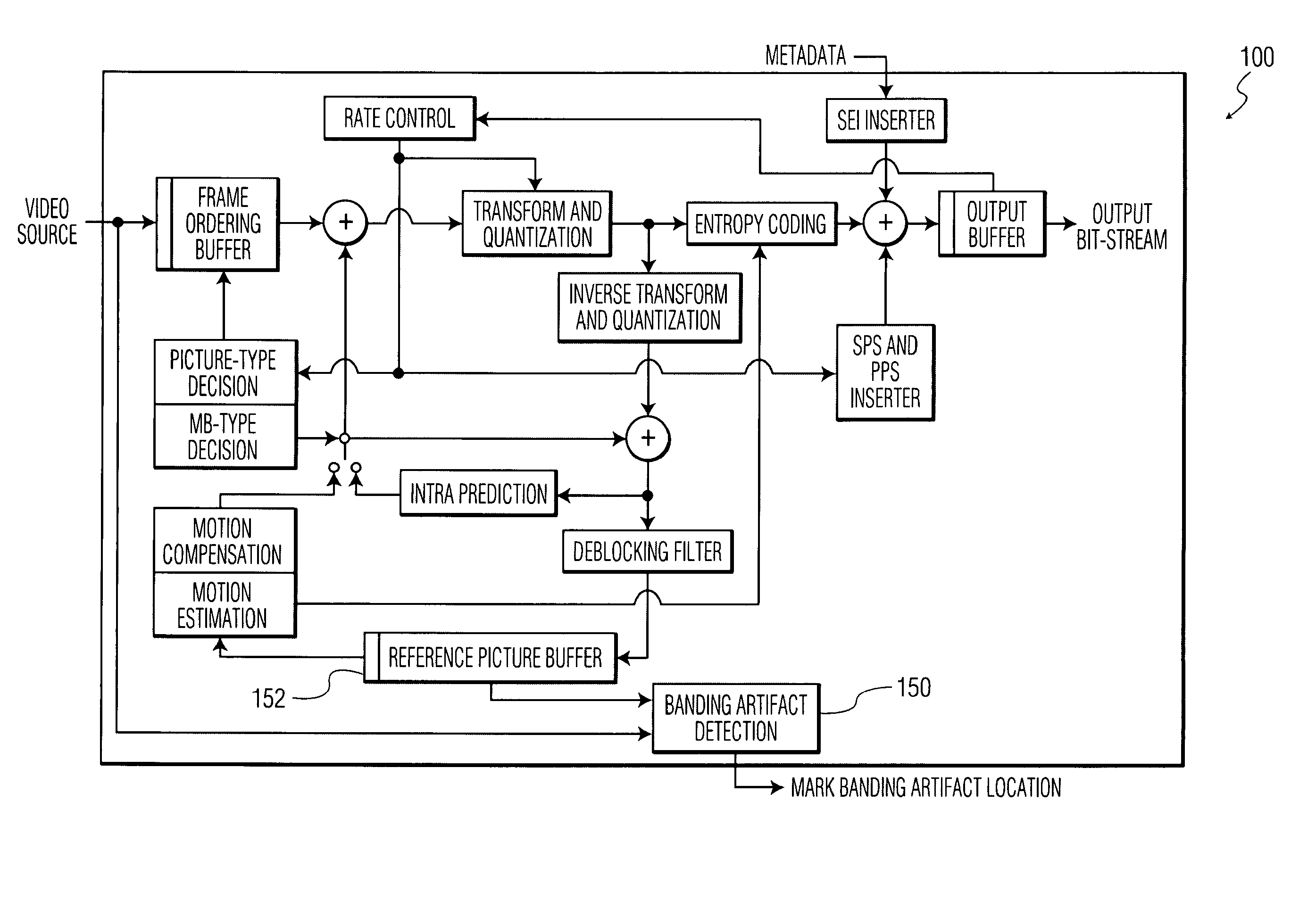
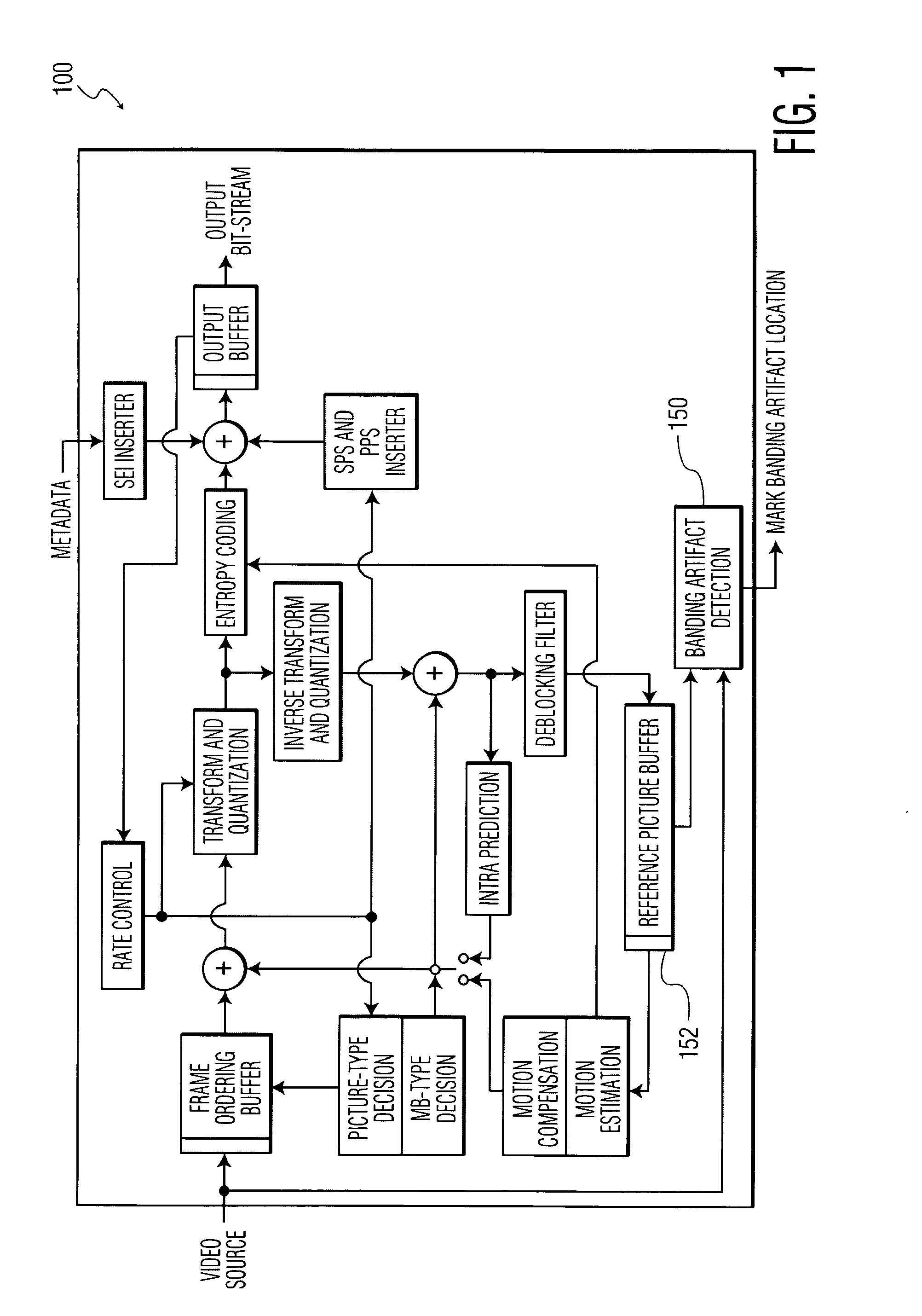
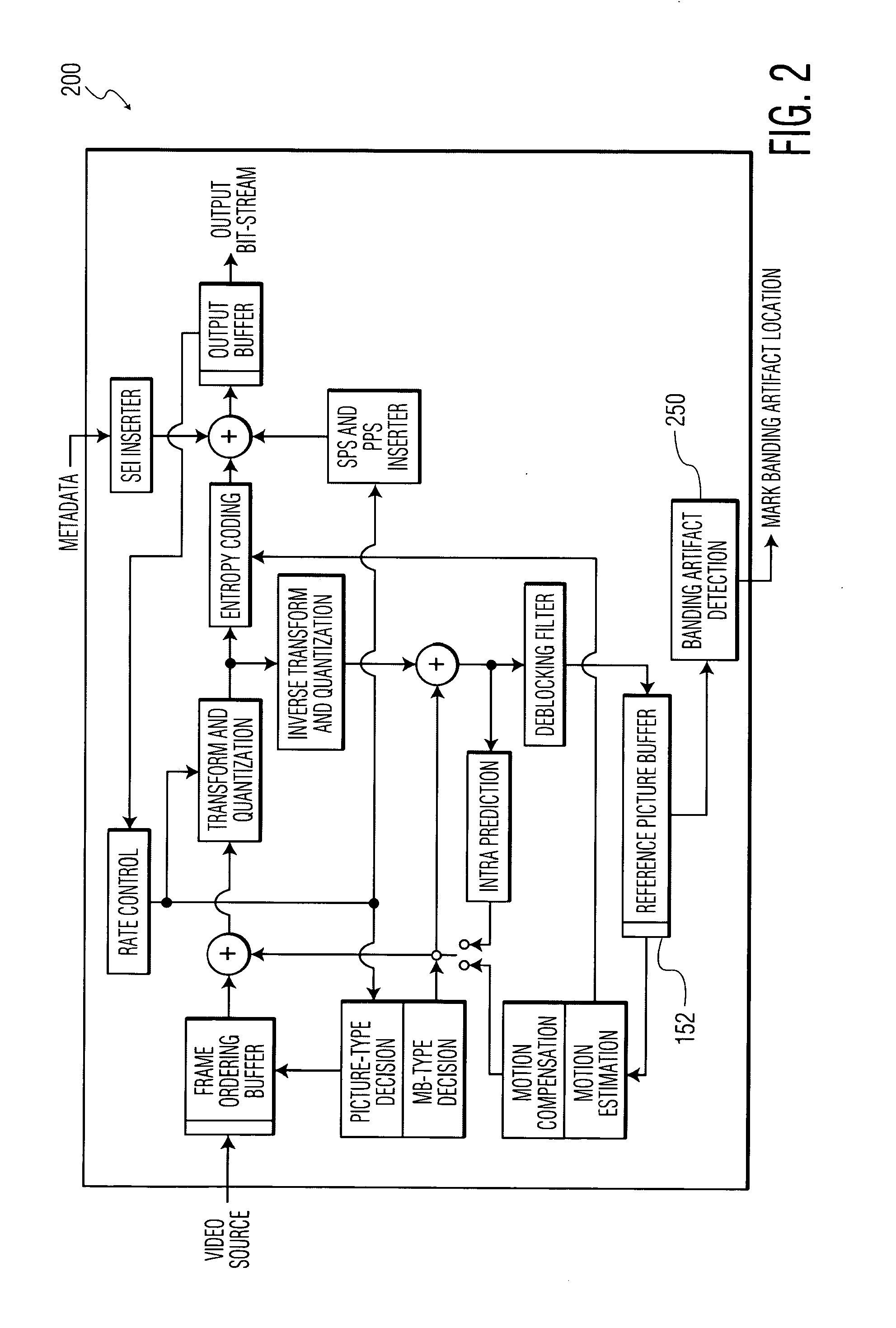
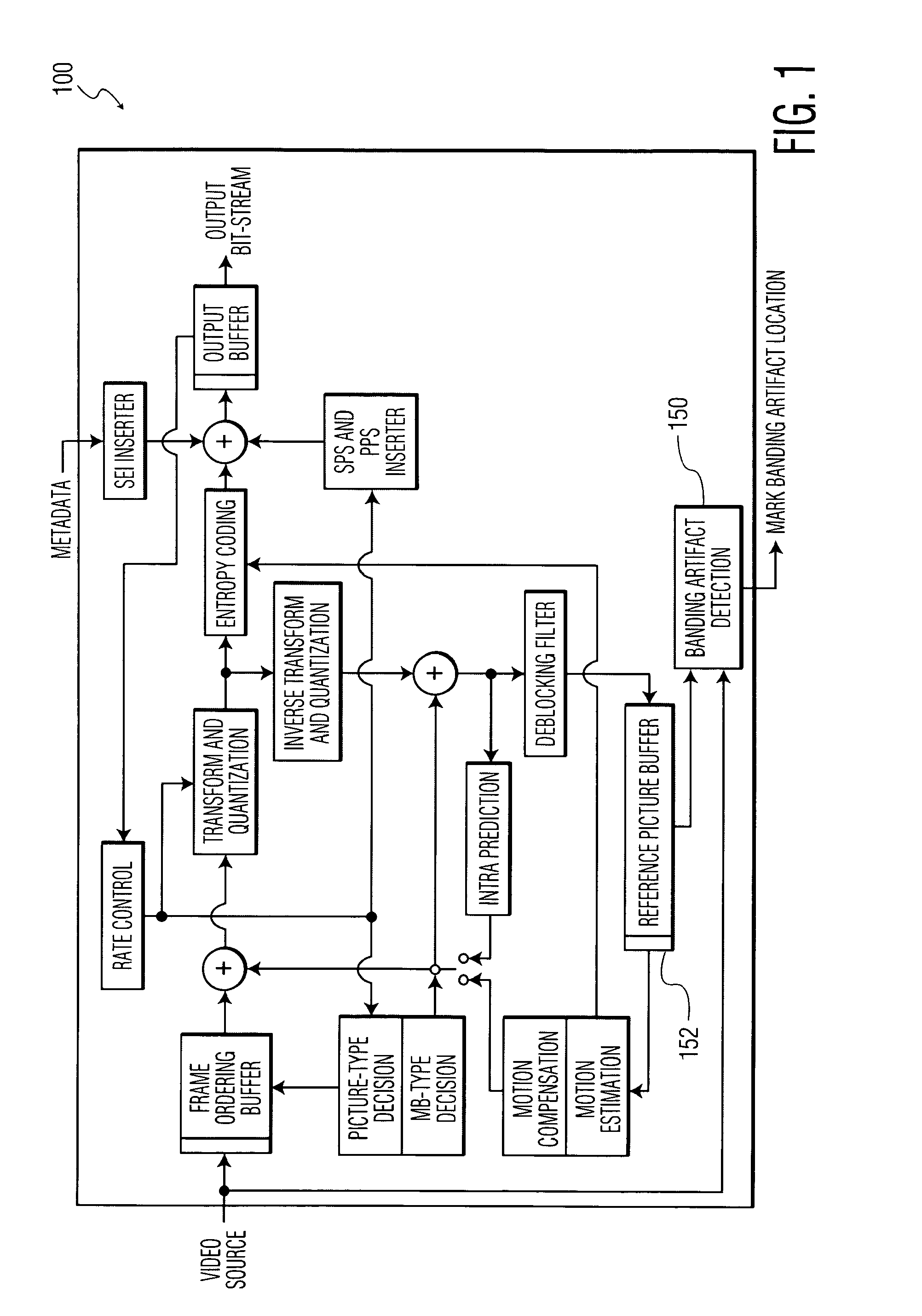
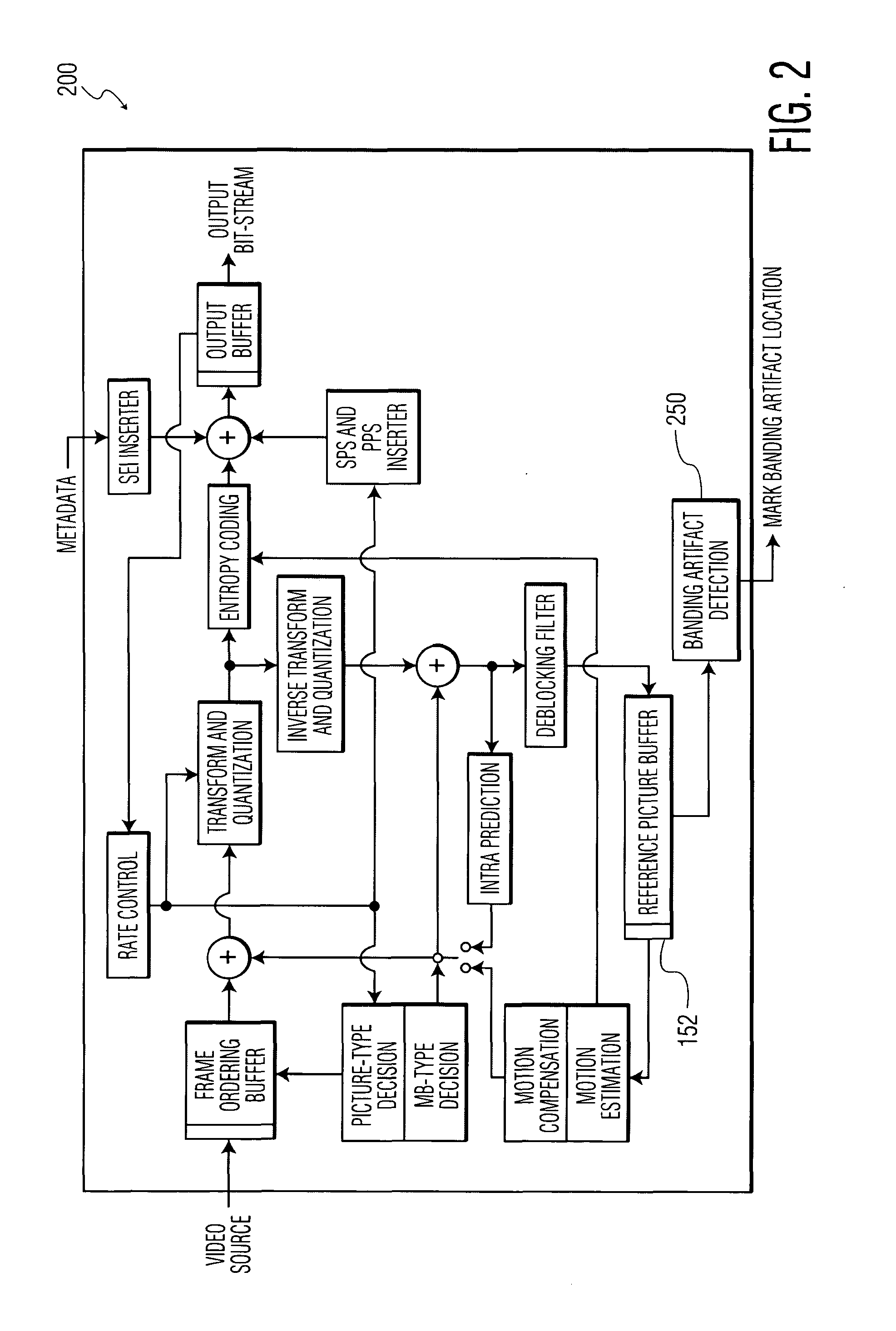
Banding artifact detection in digital video content
A method and system for identifying and determining banding artifacts in digital video content composed of a sequence of moving video pictures includes creating a mask image corresponding to a picture from said sequence of moving video pictures based on global gradient changes to detect potential areas containing banding artifacts. The values of the mask image are scaled thereby making banding artifact detection possible using gradient operators. The banding artifacts are then identified / detected based on the local gradients.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
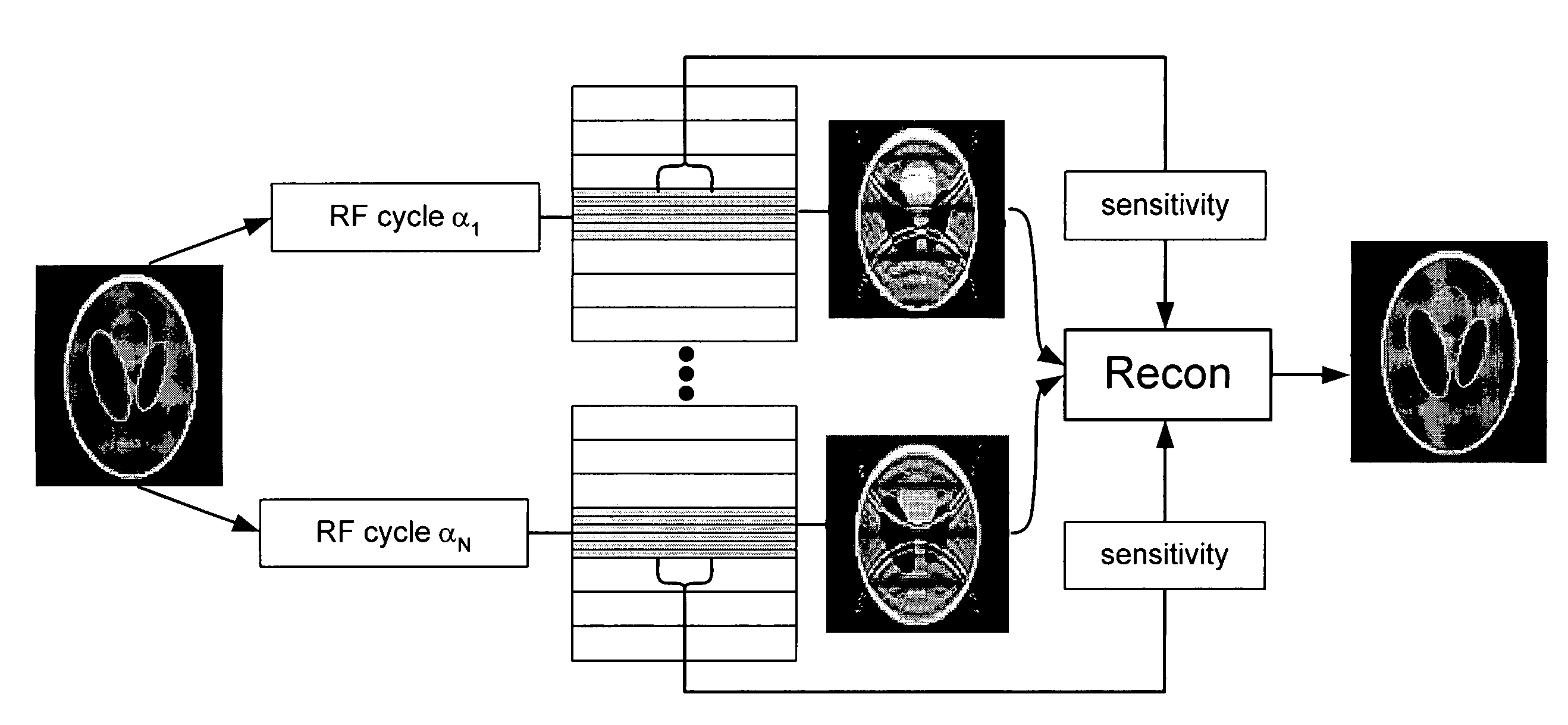
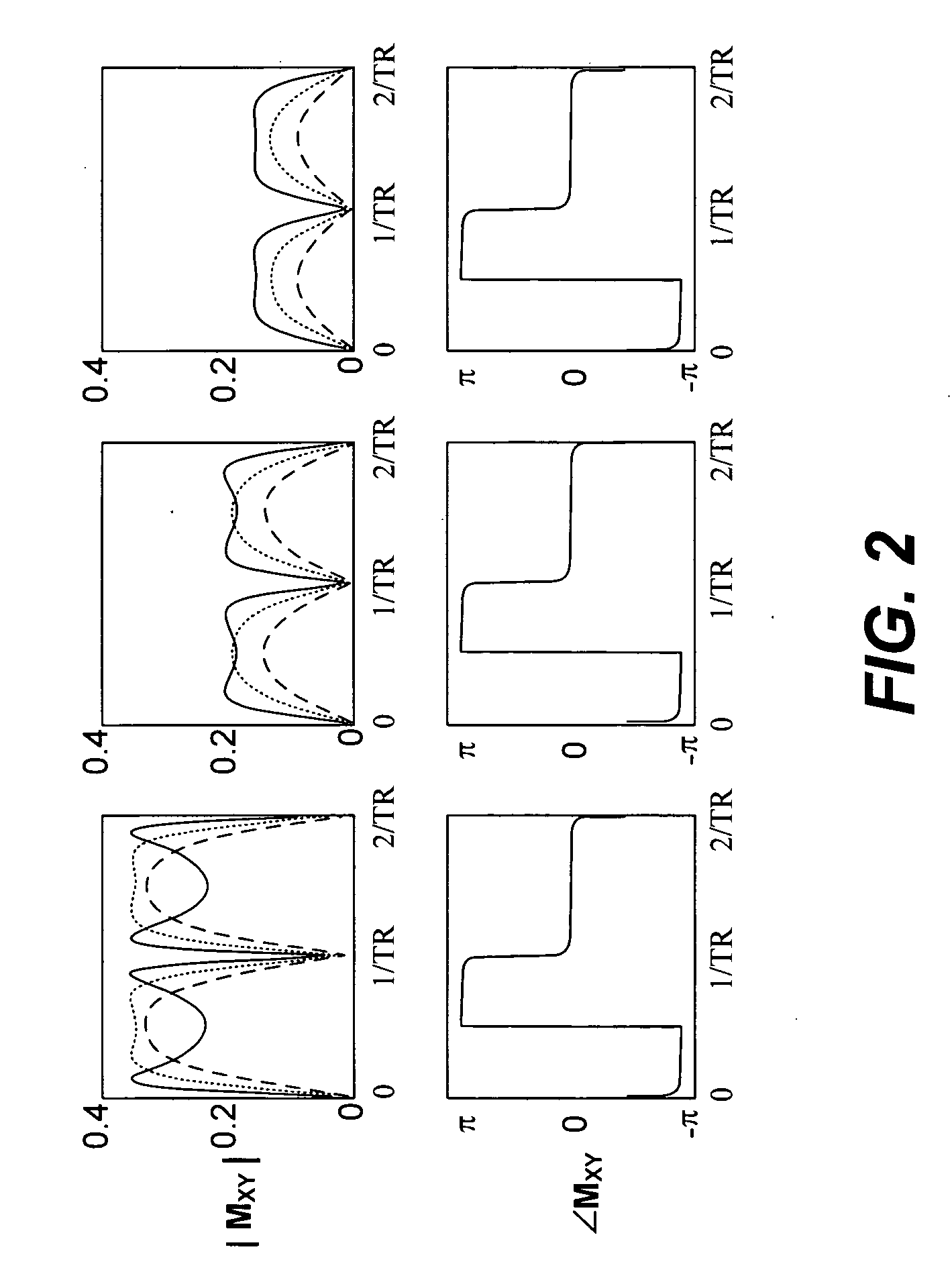
Artifact reduction in SSFP MRI using super field view reconstruction
ActiveUS7132828B2Reduce artifactsReduce scan timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionAugmented matrixDistortion
Banding artifacts in steady state free precession (SSFP) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are reduced by acquiring and combining multiple SSFP images in an augmented matrix where an acquisition vector in k-space is equal to a Fourier matrix of the trajectory on a known distortion operator for each trajectory in k-space.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method and apparatus for banding artifact detection
InactiveUS20110129020A1Eliminate areaLess noticeableImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionDigital image
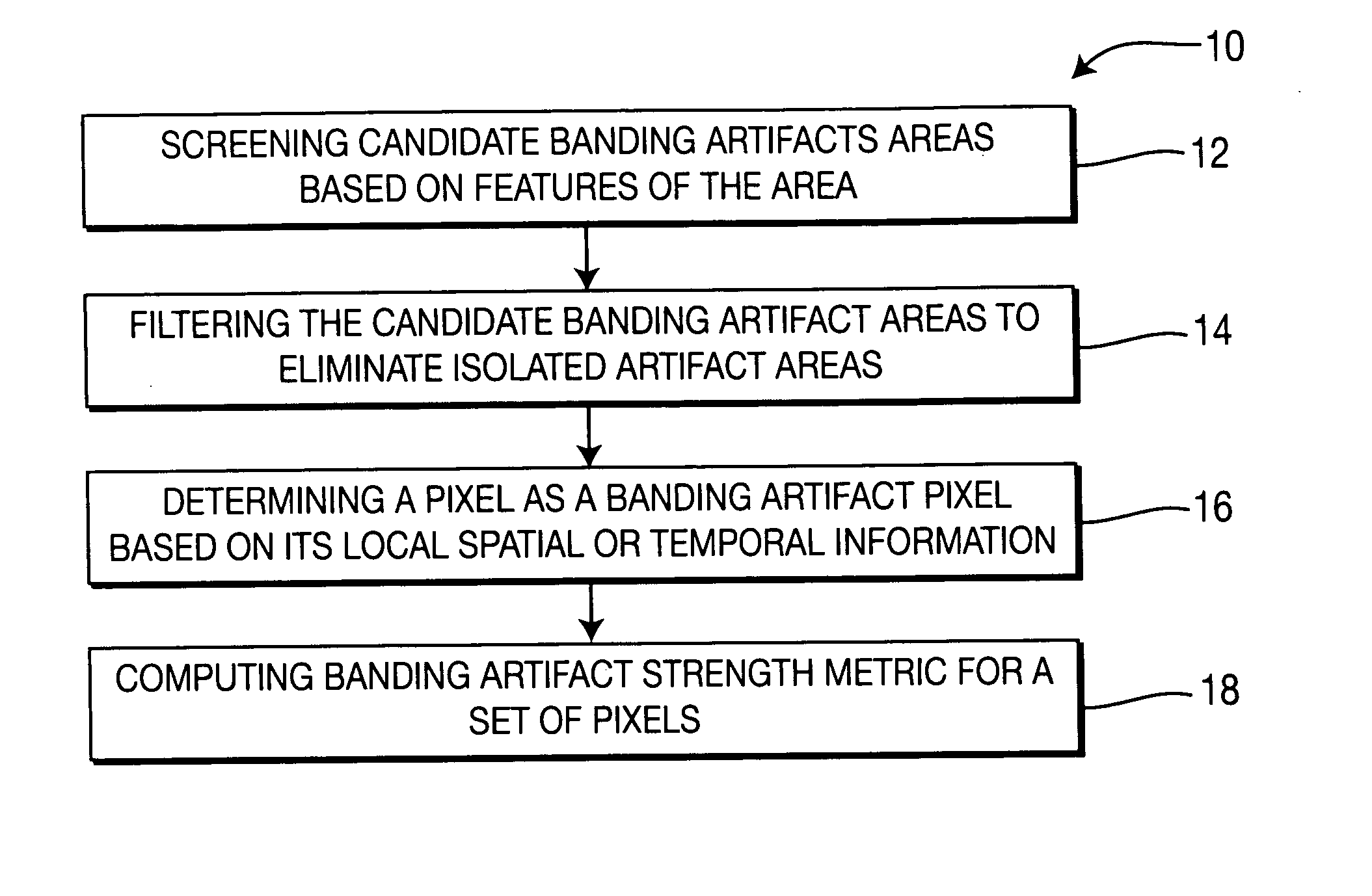
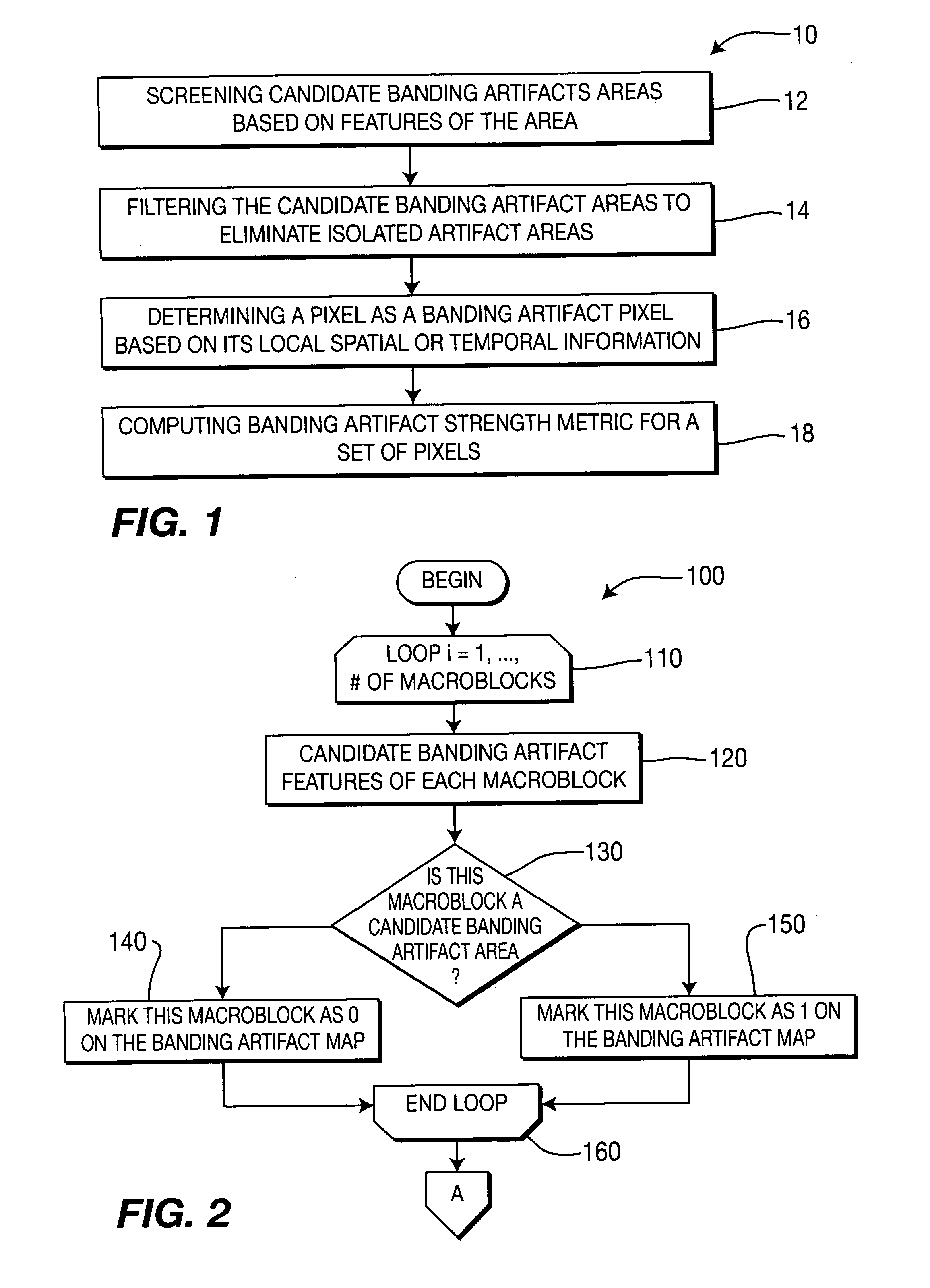
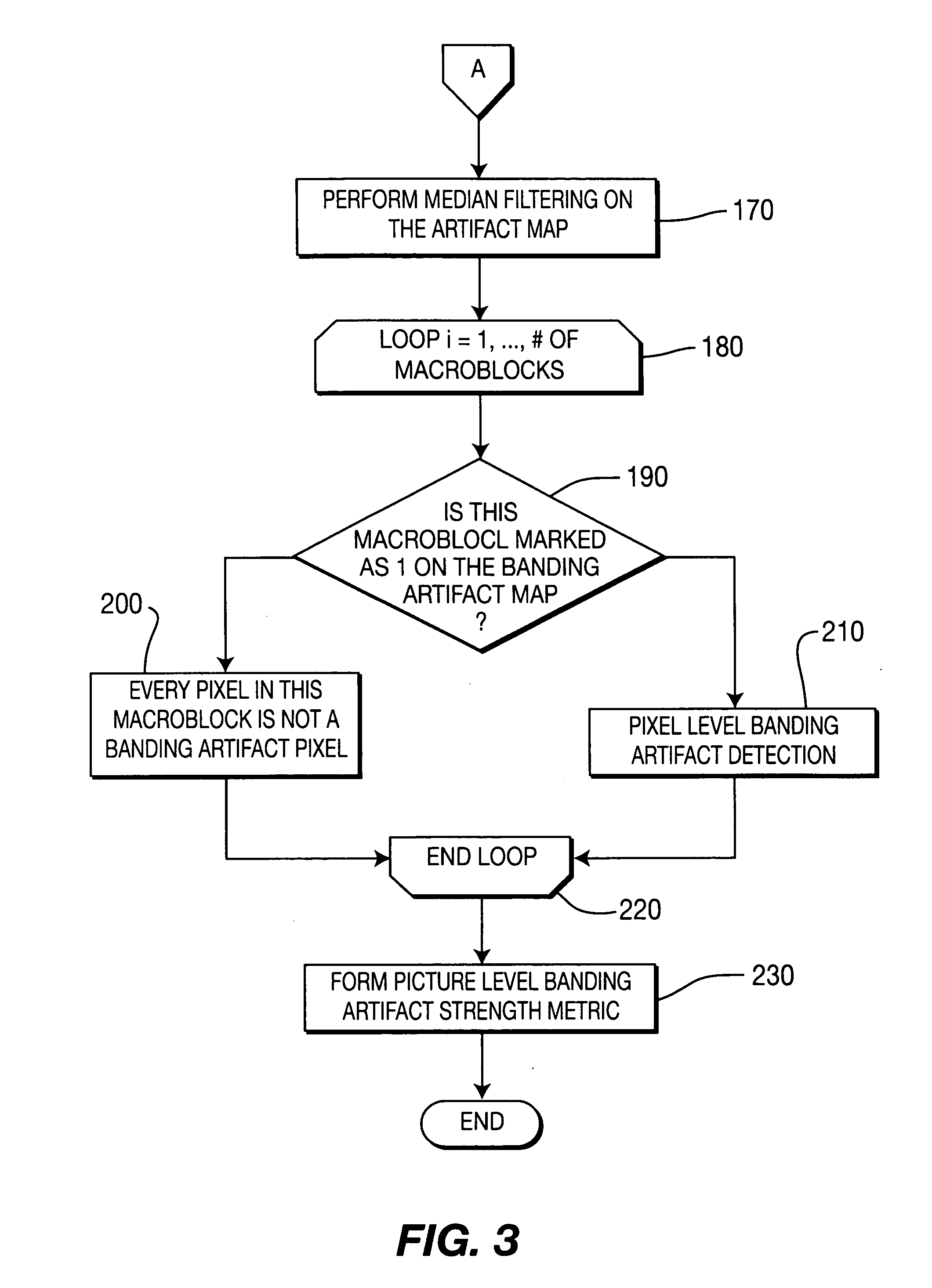
A method and apparatus for detecting banding artifacts in digital images and video contents. The method operates to (i) find the locations of the banding artifacts, (ii) determine the strength of the banding artifact per block, and (iii) determine overall banding artifact strength per picture. The banding artifact detection and strength assignment is done by first finding areas that are prone to banding artifact and then considering the local characteristics of the area to reduce the false detection. The banding artifact strength of a picture is determined by considering the size and the strength of the artifact areas in this picture as well as the artifact strength in the neighboring pictures.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
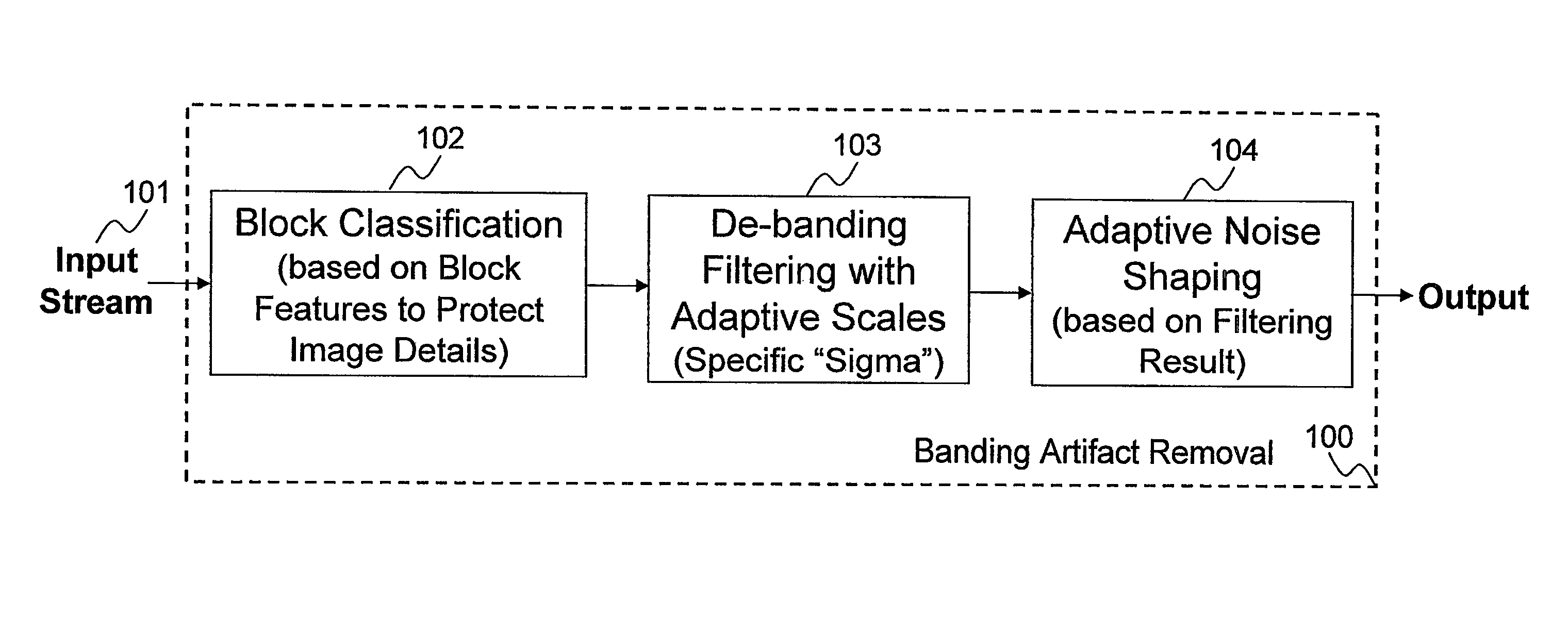
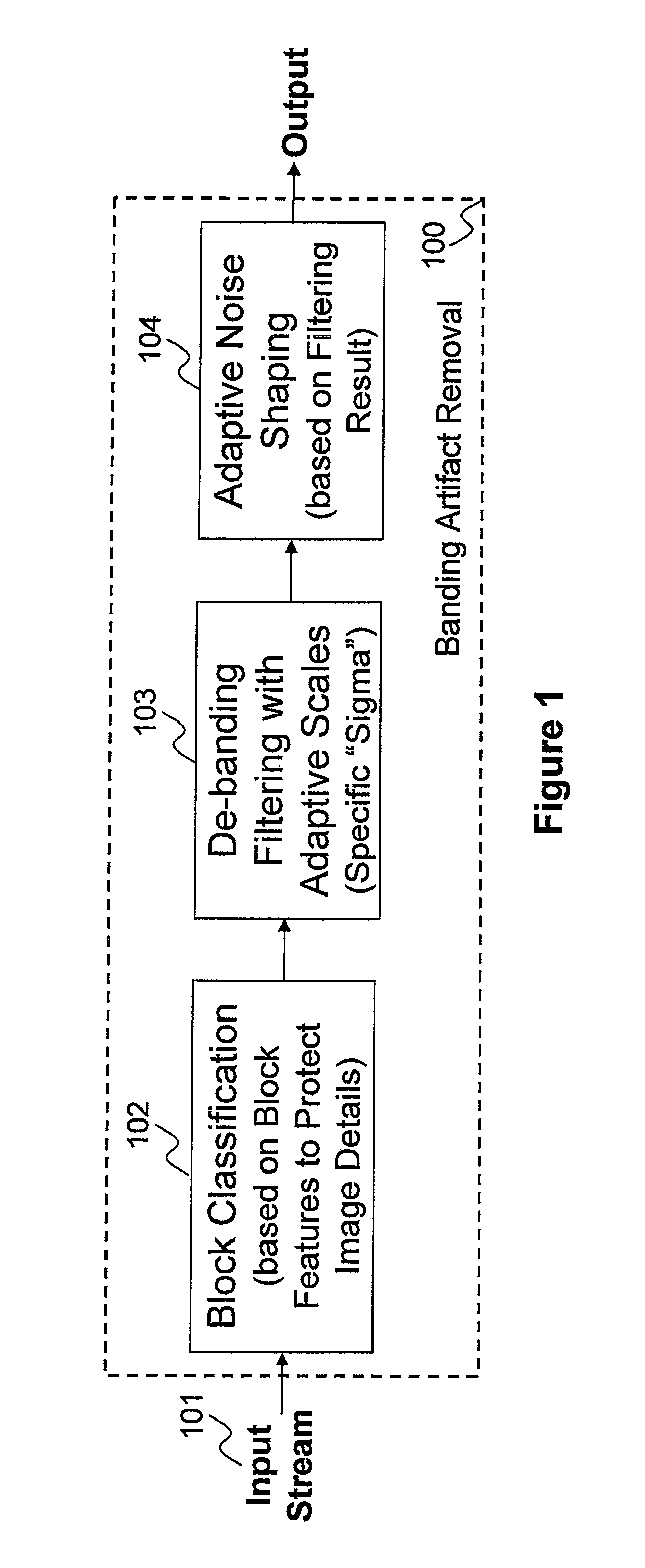
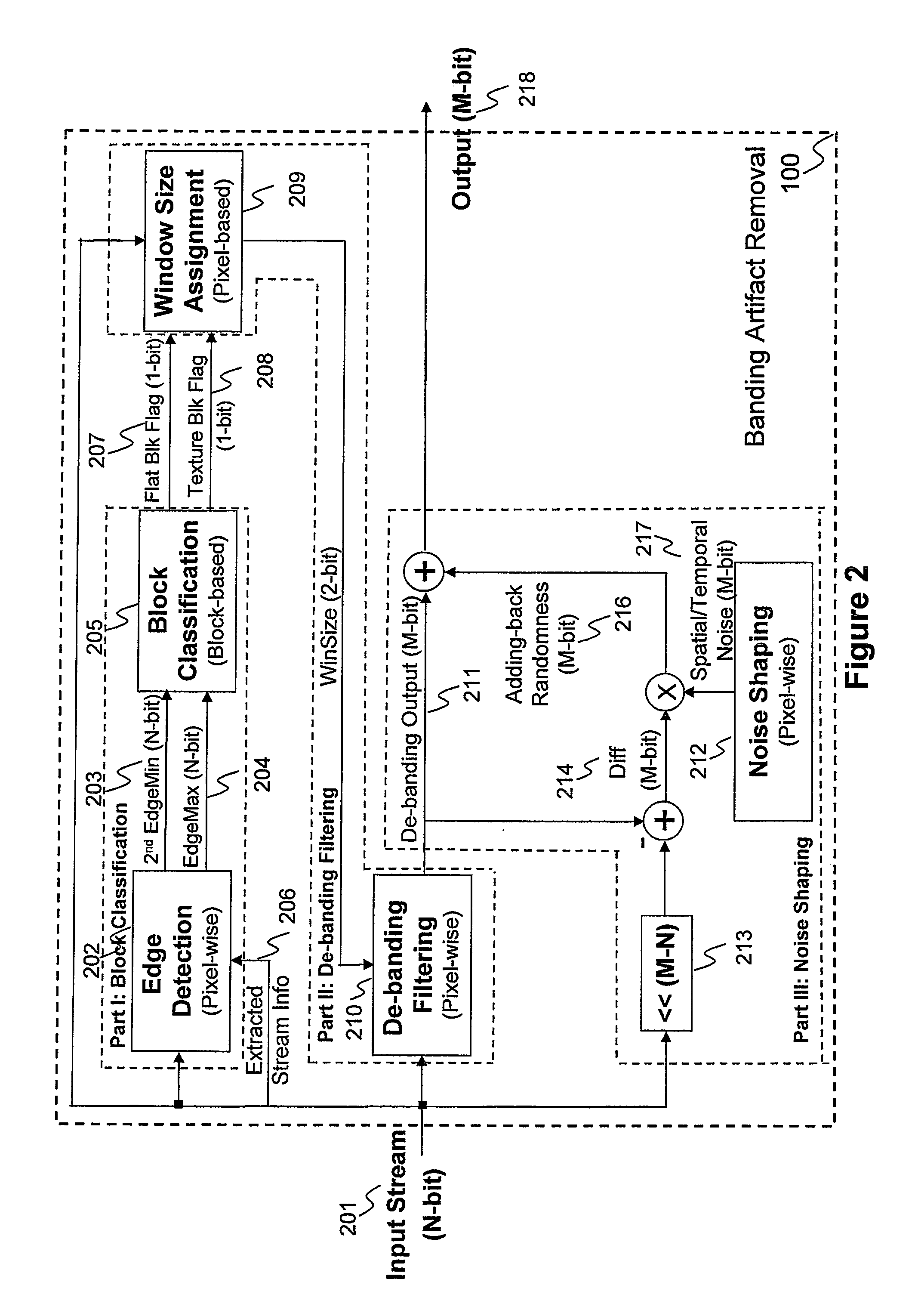
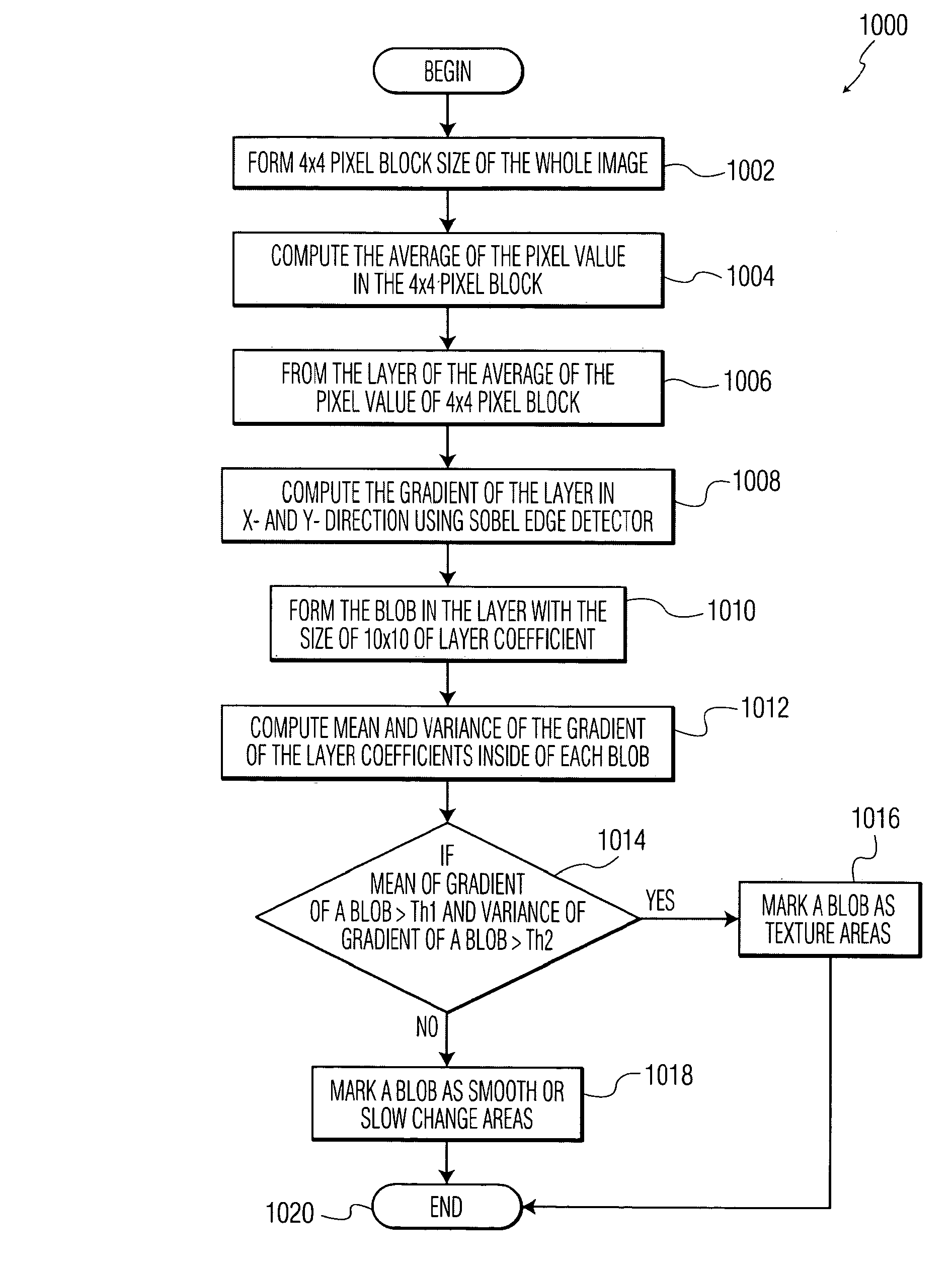
General banding and codec banding artifact removal
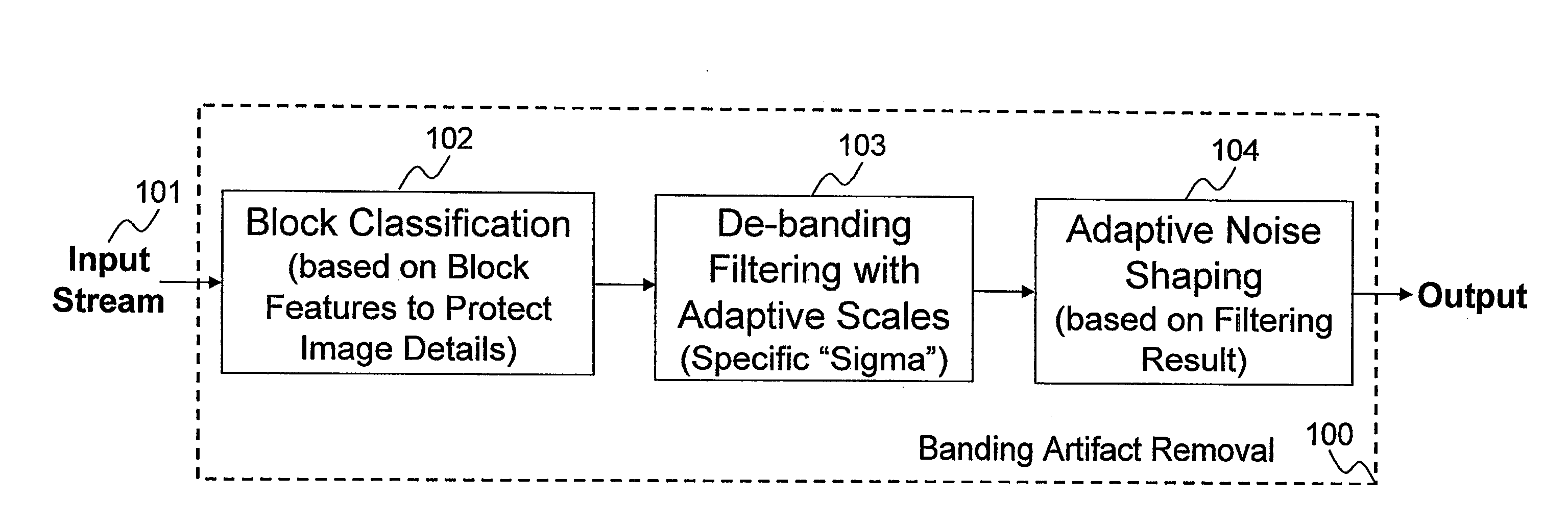
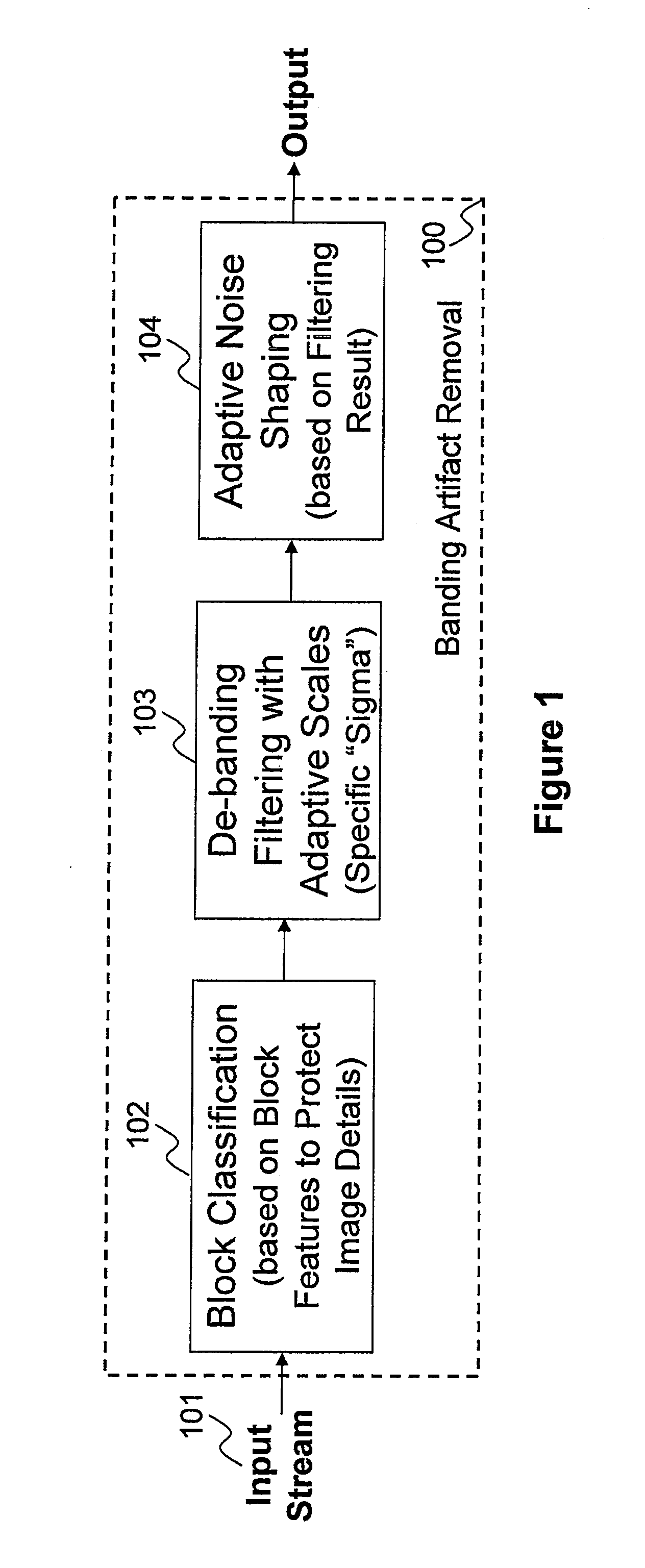
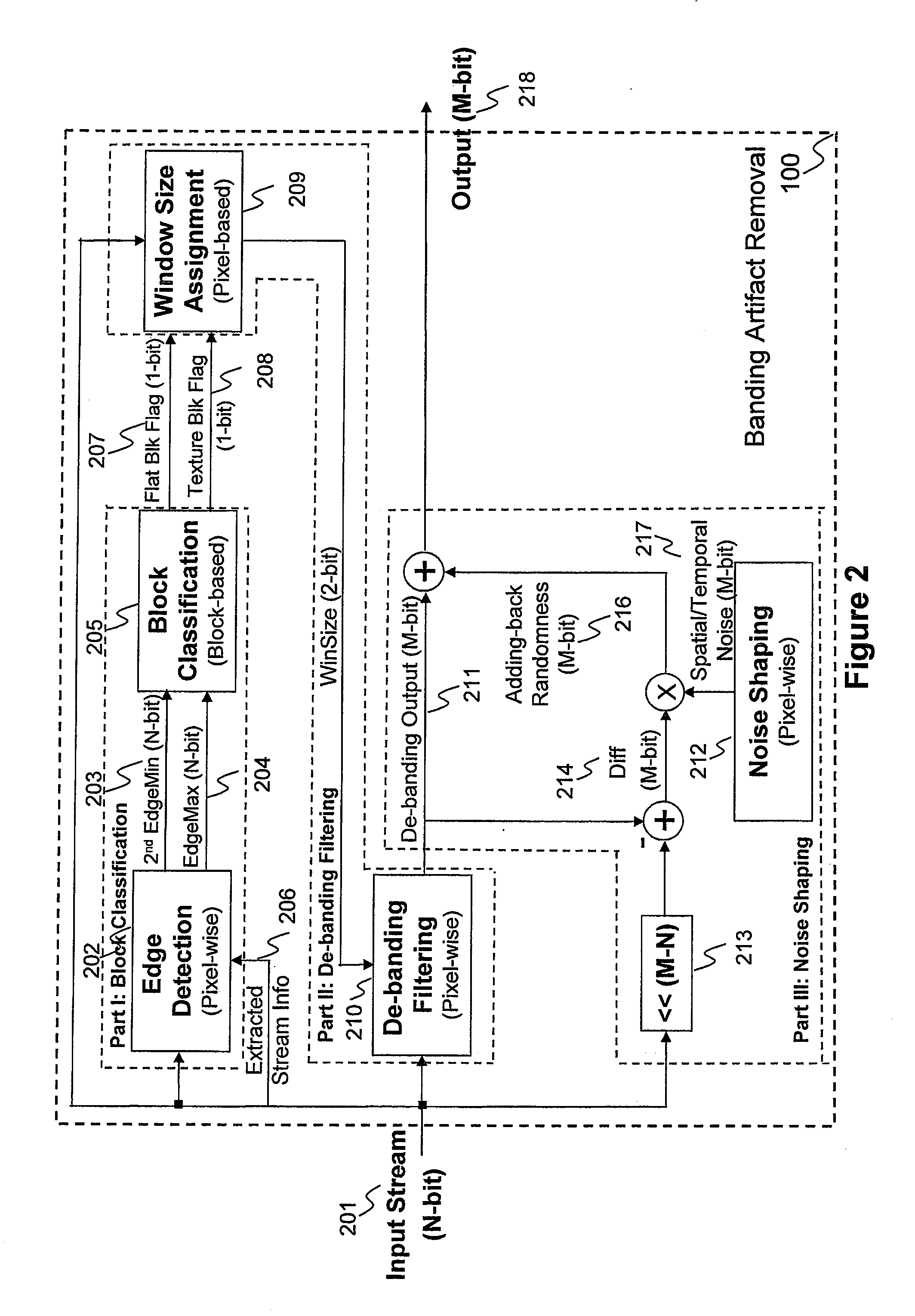
A method and apparatus are disclosed for identifying and removing banding artifacts (i.e., false contours) resulting from insufficient bit depth caused by digital image quantization, conversion, and / or compression. This method includes: explicitly identifying texture block and flat block; de-termination of filter window sizes with the consideration of handling transitions between texture block and flat block; de-banding filtering with edge protection; and noise shaping according to de-banding filter result.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
Methods and systems to facilitate reducing banding artifacts in images
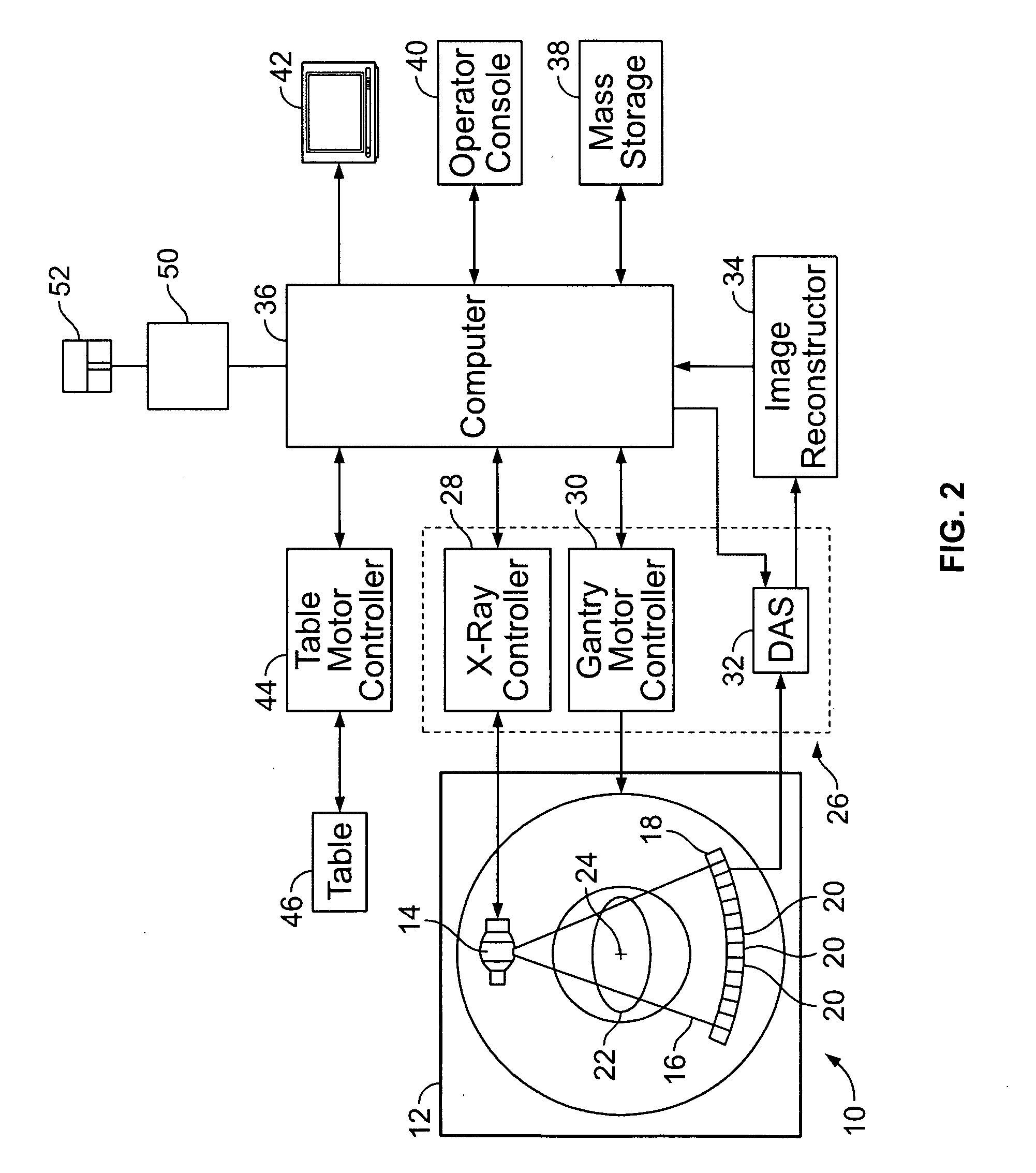
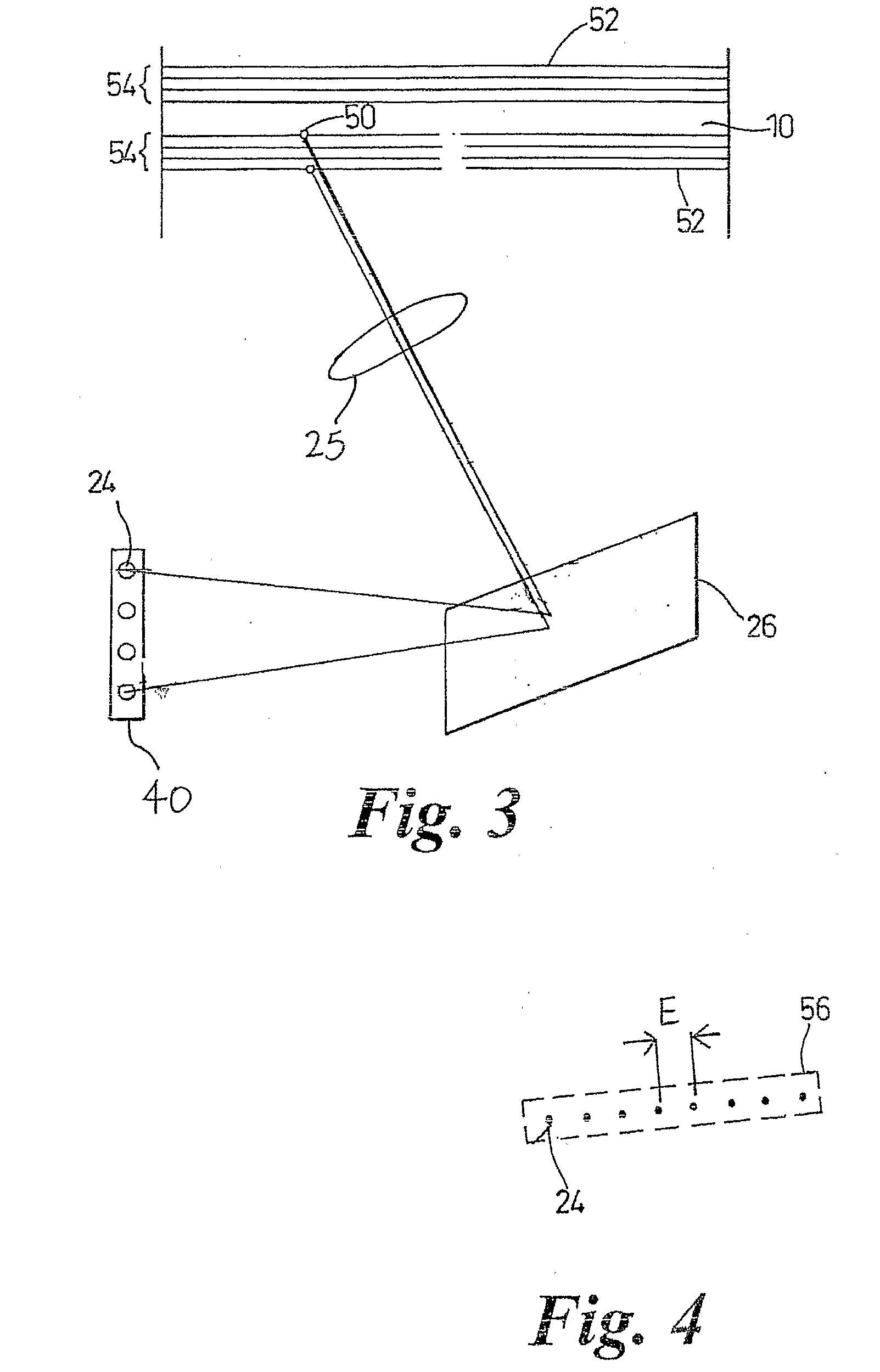
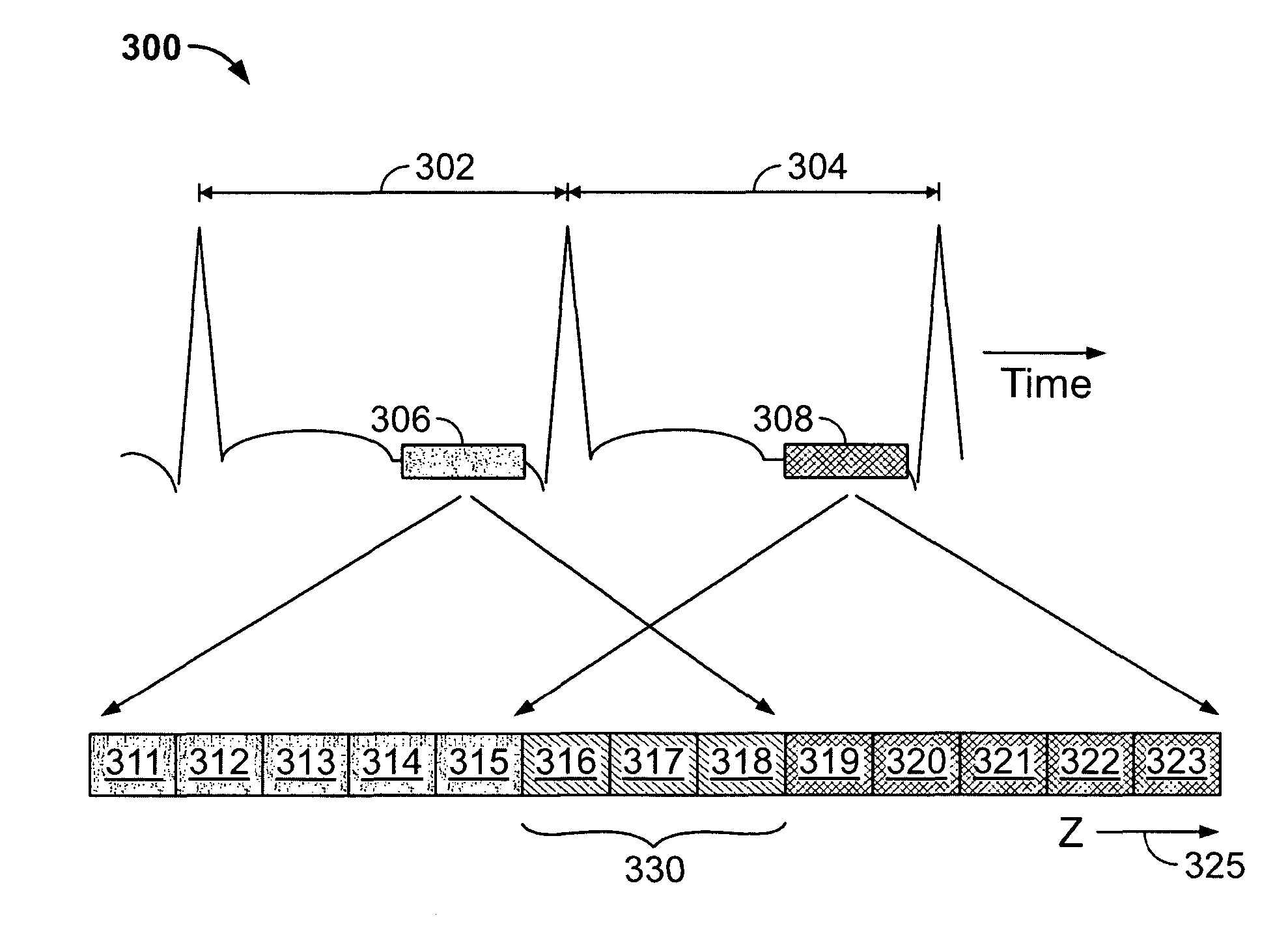
ActiveUS20070127797A1Reconstruction from projectionOrgan movement/changes detectionBiological cyclesComputer science
Methods and systems for generating computed tomographic (CT) images from image data acquired during different biological cycles are provided. A computer is programmed to receive a plurality of scan data acquired during a gated acquisition window of each of a plurality of biological cycles, blend the scan data acquired during a first of the plurality of biological cycles with the scan data acquired during a second of the plurality of biological cycles, and construct a final image from the blended data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
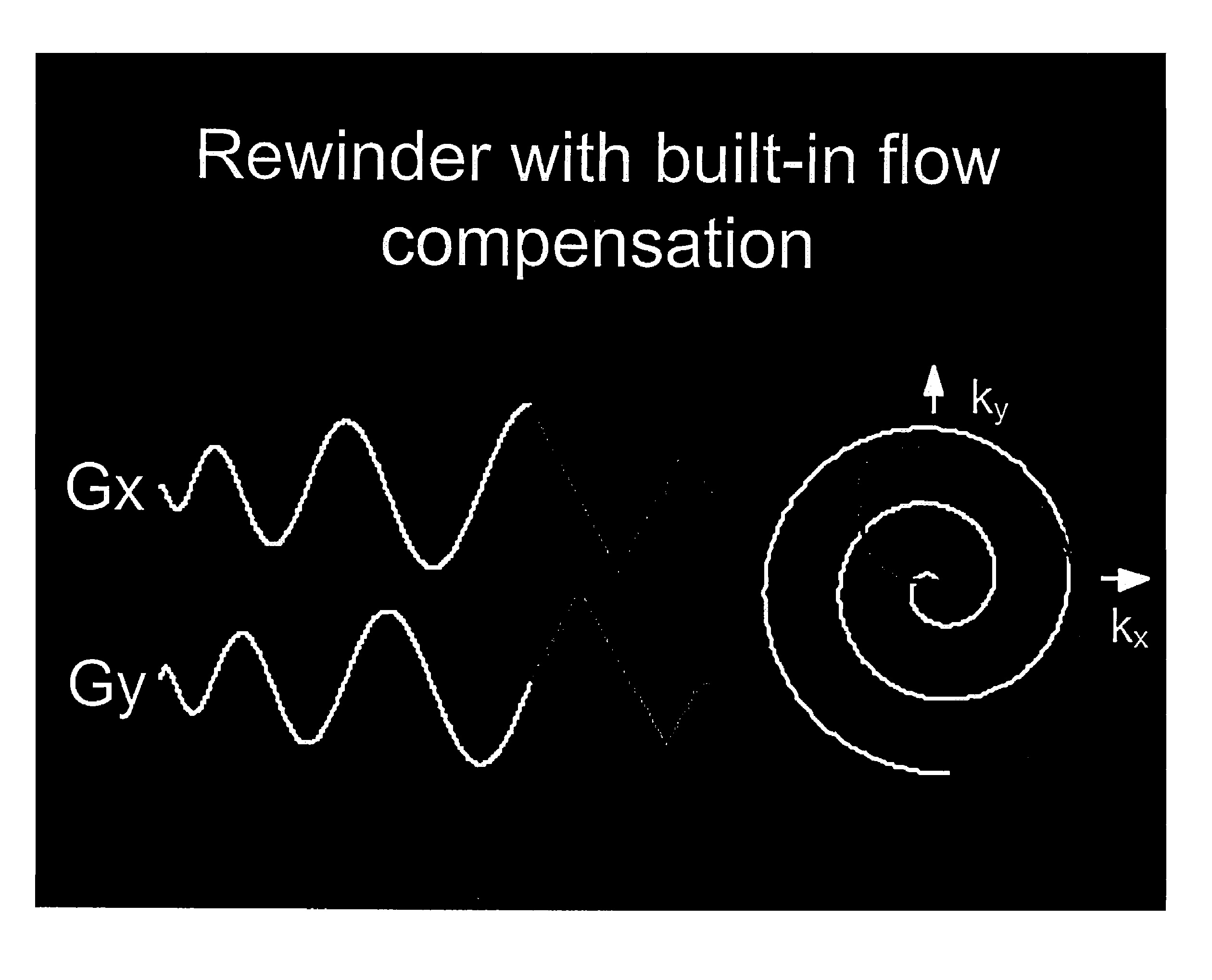
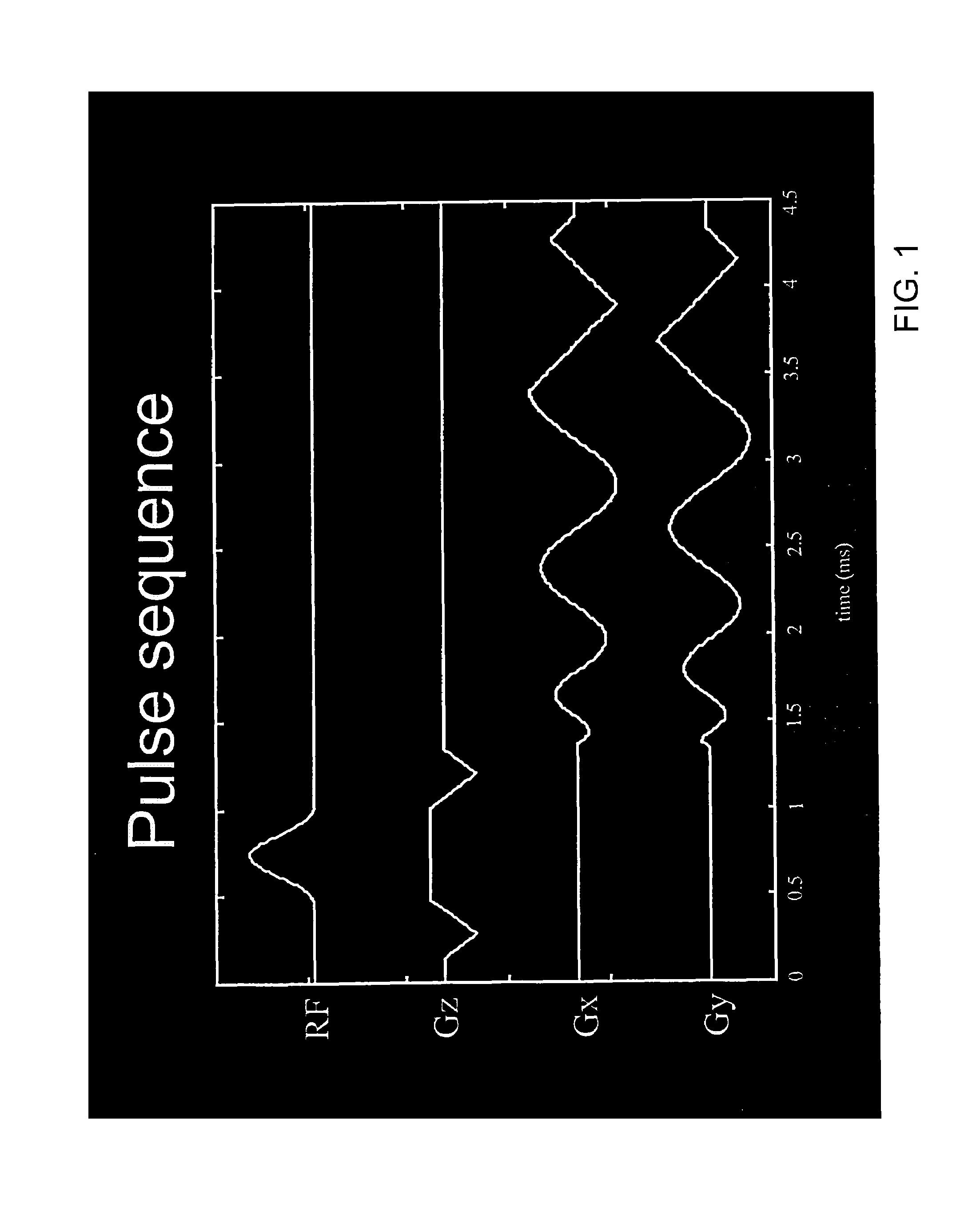
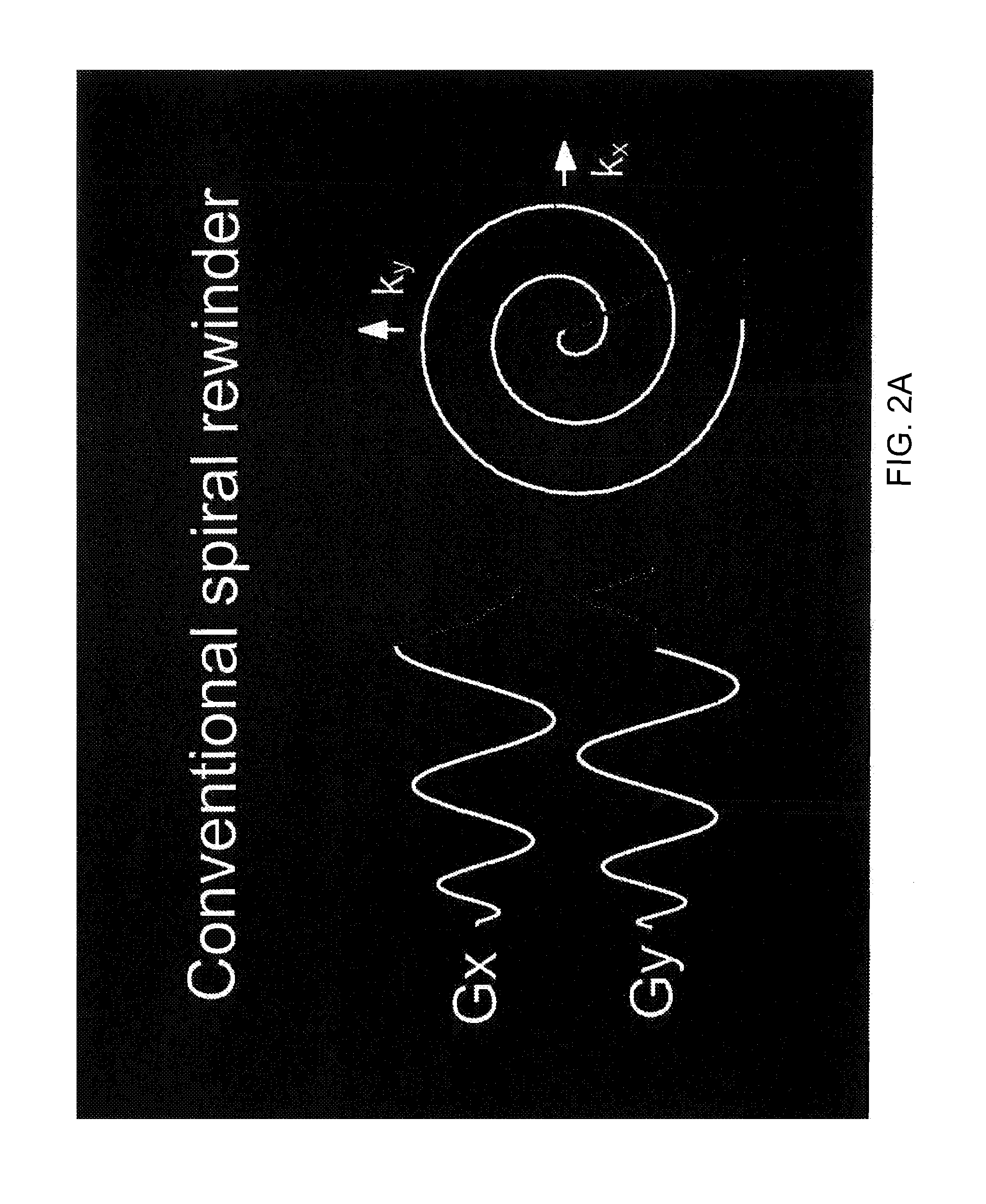
Motion compensated spiral FISP MRI
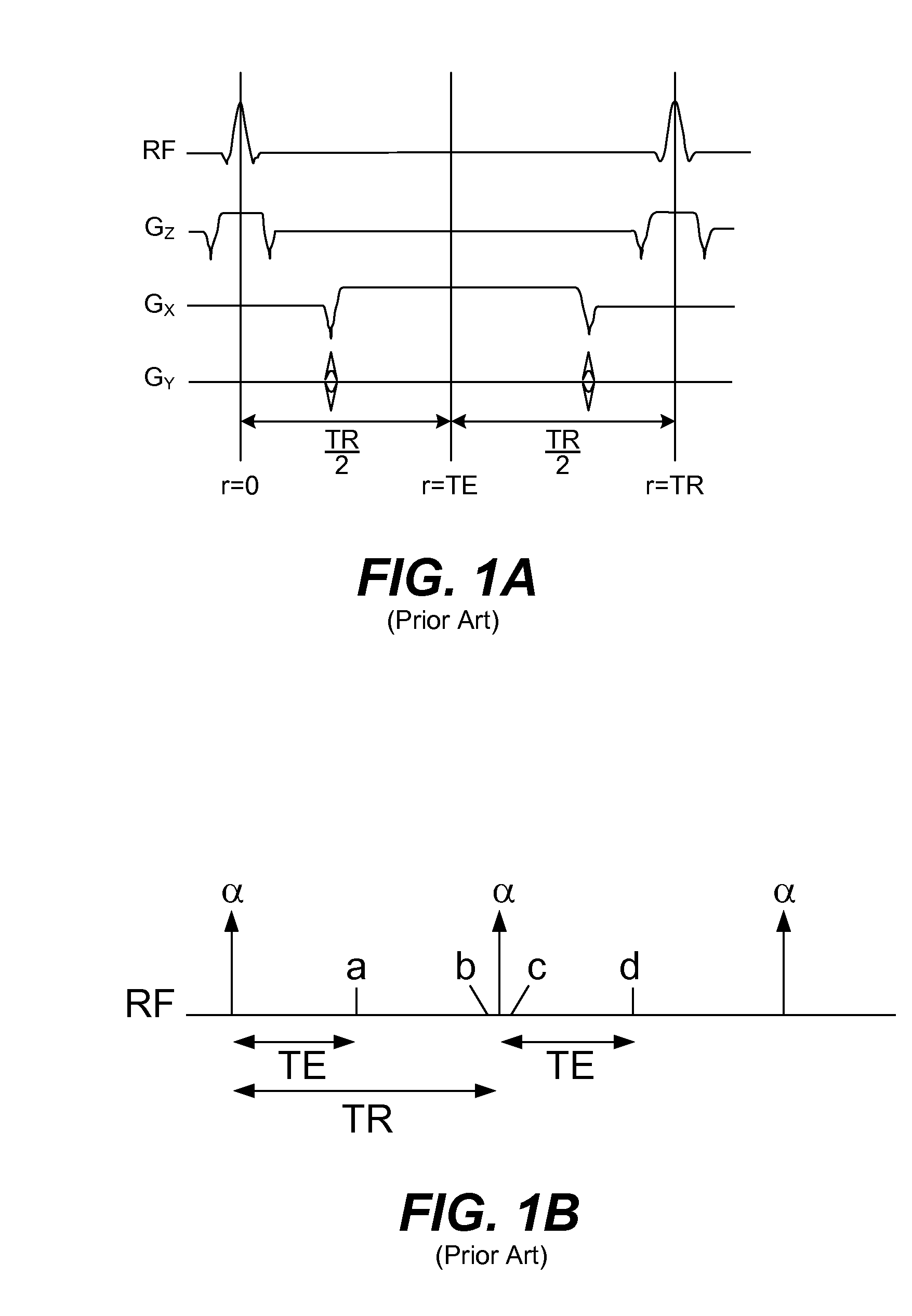
ActiveUS7558612B2Reduced repetition timePrevents banding artifactMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic field gradientPrecession
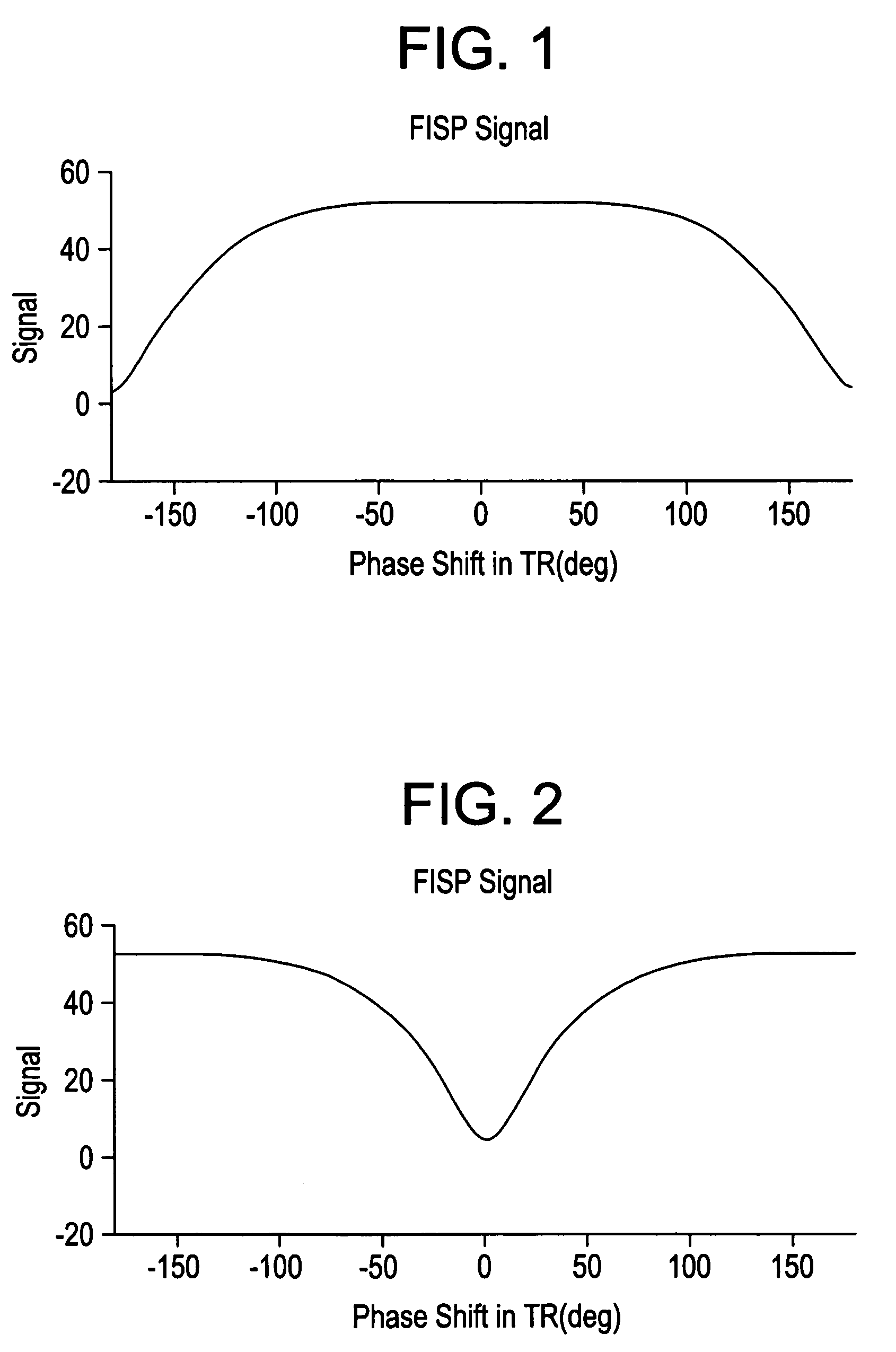
Real-time imaging of a moving object such as the heart uses fast imaging with steady precession (FISP) traversing spirals in k-space. After flipping nuclear spins in the object within a slice to be imaged, signals are read out from the nuclear spins while applying read-out magnetic field gradients whereby read-out signals traverse spirals in k-space. Thereafter, the zero moment and first moment of the read-out gradients are driven to zero quickly so that fast imaging with steady state precession is realized without banding artifacts. Motion compensated rewinders are applied after the read-out magnetic field gradients which can be integral with the read-out gradients or comprise separate compensation lobes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Lenticular image articles and method and apparatus of reducing banding artifacts in lenticular image articles
A method of creating a lenticular imaging article. The method comprises printing an interlaced composite image according to a reference grid of a printer, providing a lenticular lens sheet having a plurality of parallel lenticular lines between a plurality of lenslets, selecting an acute angle for an intersection between the first and second axes according to a function of a resolution of the interlaced composite image and a pitch of the lenticular lens sheet, and positioning the lenticular lens sheet so that the intersection forms the acute angle.
Owner:HUMANEYES TECH
Nonuniform mask circulation for irregular page advance
InactiveUS20100091051A1Reduction in banding artifactReduce artifactsDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsComputer graphics (images)Engineering
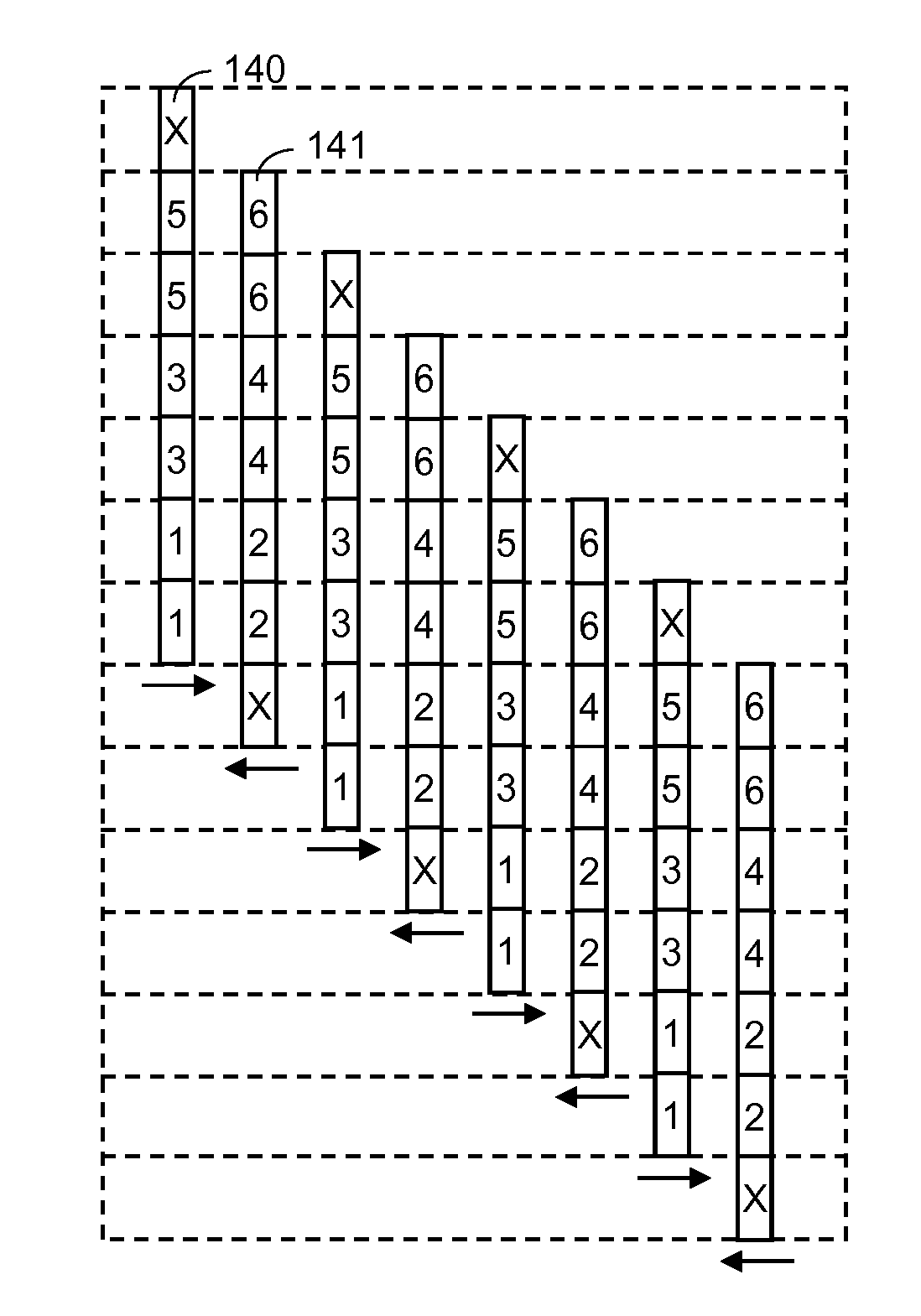
A method for reducing banding artifacts in a printed image, including irregularly advancing a media that will be printed upon while employing an entire single mask for marking elements of a printhead; and calculating a difference between an irregular advance amount of the media versus a nominal advance amount of the media. Finally, the single mask is nonuniformly circulated by the difference calculated in order to compensate for the media being irregularly advanced.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
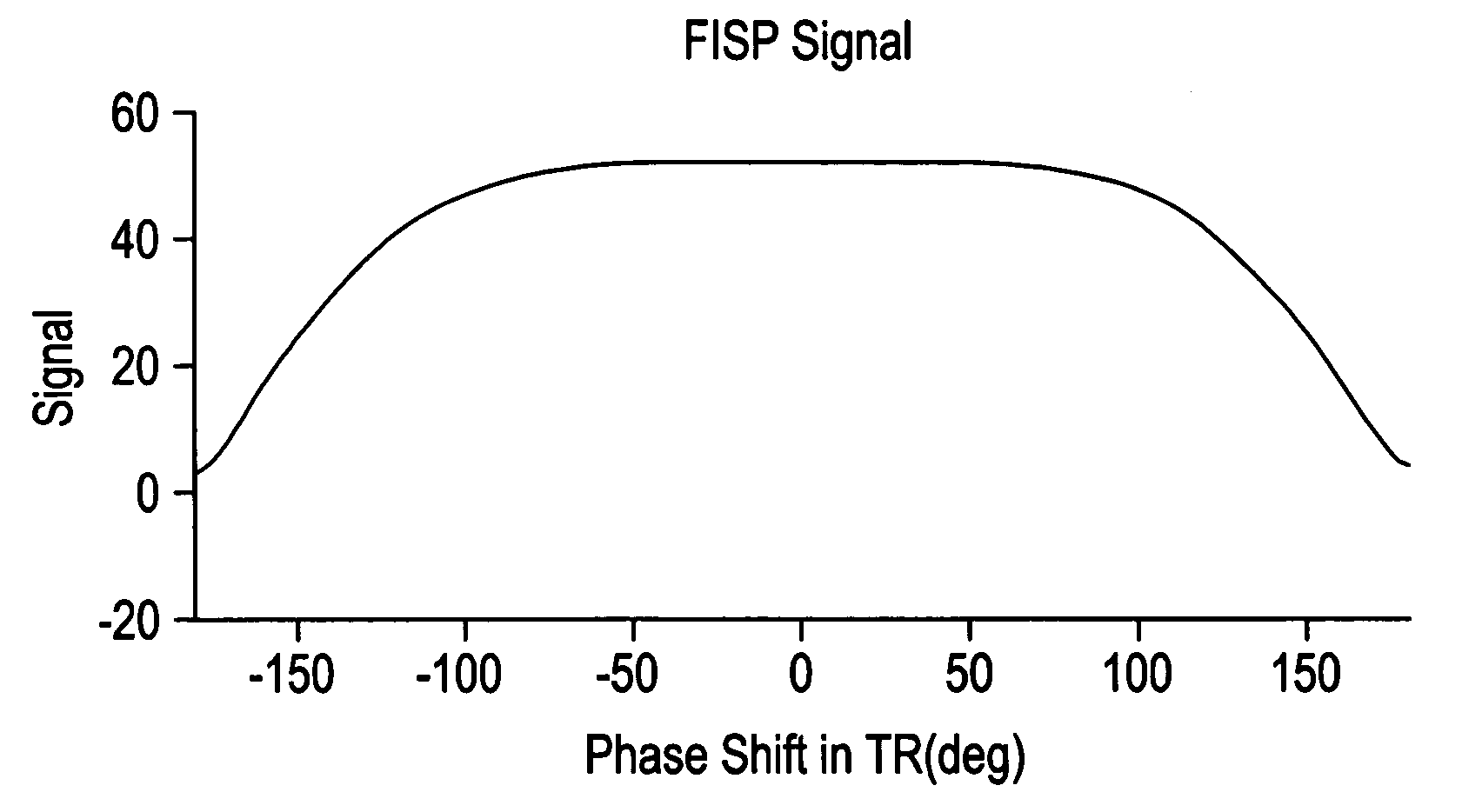
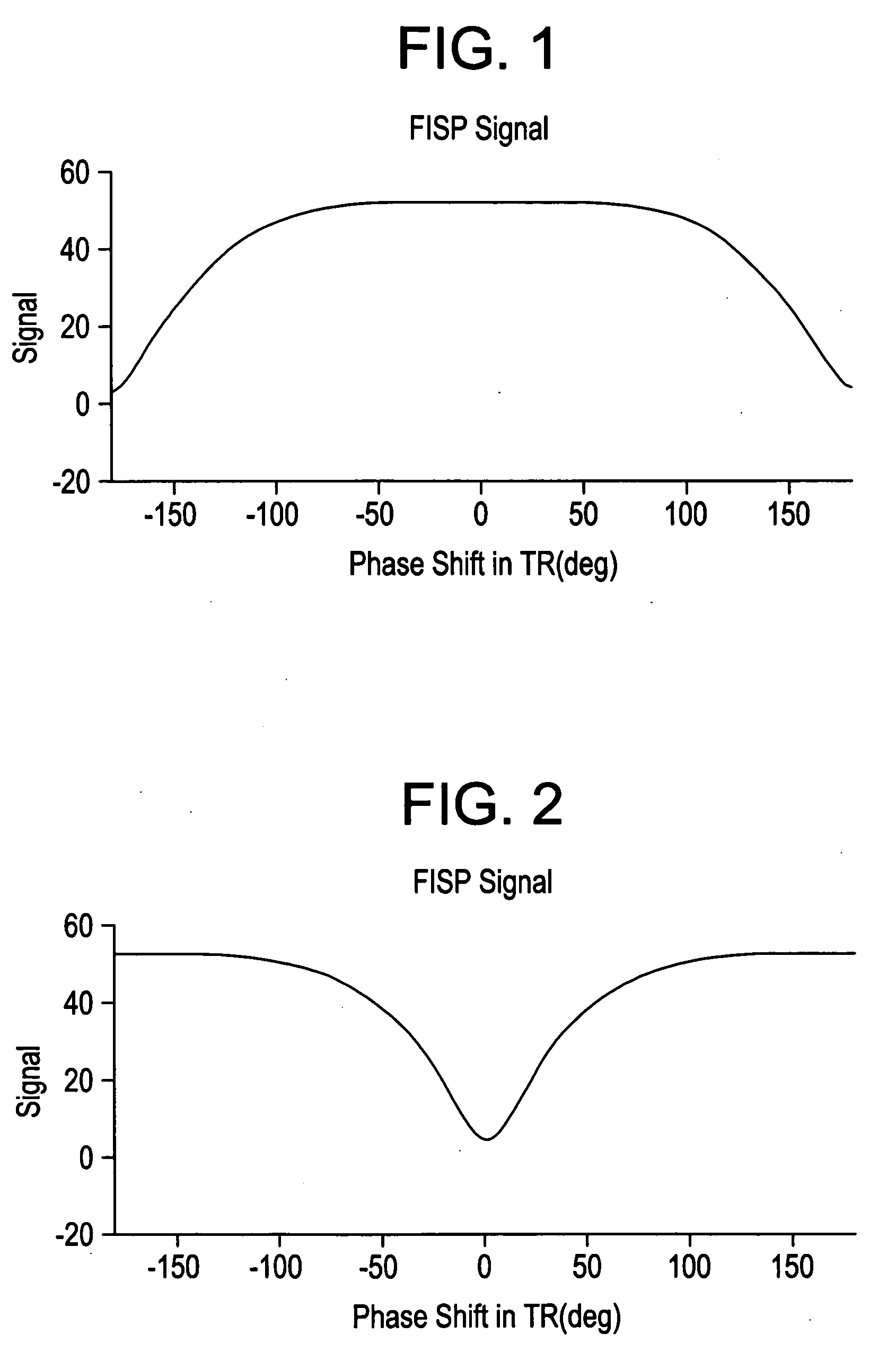
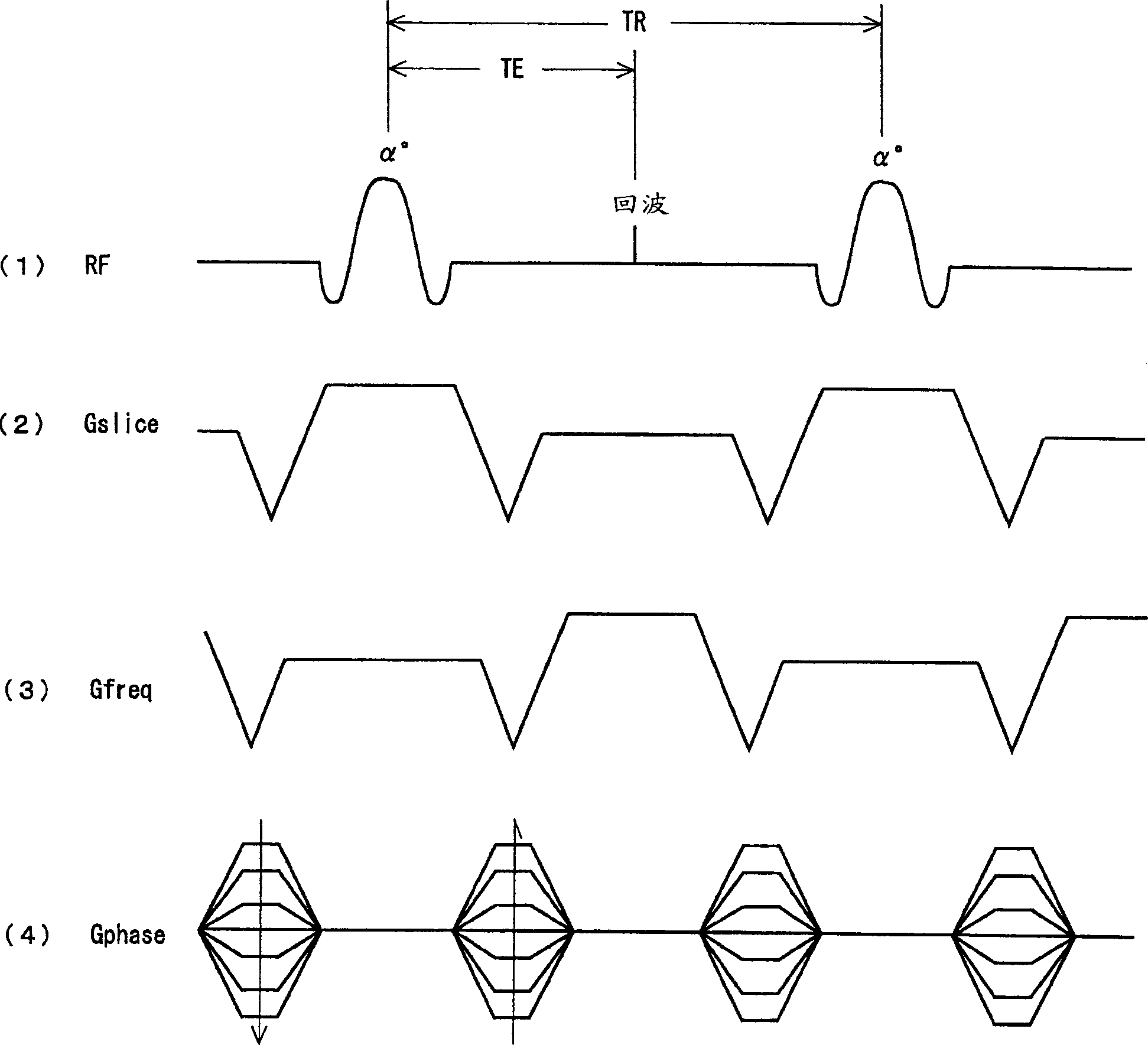
Phase cycling method in SSFP pulse sequence and magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20060088083A1Reduce artifactsUnuniformity of magnetic field is relatively satisfactoryDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhase shiftedMagnetization
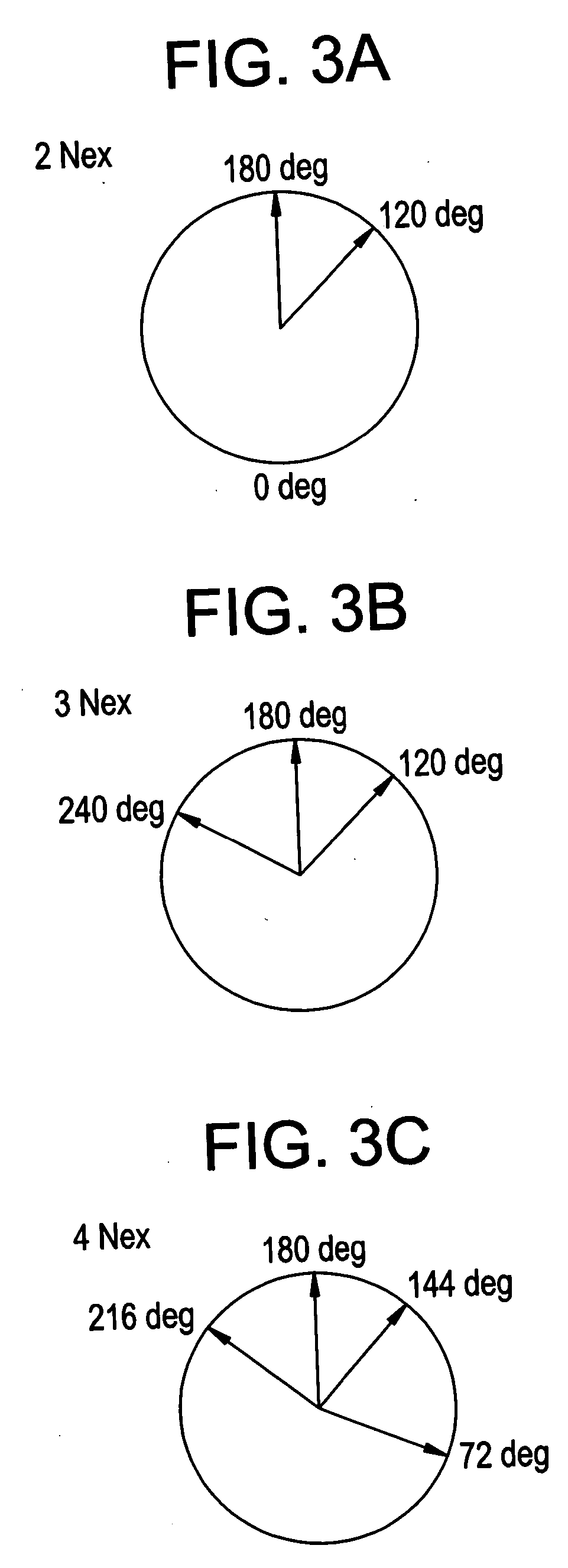
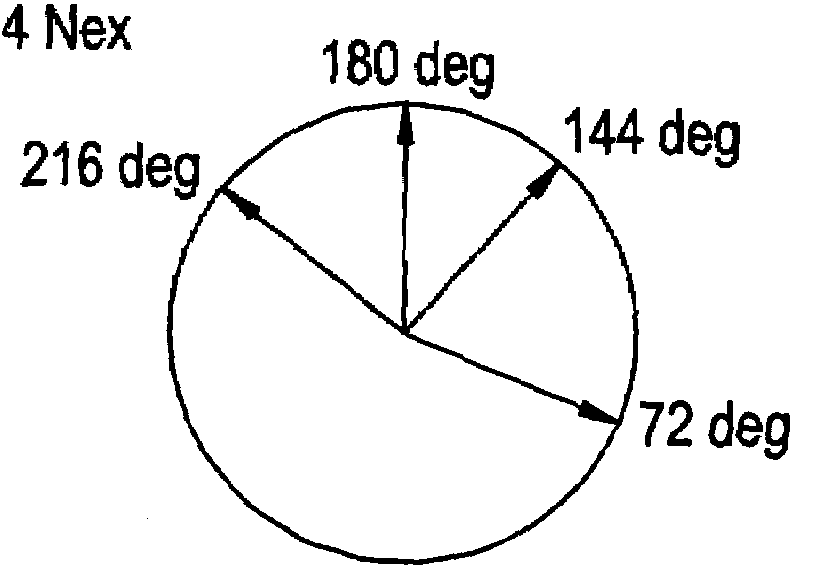
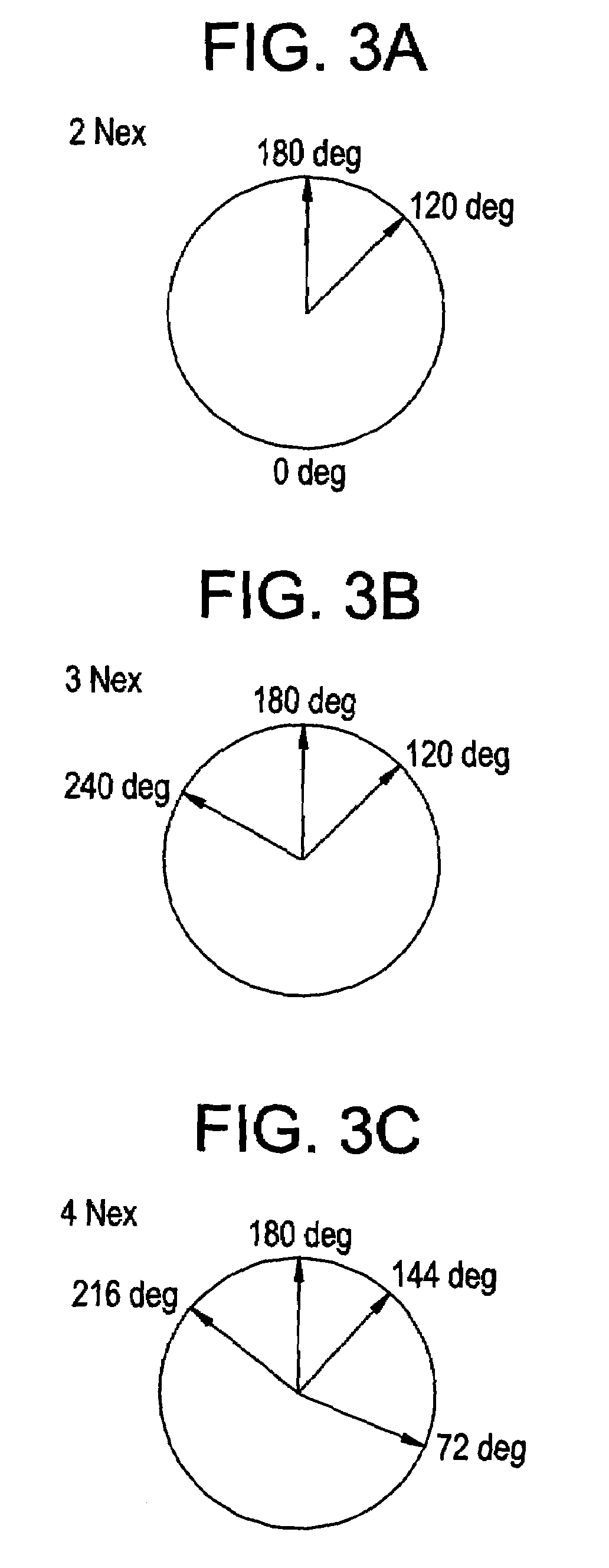
In order to positively decrease the band artifact on the middle of image when the field ununiformity is relatively fair and Nex is small, the present invention provides a phase cycling method for use in SSFP pulse sequence of a gradient echo system for rolling back the phase shift of lateral magnetization developed in TR by the gradient field prior to the next RF excitation, by identifying the RF transmission phase developing the band artifact in the vicinity of zero amount of phase shift, namely the repetition of 0-0-0-0 (degrees) as unusable RF transmission phase to use a plurality of RF transmission phases other than the unusable RF transmission phase for the phase cycling.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Bi-directional print masking
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
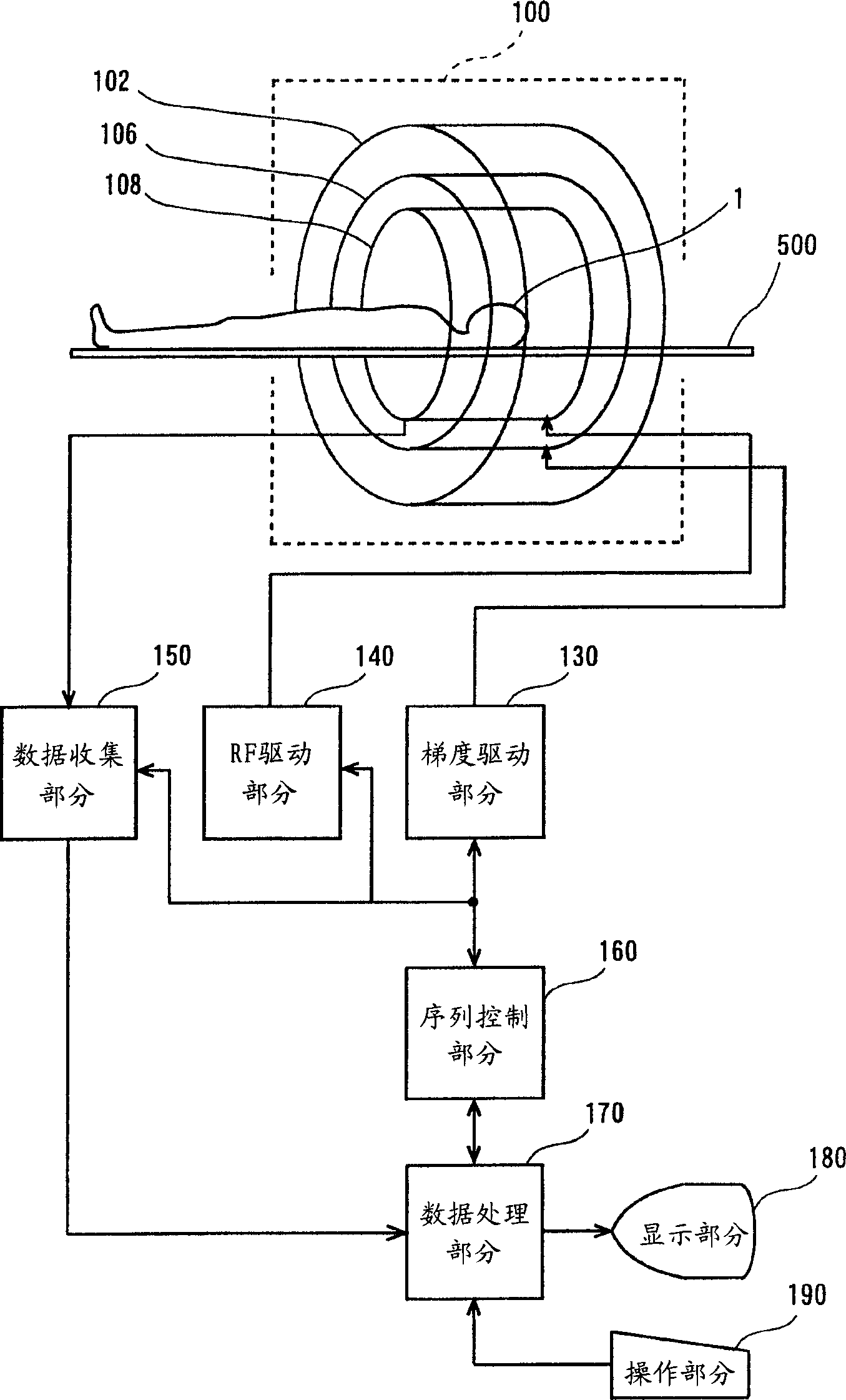
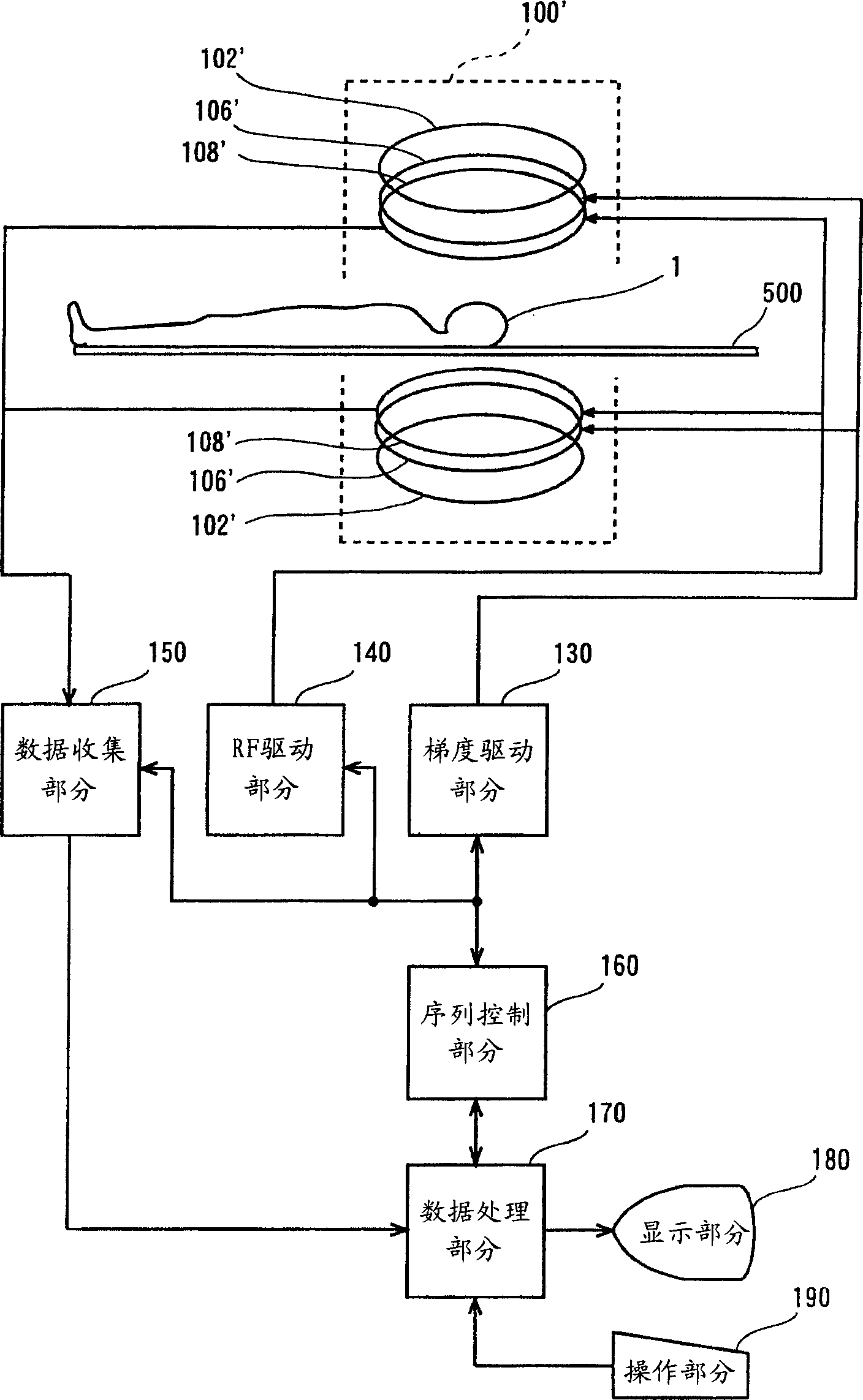
Magnetic resonance image forming equipment
InactiveCN1496706AMagnetic property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringPhase differenceResonance
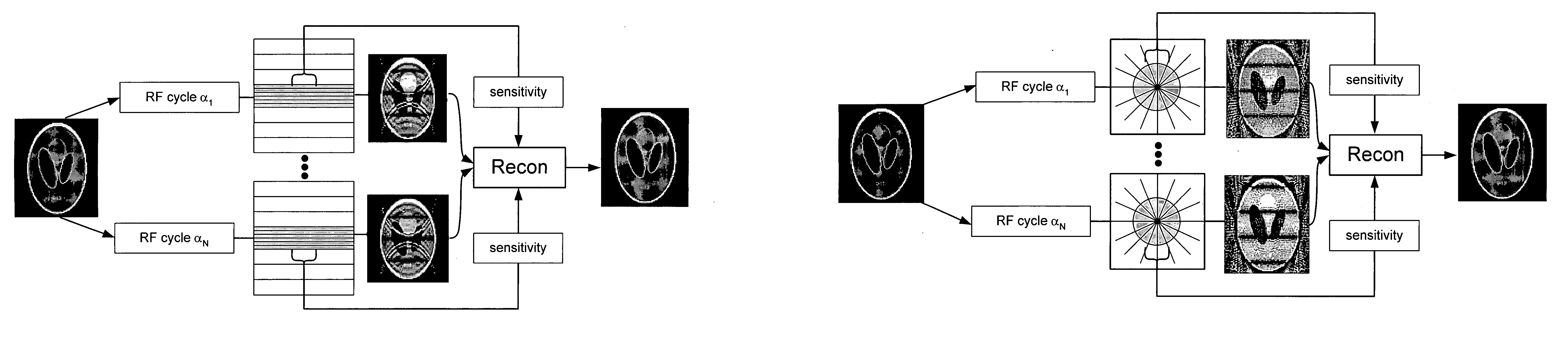
For the purpose of providing a magnetic resonance imaging apparatus for capturing water / fat-separated images free of banding artifacts in an SSFP state, an apparatus comprises: acquiring means (202) for acquiring echo data of a plurality of views in which a phase difference between water and fat is 2pi / m (m>=2) with spins within a subject brought to the SSFP state and repeating the acquisition for k=0 through M-1 with a step difference in a phase of an RF pulse of 2pi.k / M; transforming means (204) for conducting Fourier transformation on the echo data based on the phase step difference; separating means (206) for separating water data and fat data respectively in F(0) term and F(1) term of the Fourier-transformed data using the phase difference between water and fat; adding means (208') for obtaining a sum of absolute values of at least the water data or fat data in the F(0) term and F(1) term; and image producing means (210') for producing an image based on the sum data.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
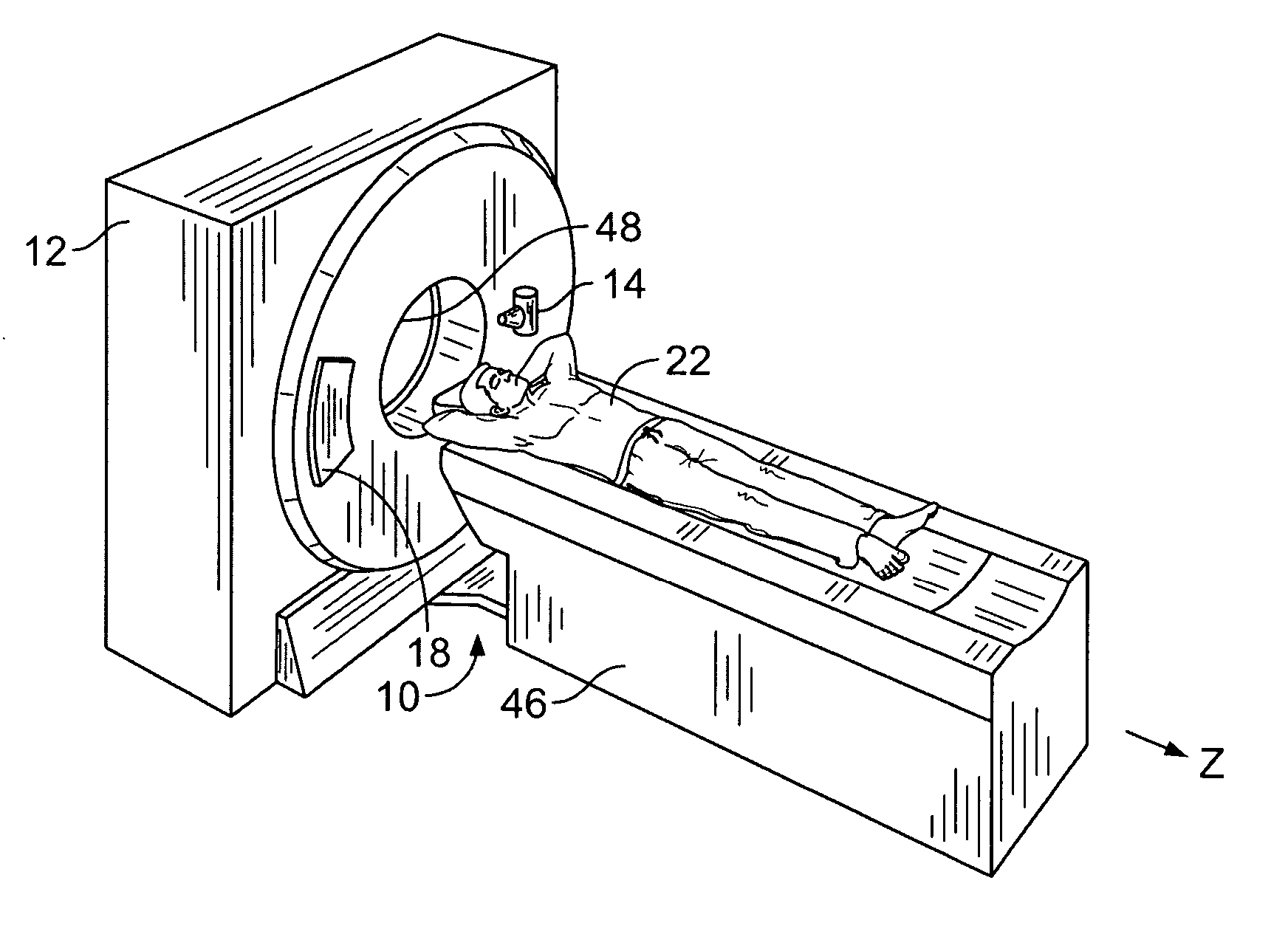
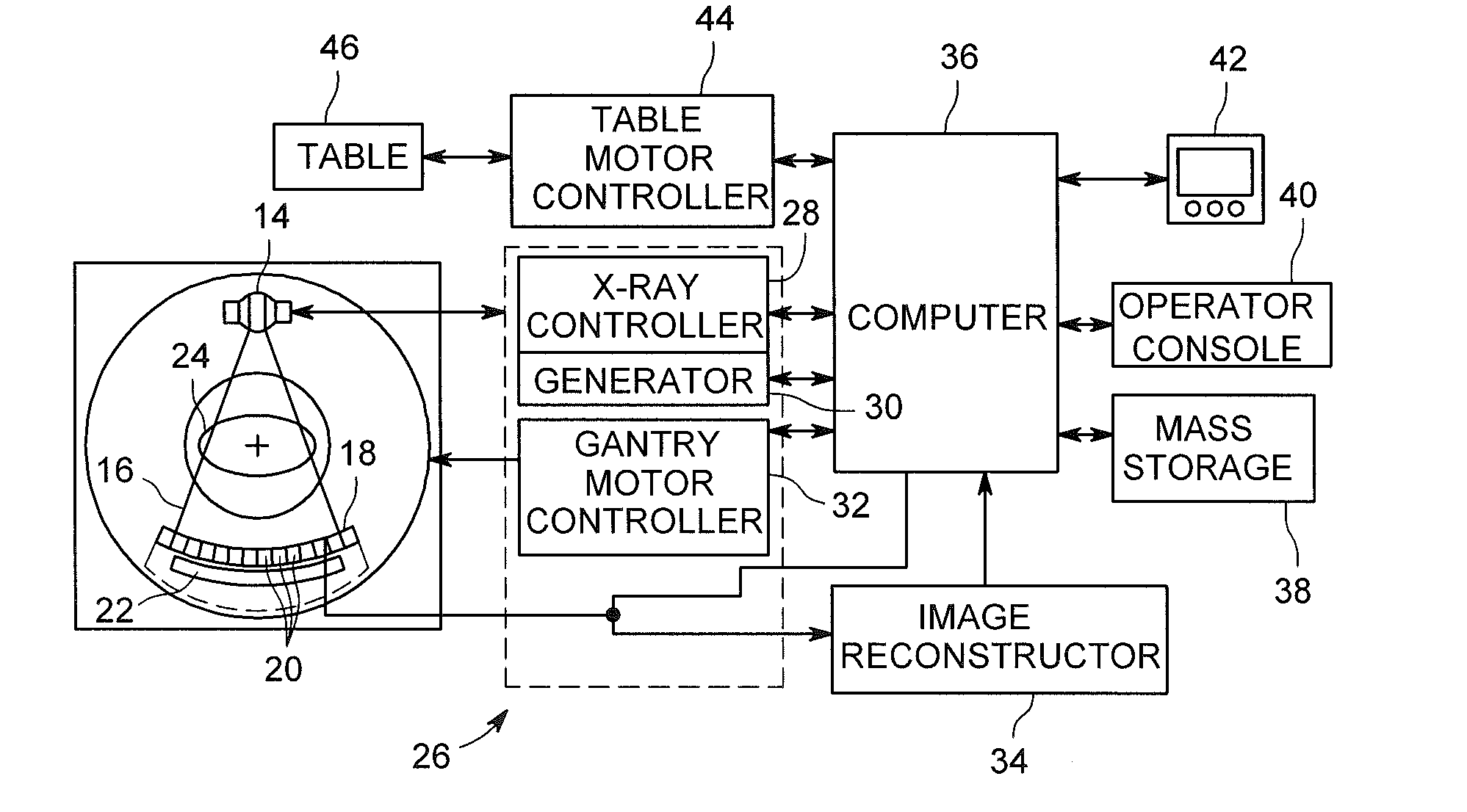
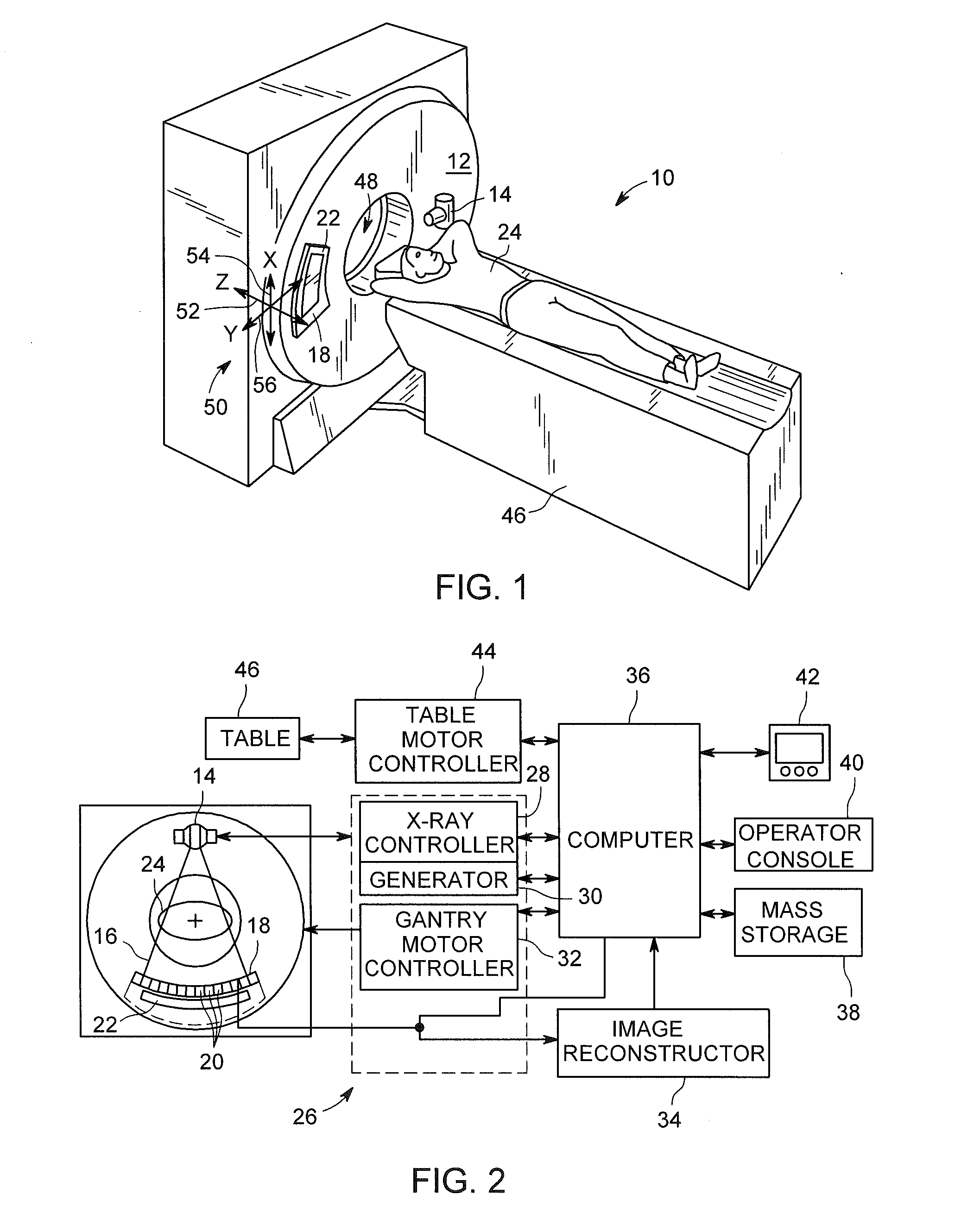
System and method of correcting banding artifacts in cardiac ct
ActiveUS20140362970A1Improve greyscale de-bandingReduce vessel mis-registrationImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionX-rayComputer vision
A CT system includes a gantry having a rotatable base and having an opening for receiving an object to be scanned, an x-ray source, a CT detector, and a computer programmed to detect a mis-registration at a slab boundary between a first slab and a second slab of a reconstructed image, quantify an amount of mis-registration at the slab boundary, and adjust the reconstructed image at the slab boundary based on the quantification.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
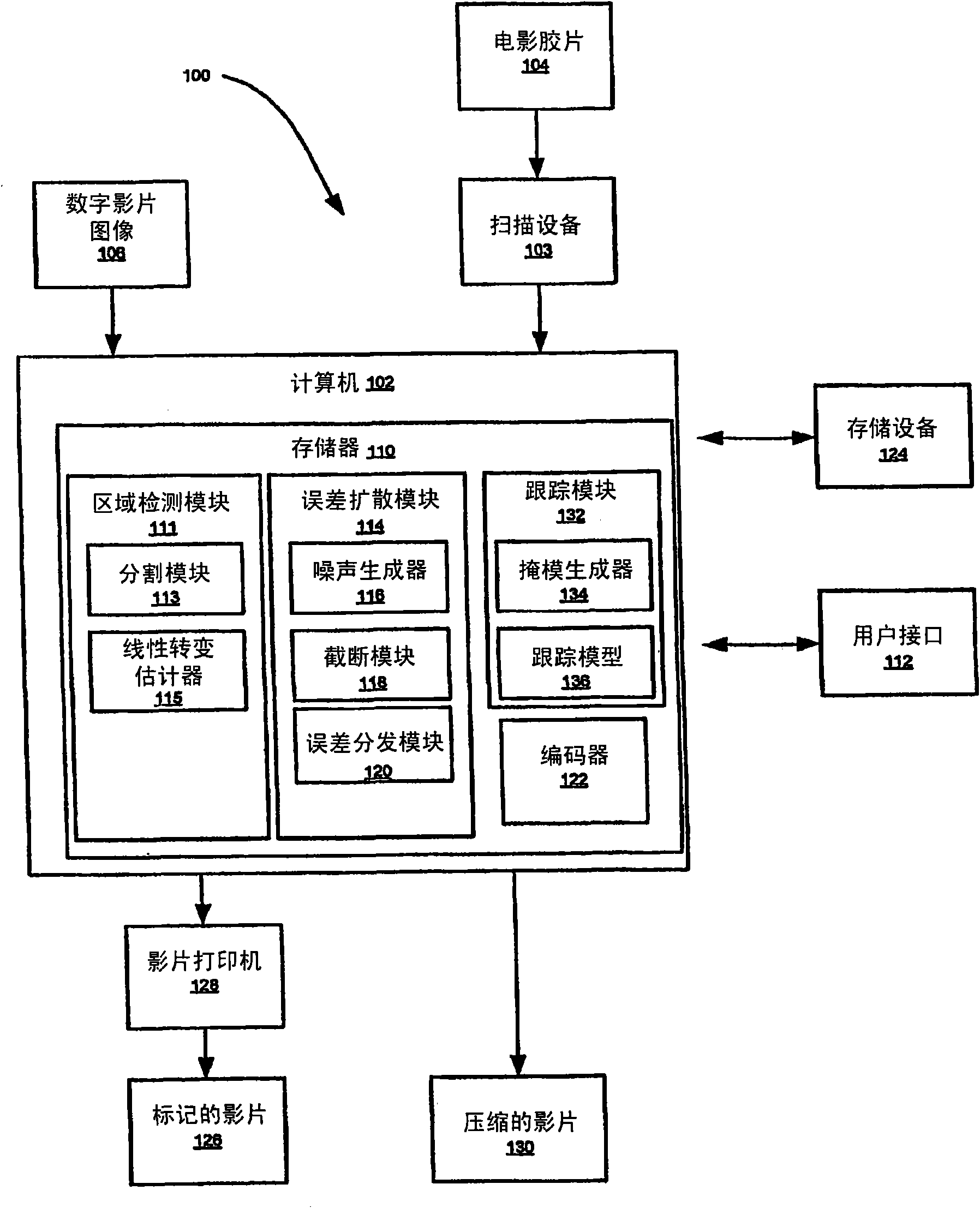
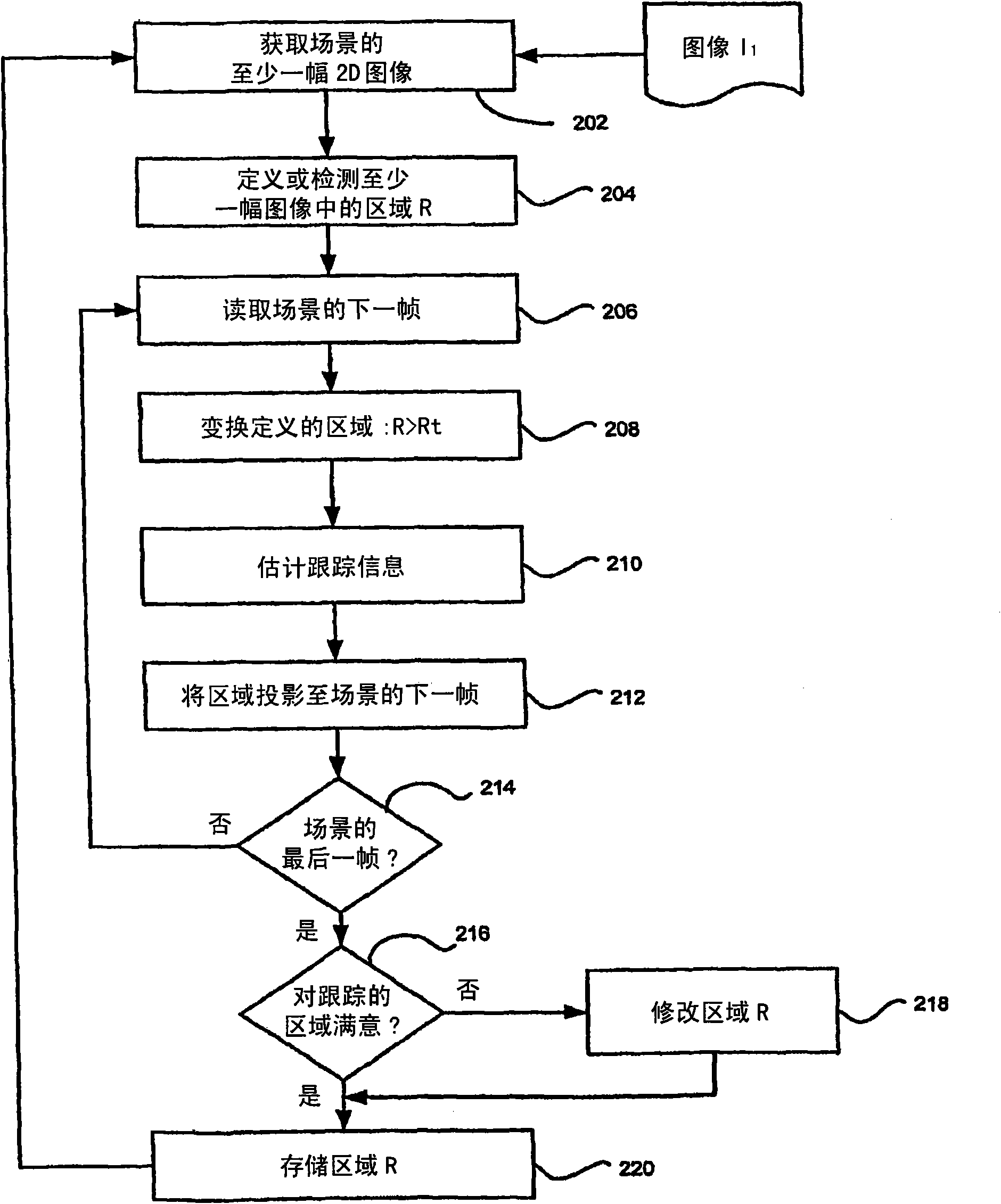
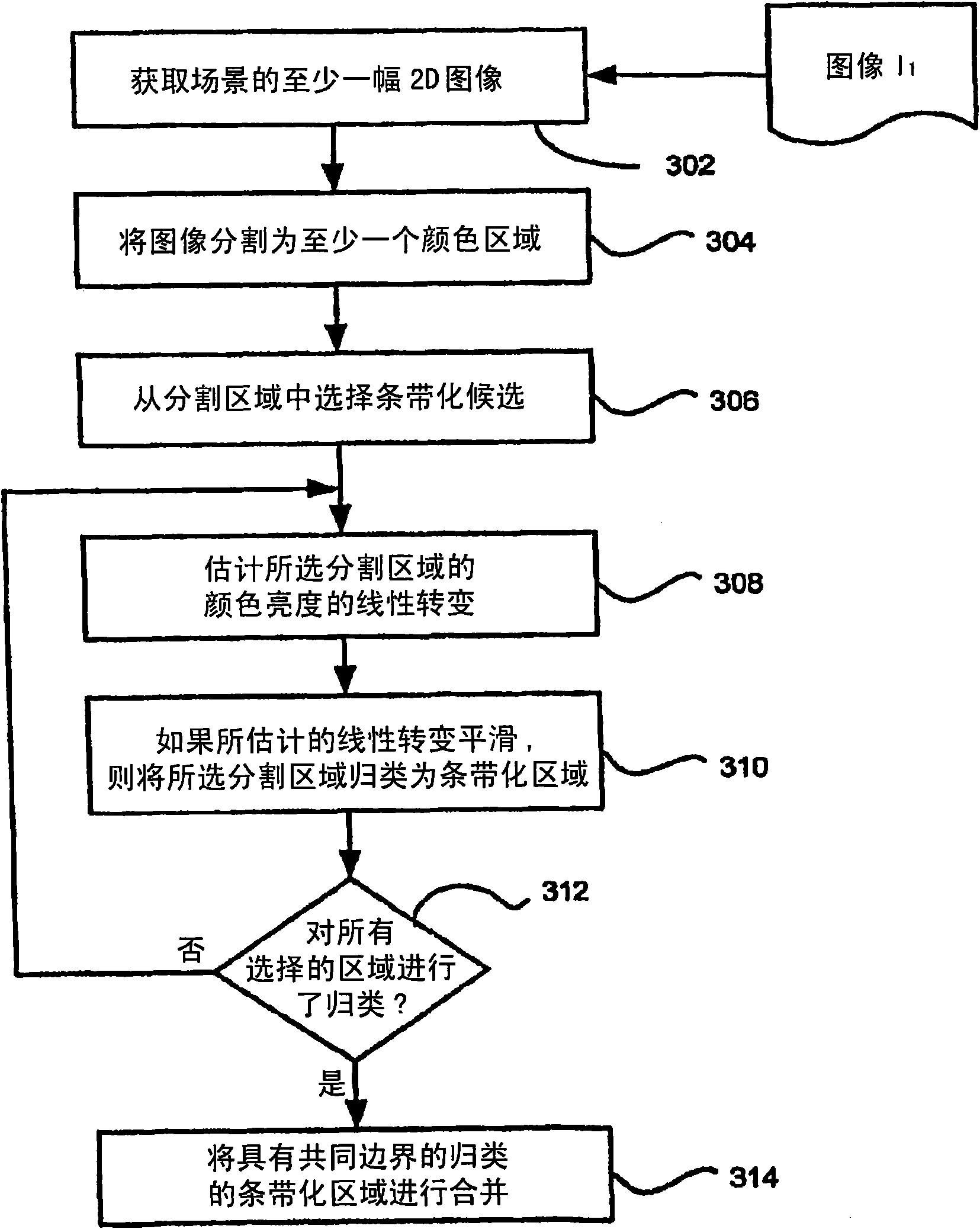
Apparatus and method for reducing artifacts in images
An apparatus and method of the present disclosure provides an automatic banding region detection function for detecting an image region that has a smooth linear transition of color intensity and is prone to have banding artifacts in image processing. The apparatus and method use a parametric model based approach to detect the banding region. The apparatus and method provide for segmenting at leastone first image into at least one homogeneous color region (304), estimating the linear transition of color intensity for the at least one homogeneous color region (308), and if the linear transitionof color intensity is substantially smooth, classifying the at least one homogenous color region as a banding region (310).
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Interactive visual card-selection process for mitigating light-area banding in a pagewide array
InactiveUS20090028585A1Cost lotPoor resultInking apparatusElectrographic process apparatusSkyEngineering
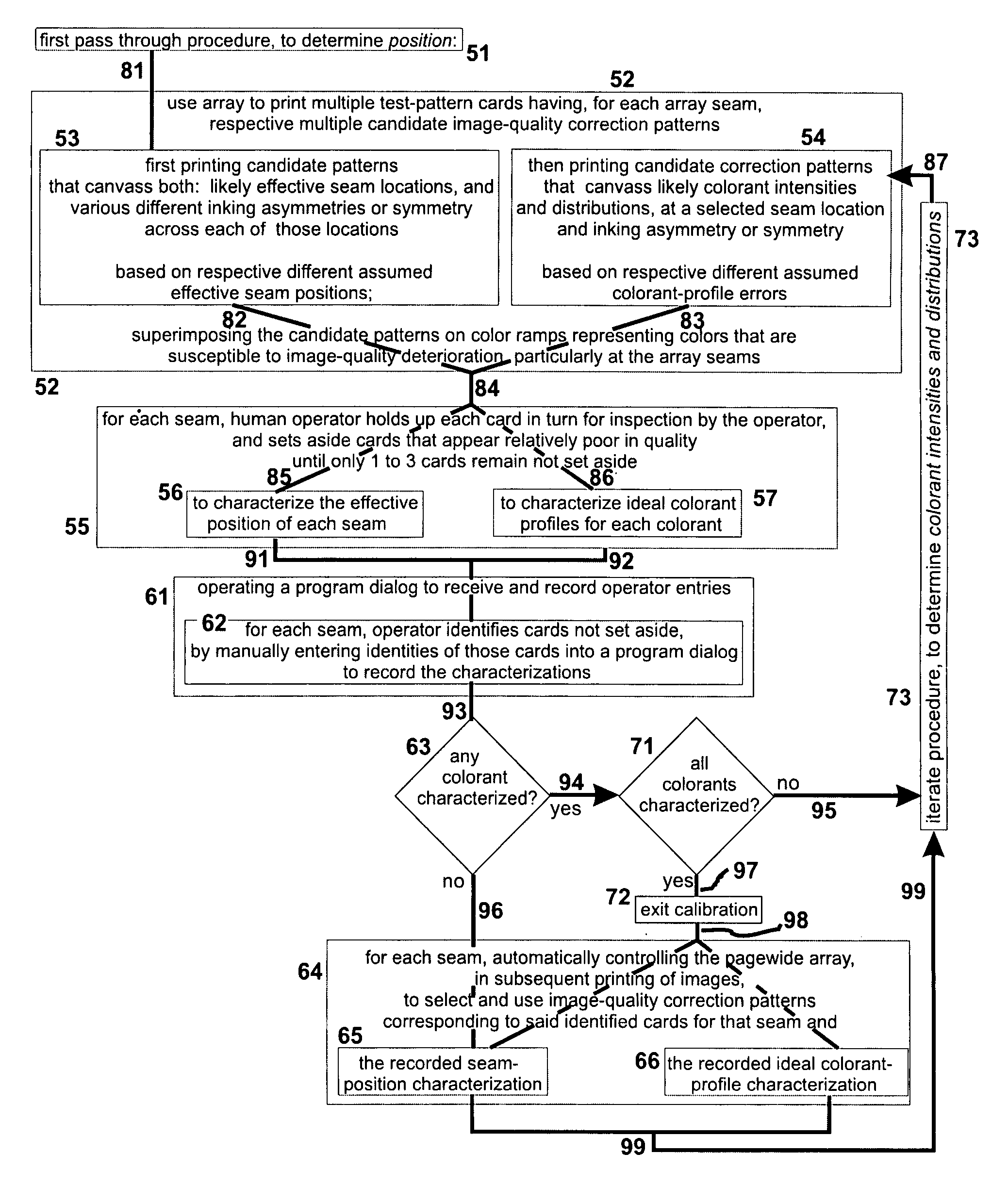
Preferably, test-patterns print on separate, multiple print-medium cards, each including a ramp with colors graded along a certain direction—and, superimposed on the ramp, a candidate add-on colorant. Ramps preferably are printed in so-called “customer colors”, common in snapshots and particularly snapshot regions that include sky. Positions or amounts of the candidate add-on colorant canvass a likely range of values that optimize camouflaging or suppression of a banding artifact (due to seams in the pagewide array) that is extended along the same certain direction. For each seam and each “customer color” used, an operator holds up several cards for comparison, selecting the best one to three. Operators thus can evaluate candidate colorant patterns in context of many different tones of the sky and other customer colors. Preferably banding suppression is integrated with linearization: at each seam a series of linearization tables is smoothly interpolated between measurement-based tables for adjacent inkjet dice.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method and apparatus for reducing artifacts in computed tomography (CT) image reconstruction
ActiveUS20150092907A1Reduce artifactsImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionMetal ArtifactTomography
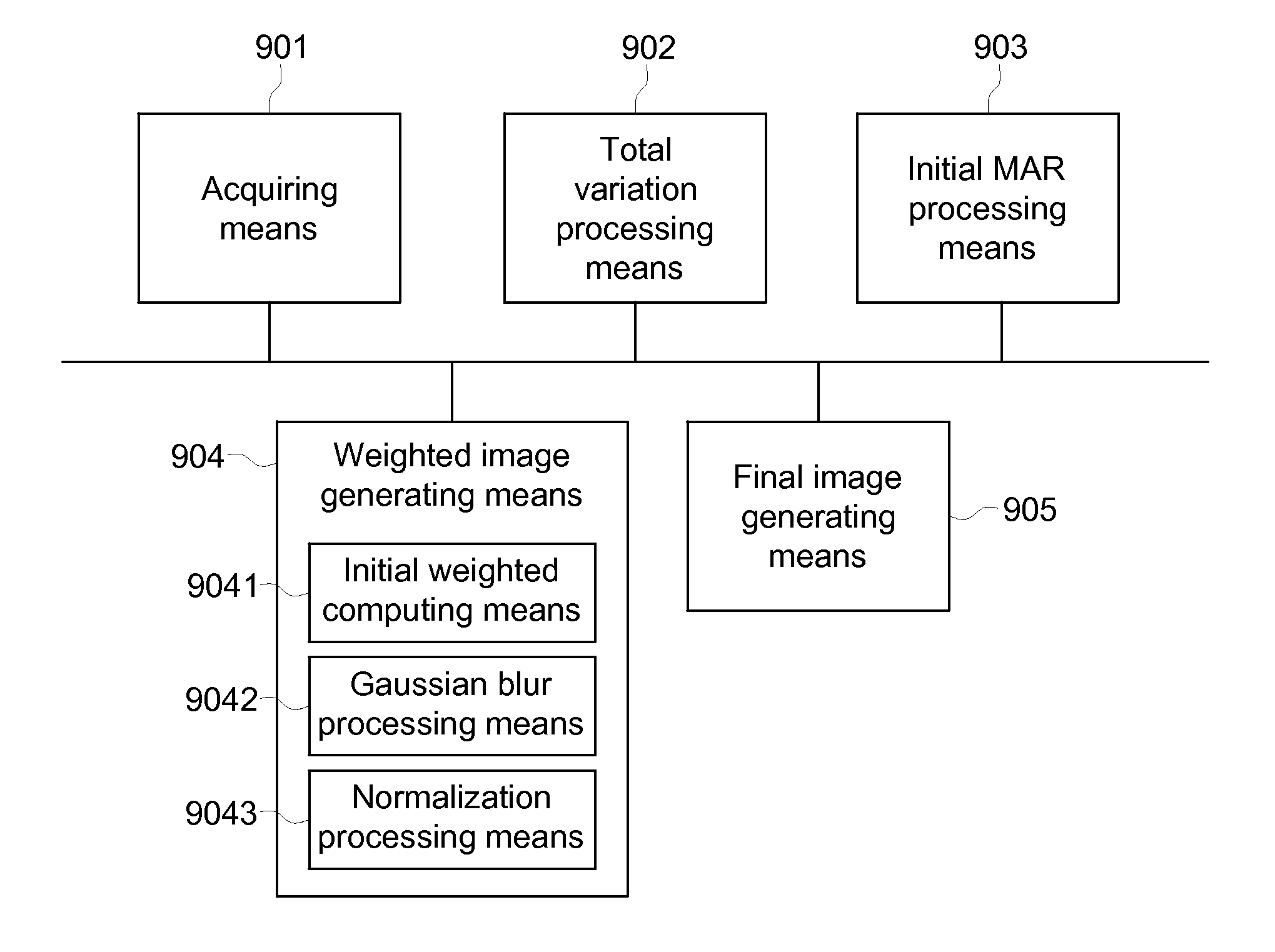
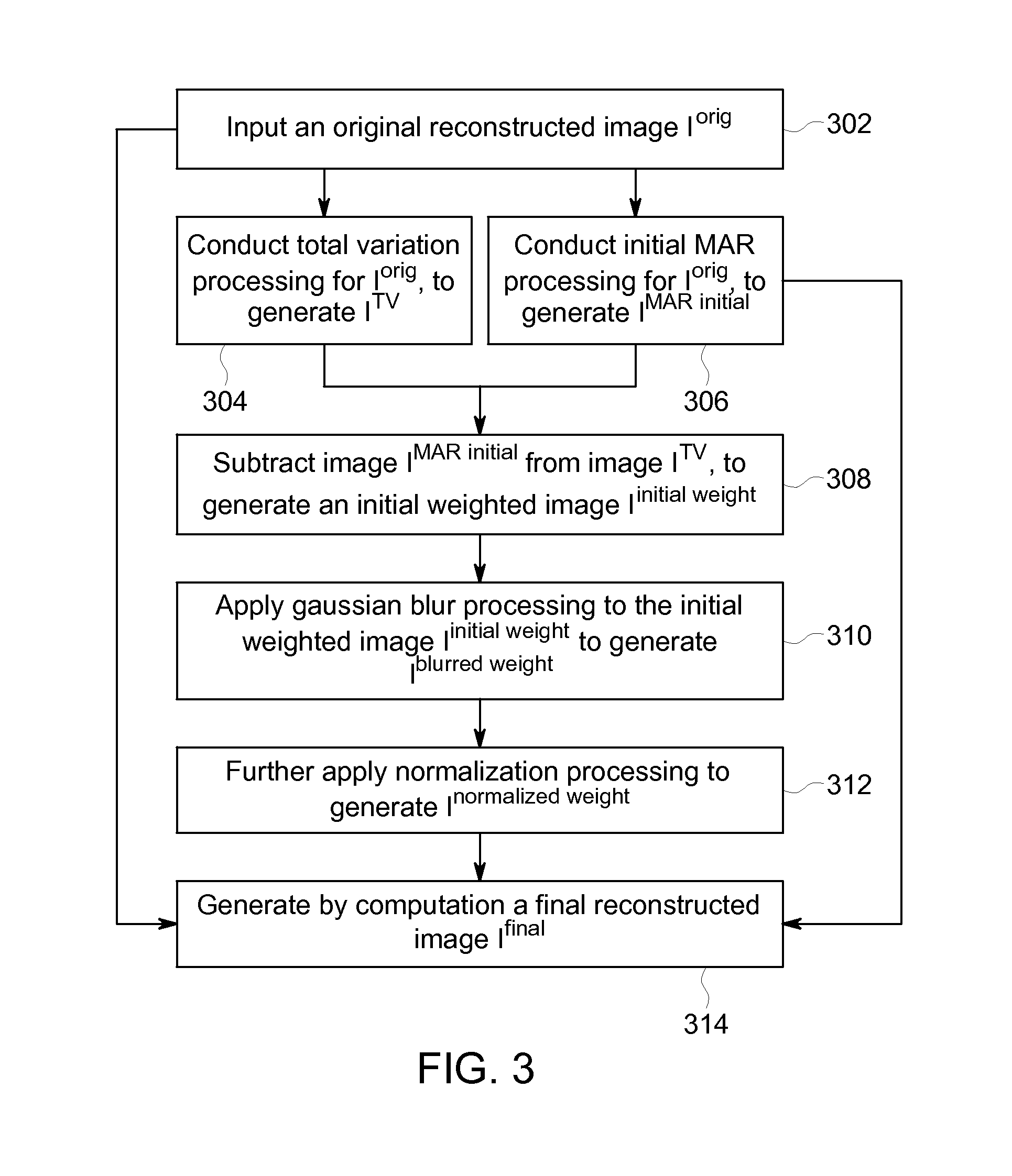
A method and apparatus for reducing artifacts in Computed Tomography (CT) image reconstruction. The method includes: acquiring an original reconstructed image; conducting total variation processing for the original reconstructed image, to generate a total variation reconstructed image; conducting initial metal artifact reduction processing for the original reconstructed image, to generate an initial metal artifact reduction reconstructed image; generating a weighted image based on the total variation reconstructed image and the initial metal artifact reduction reconstructed image, wherein the weighted image reflects that the original reconstructed image contains white-band artifacts; and combining a portion of the original reconstructed image and a portion of the initial metal artifact reduction reconstructed image through the weighted image to generate a final image, wherein the final image does not contain white-band artifact.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Artifact reduction in ssfp MRI using super field view reconstruction
ActiveUS20060214660A1Reduction in banding artifactReduce scan timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionAugmented matrixCondensed matter physics
Banding artifacts in steady state free precession (SSFP) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are reduced by acquiring and combining multiple SSFP images in an augmented matrix where an acquisition vector in k-space is equal to a Fourier matrix of the trajectory on a known distortion operator for each trajectory in k-space.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
General banding and codec banding artifact removal
A method and apparatus are disclosed for identifying and removing banding artifacts (i.e., false contours) resulting from insufficient bit depth caused by digital image quantization, conversion, and / or compression. This method includes: explicitly identifying texture block and flat block; de-termination of filter window sizes with the consideration of handling transitions between texture block and flat block; de-banding filtering with edge protection; and noise shaping according to de-banding filter result.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
Phase cycling method in SSFP pulse sequence and magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
ActiveUS7327139B2Reduce artifactsUnuniformity of magnetic field is relatively satisfactoryDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPhase shiftedMagnetization
In order to positively decrease the band artifact on the middle of image when the field ununiformity is relatively fair and Nex is small, the present invention provides a phase cycling method for use in SSFP pulse sequence of a gradient echo system for rolling back the phase shift of lateral magnetization developed in TR by the gradient field prior to the next RF excitation, by identifying the RF transmission phase developing the band artifact in the vicinity of zero amount of phase shift, namely the repetition of 0-0-0-0 (degrees) as unusable RF transmission phase to use a plurality of RF transmission phases other than the unusable RF transmission phase for the phase cycling.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
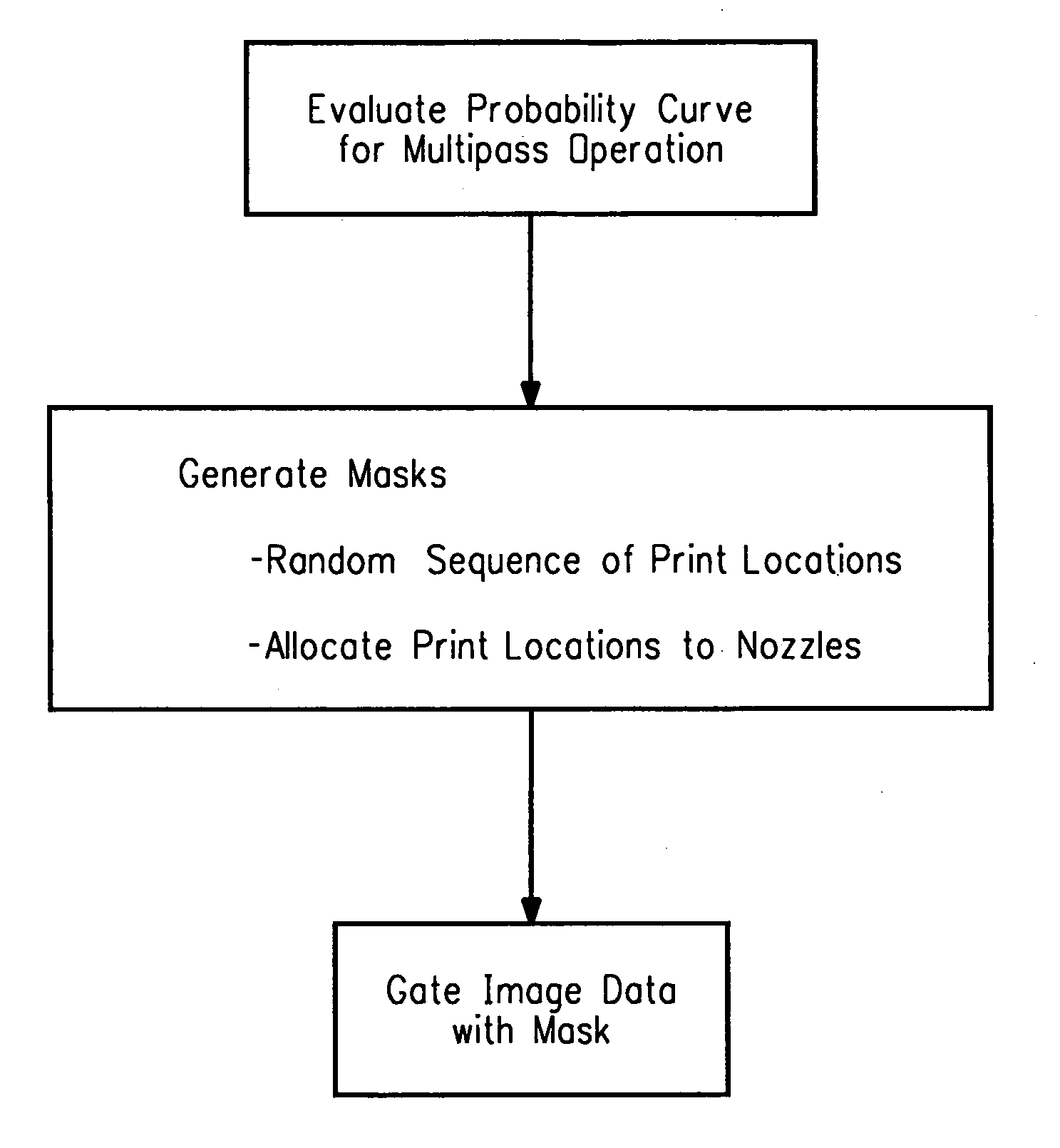
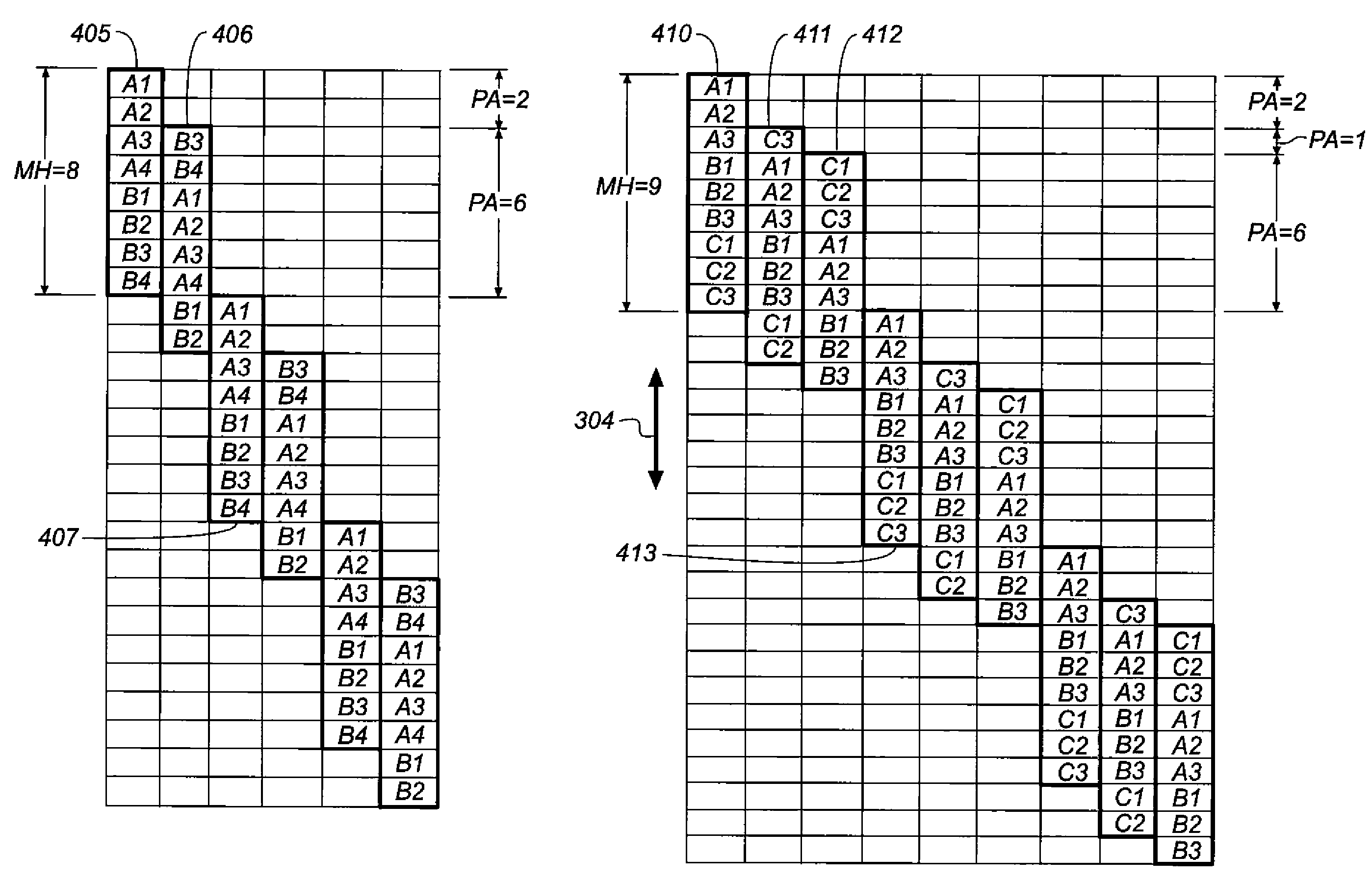
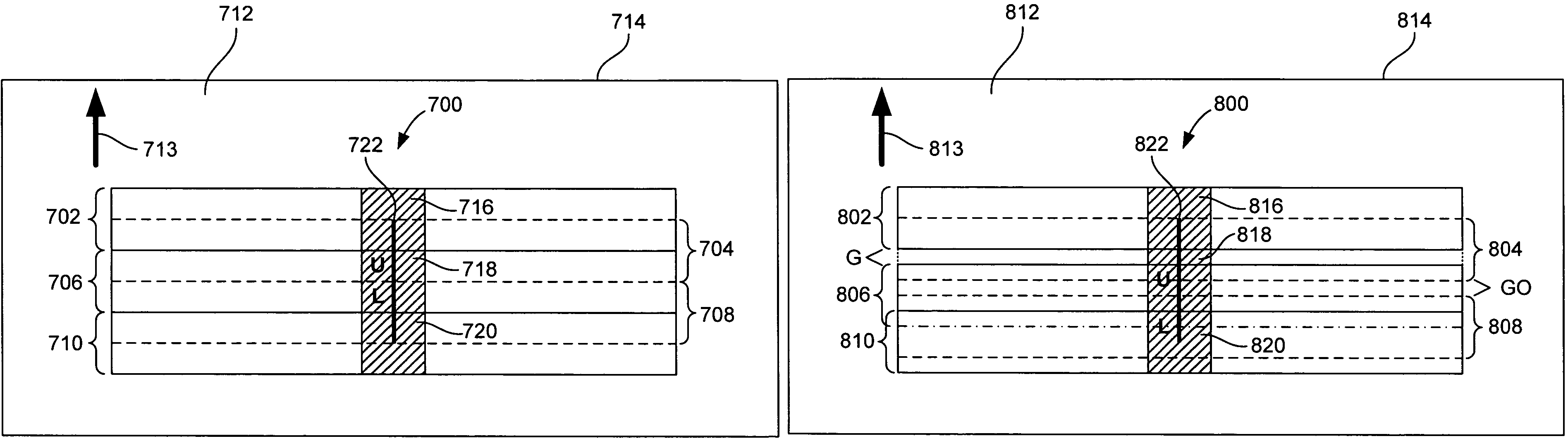
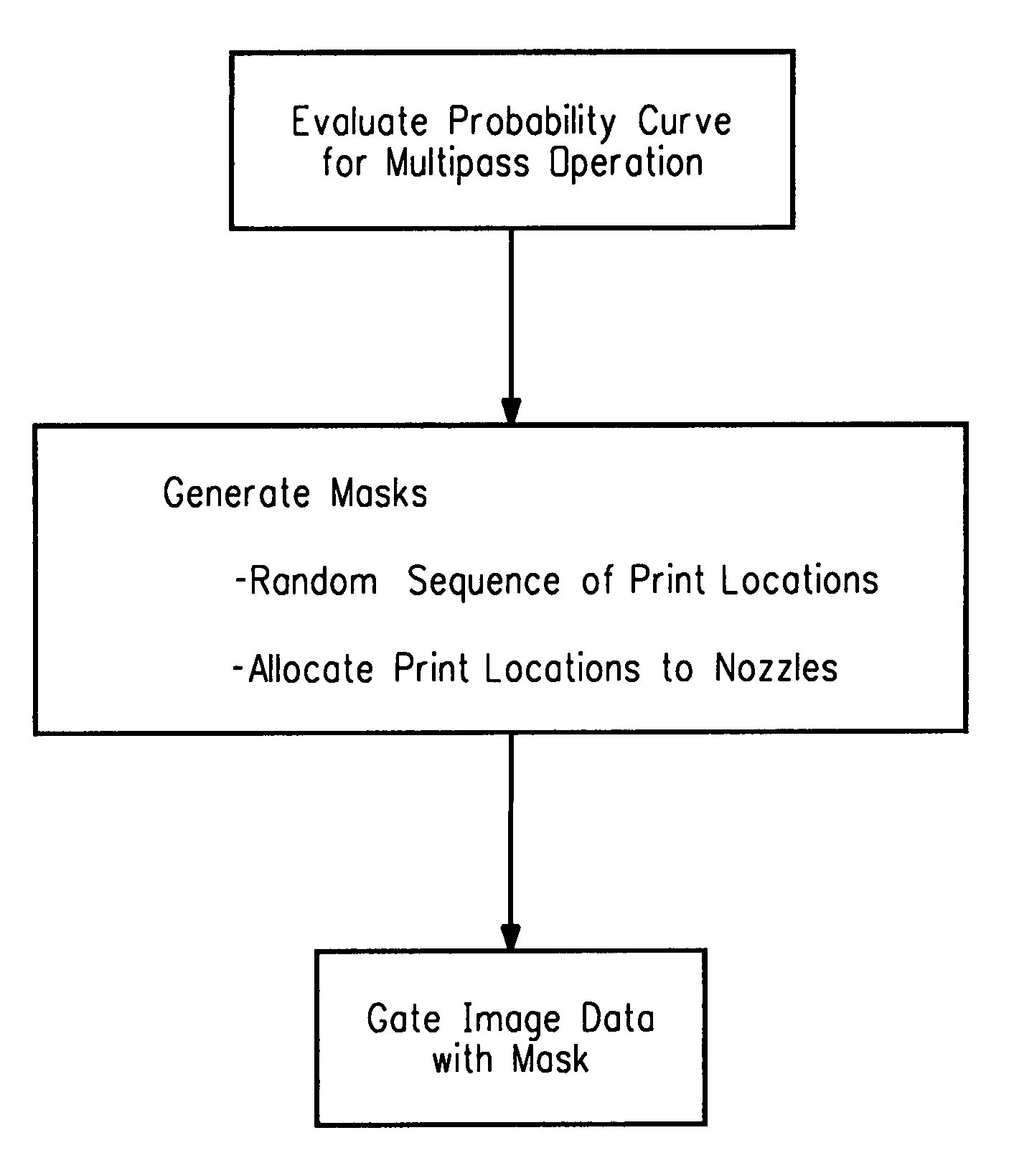
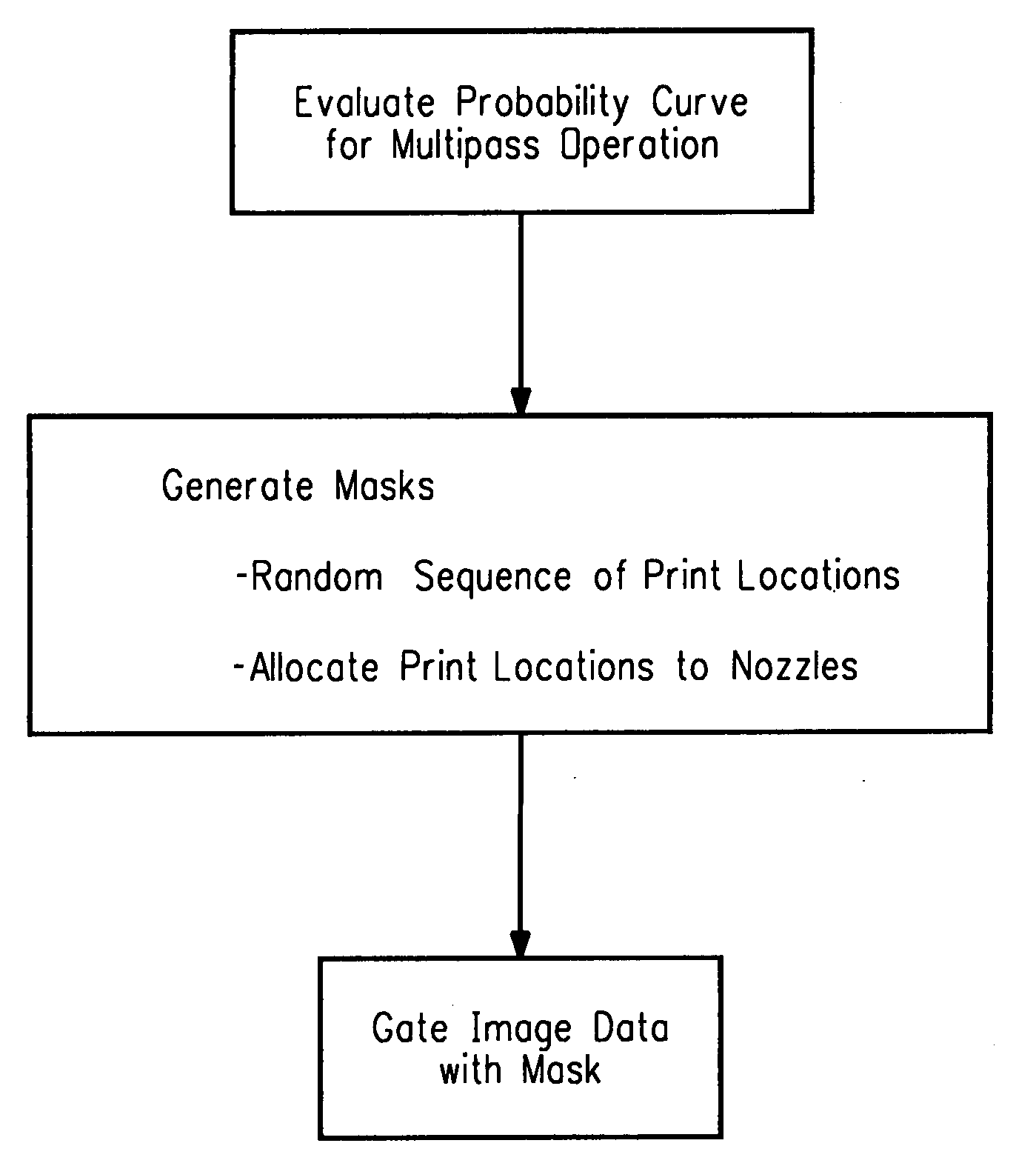
Computer readable medium with a program for minimizing banding artifacts in an ink jet printing apparatus
InactiveUS20080316258A1Minimizes deleterious banding effectDeleterious effectOther printing apparatusComputer printingEngineering
A computer readable medium contains a program for causing a printer to execute a multipass printing method characterized in that, on any given pass, the number of selected print locations onto which printing ink is deposited by each of N nozzles varies from nozzle to nozzle. The variation is governed in accordance with a weighted smoothing spline function, particularly a polynomial B-spline function of the order “j”, where j is a value equal to one less than the number of passes.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Image printing method with reduced banding
InactiveUS20110243587A1Reduce artifactsReduce wearElectrographic process apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Banding artifact detection in digital video content
A method and system for identifying and determining banding artifacts in digital video content composed of a sequence of moving video pictures includes creating a mask image corresponding to a picture from said sequence of moving video pictures based on global gradient changes to detect potential areas containing banding artifacts. The values of the mask image are scaled thereby making banding artifact detection possible using gradient operators. The banding artifacts are then identified / detected based on the local gradients.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Nonuniform mask circulation for irregular page advance
InactiveUS7845751B2Reduce artifactsDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsComputer scienceBanding Artifact
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
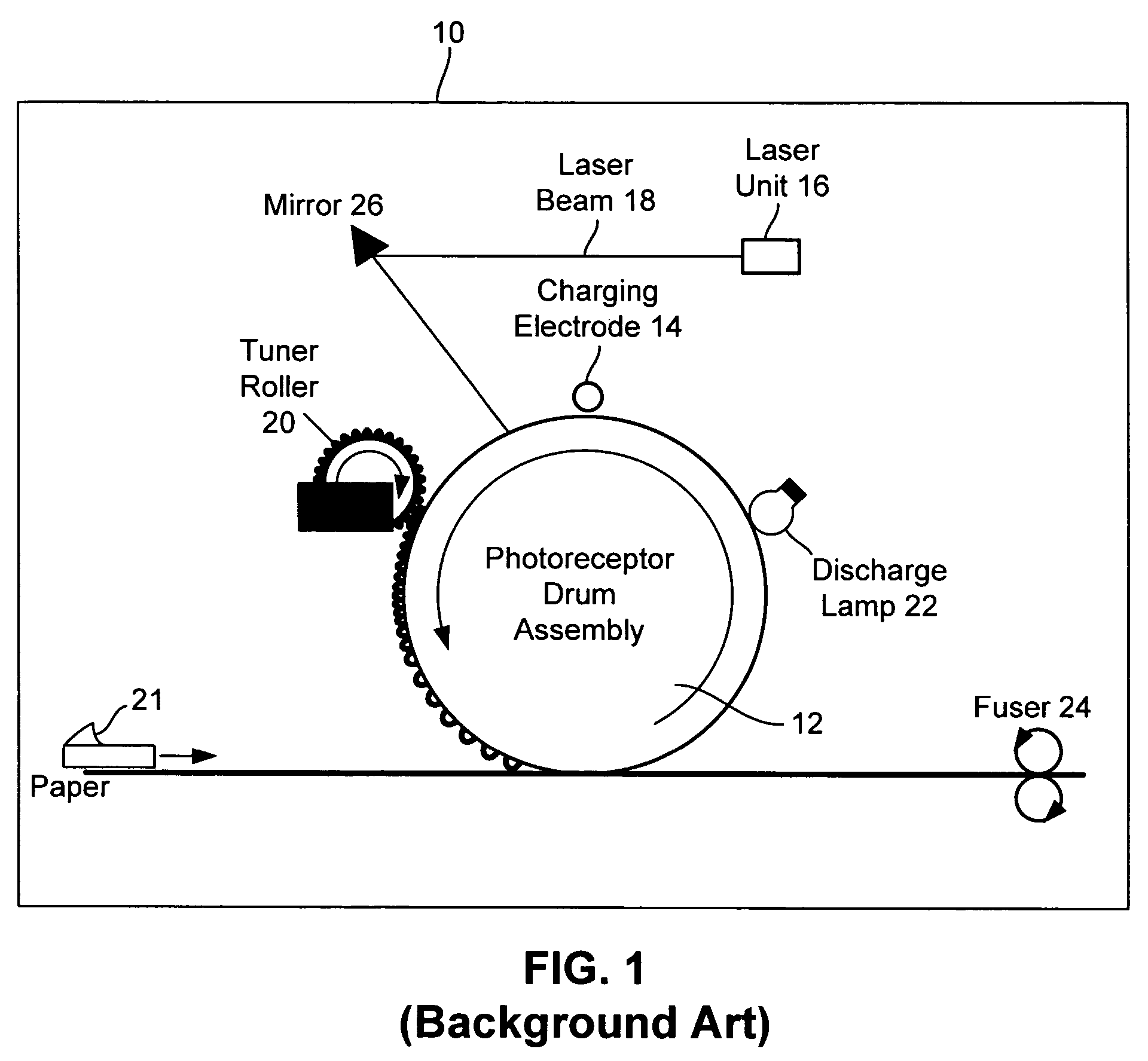
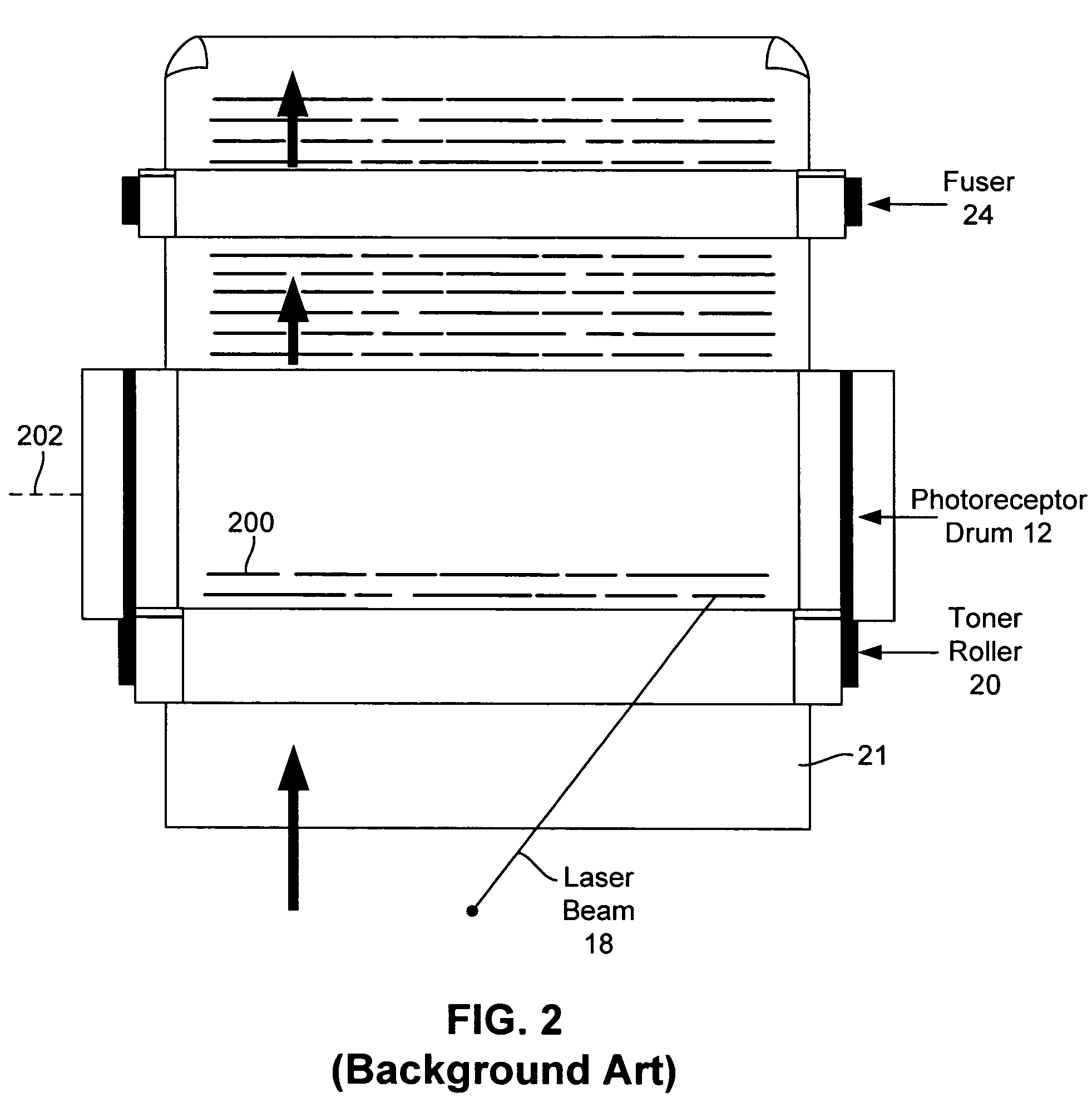
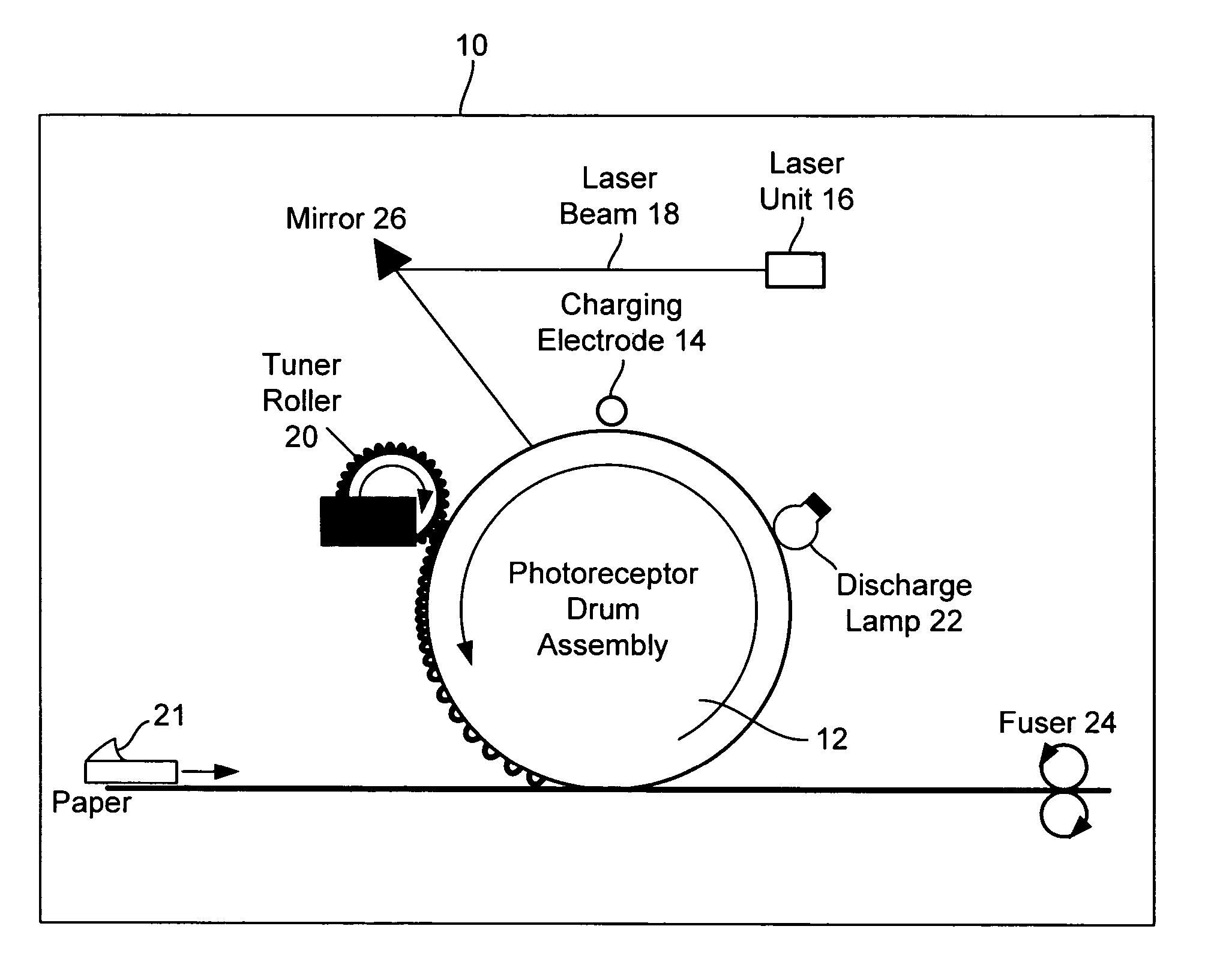
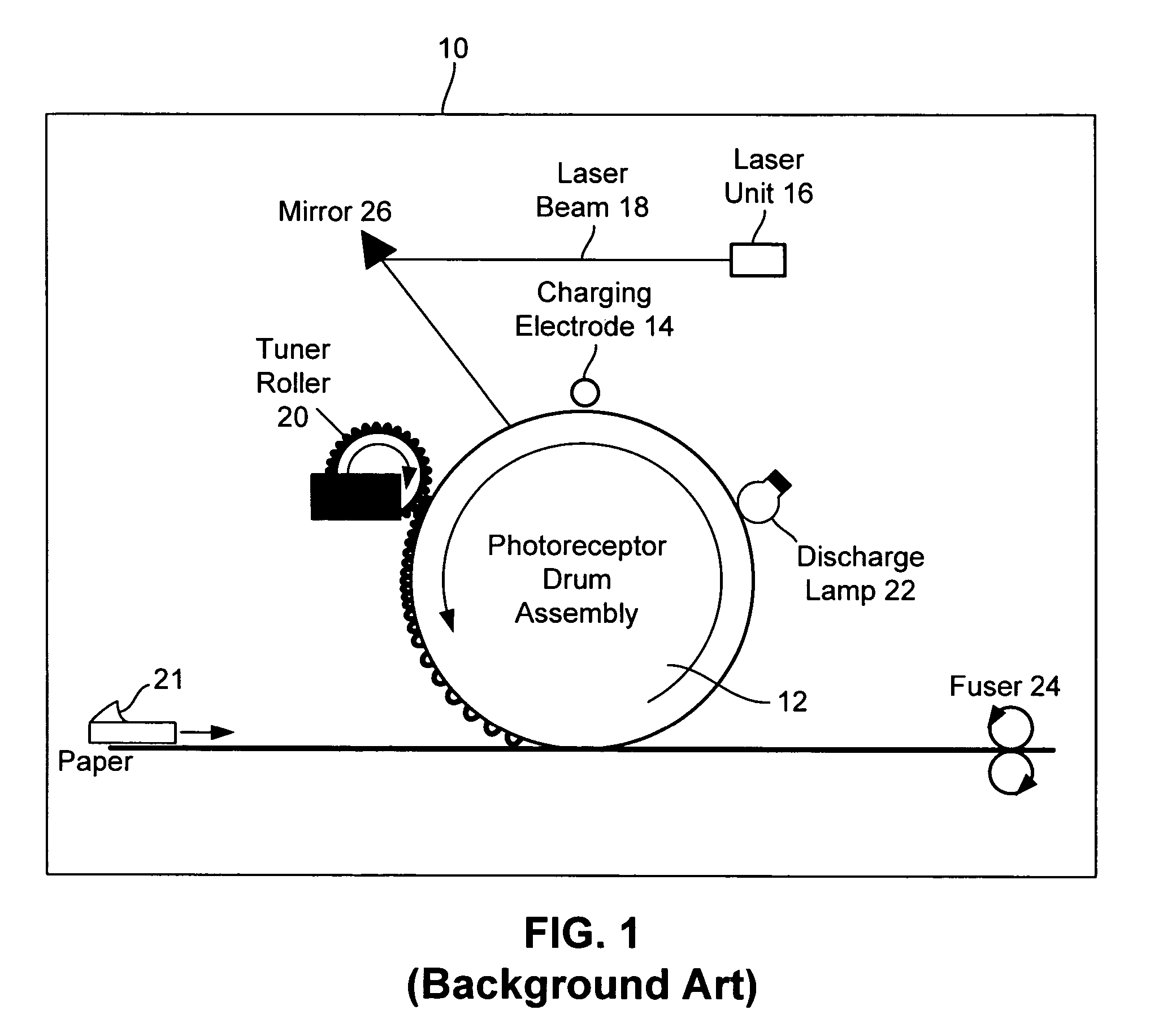
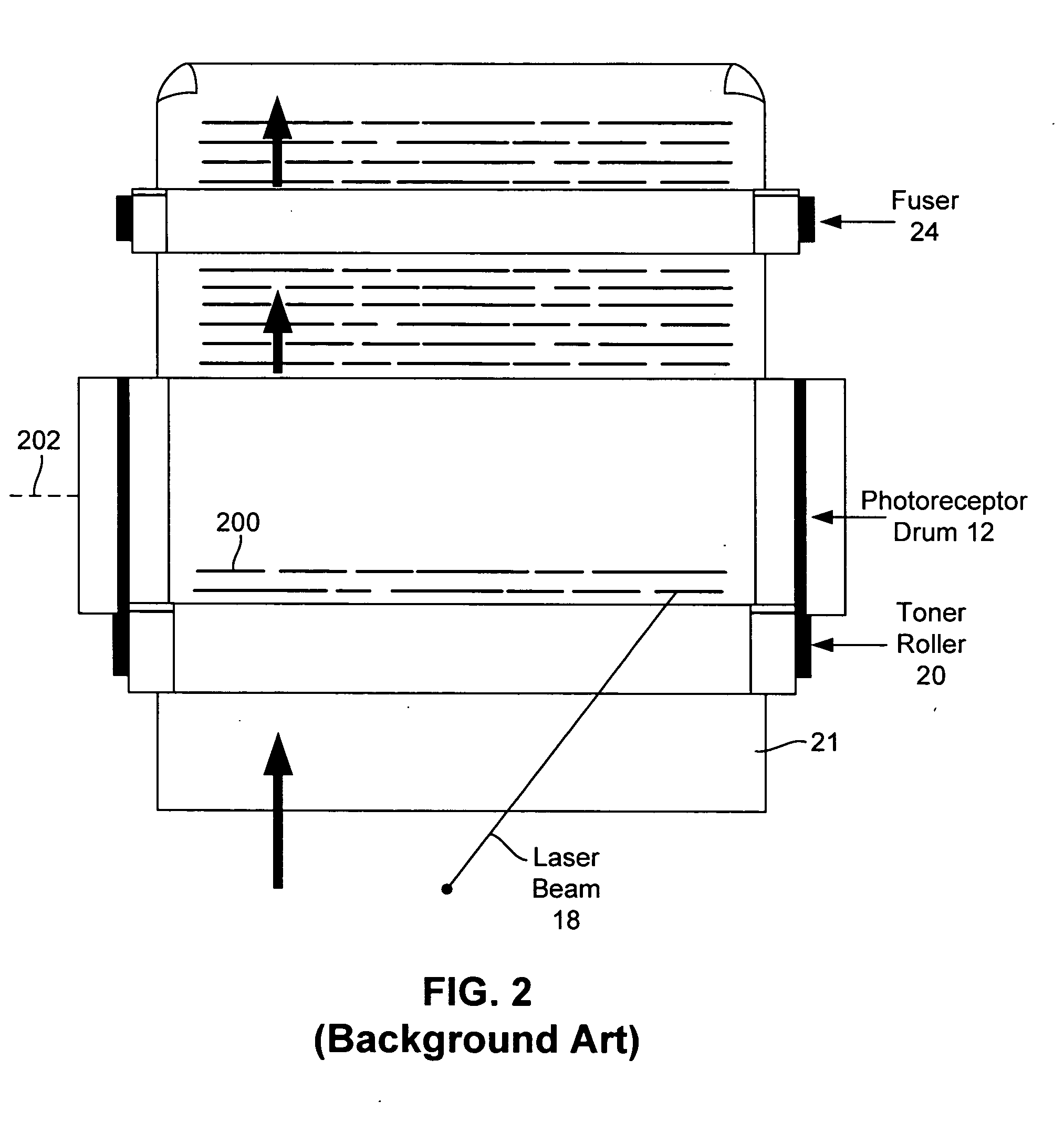
Laser printer with reduced banding artifacts
A laser scanning assembly generates a laser beam and scans the laser beam through a plurality of scan lines to form desired dots. Each scan line is positioned to overlap an adjacent scan line and each dot includes a plurality of segments. The scanning assembly scans the laser beam through multiple scan lines to fully discharge each segment of each dot. The laser scanner assembly would typically be part of a laser printer.
Owner:MARVELL INT TECH
Ink jet printing apparatus having a programmed controller that minimizes banding artifacts
A multipass printing apparatus is characterized by a computer-implemented controller that controls printing operation so that, on any given pass, the number of selected print locations onto which printing ink is deposited by each of N nozzles varies from nozzle to nozzle. The variation is governed in accordance with a weighted smoothing spline function, particularly a polynomial B-spline function of the order “j”, where j is a value equal to one less than the number of passes.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Apparatus and method of reducing banding artifact visibility in a scanning apparatus
A method of, and apparatus for, reducing the visibility of banding artifacts on a printed medium comprising producing synthetic artifacts on the printed medium, overlapping scan lines at swath boundaries and controlling exposure along a scan line to reduce the visibility of the banding artifacts.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Methods and systems to facilitate reducing banding artifacts in images
ActiveUS8364244B2Reconstruction from projectionRadiation/particle handlingBiological cyclesComputer science
Methods and systems for generating computed tomographic (CT) images from image data acquired during different biological cycles are provided. A computer is programmed to receive a plurality of scan data acquired during a gated acquisition window of each of a plurality of biological cycles, blend the scan data acquired during a first of the plurality of biological cycles with the scan data acquired during a second of the plurality of biological cycles, and construct a final image from the blended data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ink jet printing apparatus having a programmed controller that minimizes banding artifacts
InactiveUS20080316259A1Minimizes deleterious banding effectDeleterious effectOther printing apparatusPrinting inkBanding Artifact
A multipass printing apparatus is characterized by a computer-implemented controller that controls printing operation so that, on any given pass, the number of selected print locations onto which printing ink is deposited by each of N nozzles varies from nozzle to nozzle. The variation is governed in accordance with a weighted smoothing spline function, particularly a polynomial B-spline function of the order “j”, where j is a value equal to one less than the number of passes.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Laser printer with reduced banding artifacts
A laser scanning assembly generates a laser beam and scans the laser beam through a plurality of scan lines to form desired dots. Each scan line is positioned to overlap an adjacent scan line and each dot includes a plurality of segments. The scanning assembly scans the laser beam through multiple scan lines to fully discharge each segment of each dot. The laser scanner assembly would typically be part of a laser printer.
Owner:MARVELL INT TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com