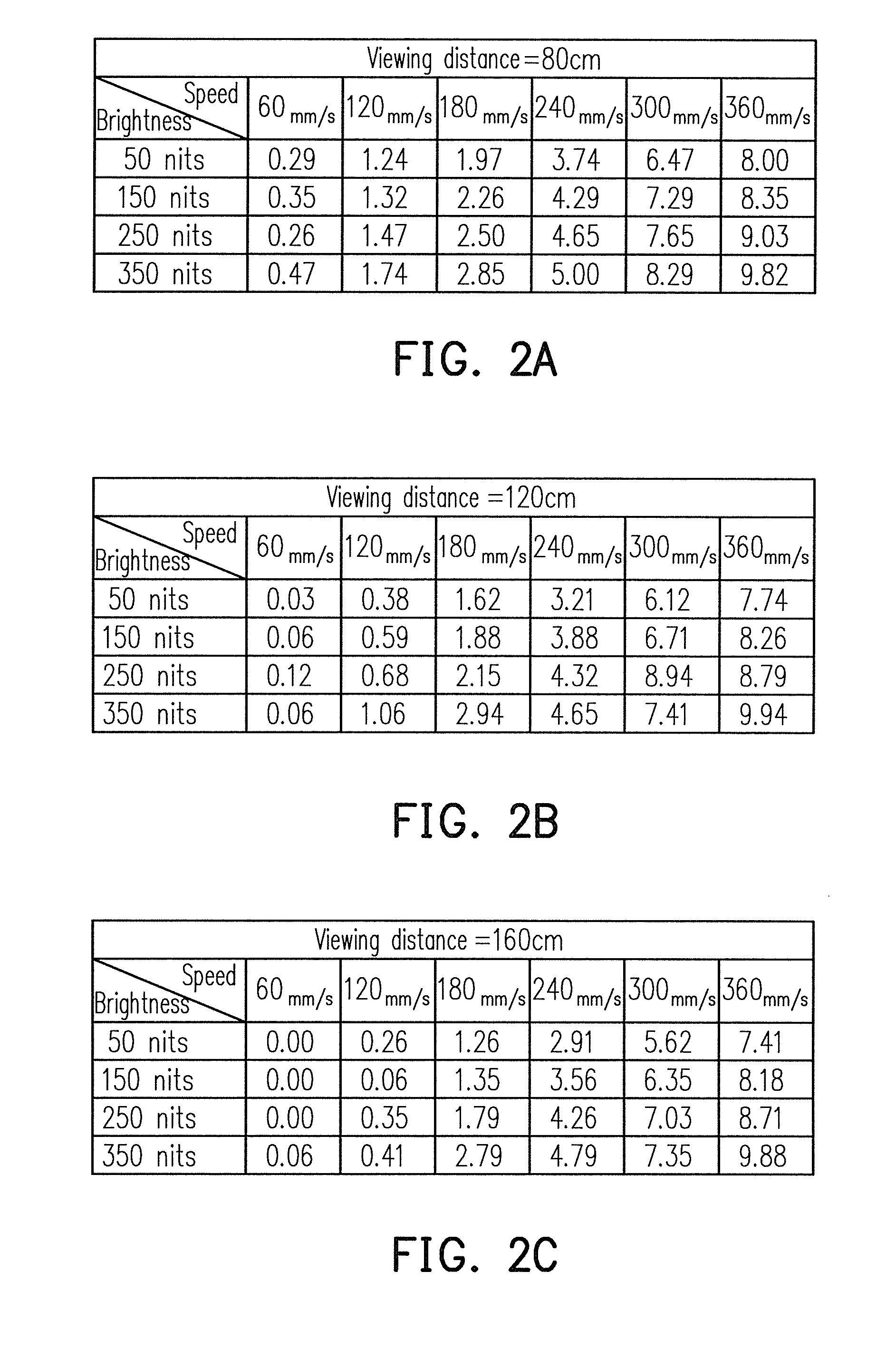
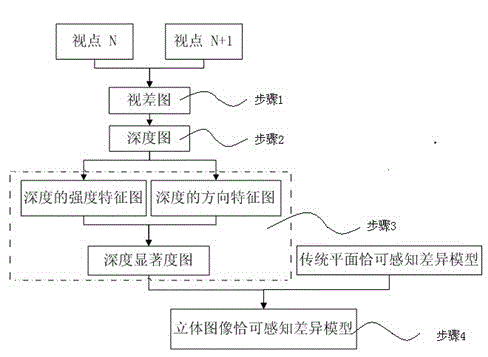
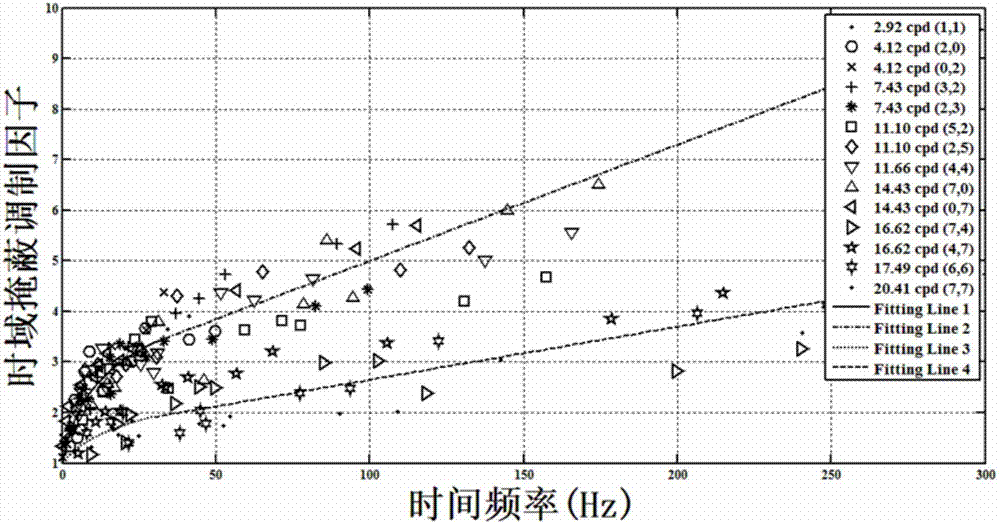
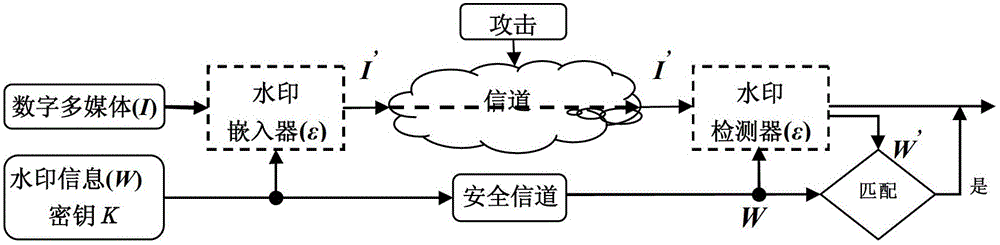
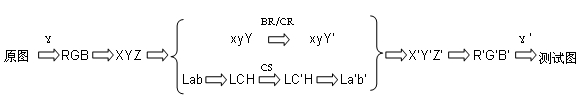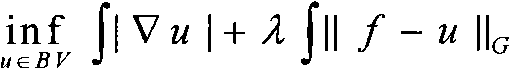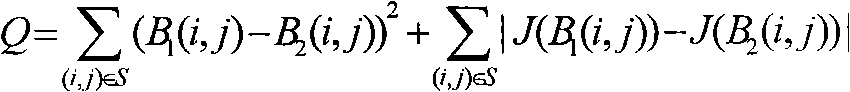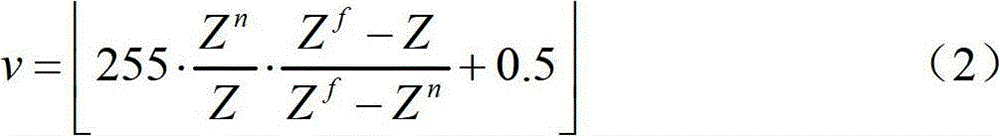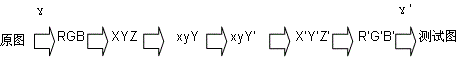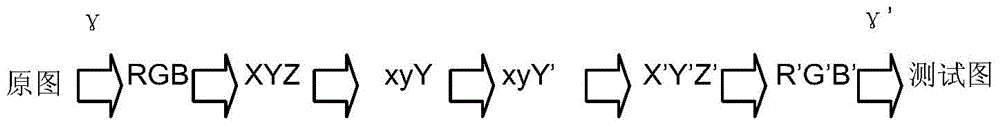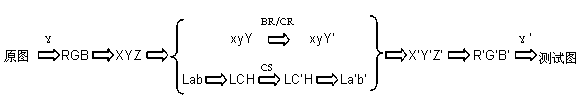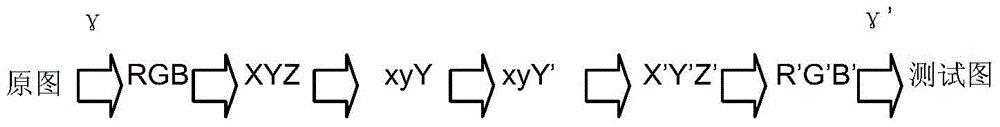Patents
Literature
45 results about "Just-noticeable difference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In the branch of experimental psychology focused on sense, sensation, and perception, which is called psychophysics, a just-noticeable difference or JND is the amount something must be changed in order for a difference to be noticeable, detectable at least half the time (absolute threshold). This limen is also known as the difference limen, difference threshold, or least perceptible difference. For many sensory modalities, over a wide range of stimulus magnitudes sufficiently far from the upper and lower limits of perception, the 'JND' is a fixed proportion of the reference sensory level, and so the ratio of the JND/reference is roughly constant (that is the JND is a constant proportion/percentage of the reference level).
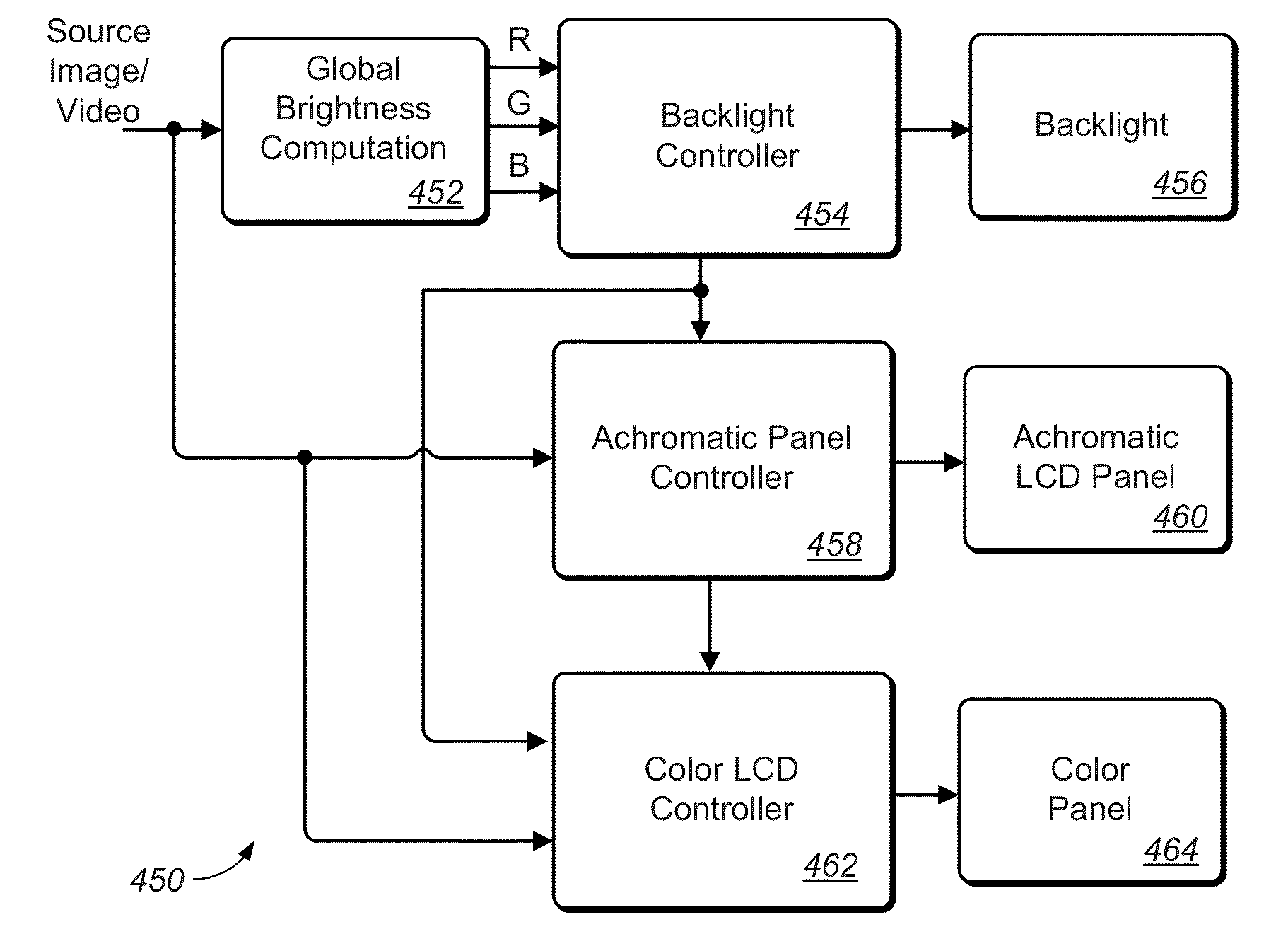
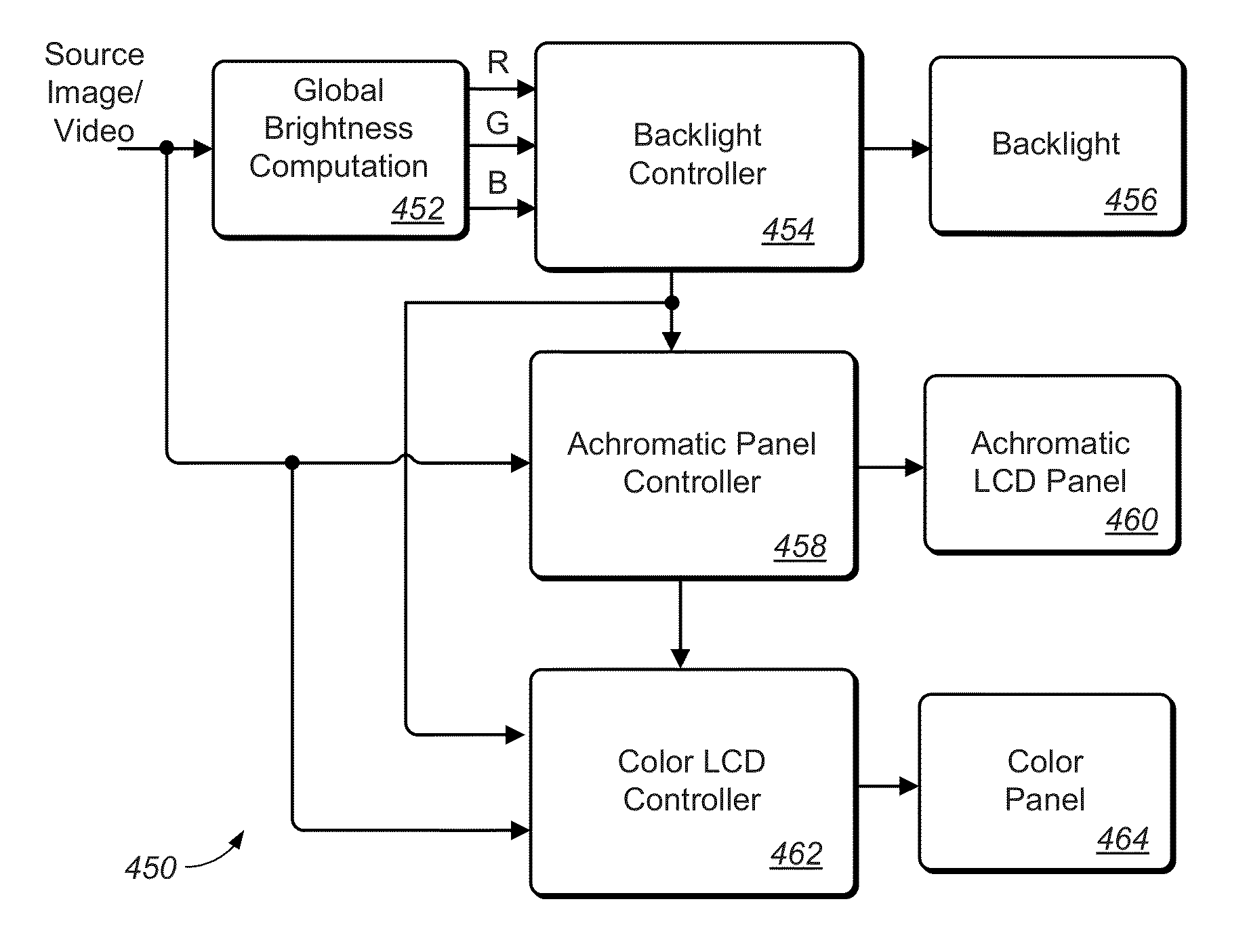
Systems and Methods for Accurately Representing High Contrast Imagery on High Dynamic Range Display Systems
ActiveUS20130106923A1Minimize number of Just Noticeable Difference (JND) stepEnhance the imageColor television detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsParallaxImaging quality
A dual-panel display system is provided that comprises control modules and algorithms to select codeword pairs (CWs) to drive a first image-generating panel and a second contrast-improving panel. The first codewords is selected by considering some characteristics of the input image data (e.g., peak luminance) and to improve some image rendering metric (e.g., reduced parallax, reduced contouring, improved level precision). The first codeword may be selected to be the minimum first codeword within a set of codeword pairs that preserves the peak luminance required by the input image data. Also, the first codeword may be selected to minimize the number of Just Noticeable Difference (JND) steps in the final image to be rendered. The second codeword may be selected to similarly improve image quality according to a given quality metric.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
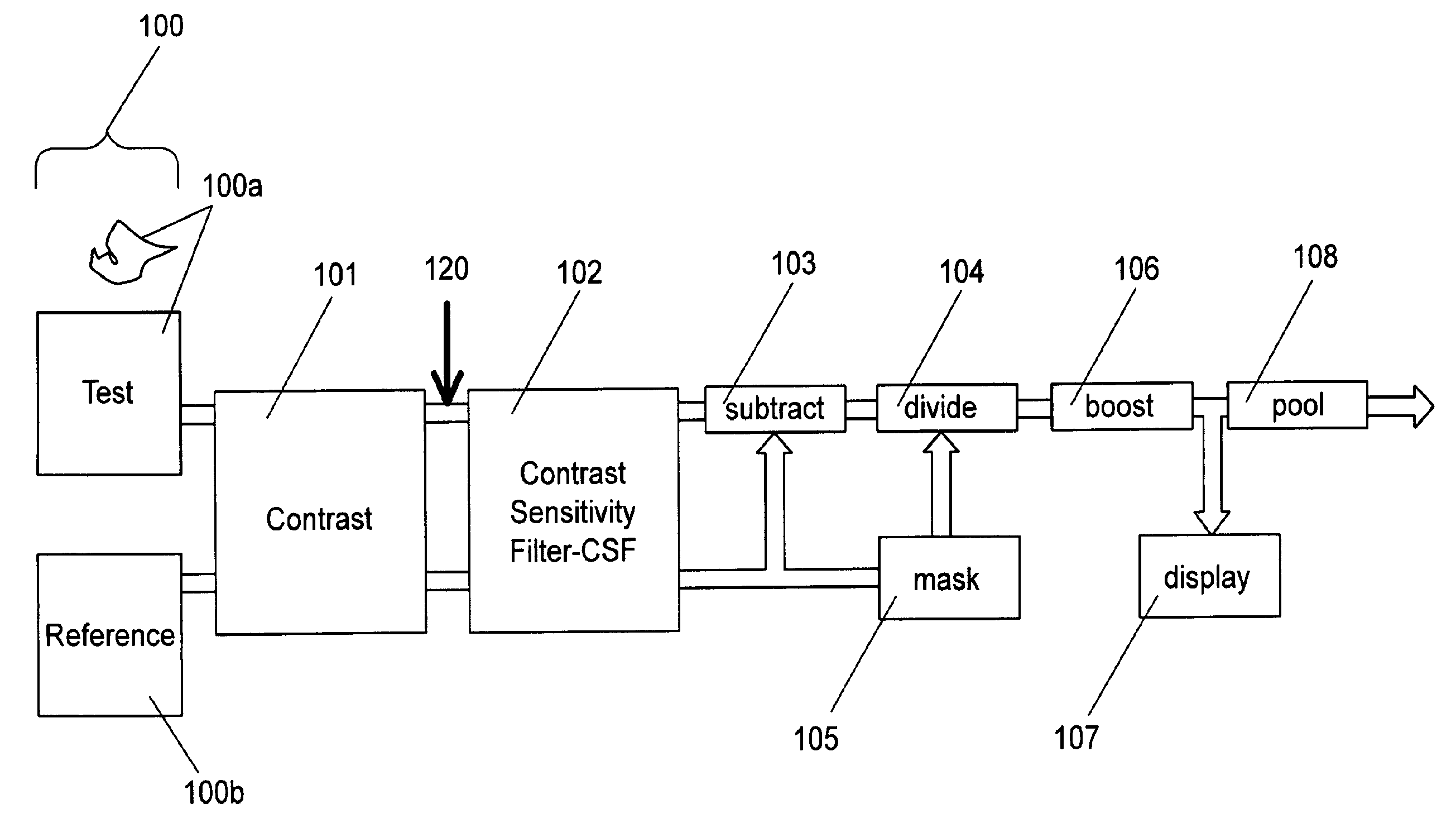
Spatial standard observer
ActiveUS7783130B2Simple and efficient designAccurate visibilityImage enhancementImage analysisReference imageLocal average
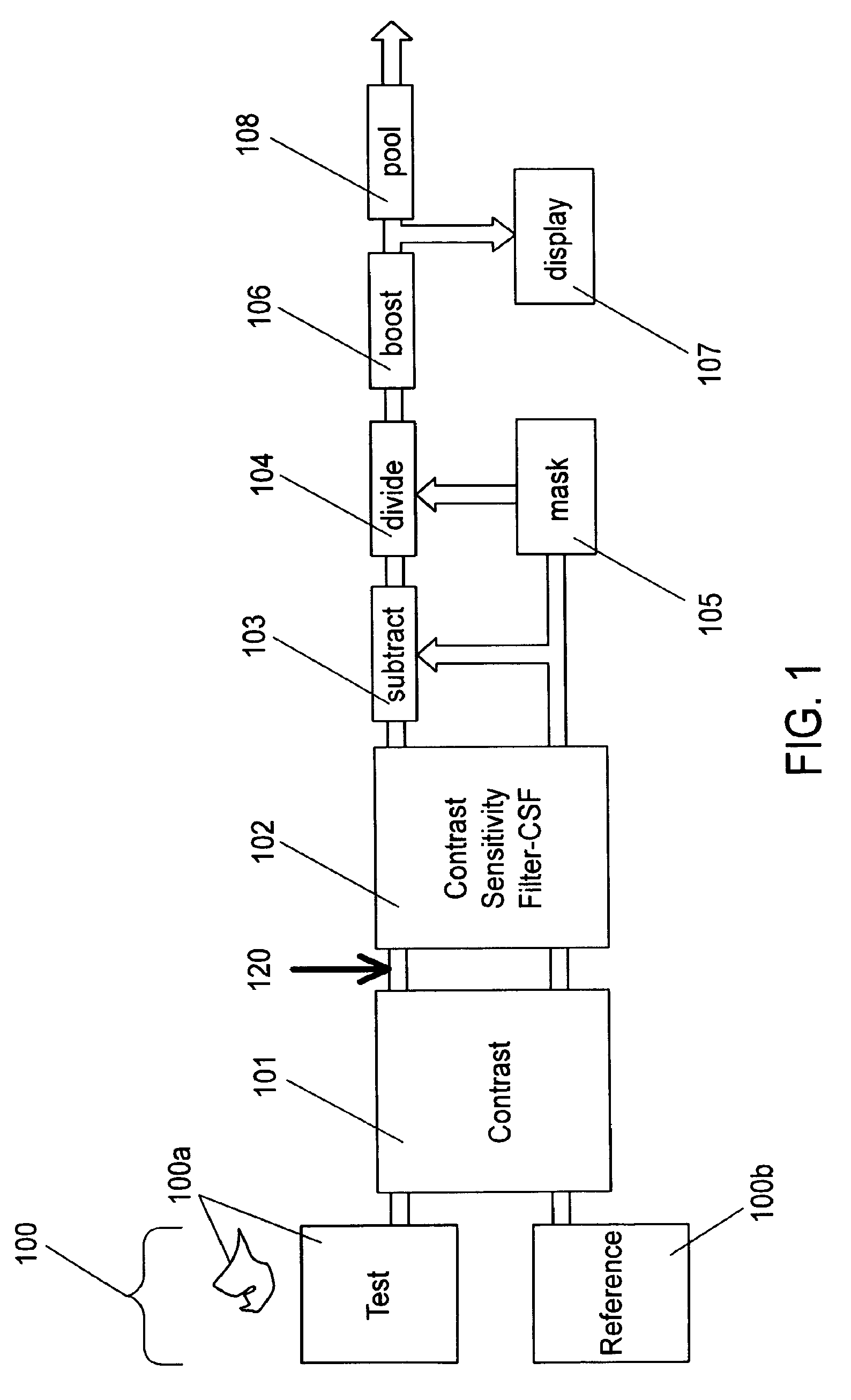
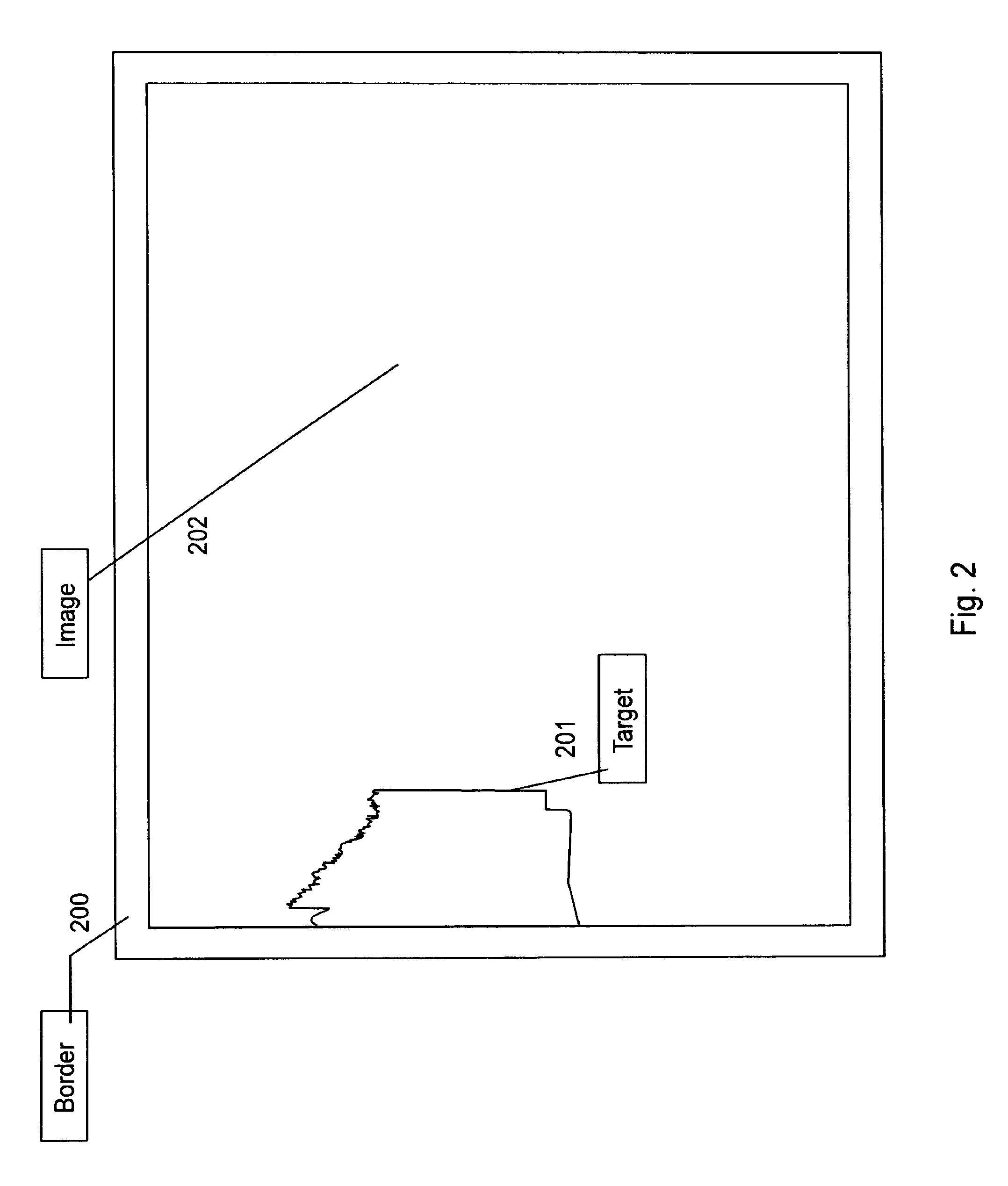
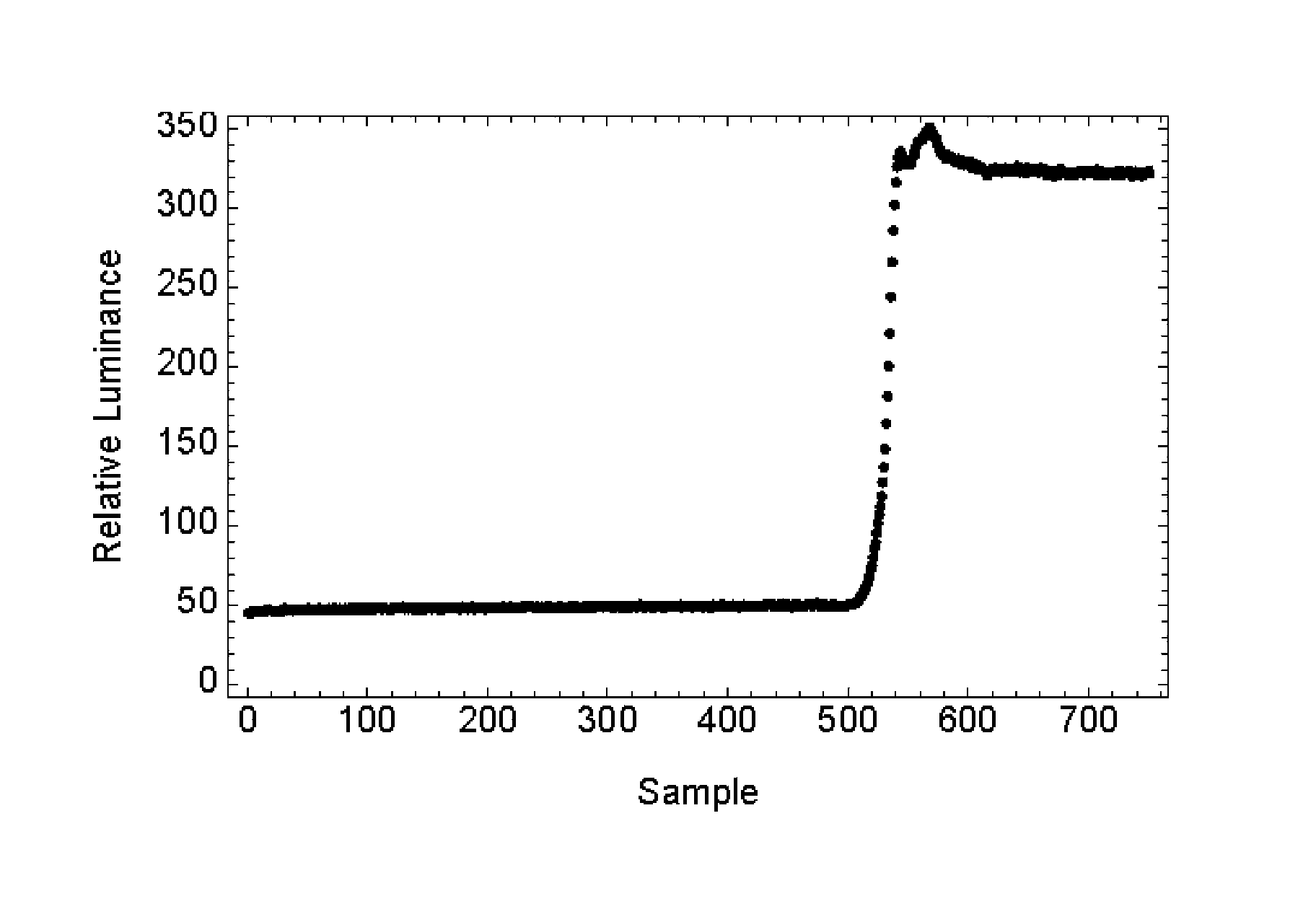
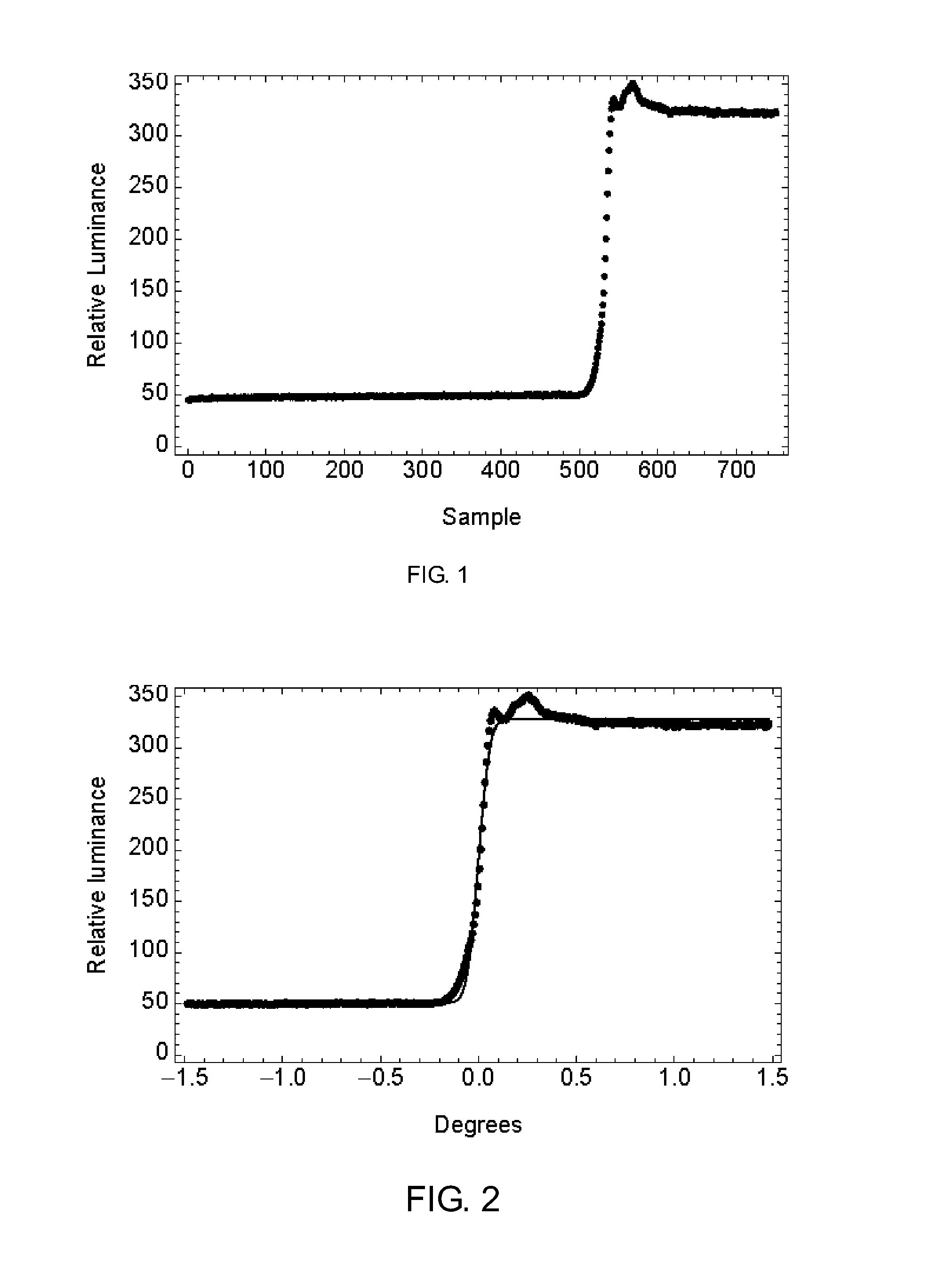
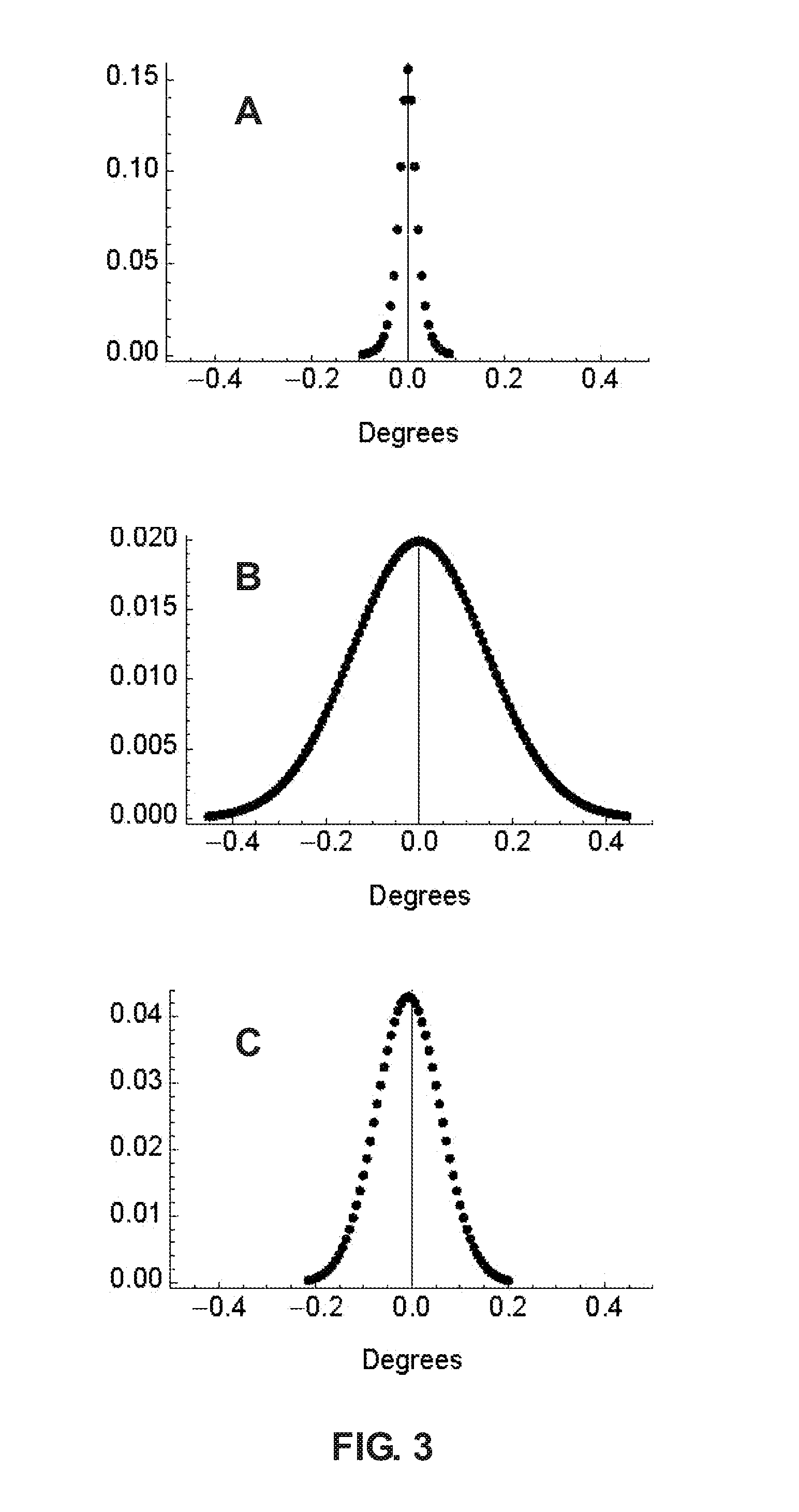
The present invention relates to devices and methods for the measurement and / or for the specification of the perceptual intensity of a visual image, or the perceptual distance between a pair of images. Grayscale test and reference images are processed to produce test and reference luminance images. A luminance filter function is convolved with the reference luminance image to produce a local mean luminance reference image. Test and reference contrast images are produced from the local mean luminance reference image and the test and reference luminance images respectively, followed by application of a contrast sensitivity filter. The resulting images are combined according to mathematical prescriptions to produce a Just Noticeable Difference, JND value, indicative of a Spatial Standard Observer, SSO. Some embodiments include masking functions, window functions, special treatment for images lying on or near borders and pre-processing of test images.
Owner:NASA
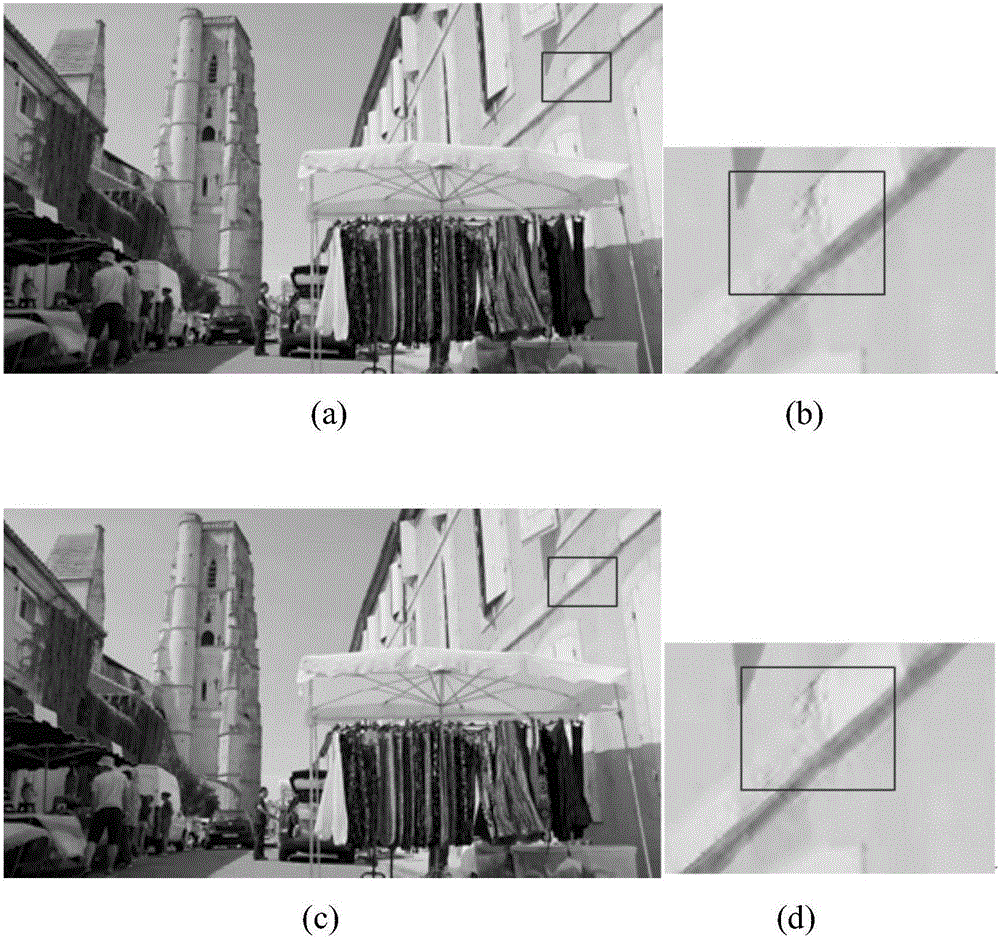
Image quality evaluation method based on visual characteristic
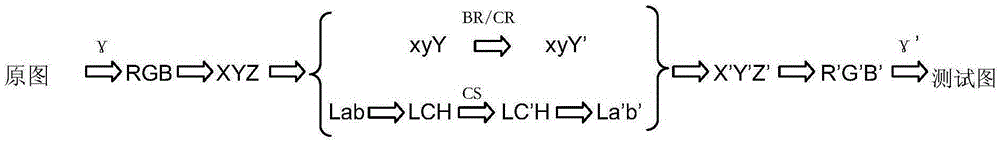
The invention discloses an image quality evaluation method based on a visual characteristic. The method is characterized by: firstly, converting original images into a xyY space or a LCH space, processing a component Y or a component C so as to obtain a group of test images; then, finding at least one JND (just noticeable difference) critical image; calculating differences of brightness (BR), color saturation (CS) and Gaussian function variance parameters in the original images and the JND critical image, wherein average values of the differences are the JND values of the BR, CS and contour rendering (CR) of the original images respectively; and then, carrying out mean calculation on the JND values of the different original images and determining the final JND values; taking the JND as a unit to change different attributes of the image at different degrees respectively; using a visual perception test to test the subjective image quality; then, using a regression analysis to establish a relation model of the image quality and the image attributes; and researching influences of the different attributes of the images according to a variance analysis. By using the method of the invention, influence on image quality which can be perceived by human eyes when improving the display parameter can be quantitatively evaluated.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Systems and methods for accurately representing high contrast imagery on high dynamic range display systems
ActiveUS9135864B2Minimize number of Just Noticeable Difference (JND) stepEnhance the imagePicture reproducers using projection devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsParallaxImaging quality
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
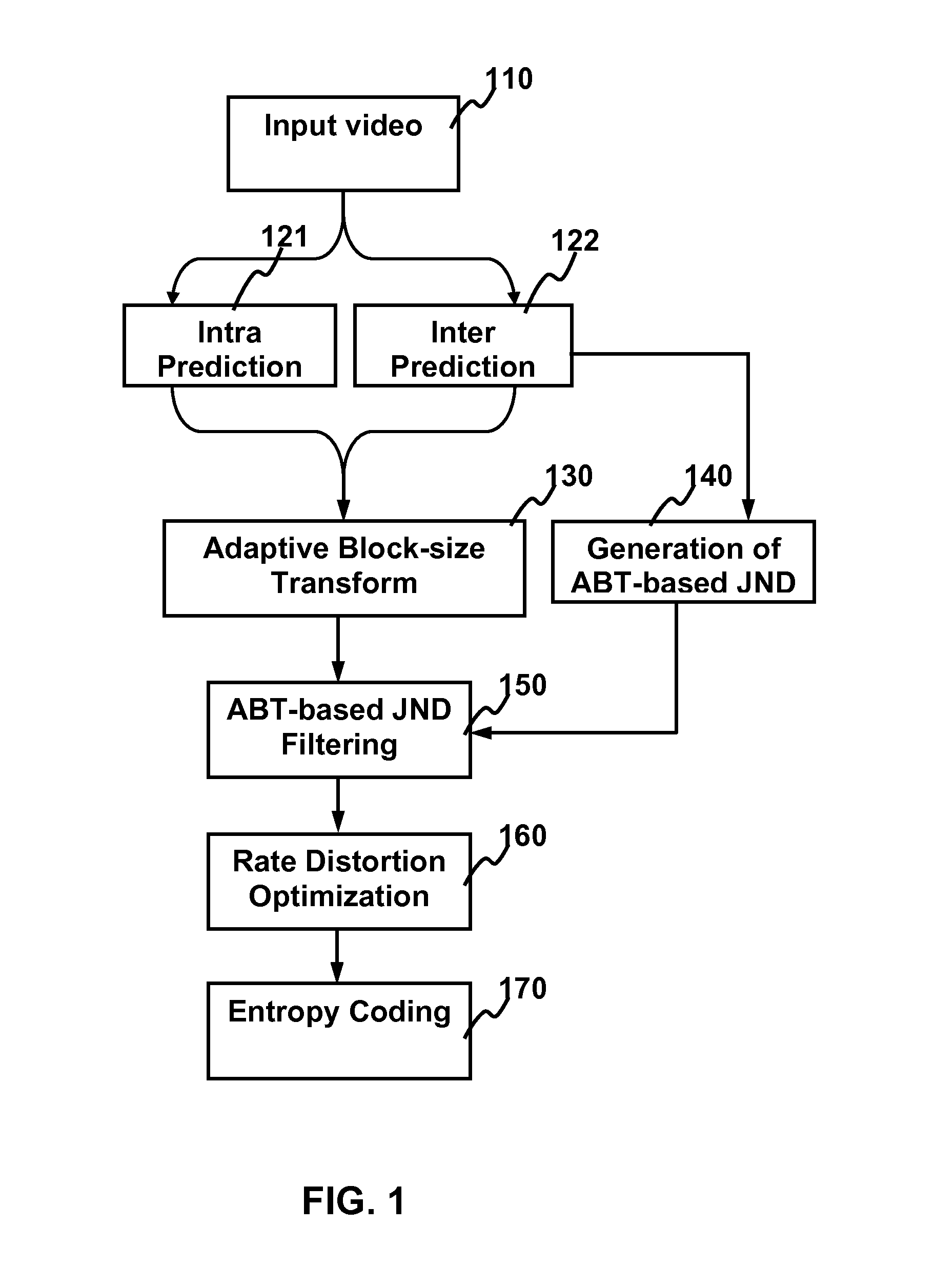
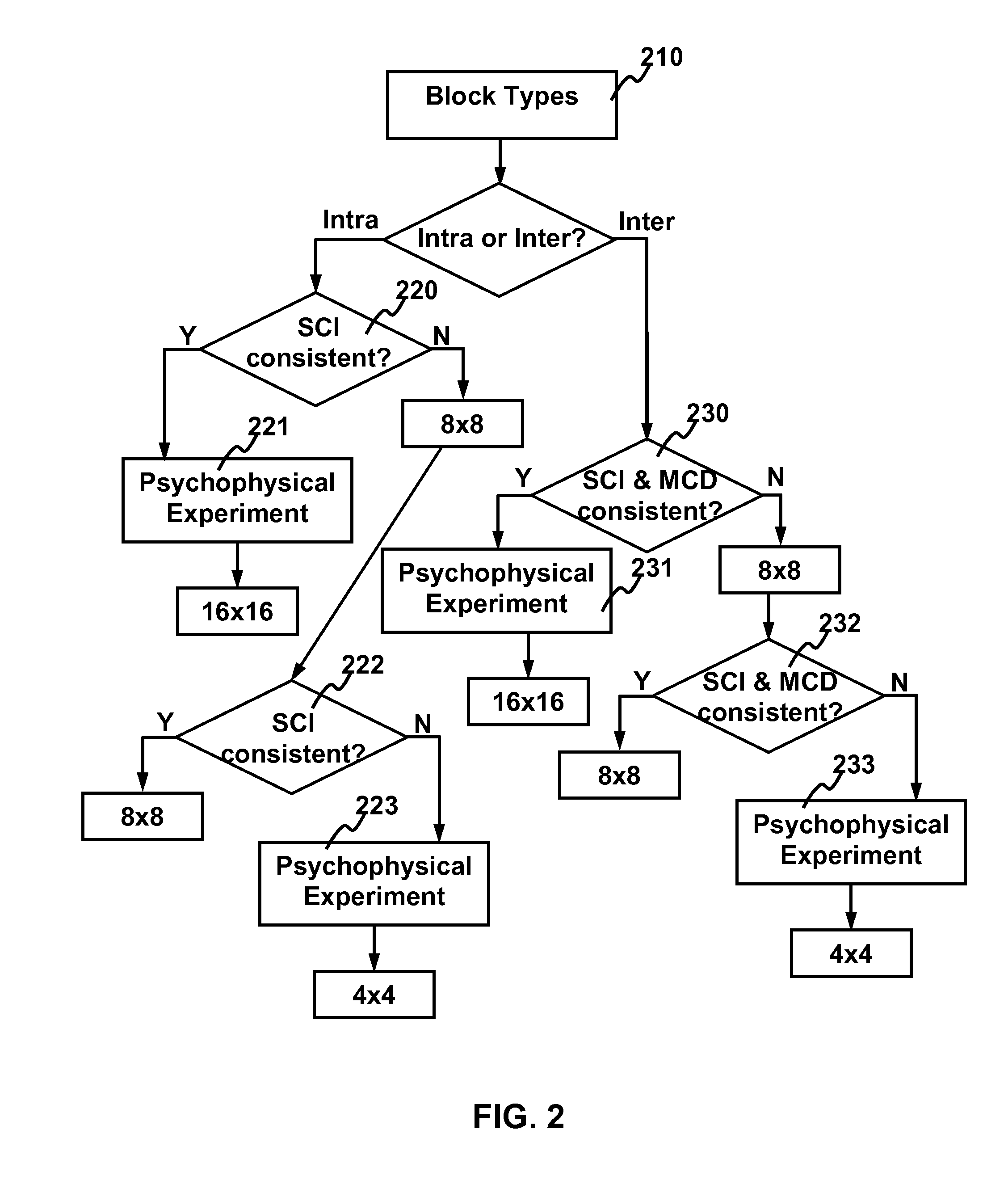
Method and apparatus for video coding by abt-based just noticeable difference model
ActiveUS20110243228A1Bit rateReduce bitrateColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionIntra-frame
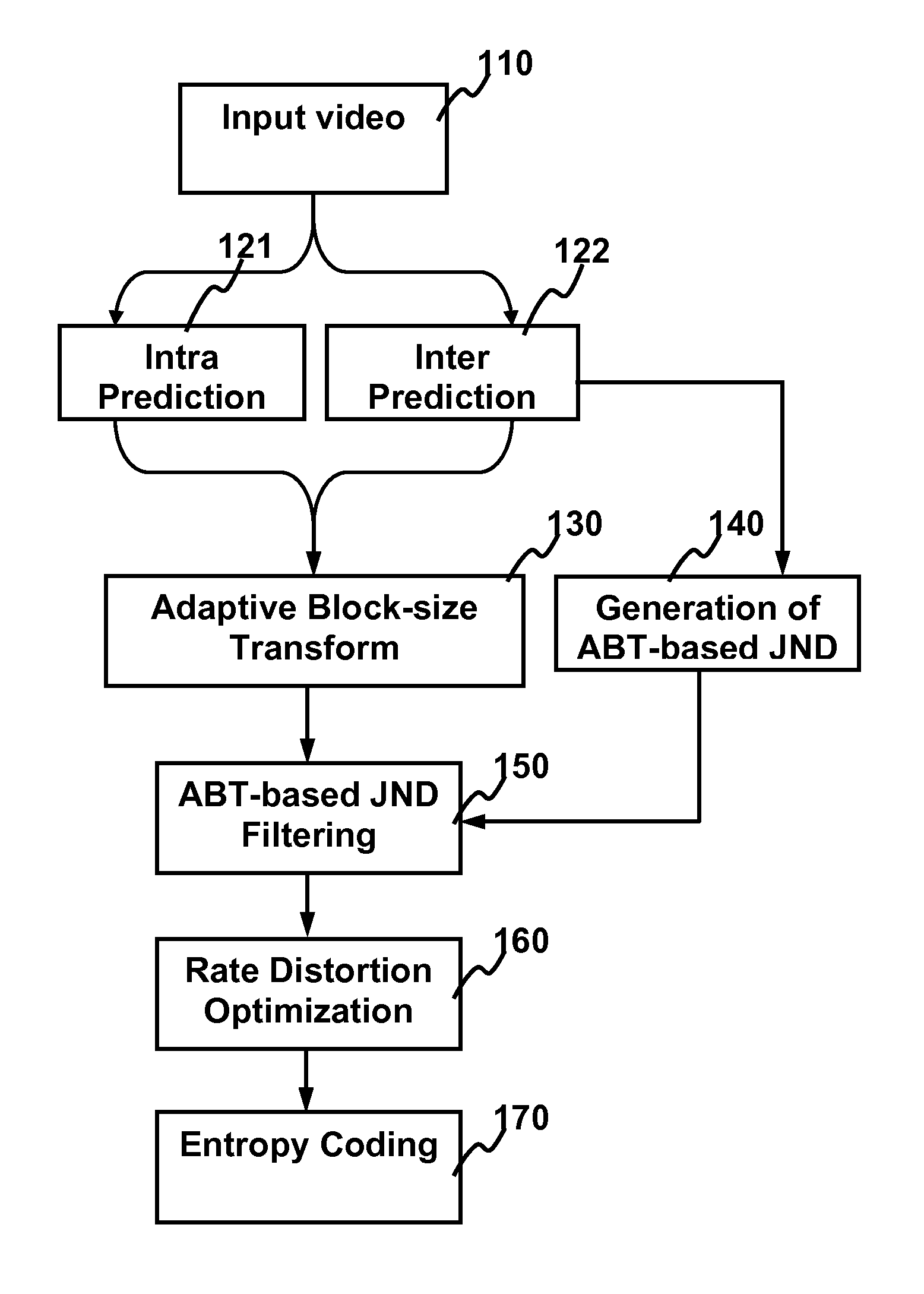
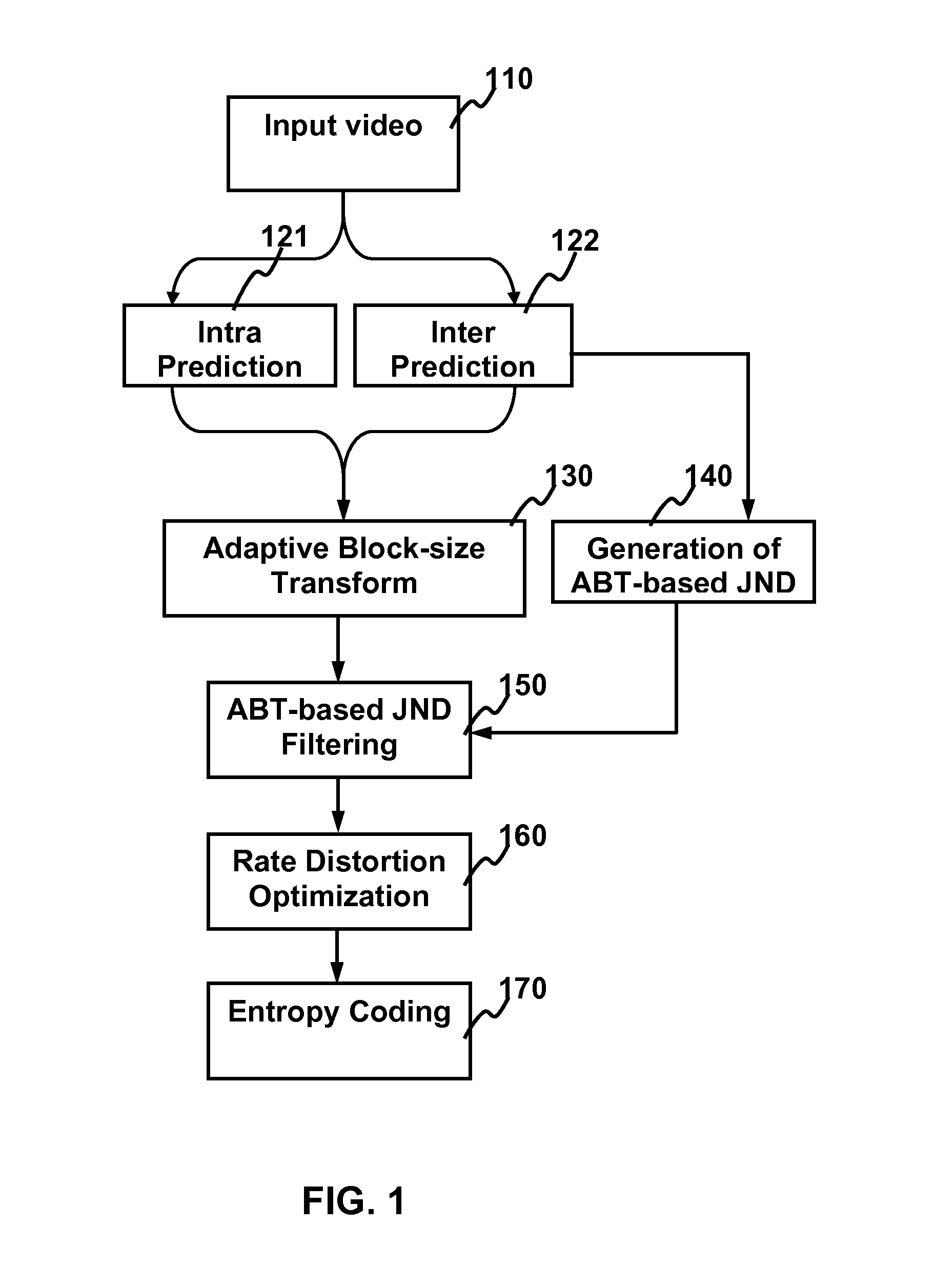
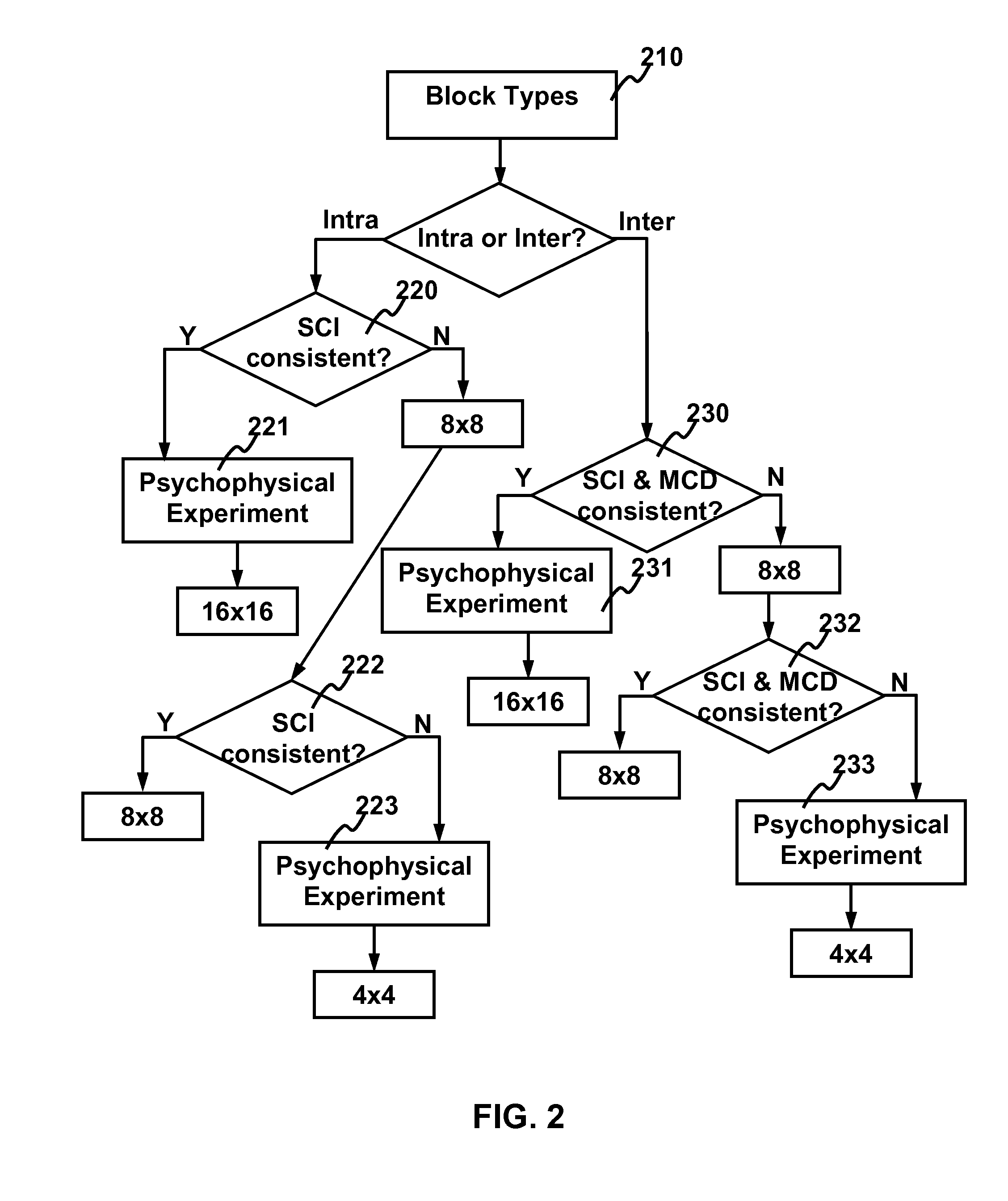
The present invention relates to method and apparatus for video coding by ABT-based just noticeable difference (JND). For building the just noticeable difference model, spatial content information (SCI) is used to represent the spatial appearance similarity between one macroblock and its sub-blocks and the motion characteristic distance (MCD) is used to represent the motion characteristics similarity between one macroblock and its sub-blocks. For intra frames, the balance strategy based on the obtained SCI of the macroblock is used to generate the ABT-based JND model. For inter frames, the balanced strategy based on the obtained SCI and MCD of the macroblock is used to generate the ABT-based JND model. Using the ABT-based JND model, the residual coefficients for each block in a frame is filtered to obtain a reduced set of residual coefficients for transmission without degradation in visual quality.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
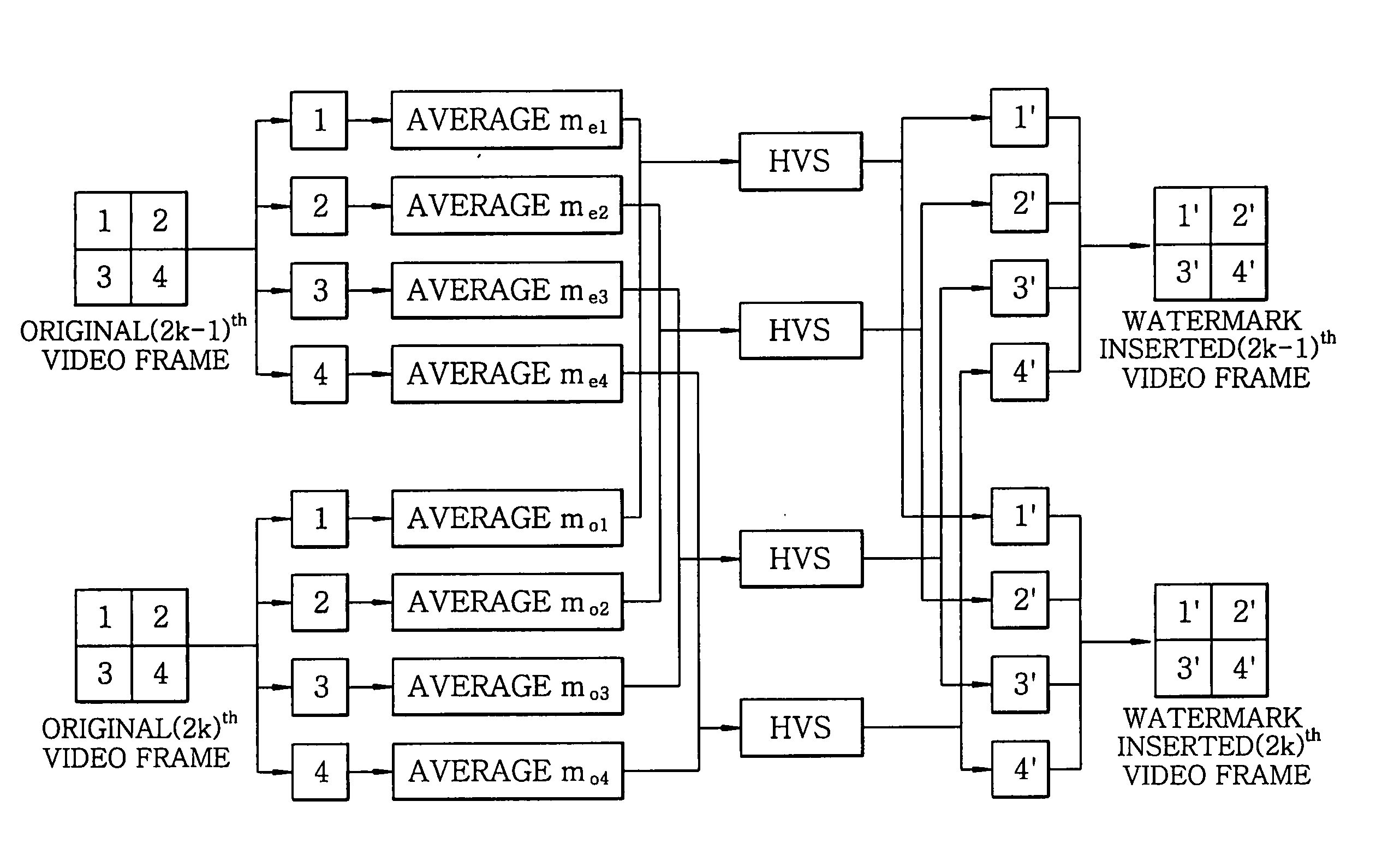
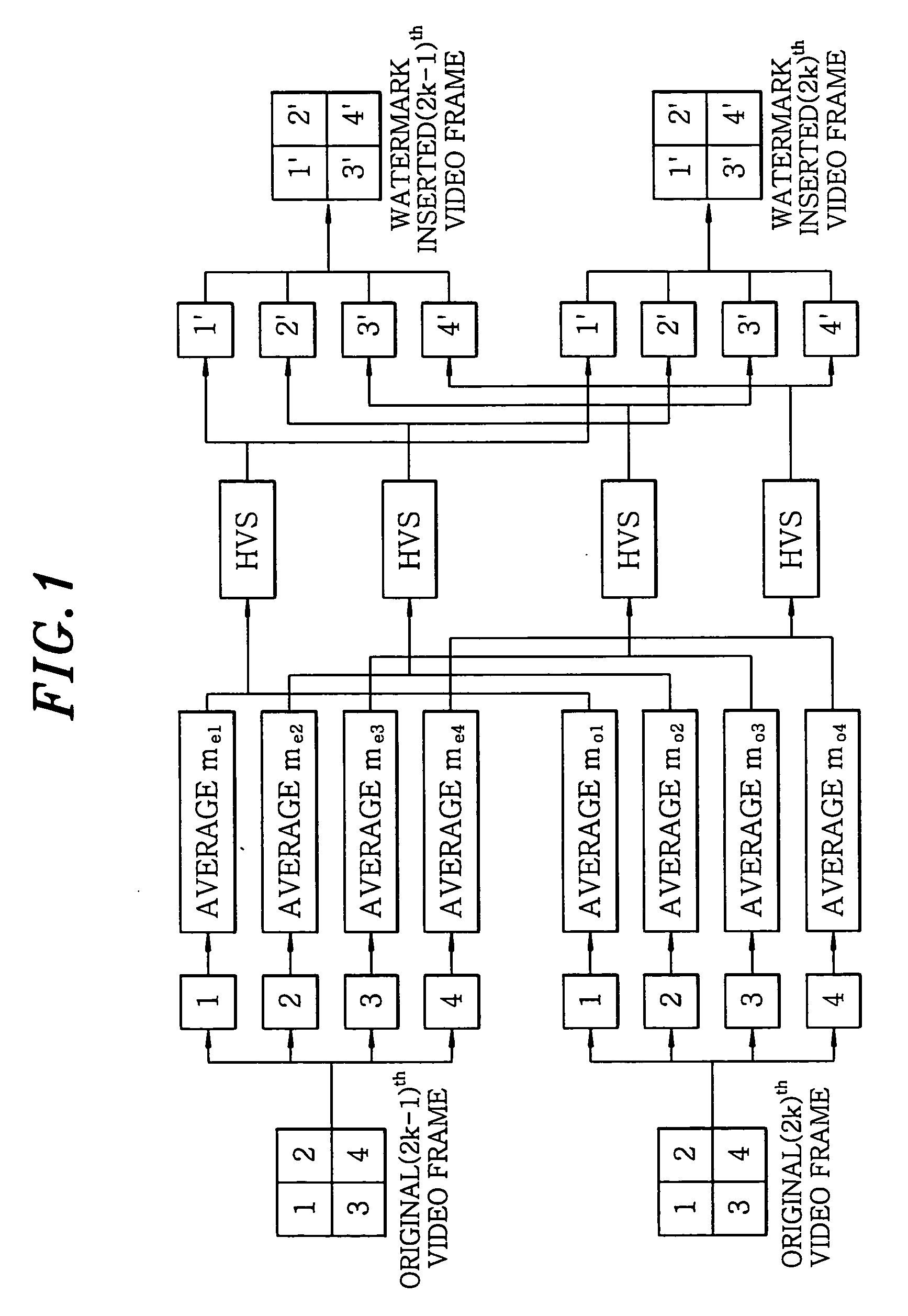
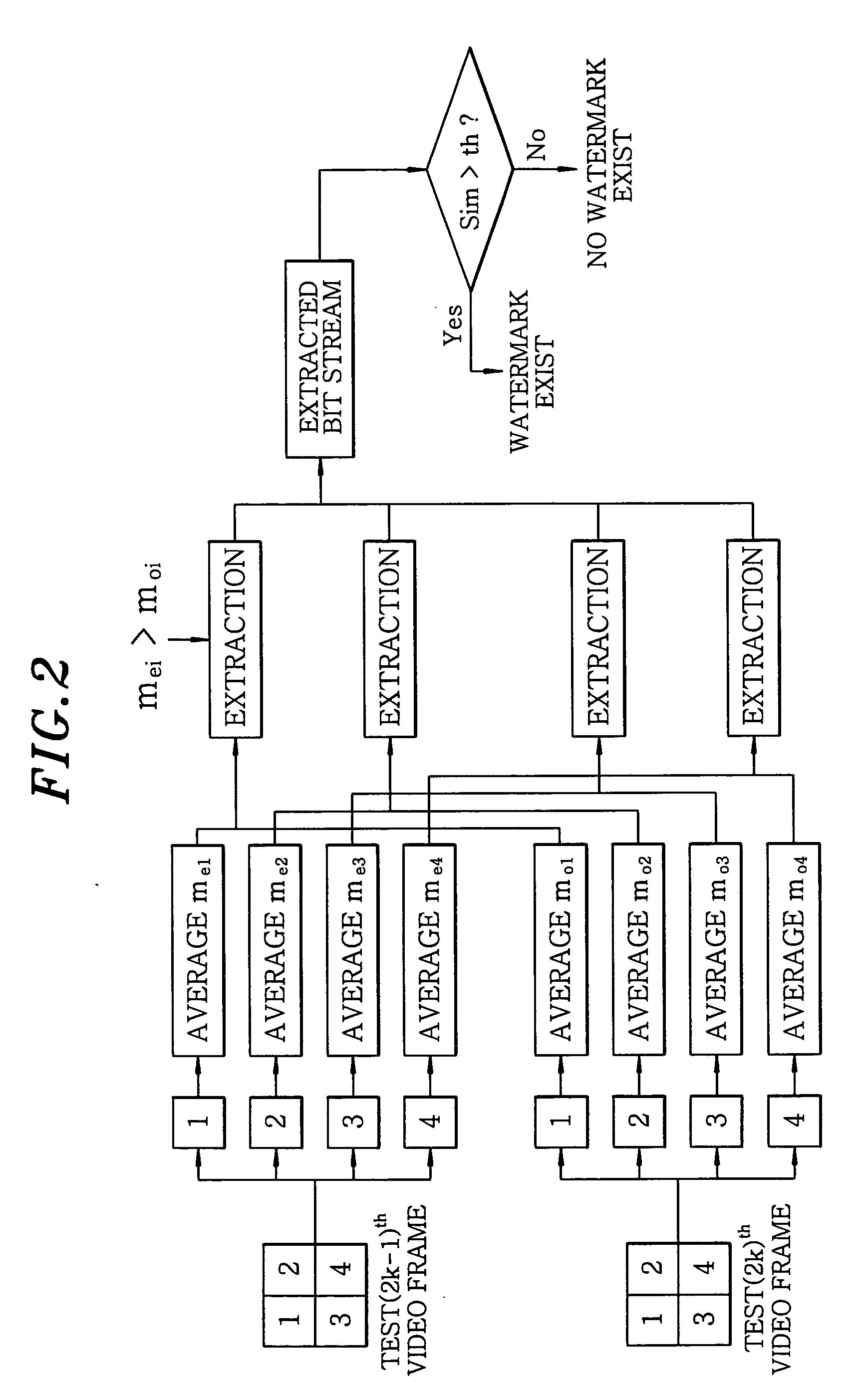
Real time video watermarking method using frame averages
InactiveUS20050105763A1Increase capacityImprove processing speedCharacter and pattern recognitionImage data processing detailsDigital dataComputer science
The present invention relates to a watermarking method for protecting the copyright of digital data, which includes the step of dividing each of two successive frames into at least two sub-groups, the step of adding and subtracting a value, which varies according to pixel locations, to and from a specific component value at each pixel location of the sub-groups using Just Noticeable Difference (JND) values and averages of the specific component value at pixel locations of corresponding sub-groups of the two successive frames, the step of adaptively embedding watermark information while modifying embedment intensity of the watermark information, the step of calculating the averages of the specific component values of the sub-groups, and the step of extracting watermark information using the calculated averages.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
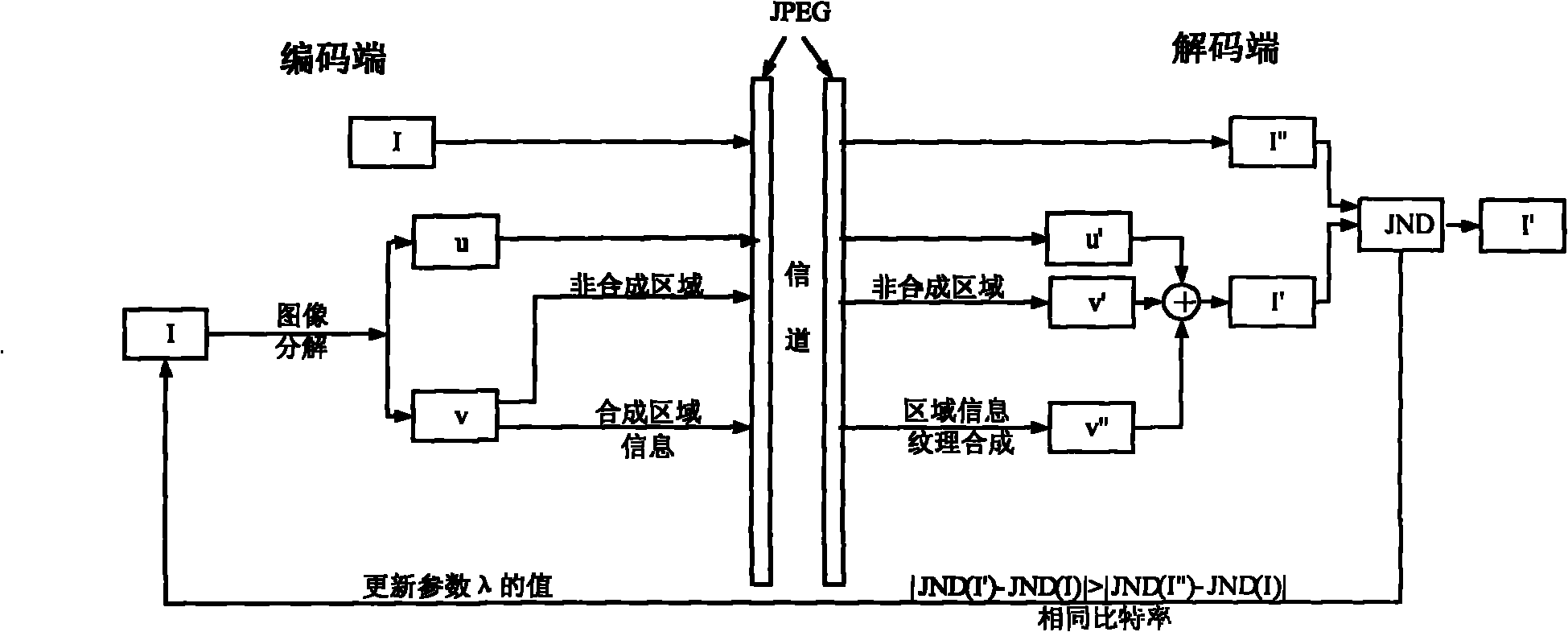
Image coding method based on total variation
ActiveCN101969567AImprove decoding performancePreserve visual featuresTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionState variation
The invention relates to an image coding method based on total variation, comprising the following steps of: (1) decomposing an input image (I) into a structure component (u) and a texture component (v); (2) analyzing the (u) at a coding end, selecting an analyzed area, mapping the (u) to the (v), and coding non-synthetic areas in the (u) and the (v) by using JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) traditional coding mode; analyzing areas which need to be analyzed in the (v) by using a block connection method at a decoding end, v'' represents an analyzed result of a texture area, and u' and v' respectively represent compressed results of the non-synthetic areas in the (u) and the (v); (3) superimposing the u', the v' and the v'' at the coding end to obtain an image I', and I'' represents a result of the input image I which is compressed by the traditional FPEG; and under the same bit rate, judging whether the I' or the I''is nearer to the I by a JND (Just Noticeable Difference) model, then, if I'' is nearer to the I, reducing a decomposable model parameter lambda, returning to the step (1) to continue a whole process until the I' is nearer to the I as compared with the I'', finishing circulation, and selecting the I'. The invention can increase the coding quality of the image at the coding end.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
JND (Just Noticeable Difference) value measurement method of image brightness
InactiveCN102447945ANot affected by JND valueTelevision systemsTesting optical propertiesComputer graphics (images)Gray level
The invention discloses a JND (Just Noticeable Difference) value measurement method of image brightness, which comprises the following steps of: converting an original image into an xyY space, respectively carrying out linear compression to a component Y according to different compression coefficients to obtain a group of test images; carrying out visual perception experiment, and finding at least one test pattern to be as a JND critical image; dividing the original image and the JND critical image into a plurality of image blocks, respectively selecting the image blocks with the largest average gray level in the original image and the JND critical image; computing the difference of the accrual display brightness corresponding to the average gray level value of the image blocks with the largest average gray level in the original image and the JND critical image, wherein the average value of the difference is the JND value of a participant to be tested to the original image brightness;and carrying out average computing to the brightness JND values of the different original images of different participants to determine a final JND value. According to the invention, when the parameter of the display is changed, the influence to the image brightness, which can be observed by the human eyes, can be quantitatively evaluated and improved, thus, evidences can be provided for the design and the research of display technology.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Color sequential method for displaying images
InactiveUS20100045707A1Increase display frequencyEfficiency problemCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingSequential methodComputer graphics (images)
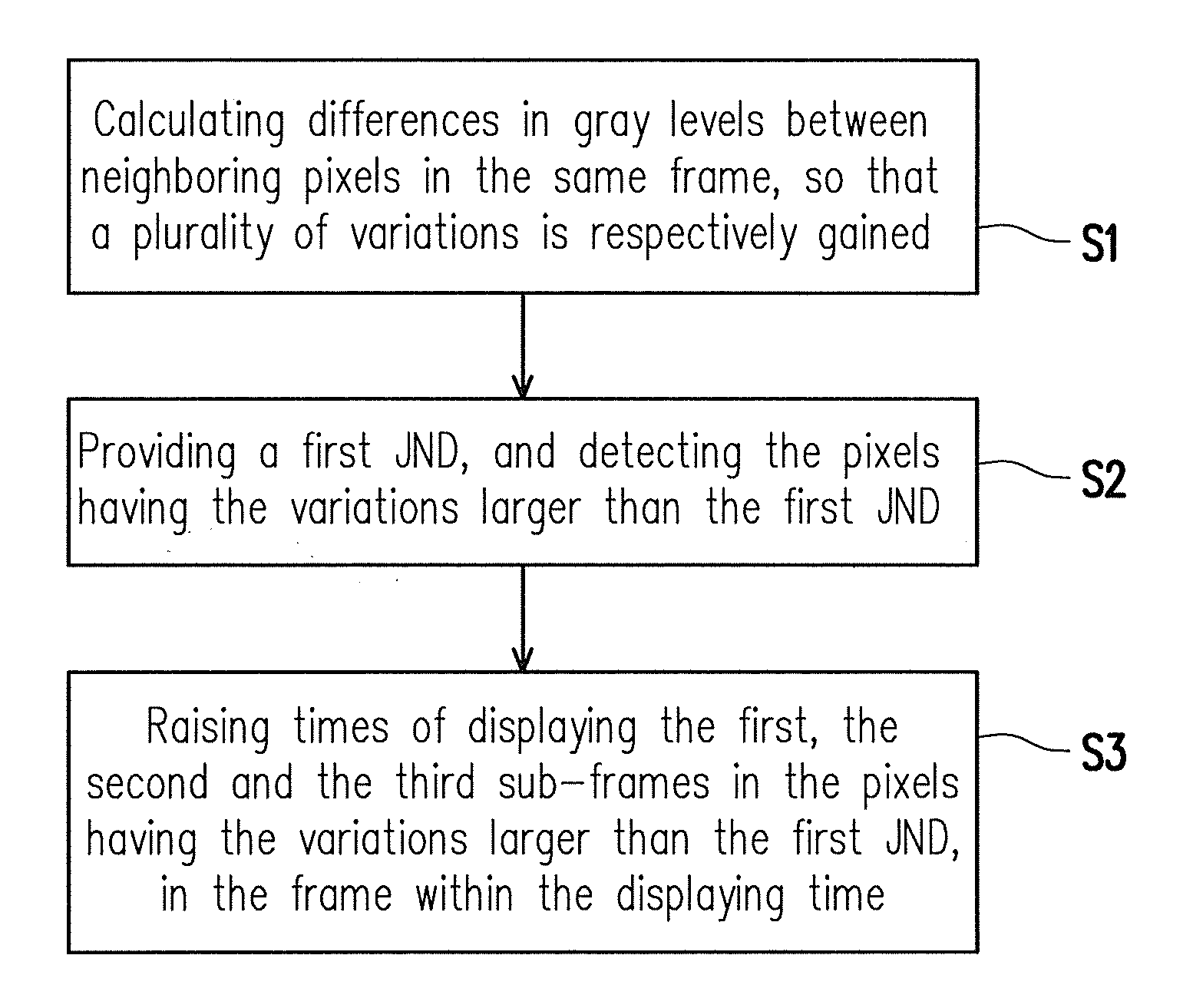
A color sequential method for displaying images is suitable for applying in a display with pixels. Each of frames is formed by displaying a first sub-frame, a second sub-frame and a third sub-frame within a displaying time by the pixels. By calculating differences in gray levels between neighboring pixels, variations are gained. Then, a first just noticeable difference is provided, and the pixels having the variations larger than the first just noticeable difference are detected. Next, times of displaying the first, the second and the third sub-frames in the pixels are raised within the displaying time.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
Depth significance-based stereopicture just noticeable difference (JND) model building method
ActiveCN102750706AAccurate response of human visual experiencePrecise visual responseImage analysisParallaxPattern recognition
The invention discloses a depth significance-based stereopicture just noticeable difference (JND) model building method. The method comprises the steps: calculating the horizontal parallax of a stereopicture pair to obtain the horizontal parallax map of the stereopicture pair; calculating the depth value of the stereopicture pair to obtain a depth map of the stereopicture pair; calculating the depth significance of the stereopicture pair to obtain the depth significance map SD of the stereopicture pair; and building a depth significance-based stereopicture JND model. The method fully considers the depth significance influence factors in stereopicture noticing, the model obtained by adopting the method can more accurately reflect the feeling of eyes, the stereopicture processed by the guidance of the model can be added with more noise under the condition of keeping the subjective quality basically unchanged, thus being capable of removing vision redundancy in the stereopicture videos.
Owner:中电科安科技股份有限公司
Visual perceptual coding method based on multi-domain JND (Just Noticeable Difference) model
ActiveCN107241607ARemove Perceptual RedundancyImprove subjective qualityDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionInformation processing
The invention discloses a visual perceptual coding method based on a multi-domain JND (Just Noticeable Difference) model and relates to video information processing. The method comprises the following steps: respectively calculating a space-domain basic JND threshold value, a luminance masking modulation factor, a contrast masking modulation factor and a time domain masking modulation factor of each transformation coefficient in a DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) block by utilizing a time-space-domain multi-domain JND model so as to obtain the time-space-domain multi-domain JND threshold value of each transformation coefficient; introducing a block perception-based distortion probability evaluative criteria in the transform coding process, and searching a correction factor of each coefficient relative to the JND threshold value through an adaptive searching algorithm so as to obtain a transformation coefficient suppression value; and finally, subtracting the original transformation coefficient from the most appropriate suppression value obtained through corresponding calculation, and taking the coefficient as a novel coefficient to be put at an entropy coding stage. According to the coded suppression strategy of the multi-domain JND model and the block perception-based distortion probability, the coding rate can be effectively reduced on the premise of guaranteeing certain subjective quality, and the compression ratio of the current coding standard is further improved.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
JND (Just Noticeable Difference) value measuring method and prediction method for dark field brightness of image
The invention discloses a JND (Just Noticeable Difference) value measuring method for the dark field brightness of an image. The method comprises the following steps: switching an original image to an xyY space, performing linear compression on a component Y according to different compression coefficients respectively, and increasing the dark field brightness of the image to obtain a group of test images; conducting a visual perception experiment to find at least one test image for serving as a JND critical image; and calculating the difference values of practical display brightness corresponding to the gray value of each pixel of the original image and the JND critical image, wherein the average value of the difference values is the JND value of the dark field brightness of the original image. The invention further discloses a JND value prediction method for the dark field brightness of an image. The JND value prediction method is used for predicting the JND value of the dark field brightness of the original image. Through adoption of the JND value measuring method and detection method, display parameters can be evaluated and improved quantitatively. In particularly, human eye noticeable influences on the dark field brightness of the image in parameter design specific to dark field brightness and contrast are lowered, so that a basis is laid for the design and research of a display technology.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
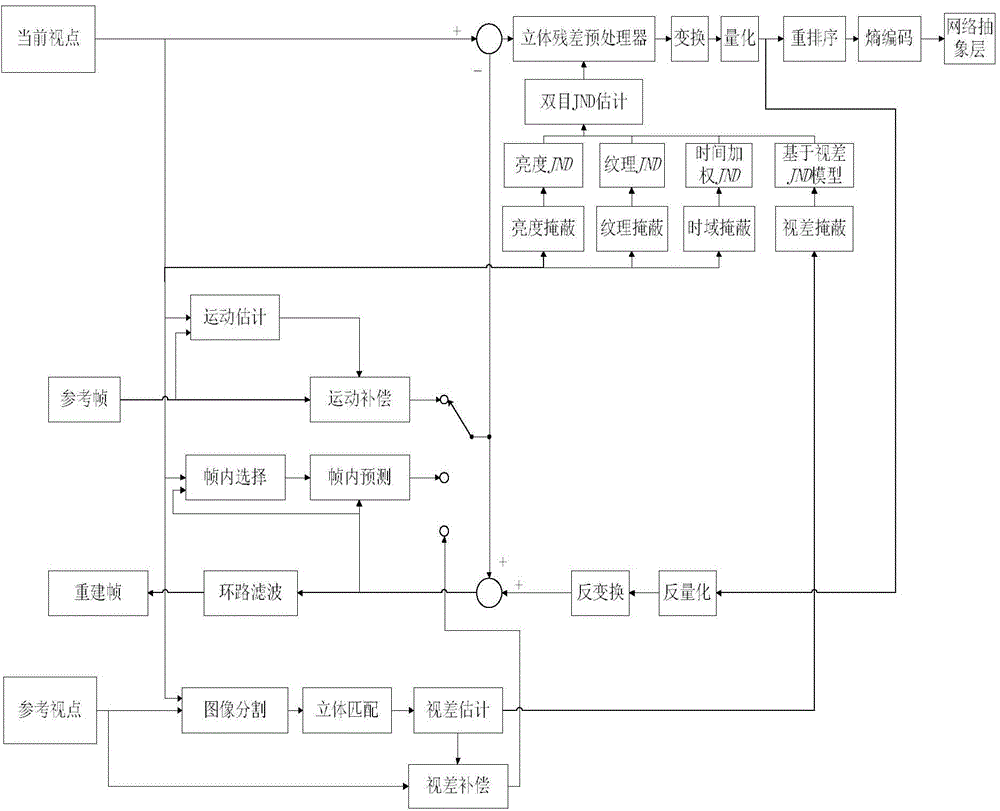
Method for sensing stereoscopic video coding based on parallax just-noticeable difference model
ActiveCN105306954AParallax estimation is accurateDistortion is easily noticeableDigital video signal modificationSteroscopic systemsStereoscopic videoAdditive model
The invention belongs to the field of video processing technology, and specifically discloses a method for sensing stereoscopic video coding based on a parallax just-noticeable difference model. The method comprises the following steps: (1) estimating parallax; (2) estimating a JND model based on the parallax; (3) calculating a brightness, texture and time weighted JND model; (4) combining the JND model based on the parallax with a spatial domain-time domain JND model by using a nonlinear additive model to obtain a binocular stereoscopic JND model based on the parallax; and (5) using the binocular stereoscopic JND model based on the parallax on a stereoscopic residual preprocessor for resetting a residual. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively eliminating inter-view redundancy of time, space and binocular stereoscopic videos, and the information of the brightness, a texture region or an object edge keeps a very natural visual effect. Therefore, the method disclosed by the invention can be used for greatly reducing the stereoscopic video code rate on the premise of generating no influence on the stereoscopic visual perceptual quality.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
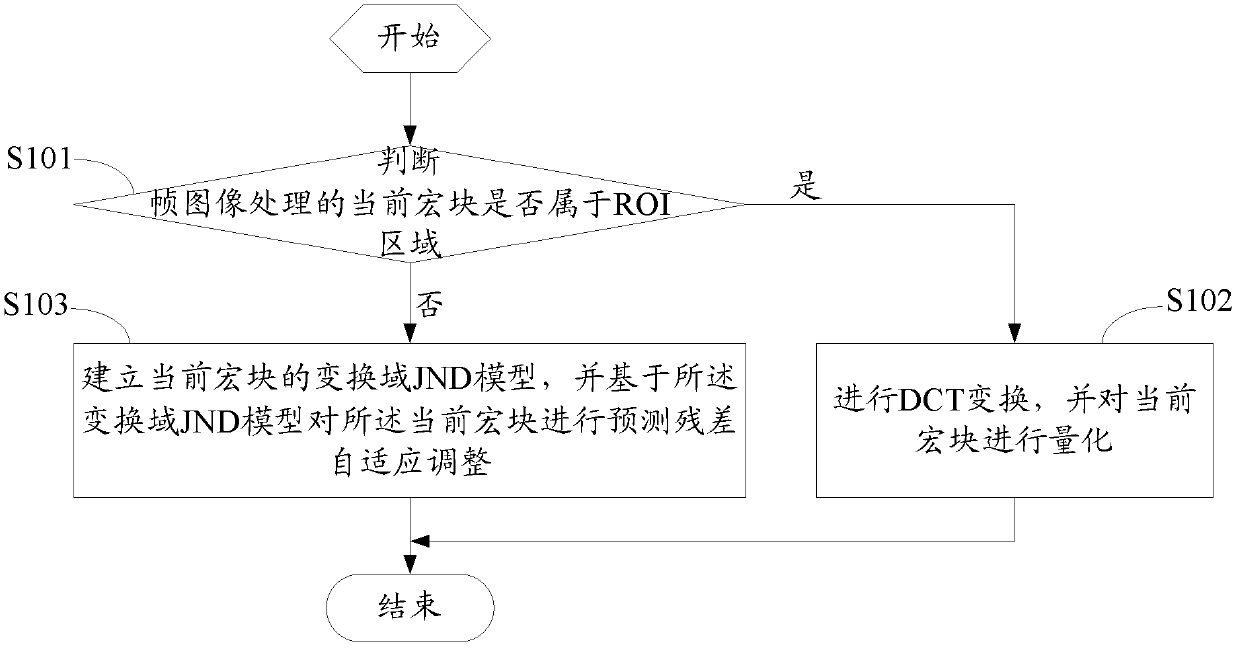
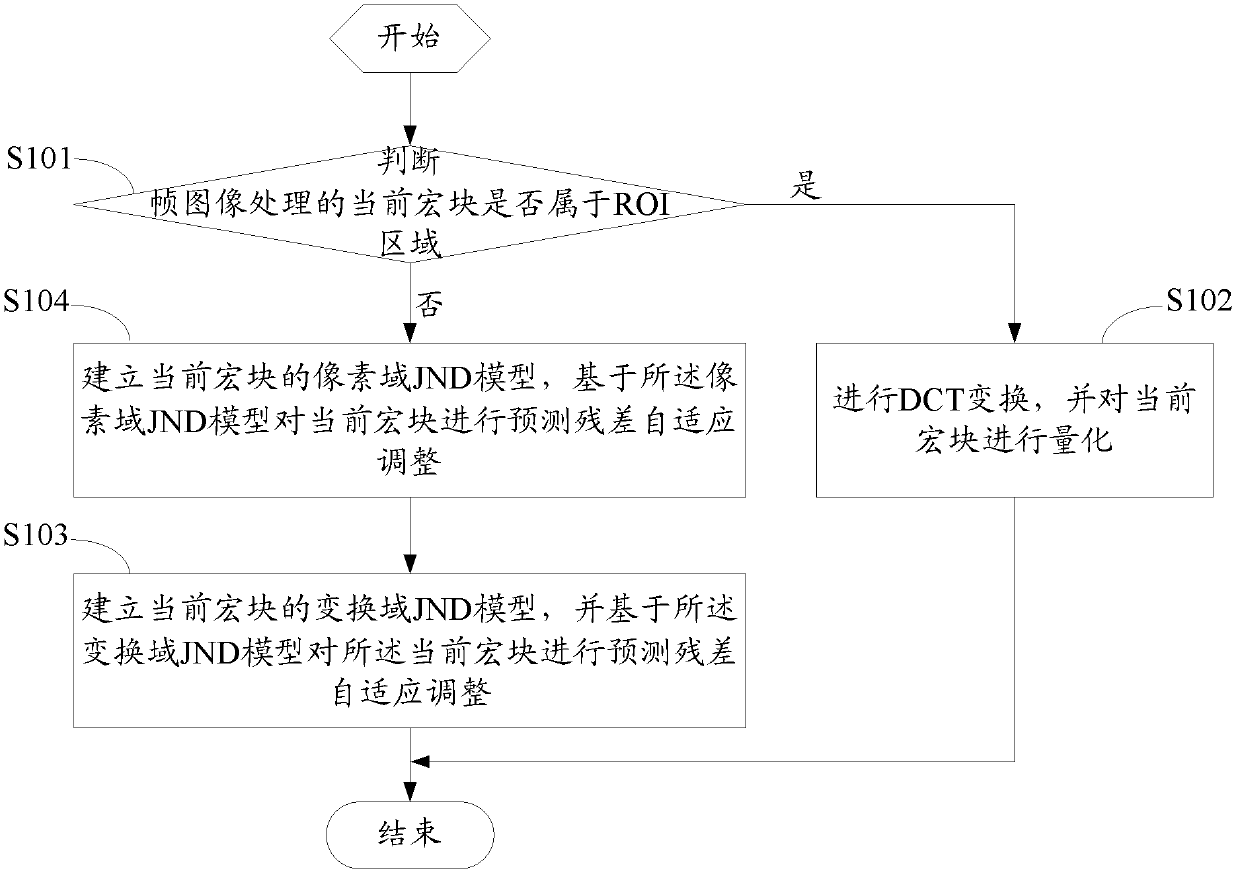
Method and device for coding video based on ROI and JND
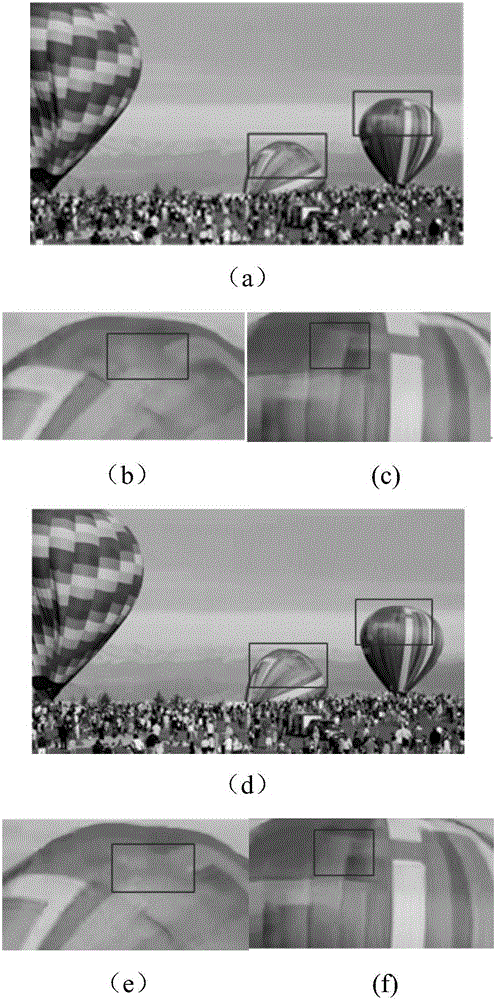
ActiveCN103379326AGuaranteed subjective qualityReduce code rateTelevision systemsImaging processingComputer architecture
The invention discloses a method and a device for coding a video based on region of interest (ROI) and just-noticeable difference (JND). The method comprises the following steps that whether the current macro block for frame image processing belongs to the ROI or not is judged; if the current macro block for frame image processing does not belong to an ROI, a transform domain JND model of the current macro block is built, and based on the transform domain JND model, forecasted residual error self-adjustment is conducted on the current macro block. The ROI and non-ROI in a frame image are separately processed, namely, conventional coding processing is conducted on macro blocks belonging to the ROI, and coding processing is conducted on macro blocks belonging to the non-ROI in the coding mode that forecasted residual error self-adjustment is carried out through transform domain JND; therefore, subjective coding quality is guaranteed, and coding rate is reduced.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Digital image watermark method based on visual attention mechanism
InactiveCN102722857ABalance imperceptibilityRobust and stableImage enhancementImage data processing detailsWatermark robustnessWatermark method
The invention discloses a digital image watermark method based on a visual attention mechanism. The digital image watermark method comprises the following steps of: firstly partitioning an image remarkable area by a visual attention mechanism module, obtaining a high-frequency area relative to the remarkable area by wavelet transform, continuously carrying out watermark embedding on dithering quantification modulation of coefficients of the high-frequency area, and dynamically regulating quantified step length depending on a JND (just noticeable difference) visual module in a quantification modulation process. Through the digital image watermark method based on the visual attention mechanism, disclosed by the invention, the step length is dynamically quantified and the watermark is embedded by combining the characteristics of human vision; when the robustness of the watermark is stabilized, the imperceptibility of the watermark is greatly balanced; and simultaneously, the influence of an image background area subjected to operations, such as filtering, noise pollution and the like, in the correctness of a watermark extracting result is further reduced to a certain extent by the introduction of a vision attention mechanism module; and the robustness of watermark detection is further improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
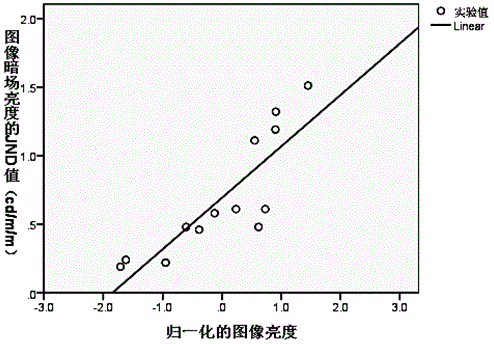
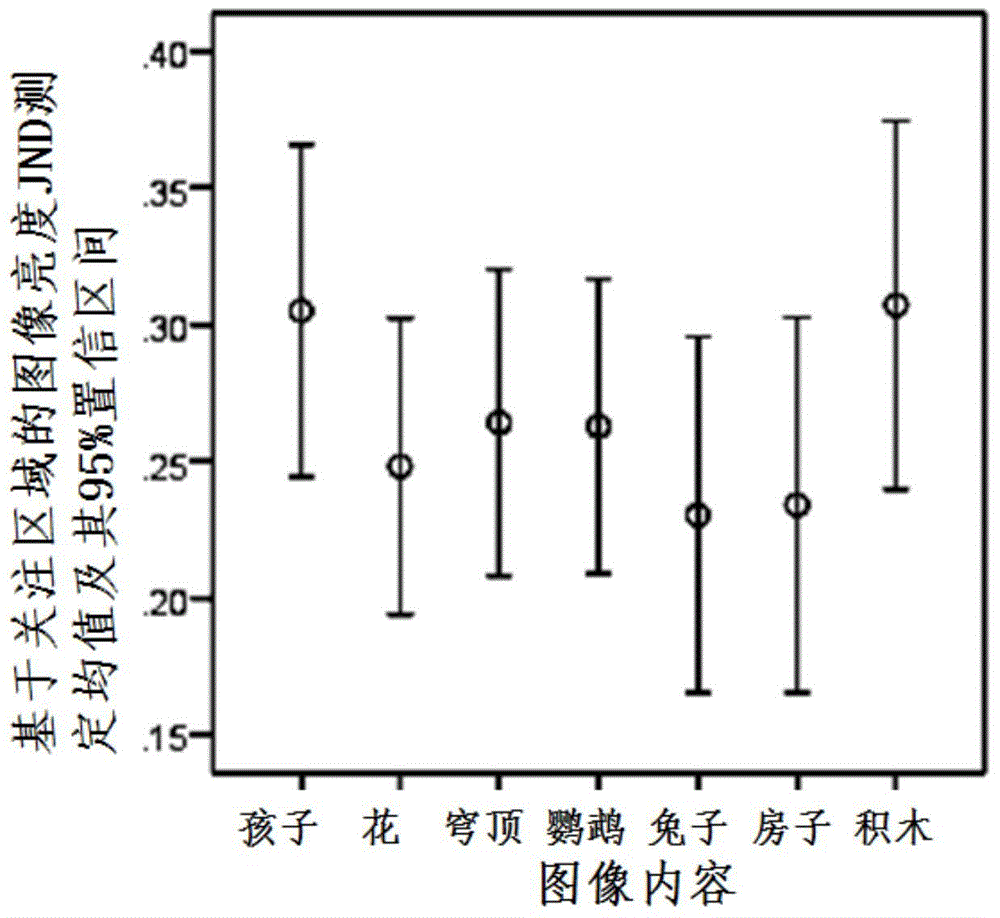
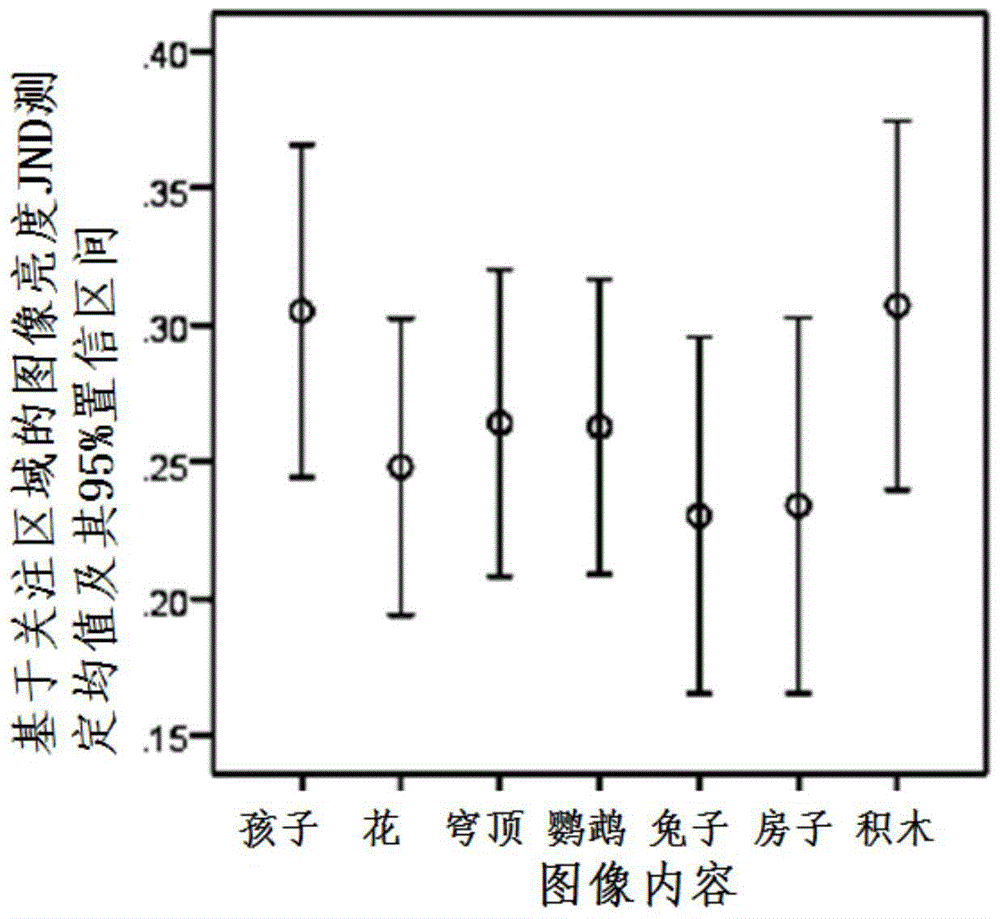
Image brightness JND value measurement method based on region of interest and prediction method
The invention discloses an image brightness just noticeable difference (JND) value measurement method based on a region of interest. According to the method, an original image is converted into an xyY space, a component Y undergoes linear compression according to different compression coefficients, and the brightness of an original image is reduced so that a set of test images is obtained; then an visual perception experiment is carried out, and at least one test image is selected to serve as a JND critical image; an image brightness JND value based on the region of interest is calculated according to a binarization image of the region of interest of the original image. The invention further discloses an image brightness JND value prediction method based on the region of interest. 0.26 is taken as the brightness JND prediction value of the image based on the region of interest. According to the image brightness JND value measurement method based on the region of interest and the prediction method, parameters of a displayer and especially influences, capable of being noticed by human eyes, of parameters of brightness and the contrast ratio on image brightness can be assessed quantitatively and improved, and accordingly bases are provided for design and researching of display techniques.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
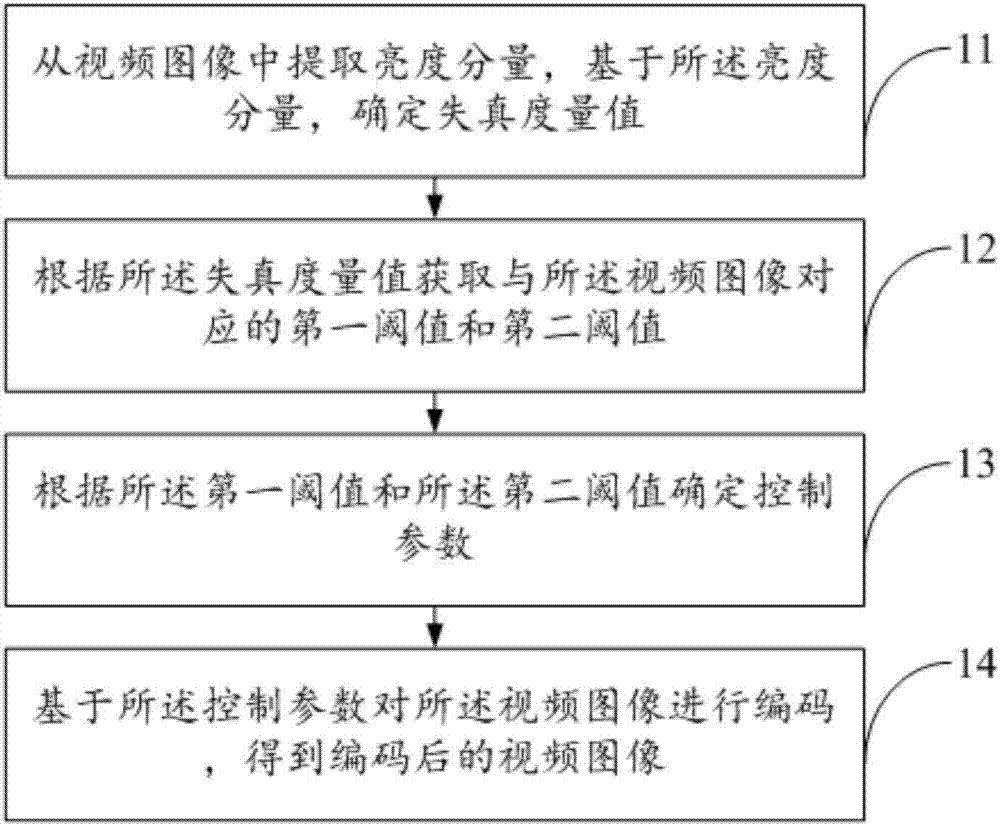
Coding method and apparatus for video images
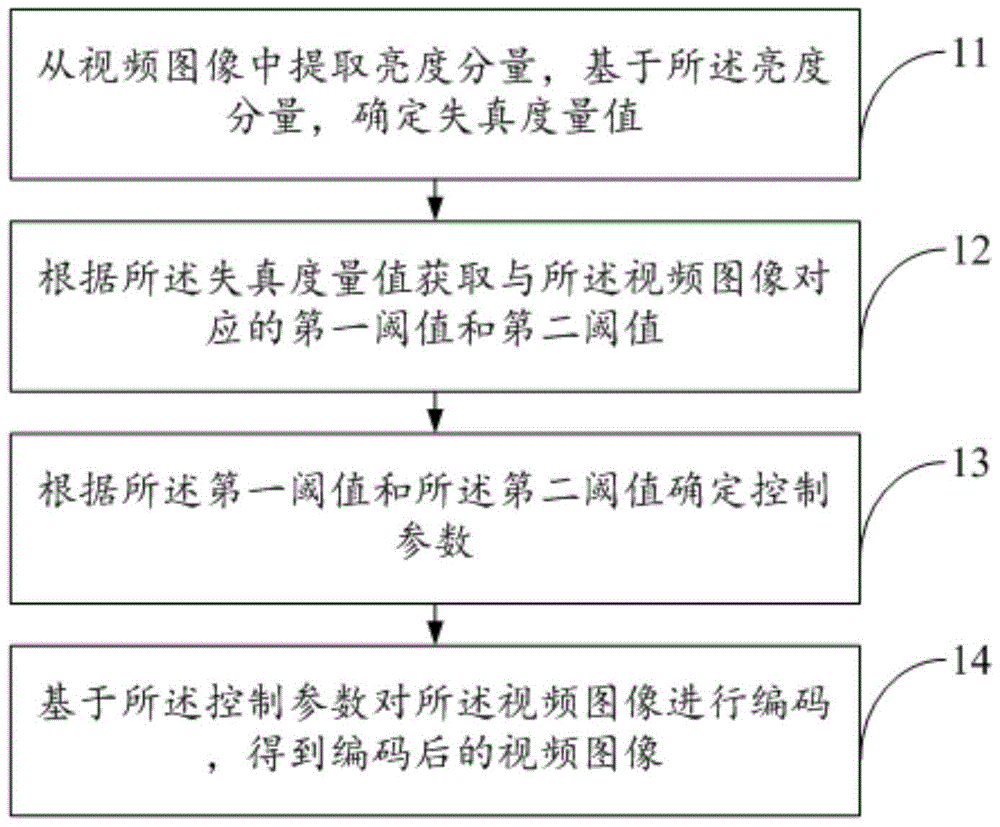
InactiveCN105812805AOvercoming the Weak Estimation ProblemAccurate estimateDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionVideo sequence
The invention discloses a coding method and apparatus for video images, and belongs to the field of video coding and decoding processing. The method comprises extracting brightness components from the video images, determining distortion magnitude, according to the distortion magnitude, obtaining a first threshold and a second threshold which are corresponding to the video images, according to the first threshold and the second threshold, determining control parameters, and obtaining coded video images by coding the video images based on the control parameters. Through utilization of a just-noticeable-difference (JND), the problem of weak estimation of a JND threshold of a disordered area in a conventional JND model is overcome, space redundancy in a video sequence is effectively eliminated, the coding amount is reduced, and the coding efficiency is improved. At the same time, a JND in an ordered area is more accurately estimated by use of an obtained brightness mask layer and a space mask layer, the perception quality of the ordered area in a video can be better improved, and the overall watching feel of the video is improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Video encoding method and apparatus
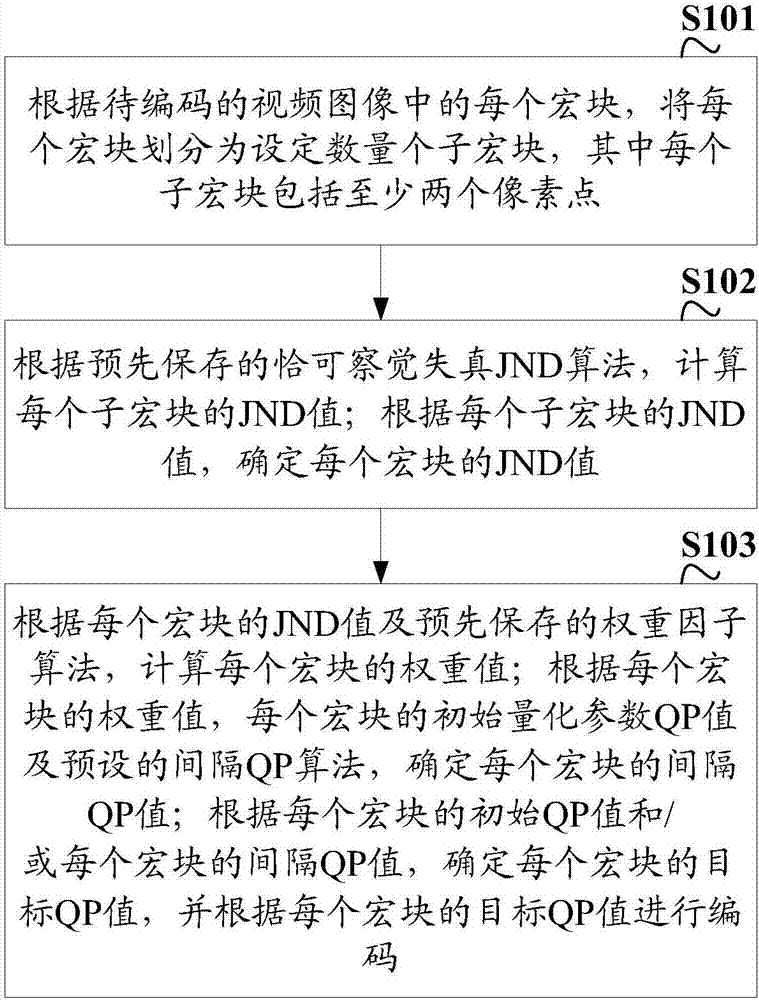
ActiveCN107147912AGuaranteed real-timeSmall amount of calculationDigital video signal modificationVideo encodingVideo image
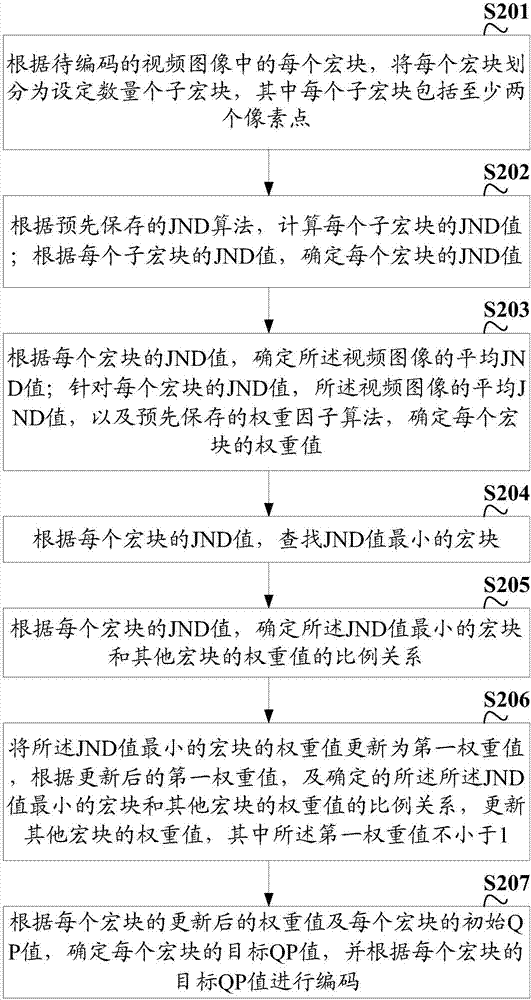
The invention discloses a video encoding method and apparatus. The method comprises the following steps: according to each macro block in a to-be-encoded video image, dividing each macro block into a set number of sub macro blocks, wherein each sub macro block comprises at least two pixel points; calculating a JND value of each sub macro block according to a pre-stored just noticeable difference (JND) algorithm; determining the JND value of each macro block according to the JND value of each sub macro block; calculating a weight value of each macro block according to the JND value of each macro block and a pre-stored weight factor algorithm; determining an interval QP value of each macro block according to the weight value of each macro block, an initial QP value of each macro block and a preset interval QP algorithm; and determining a target QP value of each macro block according to the initial QP value of each macro block and / or the interval QP value of each macro block, and performing encoding according to the target QP value of each macro block. The encoding time consumption is reduced, and the encoding instantaneity is guaranteed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DAHUA TECH CO LTD
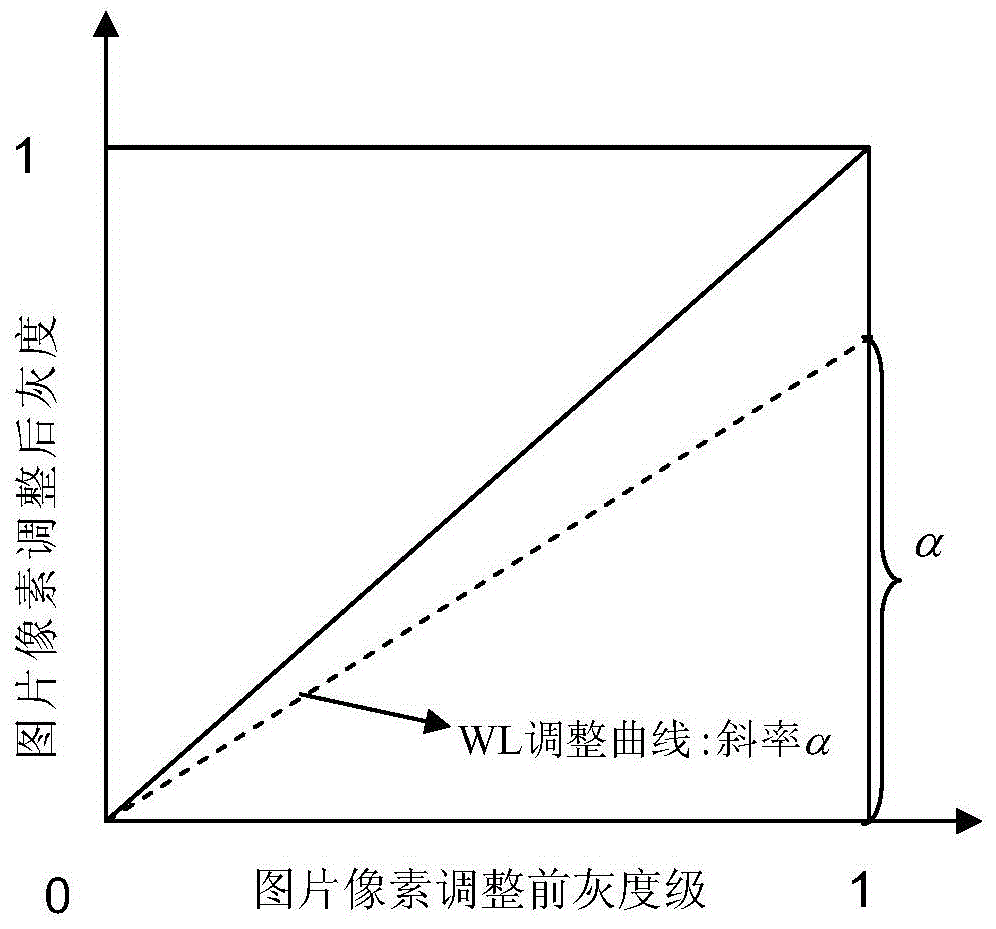
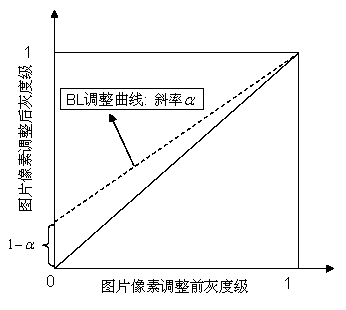
Method for generating target gamma curve of display based on visual discrimination requirement
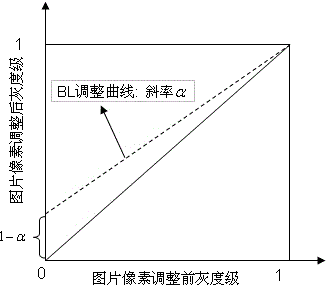
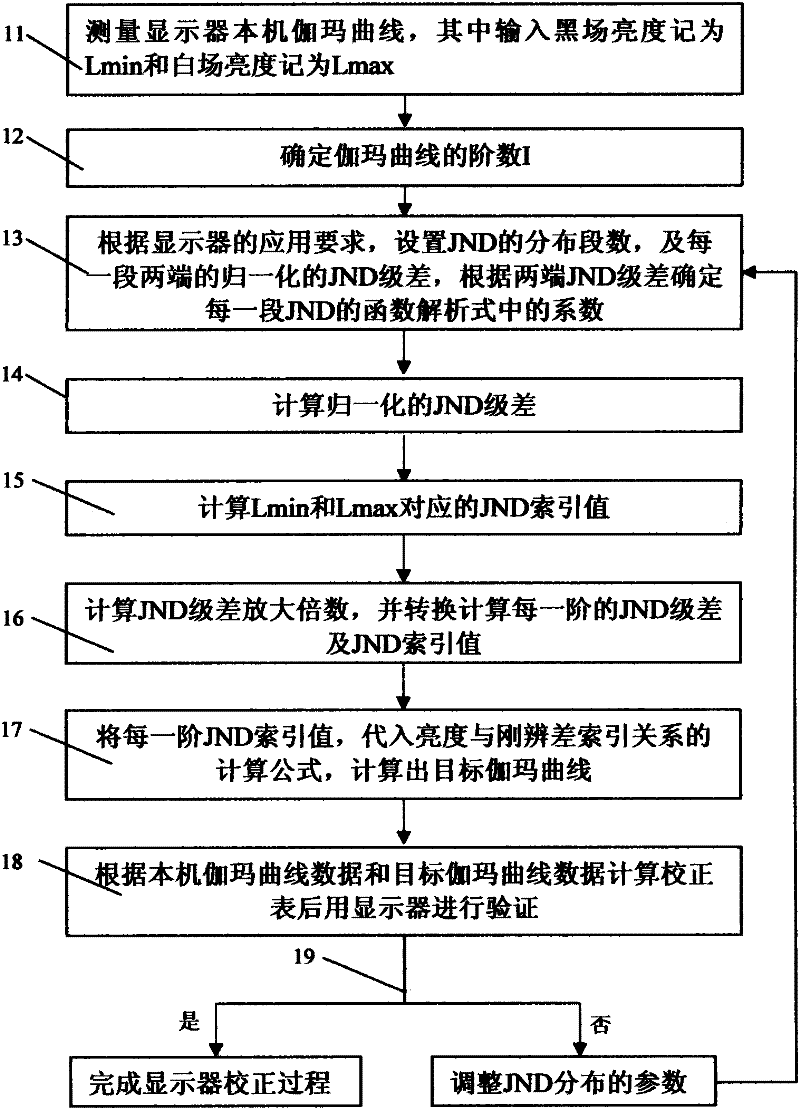
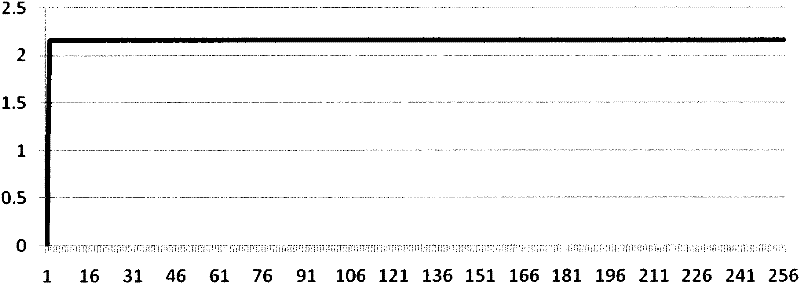
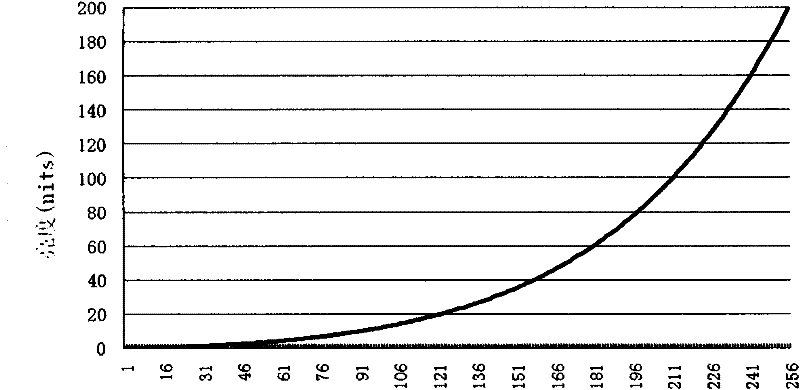
The invention discloses a method for generating a target gamma curve of a display based on a visual discrimination requirement. A just-noticeable difference (JND) is subjected to segment and distributed calculation according to a calculation formula and an inverse operation formula of an index relationship between brightness and the JND by combining the native gamma curve of the display on the basis of a display requirement, a JND index value is calculated, the target gamma curve is finally obtained, and all or part of gray scales of the generated target gamma curve can completely accord with equal-difference discrimination of human vision on the basis of the display requirement after the generated target gamma curve passes the verification of the display. The method is simple and effective, can be suitable for effectively generating the target gamma curves of various displays and is also suitable for other application of the curve, and data is simply and conveniently calculated and accurately and reliably corrected.
Owner:德为显示科技股份有限公司
Image quality evaluation method based on visual characteristic
The invention discloses an image quality evaluation method based on a visual characteristic. The method is characterized by: firstly, converting original images into a xyY space or a LCH space, processing a component Y or a component C so as to obtain a group of test images; then, finding at least one JND (just noticeable difference) critical image; calculating differences of brightness (BR), color saturation (CS) and Gaussian function variance parameters in the original images and the JND critical image, wherein average values of the differences are the JND values of the BR, CS and contour rendering (CR) of the original images respectively; and then, carrying out mean calculation on the JND values of the different original images and determining the final JND values; taking the JND as a unit to change different attributes of the image at different degrees respectively; using a visual perception test to test the subjective image quality; then, using a regression analysis to establish a relation model of the image quality and the image attributes; and researching influences of the different attributes of the images according to a variance analysis. By using the method of the invention, influence on image quality which can be perceived by human eyes when improving the display parameter can be quantitatively evaluated.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
JND (Just-noticeable difference) based video encoding method and device
ActiveCN106454386ASolve inaccurateSolve quality problemsDigital video signal modificationWeight coefficientVideo encoding
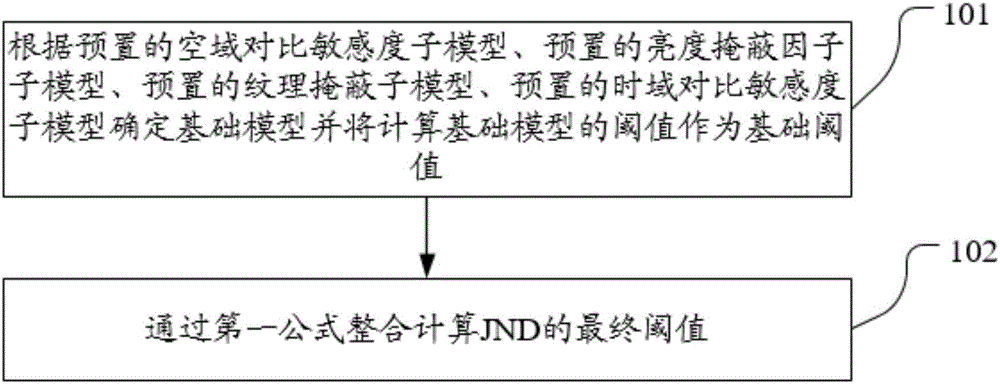
The embodiment of the invention discloses a JND (Just-noticeable difference) based video encoding method and device. According to the invention, a plurality of sub-models of a JND model are built, a foundational model is determined from the sub-models, threshold superposition is performed according to weighting coefficients of other sub-models except for the foundational model by taking the foundational model as a foundational threshold, and an offset effect of different sub-models is deducted at the same time so as to acquire a more accurate JND model and a more accurate threshold. The method and the device disclosed by the invention solve technical problems that the JND model is inaccurate and the quality of compressed video is reduced in the prior art because of the direct superposition threshold calculated via multiplication by taking effects of the plurality of sub-models as weighting coefficients.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Region-of-interest-based image dark field brightness JND value determination method and prediction method
The invention discloses a region-of-interest-based image dark field brightness JND (Just Noticeable Difference) value determination method and prediction method. The determination method includes the steps that firstly, an original image is converted into an xyY space, linear compression is conducted on the component Y according to different coefficients of compressibility, the dark field brightness of the original image is increased, and a set of test images is obtained; the visual perception experiment is conducted, and at least one test image is found out to serve as a JND critical image; next, the image dark field brightness JND value based on the region-of-interest is worked out according to the region-of-interest weight map of the original image. The invention further discloses a region-of-interest-based image dark field brightness JND value prediction method, wherein 0.20cd / m<2> serves as the image dark field brightness JND prediction value based on the region-of-interest of the image. By means of the region-of-interest-based image dark field brightness JND value determination method and the prediction method, quantitative evaluation and improvement can be conducted on display parameters, especially the influence, which human eyes can perceive, on the image dark field brightness when the parameters of the dark field brightness and contrast ratio are designed, and thus a basis is provided for display technology design and research.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Coding method and device for video image
PendingCN107027031AOvercoming the Weak Estimation ProblemAccurate estimateDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionVideo sequence
The invention discloses a coding method and device for a video image, and belongs to the field of video coding and decoding. The coding method disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of: extracting a luminance component from a video image, determining a distortion measurement value, obtaining a first threshold value and a second threshold value corresponding to the video image according to the distortion measurement value, determining control parameters according to the first threshold value and the second threshold value, and coding the video image based on the control parameters, so that a coded video image is obtained. The just-noticeable difference (JND) is utilized; therefore, the weak estimation problem for the JND threshold value of a disordered region in the previous JND model is overcome; the spatial redundancy in a video sequence is effectively eliminated; the coding amount is reduced; the coding efficiency is increased; simultaneously, the JND of an ordered region is estimated more accurately by utilization of the obtained luminance mask and spatial mask, so that the perceived quality of the ordered region in a video can be well improved conveniently; and thus, the overall viewing experience of the video can be improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Image brightness jnd value measurement method based on attention area
The invention discloses an image brightness just noticeable difference (JND) value measurement method based on a region of interest. According to the method, an original image is converted into an xyY space, a component Y undergoes linear compression according to different compression coefficients, and the brightness of an original image is reduced so that a set of test images is obtained; then an visual perception experiment is carried out, and at least one test image is selected to serve as a JND critical image; an image brightness JND value based on the region of interest is calculated according to a binarization image of the region of interest of the original image. The invention further discloses an image brightness JND value prediction method based on the region of interest. 0.26 is taken as the brightness JND prediction value of the image based on the region of interest. According to the image brightness JND value measurement method based on the region of interest and the prediction method, parameters of a displayer and especially influences, capable of being noticed by human eyes, of parameters of brightness and the contrast ratio on image brightness can be assessed quantitatively and improved, and accordingly bases are provided for design and researching of display techniques.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
JND (Just Noticeable Difference) value measurement method of image brightness
InactiveCN102447945BNot affected by JND valueTelevision systemsTesting optical propertiesComputer graphics (images)Gray level
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
3D (Three Dimensional)-mode color cast improving method
InactiveCN102868892AImprove color castAvoid duplicationColor signal processing circuitsSteroscopic systemsColor correctionComputer science
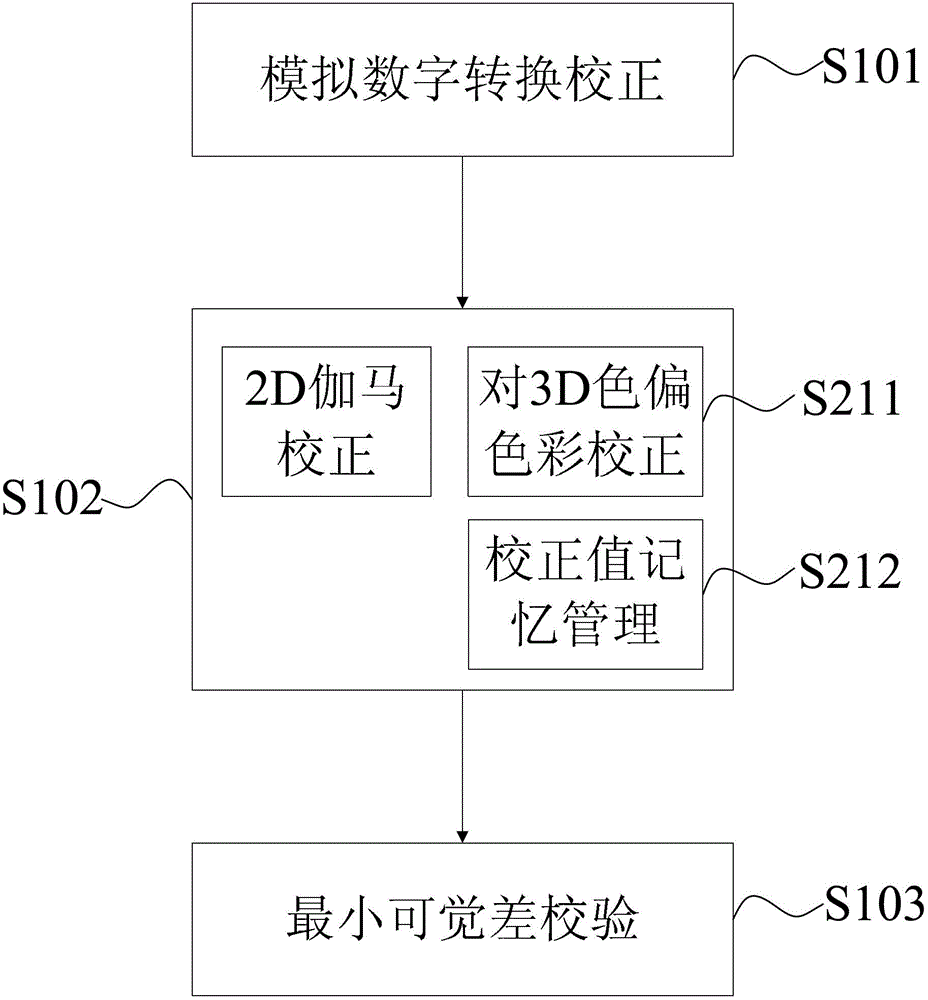
The invention provides a 3D (Three Dimensional)-mode color cast improving method, which comprises the steps of: 1, correction of analog / digital conversion; 2, gamma correction; 3, verification of just noticeable difference, wherein the gamma correction comprises 2D-mode gamma correction and 3D-mode gamma correction, and the 3D-mode gamma correction comprises color correction of 3D-mode color cast and correction value memory management. Compared with the prior art, the 3D-mode color cast improving method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that by means of the color correction of the 3D-mode color cast and the correction value memory management, the repeated gamma correction and the verification of the just noticeable difference under the 3D mode are avoided, and thus, the gamma correction and the verification of the just noticeable difference only need to be carried out under the 2D mode. Accordingly, the 3D-mode color cast problem can be improved effectively, the time for the gamma correction and the verification of the just noticeable difference is shortened, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:QISDA OPTRONICS (SUZHOU) CO LTD +1
Image enhancing method and device
ActiveCN104504653ASmall enhancementResolve distortionImage enhancementImaging processingHistogram equalization
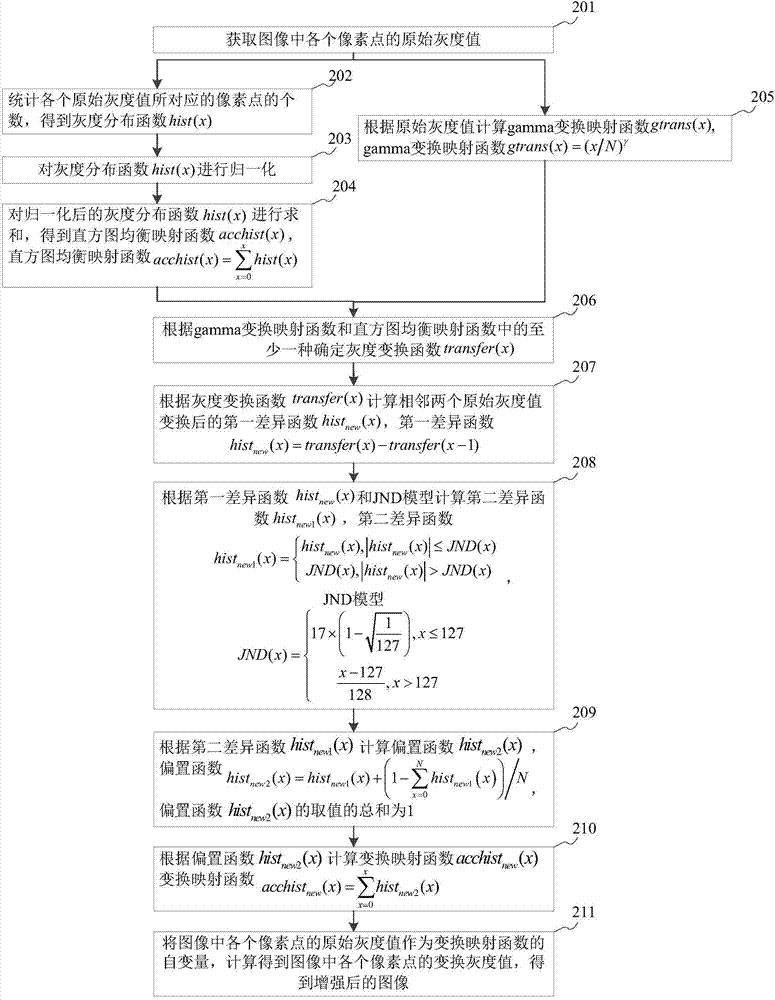
The disclosure discloses an image enhancing method and device, and belongs to the technical field of image processing. The image enhancing method comprises the following steps: acquiring the original gray-scale value of each pixel point in an image, and calculating the gamma transform mapping function of the image according to the original gray-scale values; and / or calculating a histogram equalization mapping function according to the original gray-scale values; calculating a transform mapping function according to at least one of the gamma transform mapping function and the histogram equalization mapping function and a just noticeable difference (JND) model; and performing transformation on the original gray-scale value of each pixel point in the image according to the transform mapping function to obtain an enhanced image. At least one mapping function in the gamma transform mapping function and the histogram equalization mapping function is modulated through the JND model, and gray-scale value transformation is performed on the image according to the modulated transform mapping function, so that the problem of image distortion due to excessive enhancement of the processed image is solved, and the effect of improving the image enhancing effect is achieved.
Owner:XIAOMI INC
Method of measuring main attributes of natural image
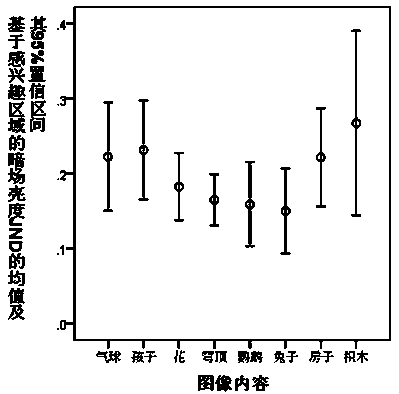
InactiveCN105427334AEasy to changeImage enhancementImage analysisStatistical analysisLevel of detail
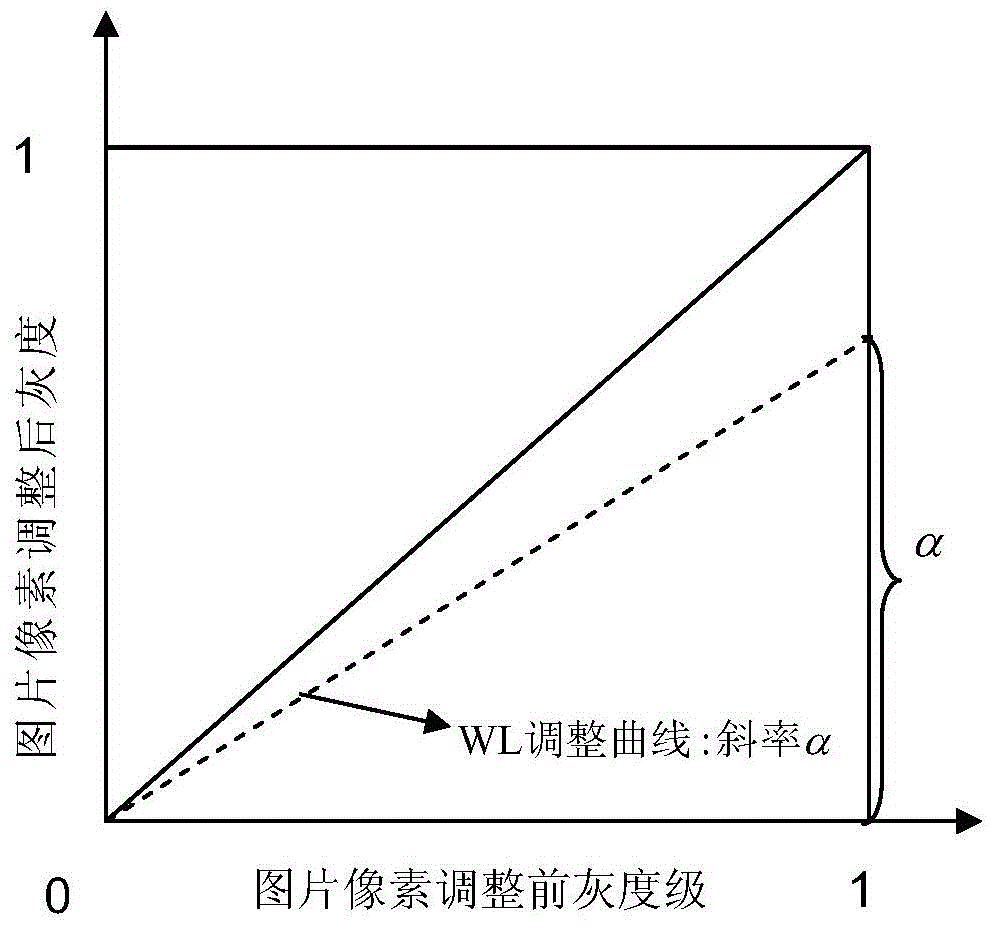
The invention discloses a method of measuring main attributes of a natural image. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1, the original image is processed according to the following methods and test images are obtained, wherein the methods are: 1, two times of JND (Just Noticeable Difference) amount of the white level of the original image are changed; 2, two times of JND amount of the black level of the original image are changed; 3, two times of JND amount of the color saturation of the original image are changed; and 4, two times of JND amount of the contour rendering of the original image are changed; 2, with the original image as a reference image, differences between any two groups of the above four groups of test images and the reference image are compared respectively, and the group of test images which has the largest difference with the reference image is found out; 3, different image contents and tested images are replaced, and the first step and the second step are repeated; and 4, a statistical model is adopted, a Z value corresponding to a different image attribute change amount is solved respectively, and significance statistical analysis is then carried out.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method and apparatus for video coding by ABT-based just noticeable difference model
ActiveUS8559511B2Bit rateReduce bitrateColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionIntra-frame
The present invention relates to method and apparatus for video coding by ABT-based just noticeable difference (JND). For building the just noticeable difference model, spatial content information (SCI) is used to represent the spatial appearance similarity between one macroblock and its sub-blocks and the motion characteristic distance (MCD) is used to represent the motion characteristics similarity between one macroblock and its sub-blocks. For intra frames, the balance strategy based on the obtained SCI of the macroblock is used to generate the ABT-based JND model. For inter frames, the balanced strategy based on the obtained SCI and MCD of the macroblock is used to generate the ABT-based JND model. Using the ABT-based JND model, the residual coefficients for each block in a frame is filtered to obtain a reduced set of residual coefficients for transmission without degradation in visual quality.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Visible motion blur
A method of measuring motion blur is disclosed comprising obtaining a moving edge temporal profile r1(k) of an image of a high-contrast moving edge, calculating the masked local contrast m1(k) for r1(k) and the masked local contrast m2(k) for an ideal step edge waveform r2(k) with the same amplitude as r1(k), and calculating the measure or motion blur Ψ as a difference function,Ω=S(ΔxΣk|m1(k)−m2(k)|β)1 / β.The masked local contrasts are calculated using a set of convolution kernels scaled to simulate the performance of the human visual system, and Ψ is measured in units of just-noticeable differences.
Owner:NASA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com