Patents
Literature
35 results about "Partial stroke testing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
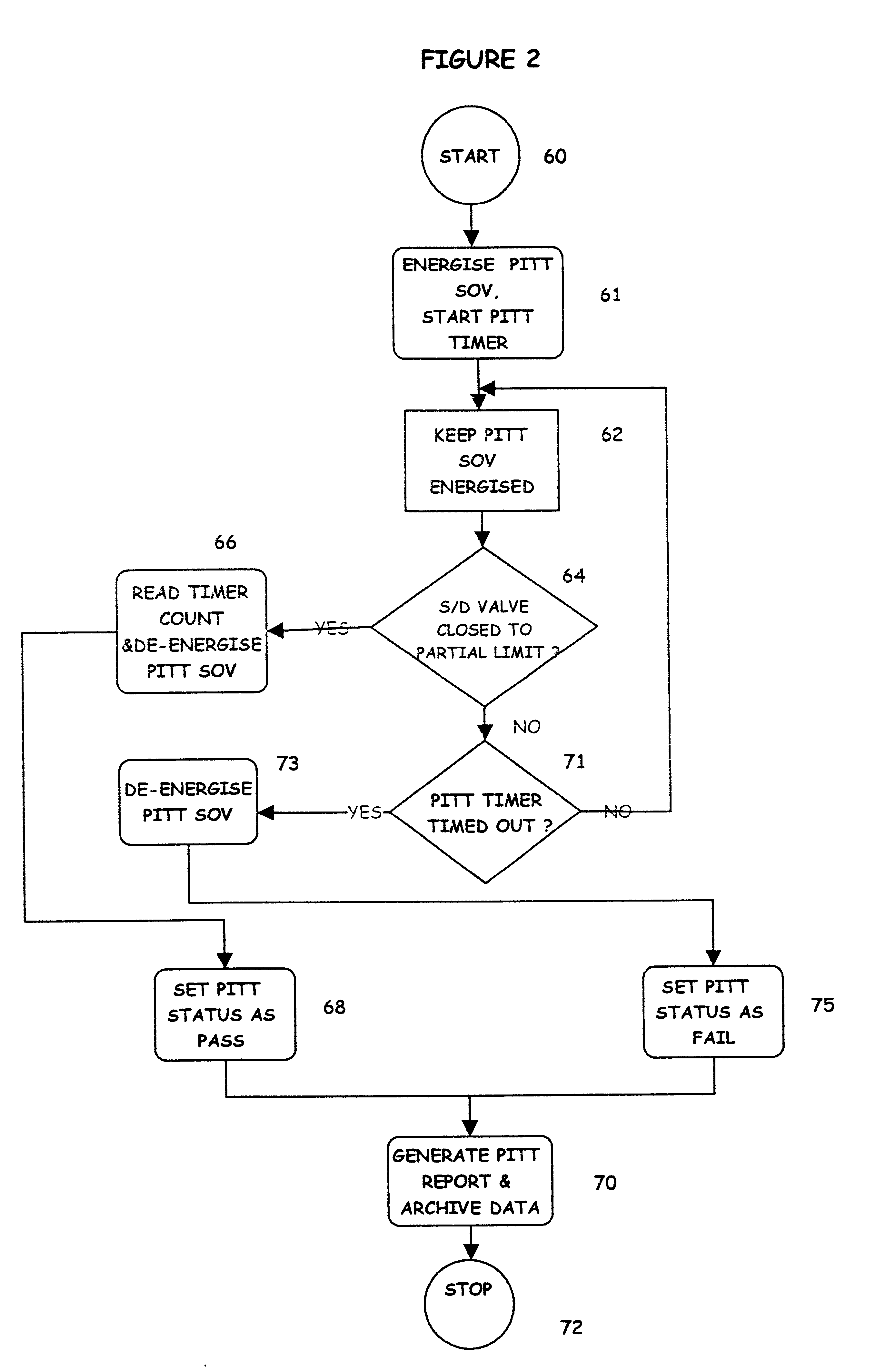
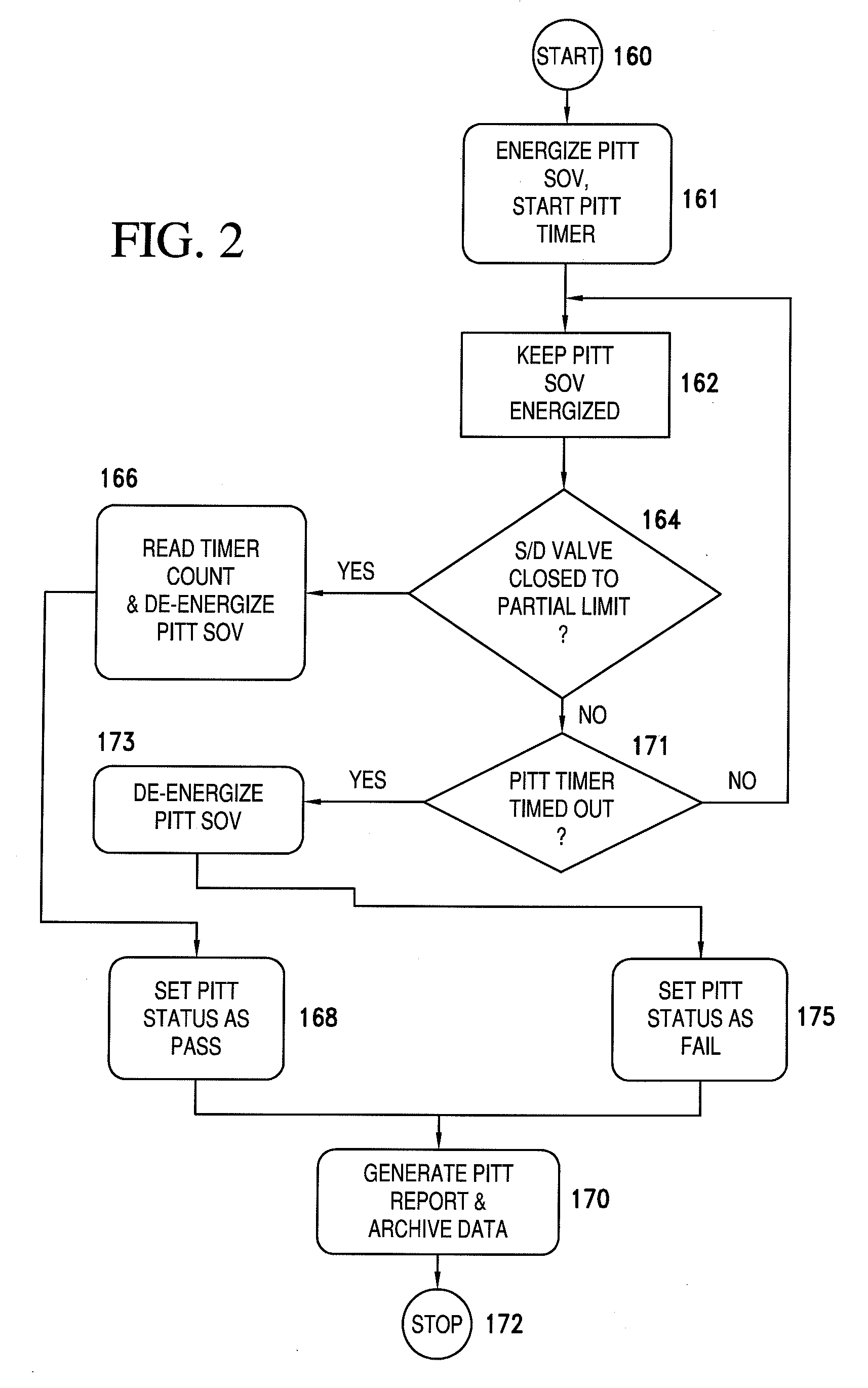
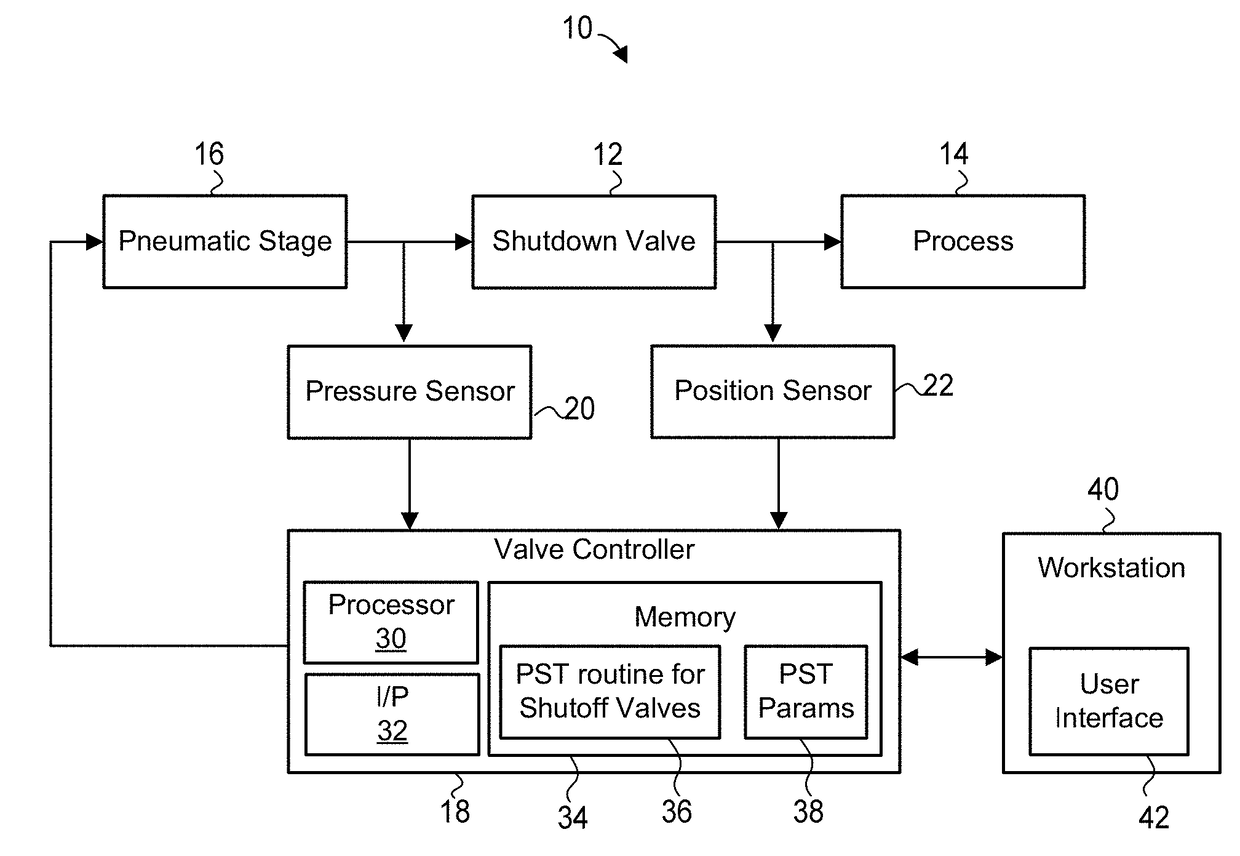
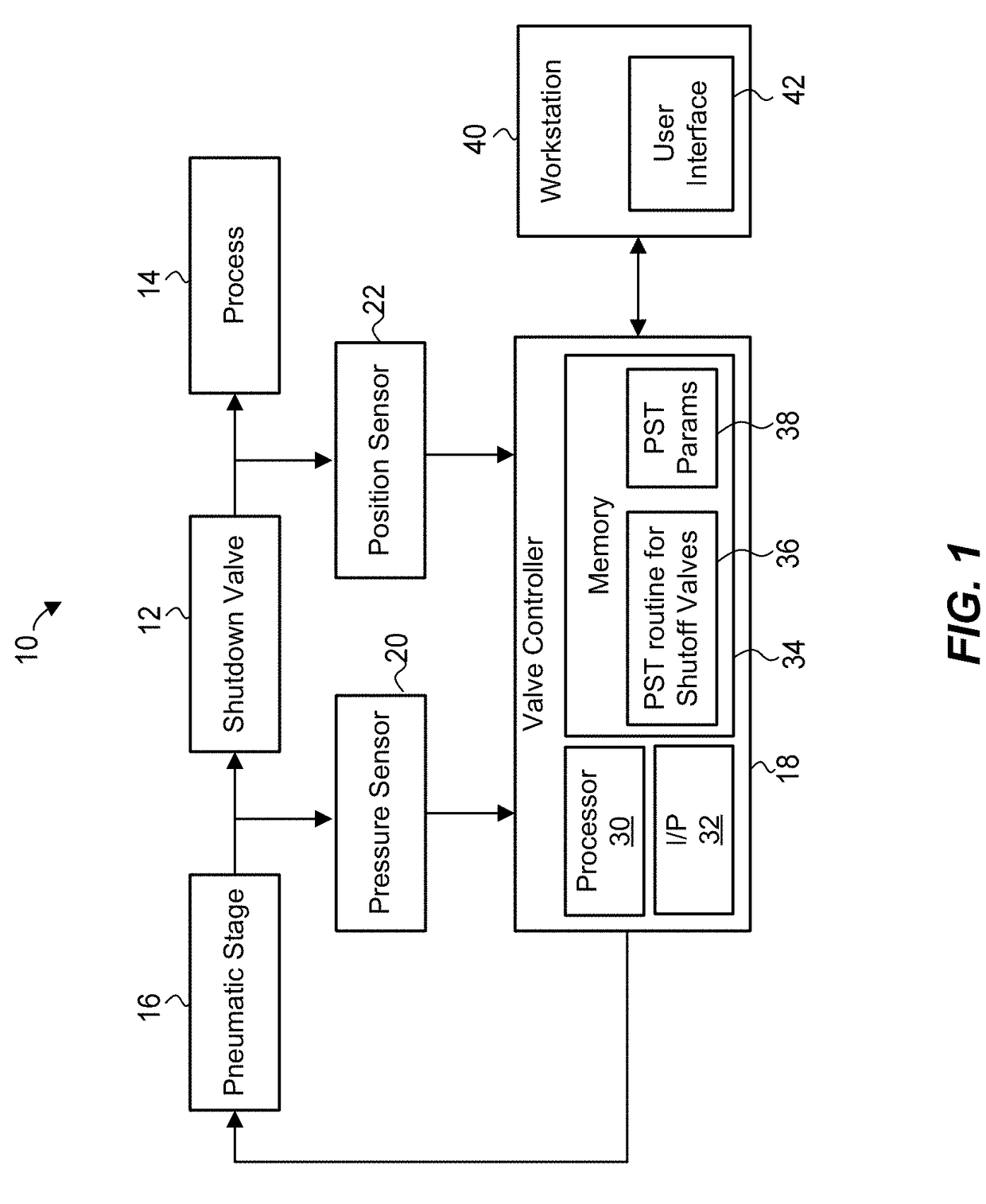
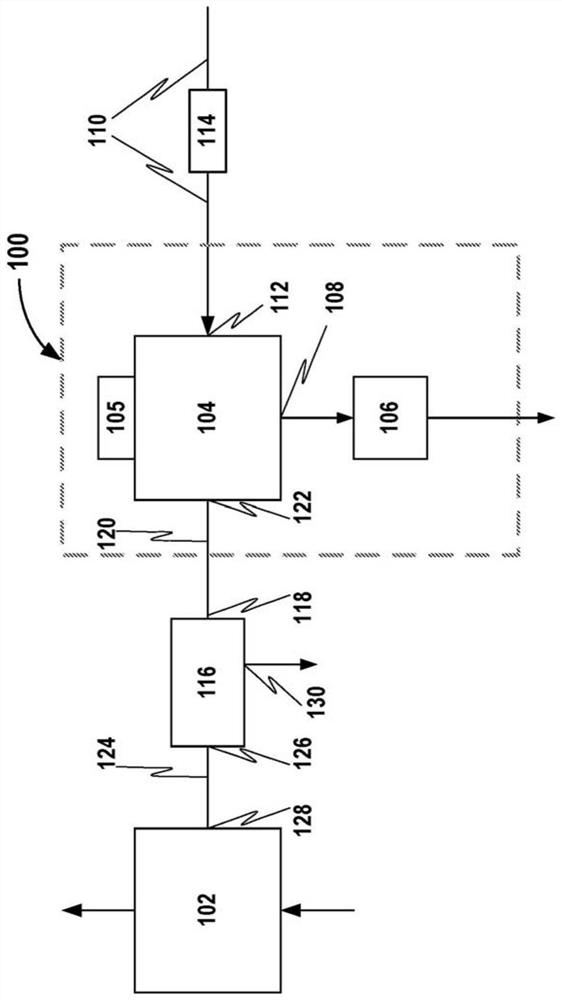
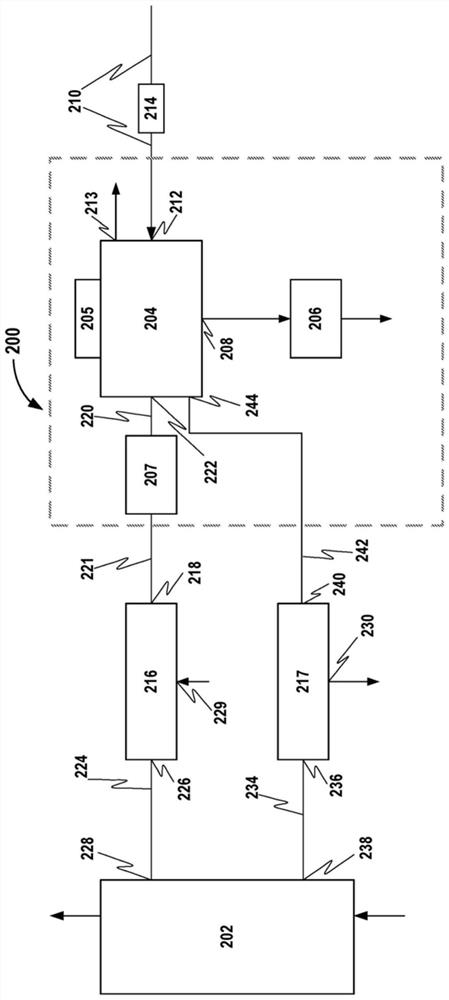
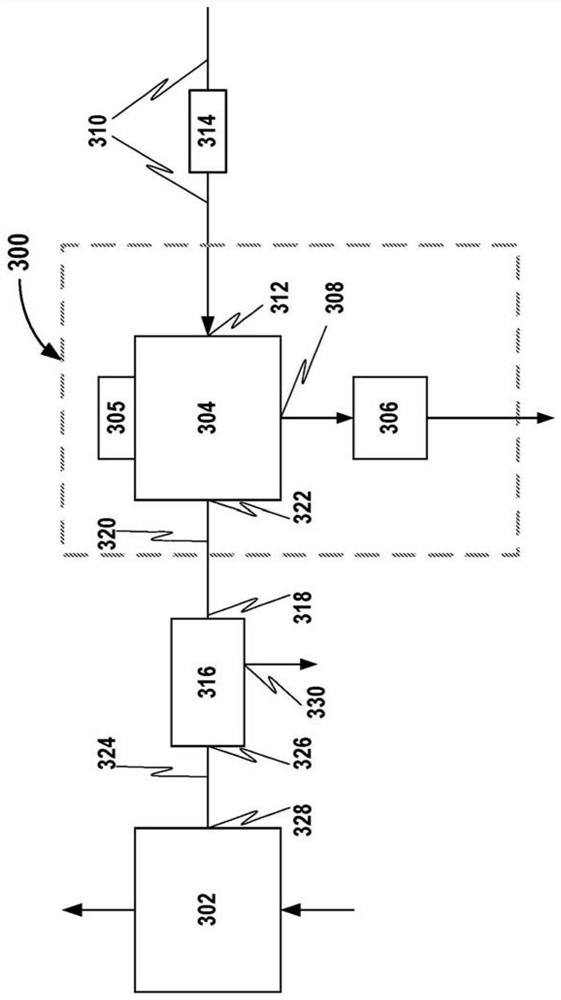
Partial stroke testing (or PST) is a technique used in a control system to allow the user to test a percentage of the possible failure modes of a shut down valve without the need to physically close the valve. PST is used to assist in determining that the safety function will operate on demand. PST is most often used on high integrity emergency shutdown valves (ESDVs) in applications where closing the valve will have a high cost burden yet proving the integrity of the valve is essential to maintaining a safe facility. In addition to ESDVs PST is also used on high integrity pressure protection systems or HIPPS. Partial stroke testing is not a replacement for the need to fully stroke valves as proof testing is still a mandatory requirement.
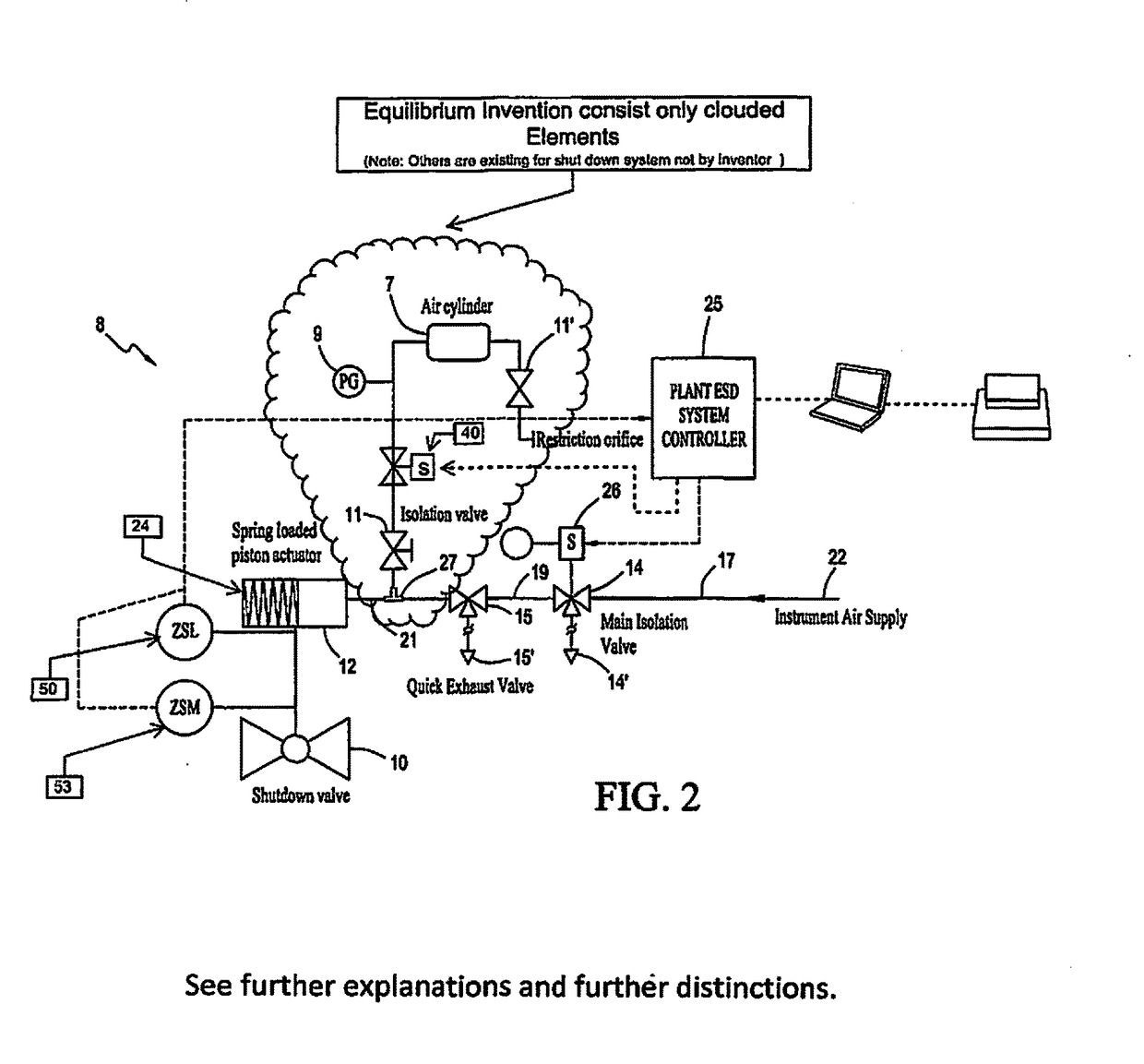
Partial stroke testing system
InactiveUS20020108436A1Quick closeLow costValve arrangementsUsing mechanical meansSystems designExhaust valve
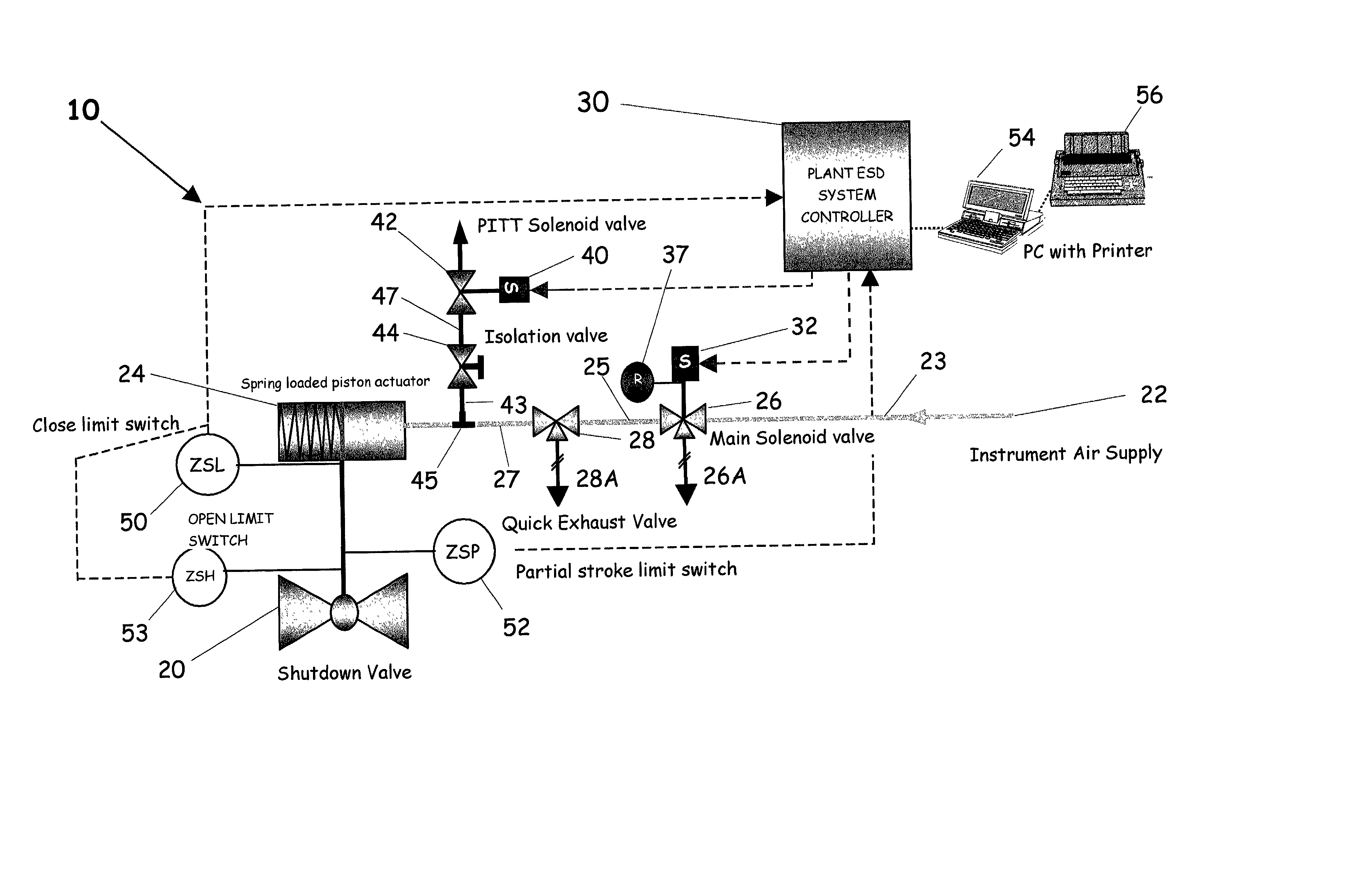
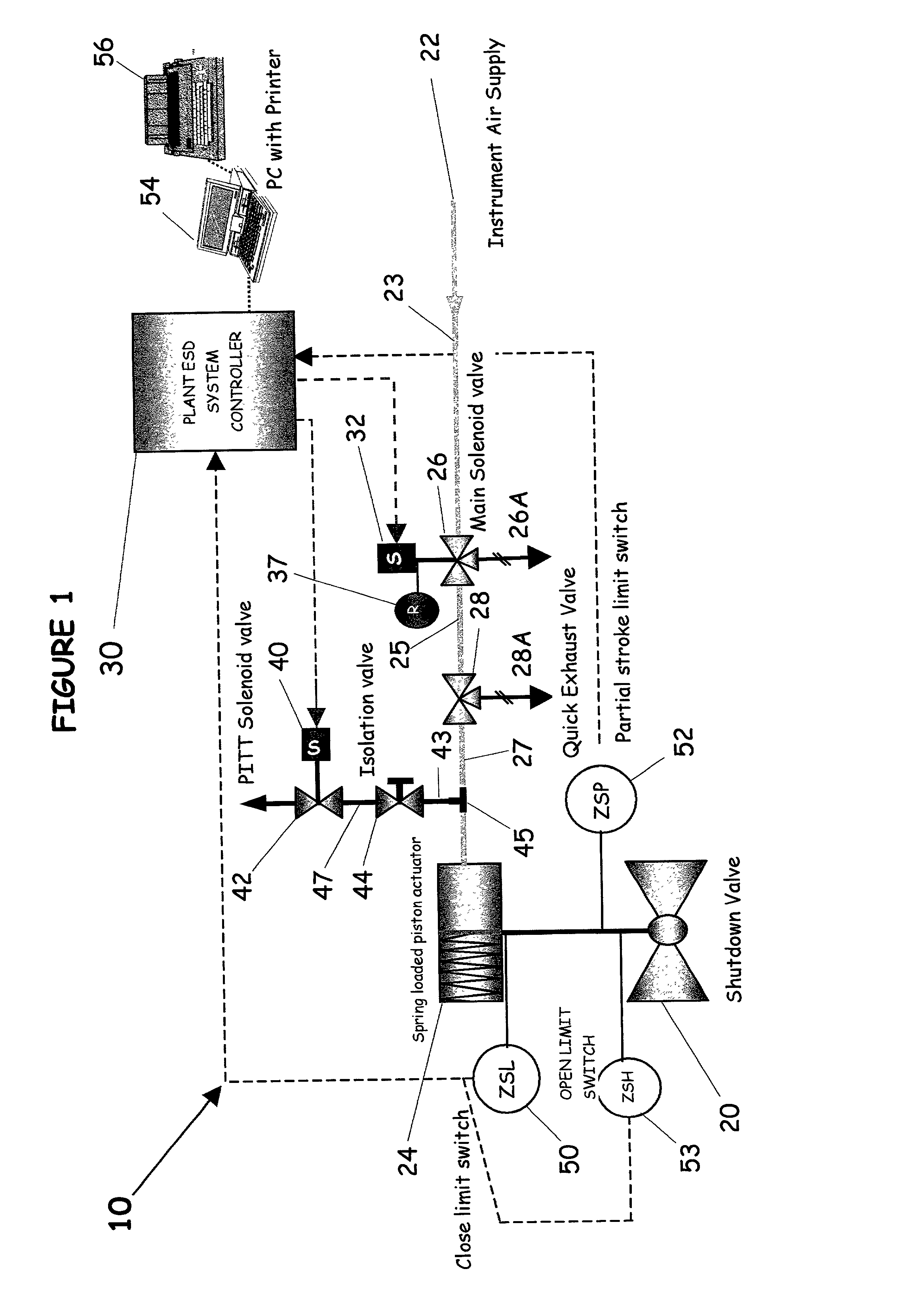
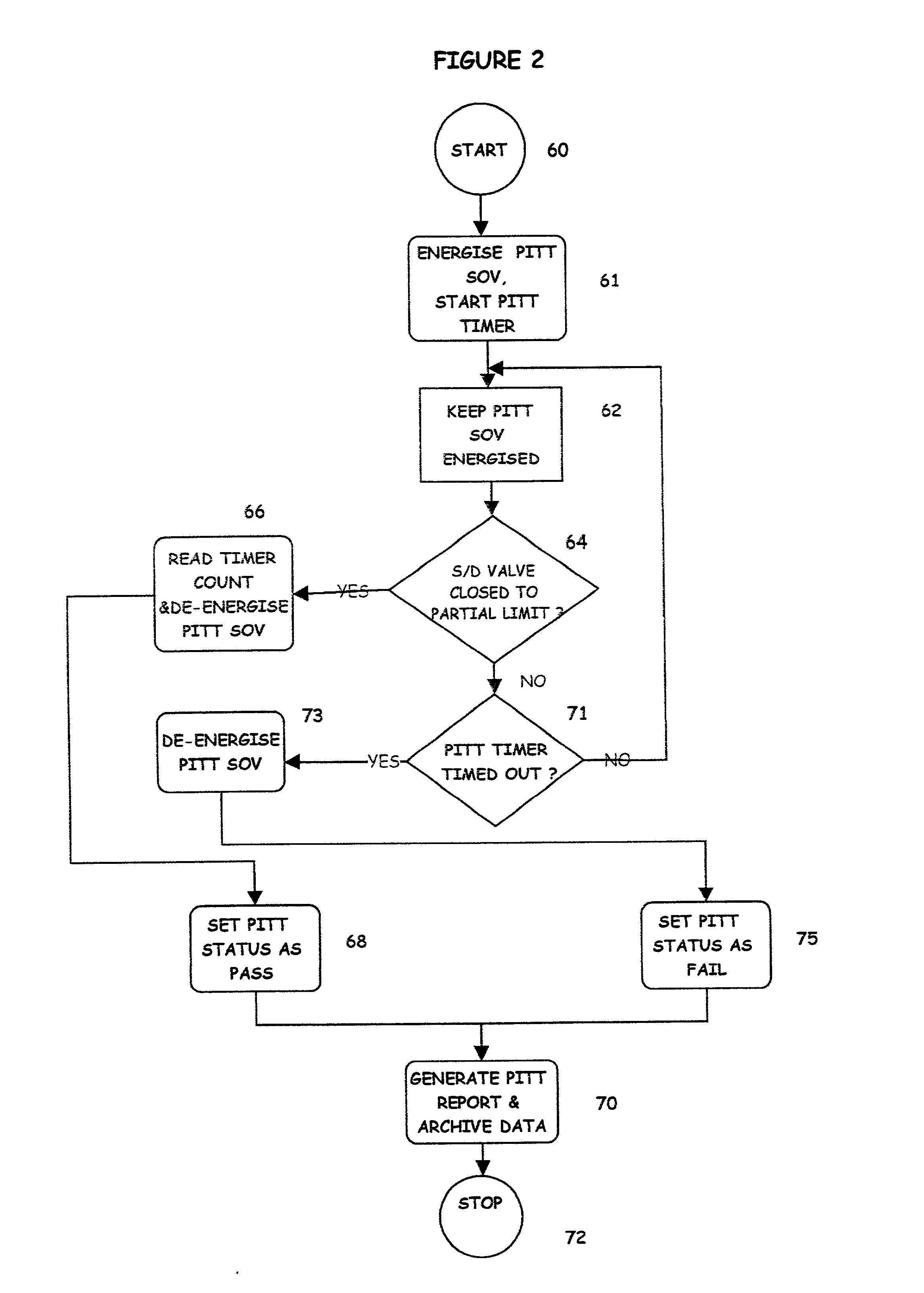
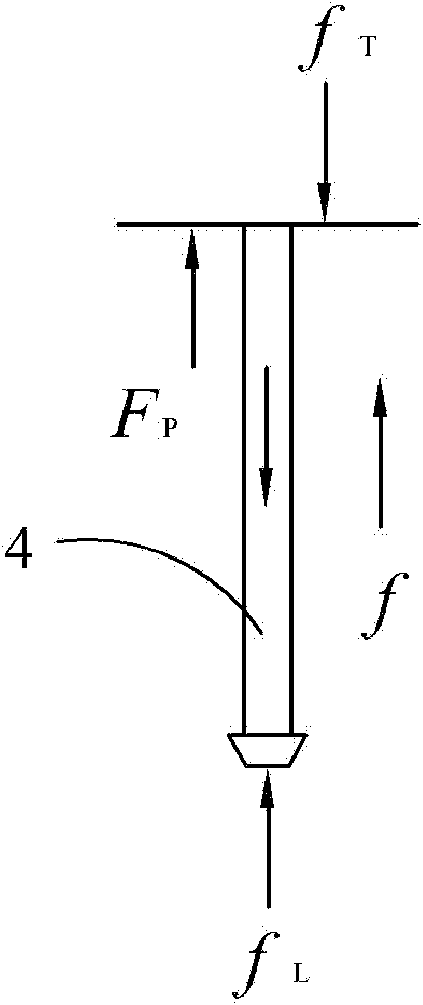
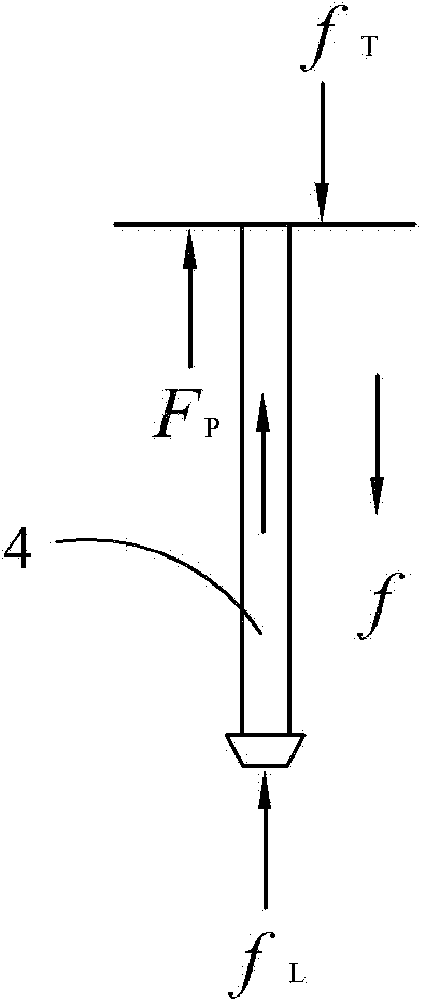
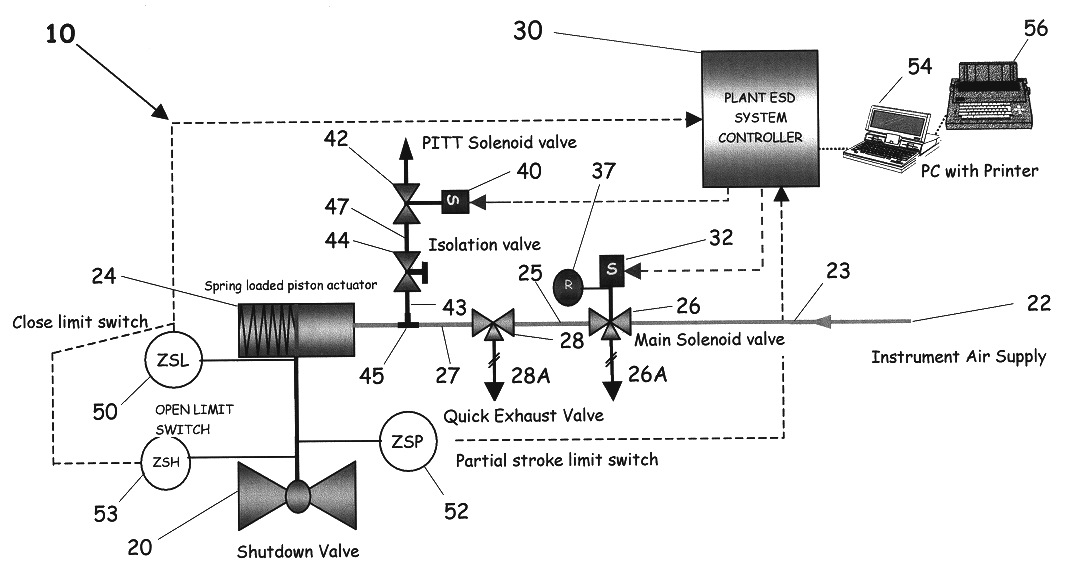
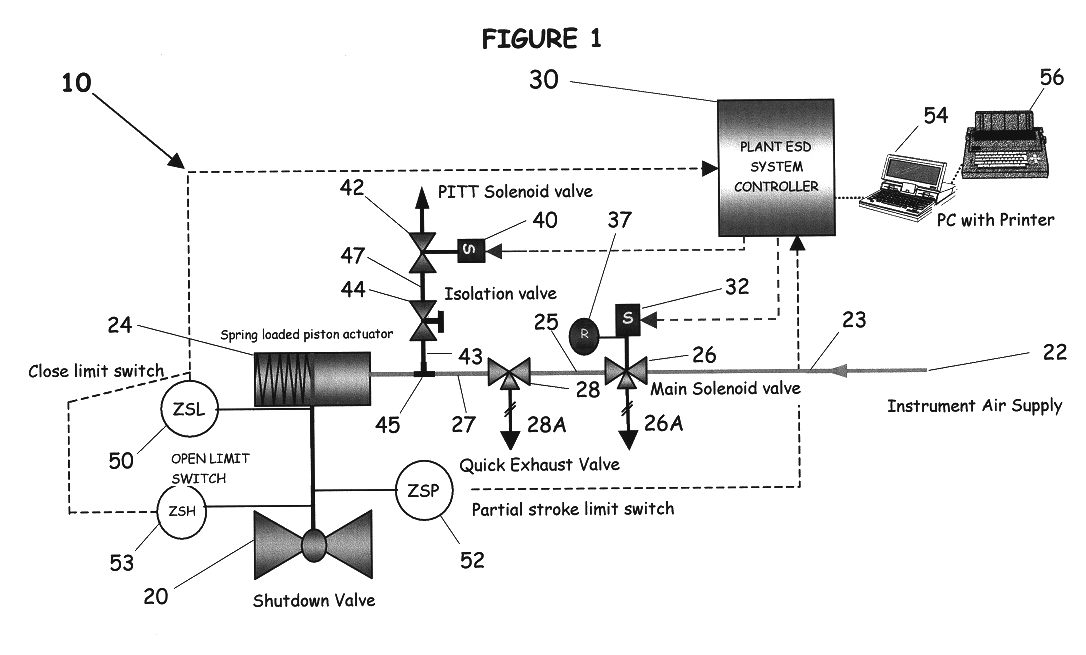
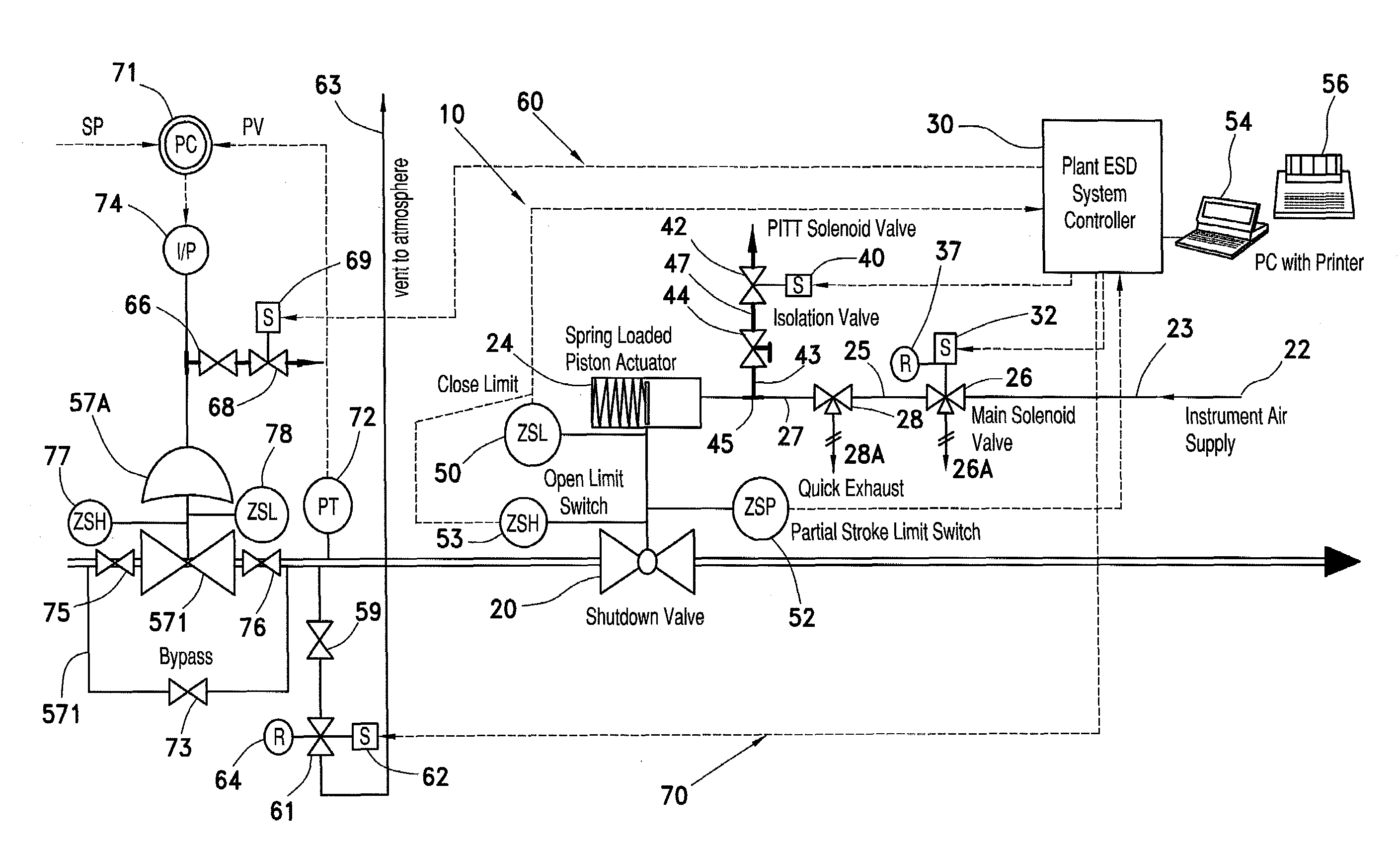
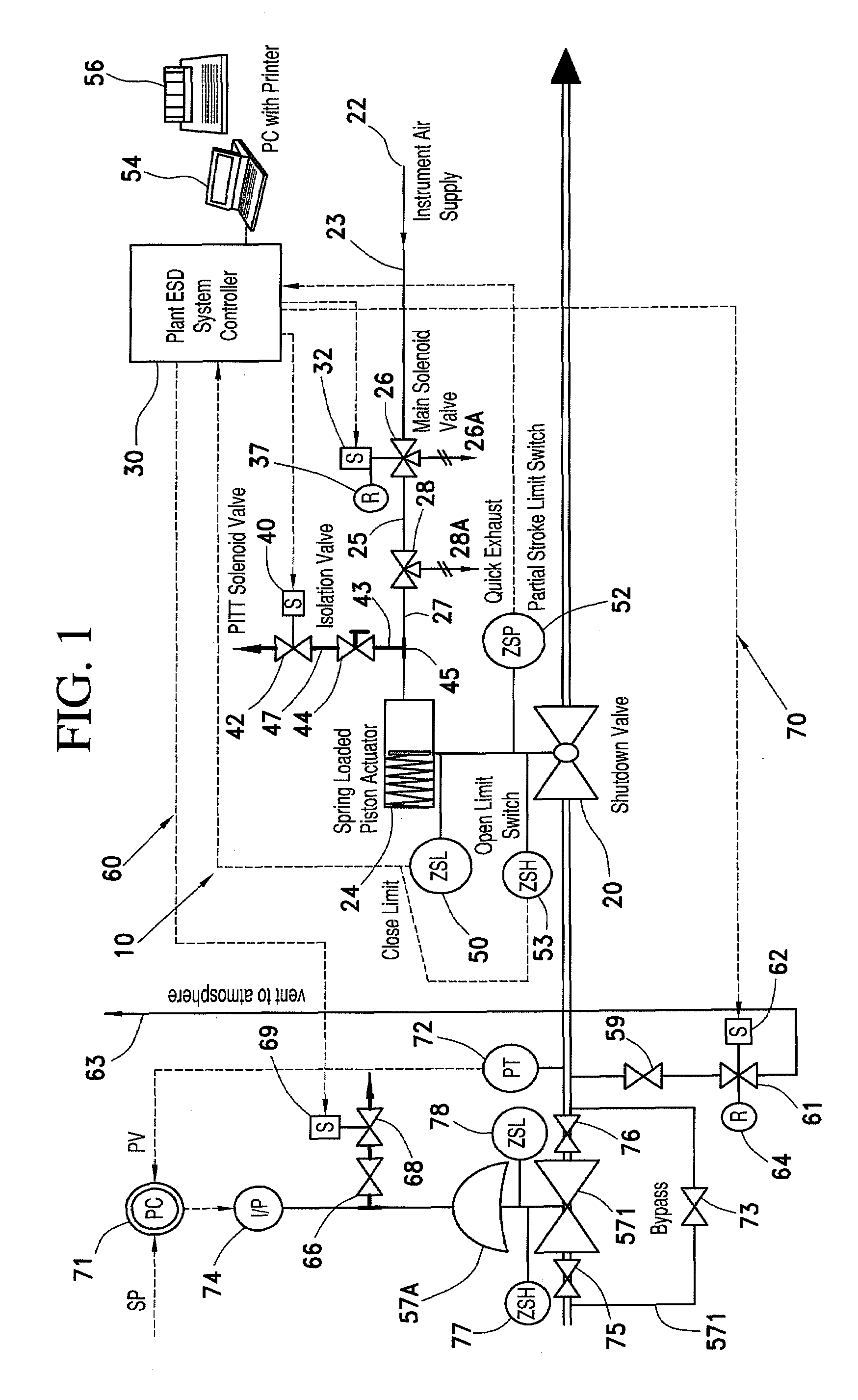
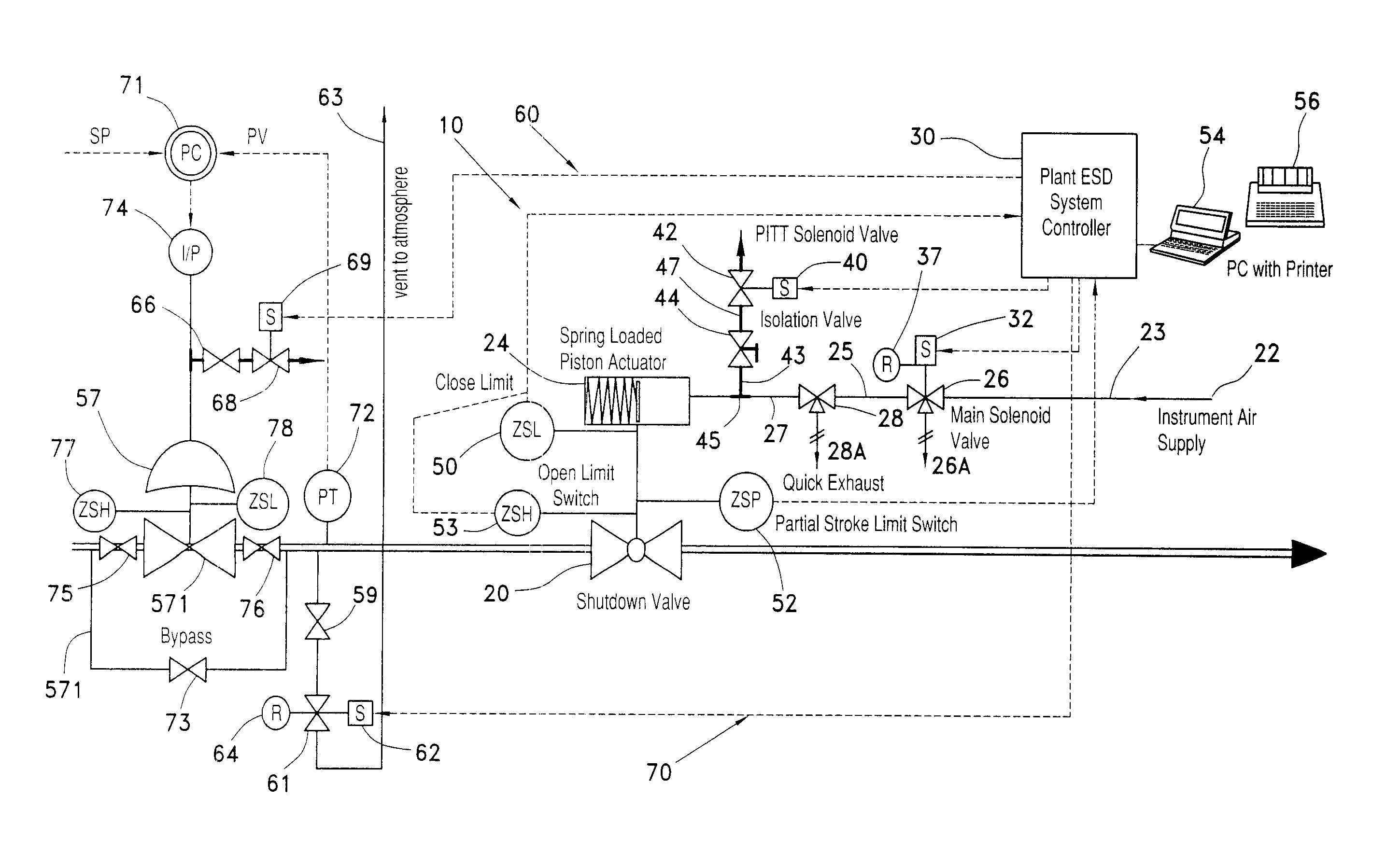
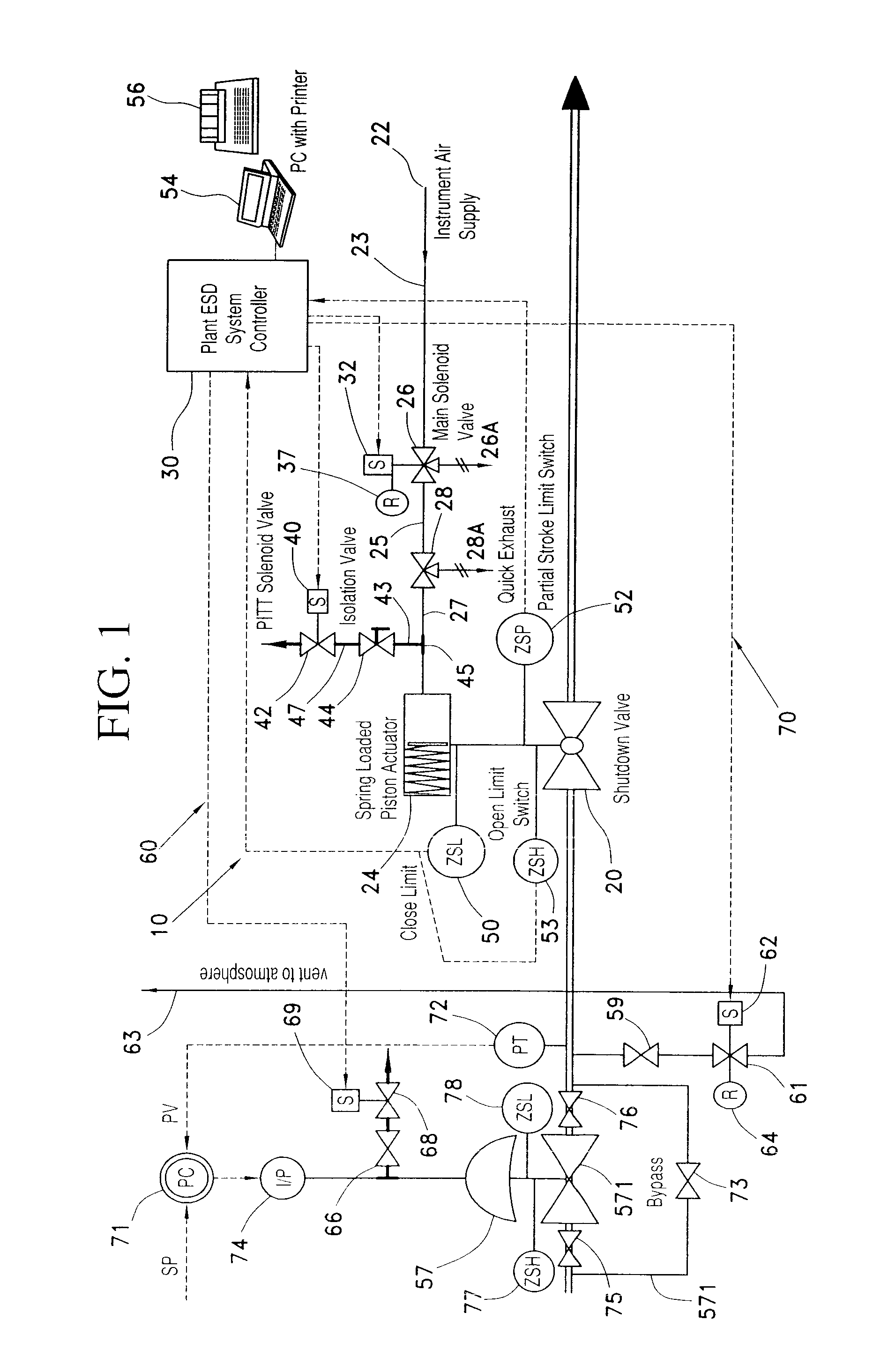
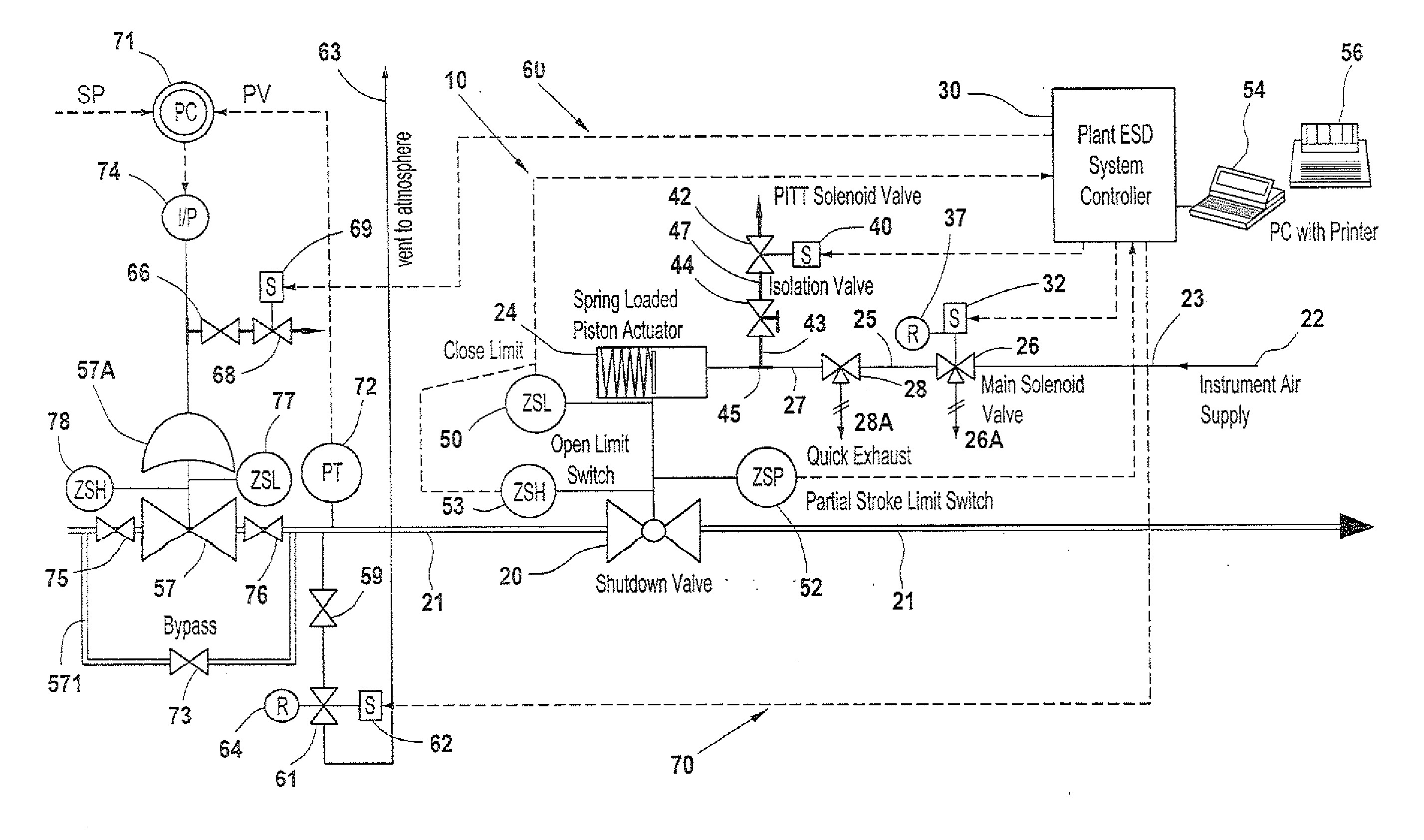
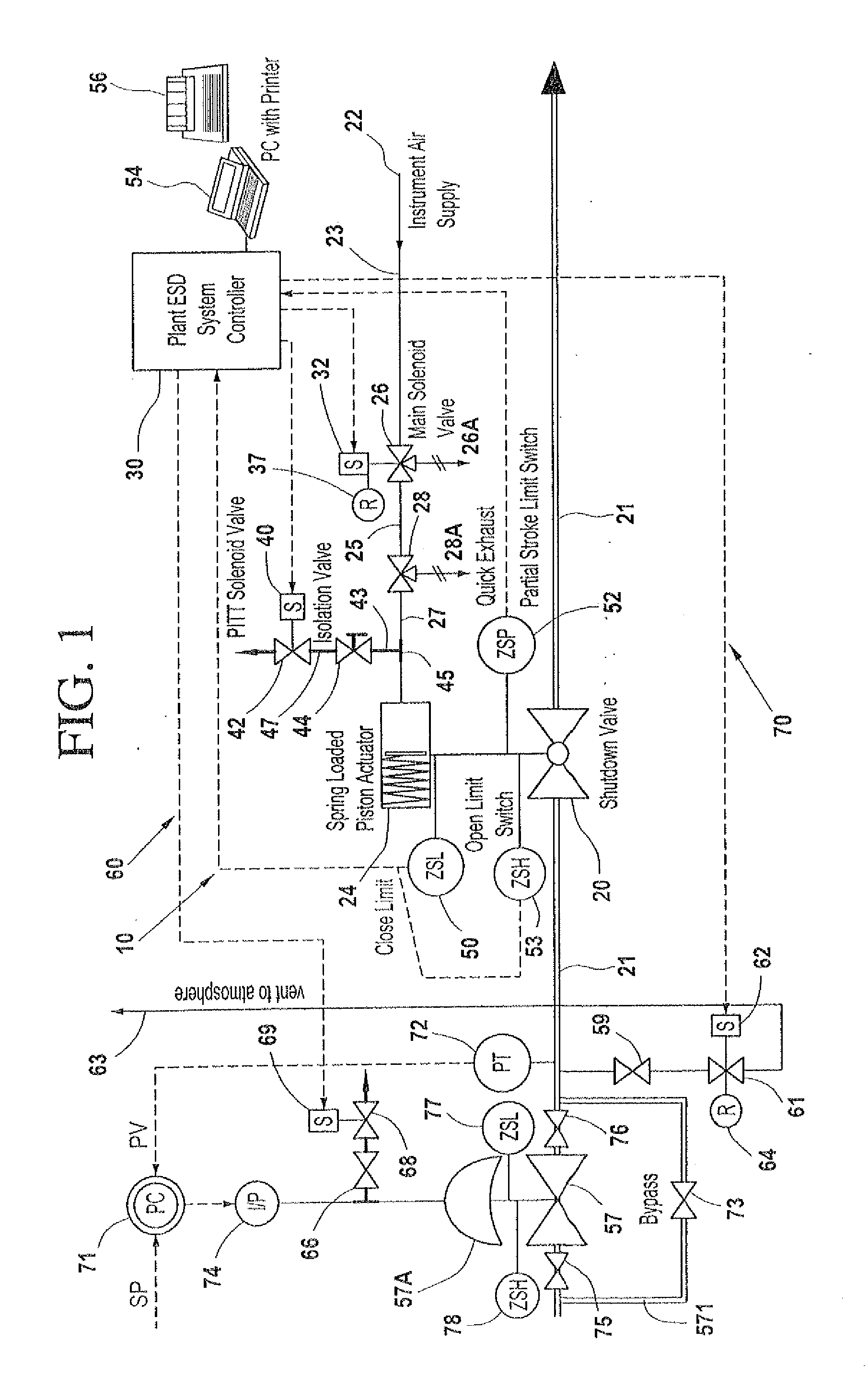
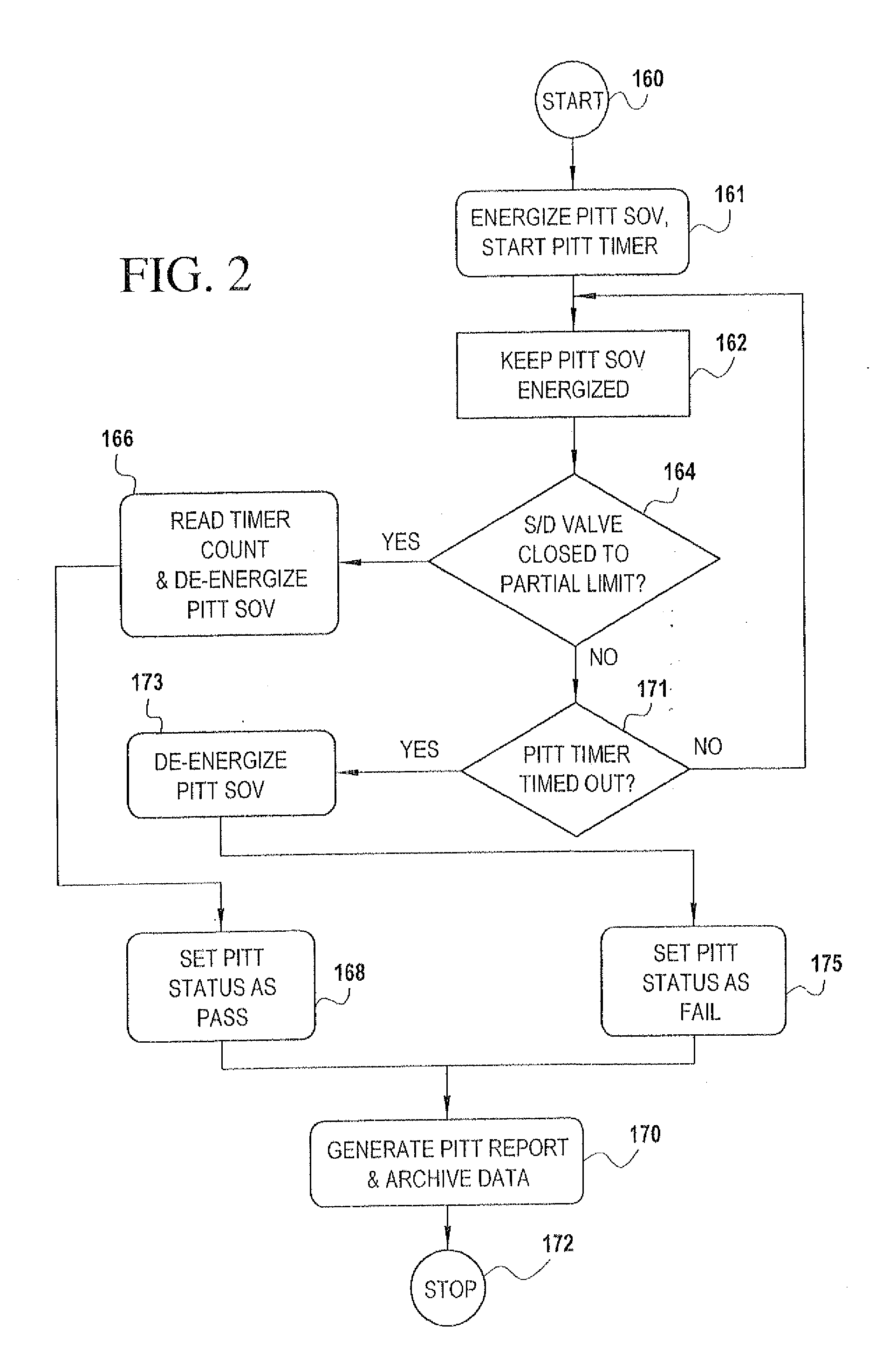
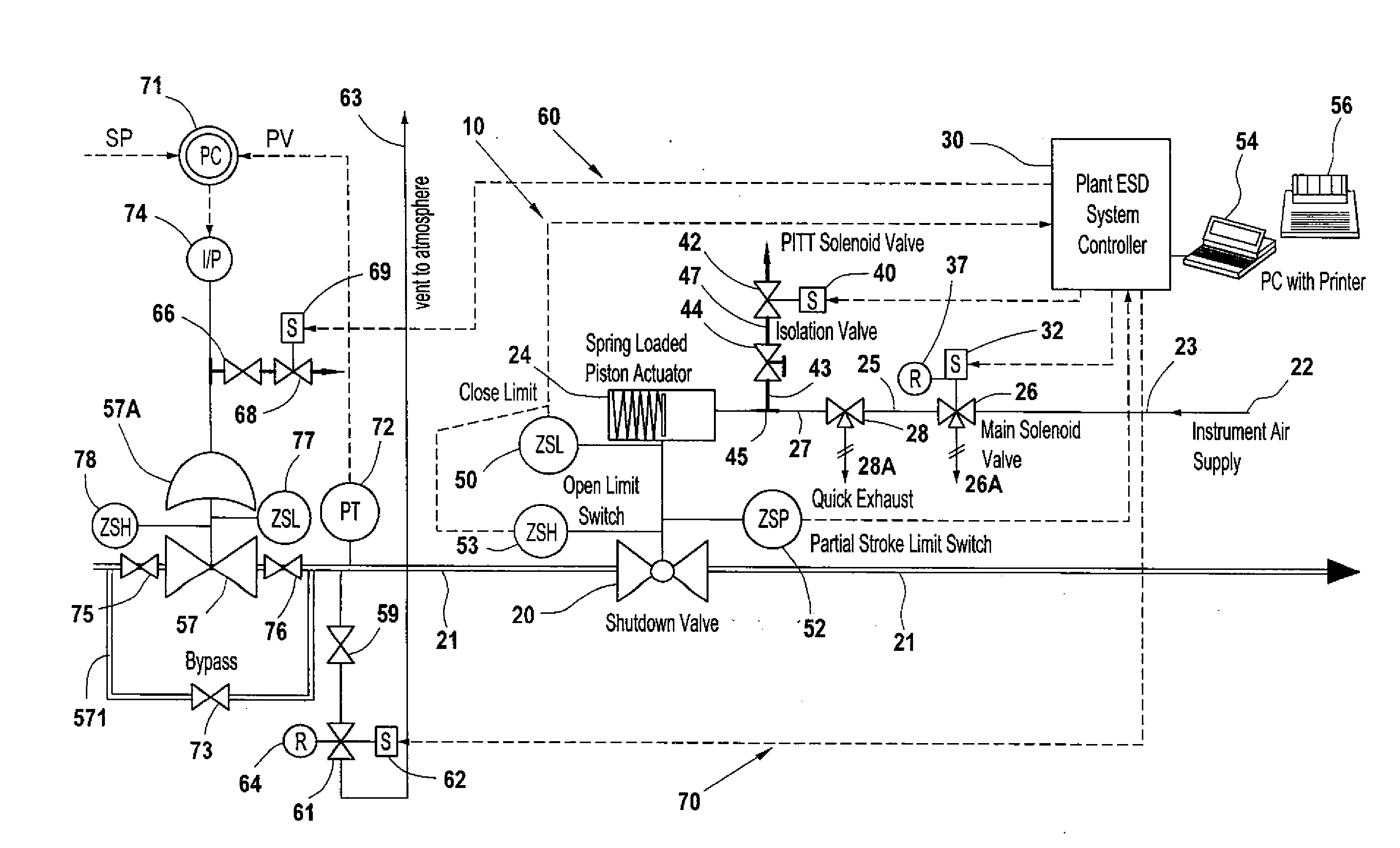
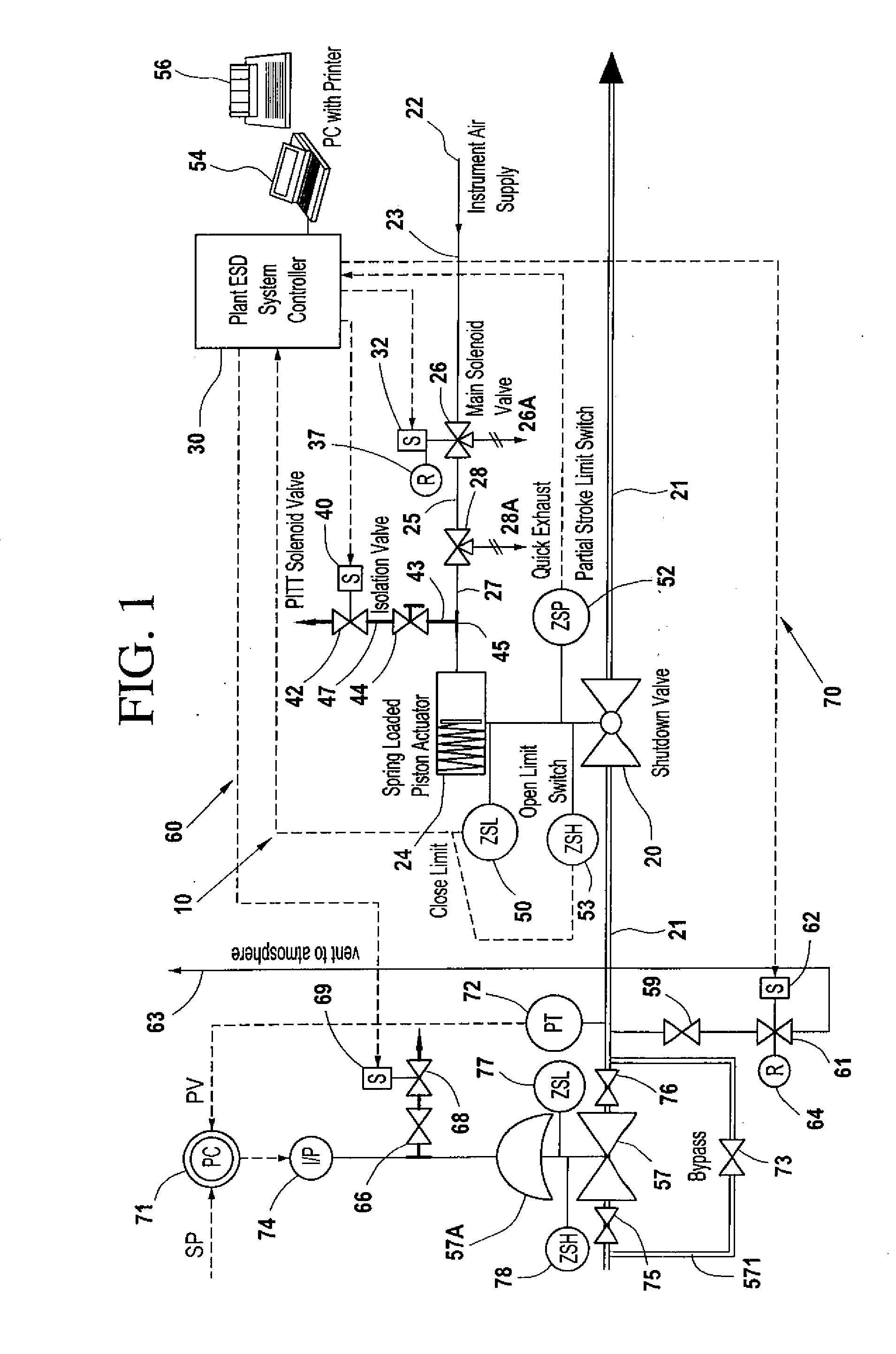
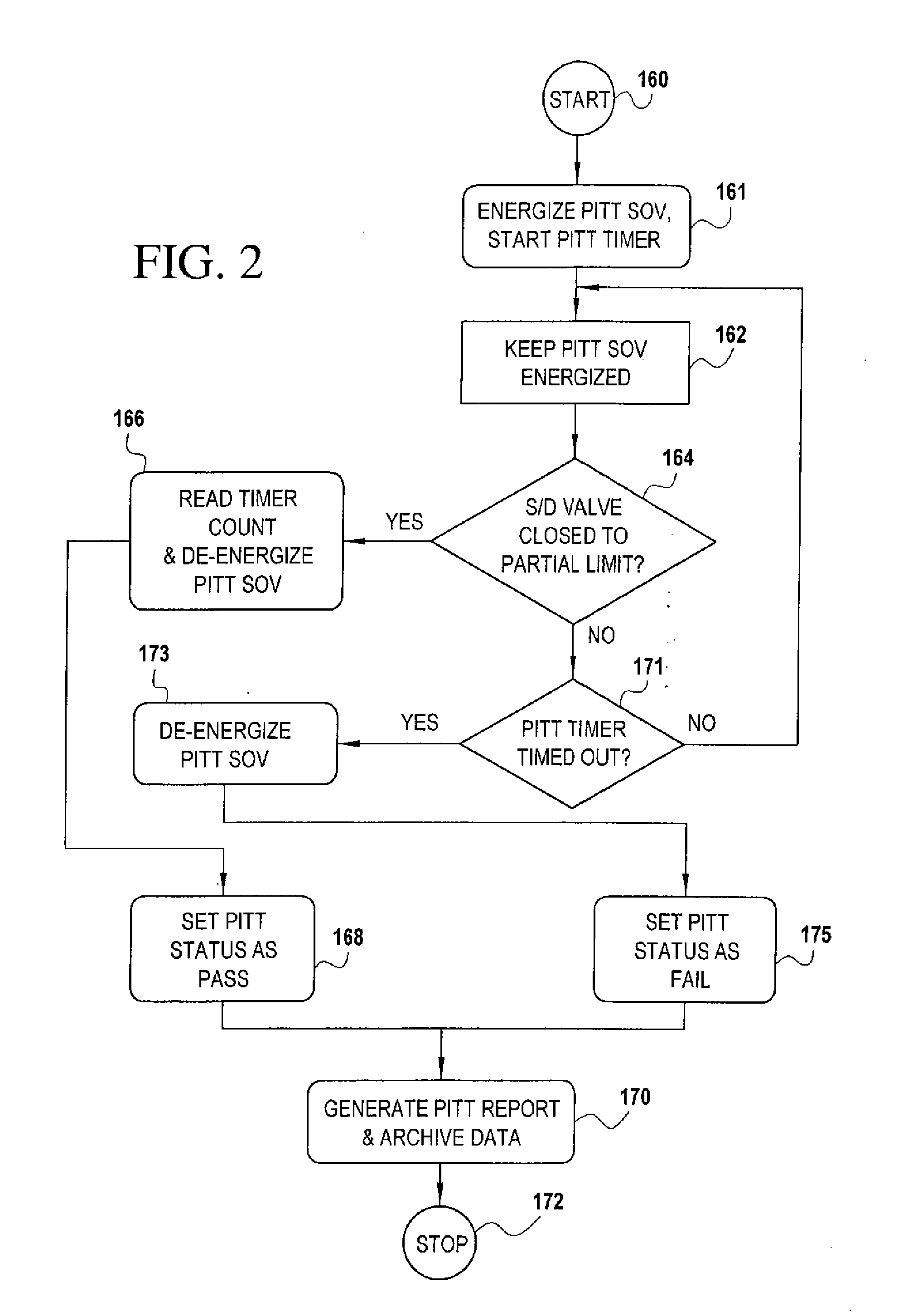
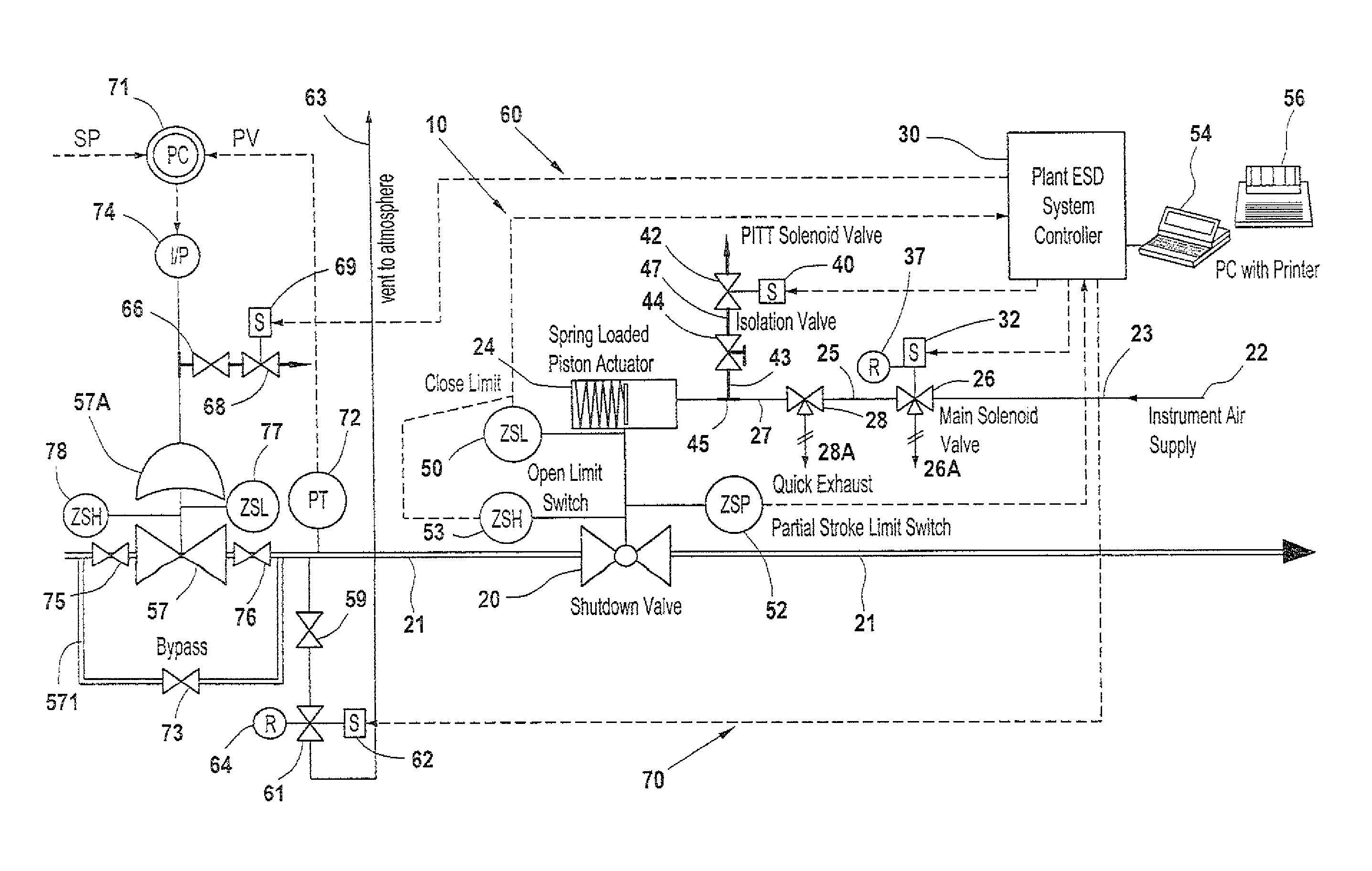
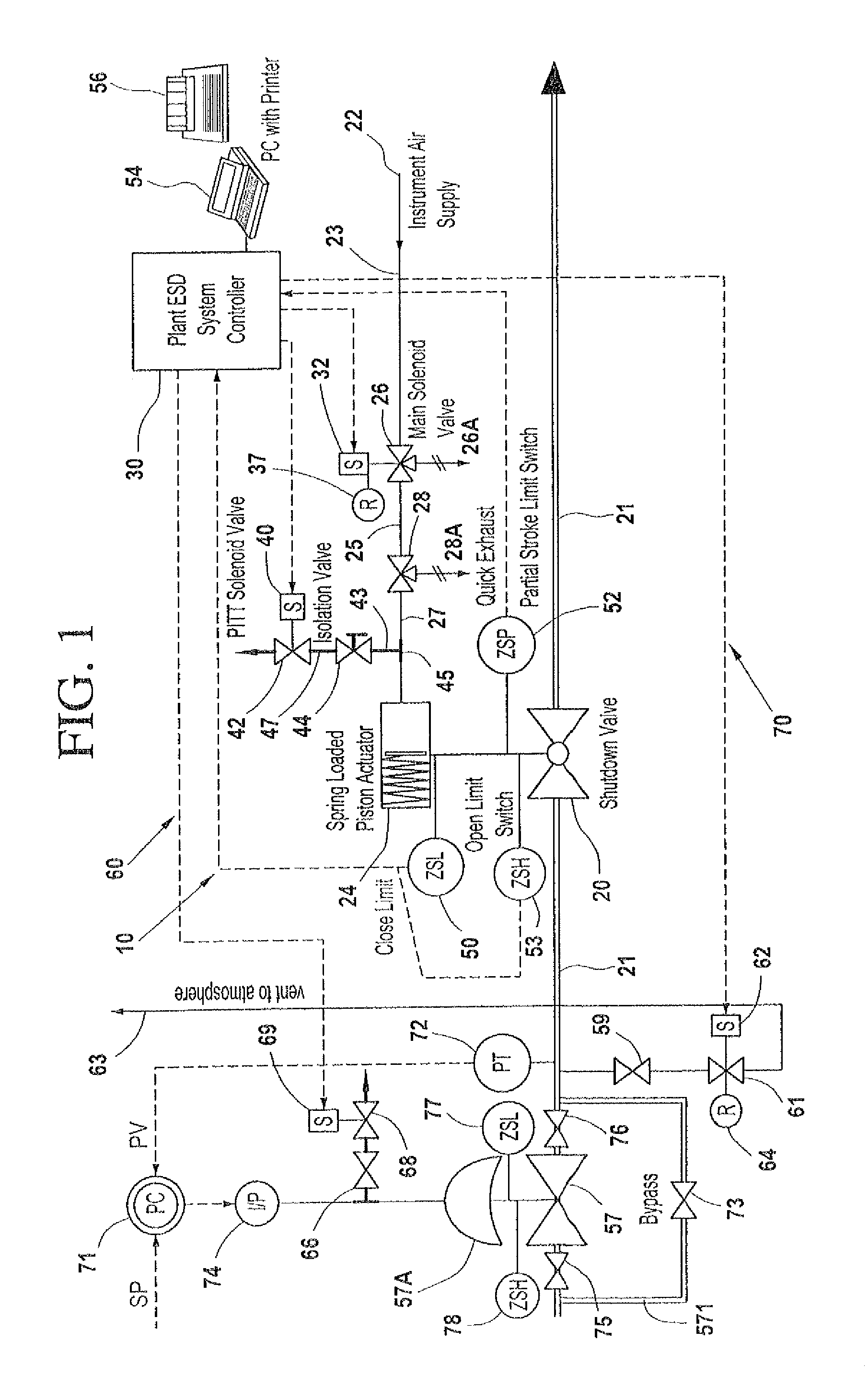
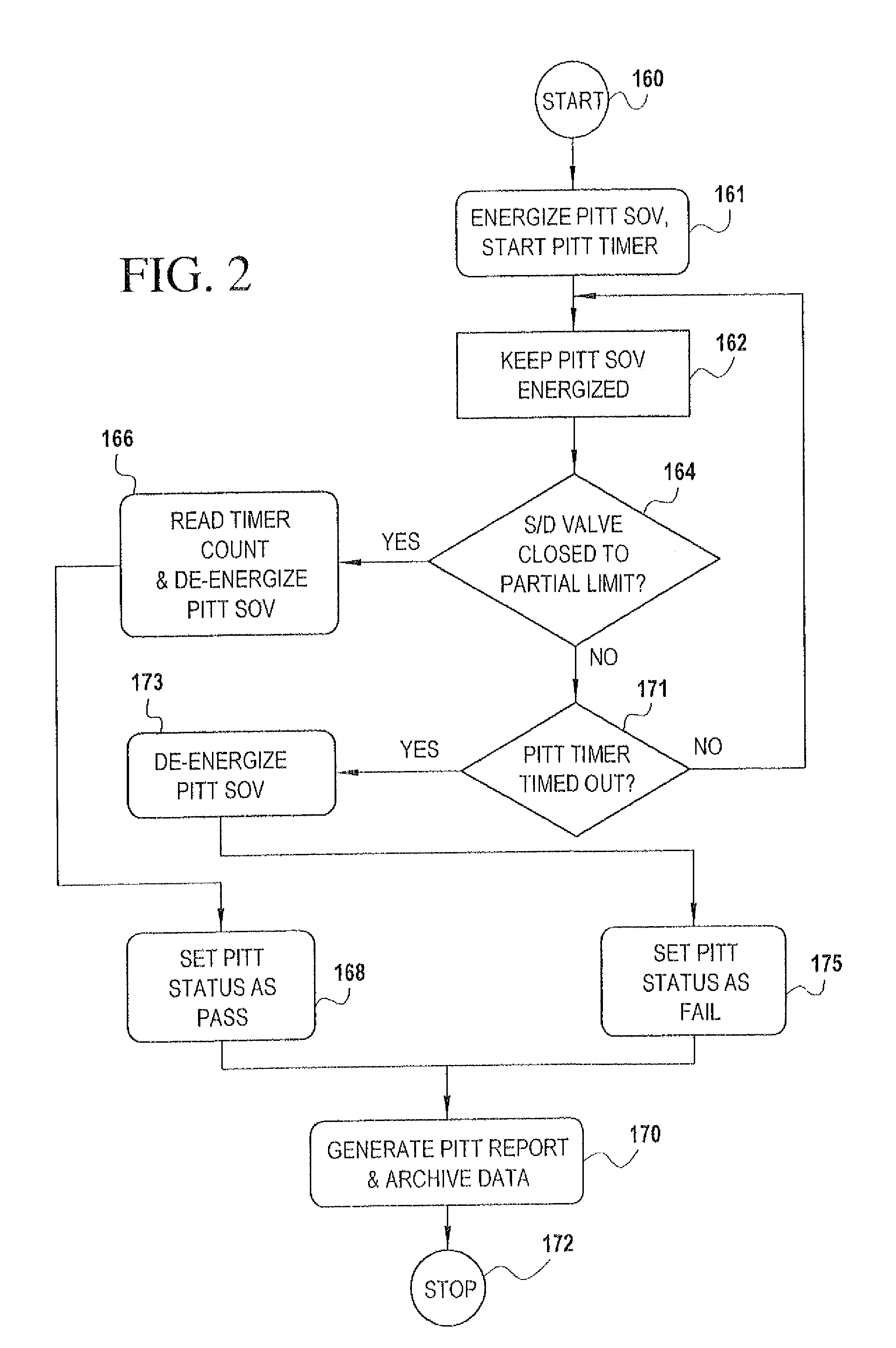
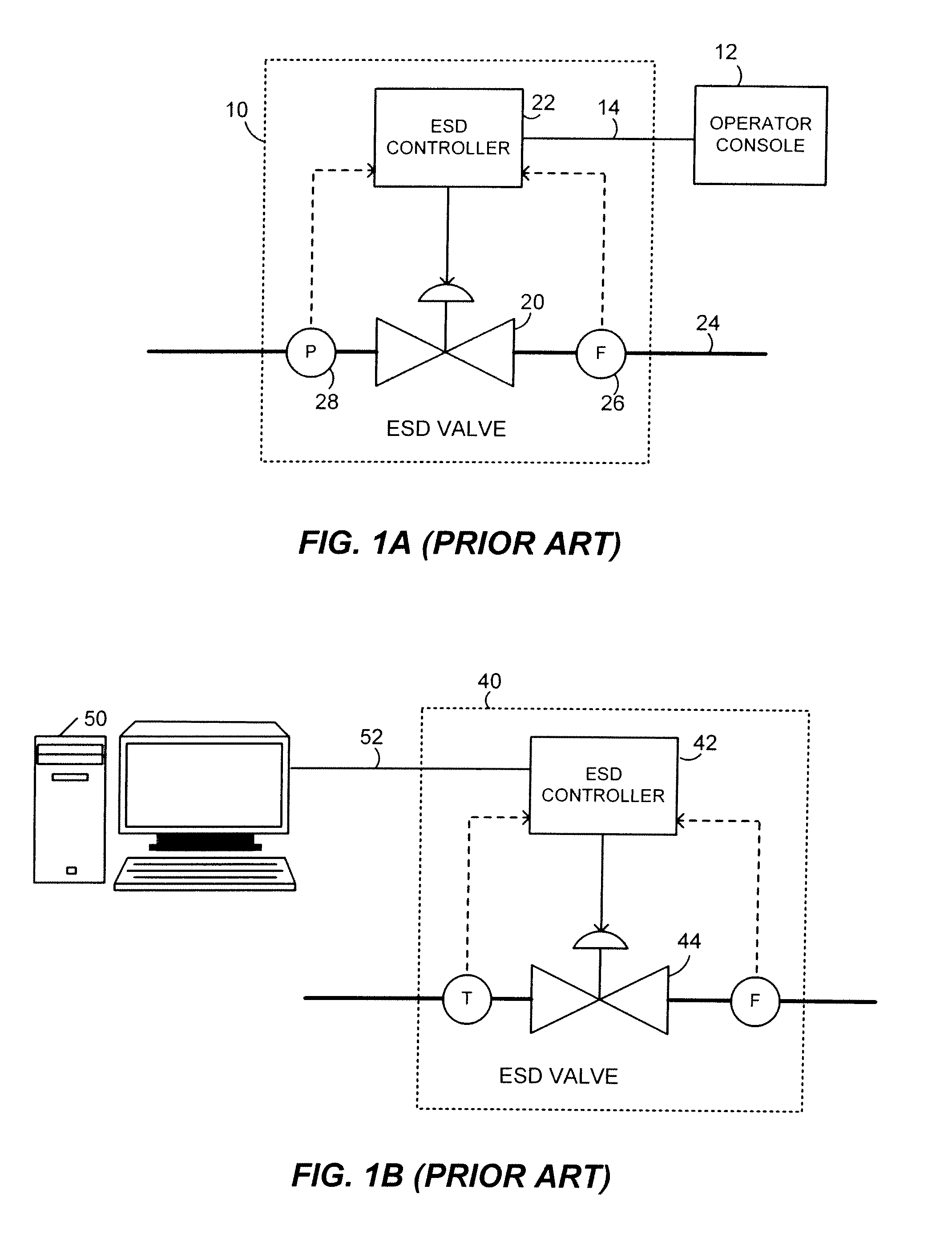
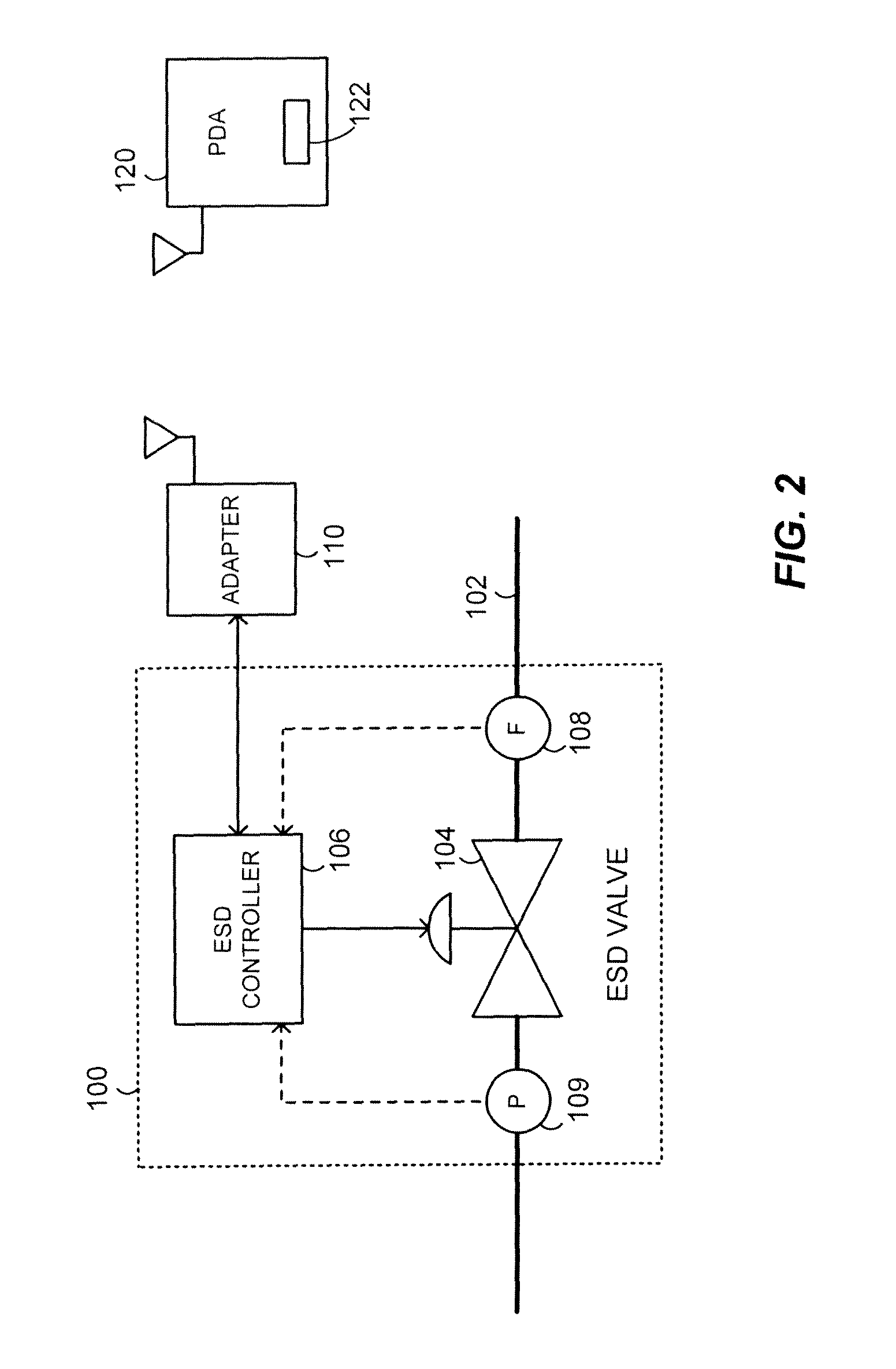
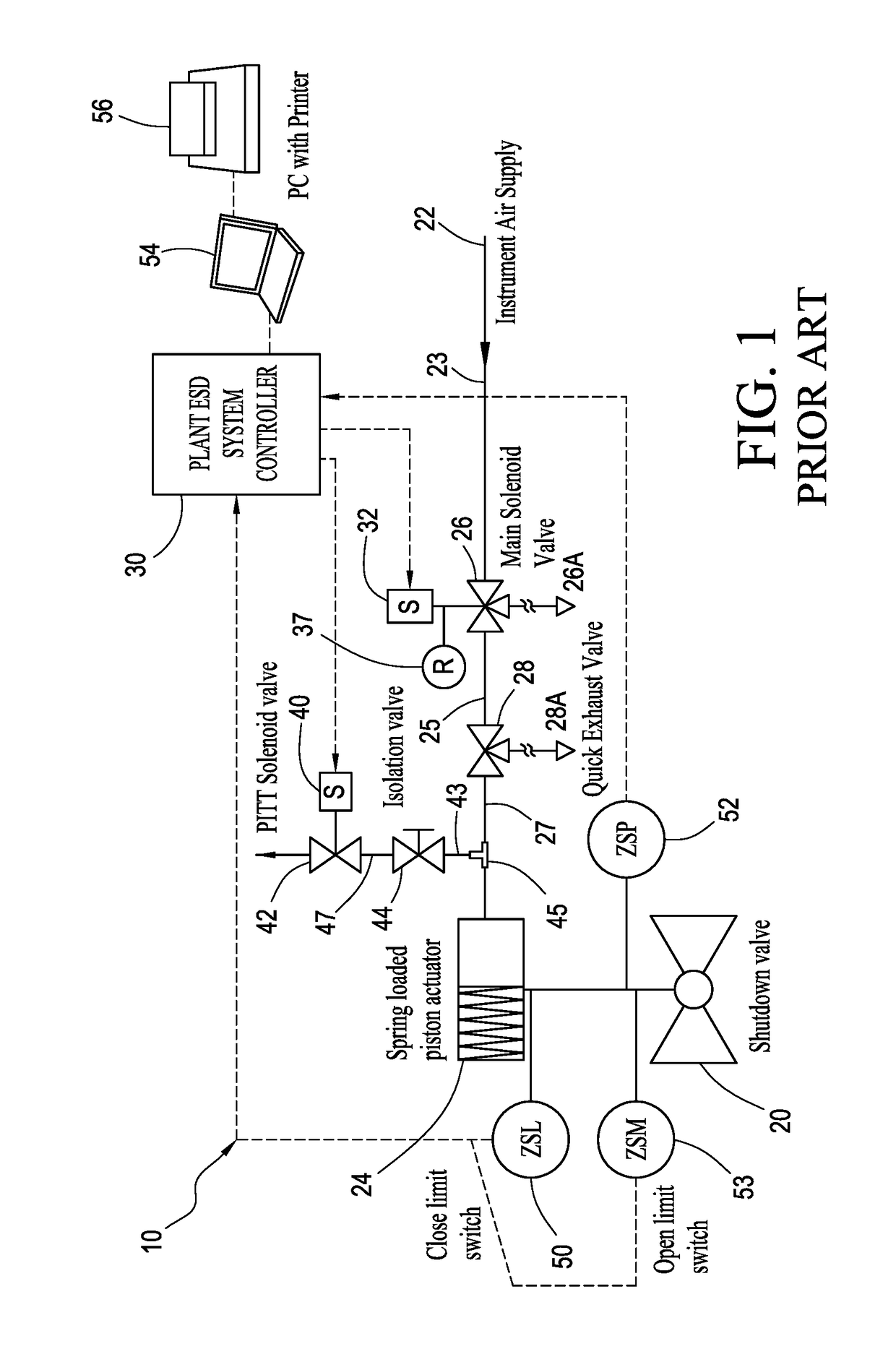
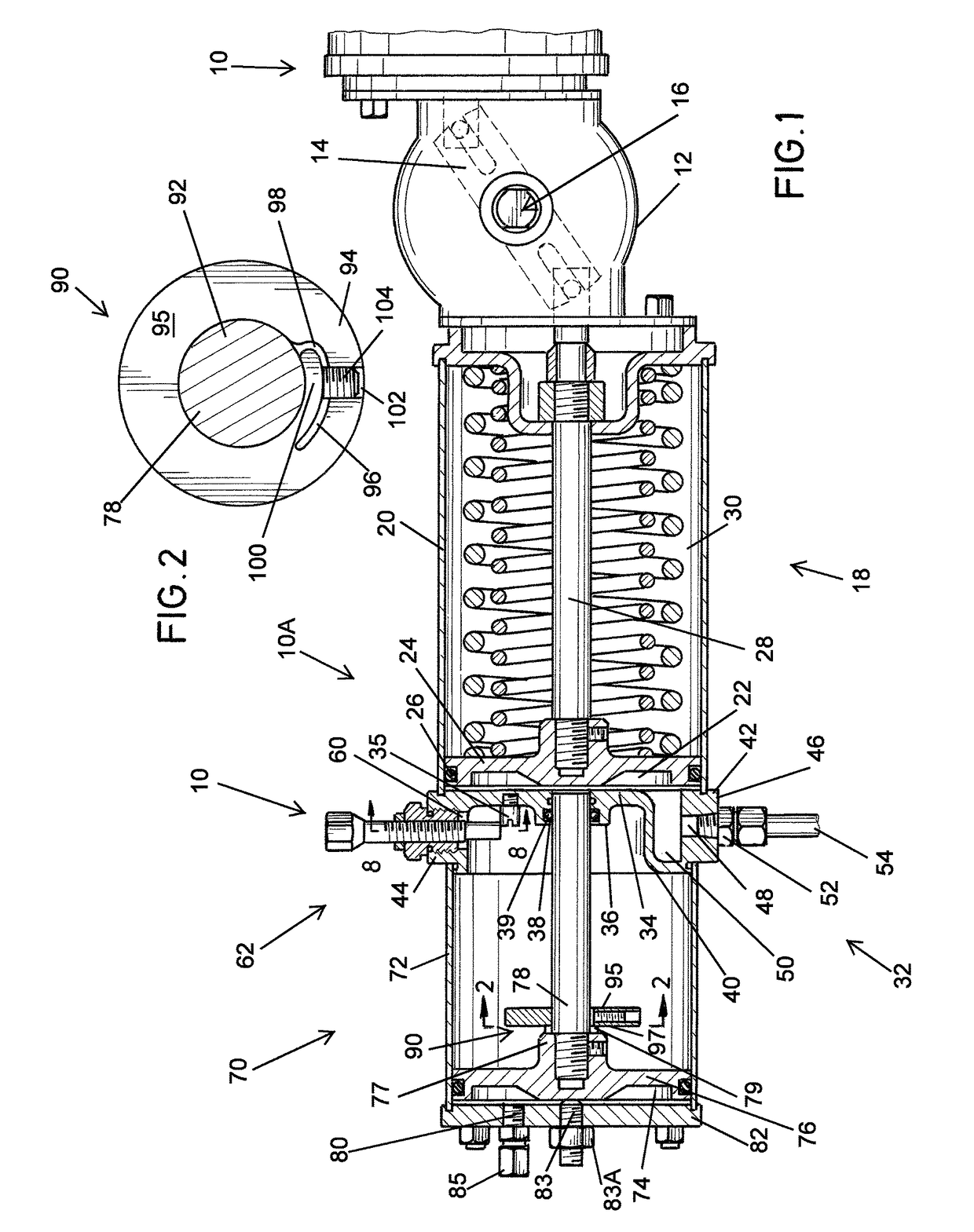
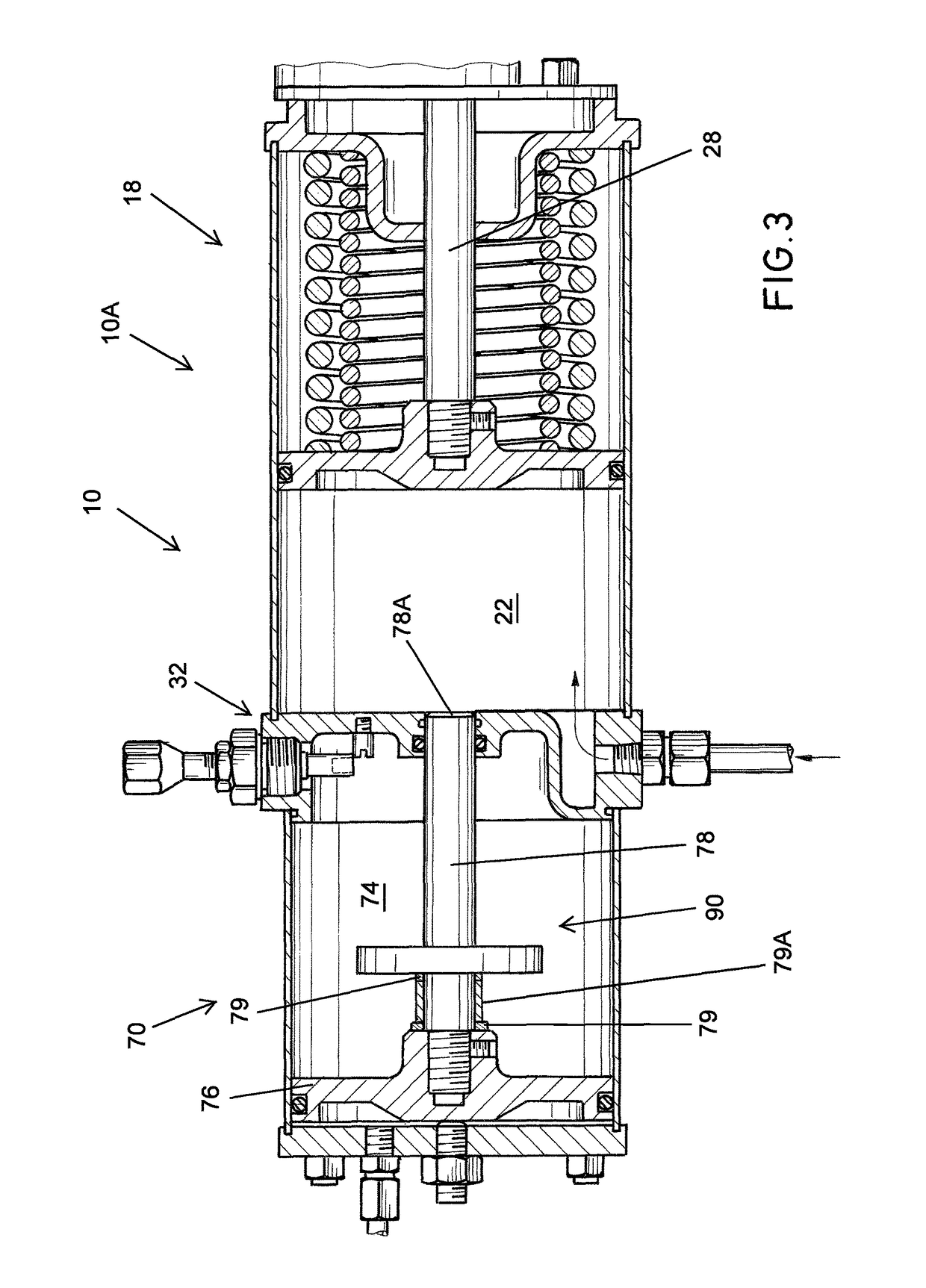
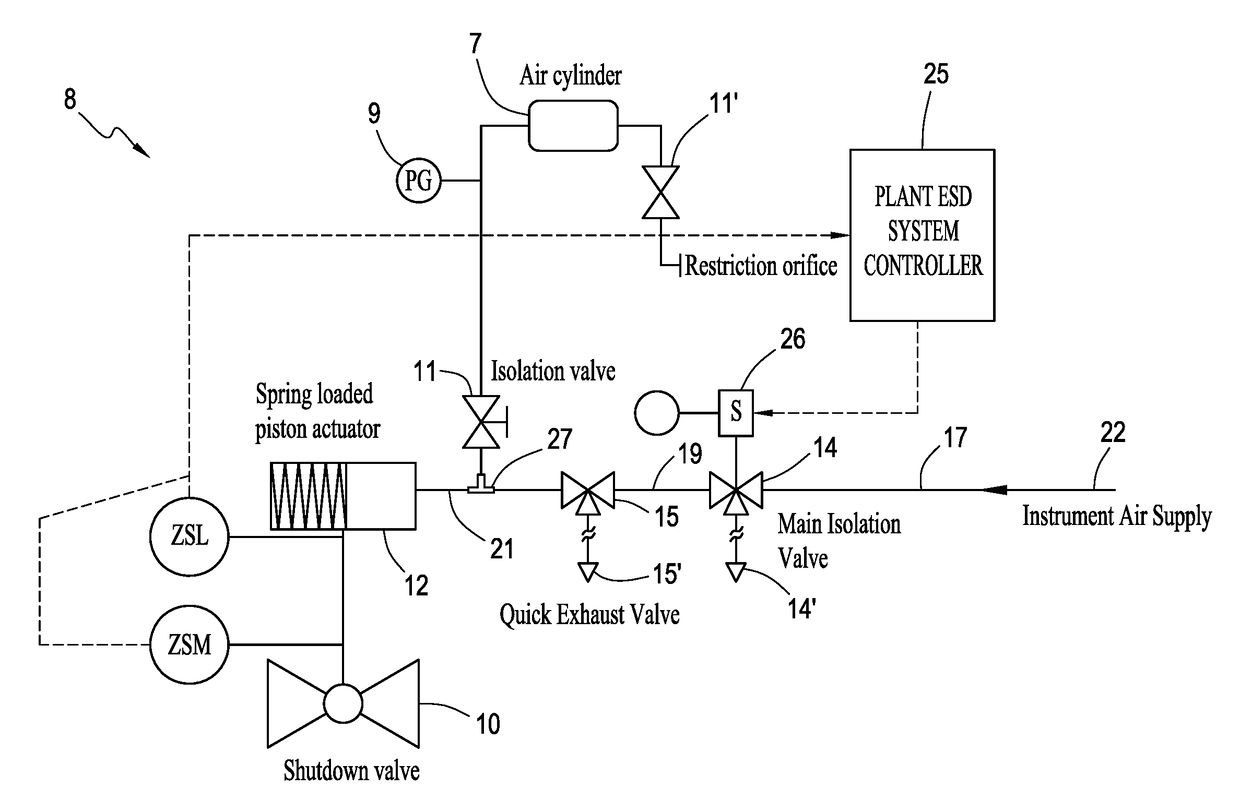
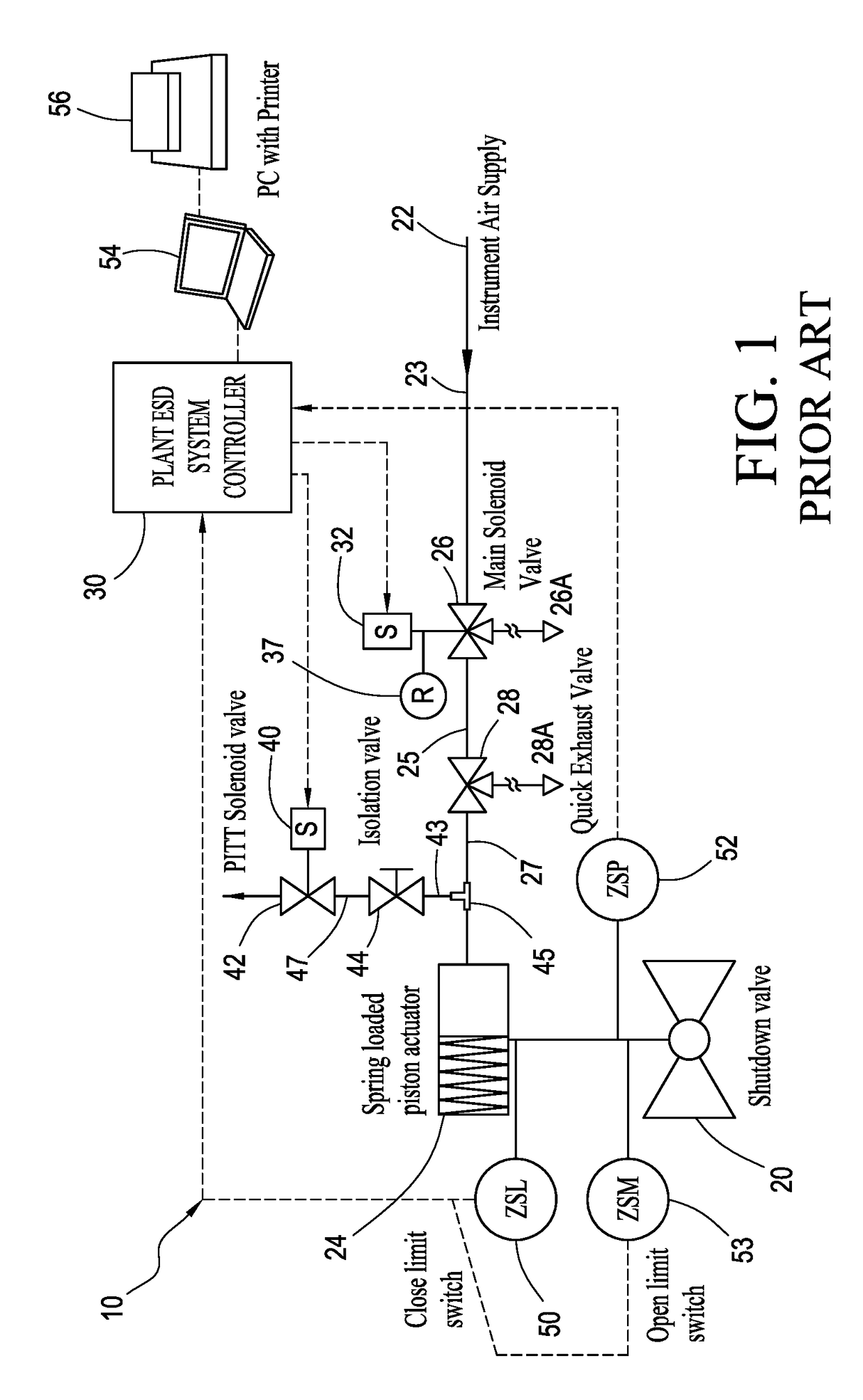
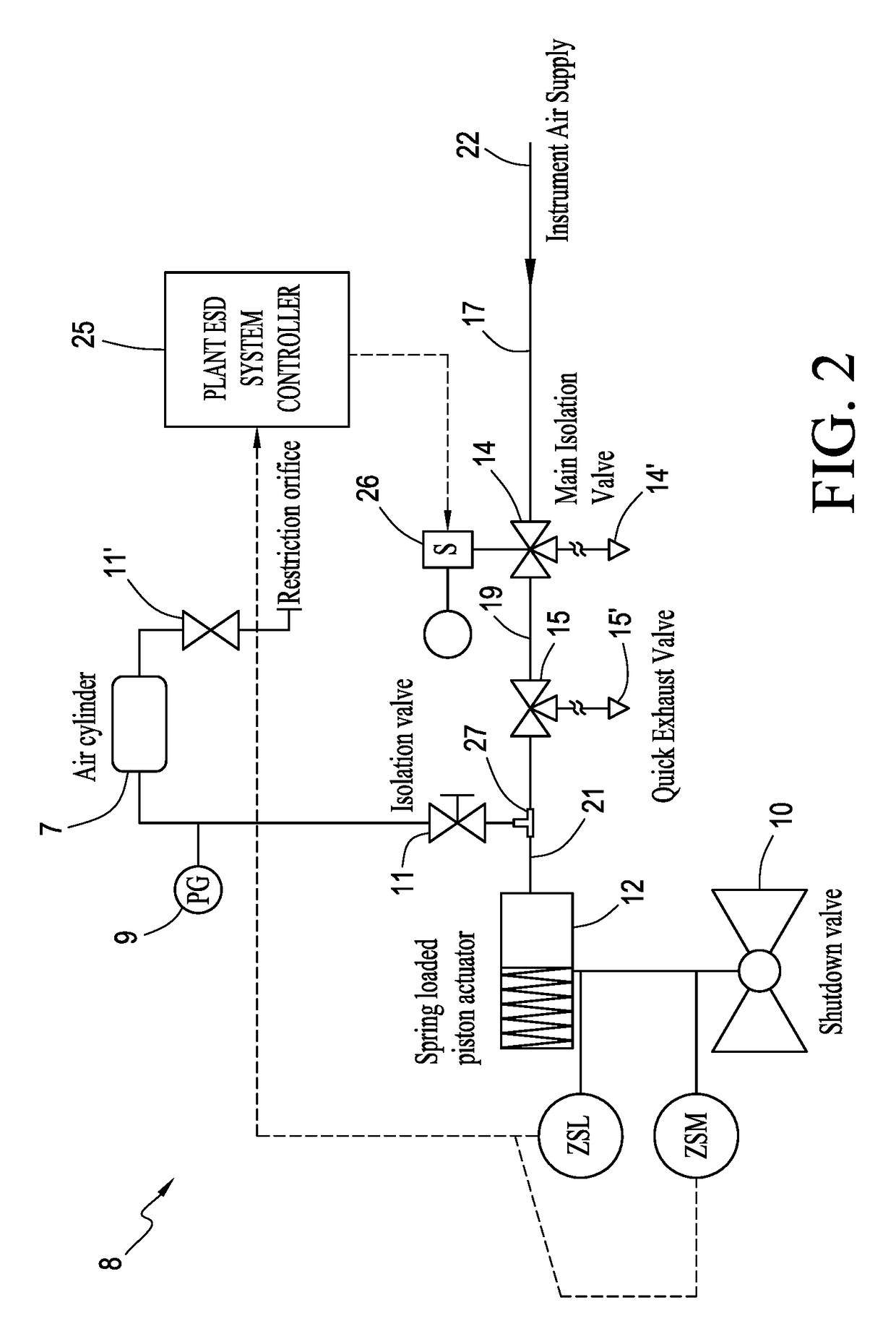
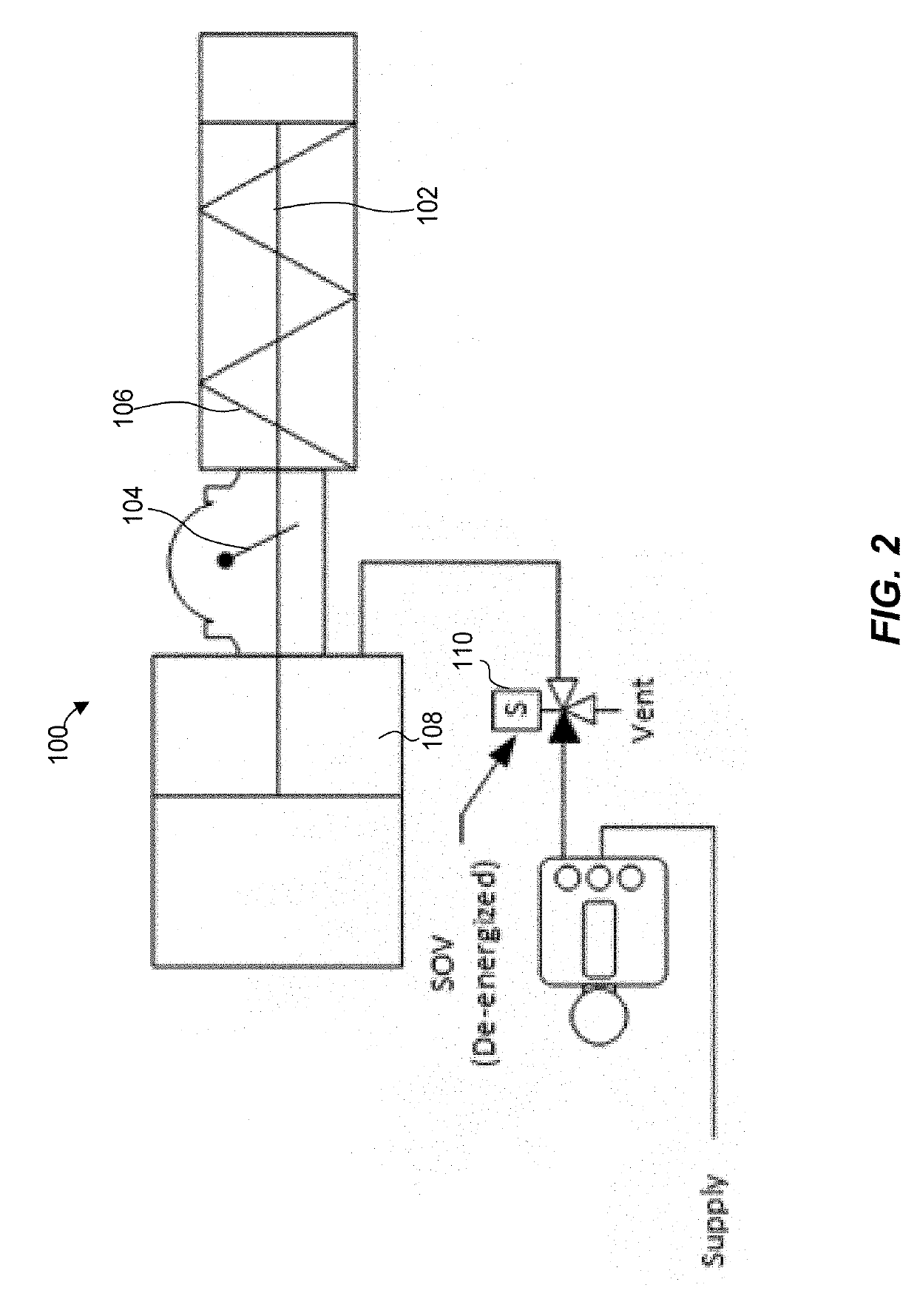
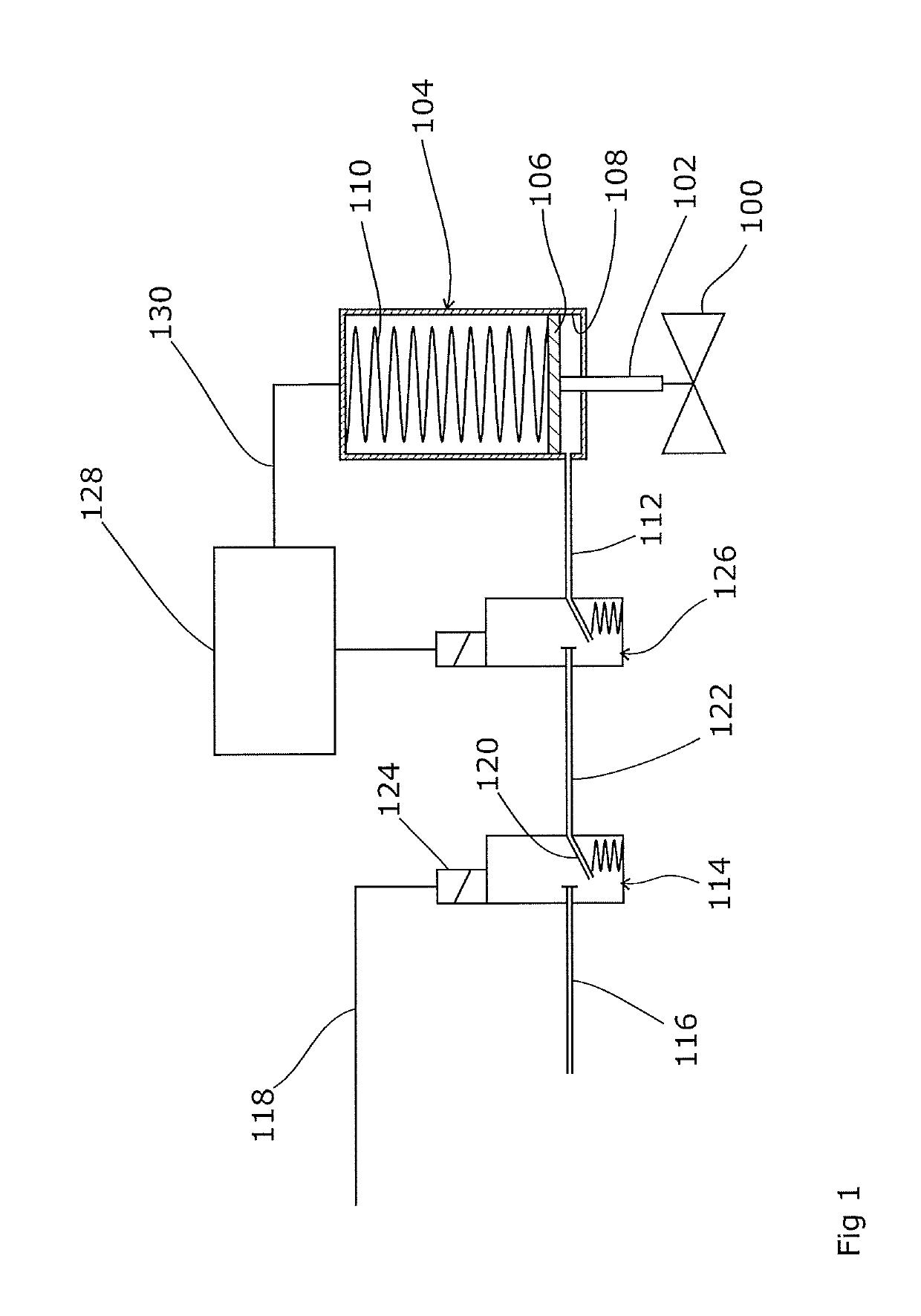
A partial stroke testing system for online testing of emergency shut-off valve, said system is designed for implementation on an emergency shut-off valve with a main solenoid with manual reset, main solenoid valve, quick exhaust valve and a pneumatic actuator connected to a source of pressurized air supply for opening and closing the said emergency shut-off valve and the said shut-off valve normally movable between a fully open and fully closed position. The system also include control means programmed into the plant emergency shutdown system controller for initiating electrical signal for initiating a test and for enhancing the bleed rate from the said pneumatic actuator in the event of a emergency trip signal. Test means for testing the said emergency shut-off valve without fully closing the emergency shut-off valve in response to signal from the said control means is included in the system. The said test means, controlled by the said control means, include a second solenoid and a second solenoid valve for bleeding off pressurized air to thereby move the said emergency shut-off valve from full opened position to partially closed position. Means for limiting the movement of said emergency shut-off valve to a partially closed position because of the bleeding of pressurized air is included in the system. The system also includes an isolation valve for isolating the said test means for maintenance purpose.
Owner:ALBUAIJAN TAREQ NASSER
Valve stroke testing system
ActiveCN102182864AAvoid damageGet motion parametersValve arrangementsMeasurement devicesControl signalBuffer tank
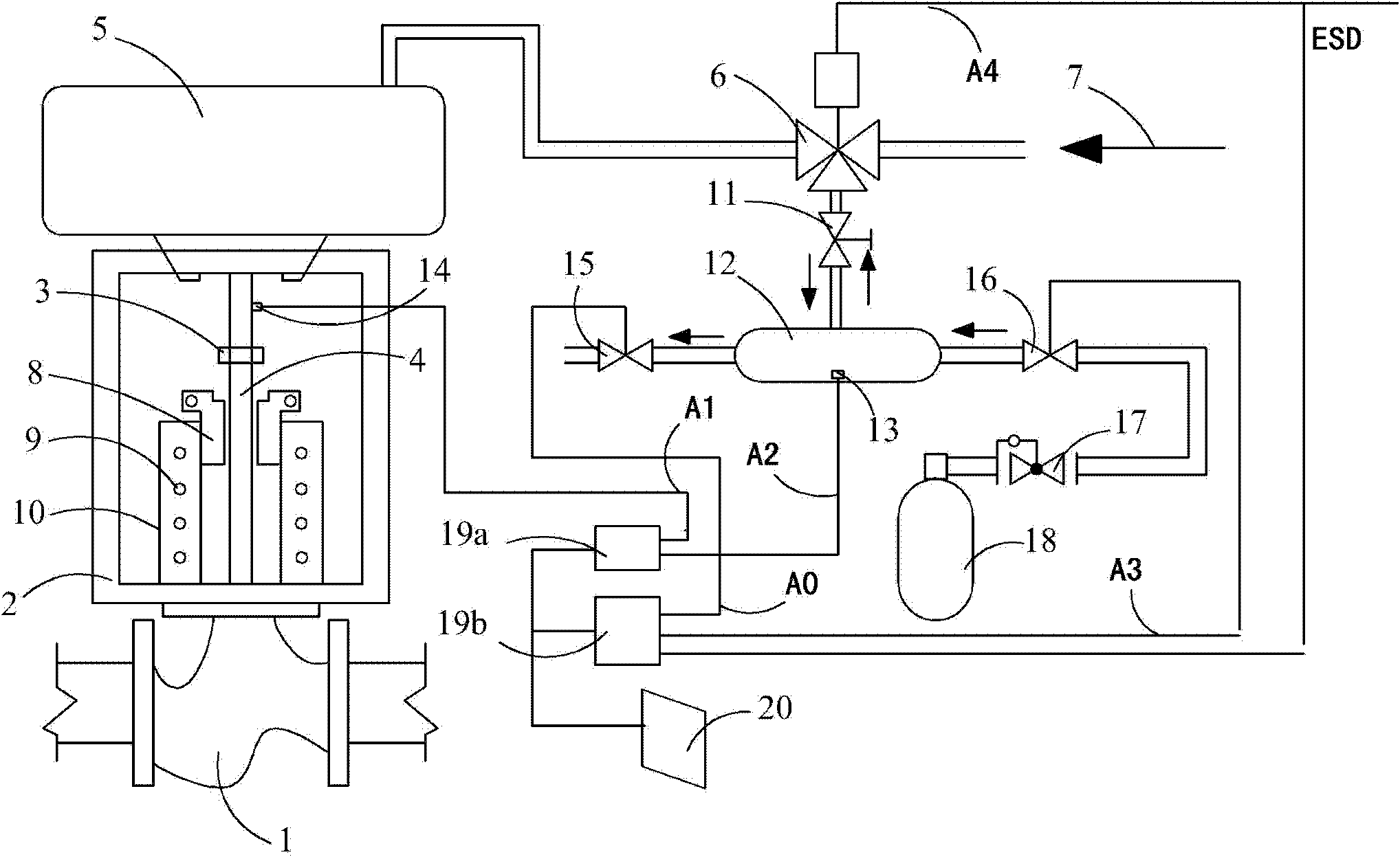
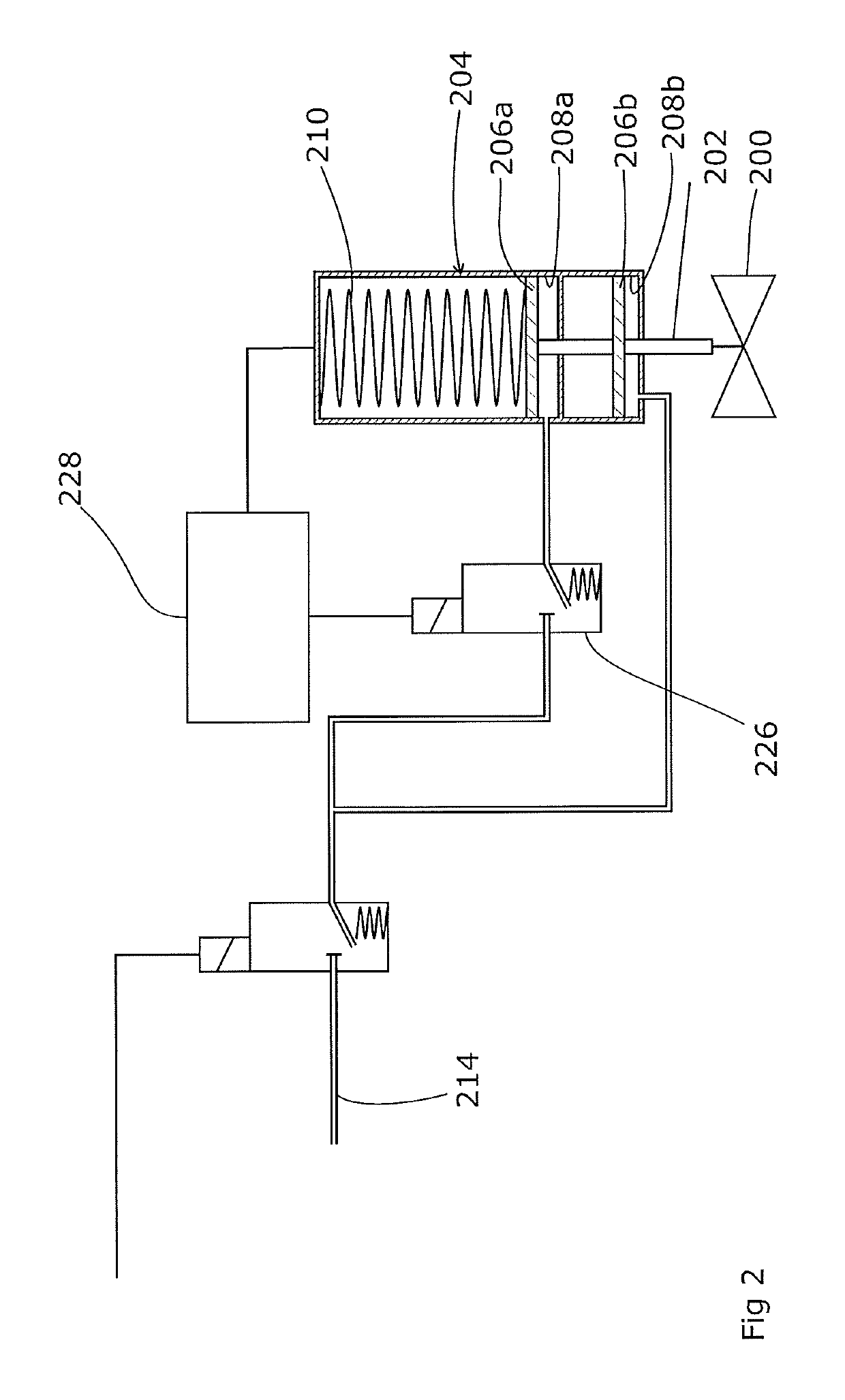
The invention discloses a valve stroke testing system which is characterized in that the system comprises a tested valve, a valve rod stroke control mechanism, an air intake and exhaust control device and a detecting unit; the tested valve comprises a pneumatic actuating mechanism and a sensor unit, wherein the pneumatic actuating mechanism controls the air intake or air exhaust through a two-position three-way electromagnetic valve; the sensor unit is used for obtaining the related information of a valve rod; the valve rod stroke control mechanism is provided with a limit sleeve; the valve rod is provided with a limit stop which is used for limiting a part of stroke of the valve rod; the air intake and exhaust control device is communicated with a circumscribed instrument air tank through an air intake electromagnetic valve according to one way of a buffer tank; the other way of the air intake electromagnetic valve is communicated with an air exhaust electromagnetic valve; one way of the air intake electromagnetic valve is communicated with the two-position three-way electromagnetic valve through a manual valve; and the detecting unit is used for collecting detecting signals and providing control signals of the two-position three-way electromagnetic valve, the air exhaust electromagnetic valve and the air intake electromagnetic valve. the valve stroke testing system provided by the invention can be used for online or off-line test of the valve stroke, can be used for full stroke or partial stroke test for the valve, and can be applied to pneumatic-type interlocked valves without mounting intelligent positioning devices in all industries.
Owner:HEFEI GENERAL MACHINERY RES INST +1
Partial stroke testing system
InactiveUS6435022B1Quick closeLow costValve arrangementsUsing mechanical meansSystems designExhaust valve
A partial stroke testing system for online testing of emergency shut-off valve, said system is designed for implementation on an emergency shut-off valve with a main solenoid with manual reset, main solenoid valve, quick exhaust valve and a pneumatic actuator connected to a source of pressurized air supply for opening and closing the said emergency shut-off valve and the said shut-off valve normally movable between a fully open and fully closed position. The system also include control means programmed into the plant emergency shutdown system controller for initiating electrical signal for initiating a test and for enhancing the bleed rate from the said pneumatic actuator in the event of a emergency trip signal. Test means for testing the said emergency shut-off valve without fully closing the emergency shut-off valve in response to signal from the said control means is included in the system. The said test means, controlled by the said control means, include a second solenoid and a second solenoid valve for bleeding off pressurized air to thereby move the said emergency shut-off valve from full opened position to partially closed position. Means for limiting the movement of said emergency shut-off valve to a partially closed position because of the bleeding of pressurized air is included in the system. The system also includes an isolation valve for isolating the said test means for maintenance purpose.
Owner:ALBUAIJAN TAREQ NASSER
Partial stroke testing system coupled with fuel control valve
ActiveUS20090222233A1Vehicle testingFluid-pressure actuator safetySafety Integrity LevelSolenoid valve
A system for on-line testing of an emergency shut-off valve includes a first emergency shut-off valve and a control for initiating a test on the first emergency shut-off valve. The system also includes a fluid actuator for opening and closing the first emergency shut-off valve. A subsystem is also provided for testing the first emergency shut-off valve without fully closing the shut-off valve in response to a signal from the control. In this system, a second solenoid valve bleeds off pressurized fluid to move the emergency shut-off valve from a fully opened to a partially closed position functions as a second emergency shut-off valve. A second emergency shut-off valve is also provided in series with the first emergency shut-off valve and a bypass around the second emergency shut-off valve allows the second emergency shut-off valve to be tested by being fully closed without shutting down the process. The use of the two emergency shut-off valves in series wherein either valve can shut down the process raises the safety integrity level to level 3.
Owner:AL BUAIJAN TAREQ NASSER
Partial stroke testing system coupled with fuel control valve
ActiveUS8074512B2Fluid-pressure actuator safetyValve arrangementsSafety Integrity LevelSolenoid valve
A system for on-line testing of an emergency shut-off valve includes a first emergency shut-off valve and a control for initiating a test on the first emergency shut-off valve. The system also includes a fluid actuator for opening and closing the first emergency shut-off valve. A subsystem is also provided for testing the first emergency shut-off valve without fully closing the shut-off valve in response to a signal from the control. In this system, a second solenoid valve bleeds off pressurized fluid to move the emergency shut-off valve from a fully opened to a partially closed position functions as a second emergency shut-off valve. A second emergency shut-off valve is also provided in series with the first emergency shut-off valve and a bypass around the second emergency shut-off valve allows the second emergency shut-off valve to be tested by being fully closed without shutting down the process. The use of the two emergency shut-off valves in series wherein either valve can shut down the process raises the safety integrity level to level 3.
Owner:AL BUAIJAN TAREQ NASSER
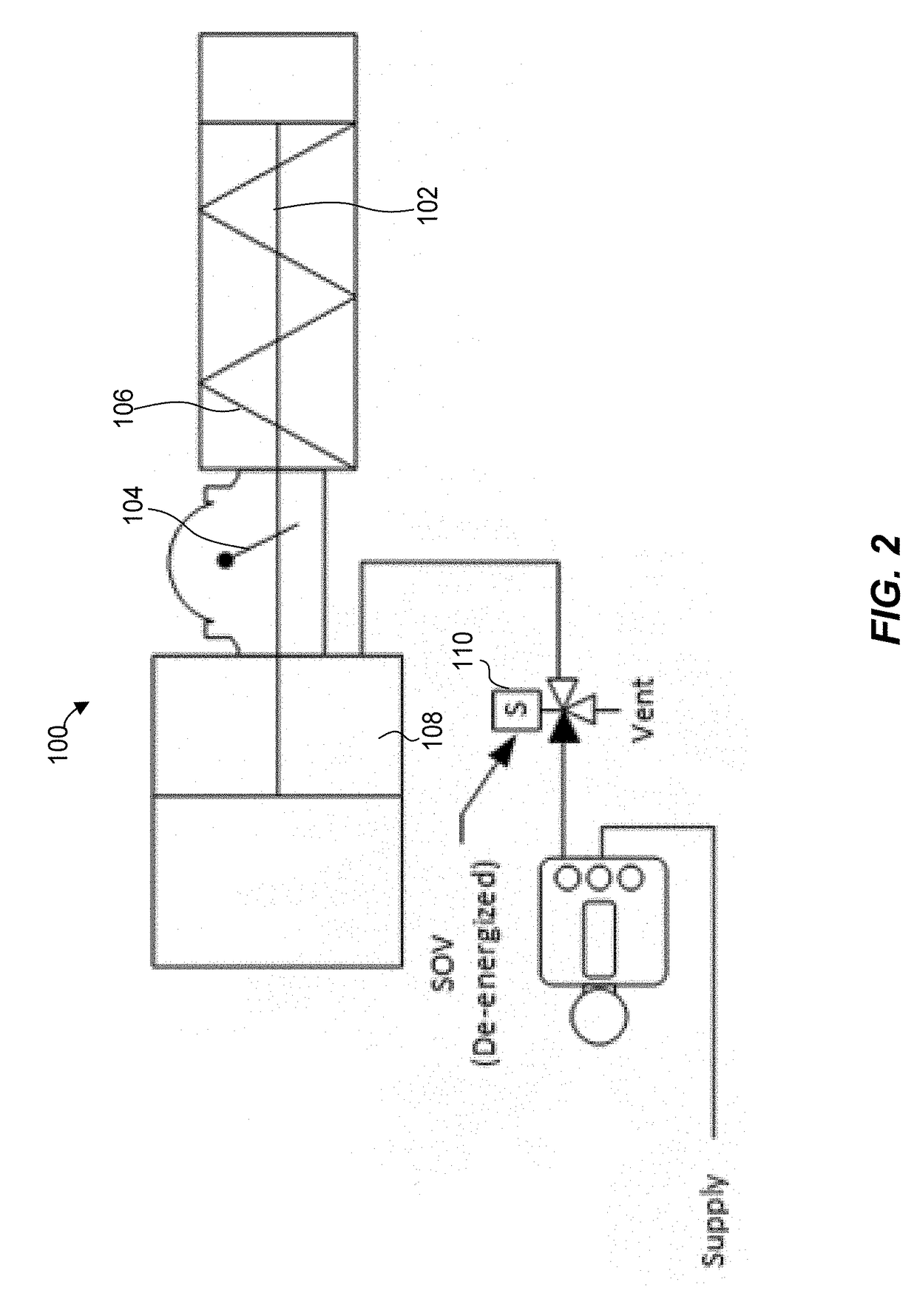
Actuating device for an on/off valve
ActiveUS8262060B2Simple and cost-effective implementationEnough timeOperating means/releasing devices for valvesTesting/monitoring control systemsSolenoid valveControl signal
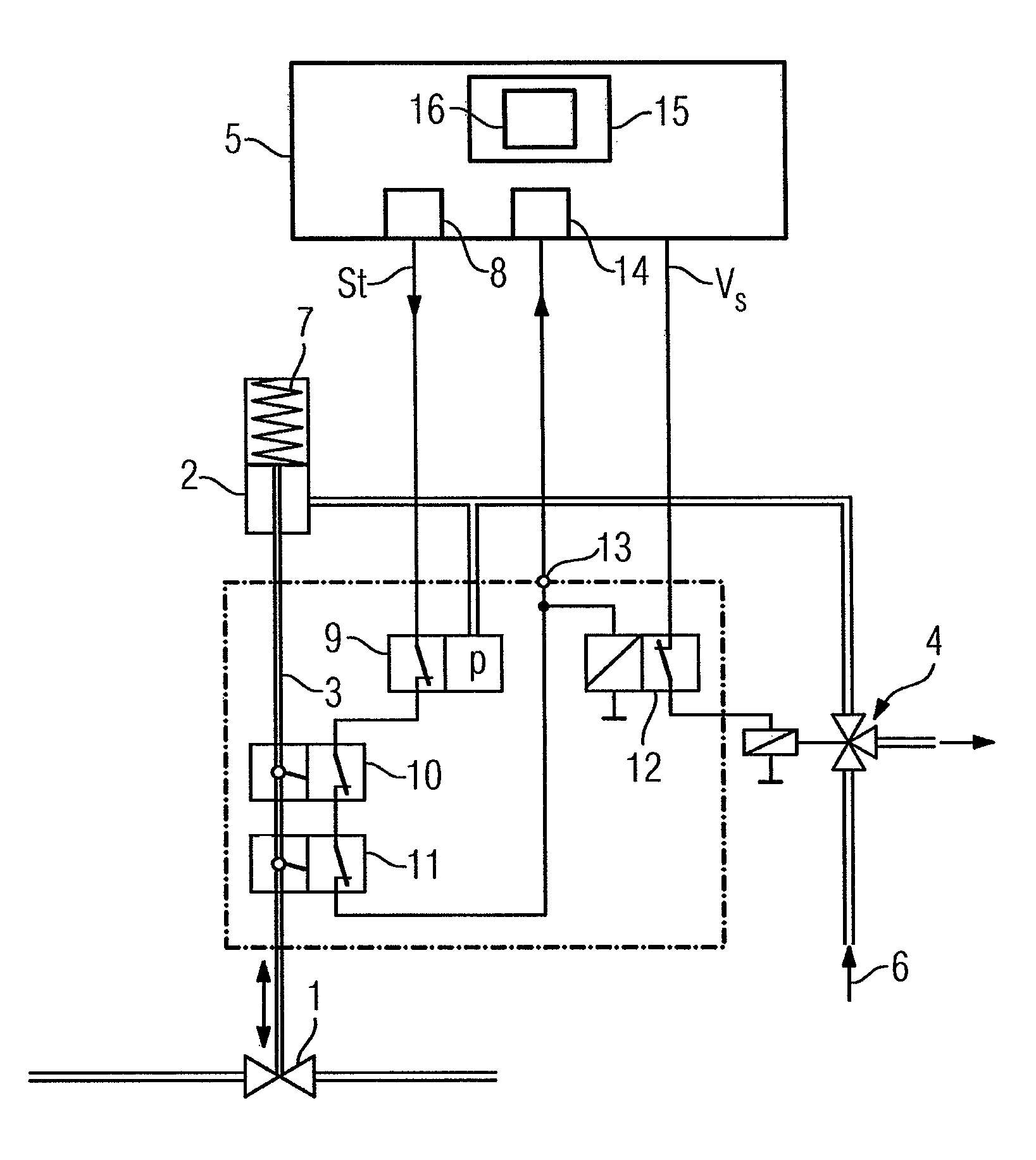
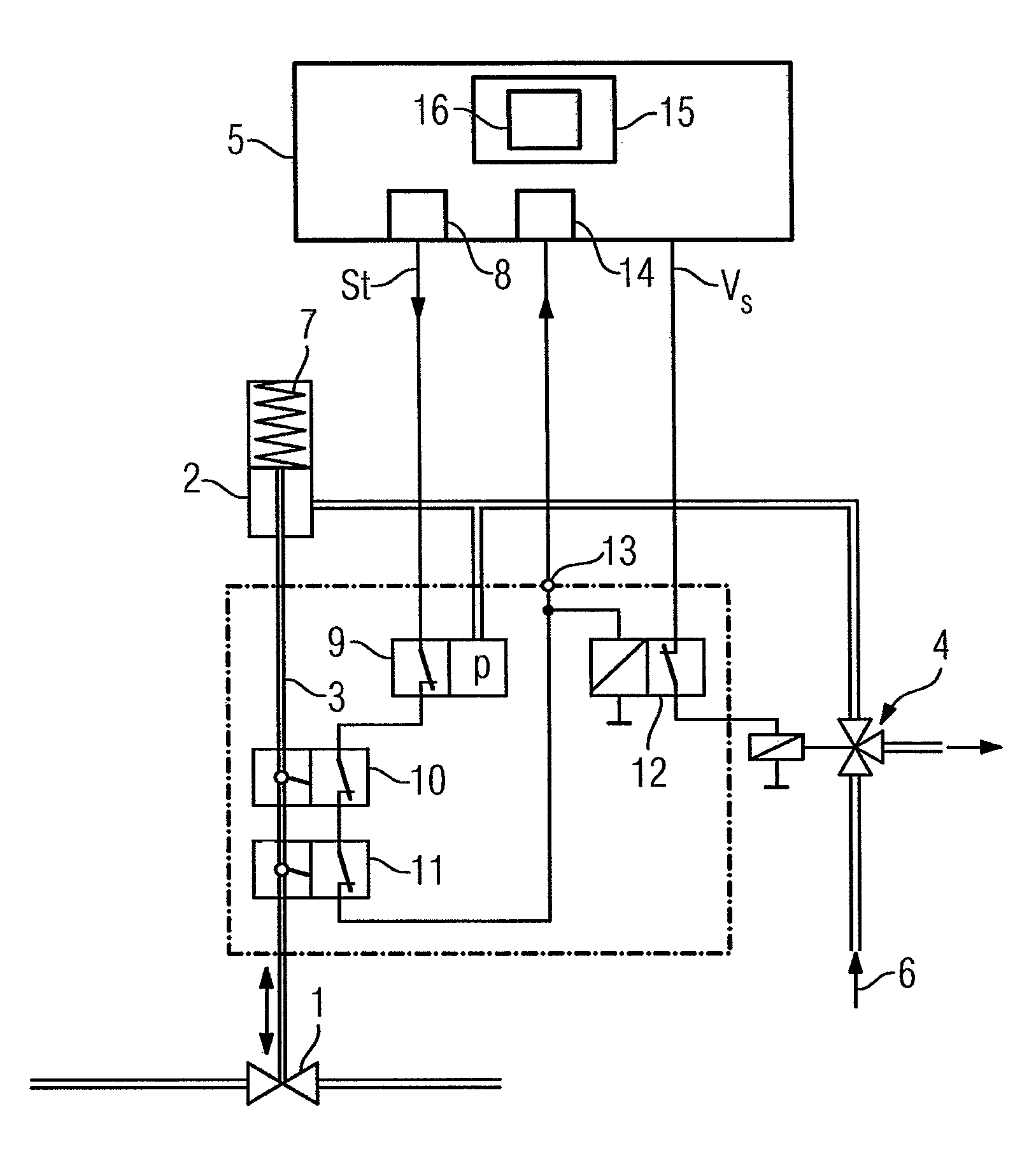
An actuating device for an on / off valve having a pneumatic drive that is connected to a compressed air supply by a solenoid valve, wherein when driven with a control voltage, the solenoid valve ventilates the pneumatic drive with the compressed air and, when the control voltage is not present, vents the pneumatic drive. The pneumatic drive moves the on / off valve into an operating position during ventilation and moves it into a safety position during venting. To permit the performance of partial-stroke tests in the simplest way possible, a device for performing the partial-stroke test includes a controllable switch which is closed in a quiescent state, and in this case supplies the control voltage to the solenoid valve. The controllable switch is opened by a control signal that is generated to perform the partial-stroke test. The control signal is supplied to the controllable switch by a position switch that is closed in the operating position of the on / off valve and is opened when the on / off valve reaches a predefined position in the direction of the safety position.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
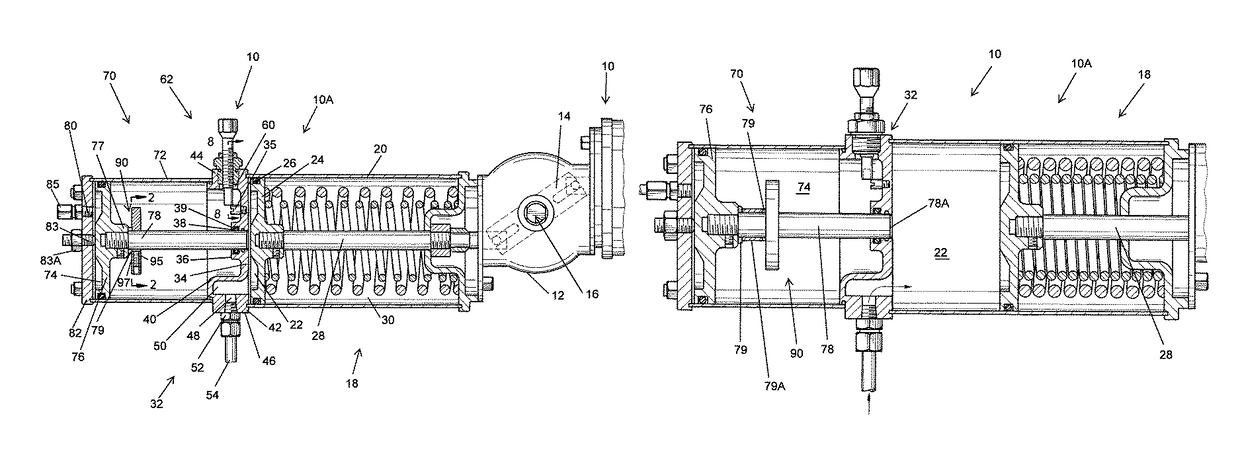
Actuator Assembly for Conducting Partial Stroke Testing
ActiveUS20170314584A1Eliminates spurious valve travelEliminate failure problemsFluid-pressure actuator testingServomotorsActuatorPartial stroke testing
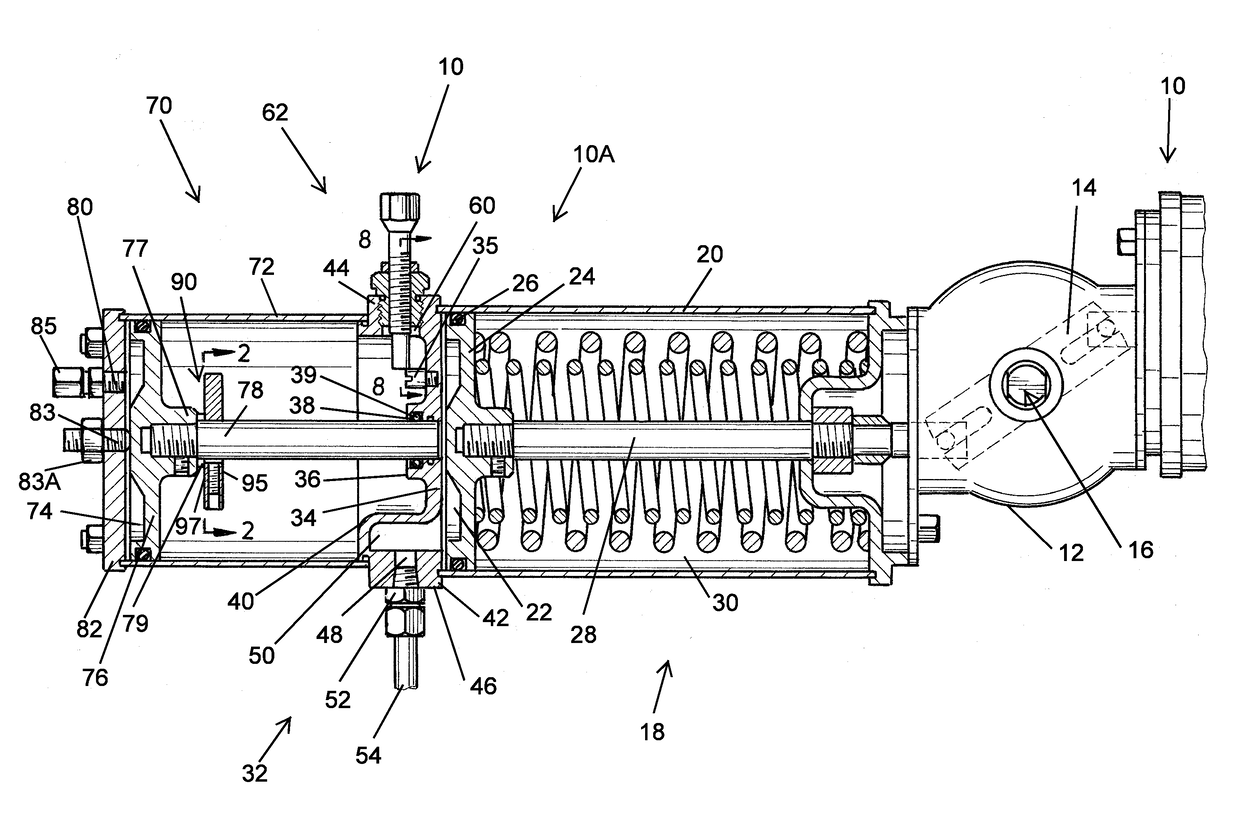
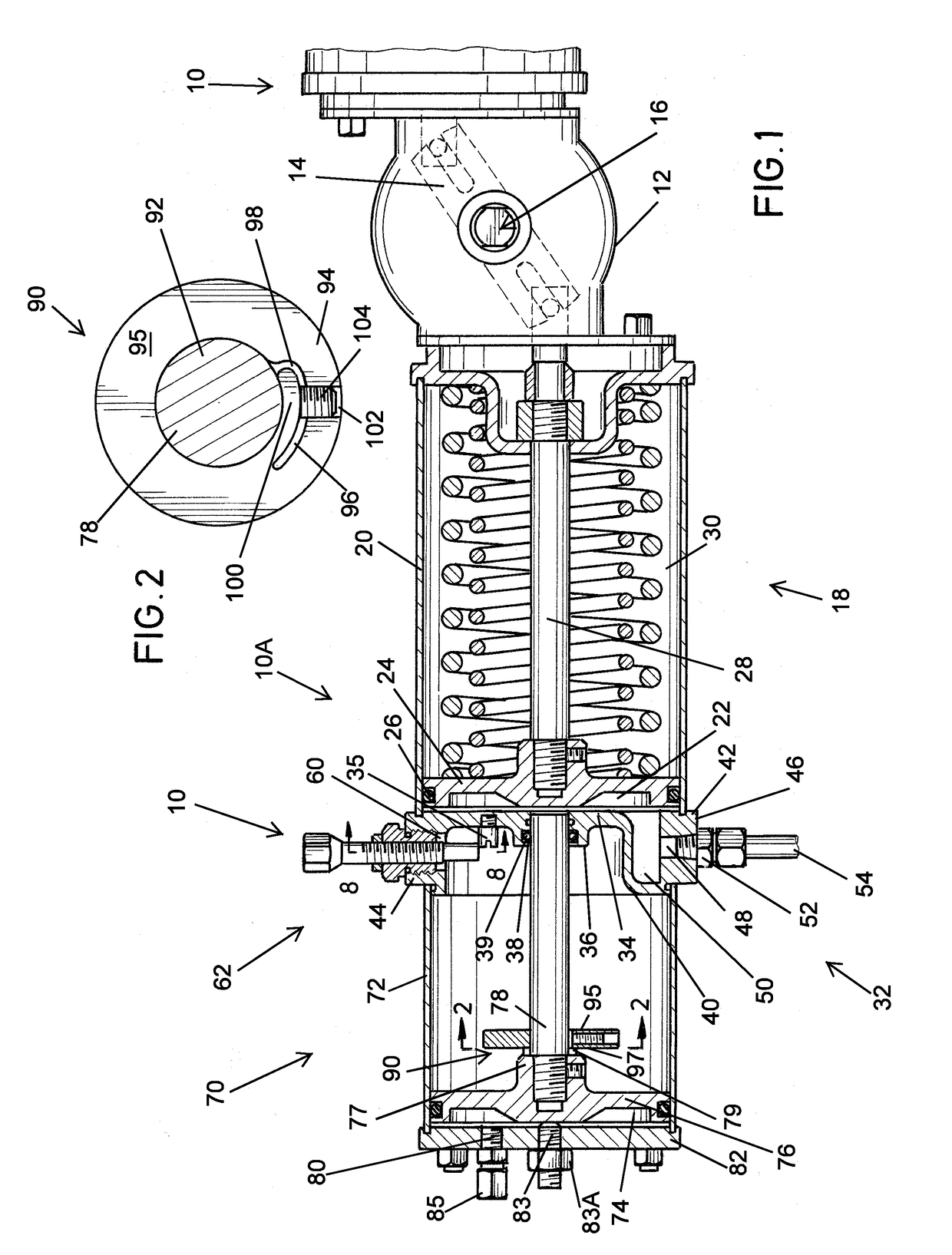
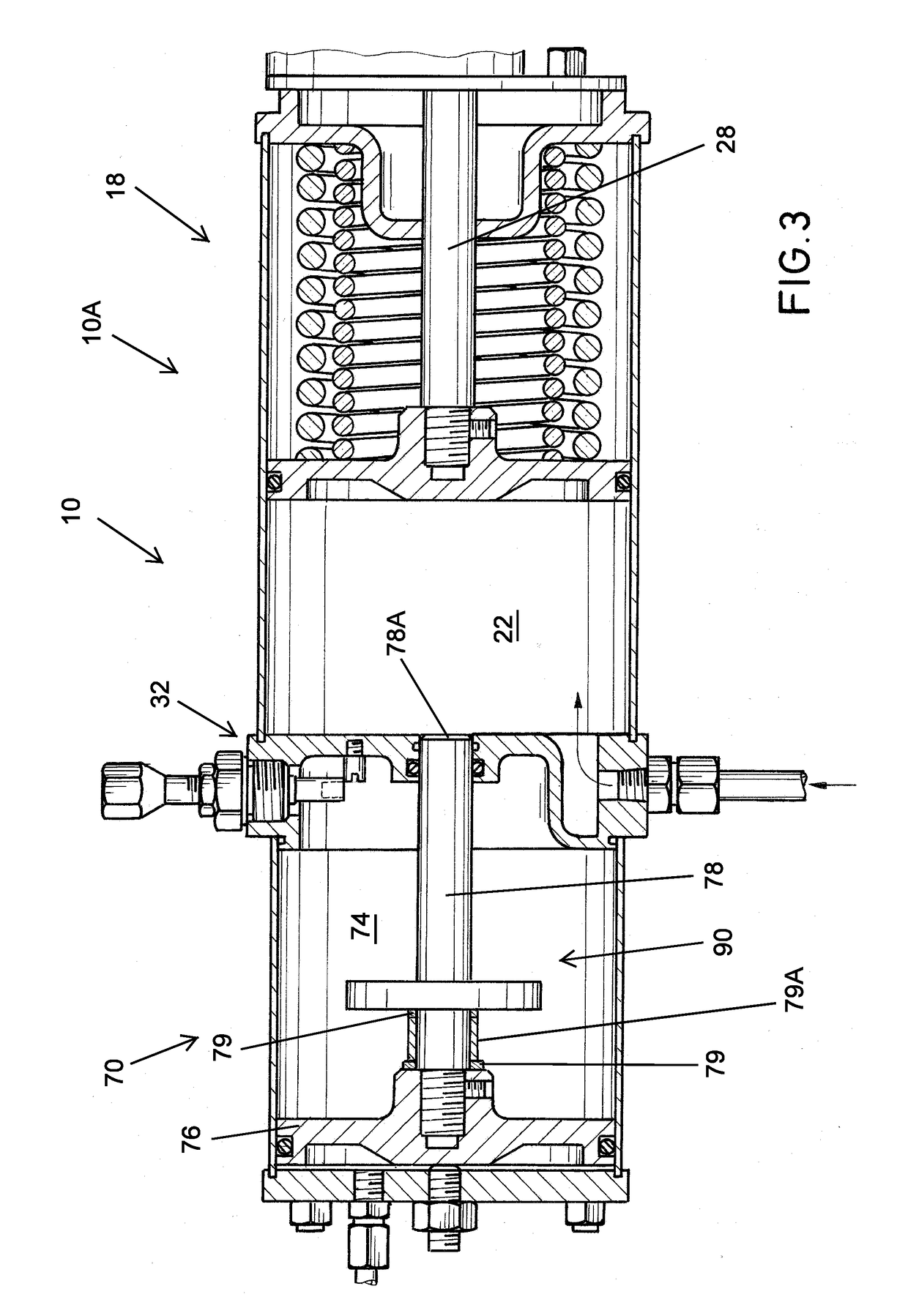
A modular actuator assembly which can be used for partial stroke testing of a valve, the assembly having a force module and a tandem piston module. The force module has a primary piston and piston rod interconnected to a shaft which is movably mounted therein. The tandem piston module is connected to the force module and has a tandem piston and piston rod. An indicator plate is connected to the piston rod and is selectively positionable on the tandem piston rod. The tandem piston rod extends into the force module and acts as a pneumatically engaged hard stop for preventing spurious travel of the primary piston and hence spurious valve travel.
Owner:QTRCO
Partial stroke testing system coupled with fuel control valve
InactiveUS20120310582A1Quick closeLow costFluid-pressure actuator safetyVehicle testingSafety Integrity LevelSolenoid valve
A system for on-line testing of an emergency shut-off valve includes a first emergency shut-off valve (first valve) and a flow control valve (second valve), with the system being configured to allow the second valve to serve as a combination flow control and second emergency shut-off valve. A subsystem is also provided for testing the first valve without fully closing the first valve in response to a signal from the control. In this subsystem, a solenoid valve bleeds off pressurized fluid to move the first valve from a fully opened to a partially closed position. A bypass around the second valve allows it to be tested as the second emergency shut-off valve, allowing the second valve to close completely without shutting down the process. The use of the two emergency shut-off valves in series wherein either valve can shut down the process provides a level 3 safety integrity level.
Owner:AL BUAIJAN TAREQ NASSER
Partial stroke testing system coupled with fuel control valve
InactiveUS20120042721A1Quick closeLow costFluid-pressure actuator safetyValve arrangementsSafety Integrity LevelSolenoid valve
A system for on-line testing of an emergency shut-off valve includes a first emergency shut-off valve (first valve) and a flow control valve (second valve), with the system being configured to allow the second valve to serve as a combination flow control and second emergency shut-off valve. A subsystem is also provided for testing the first valve without fully closing the first valve in response to a signal from the control. In this subsystem, a solenoid valve bleeds off pressurized fluid to move the first valve from a fully opened to a partially closed position. A bypass around the second valve allows it to be tested as the second emergency shut-off valve, allowing the second valve to close completely without shutting down the process. The use of the two emergency shut-off valves in series wherein either valve can shut down the process provides a level 3 safety integrity level.
Owner:AL BUAIJAN TAREQ NASSER
Method for testing the functionality of armatures
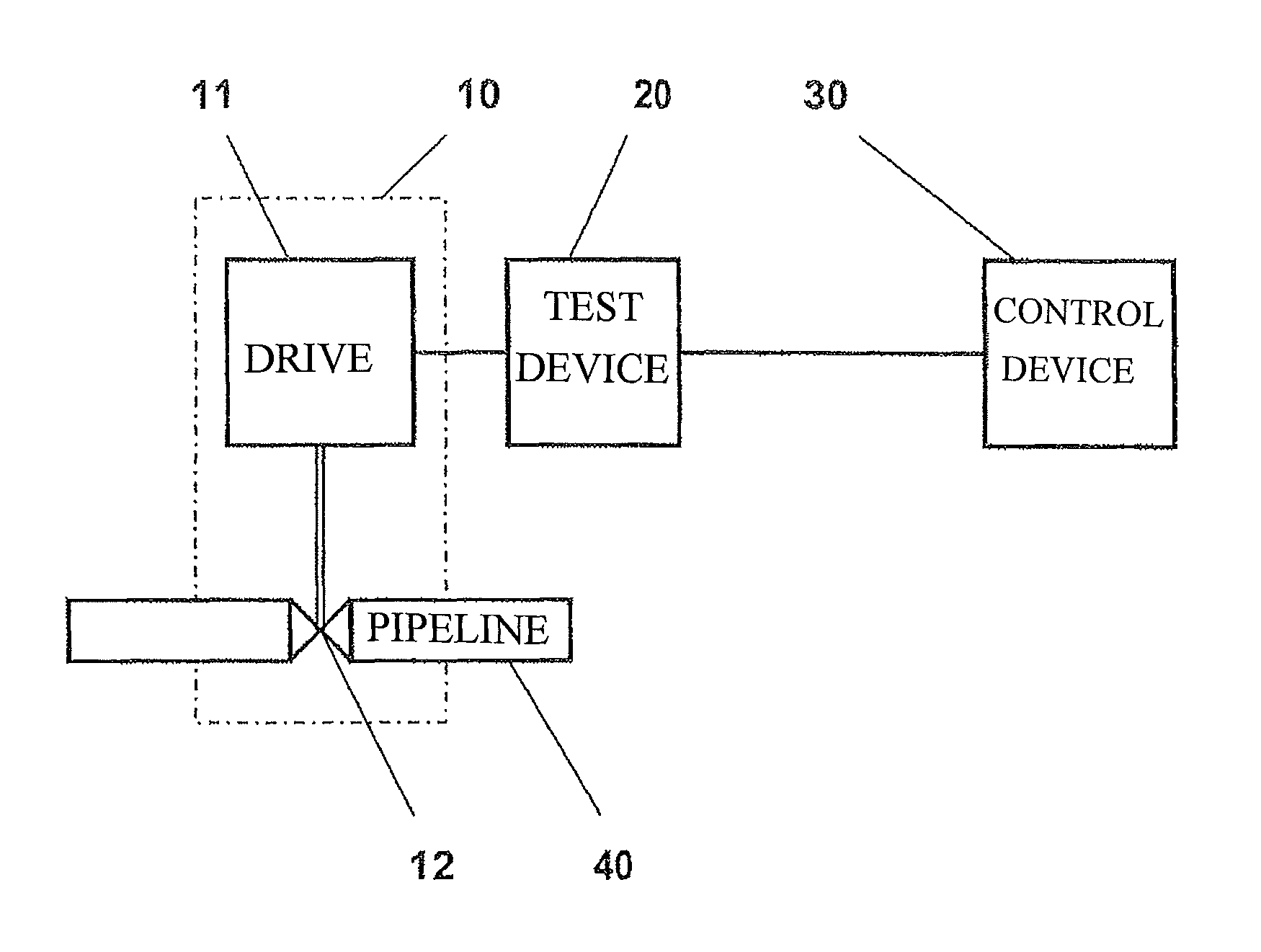
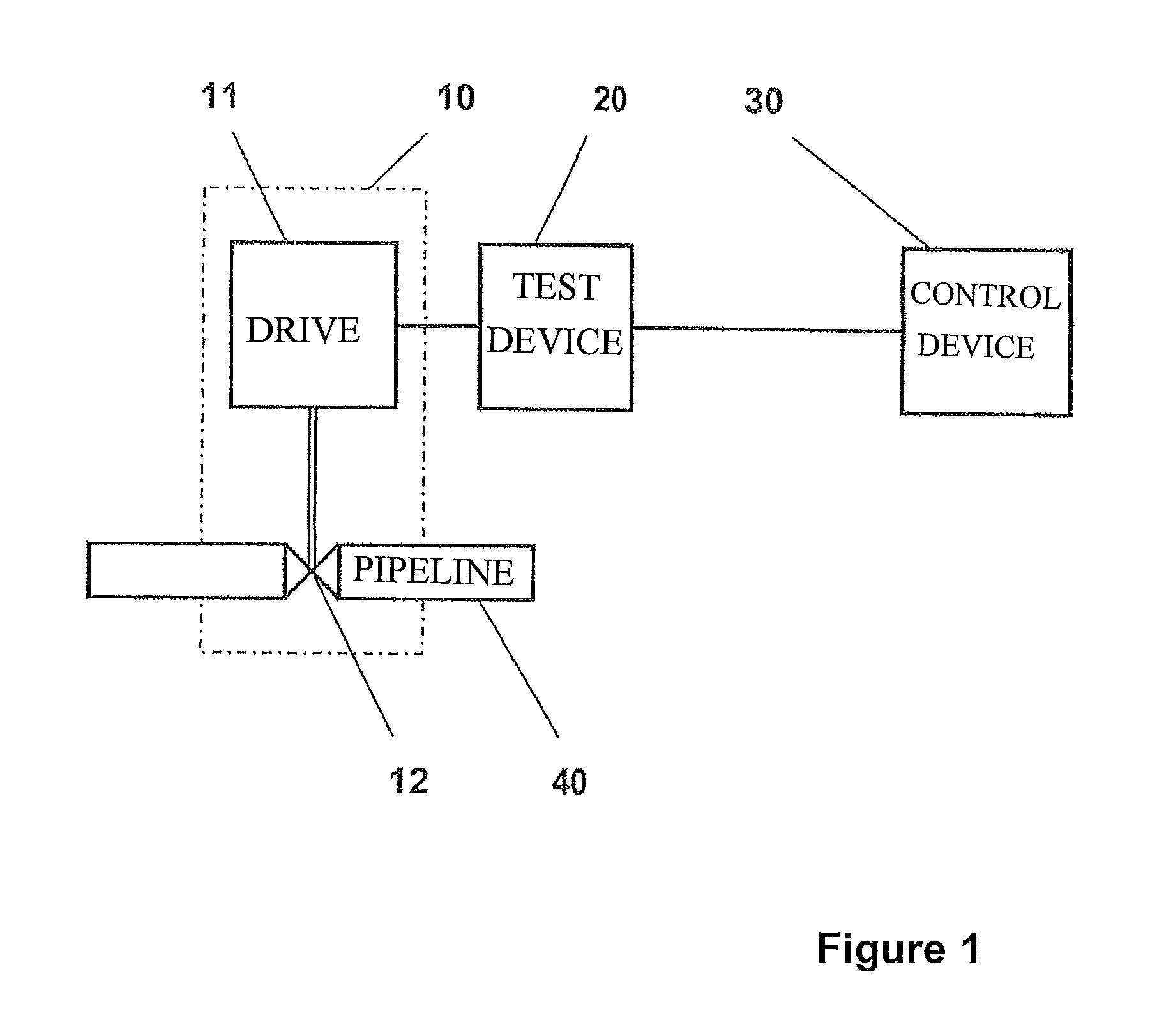
ActiveUS20080314170A1Avoid influenceContinuous monitoringElectrical testingStructural/machines measurementControl systemIn process control
The disclosure relates to a method for testing the functionality of armatures, e.g., of safety armatures, in process control systems which are assigned a test device for implementing partial stroke testing and which are connected to a control device, which brings about actuation, in accordance with regulations, of the safety armature in an emergency. Prior to the start of the implementation of the partial stroke testing, a request signal is transmitted from the test device to the control device which is answered by the control device with an enable signal, the enable signal being issued as a function of the current process sequence at the armature.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
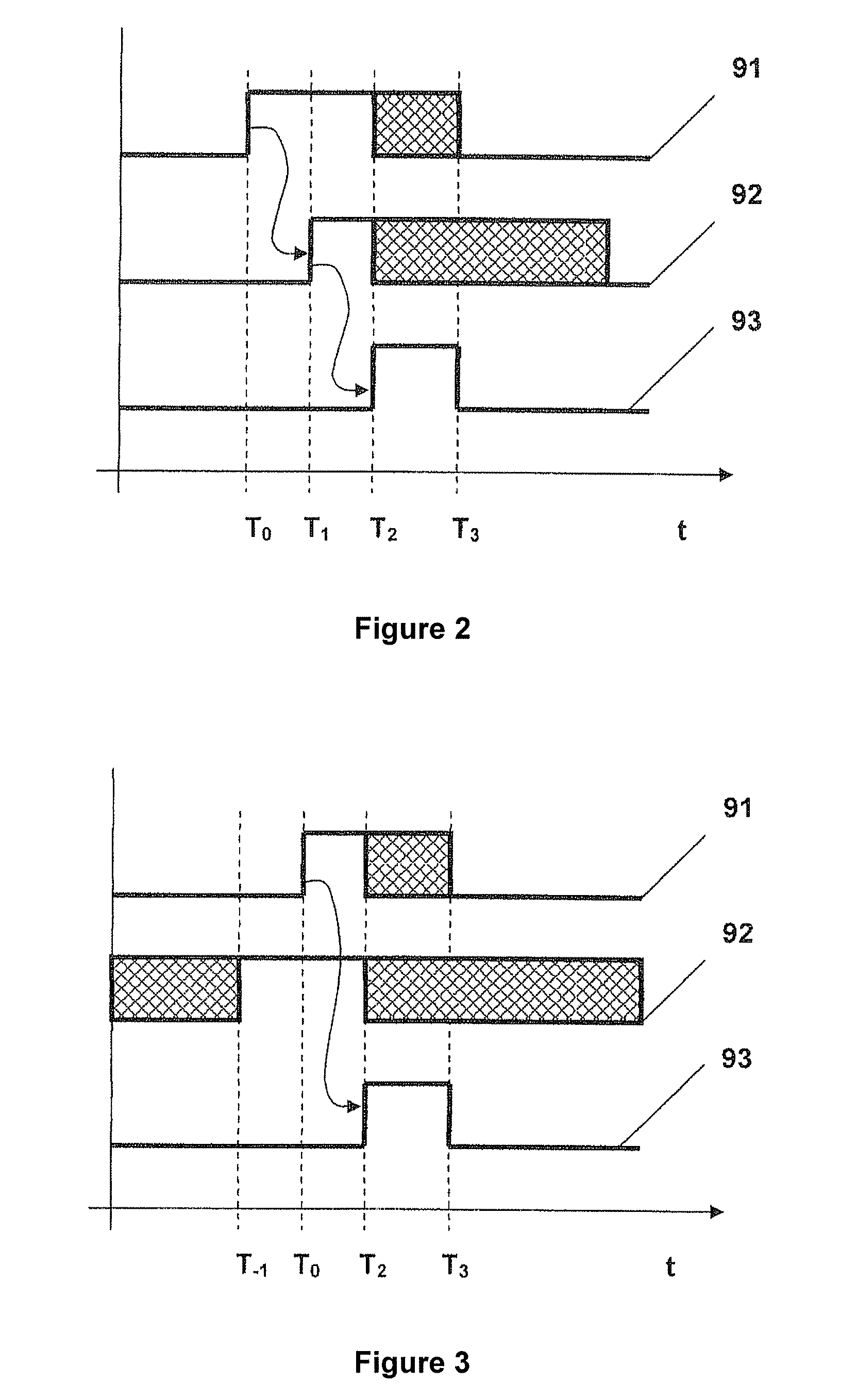
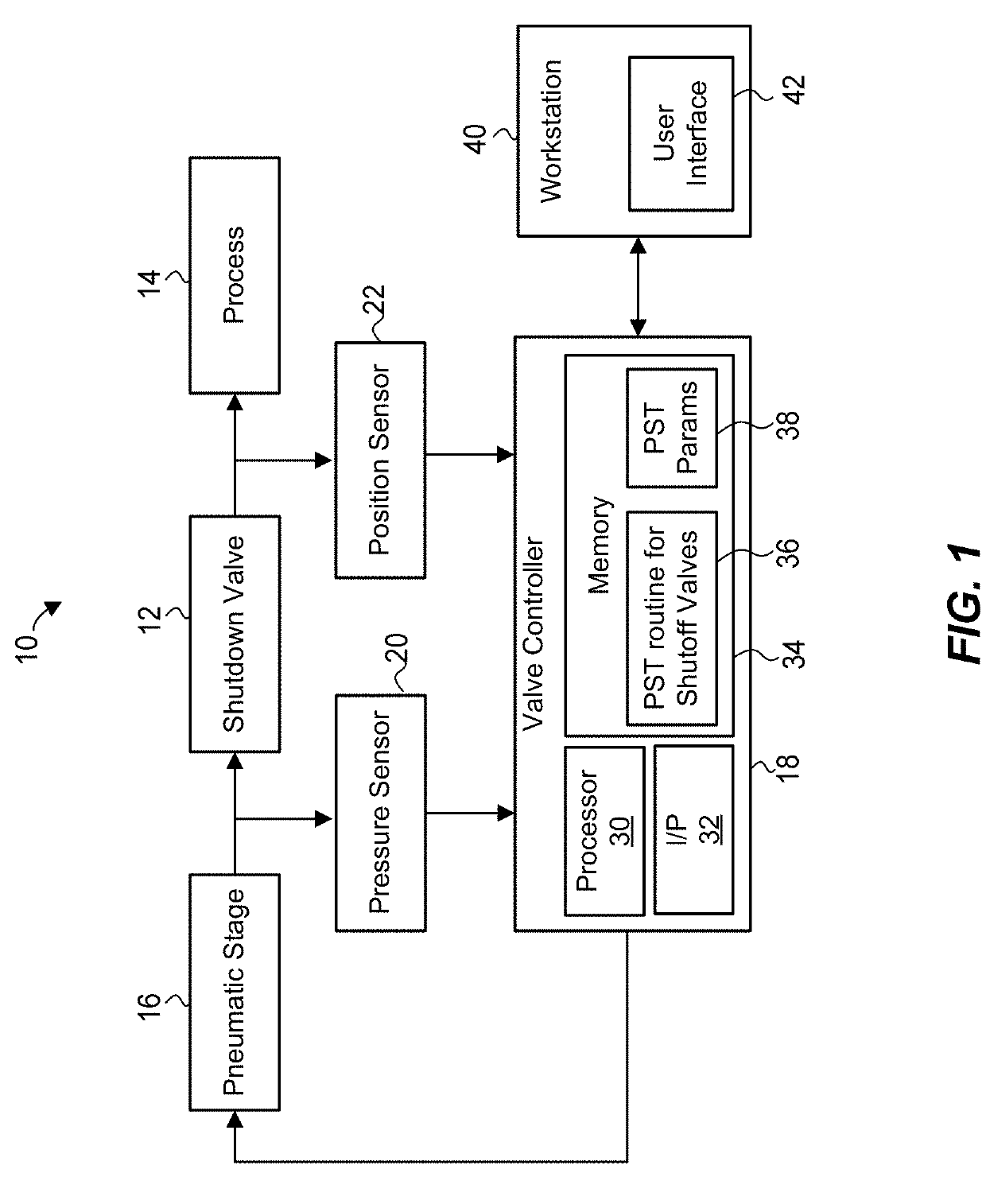
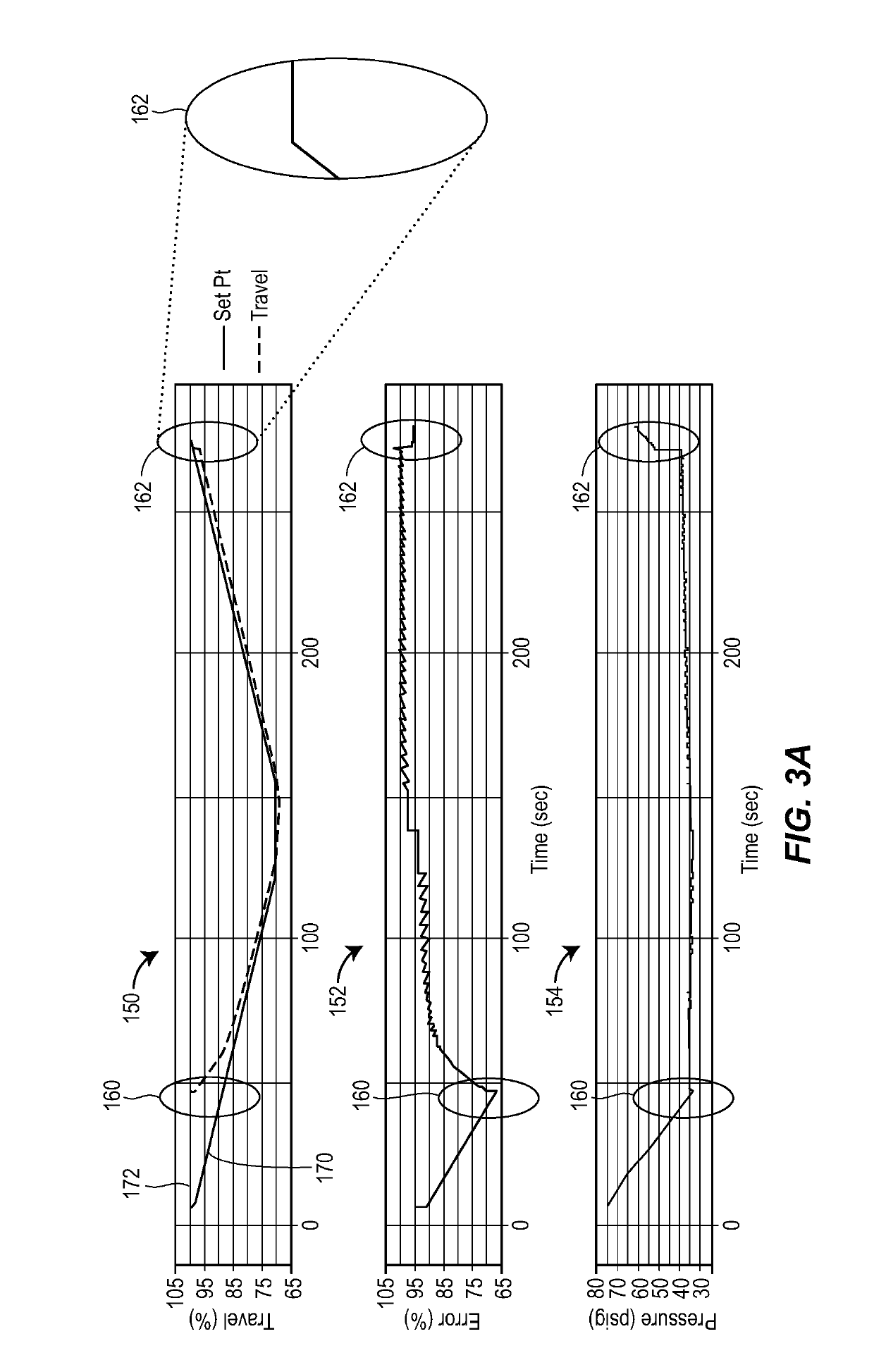
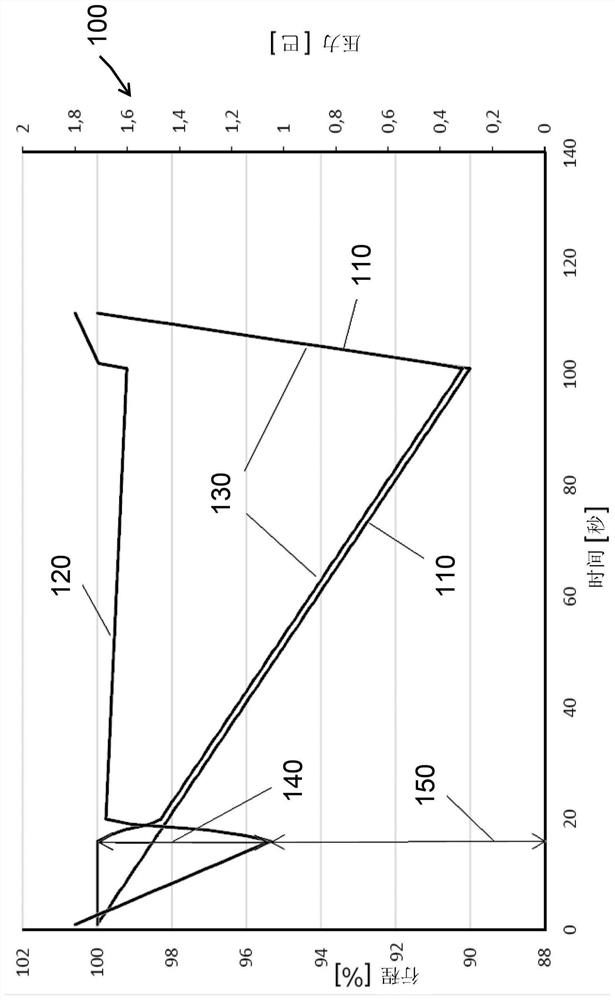
Partial stroke tests for shutdown valves
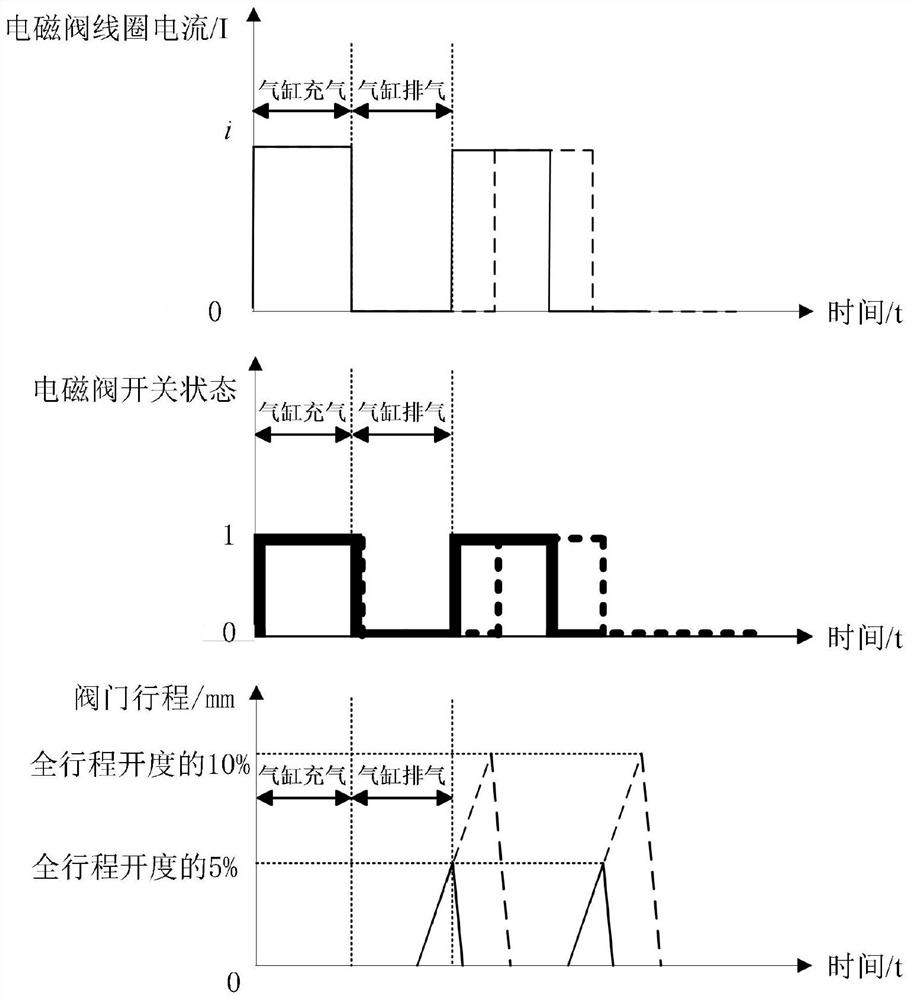
ActiveUS20170184215A1Accurately determineMinimal amountFluid-pressure actuator safetyMachine part testingEngineeringPartial stroke testing
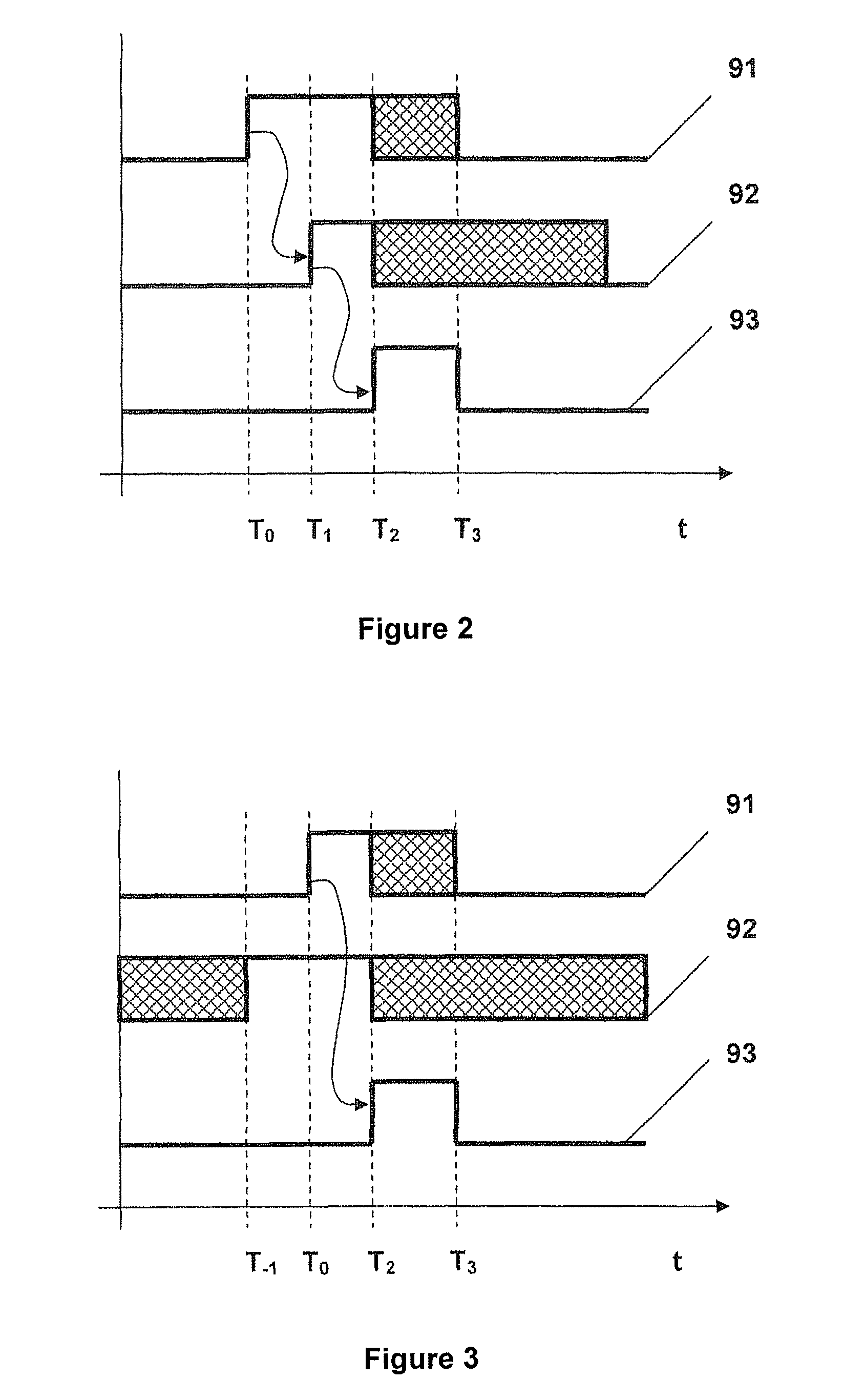
To generate a setpoint signal to stroke a valve during a partial-stroke test, a first target is determined for the setpoint signal based at least on a travel displacement threshold, the travel displacement threshold corresponding to a desired extent of travel of the valve during the partial-stroke test; the setpoint signal is ramped from an initial value to the first target, during a first time interval; subsequently to the first time interval, the setpoint signal is maintained at the first target during a second time interval; a second target is determined for the setpoint signal based at least on the initial value; and during a third time interval subsequent to the second interval, the setpoint signal is ramped from the first target to the second target in a direction opposite to the ramping of the setpoint signal during the first time interval.
Owner:FISHER CONTROLS INT LLC
Partial stroke testing system coupled with fuel control valve
InactiveUS8720267B2Quick closeLow costFluid-pressure actuator safetyVehicle testingSafety Integrity LevelSolenoid valve
A system for on-line testing of an emergency shut-off valve includes a first emergency shut-off valve (first valve) and a flow control valve (second valve), with the system being configured to allow the second valve to serve as a combination flow control and second emergency shut-off valve. A subsystem is also provided for testing the first valve without fully closing the first valve in response to a signal from the control. In this subsystem, a solenoid valve bleeds off pressurized fluid to move the first valve from a fully opened to a partially closed position. A bypass around the second valve allows it to be tested as the second emergency shut-off valve, allowing the second valve to close completely without shutting down the process. The use of the two emergency shut-off valves in series wherein either valve can shut down the process provides a level 3 safety integrity level.
Owner:AL BUAIJAN TAREQ NASSER
Testing of safety devices
ActiveUS20170268695A1Avoid excessive movementFluid-pressure actuator safetyFluid-pressure actuator testingValve actuatorEngineering
Many operators choose not to utilise partial-stroke testing arrangements even when the equipment required for it to be performed is available, due to a perceived risk of over-travel and / or spurious trip. To alleviate this, we describe a safety valve system comprising a valve operable to move between an operating state and a safe state, a valve actuator operatively connected to the valve to control its state, and including a bias toward the safe state, a pair of drive members powered by a pressure media, each acting against the bias to urge the valve toward the operating state, a first control valve arranged to selectively convey pressure media to both drive members and to withdraw supply on receipt of a safety trigger, and a second control valve arranged to selectively convey pressure media to one drive member only of the pair and to withdraw supply on receipt of a test signal. In this way, a partial stroke test is possible via the second control valve, but the other drive member of the pair will remain active thus acting as a buffer that prevents excessive movement of the valve.
Owner:IMTEX CONTROLS
Method and apparatus for partial stroke testing of an emergency shutdown valve
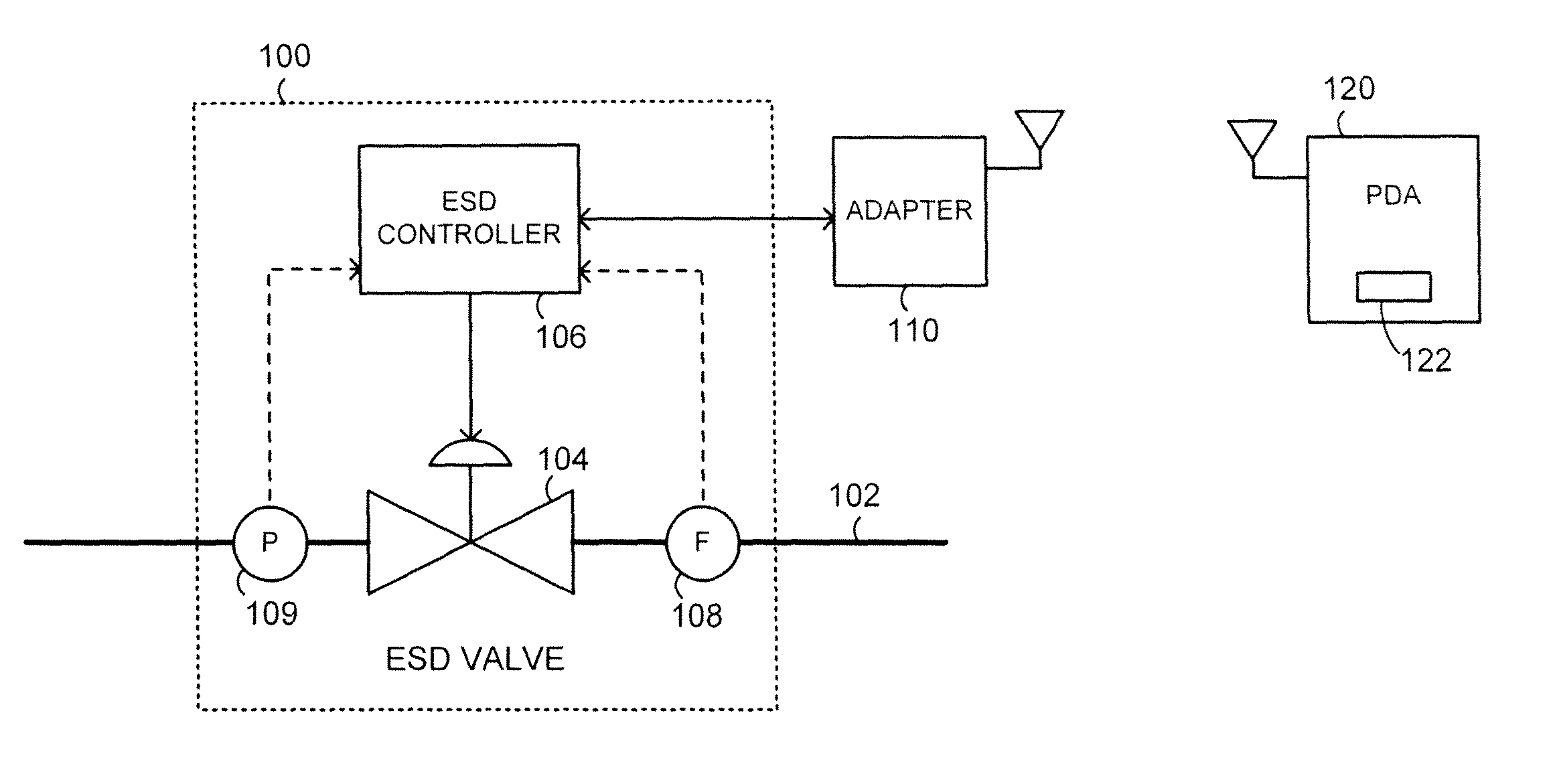
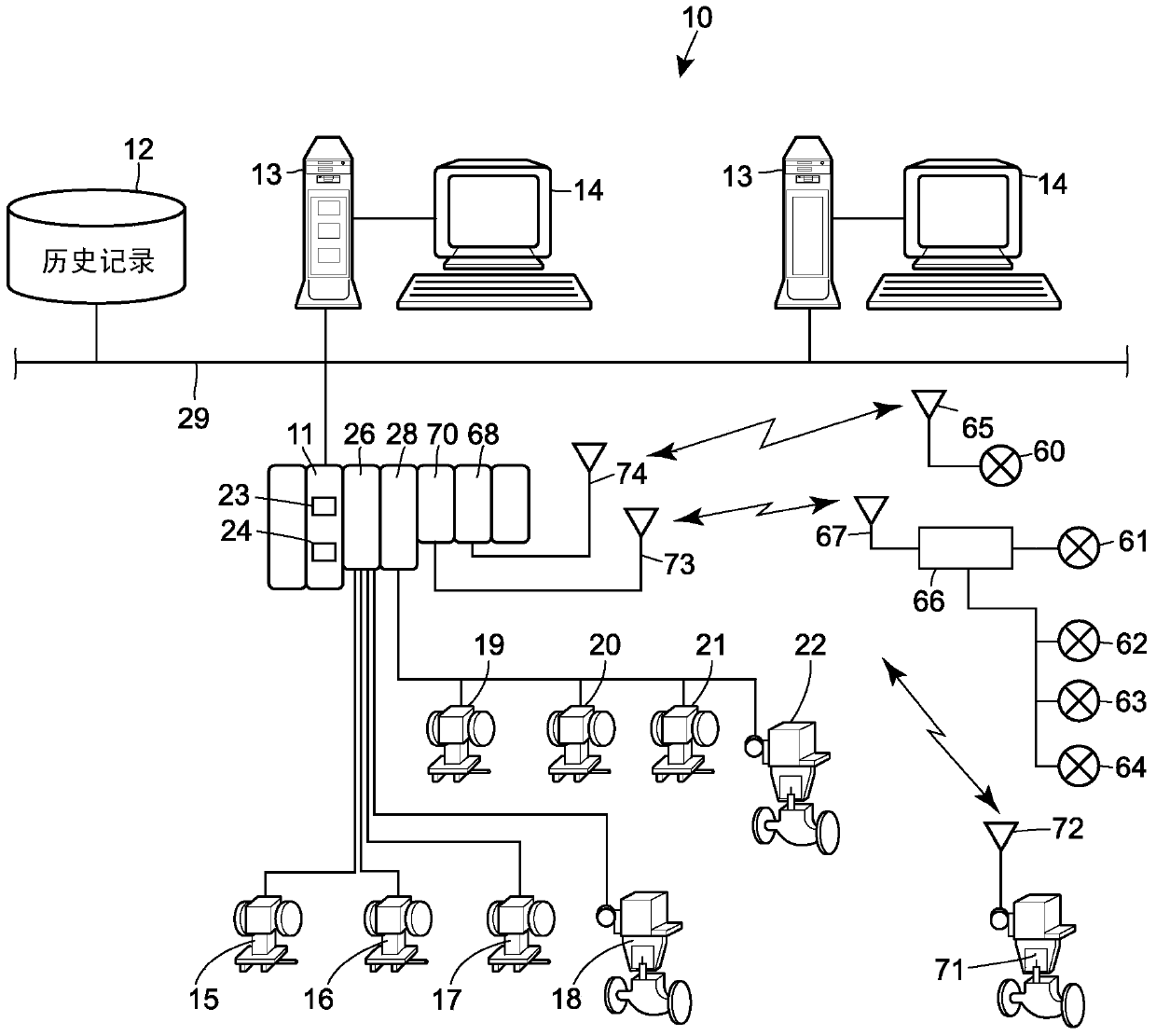
ActiveUS9080683B2Valve arrangementsHydraulic programme controlTelecommunications linkCommunication link
A method for conducting a partial stroke test of an emergency shutdown valve includes receiving a request to initiate the partial stroke test from a user interface or another source, establishing a direct or an indirect wireless communication link with the emergency shutdown valve, and generating one or more commands of a digital industrial automation protocol to be transmitted to the emergency shutdown valve via the wireless communication link, so that a partial stroke test of the emergency shutdown valve is initiated in response to these commands.
Owner:FISHER CONTROLS INT LLC
Partial stroke testing system for emergency shut-off valves
ActiveUS20170198829A1Low costNot adversely interrupt processValve arrangementsFluid-pressure actuator testingExhaust valveSolenoid valve
An emergency shut-off valve and means for initiating a test on said emergency shut-off valve includes a source of pressurized gas, a main solenoid responsive to a signal from said means for initiating a test and a source of pressurized gas are included. Further, means including a main solenoid responsive to a signal from said means for initiating a test and a main solenoid valve and a quick exhaust valve connected to the source of pressurized gas. Further, a pneumatic actuator for opening and closing the shut-off valve and test means for testing the emergency shut-off valve without fully closing the emergency shut-off valve in response to a signal from the means for initiating a test. The test means includes a second solenoid.
Owner:ALKANDARI HASSAN ABDULLAH AHMAD
Safety instrument system and method for permitting PST
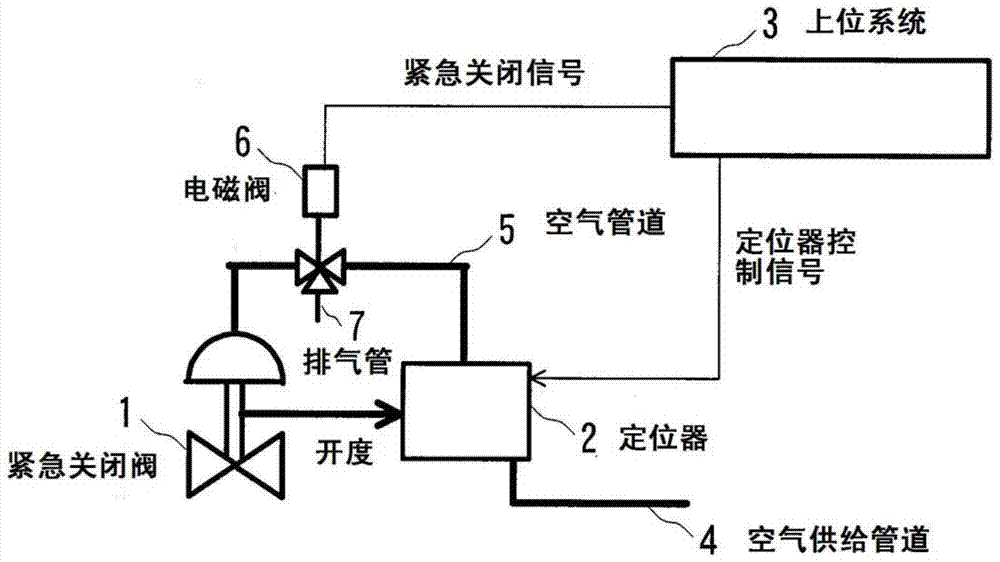
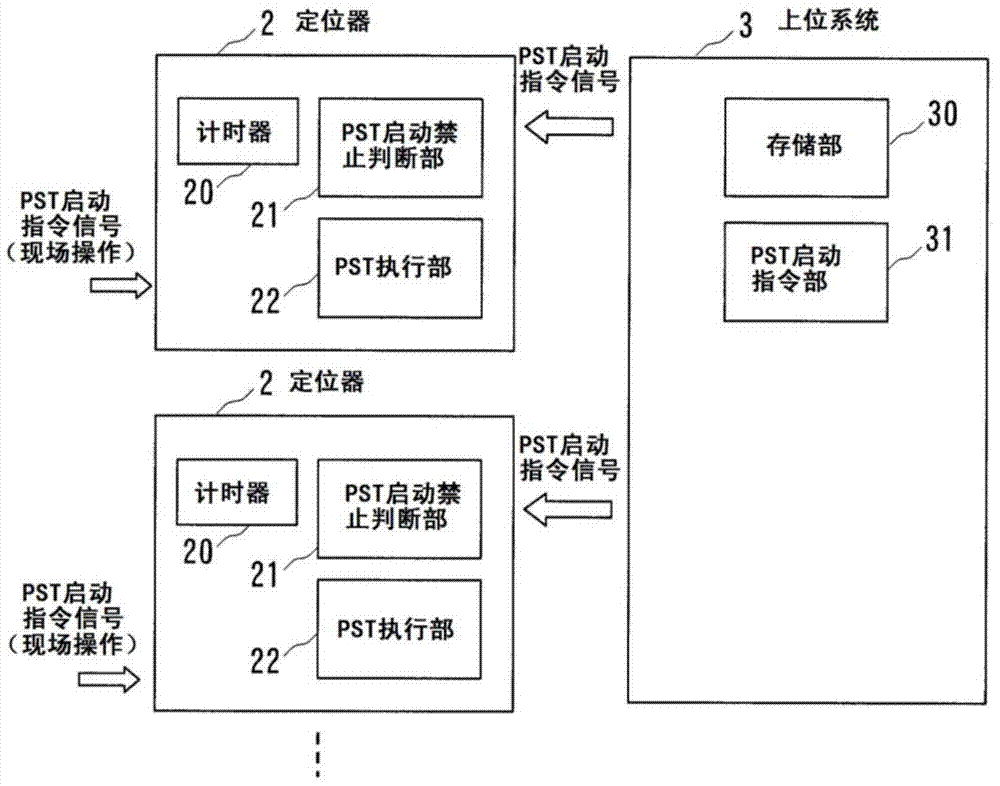
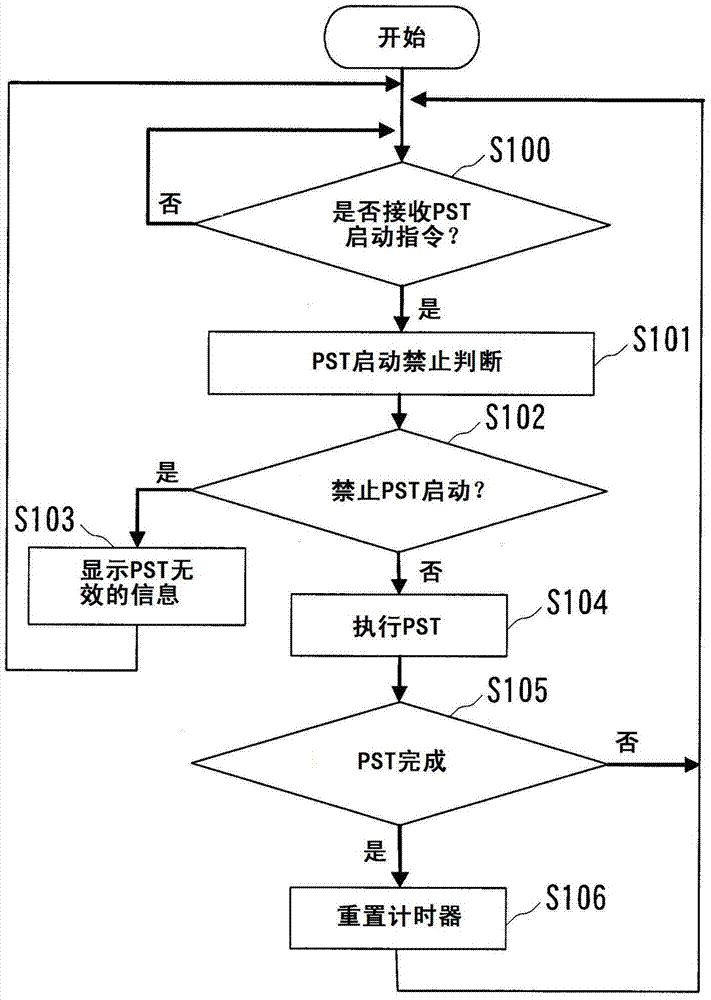
InactiveCN103901872AStart inhibitAvoid bad influenceProgramme controlValve arrangementsSafety instrumented systemProcess equipment
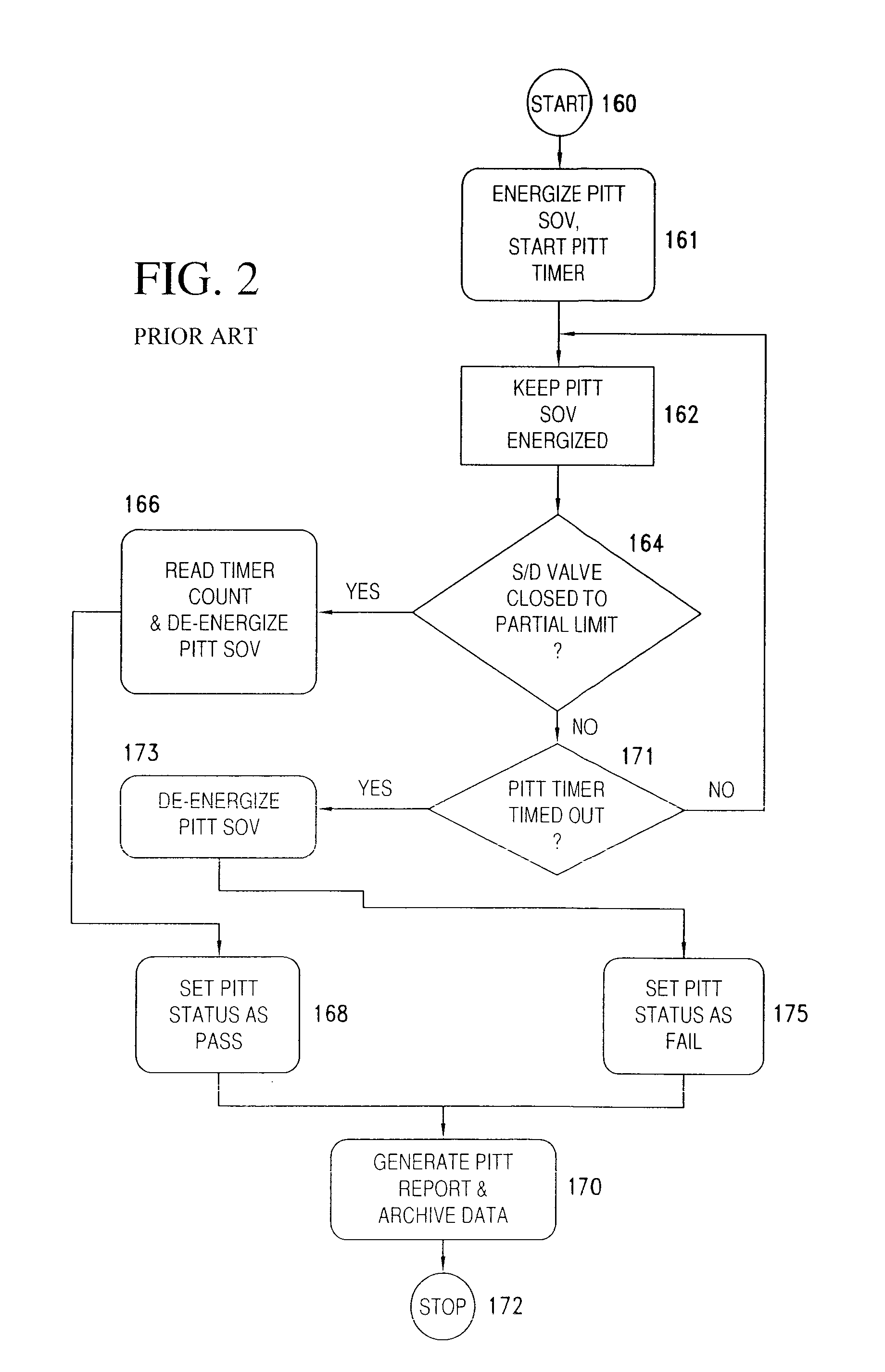
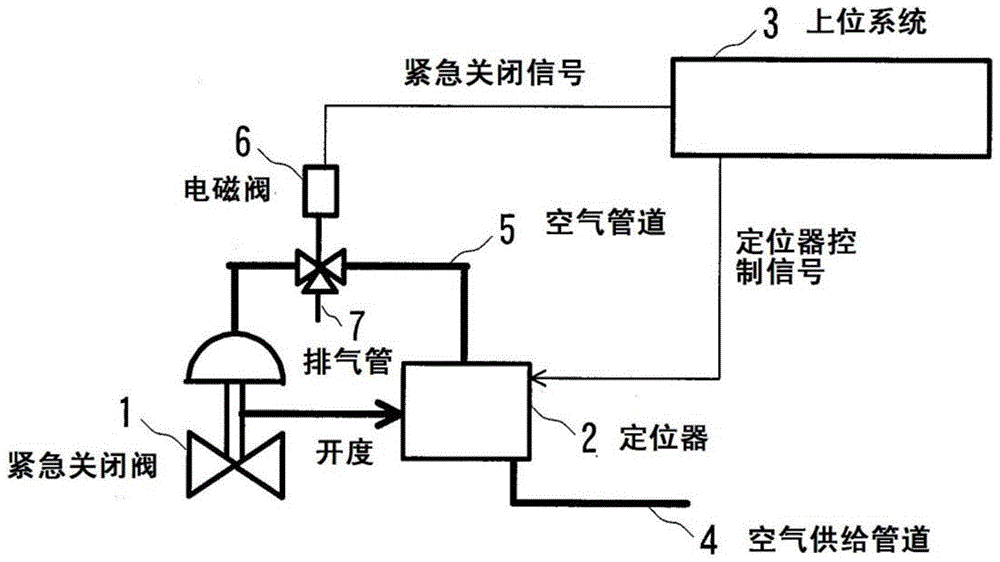
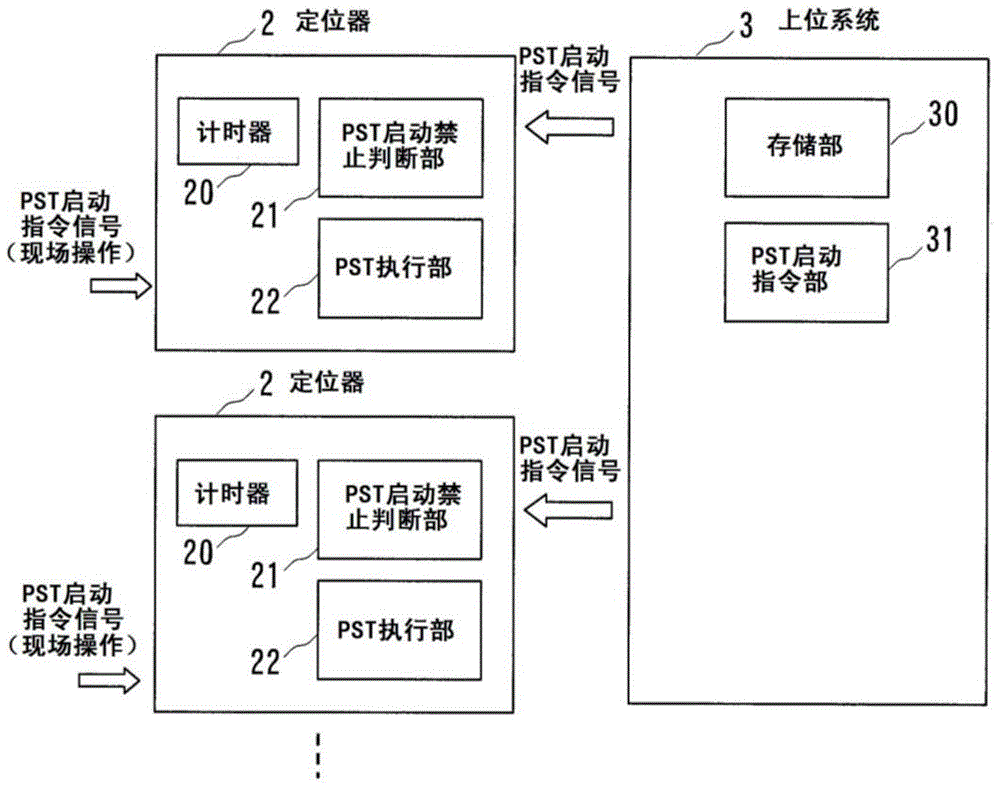
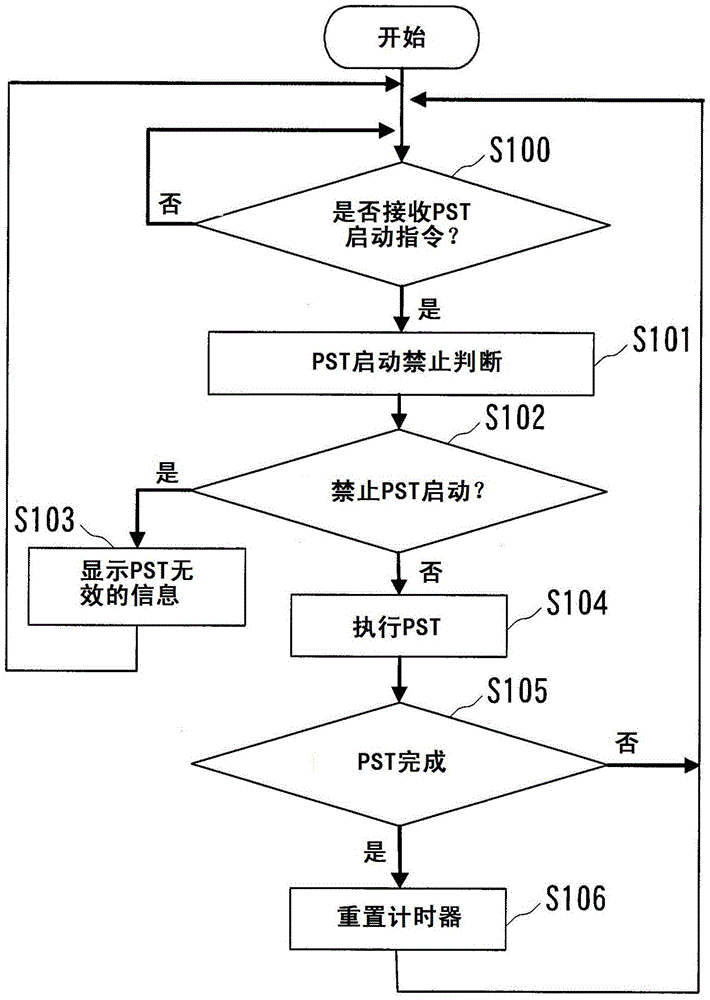
A safety instrument system comprises a positioner for controlling the degree of opening of an emergency cutoff valve that is provided in a pipe in a plant, and a higher-level system for controlling the PSTs (partial stroke tests) of the emergency cutoff valve. The positioner has: a portion for executing a PST on the emergency cutoff valve in response to an initiating instruction from the higher-level system or to an initiating instruction from an operating panel on the plant floor wherein the positioner is provided; a timer for measuring elapsed time from the completion of a PST on the emergency cutoff valve; and a portion for evaluating whether or not a PST is permitted, by comparing elapsed time from the previous PST, to a PST minimum interval that is set in advance.
Owner:YAMATAKE HONEYWELL CO LTD
Manual and pneumatic integrated valve
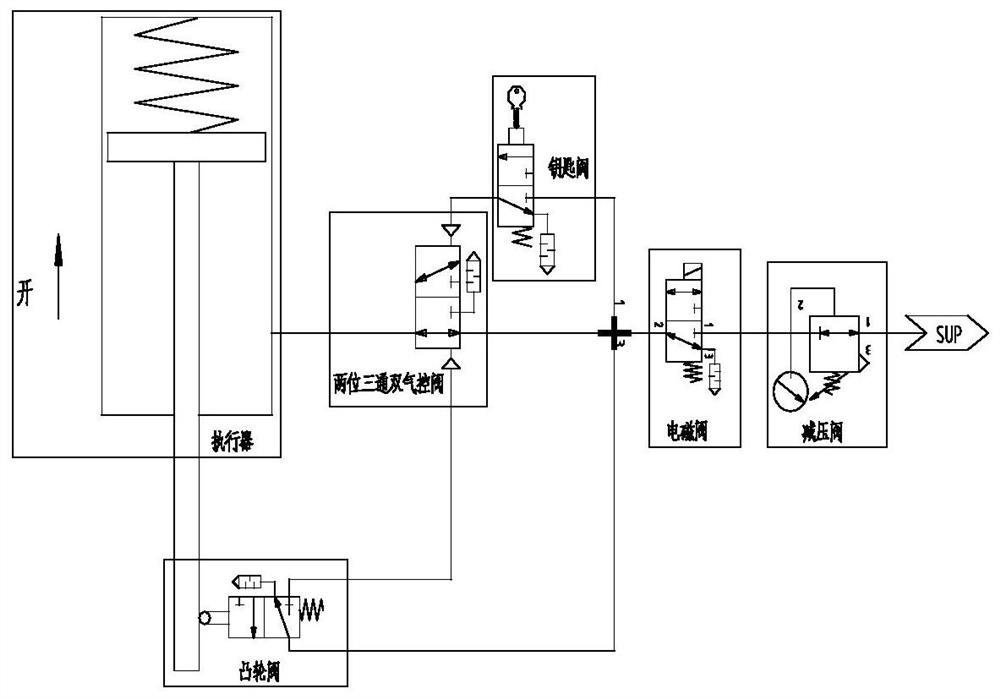
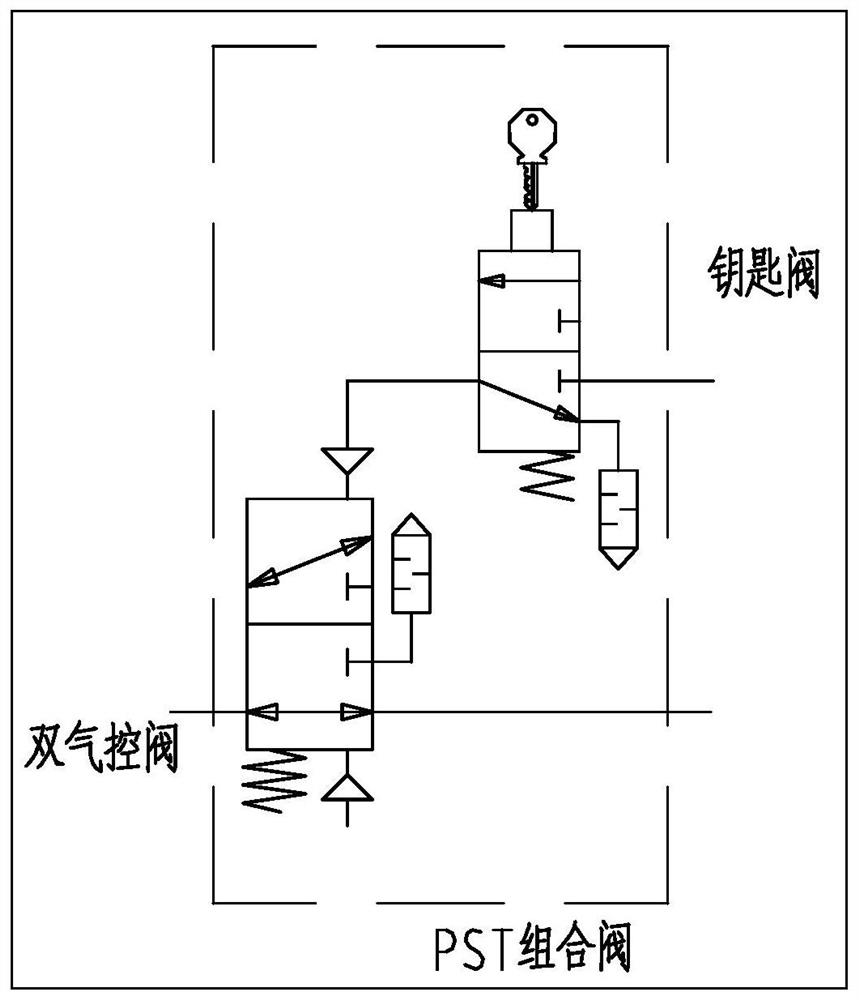
A manual and pneumatic integrated valve comprises a pressing plate, a first sealing gasket, a valve body, a limiting base, a first polyurethane seal ring, an O-ring, a shaft sleeve, a first valve element, a pressing cap, a second sealing gasket, a second polyurethane seal ring, a first upper cover, a button support, a key valve button, a second upper cover and a second valve element. The limitingbase and the first polyurethane seal ring are arranged on the valve body. The O-ring is arranged on the shaft sleeve and used for sealing between the shaft sleeve and the valve body. The valve elementis arranged in the shaft sleeve. A slide valve sealing mode is adopted between the valve element and the shaft sleeve. The pressing cap is arranged at the upper portion of the valve element. The second polyurethane seal ring is arranged in the first upper cover. The button support is arranged on the first upper cover. The second sealing gasket and the first upper cover are assembled together andarranged in the valve body. The key valve button is arranged on the second upper cover. The second upper cover is arranged on the valve body. The manual and pneumatic integrated valve has functions ofa key valve, also has functions of a two-position three-way double-air-control valve and can make a PST partial stroke test loop simpler and more reliable.
Owner:YINCHUAN INAUTO AUTOMATION
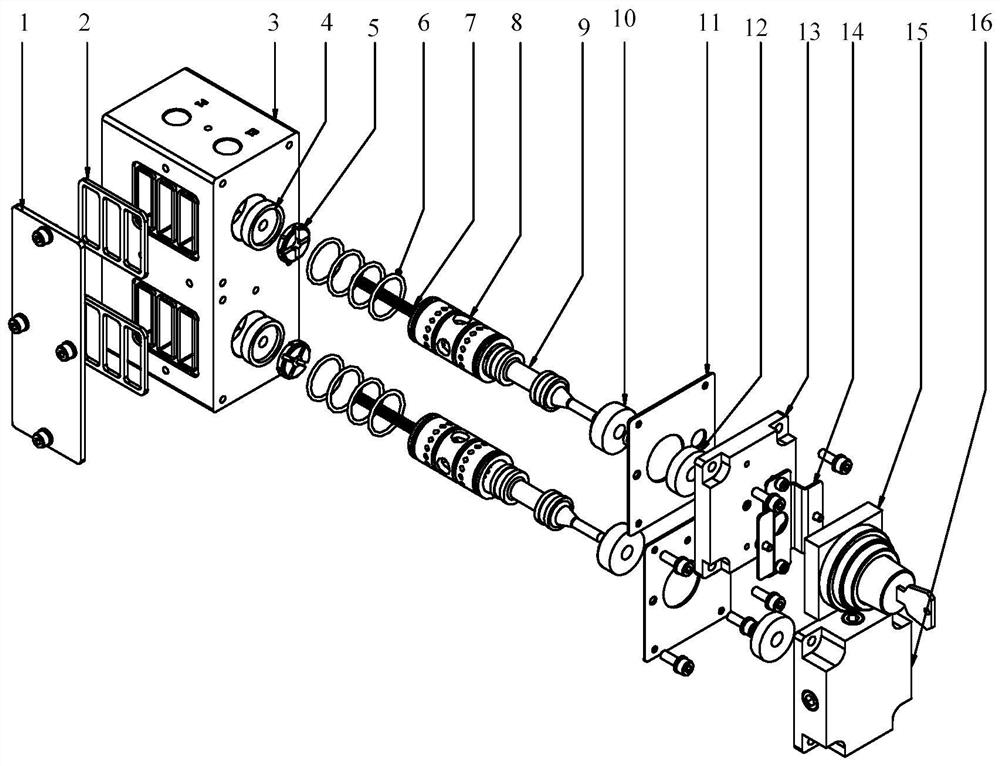
Actuator assembly for conducting partial stroke testing
ActiveUS10132337B2Eliminates spurious valve travelEliminate failure problemsFluid-pressure actuator testingServomotorsEngineeringActuator
A modular actuator assembly which can be used for partial stroke testing of a valve, the assembly having a force module and a tandem piston module. The force module has a primary piston and piston rod interconnected to a shaft which is movably mounted therein. The tandem piston module is connected to the force module and has a tandem piston and piston rod. An indicator plate is connected to the piston rod and is selectively positionable on the tandem piston rod. The tandem piston rod extends into the force module and acts as a pneumatically engaged hard stop for preventing spurious travel of the primary piston and hence spurious valve travel.
Owner:QTRCO
Partial stroke testing system for emergency shut-off valves
ActiveUS9732878B2Low costNot adversely interrupt processValve arrangementsFluid-pressure actuator testingExhaust valveSolenoid valve
An emergency shut-off valve and means for initiating a test on said emergency shut-off valve includes a source of pressurized gas, a main solenoid responsive to a signal from said means for initiating a test and a source of pressurized gas are included. Further, means including a main solenoid responsive to a signal from said means for initiating a test and a main solenoid valve and a quick exhaust valve connected to the source of pressurized gas. Further, a pneumatic actuator for opening and closing the shut-off valve and test means for testing the emergency shut-off valve without fully closing the emergency shut-off valve in response to a signal from the means for initiating a test. The test means includes a second solenoid.
Owner:ALKANDARI HASSAN ABDULLAH AHMAD
Method for testing the functionality of armatures
ActiveUS7954391B2Continuous monitoringValve arrangementsFluid-pressure actuator testingControl systemIn process control
The disclosure relates to a method for testing the functionality of armatures, e.g., of safety armatures, in process control systems which are assigned a test device for implementing partial stroke testing and which are connected to a control device, which brings about actuation, in accordance with regulations, of the safety armature in an emergency. Prior to the start of the implementation of the partial stroke testing, a request signal is transmitted from the test device to the control device which is answered by the control device with an enable signal, the enable signal being issued as a function of the current process sequence at the armature.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Locally actuated partial stroke test system
ActiveCN110168233BValve arrangementsFluid-pressure actuator testingPhysical medicine and rehabilitationIsolation valve
Embodiments of the present invention describe mechanically and electrically operated, locally actuated partial stroke test devices and systems for testing the operation of emergency isolation valves.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
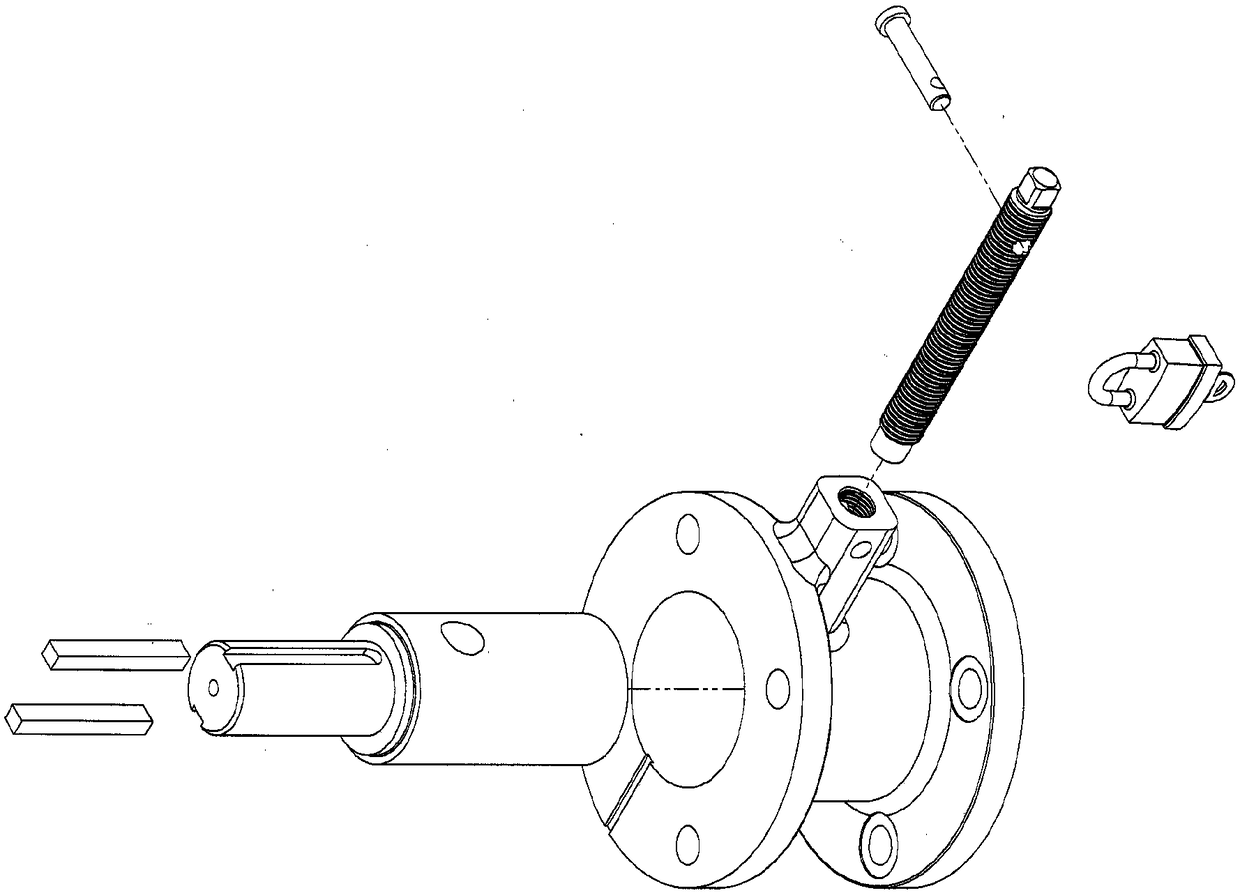
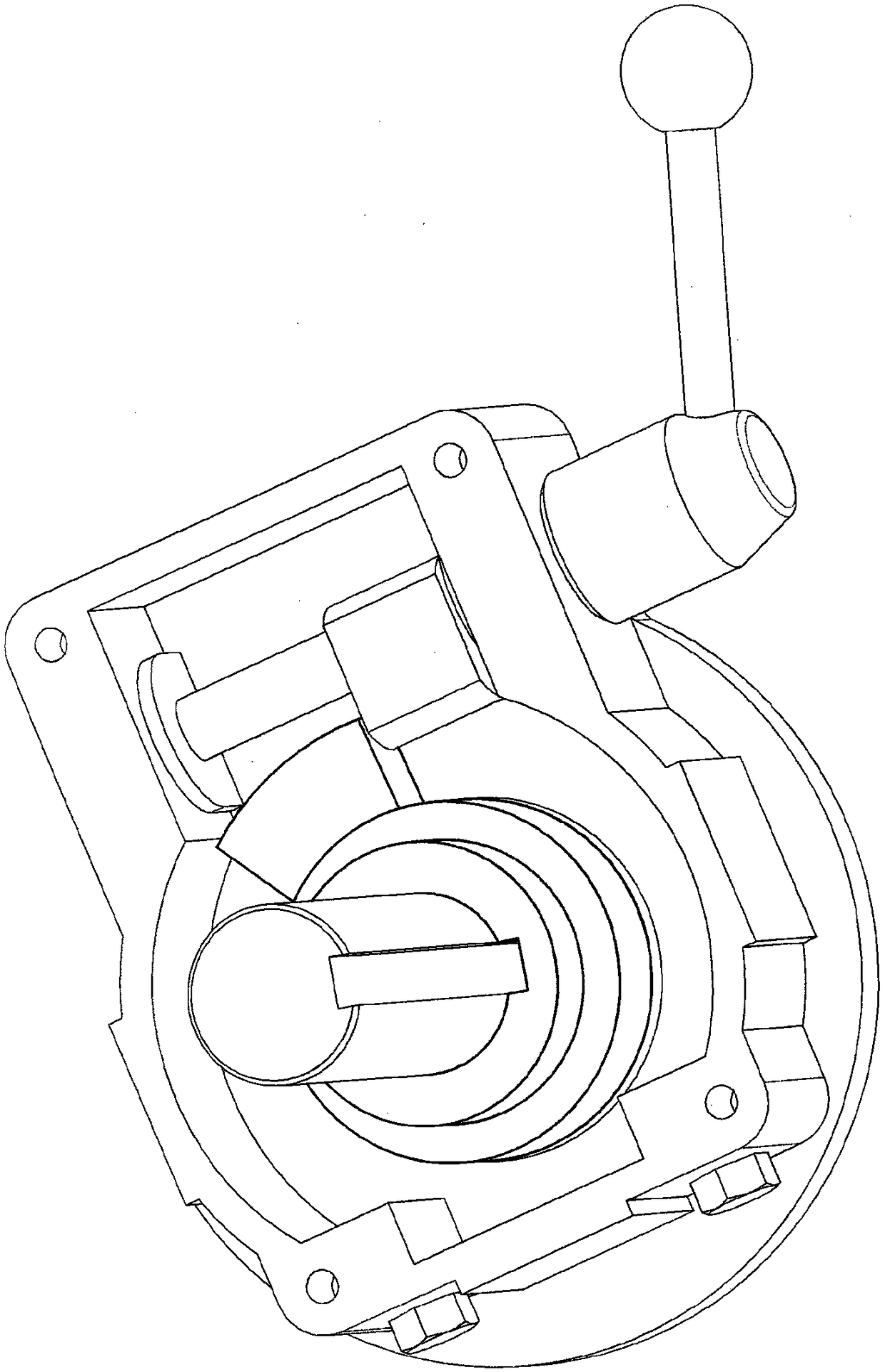
Combination device for lockout and partial stroke test of valve actuators
ActiveCN108138986AAvoid unauthorized operationsFluid-pressure actuator testingOperating means/releasing devices for valvesLinear motionValve actuator
A combination device (102) configured to effect lockout and partial stroke testing for an actuator having a piston rod (104) providing linear motion and connected to a guide block (108) in an actuator, wherein the combination device includes a device housing (102a) having a housing bore, wherein the device housing is adapted to mount on a receptacle on the actuator that aligns a device housing bore coaxially to the translatory motion axis of the piston rod; an extension rod (109) adapted to be attached to the guide block connected to the piston rod; at least two slides or a profiled bore indexsleeve (106) disposed in the device housing that when engaged provide means of restraining the movement of the extension rod in a manner that prevents said extension rod from moving and, in use, a driver element of the actuator from rotating relative to an actuator housing; a housing cover mounted over the device housing wherein the housing cover protects and retains the extension rod, and the slides or the index sleeve in the device housing and a spring biased safety pin mounted on the housing cover wherein the spring biased safety pin is configured to prevent unintended actuation of the actuator; and a tubular cover to protect the extension rod.
Owner:BRAY INT INC
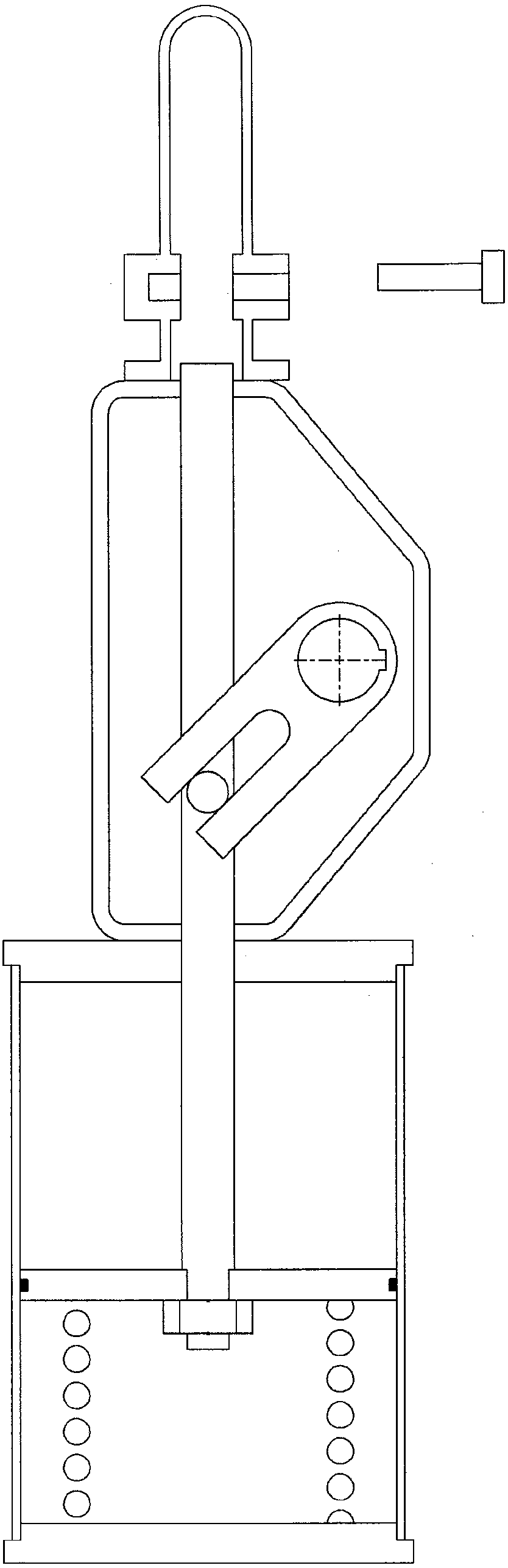
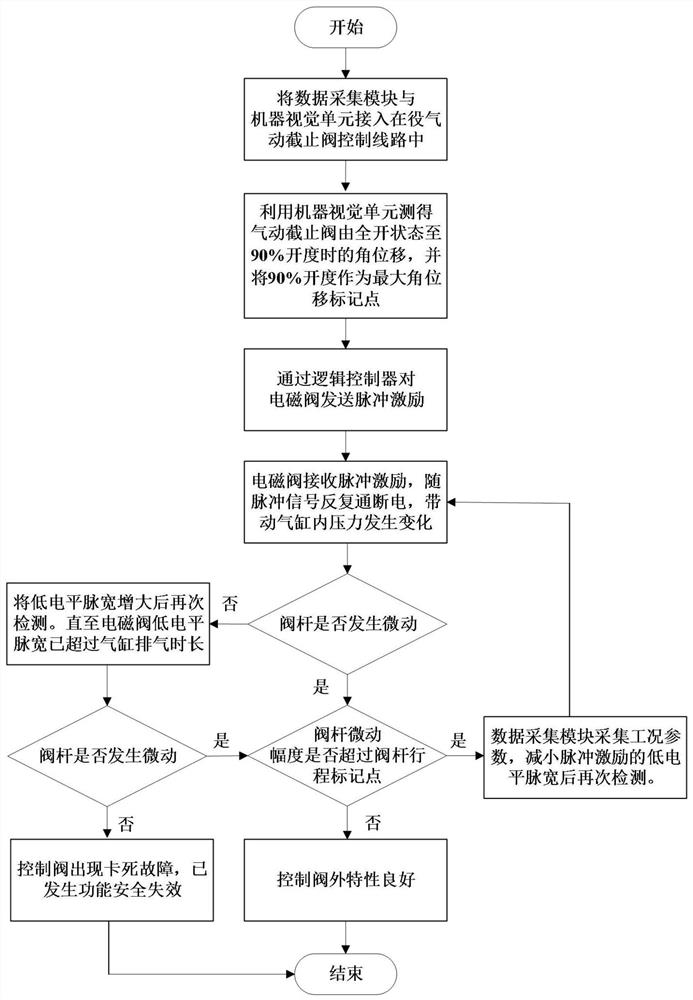
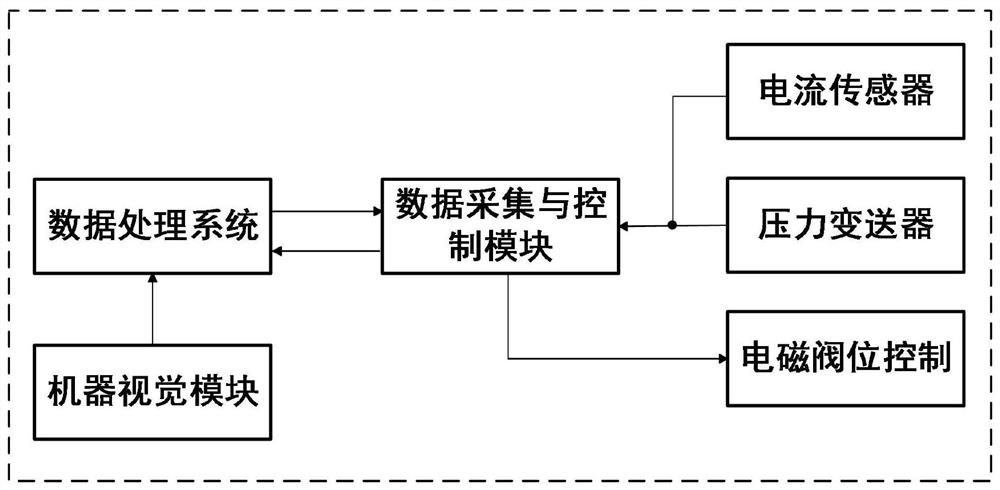
Online detection method for external characteristics of in-service pneumatic stop valve based on pulse excitation
PendingCN113466585AThe impact of low productionJudging that the external characteristics of the control valve are goodElectrical testingSafety instrumented systemControl system
The invention discloses an online detection method for external characteristics of an in-service pneumatic stop valve based on pulse excitation, and belongs to the field of functional safety detection and evaluation. According to the invention, an external characteristic detection method based on pulse excitation is used for carrying out external characteristic online detection on the in-service pneumatic stop valve, a control system sends current pulse excitation to an electromagnetic valve of the pneumatic stop valve so as to enable the electromagnetic valve to be repeatedly powered on and powered off, a valve rod of an executing mechanism is driven to repeatedly rotate by a small amplitude, the rotation angle of the valve is regulated and controlled by adjusting the duration time of the low-level pulse width within the allowable range of equipment, the output characteristic of the maximum angular displacement is detected, and online detection of the external characteristics of the in-service pneumatic stop valve is achieved. The problem of external characteristic online detection of the in-service pneumatic stop valve without a partial stroke test function is solved, the situation that normal production is affected by too large rotation amplitude of the valve rod in the detection process is avoided, and a basis is provided for evaluating the functional safety integrity of the pneumatic stop valve of a safety instrument system in a safety life cycle.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Pressure control for partial stroke testing
A method for testing a valve to control the device for coupling to control the device includes the following steps: using the process to control the pressure in the device control valve from the initial pressure to the pre -determined pressure limit;The location of the device to detect the itinerary of the valve caused by the driver; and once the pressure in the valve reaches the pre -determined pressure limit or detects one of the strokes of the valve,Back to the initial pressure.
Owner:FISHER CONTROLS INT LLC
Partial stroke tests for shutdown valves
ActiveUS10480681B2Accurately determinedMinimal amountFluid-pressure actuator safetyMachine part testingEngineeringPartial stroke testing
To generate a setpoint signal to stroke a valve during a partial-stroke test, a first target is determined for the setpoint signal based at least on a travel displacement threshold, the travel displacement threshold corresponding to a desired extent of travel of the valve during the partial-stroke test; the setpoint signal is ramped from an initial value to the first target, during a first time interval; subsequently to the first time interval, the setpoint signal is maintained at the first target during a second time interval; a second target is determined for the setpoint signal based at least on the initial value; and during a third time interval subsequent to the second interval, the setpoint signal is ramped from the first target to the second target in a direction opposite to the ramping of the setpoint signal during the first time interval.
Owner:FISHER CONTROLS INT LLC
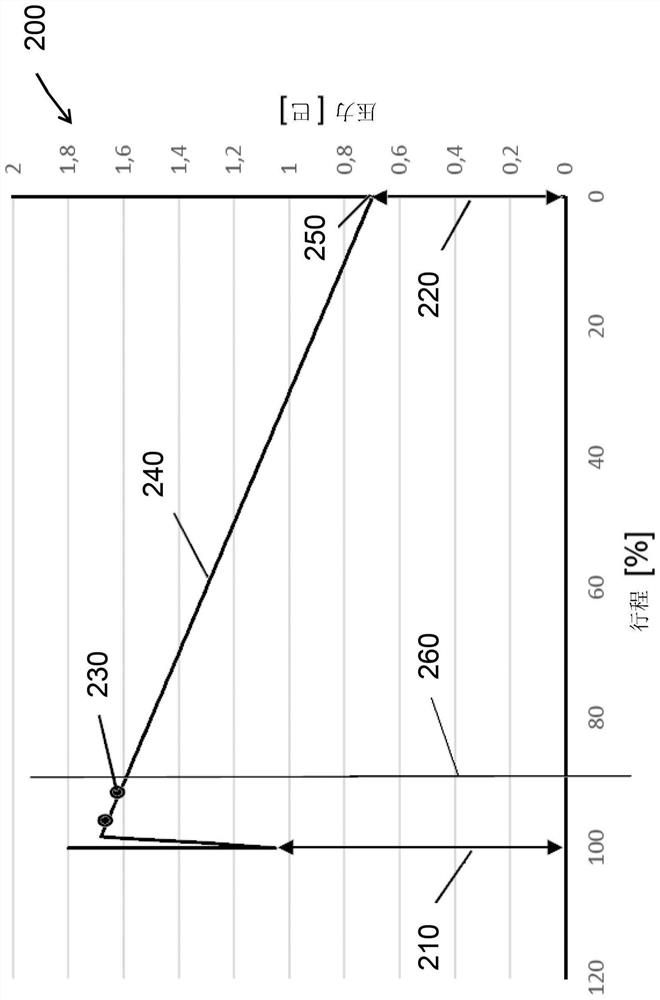
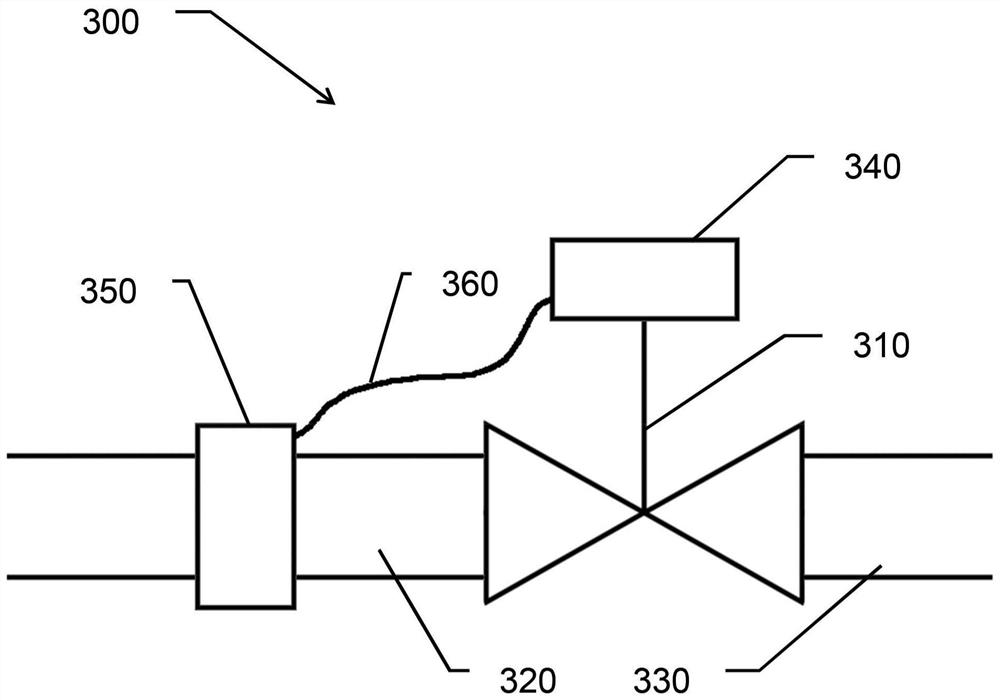
Method for verifying the operability of a safety valve
A method for verifying the operation of a safety valve(310) having a valve member and a positioner(340) for controlling the position of the valve member is proposed. The safety valve (310) is part of a plant on which a process with a process medium runs. The plant has a sensor (350)for monitoring the state of the plant, the procdess and the process medium. A sensor(350)'s measured value is used to determine a point in time during ongoing plant operation at which the operability of the valve (310) can be verified in the context of a partial stroke test. The test can also be monitored with the sensor(350) and the stroke range traversed therein can be dynamically adapted to the state. The test can thus be performed safely during operation and with an optimized stroke range. The method enables more frequent testing of and more reliable statements about the operability of the safety valve(310).
Owner:SAMSON AG
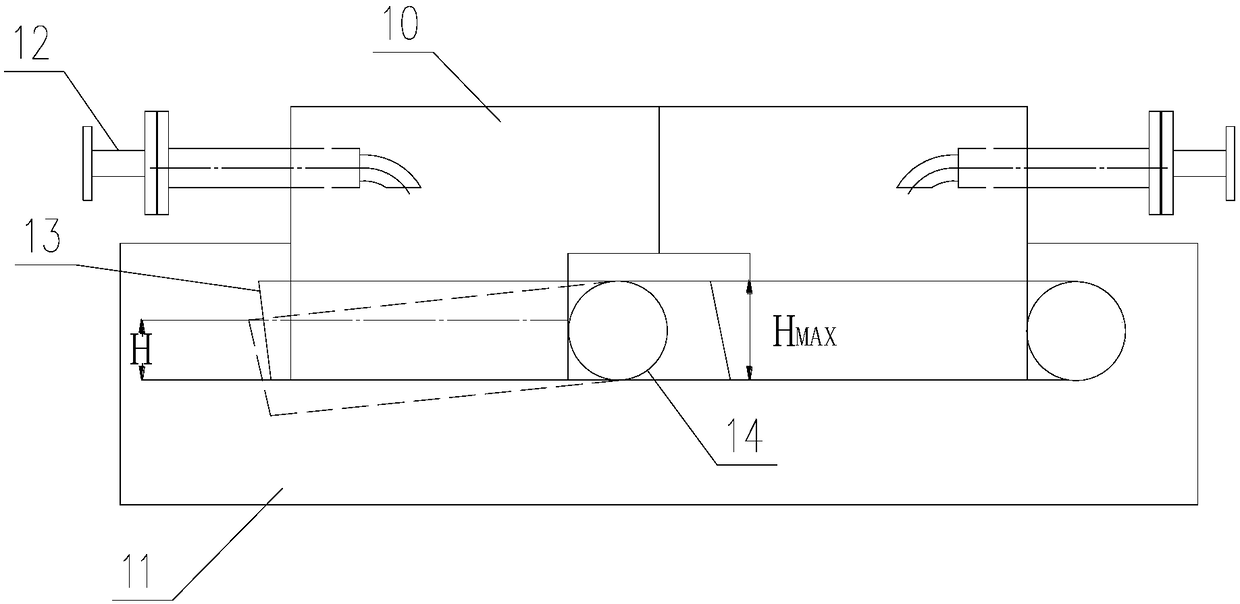
Partial stroke testing method for gas safety diffuse water seal valve for coke oven gas collector
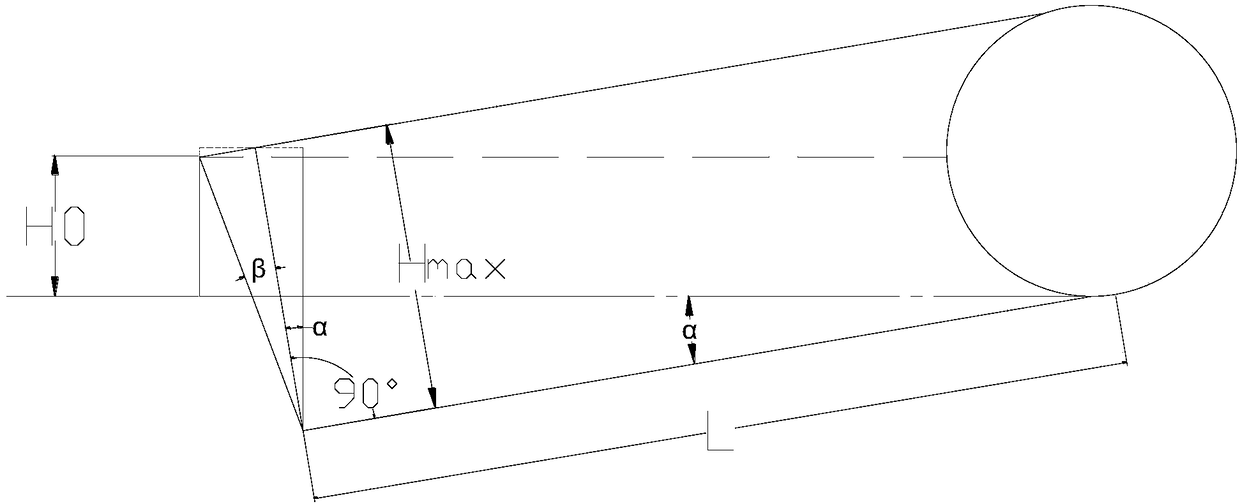
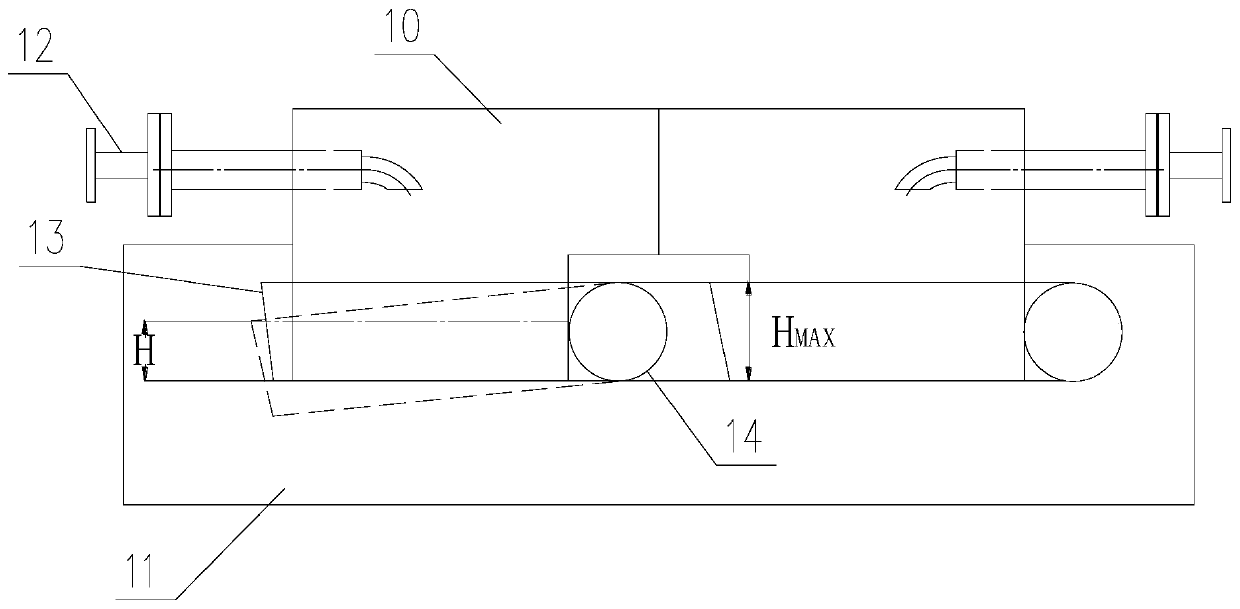
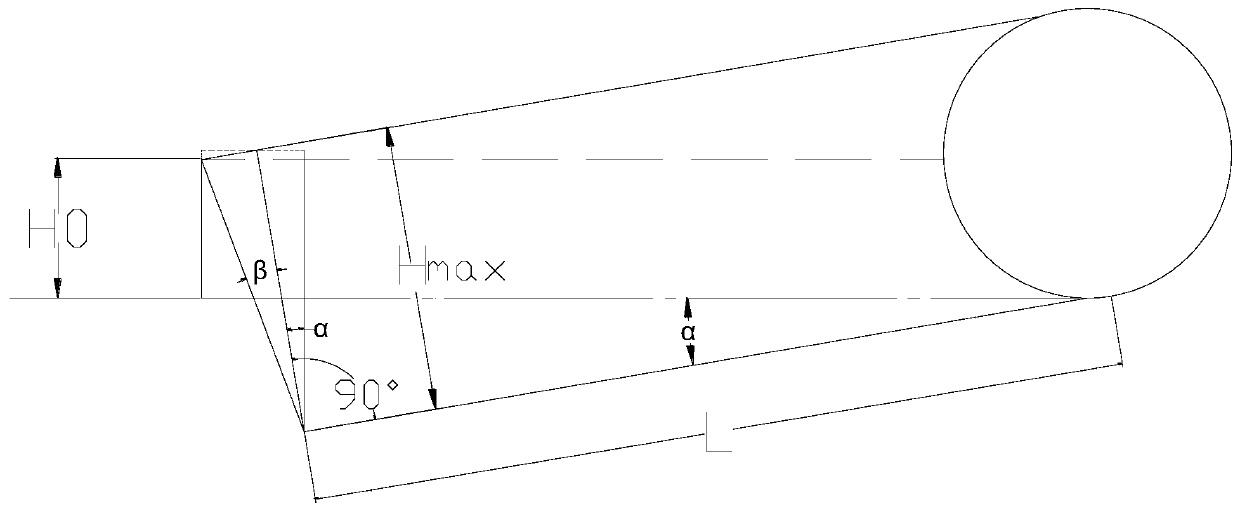
The invention provides a partial stroke testing method for a gas safety diffuse water seal valve for a coke oven gas collector. The partial stroke testing method comprises the following steps: arranging a plurality of pressure sensors in the coke oven gas collector and calculating maximal pressure P' according to a plurality of pressure measuring points P_1, P_2 until P_N; calculating the minimumwater seal liquid level height H0 at the position of no gas leakage according to maximum pressure P'; calculating a maximum rotation angle alpha in the stroke test according to the minimum water sealliquid level height H0, the actual length L of a valve plate, a dip angle beta of a baffle and normal water seal height Hmax. According to the partial stroke testing method disclosed by the invention,stroke test of the diffuse water seal valve can be performed at fixed period, and the phenomena of corrosion or blockage caused by long-time inaction of the valve can be prevented; when the pressureof the gas collector pressure is overhigh, the diffuse valve can be opened in time; in the stroke testing process of the valve, the opening degree of the valve is increased as much as possible while no gas breaks through a water seal cover and the testing adequacy is ensured.
Owner:ACRE COKING & REFRACTORY ENG CONSULTING CORP DALIAN MCC
Testing of safety devices
ActiveUS10302221B2Avoid excessive movementFluid-pressure actuator safetyFluid-pressure actuator testingValve actuatorSecure state
Owner:IMTEX CONTROLS
Safety instrumented system and pst startup method
InactiveCN103901872BStart inhibitAvoid bad influenceProgramme controlValve arrangementsSafety instrumented systemProcess equipment
The safety instrumented system of the present invention and the PST start method may inhibit the adverse effects on the process equipment caused by unnecessary PST start. Safety instrumented system having: a positioner that controls the opening of the emergency shut-off valve set on the pipe of the process equipment (2); Upper system (3) that manages the PST (Partial Stroke Test) of the emergency shut-off valve. Positioner (2) having: PST execution department (22), which performs the PST of the emergency shut-off valve according to the start instructions from the upper level system or from the operation panel of the scene where the positioner (2) is provided; A timer that measures the time elapsed since the completion of the PST of the emergency shut-off valve (20); And the PST start inhibit judgment section (21), which receives the start instruction from the PST of the host system or the operation panel, the time elapsed since the last PST and the predetermined minimum period of PST are compared to determine whether PST can be started.
Owner:YAMATAKE HONEYWELL CO LTD
A Partial Stroke Test Method of Coke Oven Collecting Pipe Gas Safety Release Water Seal Valve
The invention provides a partial stroke testing method for a gas safety diffuse water seal valve for a coke oven gas collector. The partial stroke testing method comprises the following steps: arranging a plurality of pressure sensors in the coke oven gas collector and calculating maximal pressure P' according to a plurality of pressure measuring points P_1, P_2 until P_N; calculating the minimumwater seal liquid level height H0 at the position of no gas leakage according to maximum pressure P'; calculating a maximum rotation angle alpha in the stroke test according to the minimum water sealliquid level height H0, the actual length L of a valve plate, a dip angle beta of a baffle and normal water seal height Hmax. According to the partial stroke testing method disclosed by the invention,stroke test of the diffuse water seal valve can be performed at fixed period, and the phenomena of corrosion or blockage caused by long-time inaction of the valve can be prevented; when the pressureof the gas collector pressure is overhigh, the diffuse valve can be opened in time; in the stroke testing process of the valve, the opening degree of the valve is increased as much as possible while no gas breaks through a water seal cover and the testing adequacy is ensured.
Owner:ACRE COKING & REFRACTORY ENG CONSULTING CORP DALIAN MCC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com