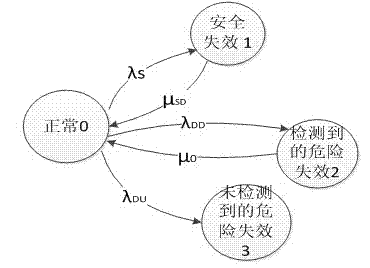
Patents
Literature
94 results about "Safety instrumented system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
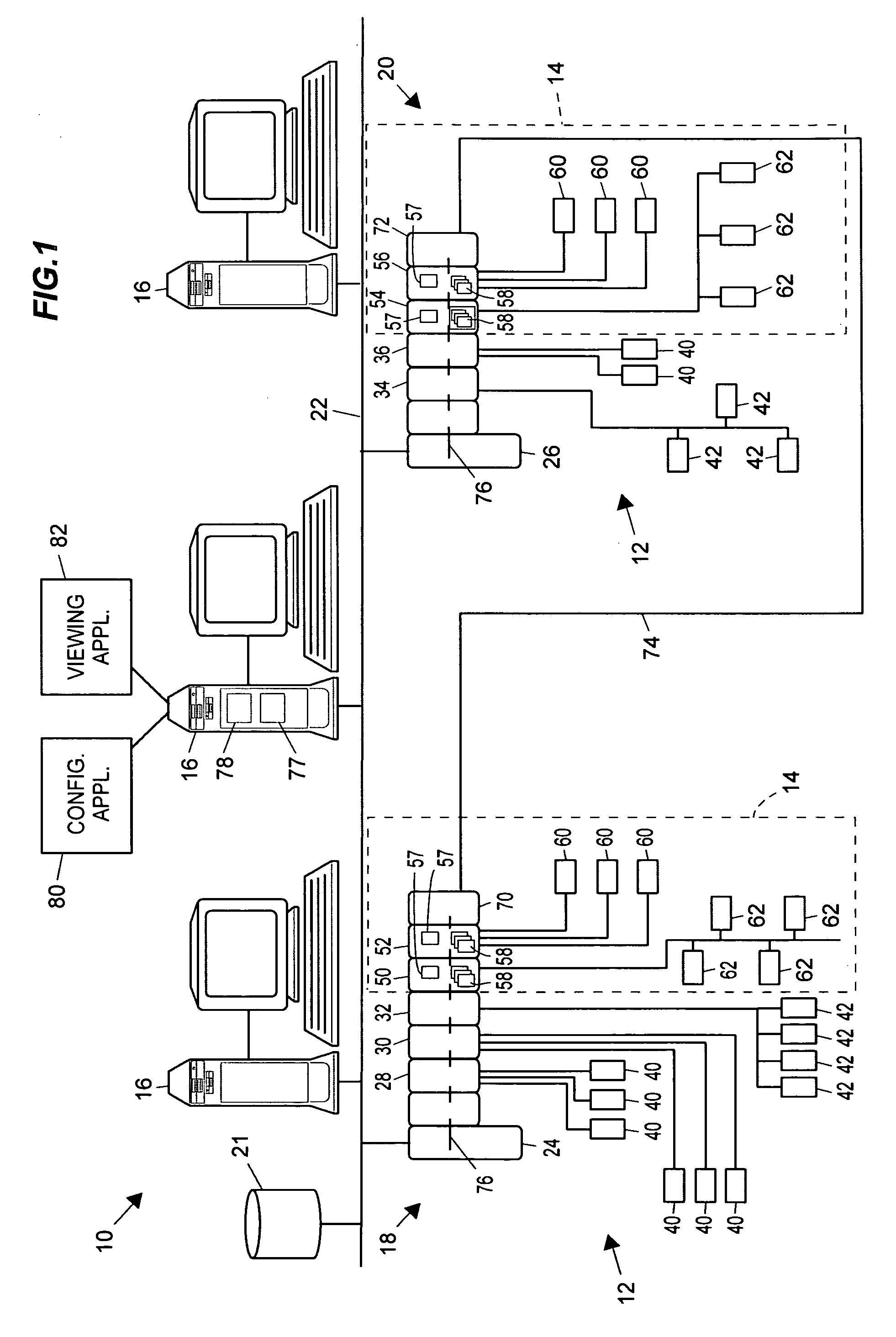
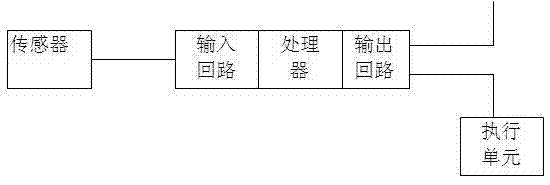
A safety instrumented system (SIS) consists of an engineered set of hardware and software controls which are especially used on critical process systems.
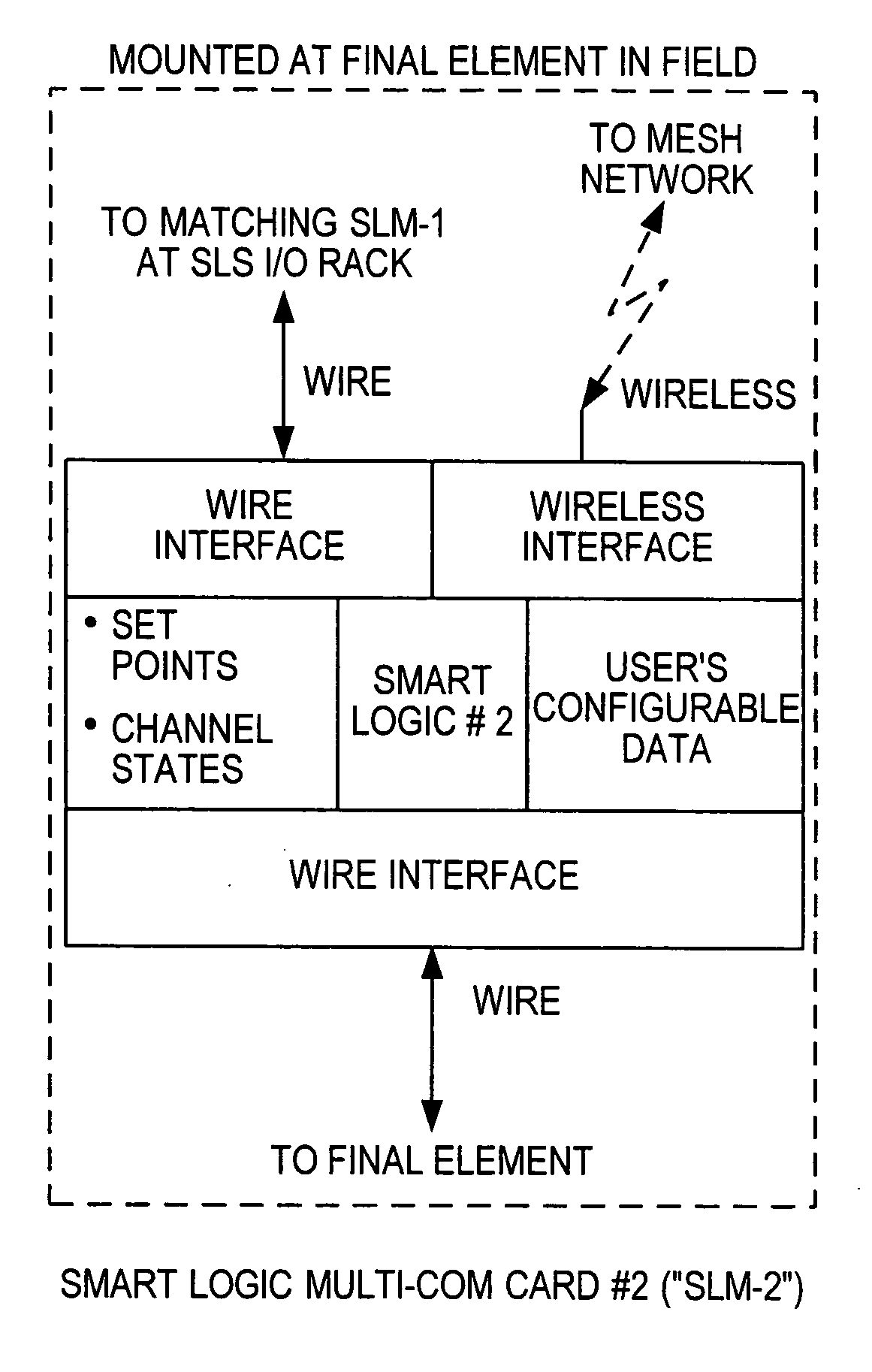
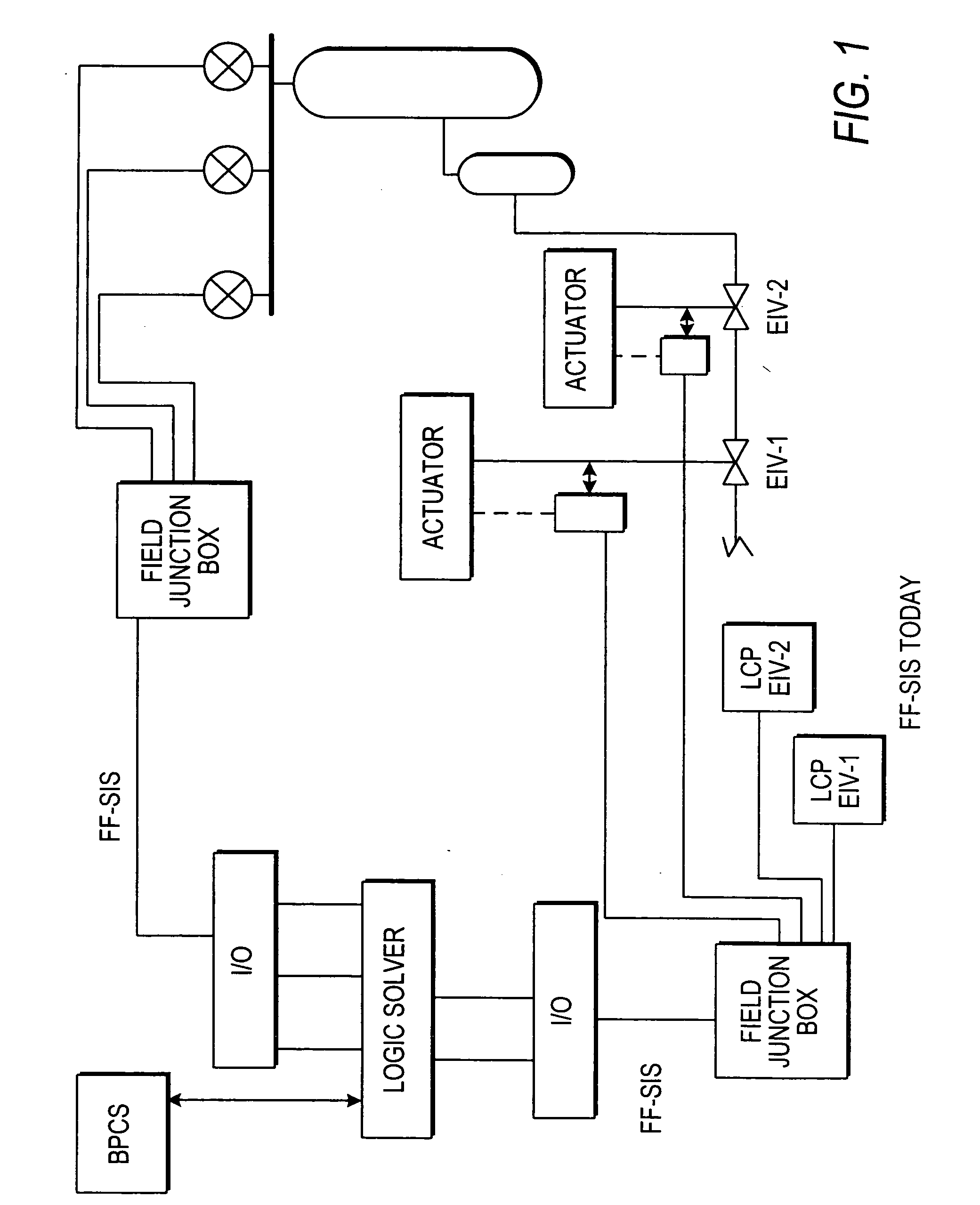
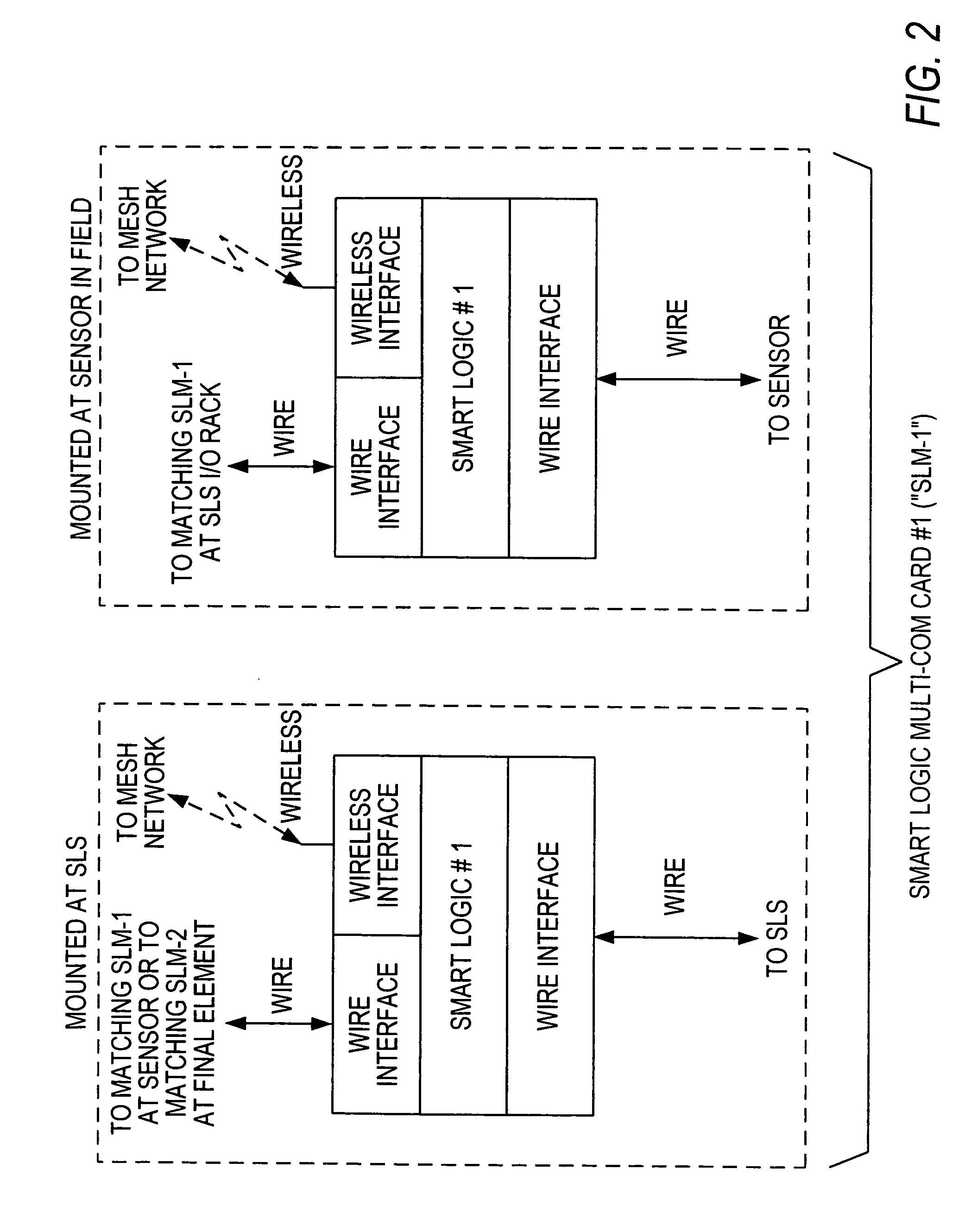
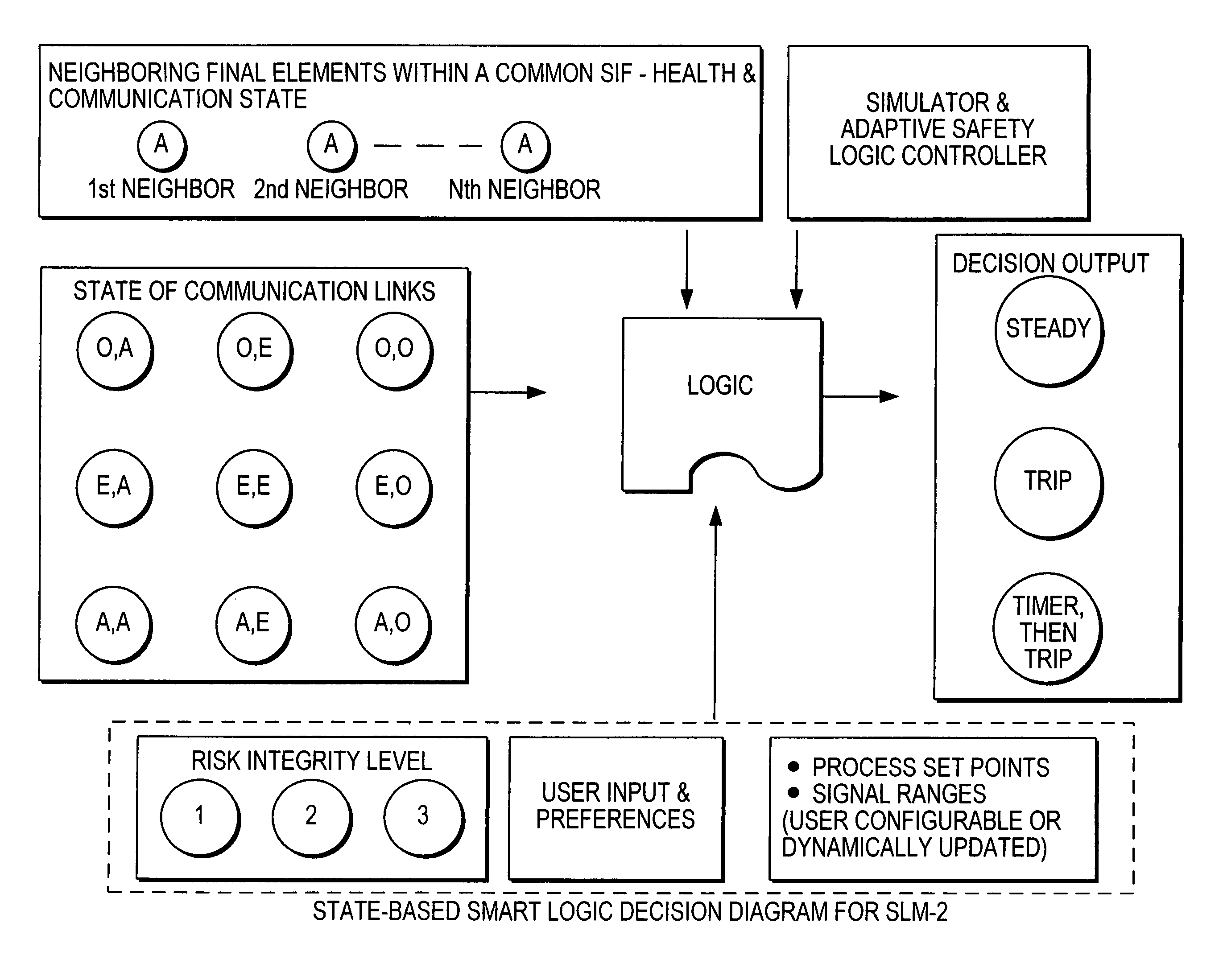
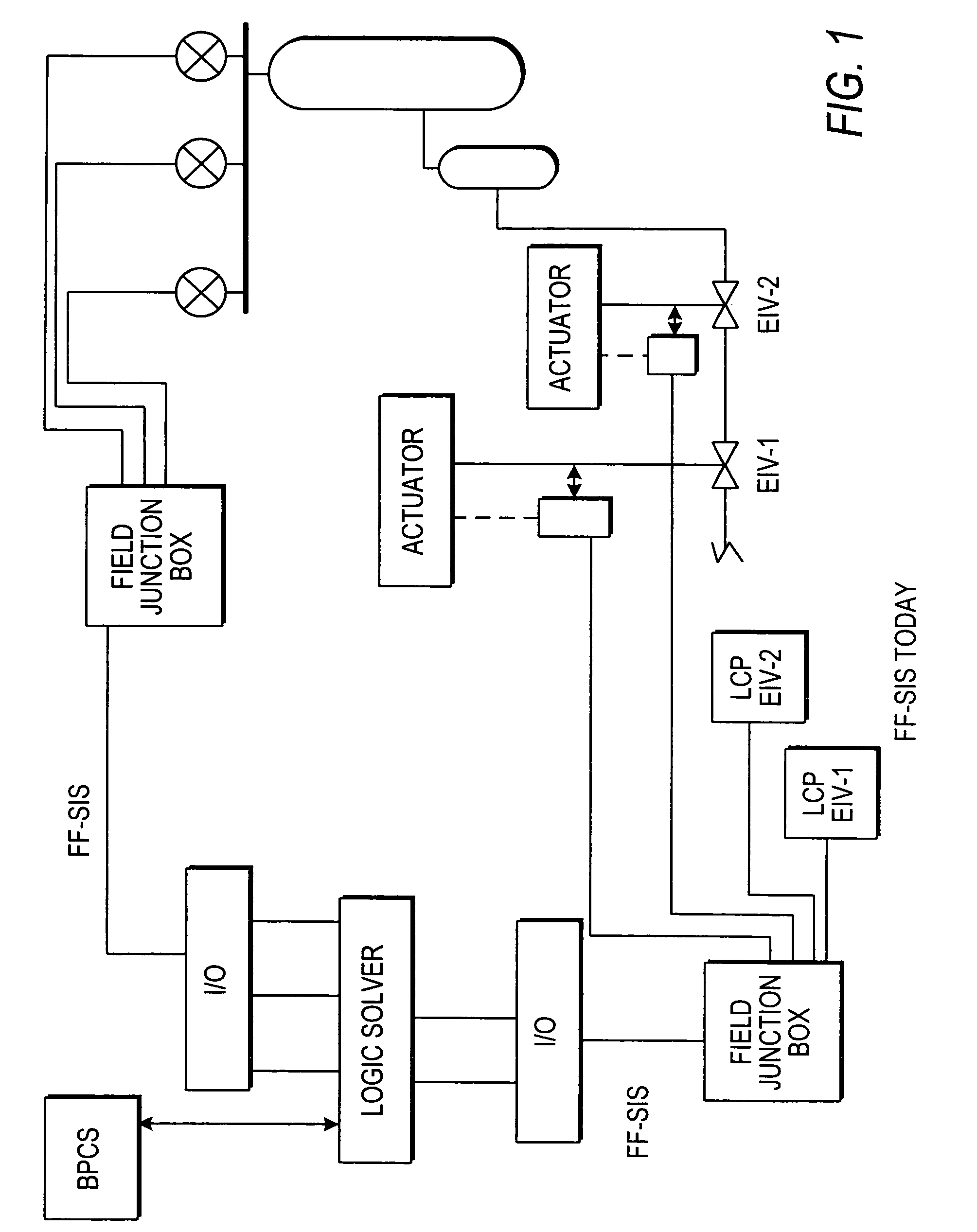
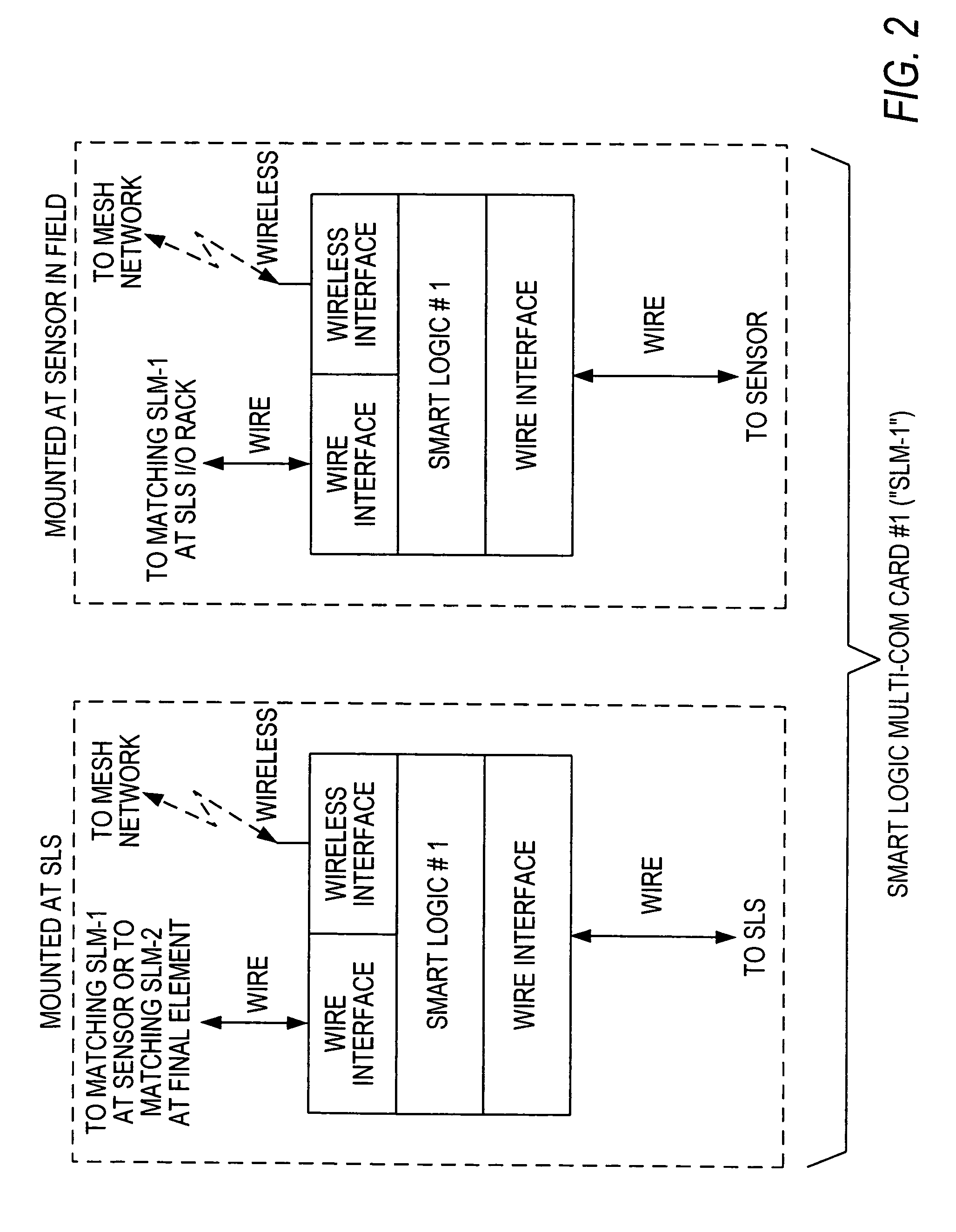
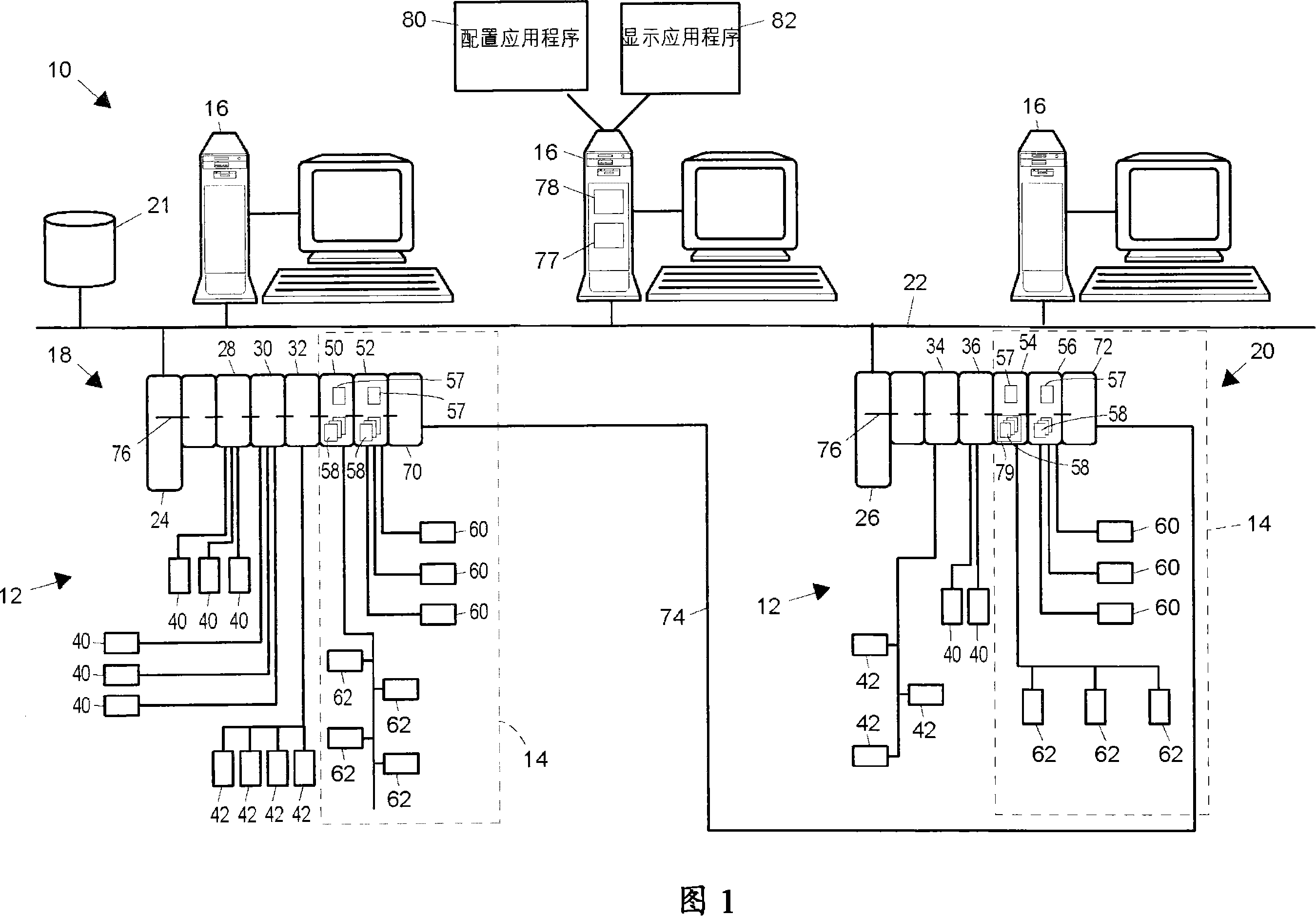
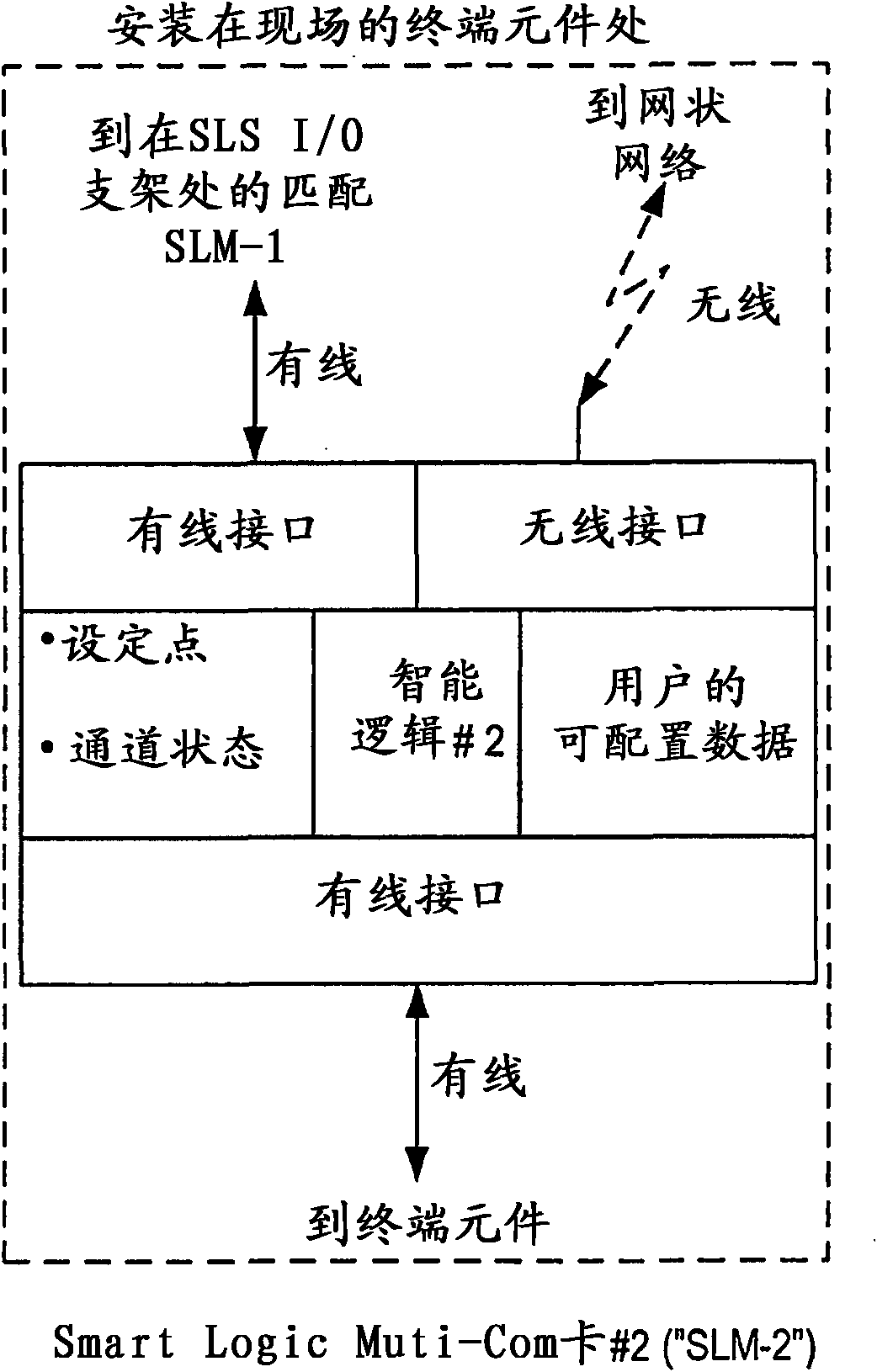
Distributed and adaptive smart logic with multi-communication apparatus for reliable safety system shutdown
InactiveUS20100004761A1Increase decision reliabilityGood flexibilityVehicle testingBurglar alarmSafety instrumented systemEngineering
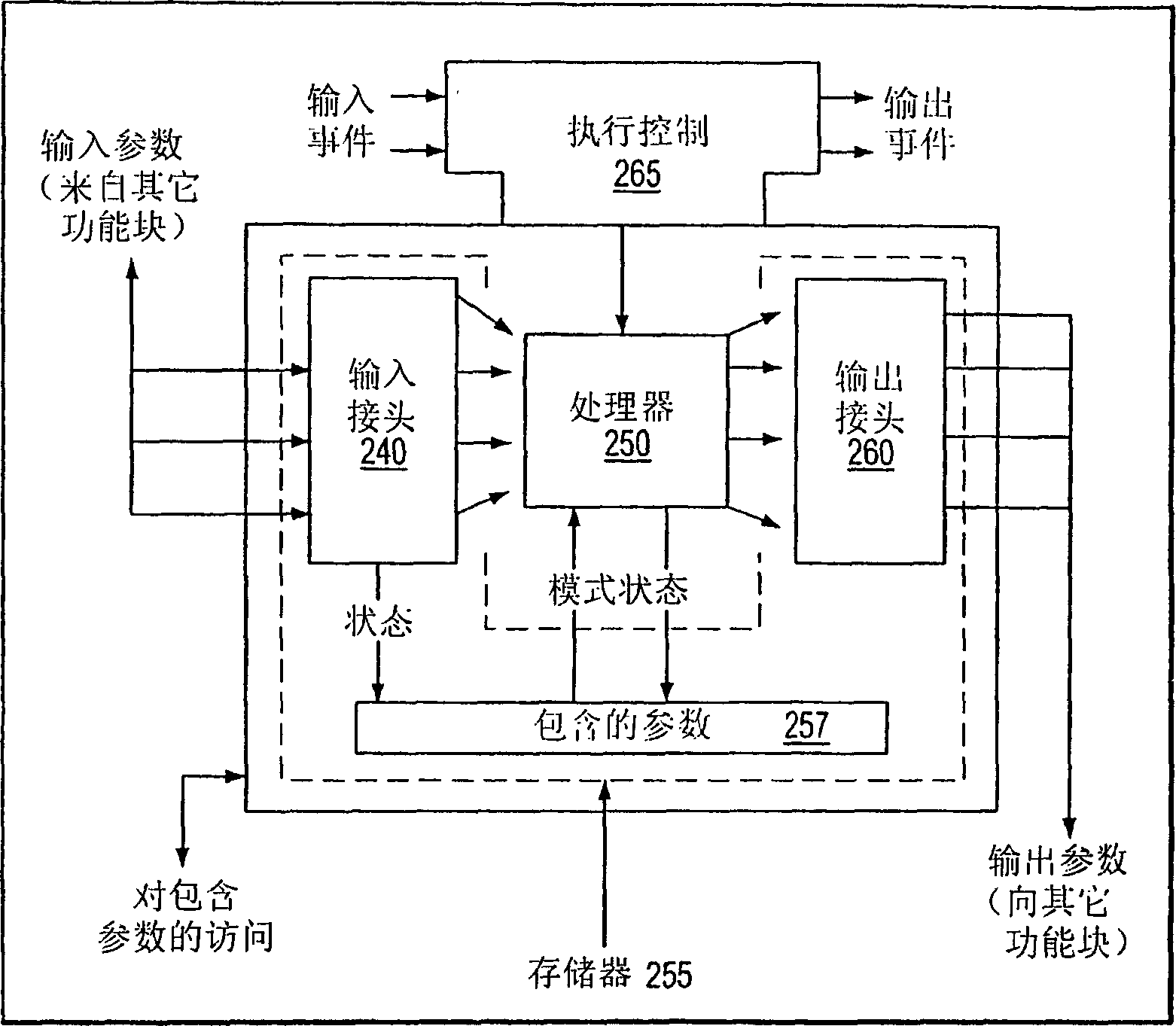
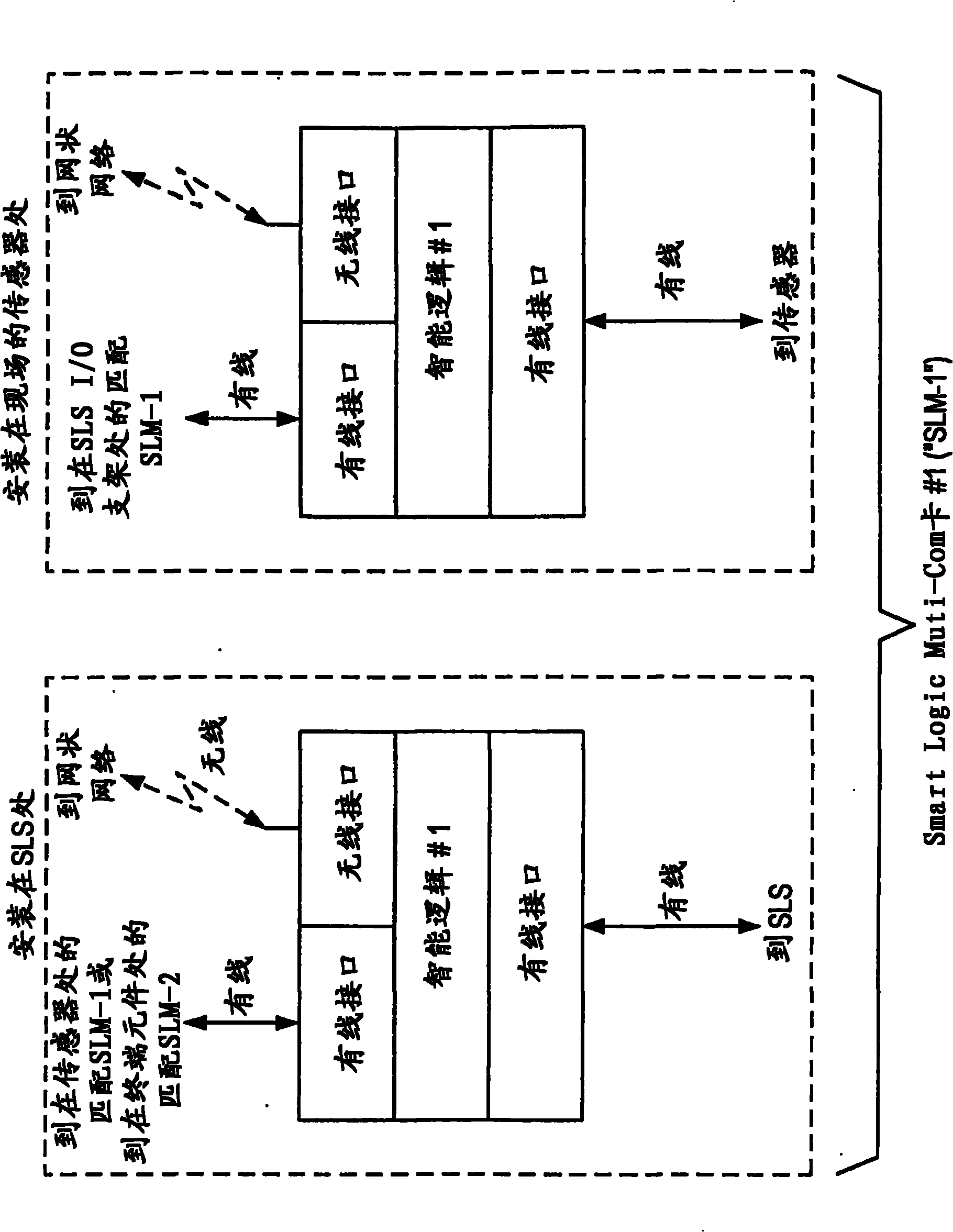
This invention relates to safety instrumented systems (“SIS”) for monitoring and controlling chemical and other industrial process field devices, and that are responsive to signals for the emergency shutdown of the process or system. The patent will significantly improve the reliability of communications within an emergency shutdown system, reduce unwanted trips, and adapt to process conditions by failing to a safe mode in dynamic conditions that are not considered by prior art logic solvers.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
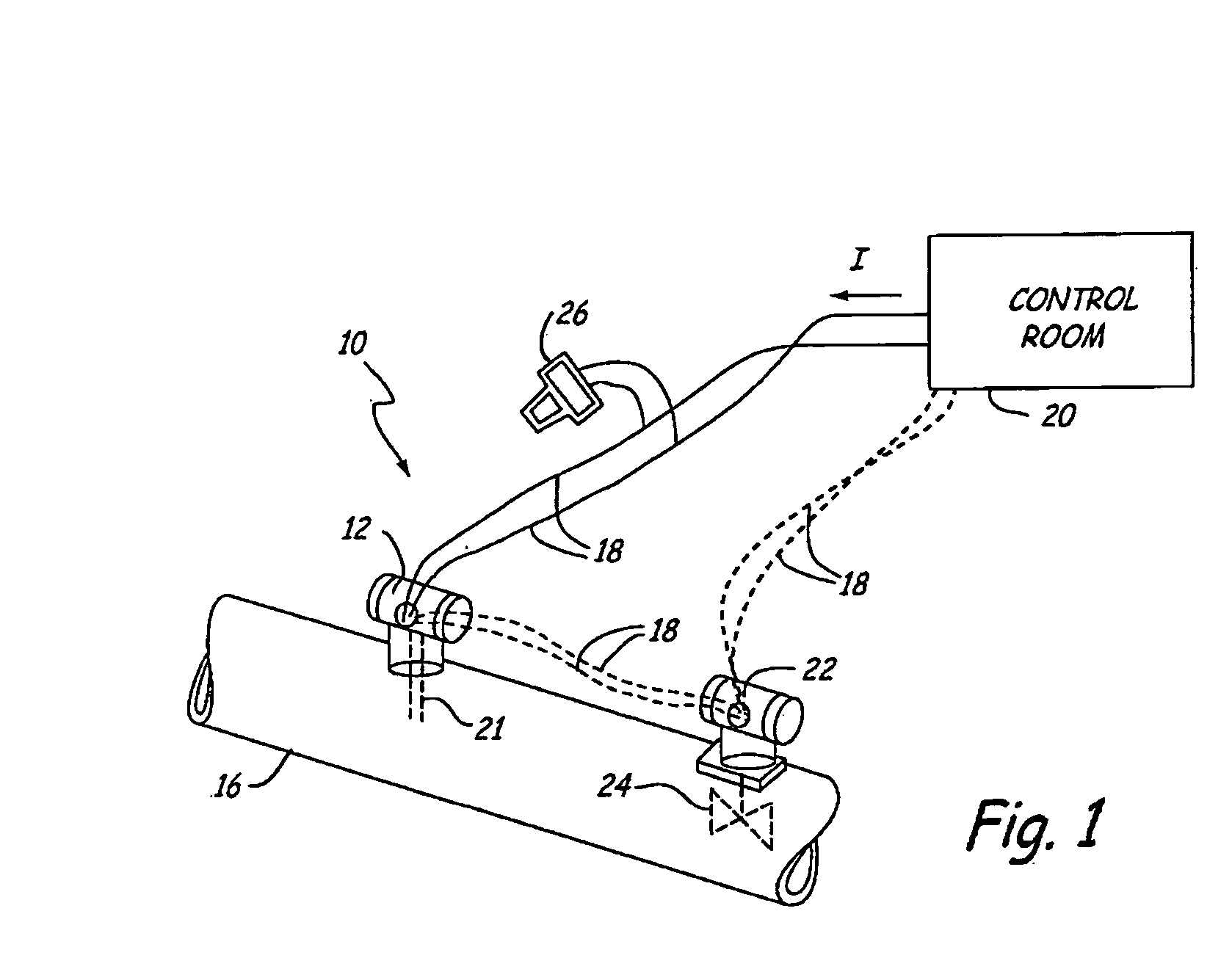
Process equipment validation
ActiveUS20050274417A1Vehicle testingElectric testing/monitoringControl flowSafety instrumented system
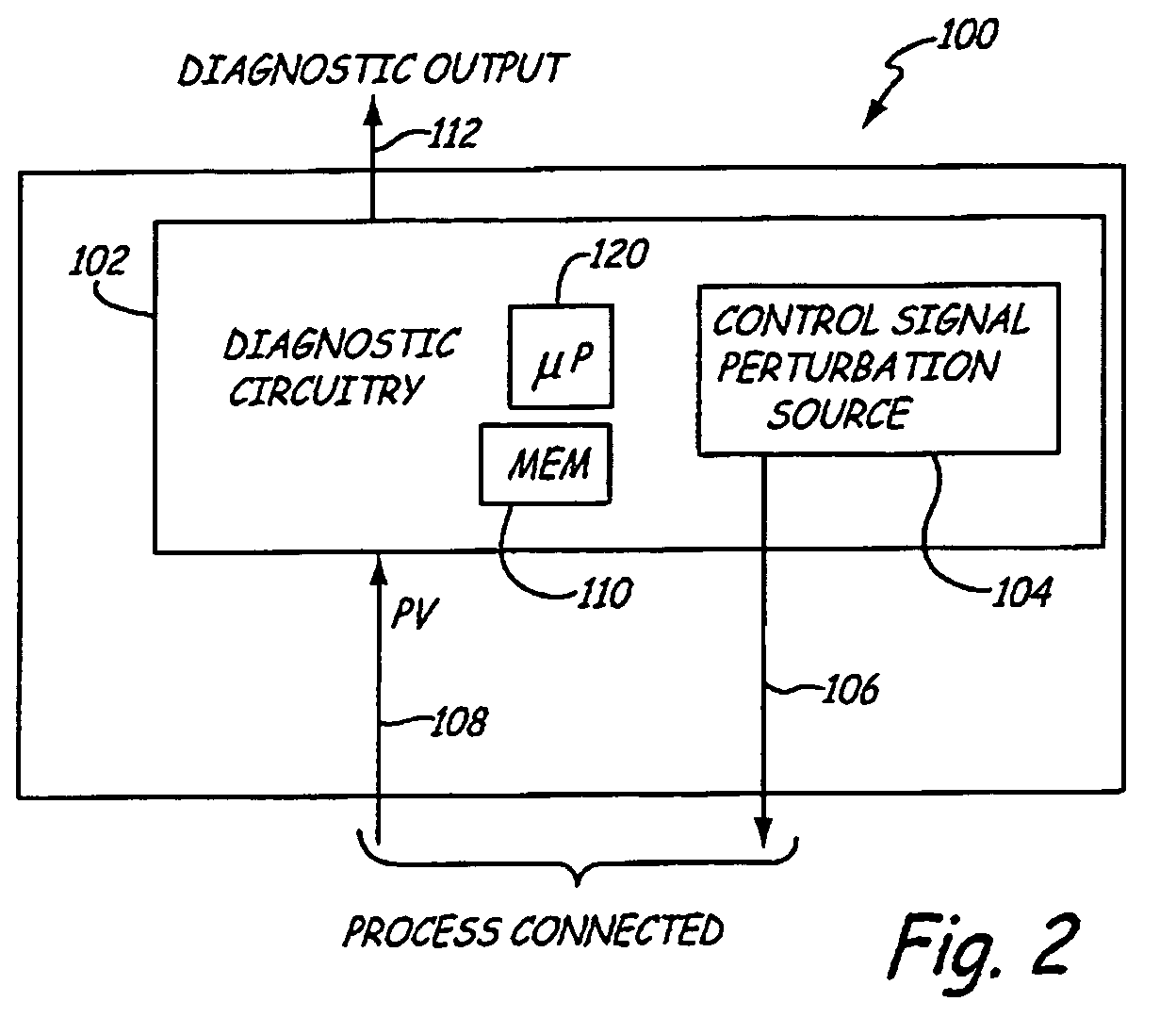
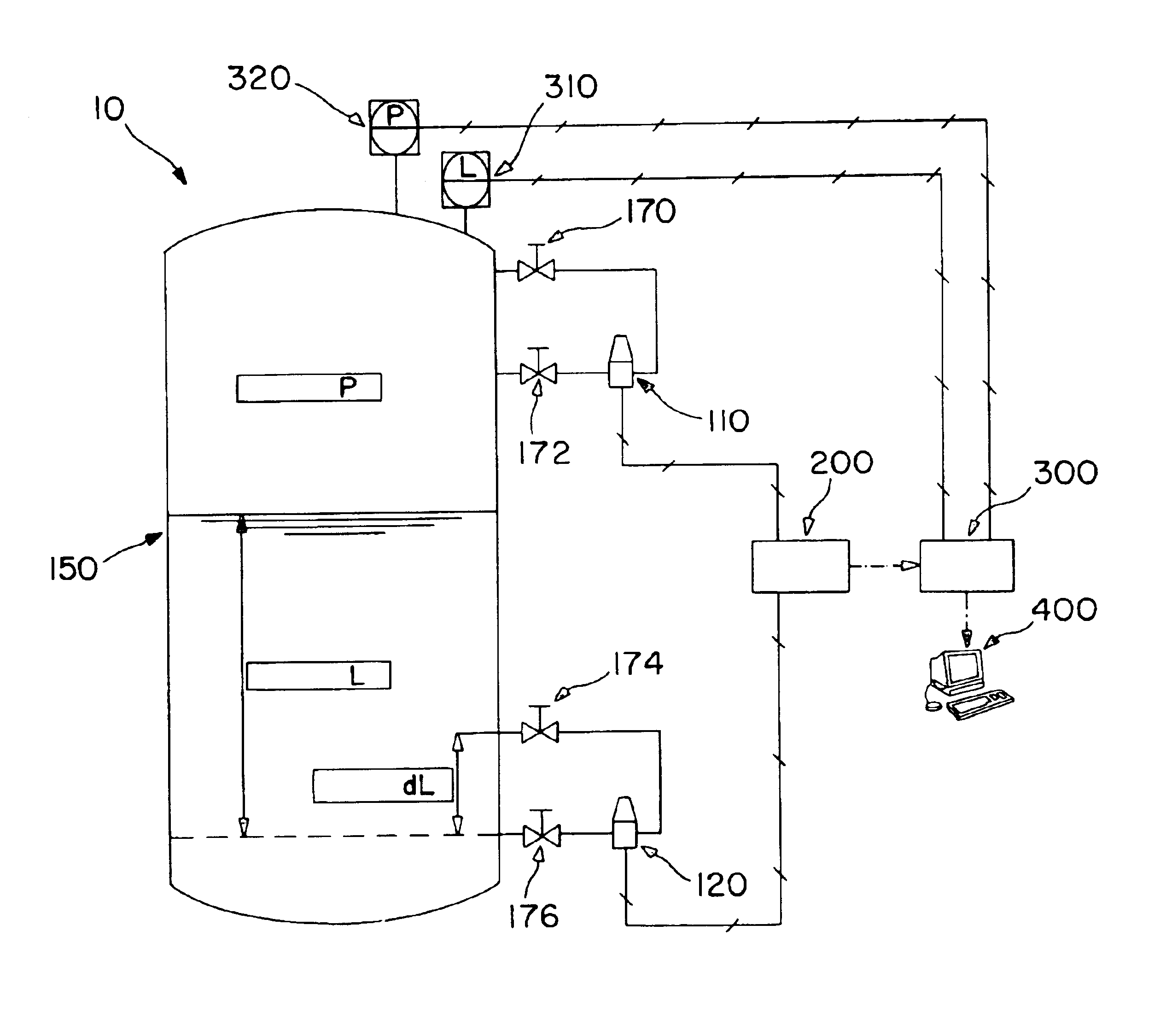
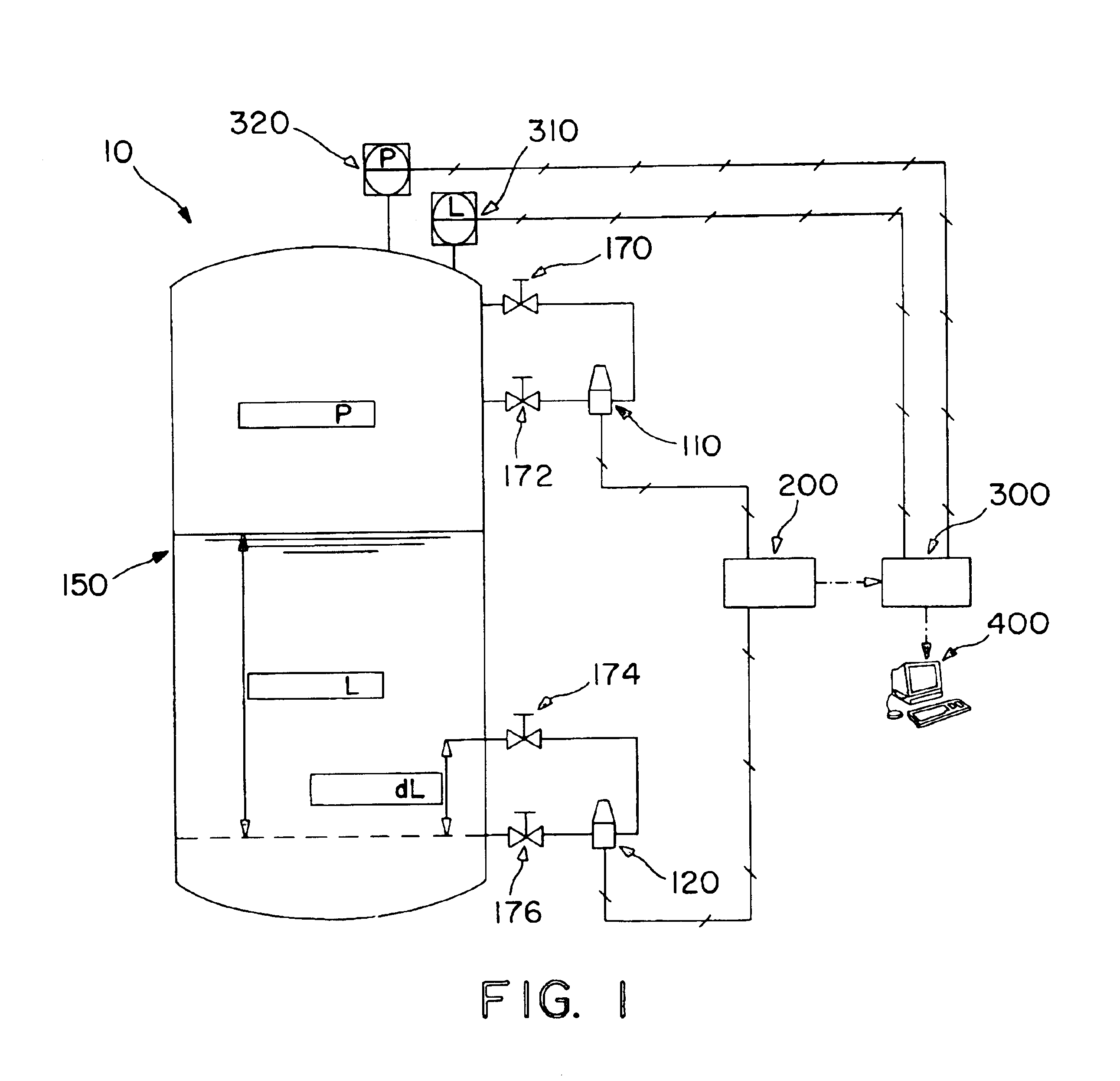
A Safety Instrumented System for use with a process control system receives pressure of process fluid in the process piping. A valve positioner positions a valve which controls flow of process fluid through the process piping. The valve positioner is caused to perform a partial stroke of the valve or otherwise introduce a perturbation into the process. A resulting change in sensed pressure due to the perturbation is used to diagnose operation of the process.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT INC
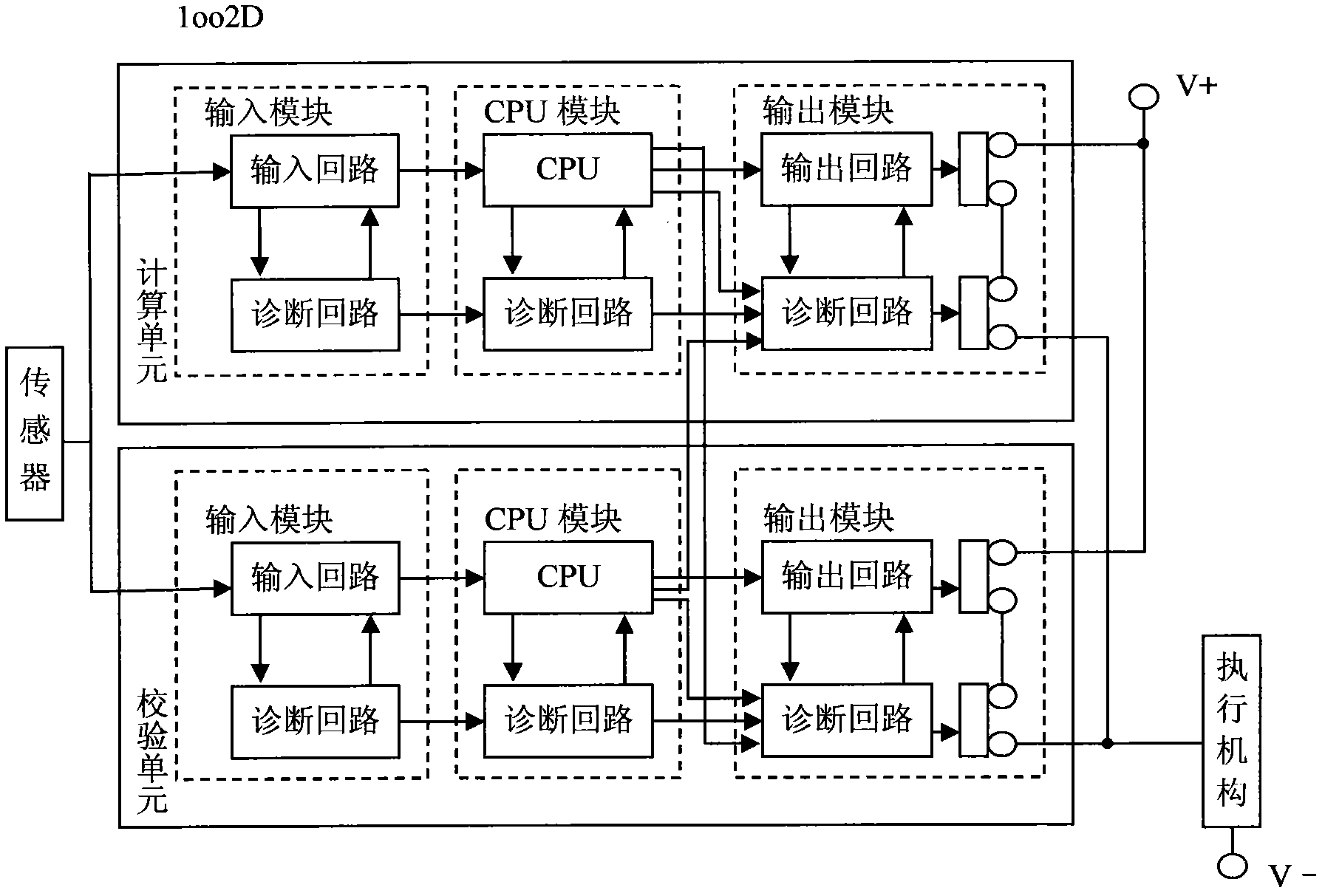
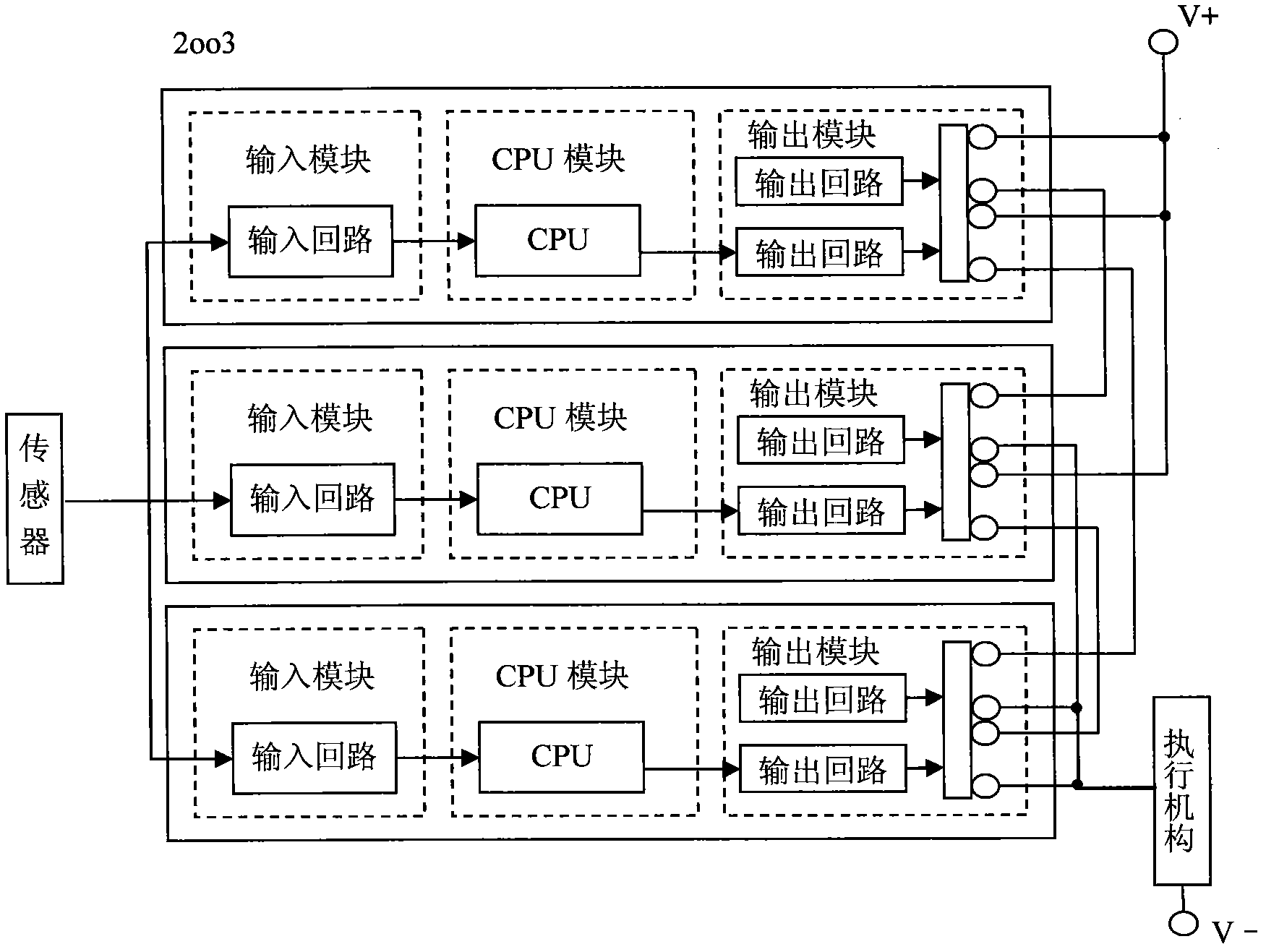
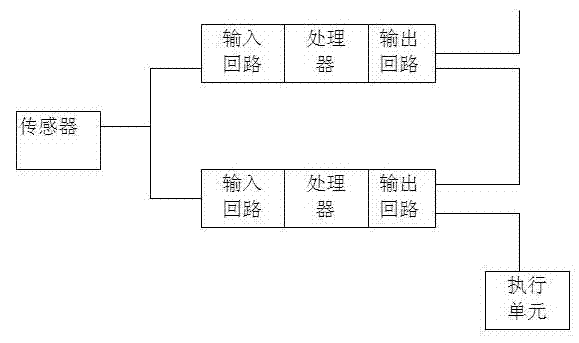
Redundant and fault-tolerant safety instrument control system based on fieldbus and ARM (advanced RISC machines)
InactiveCN102096401ATotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlSafety instrumented systemArea network
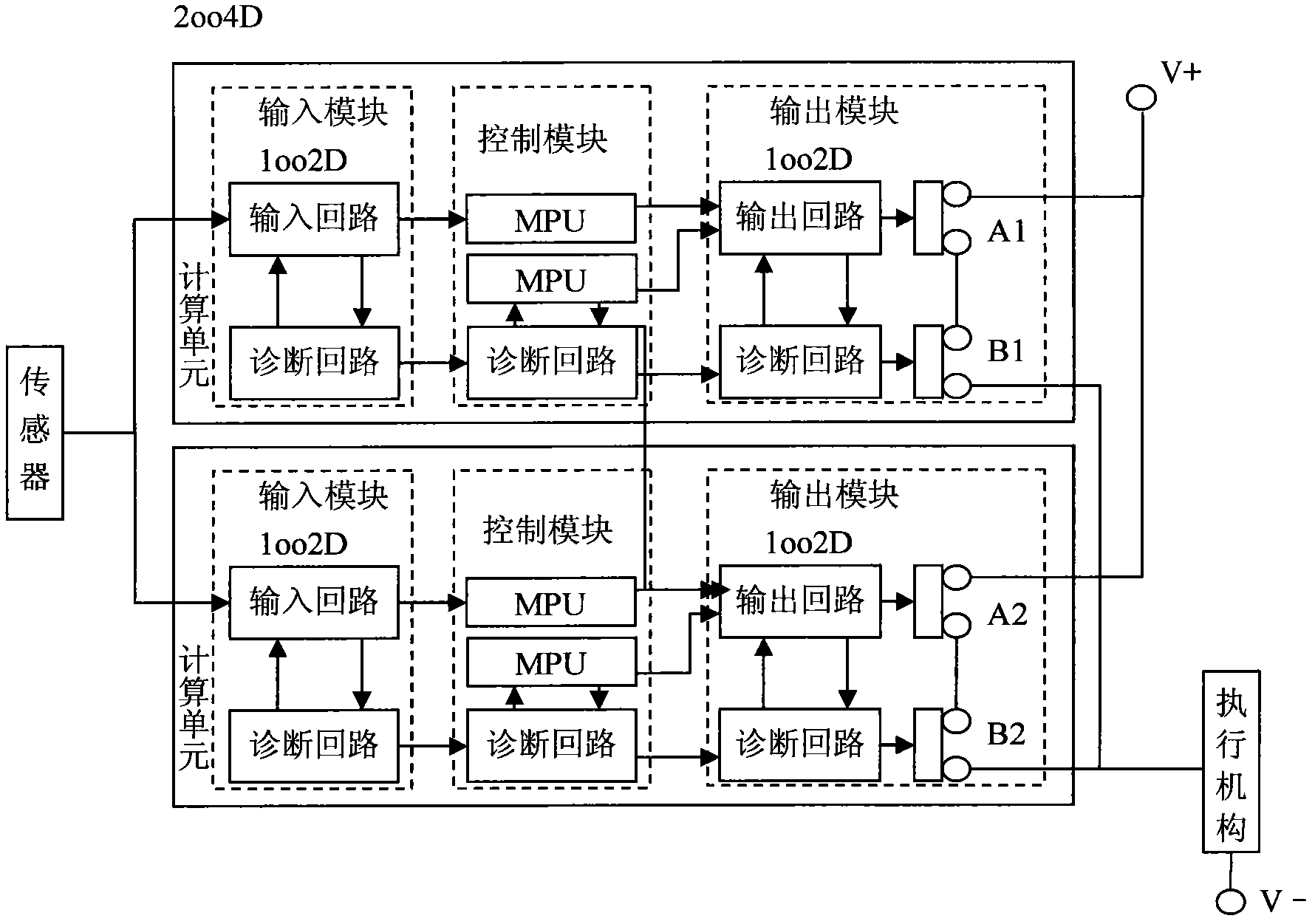
The invention provides a design and realization method of a redundant and fault-tolerant safety instrument control system based on a fieldbus and ARM (advanced RISC machines), comprising the following steps: by virtue of redundant and fault-tolerant configuration of a system power supply, input modules, a CPU (central processing unit) and output modules, four core processors communicate with respective and corresponding I / O (input / output) modules by a CAN (controller area network) bus so as to carry out field signal acquisition and control command output, and hardware 2oo4 redundant and fault-tolerant voting is carried out on the output signals of four channels on an output voting module, so that mis-stop of the system caused by single-channel hardware failure is avoided, the function safety level of the redundant and fault-tolerant safety instrument control system is ensured to reach SIL3 (safety integrity level 3), in-time and fast response and protection are carried out on dangerous states of protected field equipment, further a production device enters a predefined working condition of safe stopping, and the safety of staffs, equipment, production and the device is guaranteed.
Owner:北京昊图科技有限公司 +1
Coordination of field device operations with overrides and bypasses within a process control and safety system
InactiveUS7010450B2Avoid procedureOperation failureElectric testing/monitoringStructural/machines measurementSafety instrumented systemHand held
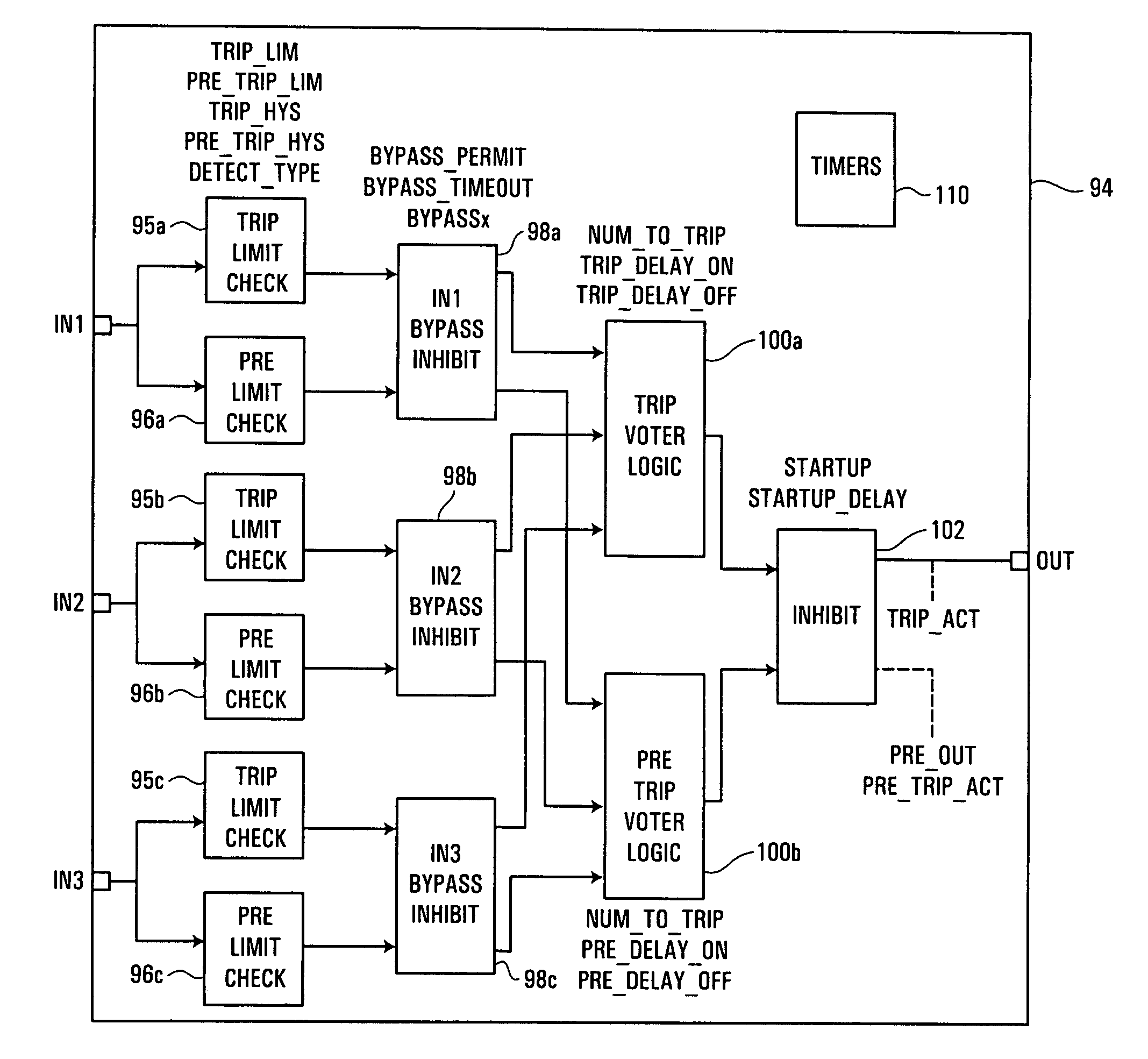
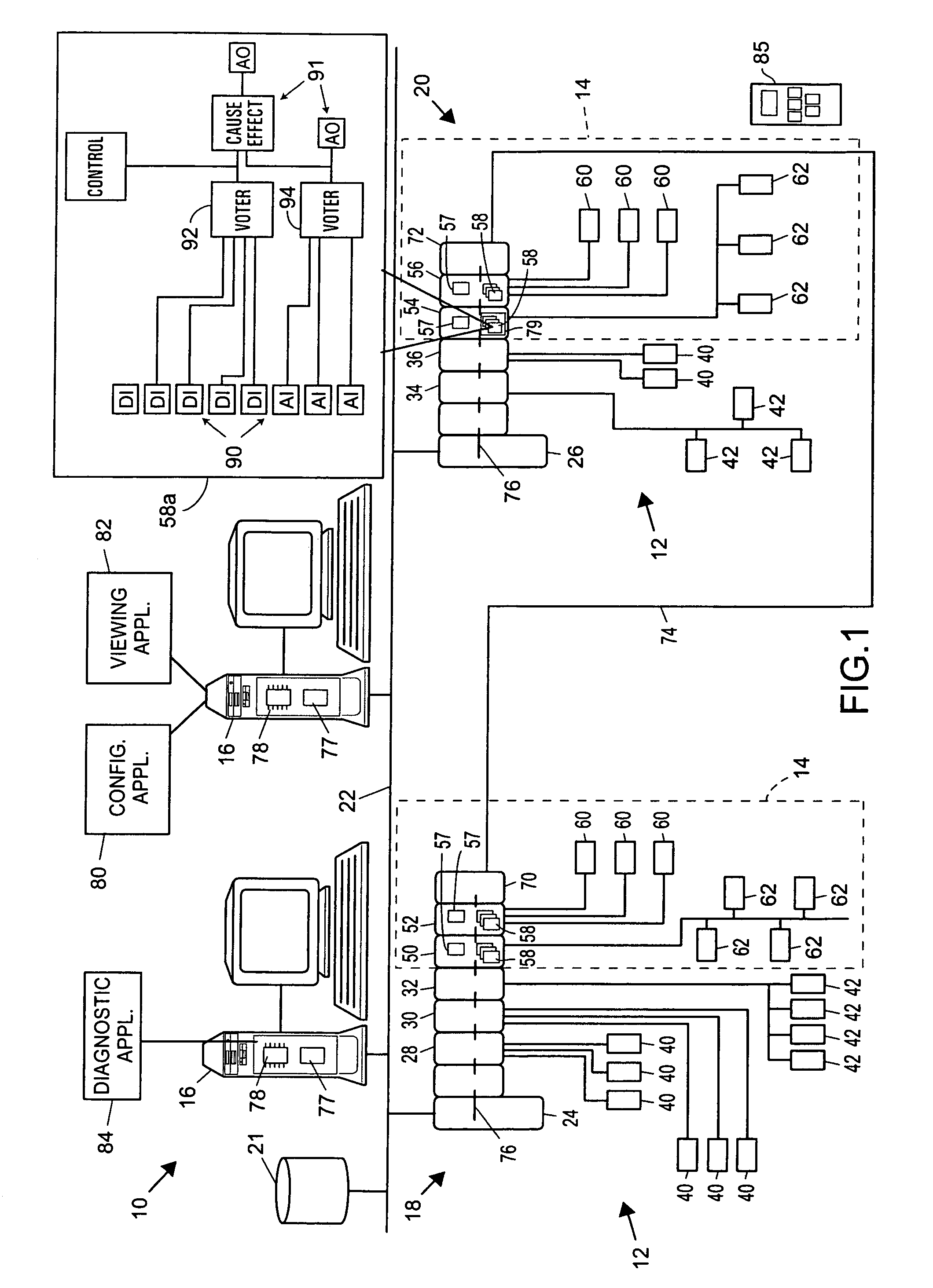
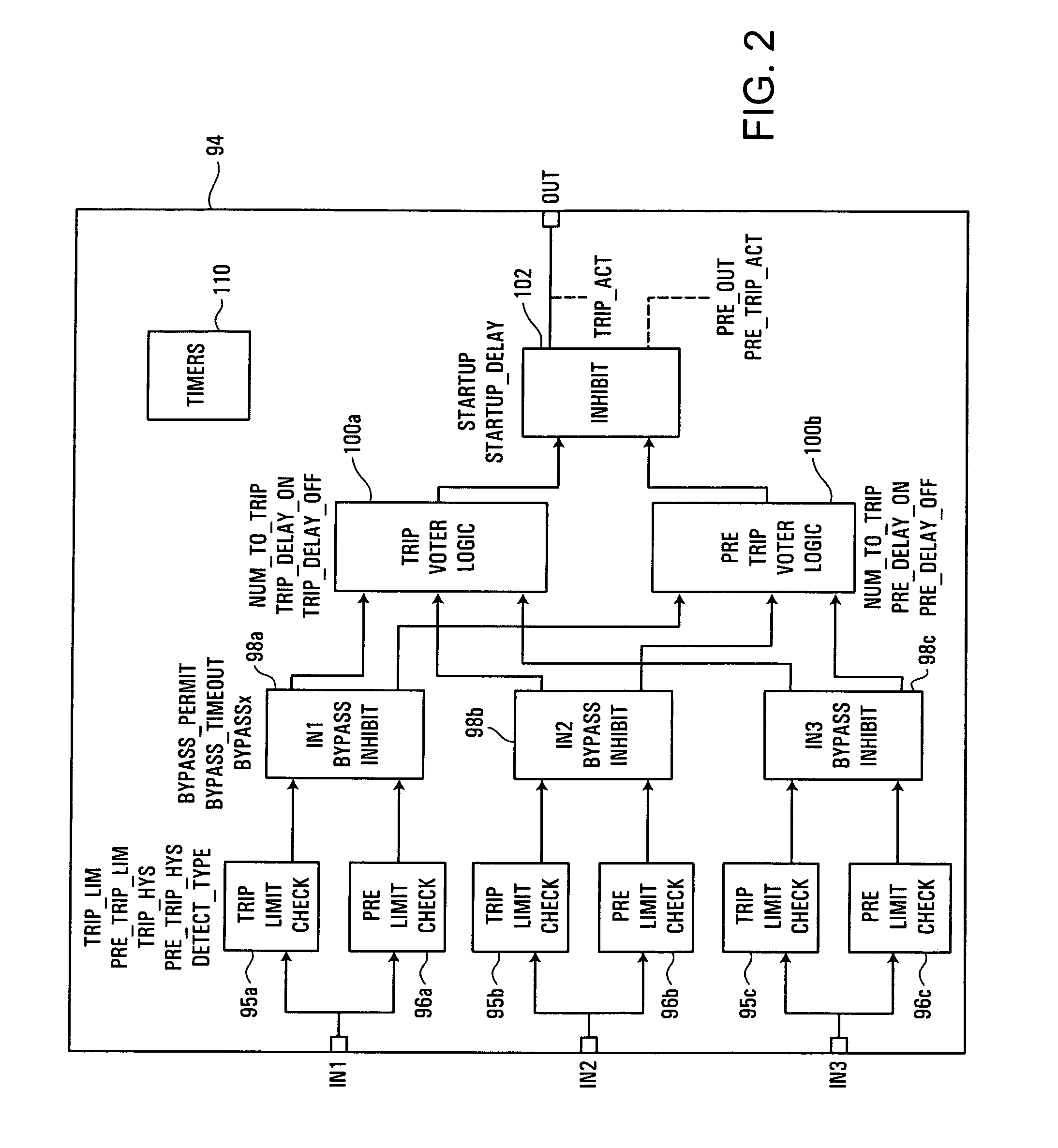
A process control or safety instrumented system uses function block logic to coordinate the logic within the process control or safety instrumented system with operational states of field devices, even when these operational states are initiated externally to the process control or safety system. Logic within input or voter function blocks associated with field devices may monitor and determine when the associated field devices are being put into testing or calibration modes and may automatically initiate appropriate bypass or override functionality in response to such detected field device configuration states. Likewise, the function block logic may automatically remove the bypass or override functionality when the field devices are placed back into their normal operational configuration states. This automatic initiation of bypasses and overrides helps to prevent a safety system within a process plant from initiating a shut-down procedure as a result of a device test initiated manually by, for example, a hand-held device attached to a field device. Likewise, the automatic removal of bypasses and overrides helps to prevent a safety system within a process plant from failing to operate properly because a user forgot to manually remove a bypass or override that was set up to allow a device test.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
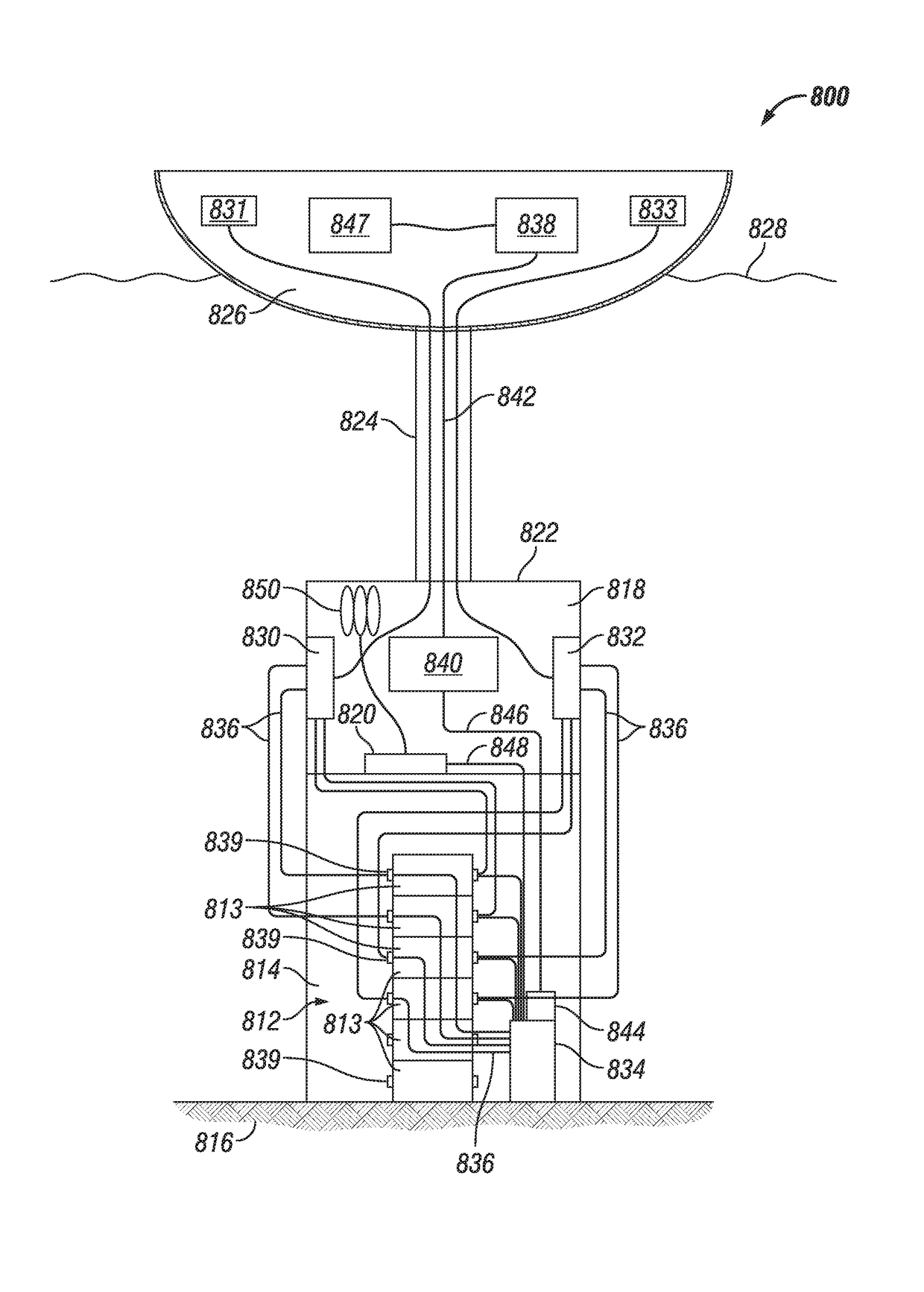
High Pressure Blowout Preventer System
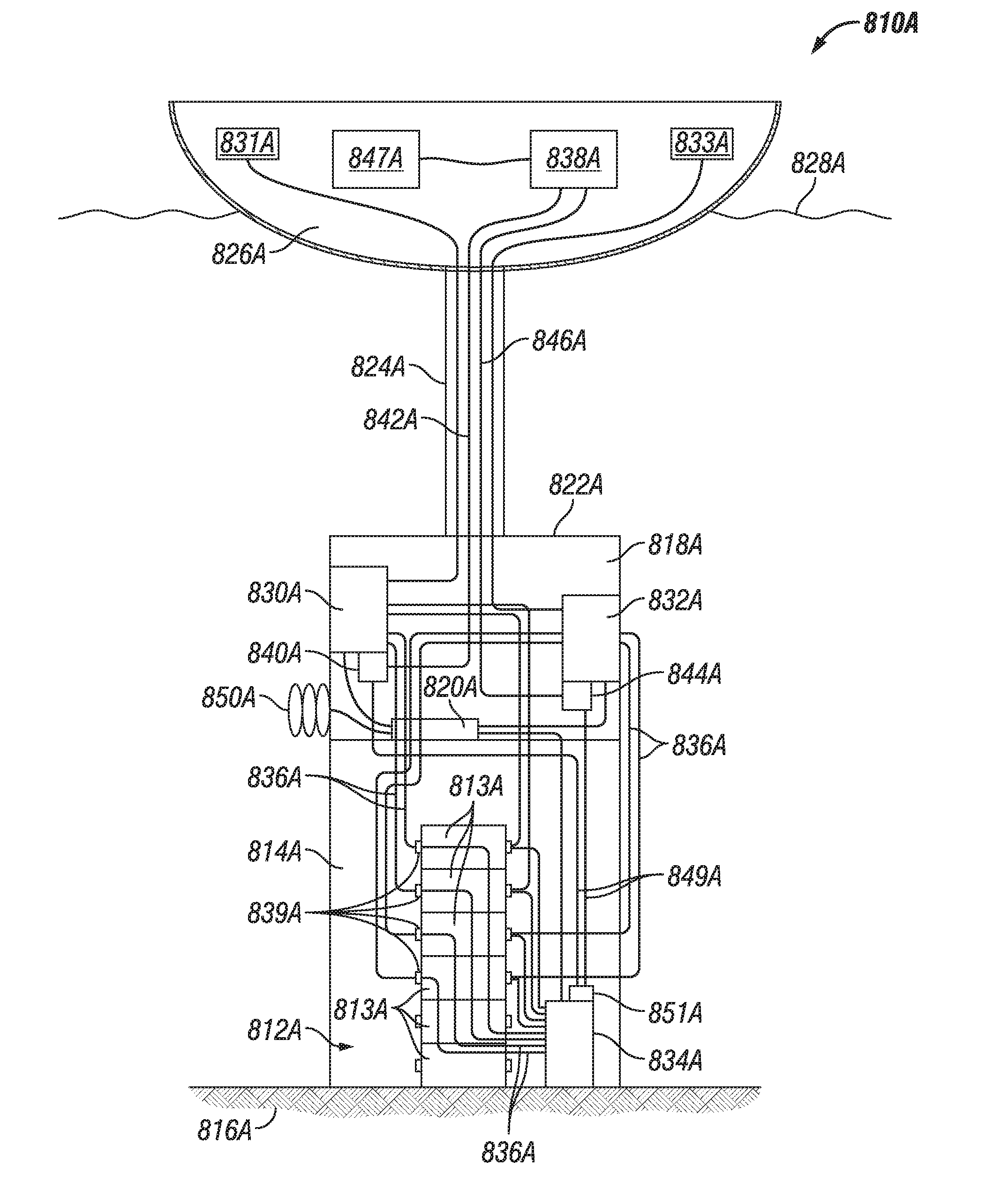
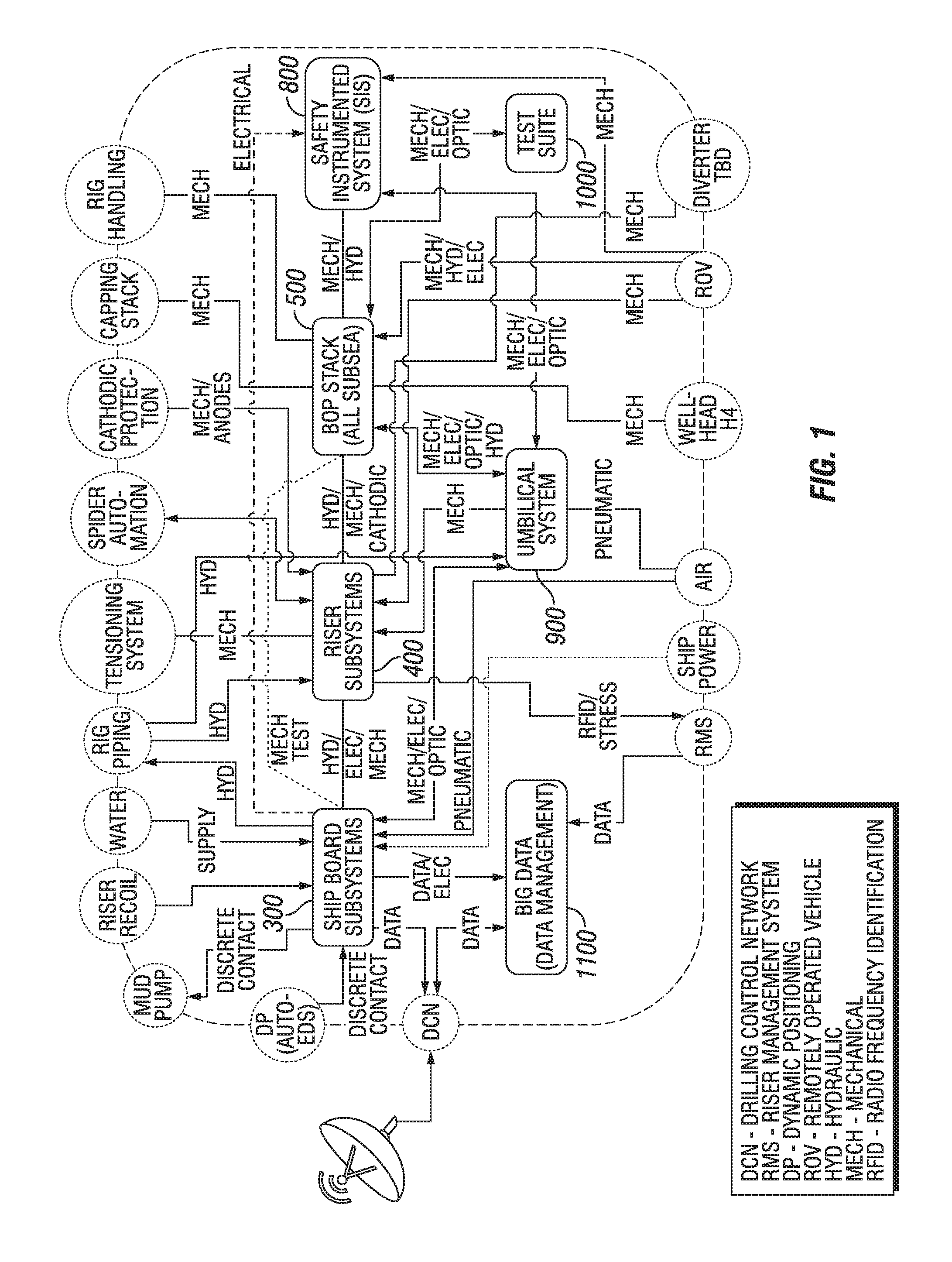
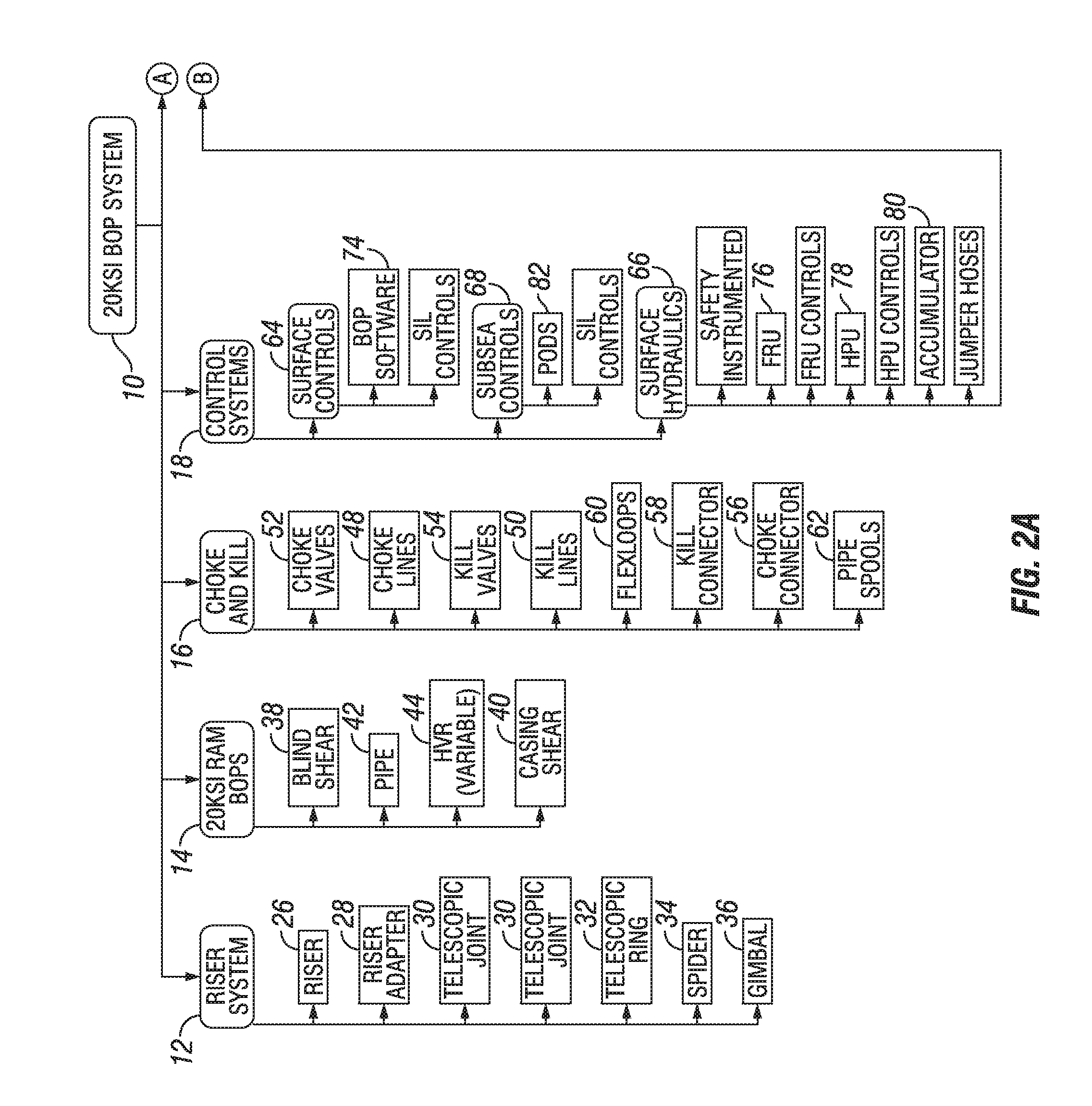
ActiveUS20160109874A1Efficient testingEnsure complianceProgramme controlSampled-variable control systemsSafety instrumented systemOcean bottom
A BOP system for use in a high pressure subsea environment, including a BOP stack including a lower marine riser package and a lower stack portion, the lower stack portion having a plurality of BOP rams attached to a subsea wellhead. The system also includes a riser subsystem extending from a drilling vessel to the BOP stack and providing fluid communication therebetween, a ship board subsystem electronically, mechanically, and hydraulically connected to the BOP stack and the riser subsystem to control the functions of the BOP stack and the riser subsystem, and a safety instrumented system having a surface logic solver and at least one subsea logic solver, the safety instrumented system in communication with at least a portion of the BOP rams to act as a redundant control system in case of failure of the ship board subsystem.
Owner:HYDRIL USA DISTRIBUTION LLC
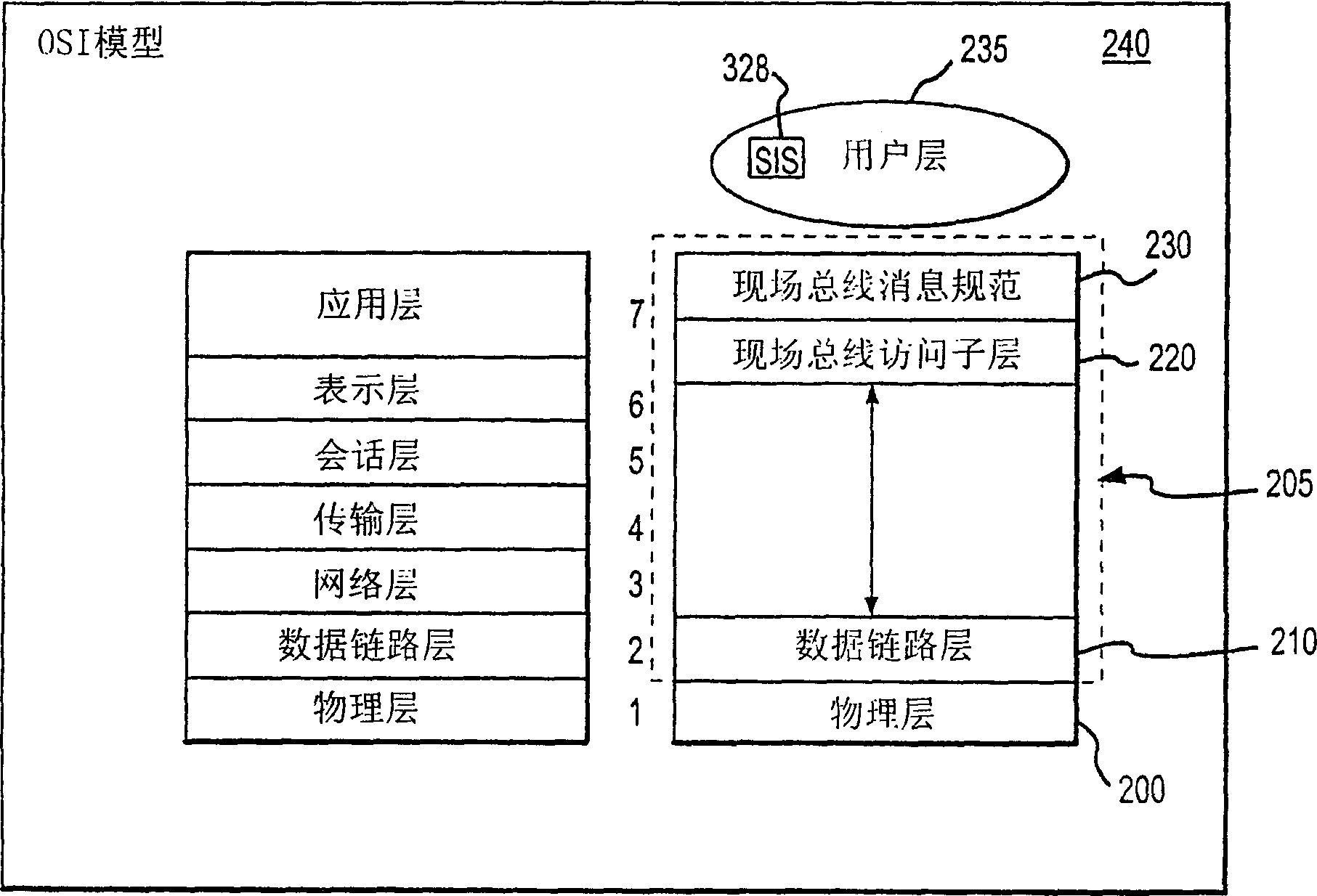
System and method for implementing safety instrumented systems in a fieldbus architecture
An apparatus, system and process is provided for communicating safety-related data, over an open system, from a sender to a receiver. Safety-related components, including function blocks, flexible function blocks, resource blocks and transducer blocks, as well as, safety-related objects are provided. Also, an extended safety-related protocol provides for authenticating communications between safety-related components over an existing black channel, such as one using a fieldbus Architecture.
Owner:FIELDBUS FOUND
Intelligent inspection system and method in thermal power plant
ActiveCN103839302AWith intelligent reverse prompt functionAccurate analysisData processing applicationsRegistering/indicating working of machinesSafety instrumented systemData center
The invention discloses an intelligent inspection system and method in a thermal power plant. The system comprises a wireless industrial Ethernet network, an inspection data center and a multifunctional inspection terminal, wherein the inspection data center and the multifunctional inspection terminal are in wireless connection with the wireless industrial Ethernet network; the inspection data center is connected with a DCS (Distributed Control System) and SIS (Safety Instrumented System) of the power plant, has synchronous clock periods and is capable of inquiring, reading and writing real-time and historic databases of the DCS and the SIS of the power plant; the inspection data center drives the multifunctional inspection terminal to sample data of an inspection target via the wireless industrial Ethernet network and exchanges data with the multifunctional inspection terminal. The invention further provides the inspection method of the system. According to the method, the clock of the DCS system of the power plant is synchronized via wireless communication, various diagnosis signals are conveniently collected by using the multifunctional inspection terminal and are integrated with original DCS data, and trend analysis and evaluation are carried out on inspection data under similar working conditions so as to prompt inspectors to master running states of equipment and parts and maintain and preserve the equipment and the parts in time, so that the equipment maintenance level and the running safety and reliability of the system are increased.
Owner:XIAN TPRI THERMAL CONTROL TECH +1
Method for evaluating functional safety of safety instrument system
InactiveCN102034025AEffective assessmentCapable of expansionSpecial data processing applicationsSafety instrumented systemSafety Integrity Level
The invention relates to a method for evaluating the functional safety of a safety instrument system, belonging to the technical field of functional safety of safety instrument systems. The invention aims at reliably simulating and monitoring the safety instrument system, evaluating the functional safety and studying the variation condition of common cause failure of the safety instrument system. The method comprises the following steps of: controlling the functional safety of a controlled system by a safety instrument system; analyzing the initial risk of the safety instrument system and determining the grade of safety integrity; verifying whether the safety instrument system reaches the determined grade of safety integrity; changing the constituting structures or devices of the safety instrument system; and repeating the above steps. In the technical scheme, the constituting structures or devices of the safety instrument system can be changed according to the studied specific condition to adapt for different application environments and requirements, and the variation condition of the common cause failure characteristic of the safety instrument system can be analyzed under different circumferences so as to provide important basis for studying the topic of common cause failure.
Owner:BEIJING MUNICIPAL INST OF LABOUR PROTECTION
Process equipment validation
A Safety Instrumented System for use with a process control system receives pressure of process fluid in the process piping. A valve positioner positions a valve which controls flow of process fluid through the process piping. The valve positioner is caused to perform a partial stroke of the valve or otherwise introduce a perturbation into the process. A resulting change in sensed pressure due to the perturbation is used to diagnose operation of the process.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT INC
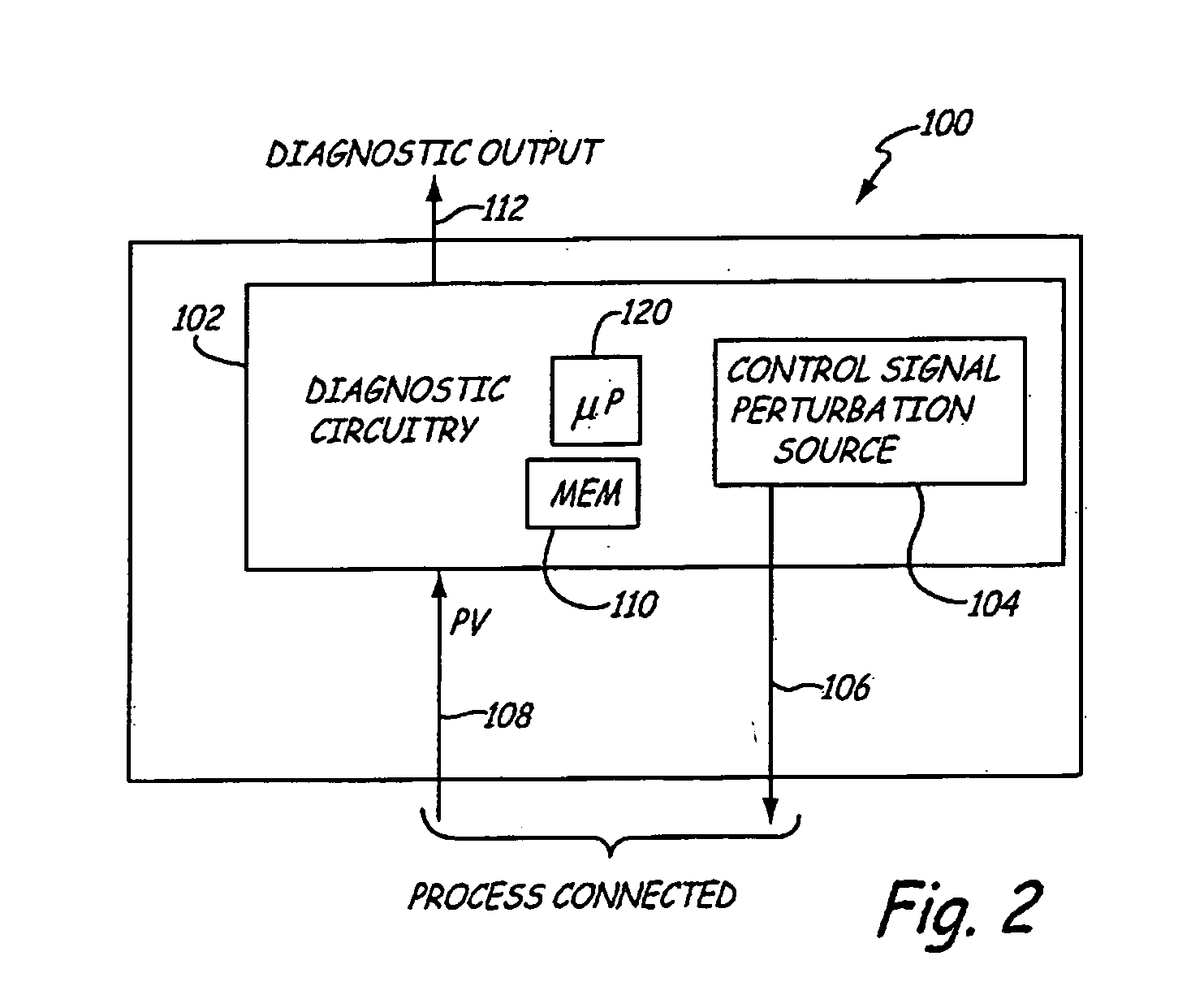
Probability of failure on demand calculation using fault tree approach for safety integrity level analysis
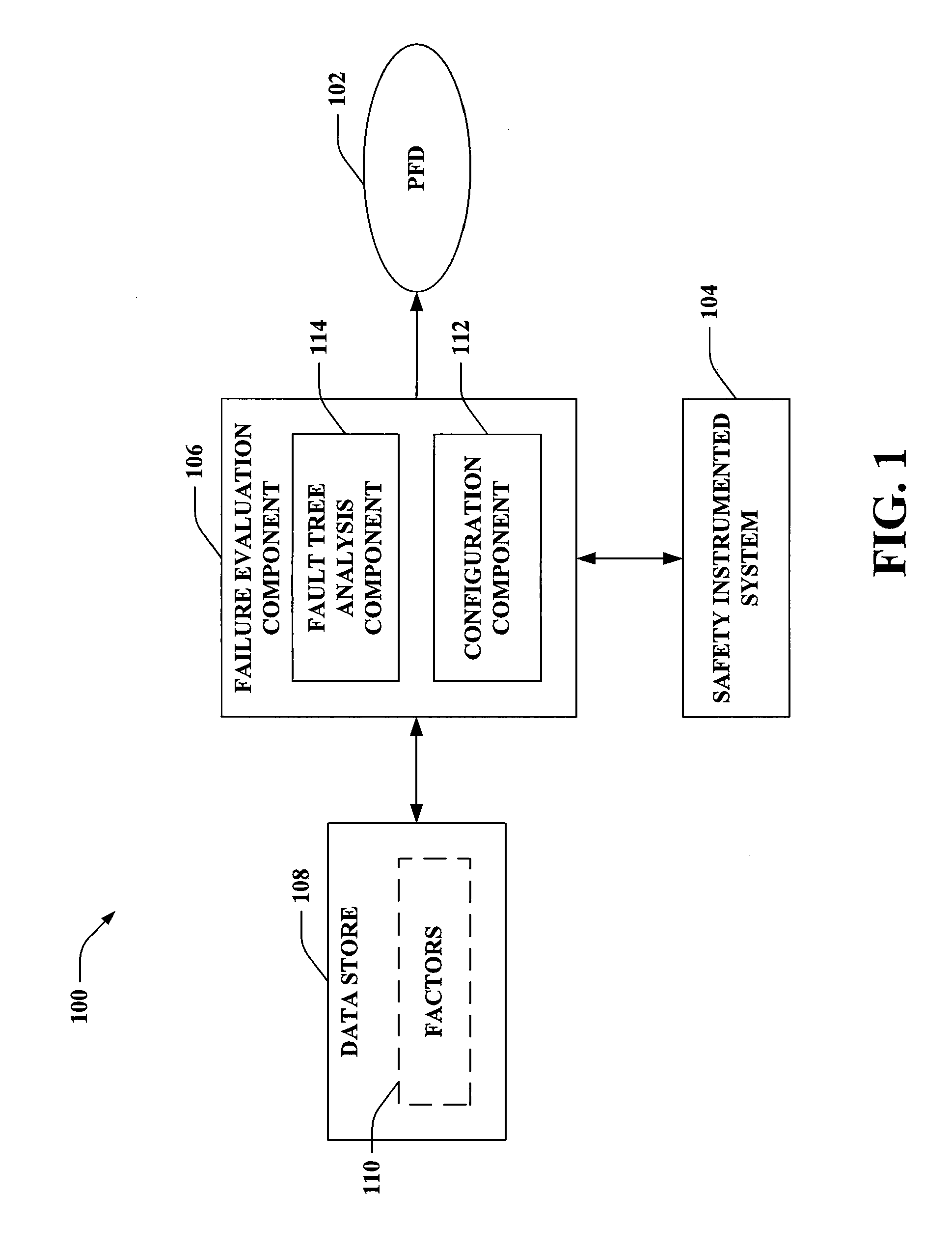
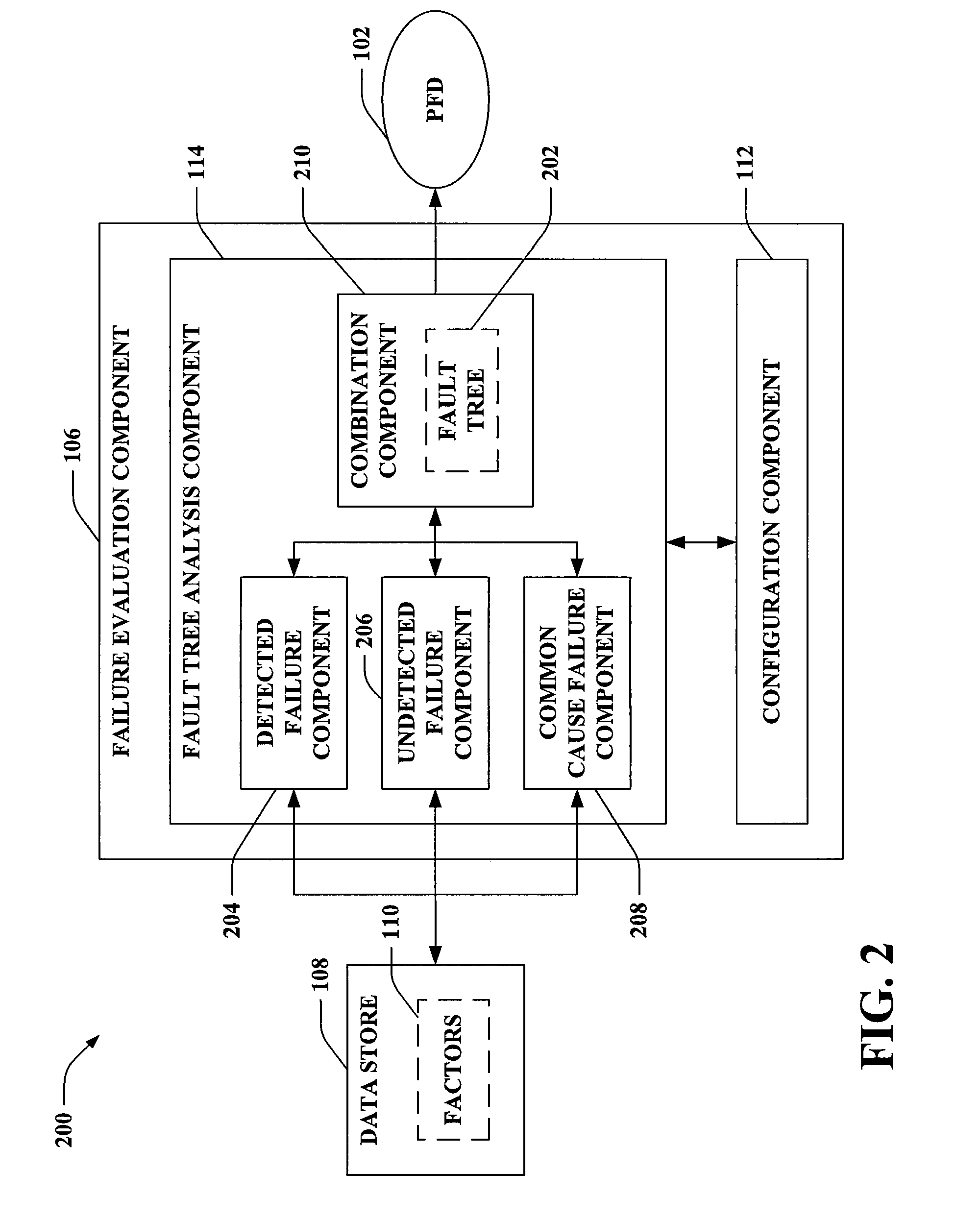
InactiveUS20130317780A1Facilitates determining a probability of failure on demand (PFD)Testing/monitoring control systemsDigital computer detailsSafety instrumented systemSafety Integrity Level
A computer-readable medium including computer-executable instructions that, when executed by a processor, cause the processor to perform acts, via an associated method that includes selecting a fault tree based upon an architecture of a safety instrumented system. The method includes evaluating at least a failure probability due to dangerous detected failures and a failure probability due to dangerous undetected failures as a function of values of factors. A portion of the failure probability due to dangerous undetected failures is based on failures detected during proof testing and a remainder of the failure probability due to dangerous undetected failures is based on failures detected during refurbishment. The method includes generating a probability of failure on demand for the safety instrumented system by combining at least the failure probability due to dangerous detected failures and the failure probability due to dangerous undetected failures according to the fault tree.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
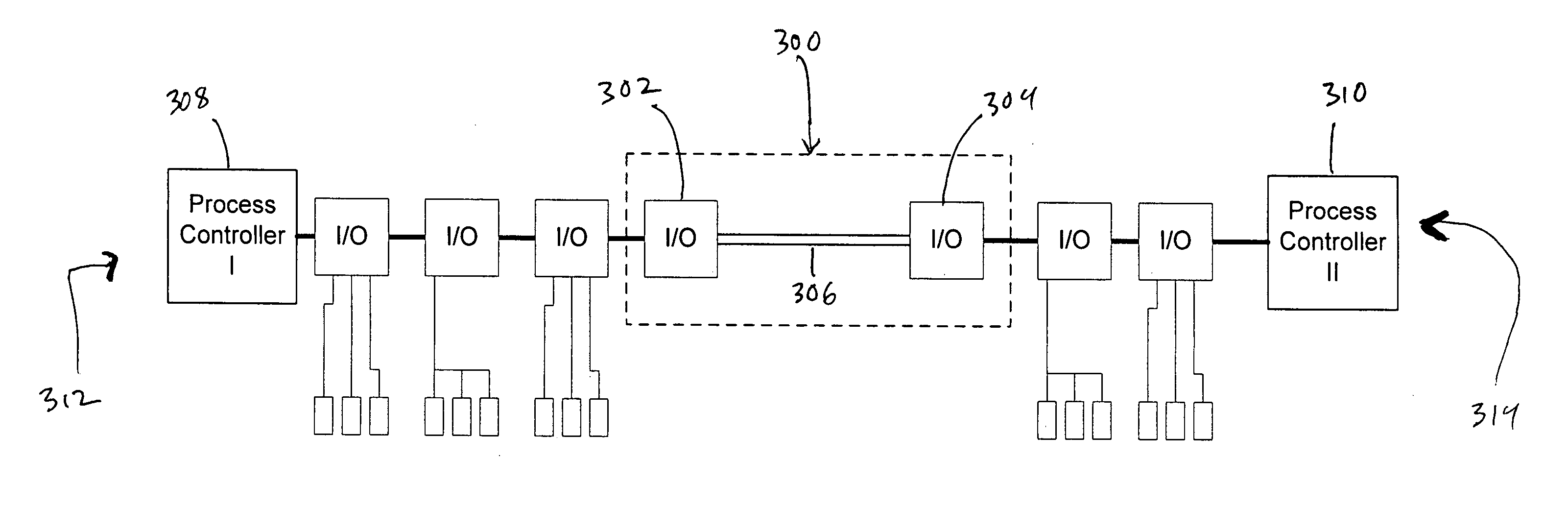
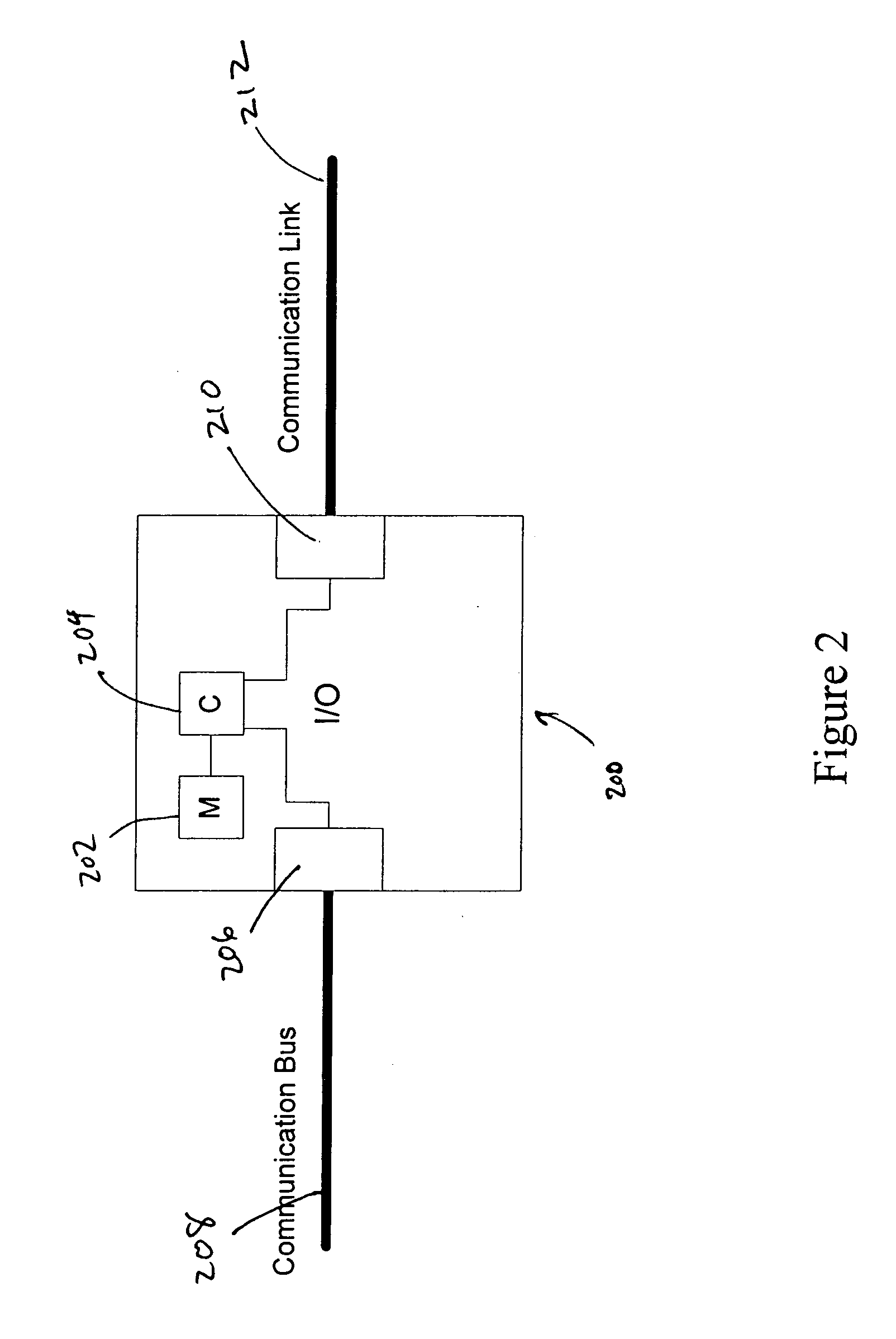
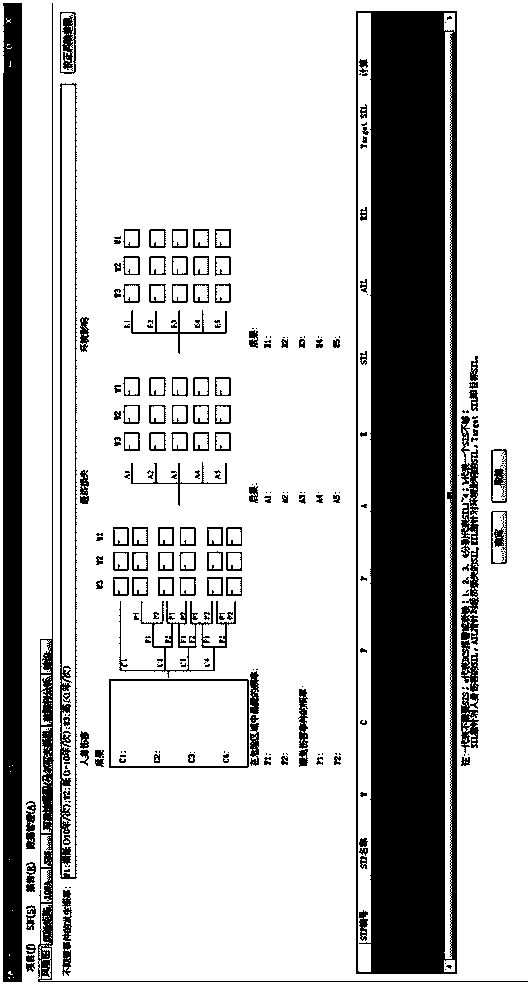
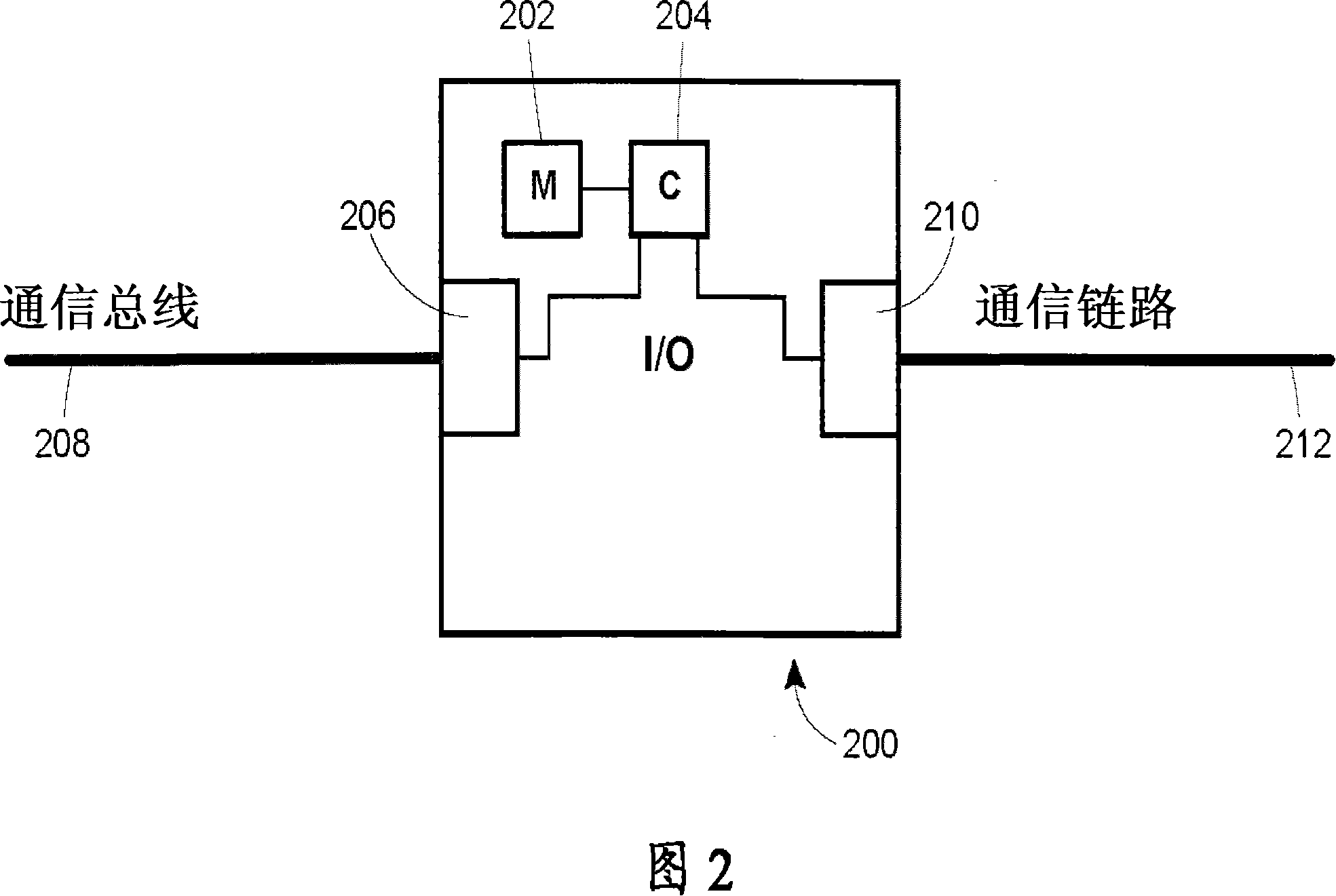
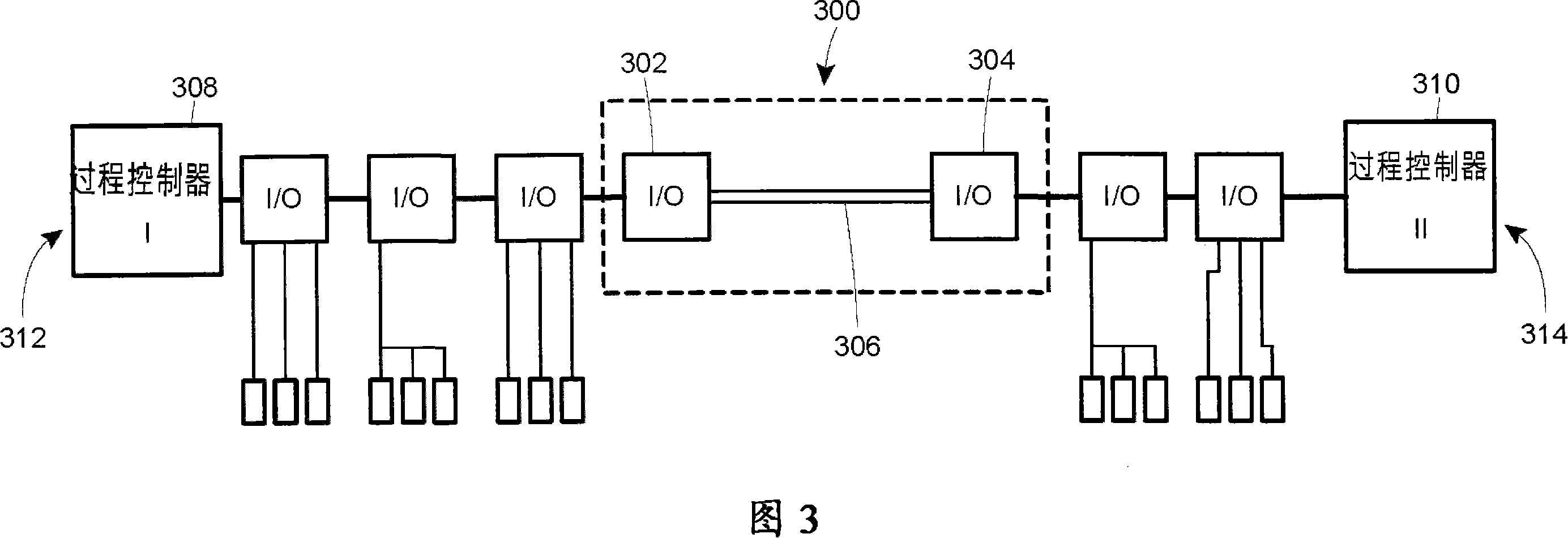
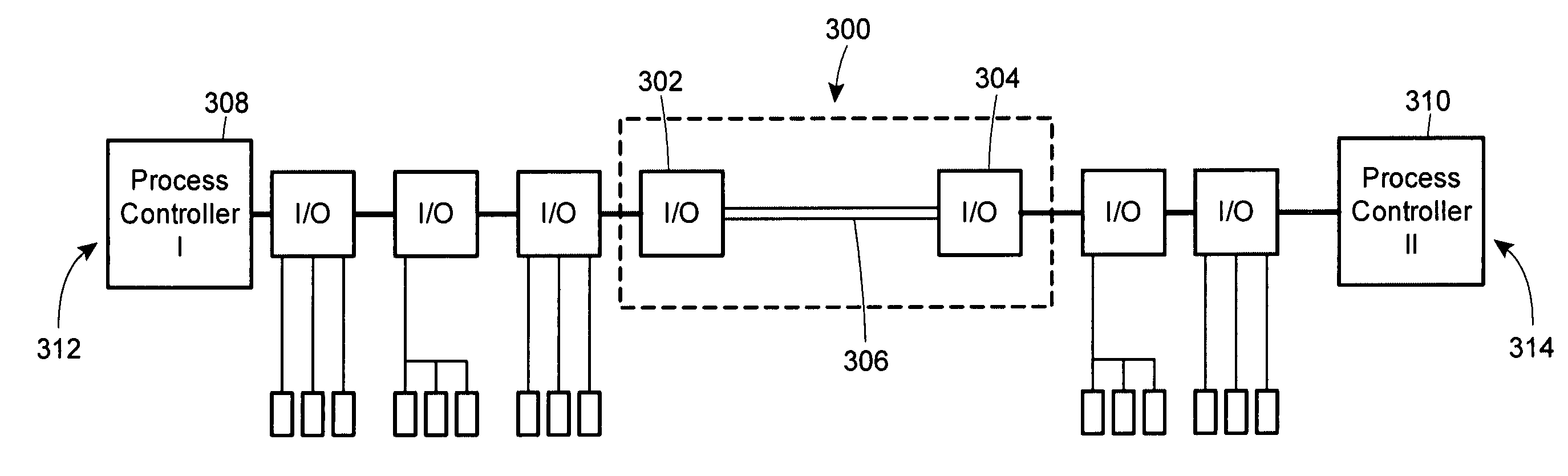
Method for intercontroller communications in A safety instrumented system or a process control system
The claimed system provides an I / O card that is used to interface two process controllers over a communication line that is separate from a primary communication line connecting the two process controllers to a workstation. The process controllers can access the I / O cards in a similar manner to I / O cards used to connect to field devices. In this manner, the physical hardware and software architecture does not need to be modified for inter-controller communications. Inter-controller communications can be programmed as general I / O communication.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
Distributed and adaptive smart logic with multi-communication apparatus for reliable safety system shutdown
InactiveUS7869889B2Increase decision reliabilityGood flexibilityVehicle testingBurglar alarmSafety instrumented systemProcess conditions
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
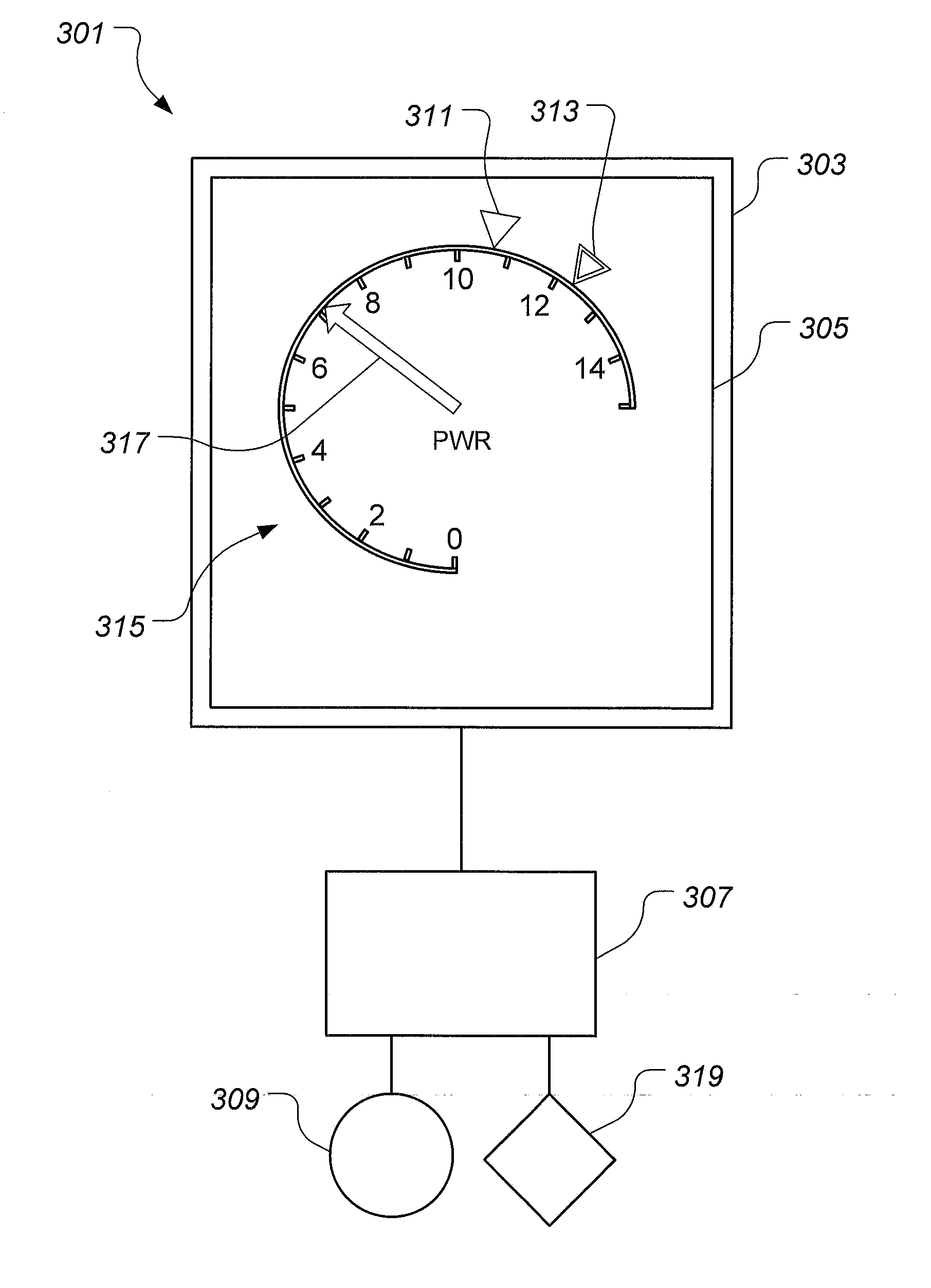
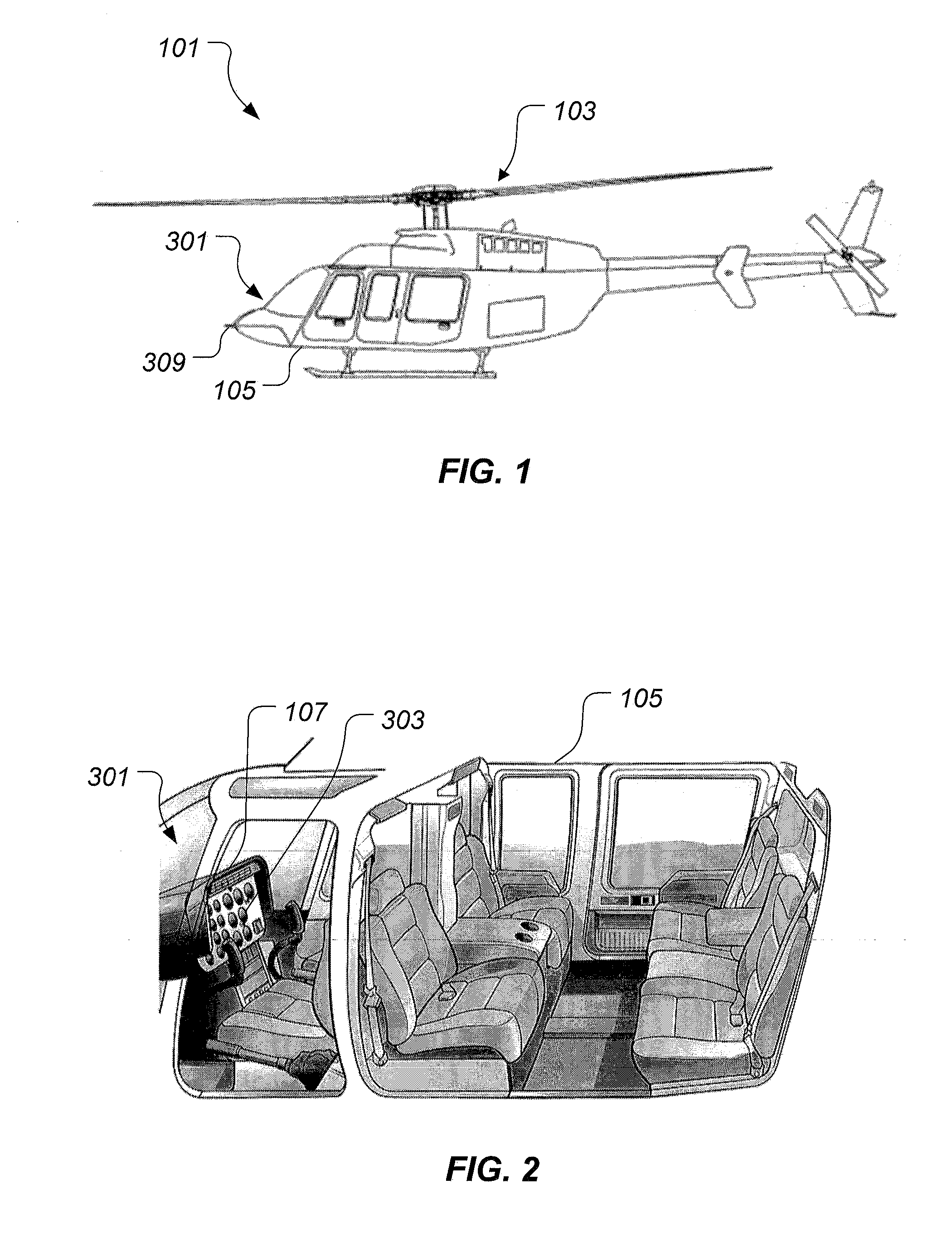
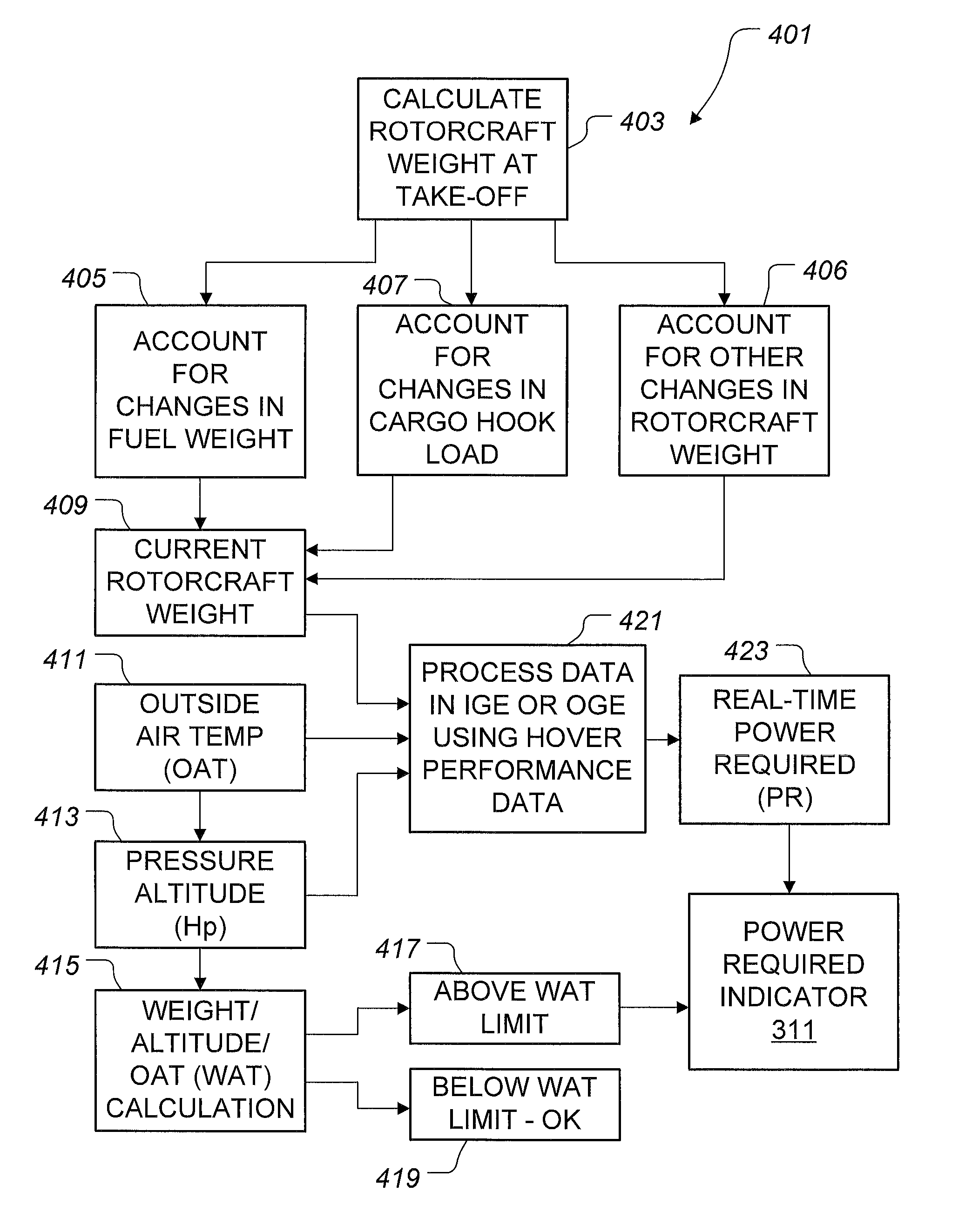
Power Safety Instrument System
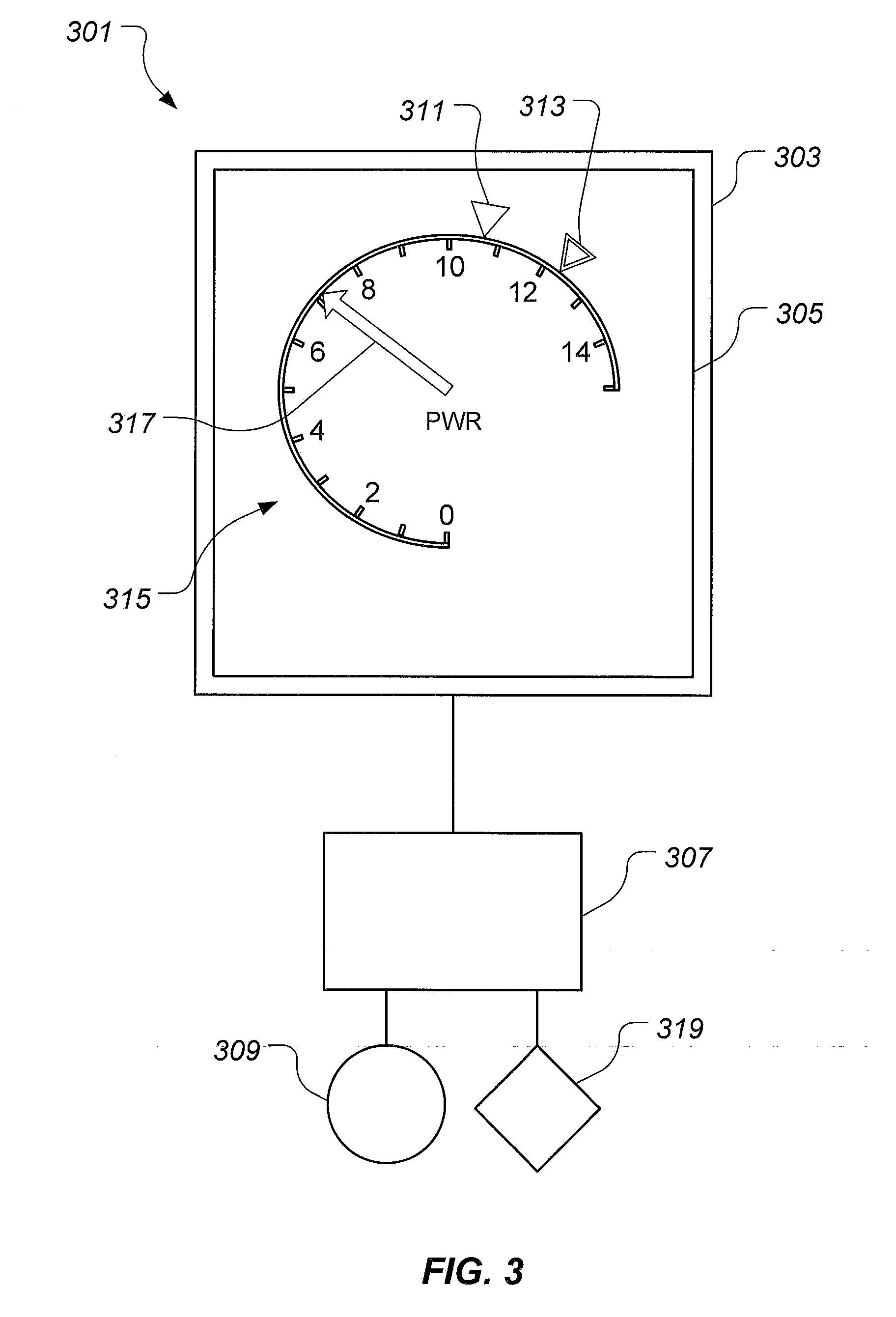
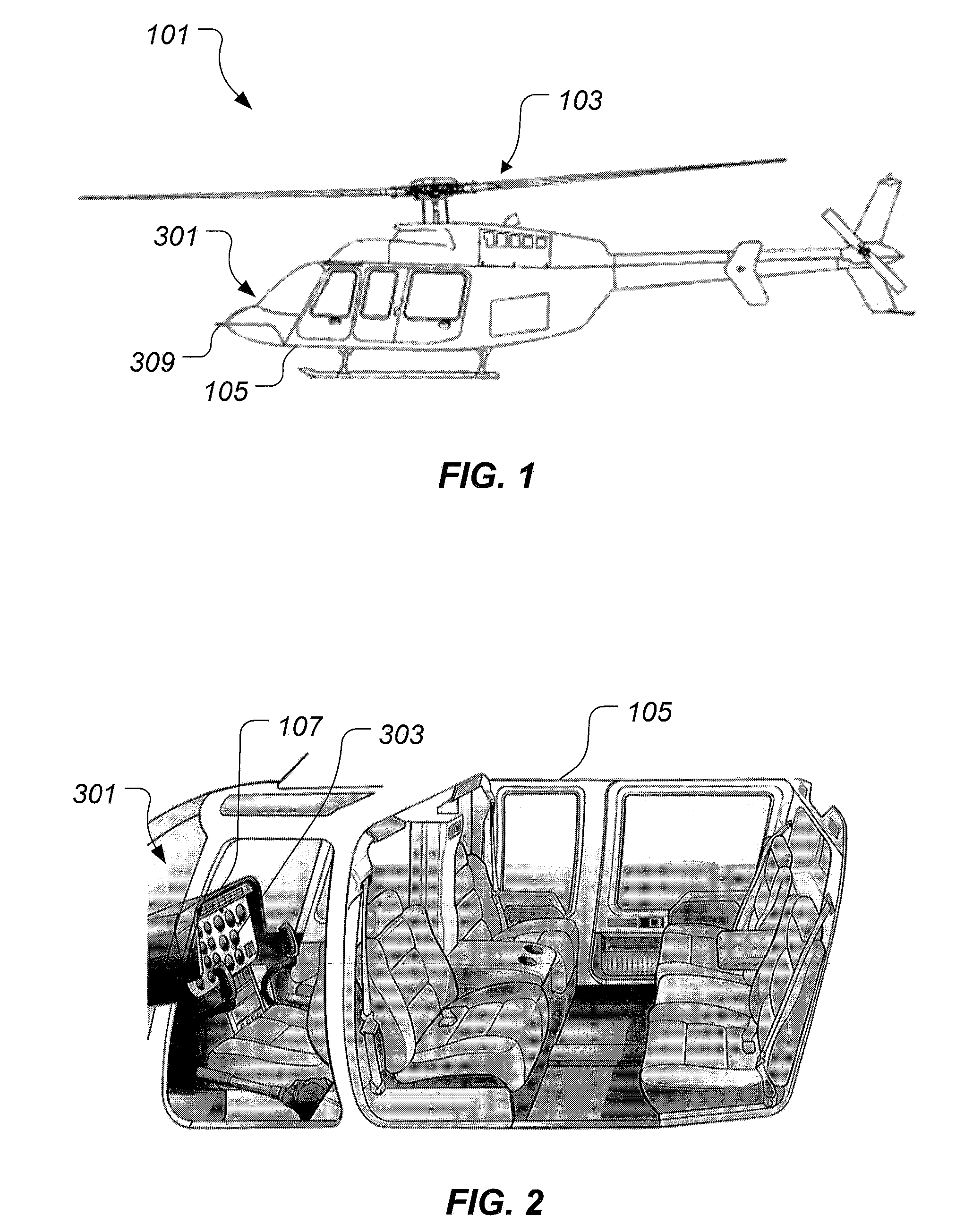
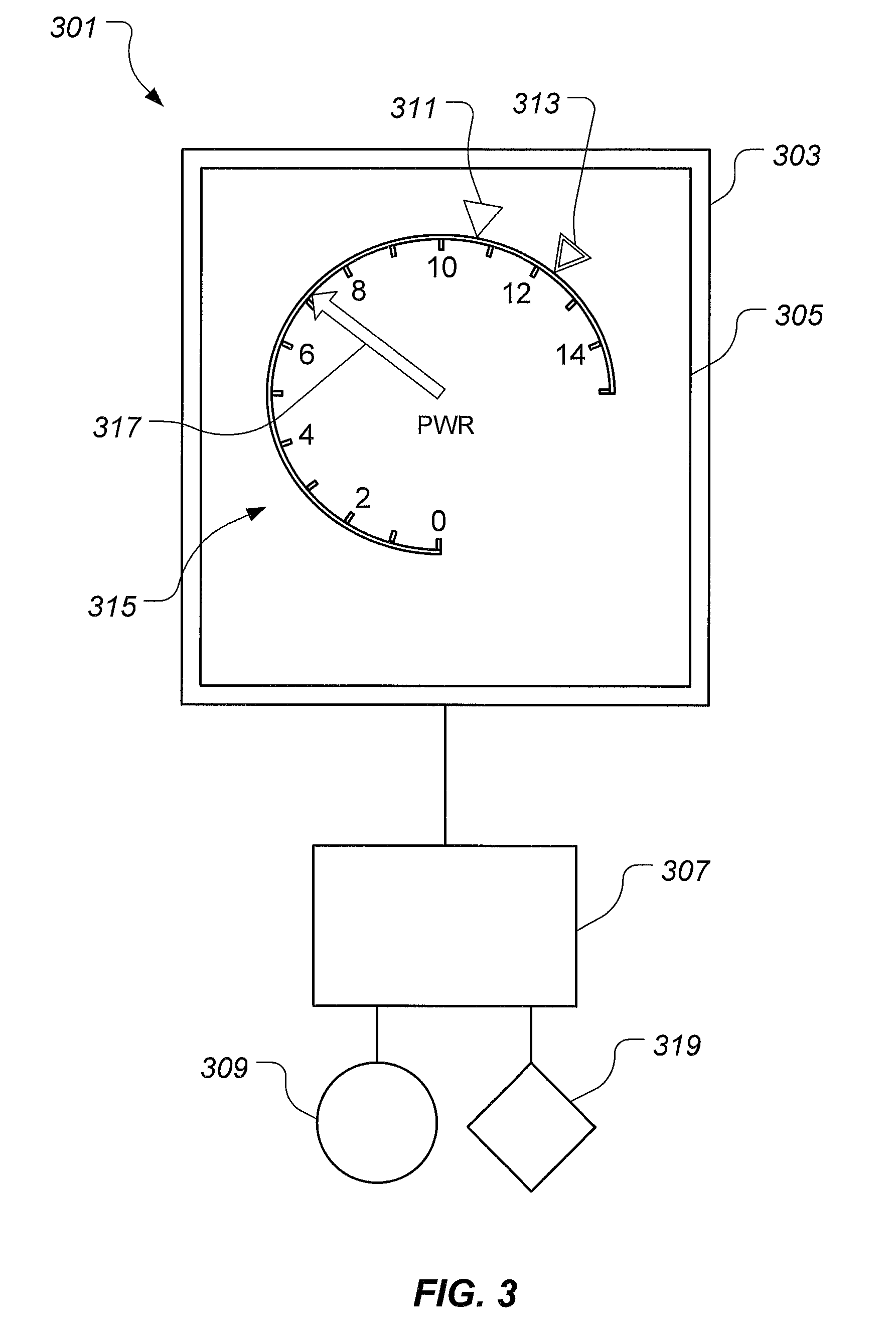
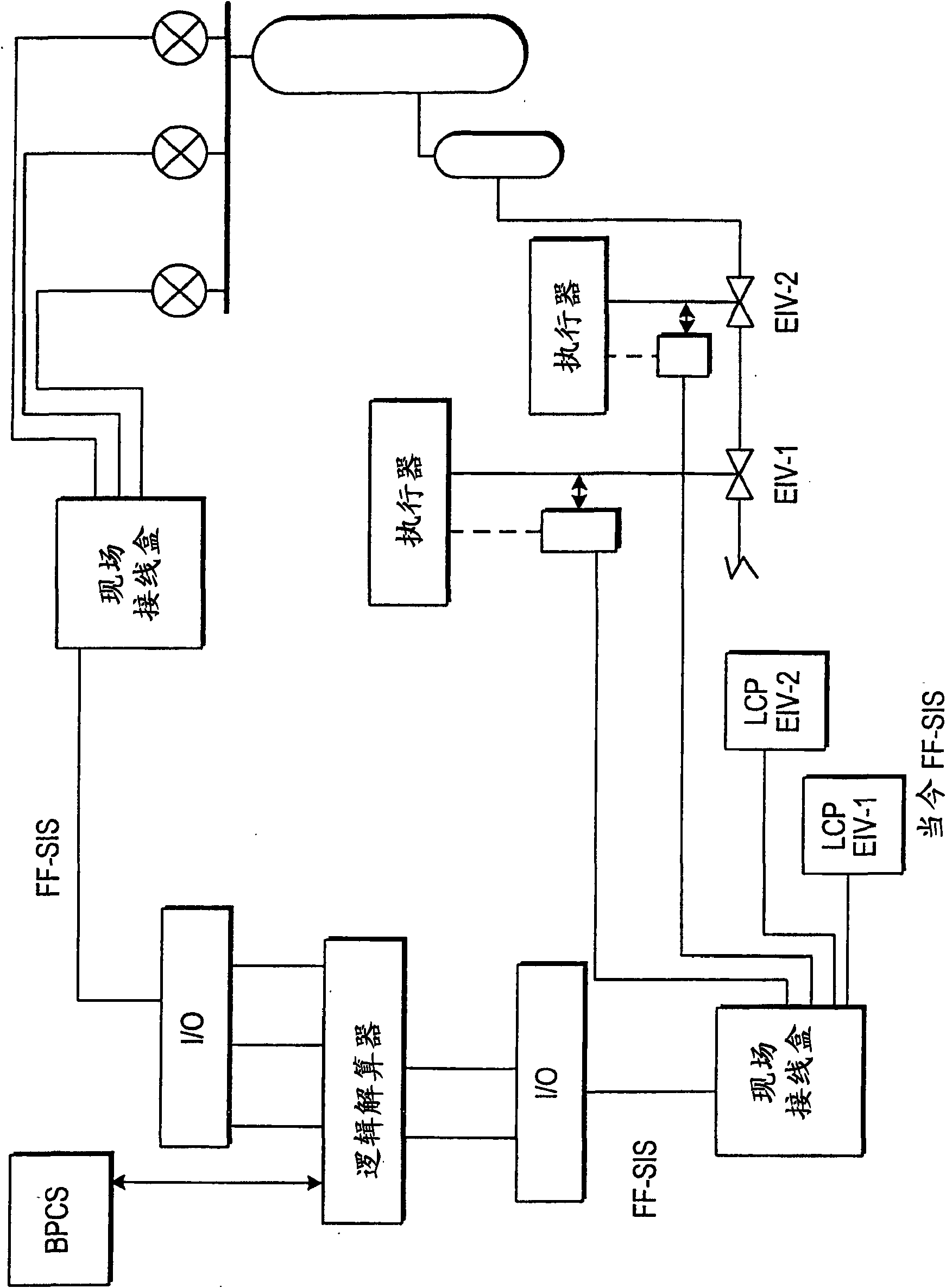
ActiveUS20130120165A1Mechanical power/torque controlSpecial tyresSafety instrumented systemDisplay device
A power safety system is configured to provide power information in an aircraft. The power safety system includes a power safety instrument having a power required indicator and a power available indicator, each being located on a display. A position of the power required indicator and the power available indicator represent the power available and power required to perform a hover flight maneuver. The power safety system may be operated in a flight planning mode or in a current flight mode. The power safety system uses at least one sensor to measure variables having an effect on the power required and the power available.
Owner:TEXTRON INNOVATIONS
Method for designing recycle hydrogen heating furnace gas pressure safe instrument system
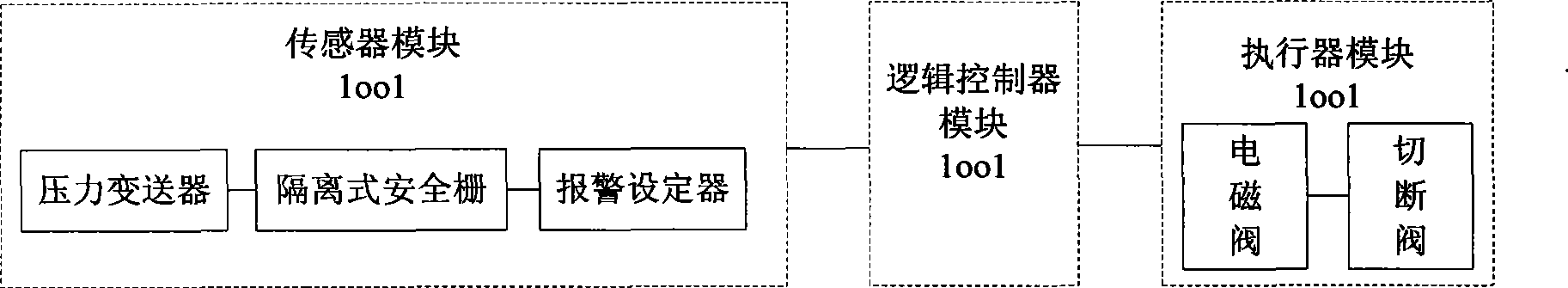
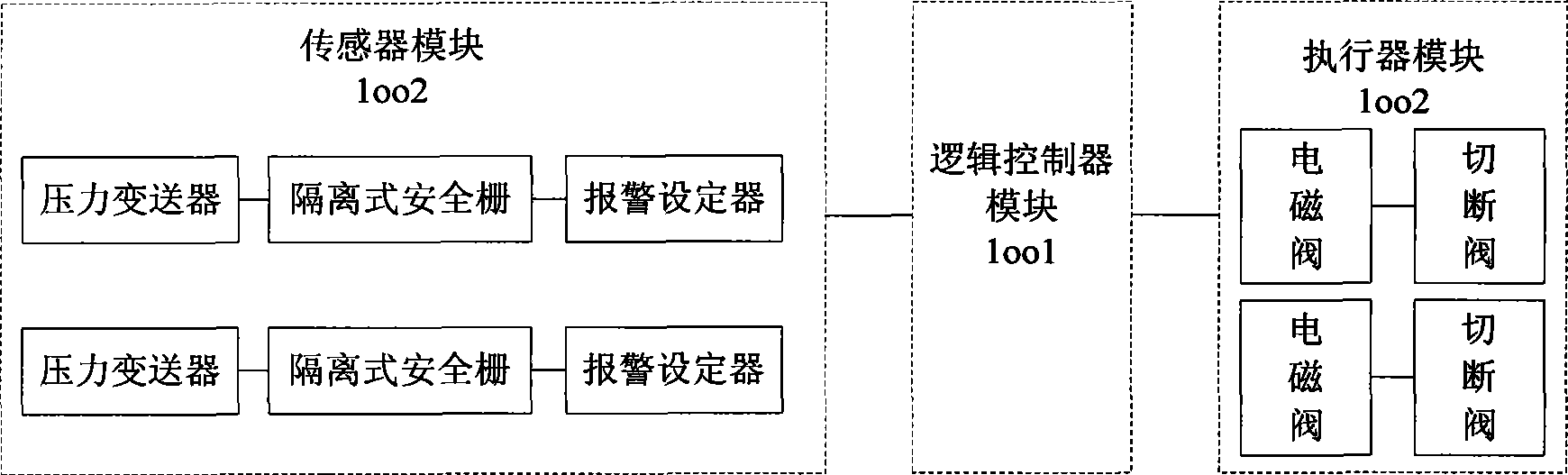
InactiveCN101414165AImprove versatilityEasy to set upProgramme controlComputer controlSafety instrumented systemHydrogen
The invention discloses a design method of a gas pressure safety instrumented system used in a circulating hydrogen heating furnace. The design method comprises the following steps: analyzing functions of the safety instrumented system based on a risk matrix to determine a required safety integrity SIL level; computing the SIL levels of an original system (1001) and a system (1002) which is provided with a redundancy unit by a Markov modeling method; and verifying whether the improved system reaches the required SIL level. The safety instrumented system has the following advantages that: 1) the SIL level required by the system is determined according to the risk matrix, and taken as the basis for improving the system, which has good generality, visual and understandable property, and facilitates document establishment and routine maintenance; 2) the SIL levels of the original system and the system which is provided with the redundancy unit are computed by a Markov model, which can reflect a static relation among the devices and dynamic changes of the system, and has high-precision quantitative analysis of reliability; and 3) the SIL level of the system is computed by the Markov modeling method, which is not affected by a dependency relationship among the devices, wherein, the model can comprise a plurality of failure modes of the devices, and a plurality of reliability indexes such as PFS, MTTFS, PFD and MTTFD can be obtained by a single modeling.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
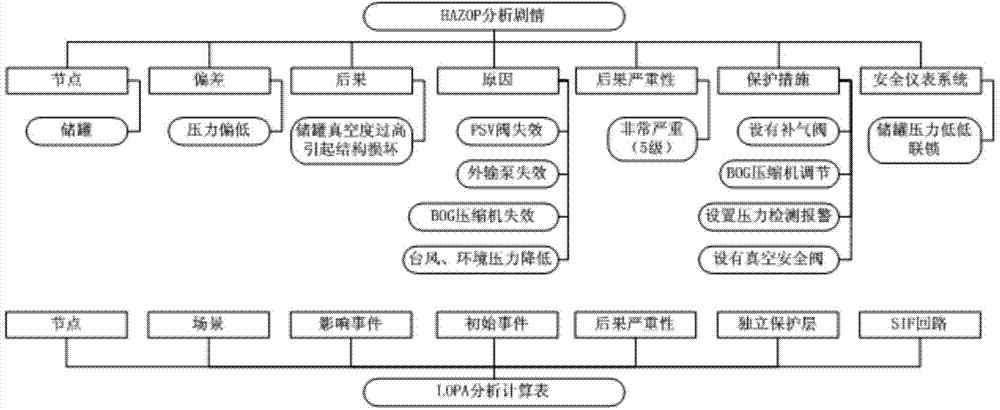
SIL (safety integrity level) judgment method for safety-instrument system for LNG (liquefied natural gas) project
InactiveCN104504502AImprove evaluation efficiencyImprove accuracyResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsSafety instrumented systemSafety Integrity Level
The invention relates to an SIL (safety integrity level) assessment unit for a safety-instrument system for an LNG (liquefied natural gas) project. The SIL assessment unit comprises a project information management module, an HAZOP (hazard and operability analysis) result import module, an intermediate data management module, an SIL assessment calculation module, a database management module and an assessment result output module, wherein the project management information module is used for building an SIL analysis project; the HAZOP result import module is used for carrying out structured processing on the HAZOP analysis result of the SIL analysis project by taking a plot as a unit; the intermediate data management module is used for managing, inquiring and editing HAZOP analysis plots stored in the HAZOP result import module; the SIL assessment calculation module is used for carrying out assessment calculation aiming at each input HAZOP analysis plot by adopting an LOPA (layer of protection analysis) method, and obtaining the to-be-set SIL; the database management module is used for providing the acceptable risk frequency of an influence event, the initial event occurrence frequency and the failure probability reference value of an independent protective layer which are required for LOPA analysis; the assessment result output module is used for automatically generating an SIL assessment report. The SIL judgment method can be widely applied to SIL assessment of the safety-instrument system for the LNG project.
Owner:CNOOC GAS & POWER GRP
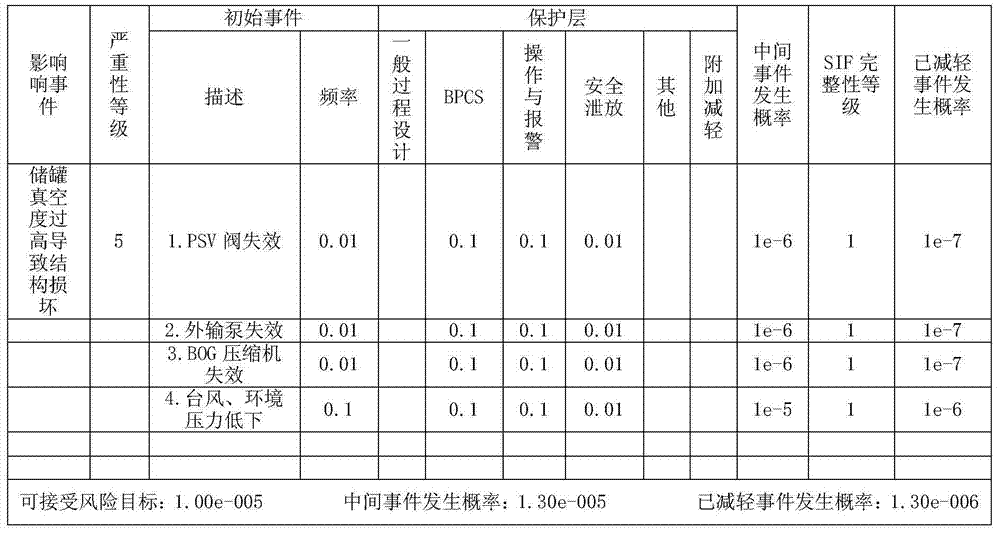
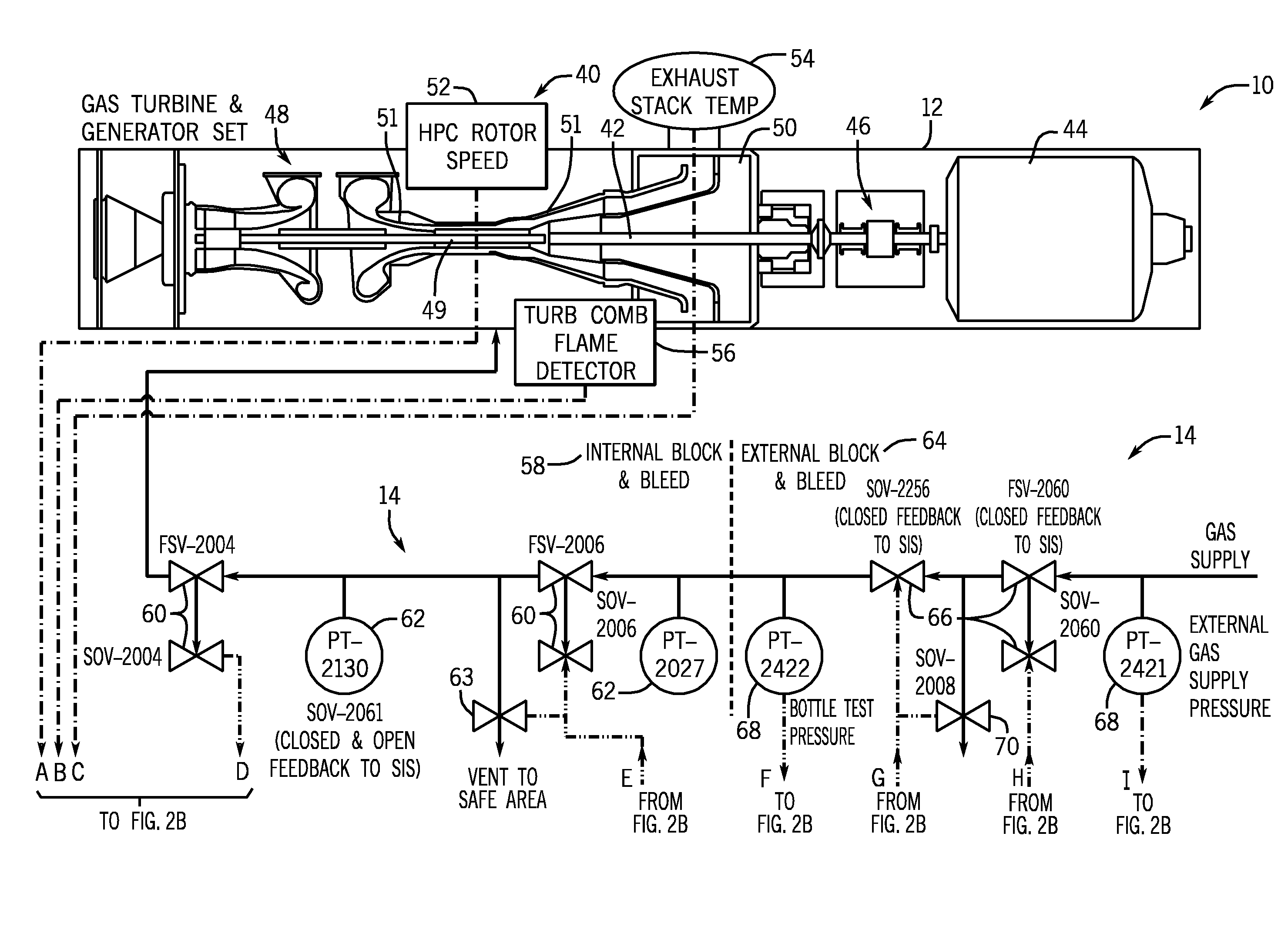
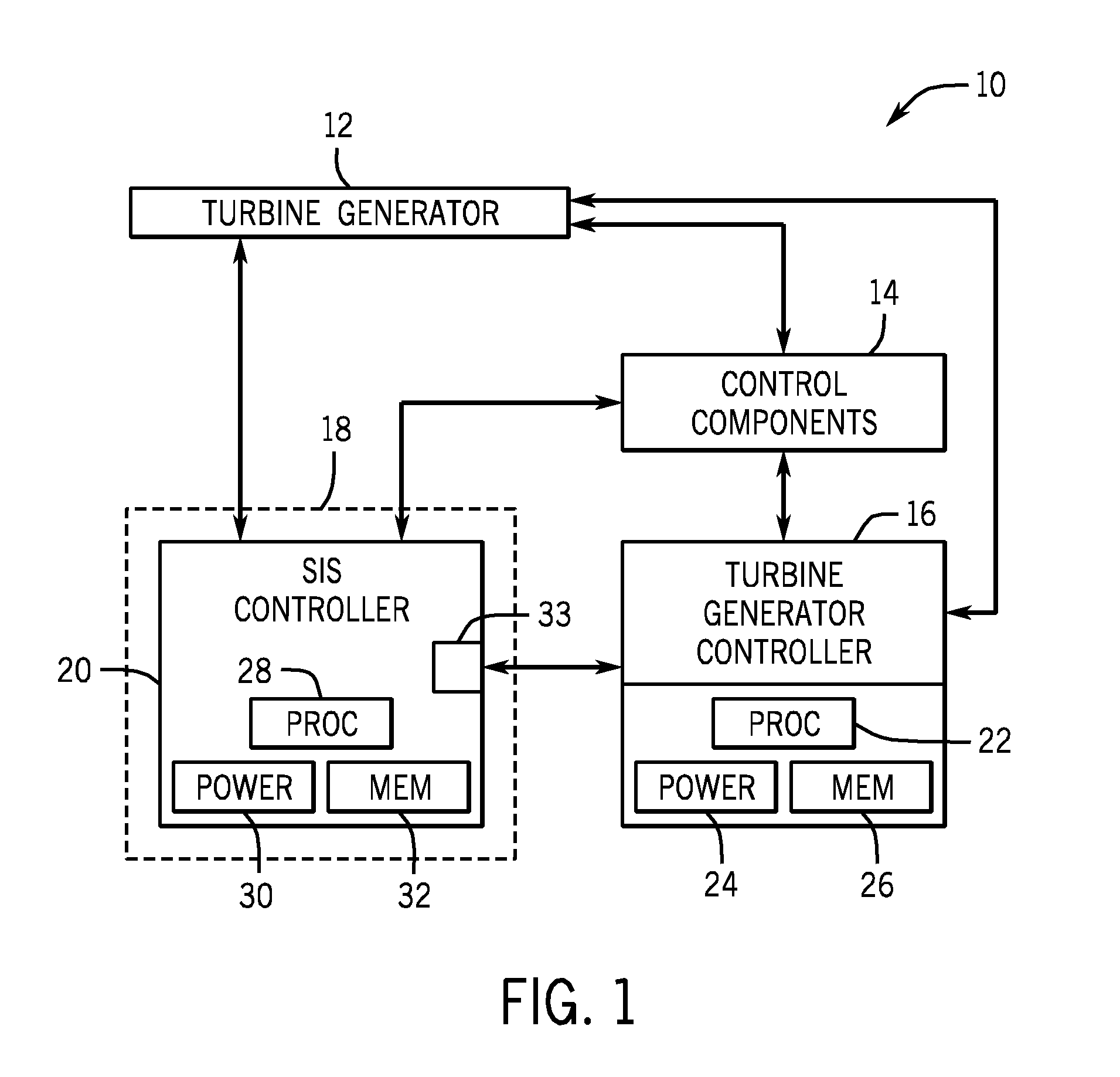
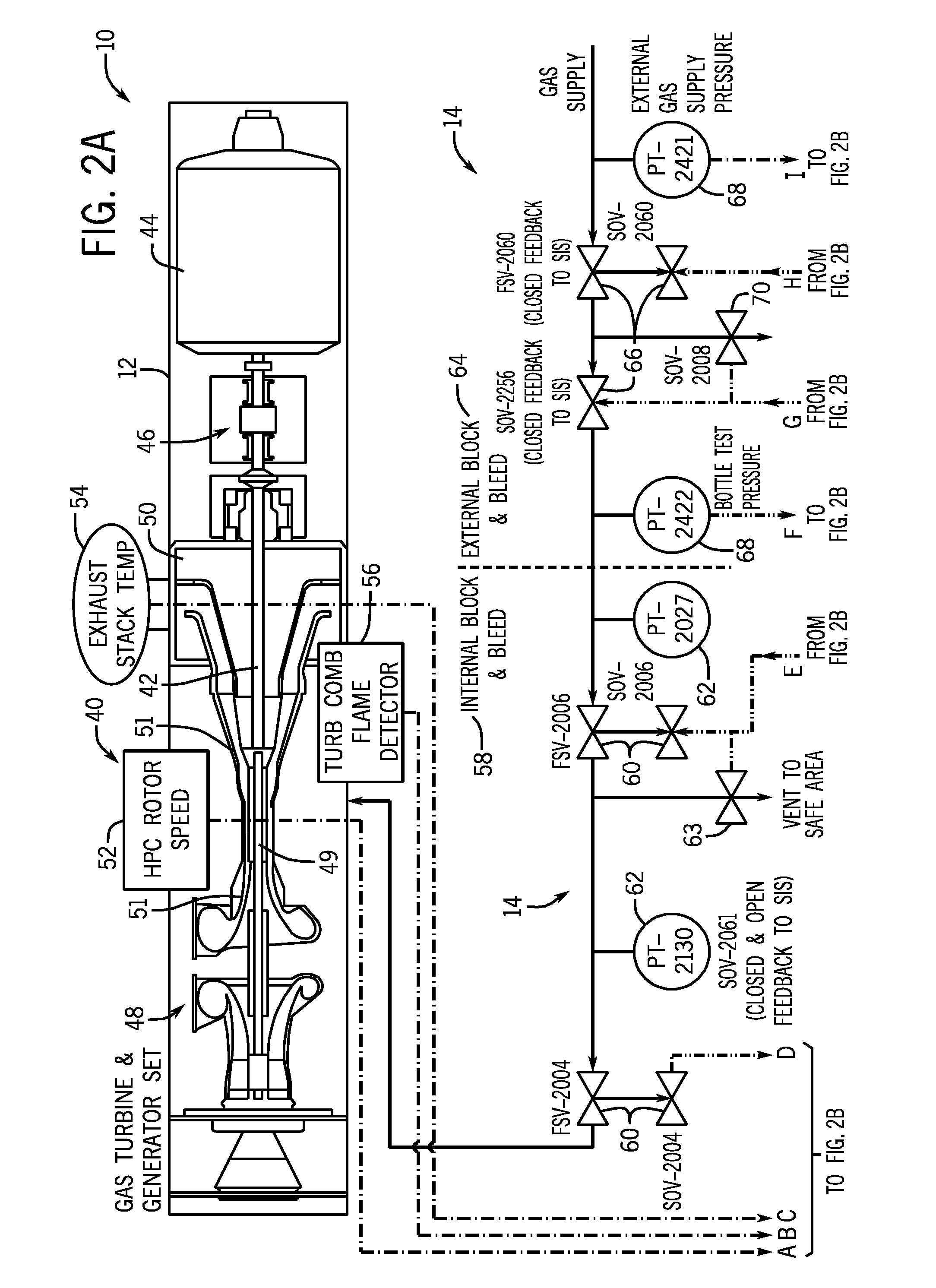
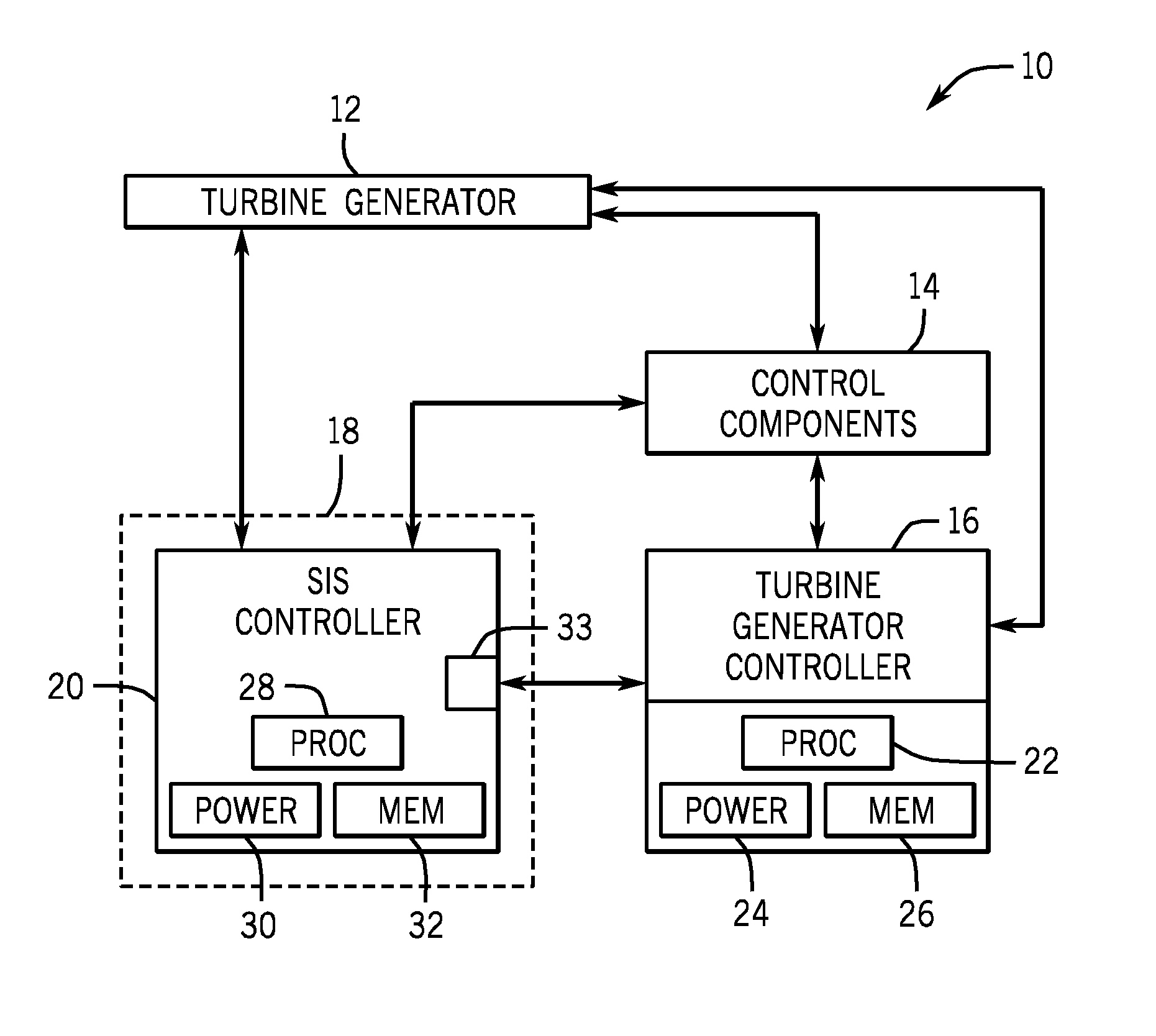
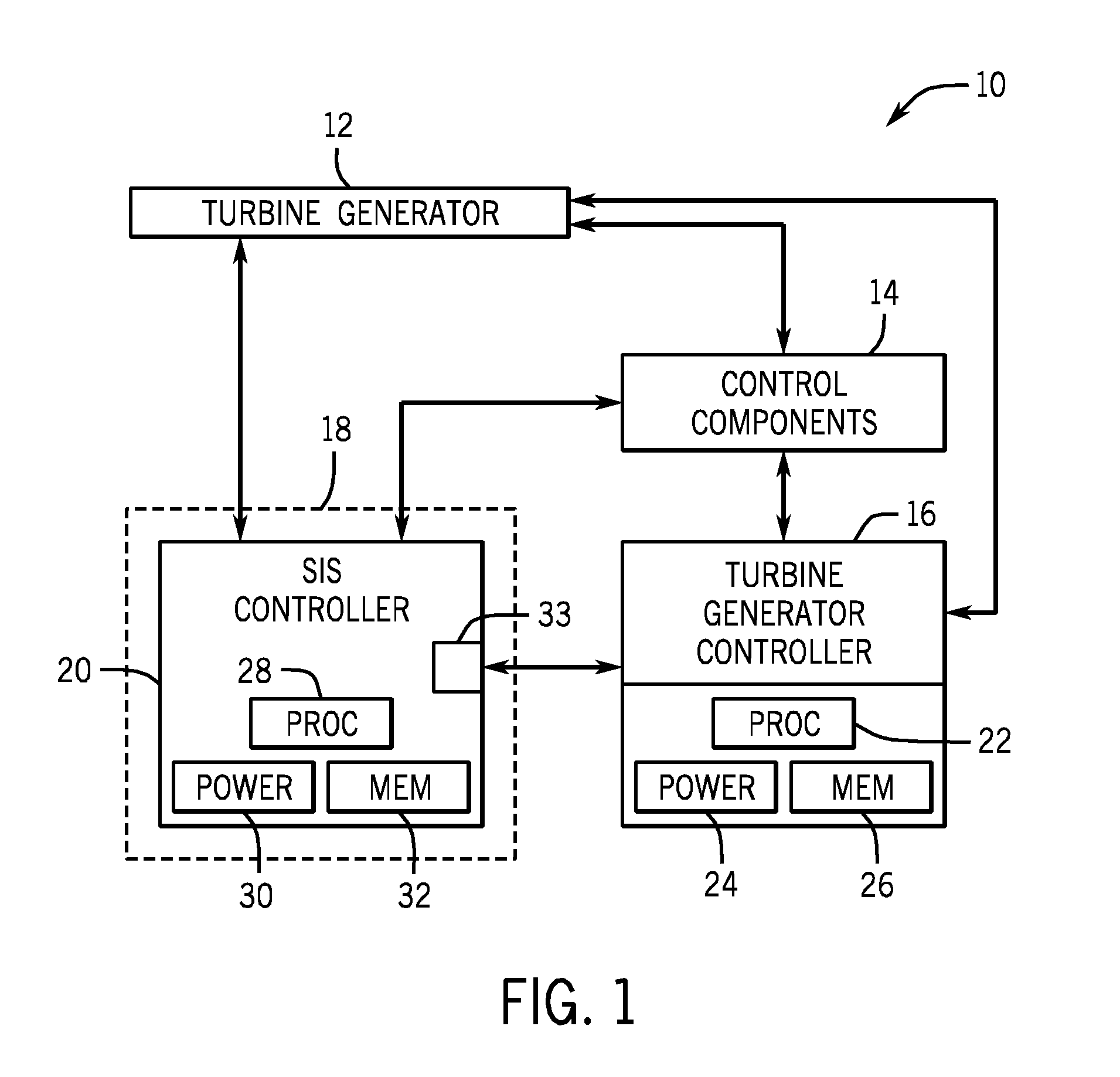
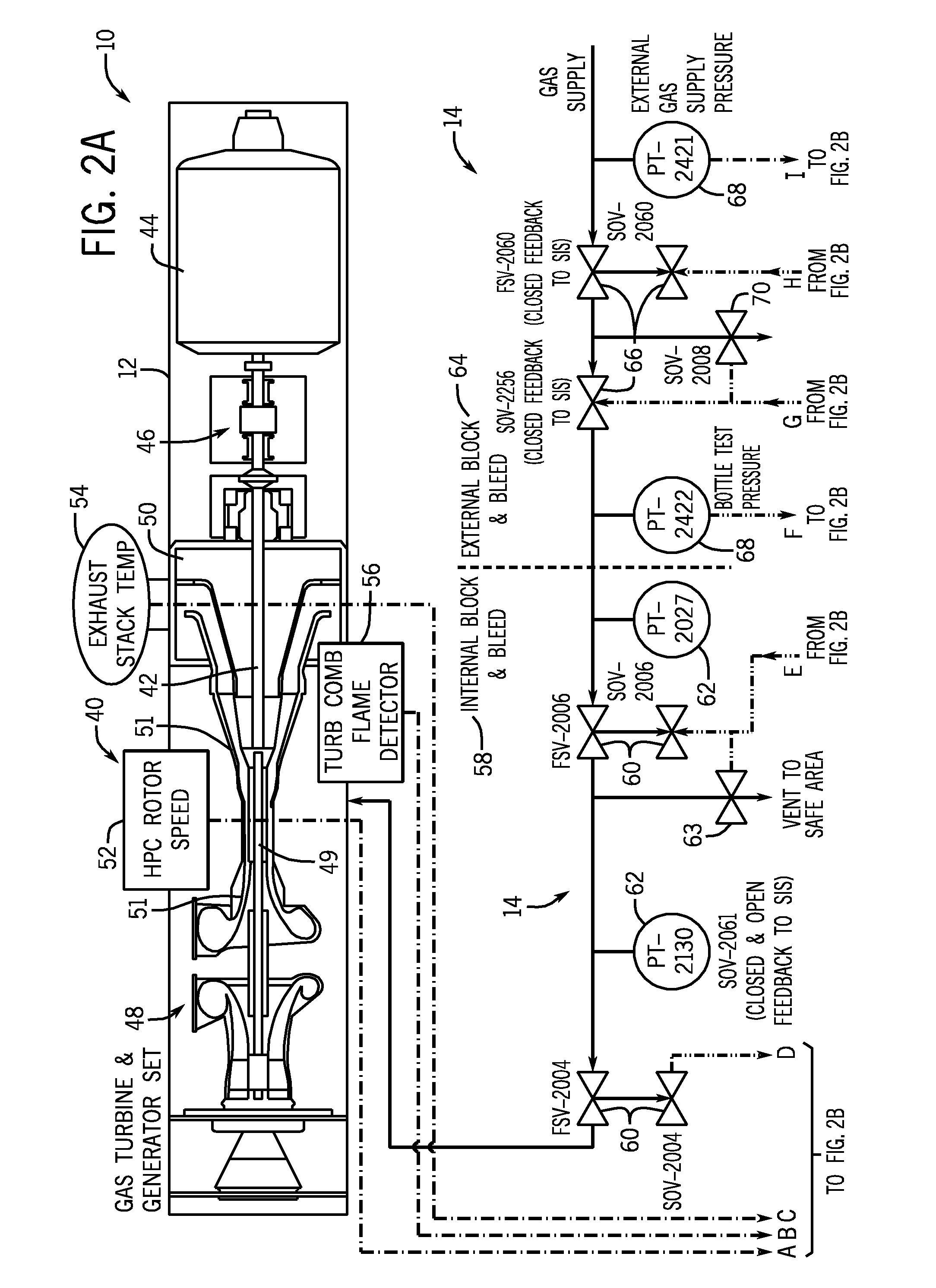
Safety instrumented system (SIS) for a turbine system
A retrofit kit for a turbine system is provided that includes a safety instrumented system (SIS) controller having a first plurality of functions and the SIS controller is configured to be coupled to a turbine-generator controller, wherein the SIS controller permits a startup function of the turbine-generator controller based on a plurality of inputs from a turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
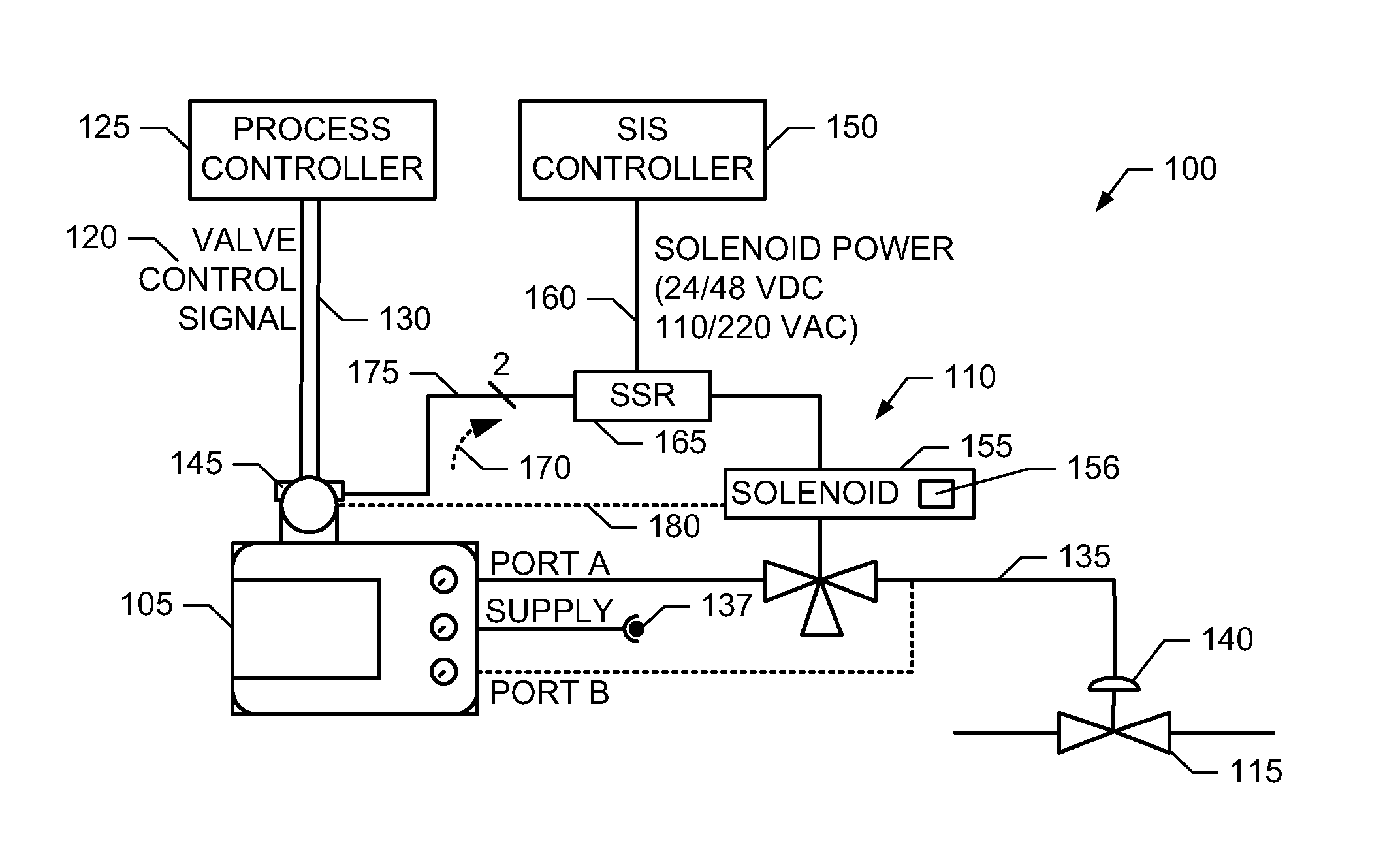
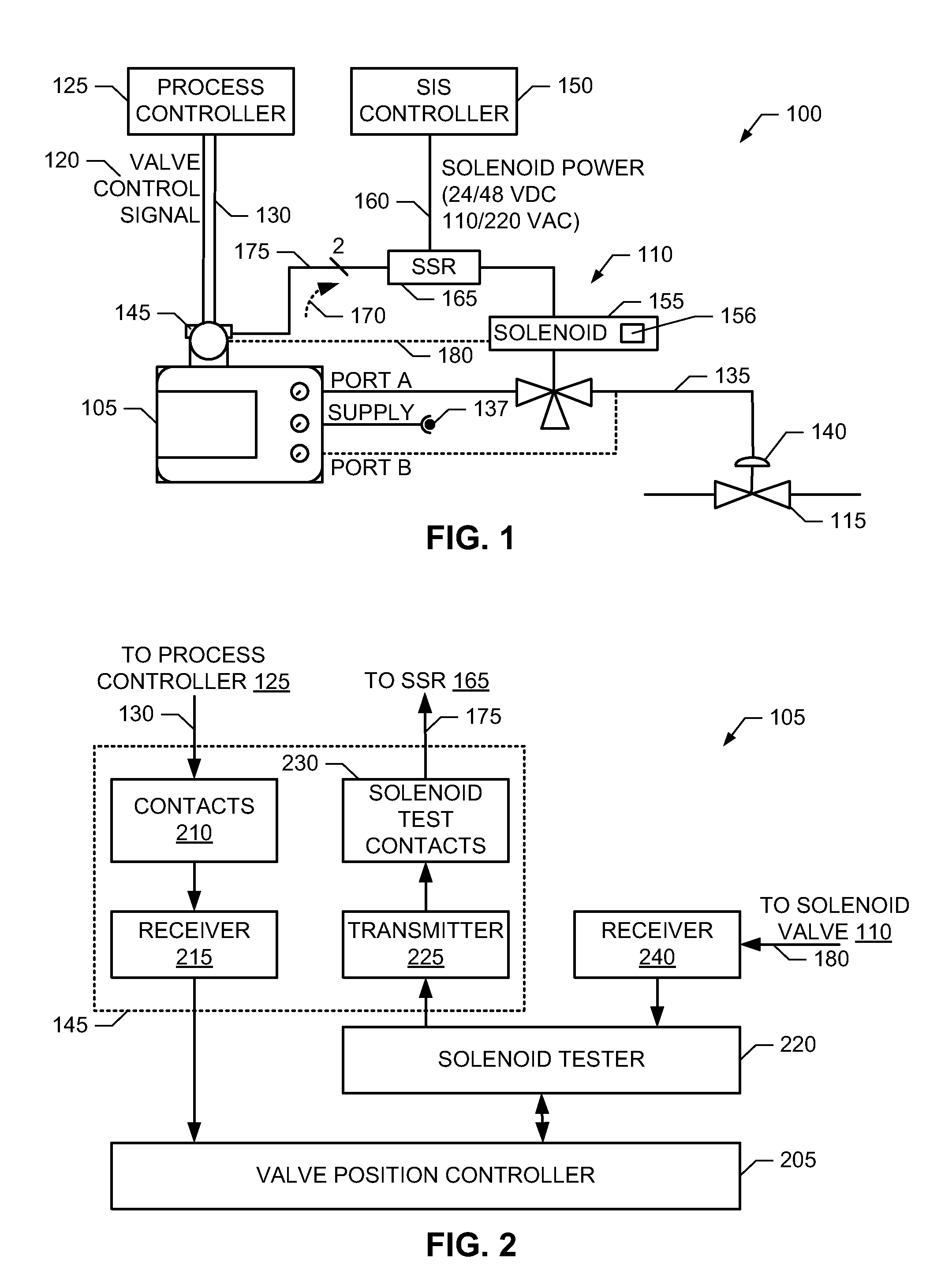
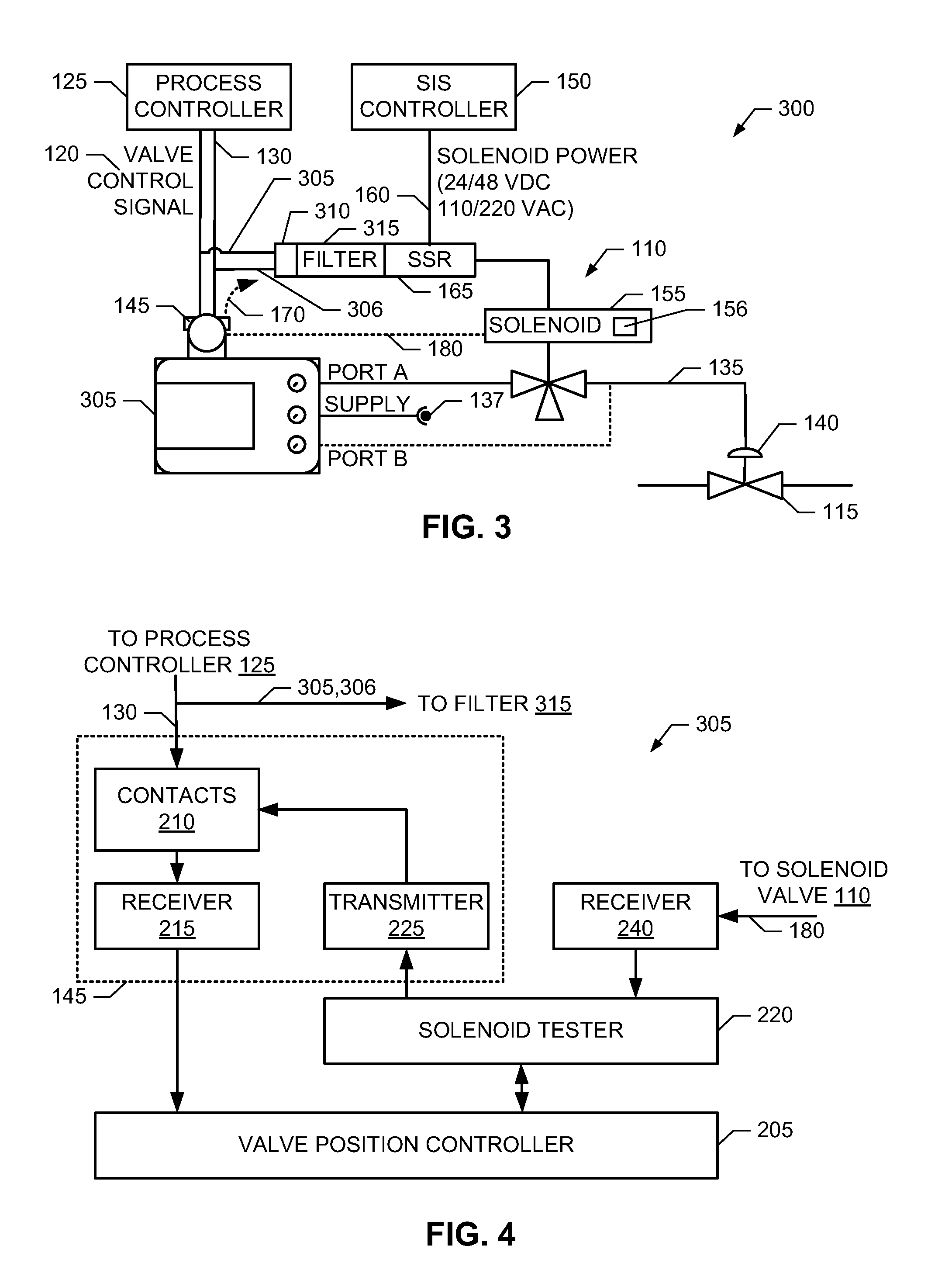
Methods, apparatus and articles of manufacture to test safety instrumented system solenoids
ActiveUS20110160917A1Mechanical power/torque controlValve arrangementsSafety instrumented systemElectricity
Example methods, apparatus and articles of manufacture to test safety instrumented system (SIS) solenoids are disclosed. A disclosed valve position control apparatus includes a relay to control a state of a solenoid and a valve positioner including a transmitter to transmit a solenoid test signal to the relay, electrical contacts to communicatively couple the solenoid test signal to the relay via one or more wires, and a solenoid tester to generate the solenoid test signal and to monitor a response of the solenoid when the solenoid test signal is transmitted to the relay to verify an operation of the solenoid.
Owner:FISHER CONTROLS INT LLC
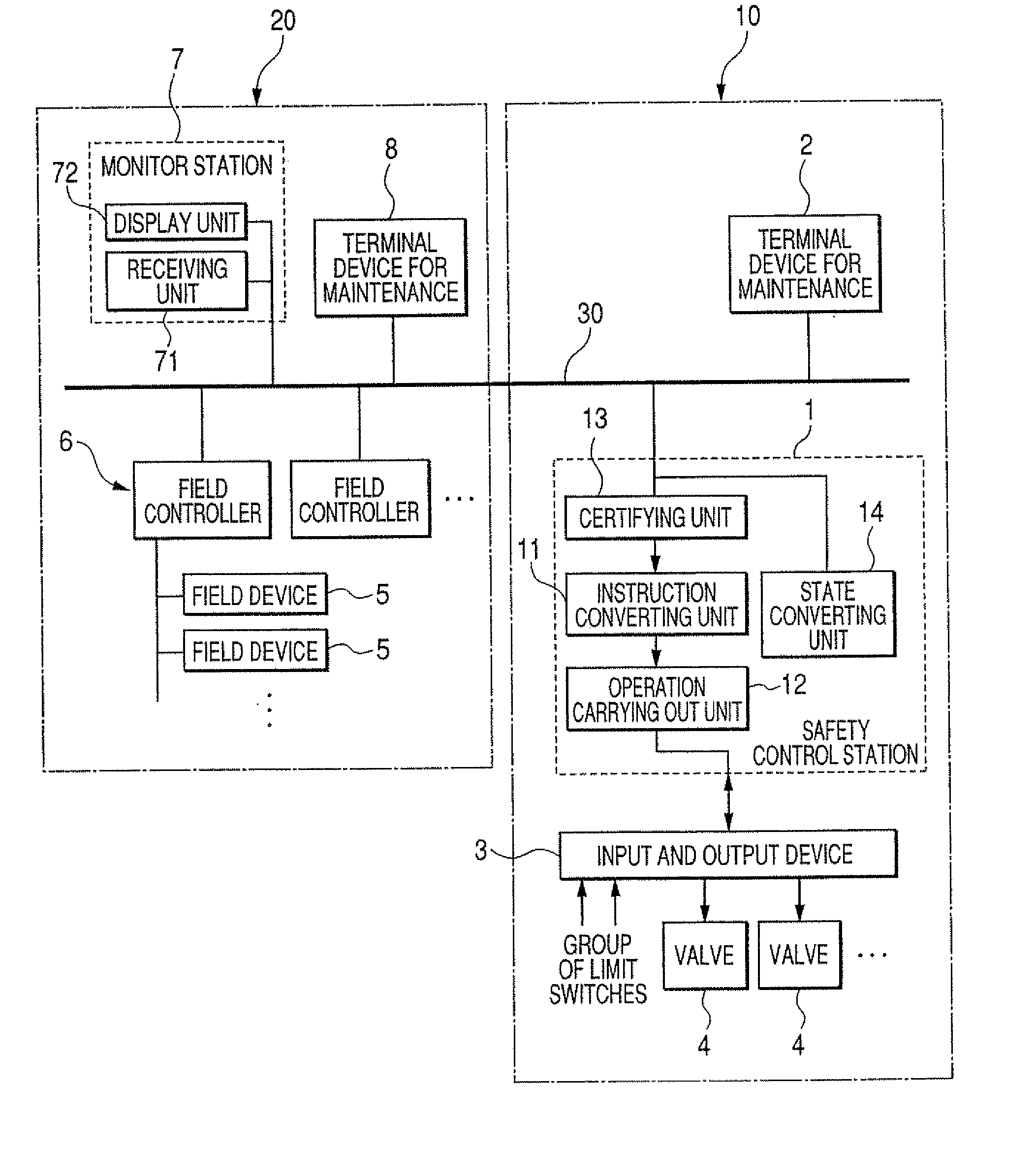
Safety instrumentation system and plant safety system
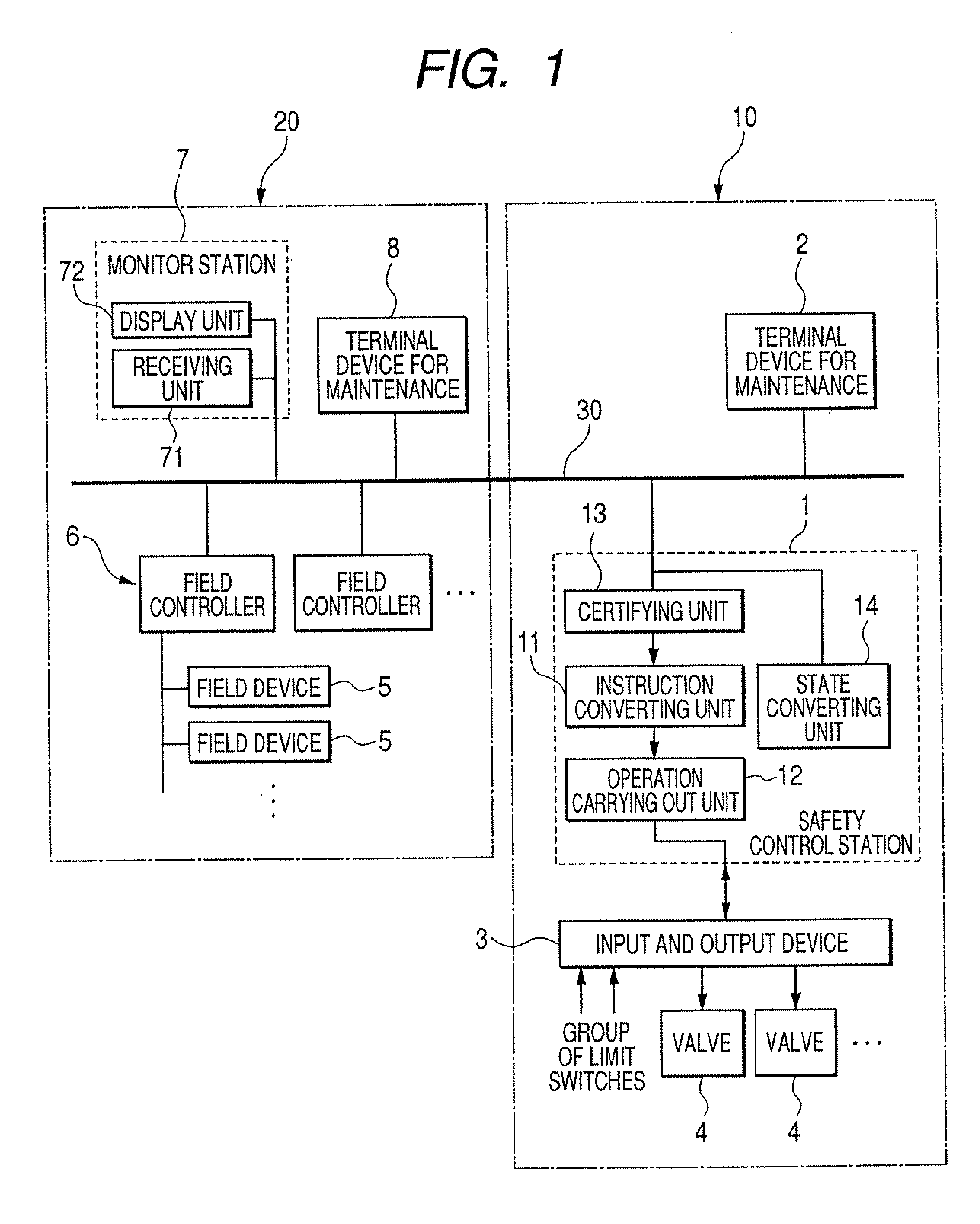
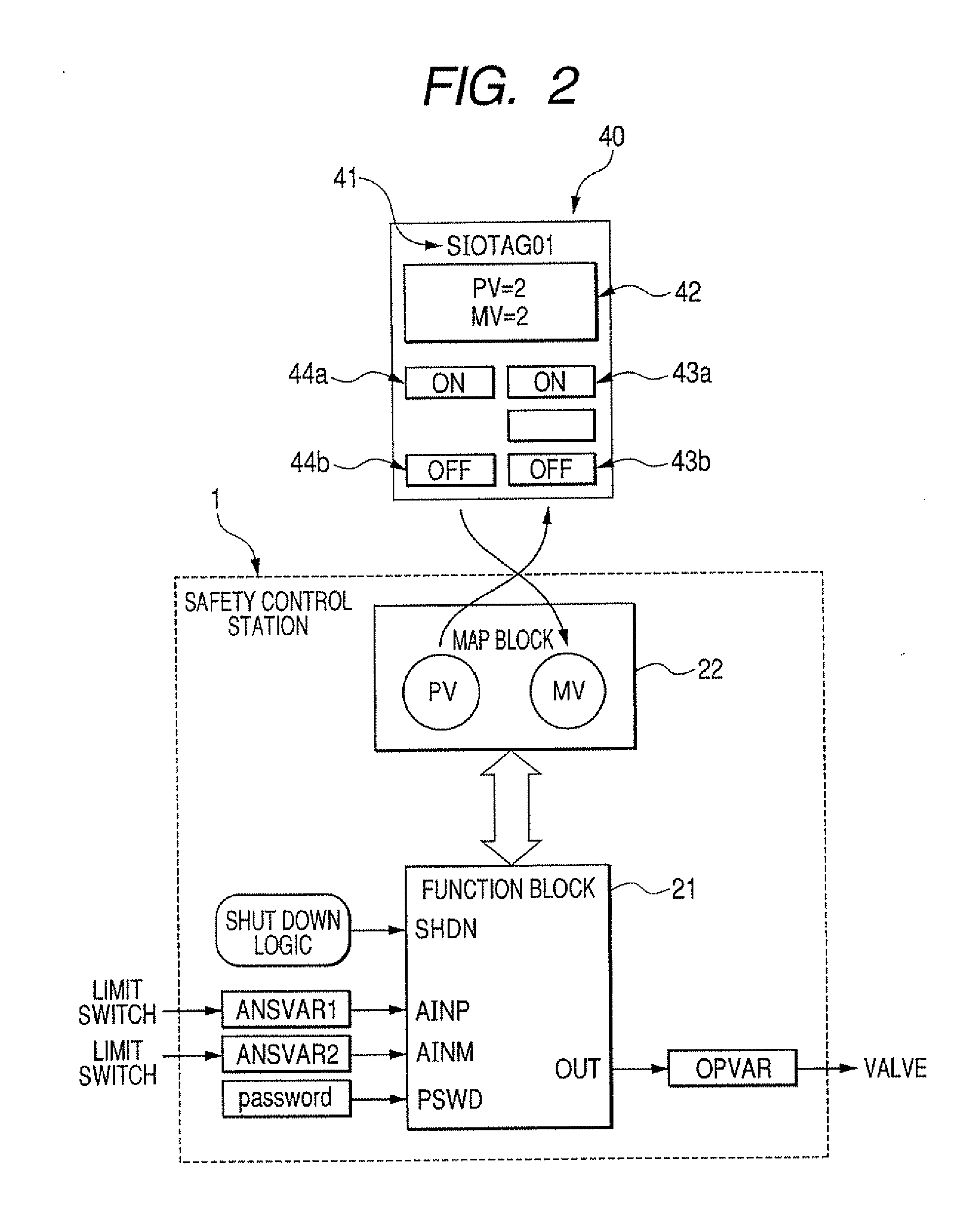
ActiveUS20080082184A1Avoid burdenBurden can be suppressedProgramme controlSafety arrangmentsSafety instrumented systemPlant safety
An instruction converting unit converts the data form of an instruction of an operation received by a receiving unit to the data form of a safety instrumentation system from the data form of a plant control system. An operation carrying out unit receives the instruction of the operation obtained by the instruction converting unit and an original instruction of the safety instrumentation system to carry out the operations, and preferentially carries out the operation of the original instruction of the safety instrumentation system when both the instructions compete with each other.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
SIL assessment unit for safety instrument system
InactiveCN104091221AReduce unscheduled parkingEnsure safe productionResourcesSafety instrumented systemSafety Integrity Level
The invention relates to an SIL (Safety Integrity Level) assessment unit of a safety instrument system and mainly solves a problem that in the prior art, a computer system, which is targeted at petrochemical devices and has functions of SIF identification, SIL allocation and SIL verification and the like, does not exist domestically yet. The SIL assessment unit for the safety instrument system is adopted and the unit includes SIFs of any number and SIL selection can be carried out for each SIF. The technical scheme of the assessment system, which has functions of safety requirement specification making, SIL verification, SIL report generation and database management solves the problem comparatively well and is applicable to the field of reliability assessment of a safety instrument system of the petroleum and petrochemical industry.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for intercontroller communications in a safety instrumented system or a process control system
ActiveCN101154103ASafety arrangmentsElectric testing/monitoringSafety instrumented systemControl system
A system provided by the present invention provides a I / O card, which is used to connect two process controllers of a same communication line. The communication line is separated from a main communication line for connecting the two process controllers to a workstation. The process controllers can access the I / O card with the mode being similar to that accessing the I / O card of field devices. After this manner, the physical hardware as well as software structure is used for communication between controllers without alteration. The communication between controllers can be programmed as generalI / O communication.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
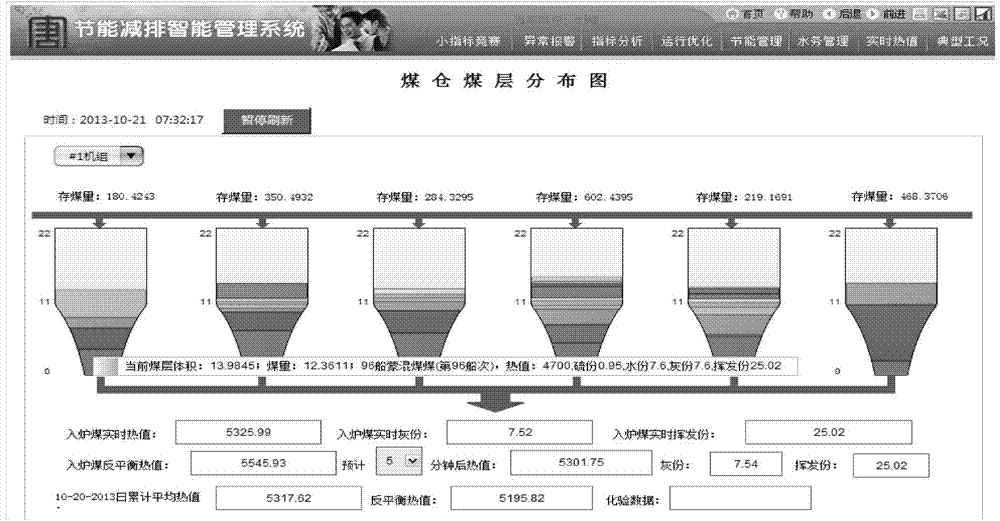
Method and system for displaying fired coal quality in real time
InactiveCN104765743AAvoid Burnout AccidentsDoes not affect calculationData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsSafety instrumented systemStart time
The invention discloses a method for displaying fired coal quality in real time. The method comprises the following steps: searching for demanded measured point data from an SIS (Safety Instrumented System) system by a measured point base via a thermal power plant system and storing searched demanded measured point data; analyzing demands by an index base according to working conditions, acquiring one or more measured point data from the measured point base, calculating index data according to an index formula and measured data acquired from the measured point base, and transmitting the generated index data to a typical working condition index database; in real time processing and updating coal storage information of each coal bunker by a real-time coal storage information management device according to the index data, wherein the coal storage information involves in beginning and terminating time of coal bed formation; acquiring the corresponding coal quality information of the coal bed including real-time fired coal by matching the beginning and terminating time with the manually inputted coal supply information, thereby obtaining the real-time fired coal heat value of the coal bunker. According to the displaying method, coal quality conditions at present and after some time can be absolutely clear.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DATANG WUSHASHAN POWER GENERATION CO LTD
Method for intercontroller communications in a safety instrumented system or a process control system
The claimed system provides an I / O card that is used to interface two process controllers over a communication line that is separate from a primary communication line connecting the two process controllers to a workstation. The process controllers can access the I / O cards in a similar manner to I / O cards used to connect to field devices. In this manner, the physical hardware and software architecture does not need to be modified for inter-controller communications. Inter-controller communications can be programmed as general I / O communication.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
Safety instrumented system (SIS) for a turbine system
A retrofit kit for a turbine system is provided that includes a safety instrumented system (SIS) controller having a first plurality of functions and the SIS controller is configured to be coupled to a turbine-generator controller, wherein the SIS controller permits a startup function of the turbine-generator controller based on a plurality of inputs from a turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Level switch with verification capability
InactiveUS6938635B2Minimal and no retrofitting effortExisting designFunctional valve typesLevel controlSafety instrumented systemRetrofitting
The present invention comprises a novel level switch which may be employed to detect liquid levels within a process vessel. The level switch of the present invention is self validating so that manual testing is not required in order to ensure proper operation and switch calibration. The switch of the present invention may be easily introduced into existing process vessel designs as a replacement for prior art level detection switches with minimal or no retrofitting effort being required. The self validating level switch of the present invention may be connected to a Safety Instrumented System (SIS) such that process control including process shutdowns to avoid overfilling and low-fluid conditions may be accomplished.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
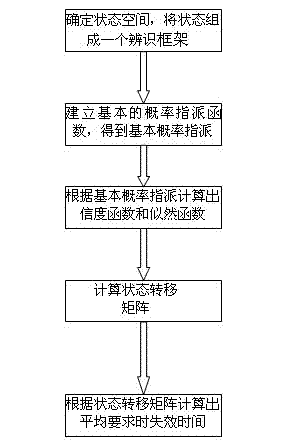
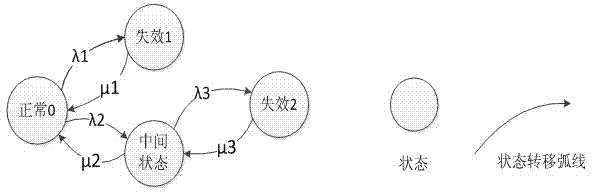
Reliability assessment method for safety instrument system based on Markov model and D-S evidence theory
InactiveCN102968569AImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsSafety instrumented systemLower limit
The invention discloses a reliability assessment method for a safety instrument system based on a Markov model and a D-S evidence theory. The reliability assessment method comprises the following steps: (1) confirming a state space according to a redundant structure of the safety instrument system and forming a discernment frame theta with states; (2) establishing a basic probability assignment function on a discernment frame power set according to various characteristics of the states and further obtaining basic probability assignment; (3) calculating a reliability function and a likelihood function according to the basic probability assignment; (4) calculating a state-transition matrix in the Markov model based on the reliability function and the likelihood function; and (5) calculating average time of failure on demand, applying the D-S evidence theory to the Markov model, calculating upper and lower limits of each state through a reliability function and a likelihood function of the D-S evidence theory, and obtaining the average probability of failure on demand of the safety instrument system. Compared with the former assessment models, the assessment model is more accurate.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Switch signal output channel detection method and structure
ActiveCN105137966AEasy to handleImprove securityElectric testing/monitoringSafety instrumented systemSwitching signal
The invention provides a switch signal output channel detection structure and a detection method. The structure comprises a switch signal output channel, an output switch, a safety switch and a power supply, wherein the safety switch is arranged between the power supply and the output switch; and the output end of the switch signal output channel is connected with the output switch. After the fact that fault happens inside or outside the switch signal output channel is detected, the safety switch is controlled to be off, the fault and the switch signal output channel can thus be isolated, the switch signal output channel is thus in a safety state, and the fault processing ability and safety of the overall safety instrument system can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUPCON TECH
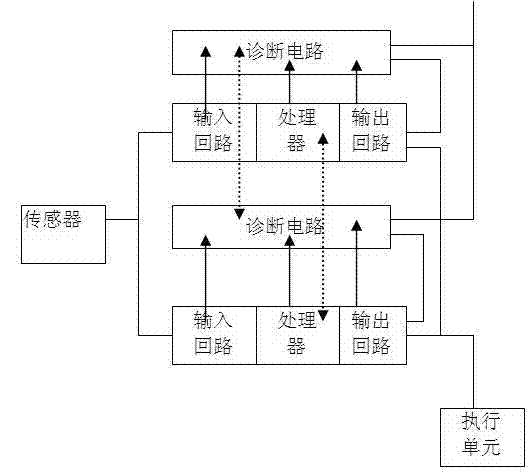
Safety instrument system based on D-S (Dempster/Shafer) evidence theory
InactiveCN102968109AStrong feedbackImprove reliabilityTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlSafety instrumented systemDecision system
The invention discloses a safety instrument system based on D-S (Dempster / Shafer) evidence theory. The safety instrument system comprises a sensor, a logic decision system and a performing unit, wherein the logic decision system comprises an input circuit, a processor, an output circuit, and a diagnosis module based on the D-S evidence theory; and the diagnosis module based on the D-S evidence theory is used for improving the reliability of the diagnosis basis through the calculation based on the D-S evidence theory in a multi-channel logical decision system according to the related feedback information among the channels. By adopting the safety instrument system based on the D-S evidence theory, the self-diagnosis function of the system can be realized through fewer hardware devices; and the safety instrument system based on the D-S evidence theory has the advantages of being lower in cost and higher in reliability and safety.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Power safety instrument system
ActiveUS9035802B2Analogue computers for trafficRemote controlled aircraftSafety instrumented systemDisplay device
A power safety system is configured to provide power information in an aircraft. The power safety system includes a power safety instrument having a power required indicator and a power available indicator, each being located on a display. A position of the power required indicator and the power available indicator represent the power available and power required to perform a hover flight maneuver. The power safety system may be operated in a flight planning mode or in a current flight mode. The power safety system uses at least one sensor to measure variables having an effect on the power required and the power available.
Owner:TEXTRON INNOVATIONS
Distributed and adaptive smart logic with multi-communication apparatus for reliable safety system shutdown
InactiveCN102077453AHigh judgment reliabilityIncrease flexibilitySafety arrangmentsAc-dc conversionSafety instrumented systemProcess safety
A safety instrumented systems (''SIS'') for monitoring and controlling chemical and other industrial process field devices that are responsive to signals for the emergency shutdown of the process or system includes associated process safety logic solver units with a hardwired communication network and a wireless communication network, each of which networks is connected to the safety logic solver and to each of the multiple field devices in order to significantly improve the reliability of communications in the event of the emergency shutdown system, reduce unwanted trips, and adapt to process conditions by failing to safe mode in dynamic conditions that are beyond the capability of prior art logic solvers.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
High pressure blowout preventer system
A BOP system for use in a high pressure subsea environment, including a BOP stack including a lower marine riser package and a lower stack portion, the lower stack portion having a plurality of BOP rams attached to a subsea wellhead. The system also includes a riser subsystem extending from a drilling vessel to the BOP stack and providing fluid communication therebetween, a ship board subsystem electronically, mechanically, and hydraulically connected to the BOP stack and the riser subsystem to control the functions of the BOP stack and the riser subsystem, and a safety instrumented system having a surface logic solver and at least one subsea logic solver, the safety instrumented system in communication with at least a portion of the BOP rams to act as a redundant control system in case of failure of the ship board subsystem.
Owner:HYDRIL USA DISTRIBUTION LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com