Patents
Literature
55results about "Wired telephone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
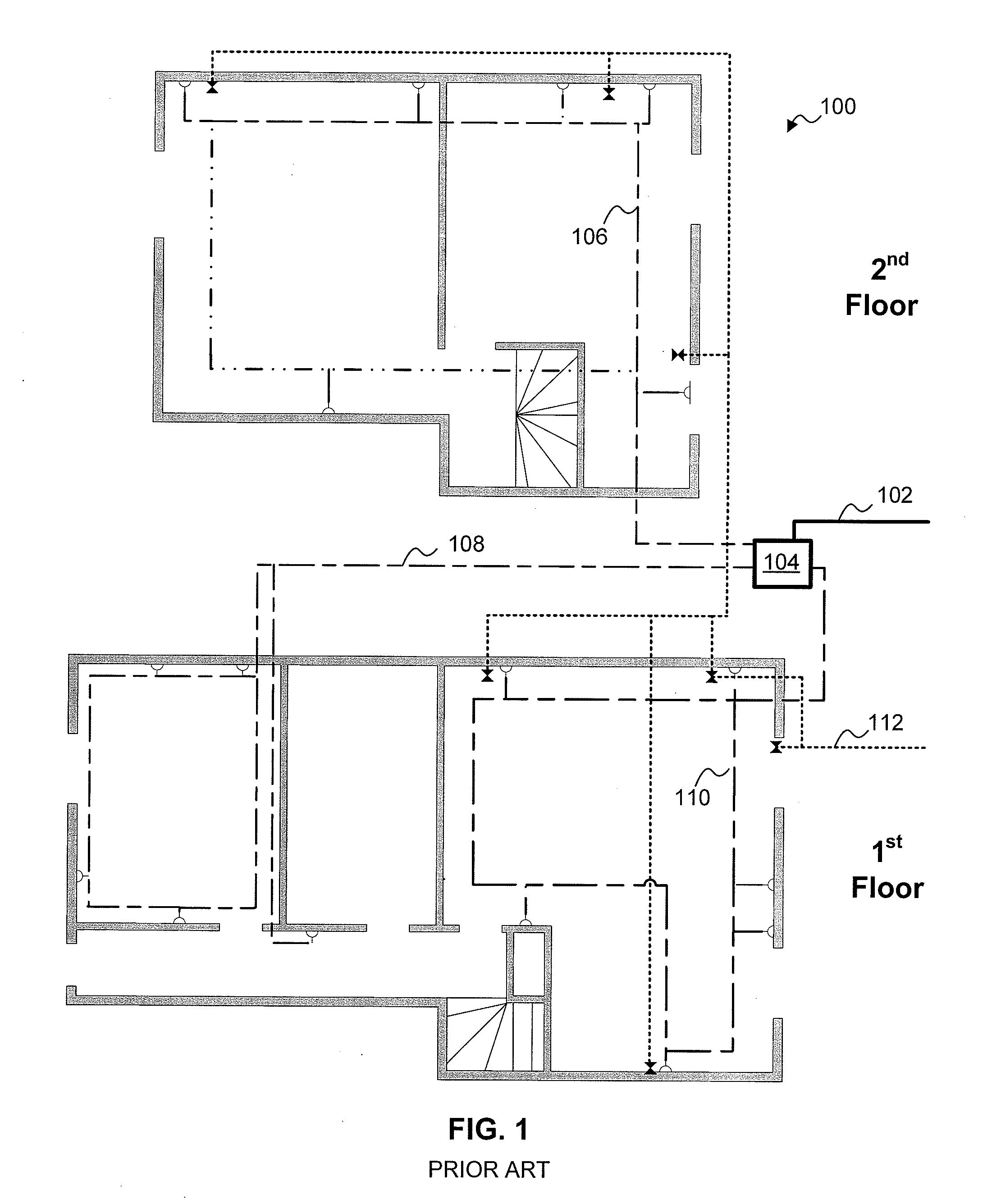
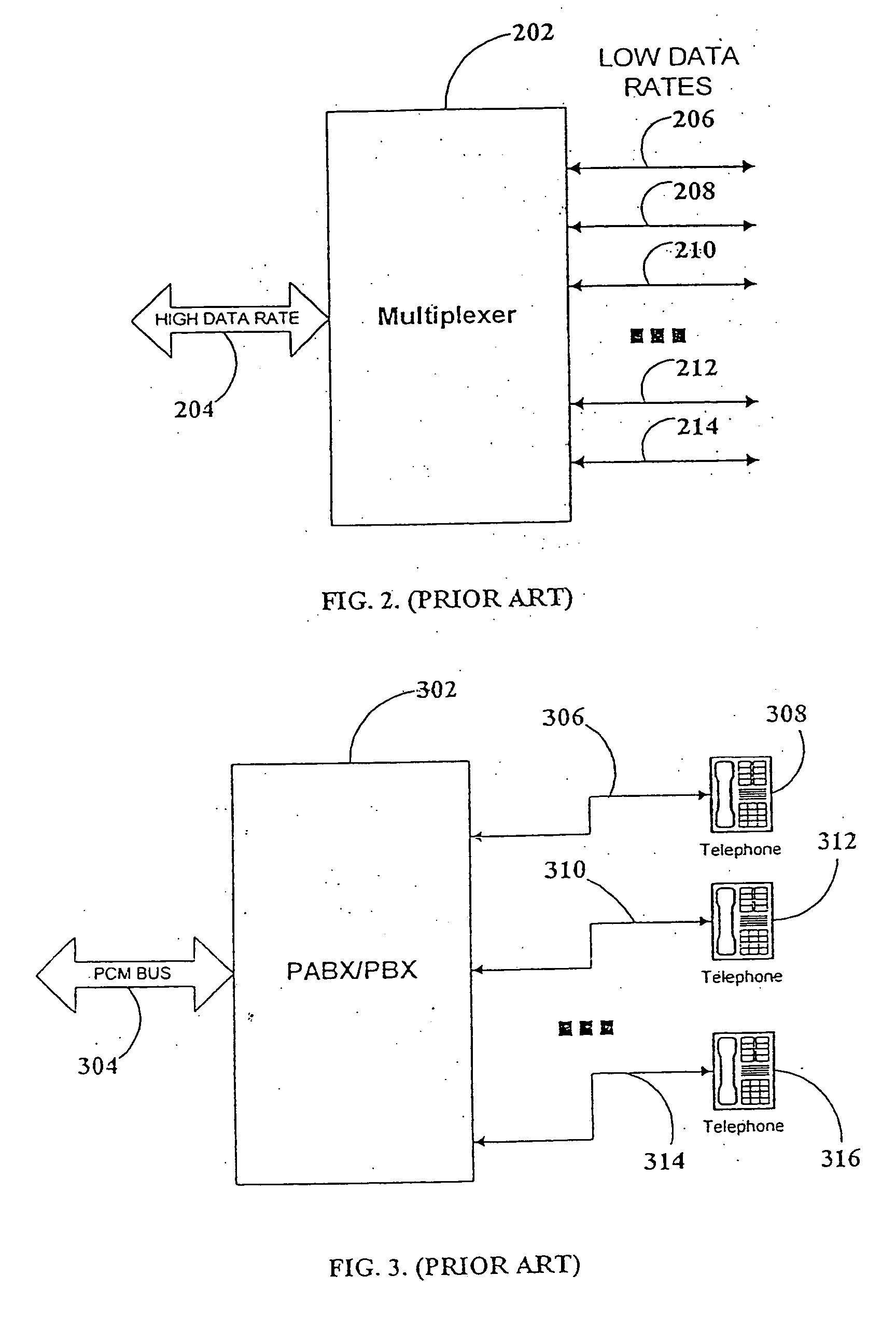
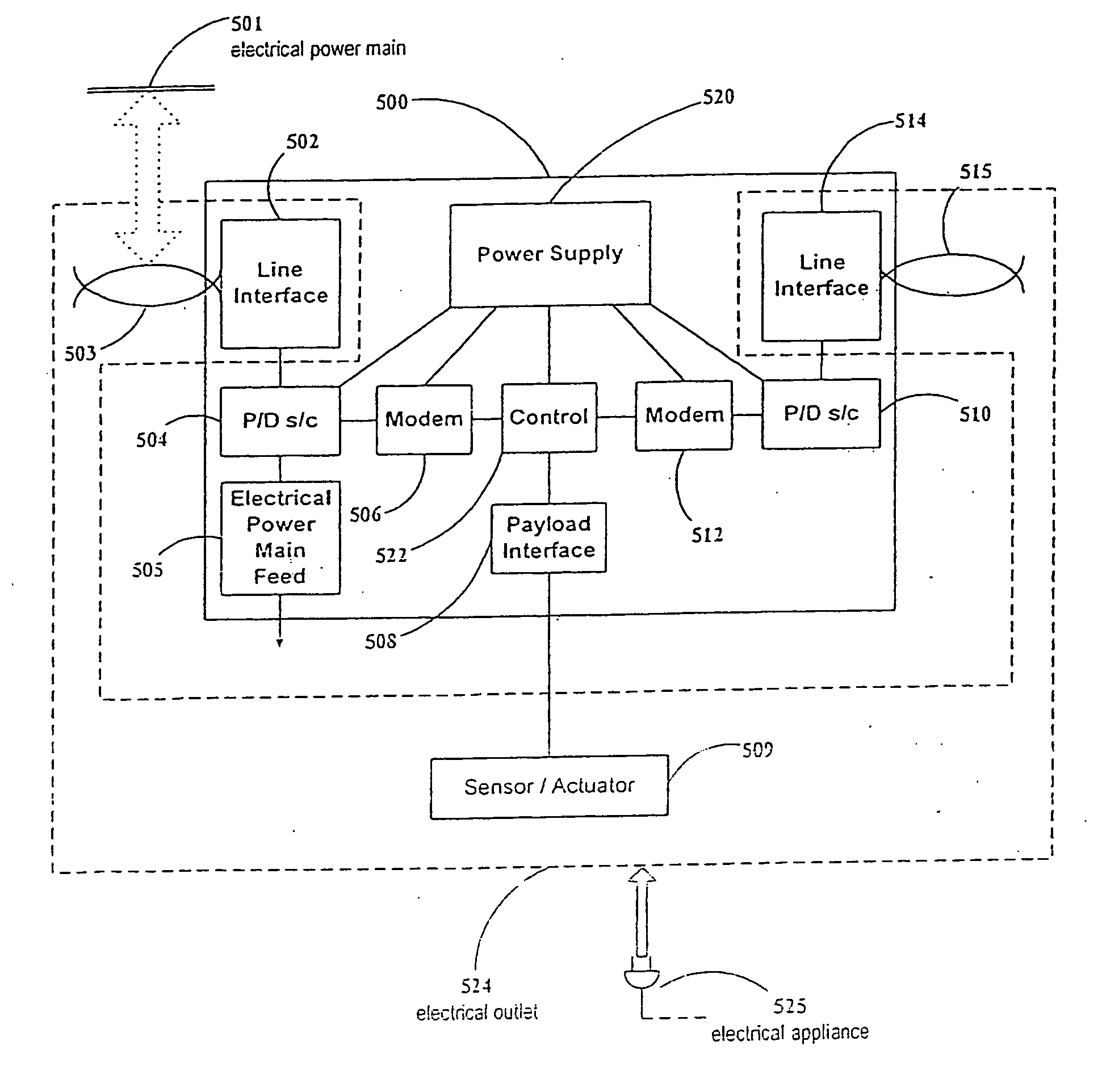
Multi-Wideband Communications over Multiple Mediums within a Network
ActiveUS20070229231A1Systems using filtering and bypassingInterconnection arrangementsQuality of serviceMultiple frequency
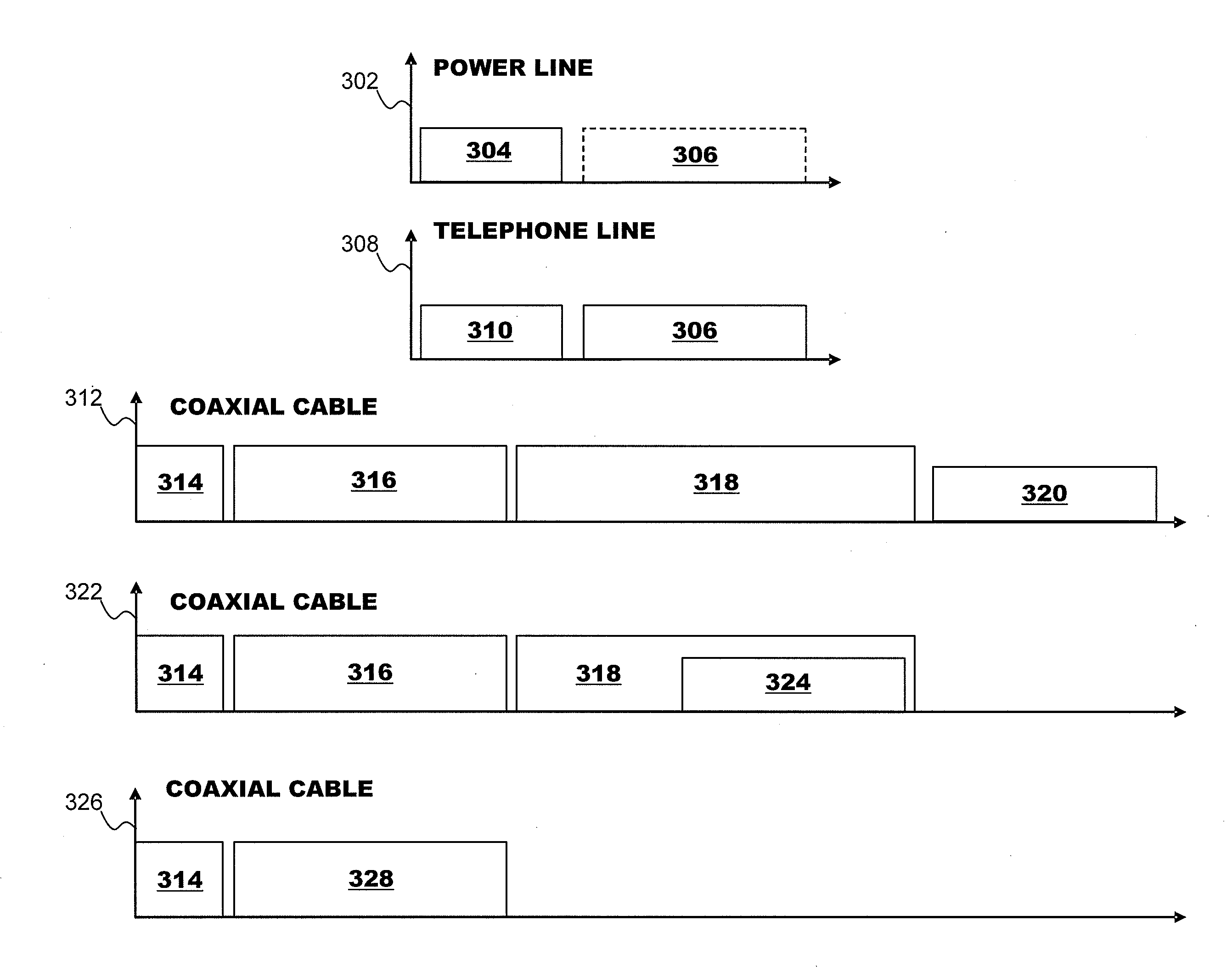
A powerline communications device comprises a powerline communications interface and at least one other communications interface configured to communicate over a computing network. The powerline communications interface is further configured to receive electrical power. The computing network may comprise mediums including powerlines, telephone lines, and / or coaxial cables. In some embodiments, the powerline communications interface may communicate with a network apparatus, such as a personal computer, via an Ethernet interface. The powerline interface, the telephone line interface, and / or the coaxial cable interface may all be associated with the same media access control (MAC) address. The powerline communications device may receive a message via a first medium and repeat the message via a second medium based on a quality of service (QoS) metric. In some embodiments, the powerline communications device may communicate using multiple frequency bands.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
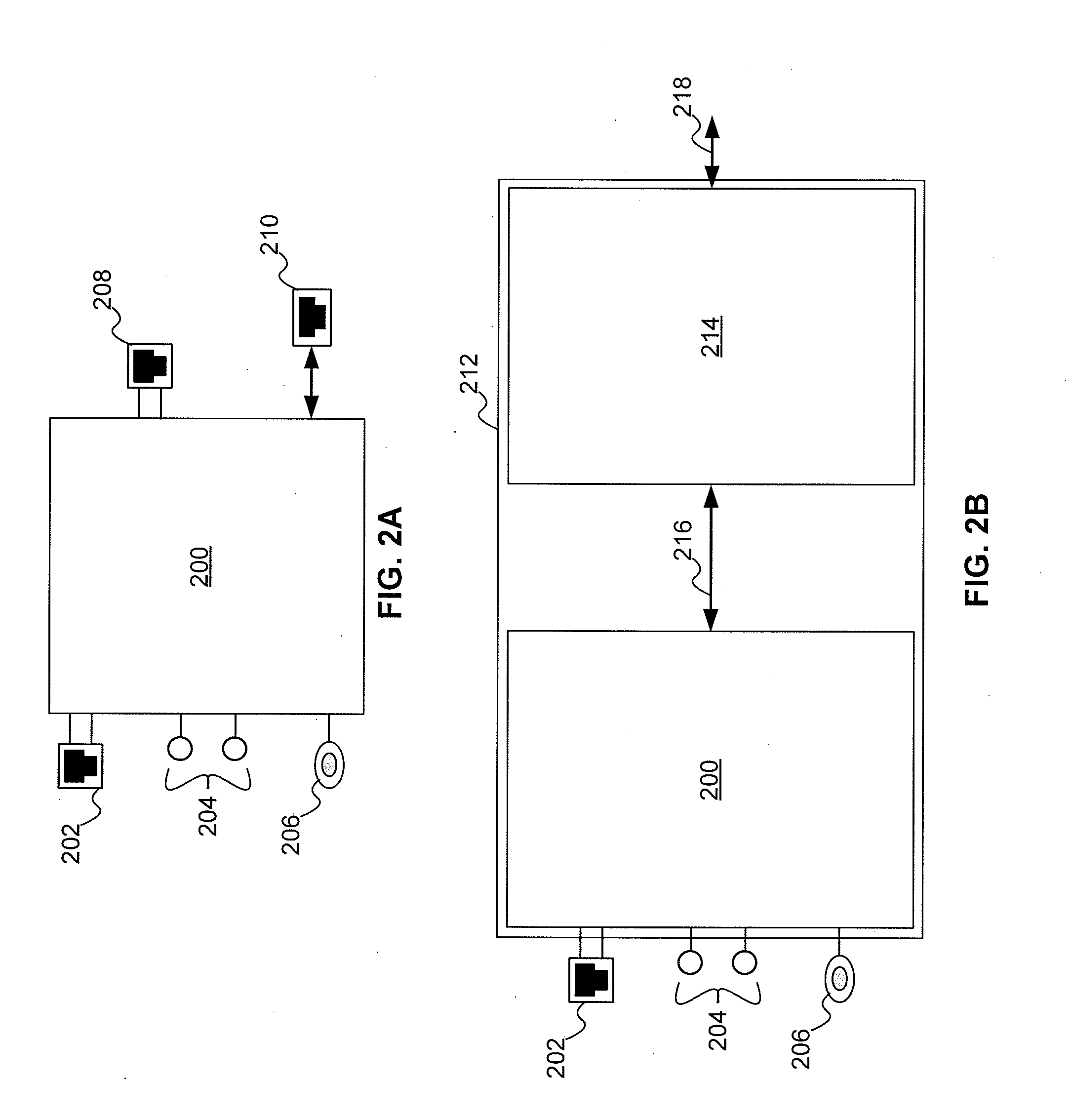
Multi-wideband communications over multiple mediums
InactiveUS8406239B2Electric signal transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceMultiple frequency
A powerline communications device comprises a powerline communications interface and at least one other communications interface configured to communicate over a computing network. The powerline communications interface is further configured to receive electrical power. The computing network may comprise mediums including powerlines, telephone lines, and / or coaxial cables. In some embodiments, the powerline communications interface may communicate with a network apparatus, such as a personal computer, via an Ethernet interface. The powerline interface, the telephone line interface, and / or the coaxial cable interface may all be associated with the same media access control (MAC) address. The powerline communications device may receive a message via a first medium and repeat the message via a second medium based on a quality of service (QoS) metric. In some embodiments, the powerline communications device may communicate using multiple frequency bands.
Owner:GIGLE SEMICON
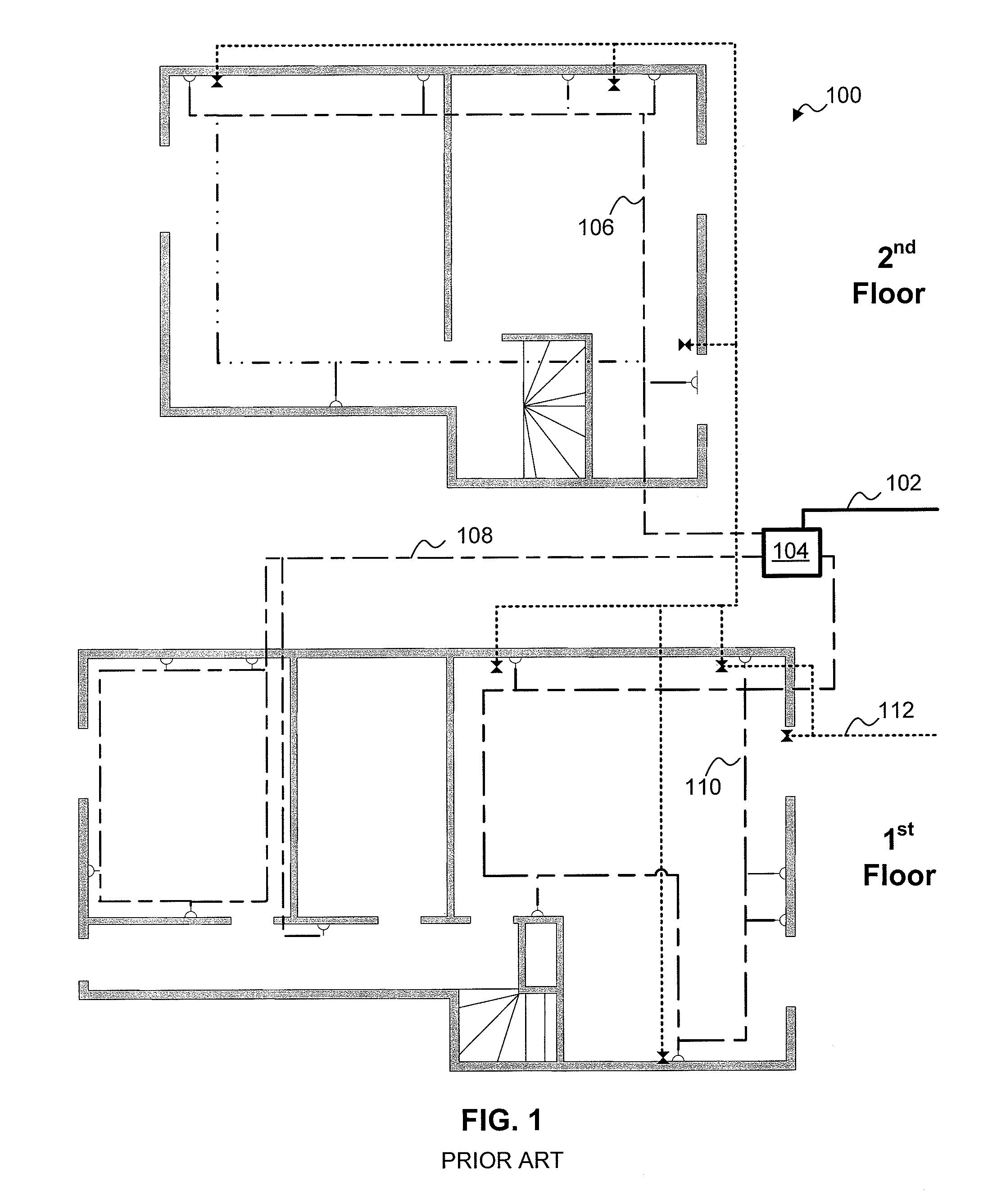
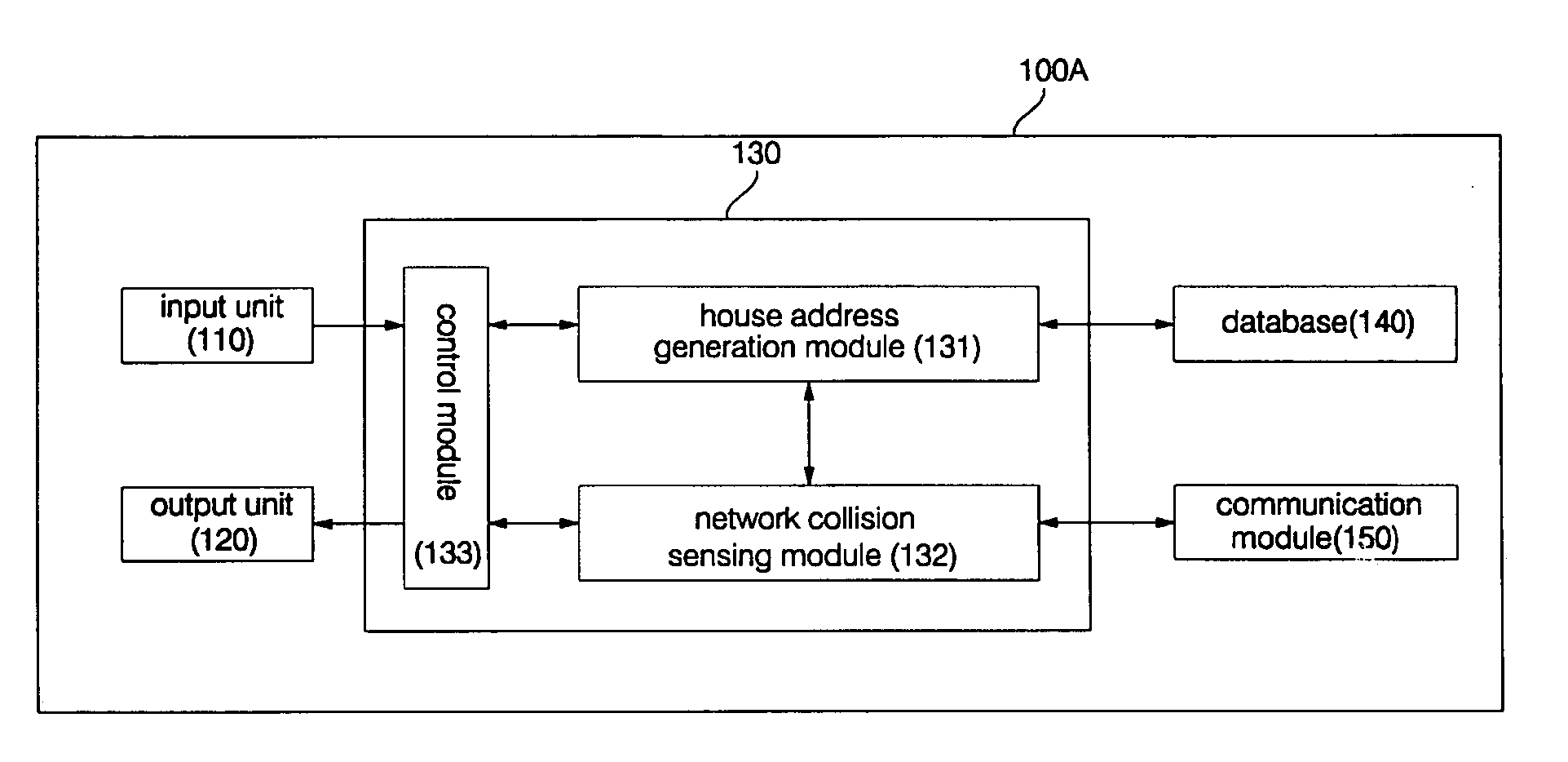
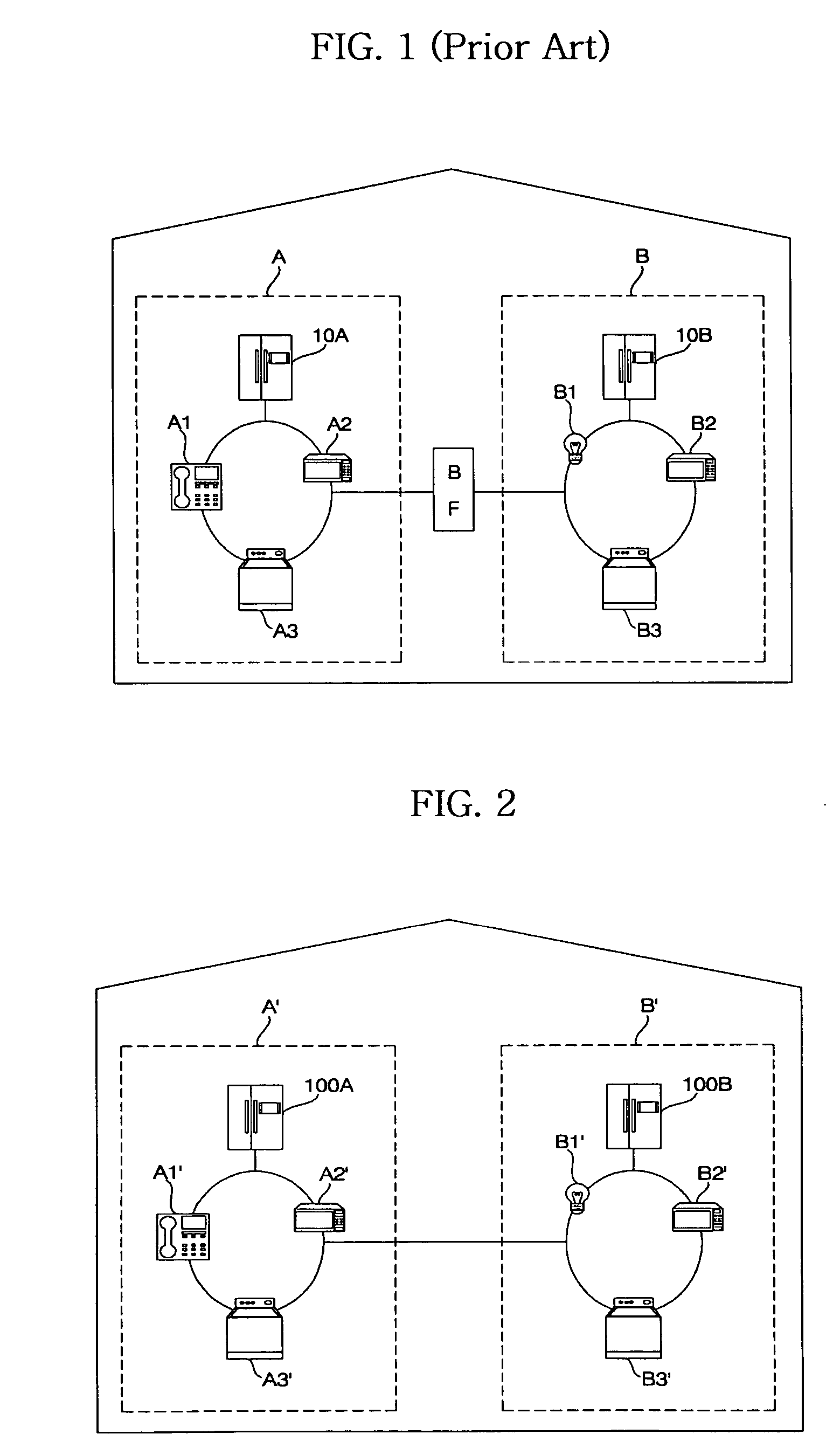
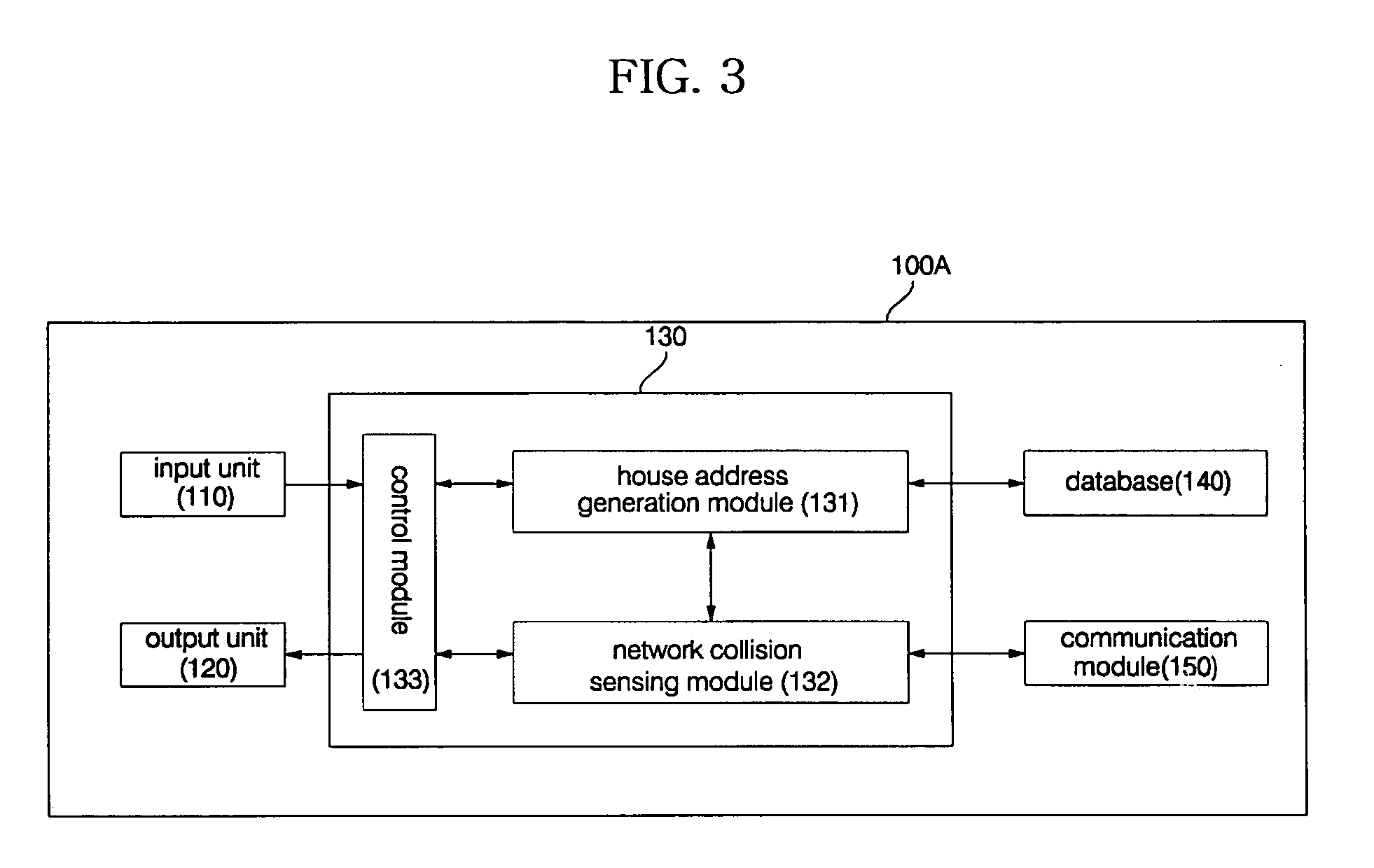
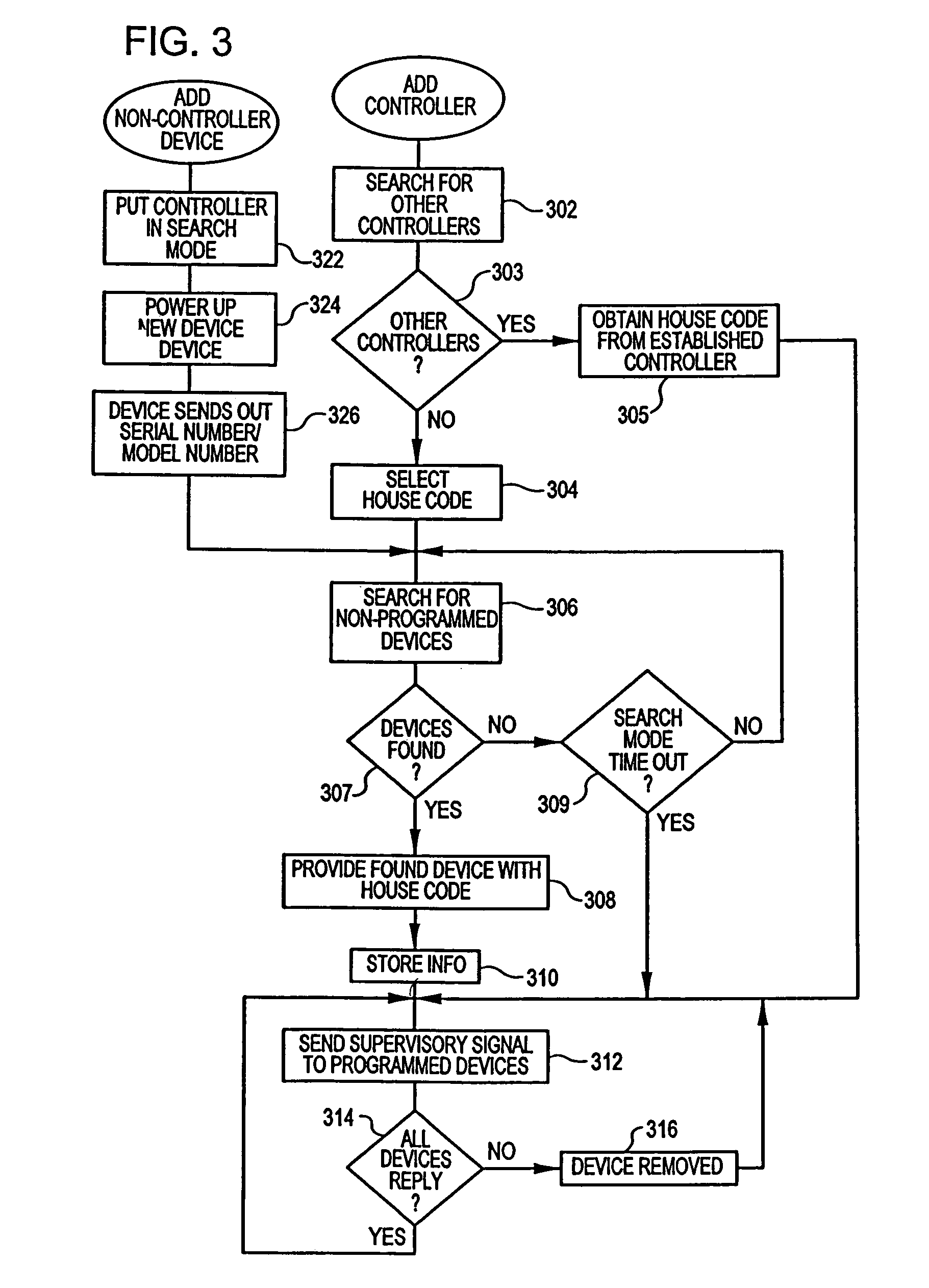
Home appliance network system and method for operating the same
InactiveUS20050002408A1Blocking in networkImprove ease of useInterconnection arrangementsPower distribution line transmissionEngineeringHome appliance
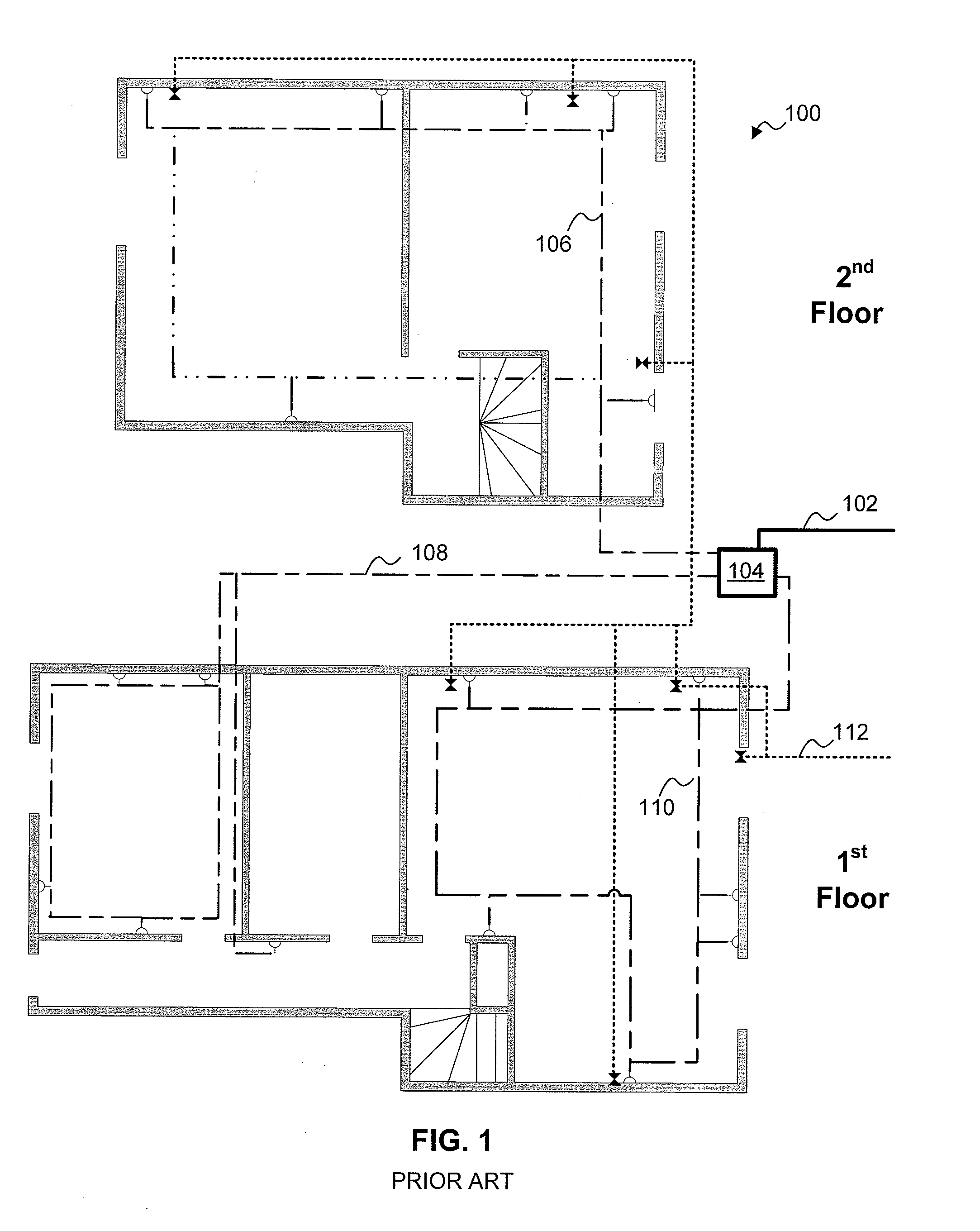
A home appliance network system and a method for operating the same, wherein a network master can not only automatically generate a unique house address of a corresponding home, but also sense a network collision of the corresponding home with a neighboring home to maintain house address uniqueness. The network master manages / controls one or more home appliances connected to a network of the corresponding home and determines whether the generated house address collides with that of the neighboring home. If the generated house address is determined to collide with that of the neighboring home, the network master automatically changes the house address to a new one to maintain house address uniqueness. As a result, the network master can prevent a network interference / collision with the neighboring home, thereby increasing security and stability of the home appliance network system at low cost.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
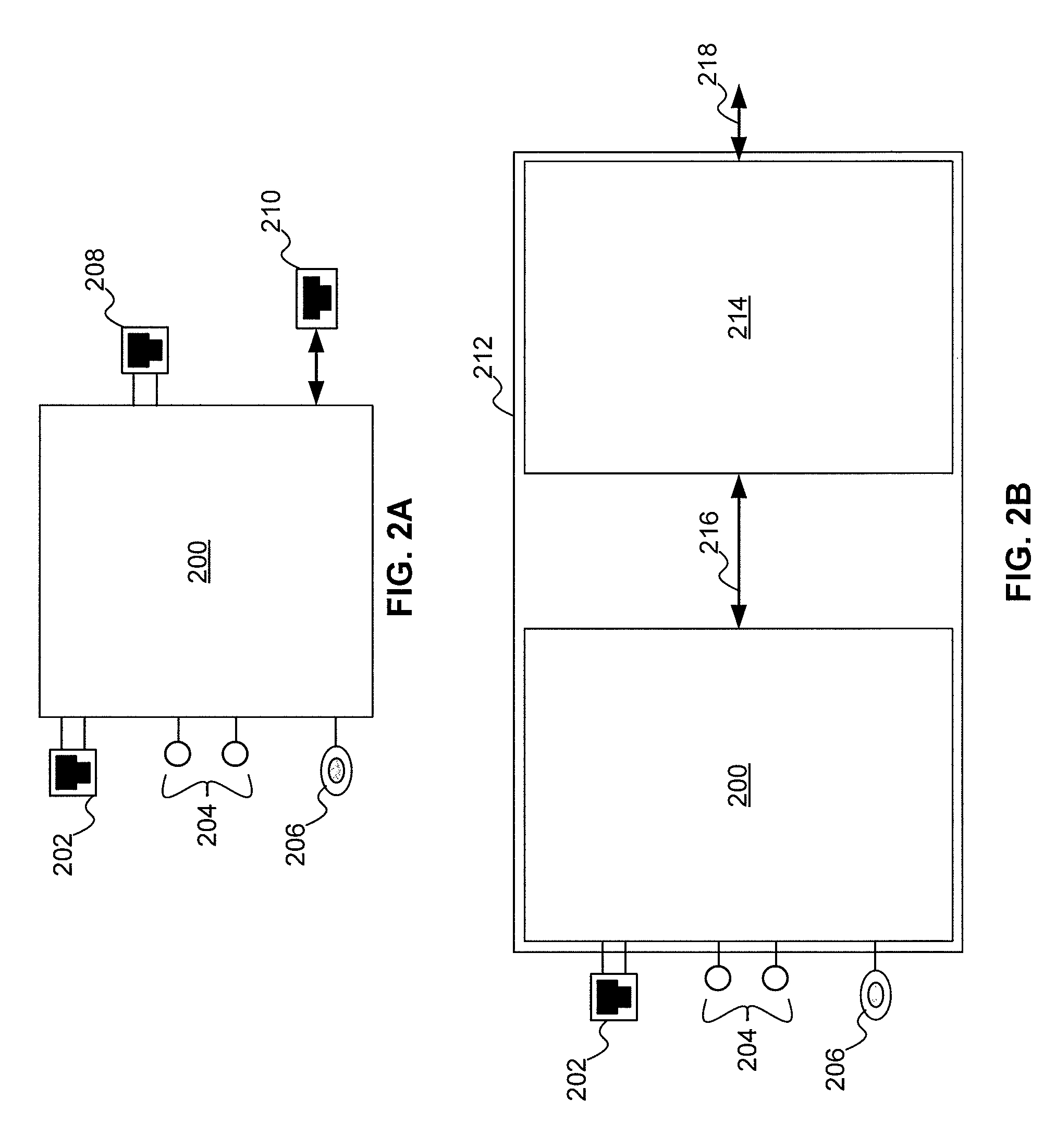
Modular outlet
ActiveUS20050010954A1Easy and simple upgradingSubstations coupling interface circuitsImproving S/N for transmission/receivingExpansion cardModularity
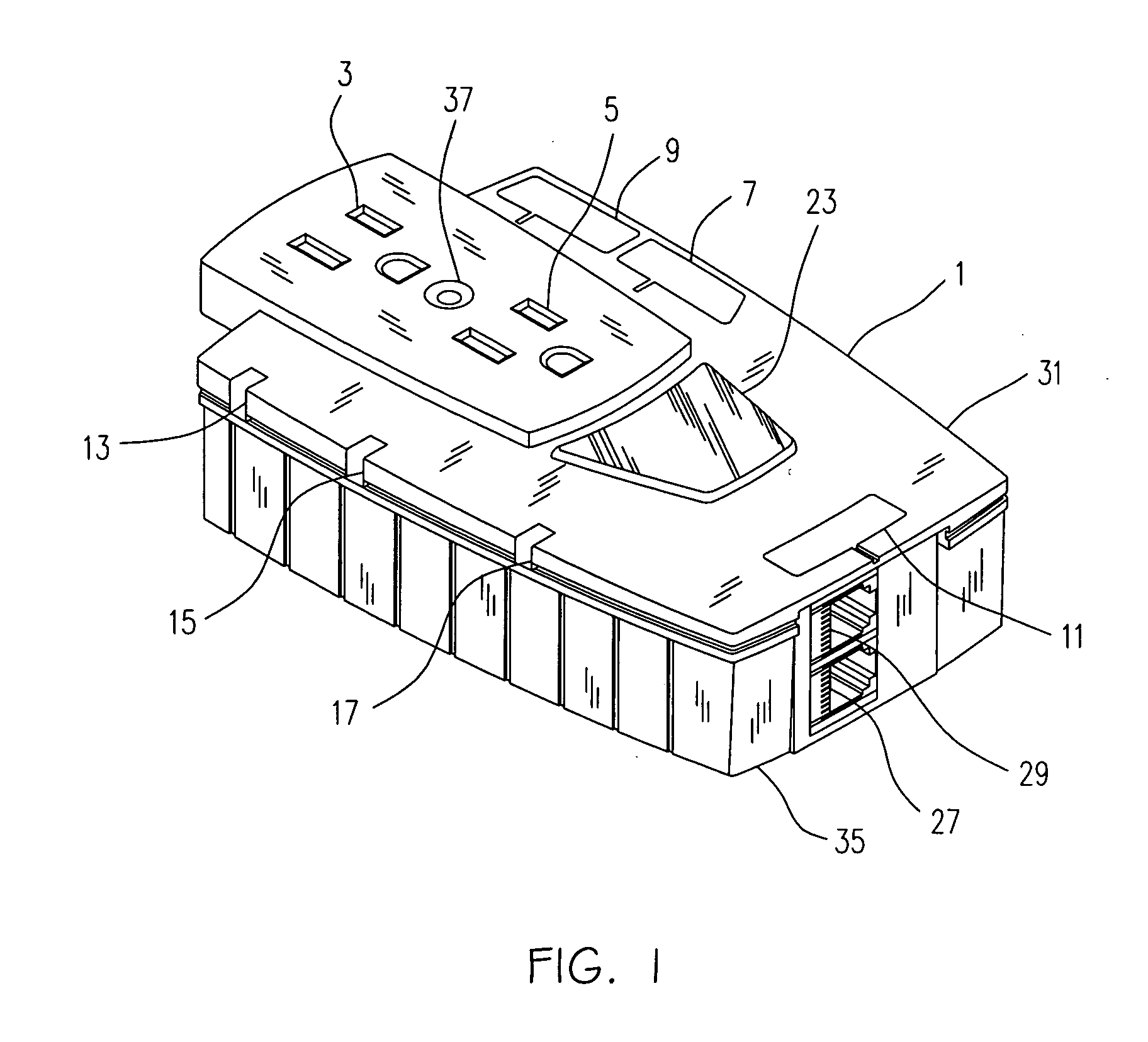
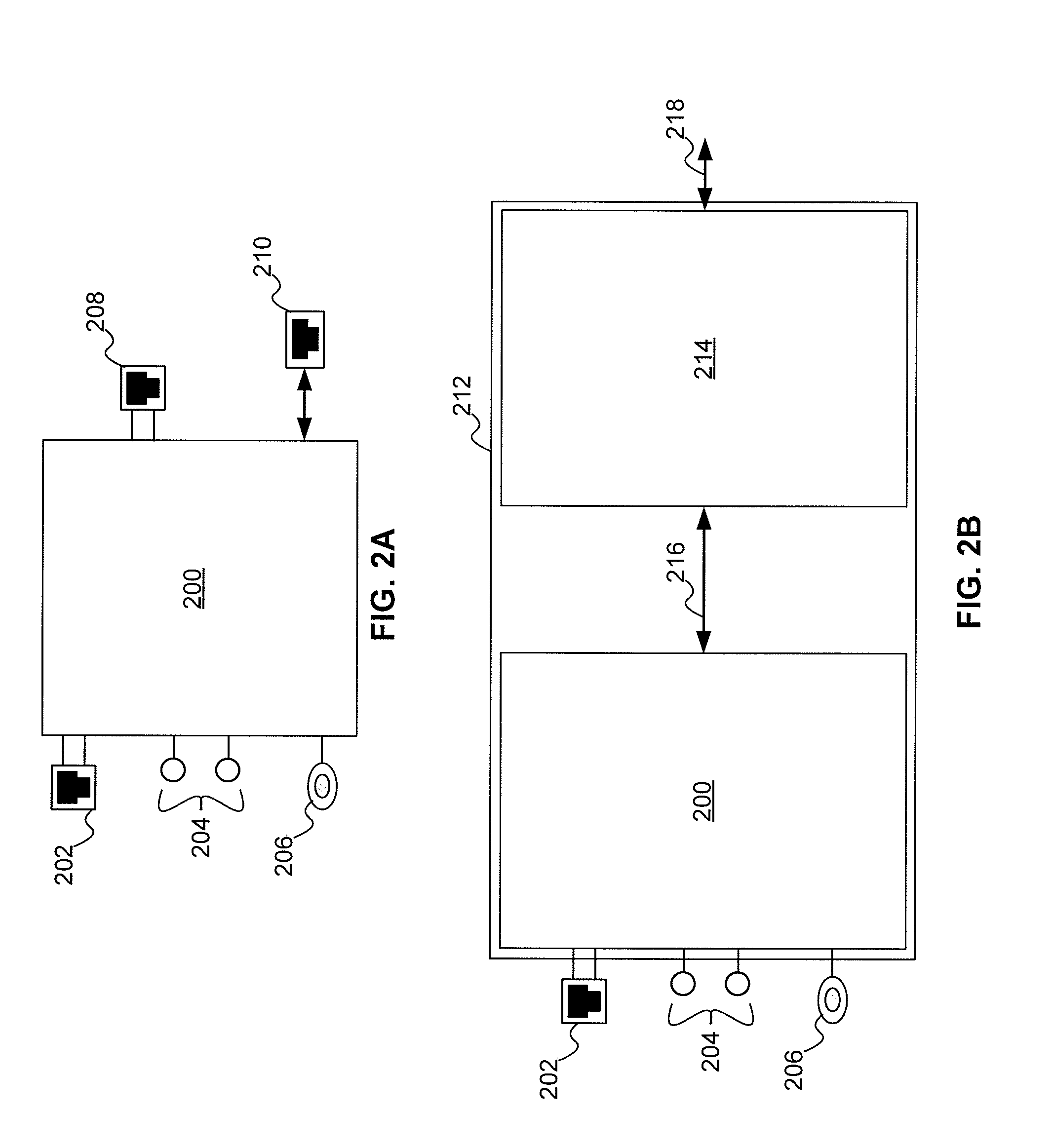
In conjunction with a wiring in a house carrying data network signal, a modular outlet comprising of a base module and interface module. The base module connects to the wiring and attached to a wall. The interface module provides a data unit connection. The interface module is mechanically attached to the base module and electrically connected thereto. The wiring may also carry basic service signal such as telephone, electrical power and cable television (CATV). In such a case, the outlet will provide the relevant connectivity either as part of the base module or as part of the interface module. Both proprietary and industry standard interfaces can be used to interconnect the module. Furthermore, a standard computer expansion card (such as PCI, PCMCIA and alike) may be used as interface module.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC +1
Two wire communication system
InactiveUS6459363B1Without loss of data transmission timeElectric signal transmission systemsTransmission/receiving by adding signal to waveElectric power transmissionElectrical conductor
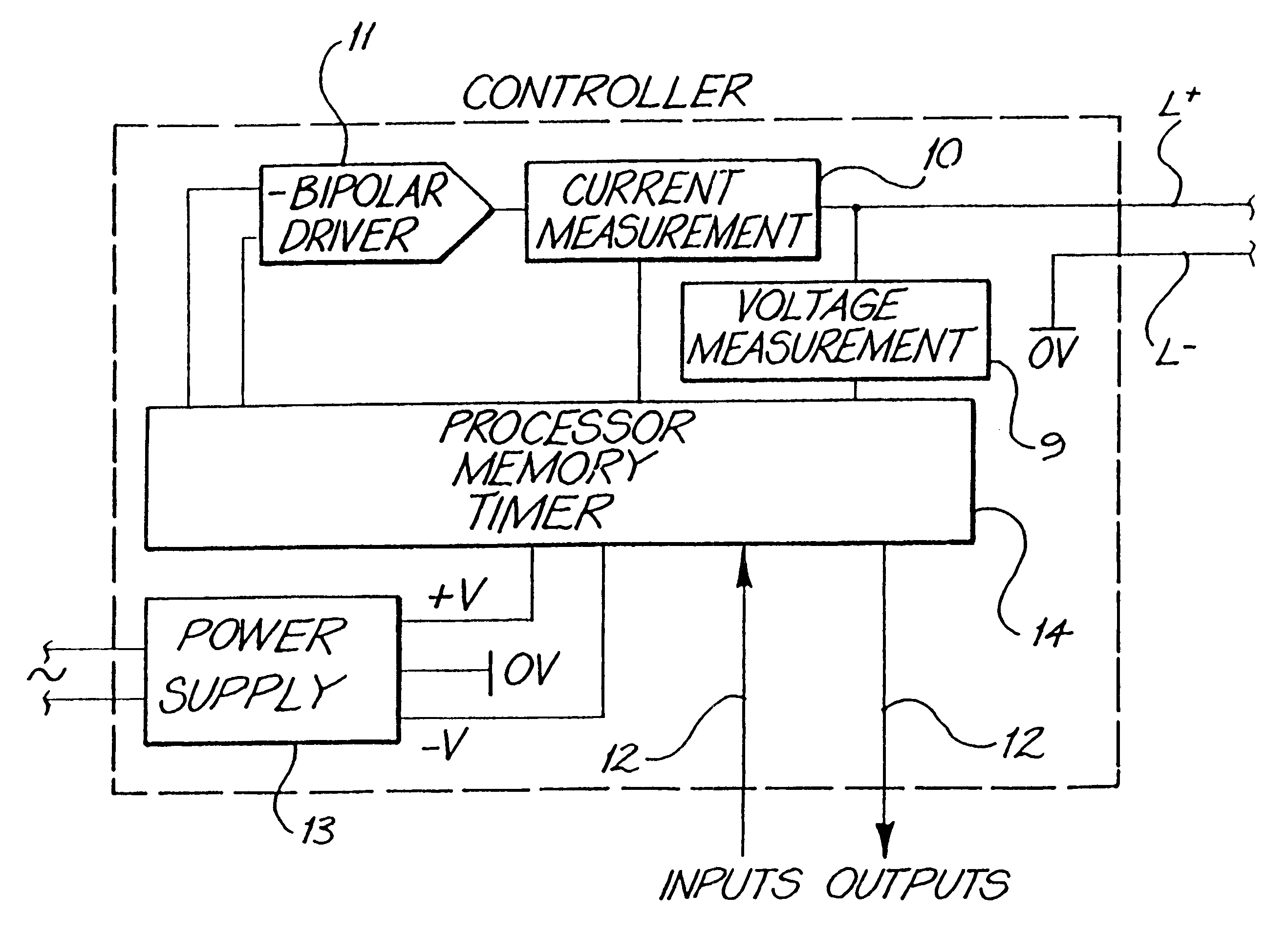
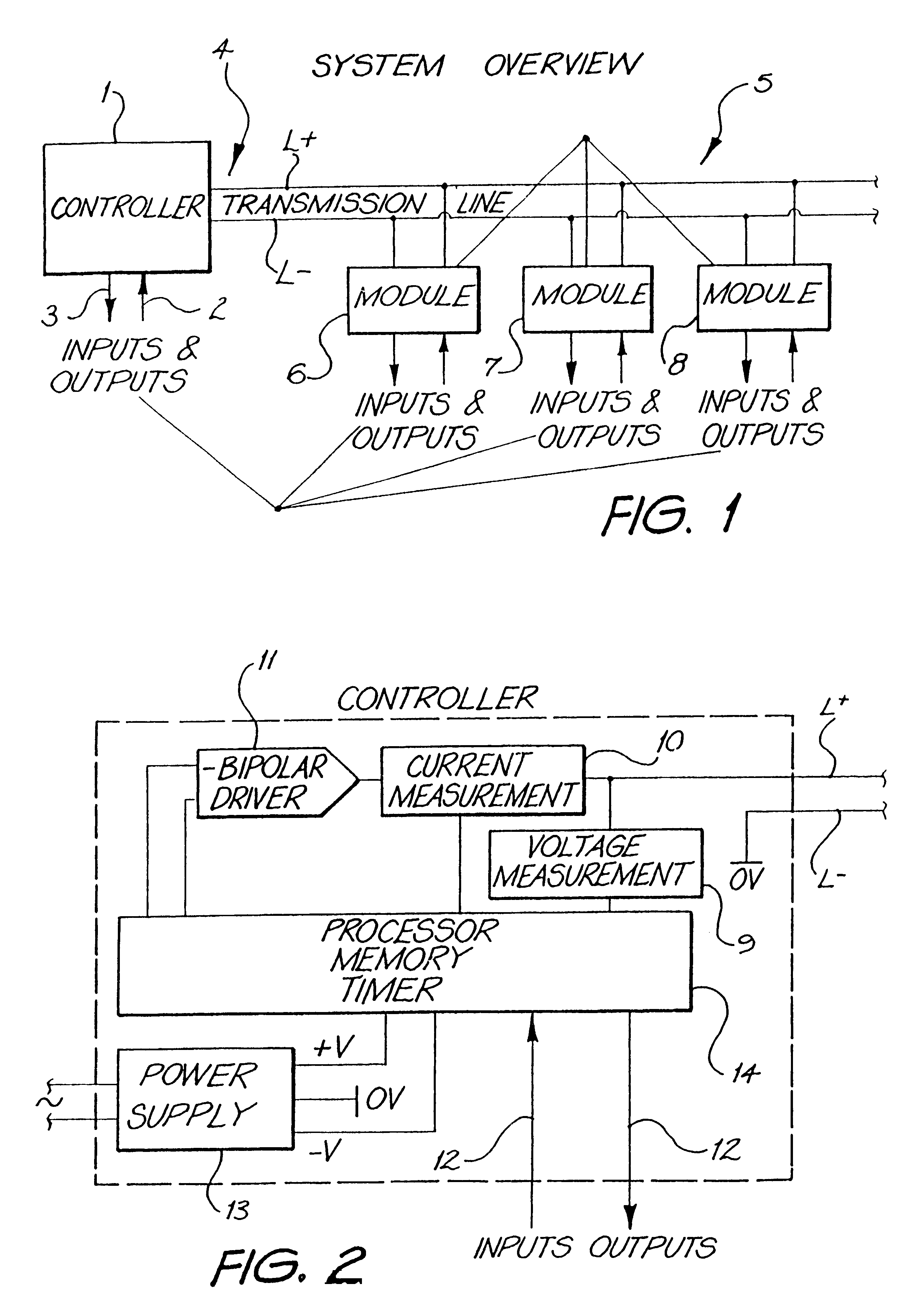
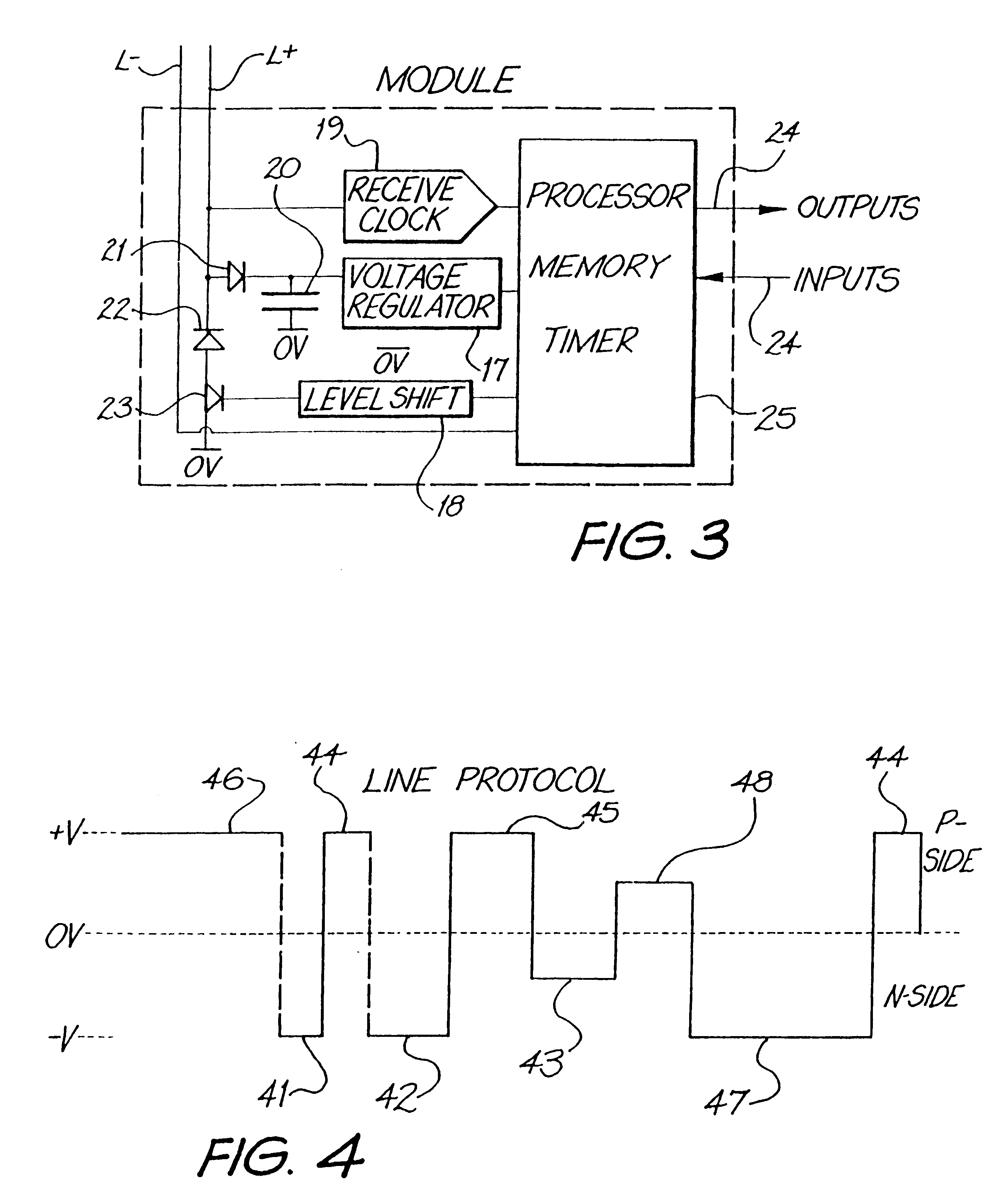
A two wire communication system capable of transmitting data and transferring power by the used of an electrical bi-polar waveform across a two wire conductor from a controller in communication with the two-wire conductor to at least one module in communication with the controller and capable of transmitting data from the module to the controller; and a remote electrical device in communication with the controller. Usable data may be continuously transmitted across the two wire conductor independent of and during power transmission between the controller and the at least one module without loss of data transmission time and without affecting the transfer of power to the at least one module. The data is transmitted across the two wire conductor to the modules by pulse duration signals at the same time power is transmitted to the modules. The system is capable of using up to 100% of transmission time to transmit data without affecting transfer of power to the at least one module.
Owner:AMPCONTROL PTY LTD
Network infrastructure integrated system
InactiveUS6904134B2Systems using filtering and bypassingInterconnection arrangementsPower line networkNetwork connection
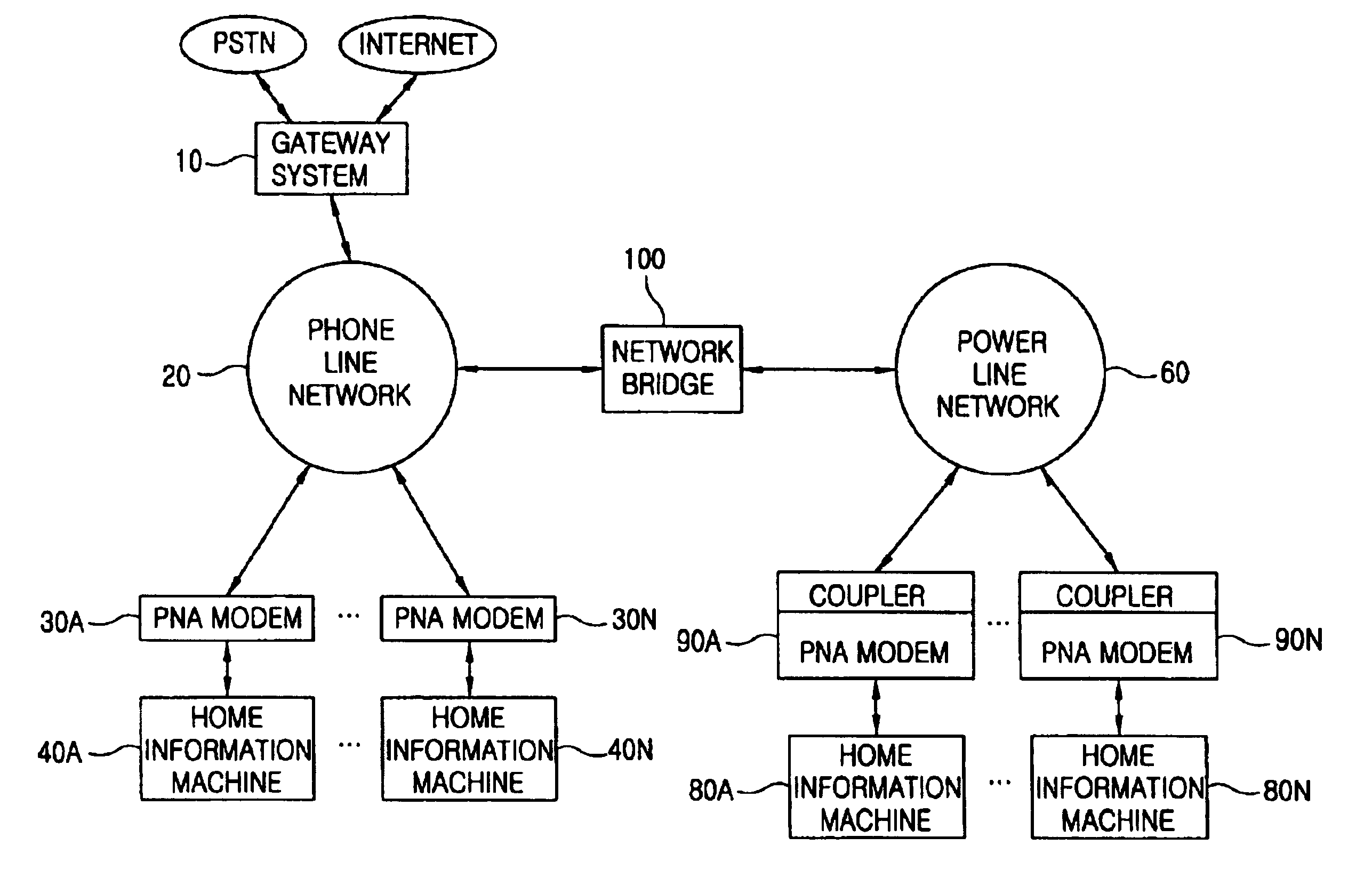
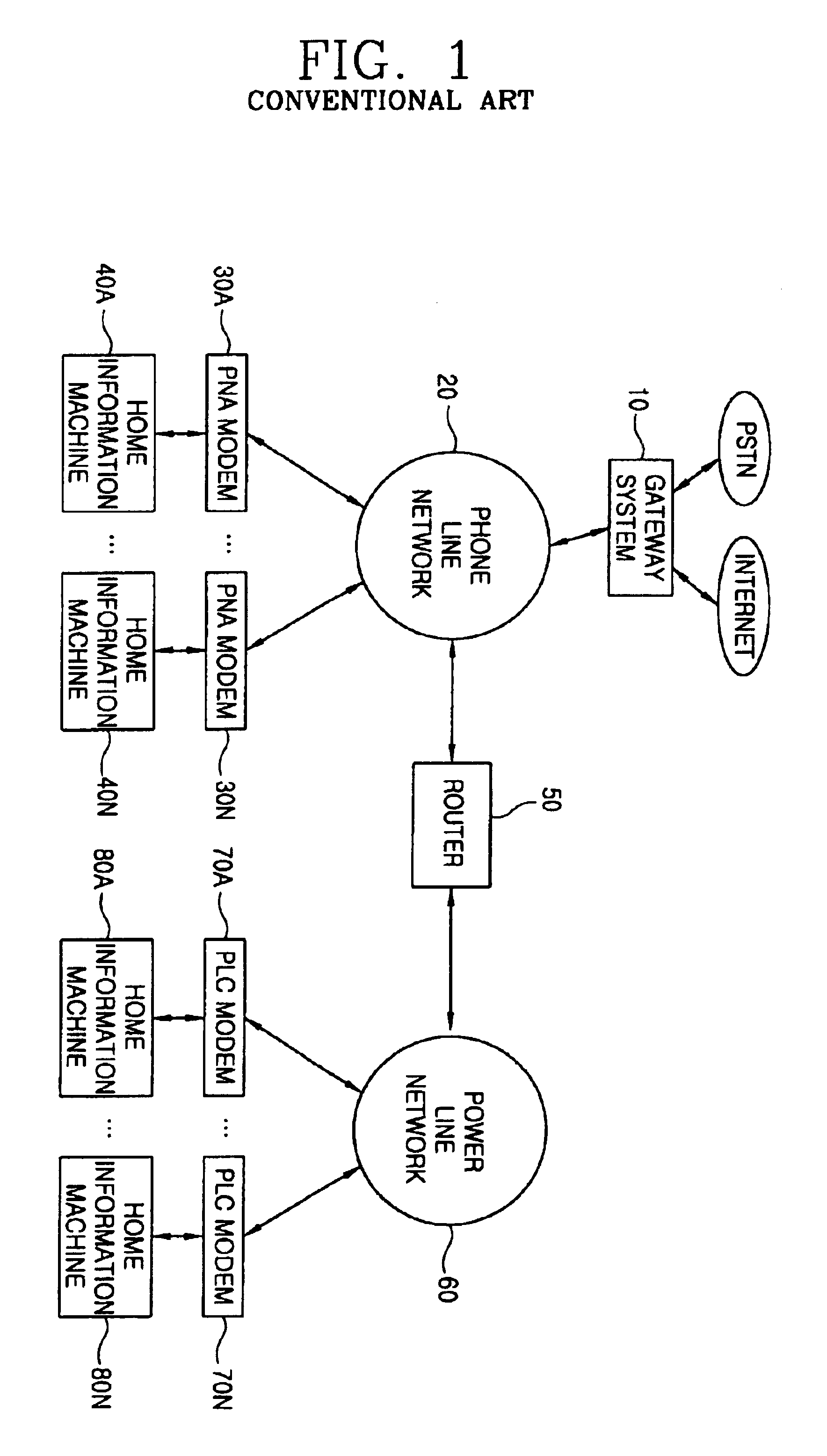
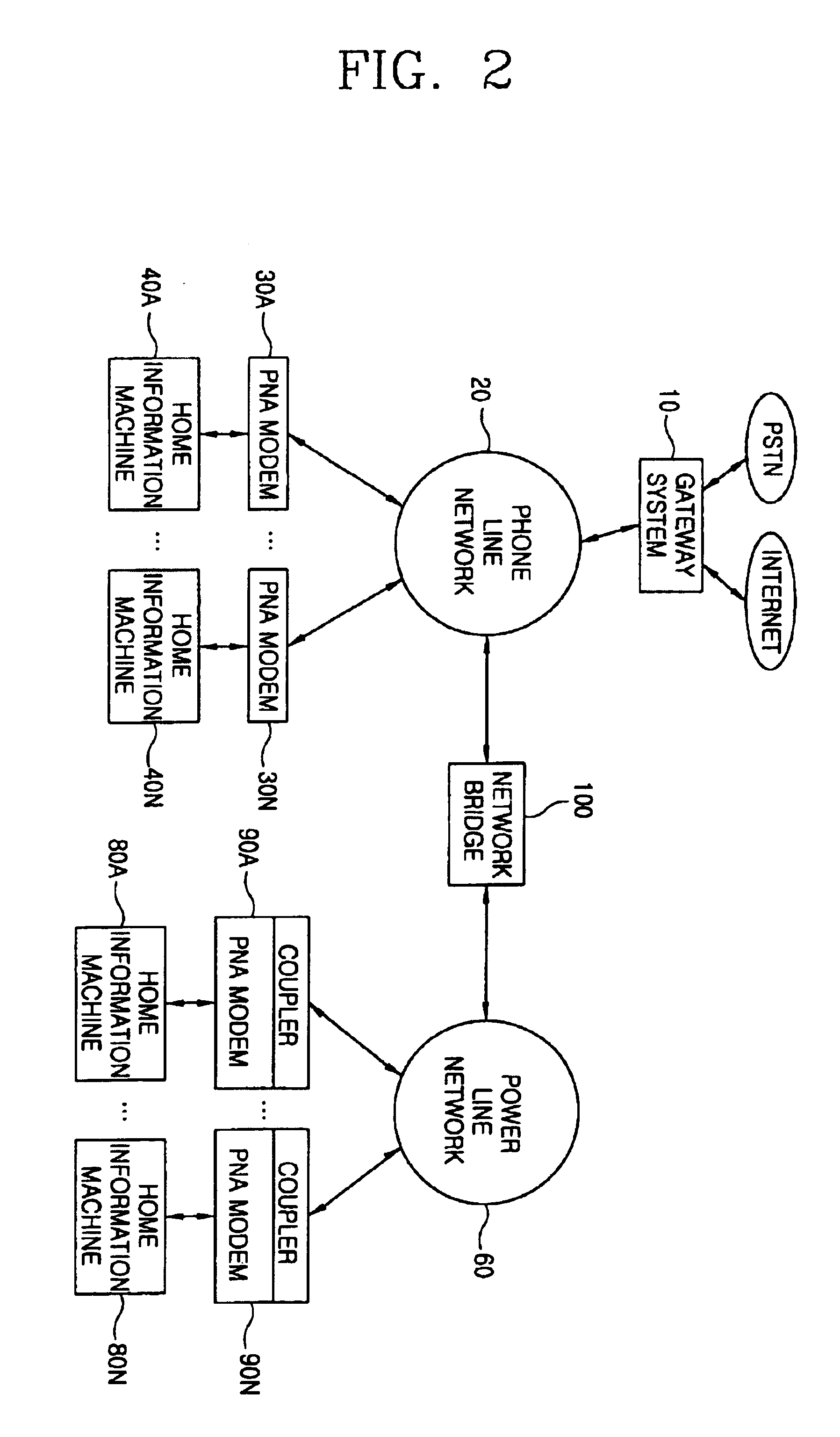
A network infrastructure integrated system which is able to integrate a telephone line network and a power line network as a single network using a simple circuit includes a first network to which a plurality of Home Information Machines are connected; a second network to which a plurality of Home Information Machines are connected; and a network bridge connected between the first and second networks and enabling the Home Information Machines to share respective applications and data with each other, whereby the cost can be reduced, the interchangeability is increased, and the accessibility to the network can be increased by using both the power lines and the telephone lines.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Multi-Wideband Communications over Multiple Mediums
InactiveUS20080130640A1Electric signal transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceMultiple frequency
A powerline communications device comprises a powerline communications interface and at least one other communications interface configured to communicate over a computing network. The powerline communications interface is further configured to receive electrical power. The computing network may comprise mediums including powerlines, telephone lines, and / or coaxial cables. In some embodiments, the powerline communications interface may communicate with a network apparatus, such as a personal computer, via an Ethernet interface. The powerline interface, the telephone line interface, and / or the coaxial cable interface may all be associated with the same media access control (MAC) address. The powerline communications device may receive a message via a first medium and repeat the message via a second medium based on a quality of service (QoS) metric. In some embodiments, the powerline communications device may communicate using multiple frequency bands.
Owner:GIGLE SEMICON
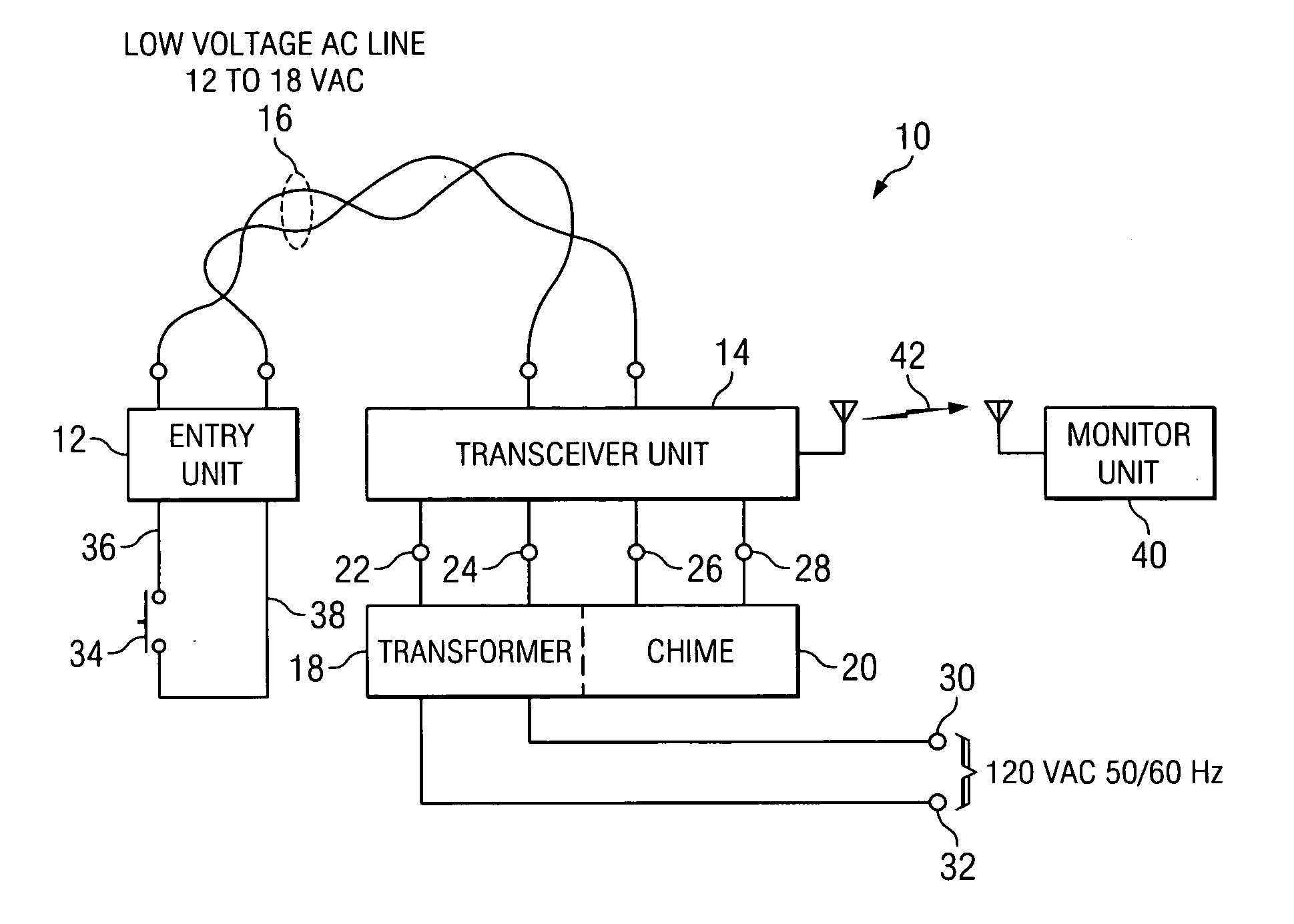
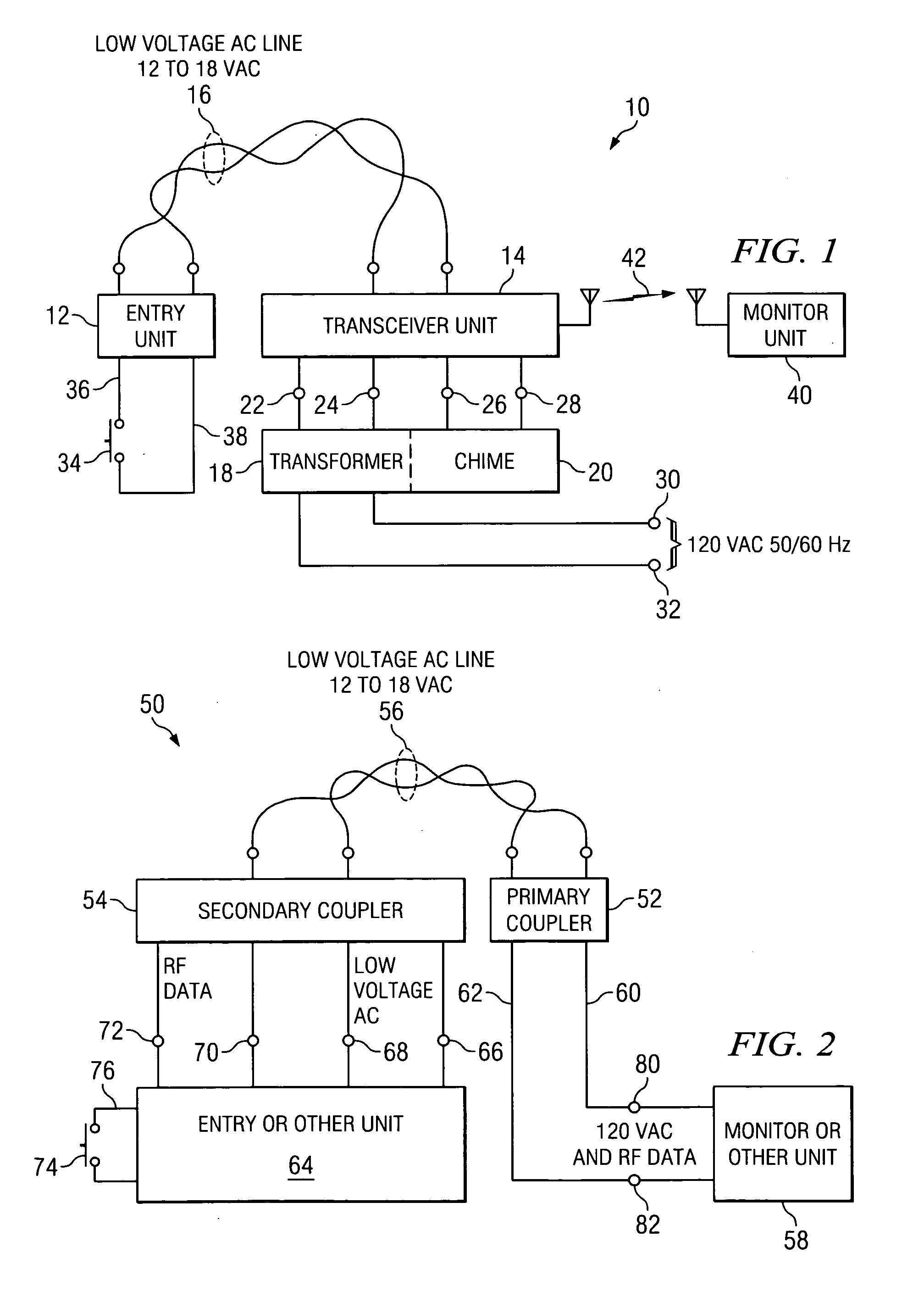
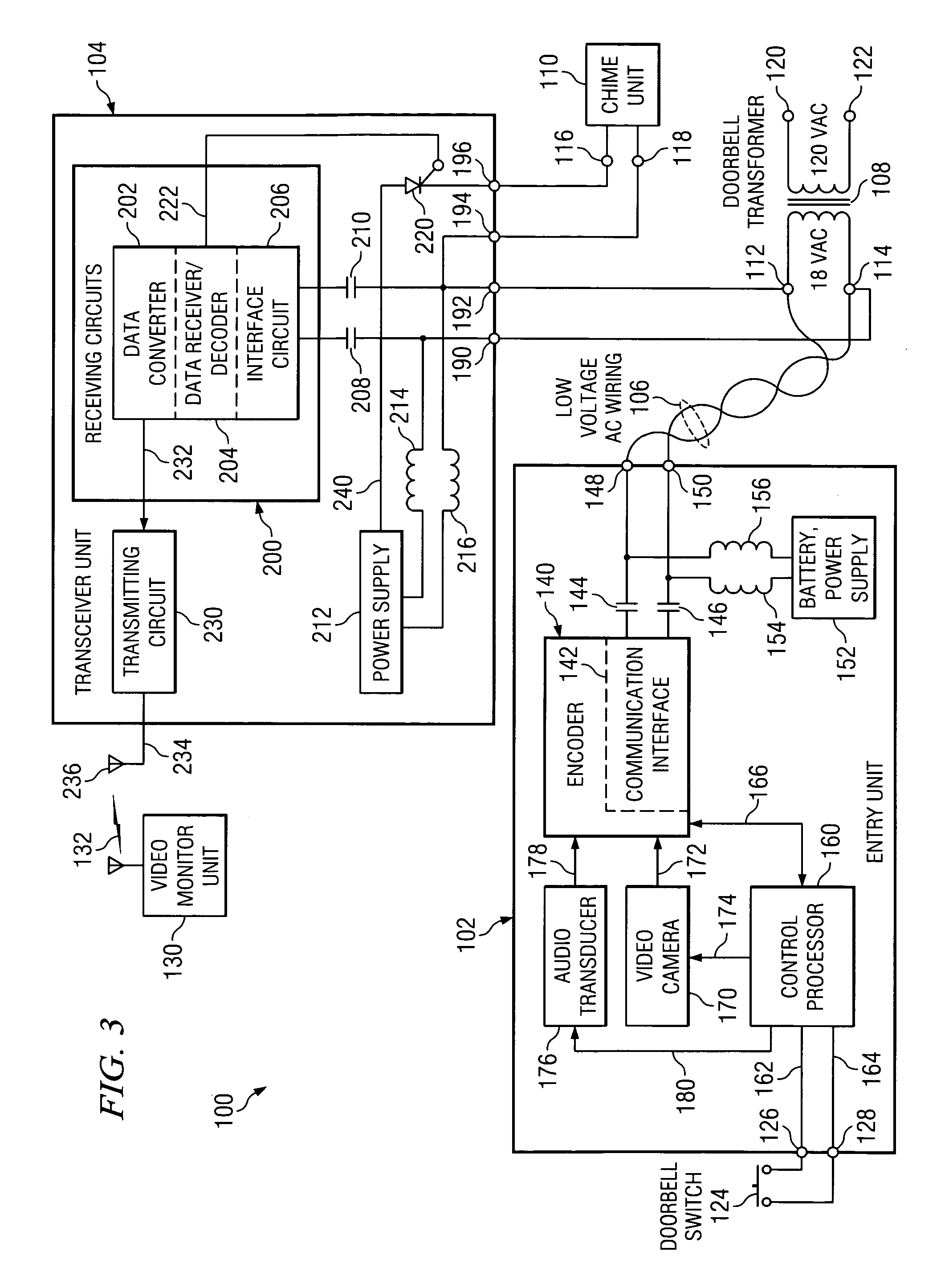
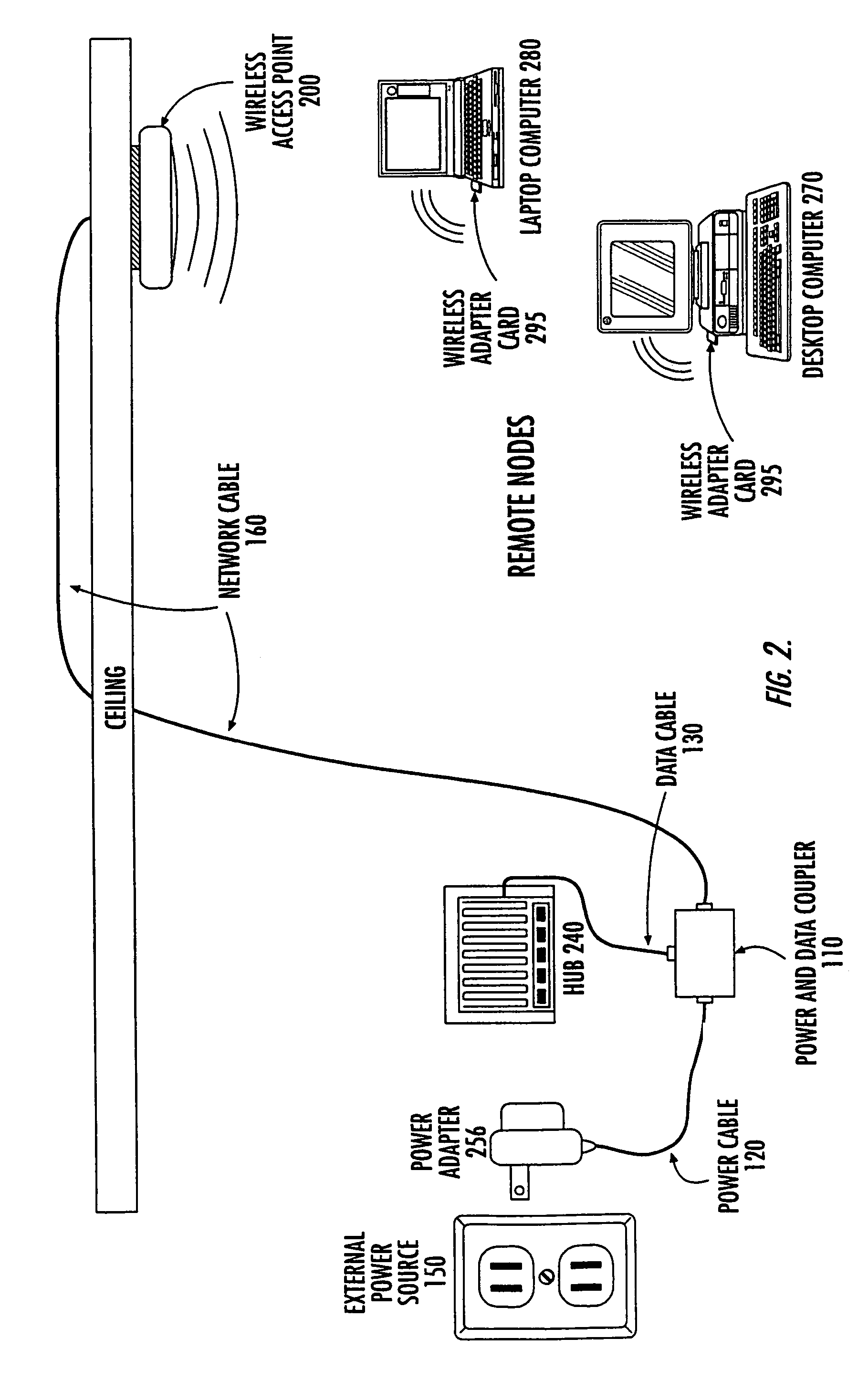
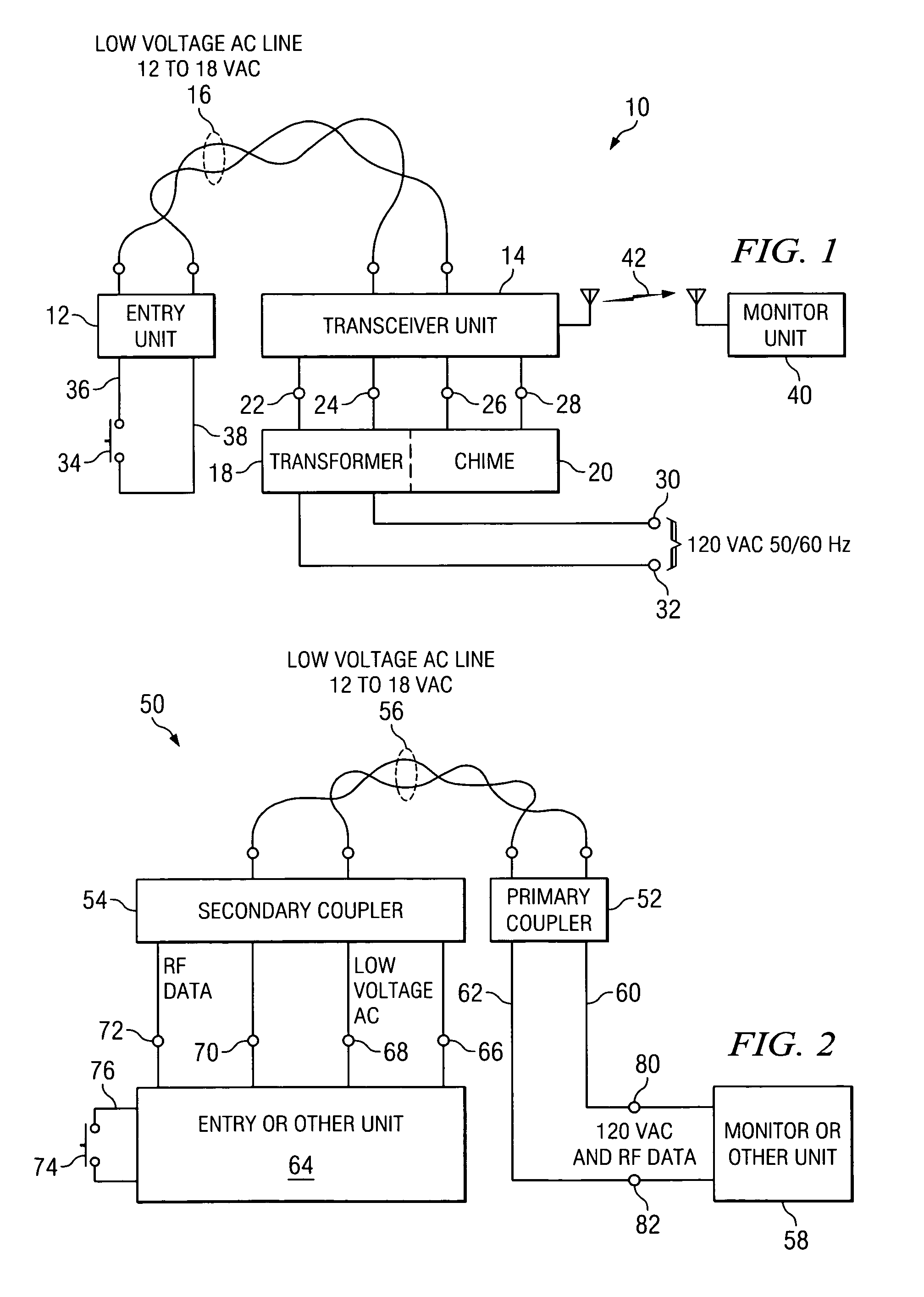
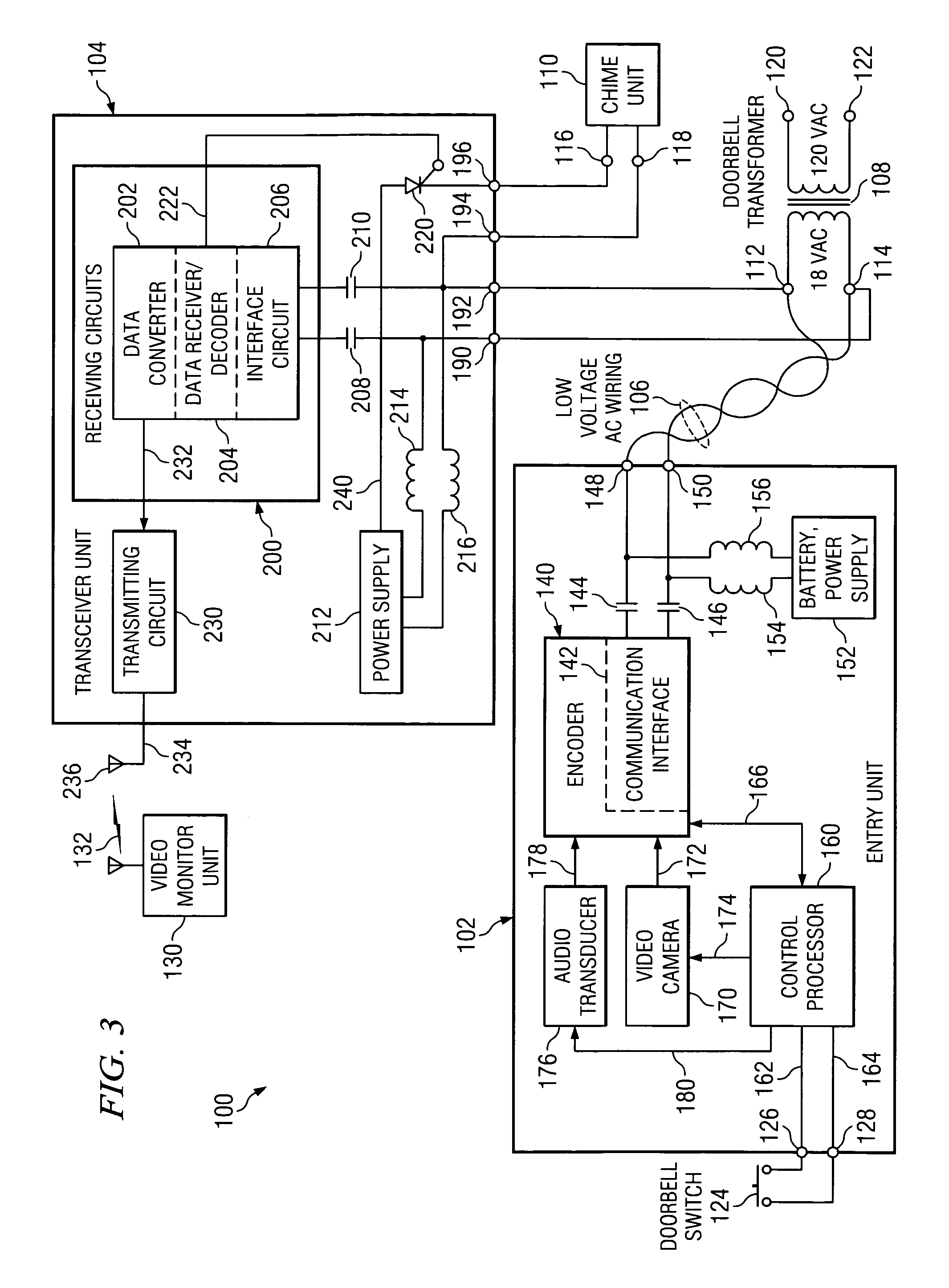
Apparatus and method for converting a low voltage AC wiring circuit to a high speed data communications link
InactiveUS20070052531A1Easy to installInexpensive and readily marketedFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelephonic communicationTelecommunications linkCoupling
An apparatus for converting a low voltage alternating current (AC) wiring circuit to a high speed data communications link, comprising a primary coupling circuit and a secondary coupling circuit. The apparatus provides low voltage AC power to a data device and couples data signals between the data device and the AC power line via the converted low voltage AC wiring circuit. An example is provided for retrofitting a door chime system to a high speed data link such as a video camera system.
Owner:THE SOURCE
Preventing unintended communication among power line communication devices associated with different premises power distribution lines of an electric power distribution system
InactiveUS20050128057A1Fast communication baud rateMany typesFrequency-division multiplex detailsImproving S/N for transmission/receivingElectricityCommunications system
An electric power line communication system operates with an electric power distribution system to provide through premises power distribution lines highly reliable communication links among power line communication devices electrically coupled or located in proximity to the premises power distribution lines. Each power line communication device associated with a set of premises power distribution lines has an identification address. A master code identifies the power line communication devices as members of a system domain of power line communication devices associated with the set of premises power distribution lines. Association of the master code with the identification addresses renders the member power line communication devices capable of operation without unintended communication with power line communication devices associated with a separate, different set of premises power distribution lines.
Owner:GE SECURITY INC
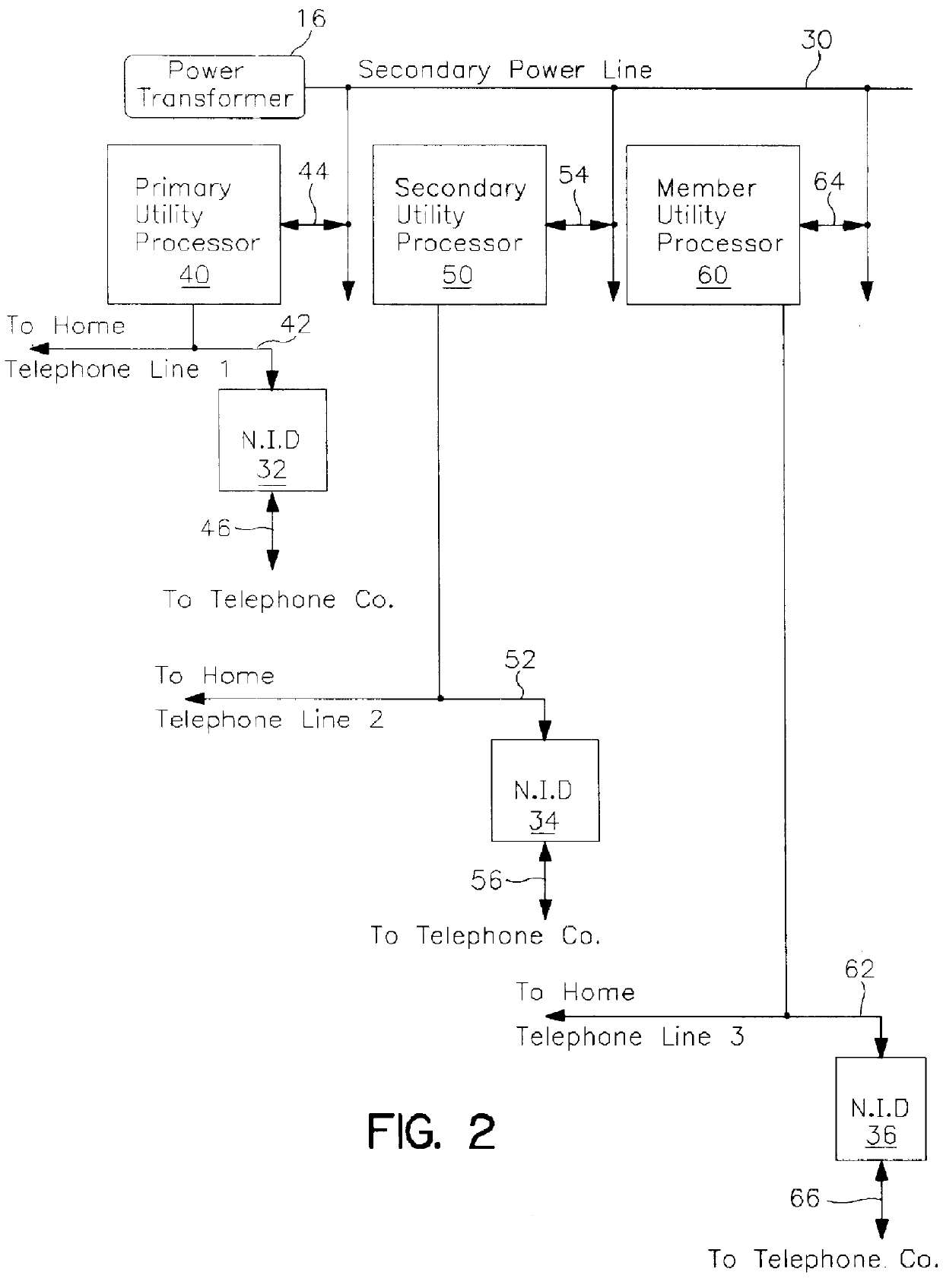
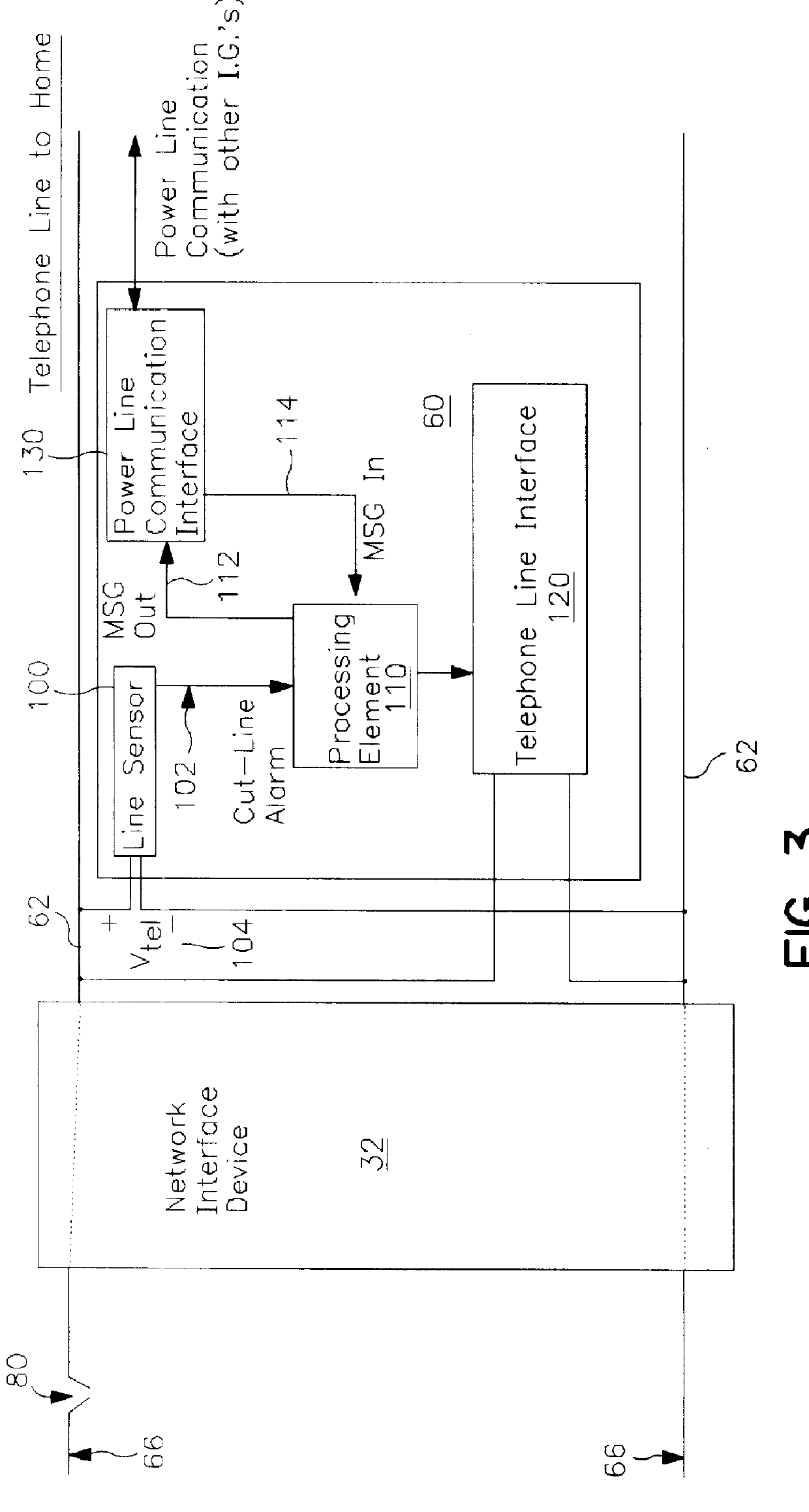
Method and apparatus for detecting and reporting a defective telecommunications line
InactiveUS6072858AElectric signal transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsLine sensorProcessing element
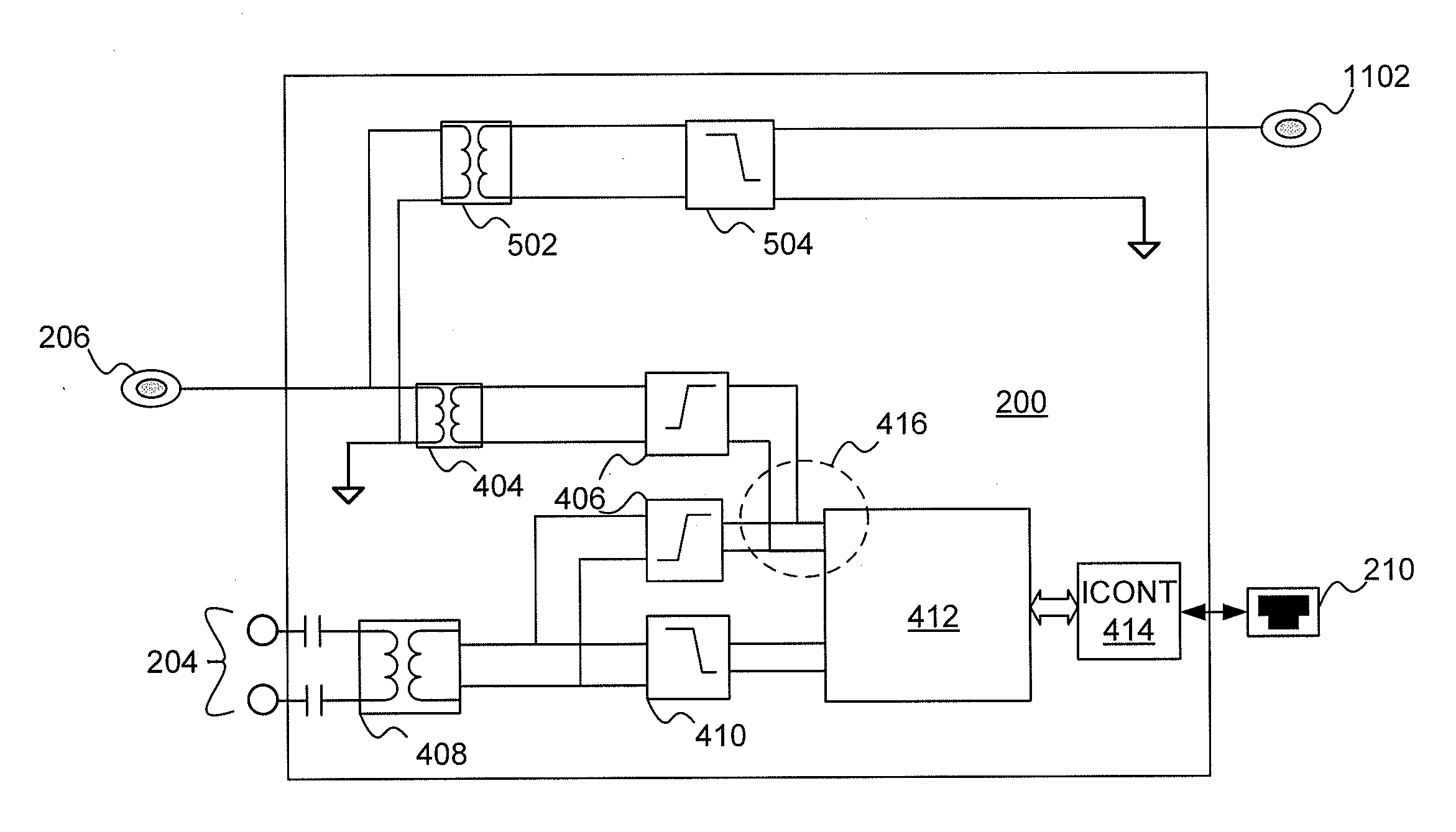
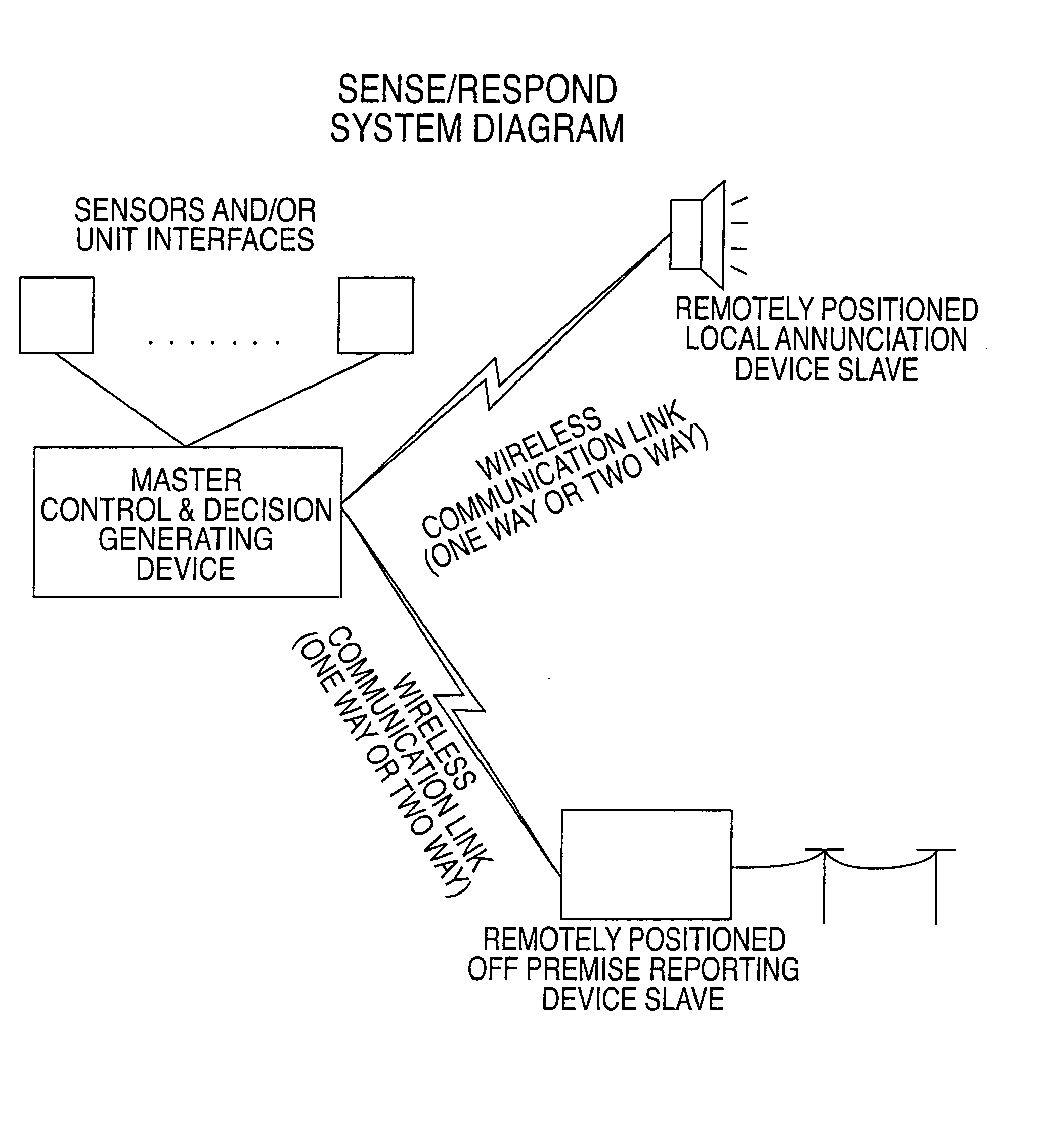
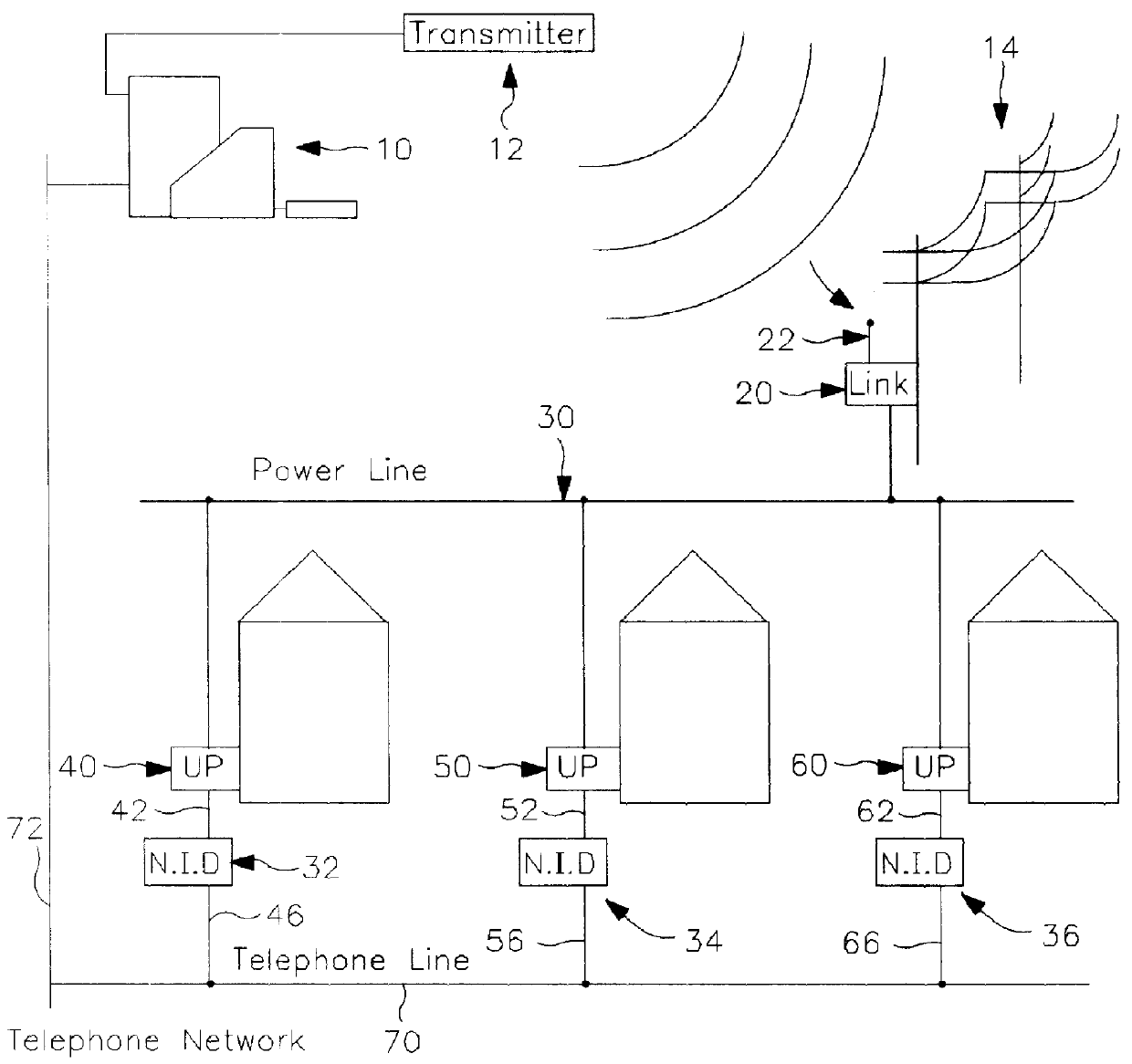
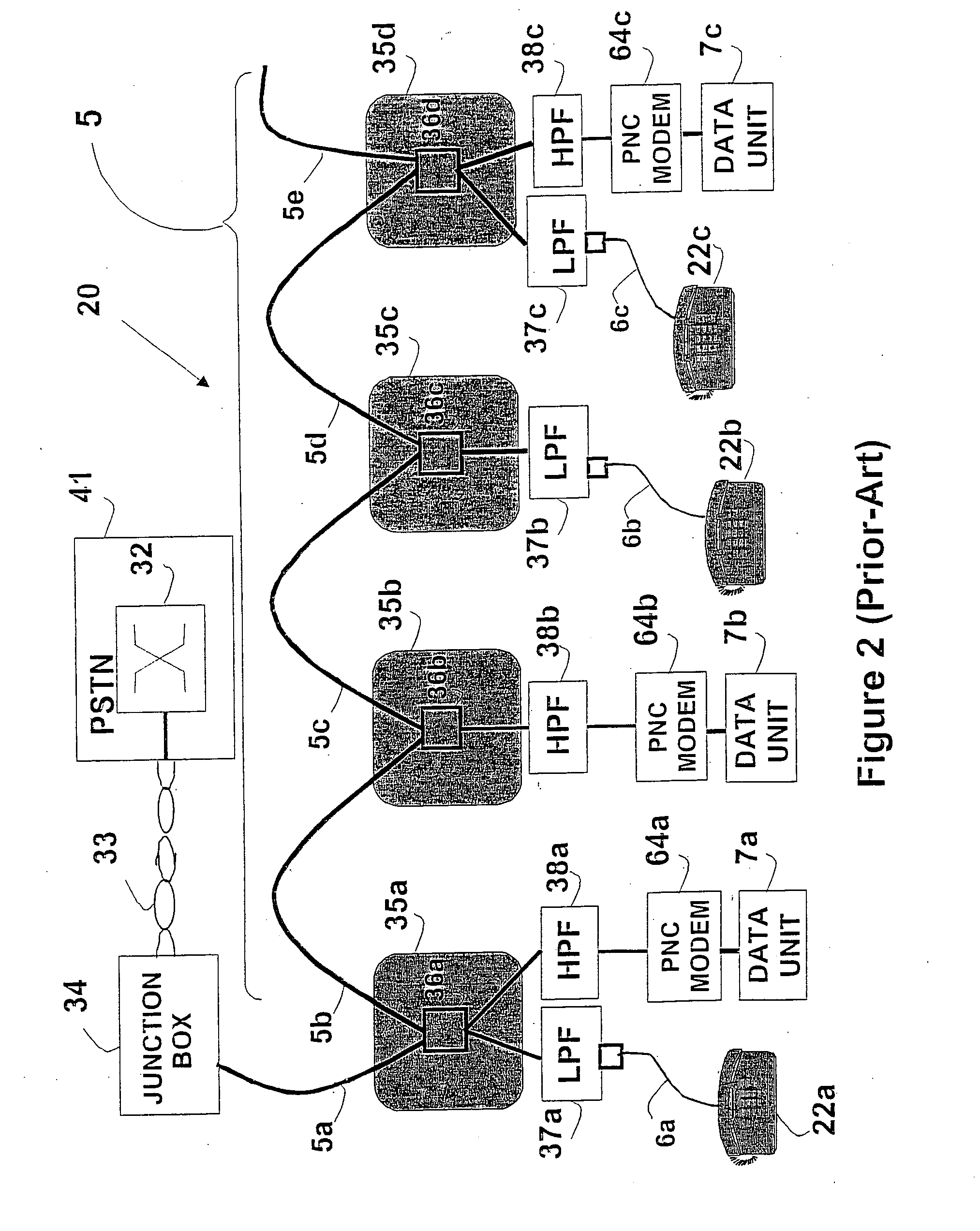
A system for detecting and reporting a defect in a telephone line includes a network of utility processors that communicate over a power line. Each utility processor monitors a telephone line connected to the processor. The utility processor includes a processing element, a line sensor, a telephone interface and a power line communication interface. Each utility processor reports a defect in the telephone line by sending message to a second utility processor via the power line. The second utility processor reports the defect to a central office via a telephone line.
Owner:COMENERGY TECH +1
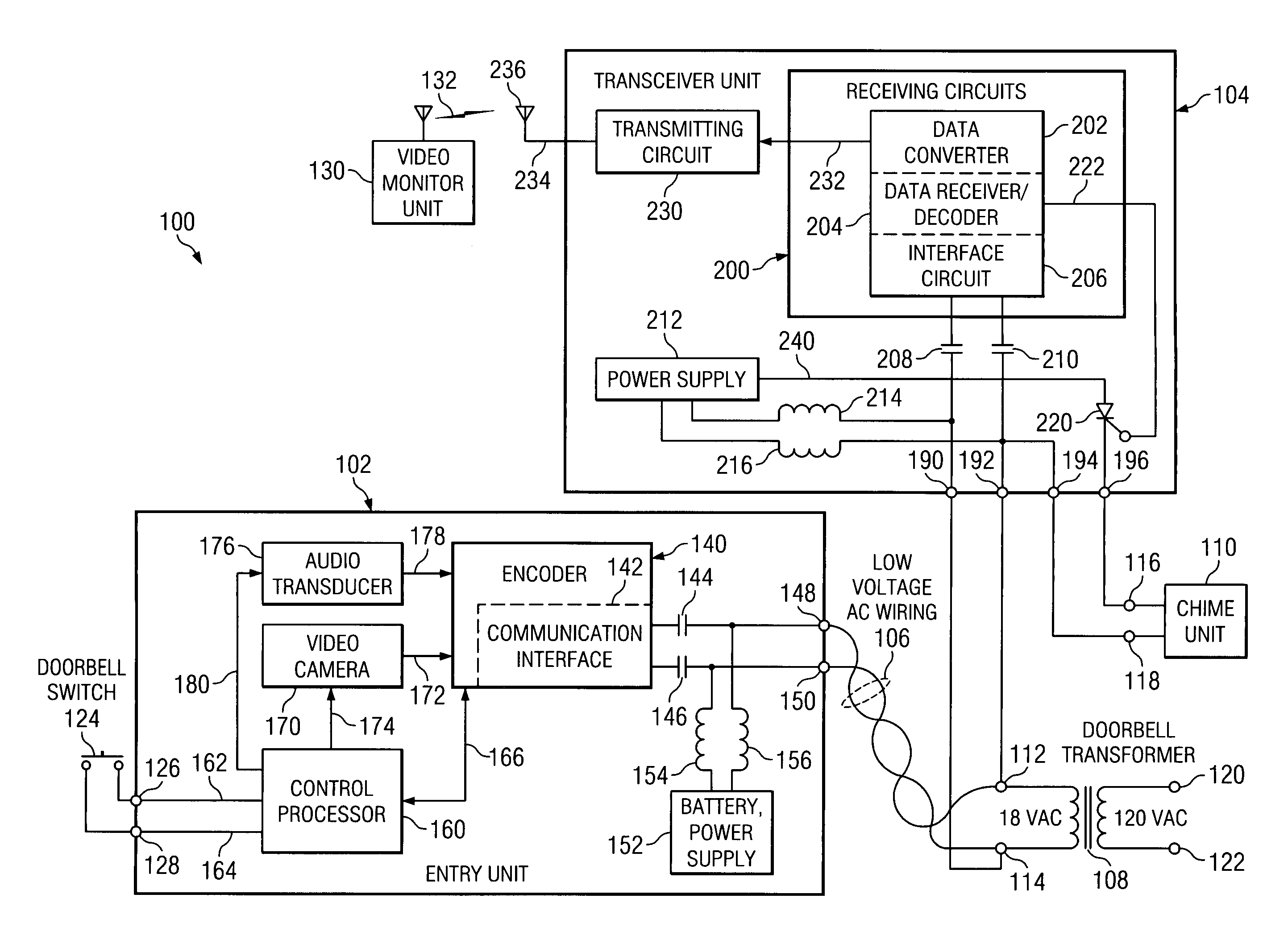
Food preparation system
InactiveUS7110829B2Electric signal transmission systemsWired telephoneCommunication interfaceControl system
A system of intelligent appliances coupled by common household power lines or wireless links. One or more of the appliances serves as a system controller and may include a further communications interface for coupling to an external communications network, such as the telephone network. The system can thus be accessed and controlled remotely. The system can also communicate with and obtain information from remote sources such as Internet-based facilities.
Owner:SUNBEAN PROD INC
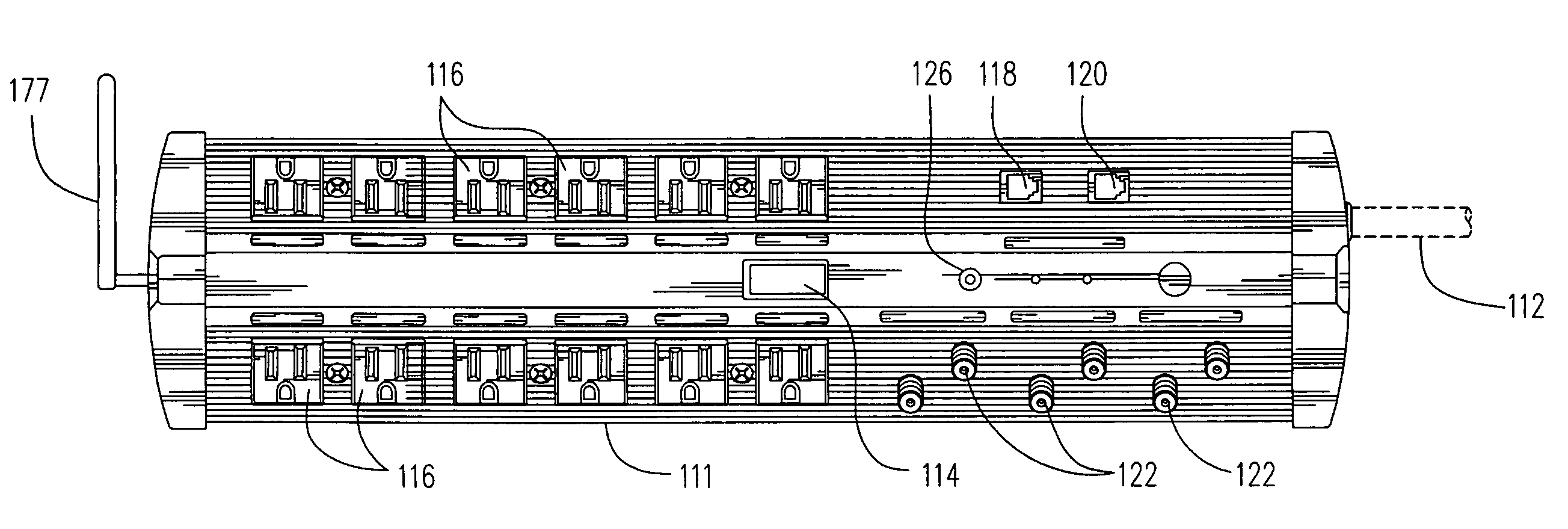
Alternating current power strip with network repeating and management
InactiveUS7239892B2Overcome riskReduce the possibilityPower managementNear-field transmissionEngineeringAlternating current
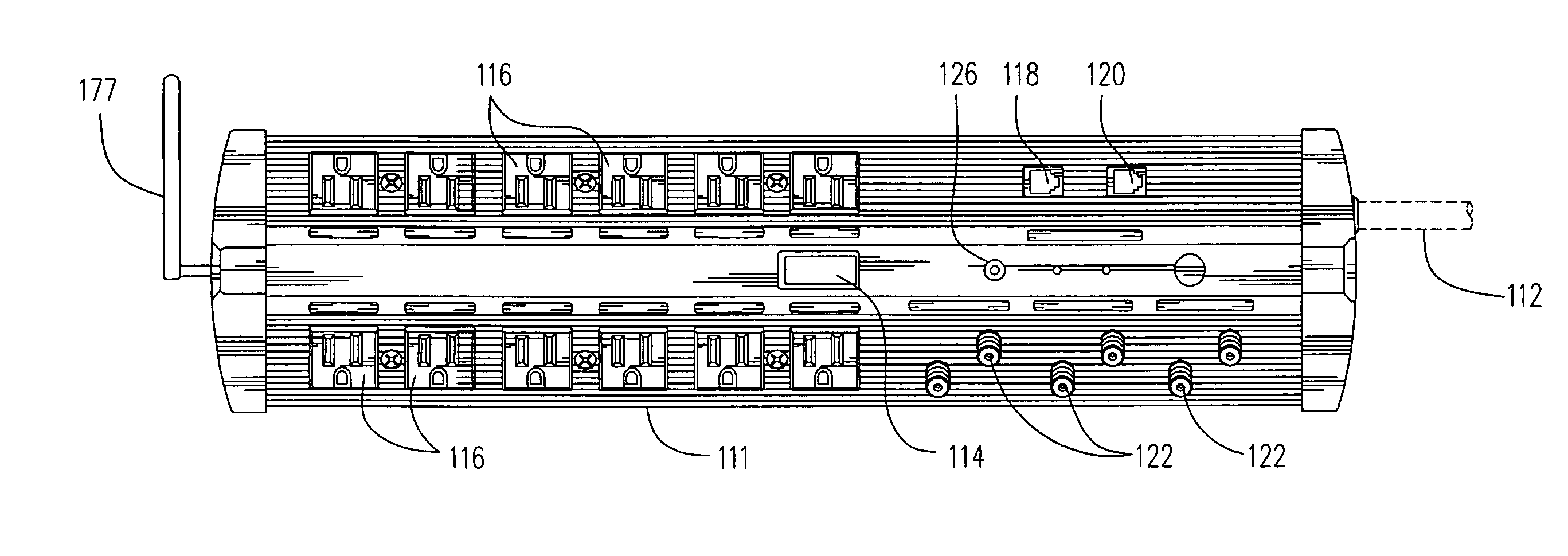
An alternating current power strip 1 with network repeating and management 23 functionality is hereby disclosed.
Owner:MONSTER
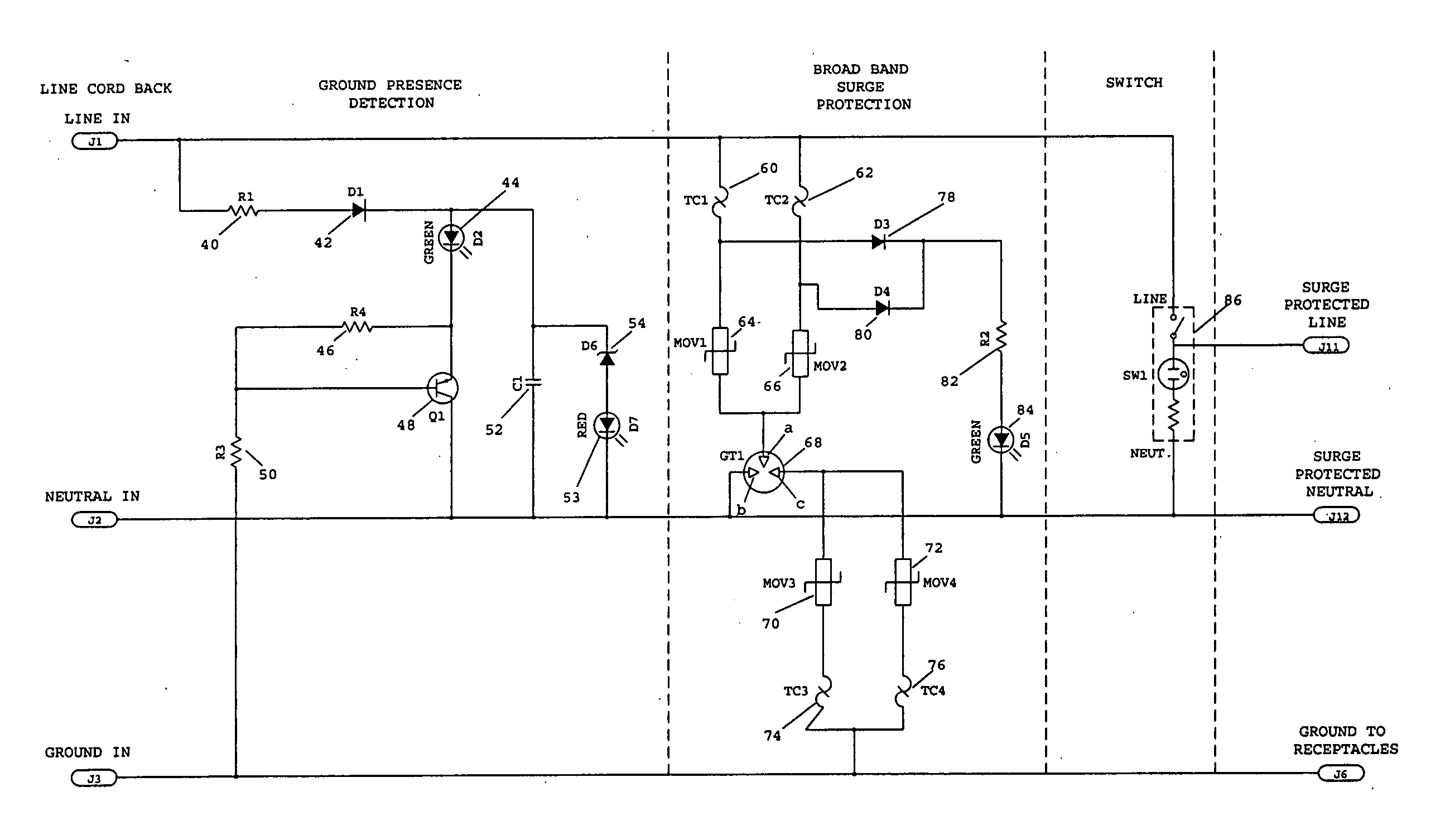
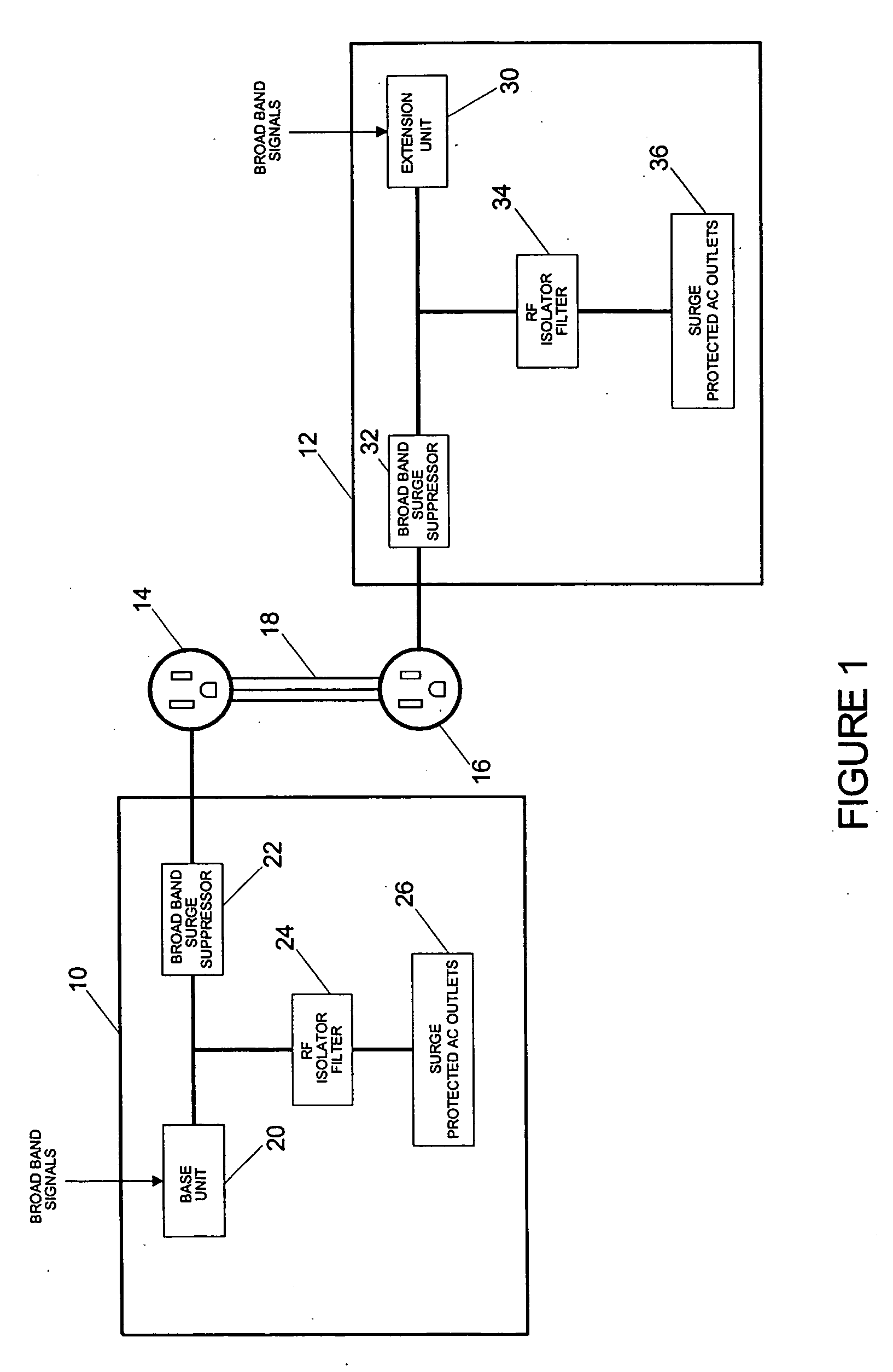
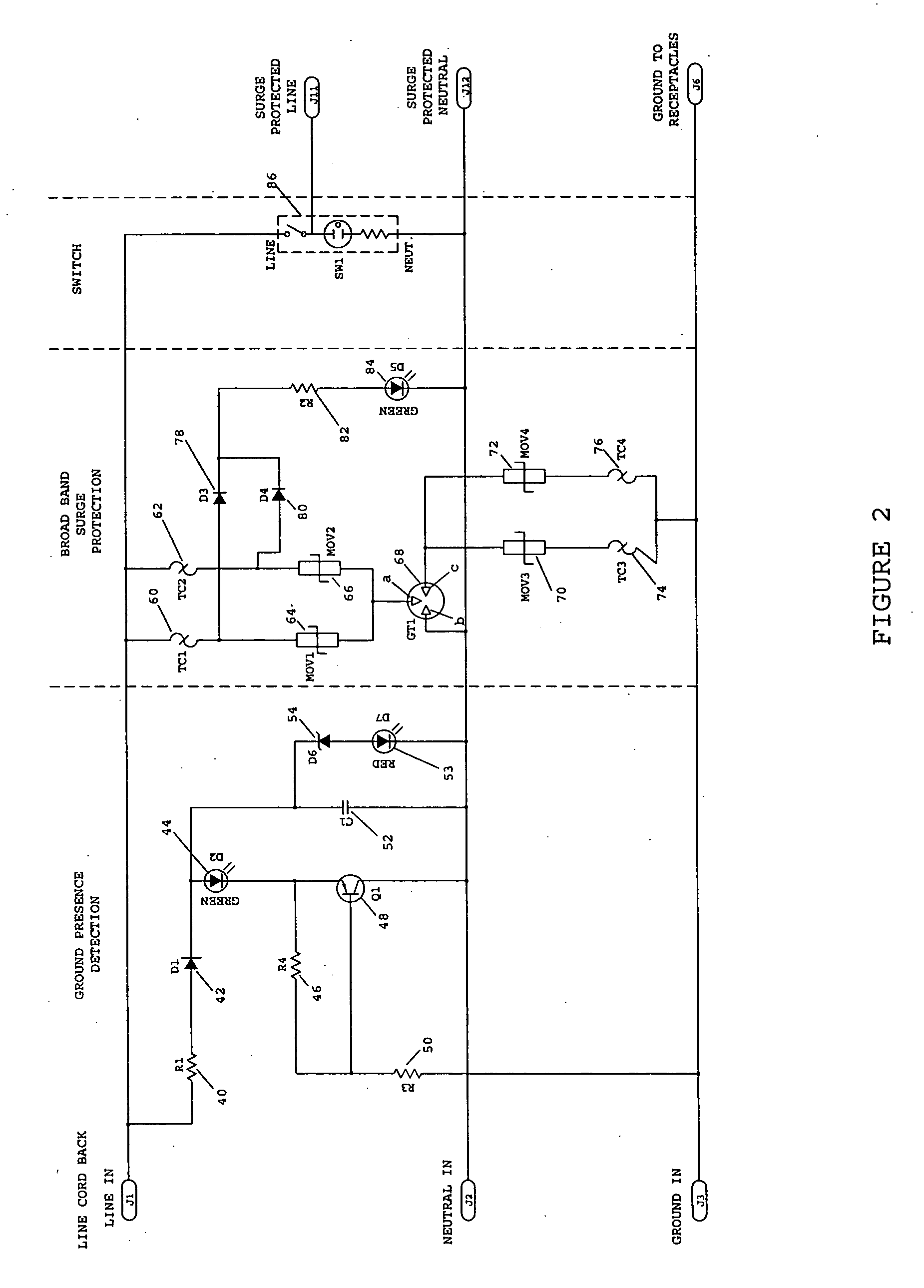
Surge protected broadband power line communication system
InactiveUS20060262478A1Wired telephoneEmergency protective arrangement detailsOptical ModuleComputer module
A surge protected broadband power line communication system is provided. The system includes a local module with a base unit and a remote module with an extension unit. Both modules include broadband surge suppressors adapted to be connected to an AC power line. The base and extension units are connected to the surge suppressors and transmit and receive broadband digital signals through the surge suppressors and over the AC power line. The local and remote modules also have RF isolator filters connected to the surge suppressors and surge protected AC outlets connected to the outputs of the isolator filters. The local module is connected to a source of broadband digital signals such as a cable modem. The system makes the cable modem available in every room in a home simply by plugging an extension unit into an outlet located in that room.
Owner:TII NETWORK TECH
Preventing unintended communication among power line communication devices associated with different premises power distribution lines of an electric power distribution system
InactiveUS7034663B2Good signalImprove reliabilityFrequency-division multiplex detailsCircuit arrangementsElectricityCommunications system
An electric power line communication system operates with an electric power distribution system to provide through premises power distribution lines highly reliable communication links among power line communication devices electrically coupled or located in proximity to the premises power distribution lines. Each power line communication device associated with a set of premises power distribution lines has an identification address. A master code identifies the power line communication devices as members of a system domain of power line communication devices associated with the set of premises power distribution lines. Association of the master code with the identification addresses renders the member power line communication devices capable of operation without unintended communication with power line communication devices associated with a separate, different set of premises power distribution lines.
Owner:GE SECURITY INC
Modular outlet
InactiveUS20070019669A1Easy and simple upgradingCoupling device connectionsSubstations coupling interface circuitsExpansion cardModularity
In conjunction with a wiring in a house carrying data network signal, a modular outlet comprising of a base module and interface module. The base module connects to the wiring and attached to a wall. The interface module provides a data unit connection. The interface module is mechanically attached to the base module and electrically connected thereto. The wiring may also carry basic service signal such as telephone, electrical power and cable television (CATV). In such a case, the outlet will provide the relevant connectivity either as part of the base module or as part of the interface module. Both proprietary and industry standard interfaces can be used to interconnect the module. Furthermore, a standard computer expansion card (such as PCI, PCMCIA and alike) may be used as interface module.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
Alternating current power strip with network repeating and management
InactiveUS20060148403A1Power reliability and protectionInteroperabilityPower managementNear-field transmissionEngineeringAlternating current
An alternating current power strip 1 with network repeating and management 23 functionality is hereby disclosed.
Owner:MONSTER
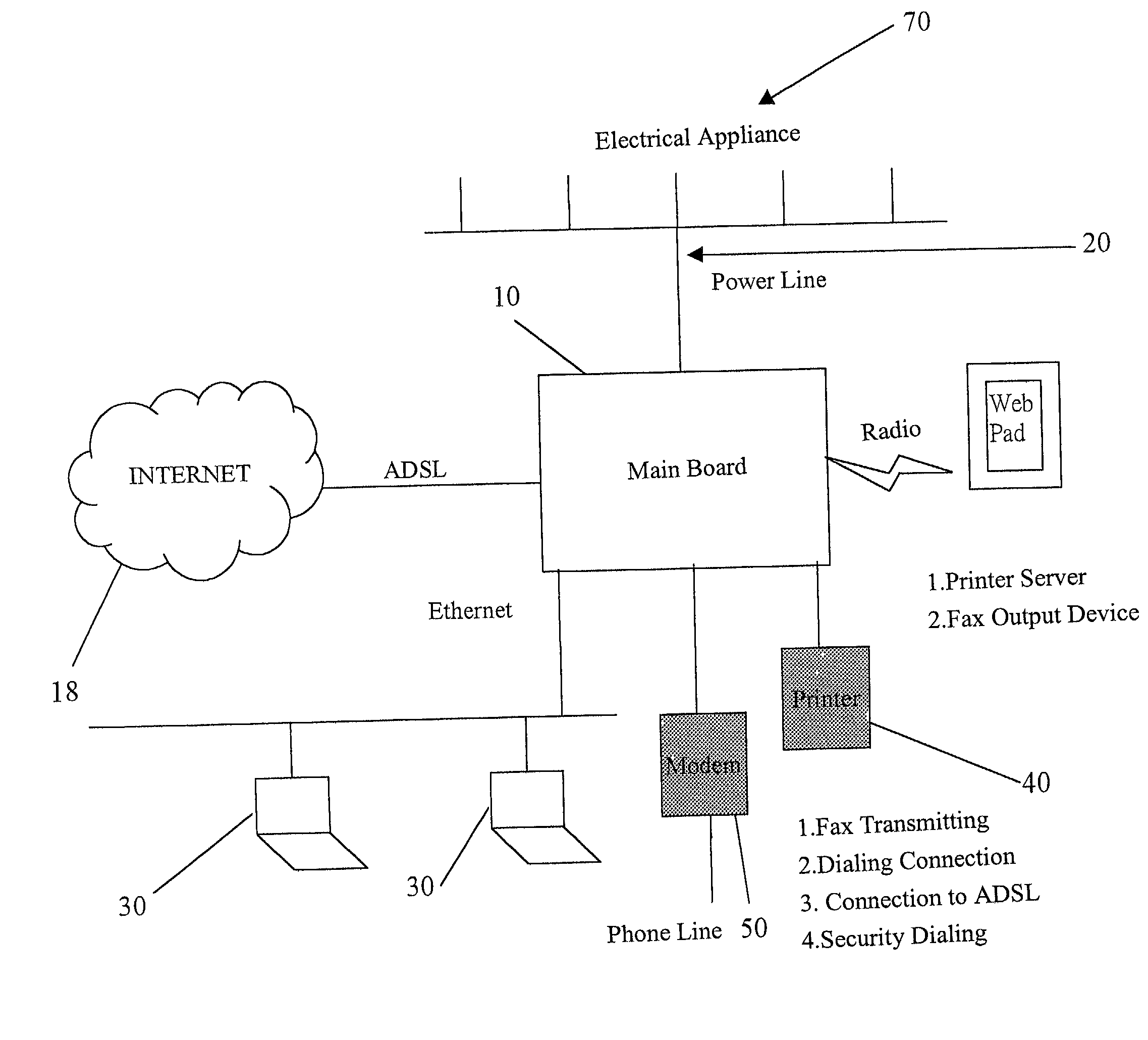
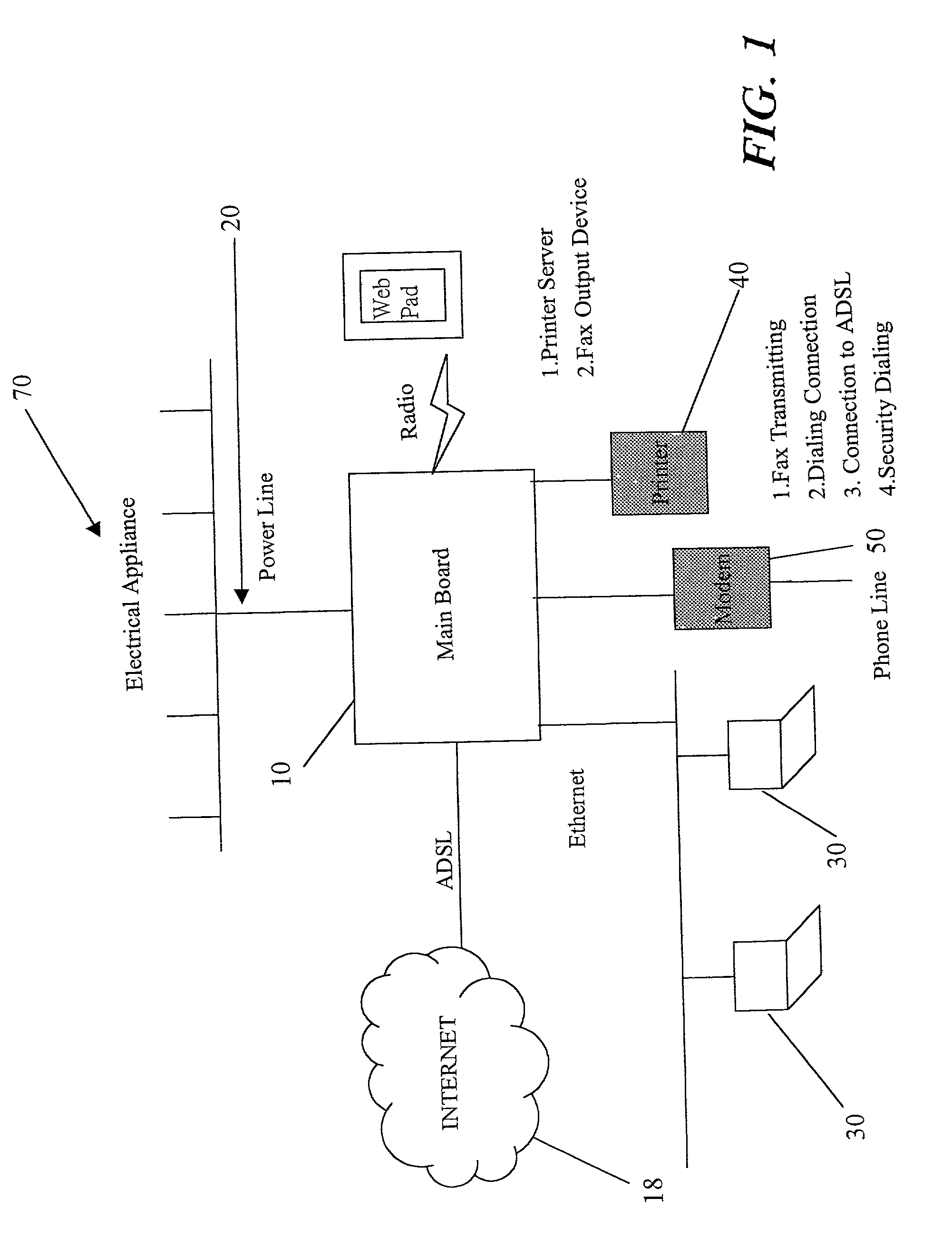
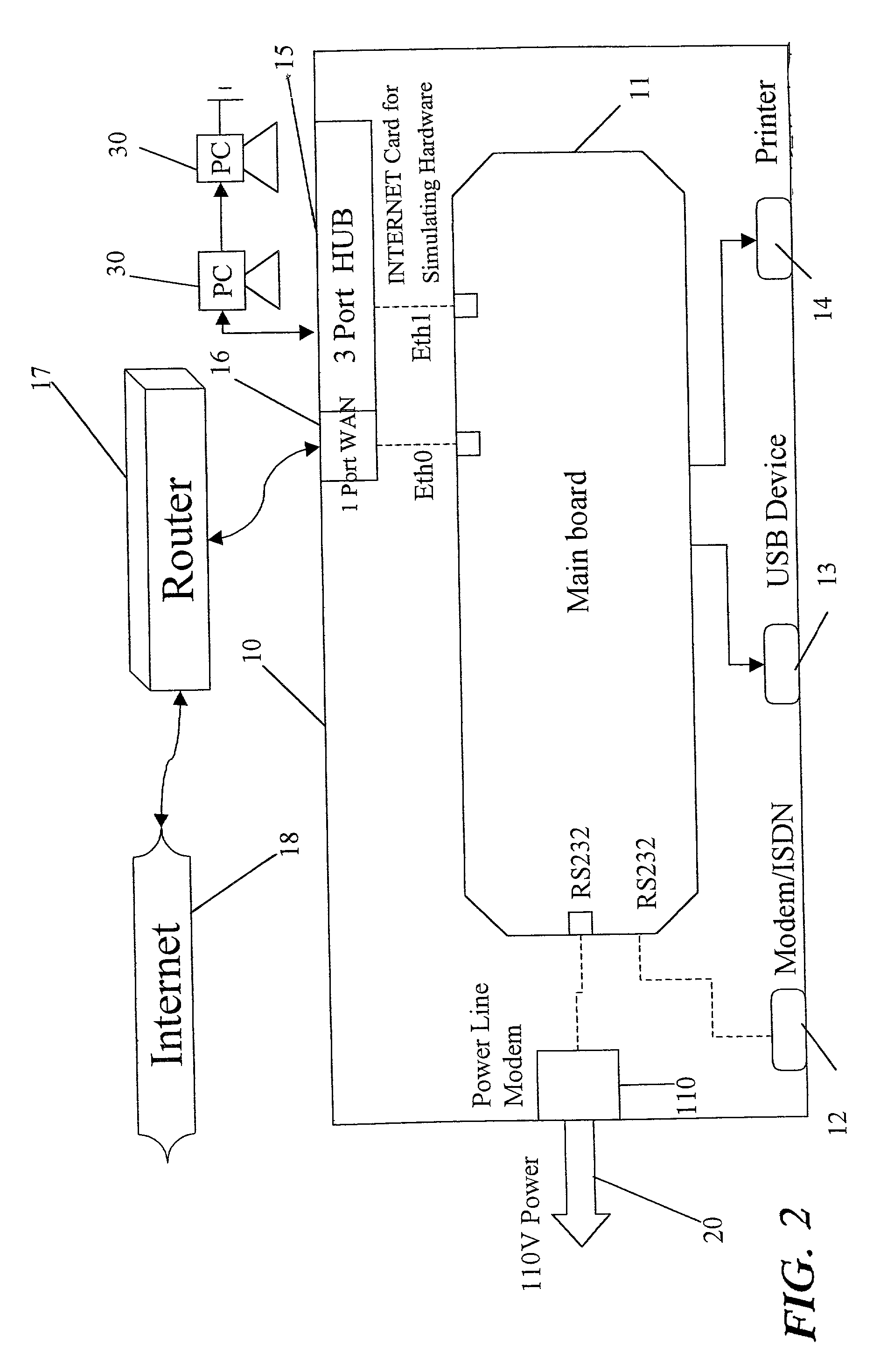
Remote control method for controlling electrical appliance via home gateway
A remote control method for controlling electrical appliance via a home gateway proceeds with an input signal by a telephone call to initiate the main board (the host) to connect to the INTERNET. After registering to the specific DNS server to have the pre-registered IP address, the user is able to control the initiation of household electrical appliances.
Owner:TECO ELECTRIC AND MACHINERY
Multichannel transceiver of digital signals over power lines
InactiveUS6950460B1Improve speed performanceSystems using filtering and bypassingPower distribution line transmissionDigital dataModem device
A data transceiving station of digital data frames includes a digital modem coupled to a transmission line, and a microprocessor receiving demodulated data from the modem according to a Packet Mode or a Bit Mode transmission through an interface circuit. The interface circuit switches between the Packet Mode and the Bit Mode transmission during transfer of a data frame to the microprocessor. The data transceiving station combines the superior speed of a Packet Mode transfer with the unlimited compatibility of a Bit Mode transfer.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Power transfer apparatus for concurrently transmitting data and power over data wires
InactiveUS7005969B2Electric signal transmission systemsWired telephoneElectric power transmissionCoupling
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Apparatus and method for converting a low voltage AC wiring circuit to a high speed data communications link
InactiveUS7417535B2Easy to installInexpensive and readily marketedFrequency-division multiplex detailsWired telephoneTelecommunications linkCoupling
An apparatus for converting a low voltage alternating current (AC) wiring circuit to a high speed data communications link, comprising a primary coupling circuit and a secondary coupling circuit. The apparatus provides low voltage AC power to a data device and couples data signals between the data device and the AC power line via the converted low voltage AC wiring circuit. An example is provided for retrofitting a door chime system to a high speed data link such as a video camera system.
Owner:THE SOURCE
Power line communication system
InactiveUS20060077047A1Improve throughputElectric signal transmission systemsBroadband local area networksTransceiverEngineering
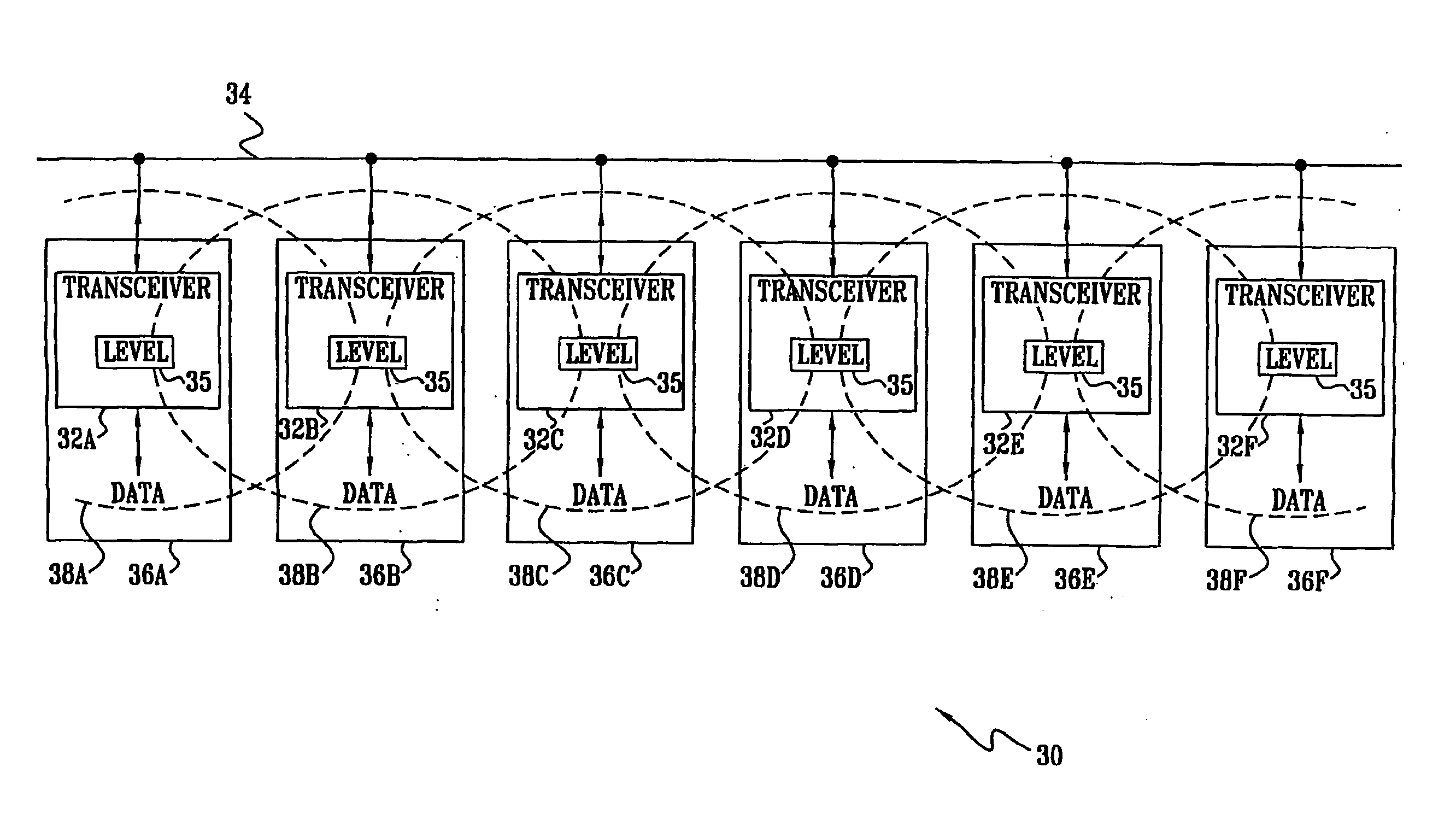
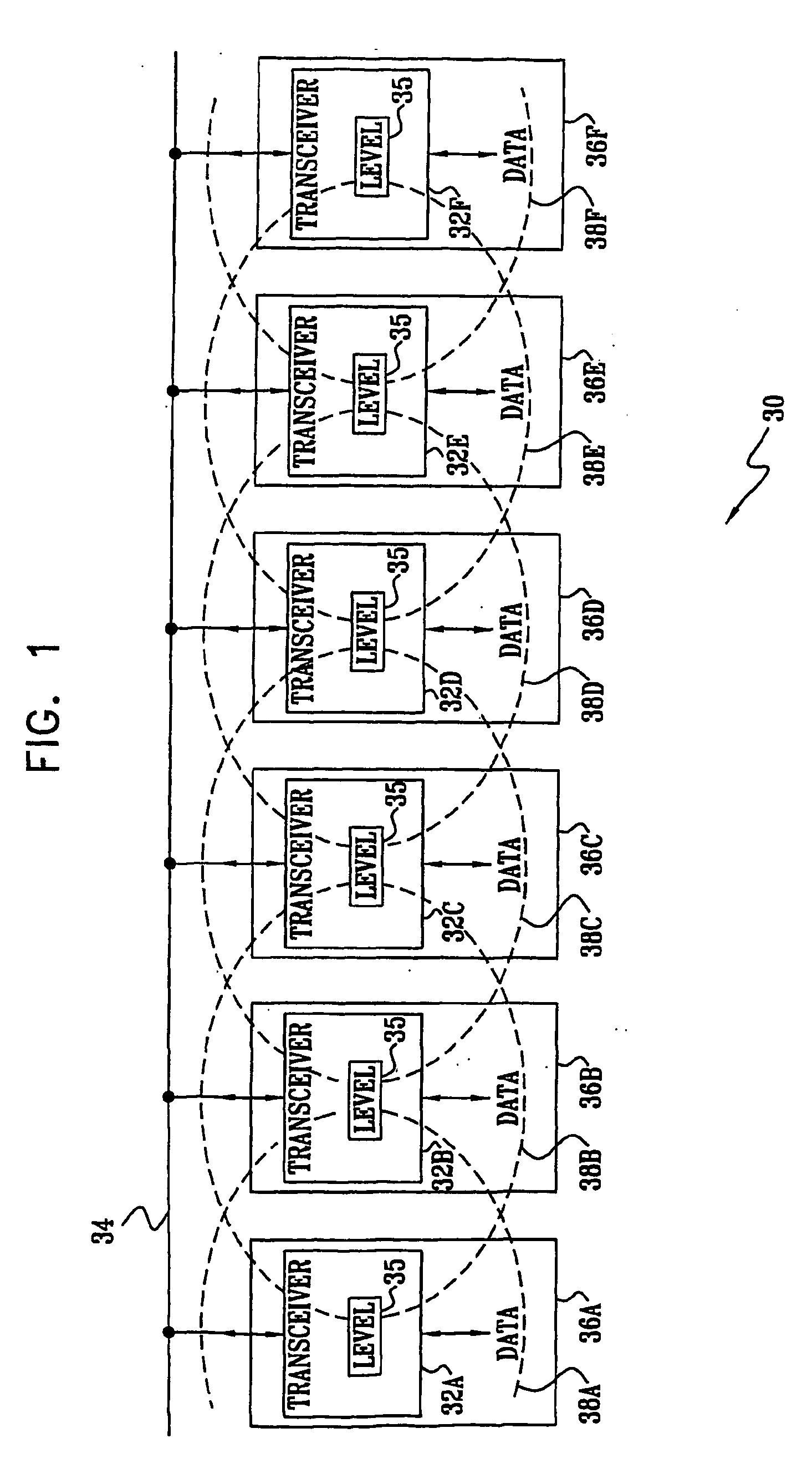
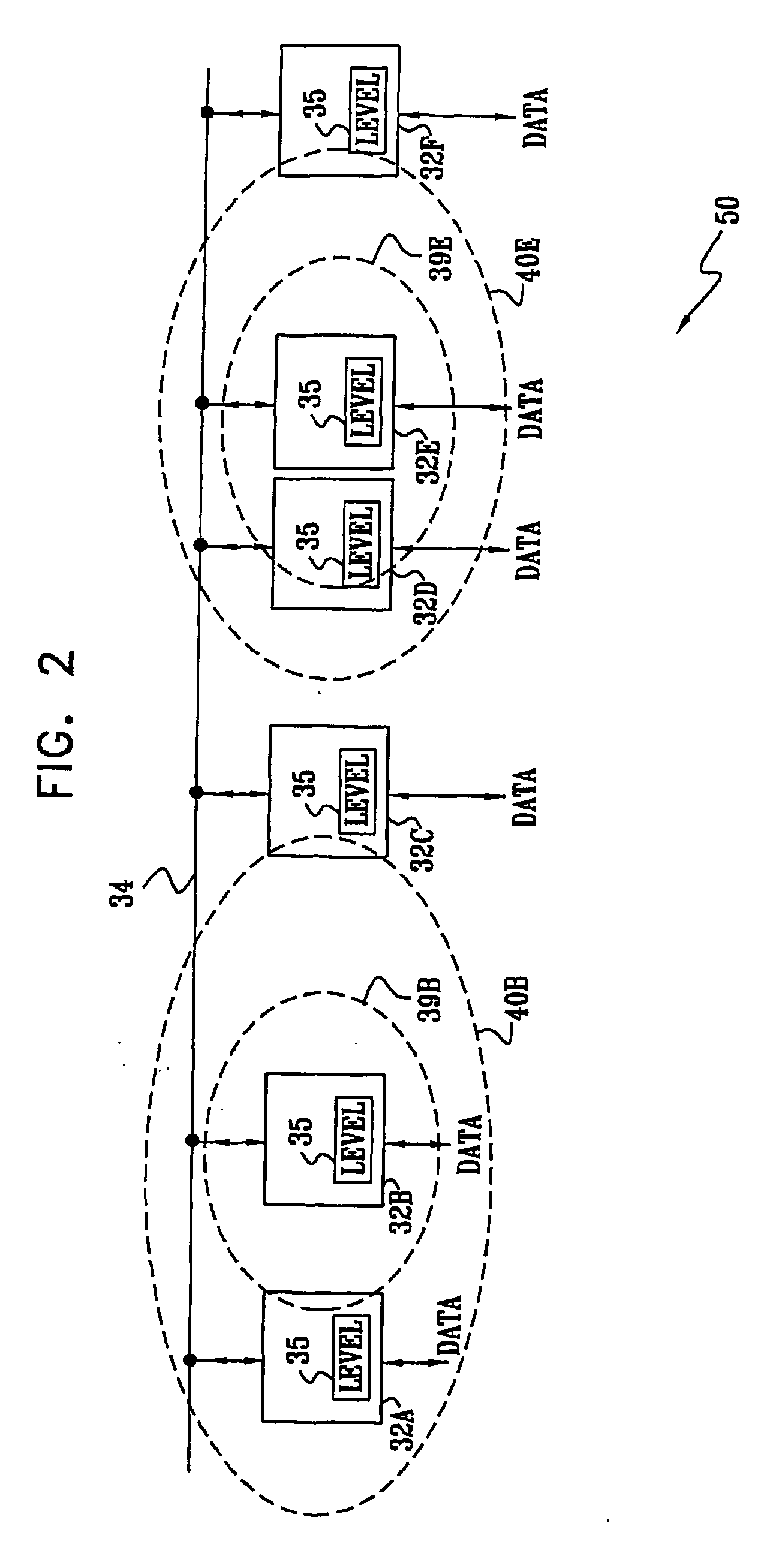
A method for communication over a network of power lines (34), including establishing a communication link within a selected frequency band over the network between a first transceiver (32B) coupled to the network and a second transceiver (32C) coupled to the network. The method further includes transmitting a first signal over the link from the first transceiver to the second transceiver at a transmission power level that is sufficiently strong that the signal can be decoded by the second transceiver, but is attenuated sufficiently when it reaches a third transceiver (32E) coupled to the network so that the third transceiver can receive a second signal over the network in the selected frequency band substantially without interference by the first signal.
Owner:MAIN NET COMM
Multi-Wideband Communications over Multiple Mediums within a Network
InactiveUS20120243621A1Systems using filtering and bypassingSystems with measurements/testing channelsCommunication interfaceQuality of service
A multi-network interface device comprises a powerline communications interface and at least one other non-power line communications interface configured to communicate over a network. The network may comprise mediums including powerlines, telephone lines, and / or coaxial cables. The multi-network interface device may receive a communications signal via a first medium and transmit the message via a second medium based on a quality of service (QoS) metric.
Owner:BROADCOM EURO
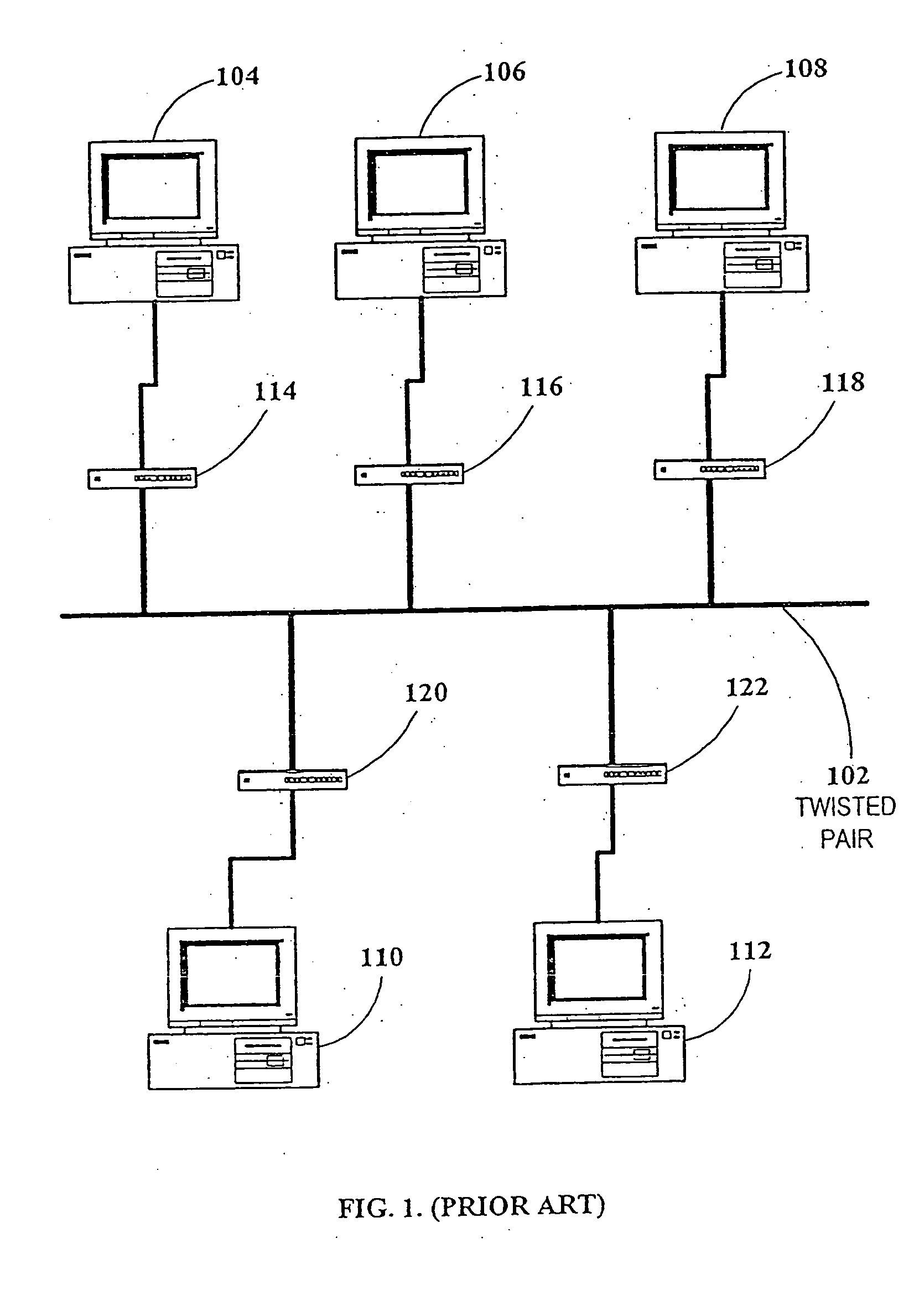
Local area network of serial intelligent cells
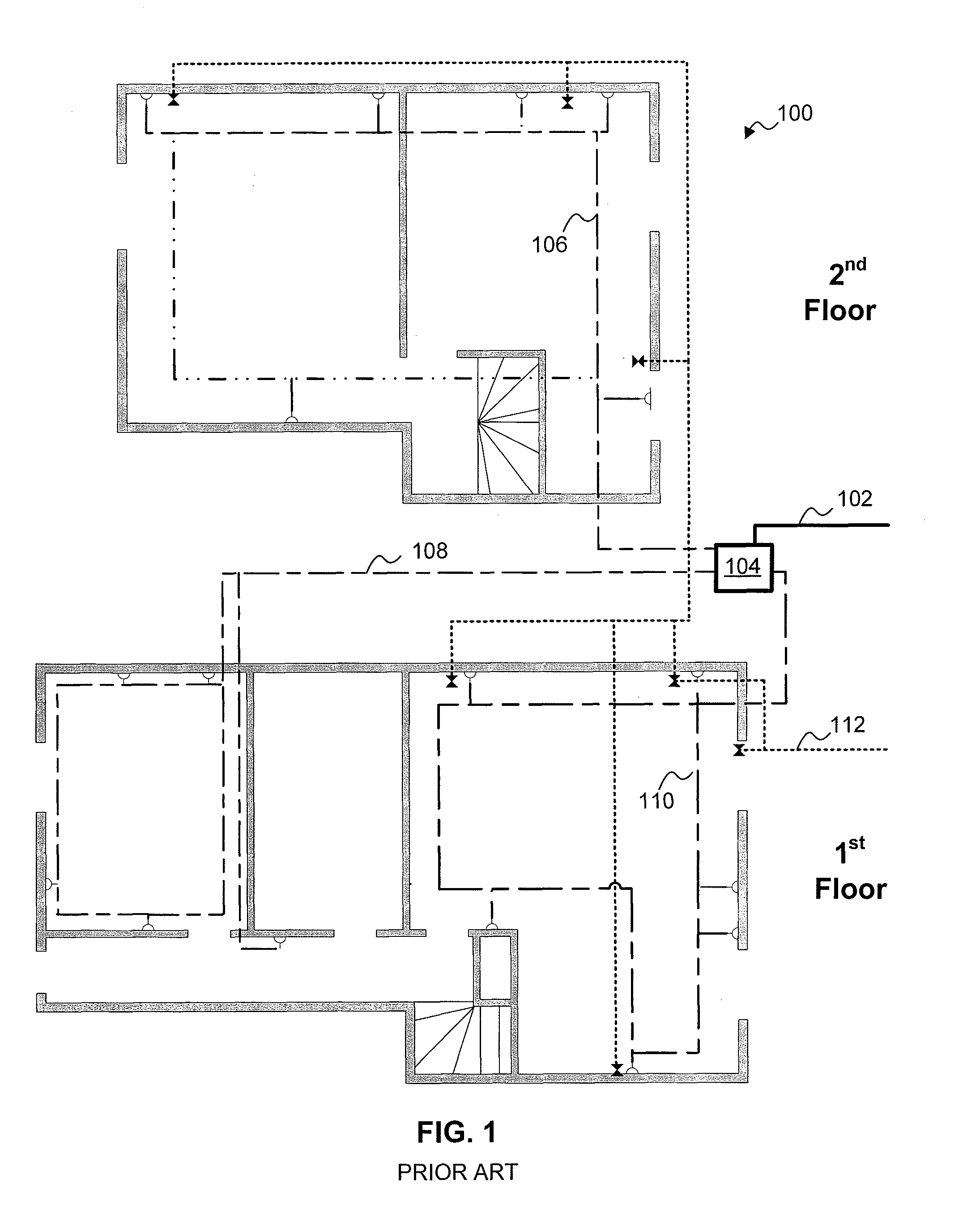
InactiveUS20050163152A1Easy to installReliable communicationBroadband local area networksPower distribution line transmissionInterconnectivityData terminal
A serial intelligent cell (SIC) and a connection topology for local area networks using Electrically-conducting media. A local area network can be configured from a plurality of SIC's interconnected so that all communications between two adjacent SIC's is both point-to-point and bidirectional. Each SIC can be connected to one or more other SIC's to allow redundant communication paths. Communications in different areas of a SIC network are independent of one another, so that, unlike current bus topology and star topology, there is no fundamental limit on the size or extent of a SIC network. Each SIC can optionally be connected to one or more data terminals, computers, telephones, sensors, actuators, etc., to facilitate interconnectivity among such devices. Networks according to the present invention can be configured for a variety of applications, including a local telephone system, remote computer bus extender, multiplexers, PABX / PBX functionality, security systems, and local broadcasting services. The network can use dedicated wiring, as well as existing wiring as the in-house telephone or electrical wiring.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Multi-wideband communications over multiple mediums within a network
ActiveUS8213895B2Systems using filtering and bypassingInterconnection arrangementsQuality of serviceMultiple frequency
A powerline communications device comprises a powerline communications interface and at least one other communications interface configured to communicate over a computing network. The powerline communications interface is further configured to receive electrical power. The computing network may comprise mediums including powerlines, telephone lines, and / or coaxial cables. In some embodiments, the powerline communications interface may communicate with a network apparatus, such as a personal computer, via an Ethernet interface. The powerline interface, the telephone line interface, and / or the coaxial cable interface may all be associated with the same media access control (MAC) address. The powerline communications device may receive a message via a first medium and repeat the message via a second medium based on a quality of service (QoS) metric. In some embodiments, the powerline communications device may communicate using multiple frequency bands.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
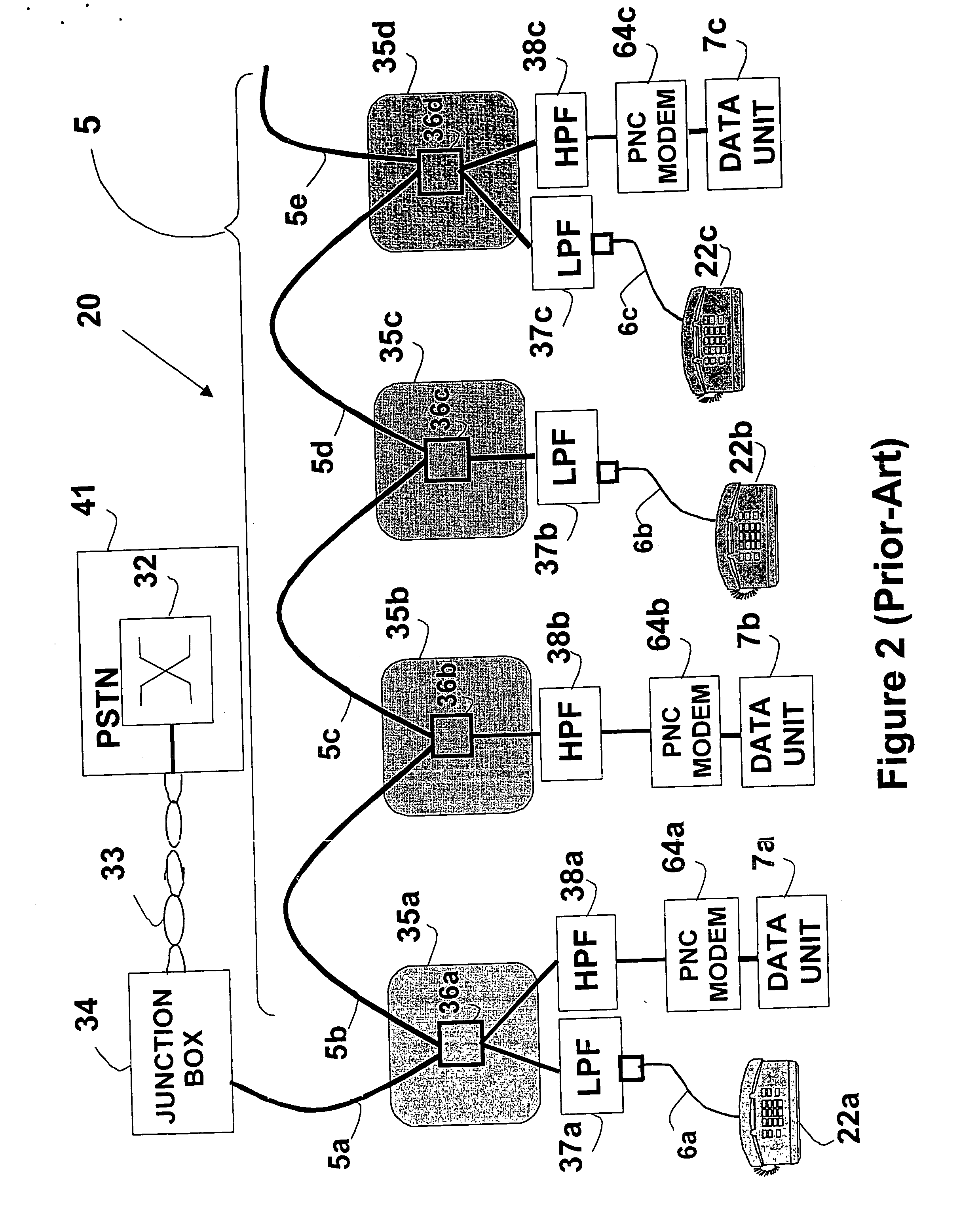
Local area network of serial intelligent cells
InactiveUS20050013320A1Precise positioningEasy to installBroadband local area networksPower distribution line transmissionDigital dataFrequency-division multiplexing
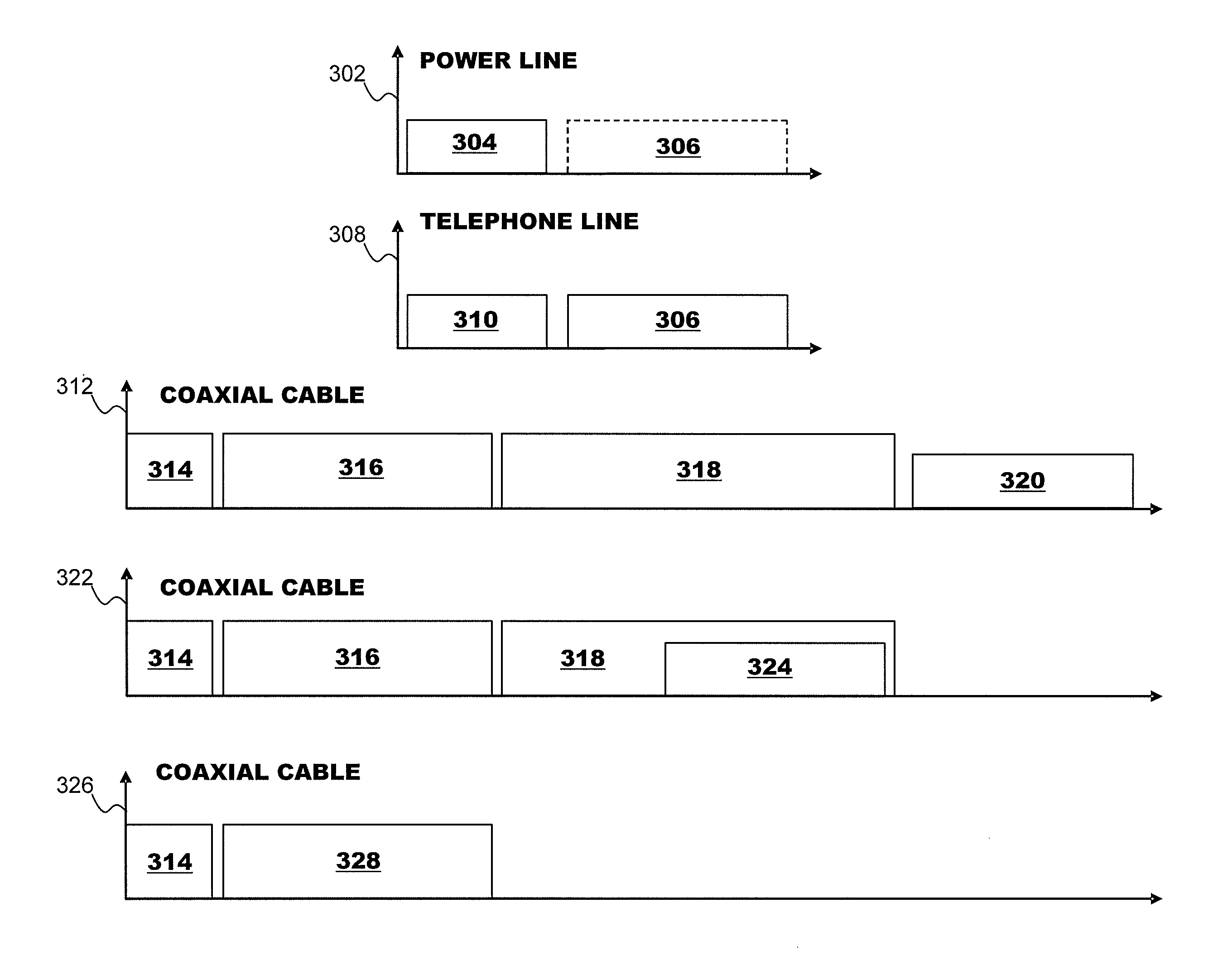
A device for coupling first and second bi-directional wired digital data signals to each other and to a data unit, for use with first and second service wire pairs installed at least in part in walls within a building. The first service wire pair concurrently carries the first bi-directional wired digital data signal and a first service signal carried over a first service signal frequency band, using frequency division multiplexing. The first wired digital data signal is carried over a frequency band distinct from the first service signal frequency band. The second service wire pair concurrently carries a second bi-directional wired digital data signal and a second service signal carried over a second service signal frequency band, using frequency division multiplexing. The second wired digital data signal is carried over a frequency band distinct from the second service signal frequency band.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
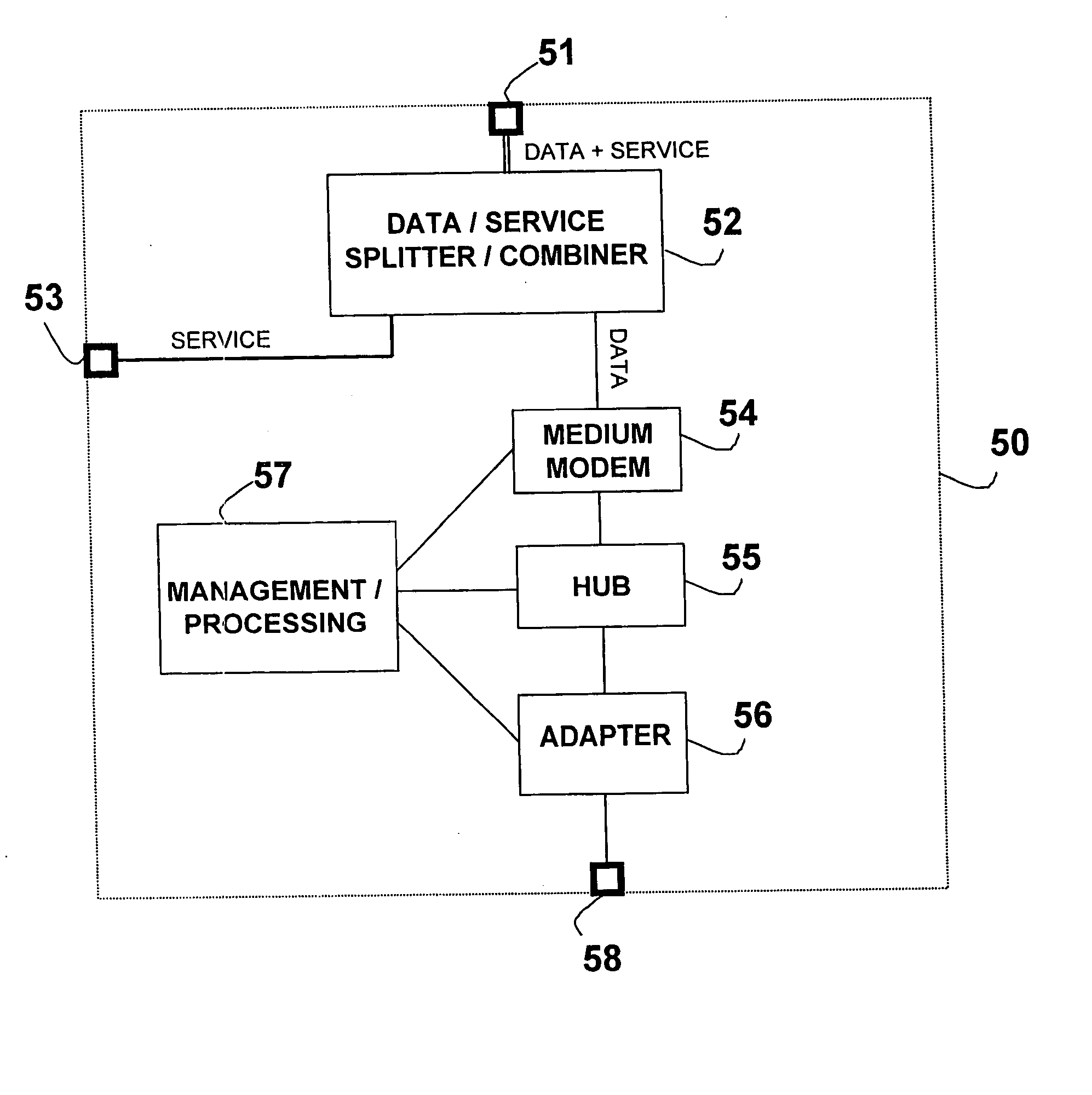
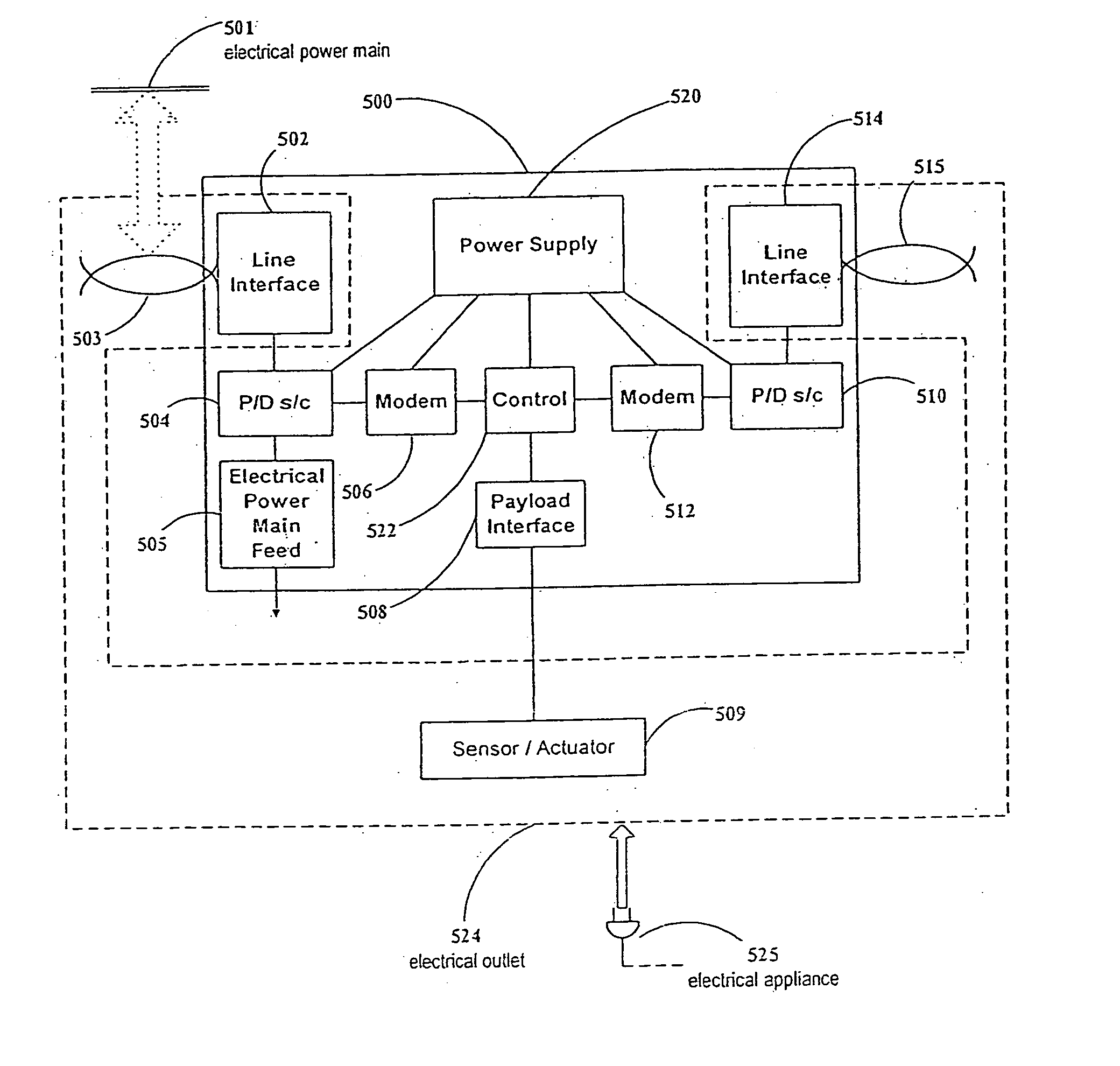
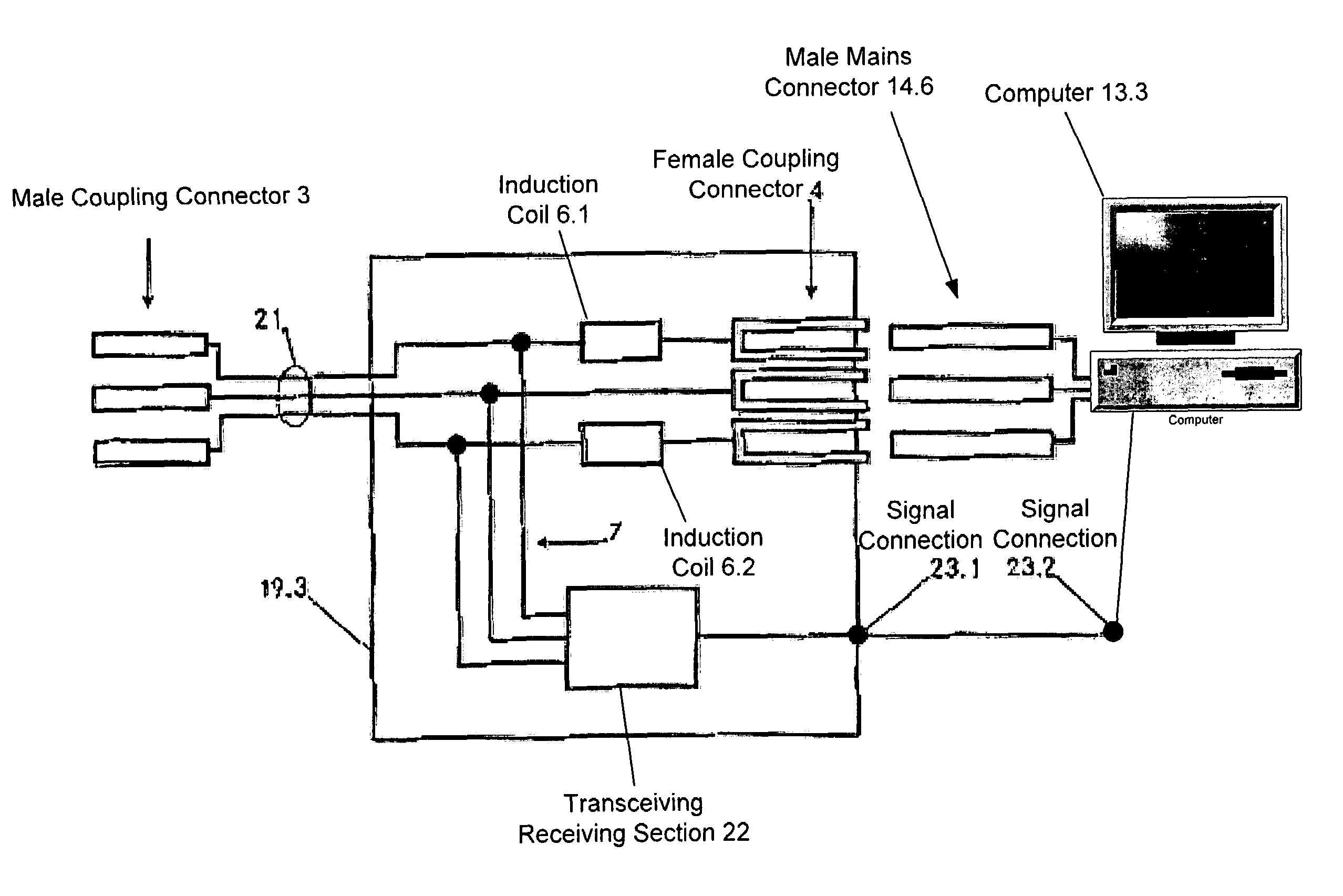
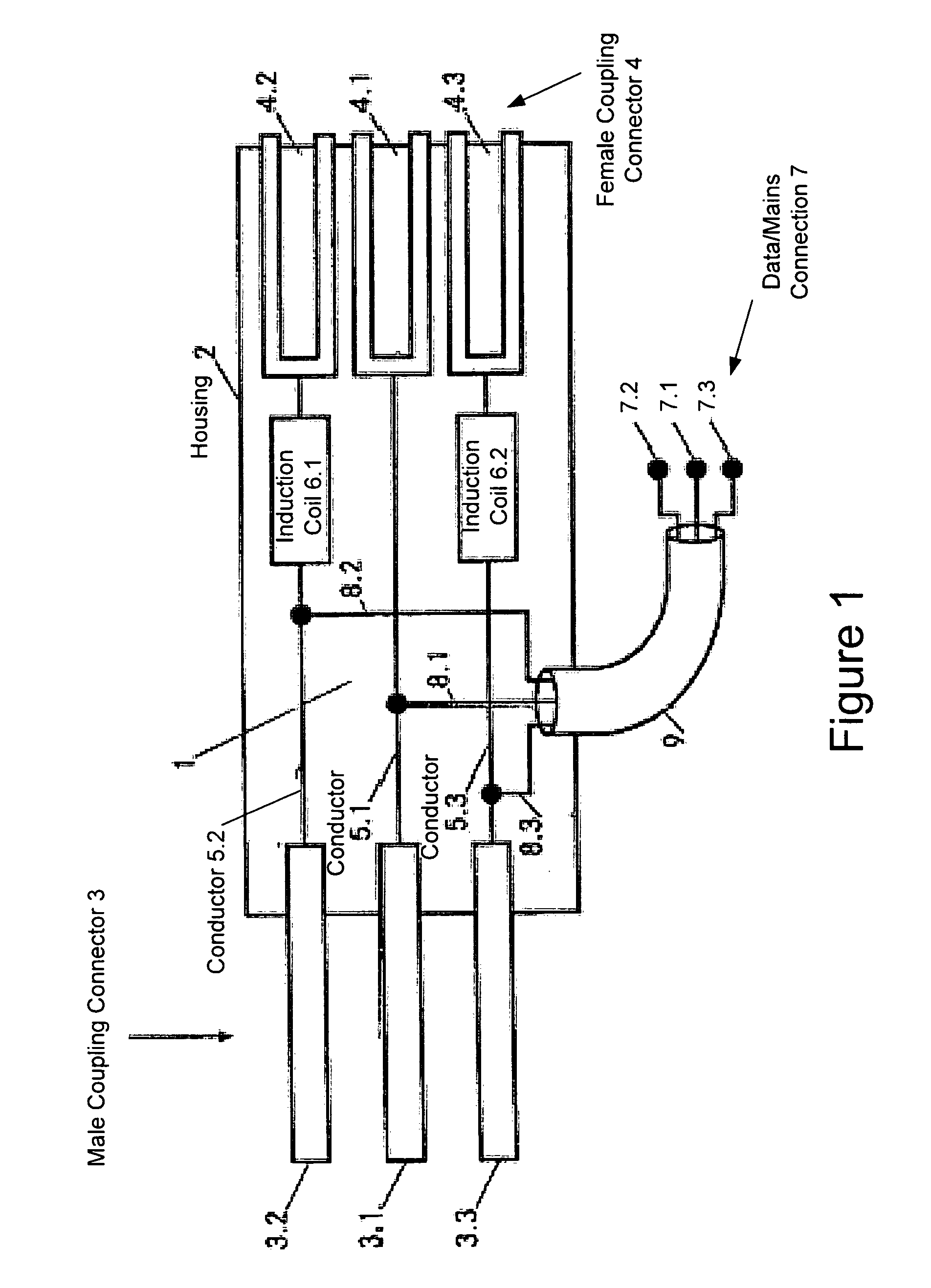
Assembly for transmitting information via a low-voltage power supply network
InactiveUS7675190B1Effect data transmissionAvoid interfering signalsCoupling for high frequencyPower distribution line transmissionModem deviceLow voltage
A coupling apparatus for facilitating communications of data signals over a low voltage electric power network is provided. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes a mains terminal configured to be connected to a low voltage electric power network carrying alternating current (AC) power and an appliance terminal configured to receive a male electric plug. The two terminals may be housed in a housing and connected via one or more inductive elements that attenuate high frequencies while allowing the AC power to pass through substantially unimpeded. Thus, interference caused by an appliance connected to the appliance terminal is filtered to prevent such interference from being conducted onto the low voltage electric power network. The apparatus also may include a third terminal that in some embodiments is electrically connected to the mains terminal to thereby output the data signals and AC power. In other embodiments, a modem may connect the third terminal to the mains terminal in which case the third terminal may communicate demodulated data to a communication device without outputting the AC power.
Owner:CURRENT COMMUNICATIONS INTERNATIONAL HOLDING GMBH
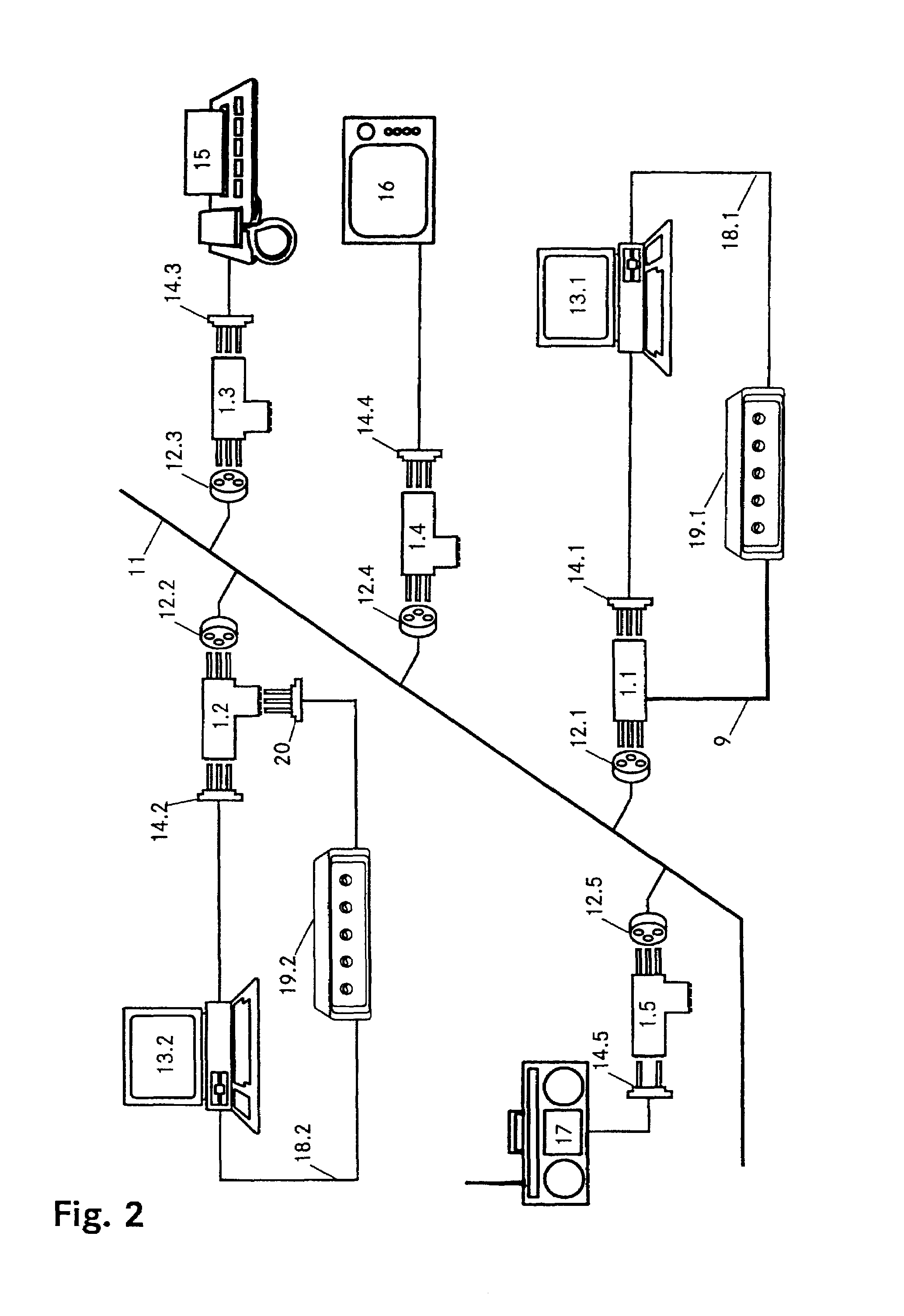
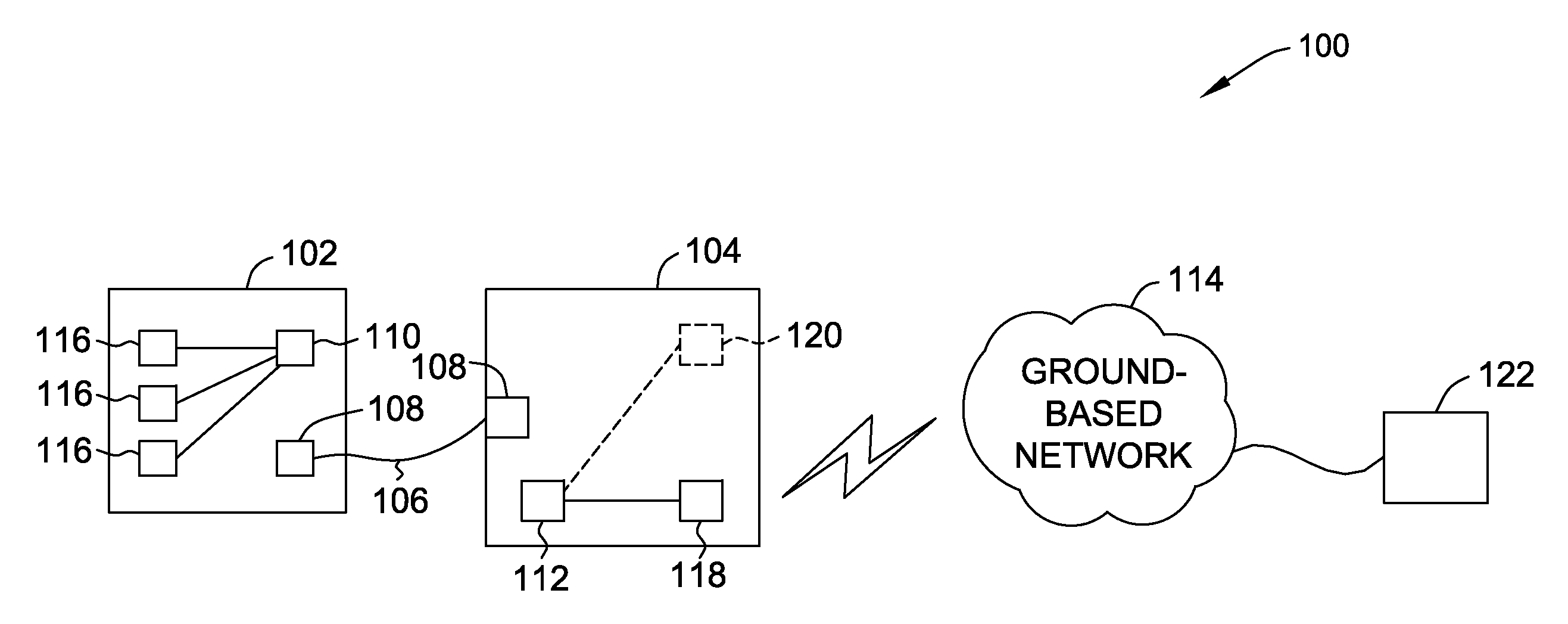
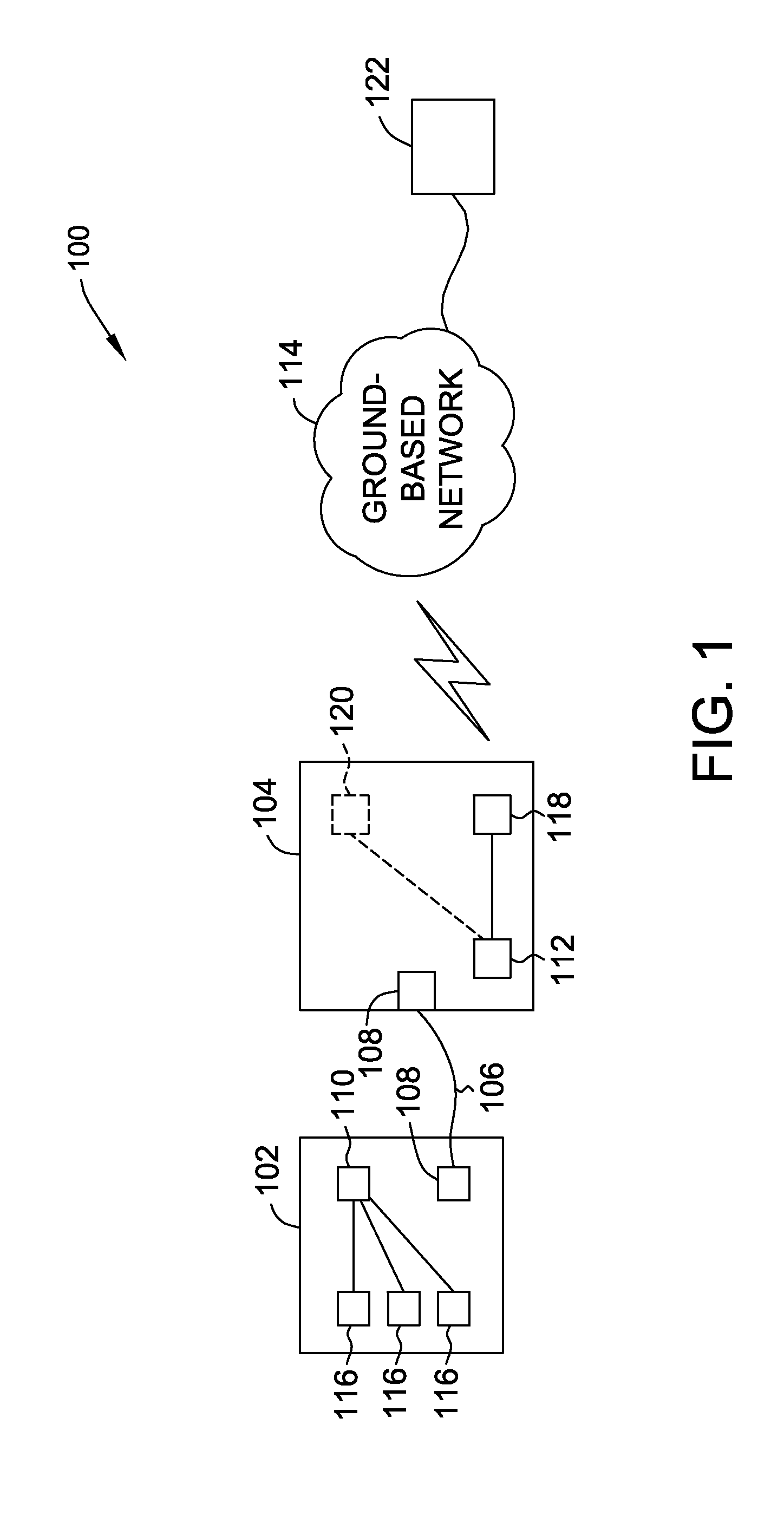
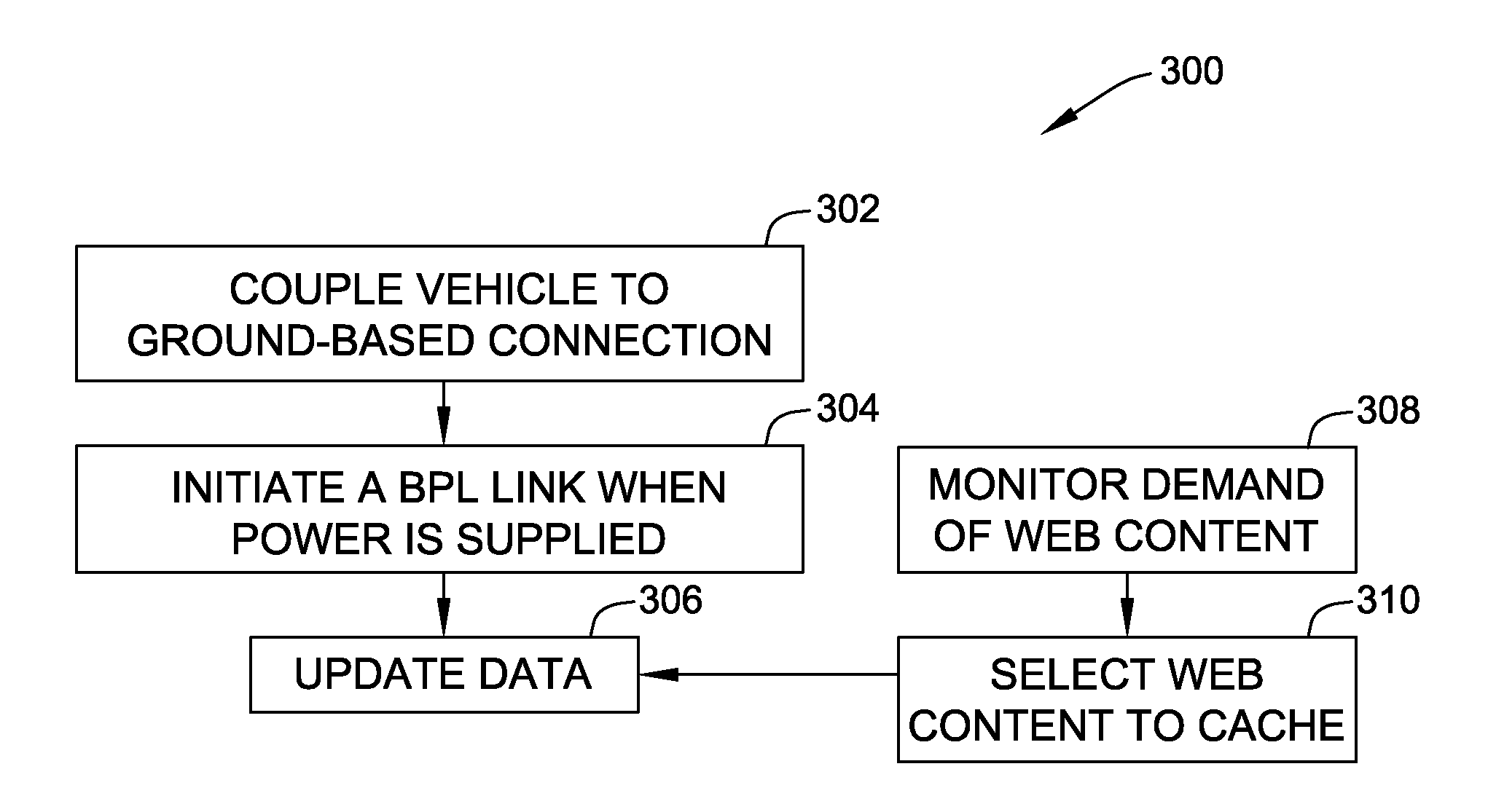
Methods and systems for vehicle broadband connection to a data network
Methods and systems for communicating data between a vehicle and a ground-based unit are provided. The method includes communicatively coupling the vehicle to the ground-based unit, initiating a Broadband over Power Line (BPL) link between the vehicle and the ground-based unit when power is supplied to the vehicle, and updating data stored in the vehicle with data received from the ground-based unit.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Methods and systems for vehicle broadband connection to a data network
ActiveUS20140074321A1Digital data processing detailsWired telephoneEngineeringBroadband over power lines
Methods and systems for communicating data between a vehicle and a ground-based unit are provided. The method includes communicatively coupling the vehicle to the ground-based unit, initiating a Broadband over Power Line (BPL) link between the vehicle and the ground-based unit when power is supplied to the vehicle, and updating data stored in the vehicle with data received from the ground-based unit.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
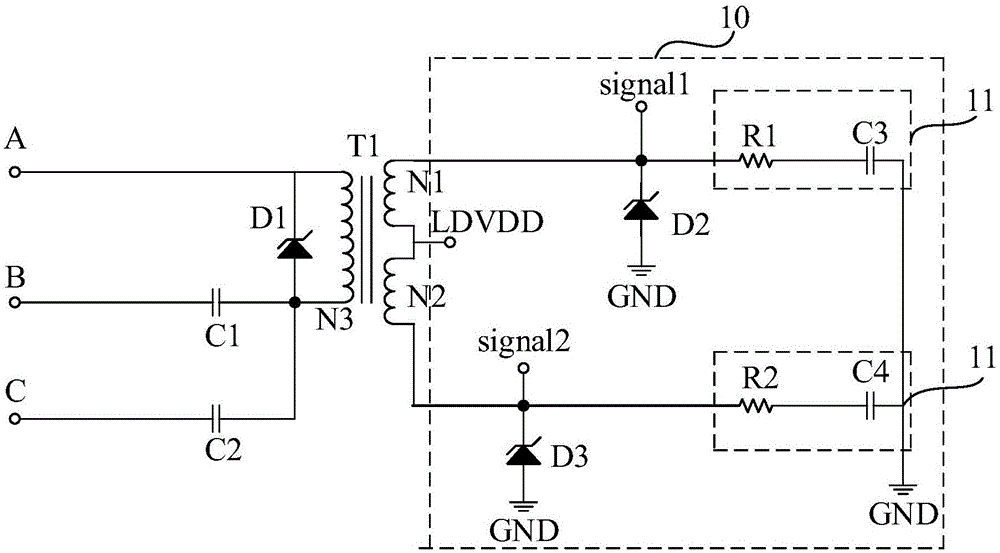
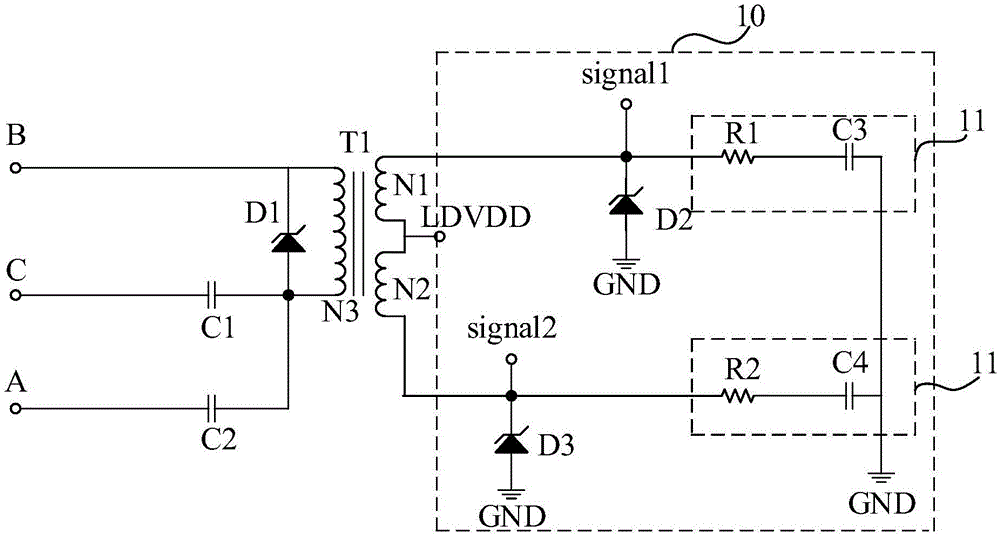
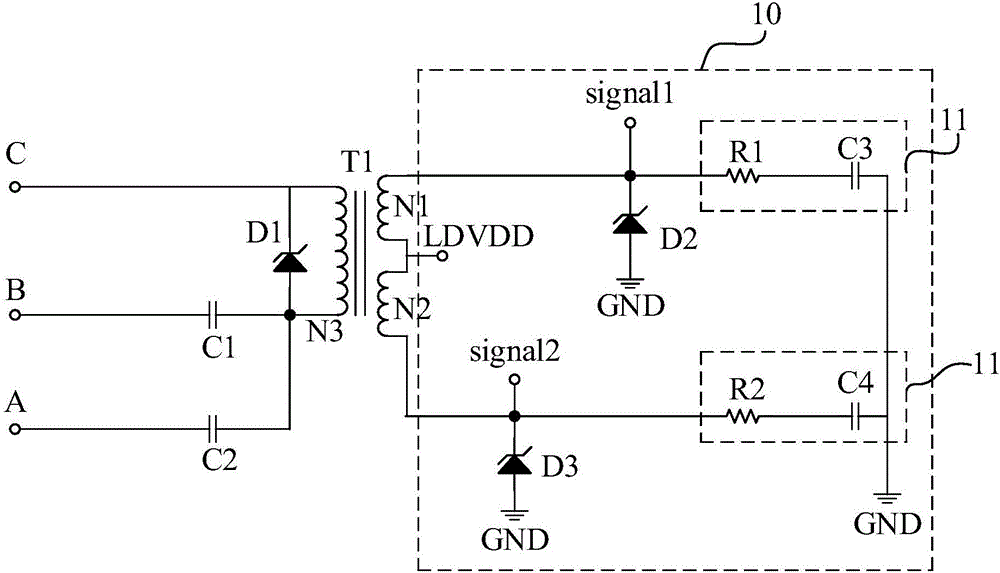
Power carrier signal coupling circuit and communication system
InactiveCN106374978ALow costReduce installation complexityPower distribution line transmissionCircuit arrangementsPower cableCommunications system
The present invention discloses a power carrier signal coupling circuit and a communication system. The power carrier signal coupling circuit comprises a first power carrier signal coupling channel and a second power carrier signal coupling channel. Any phase of three phases of alternating current power cable is used as a public channel. The first power carrier signal coupling channel is disposed between another phase of power cable and the public channel. The second power carrier signal coupling channel is disposed between the last phase of power cable and the public channel. Through adoption of the method, the reliability of the power carrier communication is improved, and the communication cost is lowered.
Owner:SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO LTD
Gateway integrating mobile communication and powerline connection
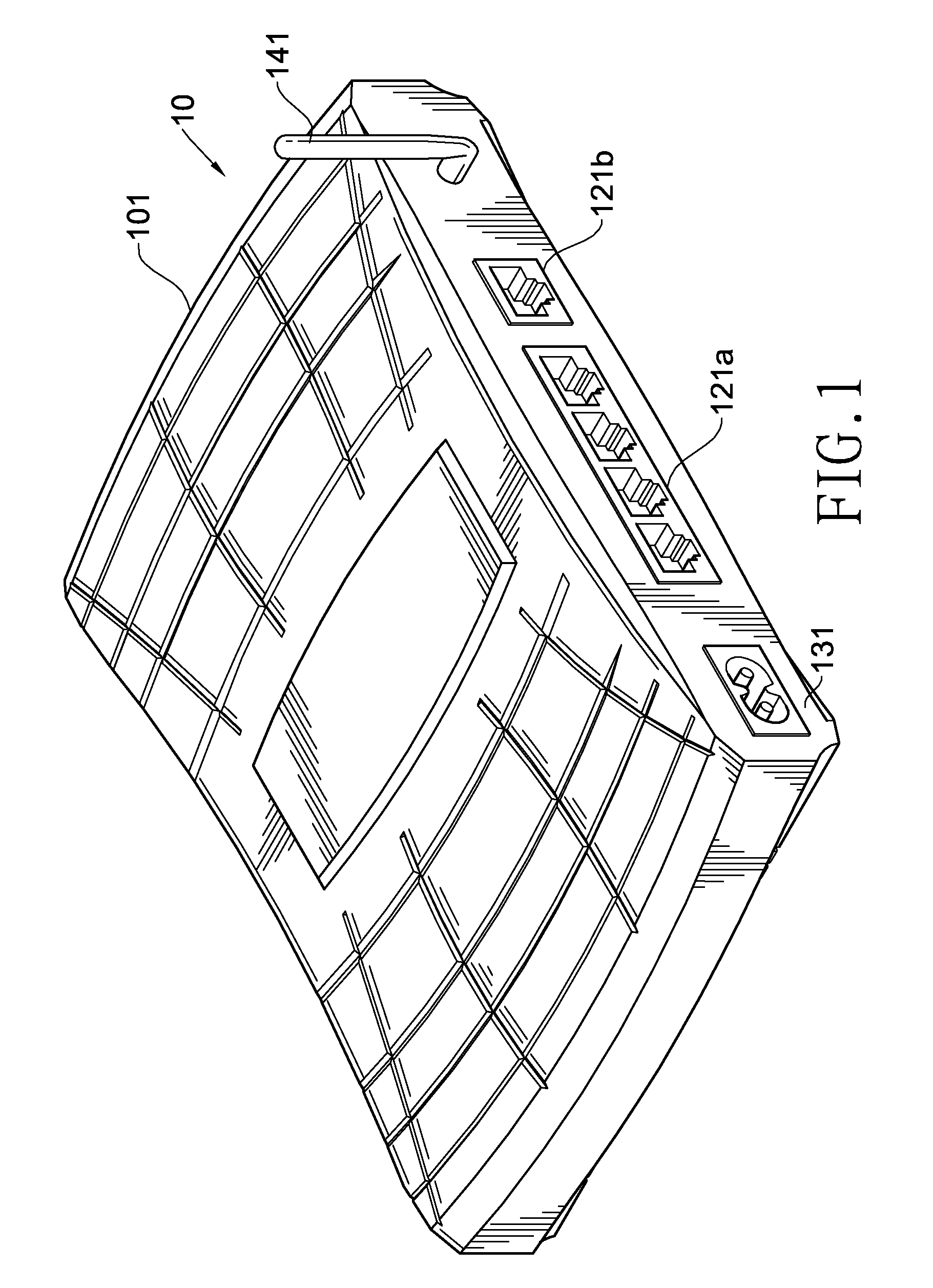
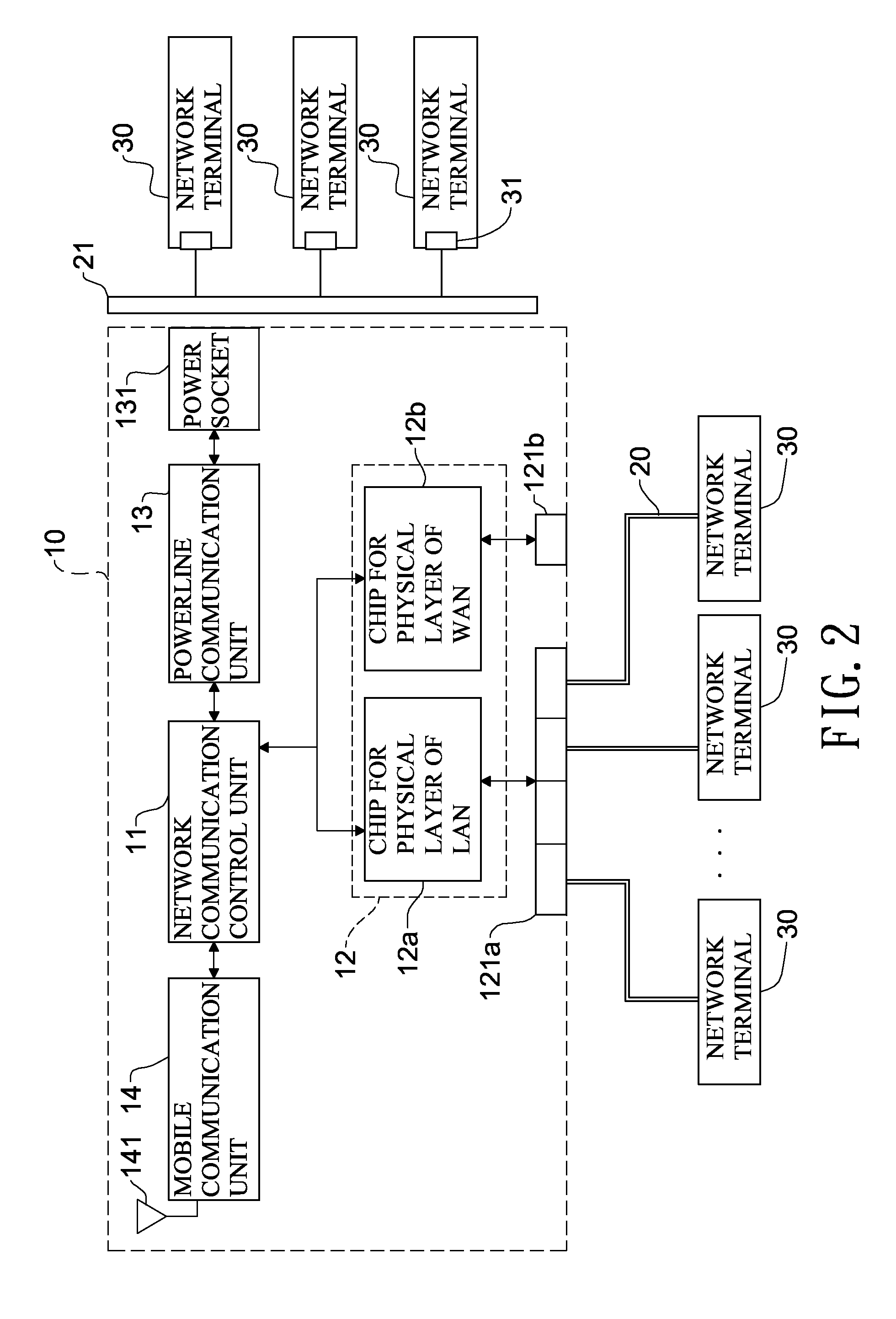
InactiveUS20100309923A1Speed up implementationDistribution is complicatedPower distribution line transmissionWired telephoneNetwork terminationCommunication unit
A gateway integrating mobile communication and powerline connection (PLC) has a network communication control unit, at least a wireline communication unit, a powerline communication unit and a mobile communication unit. The network communication control unit is connected with the wireline communication unit, the powerline communication unit and the mobile communication unit to convert, process and transmit network packets from the wireline communication unit, the powerline communication unit and the mobile communication unit. As such, the present invention is compatible with the network terminal using network cable, power line and mobile communication, thereby realizing the gateway integrating mobile communication and PLC.
Owner:ACBEL POLYTECH INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com