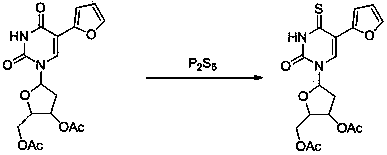
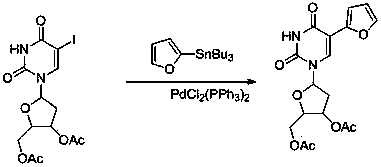Sulfur-bearing uridine anticancer drug, intermediate and synthesis method
A technology of anticancer drugs and synthetic methods, which is applied in the direction of drug combinations, chemical instruments and methods, and antineoplastic drugs. The effect of easy access to raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056]
[0057] Dissolve uridine (0.55 g, 2 mmol) in 10 mL of 0.3 mol / L dilute nitric acid, add simple iodine (0.504 g, 1.98 mmol), and heat under reflux for 100 min until the raw material is completely reacted (monitored by thin-layer chromatography). . After stopping the reaction, heat filtration to remove excess elemental iodine, the filtrate was extracted with petroleum ether until the solution was clear, and placed at 4°C to obtain a large amount of colorless needle-like crystals of 5-iodouridine, which were weighed to obtain 0.63 g after drying. 75%. m.p. 205-207℃, (literature value m.p. 208-210℃);
[0058] 1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ) (ppm): 11.71(br s,1H, N-H), 8.50(s, 1H, 6-H), 5.74(d, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz, 1'-H), 5.10, 5.29, 5.44(d , t, d, 1H, 1H, and 1H, OH), 4.05 (dd, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz, 8.0Hz, 2'-H), 4.00 (dd, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz, 8.0 Hz, 3 '-H), 3.89 (d, 1 H, J =4.0 Hz, 4'-H), 3.54-3.73 (m, 2H, 5'-H); UV-Vis (in CH 3 CN), λmax / nm: 280.0, λmax / nm: 243.0.
[0059] (2)...
Embodiment 2
[0076]
[0077] Dissolve uridine (0.55 g, 2 mmol) in 10 mL of 0.3 mol / L dilute nitric acid, add simple iodine (0.504 g, 1.98 mmol), and heat under reflux for 100 min until the raw material is completely reacted (monitored by thin-layer chromatography). . After stopping the reaction, heat filtration to remove excess elemental iodine, the filtrate was extracted with petroleum ether until the solution was clear, and placed at 4°C to obtain a large amount of colorless needle-like crystals of 5-iodouridine, which were weighed to obtain 0.63 g after drying. 75%. m.p. 205-207℃, (literature value m.p. 208-210℃);
[0078] 1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ) (ppm): 11.71(br s,1H, N-H), 8.50(s, 1H, 6-H), 5.74(d, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz, 1'-H), 5.10, 5.29, 5.44(d , t, d, 1H, 1H, and 1H, OH), 4.05 (dd, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz, 8.0 Hz, 2'-H), 4.00 (dd, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz, 8.0 Hz, 3 '-H), 3.89 (d, 1 H, J =4.0 Hz, 4'-H), 3.54-3.73 (m, 2H, 5'-H); UV-Vis (in CH 3 CN), λmax / nm: 280.0, λmax / nm: 243.0.
[0079] (2...
Embodiment 3
[0097]
[0098] In a 100 mL three-necked flask, add 5-iodo-2'-deoxyuridine (1.0 g, 2.82 mmol), anhydrous pyridine (15 mL, 183 mmol), and add purified acetic anhydride after it is fully dissolved (3.0 mL, 32 mmol), reacted under ice bath conditions for 16 h, removed the solvent under reduced pressure, then added 10 mL each of dichloromethane and benzene, removed the solvent again under reduced pressure, and added dichloromethane (20 mL), the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The crude product was dissolved in dichloromethane (250 mL), and saturated NaHCO 3 (80 mL), extracted three times with dichloromethane. Anhydrous NaSO for organic phase 4 Dry, filter, and remove the solvent from the filtrate under reduced pressure. Add 1.5 mL of 95% ethanol, and then place the mixture in the freezer for 24 h to precipitate a white solid 3',5'-O-dioxoacetyl-5-iodo-2'-deoxyuridine (1.13 g , 2.58 mmol), the yield is 91%, m. p. 156-157 ℃.
[0099] 1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com