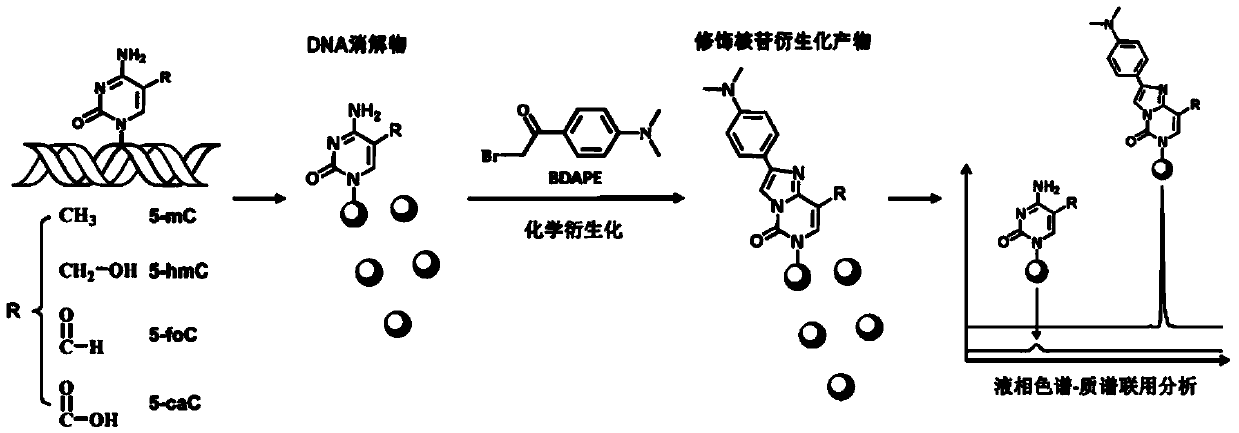
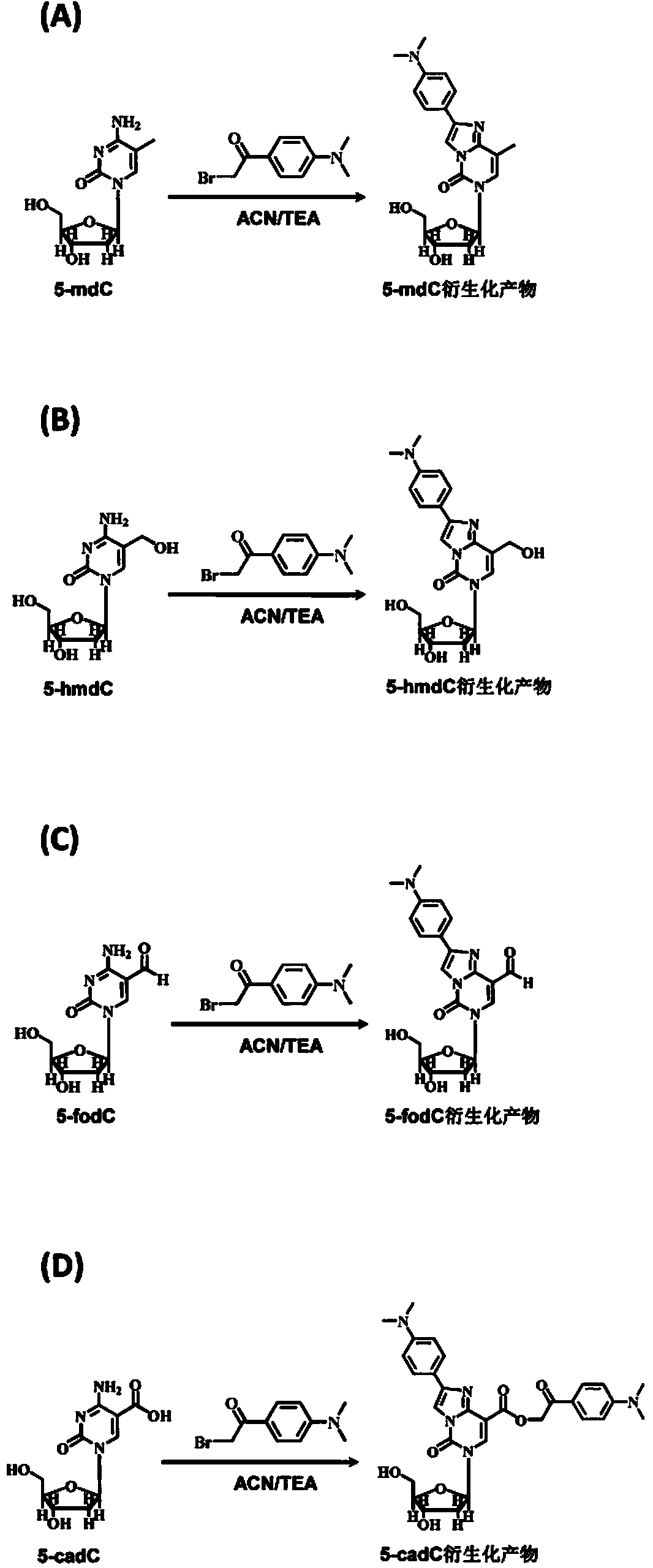
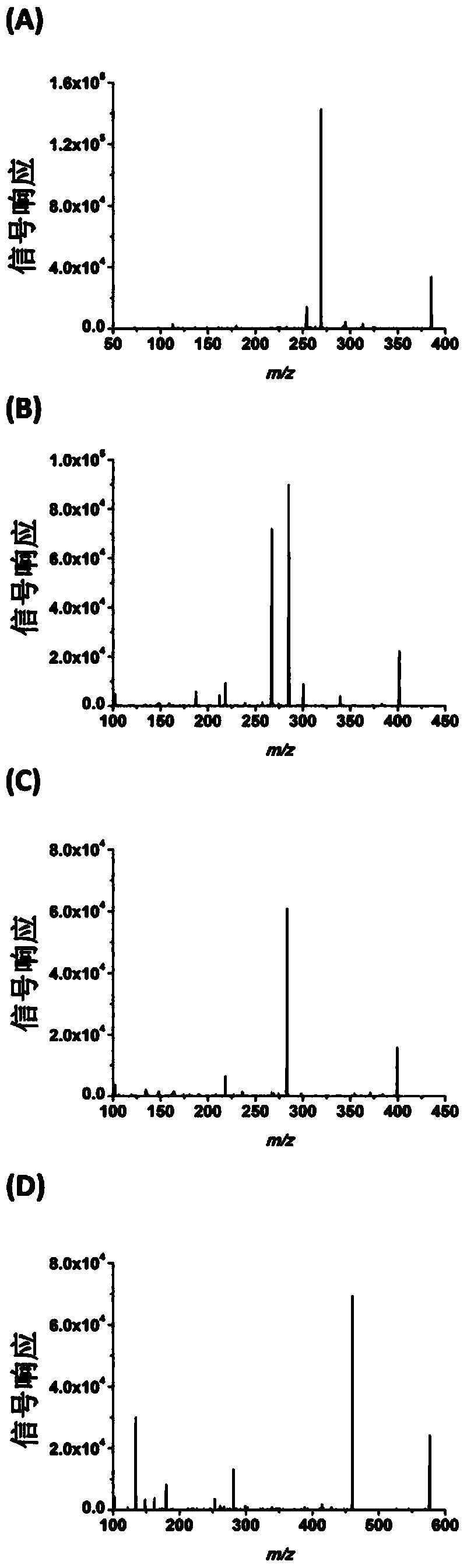
Chemical derivatization method and application thereof to nucleic acid modification detection by liquid chromatogram-mass spectrometer (LC-MS) method
A derivatization and chemical technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, measurement devices, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient sensitivity to detect, cumbersome operation, time-consuming and labor-intensive, etc., to facilitate quantitative analysis, avoid Contamination mass spectrometry, the effect of broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1: Human Cell DNA Analysis
[0045] Three human cell lines: HeLa (cervical carcinoma cells), Jurkat-T (leukemic lymphocytes) and 293T (human embryonic kidney cells). Take a certain number of cultured cells and wash them with PBS buffer, put them in a 1.5mL centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 2000g for 20s to pellet the cells, and discard the supernatant. Add 0.5mL cell lysate A (320mM sucrose, 5mM MgCl 2 , 10mM Tris, 0.1mM deferoxamine, pH 7.5, 1% Triton X-100), shake vigorously for 30s with a micro-vortex mixer. The sample was centrifuged at 16000g for 20s, the supernatant was discarded, and the previous process was repeated. Then add 0.2 mL of cell lysate B (10 mM Tris, 5 mM EDTA, 0.15 mM deferoxamine, pH 8.0, 1% sodium lauryl sarcosine), and shake vigorously for 30 s with a micro-vortex mixer. Add 10 μL RNaseA (1 mg / mL) and 3 μL RNaseT1 (1 U / μL), and incubate in a water bath at 50° C. for 15 minutes to remove RNA. Then add 10 μL proteinase K (20mg / ml in H 2 O...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: DNA Analysis of Cancer Tissues and Paracancerous Tissues of Colorectal Cancer Patients
[0050] Take formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded colorectal patient tissue sections (5-10 slices, about 30 mg), and use a paraffin-embedded tissue DNA extraction kit ( FFPE DNA Kit, Omega Co.) to extract DNA from tissues. The extracted DNA was dissolved in water and quantified by an ultra-micro ultraviolet spectrophotometer. Take 2-20μg DNA, dry it in vacuum, add 17μL water and 2μL S1 nuclease buffer (300mM sodium acetate, pH 4.6, 2800mM sodium chloride, 10mM zinc sulfate) in sequence, put it in a 95℃ water bath for 5 minutes, then place it quickly Quench in an ice-water bath for 2 minutes to untangle the DNA double strands, add 1 μL of S1 nuclease (180 U / μL) and incubate in a 37°C water bath for 12-16 hours. Then add 65 μL water, 10 μL alkaline phosphatase buffer (500 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM magnesium chloride, pH 9.0), 1 μL alkaline phosphatase (30 U / μL), 4 μL snake venom p...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3: Yeast Cell DNA Analysis
[0054]Ten yeast strains: Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741, Saccharomyces cerevisiae W1588-4C, Debaryomyces hansenii, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Maxk Kluyveromyces marxianus, Schizosaccharomyces octosporus, Yarrowia lipolytica, Pichia pastoris, Saccharomyces boulardii, Krull lactis After the culture of Kluyveromyces lactis, the yeast cell suspension was centrifuged at 4600g for 5 minutes, the cell pellet was collected and washed with water, and the residual medium was removed. Disperse the yeast cells in 1 mL of cell lysate (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 1 mM EDTA, 100 mM NaCl, 10 g / L SDS, 20 g / L Triton X-100), and then add an equal volume of phenol / chloroform (1: 1. v / v, phenol is saturated with 10mM Tris, 1mM EDTA, pH 8) and 1.5g glass beads (425-600μm), and shake vigorously for 10min with a micro-vortex mixer. Then 1 mL of TE buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0) was added to the solution, and centrifuged at 13500 g for 5 minutes. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com