Hydrogenation catalyst based on dicyclopentadiene (DCPD) resin undergoing heat polymerization by dicyclopentadiene in ethylene pyrolysis C9 and preparation method thereof and application
A technology for dicyclopentadiene and hydrogenation catalysts, applied in the direction of metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, physical/chemical process catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the cumbersome activation process, serious resin degradation, inability to To meet the needs of hydrogenation and other issues, to achieve the effect of simple activation process and improved sulfur resistance performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
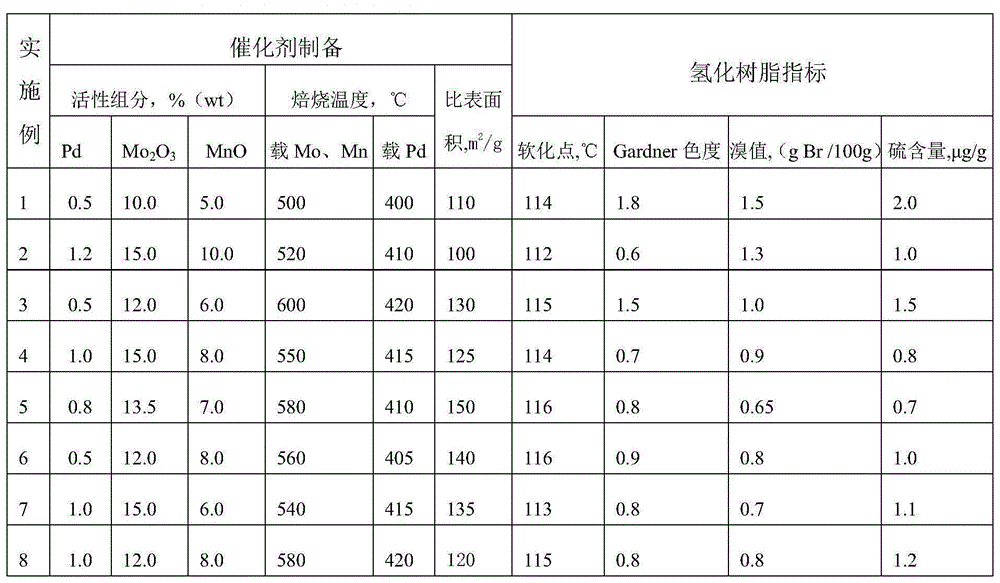
[0035] The preparation of catalyst: the preparation and evaluation data of table 3 catalyst:
[0036] Weigh a certain amount of formed γ-alumina carrier, use soluble salts of molybdenum and manganese to make a loading solution equal to the volume of the carrier, soak the carrier in the loading solution for a certain period of time at room temperature, and pour out the remaining The soaking solution is dried, roasted and cooled, then soaked in an equal volume of palladium soluble salt solution for a certain period of time, and then dried and roasted to obtain the required catalyst.
[0037] The catalyst is reduced in a hydrogen atmosphere, first raised to 120°C at 3-5°C / min, and kept at a constant temperature for 2h to 3h, then raised to 300°C at a rate of 3-5°C / min, kept at a constant temperature for 4h to 6h, and then put the bed in a hydrogen atmosphere. The temperature of the layer was lowered to 260°C for the hydrogenation reaction.
[0038] Catalyst hydrogenation reactio...
Embodiment 1-8
[0046] Examples 1-8 are catalyst preparation and evaluation experiments.
[0047] Weigh 30 g of strip-shaped γ-alumina carrier after molding, and carry the required Mo content on the catalyst according to Table 3. 2 o 3 , MnO weight percent content Weigh required ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate and 50% manganese nitrate to prepare 45ml solution. Soak the carrier in the solution for 12 hours at room temperature, and pour off the remaining soaking solution. After drying at 118-120°C, calcining at 500-600°C for 6 hours, loaded with high content of molybdenum and manganese, the catalyst has the performance of anti-sulfur poisoning and hydrogenation performance of sulfide. The gamma-alumina carrier after loading molybdenum and manganese is soaked with an equal volume of palladium chloride solution for 12 hours (weighing the amount converted into palladium chloride according to the palladium content required for loading), and then dried, The catalyst is prepared by roasting, and ...
Embodiment 9-20
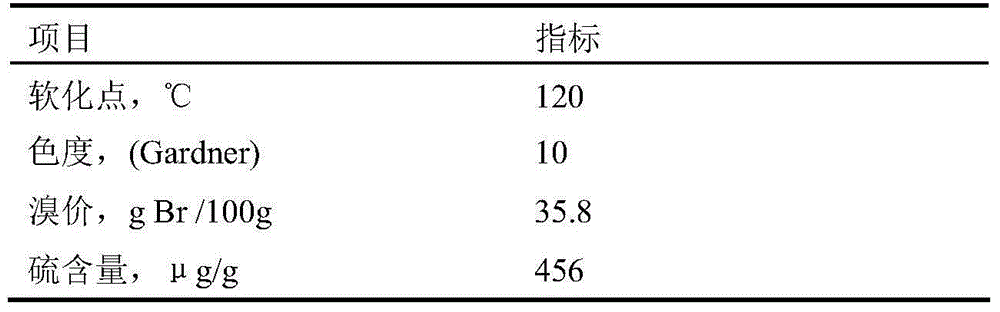
[0053] Embodiment 9-20 is based on ethylene cracking C 9 The reaction condition experiment of the DCPD petroleum resin of medium dicyclopentadiene thermopolymerization, catalyzer is the catalyzer among the embodiment 5.
[0054] Catalyst evaluation was carried out in a 10 ml fixed bed reactor.
[0055] The prepared catalyst is reduced in a hydrogen atmosphere in a 10ml fixed-bed reactor, first raised to 120°C at 3-5°C / min, and kept at a constant temperature for 2h-3h, then raised to 300°C at a rate of 3-5°C / min, and kept at a constant temperature for 4h- 6h, and then lower the bed temperature to 260°C in a hydrogen atmosphere for hydrogenation reaction.
[0056]The experimental process of catalyst hydrogenation reaction conditions is as follows: use one of n-heptane, methylcyclohexane or n-octane to make DCPD resin into a solution with a concentration of 10-20%, preheat to 250-260°C and enter the fixed bed Reactor, control the reactor temperature at 260-280°C, the reaction p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com