A negative electrode material for a zinc-nickel battery and its preparation method and application
A technology of zinc-nickel battery and negative electrode material, applied in nickel battery, electrode manufacturing, battery electrode and other directions, can solve the problems of unsuitable negative electrode material for lithium ion battery, inability to perform lithium ion intercalation and deintercalation, unstable thermodynamic properties, etc. Achieve excellent electrochemical performance, stable and reliable process conditions, high energy density and power density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1, urea prepares the method for basic zinc carbonate (zinc salt is example with zinc chloride)
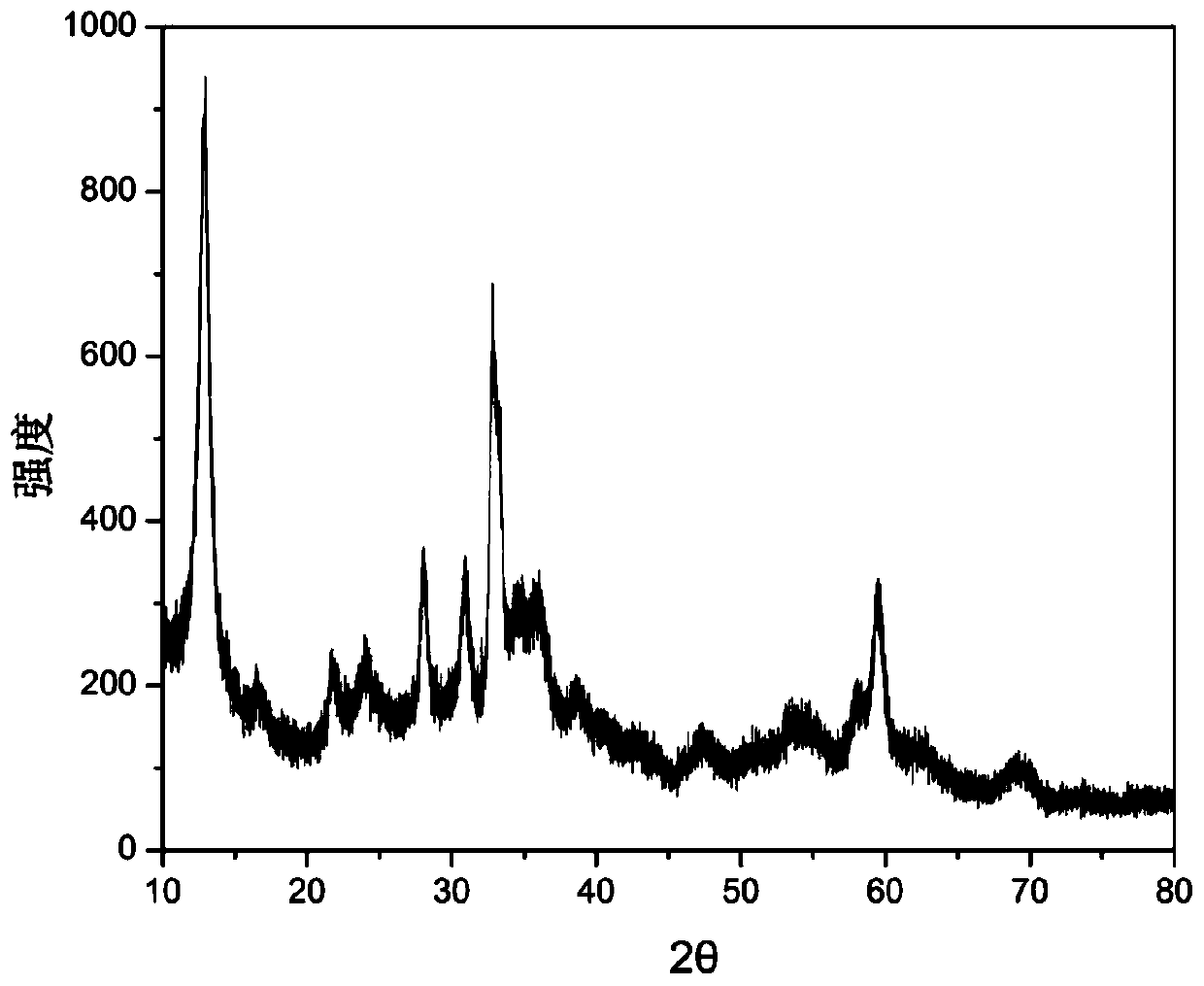
[0036] 1g of zinc chloride was added into 50mL of water to obtain a zinc chloride solution, a certain amount of urea (the quality of urea was 1.33g, 1.55g or 1.77g) was dissolved in 30mL of water to obtain a urea solution, and the two solutions were mixed and transferred to the reactor. React at 90°C for 12h while stirring magnetically. After the reaction is completed, filter, wash with deionized water until neutral, and dry at a temperature of 50°C to obtain basic zinc carbonate. The scanning electron microscope picture is as follows: figure 1 As shown, its XRD pattern is shown in image 3 shown.
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2, ammonium bicarbonate prepare the method for basic zinc carbonate (zinc salt is example with zinc nitrate)
[0038] Add 1g of zinc nitrate to 50mL of water to obtain zinc nitrate solution, weigh a certain mass of ammonium bicarbonate (1.08g, 1.15g or 1.23g respectively) and dissolve it in 15mL of water, slowly add the ammonium bicarbonate solution dropwise to the zinc salt solution At the same time, magnetic stirring was carried out, and the reaction temperature was 60°C. After the dropwise addition, the reaction was continued for 2h. After the reaction is completed, filter, wash with deionized water until neutral, and dry at a temperature of 50°C to obtain basic zinc carbonate. The scanning electron microscope picture is as follows: figure 2 As shown, its XRD pattern is shown in Figure 4 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0039] Embodiment 3, basic zinc carbonate as the negative electrode sheet preparation method of active material
[0040] In this embodiment, basic zinc carbonate is mixed with carbon materials (carbon nanotubes, carbon fibers or graphene), calcium hydroxide, bismuth oxide, and binder PTFE in a ratio of 82:10:1:3:4 to form a paste , apply it to brass mesh or three-dimensional tinned copper mesh, dry, press, and cut to obtain the negative plate; the PTFE used is a commercially available PTFE water emulsion with a mass concentration of 60%, and then diluted to 0.1%wt for use , converted to pure PTFE when calculating the PTFE ratio.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com