A method for extracting rare earth from ion adsorption type rare earth ore
An ion adsorption type, rare earth ore technology, applied in the field of rare earth extraction, can solve the problems of unavailable products, good effect, unqualified product purity, etc., to reduce the formation of calcium sulfate, reduce the generation of calcium sulfate, and weaken the migration speed Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
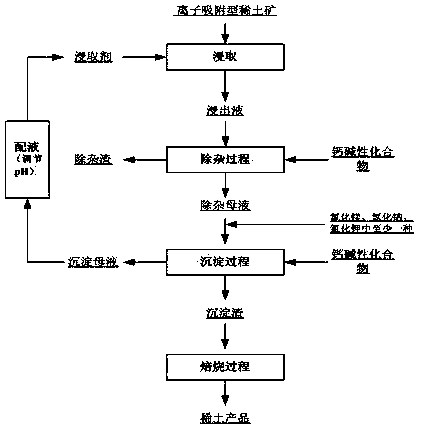
[0037] Example 1: Using a magnesium-containing sulfate and chloride mixed solution (the molar ratio of sulfate and chloride is 0.5:1) to leach ion-adsorbed rare earth ores, the obtained aluminum content is 0.05g / L, and the rare earth content is 0.3g / L (calculated as REO) leach solution; add calcium oxide to the leach solution obtained in step (1), adjust the pH of the solution to 5.2 for impurity removal, filter and wash with water after impurity removal to obtain impurity removal residue and impurity removal mother liquor. Add magnesium chloride to the impurity-removing mother liquor obtained in step (2), and control the chloride ion concentration in the impurity-removing mother liquor to 0.30 mol / L. Calcium oxide is then added to the impurity removal mother liquor for precipitation, the precipitation temperature is 25°C, and the pH of the precipitation end point is controlled to be 8.5; after the precipitation is completed, solid-liquid separation is carried out, and the prec...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: Using a mixed solution of sulfate and chloride containing magnesium (the molar ratio of sulfate and chloride is 0.5:1) to leach ion-adsorption type rare earth ore, the obtained aluminum content is 0.1g / L, and the rare earth content is 0.5g / L (calculated by REO) leachate; add calcium hydroxide to the leachate, adjust the pH of the solution to 5.2 for impurity removal, filter and wash with water after impurity removal to obtain impurity removal residue and impurity removal mother liquor. Add magnesium chloride to the impurity removal mother liquor, and control the chloride ion concentration in the impurity removal mother liquor to be 0.30mol / L. Calcium hydroxide is then added to the impurity removal mother liquor for precipitation, the precipitation temperature is 25°C, and the pH of the precipitation end point is controlled to be 8.5; after the precipitation is completed, solid-liquid separation is carried out, and the precipitation mother liquor and precipitat...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3: Using a mixed solution of sulfate and chloride containing magnesium and potassium (the molar ratio of sulfate and chloride is 2:1) to leach ion-adsorbed rare earth ores to obtain a rare earth mineral with an aluminum content of 0.3g / L. Leach solution with a content of 2g / L (calculated as REO); add calcium oxide to the leach solution, adjust the pH of the solution to 5.4 for impurity removal, filter and wash with water after impurity removal to obtain impurity removal residue and impurity removal mother liquor. Add magnesium chloride and potassium chloride to the impurity removal mother liquor, and control the chloride ion concentration in the impurity removal mother liquor to be 0.40mol / L. Calcium oxide is then added to the impurity removal mother liquor for precipitation, the precipitation temperature is 40°C, and the pH of the precipitation end point is controlled to be 8.8; after the precipitation is completed, solid-liquid separation is carried out, and th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com