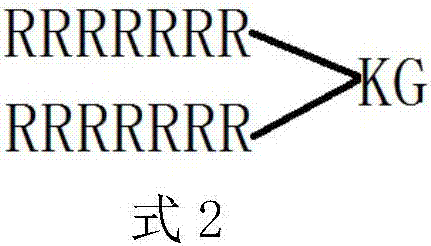Protamine active peptide analogs, and preparation method and application thereof
A protamine and active peptide technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of drug safety, drug uncontrollability, and difficulty in maintaining the quality of preparation batches.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
[0046] Experimental example 1. The inhibitory effect of protamine-like active peptides on Staphylococcus aureus
[0047] Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive bacterium (G + ), is the most common pathogenic bacteria that causes suppurative infection of human wounds, and is also the culprit that causes enteritis, pneumonia, sepsis, and sepsis. This experiment reflects the antibacterial effect of protamine-like active peptides by detecting the inhibitory rate of protamine-like active peptides on Staphylococcus aureus.
[0048] Preparation of LB culture medium:
[0049] Tryptone (Tryptone) 10g / L, yeast extract (Yeast extract) 5g / L, sodium chloride (NaCl) 10g / L, add distilled water to 1000ml, shake gently until the content dissolves, wrap the mouth of the bottle with tinfoil, and It can be used after high temperature and high pressure sterilization.
[0050] 1. Weigh the following 2mg samples of protamine-like active peptide freeze-dried powder:
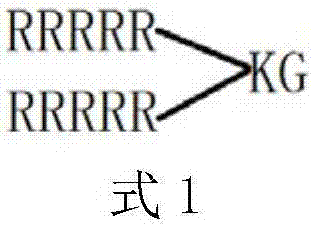
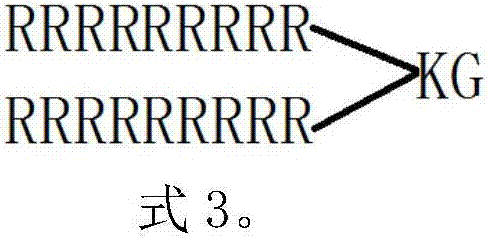
[0051] (R 9 ) 2 KG, mole...
experiment example 2
[0065] Experimental example 2. The inhibitory effect of protamine-like active peptides on Pseudomonas aeruginosa
[0066] Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a Gram-negative bacteria (G - ), is the main pathogenic bacteria that commonly causes burn wounds and wound infection and suppuration in clinical practice, and is the main pathogenic bacteria that causes diseases such as otitis media, keratitis, urethritis, gastroenteritis, and pneumonia. This experiment reflects the antibacterial effect of protamine-like active peptides by detecting the inhibitory rate of protamine-like active peptides on Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
[0067] Steps 1-3 are the same as Experimental Example 1;
[0068] 4. After burning the inoculation loop on the flame of the alcohol lamp, pick a little Pseudomonas aeruginosa and mix it in 1ml of normal saline to get the bacteria solution. Take 100μl of the bacteria solution and add it to the #0-#5 culture tube of Group A-E get culture fluid;
[0069] 5. Cultivate in ...
experiment example 3
[0074] Experimental Example 3: Allergenicity Detection of Protamine-like Active Peptides
[0075] 1. Take 4 healthy New Zealand white rabbits for 8 weeks and divide them into 2 groups (2 rabbits / group): protamine-like peptide group and natural protamine group (protamine sulfate injection, 50mg / 5ml, purchased from Beijing Yue Kangkaiyue Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.), the immune antigens in the two groups were protamine-like peptide and natural protamine;
[0076] 2. Initial immunization: subcutaneously inject Freund's complete adjuvant emulsion containing 1 mg / 1 ml immune antigen at 3 points on the back of each group of white rabbits;
[0077] The first booster immunization: 4 weeks after the initial immunization, the white rabbits in each group were subcutaneously injected with Freund's incomplete adjuvant emulsion containing 1mg / 1ml immune antigen again at 3 points;
[0078] The second booster immunization: 2 weeks after the first booster immunization, the white rabbits in each ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com