Injection liquid containing small molecular hyaluronic acid and application thereof
A technology of hyaluronic acid and human hyaluronidase, applied in the field of disease treatment drugs, can solve the problems of complex, difficult to determine clinical indications, difficult to predict the success of clinical research and druggability of small molecule hyaluronic acid, etc. , to achieve the effect of convenient production and stable preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Objective: To study the production process of injections, and to manufacture injections with and without recombinant human hyaluronidase PH20 residual protein.
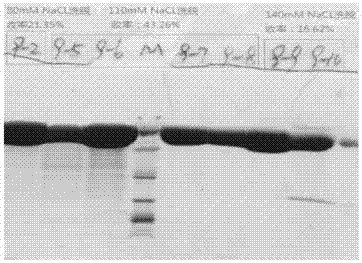
[0076] Method: Using animal cells (CHO cells) to produce glycosylated recombinant human hyaluronidase PH20, including: artificially synthesizing the gene cDNA of glycosylated recombinant human hyaluronidase PH20, inserting GC-rich pMH3, pMH4, pMH5 Empty expression vector, build up pMH3-PH20, pMH4-PH20, pMH5-PH20 expression vector (adopting the technology construction expression vector described in the patent document of CN102124019A here to express recombinant protein so that pMH3-PH20, pMH4- The cDNA expression vectors of PH20 and pMH5-PH20 were transferred into CHO-S cell line, and the CHO-S cell line with high expression of PH20 was screened. figure 1 The scale-up and large-scale cultivation of the torrent-type animal cell reactor is shown; the harvest liquid containing PH20 is filtered at 0.22um, and then s...
Embodiment 2
[0085] Objective: To study the anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects of Hyaluronic Acid Injection 1 of Example 1 in vitro experiments, molecular cytology experiments, and small animal experiments.
[0086]Method: The Hyaluronic Acid Injection 1 of Example 1 diluted 1-fold with normal saline was used to conduct in vitro antibacterial experiments, molecular cytology experiments, and small animal experiments to detect the anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects of Hyaluronic Acid Injection.
[0087] result: Figure 4 It shows that hyaluronic acid injection inhibits the growth of Porphyromonas gingivalis colony in vitro, suggesting that hyaluronic acid injection materials are not conducive to the growth of Porphyromonas gingivalis (Note: the negative control is normal saline, and the positive control is antibiotics Metronidazole); Figure 5 Show the anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects of hyaluronic acid injection on skin wounds of small animals; Image 6 It is ...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Purpose: To study the beauty and anti-aging effects of two kinds of hyaluronic acid injections containing (experimental group 1) and not (experimental group 2) hyaluronic acid fragments of recombinant human hyaluronidase PH20 residual protein in the above embodiment 1 efficacy and safety.
[0091] Method: Use the injection solution containing hyaluronic acid fragments of recombinant human hyaluronidase PH20 residual protein (100mg of hyaluronic acid fragments with a molecular weight of 10KD-60KD, 115-125mM sodium chloride, 1mM magnesium ions, no degraded hyaluronic acid The active recombinant human hyaluronidase residual protein is less than 20 micrograms) is the experimental group 1, which is used for various diseases or subclinical problems frequently occurring or aging and aging-related diseases frequently occurring in China's current air pollution, drinking water pollution and work pressure environment 38 subjects (average age 61±26 years old, 20 males, 18 females) ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com