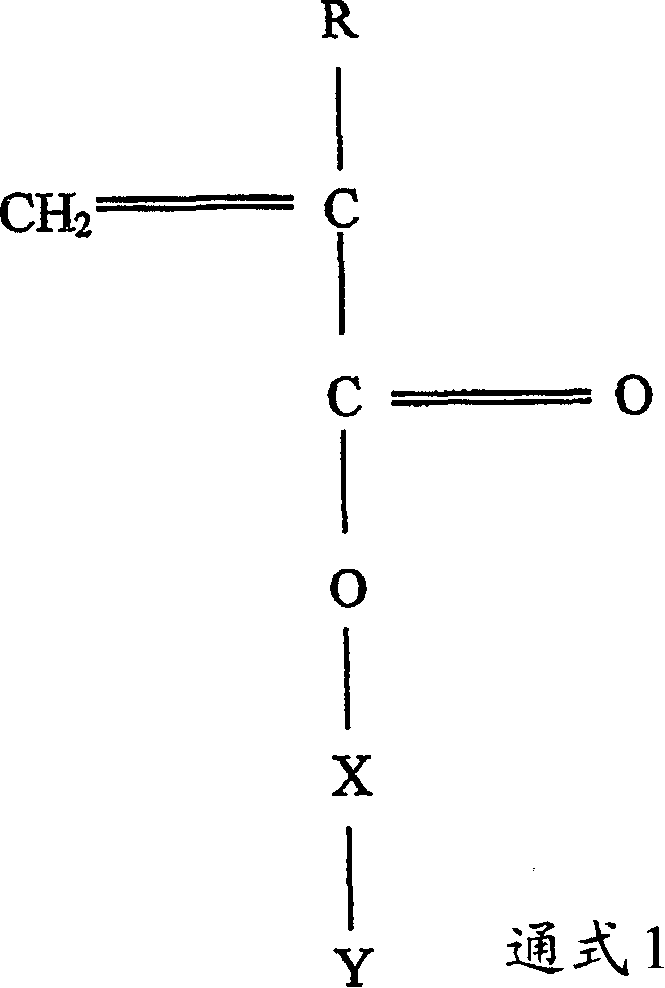
Polymerizable monomers and process of preparation thereof
A technology for polymerizing monomers and monomers, applied in the field of polymerizable monomers, to achieve the effects of easy preparation, no microbial contamination, and stable microbial contamination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0084] Preparation of acryloyl N-acetylglucosamine (Ac.NAG)
[0085] 11.1 gm N-acetylglucosamine and 4.2 gm sodium bicarbonate were dissolved in a beaker equipped with a dropping funnel and pH meter. The resulting clear solution was continuously stirred at 5°C on a magnetic stirrer. 5 ml of acryloyl chloride dissolved in 5 ml of dichloromethane was added dropwise.
[0086] The reaction mixture was maintained at pH 7.5 by adding a saturated solution of sodium bicarbonate. After adding acryloyl chloride, unreacted acryloyl chloride was extracted into 100 ml ethyl acetate. The clear aqueous solution was separated and acidified to pH 5.0 by addition of concentrated hydrochloric acid. Finally the acryloyl N-acetylglucosamine is precipitated in distilled acetone. The product was reprecipitated in acetone.
Embodiment 2
[0088] Preparation of methacryloyl 6-aminocaproic acid (M.Ac.6-ACA)
[0089] A dropping funnel and a pH meter were assembled on a 250ml capacity beaker. 13.16 gm of 6-ACA, 4 gm of sodium hydroxide and 80 ml of water were continuously stirred at 5°C on a magnetic stirrer. To the above solution was added dropwise 9 ml of methacryloyl chloride dissolved in 10 ml of dichloromethane (dichlorQmeJhane). The pH of the reaction mixture was maintained at 7.5 by addition of 10M NaOH solution. Unreacted acid chloride was extracted with 100 ml of ethyl acetate. The clear aqueous solution was acidified to pH 5.0 using concentrated hydrochloric acid and the product was extracted into ethyl acetate (3 x 100ml). The resulting organic phase was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated in vacuo. The viscous liquid was added into 500ml petroleum ether to obtain the solid phase product, which was dried in vacuum for 48 hours.
Embodiment 3
[0091] Preparation of acryloyl 6-aminocaproic acid N-acetylglucosamine (Ac.6-ACA.NAG)
[0092] 5 gm of acryloyl 6-aminocaproic acid (Ac.6-ACA) and 5.97 gm of N-acetylglucosamine were dissolved in 20 ml of dry dimethylformamide (DMF). A clear solution was obtained by continuous stirring and addition of 5.57 gm of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) as coupling agent. Stirring of the reaction mixture was continued at room temperature for 24 hours. Dicyclohexyl urea (DCU) was filtered off and the monomer containing the spacer and ligand NAG was precipitated in distilled acetone. Vacuum dried for 48 hours.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com