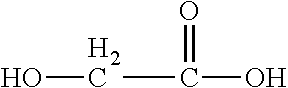Implantable polymer for bone and vascular lesions
a technology of vascular lesions and implants, which is applied in the direction of biocide, drug compositions, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of large bone defects created by trauma, inability to reverse pre-collapsed vertebrae, and inability to provide wholesome treatment to those experiencing osteoporosis-induced fractures, etc., to achieve the effect of improving load bearing capacity and strengthening bone structur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
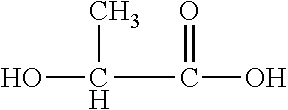
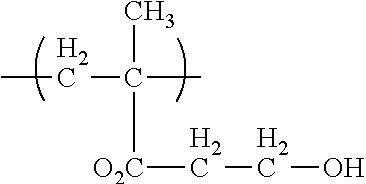
[0086]This invention is defined by its ability to control several important functional parameters of an injectable scaffold. This invention primarily features a polymer or co-polymer mix of biodegradable polymers, a crosslinking agent and, optionally, a solvent, e.g., a water miscible solvent. In this example, a PLA-PGA co-polymer with a triol cross-linker, such as glycerol, in a DMSO solvent was used. This combination is henceforth known as the “mix.” The nature of the delivery of this scaffold is unique in that: the mix will retain its viscous liquid form prior to injection; upon injection and contact with bodily tissues and fluids the solvent will diffuse from the mix; and, as the solvent diffuses the cross-linked, cohesive co-polymer will be left behind.
[0087]Alone and uncontrolled, this co-polymer scaffold is mechanically limited. Controlling the ratio of PLA-PGA in this mix is essential in controlling not only the mechanical integrity, but also the degradation rate and porosit...
example 2
[0099]The material includes a polymeric composition in a biocompatible solvent. Such a polymeric composition can contain two biodegradable polymers combined as a copolymer, which are both soluble in the solvent. This can also contain a second composition including a monomer, which can be polymerized into a gel by a catalyst agent or a redox couple, which is mixed with the first composition. Additional insoluble particles can be added in the solvent solution or the gel for mechanical support of the resulting material.
[0100]Specifically, a first composition of PLA-co-PGA in a solvent, such as DMSO, can be combined with a second composition of a HEMA monomer. When these are combined, a catalyst, such as an enzyme or a redox couple—ammonium persulphate (in composition 1) and ethylenediaminetetracetic acid (in composition 2), polymerize the HEMA into a gel. Insoluble particles, such as hydroxyapatite could then be mixed into the material either in the solvent or in the gel.
example 3
[0101]The material includes a polymeric composition in a biocompatible solvent. Such a polymeric composition can contain two biodegradable polymers, which are both soluble in the solvent. This can also contain a second composition comprising a monomer, which can be polymerized by a catalyst agent or a redox couple, which is mixed with the first composition. Additional insoluble particles can be added in the solvent solution or the gel for mechanical support of the resulting material.
[0102]Specifically, a composition of PLA and PCL in a solvent, such as DMSO, can be combined with a second composition of an AA (acrylic acid) monomer. When these are combined, a catalyst, such as an enzyme or a redox couple—ammonium persulphate (in composition 1) and ethylenediaminetetracetic acid (in composition 2), polymerize the AA. Insoluble particles, such as hydroxyapatite can then be mixed into the material either in the solvent or in the gel.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore sizes | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com