Patents
Literature
35 results about "Compressive stiffness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
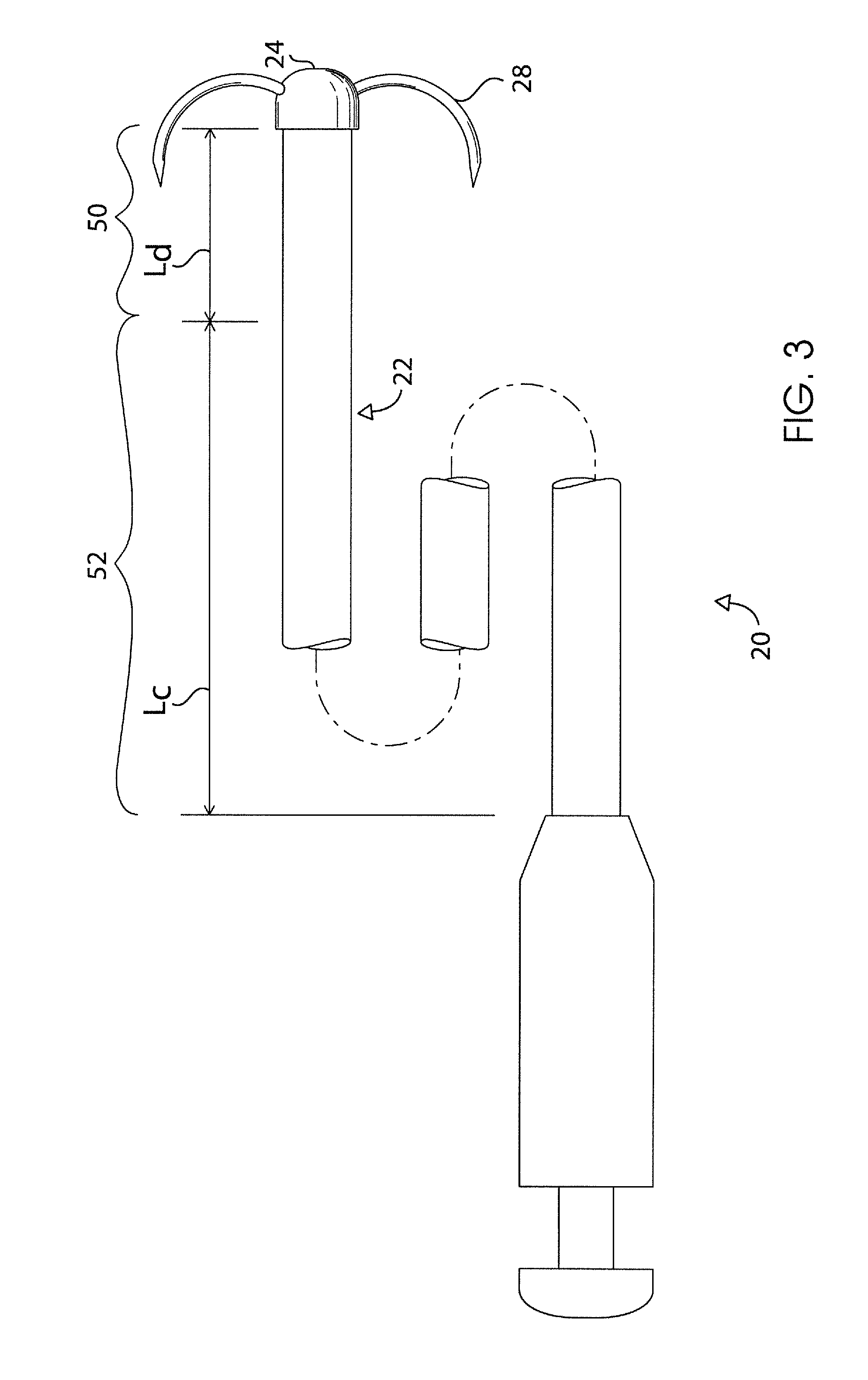
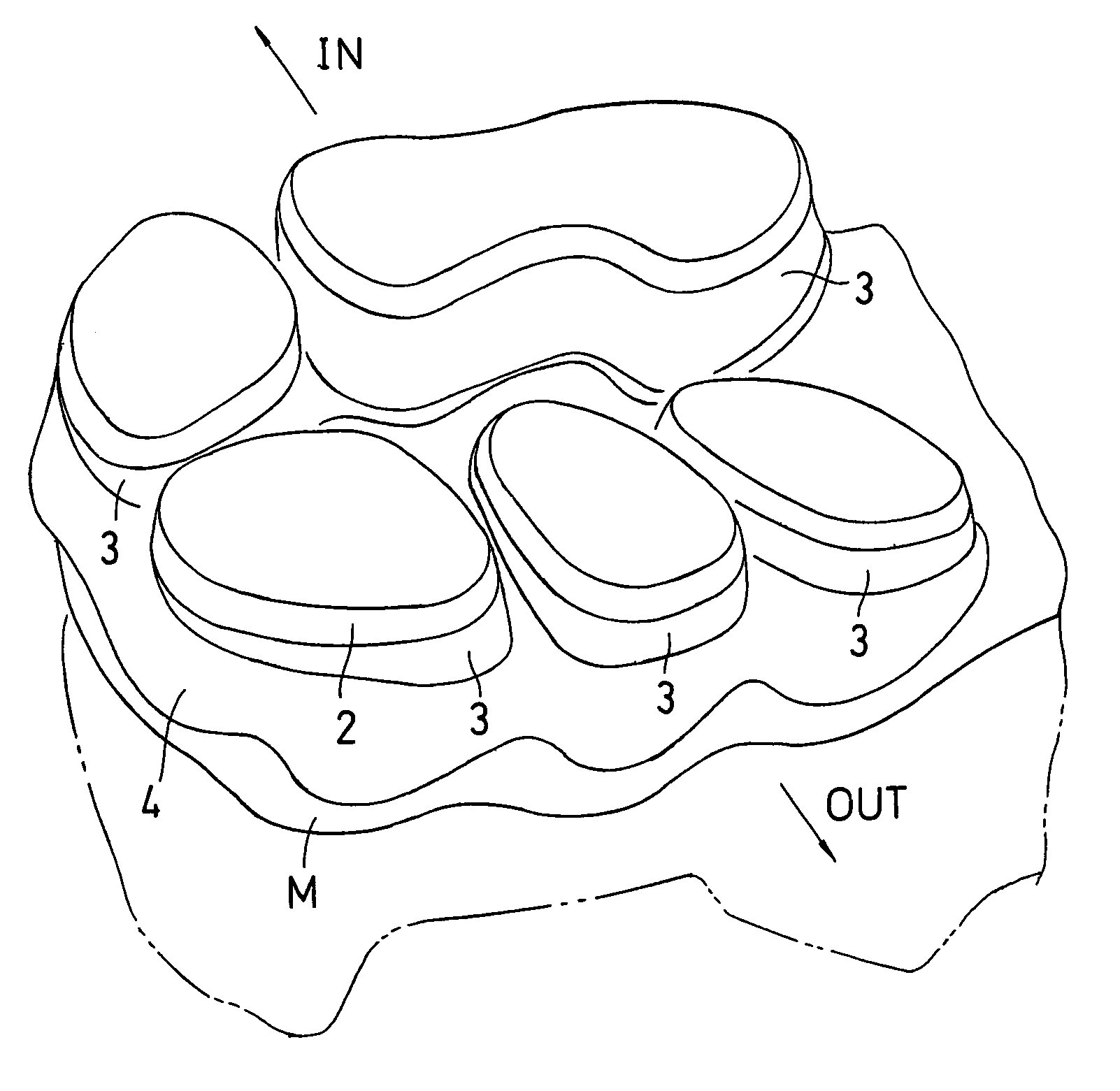
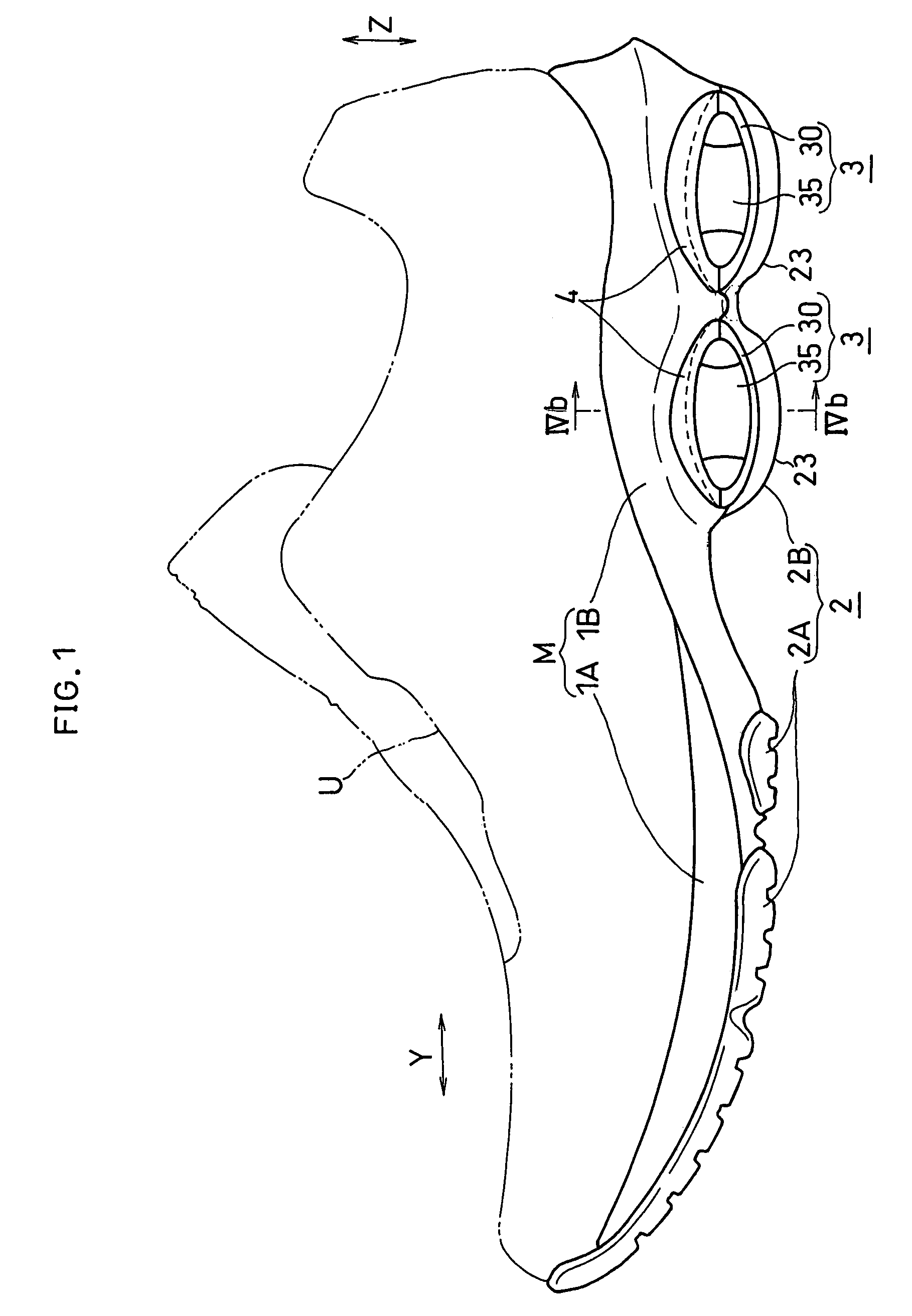
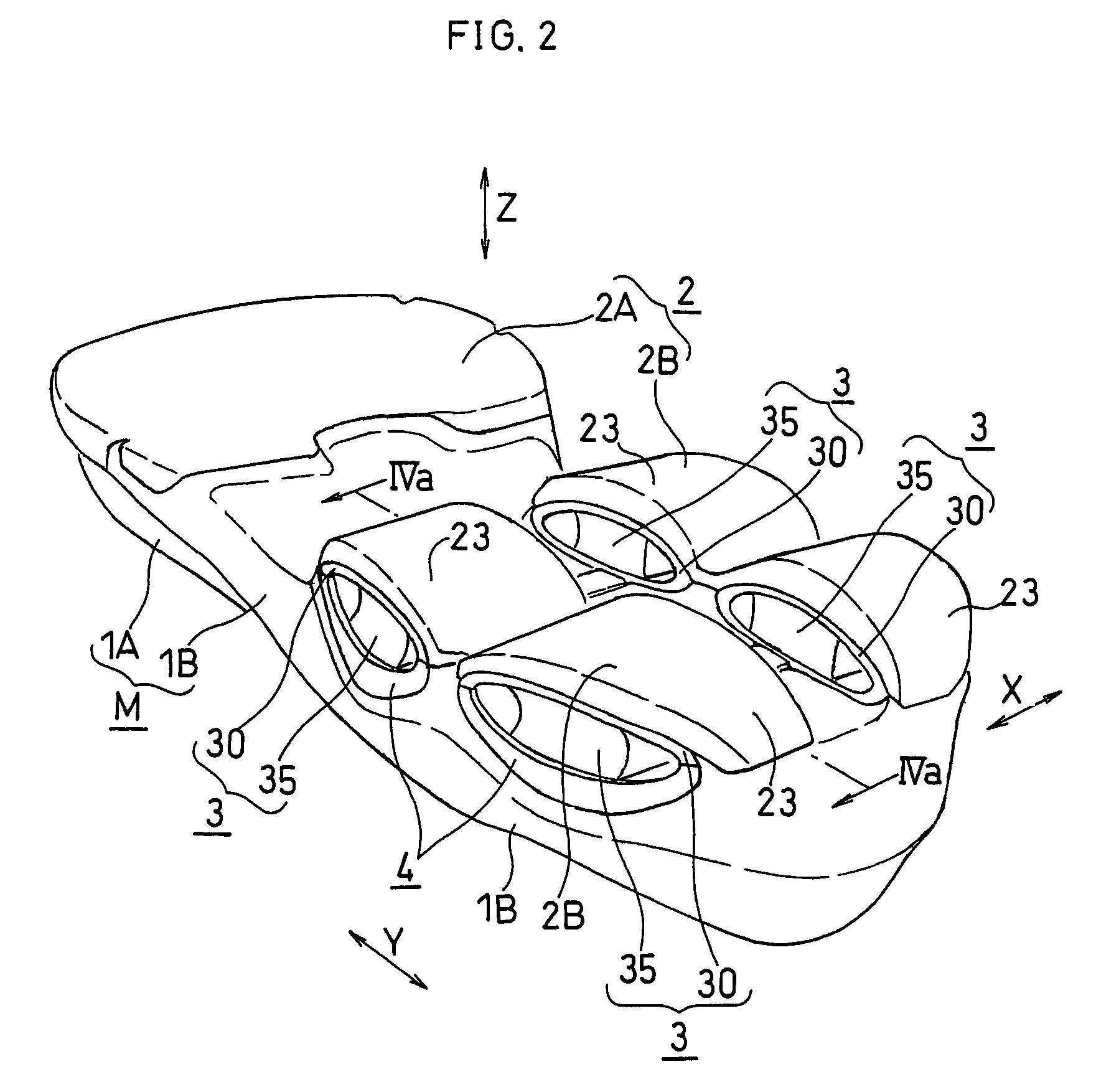
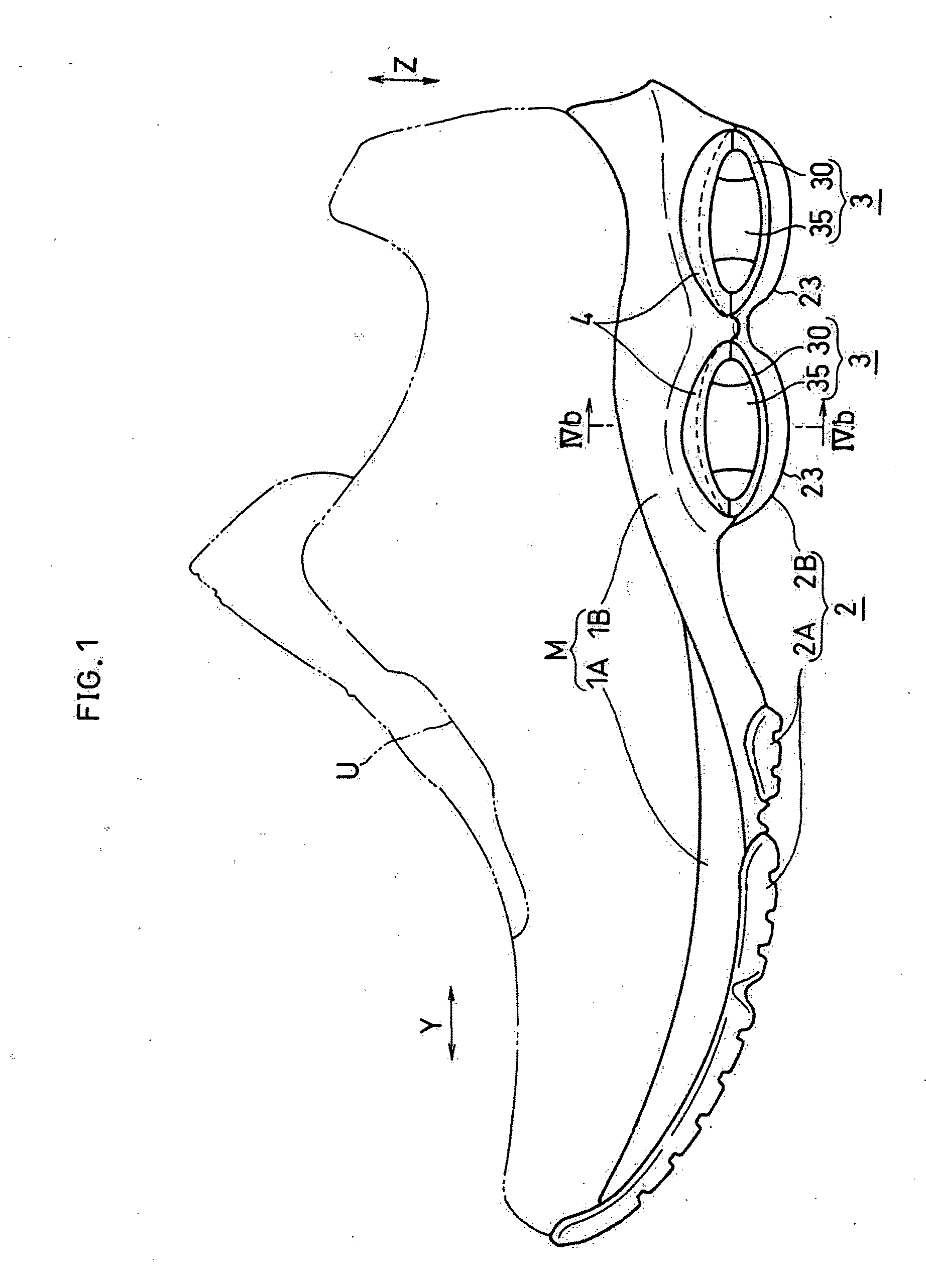
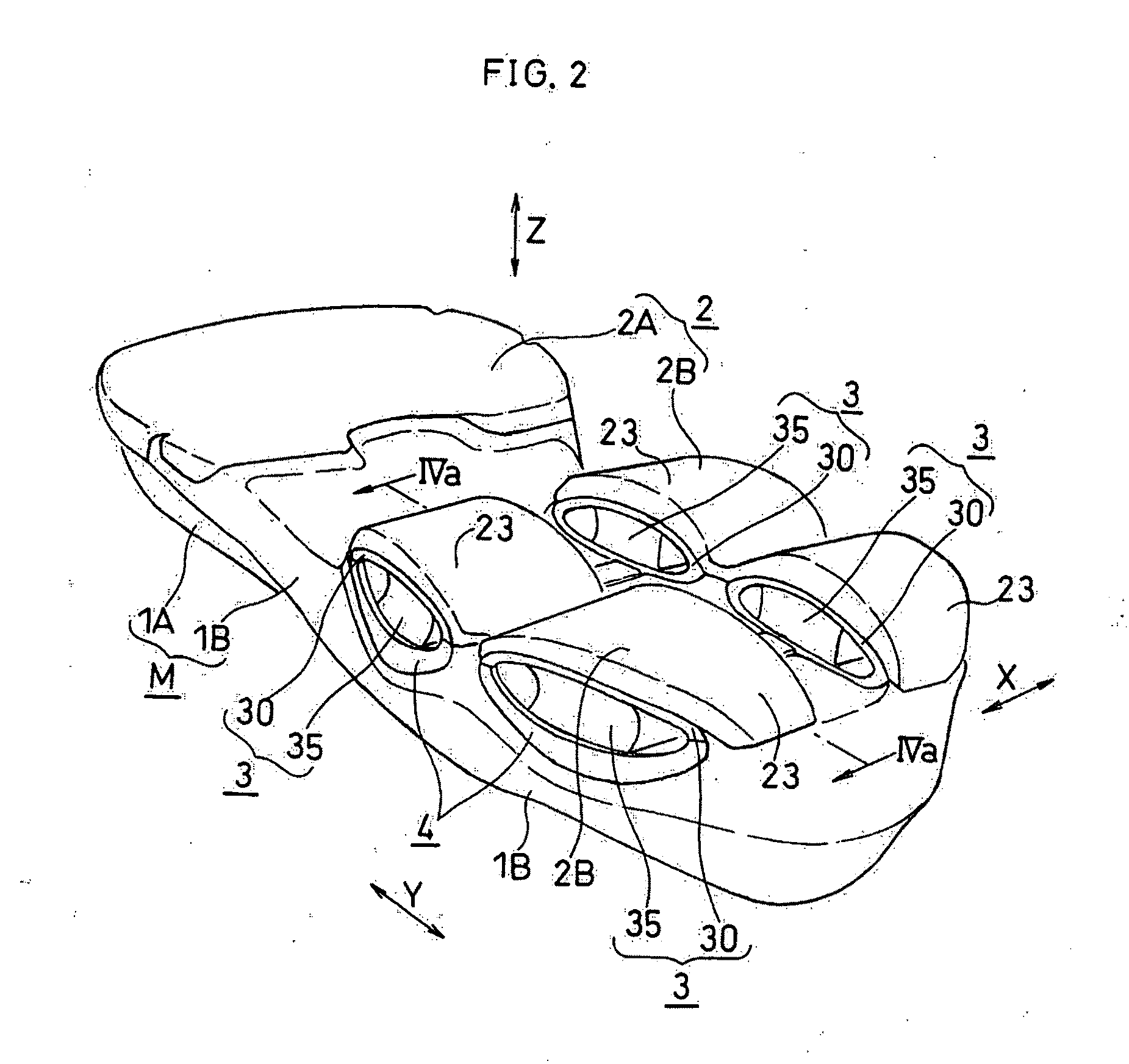
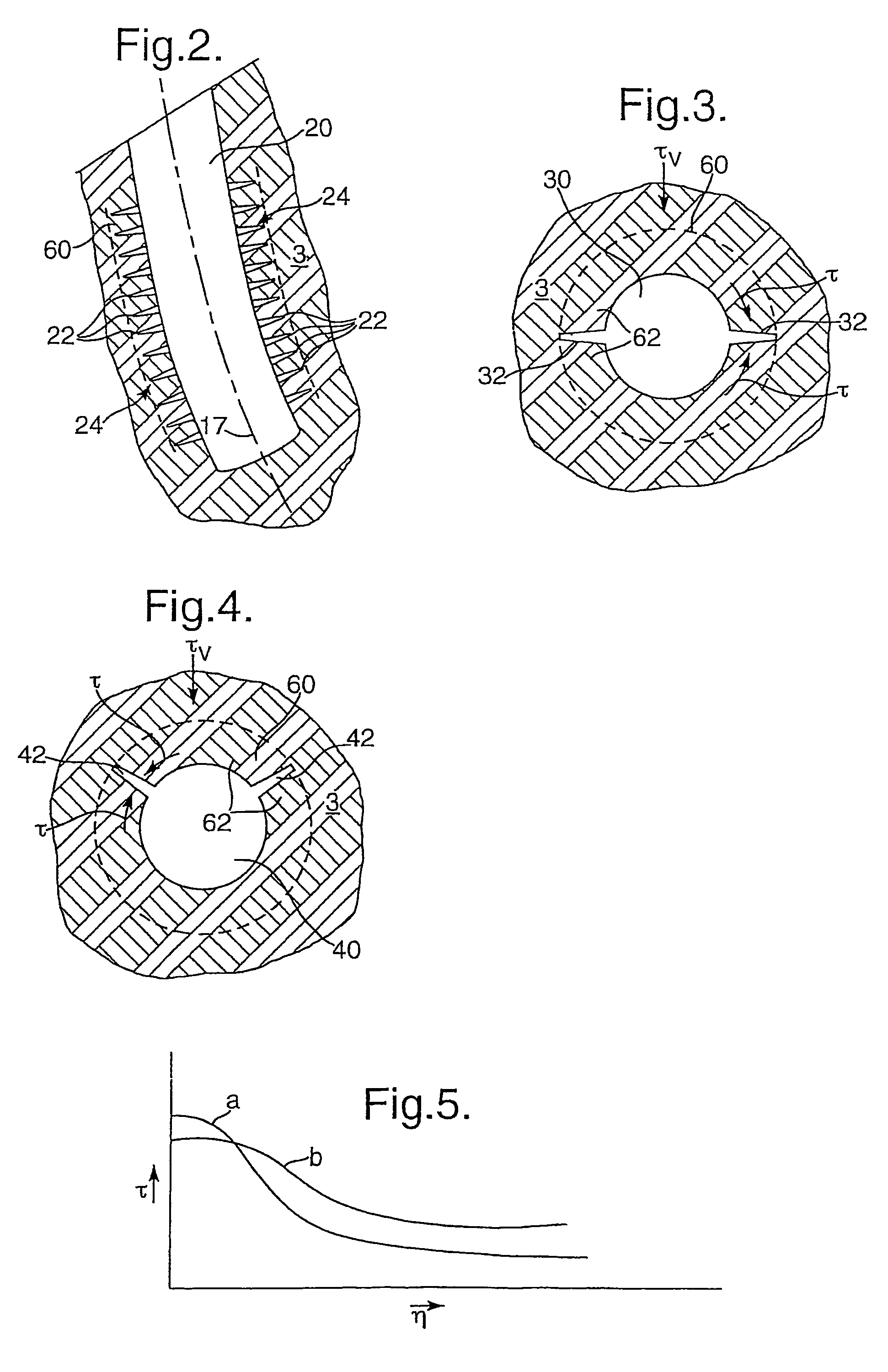
Shock absorbing device for shoe sole in rear foot part
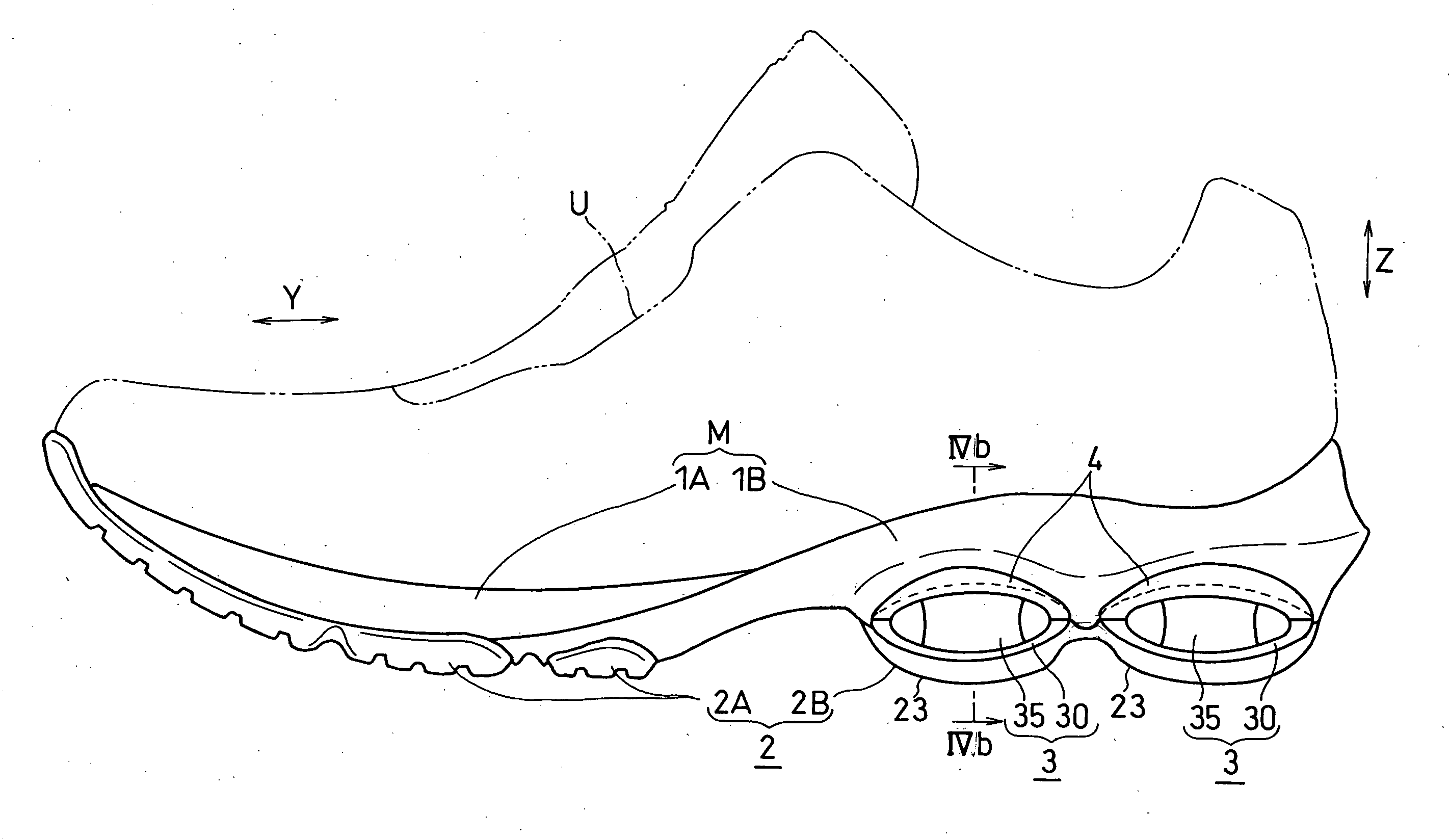
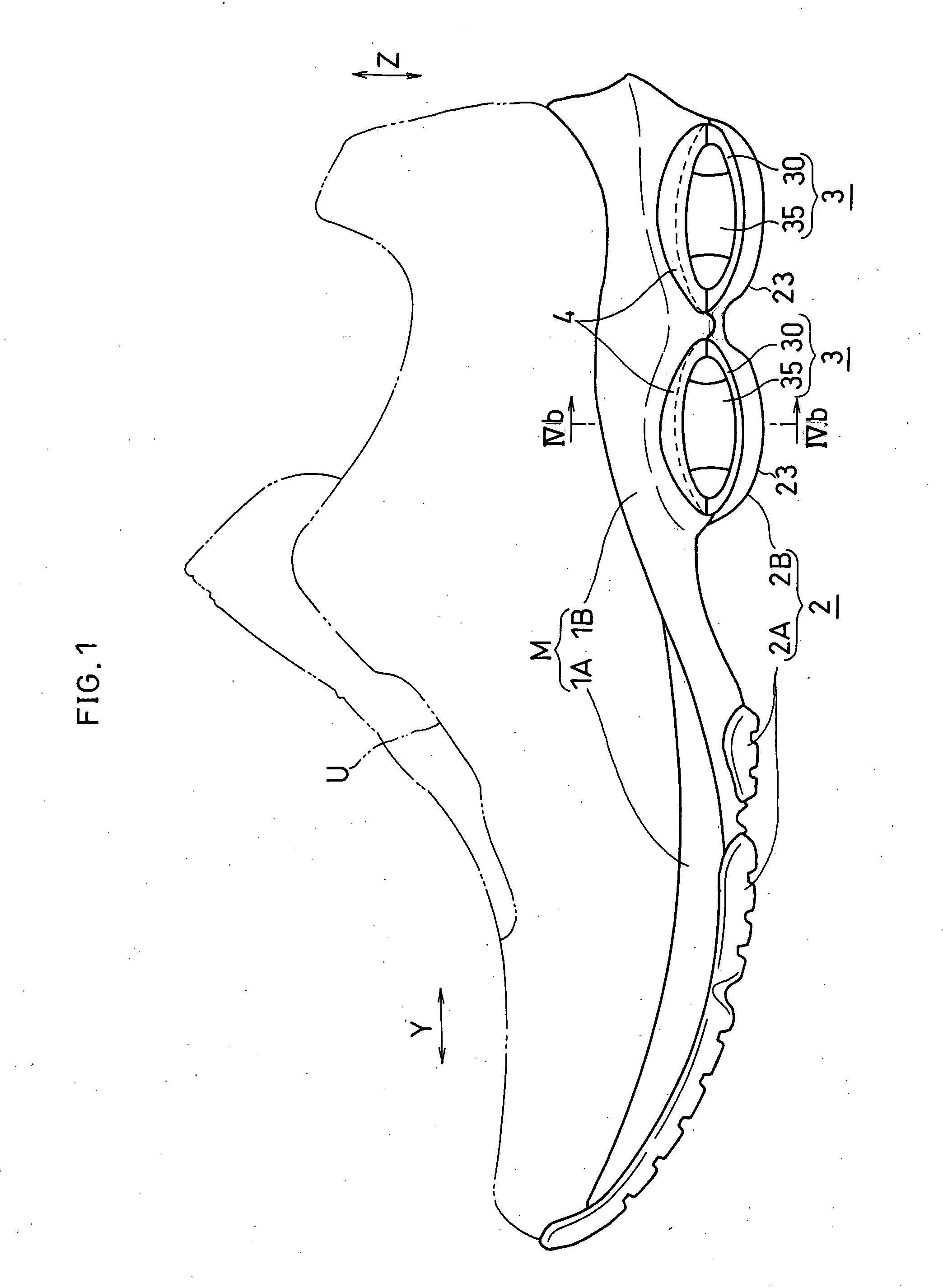
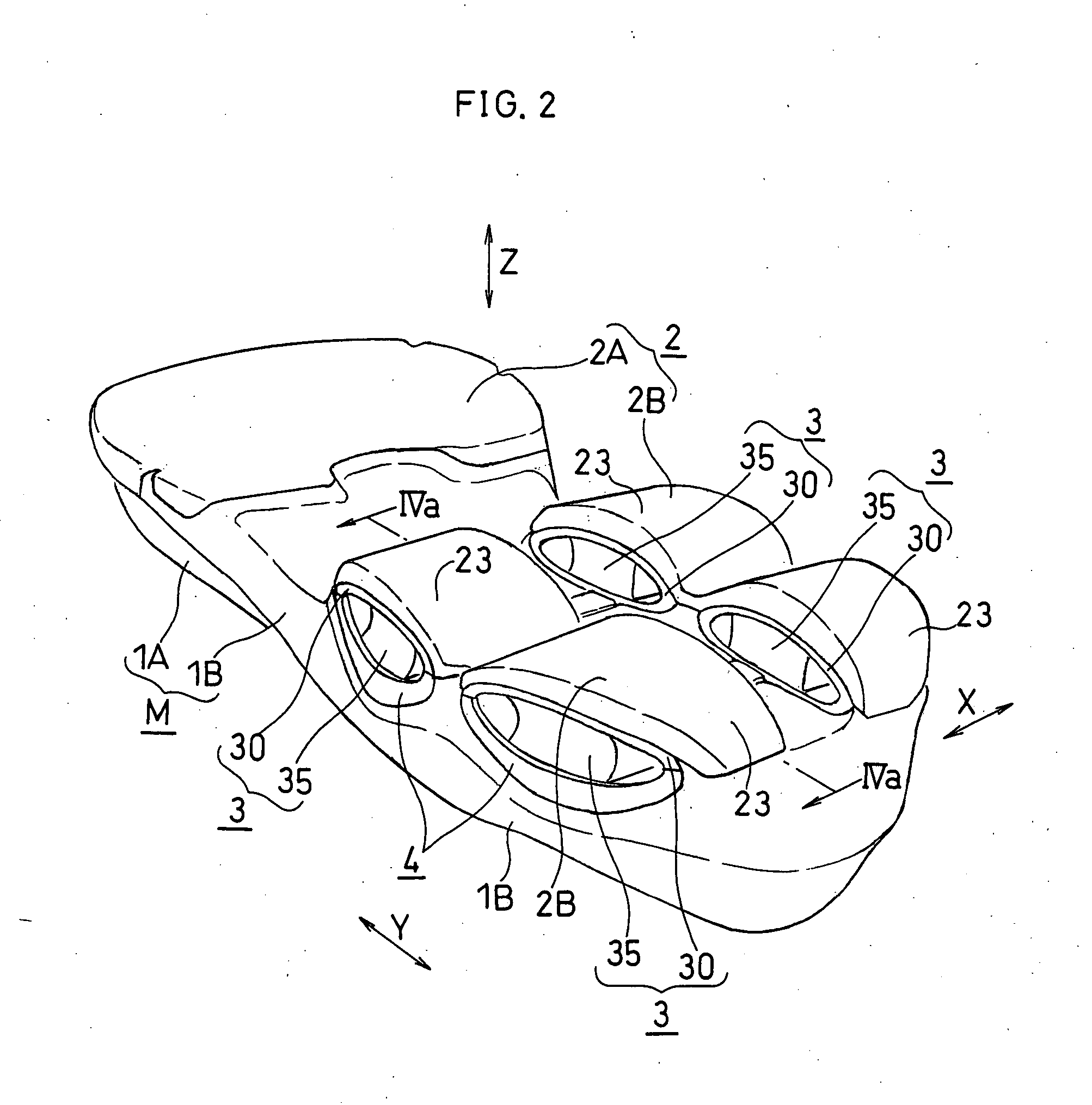
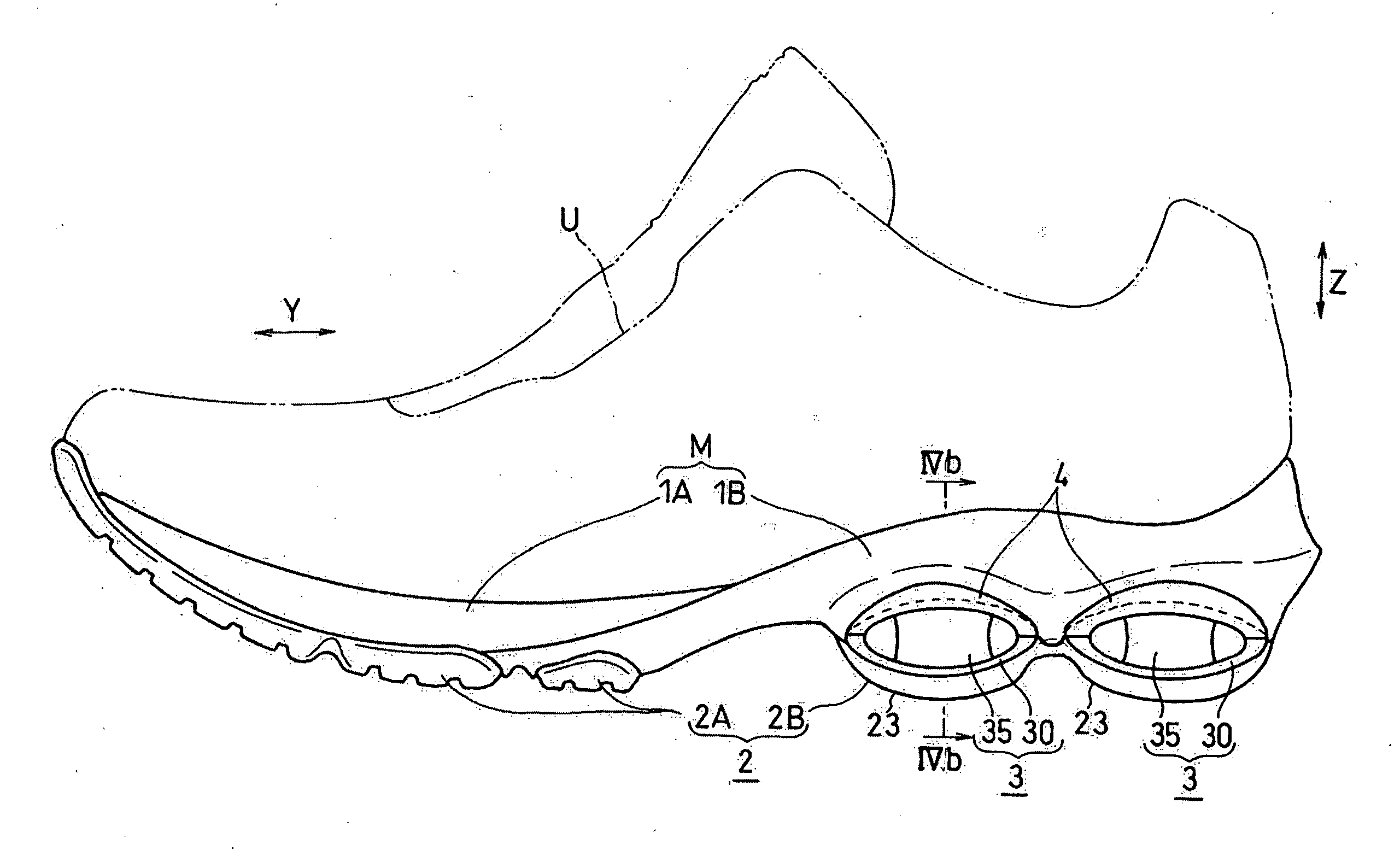
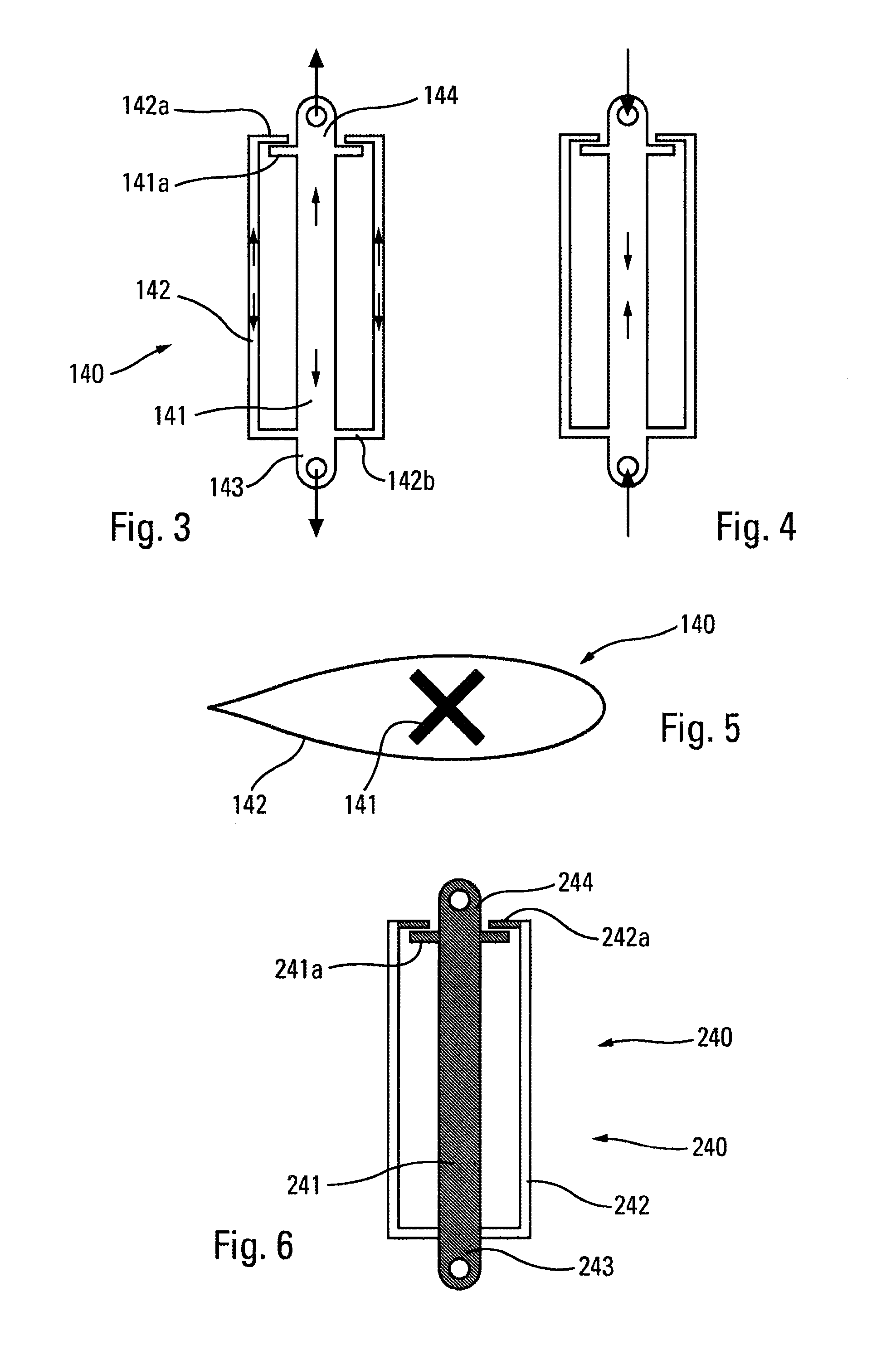
The present invention provides a shock absorbing device for a shoe sole in a rear foot part which can restrain the inclination of the foot toward the medial side while absorbing the shock of landing on the lateral side of the foot. A shock absorbing device for a shoe sole in a rear foot part according to the present invention, includes: a support element M; deformation elements 3 disposed below the support element, the deformation elements deforming to be compressed vertically at landing; and outer sole elements 2 contacting a ground at landing, each outer sole element being joined to a bottom surface of the respective deformation element. Both the deformation elements 3 and the outer sole elements 2 are substantially separated in a medial-lateral direction in the rear foot part to be arranged at least three regions of the rear foot part. A quotient obtained by dividing an area of a bottom surface of the support element M by an area of bottom surfaces of the outer sole elements 2 is set at about 1.3 or more in the rear foot part. A vertical compressive stiffness of the deformation element 3 disposed on the lateral side is smaller than that of the deformation element 3 disposed on the medial side.
Owner:ASICS CORP
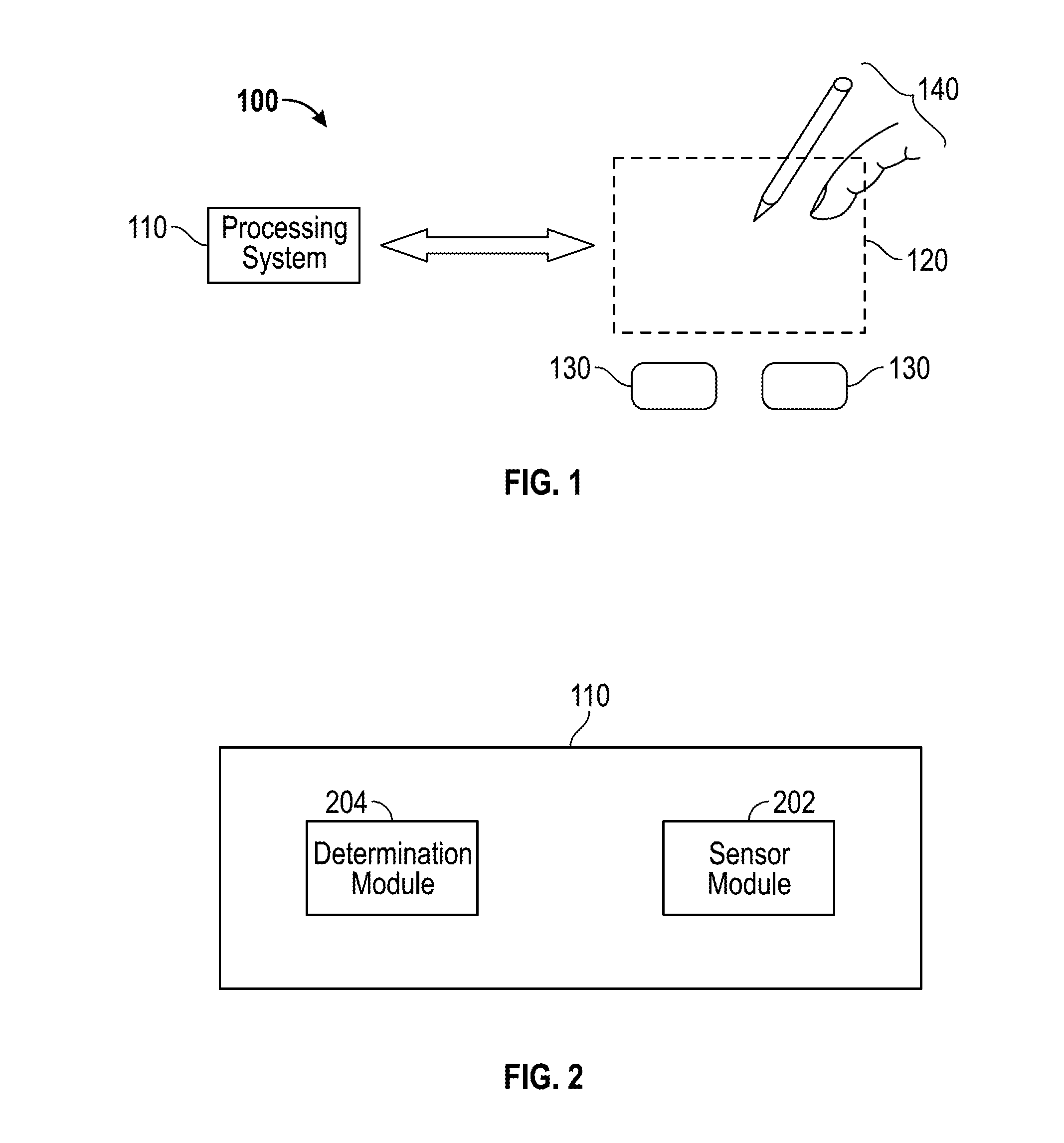
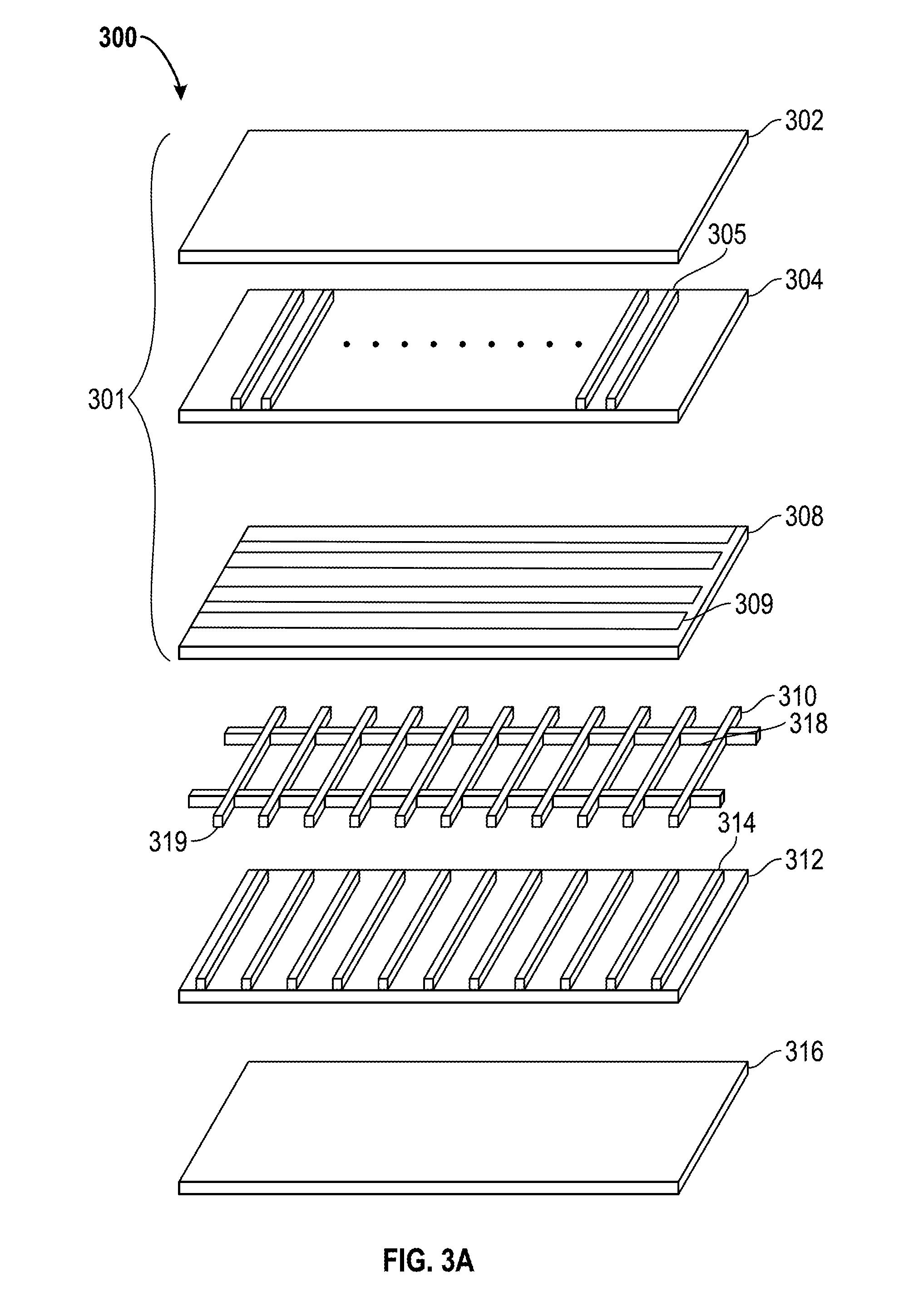
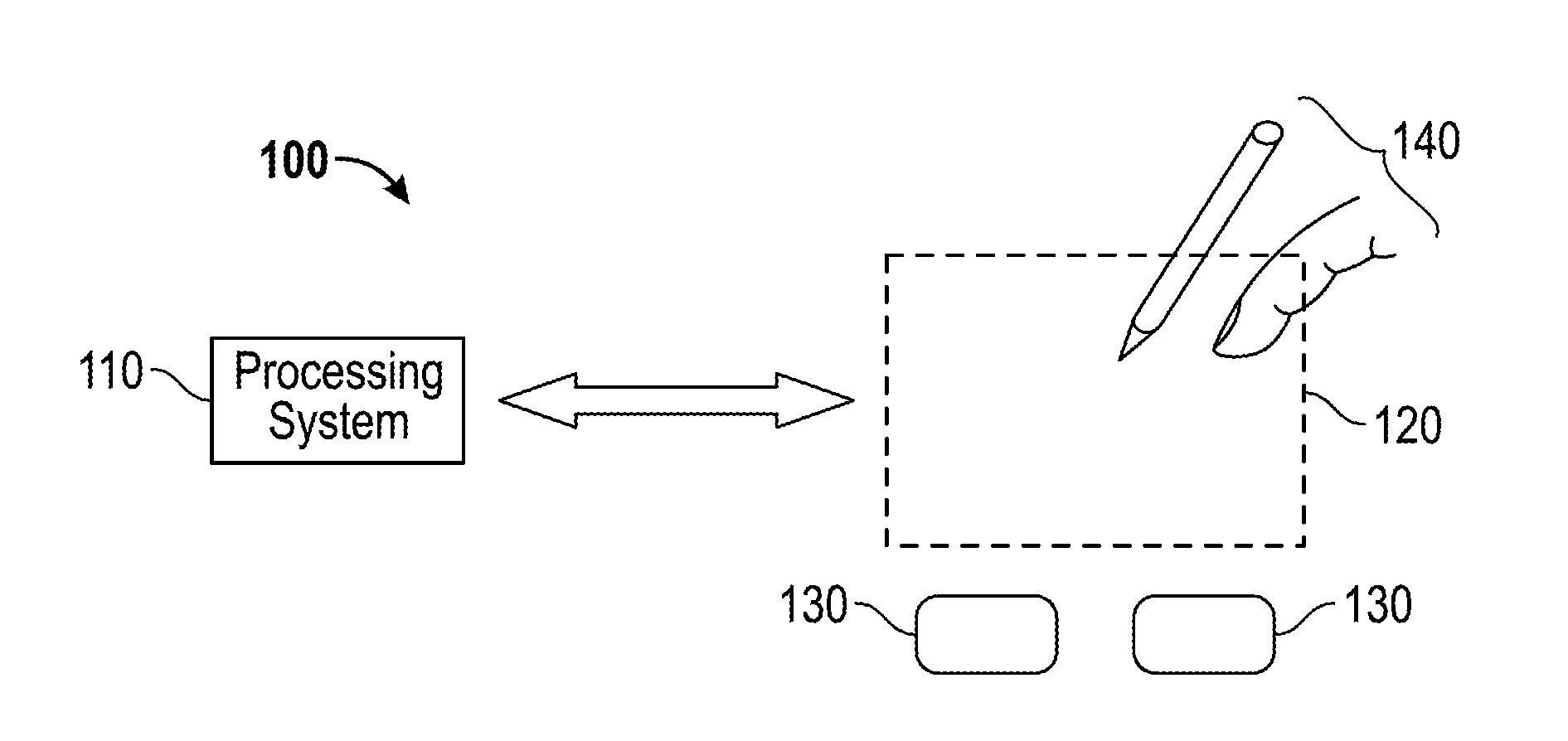
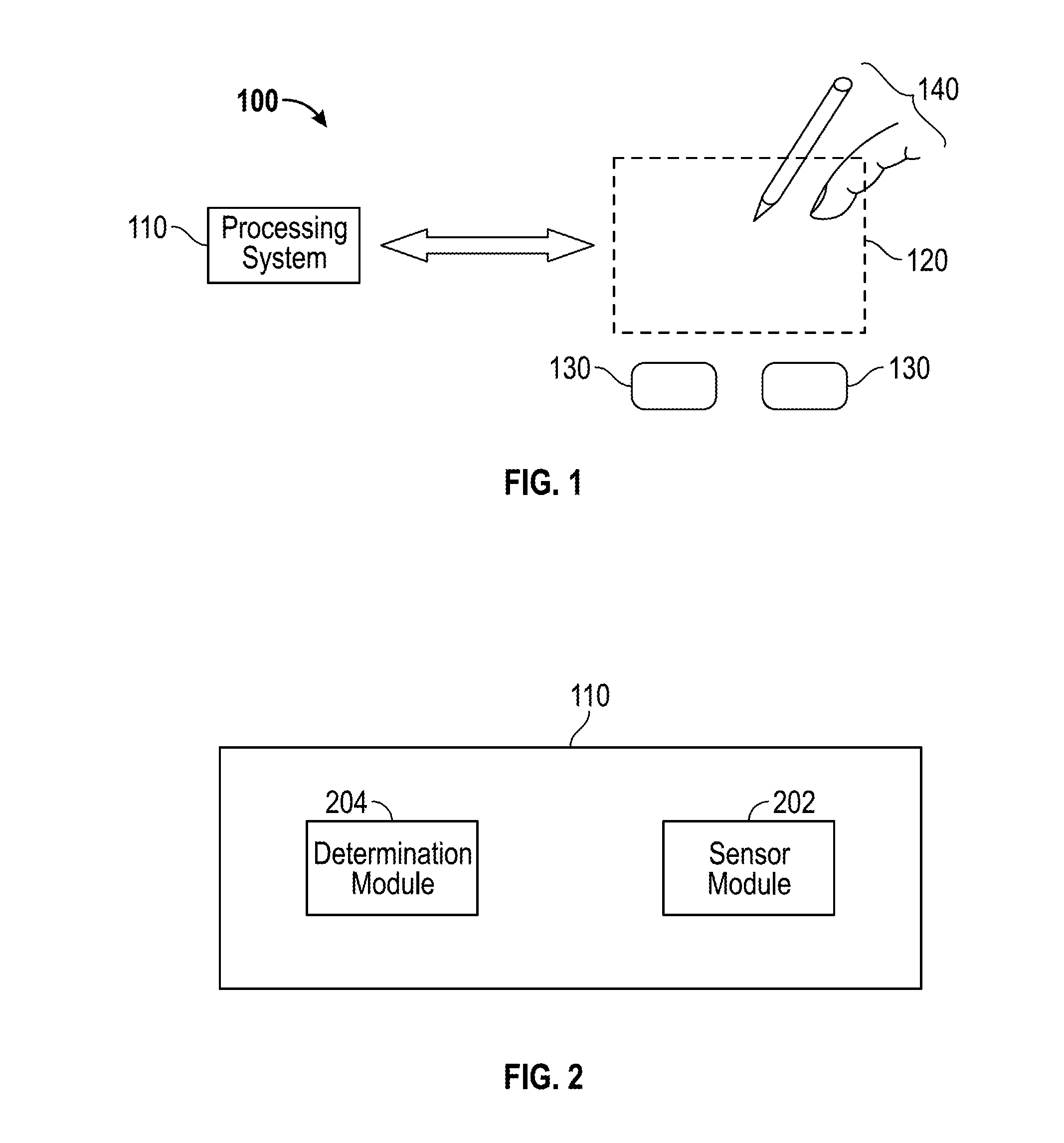
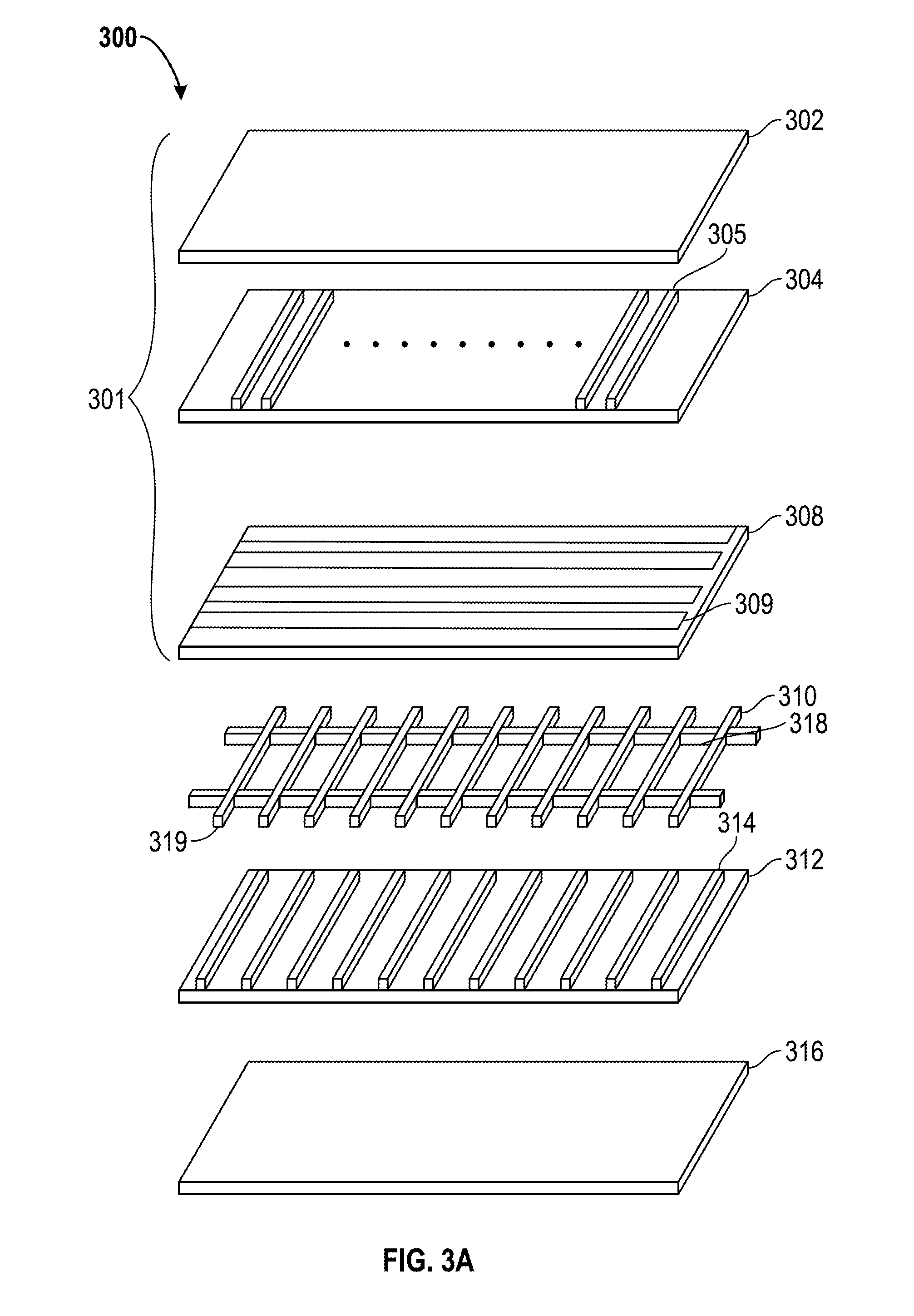
Device and method for localized force sensing
ActiveUS20140238152A1Facilitates improved device usabilityAccurately determineCapacitance measurementsForce measurementCapacitanceCompressive stiffness
A device and method for operating a capacitive input device configured to sense input objects and their applied force in a sensing region, the device including a pliable component having an input surface and characterized by a bending stiffness, and first and second arrays of sensor electrodes. The input device further includes a third array of sensor electrodes and a spacing layer disposed between the third array. The pliable component is characterized by a compressive stiffness and configured to deform in response to a force applied to the input surface and to deflect the second array of sensor electrodes towards the third array of sensor electrodes, wherein the deformation of the input surface and the deflection of the second array of sensor electrodes is a function of the ratio of the bending stiffness of the pliable component and the compressive stiffness of the spacing layer.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
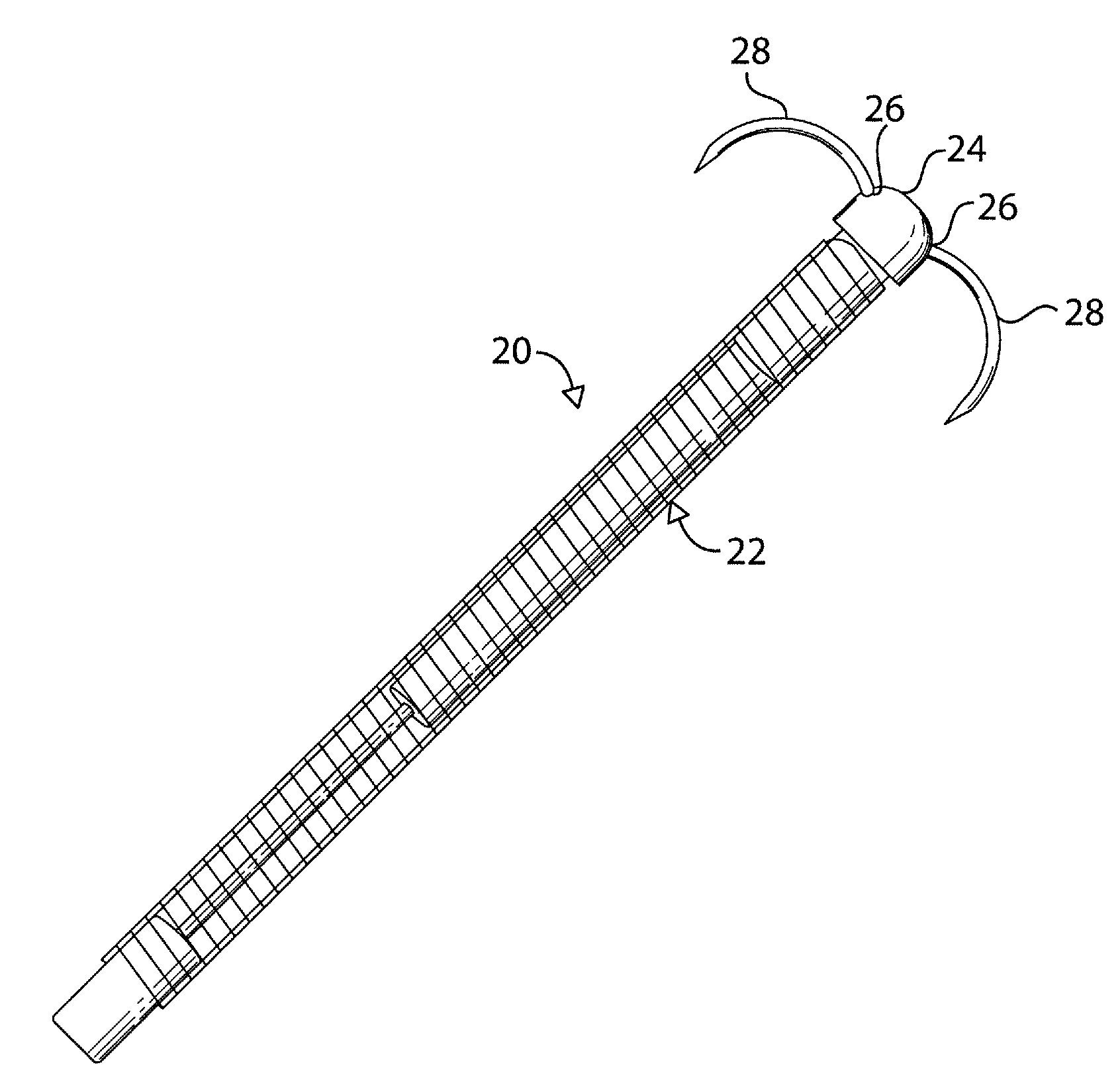
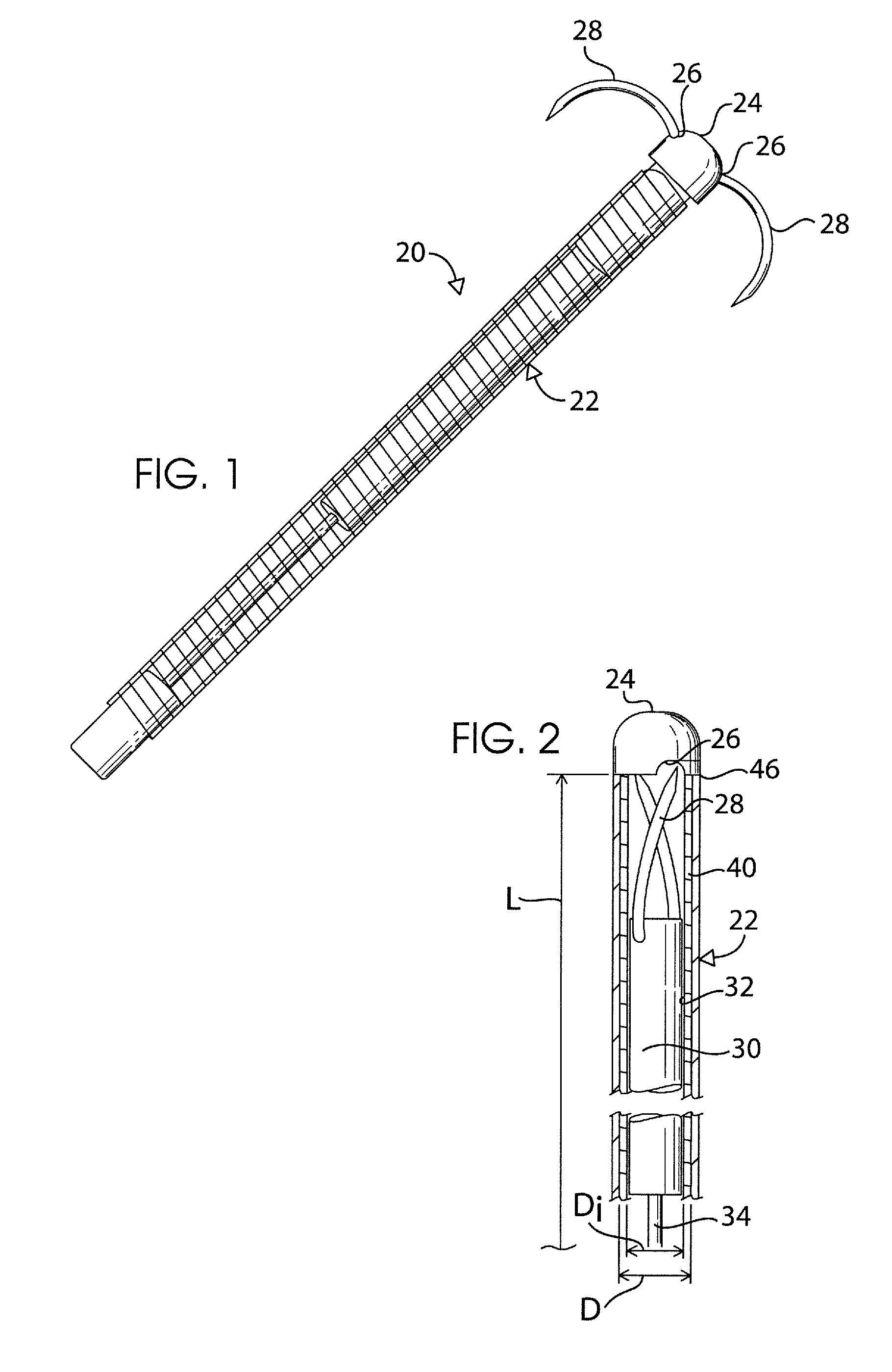
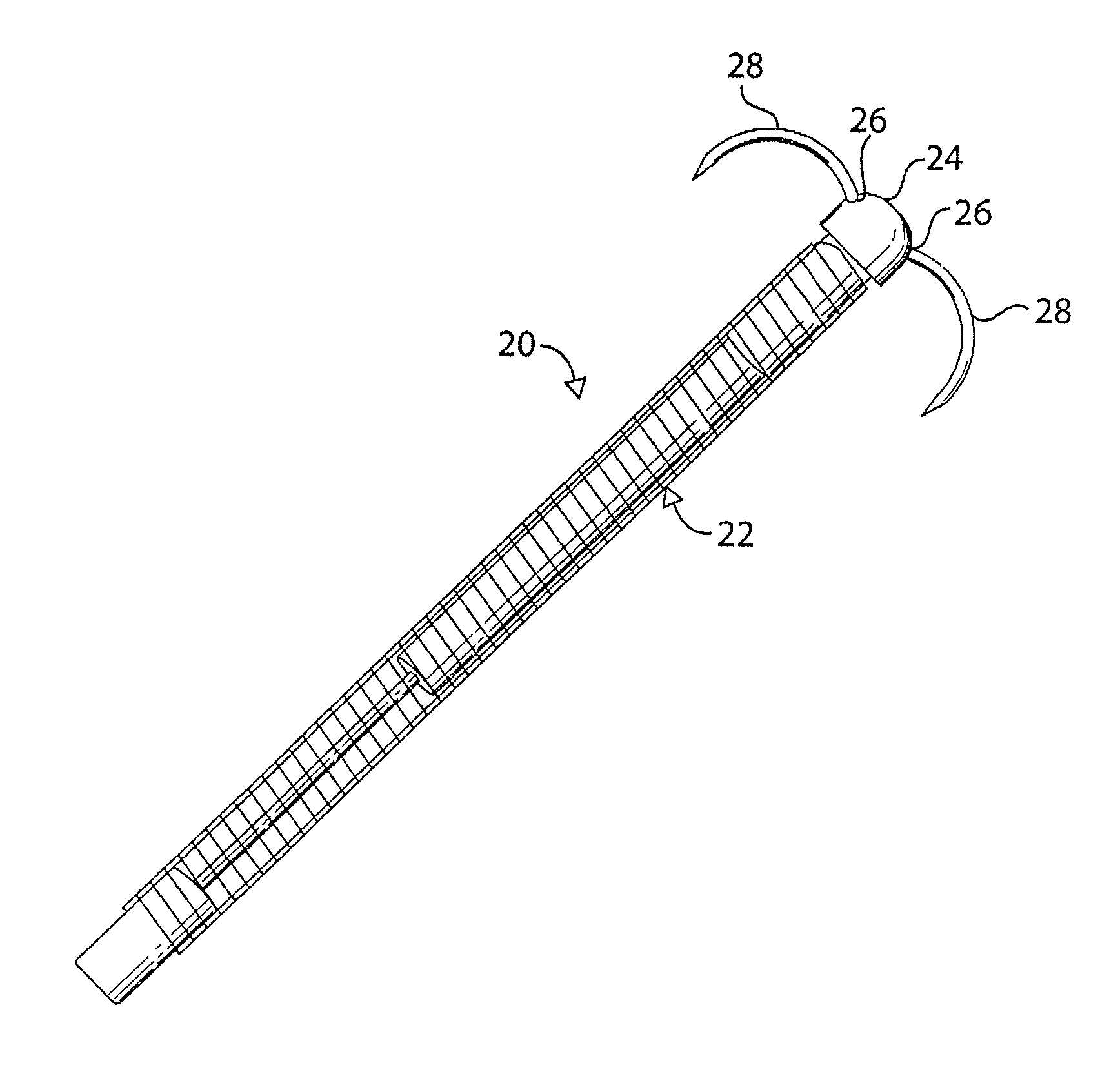
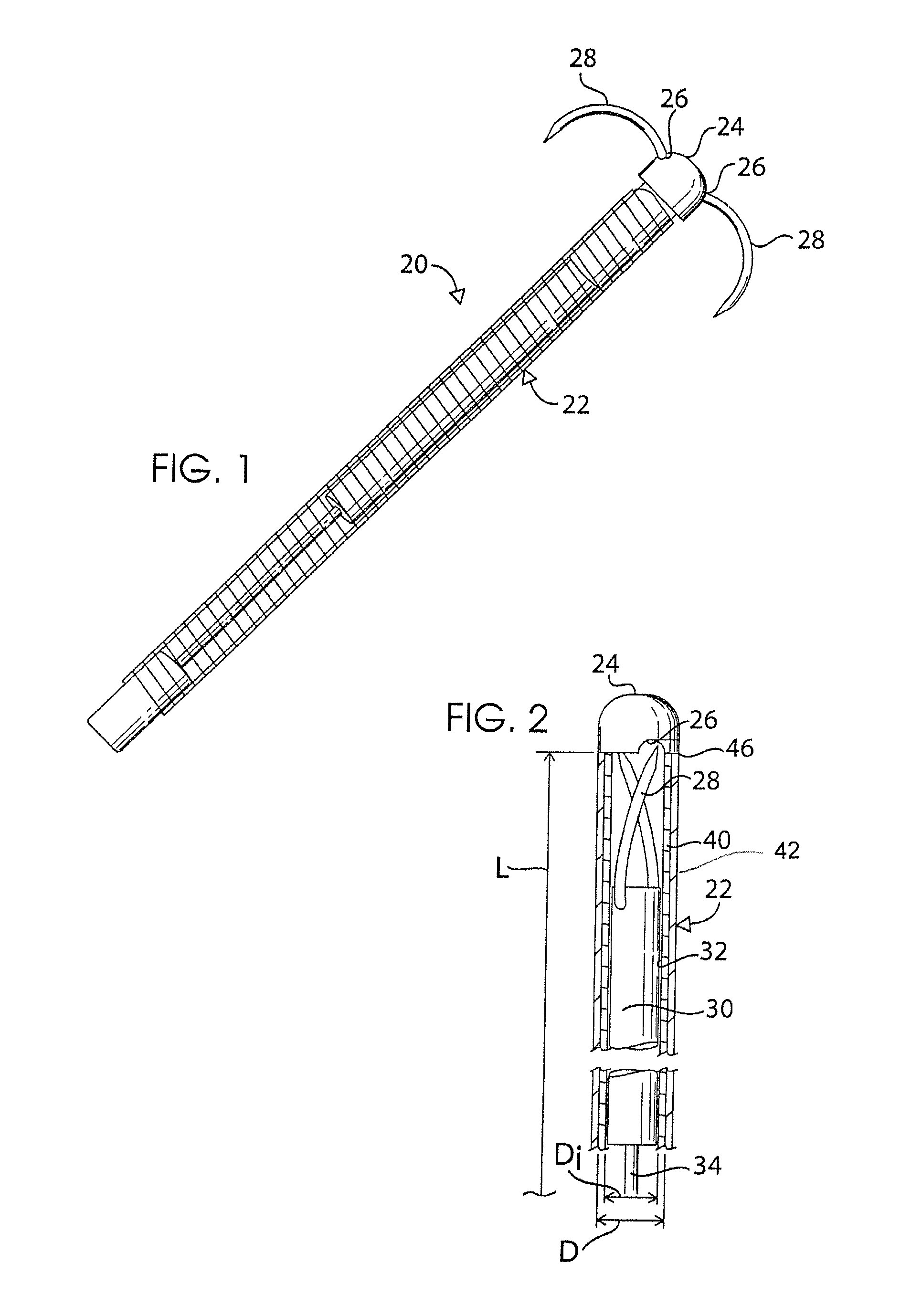
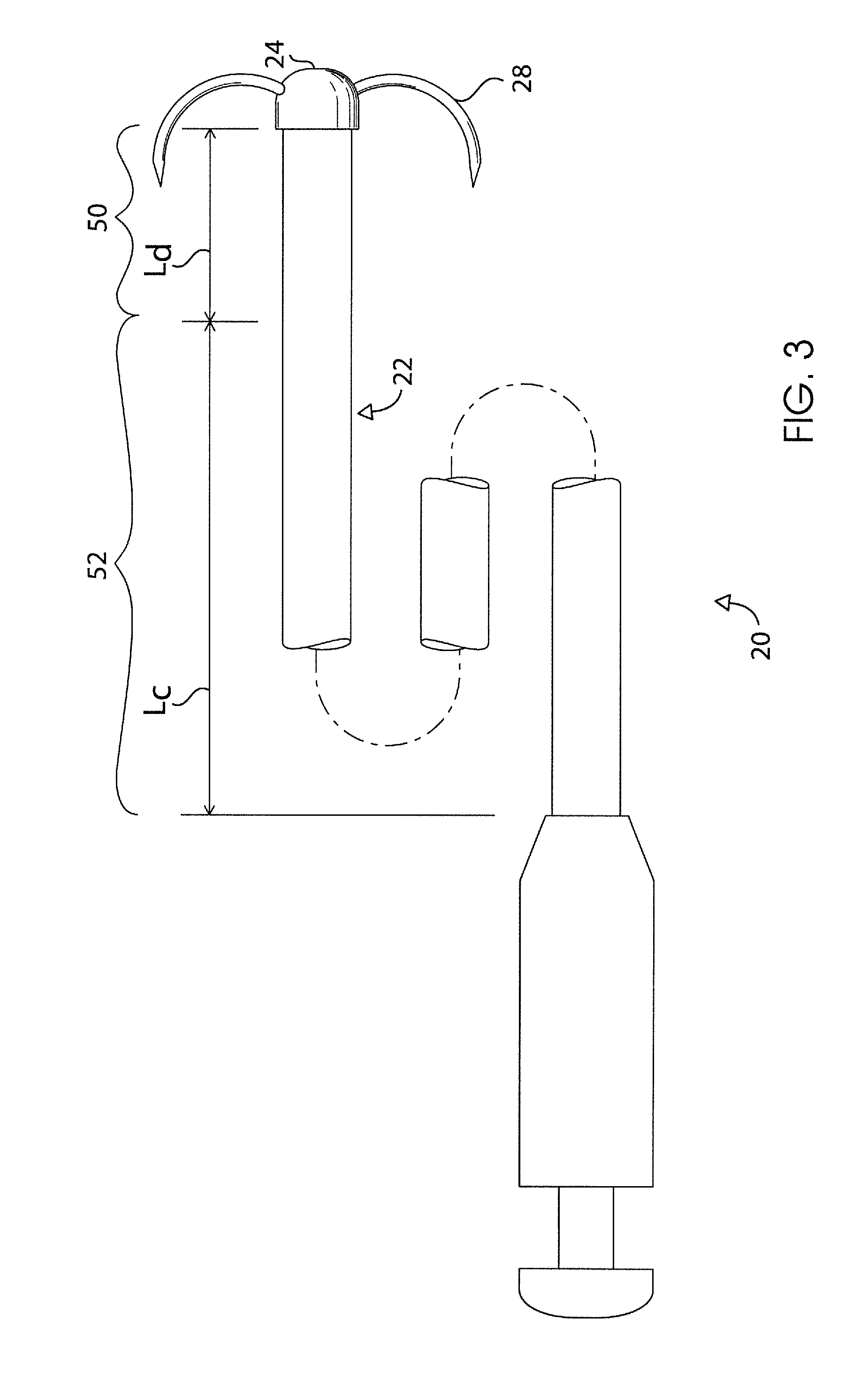
Endoscopic device
An endoscopic instrument for performing surgical procedures. The instrument includes an elongate member having a distal end for insertion into a patient's body and a proximal end opposite the distal end. The member has a distal portion adjacent the distal end and a central portion adjacent the distal portion. The distal portion has a first mechanical stiffness of a stiffness type selected from a tensile stiffness, a compressive stiffness and / or a bending stiffness. The central portion has a second mechanical stiffness of the stiffness type of the first mechanical stiffness. The first mechanical stiffness is different from the second mechanical stiffness.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Shock absorbing device for shoe sole in rear foot part
Owner:ASICS CORP
Device and method for localized force sensing
ActiveUS9075095B2Accurately determinedImprove usabilityCapacitance measurementsForce measurementCompressive stiffnessEngineering
A device and method for operating a capacitive input device configured to sense input objects and their applied force in a sensing region, the device including a pliable component having an input surface and characterized by a bending stiffness, and first and second arrays of sensor electrodes. The input device further includes a third array of sensor electrodes and a spacing layer disposed between the third array. The pliable component is characterized by a compressive stiffness and configured to deform in response to a force applied to the input surface and to deflect the second array of sensor electrodes towards the third array of sensor electrodes, wherein the deformation of the input surface and the deflection of the second array of sensor electrodes is a function of the ratio of the bending stiffness of the pliable component and the compressive stiffness of the spacing layer.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
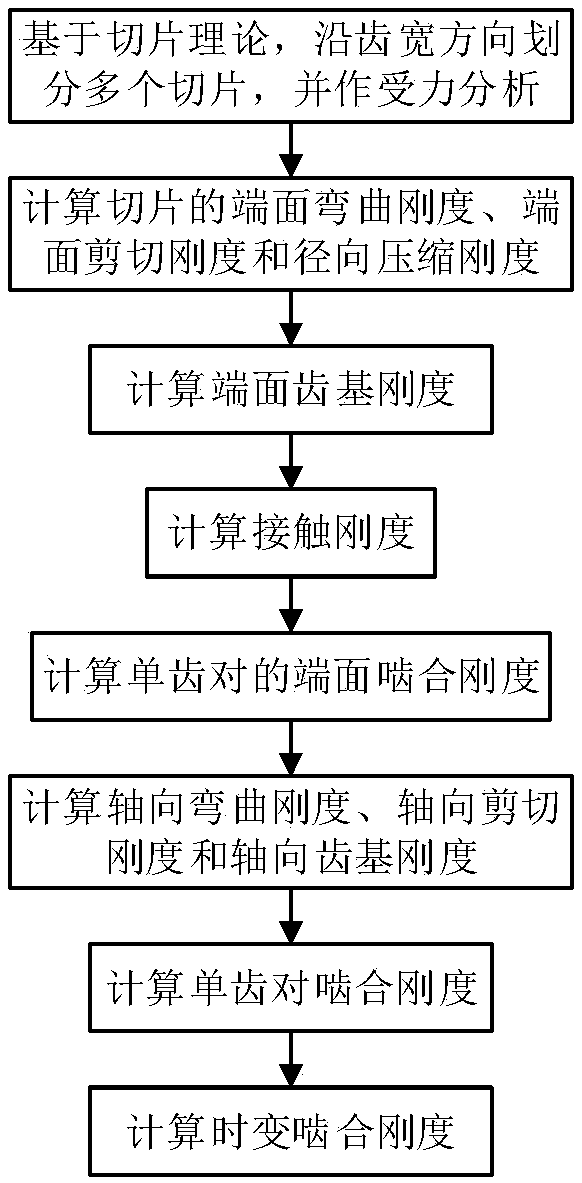
Method considering axial deformation for calculating time-varying meshing stiffness of helical gear
ActiveCN107798200AHigh precisionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationRadial compressionEngineering
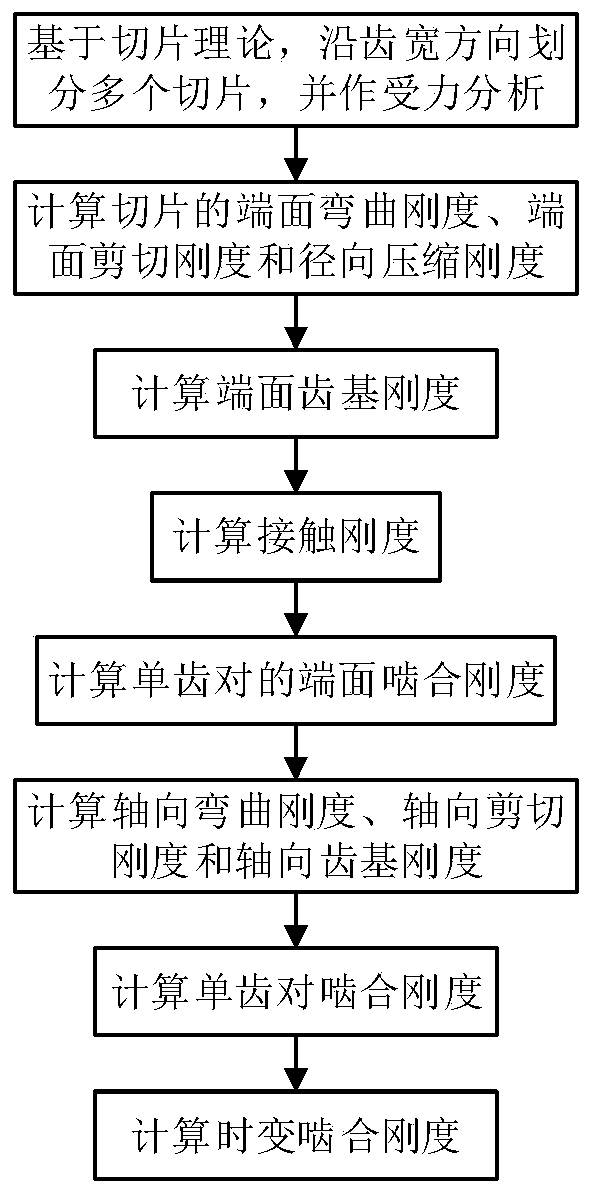
The invention proposes a method considering axial deformation for calculating time-varying meshing stiffness of a helical gear. The method aims at improving the accuracy of calculating the meshing stiffness of the helical gear. The method comprises the implementation steps of calculating the end surface bending stiffness, end surface shearing stiffness, radial compression stiffness and end surfacetooth base stiffness of the helical gear; calculating contact stiffness; calculating the end surface meshing stiffness of a single tooth pair; deducing and calculating axial bending stiffness, axialshearing stiffness and axial tooth base stiffness; calculating the meshing stiffness of the single tooth pair; calculating the time-varying meshing stiffness. According to the method, the influence ofaxial meshing force on the time-varying meshing stiffness of the helical gear is considered, a calculation expression for the quantitative calculation of the axial bending stiffness, axial shearing stiffness and axial tooth base stiffness of the helical gear is deduced, the time-varying meshing stiffness of the helical gear is calculated by combining all the stiffness in the end surface direction, the calculation accuracy is improved, and the method can be used for the dynamic performance analysis and optimization design of the helical gear.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Determination method for predicting material uniaxial constitutive relation through circular ring radial compression energy
InactiveCN104931348AConvenient and effective accessGood effectMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesSpecial data processing applicationsCompressive stiffnessNuclear power
The invention discloses a determination method for predicting material uniaxial constitutive relation through circular ring radial compression energy. According to the method, quasi-static pressing loading is carried out on a size-variable circular ring by adopting a compression clamp with a limiting groove, after a continuous load P- displacement V curve is obtained, radial compressive stiffness S of the circular ring is marked though the elastic region data of the load-displacement curve, and the material uniaxial constitutive relation is predicted through post processing. By adopting the method, the defects that both time and labor are consumed since finite element iteration is required to be carried out for multiple times and astringency cannot be evaluated in advance in the prior art are overcome, obtaining of the material uniaxial constitutive relation can be realized simply, conveniently and efficiently and an ideal effect is realized. Particularly, the method has important significance in obtaining of the material uniaxial mechanical properties of important pipeline structures existing in aerospace, nuclear power, high-speed rail, oil and gas transportation and other key projects.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Collagen/hydroxyapatite composite scaffold, and process for the production thereof
ActiveUS20100158976A1Good biocompatibilityPromotes cell adhesionPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsCompressive stiffnessCross-link
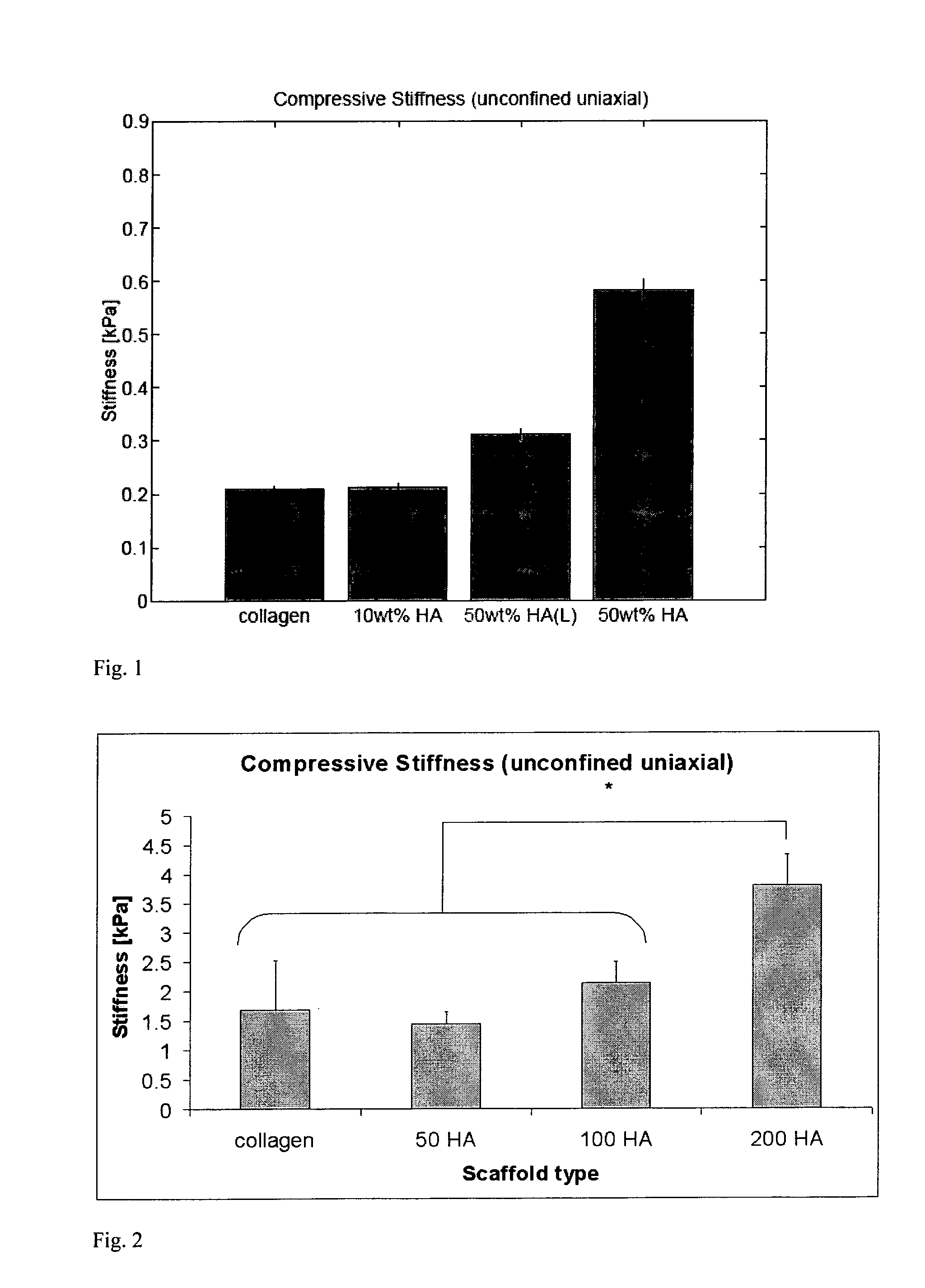
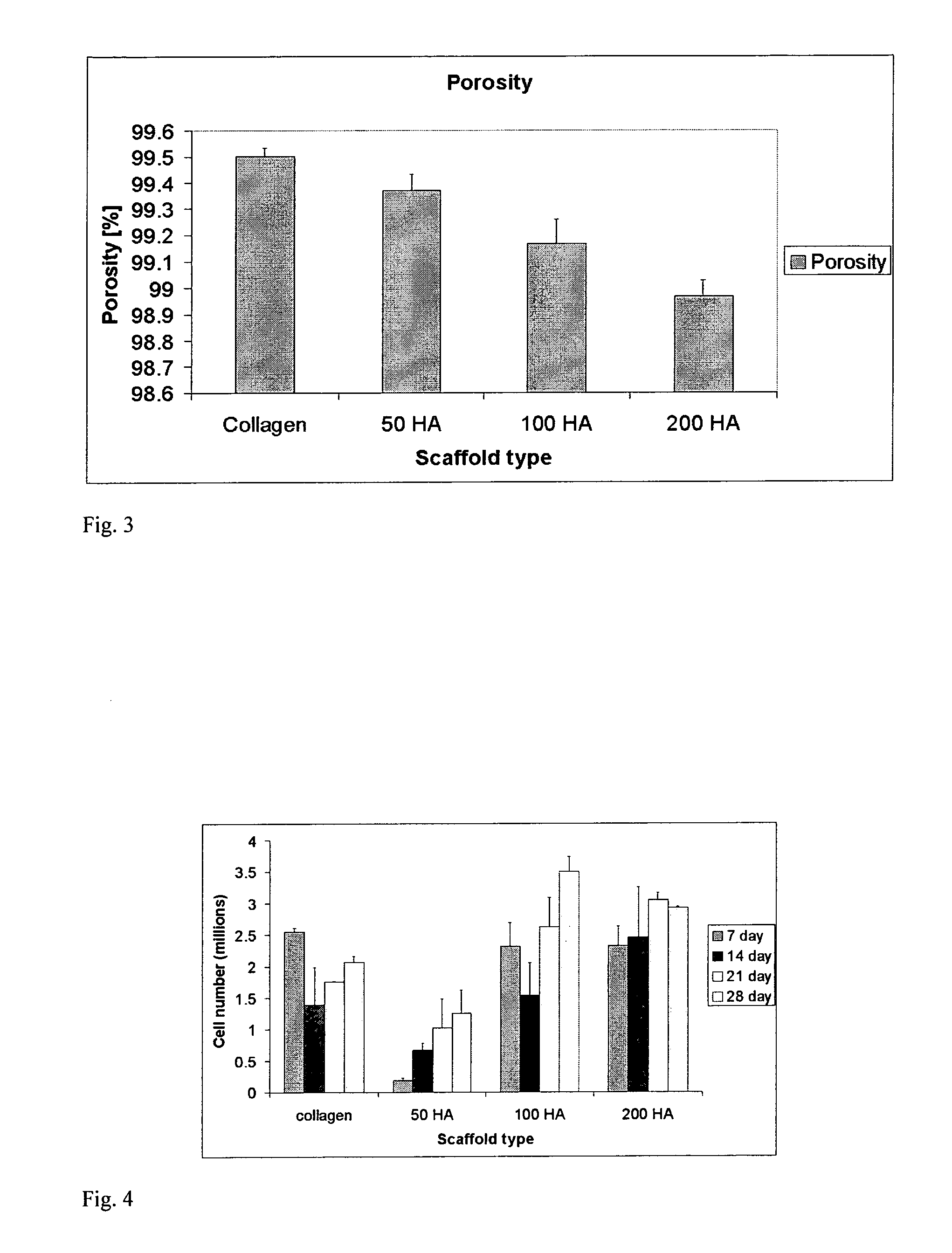
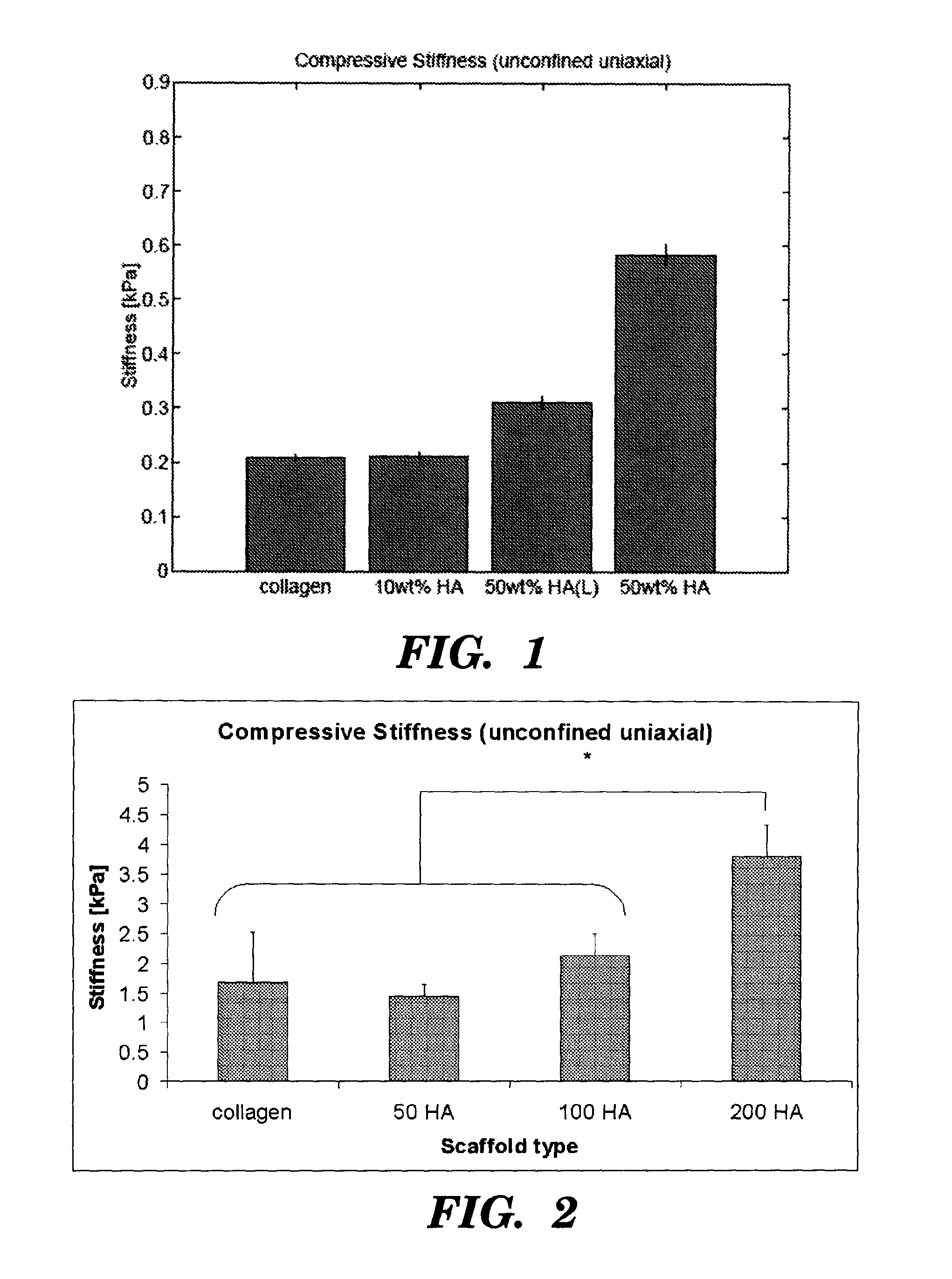
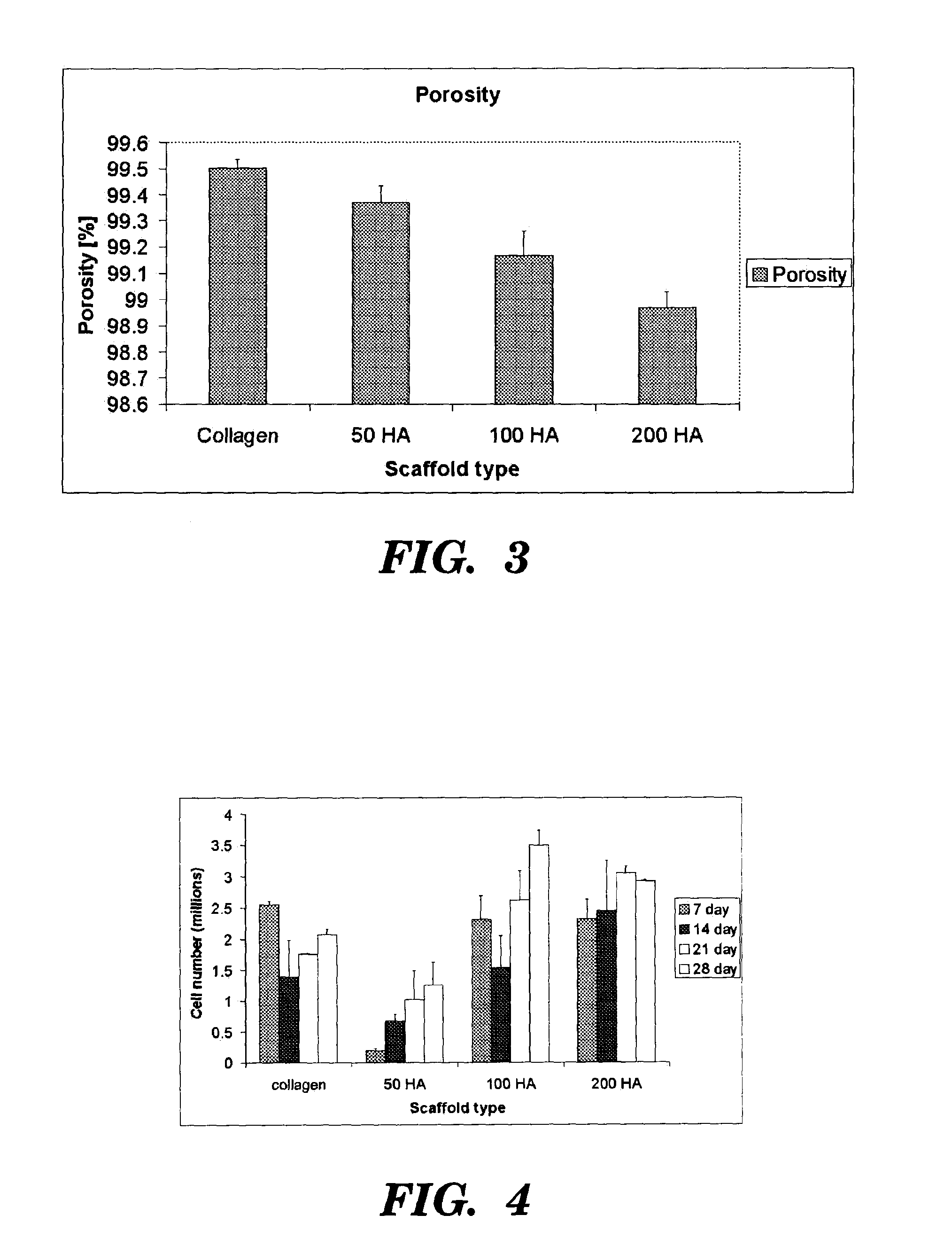
A process for producing a collagen / hydroxyapatite (HA) composite scaffold comprises the steps of forming a homogenous suspension of collagen and HA in an acidic solution, lyophilising the suspension until a desired final freezing temperature is reached to produce the composite scaffold, and optionally cross-linking the composite scaffold, wherein the ratio of HA to collagen is at least 1:10 (w / w). Also provided is a collagen / hydroxyapatite (HA) composite scaffold comprising a homogenous distribution of hydroxyapatite within a porous, crosslinked, collagen matrix, wherein the ratio of HA to collagen is at least 1:10 (w / w). Suitably, the composite scaffold has a porosity of at least 99% (v / v), and a compressive stiffness of at least 0.3 KPa. Composite scaffolds of the invention may be used to provide osteoconductive bone implants and tissue engineering implants.
Owner:ROYAL COLLEGE OF SURGEONS & IRELAND
Shock absorbing device for shoe sole in rear foot part
ActiveUS20110138651A1Increase the buffer functionFunctionalSolesHeelsCompressive stiffnessEngineering
The present invention provides a shock absorbing device for a shoe sole in a rear foot part which can restrain the inclination of the foot toward the medial side while absorbing the shock of landing on the lateral side of the foot. A shock absorbing device for a shoe sole in a rear foot part according to the present invention, includes: a support element M; deformation elements 3 disposed below the support element, the deformation elements deforming to be compressed vertically at landing; and outer sole elements 2 contacting a ground at landing, each outer sole element being joined to a bottom surface of the respective deformation element. Both the deformation elements 3 and the outer sole elements 2 are substantially separated in a medial-lateral direction in the rear foot part to be arranged at least three regions of the rear foot part. A quotient obtained by dividing an area of a bottom surface of the support element M by an area of bottom surfaces of the outer sole elements 2 is set at about 1.3 or more in the rear foot part. A vertical compressive stiffness of the deformation element 3 disposed on the lateral side is smaller than that of the deformation element 3 disposed on the medial side.
Owner:ASICS CORP
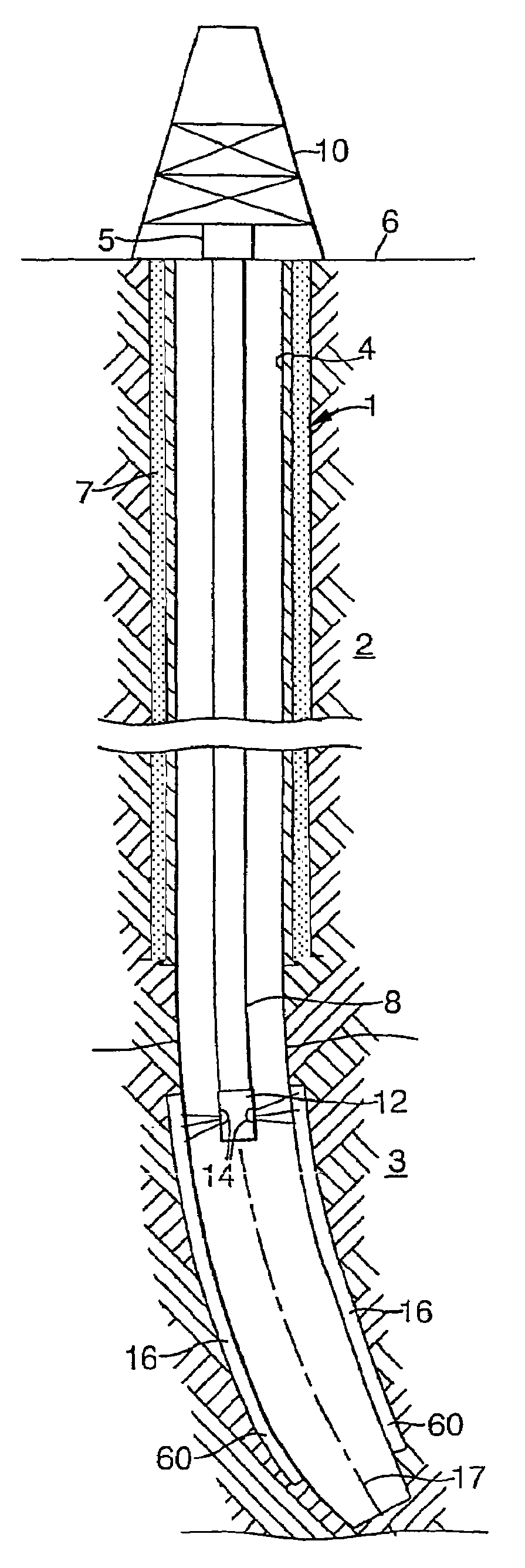
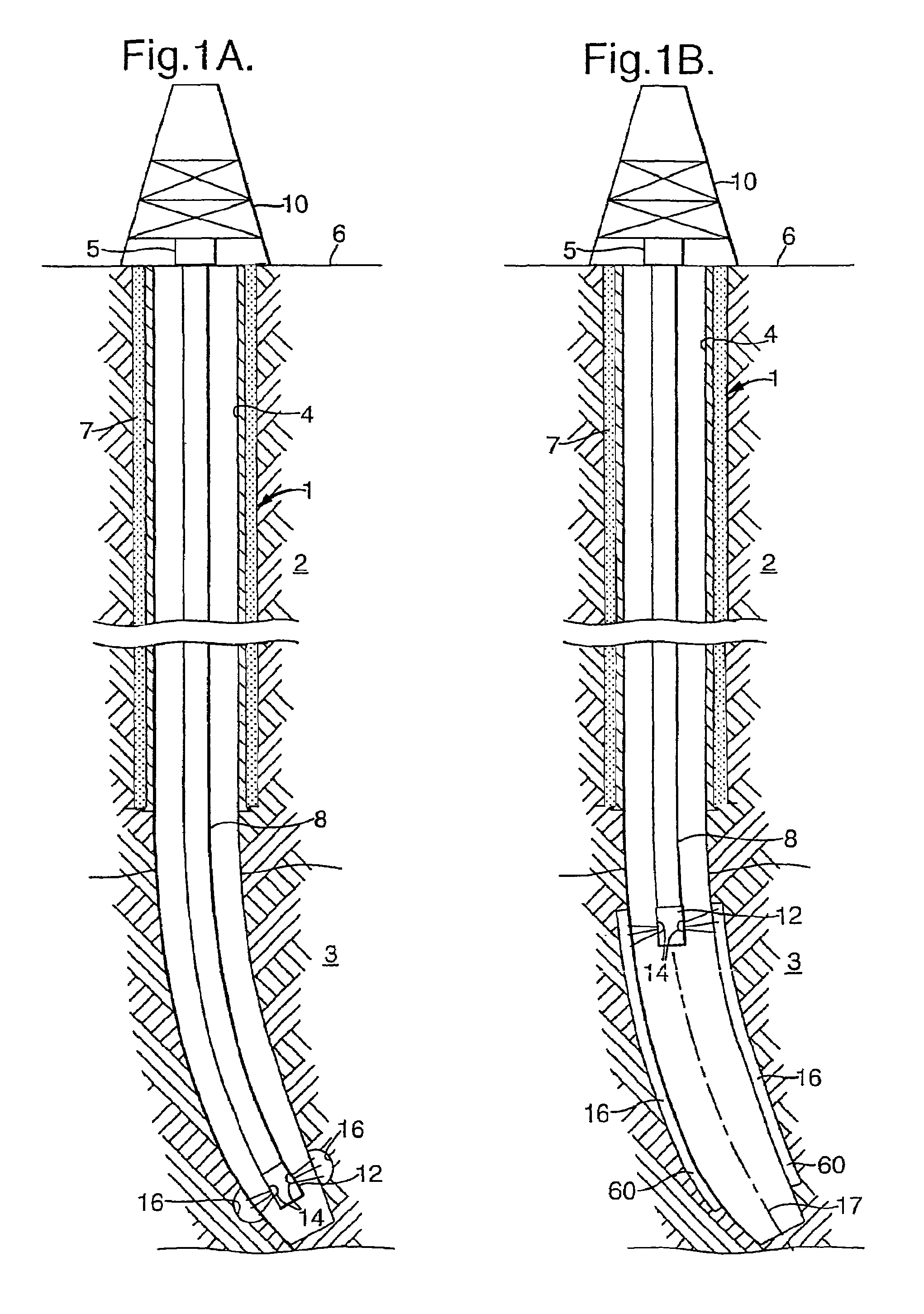
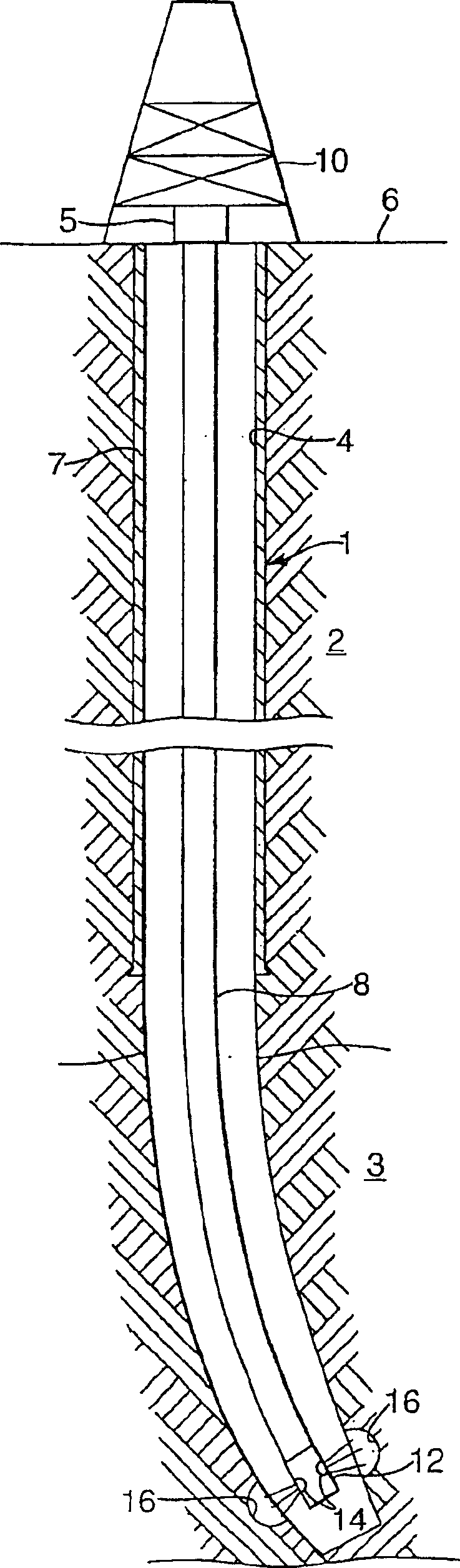
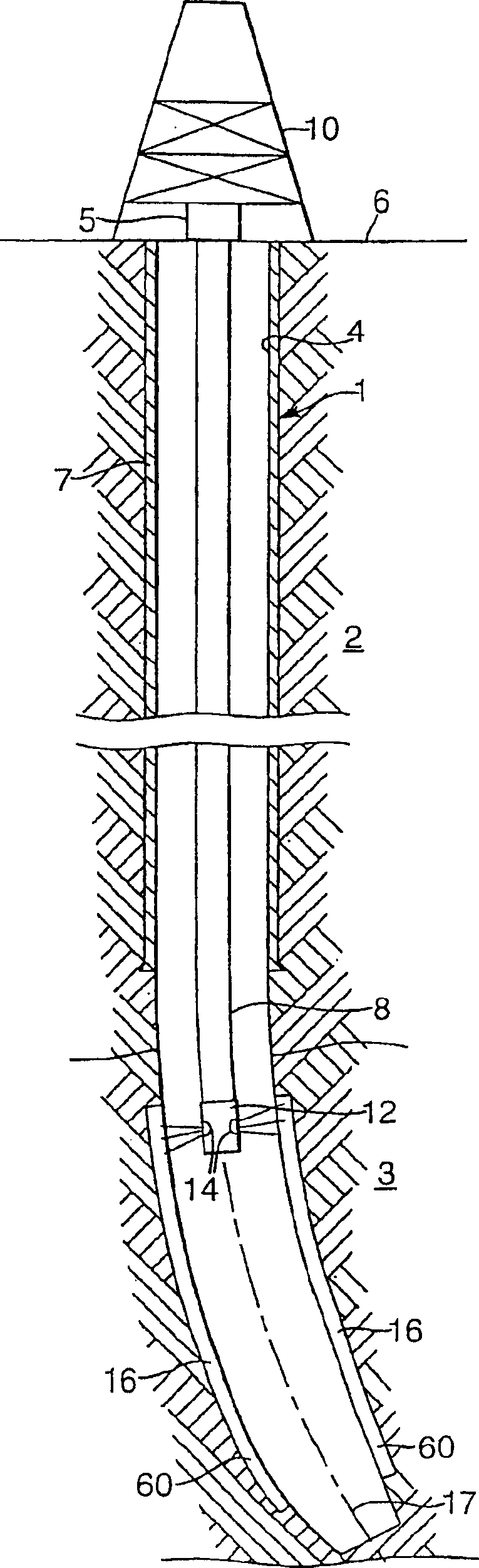
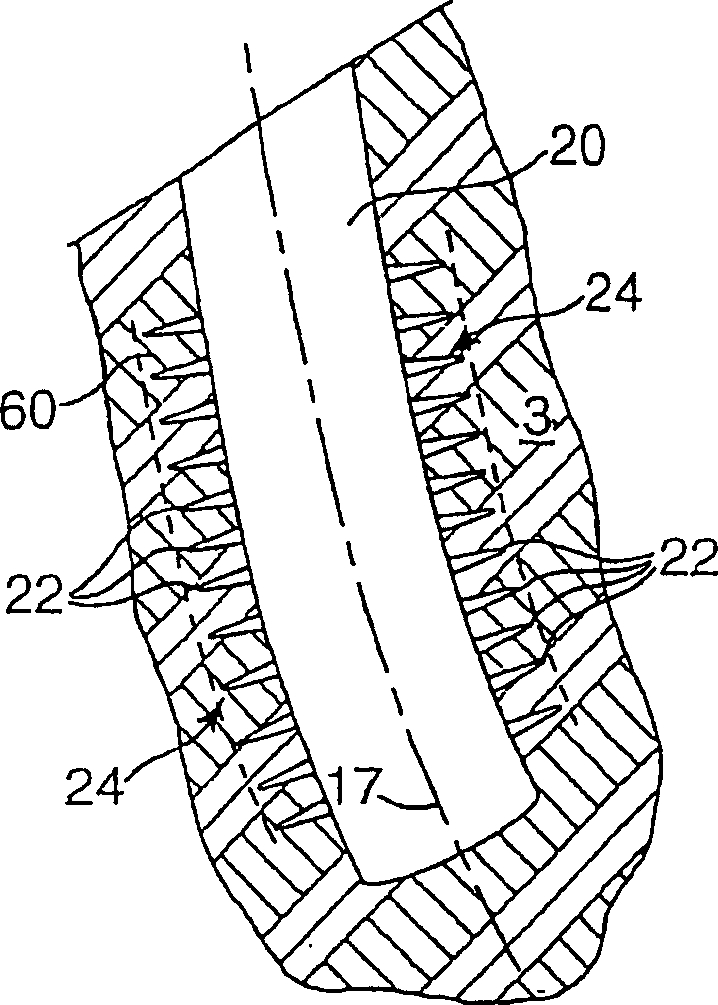
Method of reducing sand production from a wellbore
InactiveUS7451818B2Reduced compressive stiffnessReduce inflowSurveyDisloding machinesCompressive stiffnessGeophysics
A method is provided for the reduction of inflow of rock particles from an earth formation into a wellbore for the production of hydrocarbon fluid. The method comprises creating a zone of reduced compressive stiffness around the wellbore by removing rock material from the wall of the wellbore.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
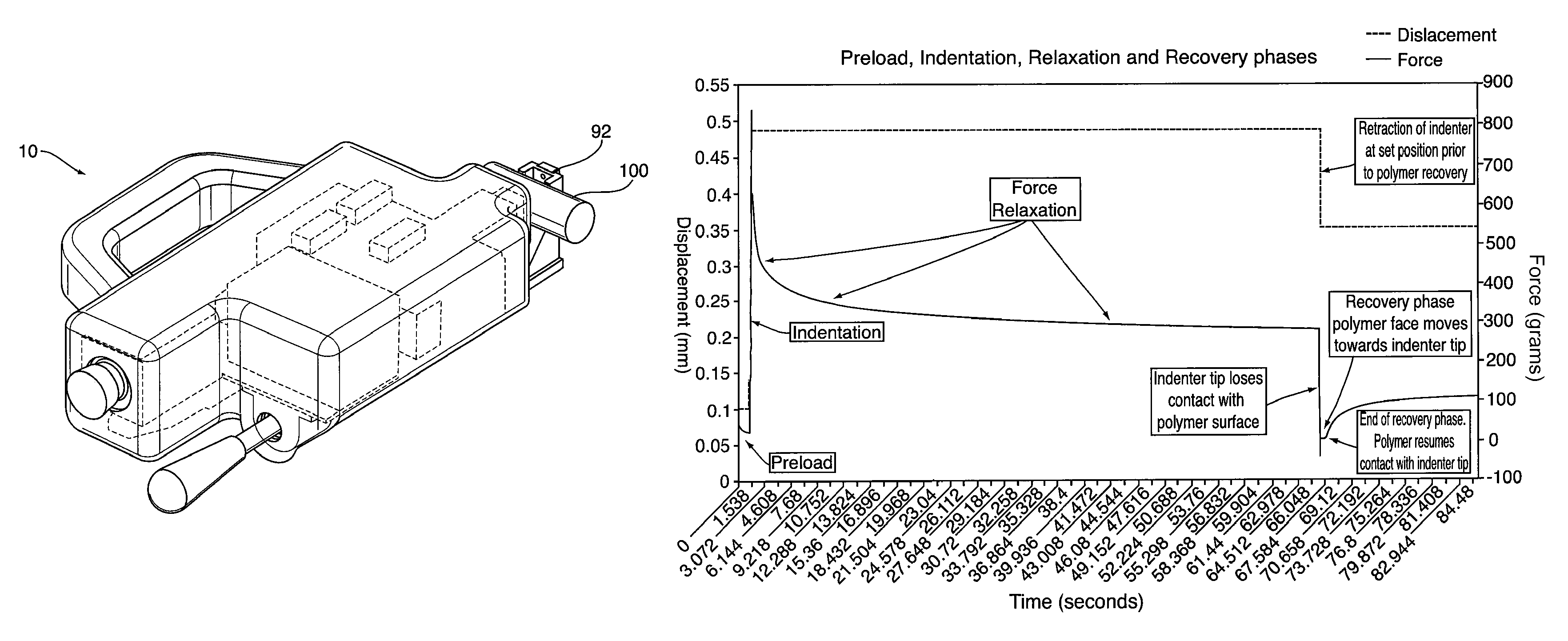
Portable polymer tester
The present invention provides a polymer indentation method and tester that includes measuring the time taken by a polymeric material to recover a set portion of an initial deformation and use this duration as a material degradation indicator. The recovery time was found to be more sensitive to cable degradation than the specific compressive stiffness (or indenter modulus) measured during the indentation phase, and this high sensitivity was achieved for both thermally aged and irradiated polymer samples.
Owner:ATOMIC ENERGY OF CANADA LIMITED
Collagen/hydroxyapatite composite scaffold, and process for the production thereof
ActiveUS8435552B2High mechanical stiffnessIncrease stiffnessPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsCross-linkCompressive stiffness
A process for producing a collagen / hydroxyapatite (HA) composite scaffold comprises the steps of forming a homogenous suspension of collagen and HA in an acidic solution, lyophilizing the suspension until a desired final freezing temperature is reached to produce the composite scaffold, and optionally cross-linking the composite scaffold, wherein the ratio of HA to collagen is at least 1:10 (w / w). Also provided is a collagen / hydroxyapatite (HA) composite scaffold comprising a homogenous distribution of hydroxyapatite within a porous, crosslinked, collagen matrix, wherein the ratio of HA to collagen is at least 1:10 (w / w). Suitably, the composite scaffold has a porosity of at least 99% (v / v), and a compressive stiffness of at least 0.3 KPa. Composite scaffolds of the invention may be used to provide osteoconductive bone implants and tissue engineering implants.
Owner:ROYAL COLLEGE OF SURGEONS & IRELAND
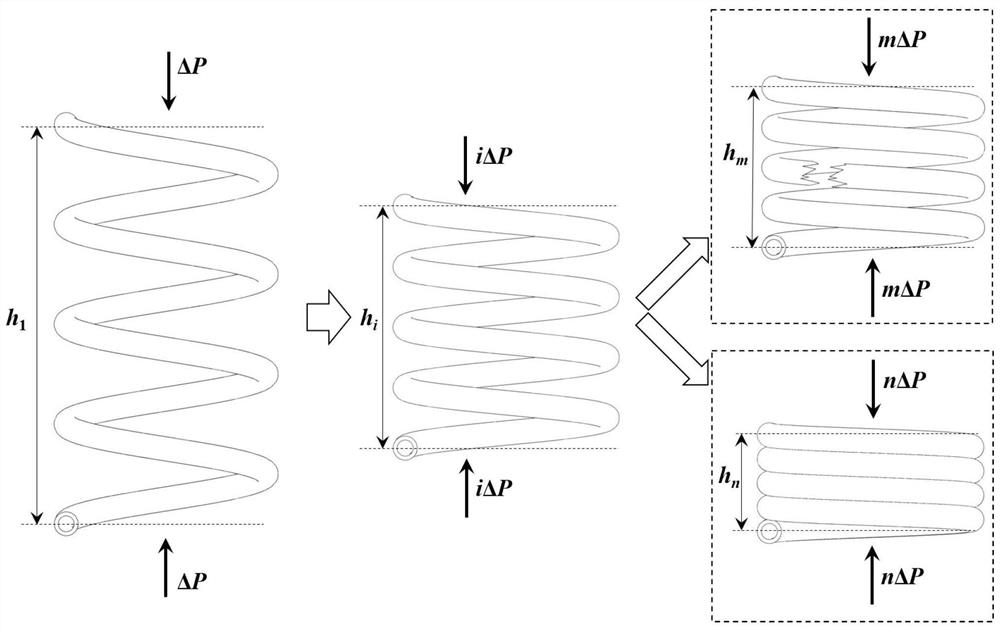
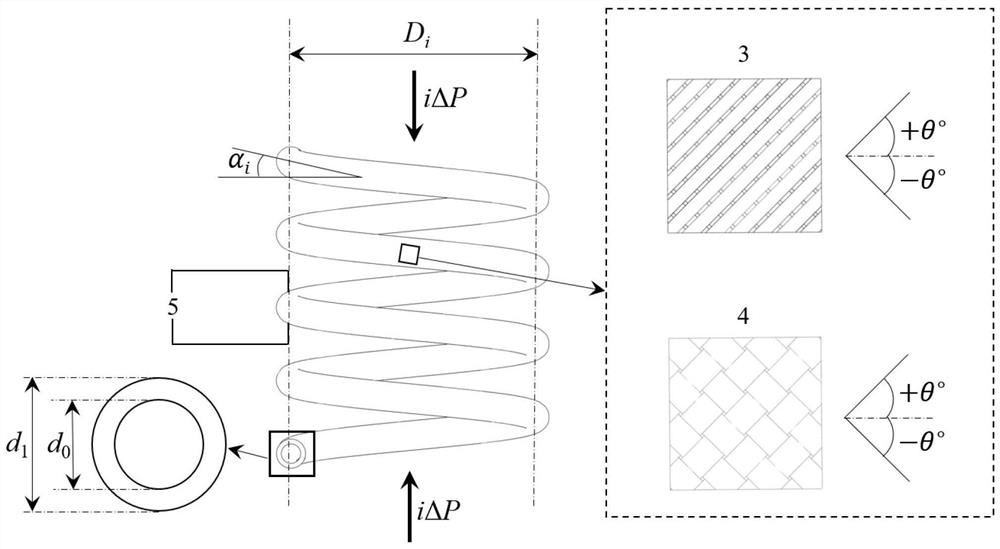
Method for predicting compression rigidity and compression strength of composite material spiral structure by considering geometric nonlinearity
ActiveCN112084616AEasy to calculateHigh precisionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationCompressive stiffnessGeometrical nonlinearity
A method for predicting compression rigidity and compression strength of a composite material spiral structure by considering geometrical nonlinearity comprises the following four steps: step 1, defining the geometrical shape and size of the spiral structure of the composite material, and determining a mathematical expression of a relationship among geometrical parameters; 2, carrying out stress analysis on any cross section A, and calculating the deformation and compression rigidity of the composite material spiral structure based on an energy principle; 3, through the compression deformationincrement and the compression load increment in the cumulative loading process, establishing a load displacement relation considering geometric nonlinearity of the composite material spiral structure, and linearly fitting a load displacement curve according to a least square method; 4, deriving a composite material helical structure compression strength analytical expression by adopting principaldirection stress and a TsaiHill failure criterion; the invention is convenient and efficient, and the compression rigidity and the compression strength of the spiral structure of the composite material can be conveniently and quickly predicted only by determining performance parameters and geometrical parameters of component materials.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Portable polymer tester
ActiveUS8857246B2Material testing goodsInvestigating material hardnessThermal ageingCompressive stiffness
The present invention provides a polymer indentation method and tester that includes measuring the time taken by a polymeric material to recover a set portion of an initial deformation and use this duration as a material degradation indicator. The recovery time was found to be more sensitive to cable degradation than the specific compressive stiffness (or indenter modulus) measured during the indentation phase, and this high sensitivity was achieved for both thermally aged and irradiated polymer samples.
Owner:ATOMIC ENERGY OF CANADA LIMITED
Analysis method for lateral limit support stiffness of curve beam
ActiveCN108629075AReasonable stiffness valueIn line with the actual situationGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationCompressive stiffnessStructural analysis
The invention discloses an analysis method for lateral limit support stiffness of a curve beam. The method comprises the following steps of building a three-dimensional model of the curve beam by adopting a solid 90 unit in an ANSYS system; setting temperature field parameters including a heat transfer coefficient, specific heat, a concrete surface and air convection coefficient, concrete densityand a temperature gradient; performing grid division; according to different boundaries, applying temperature loads changed with time; solving a temperature field; by adopting a sequential coupling method, converting a thermodynamic analysis unit Solid 90 into a structural analysis unit Solid 95, and loading temperature field solving data as the temperature load together with a vehicle centrifugalforce; performing structural mechanic solving; and adjusting compressive stiffness of lateral limit support, repeating the step for adjusting the compressive stiffness of the lateral support and performing calculation, and comparing calculation results to obtain reasonable lateral limit support stiffness. The structural analysis is performed in combination with the centrifugal force based on thetemperature field analysis; temperature calculation data and centrifugal force data jointly serve as loads and are loaded for calculation; and the actual condition of the curve beam is better met.
Owner:CHINA COMM NORTH ROAD & BRIDGE
Shock absorber capable of changing damping and adjusting mass and rigidity and rigidity quantitative regulation method
ActiveCN111810567APosition vibration precise controlPrecise Control of VibrationNon-rotating vibration suppressionShock absorbersPhysicsCompressive stiffness
The invention discloses a shock absorber capable of changing damping and adjusting mass and rigidity and a rigidity quantitative regulation method. The shock absorber comprises a base, two rubber washers, a mass block, a top end cover, a nut, a screw rod, an internal end cover, a lining, a regulating stopper, a rubber sleeve and a guide rail seat. When a system vibrates, the mass block vibrates under support of the rubber washers to absorb part of energy, and the interior of each of the rubber washers vibrates to consume part of energy, so that the purpose of realizing vibration attenuation ofa main system is realized. Mass regulation of the shock absorber is realized through the number of the mass block; vibration of the external diameter of the lining is controlled through the depth screwed into the regulating stopper to adjust damping of the shock absorber; the top end nut is screwed to adjust the compressing degree of the upper and lower rubber washers; quantitative regulation ofthe shock absorber rigidity is realized according to the relationship of the compression amount and the compressing rigidity of the rubber washers, and a better damping effect is realized without an experiment. The shock absorber is simple and compact in structure, can realize quantitative regulation of rigidity and mass and is wide in applicable range.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Motorcycle tire
InactiveCN108688408AIncreased durabilityMotorcycle tyresPneumatic tyre reinforcementsCompressive stiffnessMotorcycle tyre
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Prestressed variable-stiffness three-dimensional seismic isolation support
InactiveCN113152972ADoes not affect the horizontal vibration isolation effectAchieving Variable Stiffness PropertiesProtective buildings/sheltersShock proofingCompressive stiffnessPre stress
The invention relates to a prestressed variable-stiffness three-dimensional seismic isolation support, and belongs to the field of seismic absorption and isolation of structural engineering. On the basis of a common rubber seismic isolation support, the tensile deformation capacity of the support is enhanced through vertical seams, prestress is applied through nuts, the rubber layer is pulled, meanwhile, springs are pressed, and therefore the prestress variable-rigidity three-dimensional seismic isolation support is formed. According to the prestressed variable-stiffness three-dimensional seismic isolation support, on the basis of the common rubber seismic isolation support, the tensile deformation capacity of the rubber seismic isolation support is enhanced through the vertical seams, then self-balancing pre-tensioning and pre-pressing deformation is applied, the vertical rigidity of the seismic isolation support is mainly controlled by the springs, and when vertical deformation after seismic isolation is larger than pre-tensioning deformation, the vertical rigidity is controlled by the sum of the vertical compression rigidity of the rubber layer and the spring rigidity, so that the variable rigidity characteristic is realized; and meanwhile, vertical seismic isolation does not affect the horizontal seismic isolation effect of the rubber layer, and therefore the three-direction seismic isolation effect is achieved. The prestressed variable-stiffness three-dimensional seismic isolation support does not increase the material cost, is simple in structure, clear in mechanical property parameter and convenient to implement, and can be widely applied to three-dimensional seismic isolation analysis and design of structures.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Endoscopic device
An endoscopic instrument for performing surgical procedures. The instrument includes an elongate member having a distal end for insertion into a patient's body and a proximal end opposite the distal end. The member has a distal portion adjacent the distal end and a central portion adjacent the distal portion. The distal portion has a first mechanical stiffness of a stiffness type selected from a tensile stiffness, a compressive stiffness and / or a bending stiffness. The central portion has a second mechanical stiffness of the stiffness type of the first mechanical stiffness. The first mechanical stiffness is different from the second mechanical stiffness.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
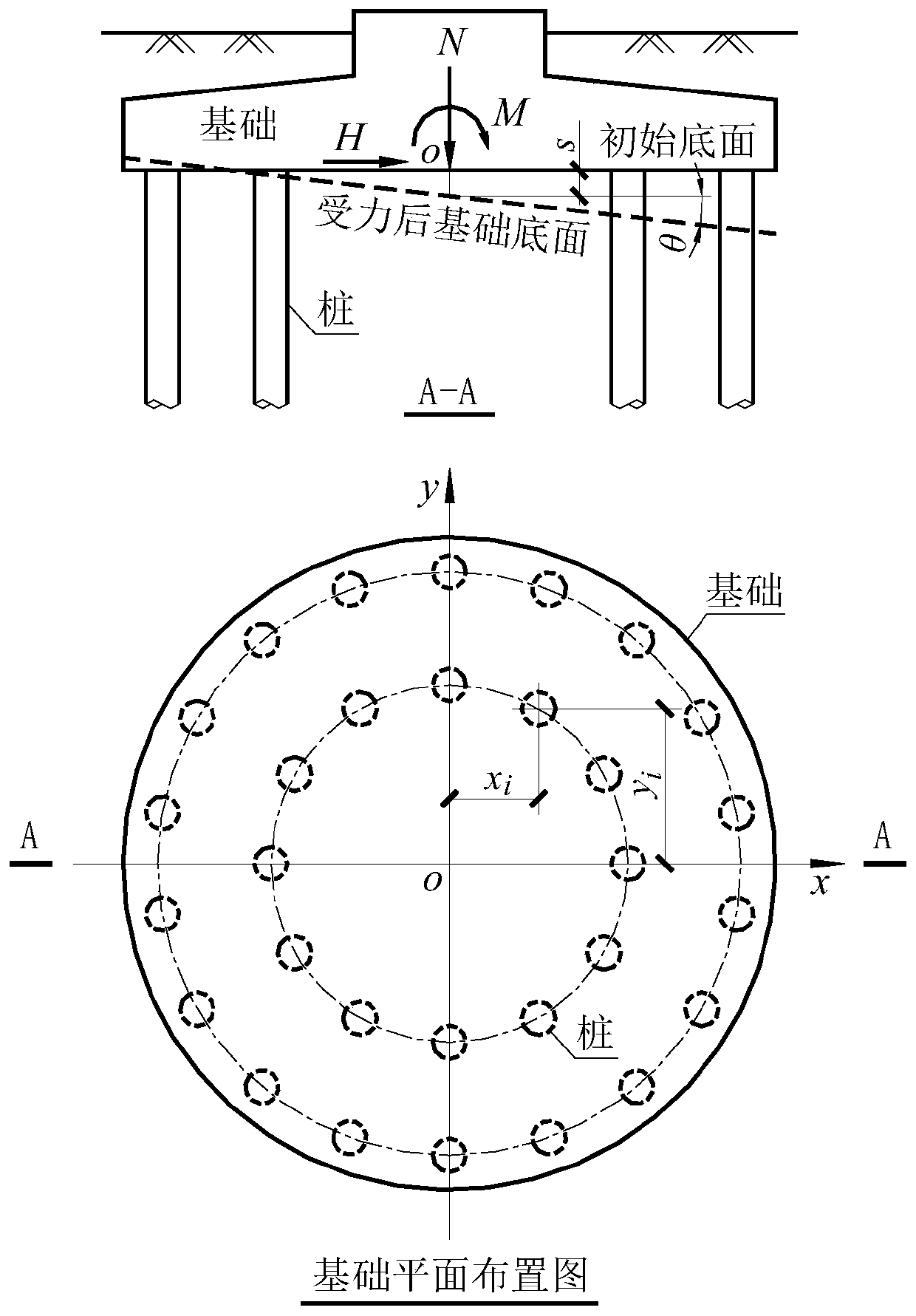
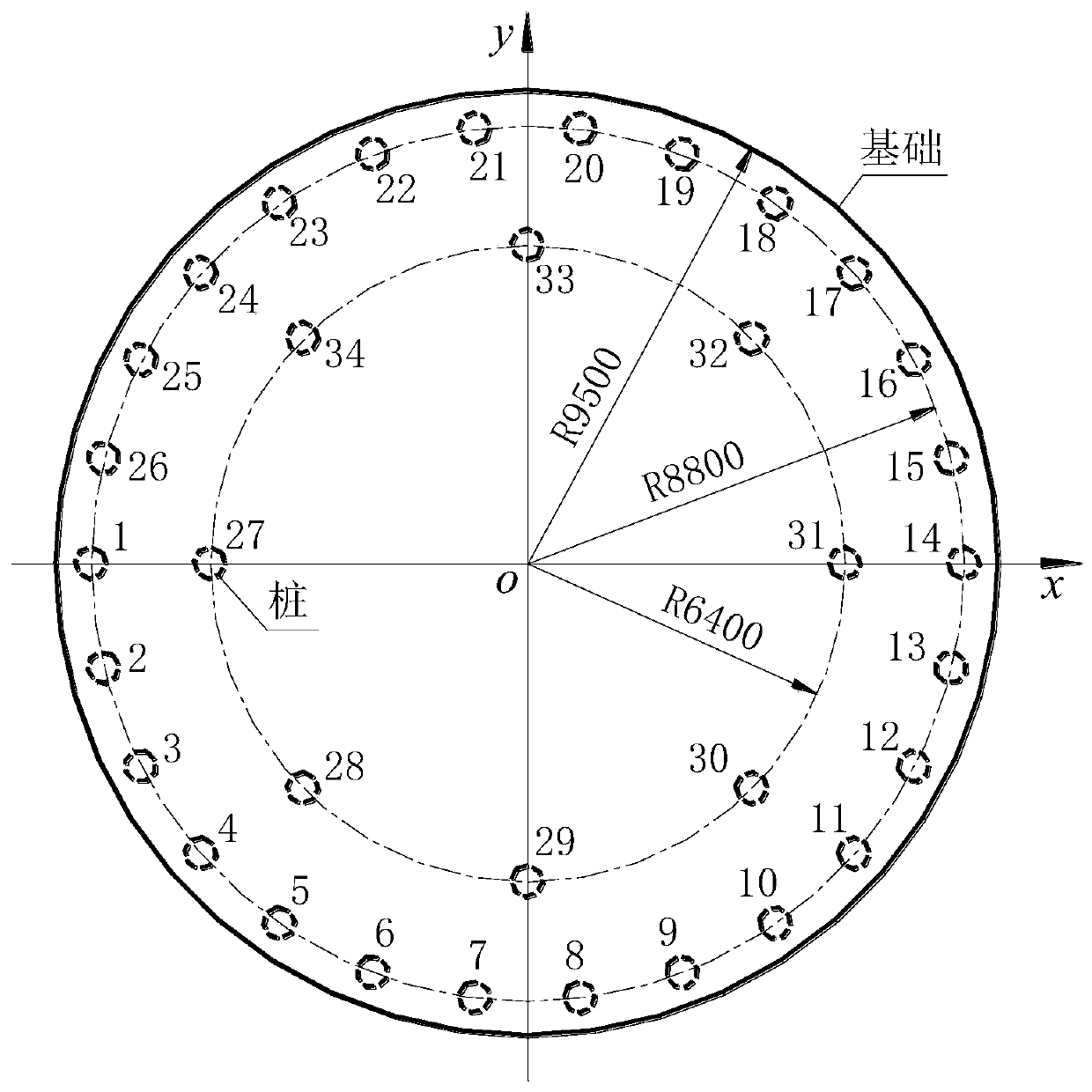
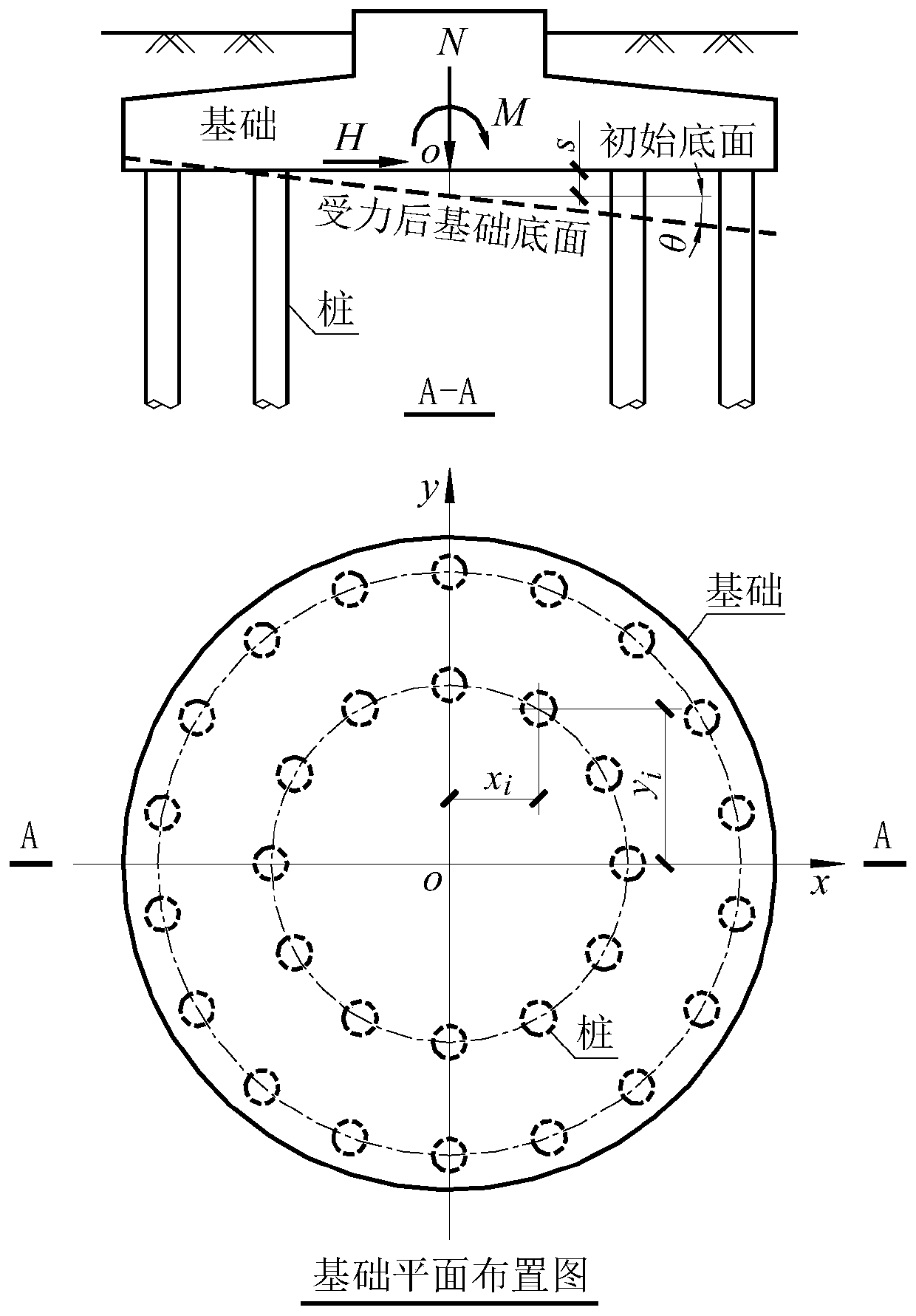
Rigid bearing platform lower pile top vertical force calculation method considering foundation pile rigidity distribution difference
The invention discloses a rigid bearing platform lower pile top vertical force calculation method considering a foundation pile rigidity distribution difference. The method comprises the following steps: the bending moment acting on a rigid bearing platform at the top of a foundation pile, the equivalent resultant force of vertical loads and the vertical deformation rigidity of each foundation pile are obtained; and the pile top vertical force is obtained through calculation according to the bending moment, the equivalent resultant force of the vertical load and the vertical deformation rigidity. Aiming at the problem of pile top vertical force calculation when the vertical stiffness of all or part of foundation piles under a rigid foundation is different and the vertical uplift stiffnessand the compressive stiffness of the same foundation pile are different, a complete pile top vertical force calculation formula and a corresponding foundation pile stiffness iterative algorithm are given; on the basis, an automatic algorithm that the vertical force of the pile top changes along with the change of the action direction of the horizontal load is provided for pile foundations needingto consider the action direction of the horizontal load, such as bearing wind load.
Owner:CEEC JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER DESIGN INST
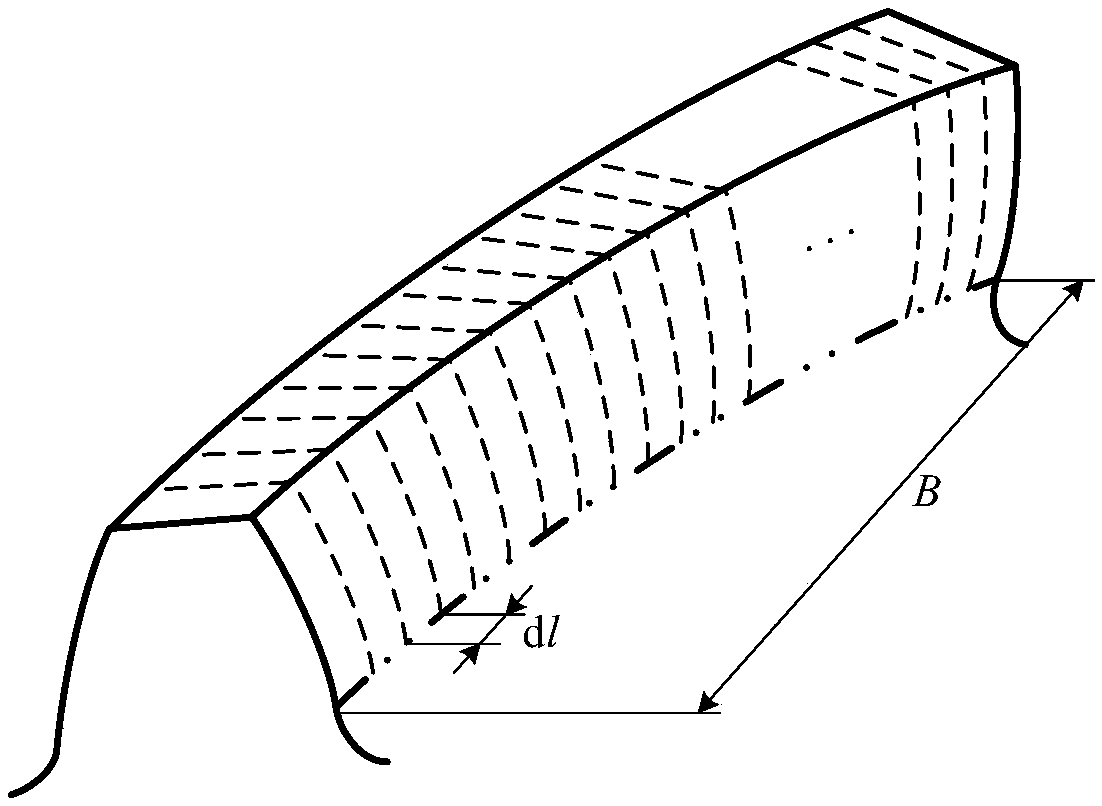
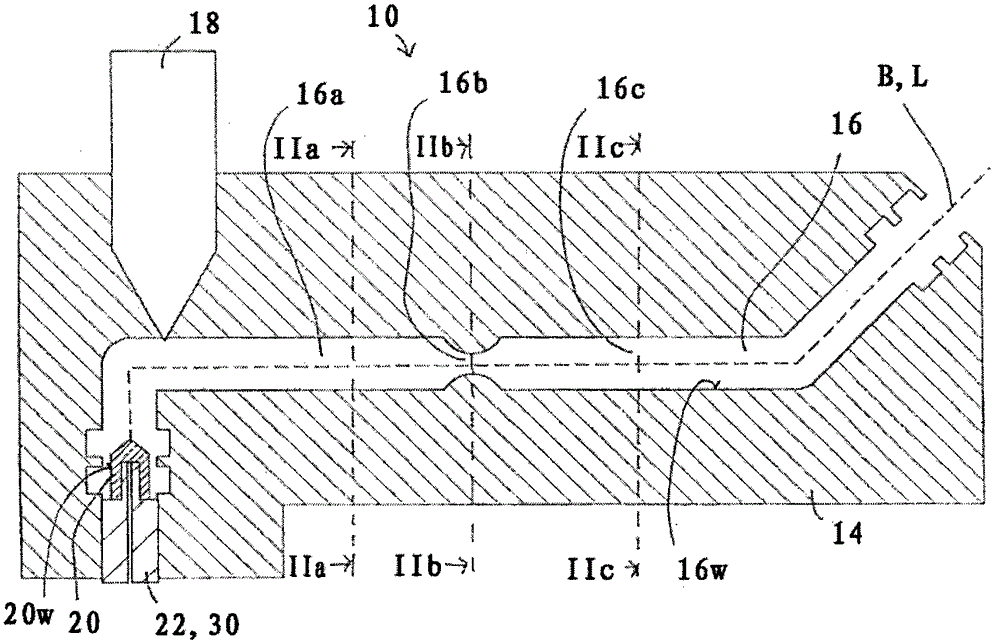
Molding device and molding method for producing hollow molded articles
ActiveCN102765167BQuality improvementPrevent flow throughTubular articlesHollow articlesCompressive stiffnessPolymer science
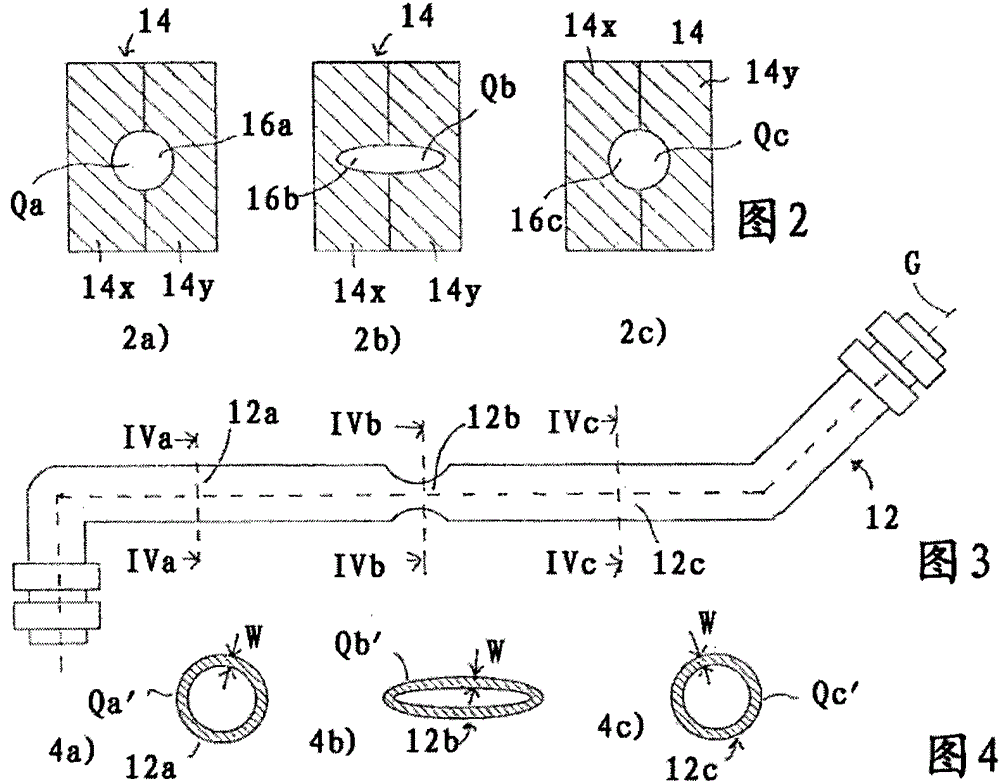
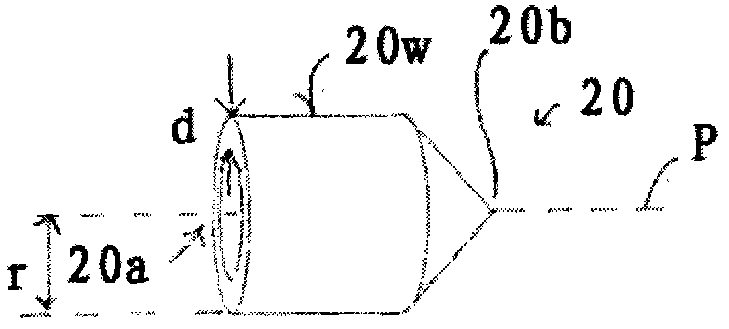
The invention relates to a molding device (10) for producing hollow molded articles (12), comprising: a mold (14) having a cavity (16), filling the cavity (16) with molding material in a free-flowing state ) filling device (18), ejector (20; 120) and displacement device (22), the displacement device is designed to drive the ejector (20) to move along the trajectory (B) into the mold for filling In the molding material of cavity (16), wherein mold cavity (16) comprises at least two mold cavity parts (16a, 16b, 16c) that are arranged successively along the trajectory (B) of motion of ejection body (20), these parts have differently shaped cross-sections (Qa, Qb, Qc) perpendicular to the trajectory of motion (B), and wherein the ejector body (20) comprises a deformed portion formed of a deformed material having a higher density than the molding material A lower elastic compressive stiffness such that a cubic test specimen composed of said deformed material has a lower elastic compressive stiffness than a test specimen of the same shape and size composed of said molded material in the cured state.
Owner:ROECHLING AUTOMOTIVE SE & CO KG
Hyperstatic truss comprising connecting rods
ActiveUS9429073B2Reduce sizeDrag minimizationPower plant constructionEfficient propulsion technologiesCompressive stiffnessEngineering
A hyperstatic truss including connecting rods, used for suspension of a first ring, forming part of an engine case, inside a second ring concentric to the first ring, the connecting rods being secured at one end to the first ring and at the other end to the second ring. The tensile stiffness of the connecting rods is greater than the compressive stiffness thereof. The truss for example can be used for suspension of a ducted-fan turbine engine with an elongate bypass duct.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
A Calculation Method of Time-varying Mesh Stiffness of Spur Gears Considering the Effect of Temperature
InactiveCN109101737BGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsCompressive stiffnessDrive wheel
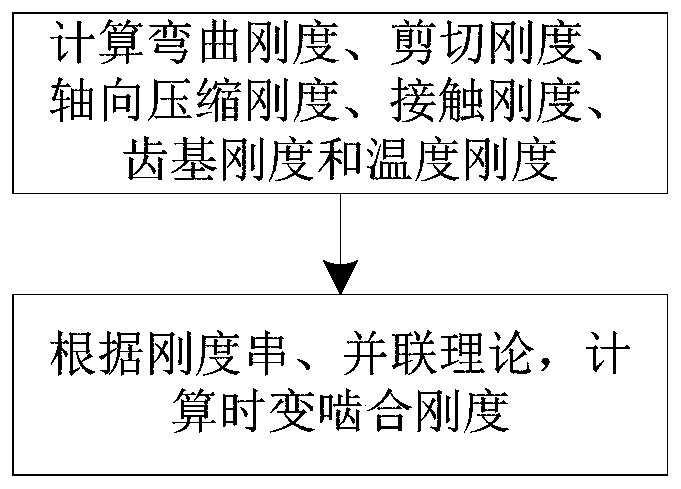
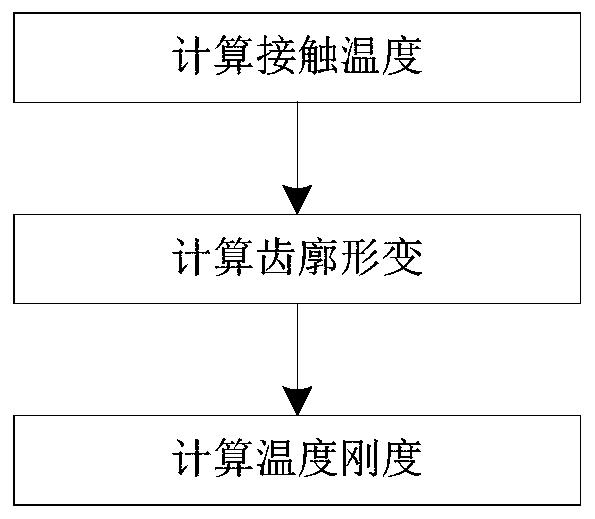
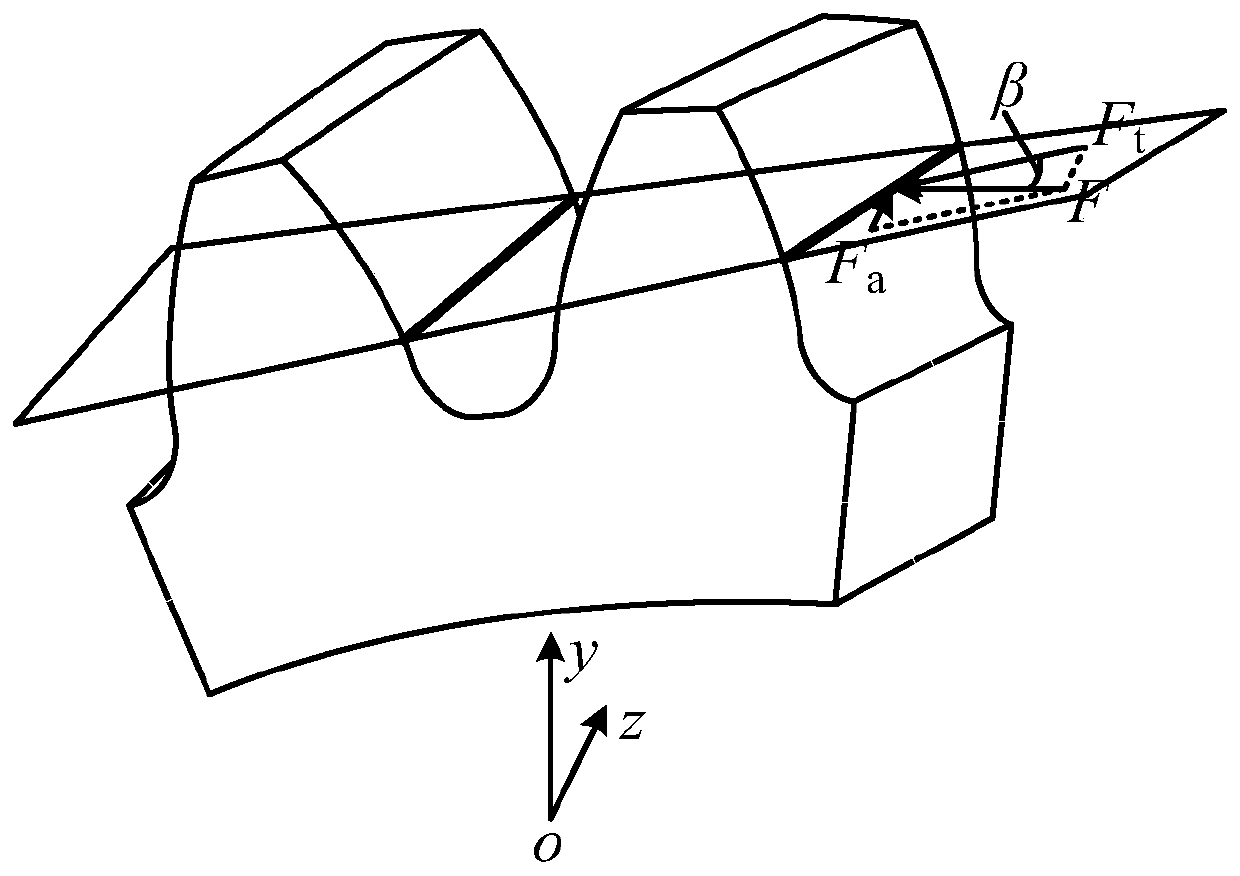
The invention discloses a method for calculating the time-varying meshing stiffness of spur gears considering the influence of temperature. This method takes into account the influence of the working environment temperature of the gear pair (steady-state ambient temperature). According to Coleman theory, the instantaneous temperature of the tooth surface generated by frictional heat when the driving wheel / driven wheel meshes is calculated, and the mathematics of the tooth surface contact temperature changing with time is derived. Expression; Calculate the tooth profile thermal deformation of the driving wheel and the driven wheel tooth caused by the contact temperature change of the tooth surface, so as to calculate the temperature stiffness of the tooth caused by the temperature change; Finally, according to the stiffness series and parallel theory, combined with the tooth bending stiffness, The shear stiffness, axial compression stiffness, contact stiffness, tooth base stiffness and temperature stiffness are used to calculate the time-varying mesh stiffness of the gear.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
A Design Method of Bead Parameters Based on Bead Pressure
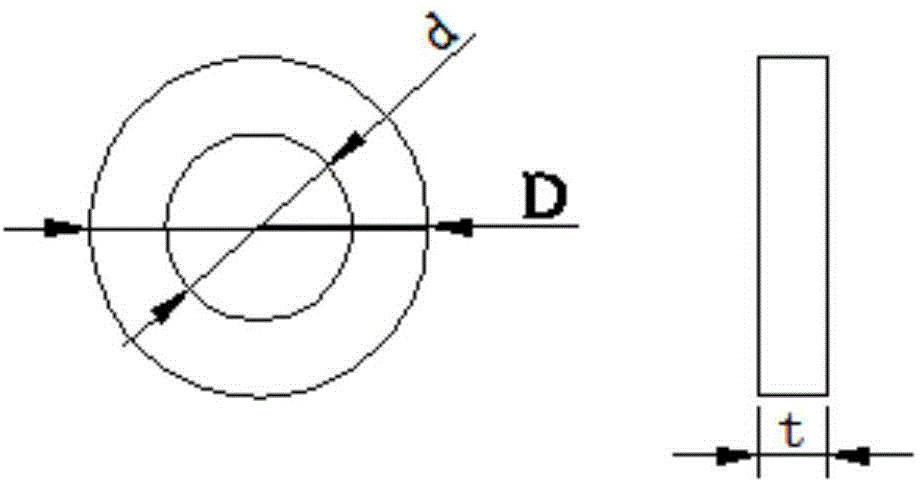
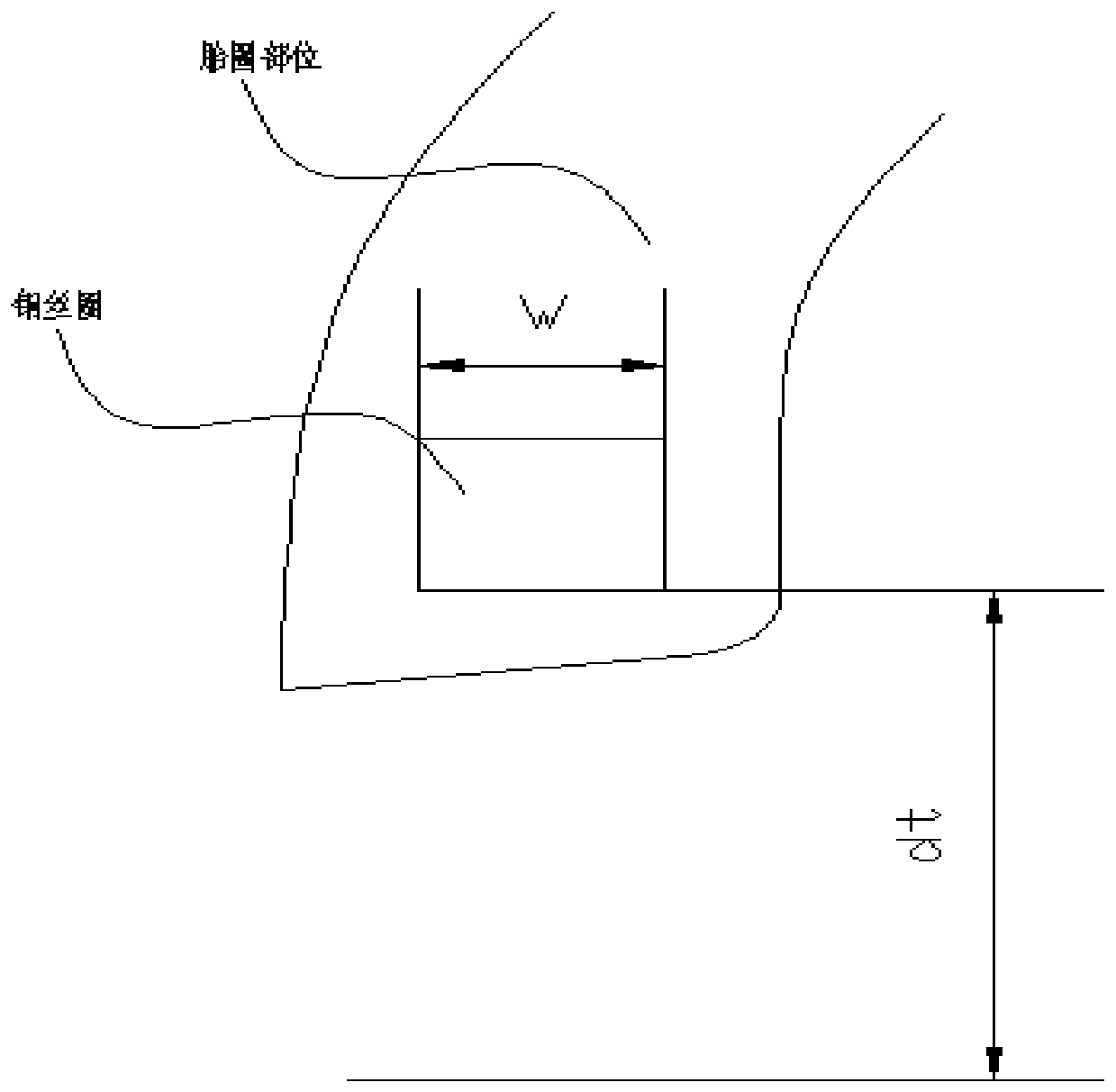
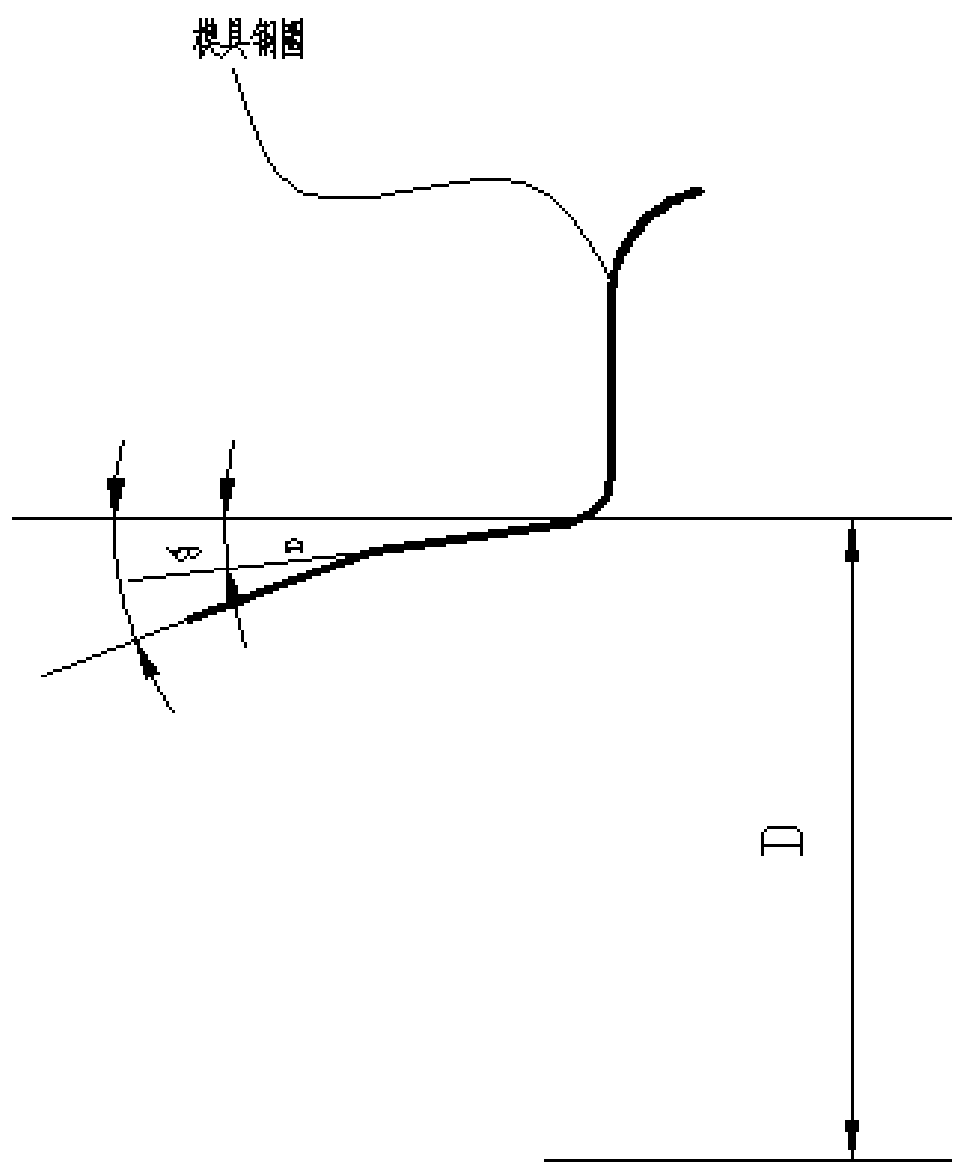
ActiveCN106599413BGuaranteed degree of interference fitShorten design timeGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationRubber materialTire bead
The invention provides a method for designing bead parameters based on bead pressure. Based on the specific required bead pressure range, the engagement diameter D of the mold steel ring and the inner diameter d of the bead ring are obtained by using the formula t The functional relationship, so as to calculate the value range of the engagement diameter D of the mold steel ring and the inner diameter d of the steel ring t The value range of the bead bottom material thickness G is used to calculate D and d respectively t value. The present invention utilizes the relationship between the compression stiffness of the rubber material in theory of tire mechanics, the size of the rubber material, and its shape to determine the size of the rubber material at the bead, so as to ensure that the degree of interference fit at the bead, that is, the pressure of the bead, is at an appropriate level. It is used to set the engagement diameter of the mold steel ring and the reference of the inner diameter of the bead ring, and shorten the time required for the design of the bead part.
Owner:GITI RADIAL TIRE (ANHUI) CO LTD
A Calculation Method for Time-varying Mesh Stiffness of Helical Cylindrical Gears Considering Axial Deformation
ActiveCN107798200BHigh precisionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationCompressive stiffnessShear stiffness
The invention proposes a method considering axial deformation for calculating time-varying meshing stiffness of a helical gear. The method aims at improving the accuracy of calculating the meshing stiffness of the helical gear. The method comprises the implementation steps of calculating the end surface bending stiffness, end surface shearing stiffness, radial compression stiffness and end surfacetooth base stiffness of the helical gear; calculating contact stiffness; calculating the end surface meshing stiffness of a single tooth pair; deducing and calculating axial bending stiffness, axialshearing stiffness and axial tooth base stiffness; calculating the meshing stiffness of the single tooth pair; calculating the time-varying meshing stiffness. According to the method, the influence ofaxial meshing force on the time-varying meshing stiffness of the helical gear is considered, a calculation expression for the quantitative calculation of the axial bending stiffness, axial shearing stiffness and axial tooth base stiffness of the helical gear is deduced, the time-varying meshing stiffness of the helical gear is calculated by combining all the stiffness in the end surface direction, the calculation accuracy is improved, and the method can be used for the dynamic performance analysis and optimization design of the helical gear.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
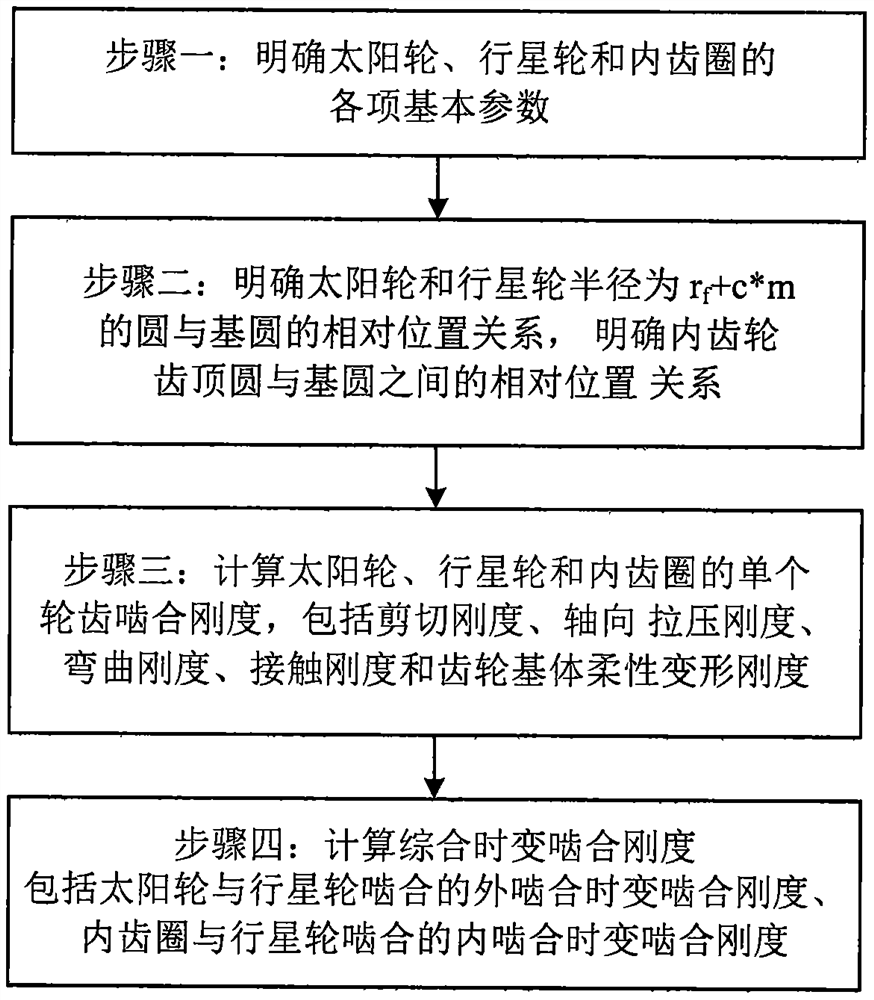
A Calculation Method of Time-varying Mesh Stiffness of Planetary Gears Based on Tooth Profile Correction Method
ActiveCN111625758BAccurate divisionImprove accuracyGearing detailsComplex mathematical operationsCompressive stiffnessKinetics
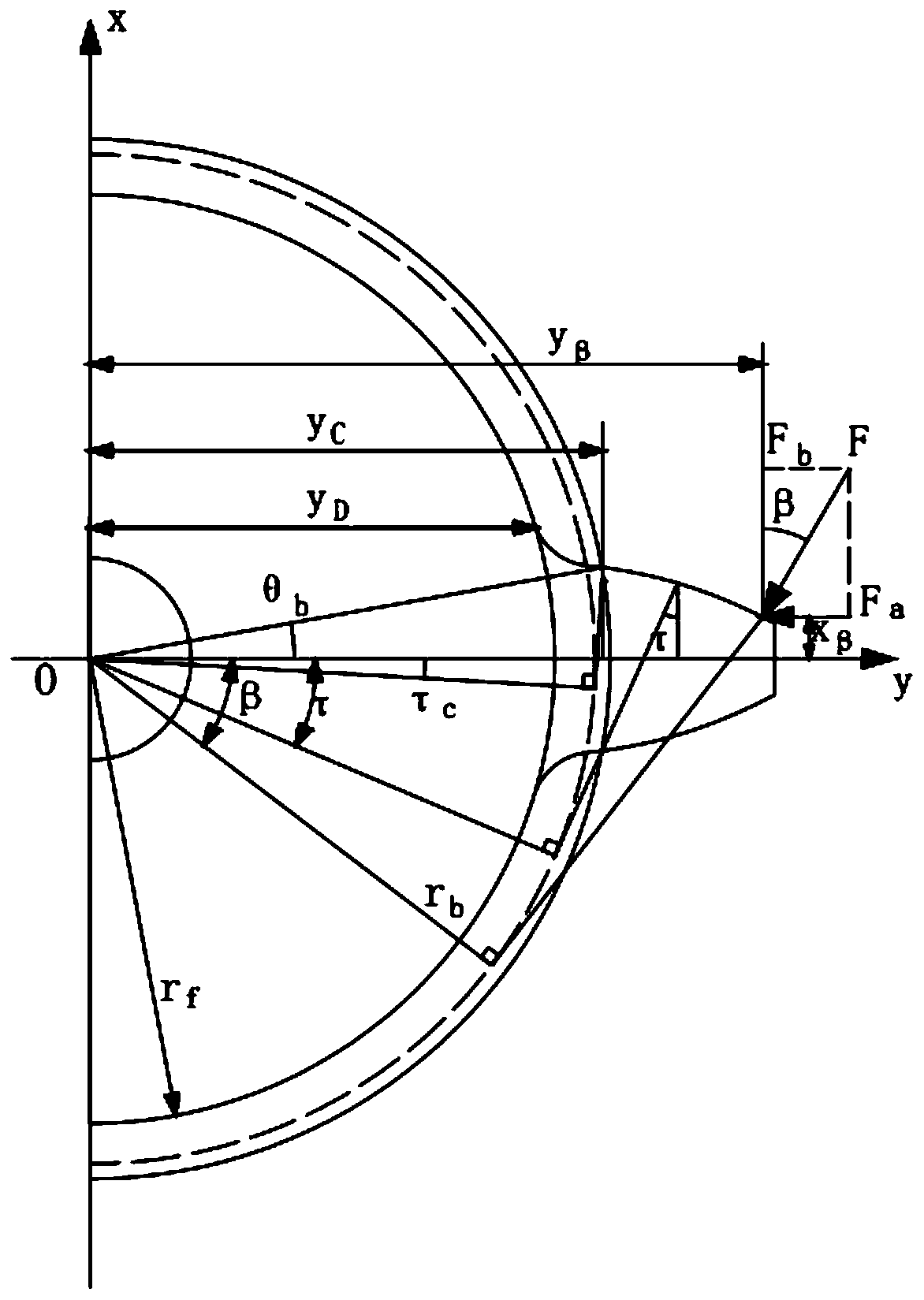
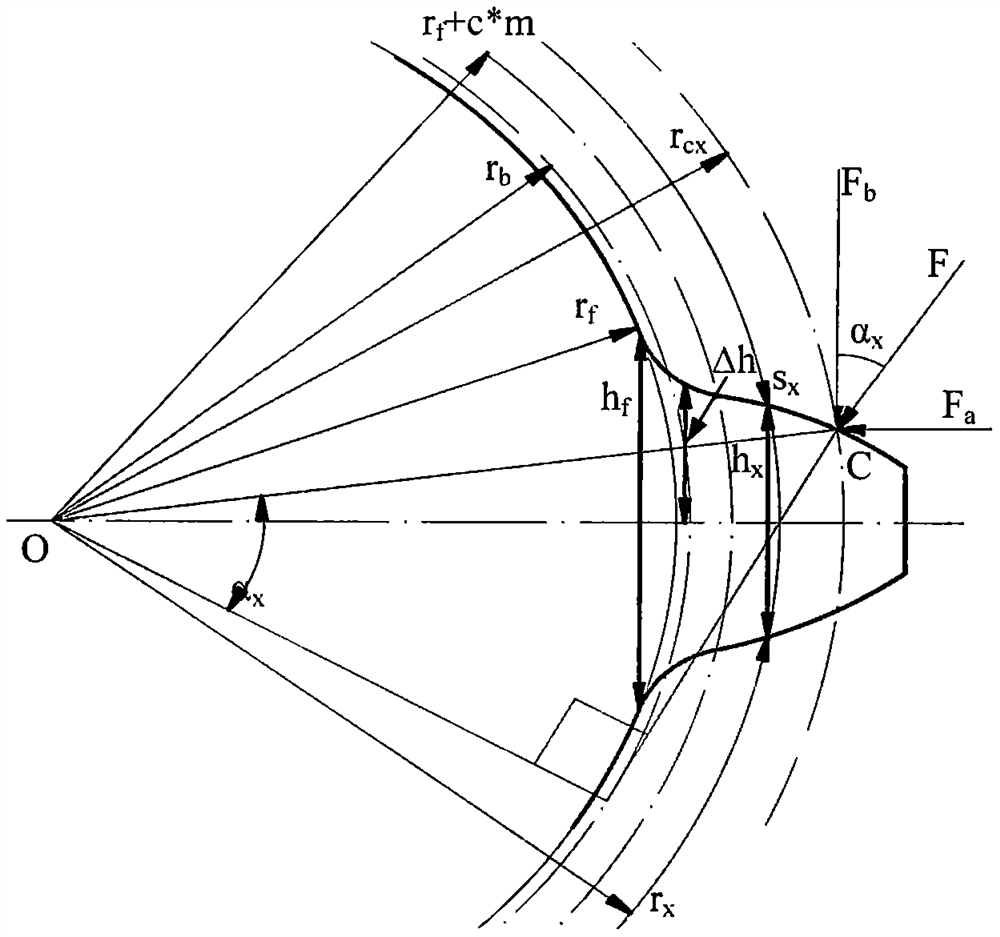
The invention discloses a method for calculating the time-varying meshing stiffness of a planetary gear based on a tooth shape correction method, which belongs to the technical field of mechanical dynamics, fully considers the influence of the tooth shape on the calculation of the comprehensive meshing stiffness, and improves the calculation accuracy of the time-varying meshing stiffness of the planetary gear , including the following specific steps: First, the basic parameters of the sun gear, planetary gear and ring gear should be specified, and then the radius of the sun gear and planetary gear should be r f The relative positional relationship between the +c*m circle and the base circle, clarify the relative positional relationship between the addendum circle and the base circle of the internal gear, and then calculate the meshing stiffness of the individual teeth of the sun gear, planetary gear and internal gear, including Shear stiffness, axial tension and compression stiffness, bending stiffness, contact stiffness and flexible deformation stiffness of the gear base, and finally calculate the comprehensive time-varying meshing stiffness, including the time-varying meshing stiffness of the outer meshing of the sun gear and the planetary gear, the inner ring gear and the planetary gear The inner meshing stiffness of the wheel meshing is time-varying, and the invention has the advantages of simple principle, easy calculation and strong practicability.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Testing method of woven composite material blade
PendingCN114720302AVerify consistencyEasy to operateMaterial strength using steady bending forcesCompressive stiffnessAviation
The invention discloses a method for testing a woven composite material blade, relates to the field of aero-engine blade testing, and is used for testing the compression performance of the woven composite material blade. The method comprises the following steps: setting a target area on the woven composite material blade; sampling from the target area to obtain a sample; loading the sample by adopting a four-point bending test device; acquiring first bending test data of the sample; establishing a finite element model of the sample; applying boundary conditions to the finite element model according to a four-point bending test; calculating second bending test data of the finite element model according to the rigidity of the finite element model; when the difference value between the first bending test data and the second bending test data is smaller than a set value, extracting the compression stiffness of the finite element model and the maximum compression stress corresponding to the maximum load; the maximum compression stress in the finite element model is the compression strength of the sample, and the ratio of the maximum compression stress to the maximum compression strain in the finite element model is the compression modulus of the sample.
Owner:AECC COMML AIRCRAFT ENGINE CO LTD
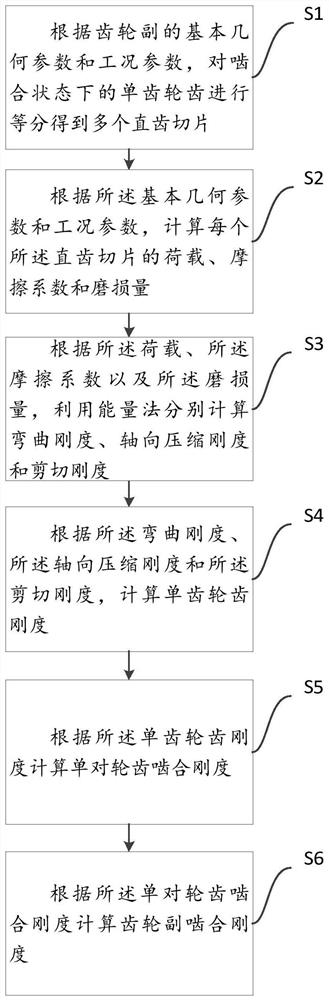
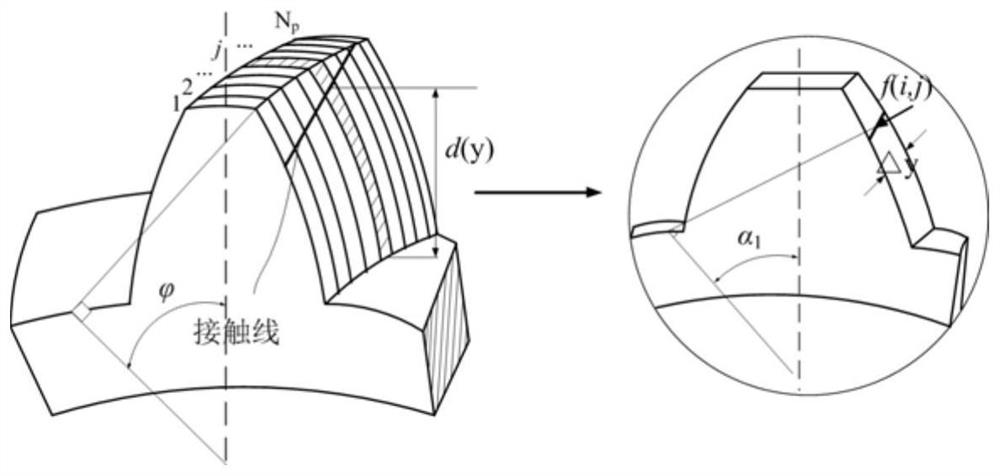
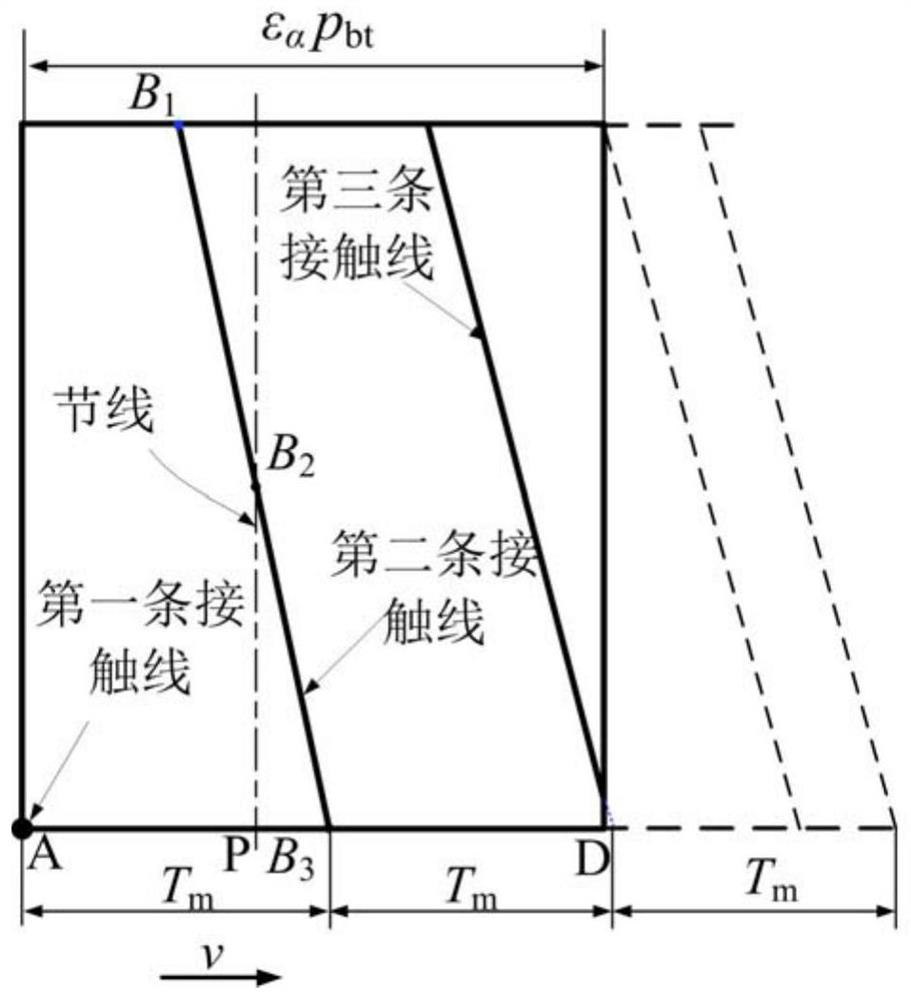
Gear pair meshing stiffness calculation method and terminal equipment
ActiveCN113051681AMesh Stiffness CalculationGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsCompressive stiffnessAxial compression
The embodiment of the invention discloses a gear pair meshing rigidity calculation method, which specifically comprises the following steps of: equally dividing single gear teeth in a meshing state according to basic geometric parameters and working condition parameters of a gear pair to obtain a plurality of straight tooth slices; according to the basic geometric parameters and the working condition parameters, calculating the load, the friction coefficient and the abrasion loss of each straight tooth slice; according to the load, calculating the friction coefficient and the abrasion loss, the bending rigidity, the axial compression rigidity and the shearing rigidity through adoption of an energy method; according to the bending rigidity, calculating the axial compression rigidity and the shearing rigidity, the single gear tooth rigidity; calculating meshing stiffness of a single pair of gear teeth according to the tooth stiffness of the single gear; calculating the meshing rigidity of the gear pair according to the meshing rigidity of the single pair of gear teeth; and therefore, the influence of friction and abrasion on the meshing rigidity of the helical gear pair is considered, and the meshing rigidity of the helical gear pair is accurately calculated.
Owner:TIANJIN HAISHENG JIAHE ENERGY TECH
Method of reducing sand production from a wellbore
InactiveCN1878928AReduce inflowFluid removalDrilling machines and methodsCompressive stiffnessGeophysics
A method is provided for the reduction of inflow of rock particles from an earth formation into a wellbore for the production of hydrocarbon fluid. The method comprises creating a zone of reduced compressive stiffness around the wellbore by removing rock material from the wall of the wellbore.
Owner:SHELL INT RES MAATSCHAPPIJ BV
A self-resetting lateral shear-resistant wall-to-floor connection device and its application method
ActiveCN112922176BGuaranteed stabilityMaintain out-of-plane stabilityFloorsProtective buildings/sheltersCompressive stiffnessCarbon fibers
The invention discloses a connection device between a self-resetting anti-lateral shear wall and a floor slab and a use method thereof, which comprises a self-resetting anti-lateral shear wall, a floor, a friction device and a carbon fiber reinforced laminated low-damping rubber bearing. The side shear wall is connected with the floor slab through the carbon fiber reinforced laminated low damping rubber bearing. Beneficial effects: It can reduce the acceleration of the floor and maintain the stability of the floor. The energy consumption section in the middle of the friction device consumes seismic energy. The carbon fiber reinforced laminated low-damping rubber bearing is fixed at the gap between the two sides of the self-resetting lateral shear wall and the floor. , this bearing has an almost linear elastic response under large shear deformations with significant compressive stiffness for maintaining the out-of-plane stability of self-resetting lateral shear walls and providing predictable and reliable postelastic stiffness for deformed connections , the carbon fiber reinforced rubber layer is used to prevent the collision damage between the self-resetting anti-lateral shear wall and the floor.
Owner:JIANGSU OCEAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com