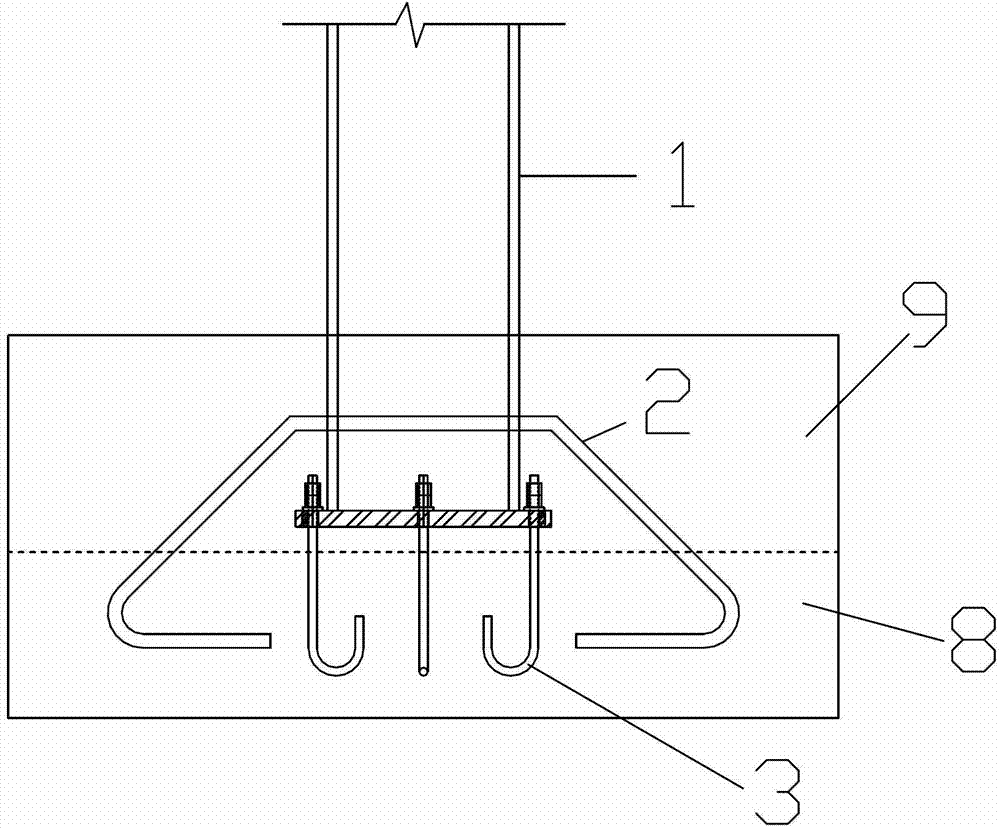
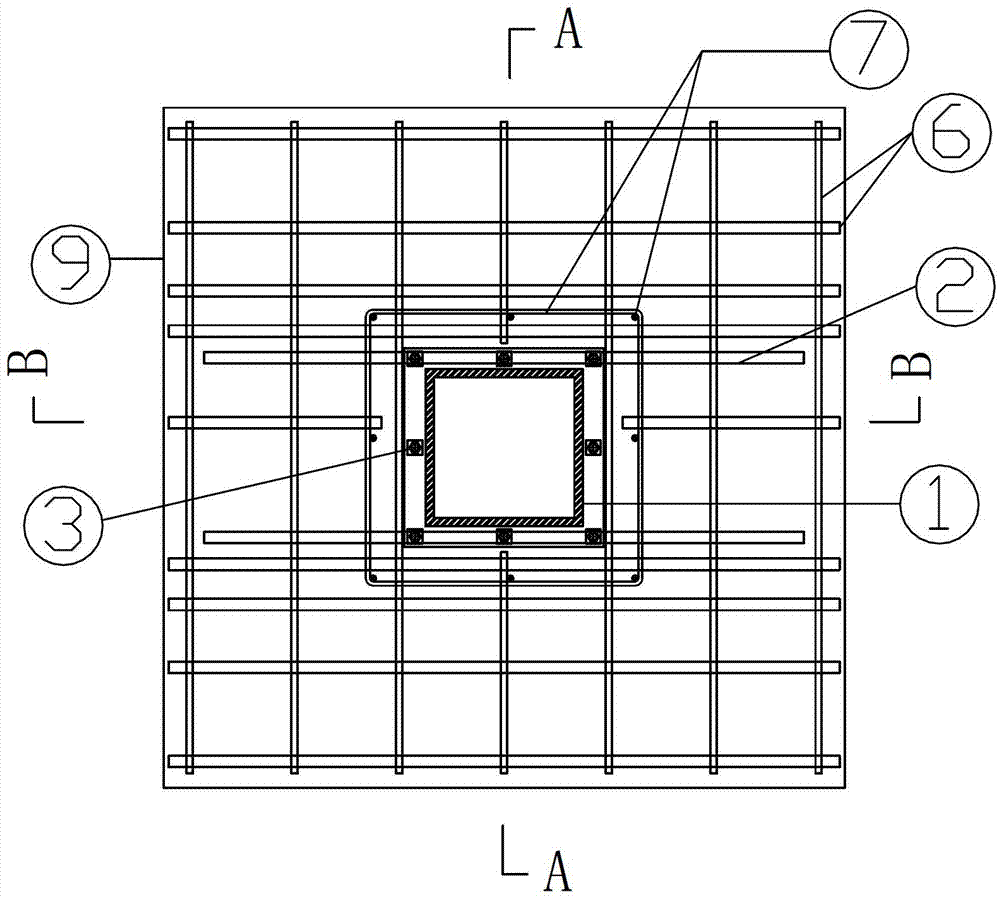
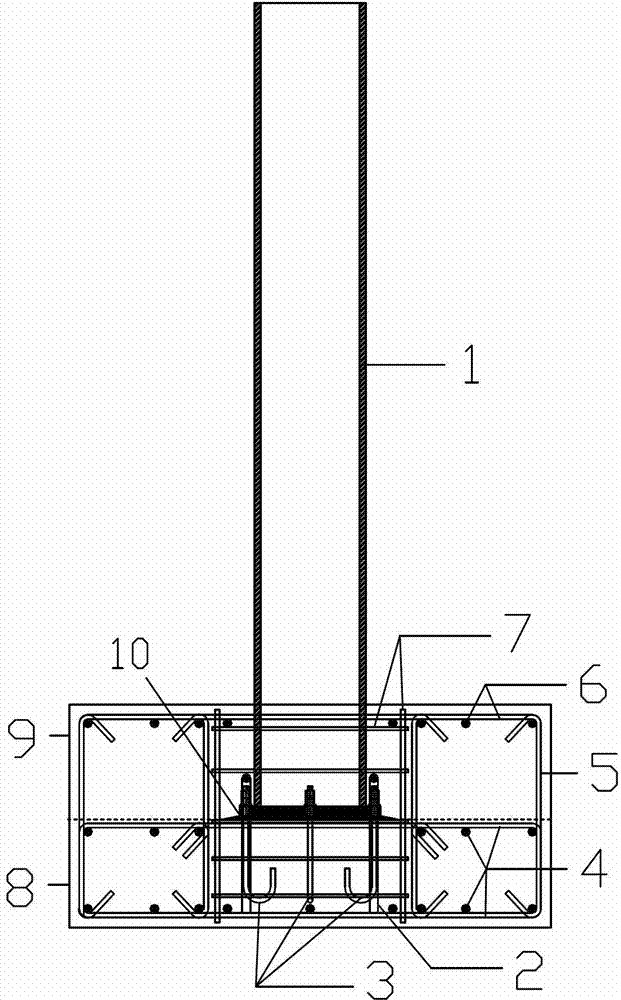
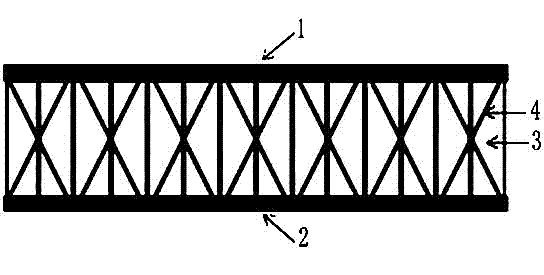
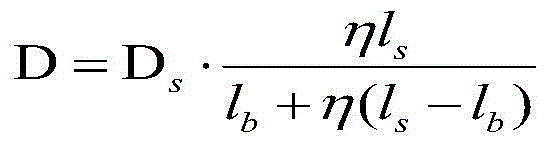Patents
Literature
124 results about "Shear stiffness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Traditionally, the shear stiffness of a cross-section of a prismatic beam is derived by setting equal the complementary energy of a slice of the beam to the complementary energy of a slice of the wire model of the beam.
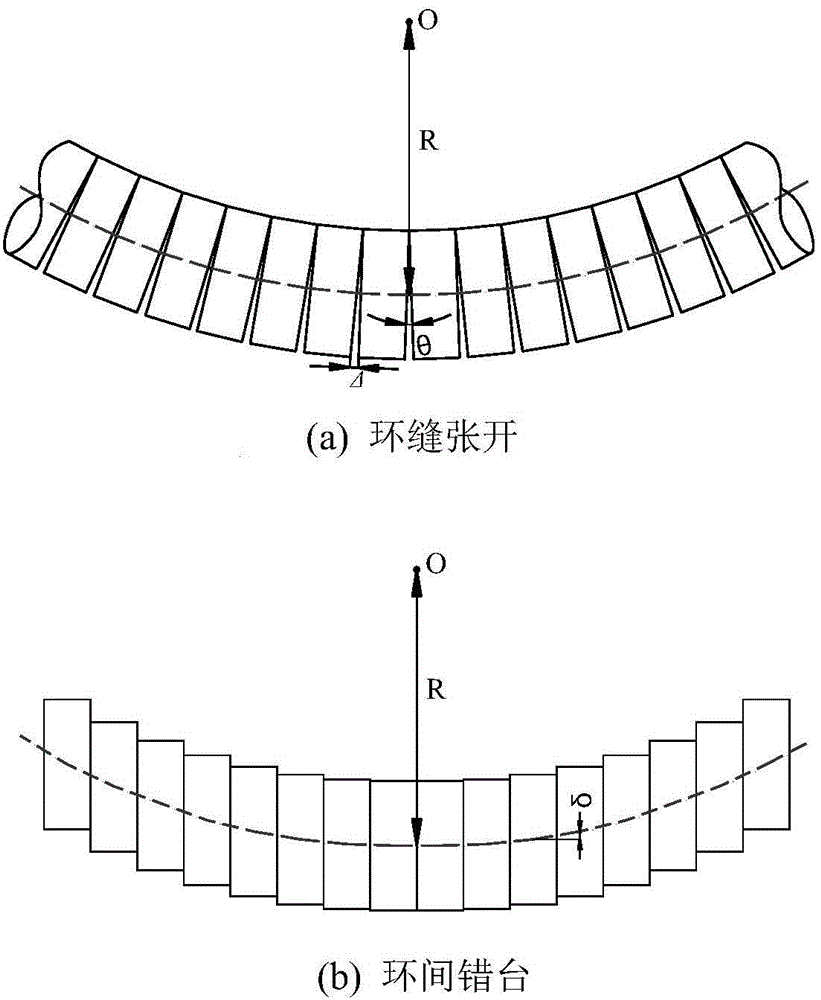
Method for determining capability of resisting slab staggering and expanding deformation of joints between shield tunnel lining rings
InactiveCN104537162AAccurate calculationSimple methodSpecial data processing applicationsShear stiffnessEngineering
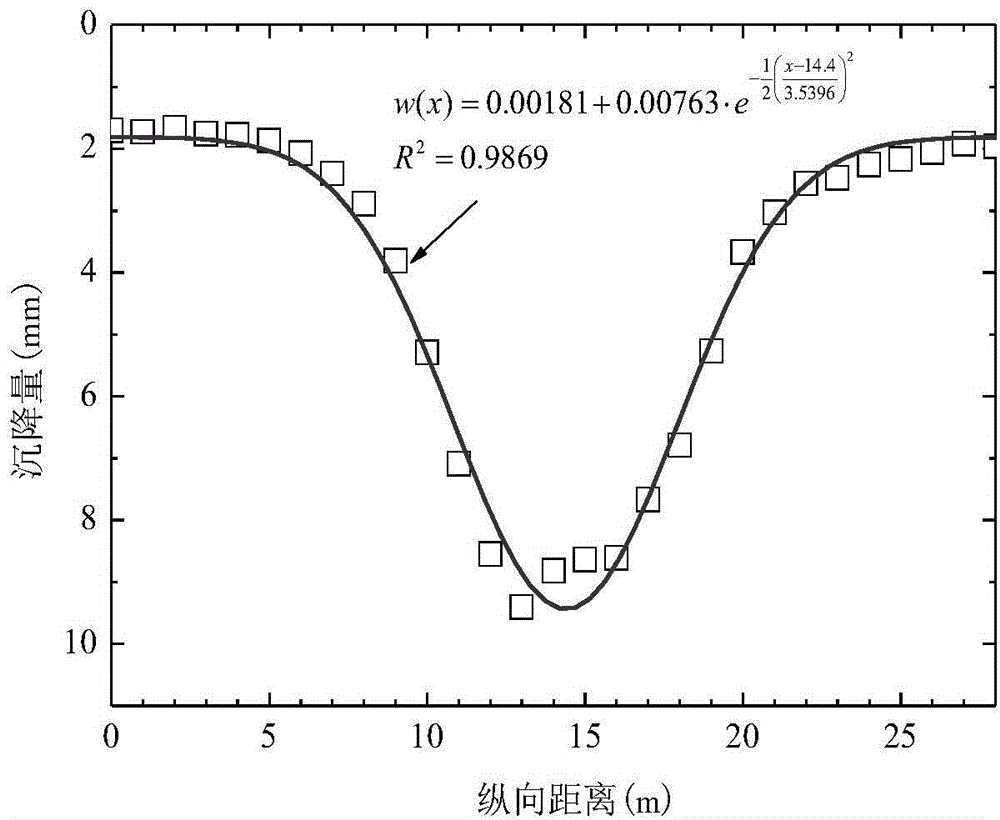
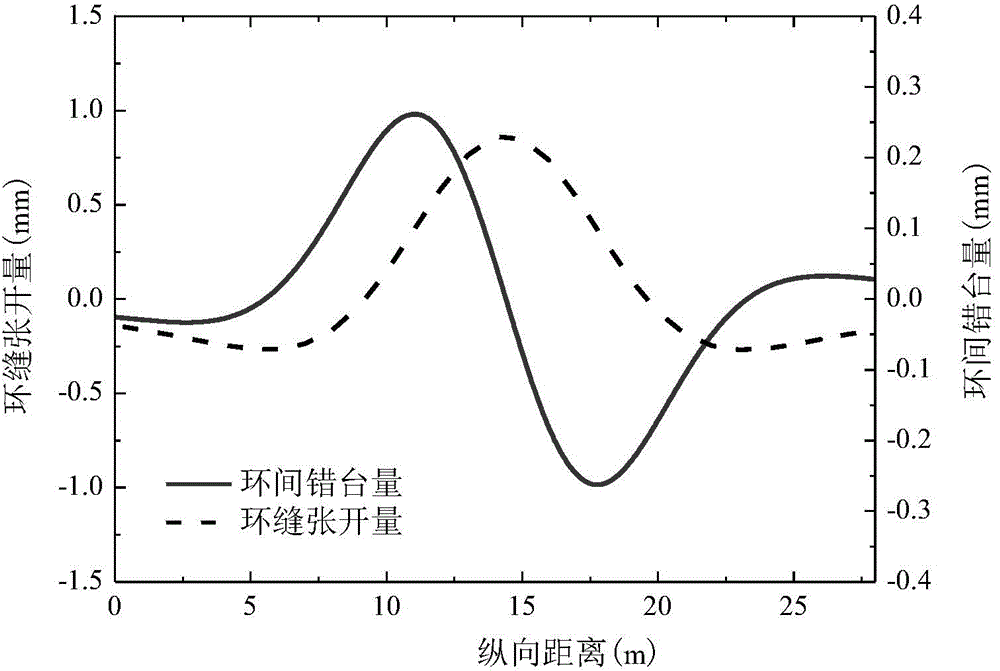
The invention provides a method for determining the capability of resisting slab staggering and expanding deformation of joints between shield tunnel lining rings. The method comprises the steps that firstly, the design information of a shield tunnel is obtained; secondly, the longitudinal equivalent bending rigidity and the longitudinal equivalent shearing rigidity of a Timoshenko beam tunnel model are determined by combining the lining design information of the tunnel and the design information of the shield tunnel; thirdly, measuring points are embedded in a track bed of the tunnel, and the settlement volumes of all the longitudinal lining rings of the tunnel are determined; fourthly, fitting is conducted on settlement monitoring values of the tunnel through the Gaussian curve, a fitting equation of a settlement curve is obtained, and the range of the influence of a settlement funnel is judged; fifthly, rotating angles of the lining rings of the tunnel are determined by using the fitting equation of the settlement curve and combining the longitudinal equivalent bending rigidity and the longitudinal equivalent shearing rigidity of the tunnel; sixthly, the expansion amount of the joints of the rings and / or the slab staggering amount between the rings are / is determined. The method is simple, practical, convenient to popularize and suitable for determining the capability of resisting slab staggering and expanding deformation of the joints between the shield tunnel lining rings.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
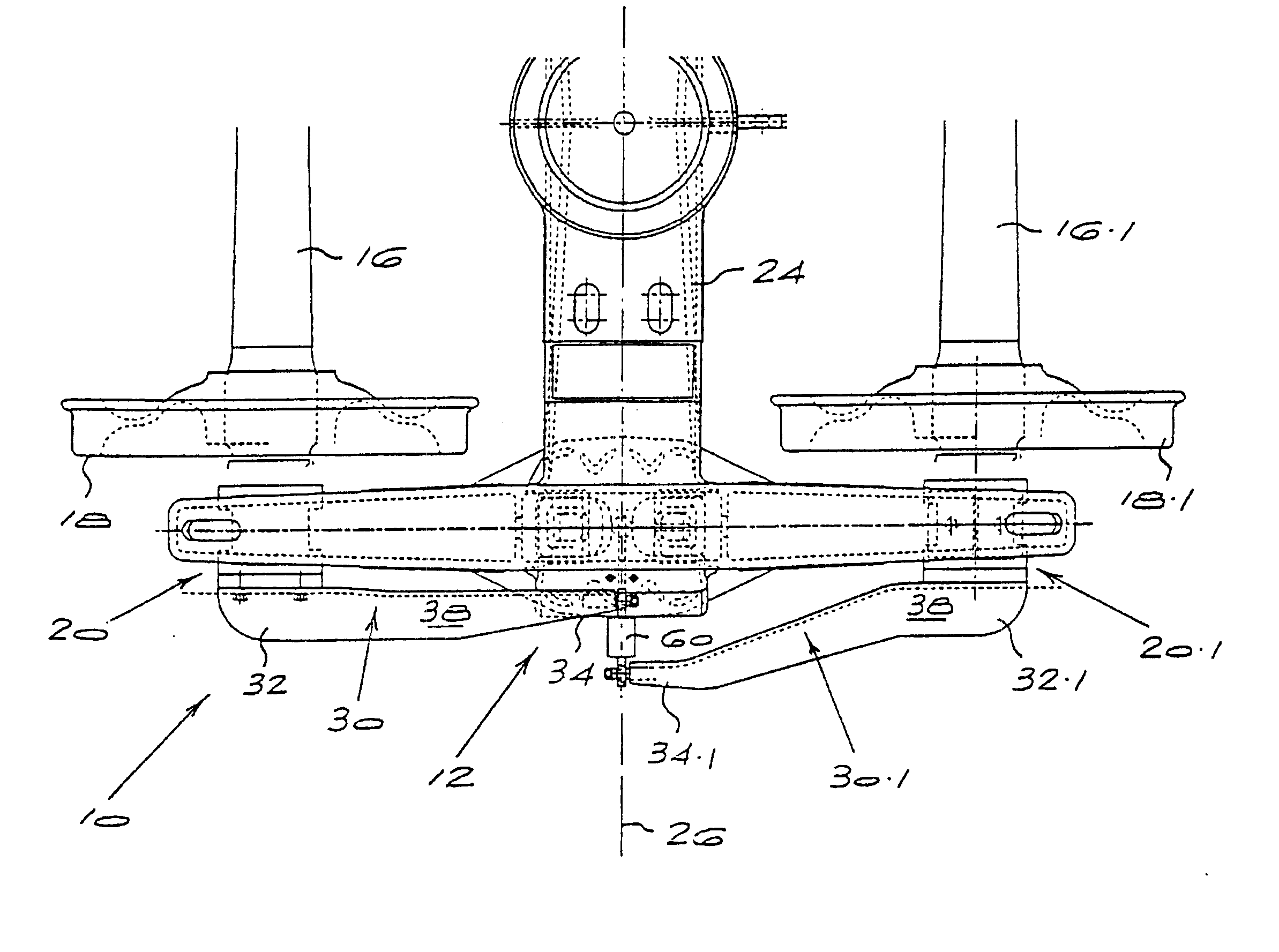
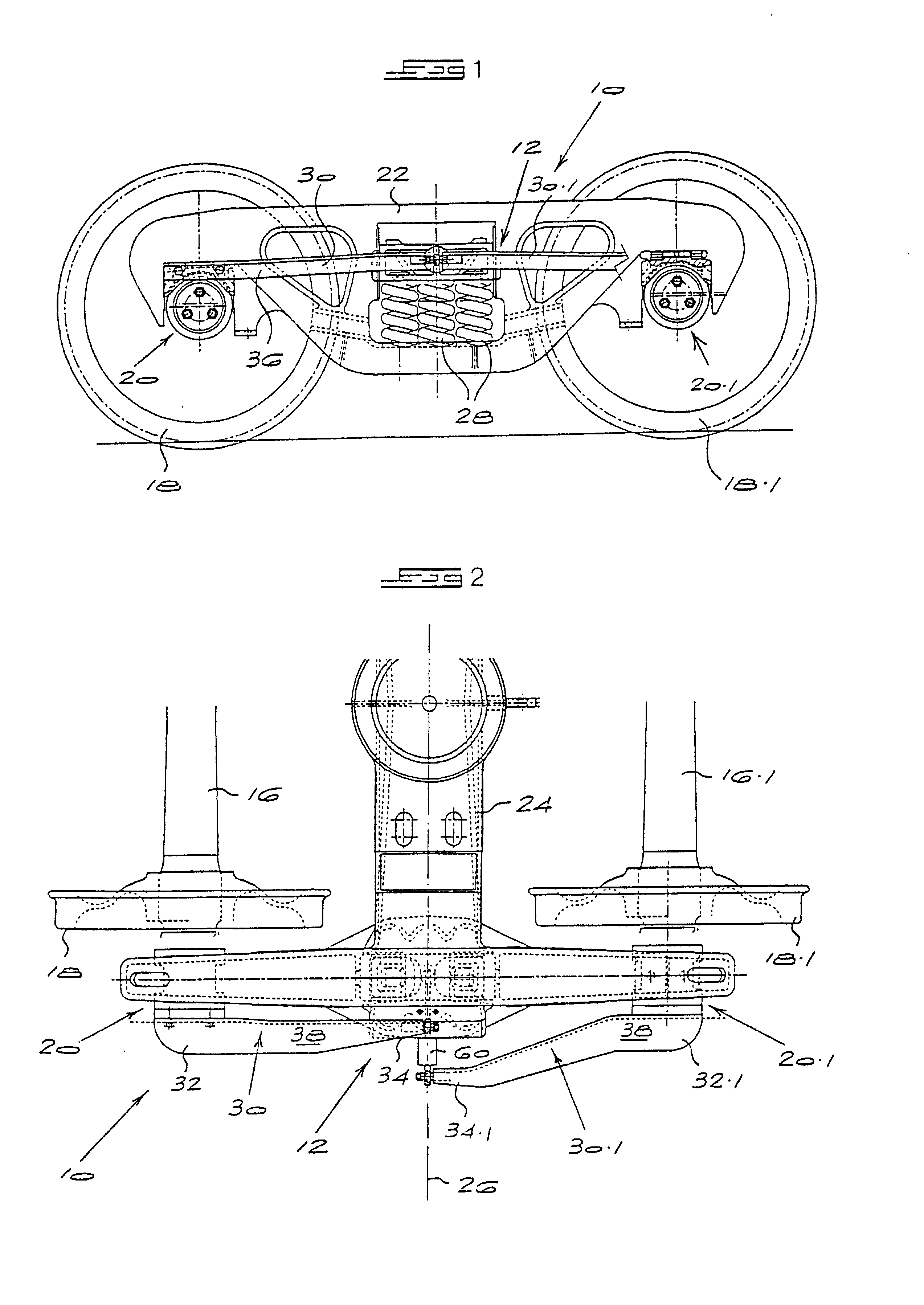
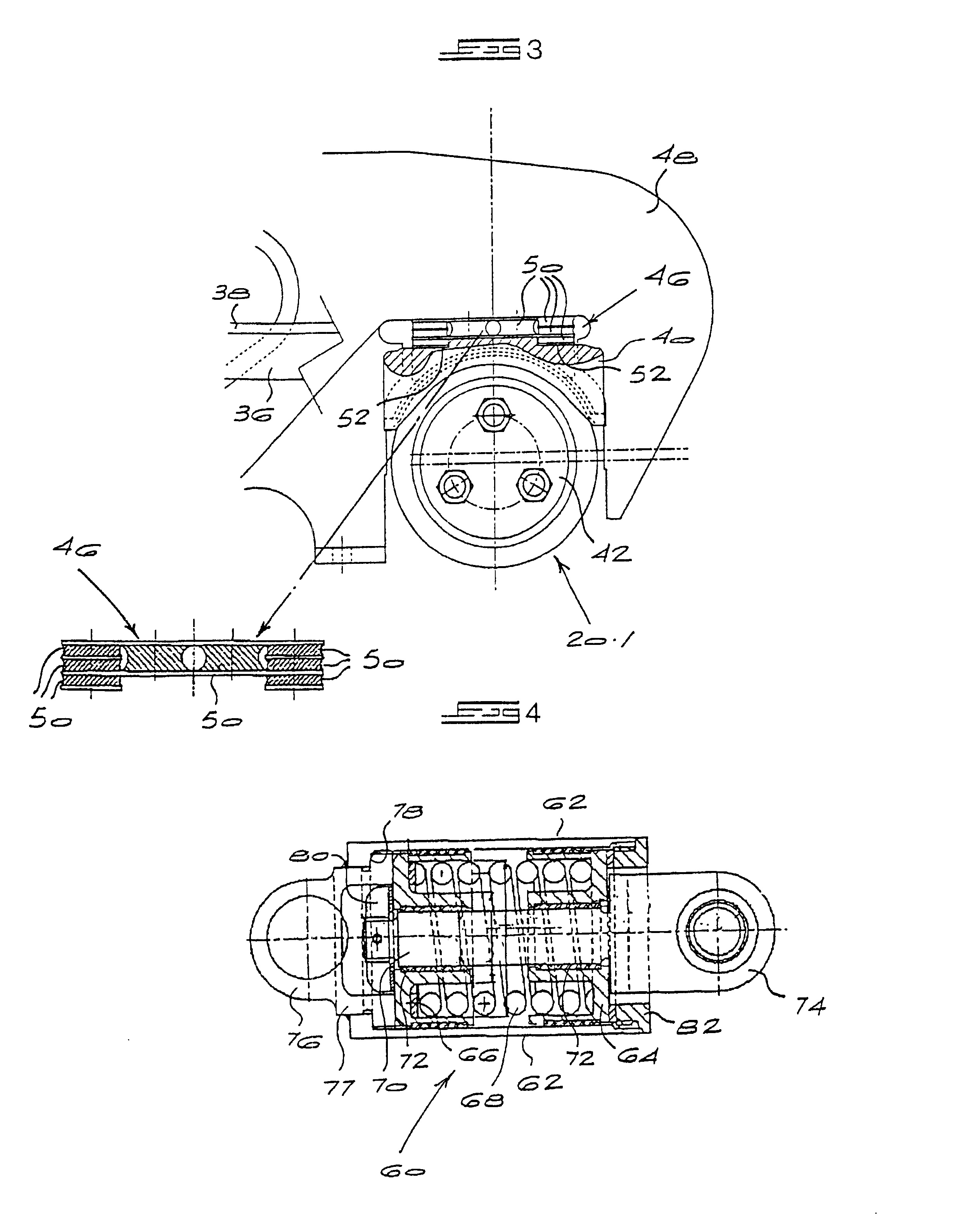
Self-steering bogies
The invention concerns an inter-axle shear stiffening apparatus for a self-steering rail bogie and a self-steering rail bogie equipped with such apparatus. The apparatus has axle structures including axles (16, 16.1) which are journalled in axle box bearings (20, 20.1). Radial arms (30, 30.1) are connected rigidly to respective axle structures of the bogie an extend towards one another in a fore and aft direction. A lateral force transmitting device (60) acts between the arms to transmit lateral forces between them while accommodating relative lateral movement between them. The design of this device is such that, irrespective of the extent of relative movement between the arms, the device can only transmit between them lateral forces of limited, predetermined magnitude. This value is chosen such that the bogie is provided with sufficient inter-axle shear stiffness to enhance its hunting stability without excessive force couples being applied to the axle box bearings.
Owner:SCHEFFEL HERBERT
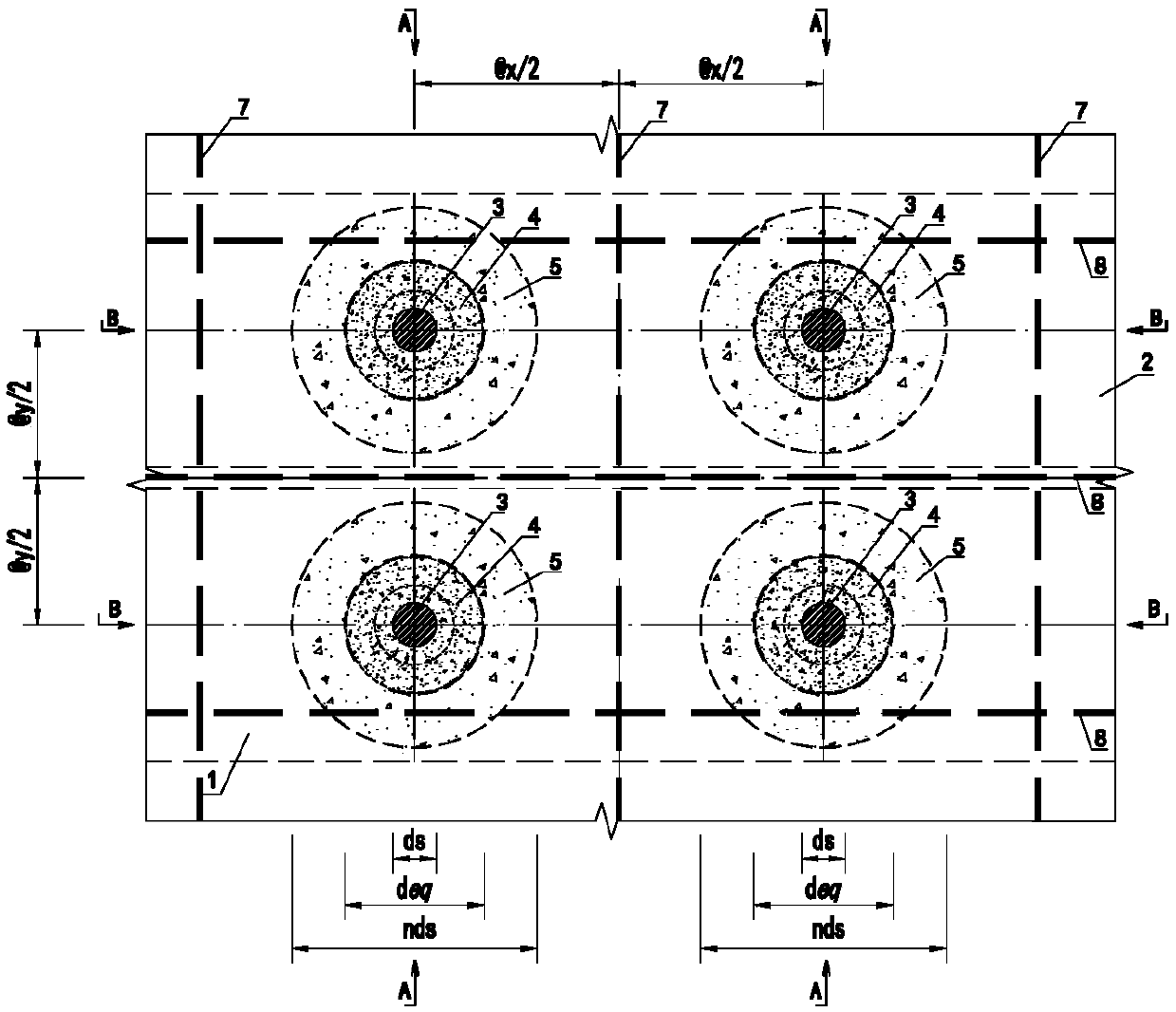
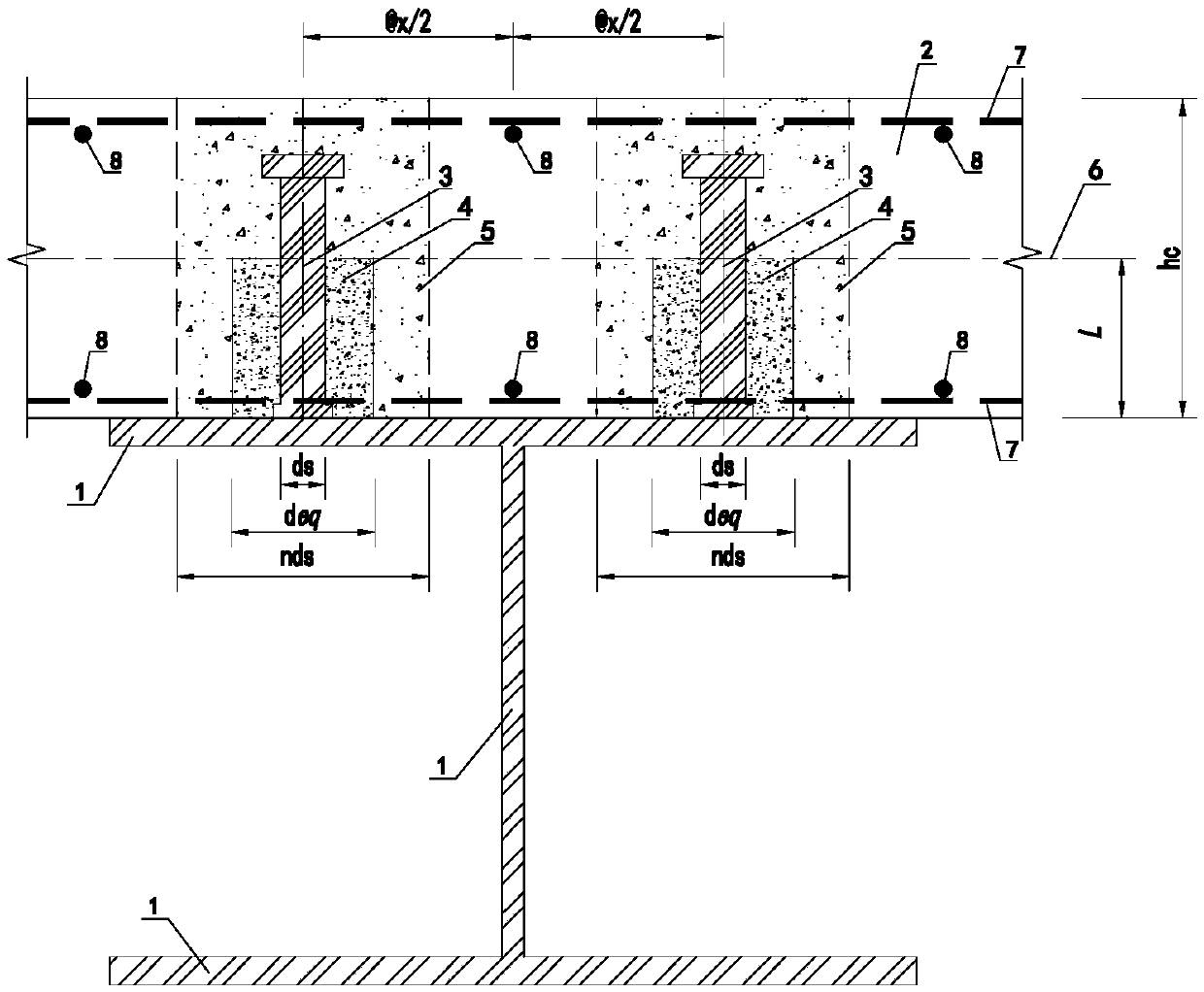
Stud connection-based steel-concrete composite beam calculation model analysis method
ActiveCN108614936AEasy to handleQuick calculationGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationShear stiffnessLateral stiffness
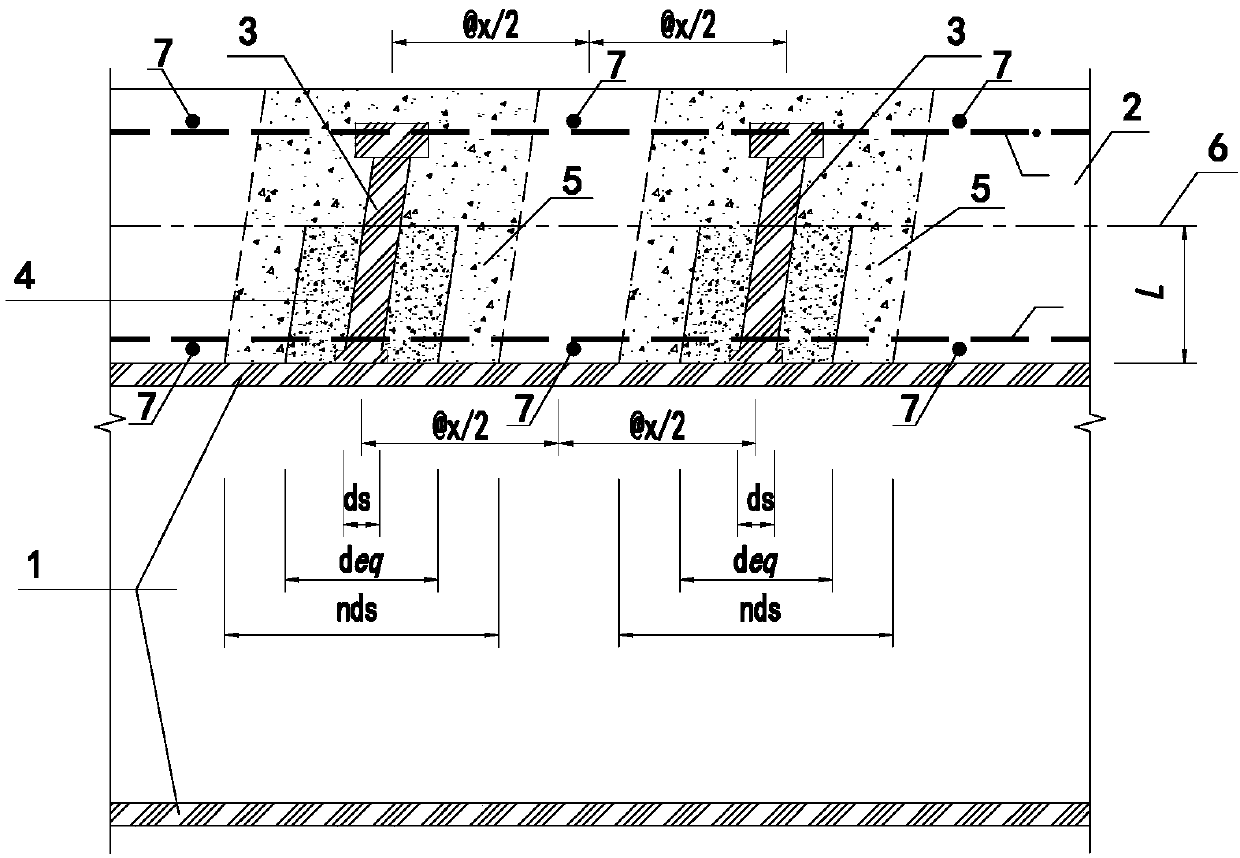
The invention relates to a stud connection-based steel-concrete composite beam calculation model analysis method. The method comprises the following steps of 1, building a stud shear connector composite beam calculation analysis model; 2, proposing that the overall shear stiffness Dsc of a stud comprises the shear stiffness Ds of the stud and the stiffness Dc of concrete in the range of a concentric circle with the diameter nds; 3, introducing a reduction coefficient beta of a working state of the overall shear stiffness of the stud to obtain equivalent lateral stiffness Deq; and 4, accordingto a lateral stiffness equivalence principle, making the stud equivalent to a short steel beam unit, and proposing that different values of the equivalent diameter deq of the short steel beam unit areused for simulating the mechanical performance of the stud in different working states. The method has the advantages that the calculation process is high in efficiency; a calculation result can quantitatively reflect interface slip of a steel-concrete composite structure and stress states of parts in stress periods of the composite structure; the practicality is high; and the method is easily understood and mastered by structure designers.
Owner:HUNAN ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN INST
Method for determining longitudinal internal force of shield tunnel under load effect
InactiveCN104537215AAccurate determination of longitudinal internal force valuesSimple methodSpecial data processing applicationsShear stiffnessDesign information
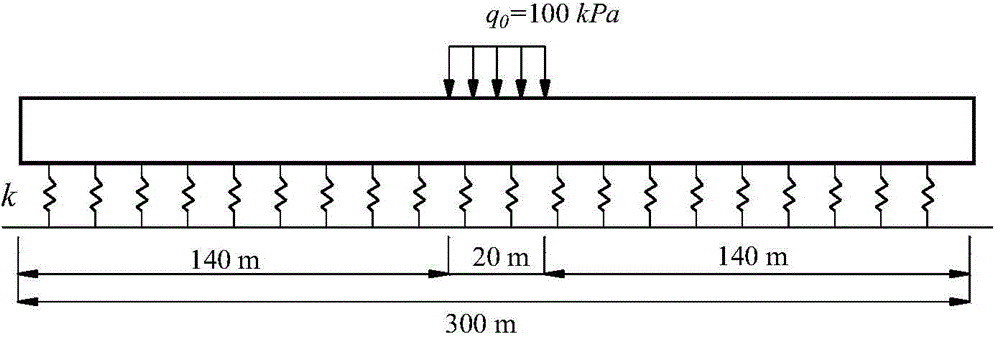
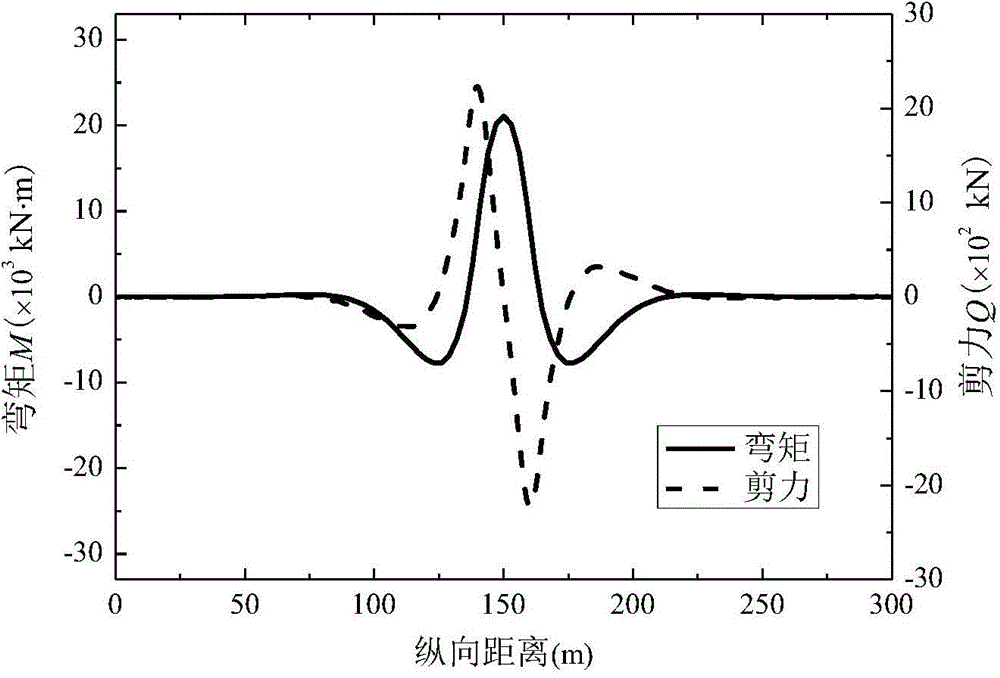
The invention provides a method for determining longitudinal internal force of a shield tunnel under the load effect. According to the method, the tunnel is simplified into a timoshenko beam capable of taking shear deformation into consideration, and the equivalent bending rigidity and equivalent shear rigidity of the timoshenko beam are determined on the basis that the design information of a tunnel structure is obtained; a deformation basic differential equation and boundary conditions of the deformation basic differential equation under the load effect are determined through a timoshenko beam model on an elastic foundation; the tunnel longitudinal settling volume and the rotating angle are obtained by solving the deformation basic differential equation, and then the longitudinal internal force value of the tunnel under the load effect above the tunnel is determined. The elastic foundation beam model based on the timoshenko beam theory is adopted, the longitudinal characteristics of tunnel bending deformation and dislocation deformation can be well reflected, accordingly, the longitudinal internal force value of the tunnel under the load effect can be determined more accurately, and a basis is provided for the longitudinal tunnel design.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
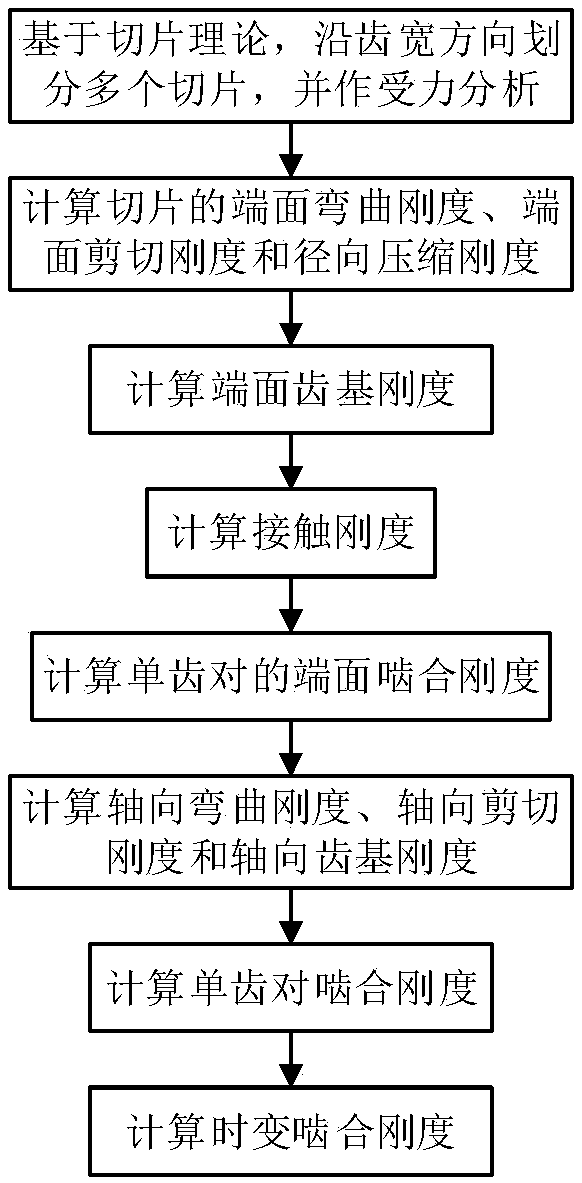
Method considering axial deformation for calculating time-varying meshing stiffness of helical gear
ActiveCN107798200AHigh precisionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationRadial compressionEngineering
The invention proposes a method considering axial deformation for calculating time-varying meshing stiffness of a helical gear. The method aims at improving the accuracy of calculating the meshing stiffness of the helical gear. The method comprises the implementation steps of calculating the end surface bending stiffness, end surface shearing stiffness, radial compression stiffness and end surfacetooth base stiffness of the helical gear; calculating contact stiffness; calculating the end surface meshing stiffness of a single tooth pair; deducing and calculating axial bending stiffness, axialshearing stiffness and axial tooth base stiffness; calculating the meshing stiffness of the single tooth pair; calculating the time-varying meshing stiffness. According to the method, the influence ofaxial meshing force on the time-varying meshing stiffness of the helical gear is considered, a calculation expression for the quantitative calculation of the axial bending stiffness, axial shearing stiffness and axial tooth base stiffness of the helical gear is deduced, the time-varying meshing stiffness of the helical gear is calculated by combining all the stiffness in the end surface direction, the calculation accuracy is improved, and the method can be used for the dynamic performance analysis and optimization design of the helical gear.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Rejuvenation of vacuum tower bottoms through bio-derived materials
ActiveUS20170247542A1Improve low temperature performanceReduce stiffnessIn situ pavingsClimate change adaptationShear stiffnessTower
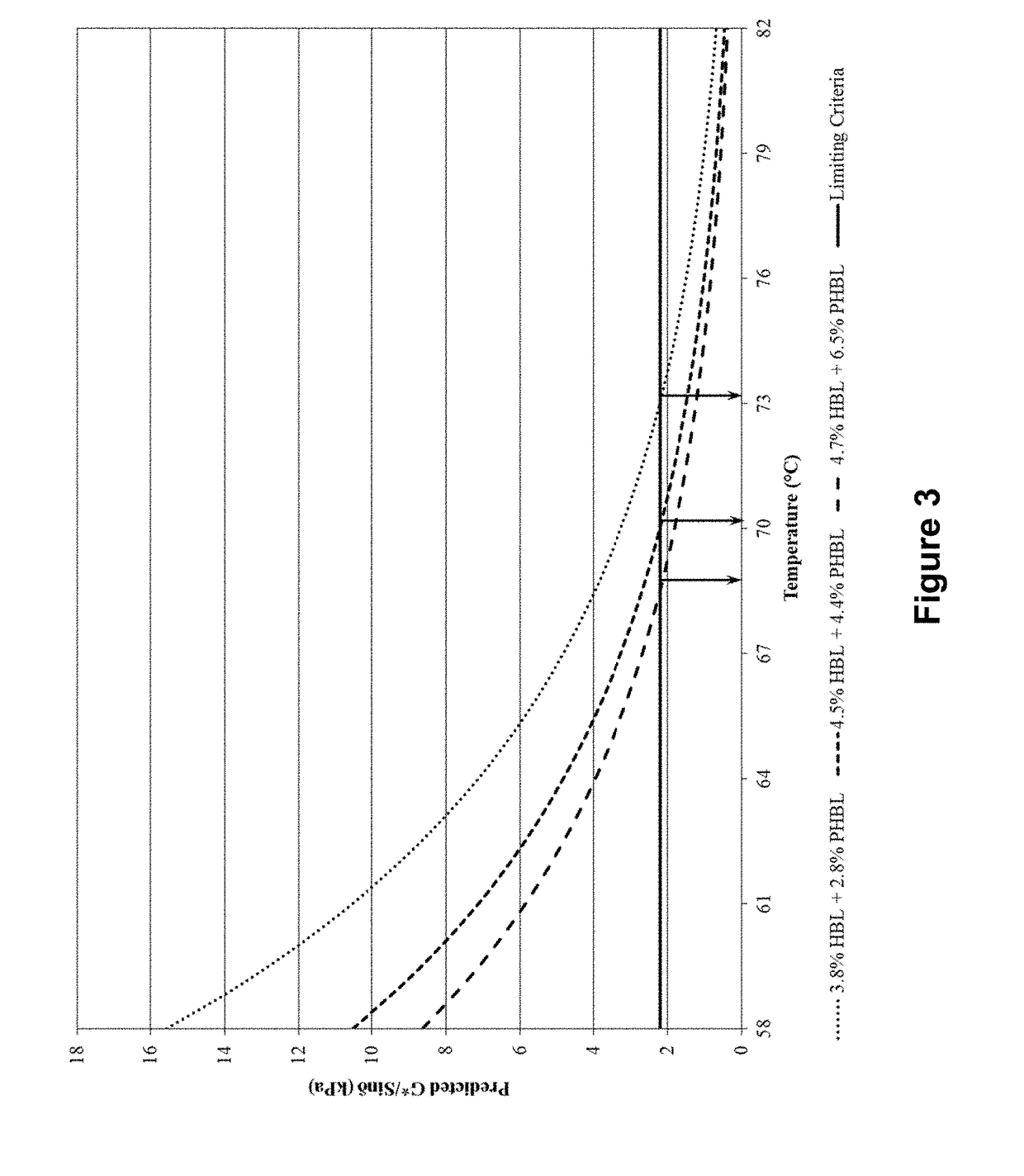
The present invention relates to an asphalt product. The asphalt product includes an asphalt binder and a bio-oil blend comprising a mixture of a non-hydrogenated bio-oil and a partially hydrogenated bio-oil, where the bio-oil blend is mixed with the asphalt binder to form an asphalt product having a shear stiffness of 0.20 kPa to 11,000 kPa at a temperature ranging from 25° C. to 85° C. and / or a viscosity of 0.15 Pa·s to 1.50 Pa·s at a temperature ranging from 120° C. to 165° C. The present invention further relates to methods of producing an asphalt product and methods of applying an asphalt product to a surface.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Flexible pipe with a permeable outer sheath and a method of its manufacturing
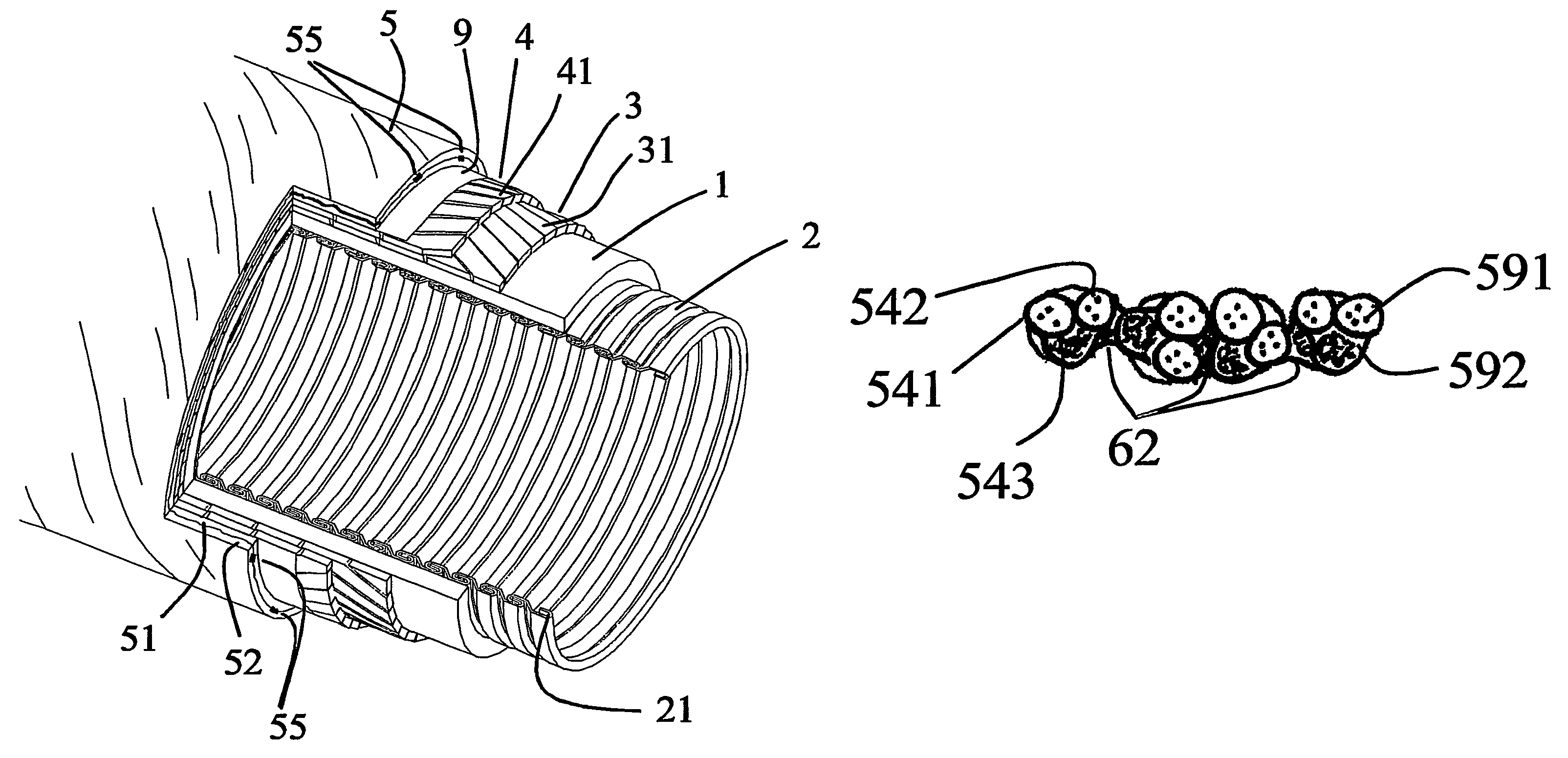
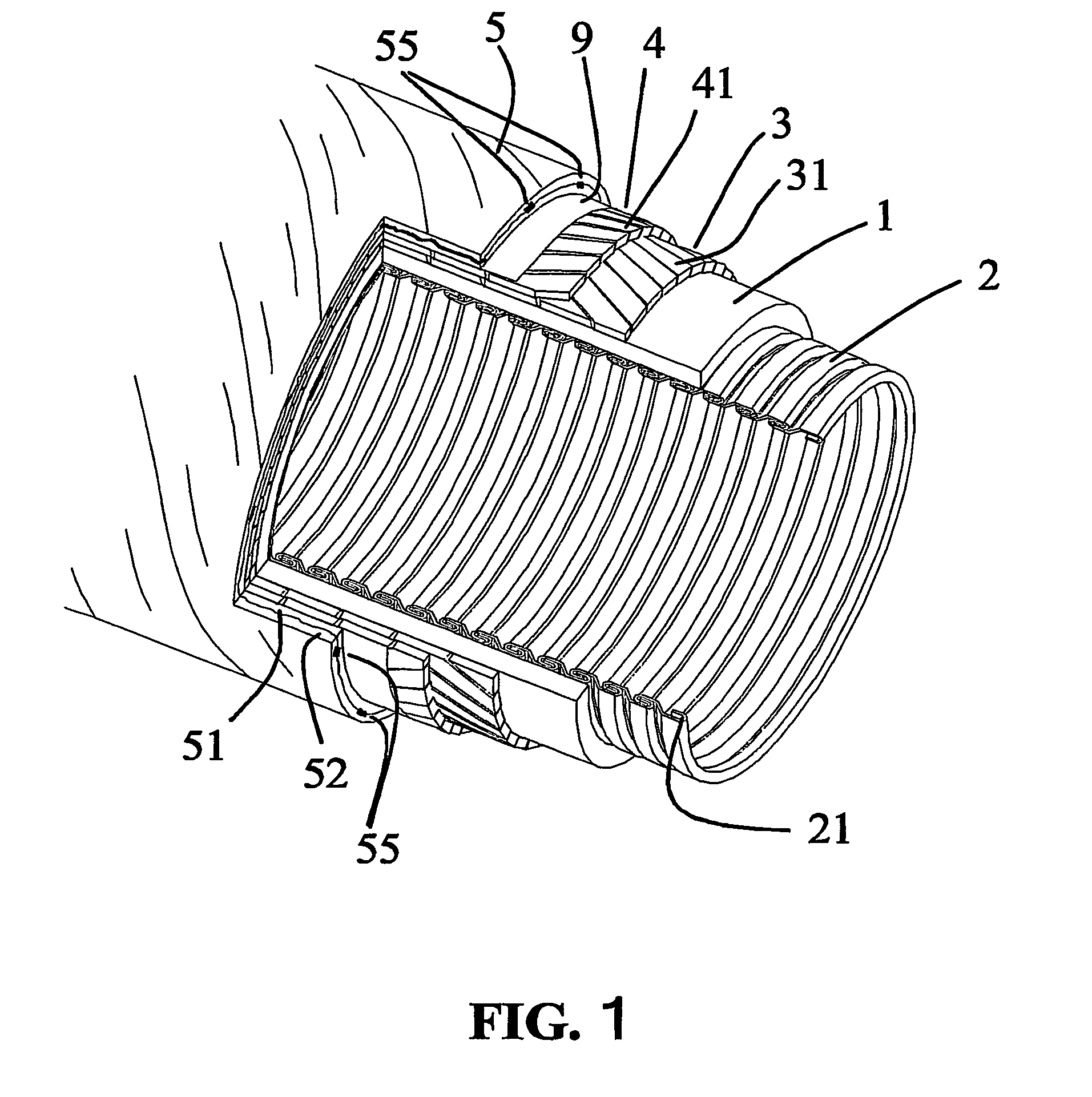
A flexible pipe for transporting a fluid in a marine environment. The pipe comprises a liner for confining the fluid, an armoring layer surrounding the liner, and an outer protective sheath surrounding the armoring layer and allowing radial expansion and contraction of the armoring layers. The outer protective sheath comprises at least two protective layers of helically wound composite wires with essentially opposite winding angles and locally held together, providing a relatively flexible yet fixed structure of the outer sheath. The outer sheath is held together in an array of discrete spots or along linear or curved paths. Flexibility is maintained because the stiffness in shear in the wires of adjacent protective layers may be made much larger in areas being locally held together than outside these areas. This allows a change of angles between the wires of two adjacent layers of the outer protective sheath during elongation or shortening of the pipe.
Owner:NAT OILWELL VARCO DENMARK
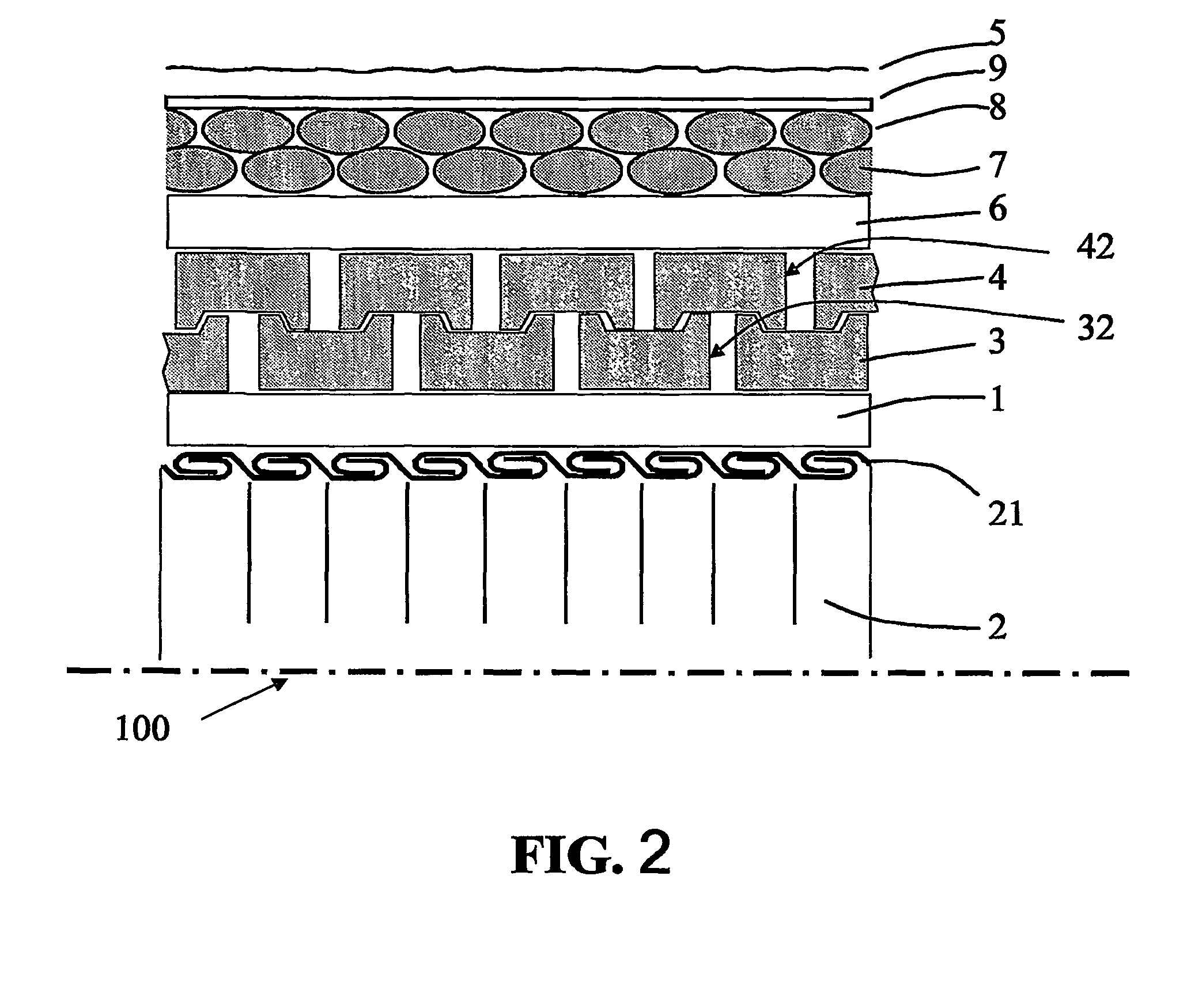
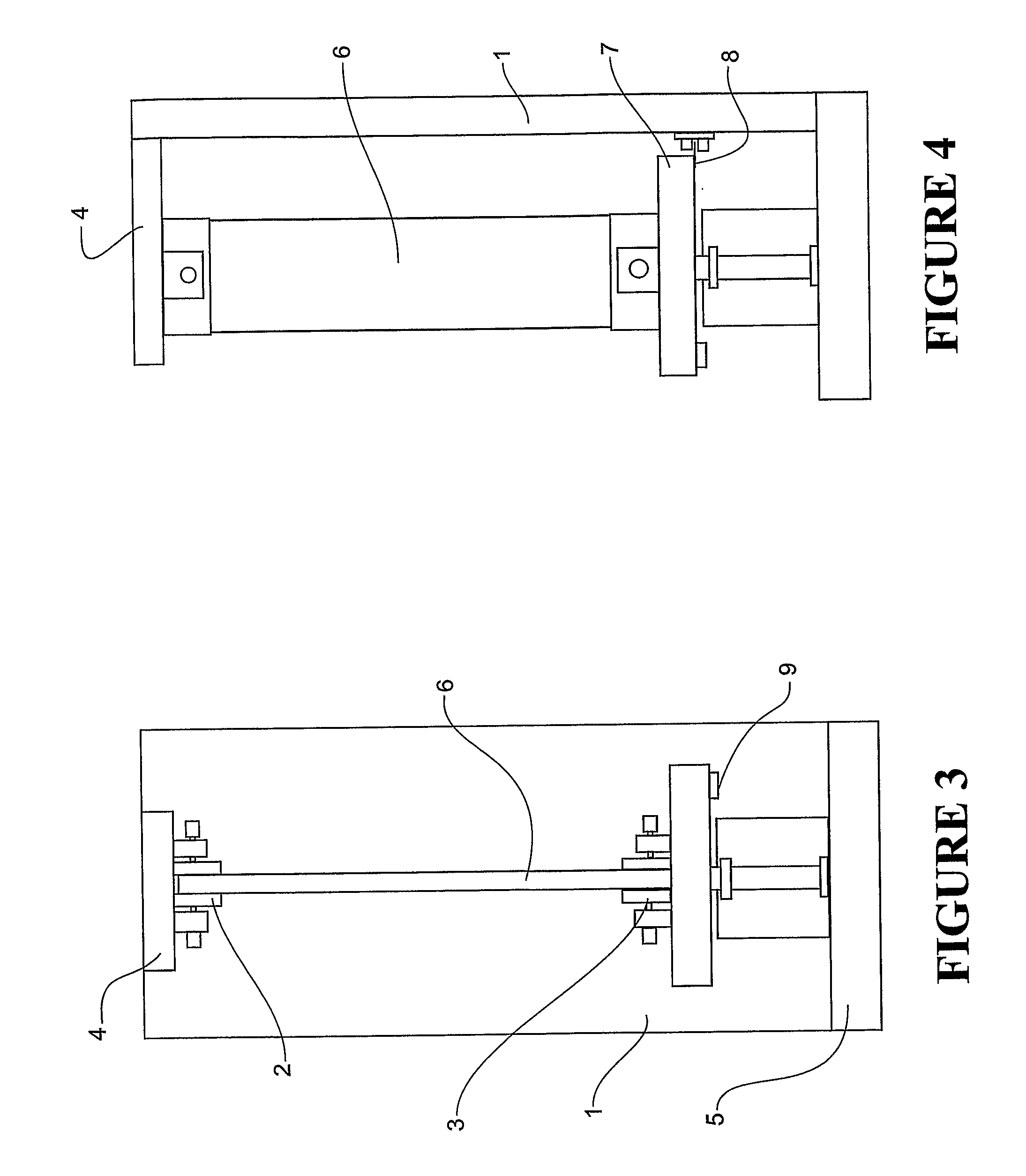
Method and apparatus for testing of shear stiffness in board
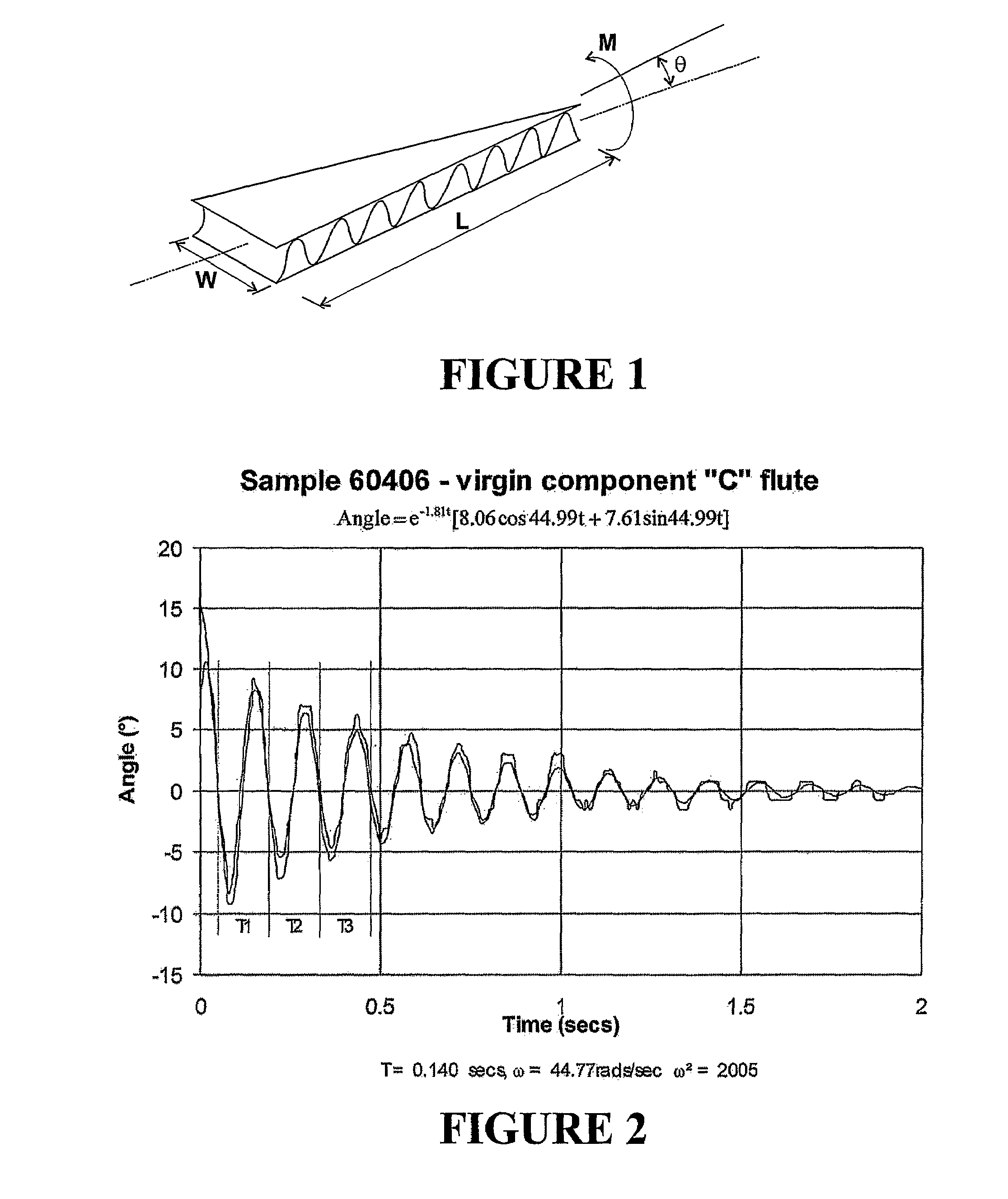
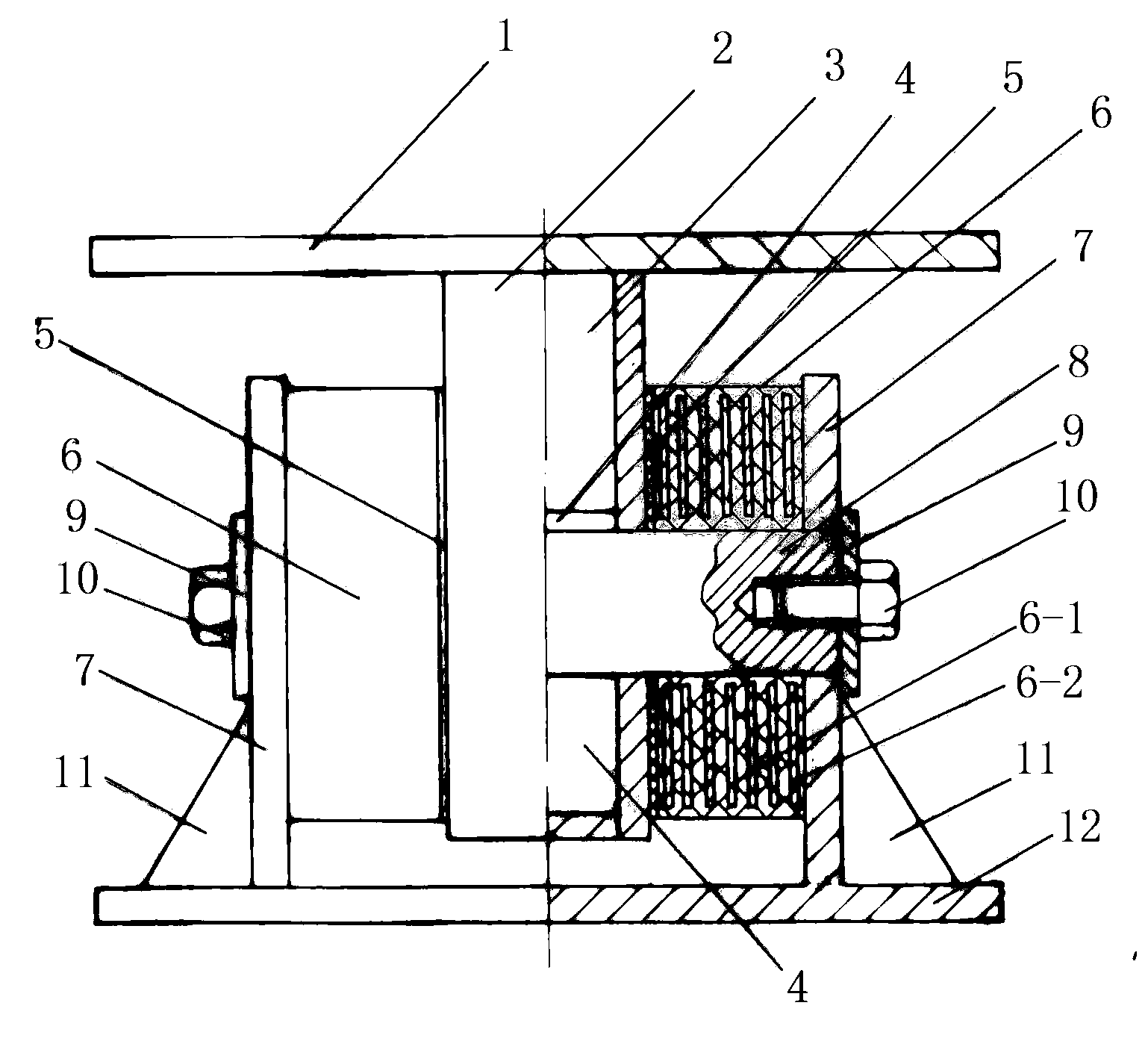
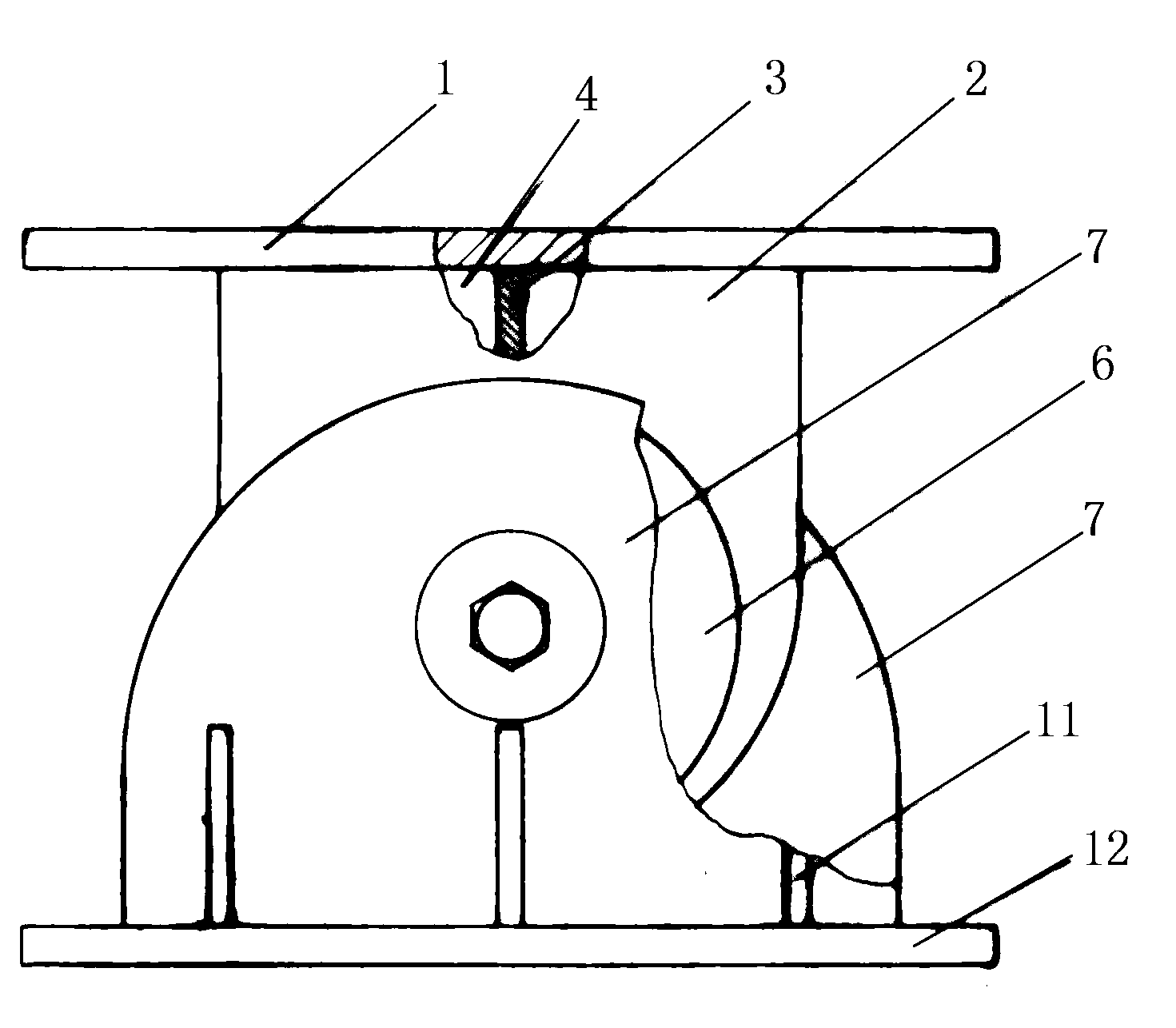
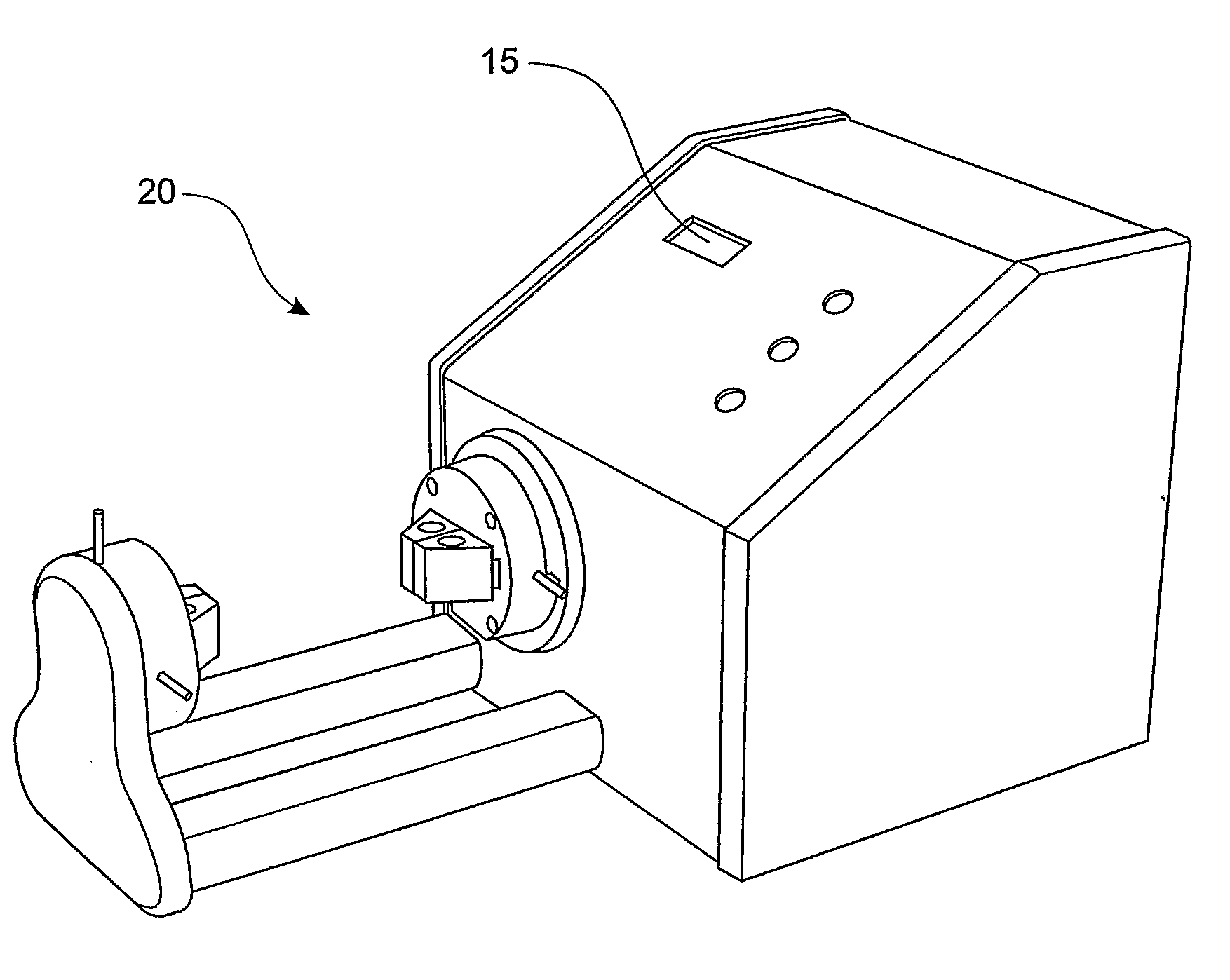
ActiveUS7621187B2Material strength using steady torsional forcesTension measurementInertial massShear stiffness
A method and apparatus for testing shear stiffness in board is disclosed. The board sample (6) is placed into stationary jaw (2) and jaw (3) which is rigidly connected to inertial mass (7). The mass (7) is twisted around the sample axis with an initial twist chosen to ensure the sample is within the elastic region, and then allowed to freely oscillate. The oscillation frequency is then measured to evaluate the torsional stiffness of the sample.
Owner:KORUTEST
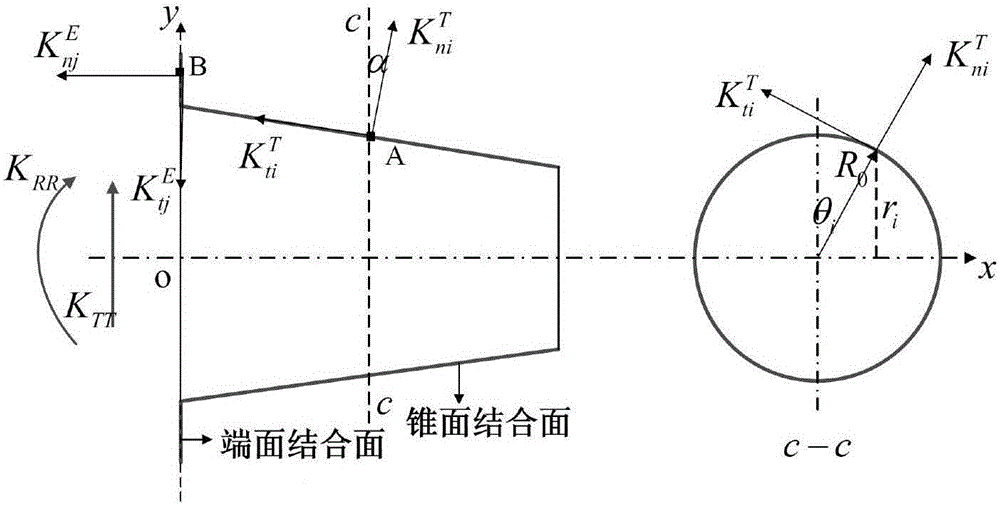
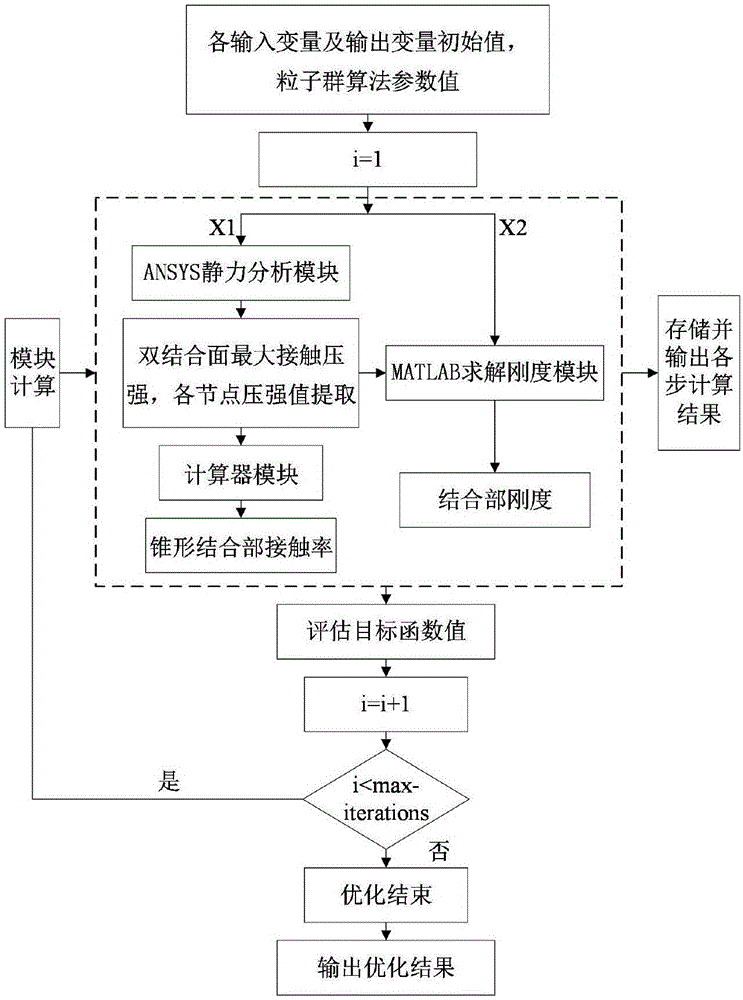
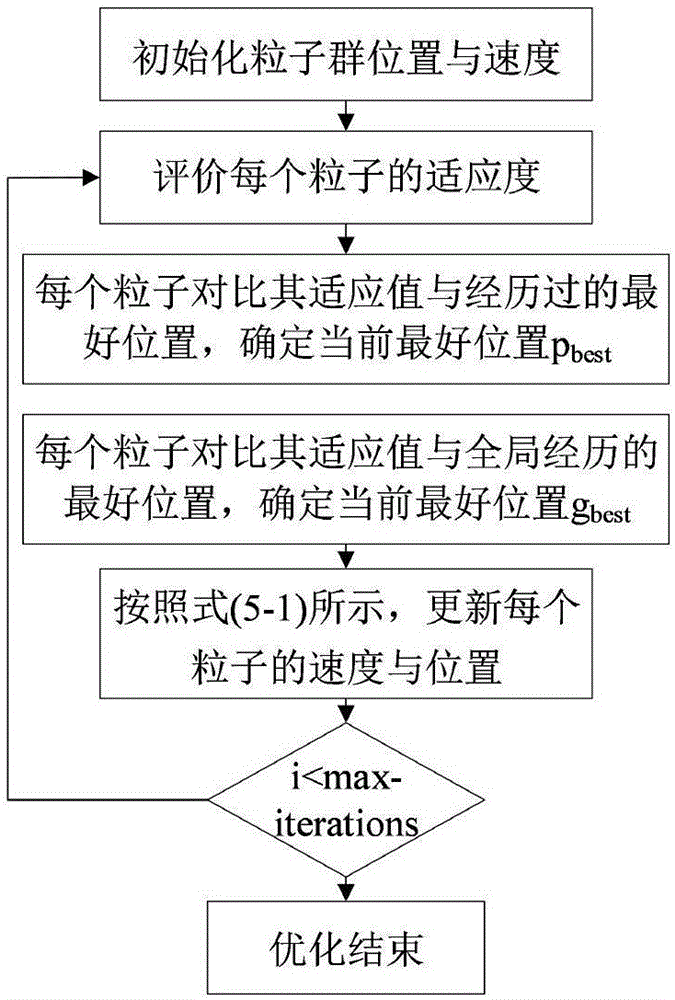
Dual-face locking knife handle-spindle system joint part stiffness characteristic optimization method based on particle swarm optimization
The invention discloses a dual-face locking knife handle-spindle system joint part stiffness characteristic optimization method based on particle swarm optimization. The dual-face locking knife handle-spindle system joint part stiffness characteristic optimization method based on particle swarm optimization adopts knife handle-spindle structural technological parameters and joint surface fractal parameters as optimization variables. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a three-dimensional fractal normal and shear stiffness model and a joint part torsion and radial stiffness model are built, and MATLAB programs are written separately; secondly, a contact-considering three-dimensional geometrical model is built for the dual-face locking knife handle-spindle system and static analysis is performed, so that an APDL file is obtained, and finally integration in Isight software and iterative optimization based on the particle swarm optimization are achieved. According to the method, the combination of the three-dimensional fractal micro contact stiffness modeling theory and finite element static analysis is adopted, the dual-face locking knife handle-spindle system joint part torsion and radial stiffness can be calculated under the high-speed condition, and the knife handle-spindle system optimization process on the Isight software platform based on the particle swarm optimization is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Combined intelligent isolation bearing of magnetorheological elastomer
ActiveCN104879431AReduce production processReduce use costSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionElastomerInsulation layer
The invention discloses a combined intelligent isolation bearing of magnetorheological elastomer and belongs to the field of structural control. The combined intelligent isolation bearing mainly comprises a stress bearer component, an exciter component, a sensor and a controller; the stress bearer component is composed of a round magnetorheological elastomer-steel plate vulcanized lamination, an annular lead core and an annular magnetorheological elastomer-steel plate vulcanized lamination which are coaxial and which are arranged from inside to outside; the exciter component comprises a core, a coil, an insulation layer and a magnetized steel ring coaxially arranged from inside to outside; a magnetic loop can form in a support; the sensor is mounted on upper and lower connecting plates; the controller adjusts shear stiffness of the support according to signals. The combined intelligent isolation bearing has the advantages that the mechanical and electromagnetic features of materials are made full use, spatial utilization rate and magnetic field utilization rate are high, the magnetic field is uniform with little flux leakage, the size of the coil is greatly reduced, production, usage and maintenance costs are reduced, and the combined intelligent isolation bearing as shaped as a lead-core rubber bearing is convenient to design and construct.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
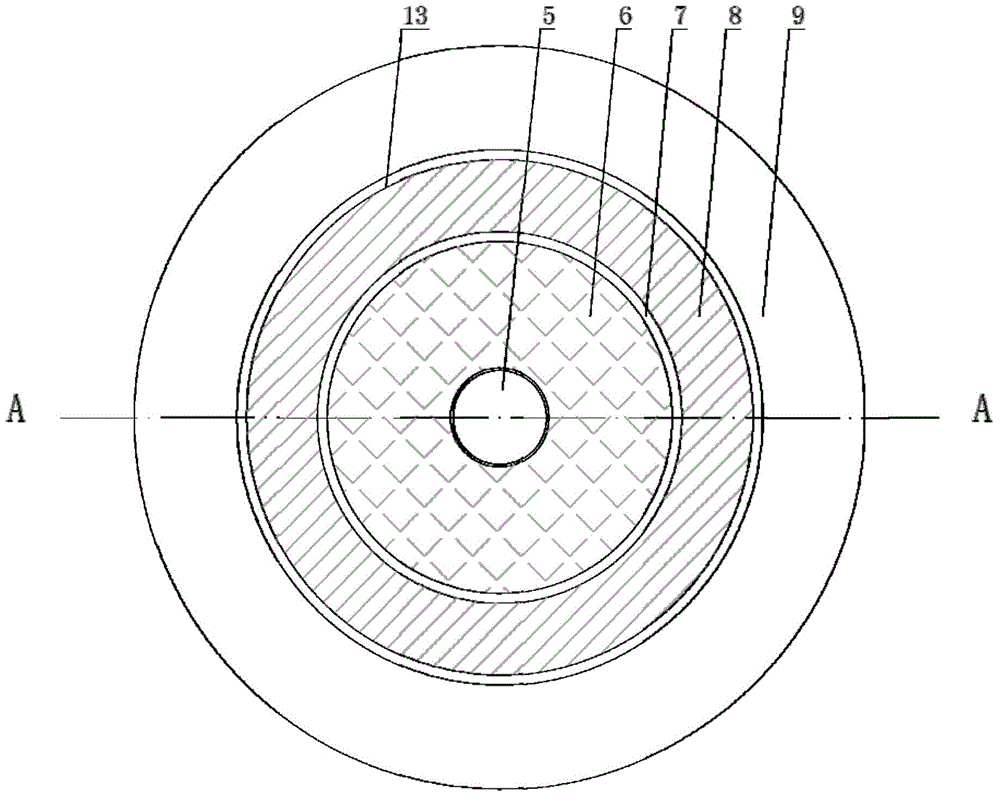
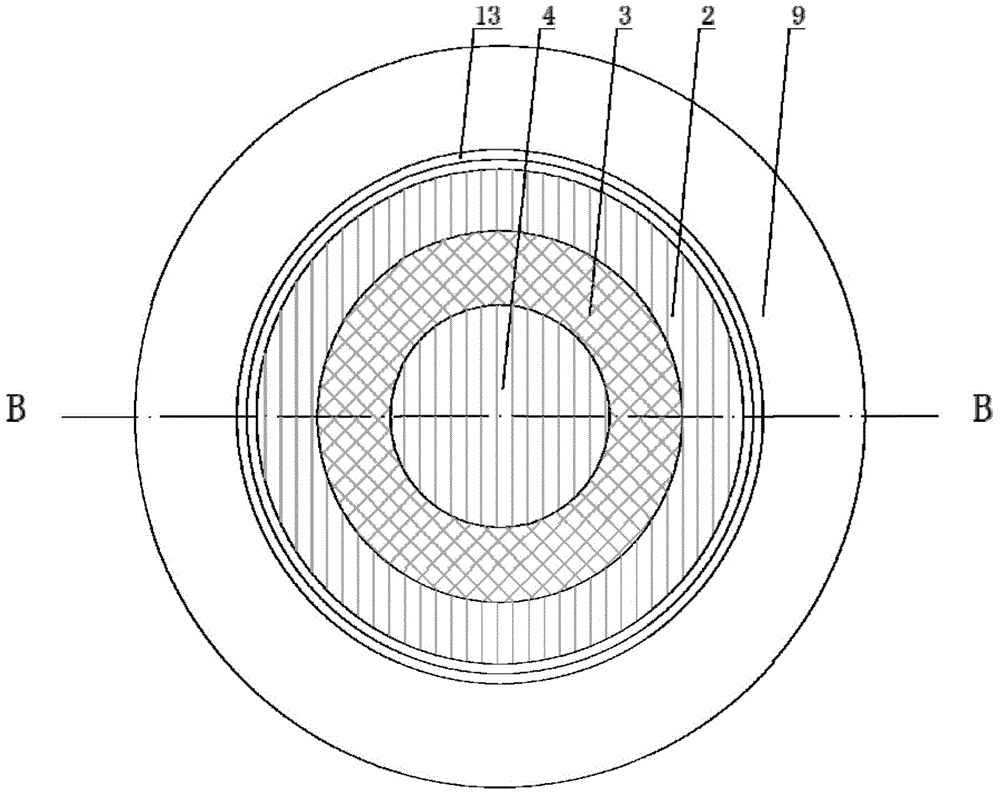
A method for calculating the time-varying meshing stiffness of spur gears considering the effect of temperature
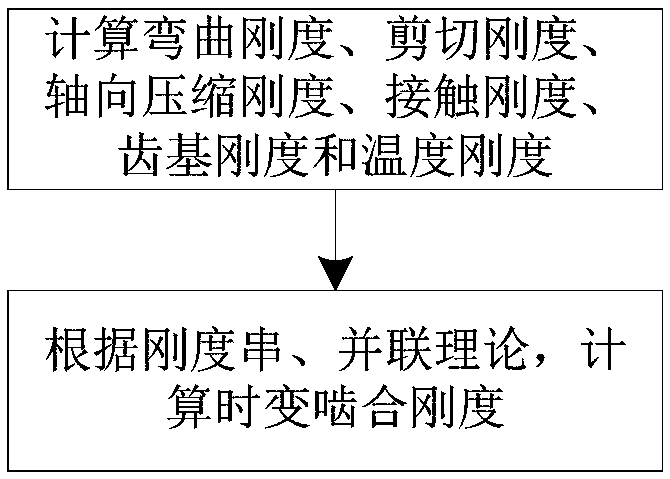
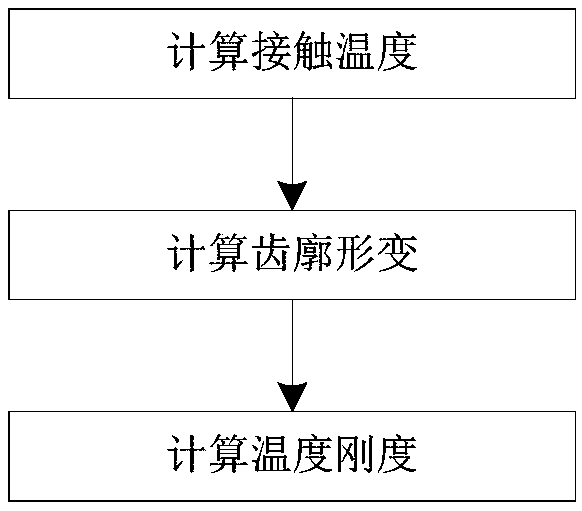
The invention discloses a method for calculating the time-varying meshing rigidity of a spur gear considering the influence of temperature. Considering the influence of the working environment temperature (steady state environment temperature) of the gear pair, the instantaneous temperature of the tooth surface generated by the friction heat of the driving wheel / driven wheel is calculated according to the Coleman theory, and the mathematical expression of the tooth surface contact temperature changing with time is derived. The results show that the contact temperature of the driving wheel / driven wheel is higher than that of the driven wheel. The thermal deformation of the tooth profile of the driven wheel and the driven wheel caused by the change of the tooth surface contact temperature iscalculated, and the temperature stiffness of the tooth caused by the change of the temperature is calculated. Finally, the time-varying meshing stiffness of gears is calculated according to the theory of rigidity series and parallel, combined with the bending stiffness, shear stiffness, axial compression stiffness, contact stiffness, tooth base stiffness and temperature stiffness of gears.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for calculating natural frequency of honeycomb sandwich plate
InactiveCN102607695ASimple calculationImprove calculation accuracySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementShear stiffnessHoneycomb
The invention relates to a method for calculating a natural frequency of a honeycomb sandwich plate, which comprises the following steps of: by measuring bending rigidities D11, D12, D22 and D66 of the sandwich plate, shear moduli Gxz and Gyz of a core layer in x-z and y-z planes, a length a and a width b of the sandwich plate, a panel thickness t, a core layer thickness h and a panel density rho<f> and a core layer density rho<c> of the sandwich plate, calculating to obtain shear stiffnesses Cxz and Cyz of the core layer and an equivalent face density rho; and substituting the measured data into a formula to calculate so as to solve the natural frequency omega<m> of an mth order of the sandwich plate. According to the invention, a bending vibration equation system form and the process of solving the natural frequency of the sandwich plate are simplified, the influence of the transverse shear deformation of the core layer and the integral orthogonal anisotropy of the sandwich plate on the mechanical property of the sandwich plate is also considered, the calculating process of the natural frequency is simplified, the calculating efficiency is improved, the calculating difficulty is reduced and the calculating accuracy of the natural frequency is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING TELECOMMUNICATION INSTITUTE
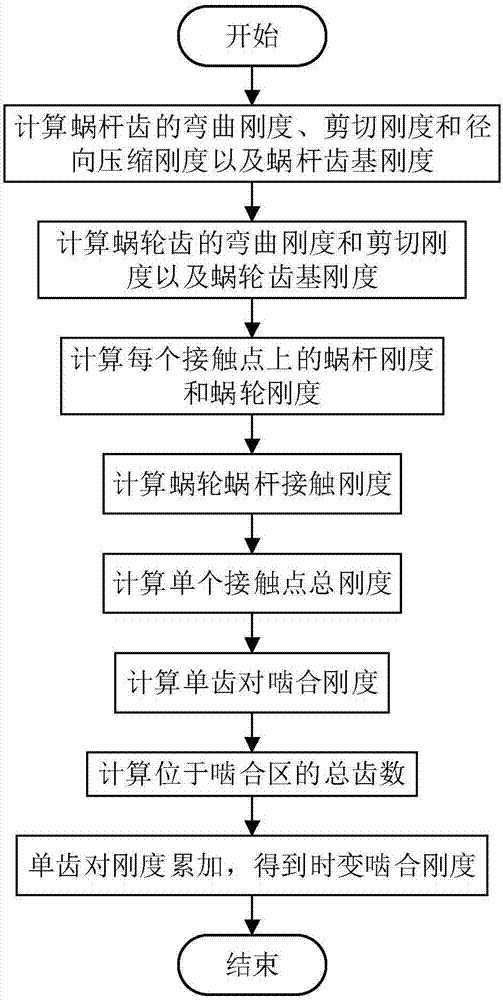
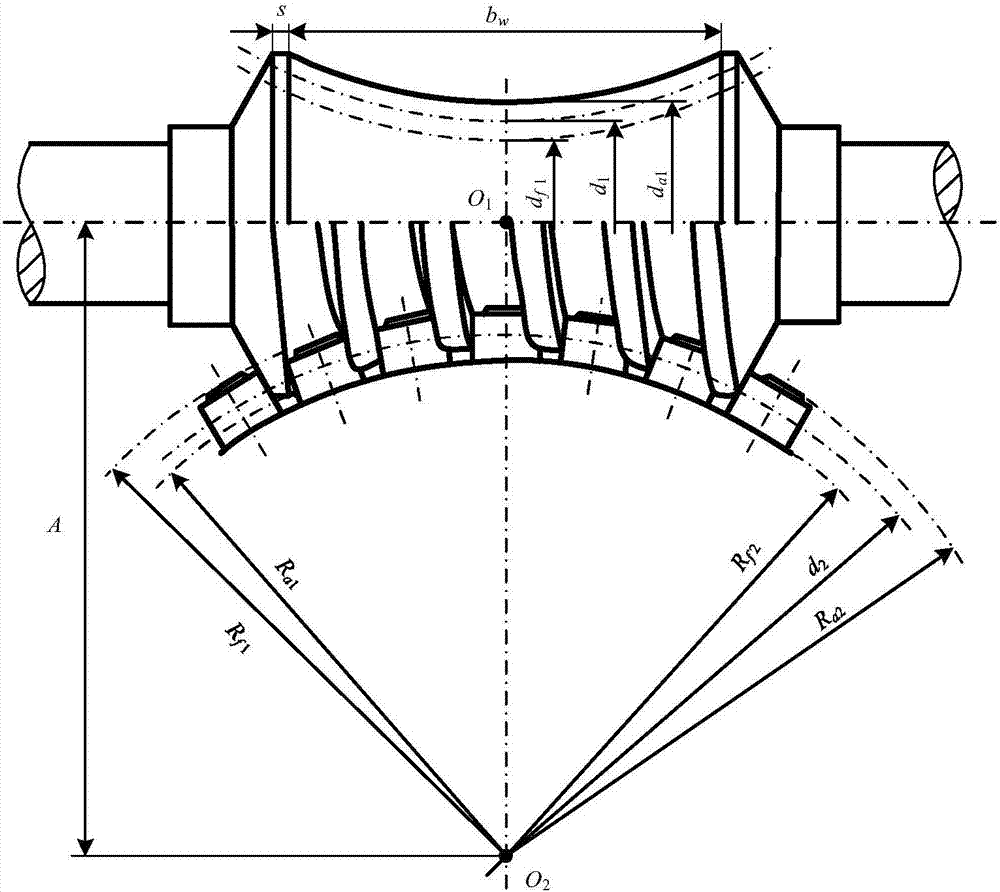
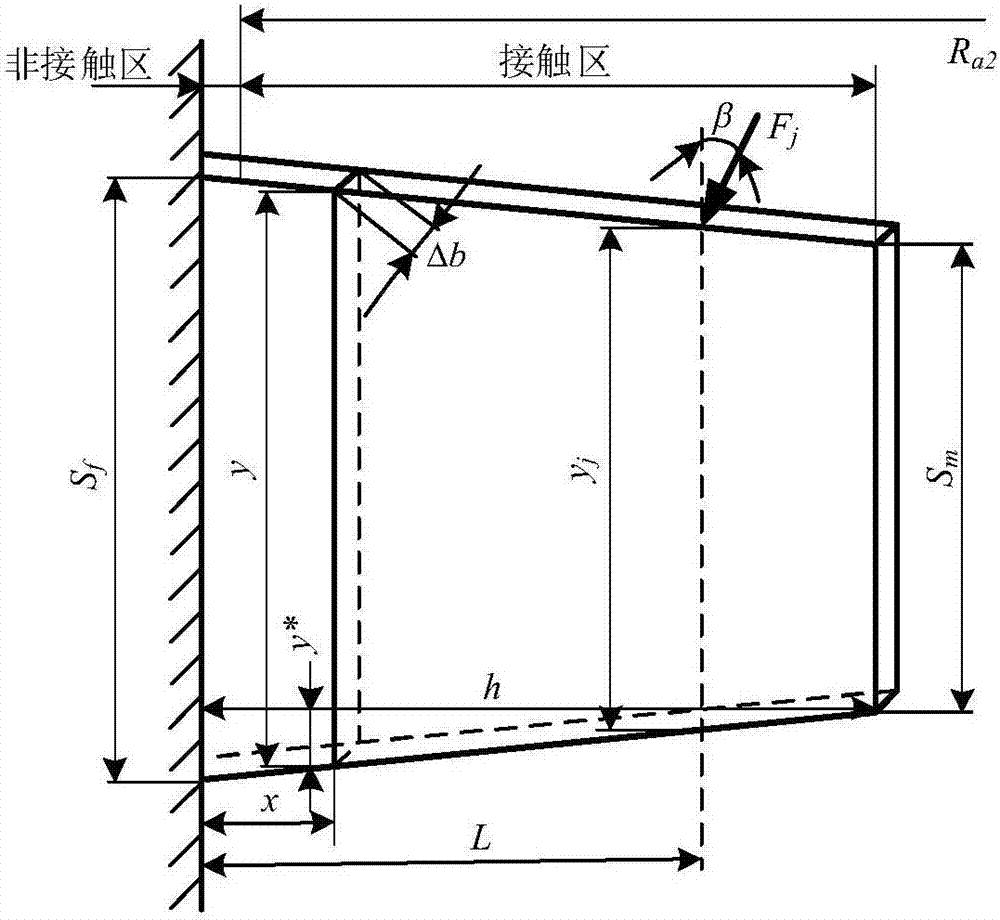
Analyzing method of time-varying mesh stiffness of single roller enveloping worm gear pair
ActiveCN107247856ABending stiffness achievedAchieve stiffnessGeometric CADPortable liftingShear stiffnessRadial compression
The invention provides an analyzing method of time-varying mesh stiffness of a single roller enveloping worm gear pair and aims to acquire the time-varying mesh stiffness of the single roller enveloping worm gear pair. The method includes: deducing worm tooth bending stiffness, shear stiffness and radial compression stiffness formulas; calculating worm tooth base stiffness; calculating worm gear tooth bending stiffness and shear stiffness; calculating worm gear tooth base stiffness; calculating worm stiffness and worm gear stiffness at a disperse contact point; calculating contact stiffness; performing serial and parallel calculation on the worm stiffness, the worm gear stiffness and the contact stiffness; calculating the time-varying mesh stiffness. The method has the advantages that the time-varying mesh stiffness of the single roller enveloping worm gear pair can be calculated, the worm gear stiffness and the worm stiffness can be further decomposed, the worm tooth bending stiffness, shear stiffness and radial compression stiffness formulas are provided, a calculation model of the number of meshing worm gear teeth in a mesh cycle is provided, and the method is applicable to the dynamic performance analysis and optimization design of the single roller enveloping worm gear pair.
Owner:西安启工数据科技有限公司
Intelligent variable-stiffness tuned mass damper system with magnetorheological elastomer bearings
ActiveCN105889381AEasy to adjustReduce energy consumptionMagnetic springsShock proofingMagnetic currentVariable stiffness
The invention discloses an intelligent variable-stiffness tuned mass damper system with magnetorheological elastomer bearings and belongs to the technical field of passive structure adaptive control. The intelligent variable-stiffness tuned mass damper system comprises a tuned mass block, a stress component, excitation components, sensors and a controller, wherein the tuned mass block is mounted on an upper connecting plate; the stress component consists of at least four magnetorheological elastomer bearings, magnetic-conducting connecting plates and the upper connecting plate; each bearing is enwrapped with a protective rubber layer; each excitation component consists of a coil, an iron core and a hard insulating layer; one sensor is mounted on each of the upper connecting plate and a lower connecting plate; the controller changes the shearing stiffness of the system according to a signal. The intelligent variable-stiffness tuned mass damper system is simple to produce and convenient to mount; the mechanical and magnetic properties of materials are fully utilized, and the space utilization rate and the magnetic field utilization rate are high; compared with a cylindrical bearing, a circular truncated cone-shaped bearing has wider stiffness adjustment range and better overall stability; each coil is not only taken as one excitation component, but also has the function of the tuned mass block; real-time and efficient adjustment can be ensured.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
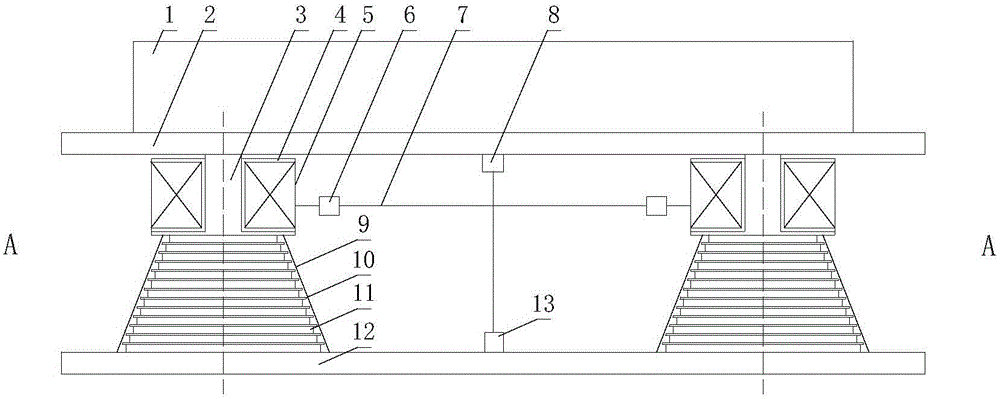
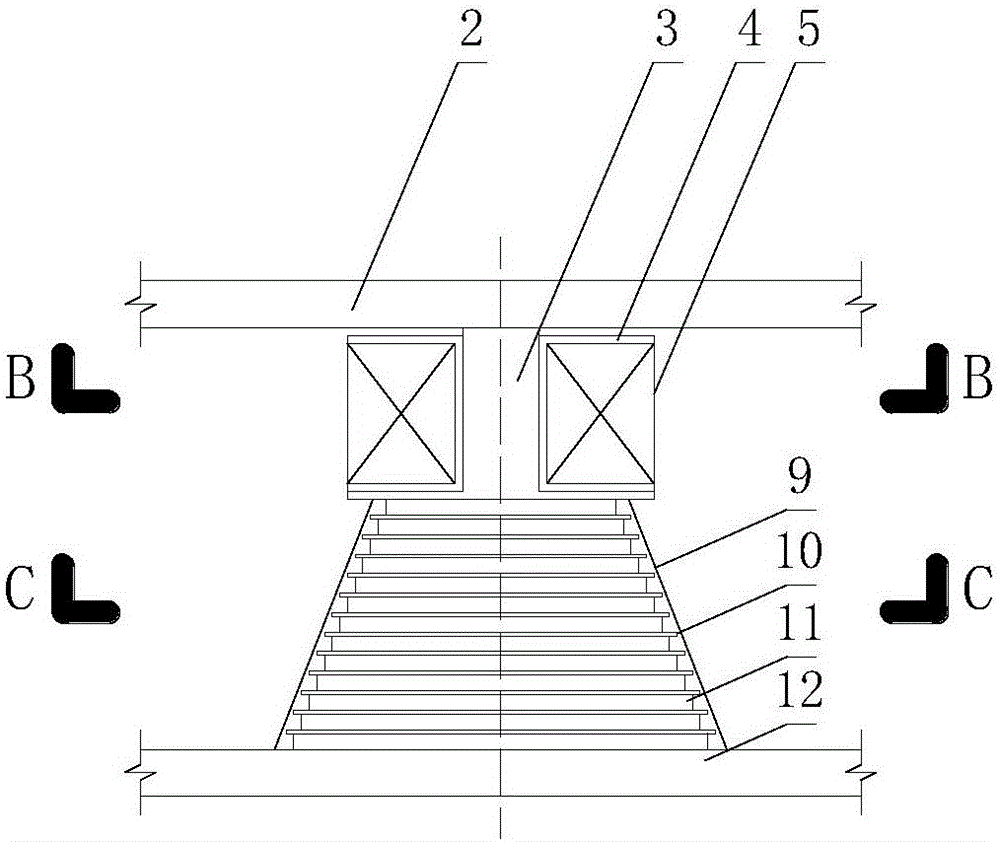
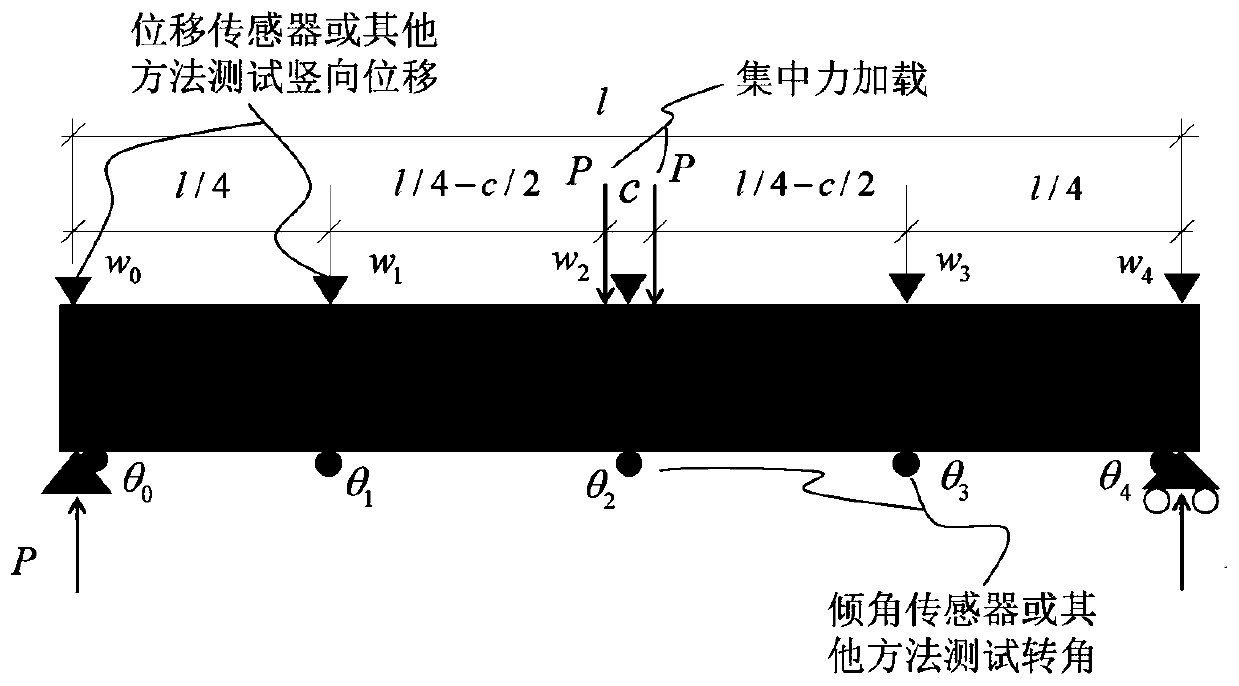
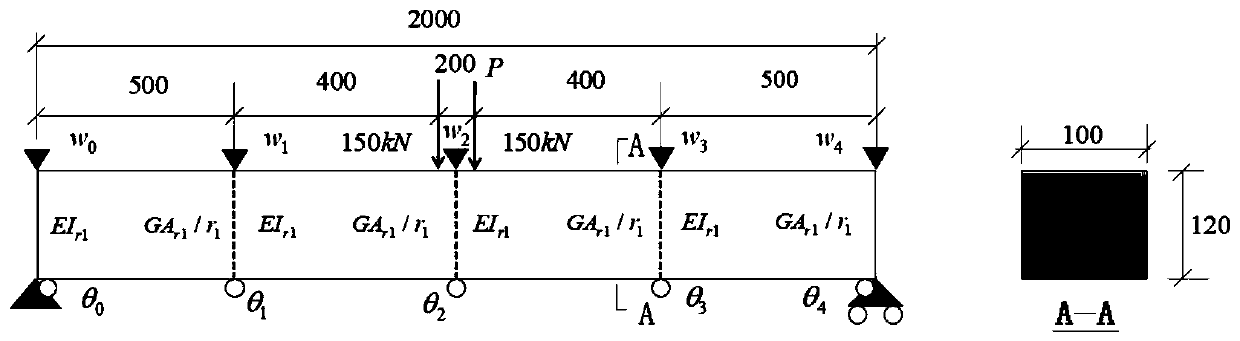
Beam structure initial state recognition method based on displacement and corner
ActiveCN111460558AIncrease credibilityEasy to operateGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelShear stiffness
The invention discloses a simply supported beam initial state recognition method based on displacement and a corner. The method comprises the following steps: segmenting a beam body; testing the vertical displacement and the rotation angle of the beam body at the subsection under the known load effect; basic mechanics principle, based on displacement and corner test values under the known load effect, the bending rigidity value and the shearing rigidity value of each beam section are obtained through backstepping, and finally according to the principle that bending strain energy and shearing strain energy are equal, the equivalent bending rigidity and shearing rigidity of the beam structure are obtained through derivation, so that important initial state information of the beam structure is obtained. According to the method, the bending resistance and the shearing rigidity of the beam structure can be identified only by knowing the vertical displacement and the corner test value underthe action of the load, and the method has the advantage of high operability; furthermore, an analysis method is adopted, a complex finite element model does not need to be established for multiple iterations, and the efficiency is higher; in addition, the method can be applied to bearing capacity evaluation, model correction and damage recognition of the beam structure, and has a wide applicationprospect.
Owner:GUANGXI TRANSPORTATION SCI & TECH GRP CO LTD
Wood-concrete composite beam shear connector pushing-out testing sample
PendingCN108412049AIncreased shear strengthIncrease stiffnessBridge structural detailsBuilding constructionsSocial benefitsMesh reinforcement
The invention discloses a wood-concrete composite beam shear connector pushing-out testing sample. The wood-concrete composite beam shear connector pushing-out testing sample comprises a wood beam, concrete slabs, a shear connector, anchoring parts and a steel mesh reinforcement. The shear connector is anchored on the upper portion of the wood beam through the anchoring parts, the steel mesh reinforcement is laid on the upper portion of the wood beam through a supported template piece, transverse reinforcements in the steel mesh reinforcement penetrate through through-holes reserved in the shear connector, the concrete slabs are poured into the template piece with the steel mesh reinforcement and the shear connector used as a skeleton, and a wood-concrete composite beam is formed. The wood-concrete composite beam shear connector pushing-out testing sample improves the shear strength and shear stiffness of the shear connector, has good fatigue resistance performance, reduces the shear deformation of the shear connector, and overall deformation of wood-concrete composite beam is reduced; and while resisting relative slip, the raising effect between the concrete slabs and the wood beam can be effectively restrained, and good social benefits and transformation prospects are achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Damping type hinge pin support
InactiveCN103883010ASolutionSolve the problem of poor multi-directional earthquake forceShock proofingShear stiffnessEngineering
The invention relates to a damping type hinge pin support which has a great capacity for energy dissipation and damping and has high flexural rigidity, shear stiffness and deformability. The damping type hinge pin support comprises an upper cover plate, a pair of lower lug plates, a hinge pin and a bottom plate, and further comprises an upper lug plate with a chamber and a pair of high damping rubber combination spring bodies with shaft holes, wherein end faces of the pair of the high damping rubber combination spring bodies are respectively provided with a teflon layer. The damping type hinge pin support solves the problem that in the prior art, a hinge pin support of a steel structure is poor in resistance in acting force caused by temperature variation and multidirectional earthquake acting force, is capable of rotating in a multidirectional mode, meanwhile has high pulling, pressing and bearing force inside a support plane in the main stress direction and especially has high deformability and energy dissipation and damping capacity.
Owner:NORTHERN ENG DESIGN & RES INST CO LTD +1
Testing method of shearing property of waveform steel-web combination beam
InactiveCN103743630AReliable structural research on dynamic performanceMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesSheet steelWave shape
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Pitch bearing
A pitch bearing for connecting first and second articles is provided. The first article includes a first curved outer surface and the second article includes a second curved outer surface opposite the first curved outer surface. The pitch bearing includes an axisymmetric structure interposed between the first and second curved outer surfaces. The axisymmetric structure includes compliant layers and stabilizing layers interleaved between the compliant layers. The compliant layers and the stabilizing layers proximate to the first article haves a curvature matching that of the first curved outer surface. The compliant layers and the stabilizing layers proximate to the second article have a curvature matching that of the second curved outer surface. A shear stiffness of each of the stabilizing layers is greater than a shear stiffness of each of the compliant layers.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Settlement calculation method of grid-type diaphragm wall bridge foundation in soft soil foundation
ActiveCN107679348AAvoid wastingAvoid the problem of foundation instabilityGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationSlurry wallShear stiffness
The invention provides a settlement calculation method of a grid-type diaphragm wall bridge foundation in a soft soil foundation. According to the method, the structural characteristics of the grid-type diaphragm wall foundation itself in the soft soil foundation are taken into account; based on the foundation settlement characteristics, calculation of the frictional resistance on the outer side of a wall body is deduced, meanwhile the concept of equivalent shear stiffness is put forward and used for calculating the frictional resistance on the inner side of the wall body, and finally based ona load transfer method, the foundation settlement amount under various levels of load can be calculated by means of iterative calculation. According to the method, it is unnecessary to conduct special geotechnical engineering investigation, and the method provides a scientific basis for engineering design and construction of the soft soil foundation to which the novel grid-type diaphragm wall bridge foundation are applied.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
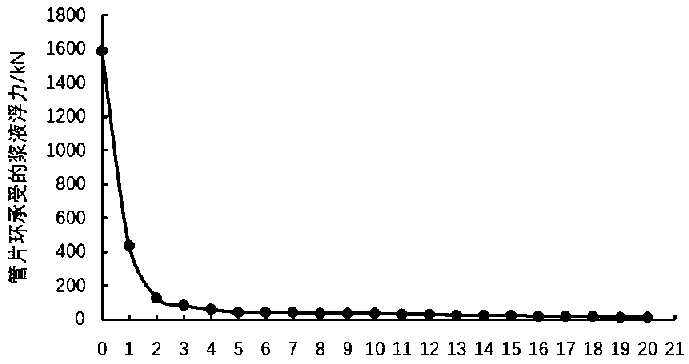
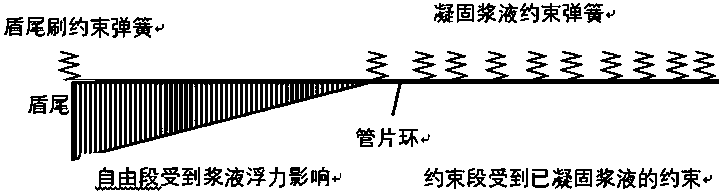
Establishment method of floating and slab staggering refined model of segment ring separated from shield tail
ActiveCN111222275AReflect the longitudinal force characteristicsReflect the impact of floatingUnderground chambersDesign optimisation/simulationShear stiffnessJackscrew
The invention relates to a method for establishing a segment ring floating and slab staggering refined model for removing a shield tail, which comprises the following steps of: after determining the design information of a tunnel structure, establishing a refined numerical model which can consider the buoyancy borne by a segment, the thrust and direction of a shield tail jack and the shearing rigidity of a joint of adjacent segment rings; the self-made buoyancy test device is used for accurately testing the buoyancy borne by the duct part, and the floating condition of the duct part in the post-wall grouting wrapping state can be better reflected. Changes, caused by posture changes of the shield tunneling machine, of the thrust and direction of the shield tail jack on the segment ring areconsidered, and the longitudinal stress characteristics of the shield tail segment ring in the actual construction process of a tunnel and the influence on upward floating of segments are better reflected. By considering the shearing rigidity of the adjacent segment ring joints, the longitudinal characteristics of bending deformation and shearing deformation of the shield tail segment ring can bebetter reflected, displacement, slab staggering and additional internal force caused by floating of the shield tail segment ring can be more accurately determined, and a basis is provided for processcontrol of construction.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Pitch bearing
A pitch bearing for connecting first and second articles is provided. The first article includes a first curved outer surface and the second article includes a second curved outer surface opposite the first curved outer surface. The pitch bearing includes an axisymmetric structure interposed between the first and second curved outer surfaces. The axisymmetric structure includes compliant layers and stabilizing layers interleaved between the compliant layers. The compliant layers and the stabilizing layers proximate to the first article haves a curvature matching that of the first curved outer surface. The compliant layers and the stabilizing layers proximate to the second article have a curvature matching that of the second curved outer surface. A shear stiffness of each of the stabilizing layers is greater than a shear stiffness of each of the compliant layers.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Method for quickly evaluating transverse force transmission capacity of hollow slab girder bridge hinge joint
ActiveCN109933936ATruly reflect the mechanical response of the structureAvoid bias in evaluation resultsSpecial data processing applicationsEvaluation resultVertical deflection
The invention discloses a method for quickly evaluating the transverse force transmission capacity of a hollow slab girder bridge hinge joint. The method comprises: firstly, measuring points are arranged on the two sides of a hinge joint of the hollow slab girder bridge; further, the relative vertical deflection of the measuring point position in the load test is obtained; substituting the proposed hinge joint rotation stiffness calculation formula and the proposed hinge joint shear stiffness calculation formula, solving the actually measured rotation stiffness and the actually measured shearstiffness of the hinge joint as evaluation indexes of the hinge joint transverse force transmission capacity, and quickly evaluating the hinge joint transverse force transmission capacity according todifferent threshold ranges of the proposed evaluation indexes. The method can also be used in related standard systems for bridge reinforcement, that is, the hollow slab bridge hinge joint is rapidlyevaluated through the method, and the degree of beam reinforcement needing to be carried out is judged according to the evaluation result.
Owner:ANHUI TRANSPORTATION HLDG GRP CO LTD +1
Beam bridge with ultrahigh pier concrete filled steel tube continuous beam anti-seismic structure system
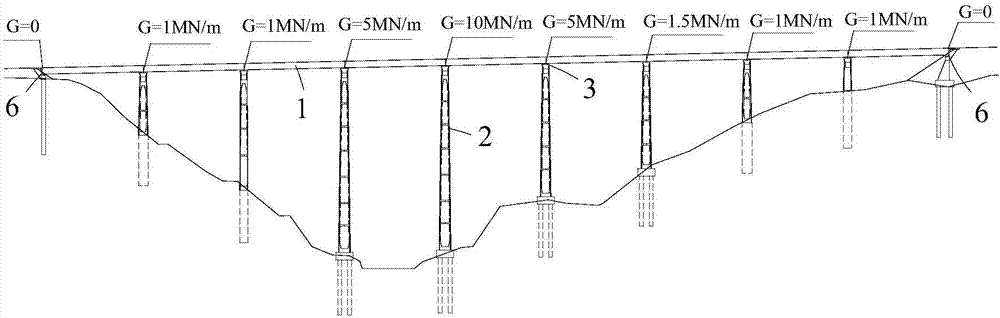
InactiveCN106988209AUniform stiffnessDisplacement and coordinationBridge structural detailsShear stiffnessContinuous beam
The invention discloses a beam bridge with an ultrahigh pier concrete filled steel tube continuous beam anti-seismic structure system. The beam bridge comprises a plurality of piers with unequal heights and a main beam arranged on the piers. The main beam and the piers are mutually connected through supports. The higher the piers are, the larger the shear rigidity values of the supports adopted by the piers for being connected with the main beam are, namely, the shear rigidity values of the supports, connected with the main beam, of the higher piers are larger, and the shear rigidity values of the supports, connected with the main beam, of the lower piers are smaller. The piers with different heights of the structure system adopt the supports with different shear rigidity values for matching, so that the total rigidity values formed by connecting of the piers with the different heights and the main beam are matched one another, and the rigid frame-limiting connecting beam structure system is formed. In the system, the piers and the supports are balanced in integral rigidity and coordinate and uniform in deflection, so that anti-seismic performance is improved by a large margin; and meanwhile the comfort of vehicle driving is improved due to the fact that the number of the supports and the lengths of expansion joints are decreased.
Owner:SICHUAN VOCATIONAL & TECHN COLLEGE OF COMM
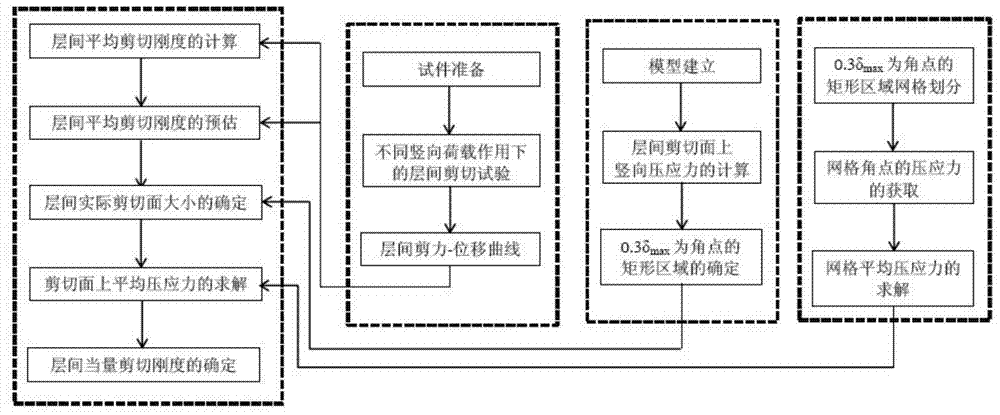
Method for determining interlayer equivalent shear stiffness between base layer and surface layer of cement concrete pavement and horizontal shear tester
ActiveCN104849210AOvercome the problem that the value cannot reflect the difference in vertical compressive stressUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisSurface layerShear stiffness
The invention provides a method for determining interlayer equivalent shear stiffness between base layer and surface layer of a cement concrete pavement and a horizontal shear tester. The horizontal shear tester capable of simulating vertical load comprises a fixing device, a loading device, a measuring device and a servo device, wherein the base layer of the cement concrete pavement is arranged in the fixing device; the surface layer of the cement concrete pavement is arranged on the upper surface of the base layer of the cement concrete pavement; the loading device and the measuring device are respectively arranged on the surface layer of the cement concrete pavement; the servo device is respectively connected with the loading device and the measuring device. The horizontal shear tester is capable of reflecting the difference of vertical pressure stress on the shear surface, displaying the size of the actual interlayer shear surface and providing accurate calculation parameters for structural analysis of the cement concrete pavement.
Owner:SHANXI PROVINCIAL RES INST OF COMM +1
Reinforcing method for touched nodes of existing beam and lacing bar type lattice steel column
ActiveCN103806672AIncrease lateral stiffnessImprove economyBuilding repairsSystems designShear stiffness
The invention discloses a reinforcing method for touched nodes of an existing beam and a lacing bar type lattice steel column. The lacing bar type lattice steel column is composed of four square steel pipe columns and lacing bars, and the existing beam penetrates through the center of the lacing bar type lattice steel column. In order to enable the existing beam to smoothly penetrate through the center of the lacing bar type lattice steel column, the lacing bars are not arranged on the lacing bar type lattice steel column at the touched nodes, so the shear stiffness of the touched nodes is weakened to some extent. The shear stiffness and the rigidity of the lacing bar type lattice steel column at the touched nodes are enhanced by utilizing a box-shaped reinforcement structural system formed by reinforced steel plates and the square steel pipe columns of the lacing bar type lattice steel column. According to the reinforcing method, the shear resistance and the stress performance at the touched nodes of the lacing bar type lattice steel column and the existing beam can be effectively improved, in addition, power transmission system design of the nodes is clear, the stress is reasonable, and on-site construction is facilitated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TIANDI ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD +1
Flexible membrane material shearing performance testing method considering tensile-shear coupling effect
InactiveCN110208113AAccurate grasp of mechanical responseAccurate acquisitionMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesStress ratioShear stiffness
The invention discloses a flexible membrane materialshearing performance testing method considering a tensile-shear coupling effect. Based on a biaxial testing method, the deflection angle and warp and weft stress ratio parameters of the membrane material are integrated to realize the coupling stress state of the flexible membrane in the coexistence of tensile and shear stresses; different shear stress levels can be set based on specific working conditions of the membrane surface in membrane structural engineering,and the correlation between shear stress and shear strain is analyzed;and basedon treatment and analysis of material mechanics theory, the shear stiffness of the flexible membrane under the tensile-shear coupling stress is obtained. The flexible membrane material shearing performance testing method considering the tensile-shear coupling effect is superior to the existing shear testing method in terms of stress stability, tensile and shear stresses synchronization, test operability and the like, the test of the mechanical properties of the flexible membrane under the true tensile-shear coupling stress state can be realized,the correlation analysis between the shear stressand the shear strain is realized, and the shortcomings of the existing flexible membrane shear performance testing method areeffectively compensated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Shallow buried steel column base and construction method thereof
InactiveCN102966113AEliminate setup requirementsMitigation or Elimination of QuantitiesFoundation engineeringReinforced concreteShear stiffness
The invention provides a shallow buried steel column base which comprises a steel column, wherein the bottom of the steel column is provided with an end plate; the end plate of the steel column is fixed by virtue of an anchor bolt; the other end of the anchor bolt is fixed in a bottom plate or base beam concrete; and the bottom of the steel column is buried in shallow buried layer concrete above the bottom plate or the base beam concrete. The shallow buried steel column base is of a shear-resistant structure due to the shallow buried layer reinforced concrete, so that the requirement for arrangement of a lower shear-resistant key on the end plate of the steel column is eliminated; and the anchor bolt is not needed to be shear-resistant, so that the difficulty in anchor bolt quantity and arrangement brought by the condition that the anchor bolt participates in shear resistance can be relieved or eliminated, and the shear stiffness and shear bearing capability of the steel column base are effectively improved. The shear-resistant design of the steel column base is simplified, the construction is convenient, and the seismic performance of the steel column base is improved. The invention further provides a construction method of the shallow buried steel column base.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Foam interlayer structure compound material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102390129AIncreased shear stiffnessLight in massSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationShear stiffnessEngineering
The invention discloses a foam interlayer structure compound material and a preparation method thereof. A foam core material in the compound material is arranged between an upper skin and a lower skin, wherein one ends of one group of pultrusion rods in the foam core material are connected with the upper skin, the other ends of the group of pultrusion rods are connected with the lower skin to form a *-shaped structure, and pultrusion rods for connecting the upper skin and the lower skin are arranged between every two adjacent *-shaped structures. In the interlayer structure compound material, a plurality of pins are arranged in a foam matrix to form a space grid structure, thus the bonding force between the skins and the core material is improved, and because of geometrical features of the grid structure, the performances such as shearing resisting rigidity can be greatly improved. The foam interlayer structure compound material can be applied to aircraft members with high rigidity and weight requirements, such as wallboards, wing surfaces, tail beams and other main load-carrying structures.
Owner:句容市育达实业投资有限公司
Method and Apparatus for Testing of Shear Stiffness in Board
ActiveUS20080276720A1Material strength using steady torsional forcesTension measurementInertial massShear stiffness
A method and apparatus for testing shear stiffness in board is disclosed. The board sample (6) is placed into stationary jaw (2) and jaw (3) which is rigidly connected to inertial mass (7). The mass (7) is twisted around the sample axis with an initial twist chosen to ensure the sample is within the elastic region, and then allowed to freely oscillate. The oscillation frequency is then measured to evaluate the torsional stiffness of the sample.
Owner:KORUTEST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com