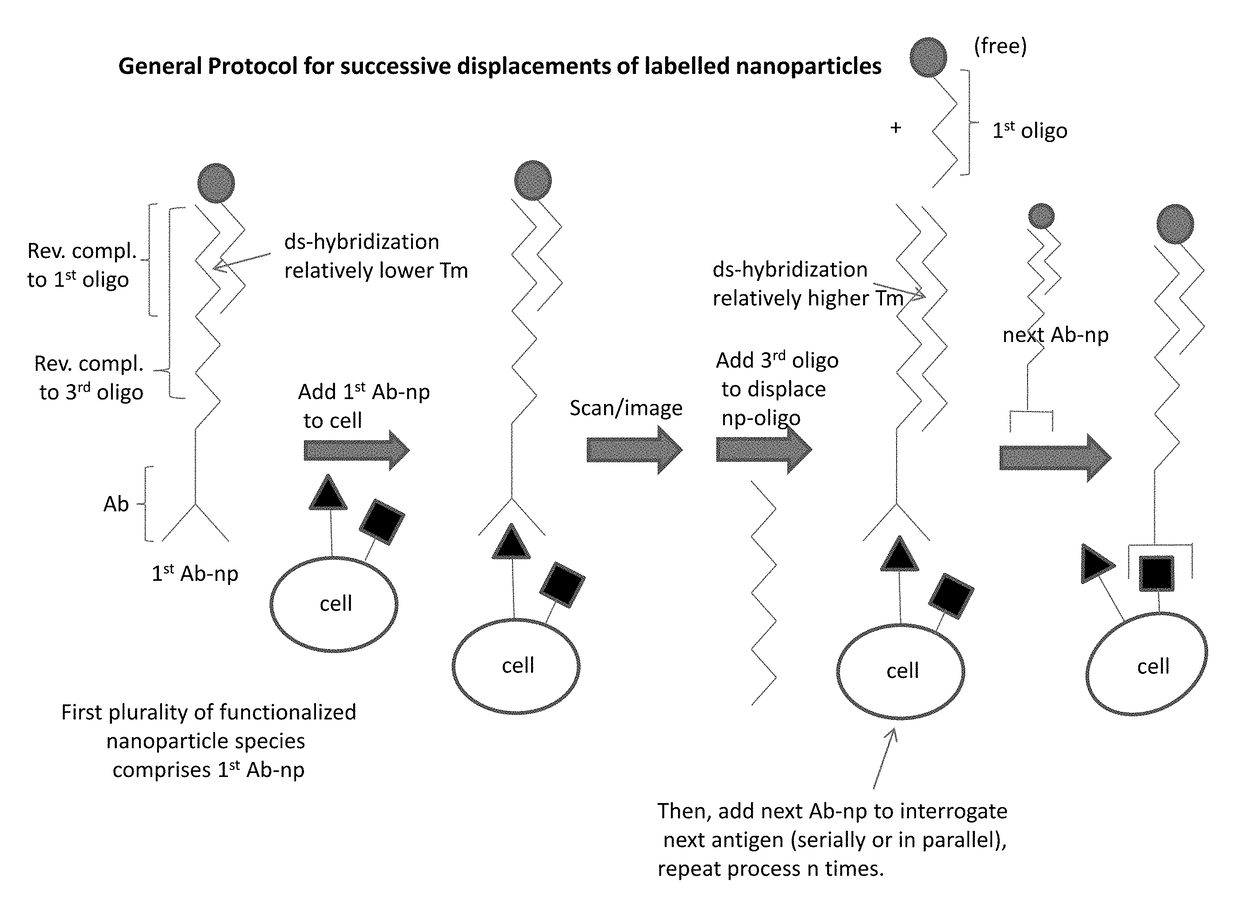
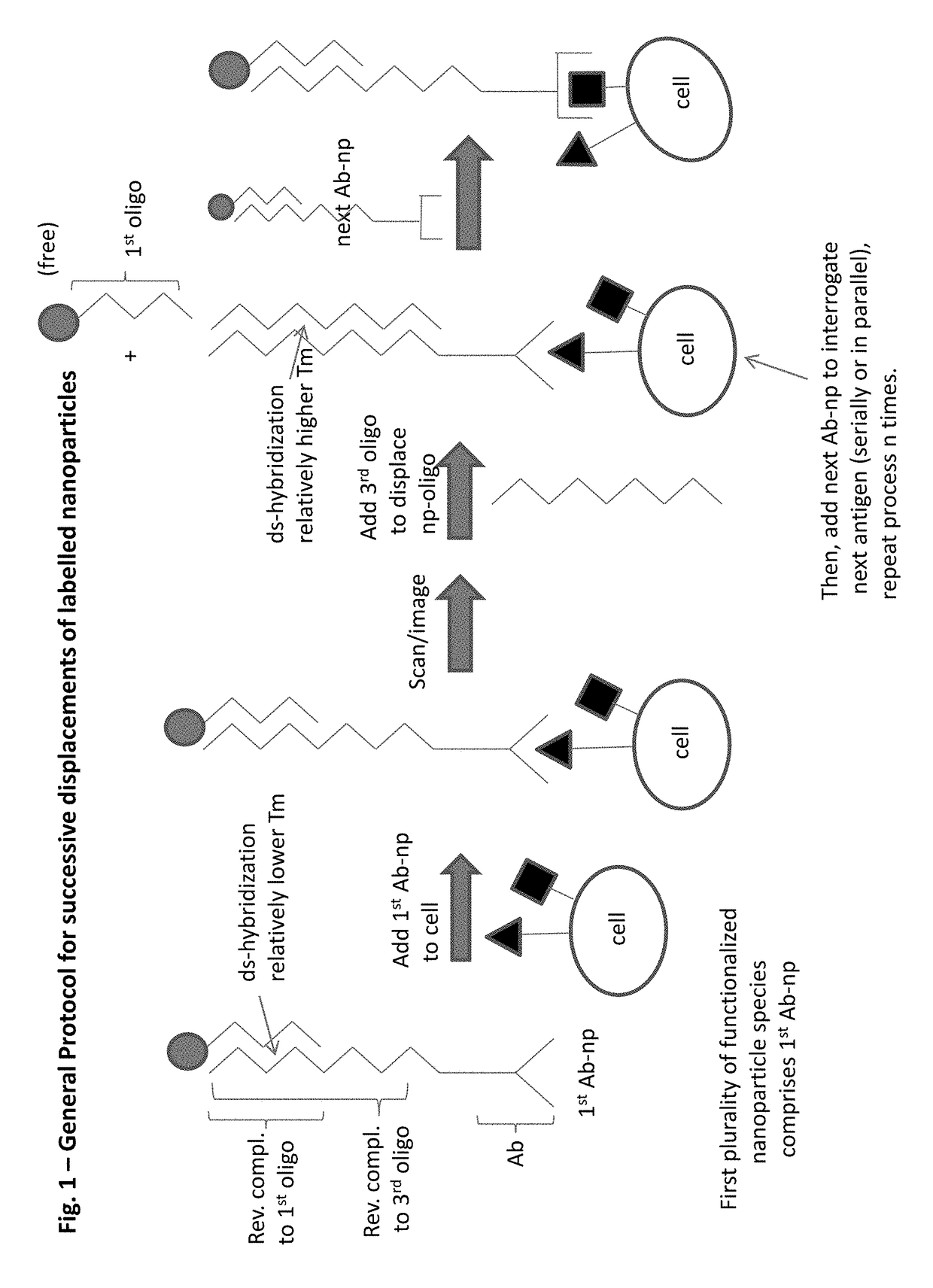
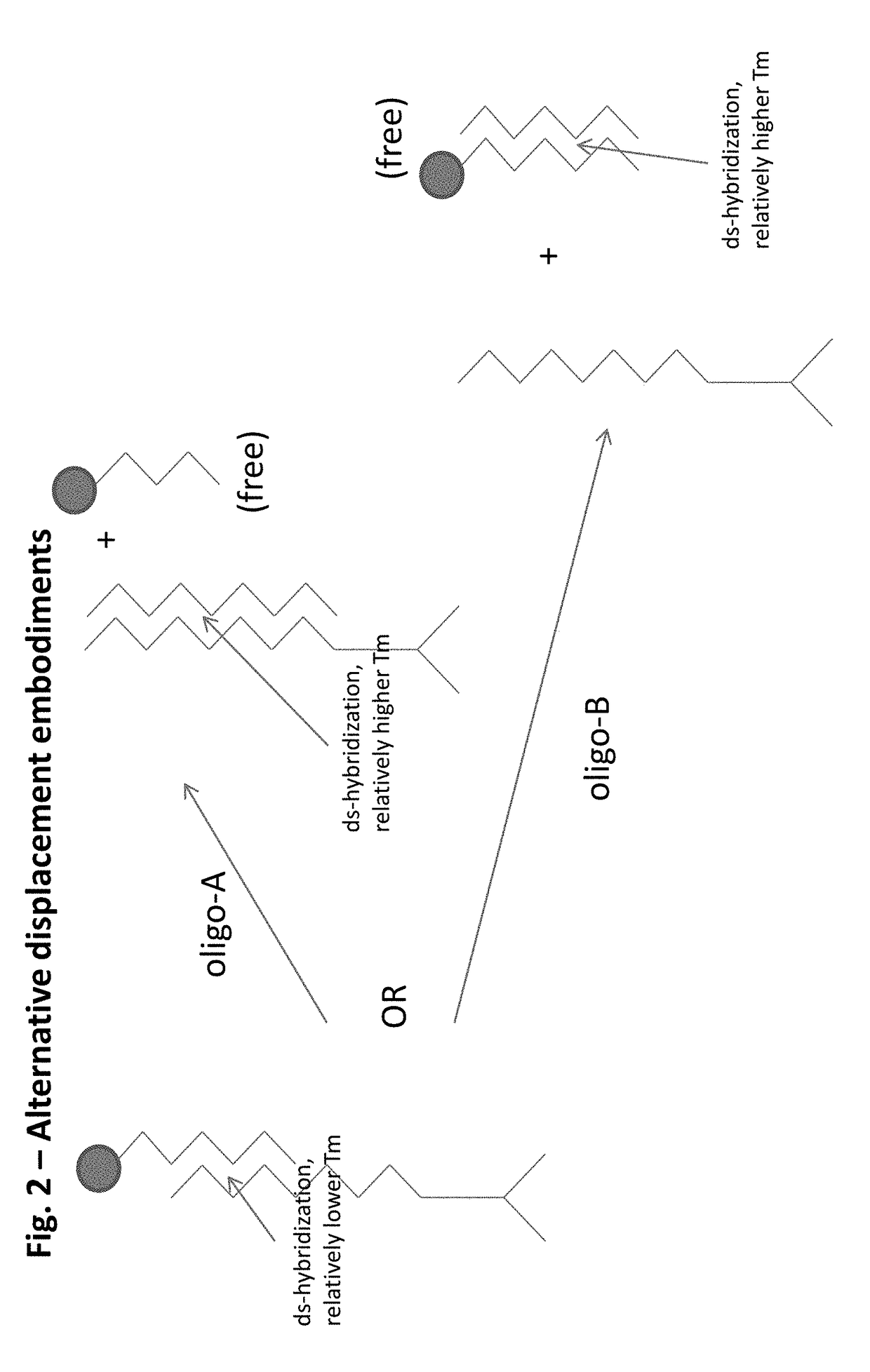
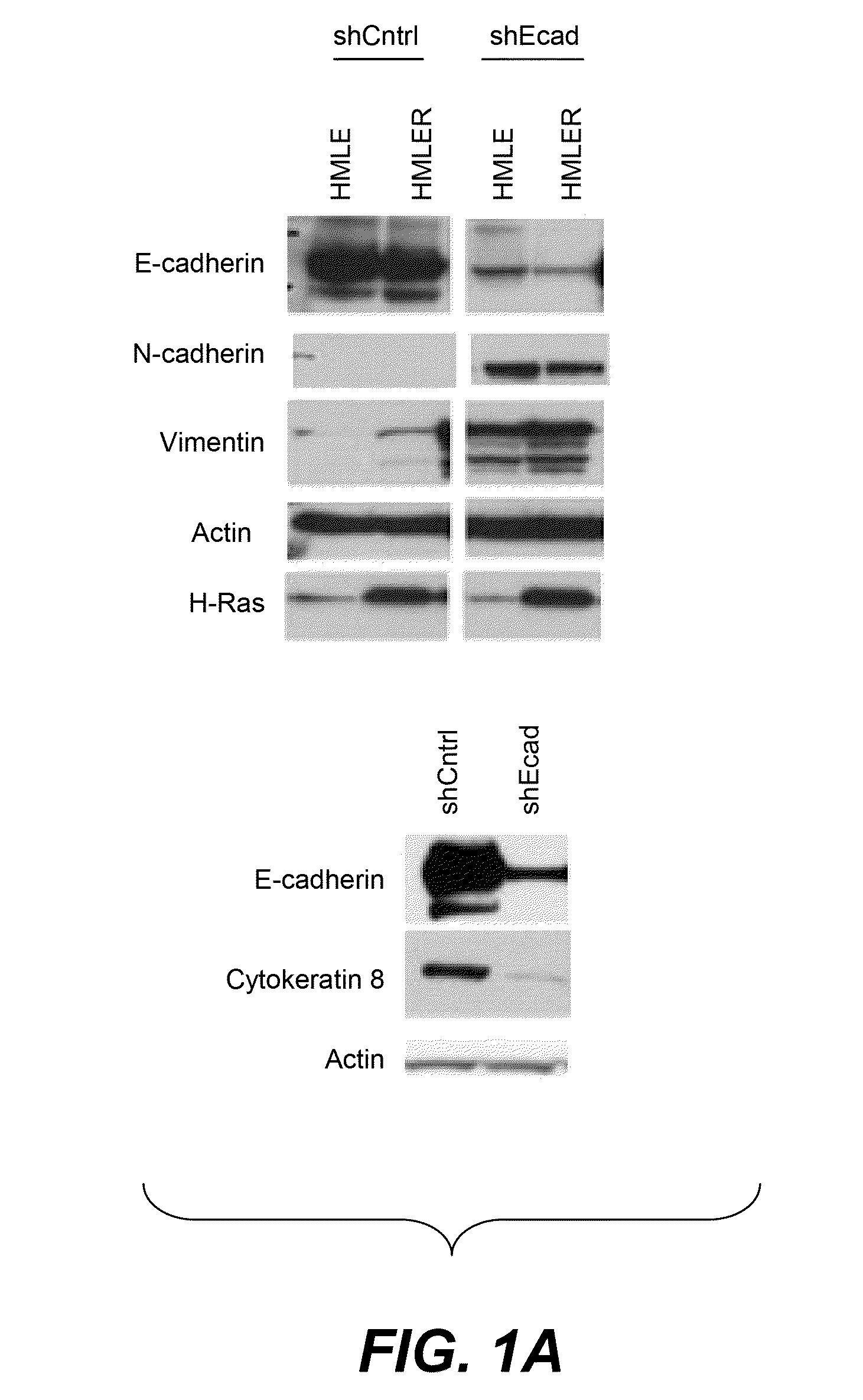
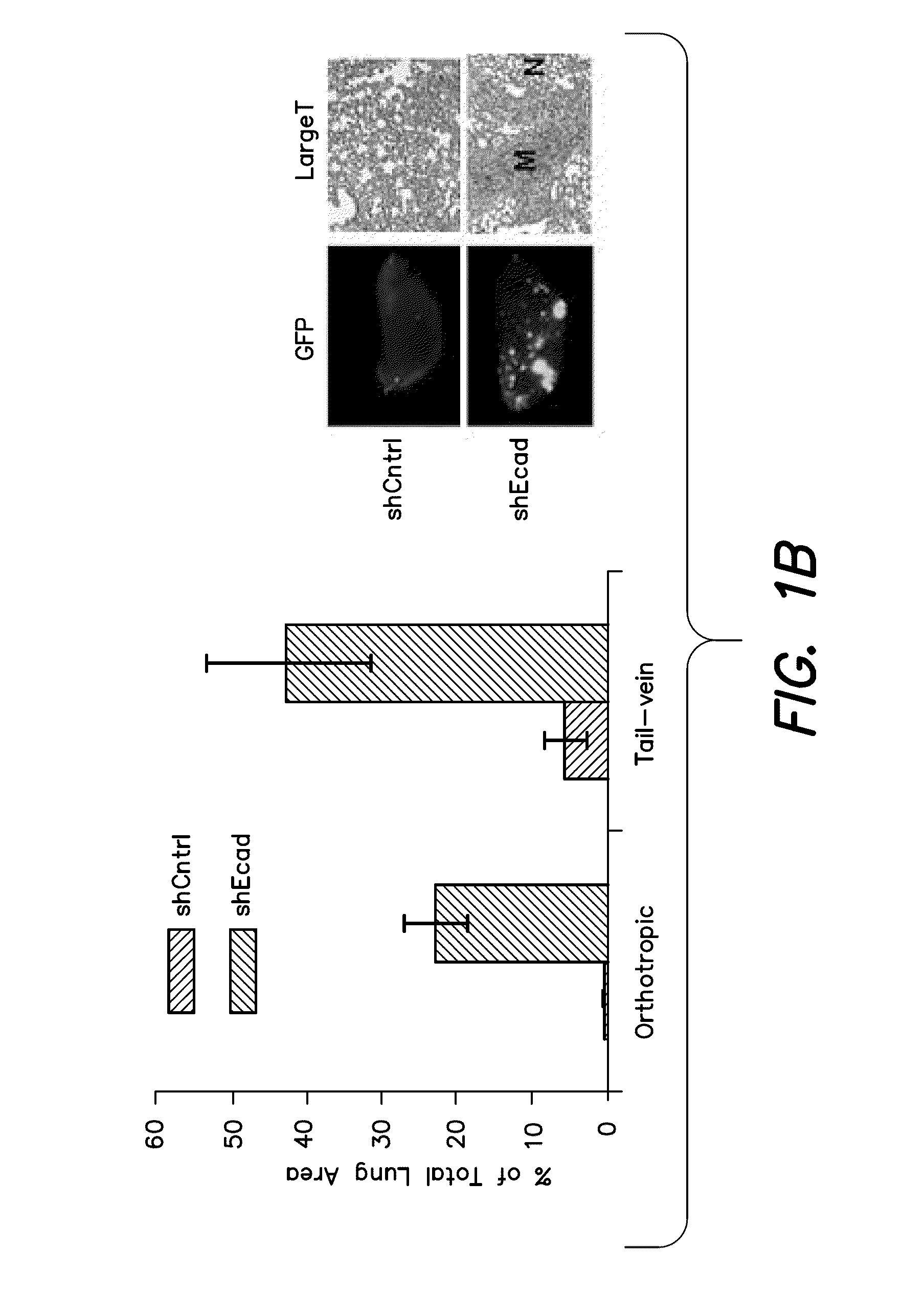
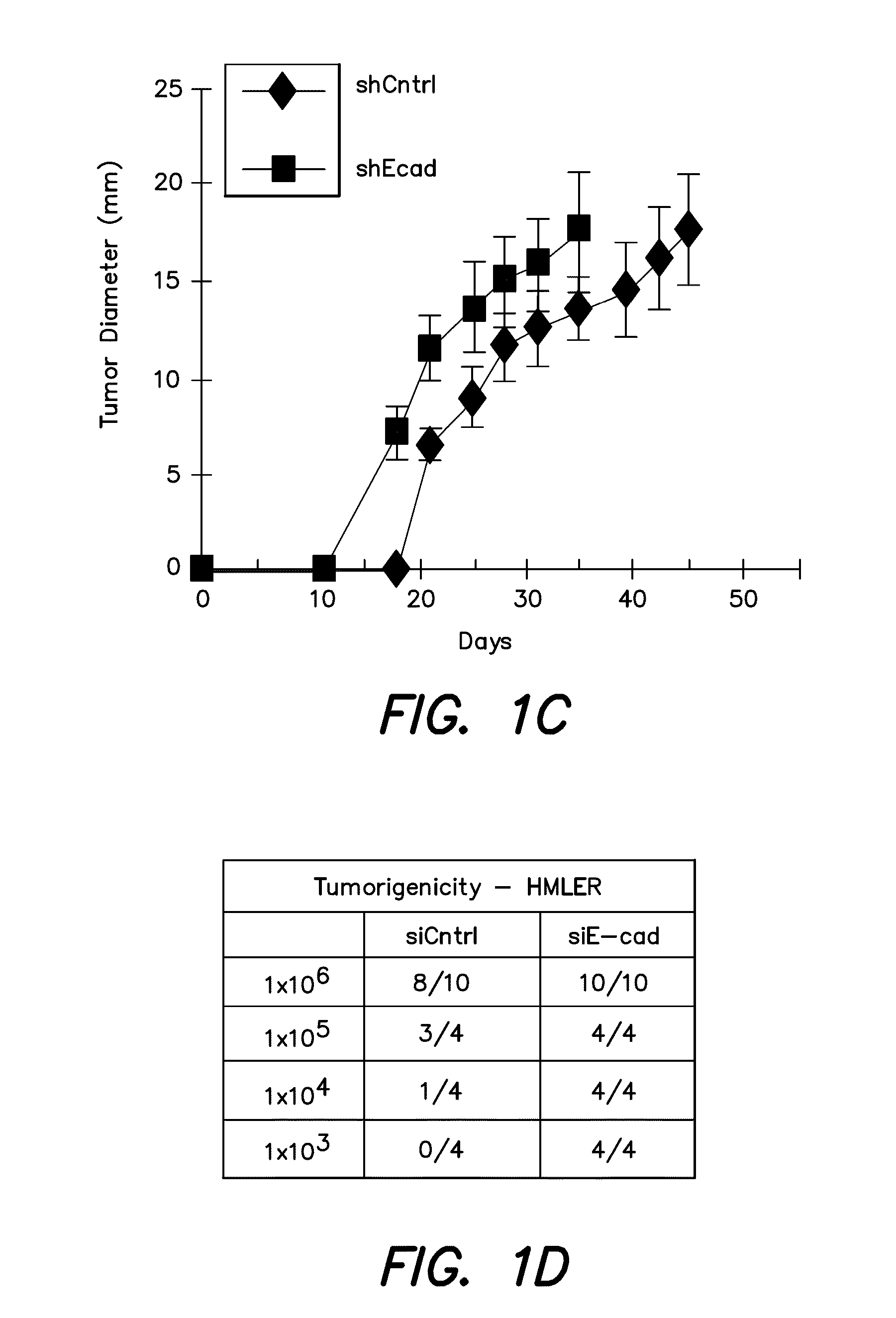
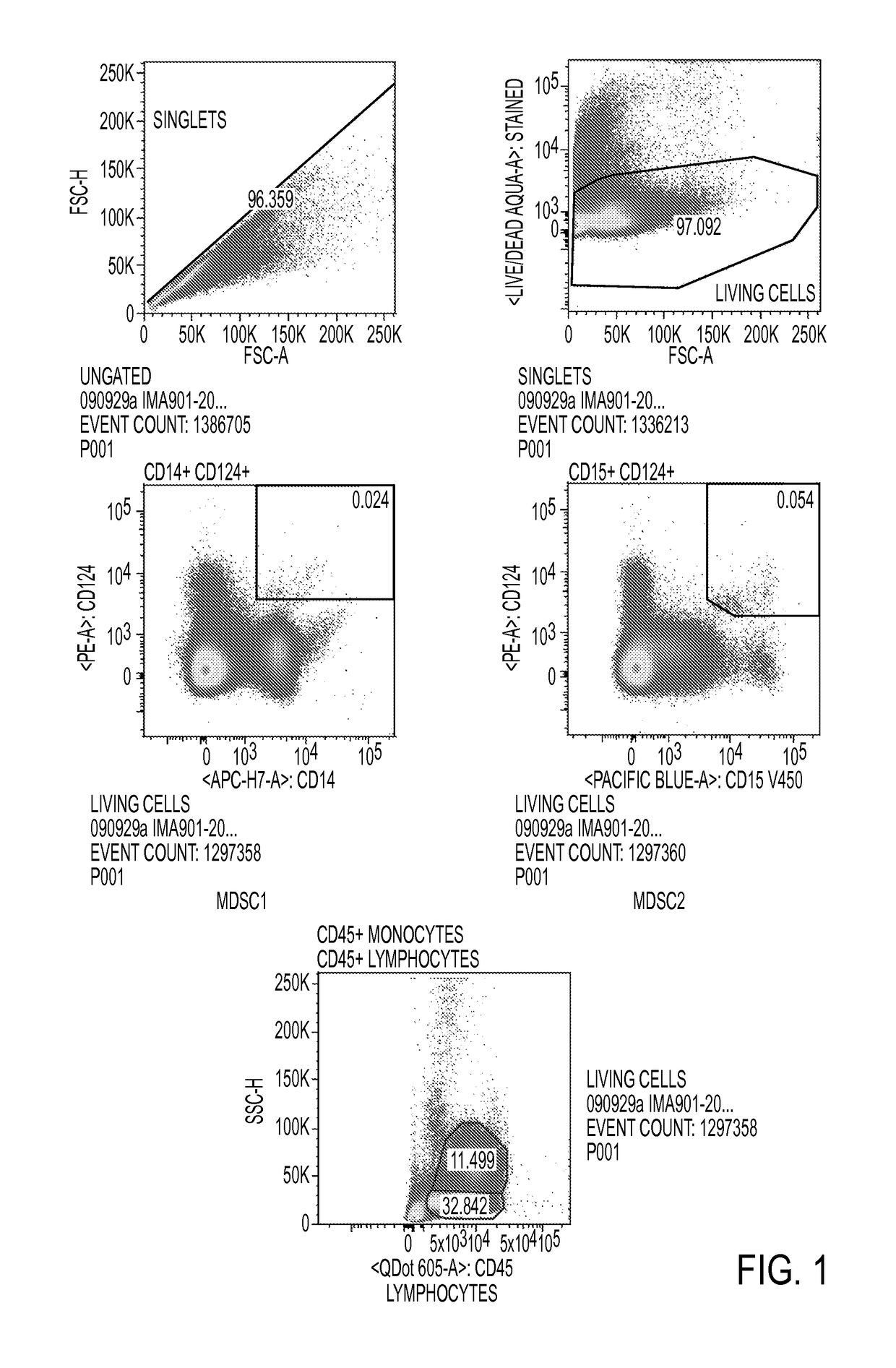
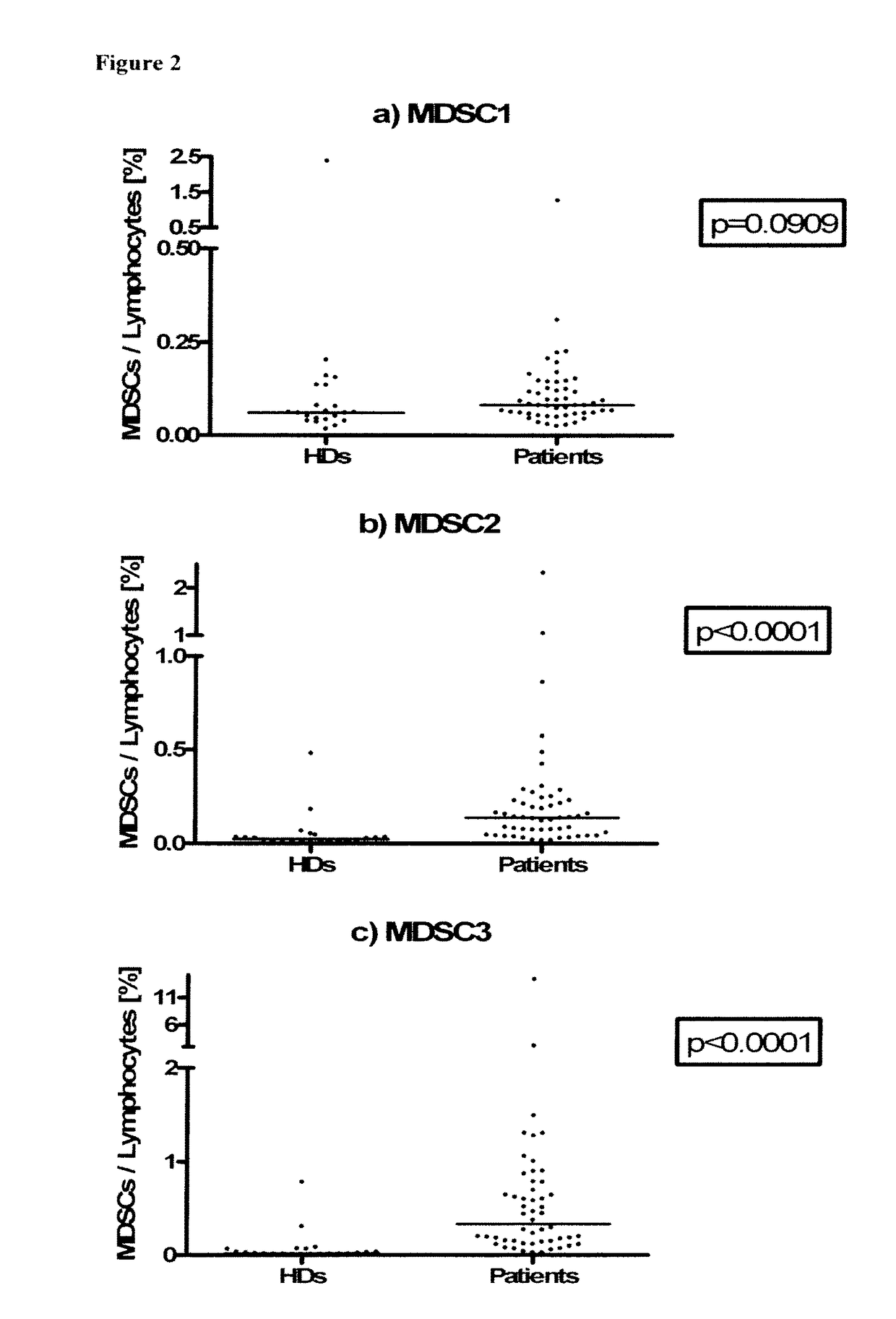
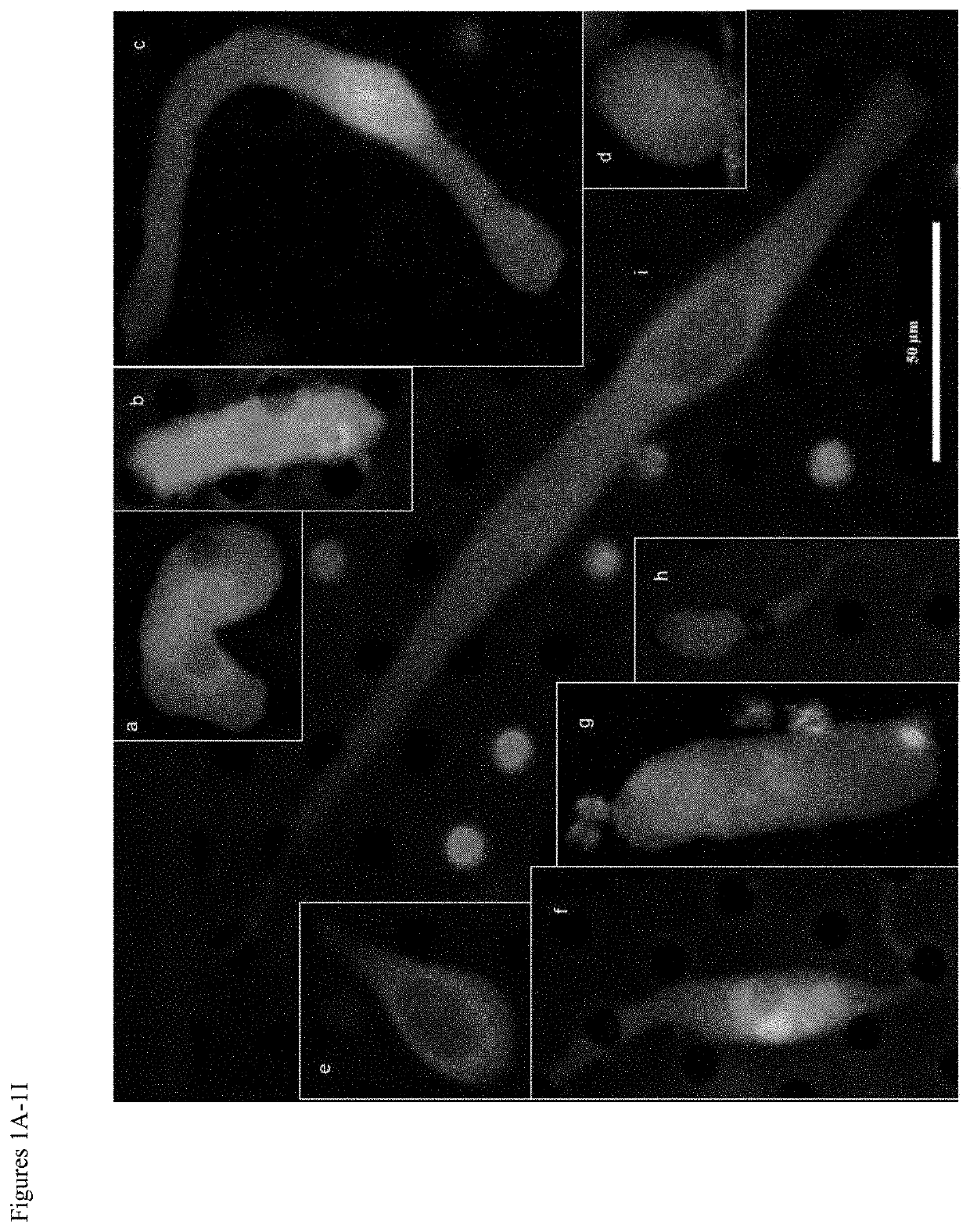
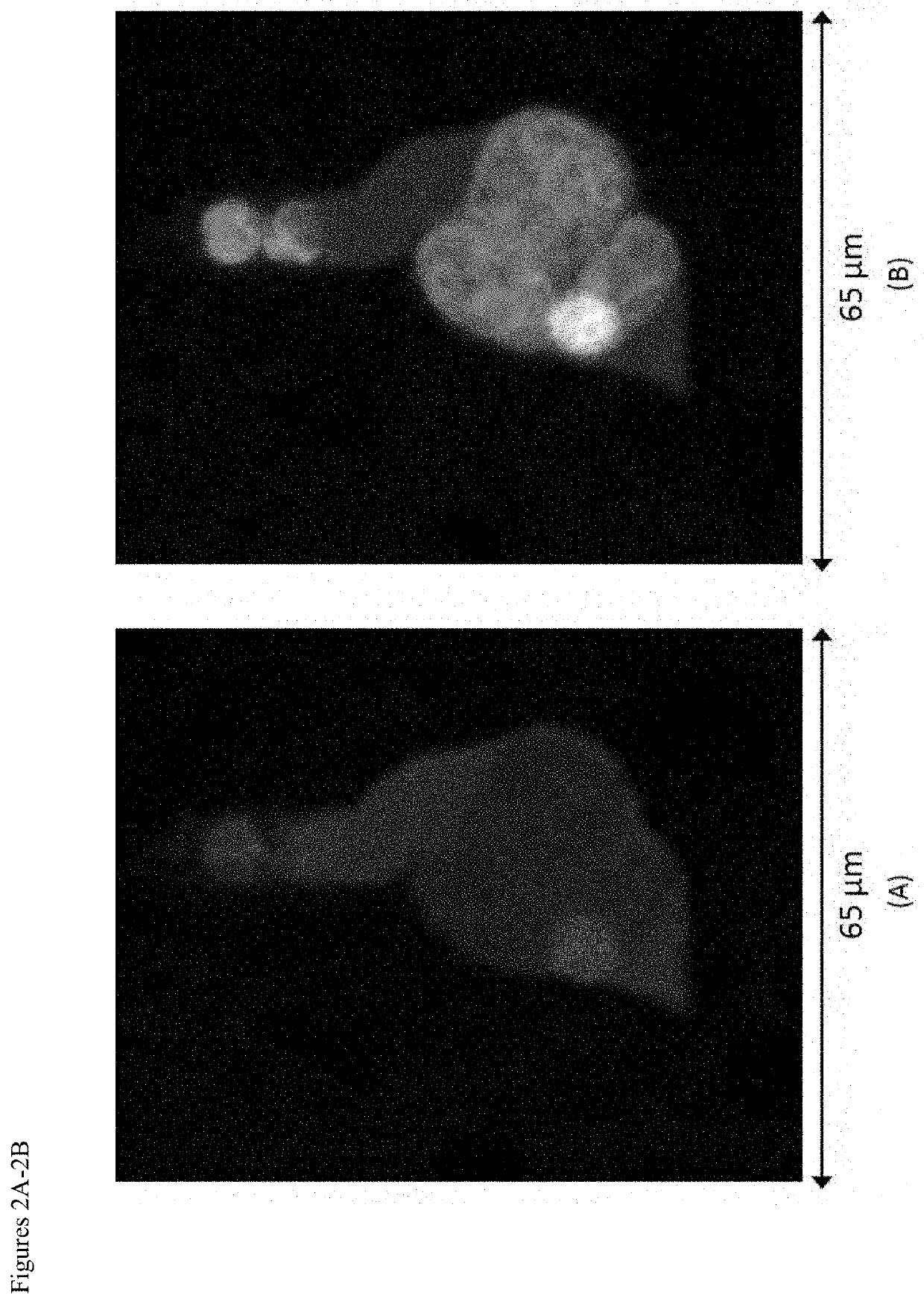
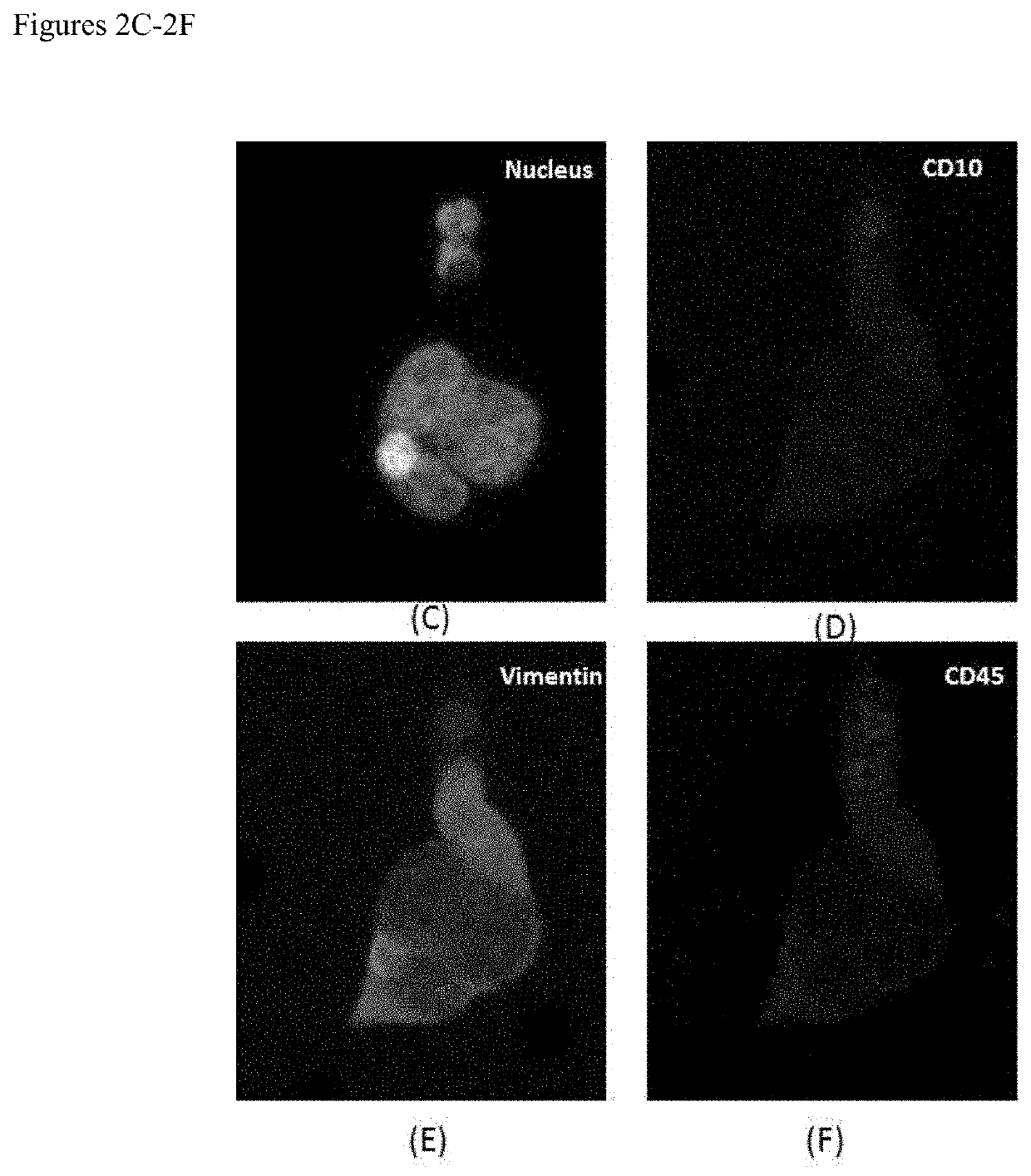
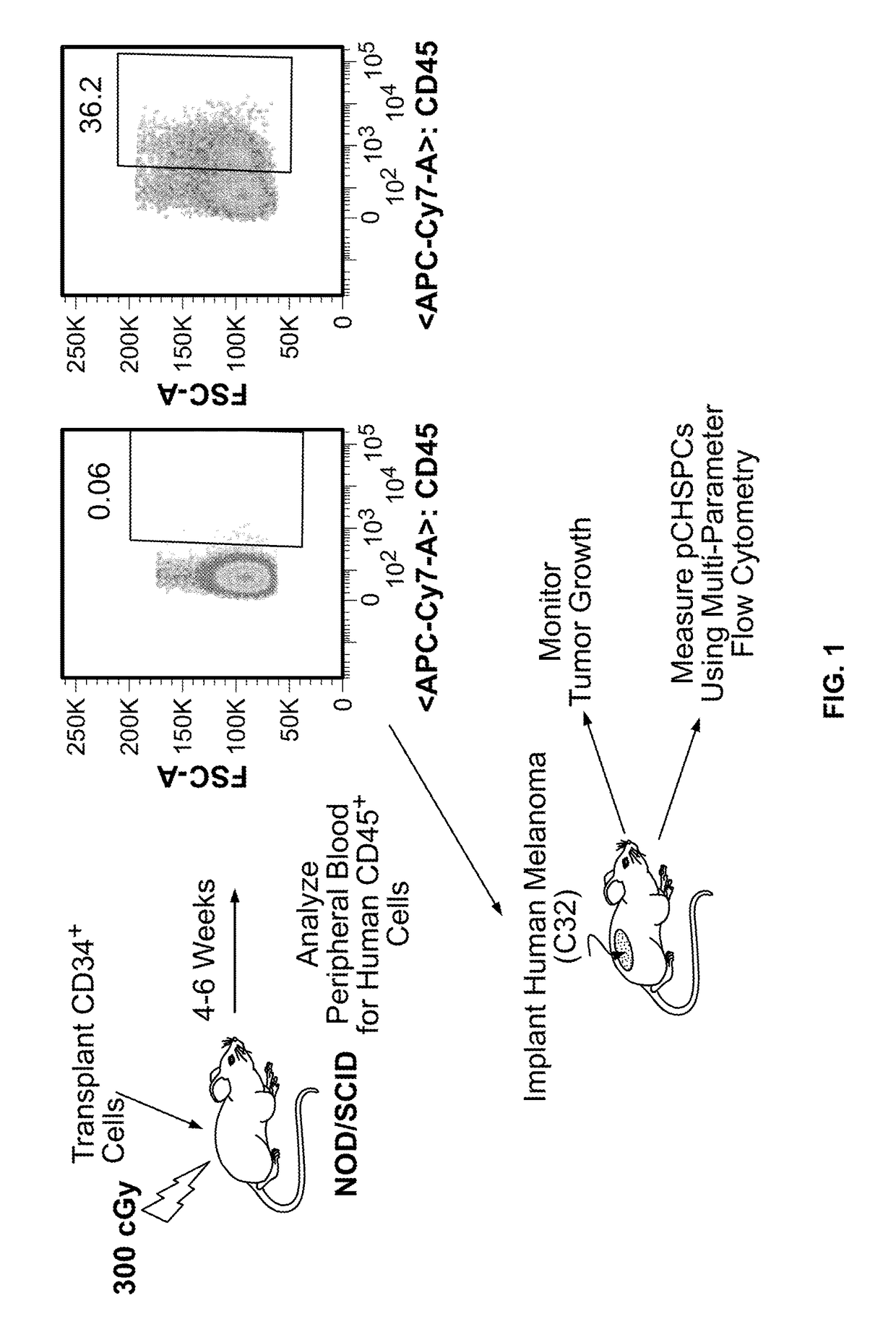
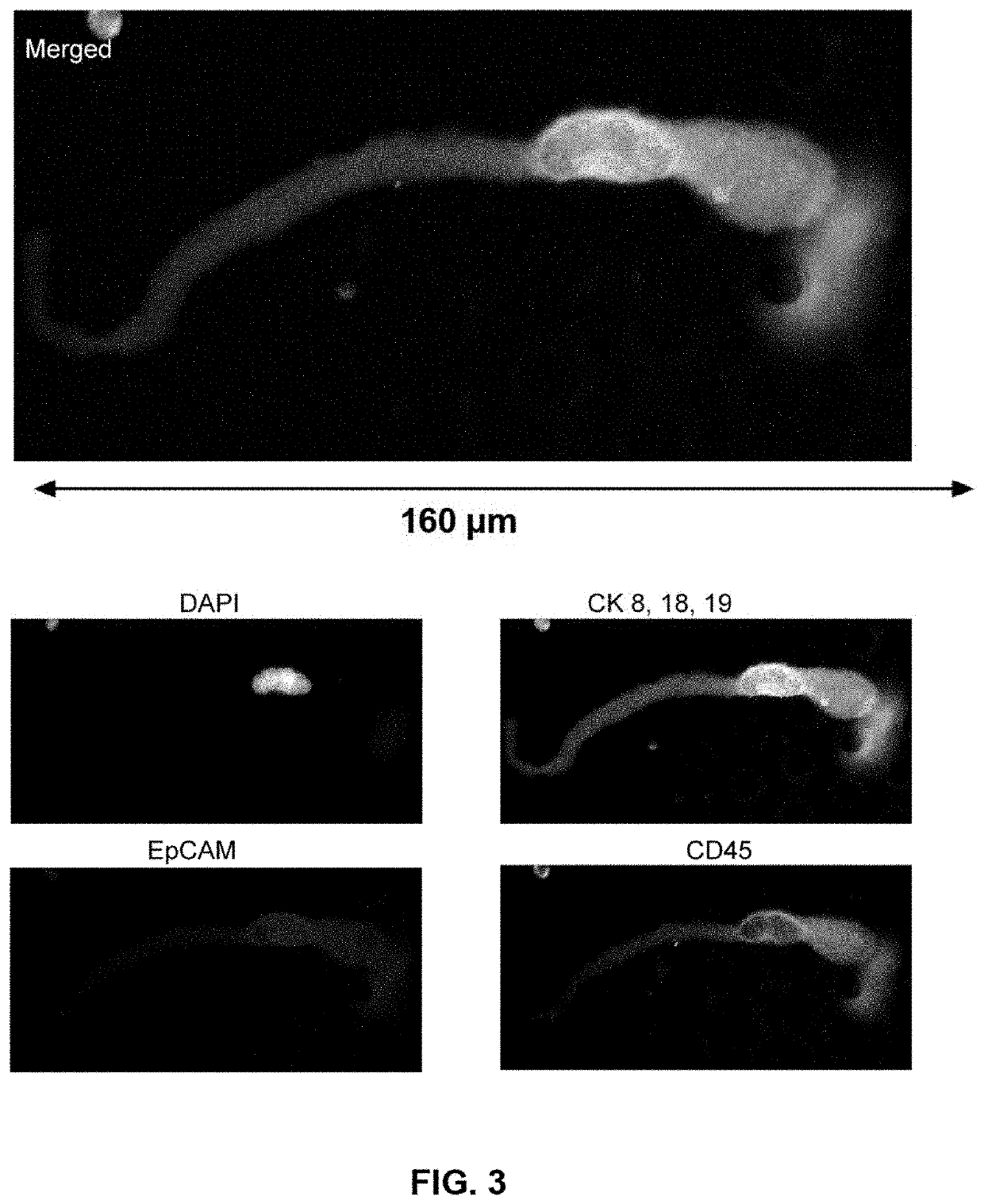
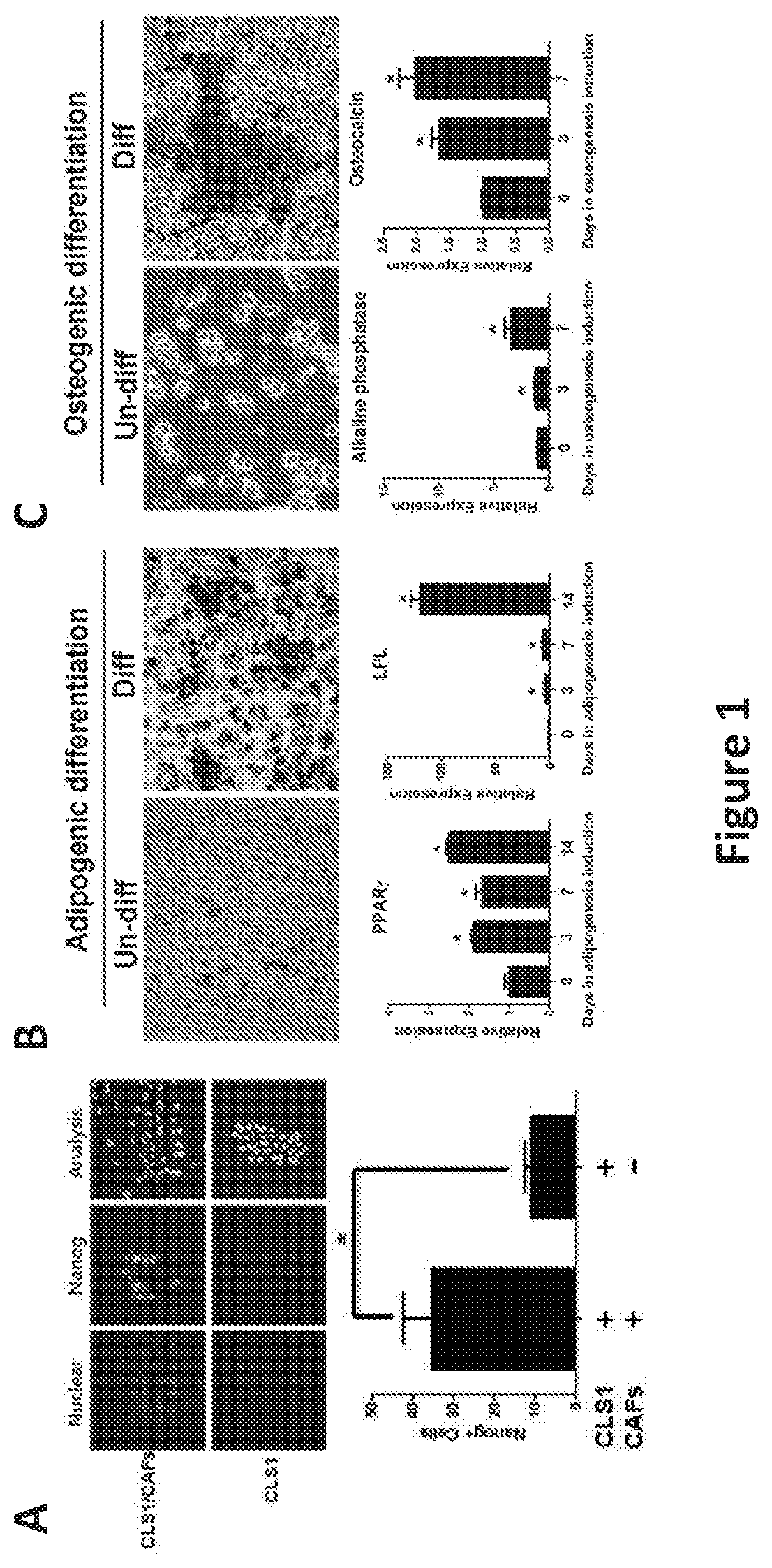
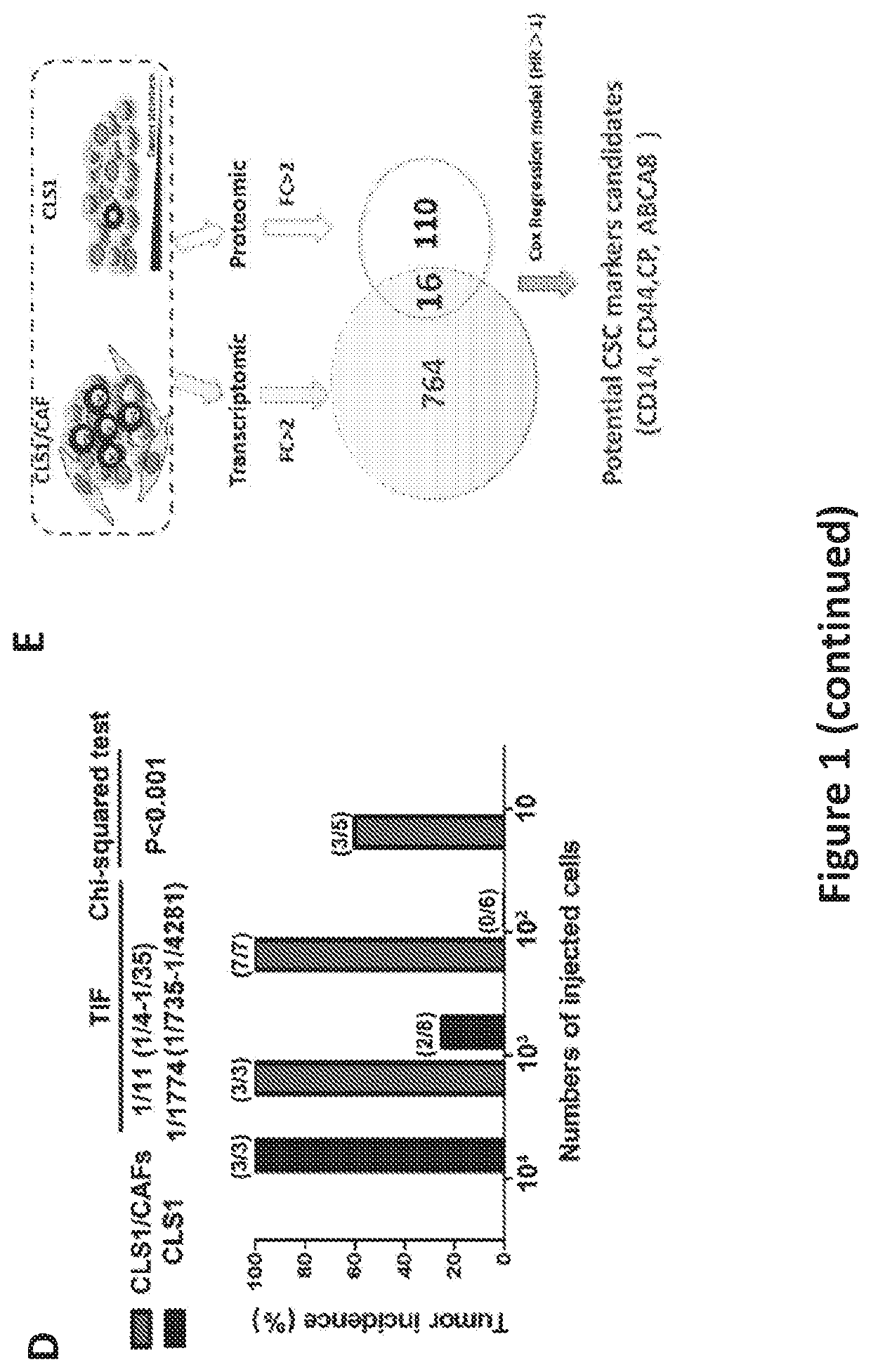
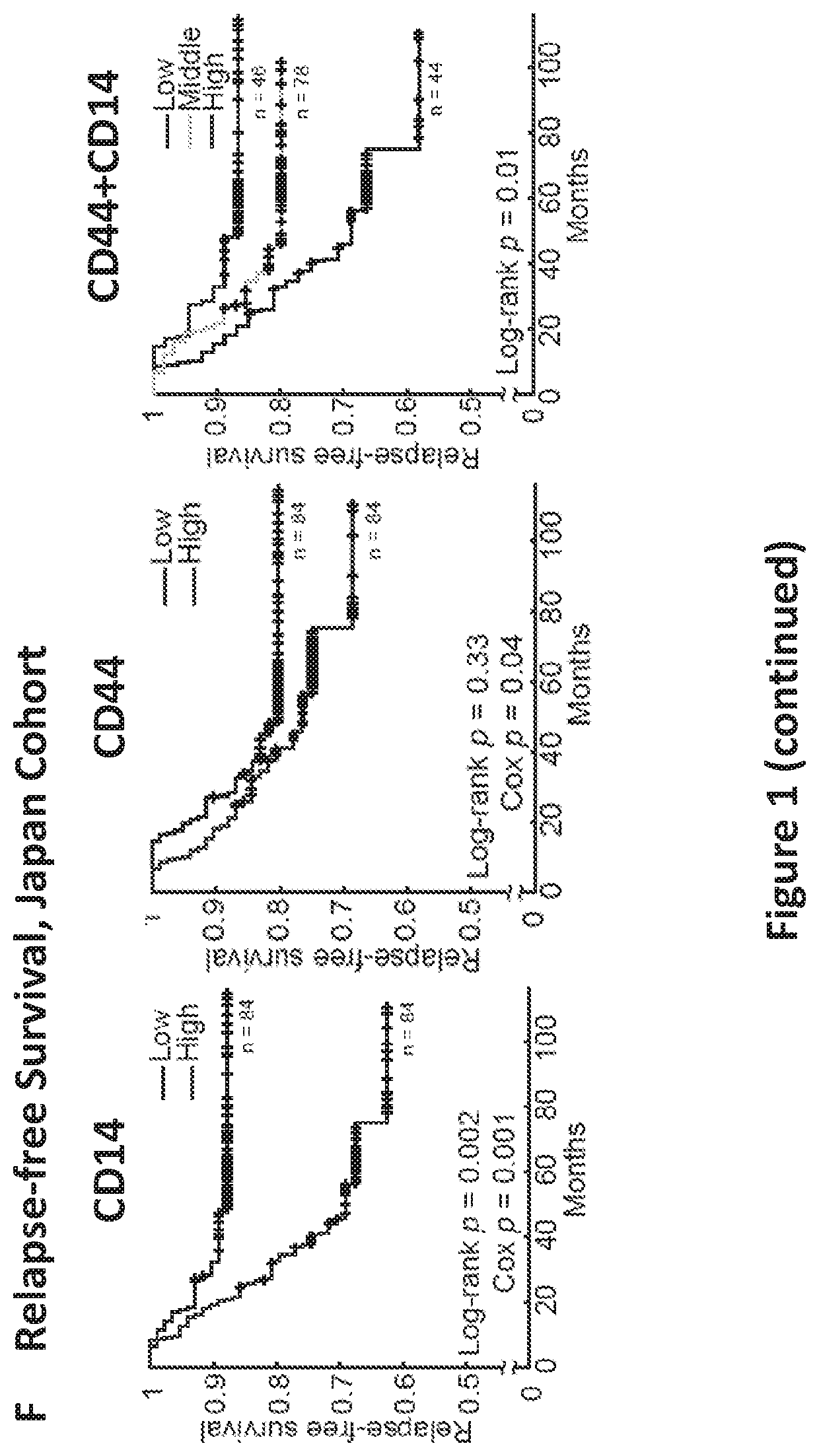
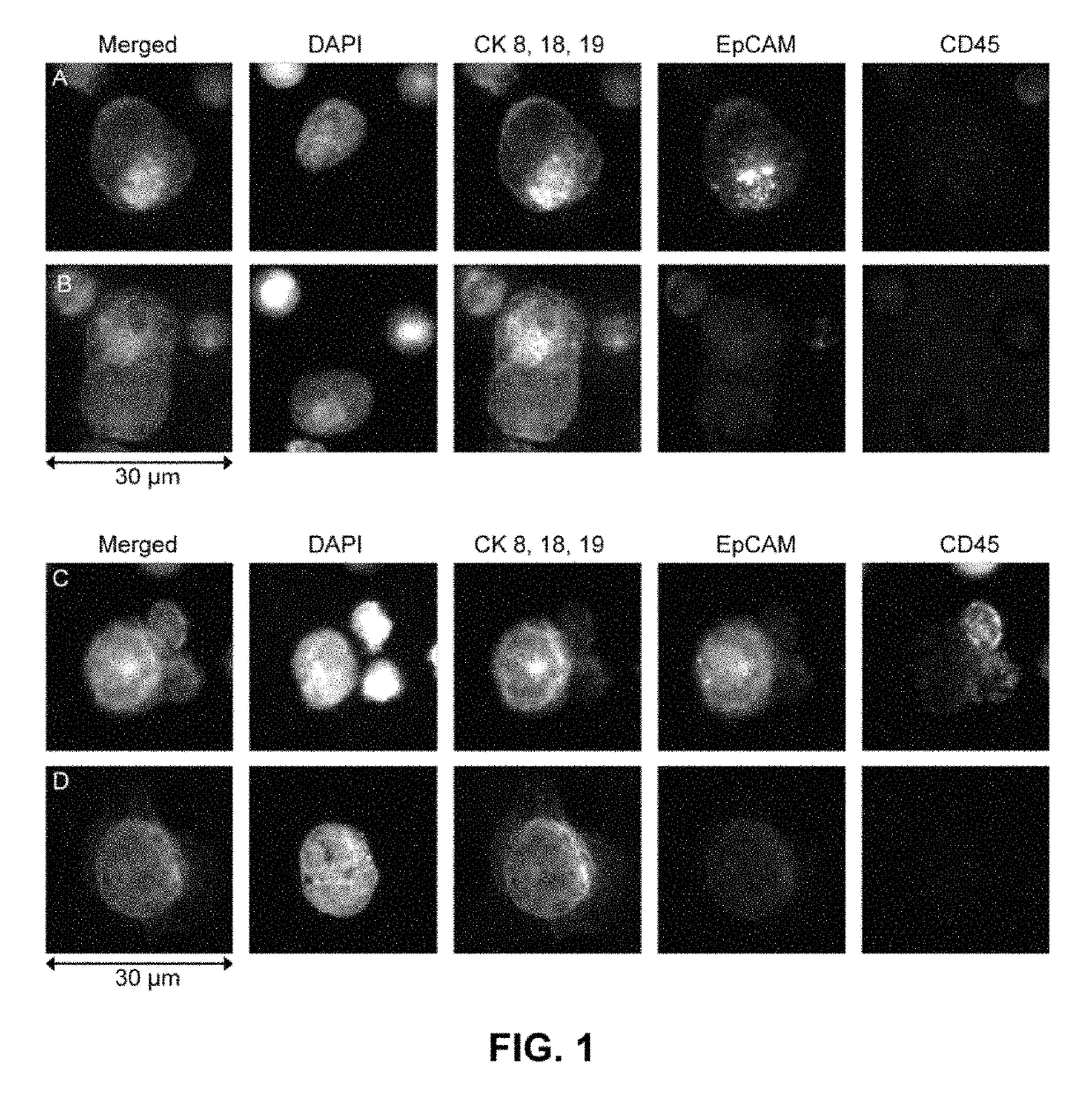
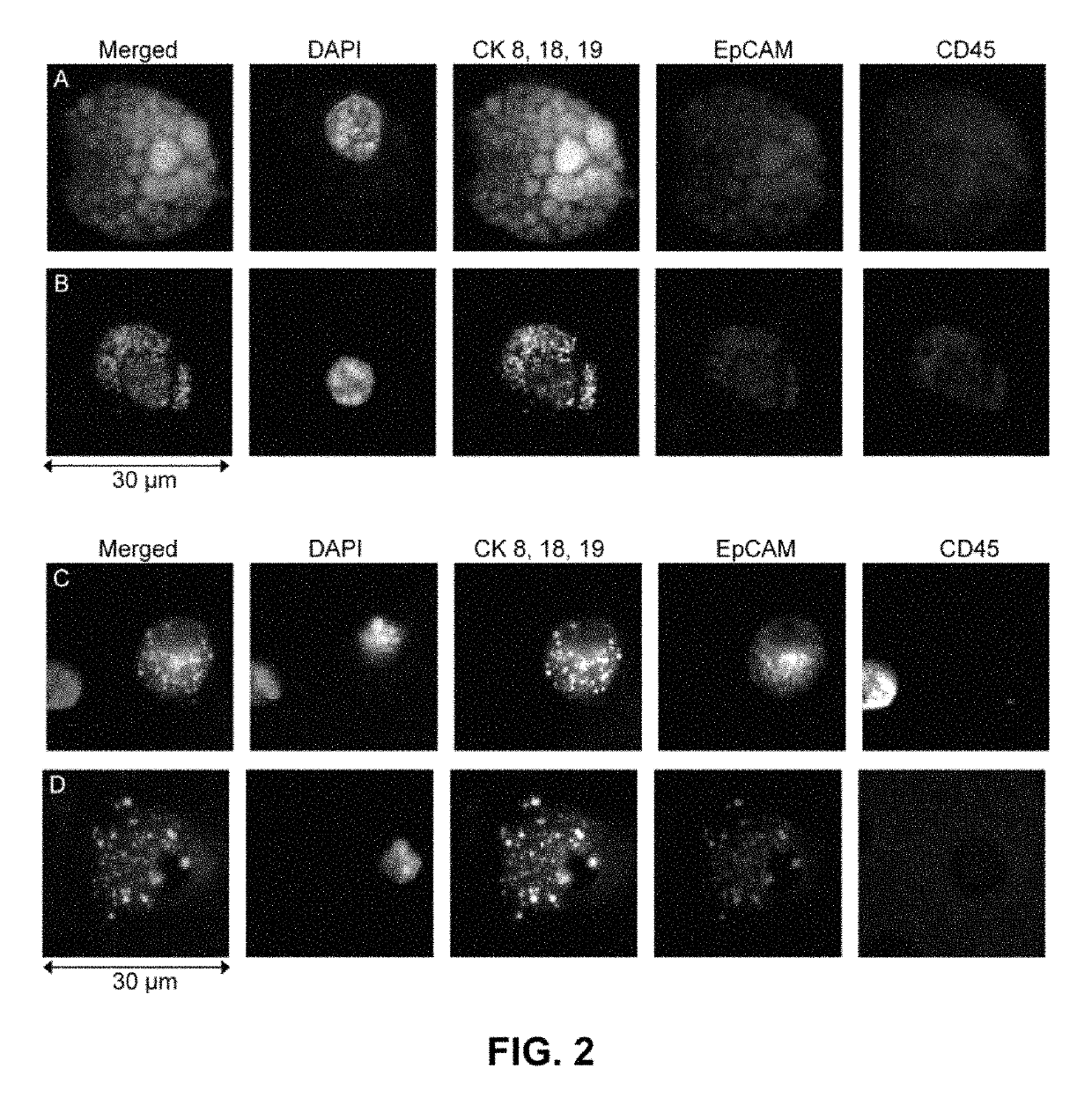
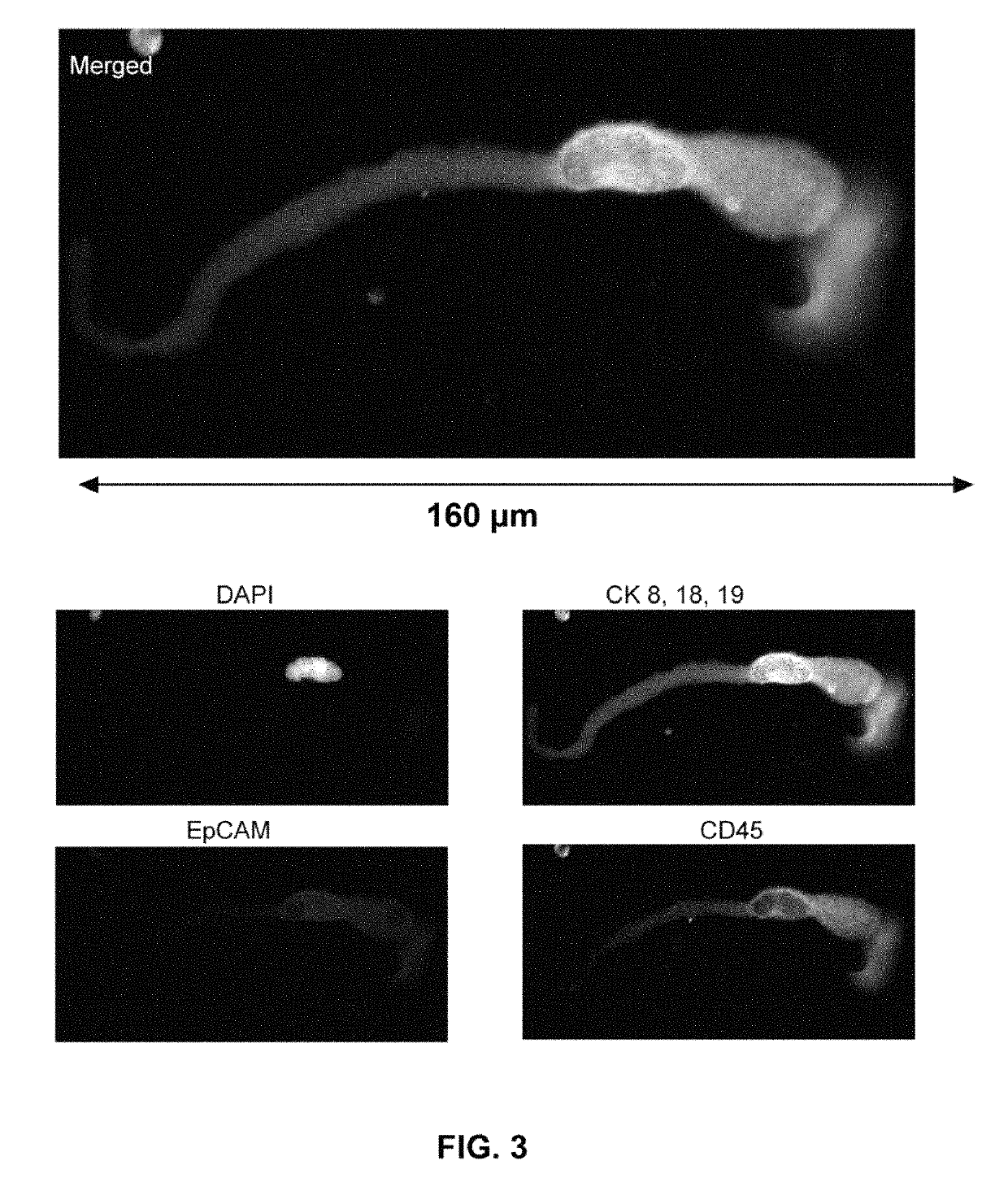
Patents
Literature
32 results about "Cellular biomarkers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
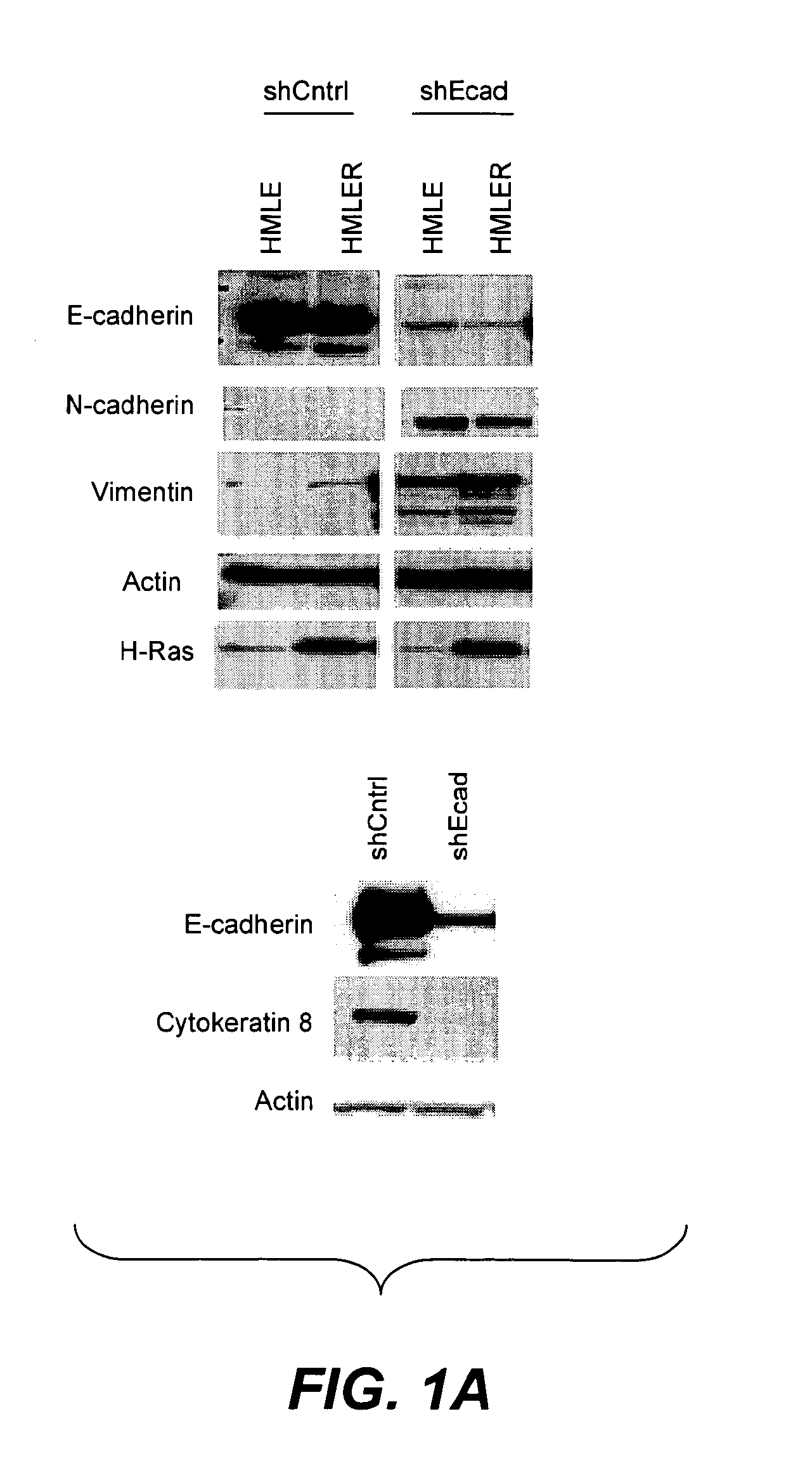
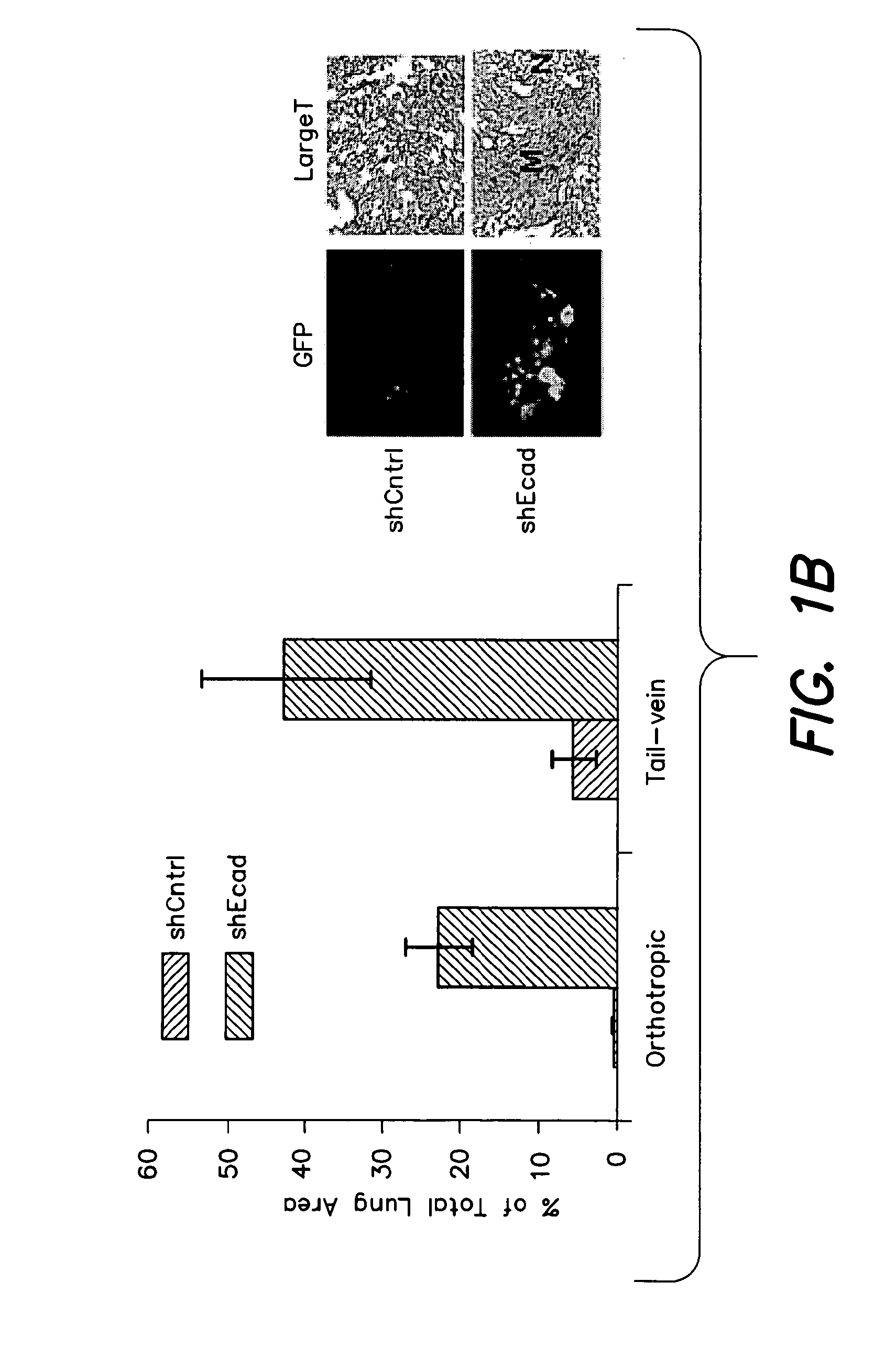
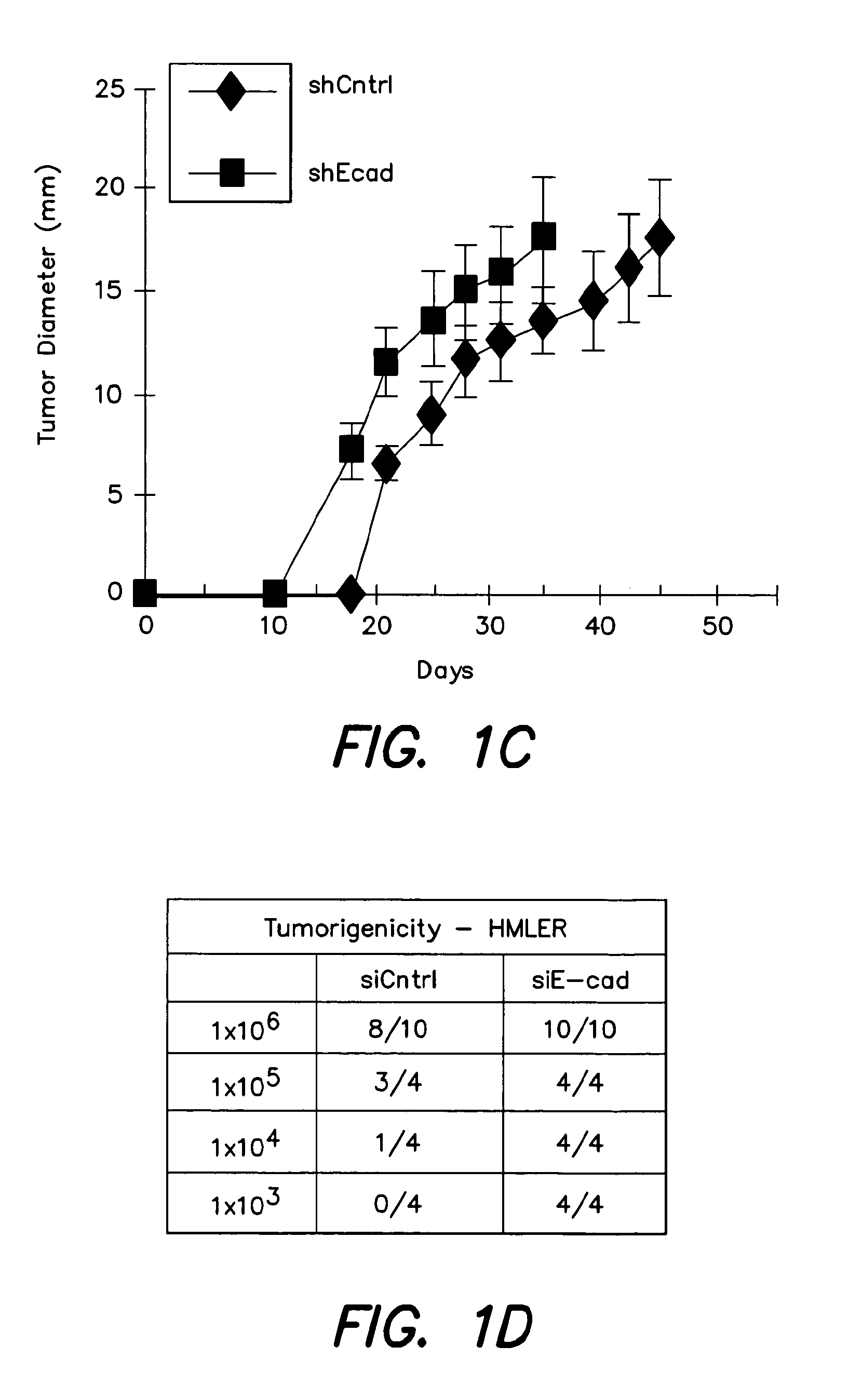
Diagnostic and prognosis methods for cancer stem cells
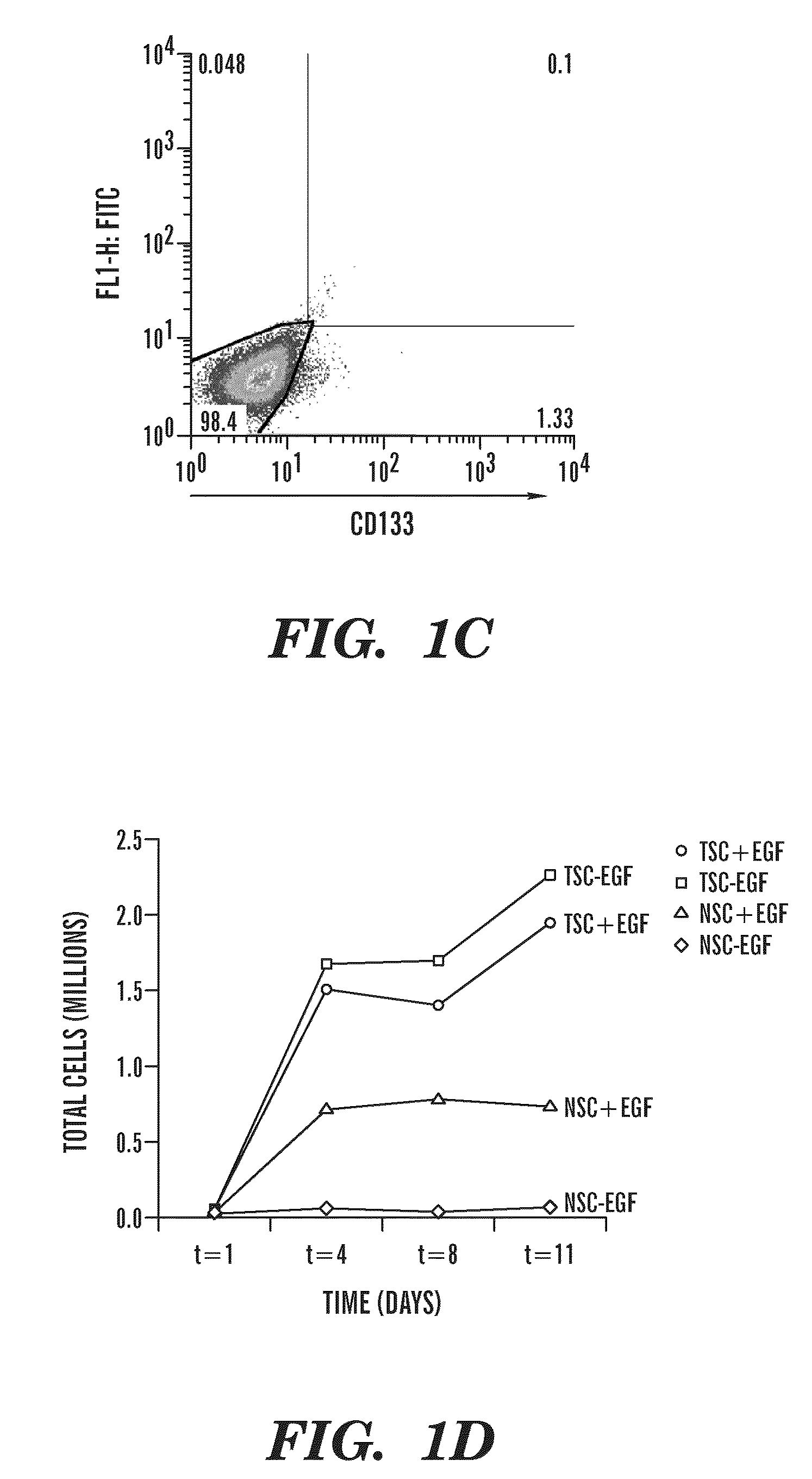
The present invention provides methods for diagnosis and prognosis of cancer stem cells (CSC) using expression analysis of one or more groups of genes, and a combination of expression analysis from a biological sample from the subject. The methods of the invention provide a method for accuracy detecting cancer stem cells in a population of cancer cells. The invention also provides methods and kits for diagnosis and prognosis of cancer in a subject using cancer stem cell biomarker expression analysis.
Owner:JACKSON LAB THE
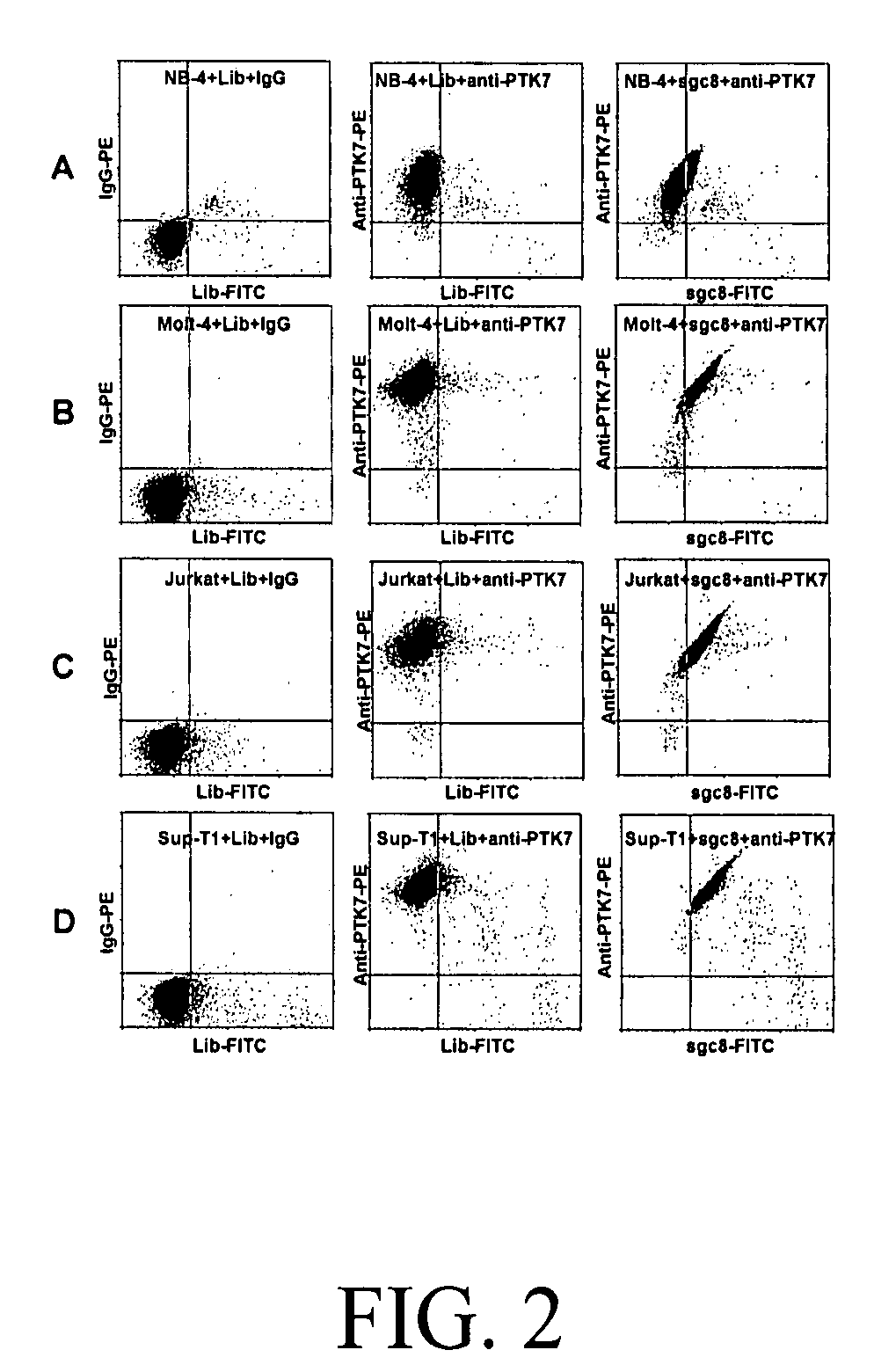
Aptamer-based methods for identifying cellular biomarkers
InactiveUS20090117549A1Easy to fixEasy to synthesizeElectrolysis componentsParticle separator tubesBiotin-streptavidin complexCancer cell
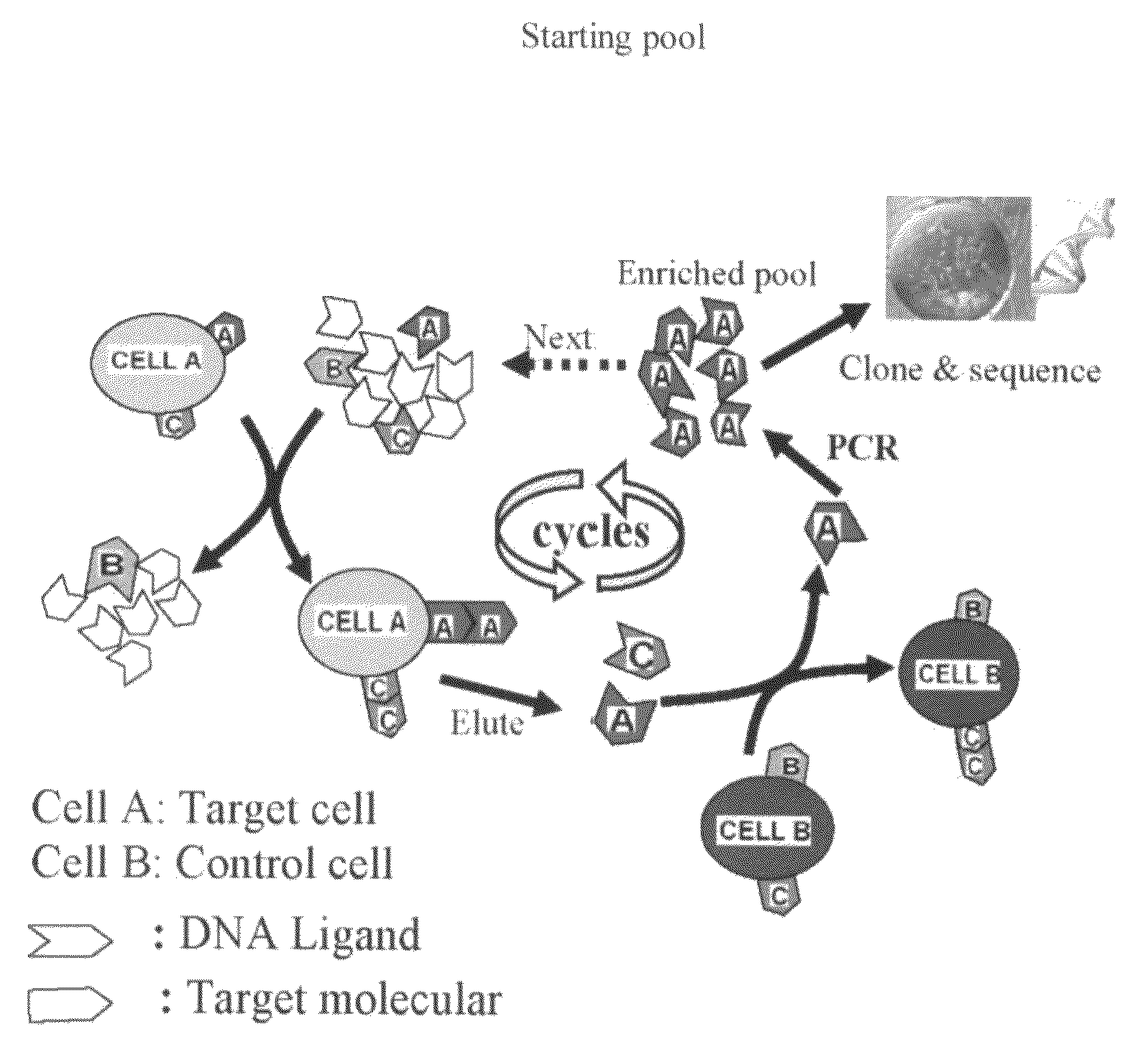
In this invention, a biomarker discovery method has been developed using specific biotin-labeled oligonucleotide ligands and magnetic streptavidin beads. In one embodiment, the oligonucleotide ligands are firstly generated by whole-cell based SELEX technique. Such ligands can recognize target cells with high affinity and specificity and can distinguish cells that are closely related to target cells even in patient samples. The targets of these oligonucleotide ligands are significant biomarkers for certain cells. These important biomarkers can be captured by forming complexes with biotin-labeled oligonucleotide ligands and collecting the complexes using magnetic streptavidin beads, whereupon the captured biomarkers are analyzed to identify the biomarkers. Analysis of biomarkers include HPLC-Mass Spectroscopy analysis, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, flow cytometry, and the like. The identified biomarkers can be used for pathological diagnosis and therapeutic applications. Using the disclosed methods, highly specific biomarkers of any kinds of cells, in particular cancer cells, can easily be identified without prior knowledge of the existence of such biomarkers.
Owner:TAN WEIHONG +1
Methods for identification and use of agents targeting cancer stem cells
The invention relates to methods for identifying compounds and compositions that target cancer stem cells. In some aspects, the invention relates to treatment methods that use compounds and compositions that specifically target cancer stem cells for inhibiting the growth and / or survival of cancer stem cells in a subject in need thereof. Other aspects of the invention relate to the use of cancer stem cell biomarkers in the selection of a treatment for inhibiting the growth and / or survival of cancer stem cells in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
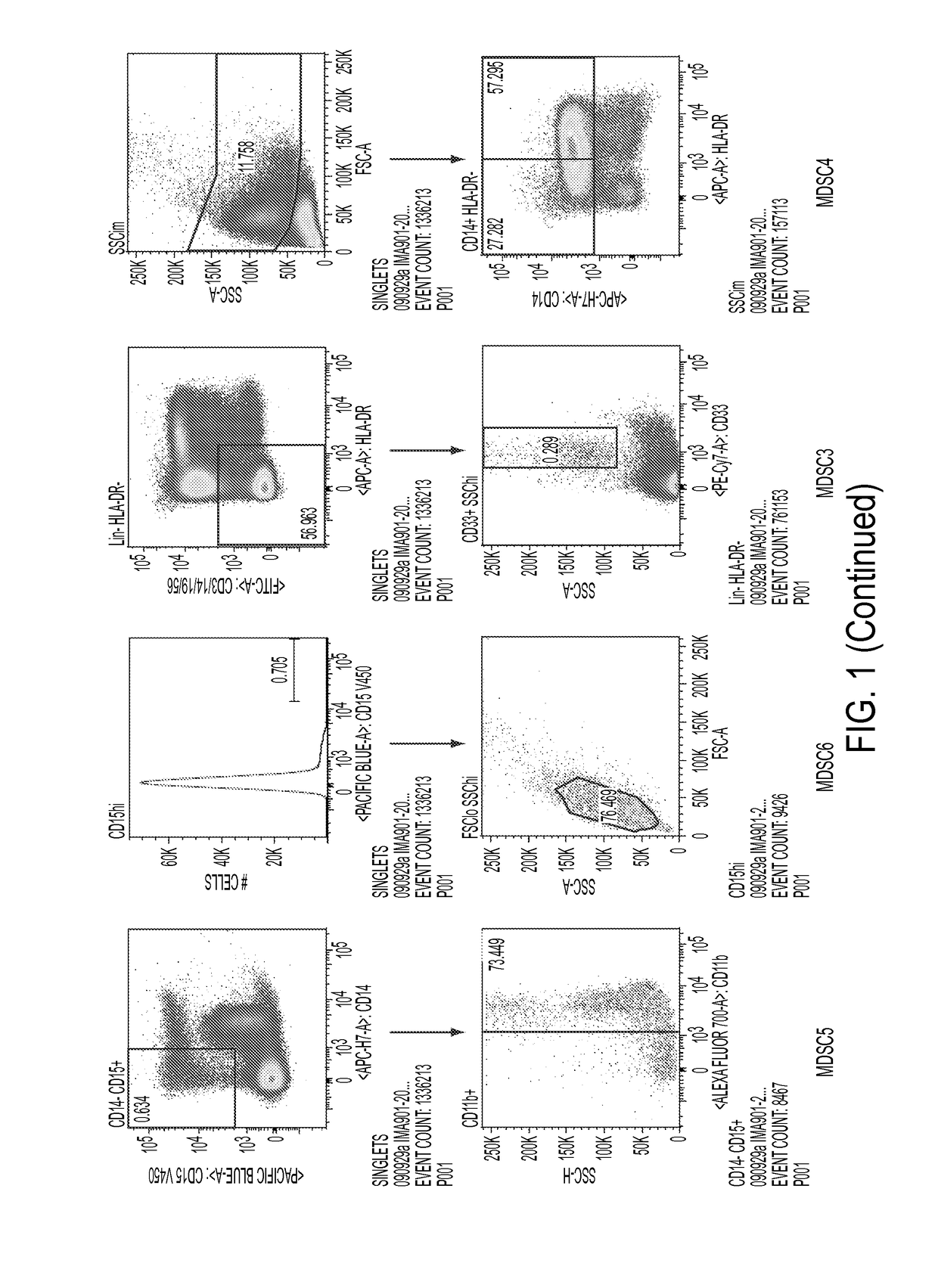
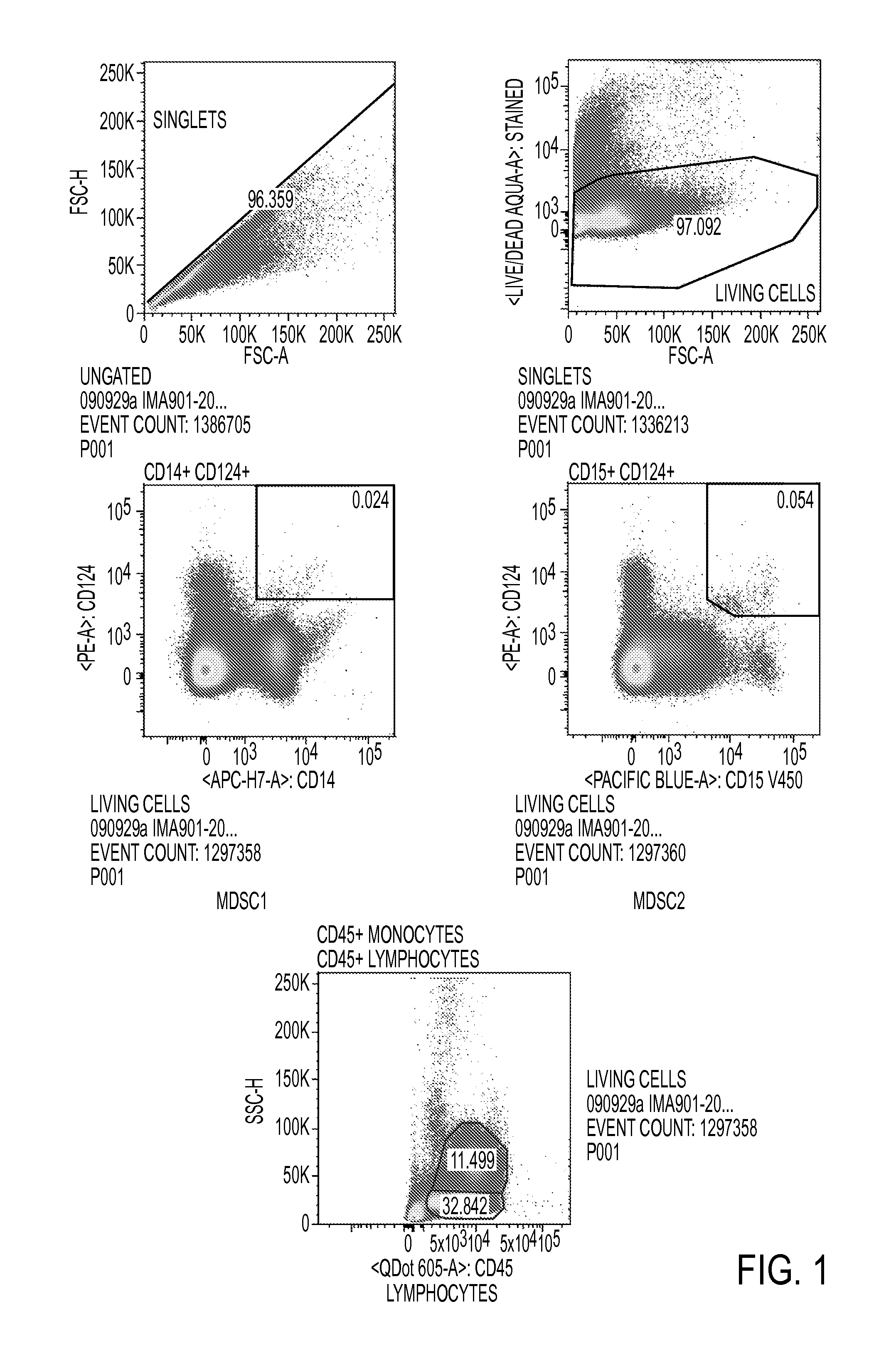
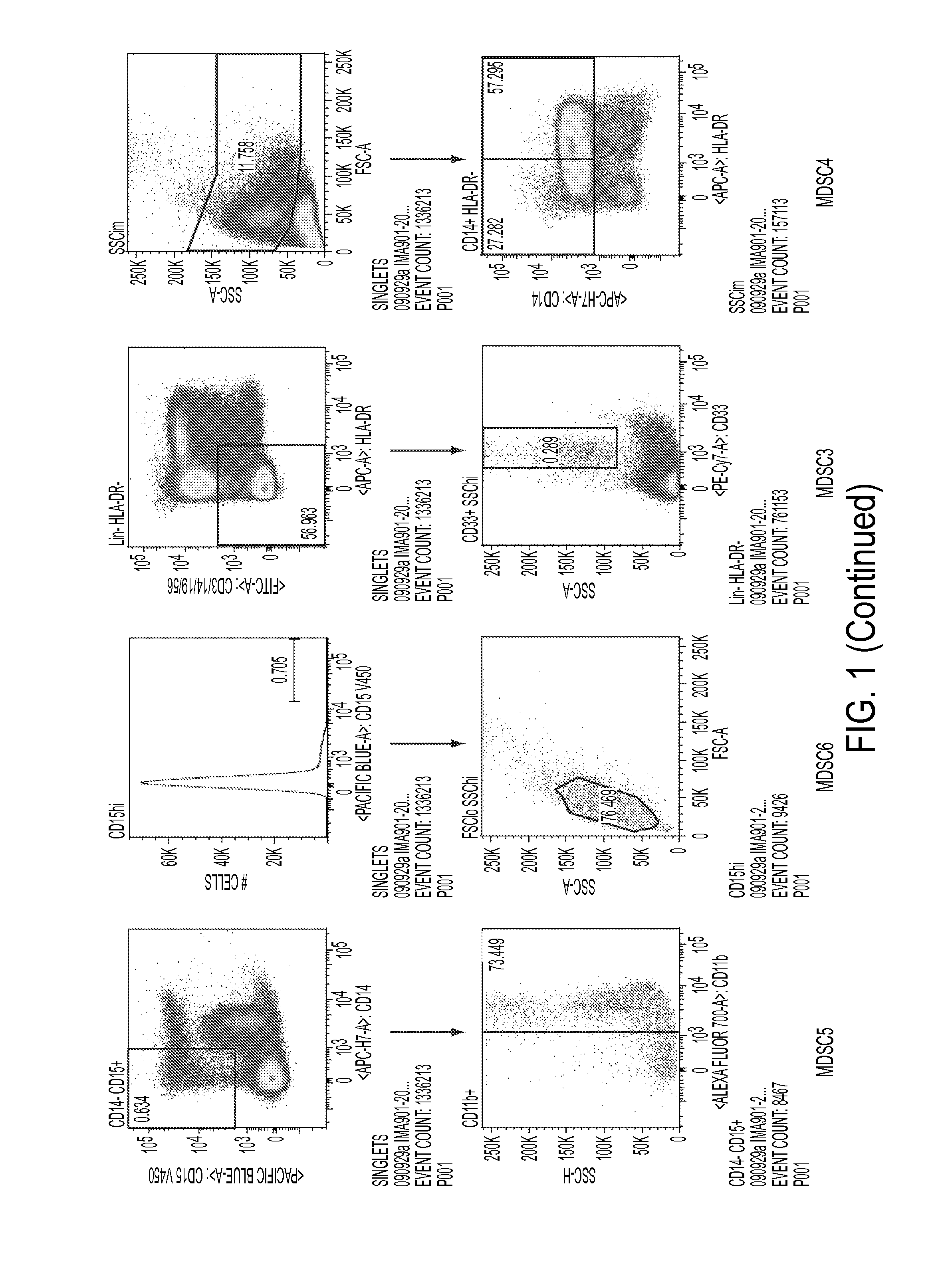
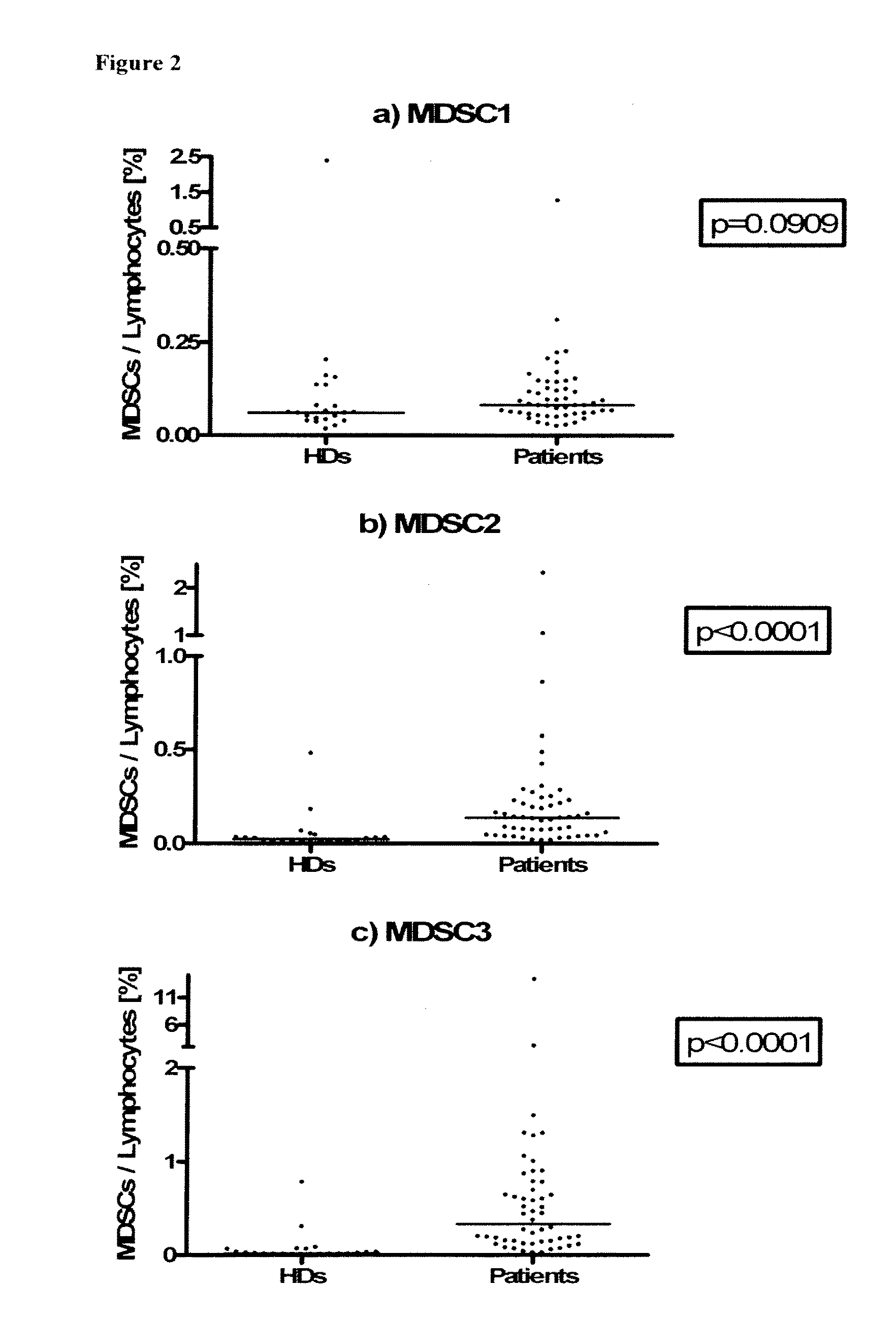
Use of myeloid cell biomarkers for the diagnosis of cancer
ActiveUS20120070461A1Diagnosing and prognosing cancerImprove the level ofBiological testingImmunological disordersCancers diagnosisTherapeutic effect
The present invention relates to the use of myeloid cell biomarkers for the differential diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) or colorectal cancer (CRC). The present invention furthermore relates to monitoring the effect of a treatment against renal cell carcinoma (RCC) or colorectal cancer (CRC), and establishing a prognosis of the outcome of the treatment of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) or colorectal cancer (CRC). The present invention furthermore relates to panels of cellular biomarkers for use in the above methods, in particular multicolor panels for measuring said biomarkers.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
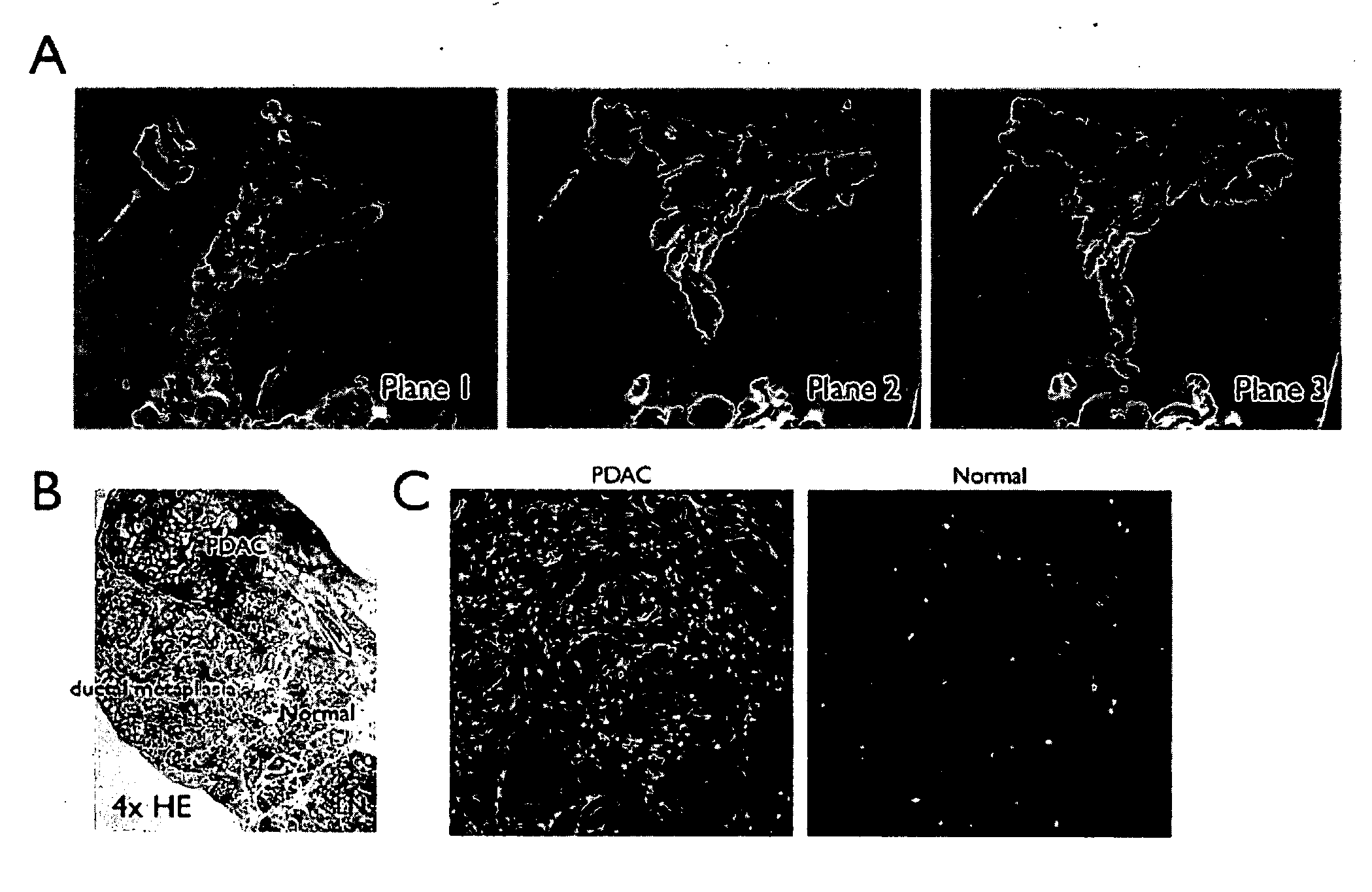
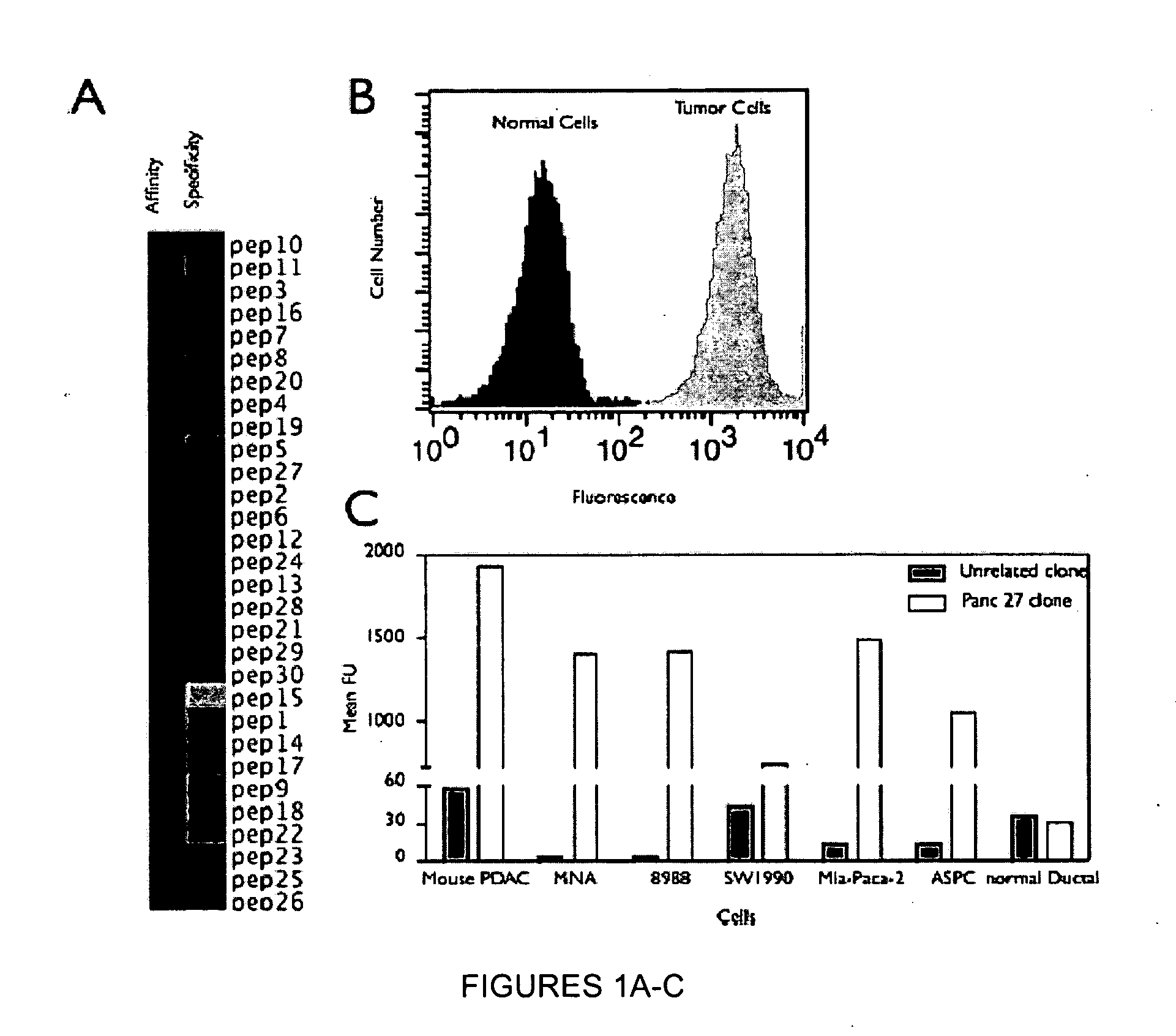
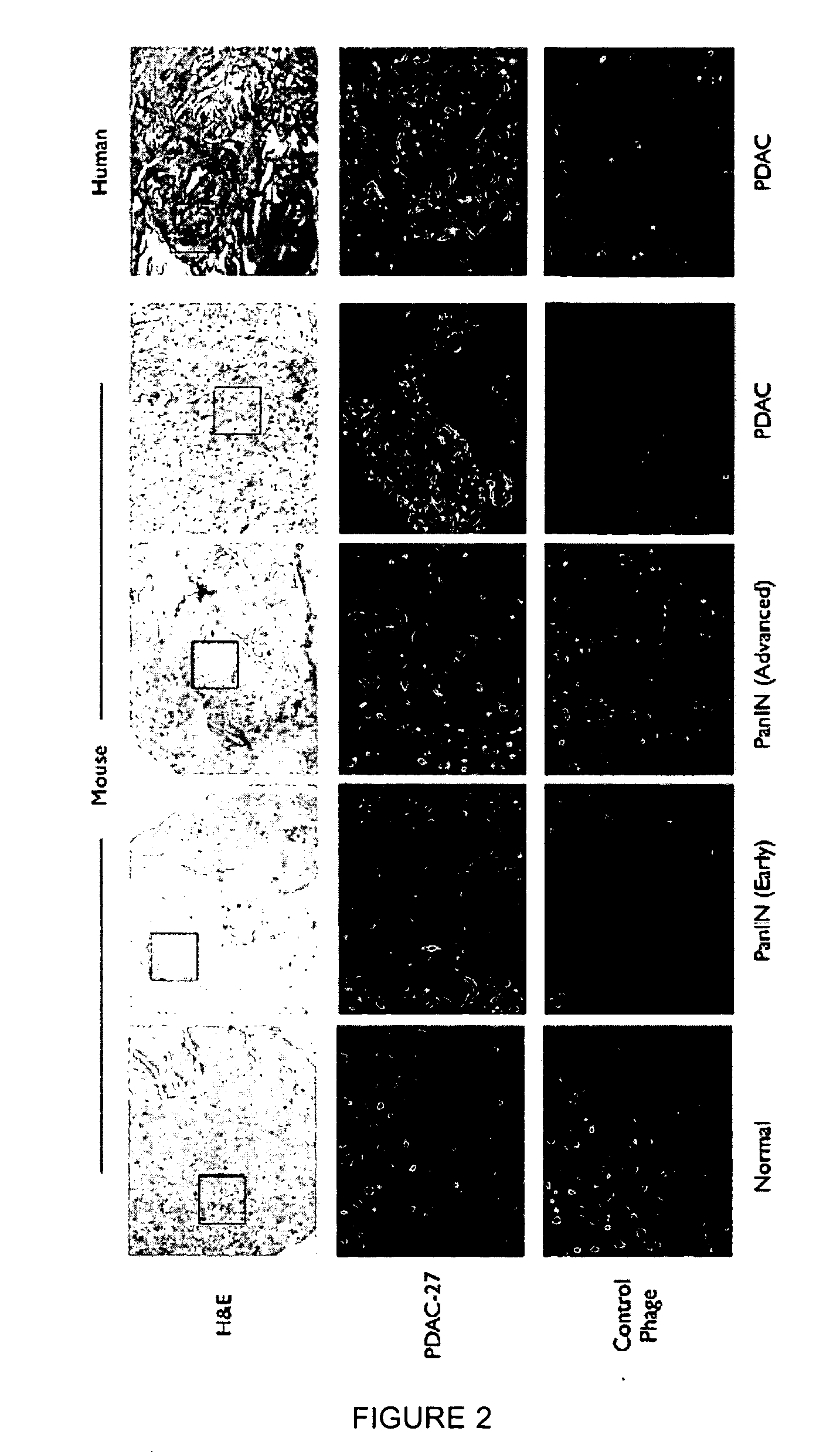
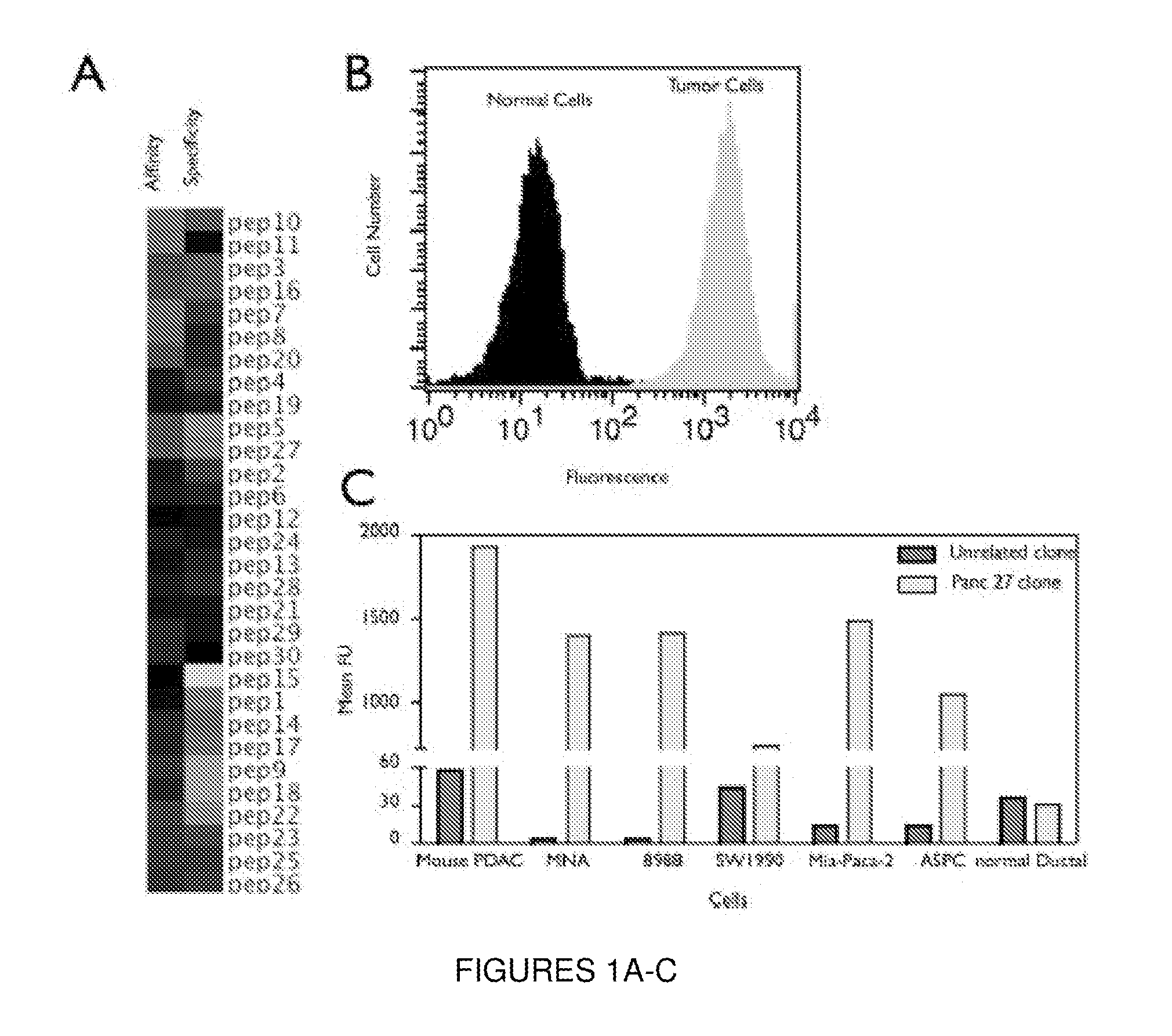
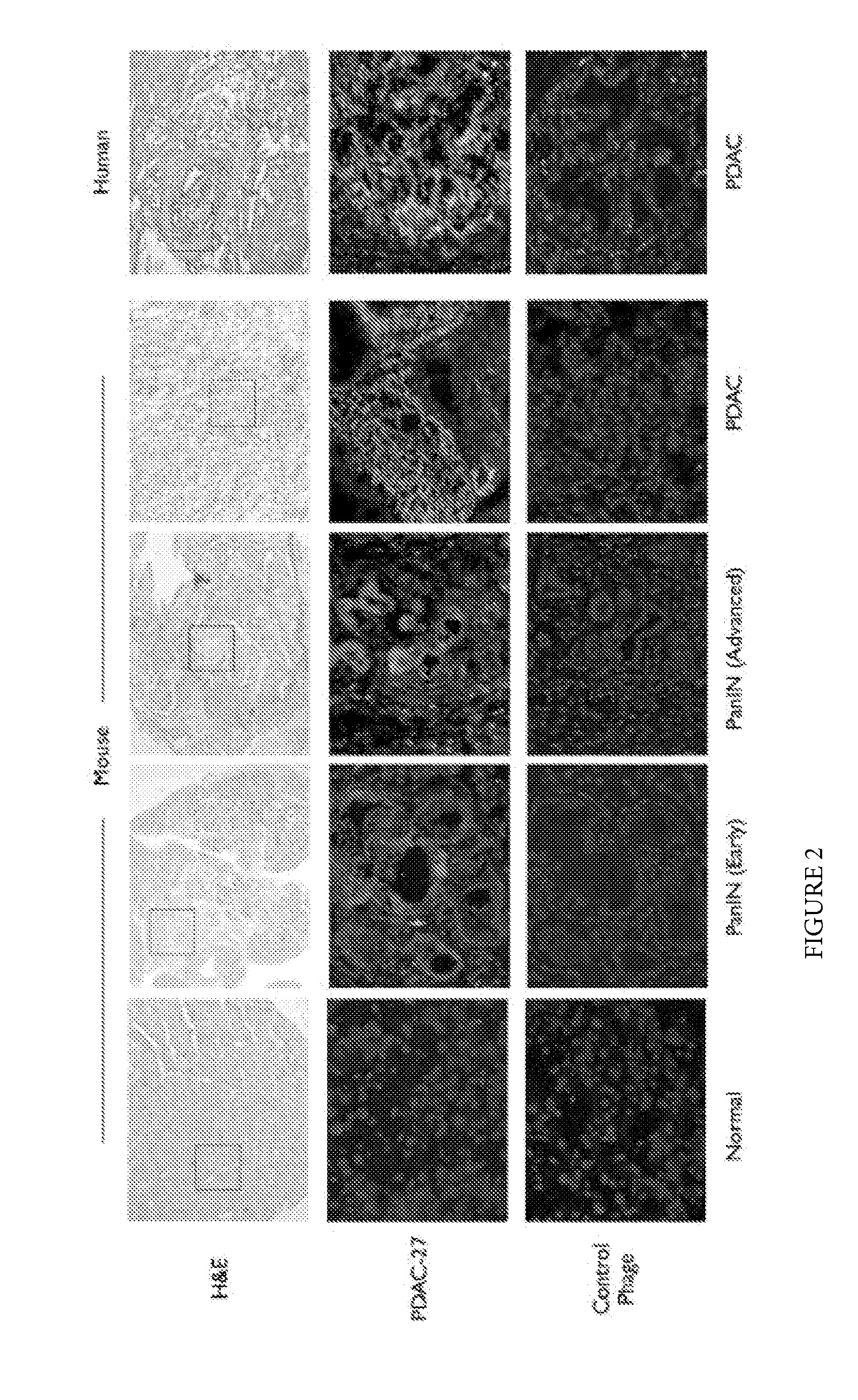
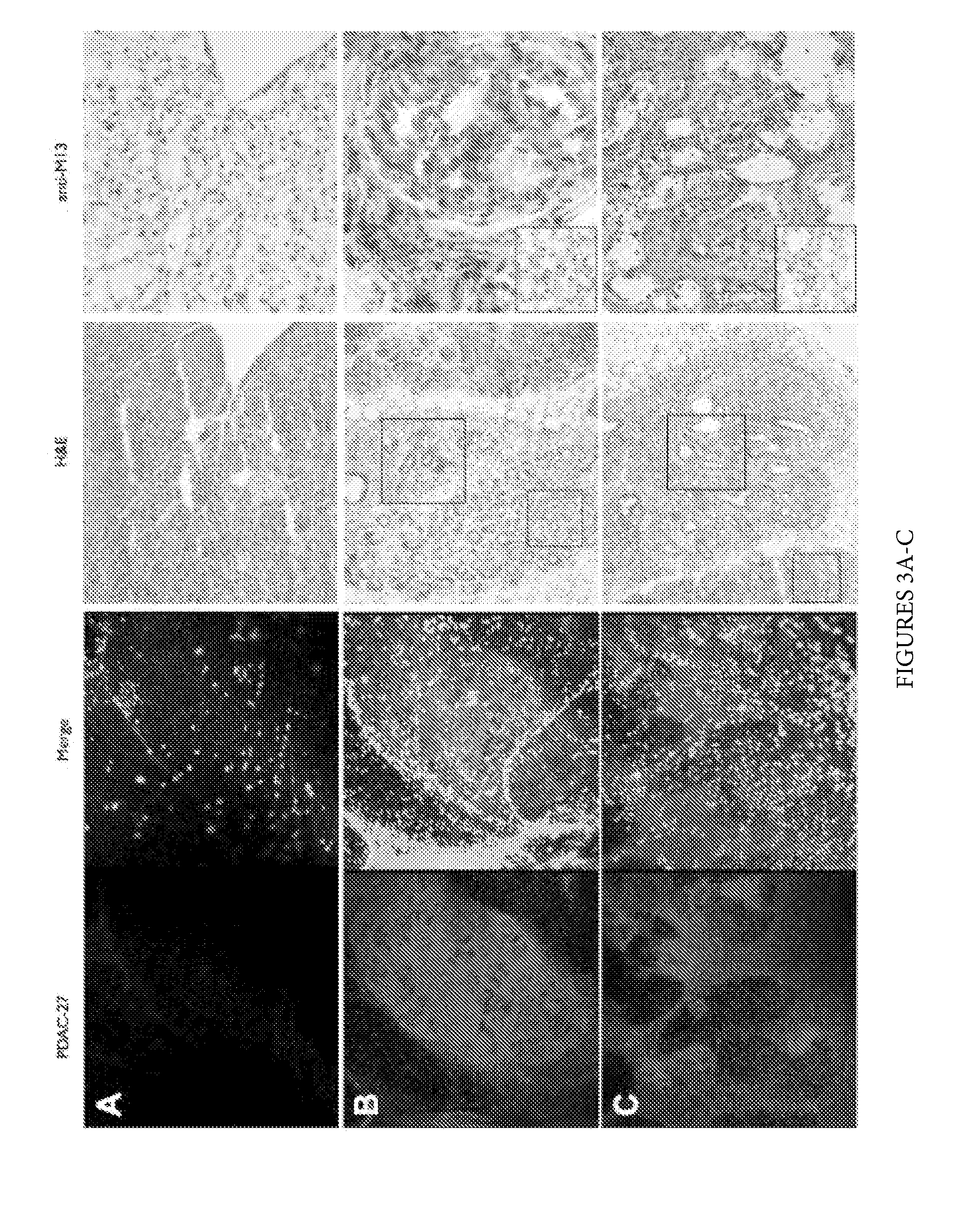
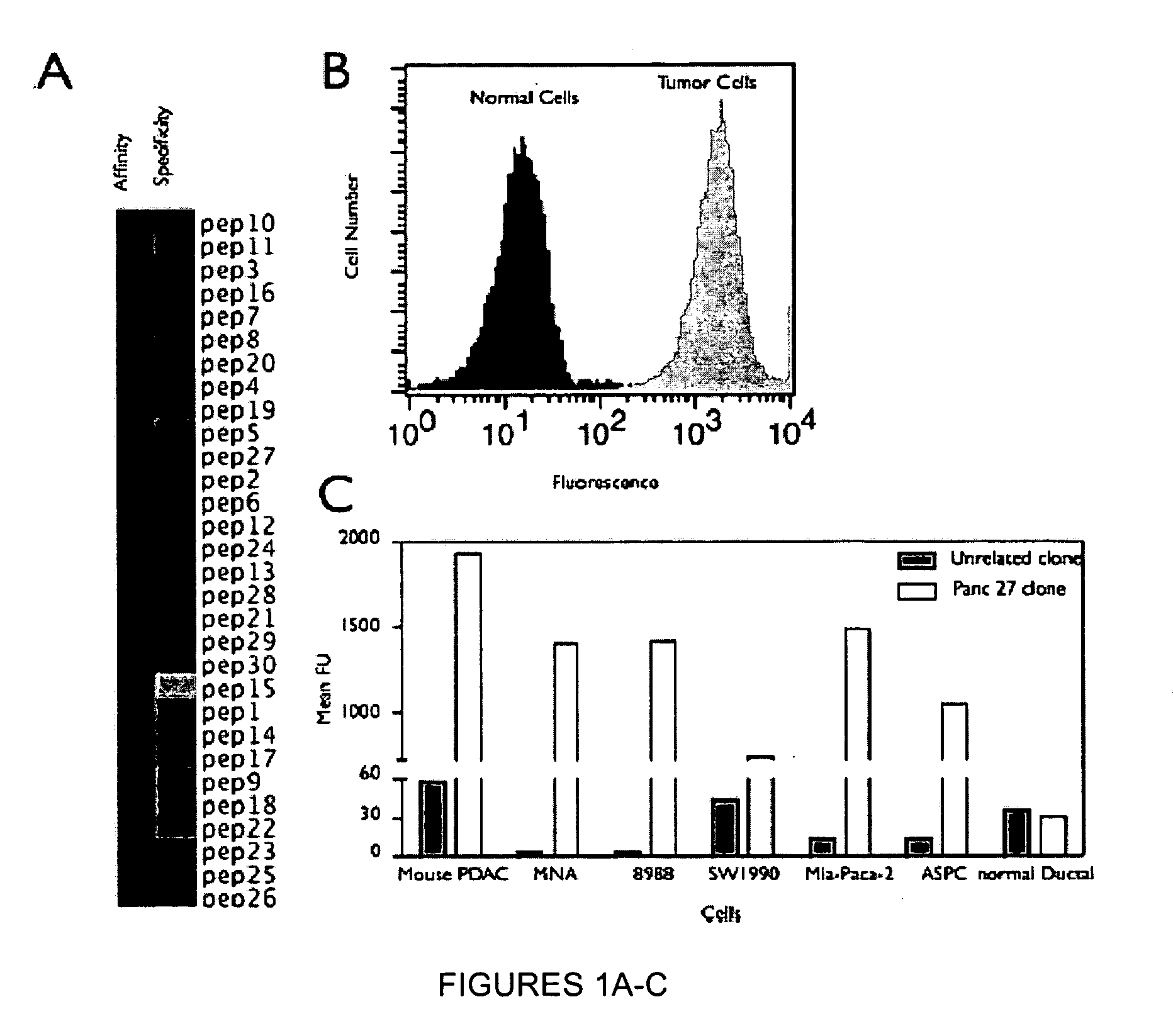
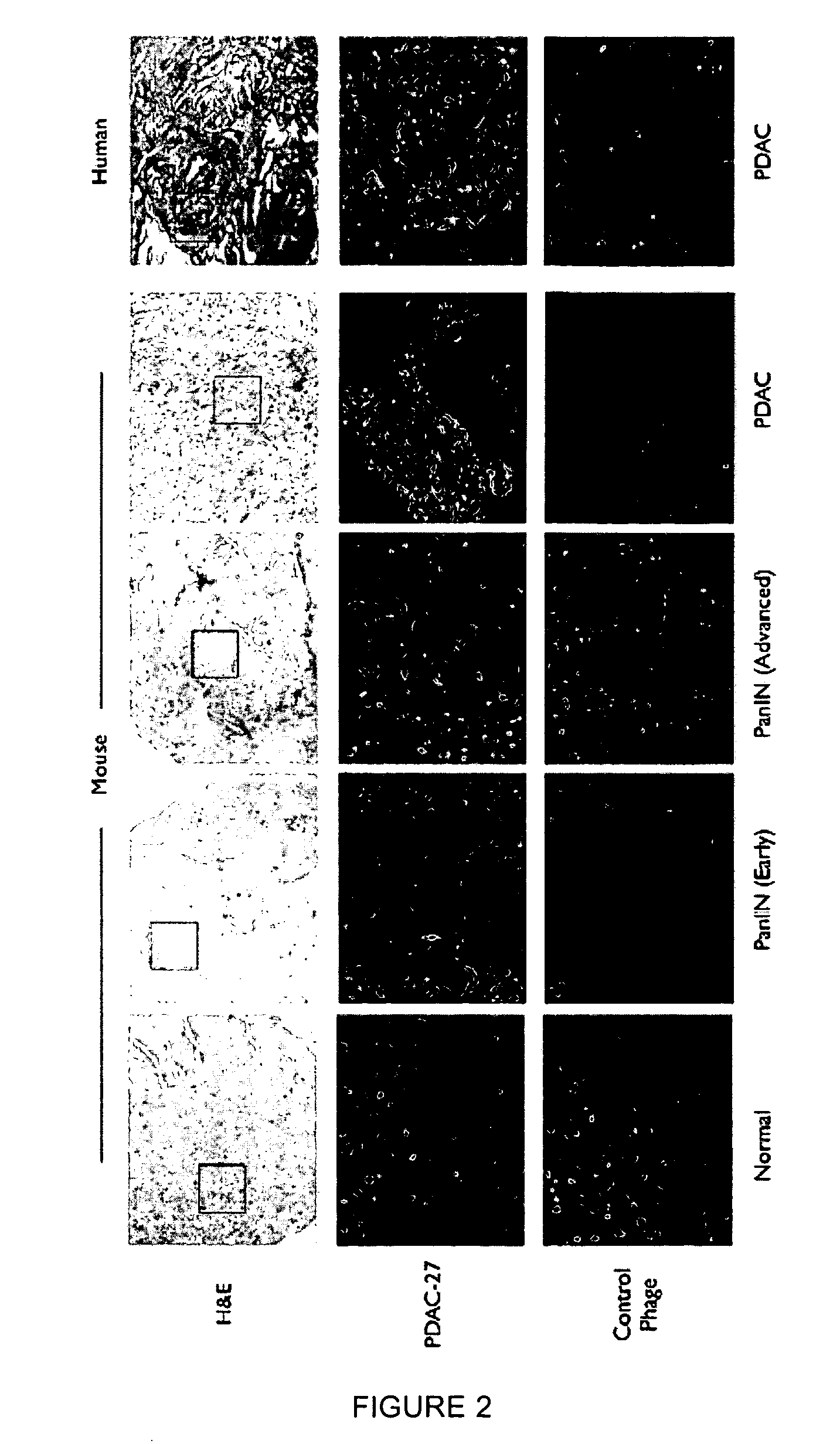
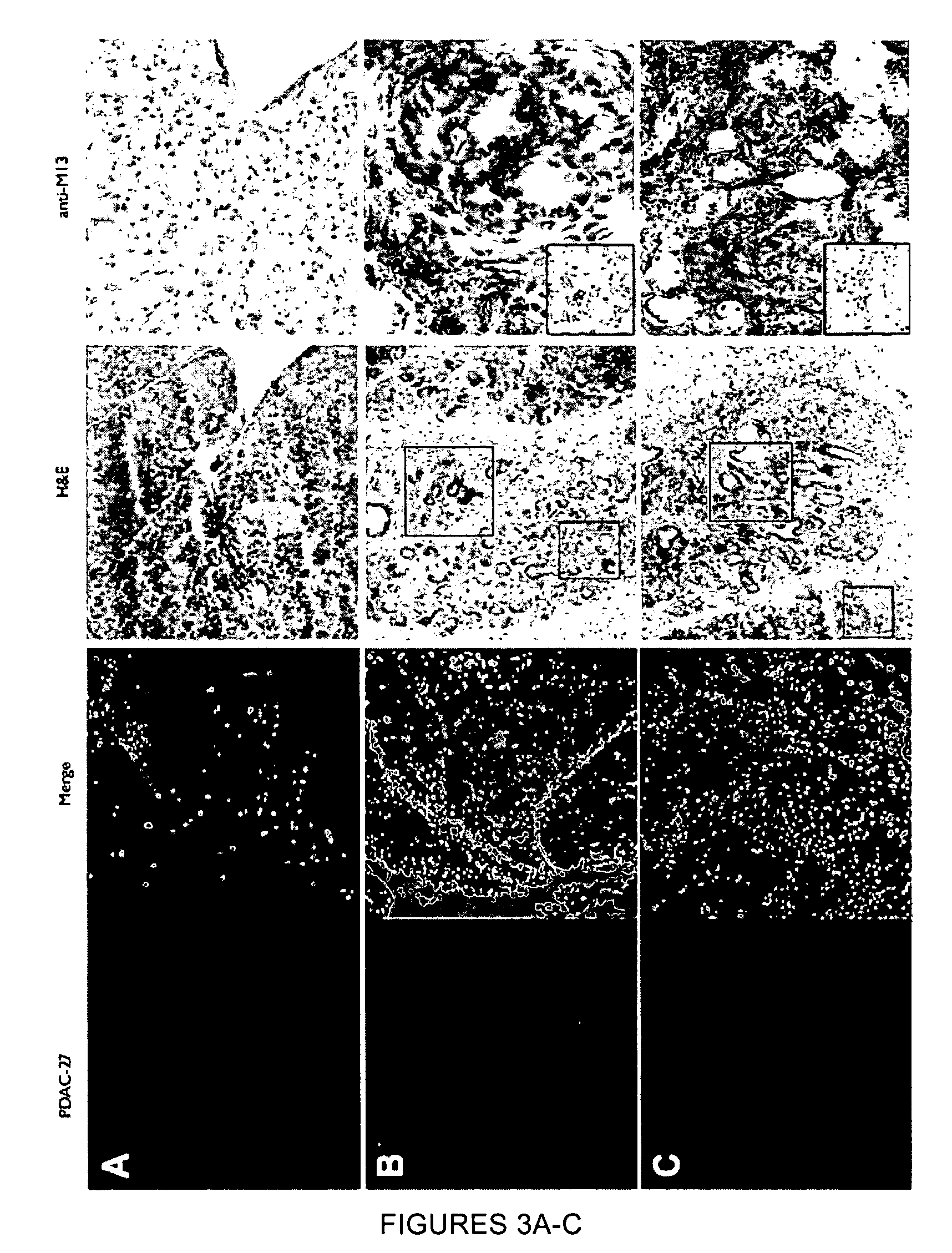
Plectin-1 targeted agents for detection and treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
ActiveUS20110182814A1Fast wayQuick identificationPeptide/protein ingredientsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsPancreas Ductal AdenocarcinomaCancer cell
Described herein are compositions and methods for cancer cell biomarkers, such as pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cell biomarkers, and binding molecules for diagnosis and treatment of cancer, e.g., PDAC. Methods of identifying “accessible” proteomes are disclosed for identifying cancer biomarkers, such as plectin-1, a PDAC biomarker. Additionally, imaging compositions are provided comprising magnetofluorescent nanoparticles conjugated to peptide ligands for identifying PDACs.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Plectin-1 Targeted Agents for Detection and Treatment of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
ActiveUS20150151010A1Fast wayQuick identificationPeptide/protein ingredientsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsCancer cellTumor Biomarkers
Described herein are compositions and methods for cancer cell biomarkers, such as pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cell biomarkers, and binding molecules for diagnosis and treatment of cancer, e.g., PDAC. Methods of identifying “accessible” proteomes are disclosed for identifying cancer biomarkers, such as plectin-1, a PDAC biomarker. Additionally, imaging compositions are provided comprising magnetofluorescent nanoparticles conjugated to peptide ligands for identifying PDACs.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Cellular Biomarker Antioxidant Assay and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080312128A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAlternative methods
The invention encompasses cell-based systems comprising biomarkers that respond to oxidative stress (OS) in a quantitative manner, and methods of use thereof. The systems are useful for screening, identifying and testing antioxidant agents, combinations, and formulations thereof for preventing, treating, or reducing symptoms of conditions associated with oxidative damage to cells. The cell-based systems are useful for identifying effective new antioxidant agents and for optimizing antioxidant formulations for targeted therapeutic applications. One cell-based system utilizes RPE cells of the eye for identifying and optimizing antioxidant compositions effective for treatment of age-related conditions such as macular degeneration. The cell-based systems provide a convenient, inexpensive and physiologically relevant in vitro alternative to human population-based methods for testing efficacy of nutritional and pharmaceutical compositions comprising antioxidants. The invention further encompasses nutritional or pharmaceutical compositions targeting particular diseases such as AMD, formulated using methods as disclosed herein.
Owner:CHAUM EDWARD +1
Aptamer-based methods for identifying cellular biomarkers
InactiveUS20110124015A1Easy to fixEasy to synthesizeElectrolysis componentsParticle separator tubesBiotin-streptavidin complexAptamer
Owner:TAN WEIHONG +1
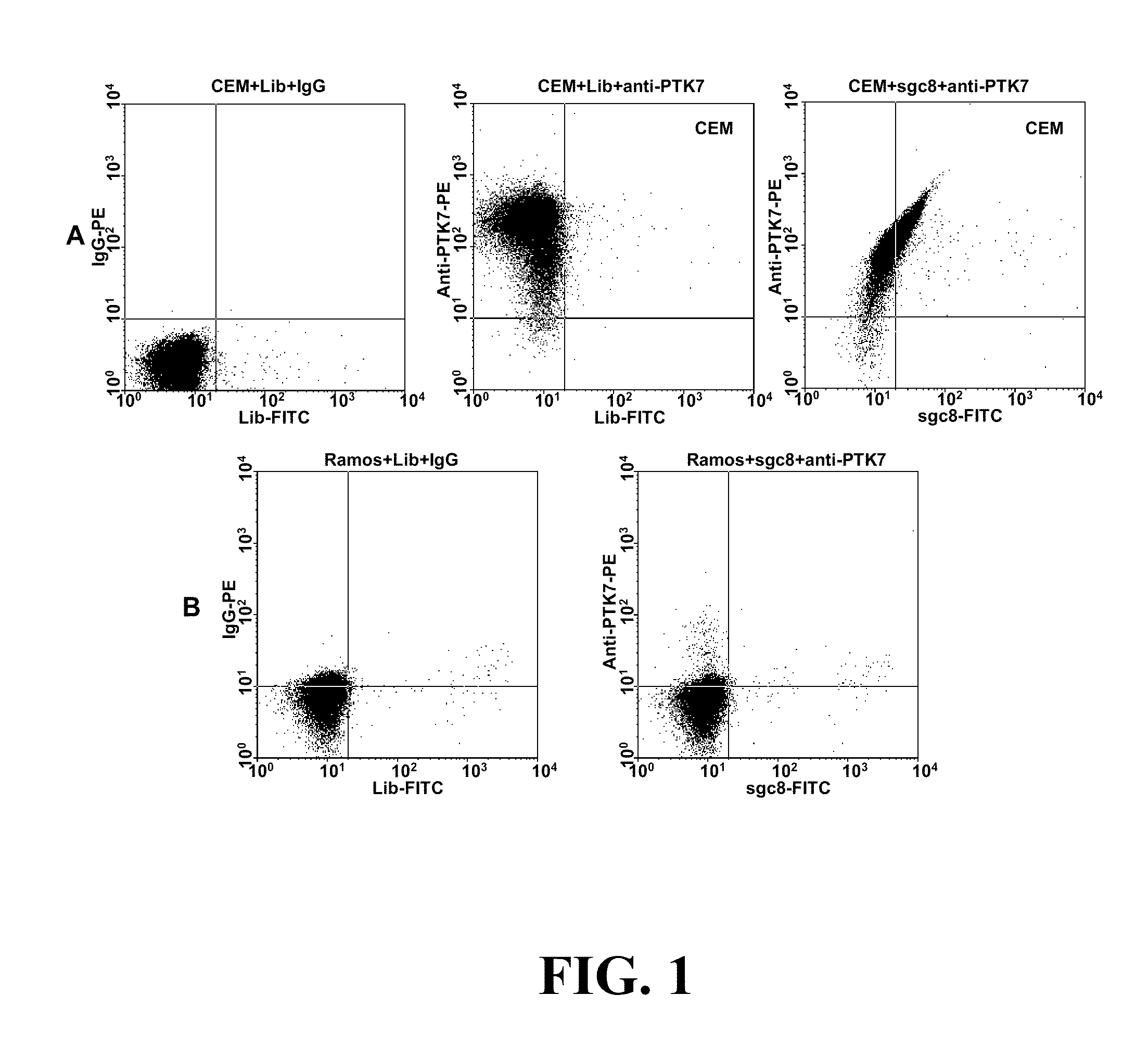
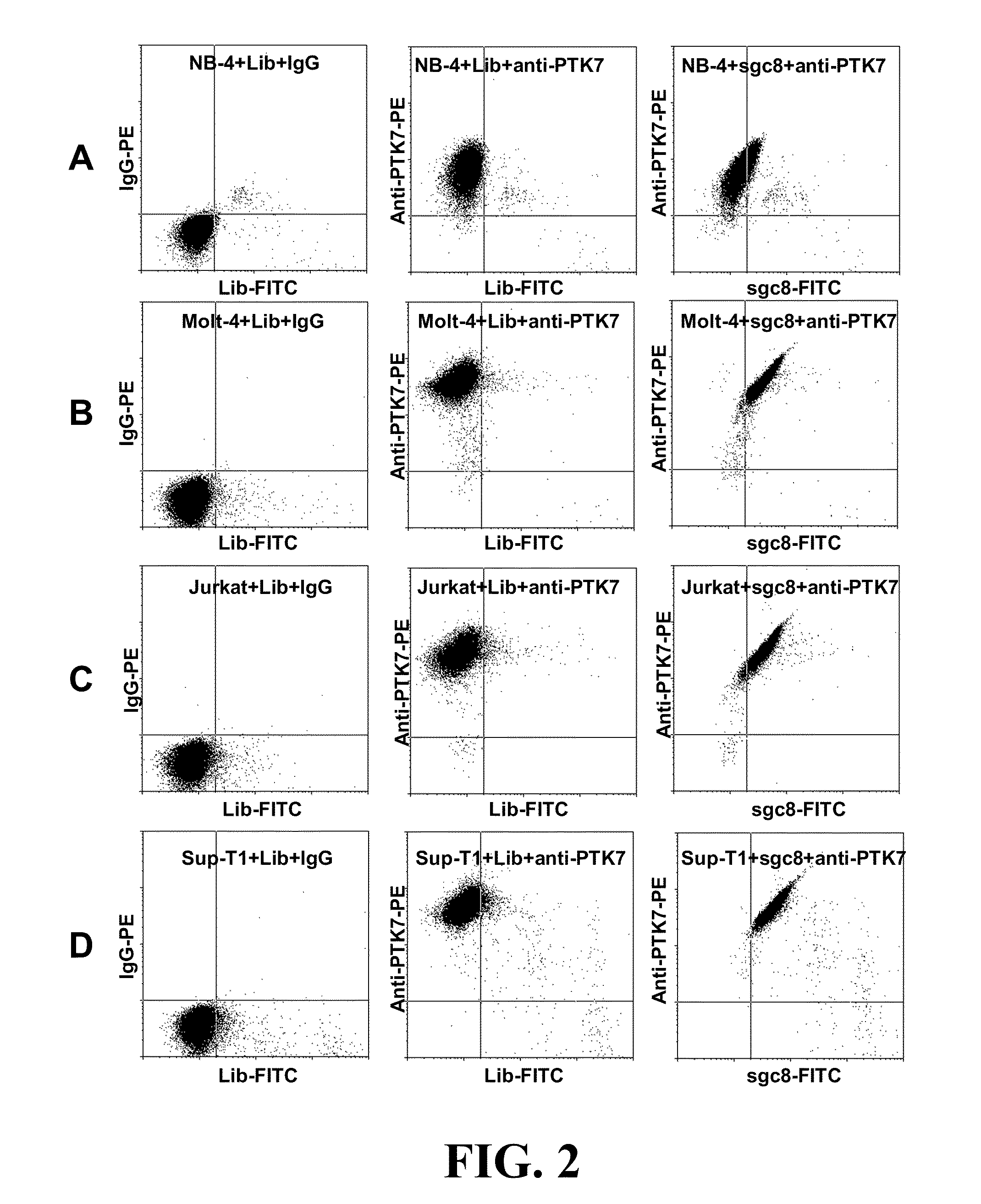
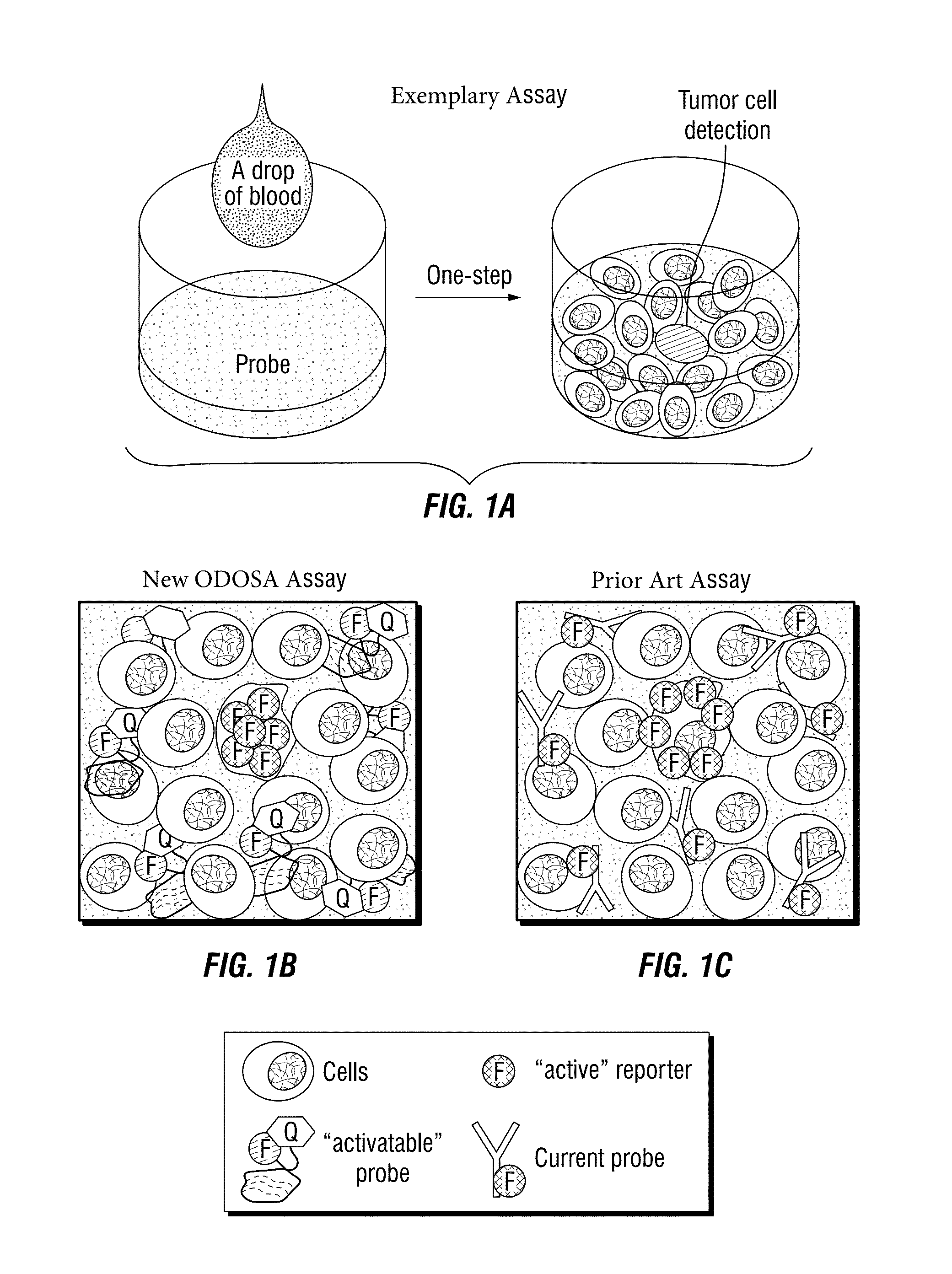
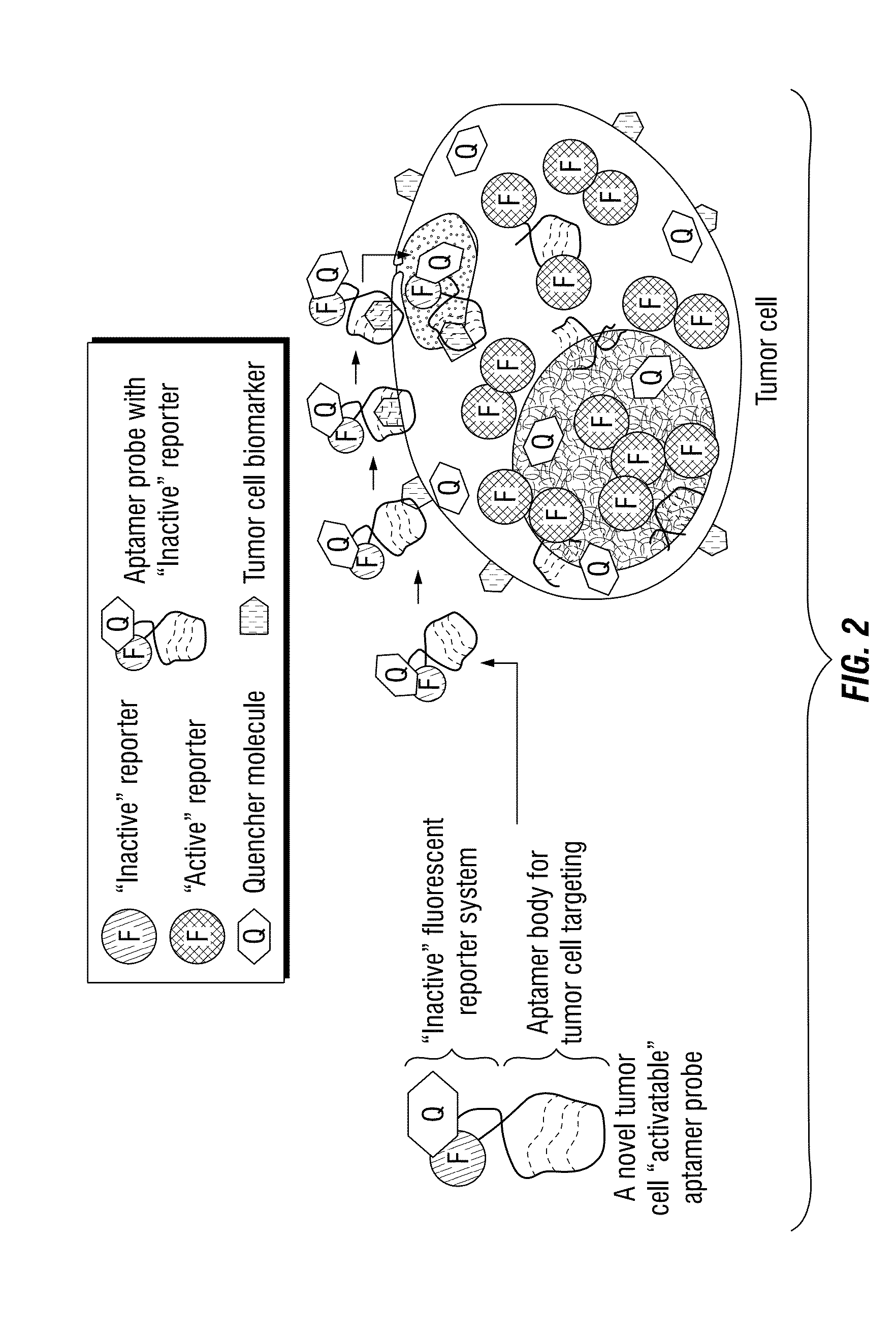
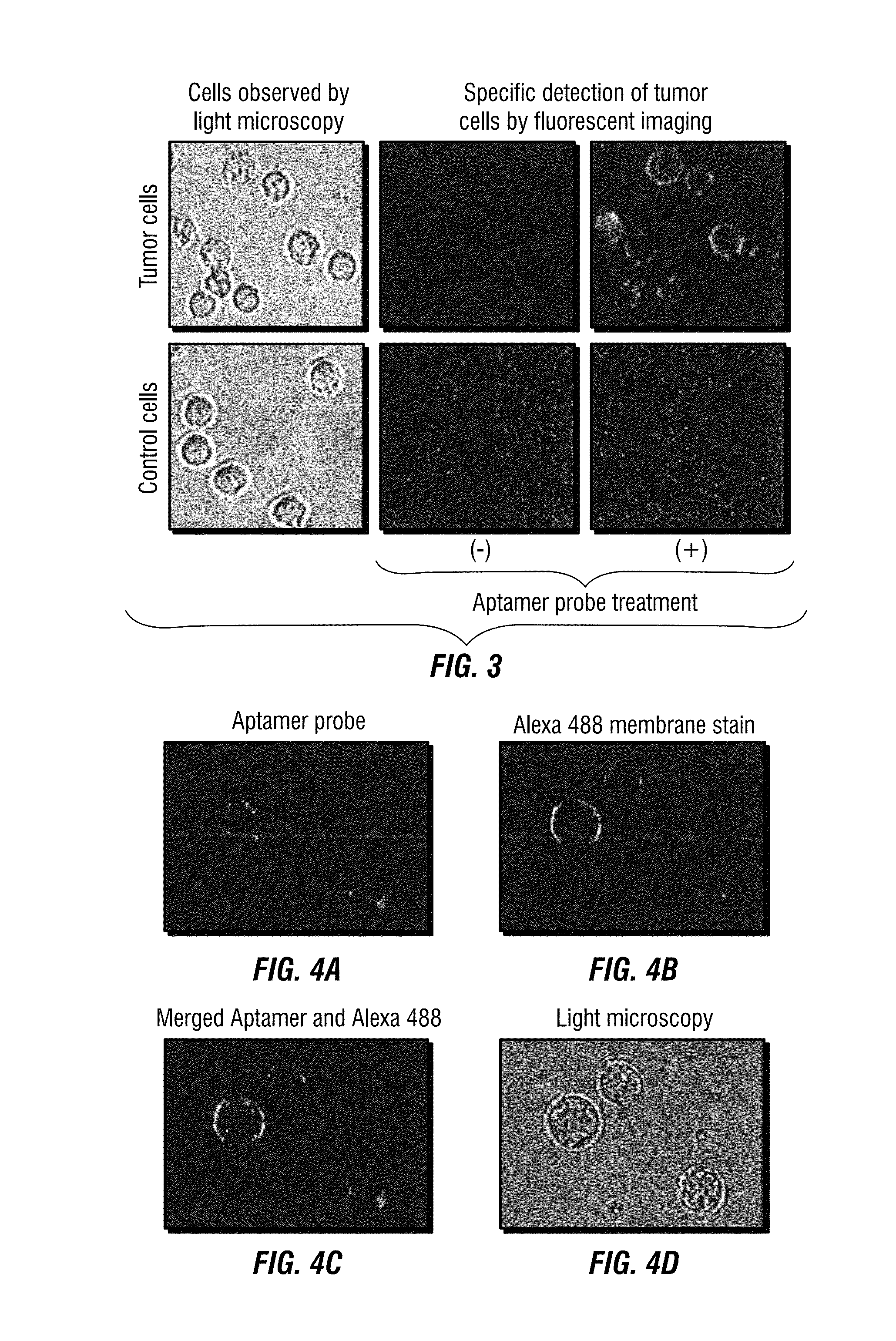
Multi-Aptamer-Based, Cell-Specific, One-Step Tumor Cell Detection Assays
ActiveUS20150276750A1Facile in implementationFacile in executionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningAptamerCell specific
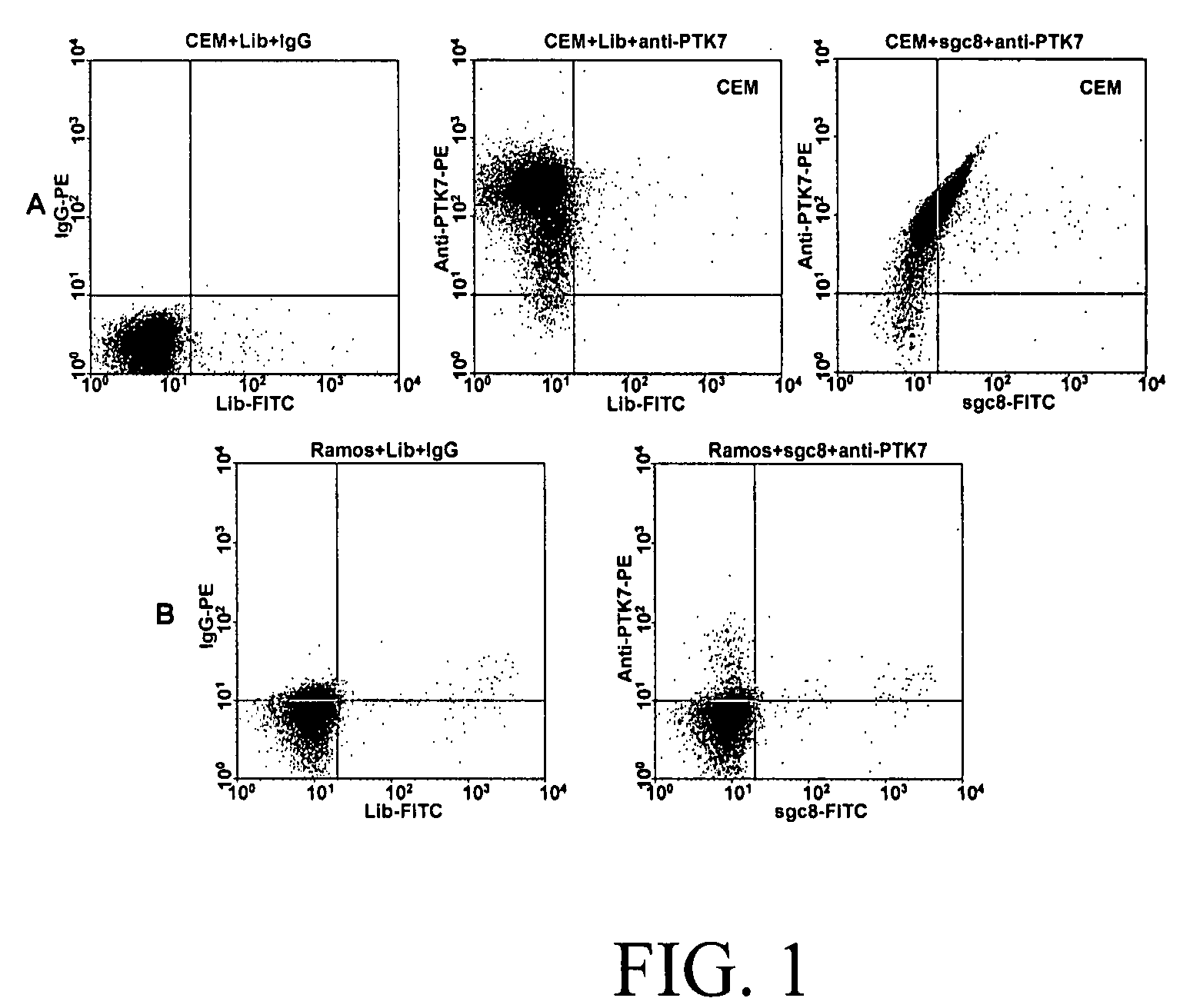
Disclosed are methods and compositions for the detection of one or more different types of cellular biomarkers in a biological sample, and in particular, methods and compositions for the rapid, one-step, highly-cell specific detection of circulating tumor cells from minute quantities of mammalian biological fluids, including, for example, from a single drop of human blood. In certain embodiments, distinctly-labeled, multi-aptamer detection reagents are provided for detecting and quantitating selected cancer cells in clinical samples such as patient specimens and / or tissues. Aptamer-based imaging methodologies are also provided for use in a variety of diagnostic assay protocols.
Owner:THE METHODIST HOSPITAL
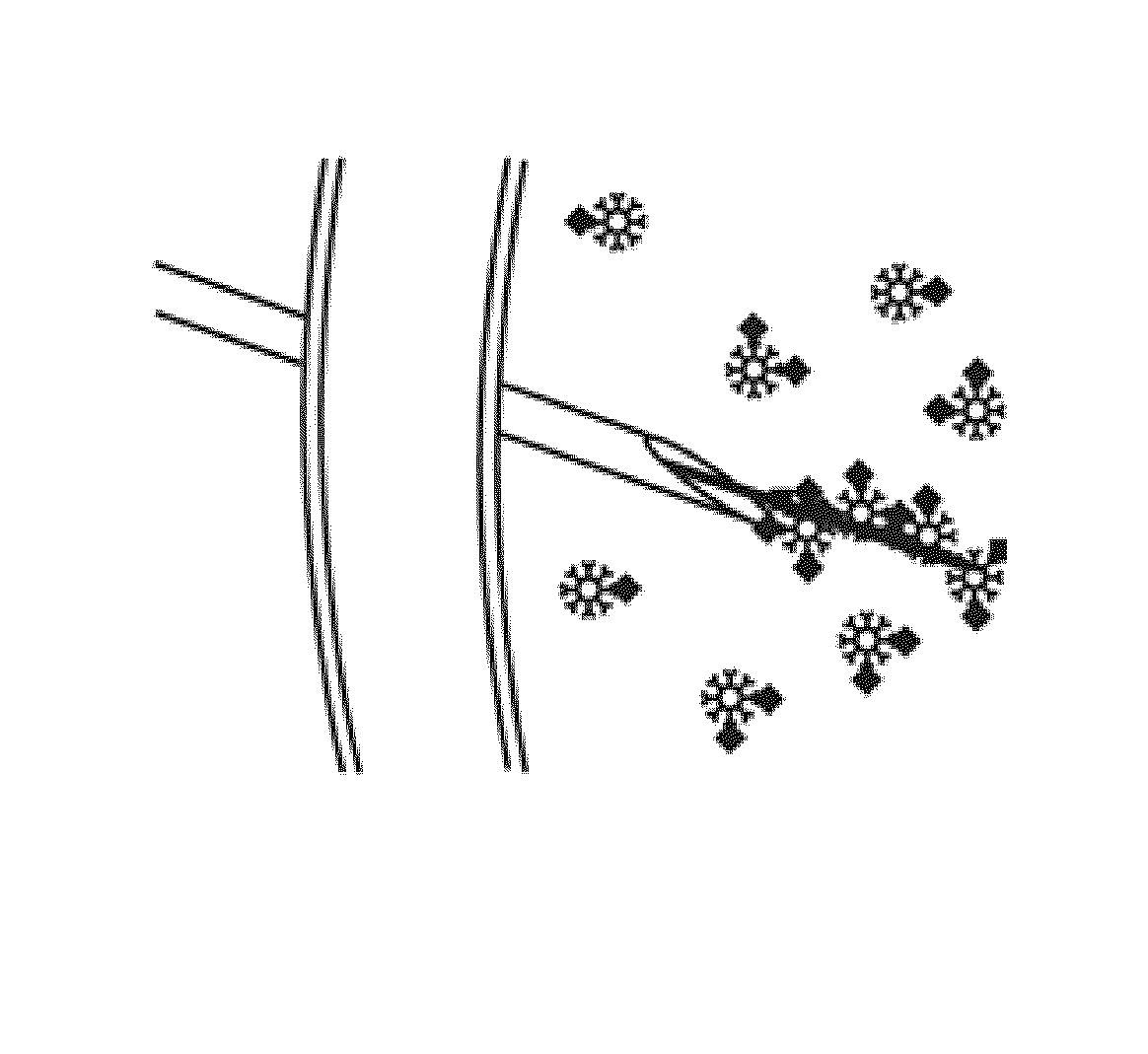
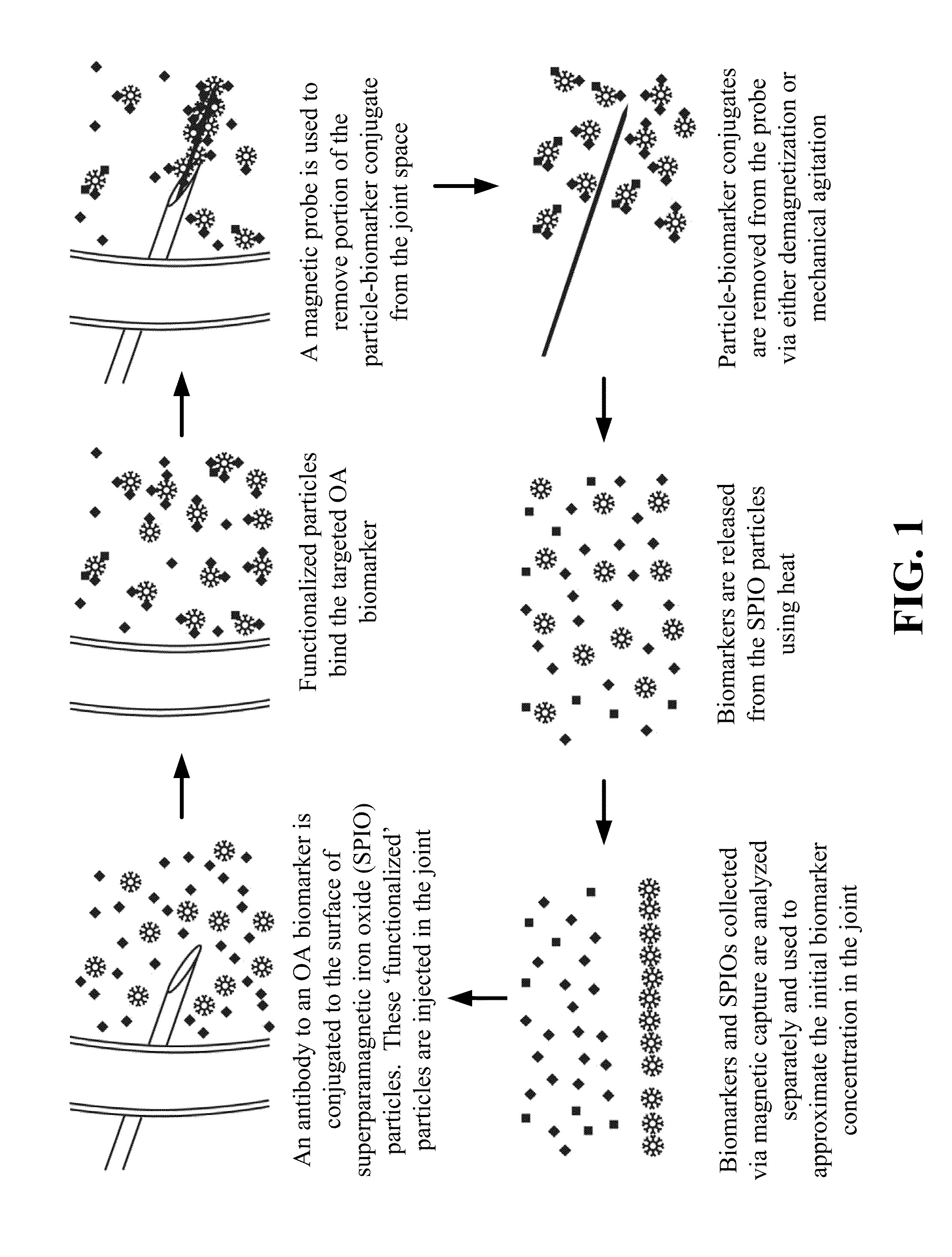
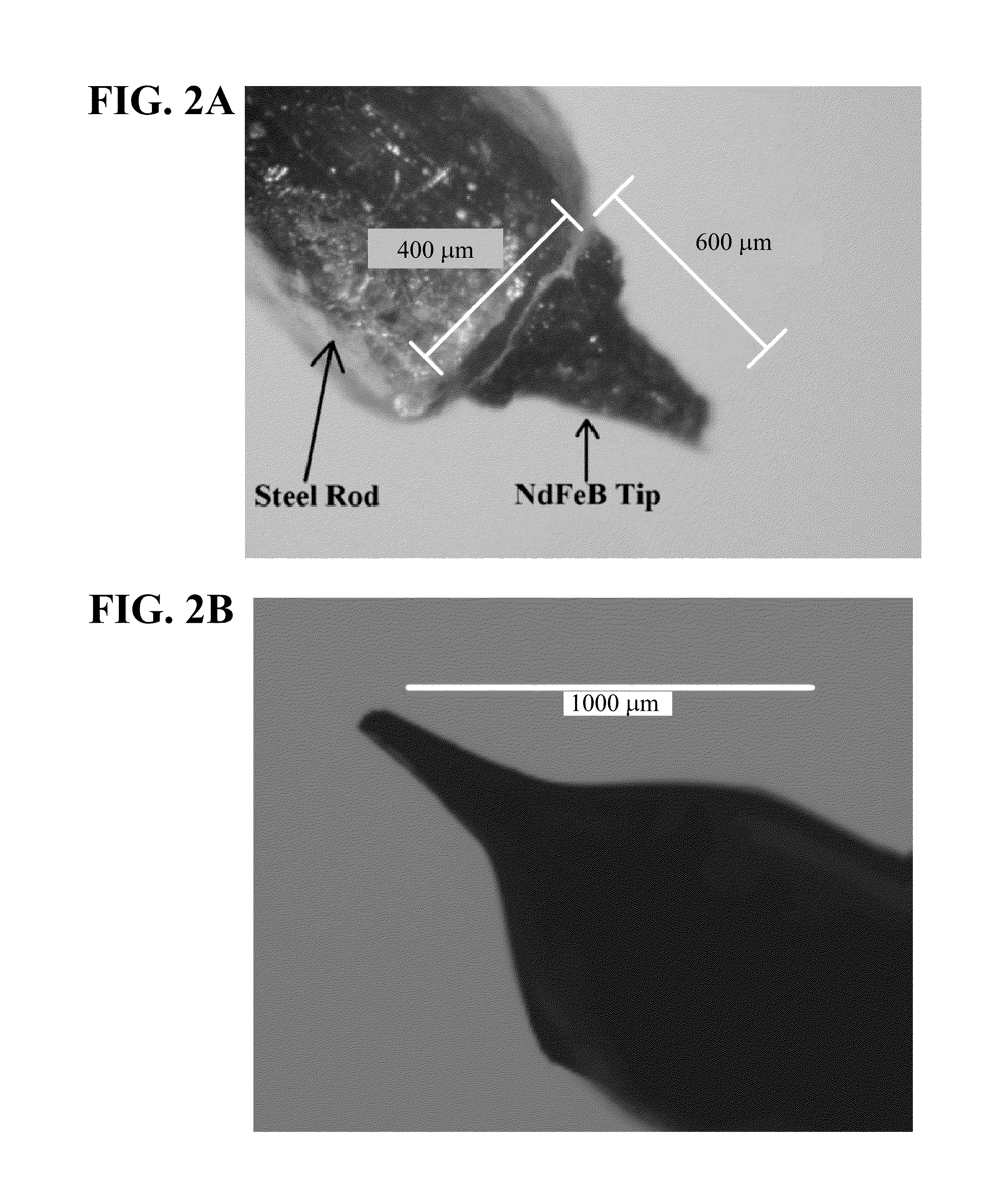
Magnetic apparatus and methods of use
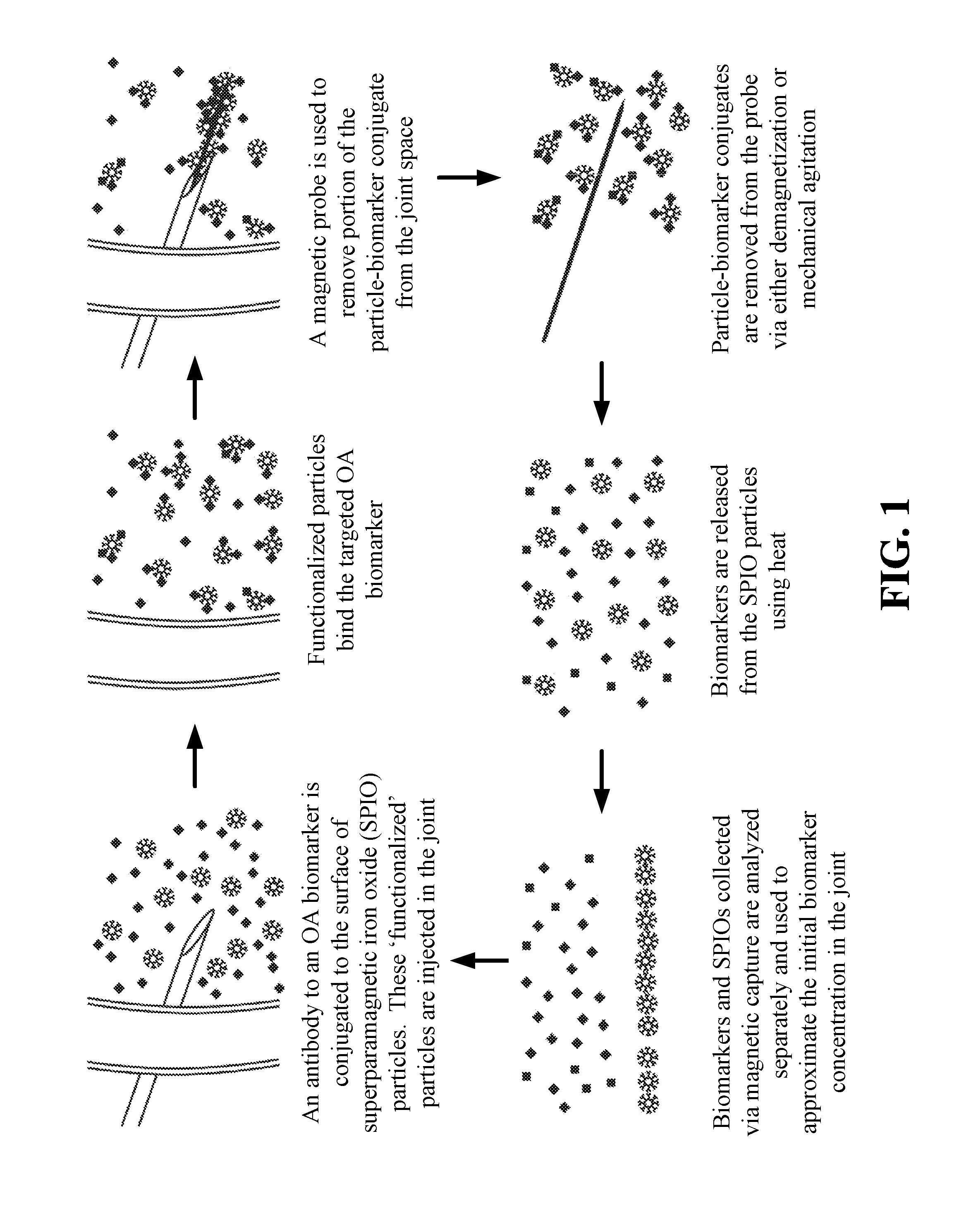
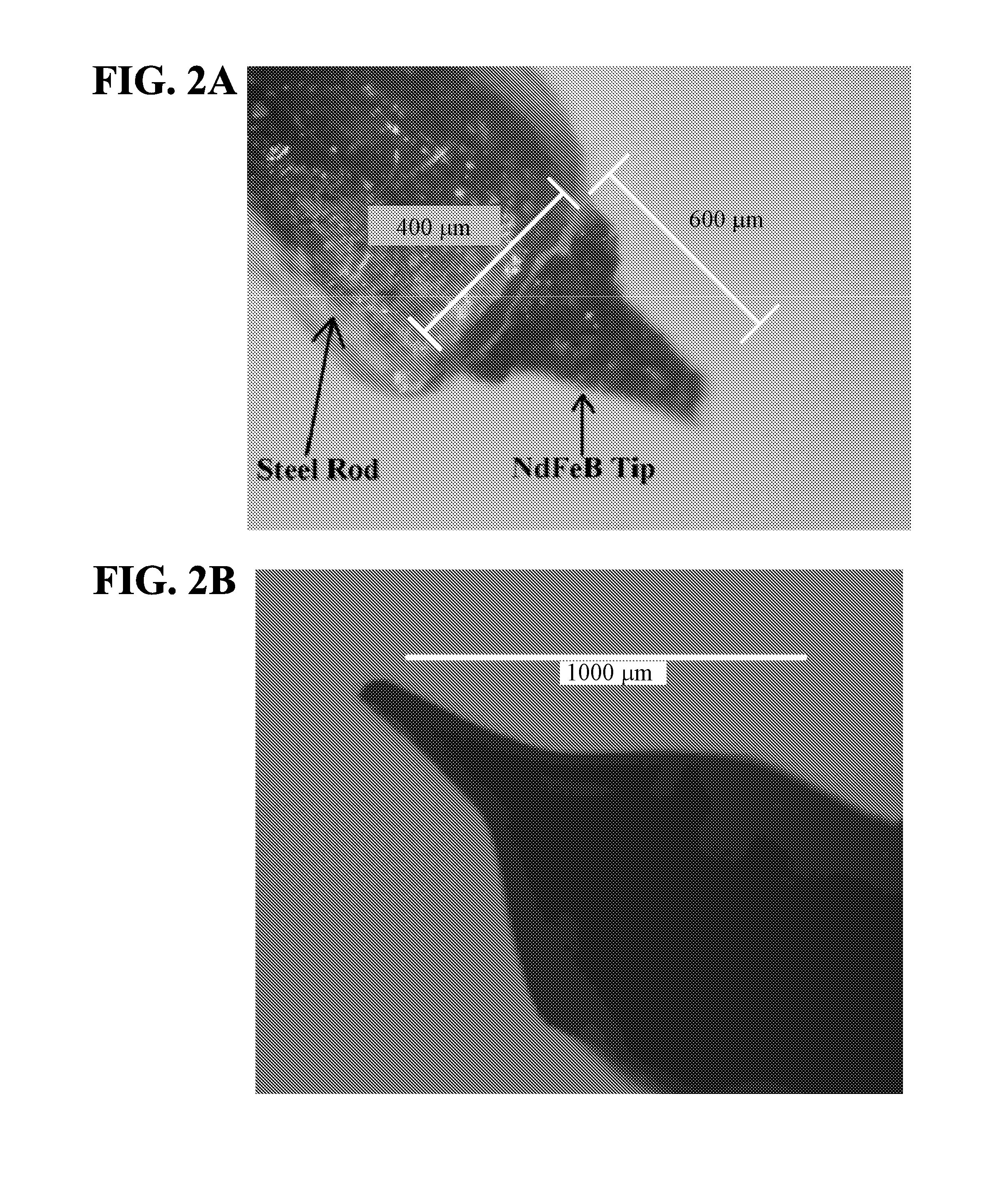
Provided herein is a magnetic apparatus for collecting superparamagnetic particles from a subject. The superparamagnetic particles are previously injected into the subject and have ligands bound thereto that are specific for one or more non-cell biomarkers. In one embodiment, the superparamagnetic particles are injected into and retrieved from a cavity such as a joint cavity. These compositions and methods allow for the sequestration and removal of inflammatory mediators, as both a diagnostic of the local immune response and a therapeutic that can reduce inflammation in the local disease environment.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Integrated visual morphology and cell protein expression using resonance-light scattering
InactiveUS20170234874A1Improve abilitiesImage analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansCellular biomarkersFunctionalized nanoparticles
The invention relates to detecting cell biomarker signatures and integrated cell biomarker-morphological profiles by detecting resonance-light scattering of functionalized nanoparticles.
Owner:CLEARBRIDGE BIOPHOTONICS PTE LTD
Methods for identification and use of agents targeting cancer stem cells
InactiveUS20140294729A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCellular biomarkersBiology
The invention relates to methods for identifying compounds and compositions that target cancer stem cells. In some aspects, the invention relates to treatment methods that use compounds and compositions that specifically target cancer stem cells for inhibiting the growth and / or survival of cancer stem cells in a subject in need thereof. Other aspects of the invention relate to the use of cancer stem cell biomarkers in the selection of a treatment for inhibiting the growth and / or survival of cancer stem cells in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES +2
Use of myeloid cell biomarkers for the diagnosis of cancer
The present invention relates to the use of myeloid cell biomarkers for the differential diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) or colorectal cancer (CRC). The present invention furthermore relates to monitoring the effect of a treatment against renal cell carcinoma (RCC) or colorectal cancer (CRC), and establishing a prognosis of the outcome of the treatment of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) or colorectal cancer (CRC). The present invention furthermore relates to panels of cellular biomarkers for use in the above methods, in particular multicolor panels for measuring said biomarkers.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
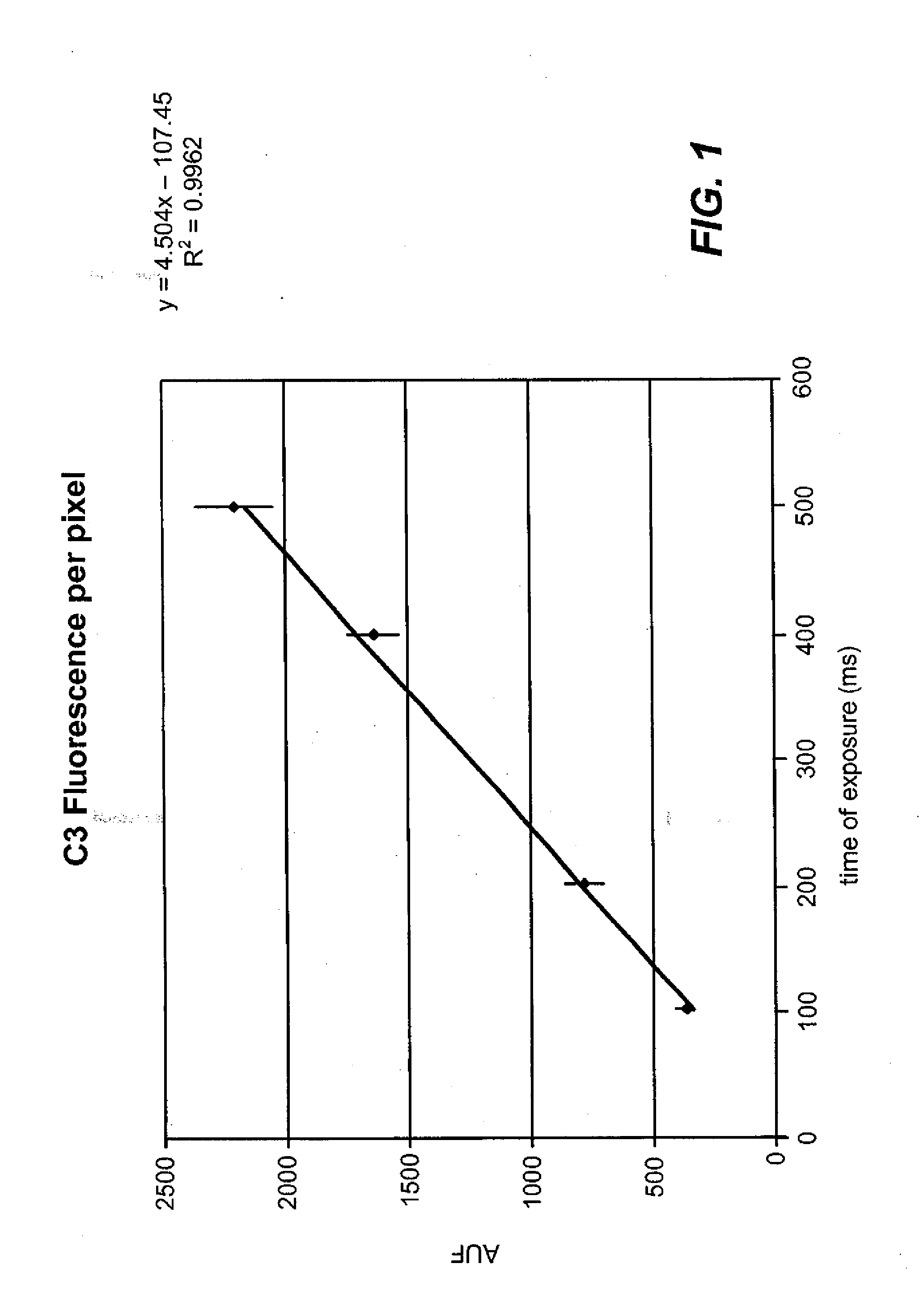
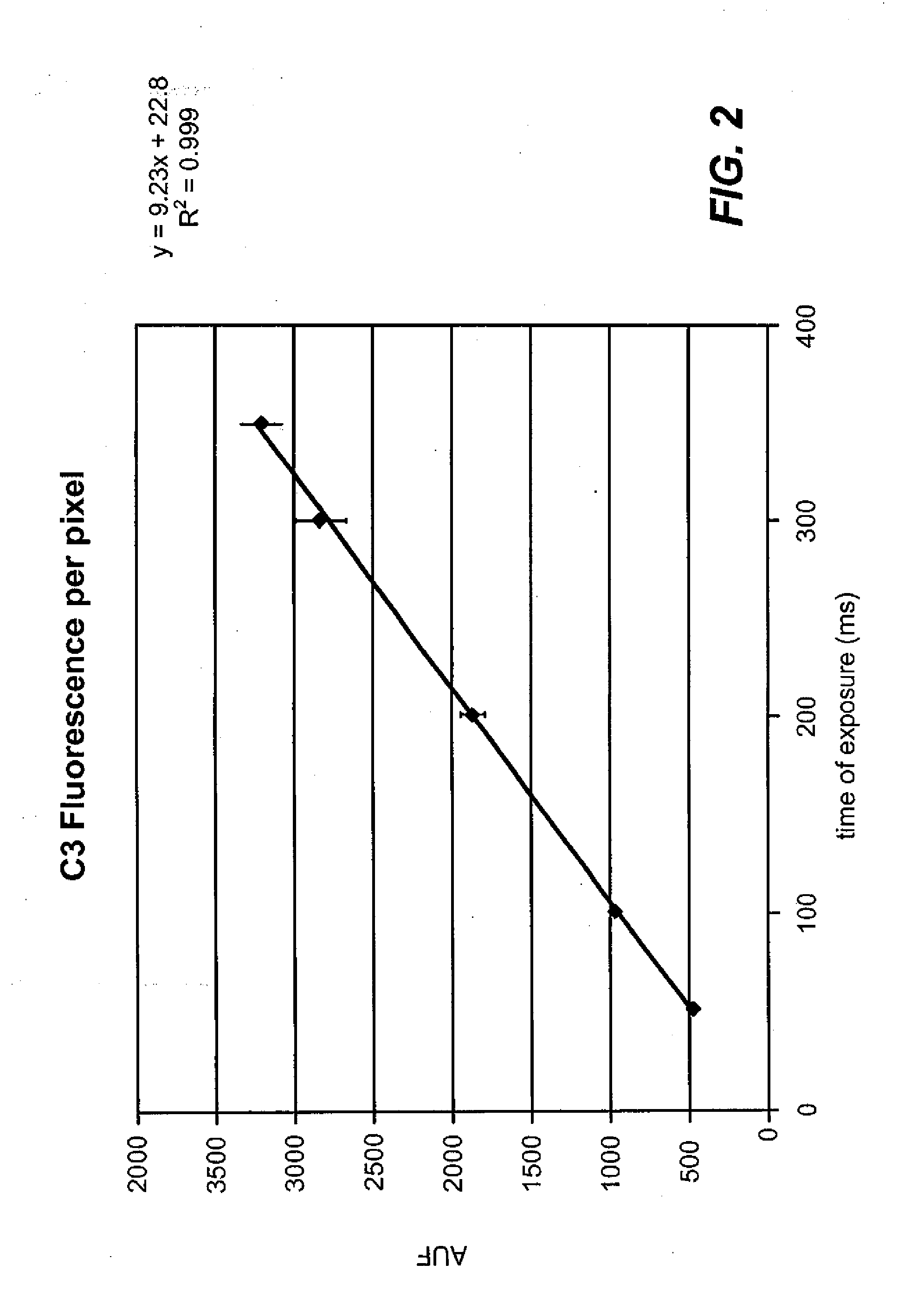
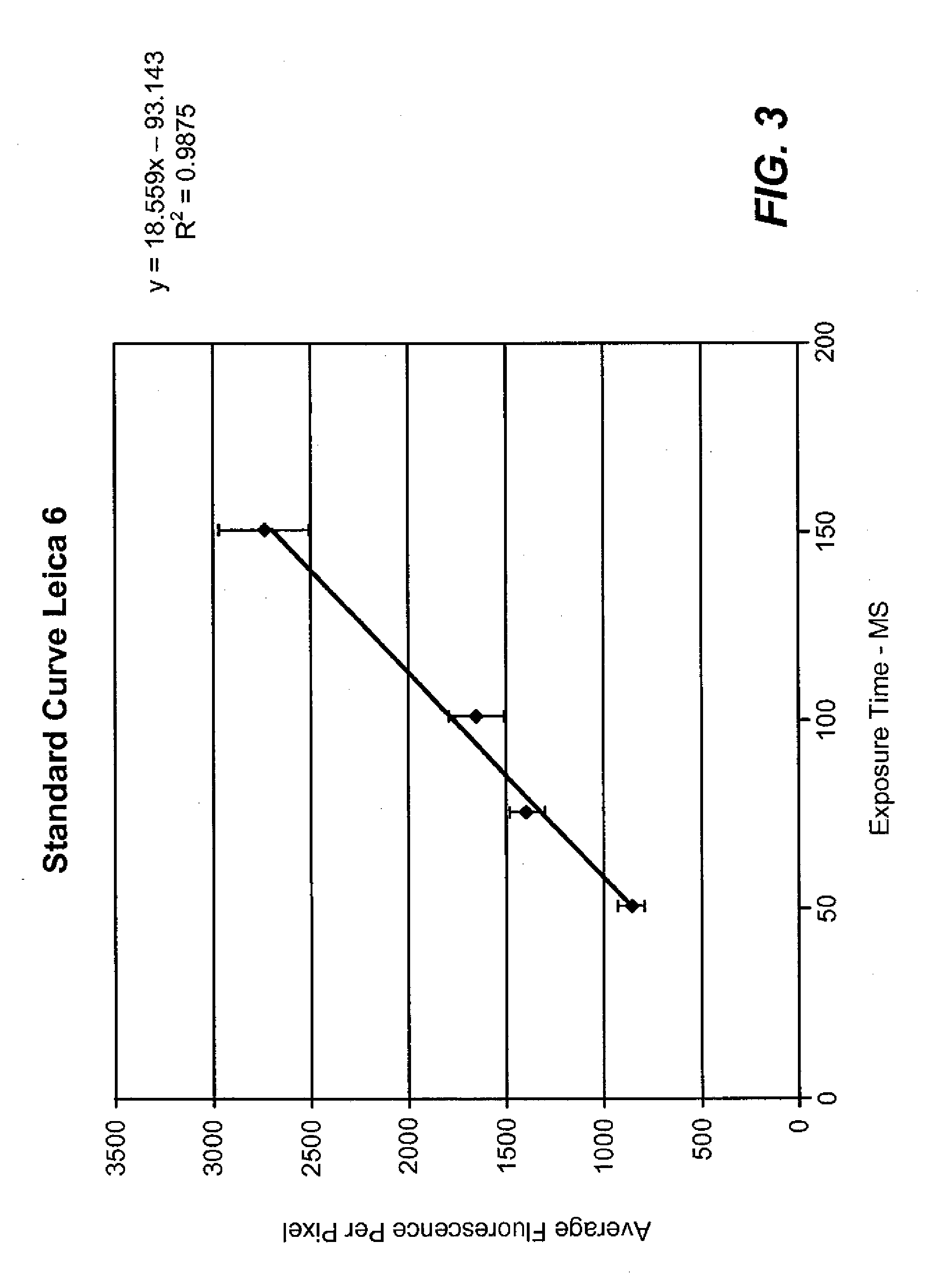
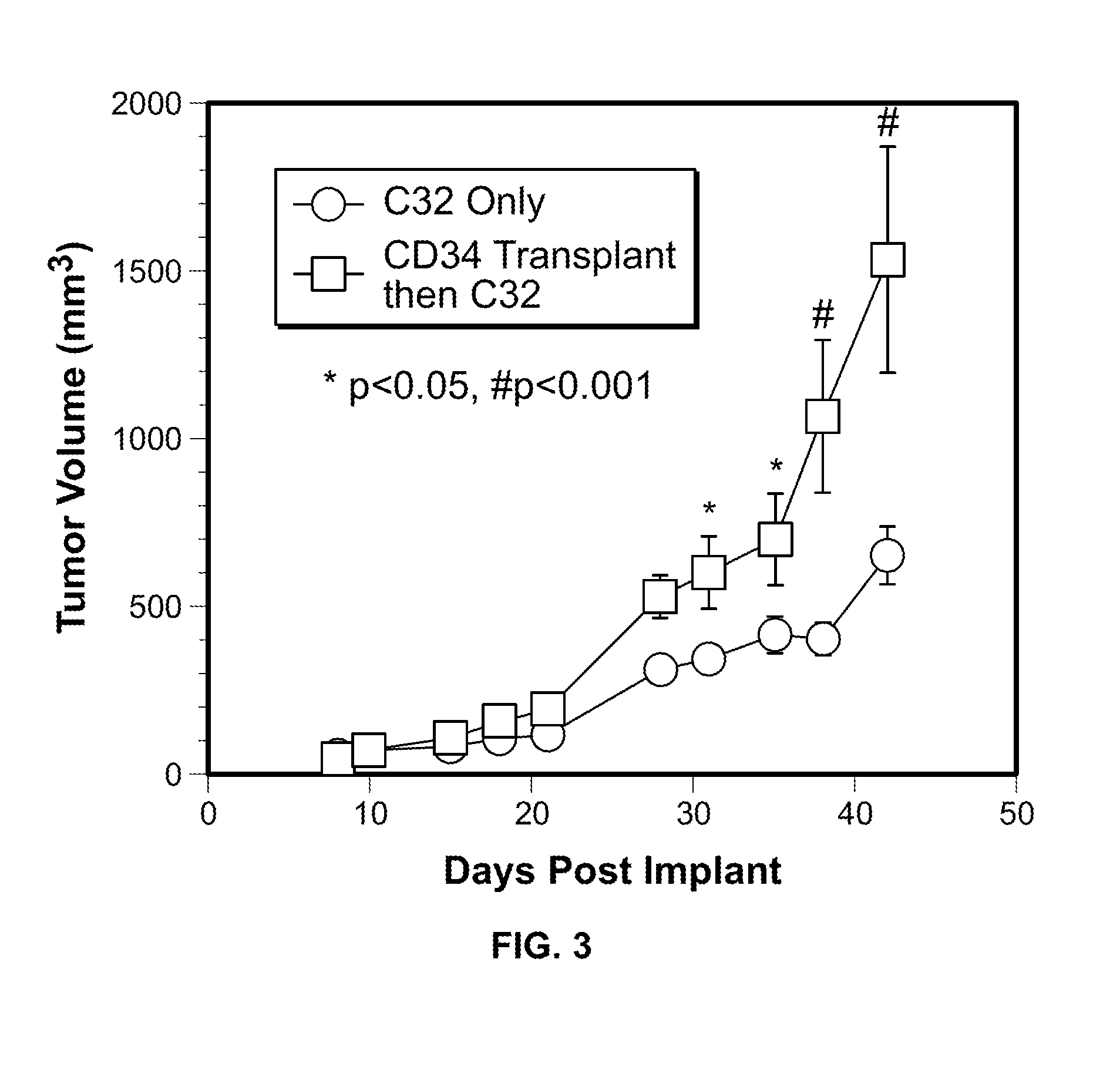
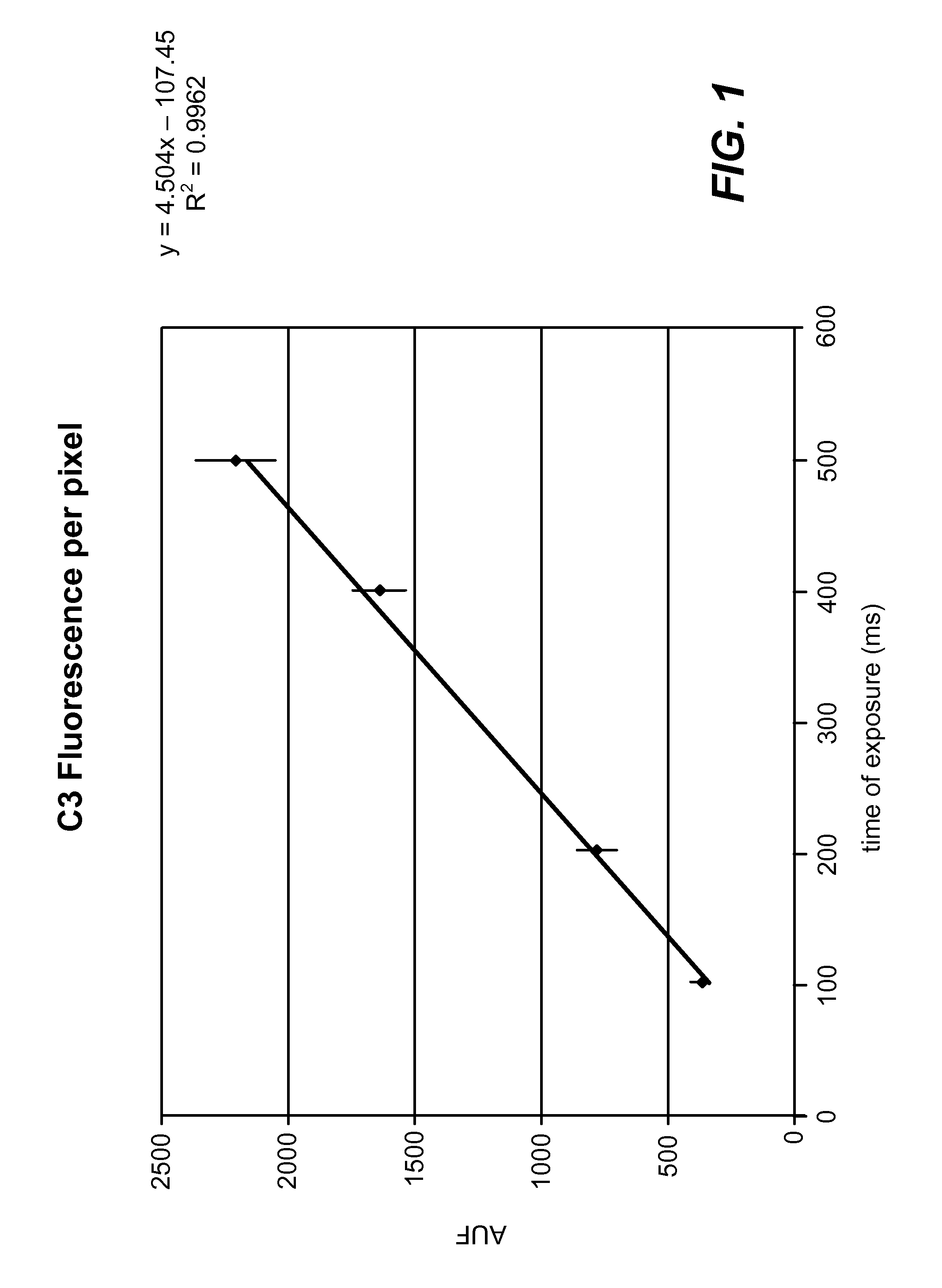
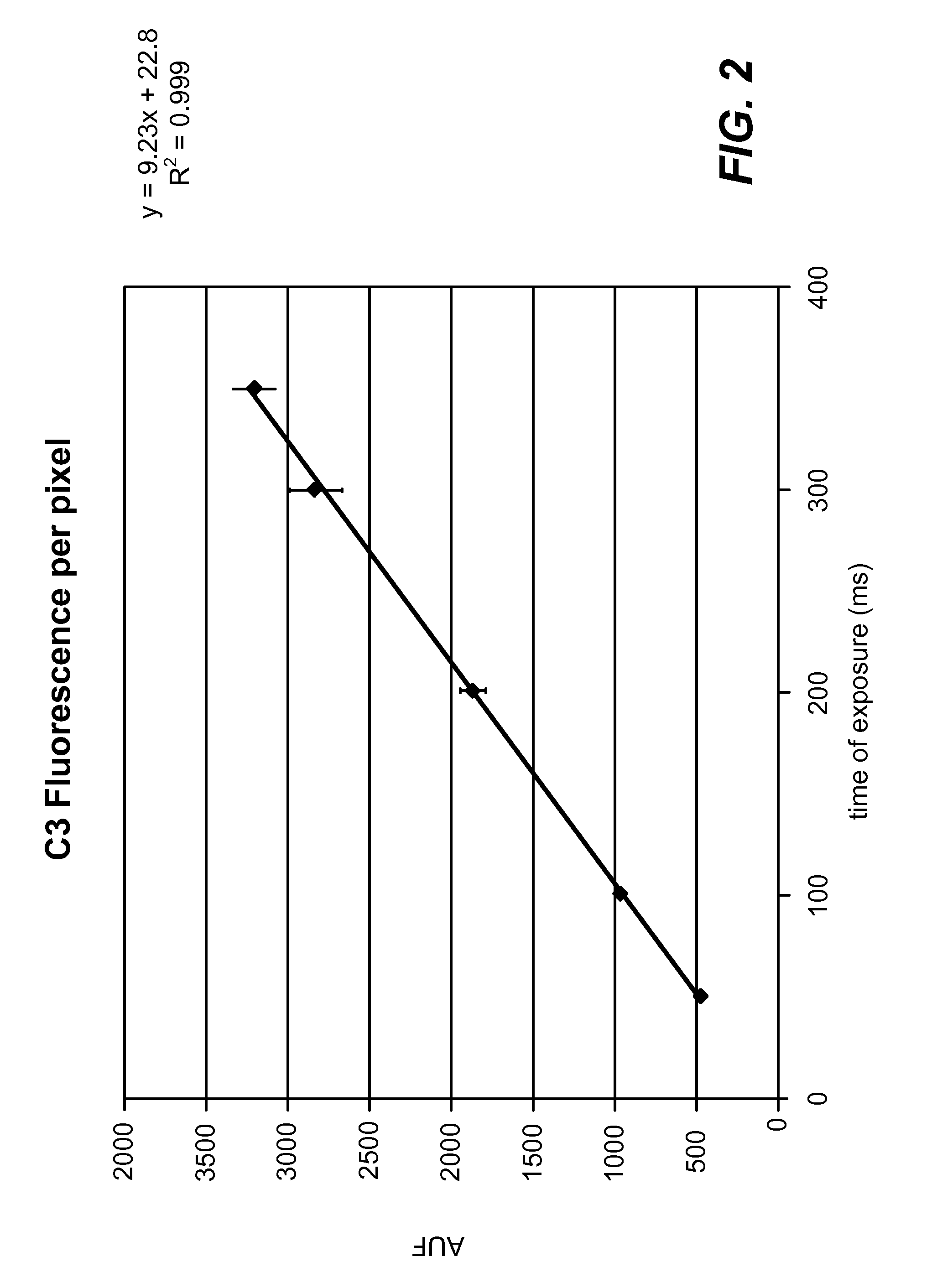
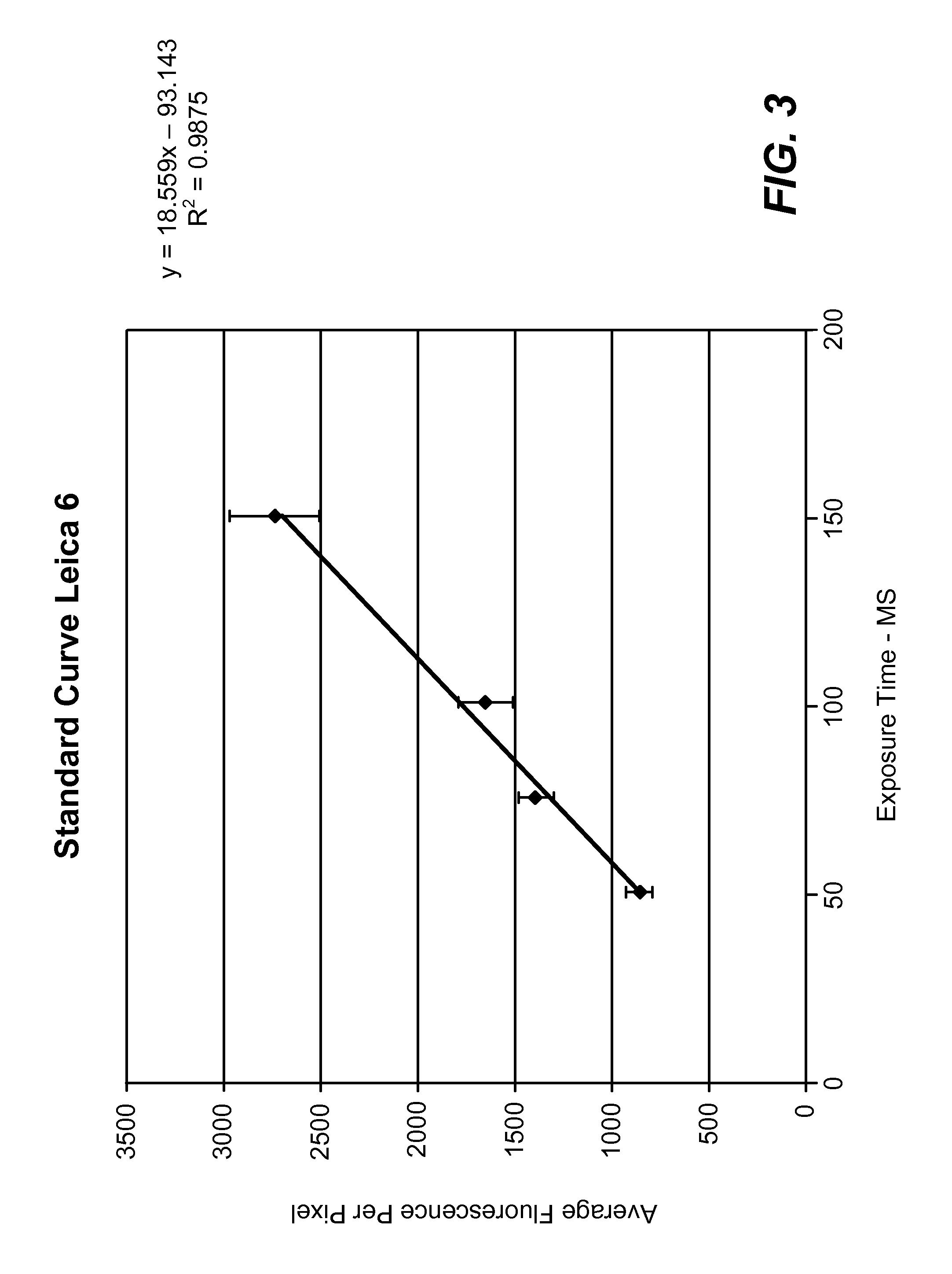
Standardized evaluation of therapeutic efficacy based on cellular biomarkers
The present invention provides materials and methods for predicting the response of a disease state to a therapeutic agent. A targeting moiety specific for a biological marker is labeled with a reporter moiety and used to analyze cells characteristic of the disease state. The output of the reporter moiety, which may be fluorescence intensity, is compared to the output of reference standard analyzed under similar or identical conditions. The use of a reference standard allows biomarker reporting to be normalized. Biomarker values can then be correlated from sample to sample and from laboratory to laboratory based on quantitative calibration on a universal reference standard.
Owner:ON Q ITY
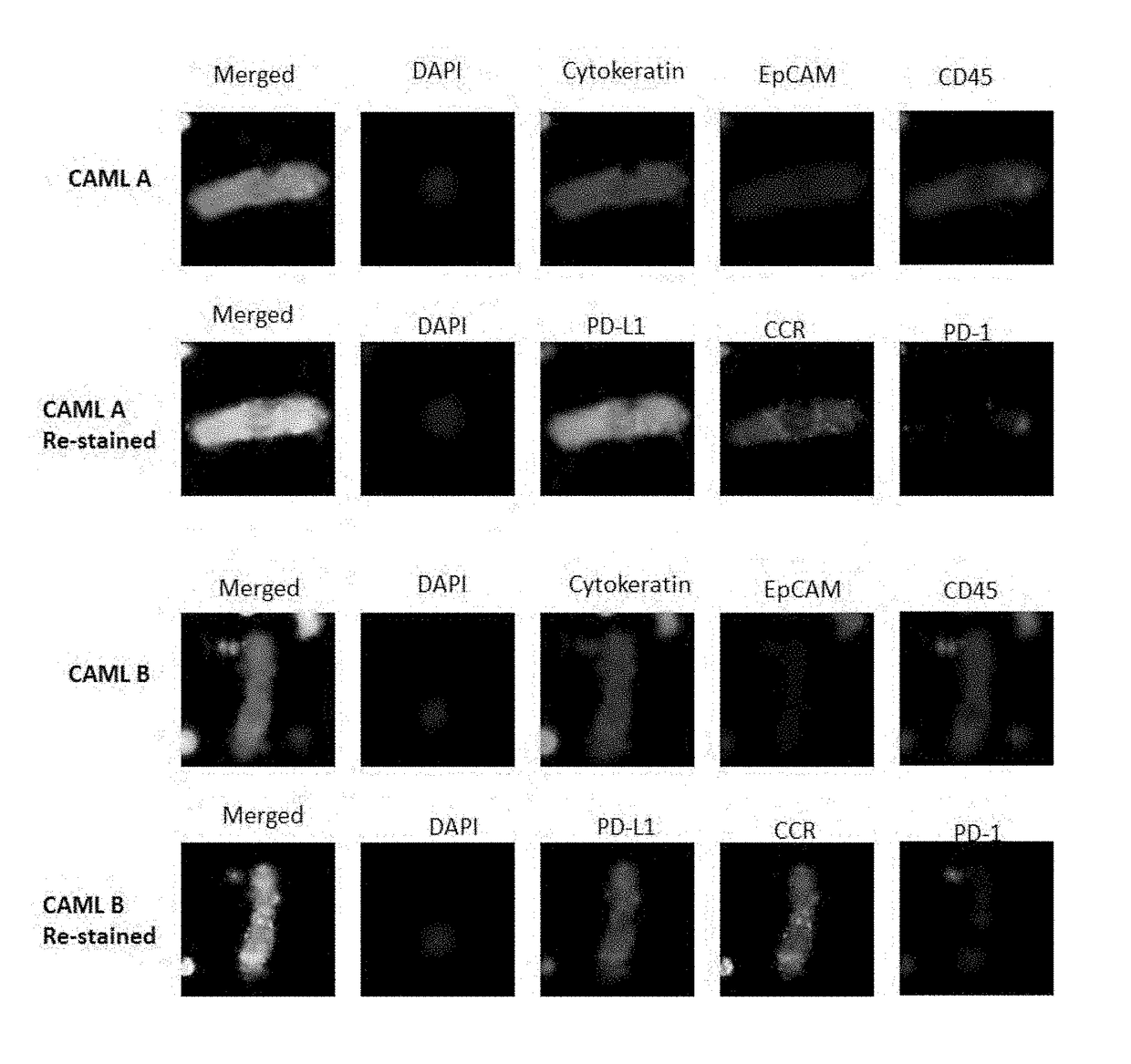
Use of circulating cell biomarkers in the blood for detection and diagnosis of diseases and methods of isolating them
ActiveUS20180238893A1Rapid determinationEarly detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisBiomarker (petroleum)Viral infection
A new sensitive cell biomarker of solid tumors and viral infection is identified in blood. This biomarker can be used to determine presence of carcinomas, sarcomas, and viruses, rapid determination of treatment response, early detection of cancer, early detection of cancer recurrence, and may be used to determine therapy.
Owner:CREATV MICROTECH
ER-stress inducing compounds and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS9316631B1Effectively de-bulkBiological testingHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsStress inducedCompound specific
The invention relates to methods for identifying ER-stress inducing compounds that target cancer stem cells. In some aspects, the invention relates to treatment methods that use ER-stress inducing compounds that specifically target cancer stem cells for inhibiting the growth and / or survival of cancer stem cells in a subject in need thereof. Other aspects of the invention relate to the use of cancer stem cell biomarkers in the selection of a treatment for inhibiting the growth and / or survival of cancer stem cells in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Capture, identification and use of a new biomarker of solid tumors in body fluids
ActiveUS20150168381A1Uniform distribution of poresRapid determinationMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisCellular biomarkersBiologic marker
A new sensitive cell biomarker of solid tumors is identified in blood. This biomarker can be used to determine presence of carcinomas, rapid determination of treatment response, early detection of cancer, early detection of cancer recurrence, and may be used to determine therapy.
Owner:CREATV MICROTECH
Use of circulating cell biomarkers in the blood for detection and diagnosis of diseases and methods of isolating them
ActiveUS10871491B2Rapid determinationEarly detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDiseaseCancer research
A new sensitive cell biomarker of solid tumors and viral infection is identified in blood. This biomarker can be used to determine presence of carcinomas, sarcomas, and viruses, rapid determination of treatment response, early detection of cancer, early detection of cancer recurrence, and may be used to determine therapy.
Owner:CREATV MICROTECH
Pro-angiogenic and Anti-angiogenic hematopoietic progenitor cell populations
InactiveUS20170328910A1Disease diagnosisBiological testingCellular biomarkersAngiogenesis growth factor
Methods for identifying active angiogenesis and vasculopathy are described. More particularly, the present disclosure relates to cellular biomarkers, and to methods of screening cellular biomarkers for identifying active angiogenesis.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Capture, identification and use of a new biomarker of solid tumors in body fluids
Owner:CREATV MICROTECH
Biomarkers for lung cancer stem cells
PendingUS20190346445A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisCellular biomarkersLung cancer
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Capture, identification and use of a new biomarker of solid tumors in body fluids
ActiveUS10247725B2Rapid determinationEarly detectionDisease diagnosisBiological testingCellular biomarkersBody fluid
A new sensitive cell biomarker of solid tumors is identified in blood. This biomarker can be used to determine presence of carcinomas, rapid determination of treatment response, early detection of cancer, early detection of cancer recurrence, and may be used to determine therapy.
Owner:CREATV MICROTECH
Magnetic apparatus and methods of use
Provided herein is a magnetic apparatus for collecting superparamagnetic particles from a subject. The superparamagnetic particles are previously injected into the subject and have ligands bound thereto that are specific for one or more non-cell biomarkers. In one embodiment, the superparamagnetic particles are injected into and retrieved from a cavity such as a joint cavity. These compositions and methods allow for the sequestration and removal of inflammatory mediators, as both a diagnostic of the local immune response and a therapeutic that can reduce inflammation in the local disease environment.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
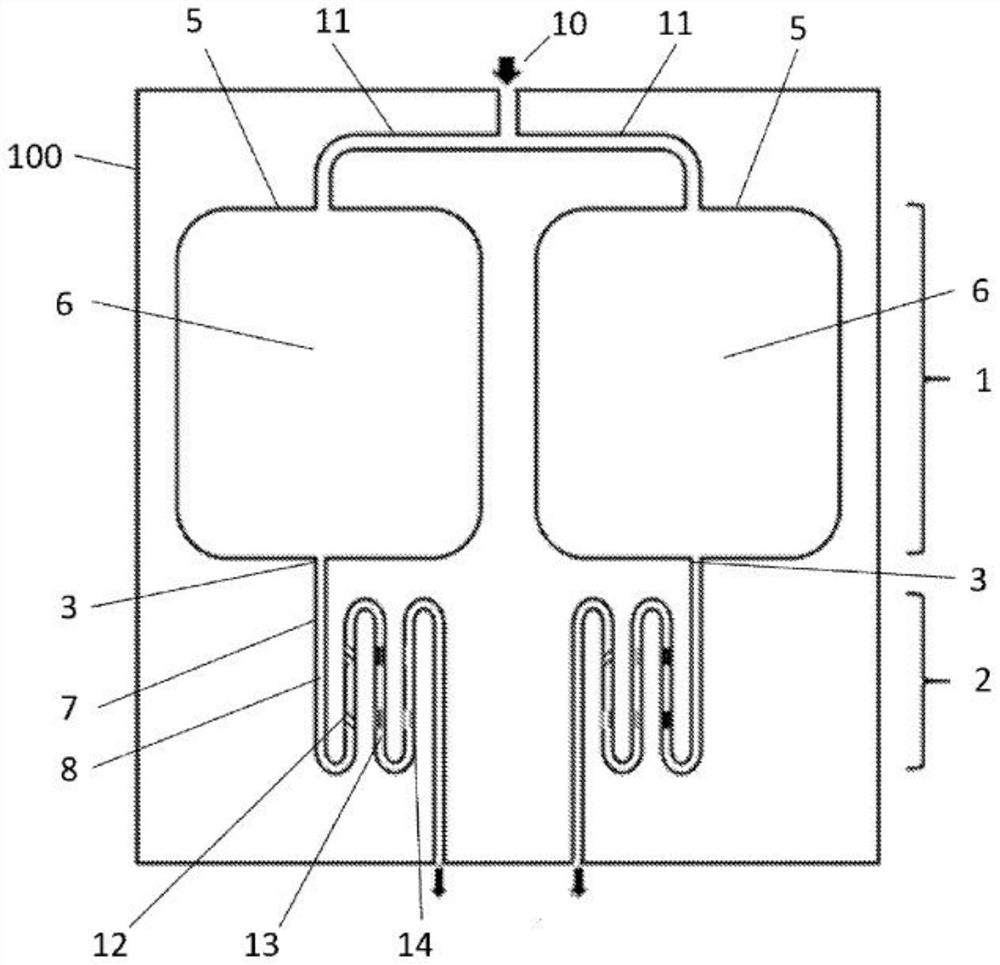
Microfluidic devices with smooth surfaces for the enrichment of rare cells and biomarkers from biological fluids
The present invention discloses microfluidic devices and methods for the enrichment and detection of rare cells such as circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and other biomarkers including proteins and DNA / RNA from biological fluid samples. The device improves upon existing microfluidic devices by optimizing the microfluidic design of its cell capture chamber at the micron level to mimic natural smooth surfaces such as those of the ocean floor or river bed. The smooth surface is characterized by creating a gentle environment and enhancing sample mixing to improve sustained cell-antibody contact and capture of rare cells while reducing shear-induced cell damage. The cell capture module is coated with a cell capture ligand. A second optional module binds acellular biomarkers with high sensitivity, enriching acellular biomarkers 100 to 1000-fold while enriching cellular biomarkers.
Owner:BEIJING NANOPEP BIOTECH CORP LTD
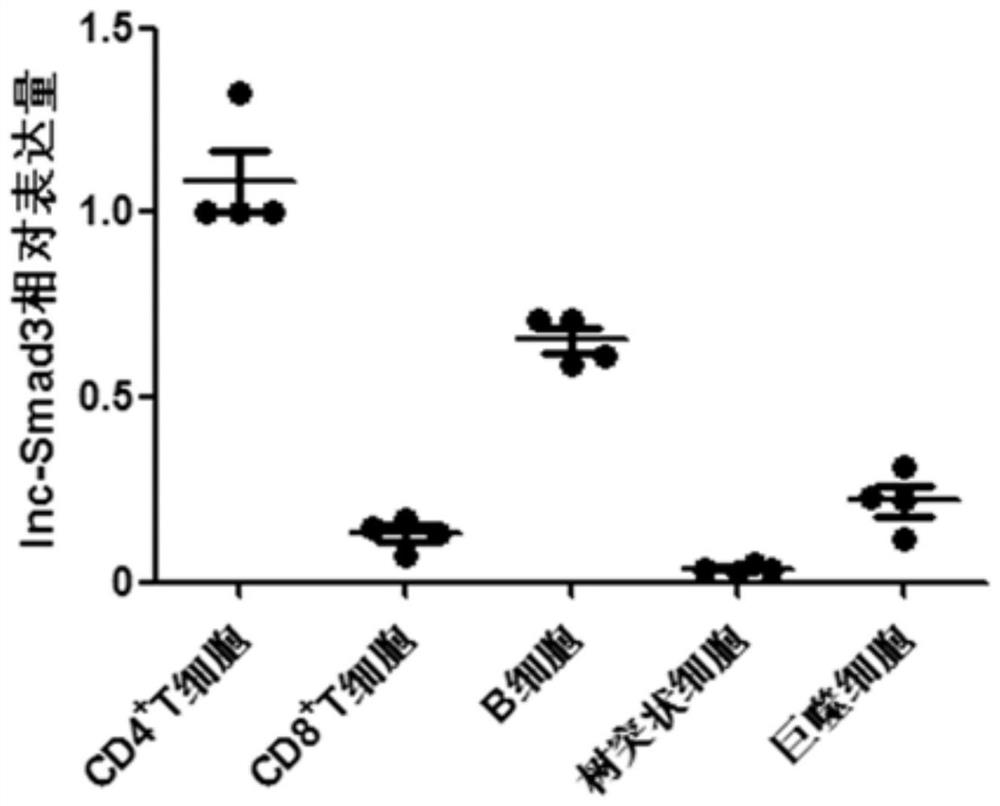
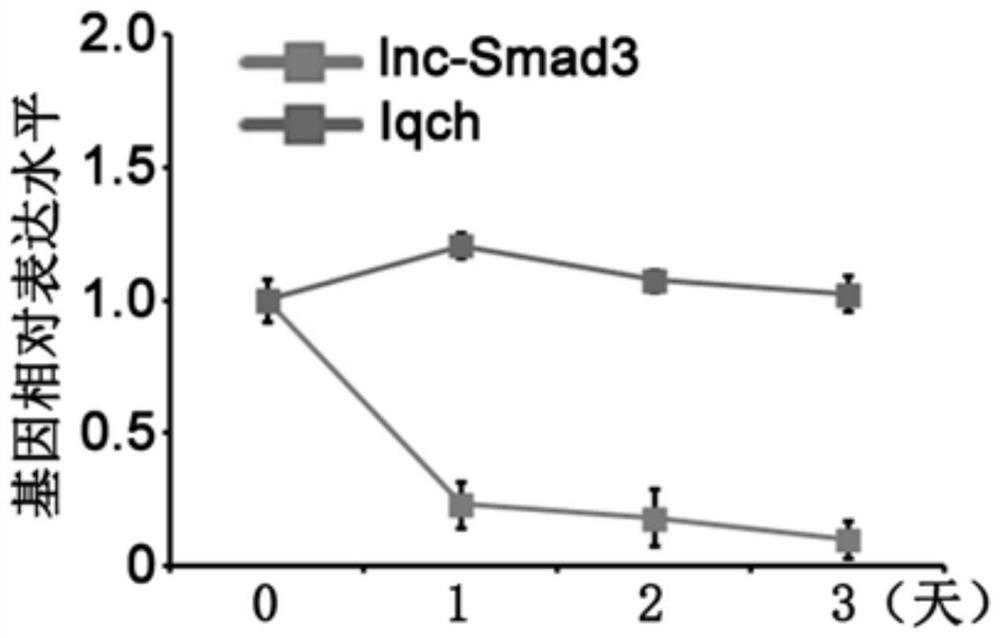
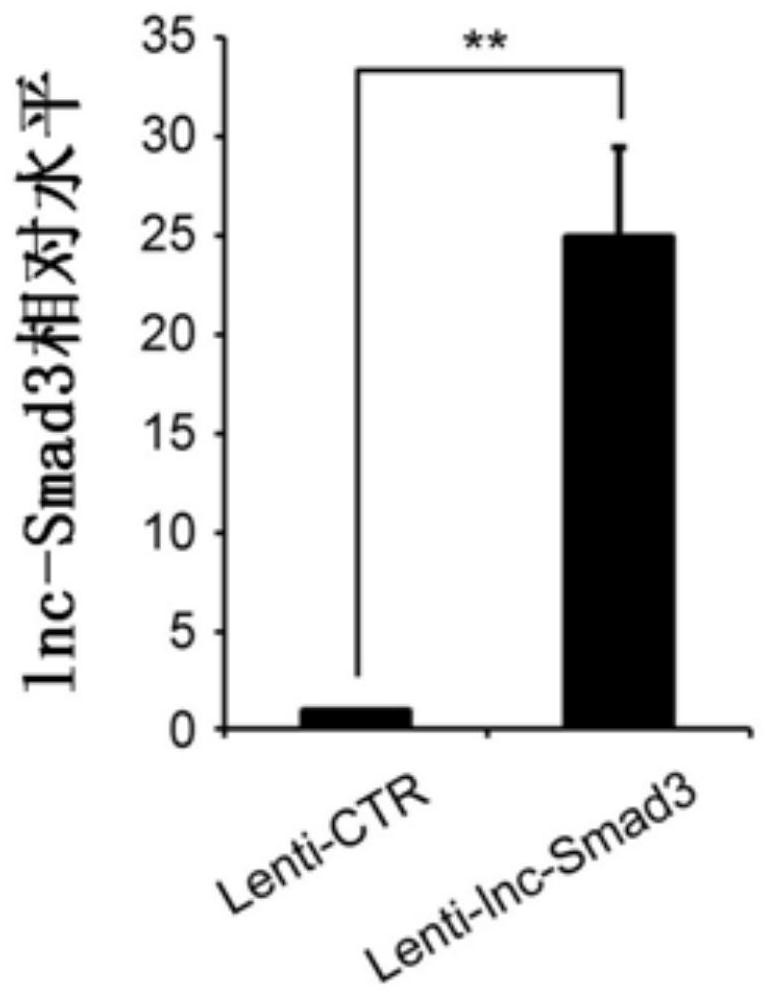
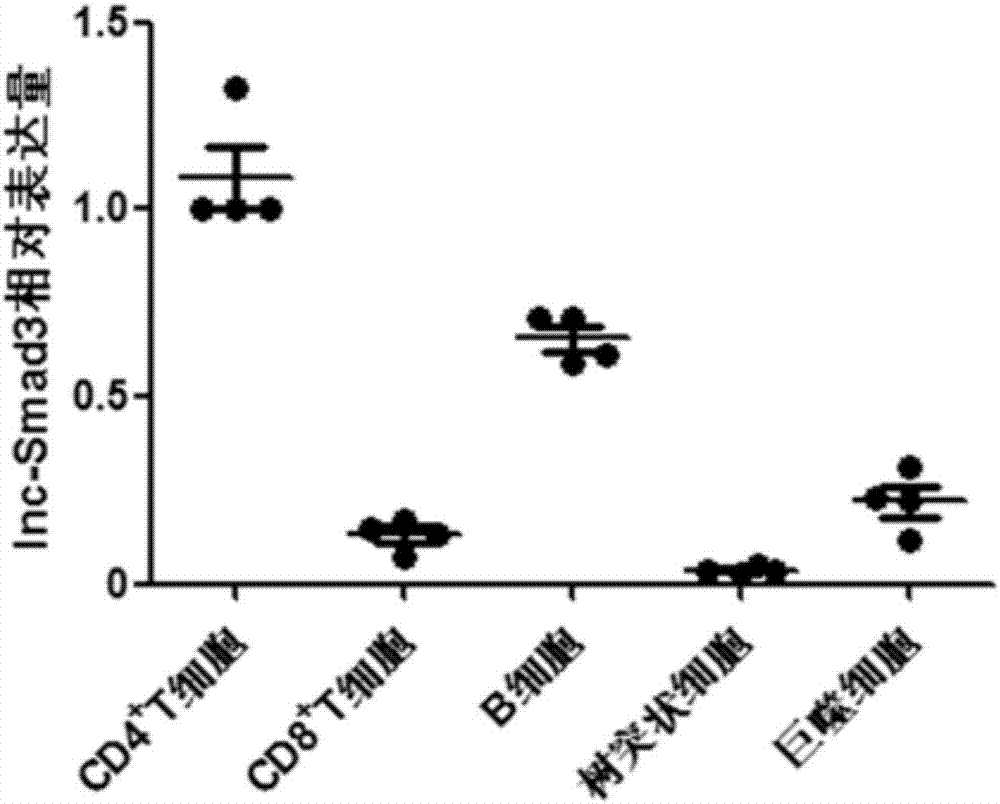
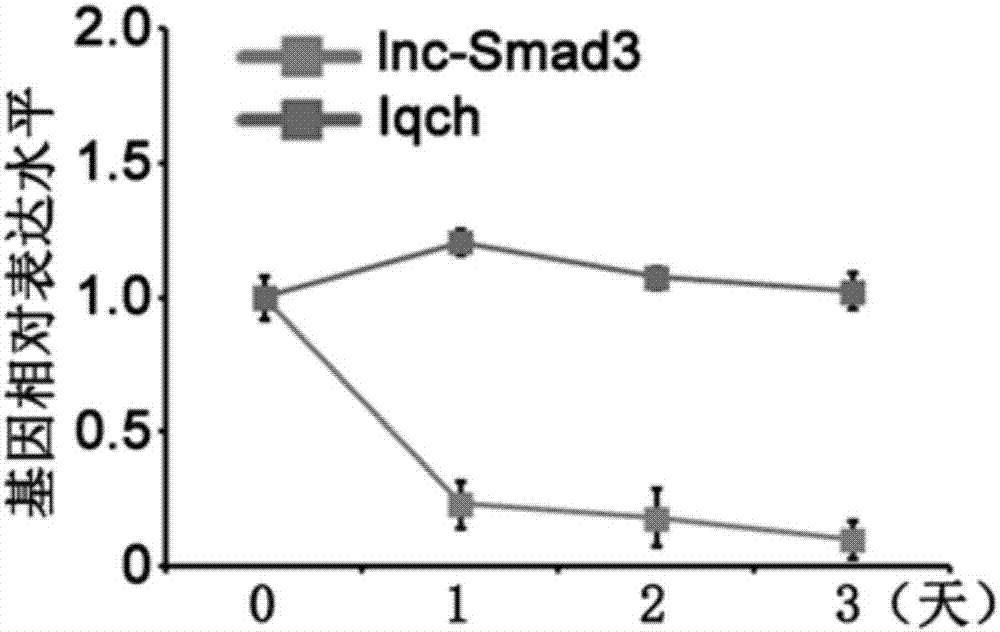
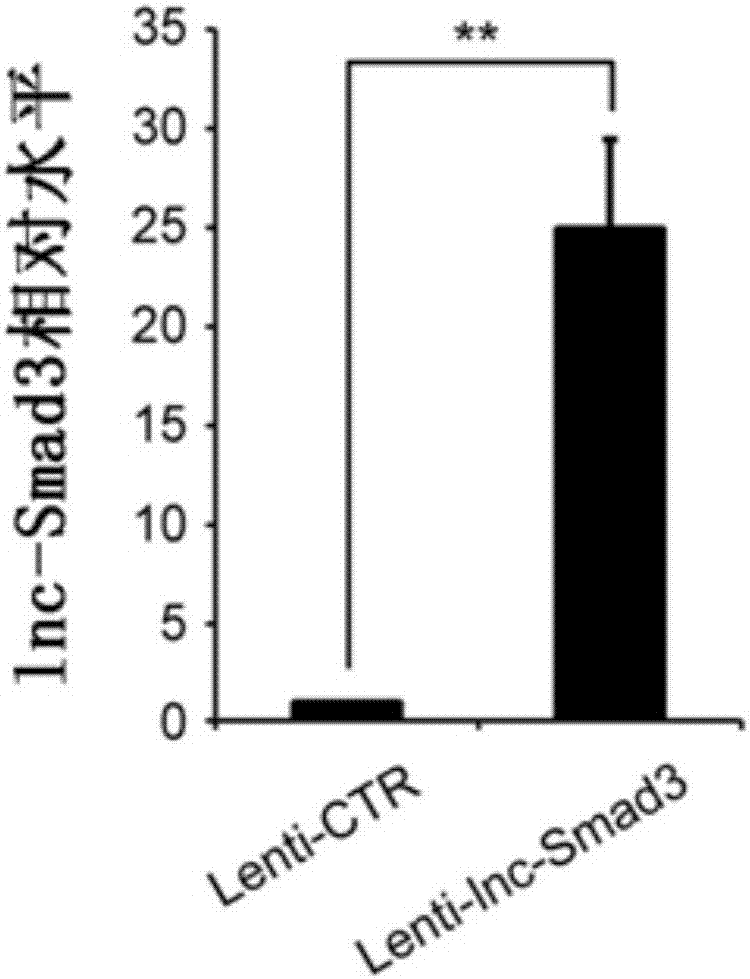
an initial state cd4 + Specific biomarkers for T cells and/or their differentiated regulatory T cells
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, specifically to a specific biomarker of an initial CD4<+>T cell and / or a regulatory T cell differentiated from the initial CD4<+>T cell and / or maturity state and function. The invention provides application of long non-coding RNA (namely lnc-Smad3) as shown in the SEQ ID NO:1 or complementary or homologous RNA sequence as a biomarker for identifying the initial CD<+>T cell and / or a regulatory T cell differentiated from the initial CD4<+>T cell, application of a reagent for detecting RNA sequence level in the preparation of a kit for identifying the an initial CD4<+>T cell and / or a regulatory T cell differentiated from the initial CD4<+>T cell, and a corresponding kit and a method thereof. The invention provides a convenient and effective specific biomarker and a method for clinical and scientific research and identification of an initial CD4<+>T cell and / or a regulatory T cell differentiated from the initial CD4<+>T cell and maturity degree thereof. The specific biomarker has a wide application prospect.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Specific biomarker of initial CD4<+>T cell and/or regulatory T cell differentiated from initial CD4<+>T cell
ActiveCN107083422AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRegulatory T cellRNA Sequence
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, specifically to a specific biomarker of an initial CD4<+>T cell and / or a regulatory T cell differentiated from the initial CD4<+>T cell and / or maturity state and function. The invention provides application of long non-coding RNA (namely lnc-Smad3) as shown in the SEQ ID NO:1 or complementary or homologous RNA sequence as a biomarker for identifying the initial CD<+>T cell and / or a regulatory T cell differentiated from the initial CD4<+>T cell, application of a reagent for detecting RNA sequence level in the preparation of a kit for identifying the an initial CD4<+>T cell and / or a regulatory T cell differentiated from the initial CD4<+>T cell, and a corresponding kit and a method thereof. The invention provides a convenient and effective specific biomarker and a method for clinical and scientific research and identification of an initial CD4<+>T cell and / or a regulatory T cell differentiated from the initial CD4<+>T cell and maturity degree thereof. The specific biomarker has a wide application prospect.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Capture, identification and use of a new biomarker of solid tumors in body fluids
ActiveUS20190242871A1Uniform distribution of poresDisease diagnosisBiological testingCellular biomarkersBody fluid
A new sensitive cell biomarker of solid tumors is identified in blood. This biomarker can be used to determine presence of solid tumors, rapid determination of treatment response, early detection of cancer, early detection of cancer recurrence, and may be used to determine therapy.
Owner:CREATV MICROTECH
Pro-angiogenic and Anti-angiogenic hematopoietic progenitor cell populations
Methods for identifying active angiogenesis and vasculopathy are described. More particularly, the present disclosure relates to cellular biomarkers, and to methods of screening cellular biomarkers for identifying active angiogenesis.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Standardized evaluation of therapeutic efficacy based on cellular biomarkers
InactiveUS20100075341A1Increase volumeFluorescence enhancementSamplingDisease diagnosisDiseaseCellular biomarkers
The present invention provides materials and methods for predicting the response of a disease state to a therapeutic agent. A targeting moiety specific for a biological marker is labeled with a reporter moiety and used to analyze cells characteristic of the disease state. The output of the reporter moiety, which may be fluorescence intensity, is compared to the output of reference standard analyzed under similar or identical conditions. The use of a reference standard allows biomarker reporting to be normalized. Biomarker values can then be correlated from sample to sample and from laboratory to laboratory based on quantitative calibration on a universal reference standard.
Owner:LESKO STEPHEN A +1
Plectin-1 targeted agents for detection and treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
ActiveUS8829159B2Fast wayQuick identificationPeptide/protein ingredientsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsCancer cellTumor Biomarkers
Described herein are compositions and methods for cancer cell biomarkers, such as pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cell biomarkers, and binding molecules for diagnosis and treatment of cancer, e.g., PDAC. Methods of identifying “accessible” proteomes are disclosed for identifying cancer biomarkers, such as plectin-1, a PDAC biomarker. Additionally, imaging compositions are provided comprising magnetofluorescent nanoparticles conjugated to peptide ligands for identifying PDACs.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com