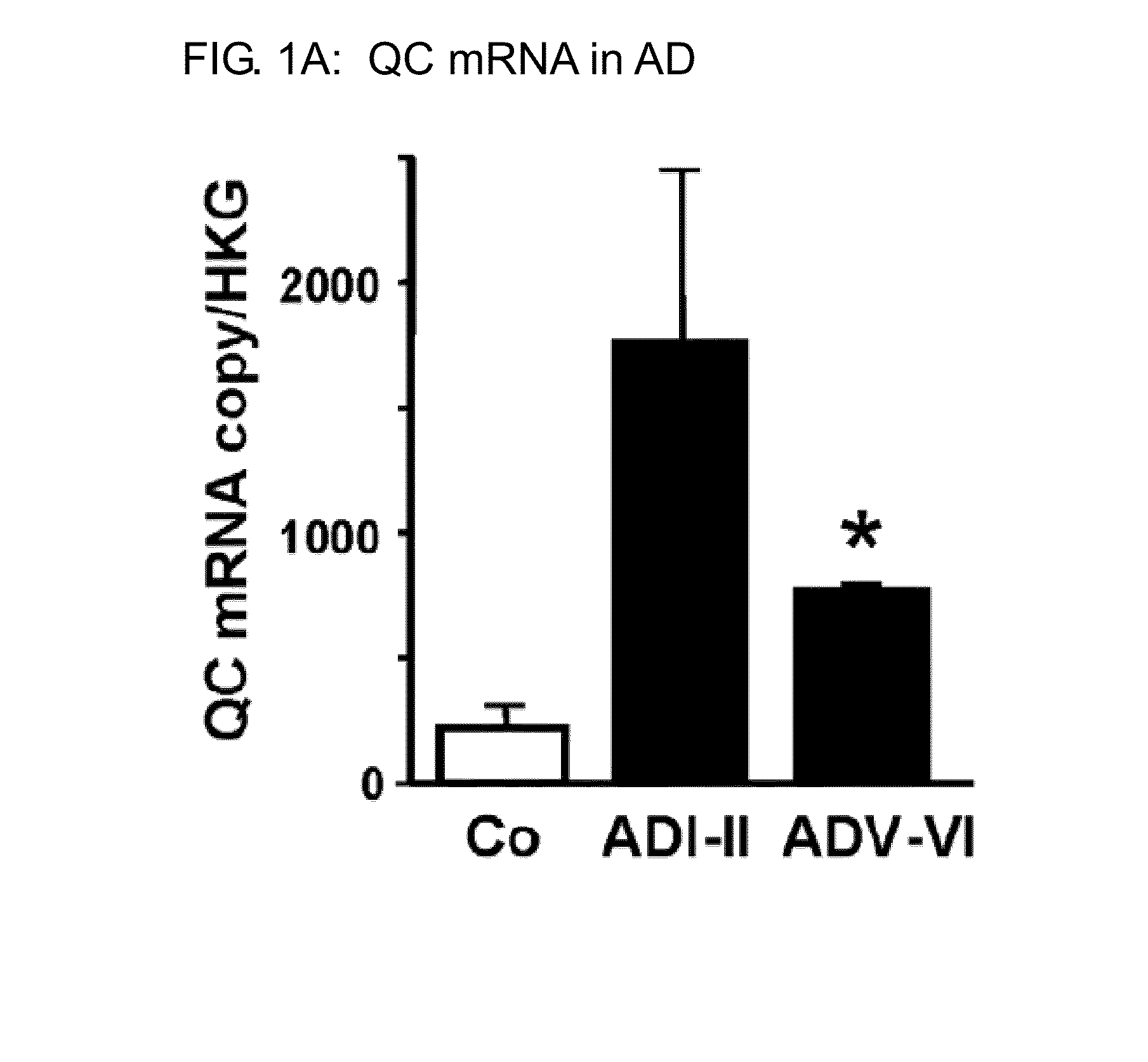
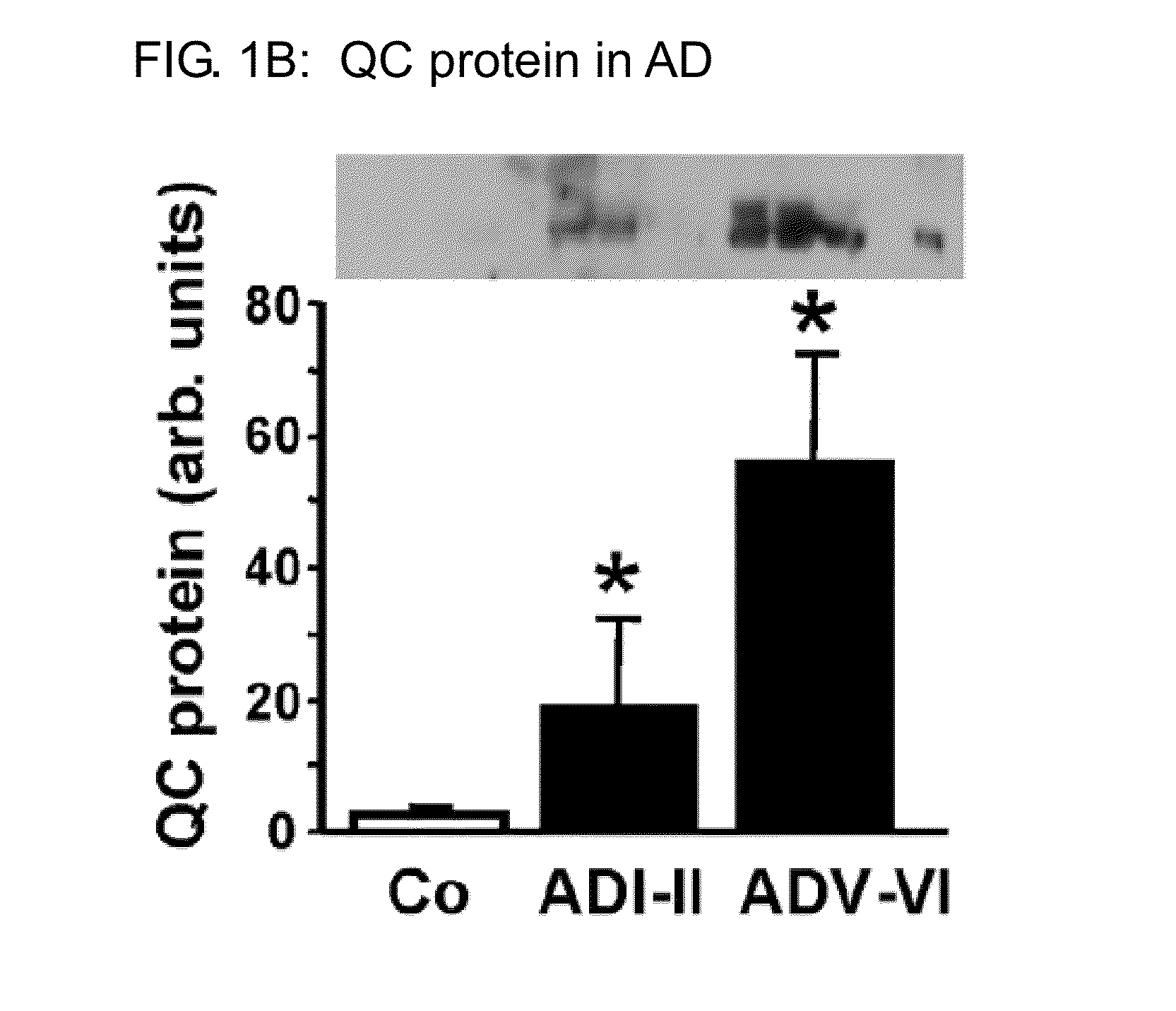
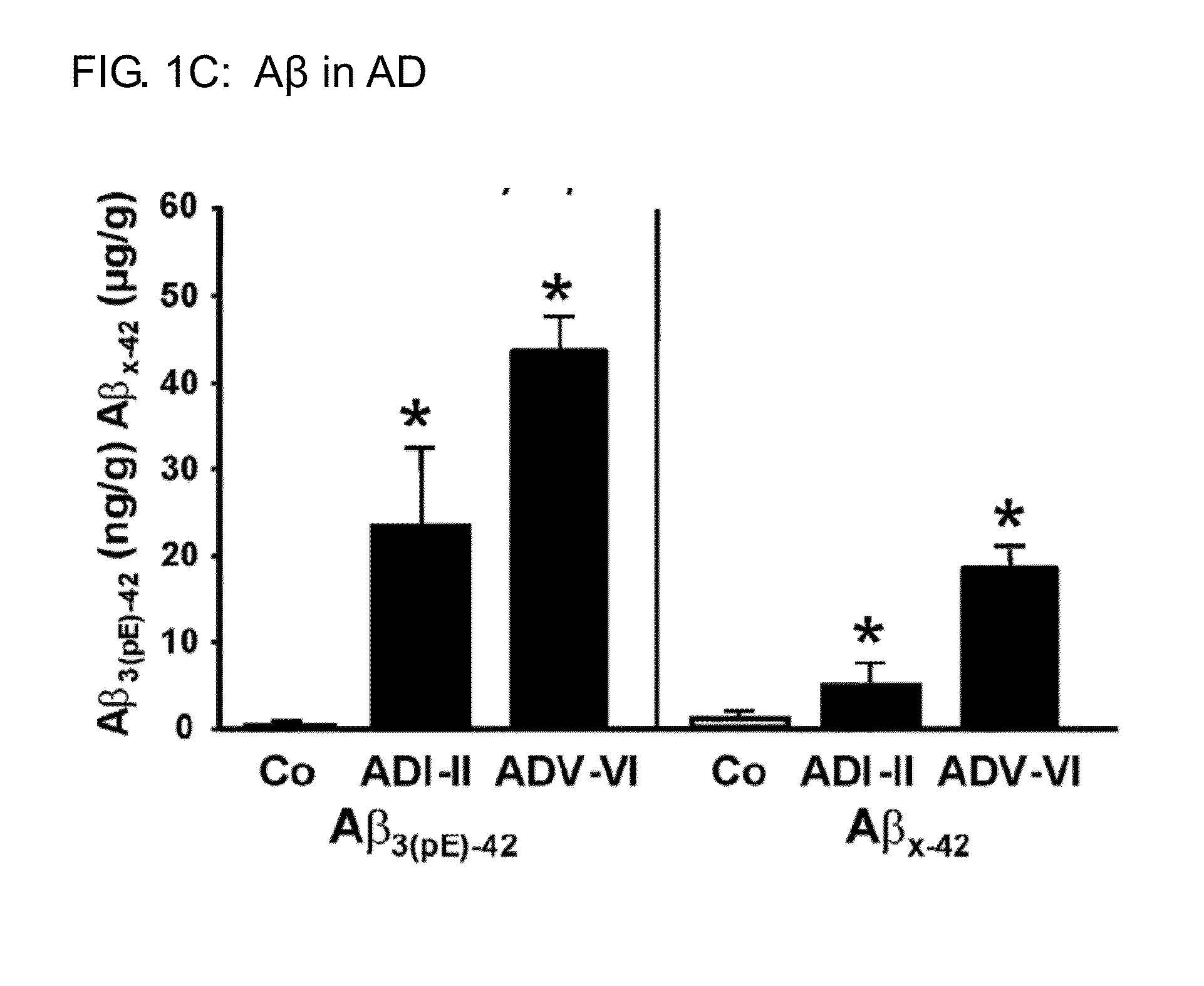
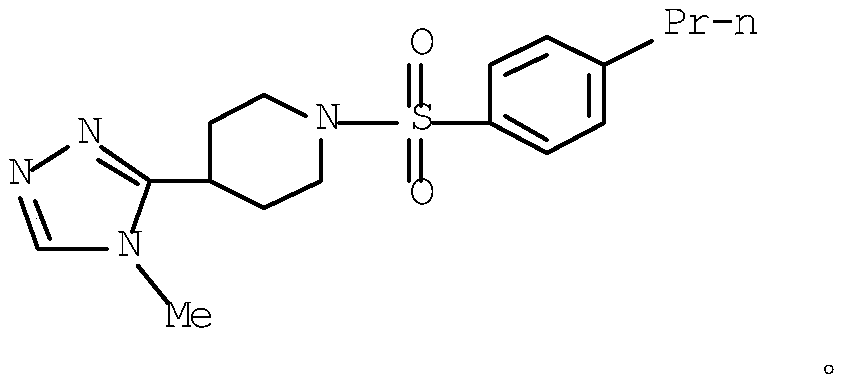
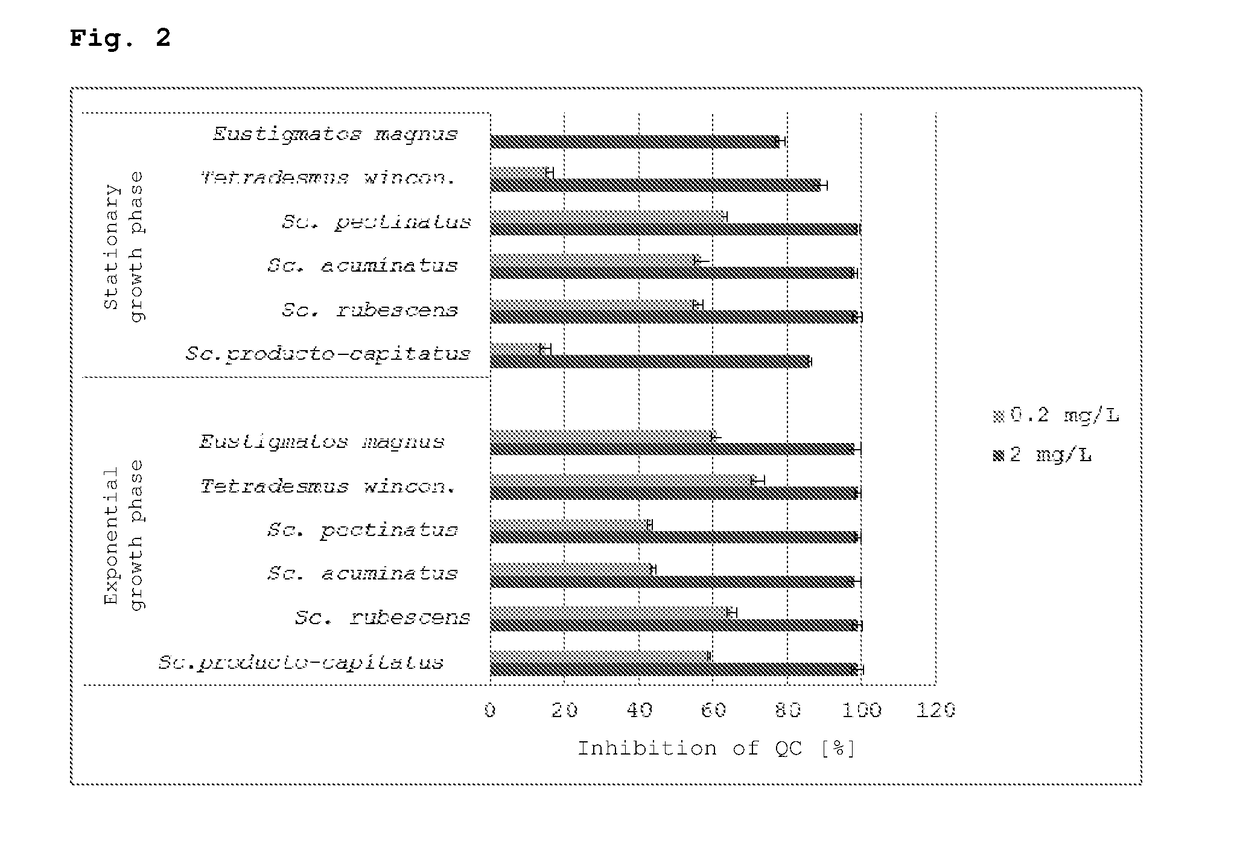
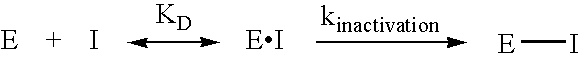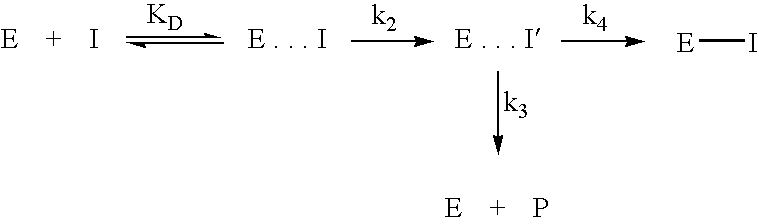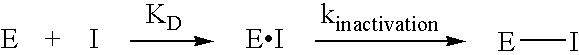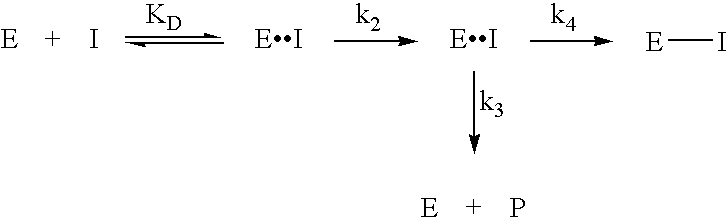Patents
Literature
54 results about "Glutaminyl cyclase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
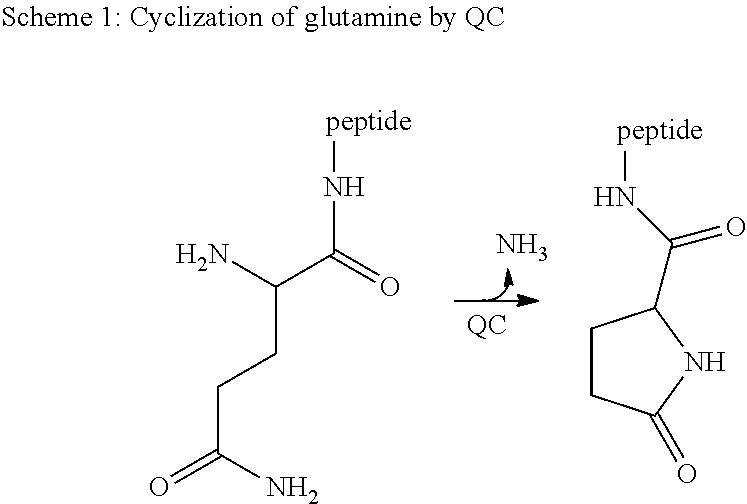
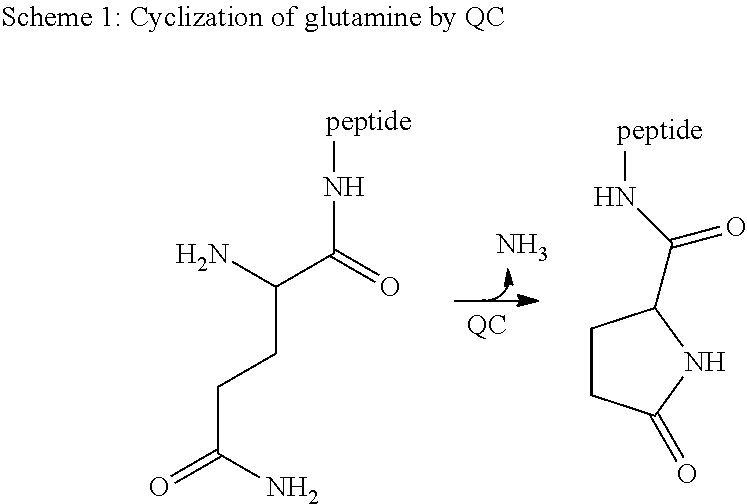
Glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the QPCT gene. [5] [6] This gene encodes human pituitary glutaminyl cyclase , which is responsible for the presence of pyroglutamyl residues in many neuroendocrine peptides .
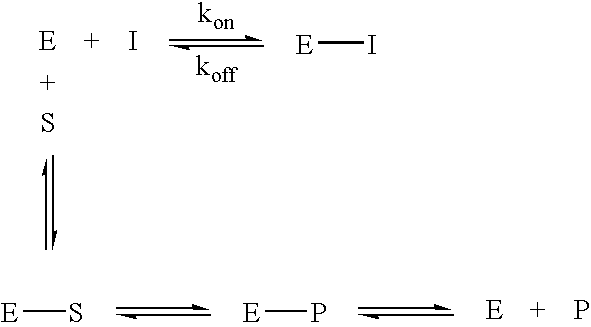
Inhibitors of glutaminyl cyclase
The present invention relates to novel inhibitors of glutaminyl cyclase and combinations thereof for the treatment of neuronal disorders, especially Alzheimer's disease, Down Syndrome, Parkinson disease, Chorea Huntington, pathogenic psychotic conditions, schizophrenia, impaired food intake, sleep-wakefulness, impaired homeostatic regulation of energy metabolism, impaired autonomic function, impaired hormonal balance, impaired regulation, body fluids, hypertension, fever, sleep dysregulation, anorexia, anxiety related disorders including depression, seizures including epilepsy, drug withdrawal and alcoholism, neurodegenerative disorders including cognitive dysfunction and dementia.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Use of effectors of glutaminyl and glutamate cyclases
ActiveUS20070191366A1Stimulate gastrointestinal tractPrevent proliferationBiocideNervous disorderCyclaseMedicine
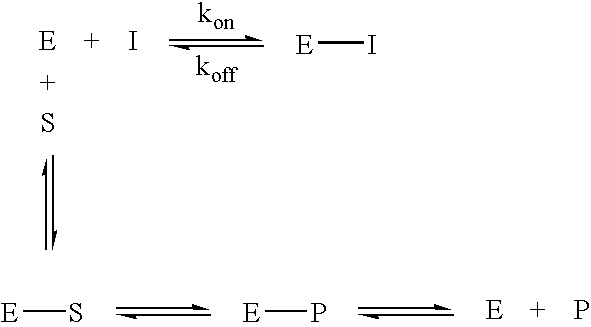
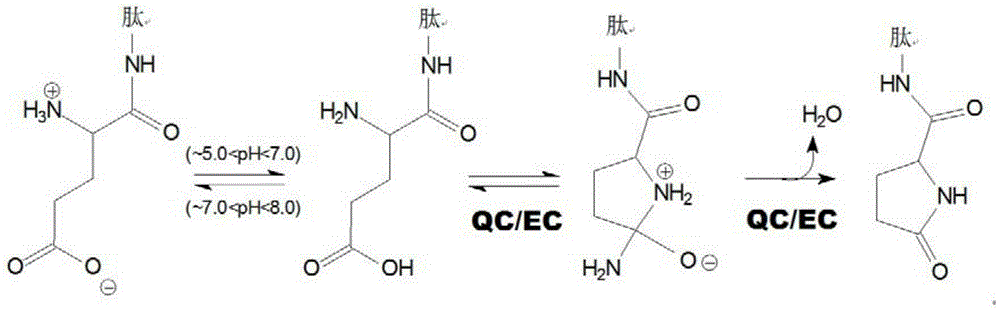
The present invention provides novel physiological substrates of mammalian glutaminyl cyclase (QC, EC 2.3.2.5), new effectors of QC, methods for screening for such effectors, and the use of such effectors and pharmaceutical compositions comprising such effectors for the treatment of conditions that can be treated by modulation of QC-activity. Preferred compositions additionally comprise inhibitors of DP IV or DP IV-like enzymes for the treatment or alleviation of conditions that can be treated by modulation of QC- and DP IV-activity.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Use of glutaminyl cyclase inhibitors
ActiveUS20090068699A1BiocideOrganic active ingredientsMild cognitive impairment (MCI)Percent Diameter Stenosis
An inhibitor of a glutaminyl peptide cyclotransferase, and use thereof for the treatment and / or prevention of a disease or disorder selected from the group consisting of inflammatory diseases selected froma. neurodegenerative diseases, e.g. mild cognitive impairment (MCI), Alzheimer's disease, neurodegeneration in Down Syndrome, Familial British Dementia, Familial Danish Dementia, multiple sclerosis,b. chronic and acute inflammations, e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, restenosis, pancreatitis,c. fibrosis, e.g. lung fibrosis, liver fibrosis, renal fibrosis,d. cancer, e.g. cancer / hemangioendothelioma proliferation, gastric carcinomas,e. metabolic diseases, e.g. hypertension,f. and other inflammatory diseases, e.g. neuropathic pain, graft rejection / graft failure / graft vasculopathy, HIV infections / AIDS, gestosis, tuberous sclerosis.Additionally disclosed are a respective diagnostic method, assay and kit.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Novel inhibitors of glutaminyl cyclase
ActiveUS20050215573A1Facilitated DiffusionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHuntingtons choreaDrug withdrawal
The present invention relates to novel inhibitors of glutaminyl cyclase and combinations thereof for the treatment of neuronal disorders, especially Alzheimer's disease, Down Syndrome, Parkinson disease, Chorea Huntington, pathogenic psychotic conditions, schizophrenia, impaired food intake, sleep-wakefulness, impaired homeostatic regulation of energy metabolism, impaired autonomic function, impaired hormonal balance, impaired regulation, body fluids, hypertension, fever, sleep dysregulation, anorexia, anxiety related disorders including depression, seizures including epilepsy, drug withdrawal and alcoholism, neurodegenerative disorders including cognitive dysfunction and dementia.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Use of inhibitors of glutaminyl cyclase and glutamate cyclase for treatment and prevention of neurodegenerative diseases
Physiological substrates of mammalian glutaminyl cyclase (QC, EC 2.3.2.5), new effectors of QC, methods for screening for such effectors, and the use of such effectors and pharmaceutical compositions comprising such effectors for the treatment of conditions that can be treated by modulation of QC-activity. Preferred compositions additionally comprise inhibitors of DP IV or DP IV-like enzymes for the treatment or alleviation of conditions that can be treated by modulation of QC- and DP IV-activity.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
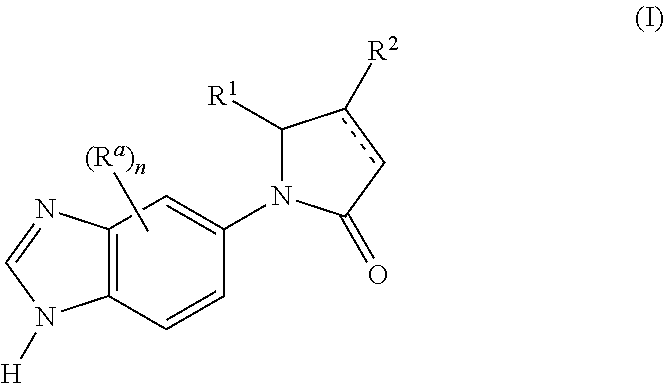
Heterocylcic derivatives as inhibitors of glutaminyl cyclase
ActiveCN102695546ALasting effectOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderCyclaseL-Pyroglutamic Acid
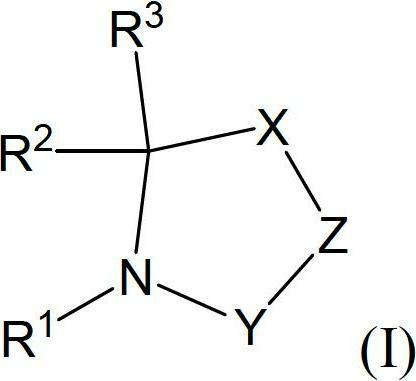
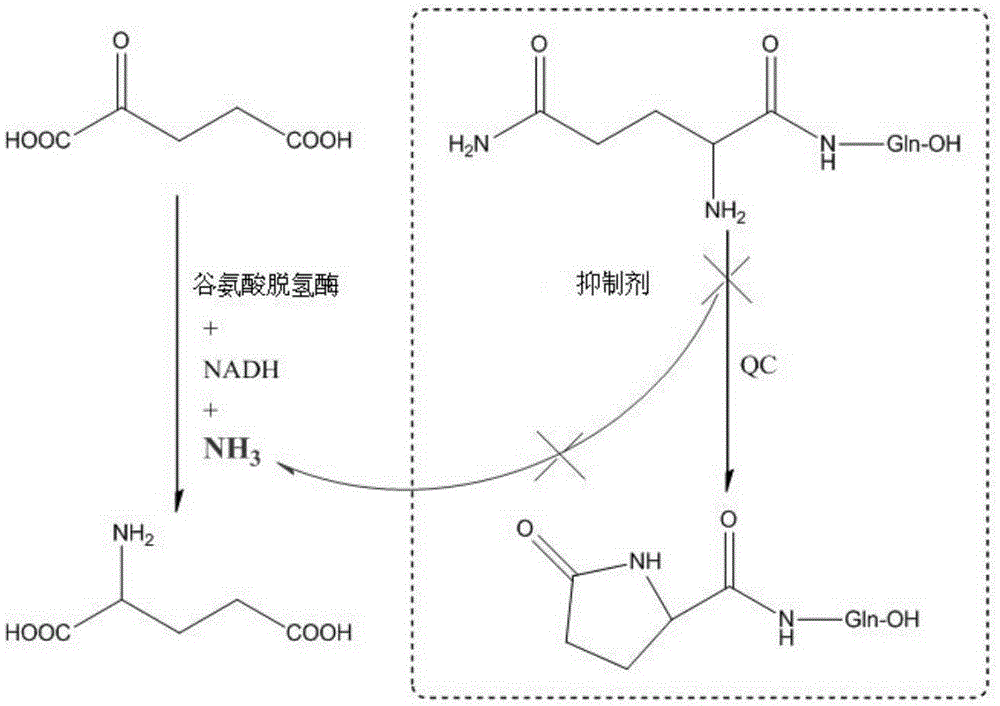
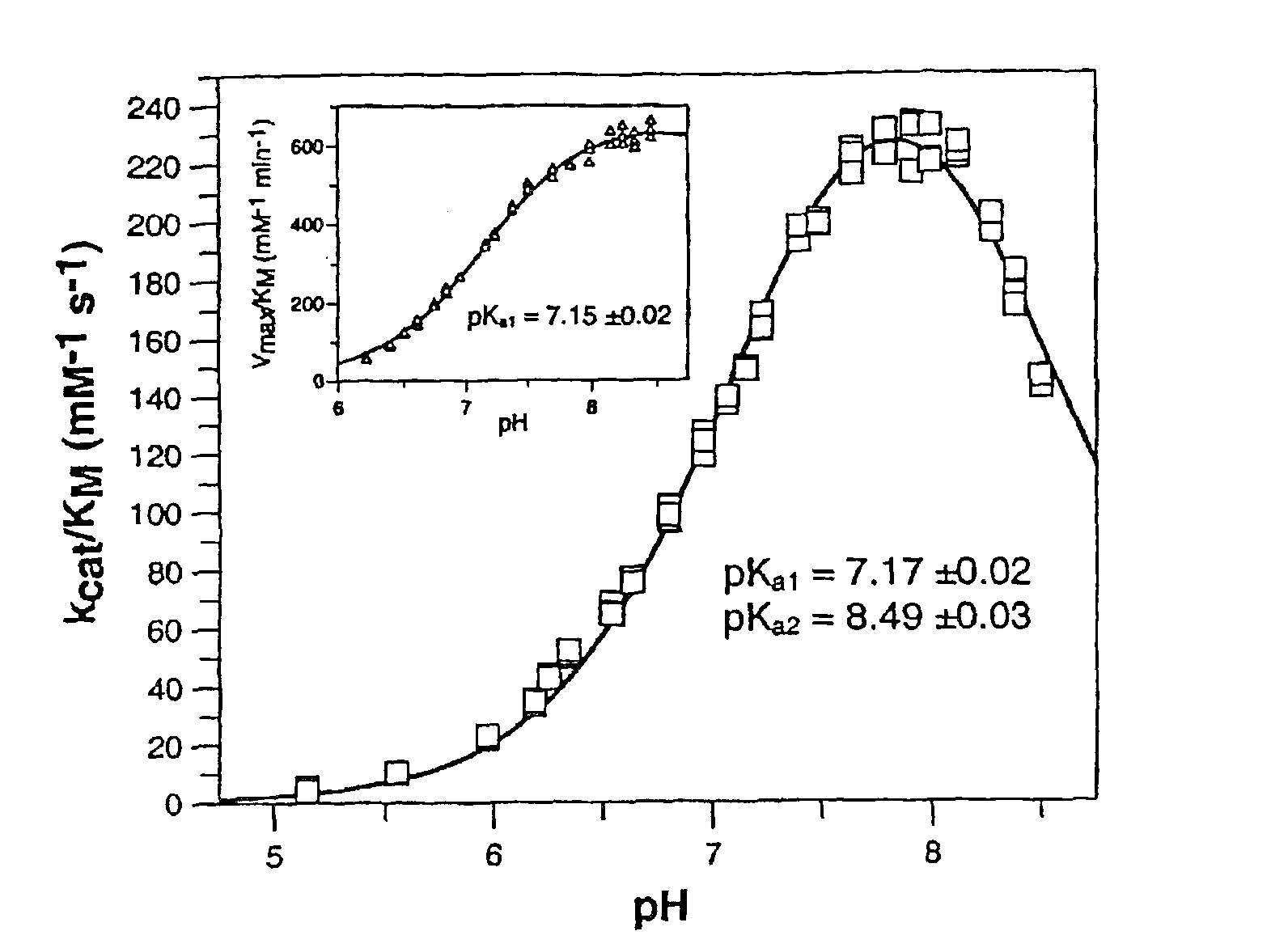
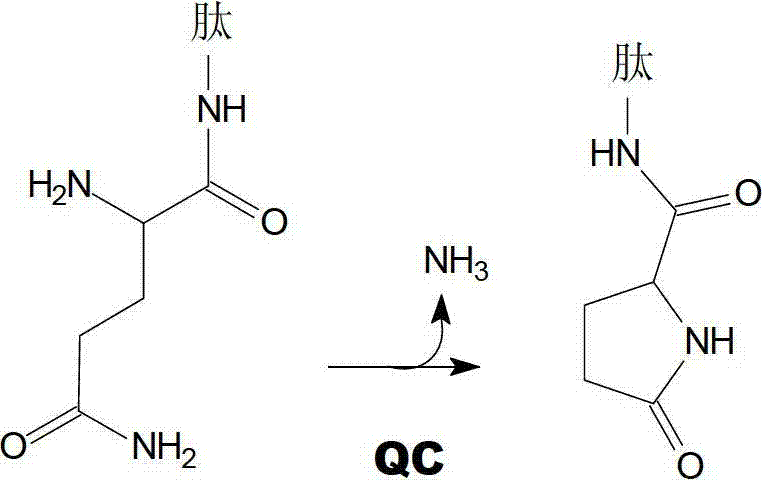
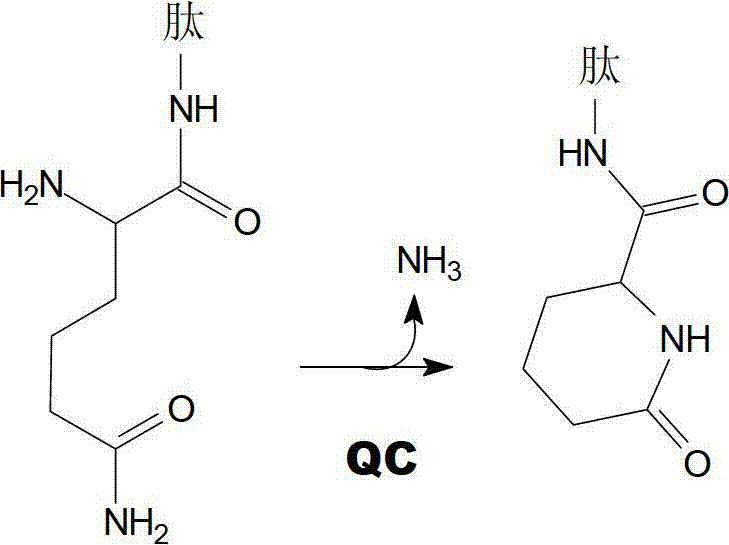
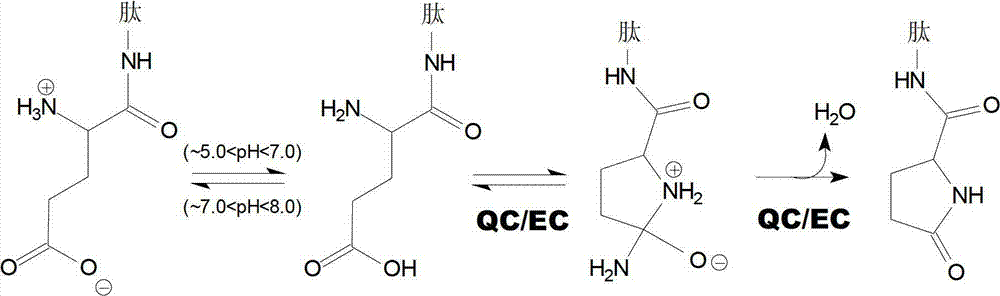
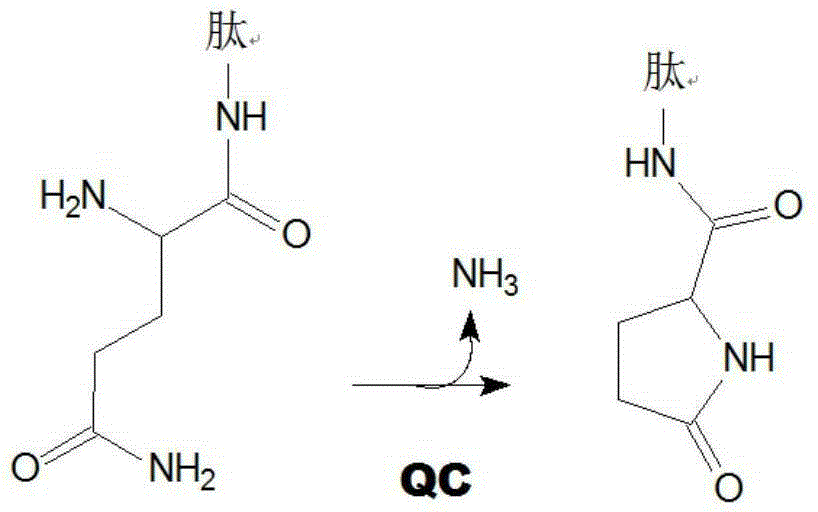
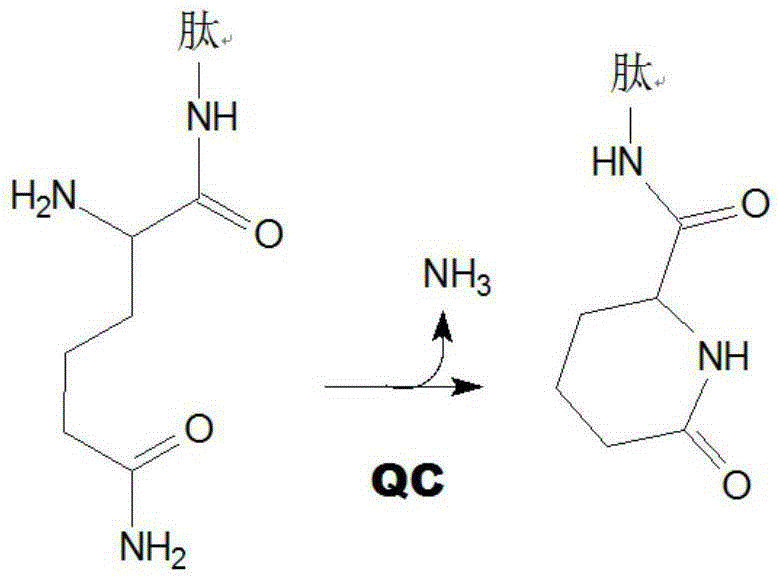
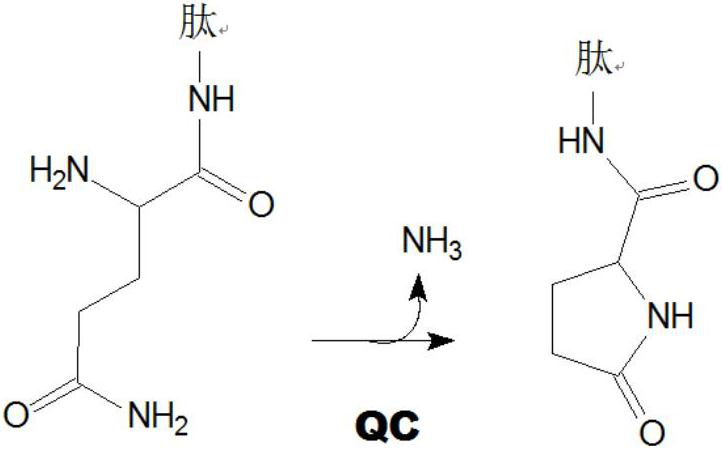
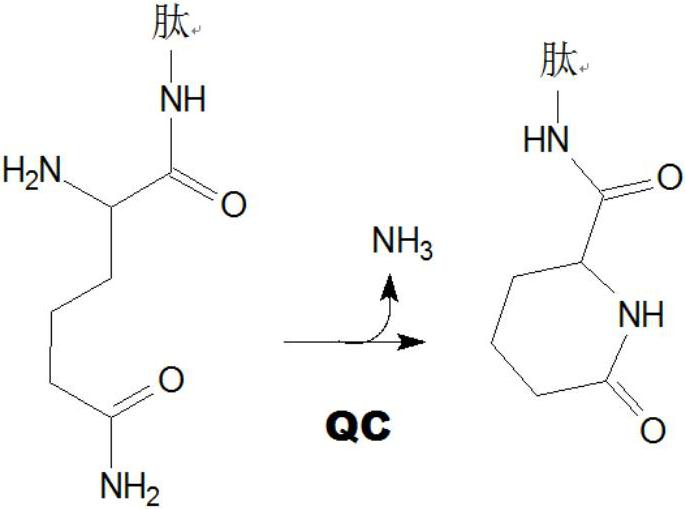
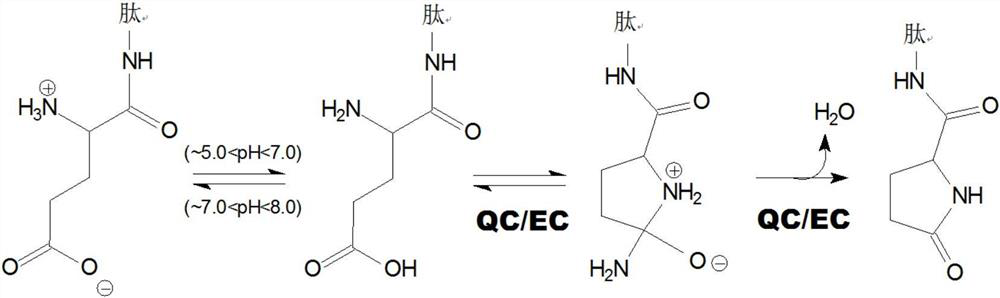
The invention relates to novel pyrrolidine derivatives of formula (I), wherein R1, R2 and R3 are as defined herein, as inhibitors of glutaminyl cyclase (QC, EC 2.3.2.5). QC catalyzes the intramolecular cyclization of N-terminal glutamine residues into pyroglutamic acid (5-oxo-prolyl, pGlu*) under liberation of ammonia and the intramolecular cyclization of N-terminal glutamate residues into pyroglutamic acid under liberation of water.
Owner:维沃永治疗公众有限公司
Glutaminyl cyclase inhibitor
ActiveCN105384692AHigh activityImprove druggabilityNervous disorderOrganic chemistryWater solubleGlutamine
The invention discloses a glutaminyl cyclase inhibitor. The structure of the glutaminyl cyclase inhibitor is shown in the following formula ( as shown in the description). The glutaminyl cyclase inhibitor (QC inhibitor) provided by the invention is designed according to the crystal structure of an active center of target pheron. The glutaminyl cyclase inhibitor shows favorable selectivity and specifity, and has higher druggability. The glutaminyl cyclase inhibitor is rich in parent structures, good in water solubility, good in transmembrane properties and high in activity.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Novel Inhibitors
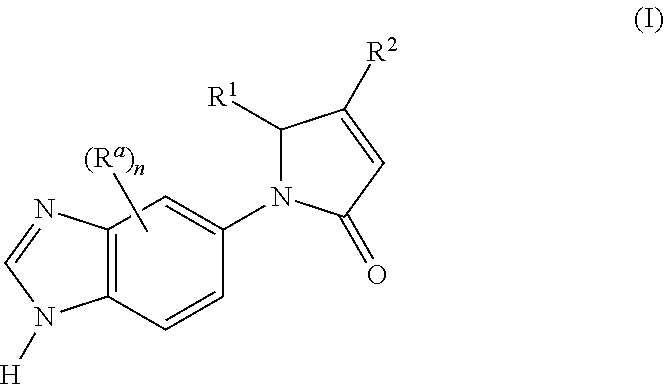
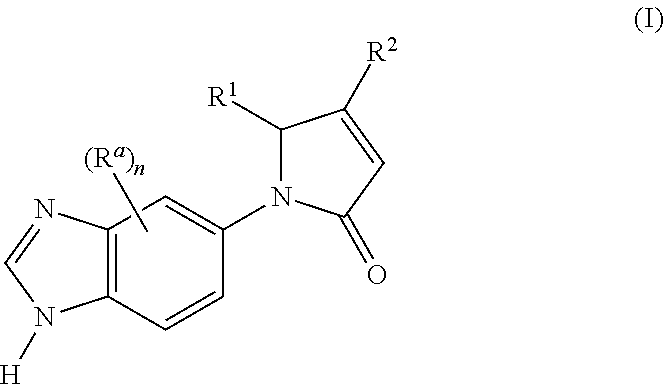
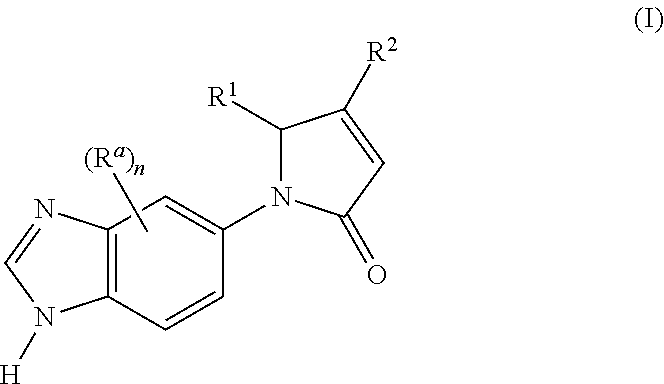
Novel heterocyclic derivatives of formula (I):or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate or polymorph thereof, including all tautomers and stereoisomers thereof, wherein Ra, n, R1 and R2 are as defined herein, as inhibitors of glutaminyl cyclase (QC, EC 2.3.2.5).
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
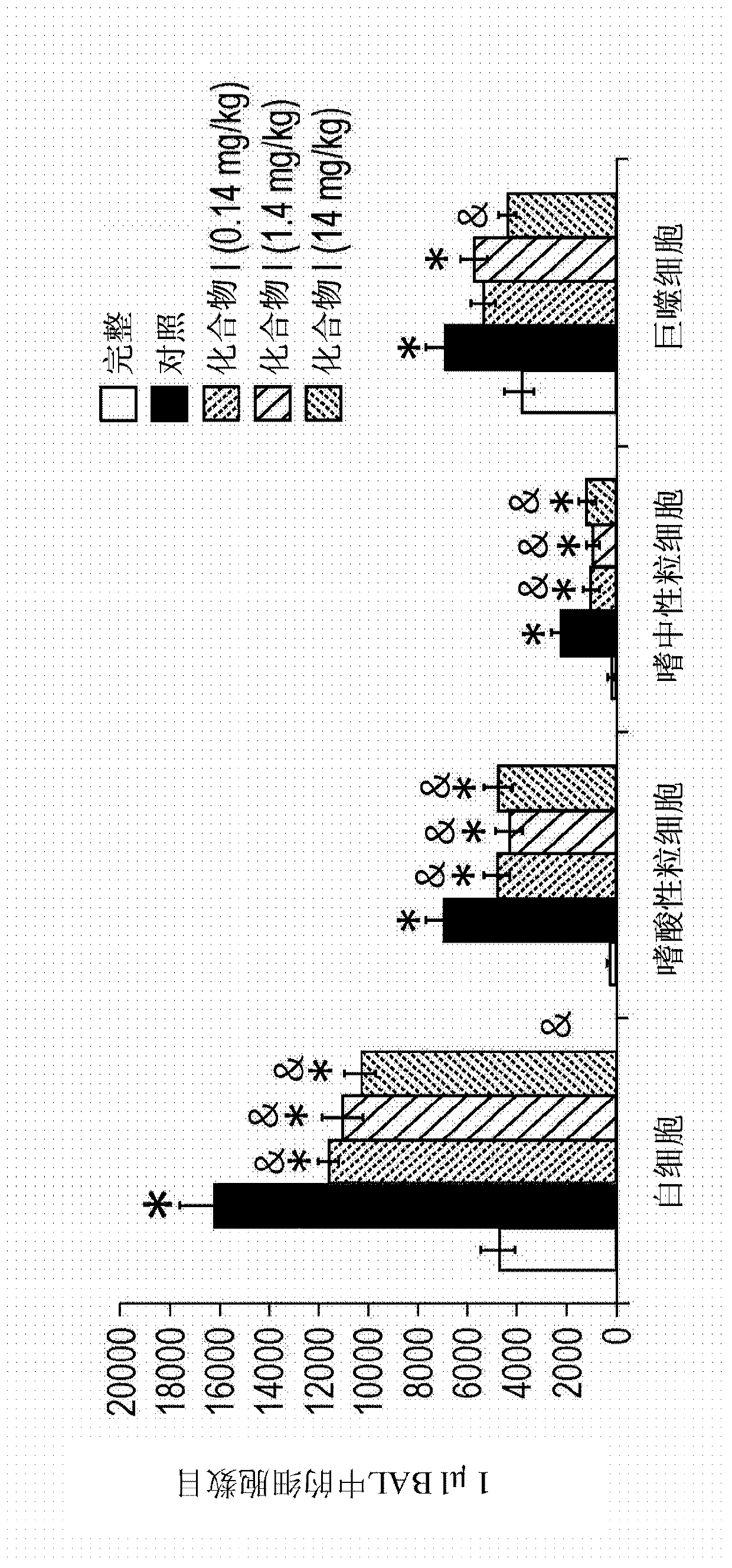
Methods of treating or preventing an inflammatory disease or condition using glutaminyl cyclase inhibitors
Methods for the treatment and / or prevention of an inflammatory disease or disorder through administration of an inhibitor of a glutaminyl peptide cyclotransferase. Inflammatory diseases or disorders treated or prevented by methods disclosed herein include mild cognitive impairment (MCI), rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, restenosis, pancreatitis, sepsis and peritonitus. Further provided are respective diagnostic methods, assays and kits.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Novel genes related to glutaminyl cyclase
ActiveCN101573450AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryIsozymeGlutaminyl-Peptide Cyclotransferase
The present invention relates to novel glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase-like proteins (QPCTLs), which are isoenzymes of glutaminyl cyclase (QC, EC 2.3.2.5), and to isolated nucleic acids coding for these isoenzymes, all of which are useful for the discovery of new therapeutic agents, for measuring cyclase activity, and for determining the inhibitory activity of compounds against these glutaminyl cyclase isoenzymes.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Method of treating inflammation with glutaminyl cyclase inhibitors
ActiveUS8338120B2Organic active ingredientsBiocideTransferase inhibitorMild cognitive impairment (MCI)
Provided herein are methods for the treatment and / or prevention of an inflammatory disease or disorder through administration of an inhibitor of a glutaminyl peptide cyclotransferase. Inflammatory diseases or disorders treated or prevented by methods disclosed herein include mild cognitive impairment (MCI), rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, restenosis and pancreatitis.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
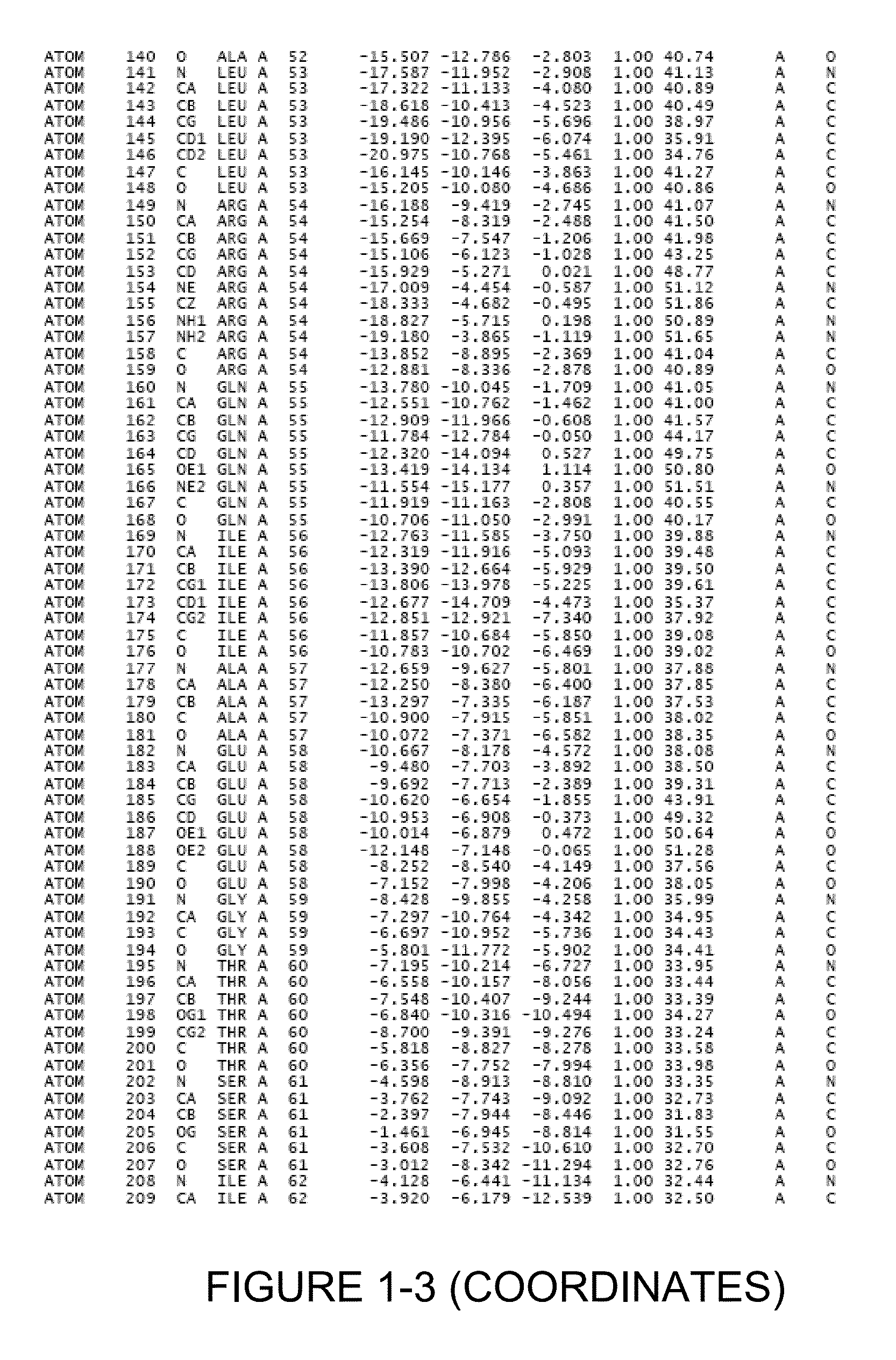
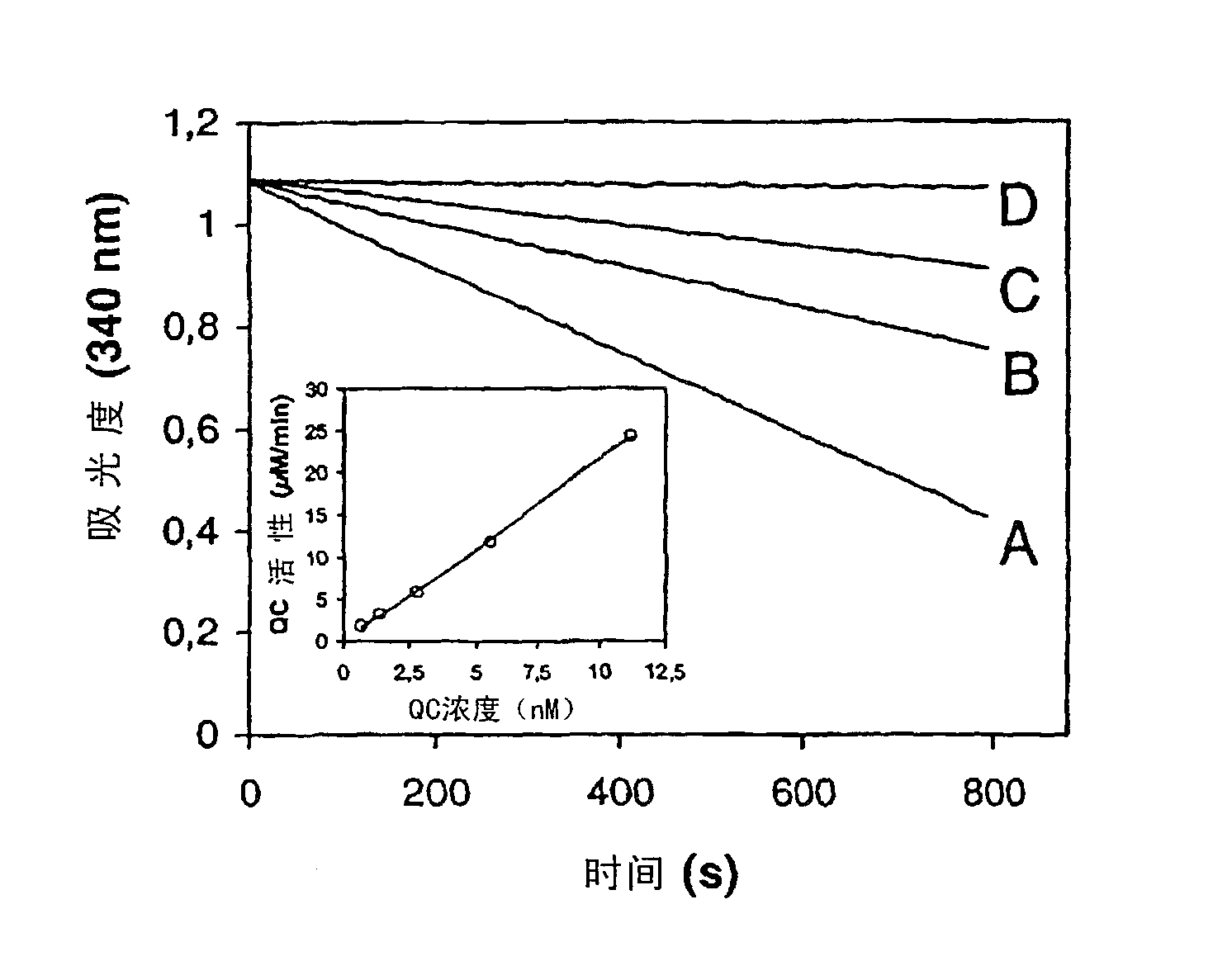
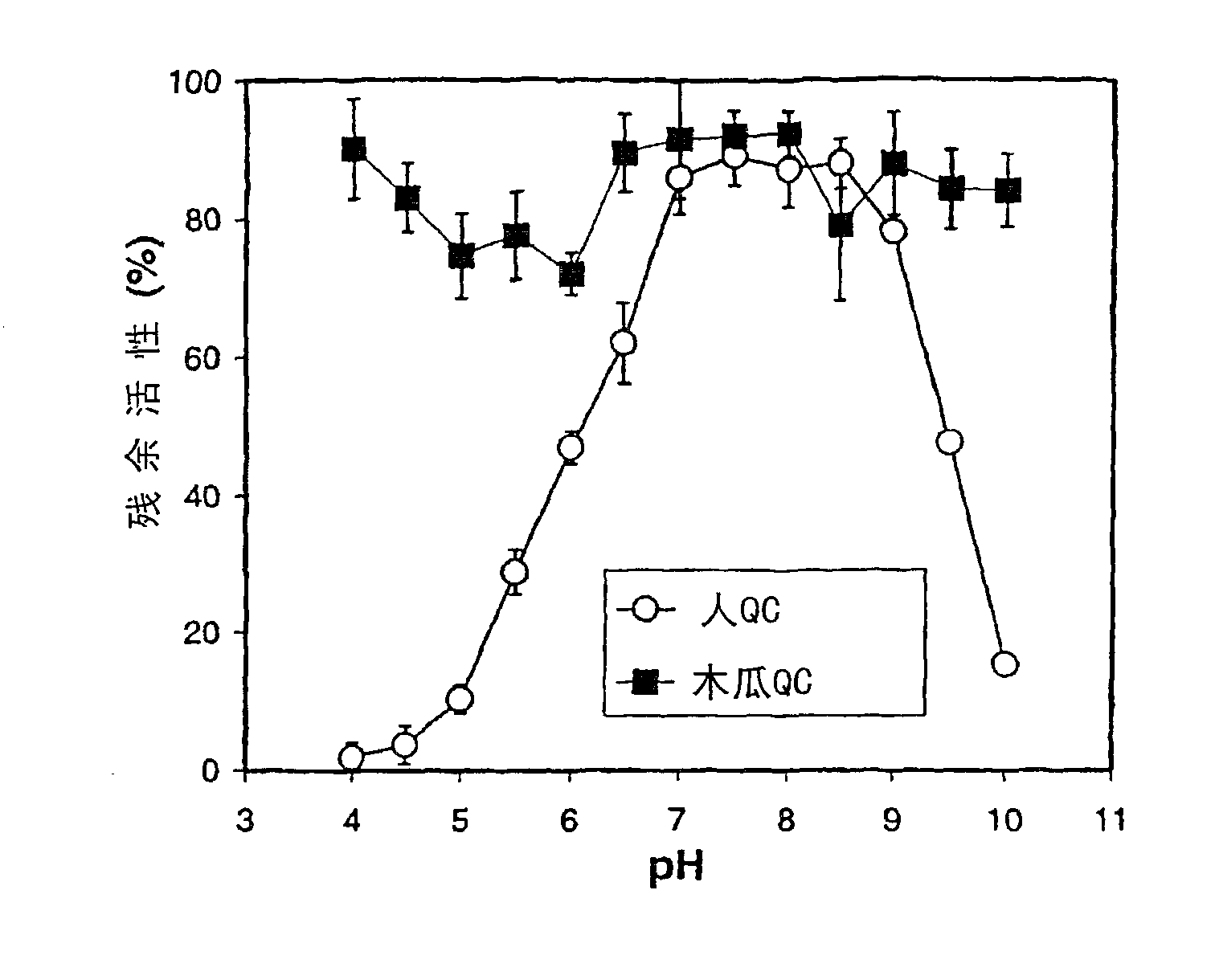
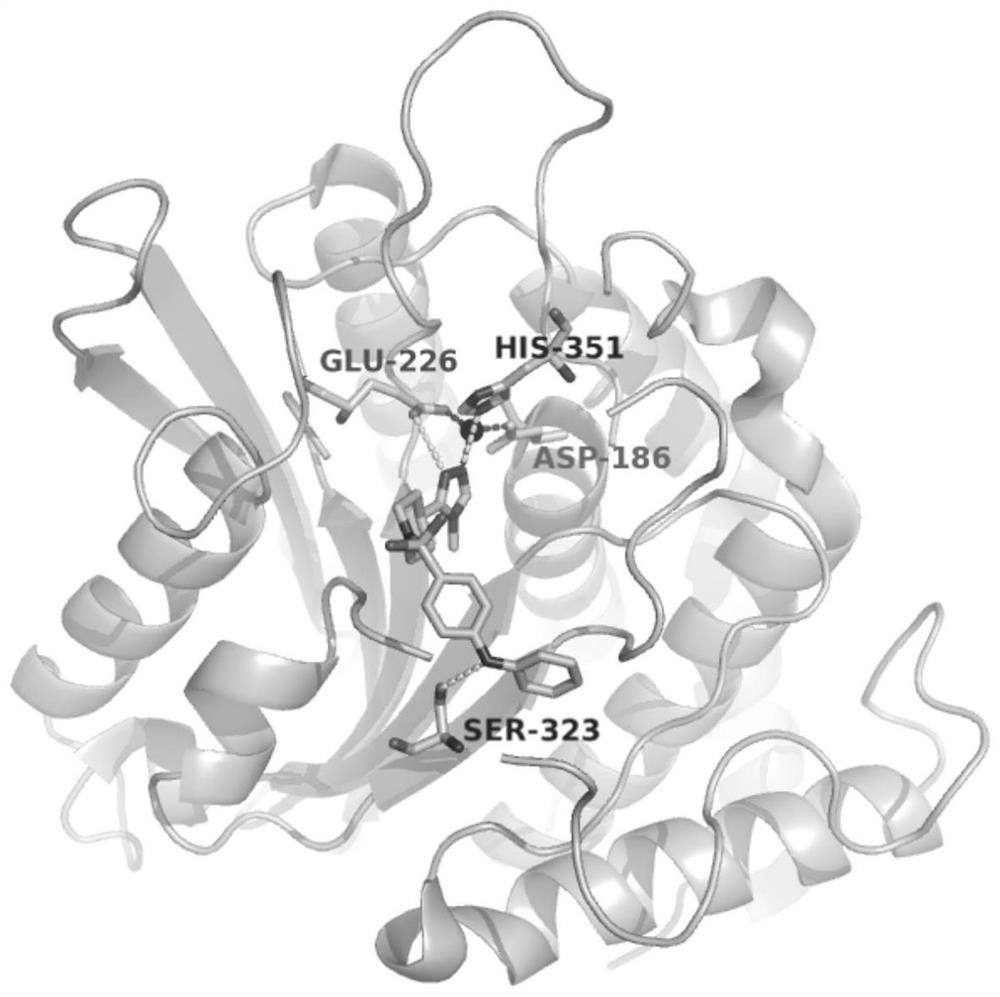
Crystal structure of glutaminyl cyclase
InactiveUS8409837B2Molecular designAnalogue computers for chemical processesCrystal structureGlutamine
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Novel diagnostic method
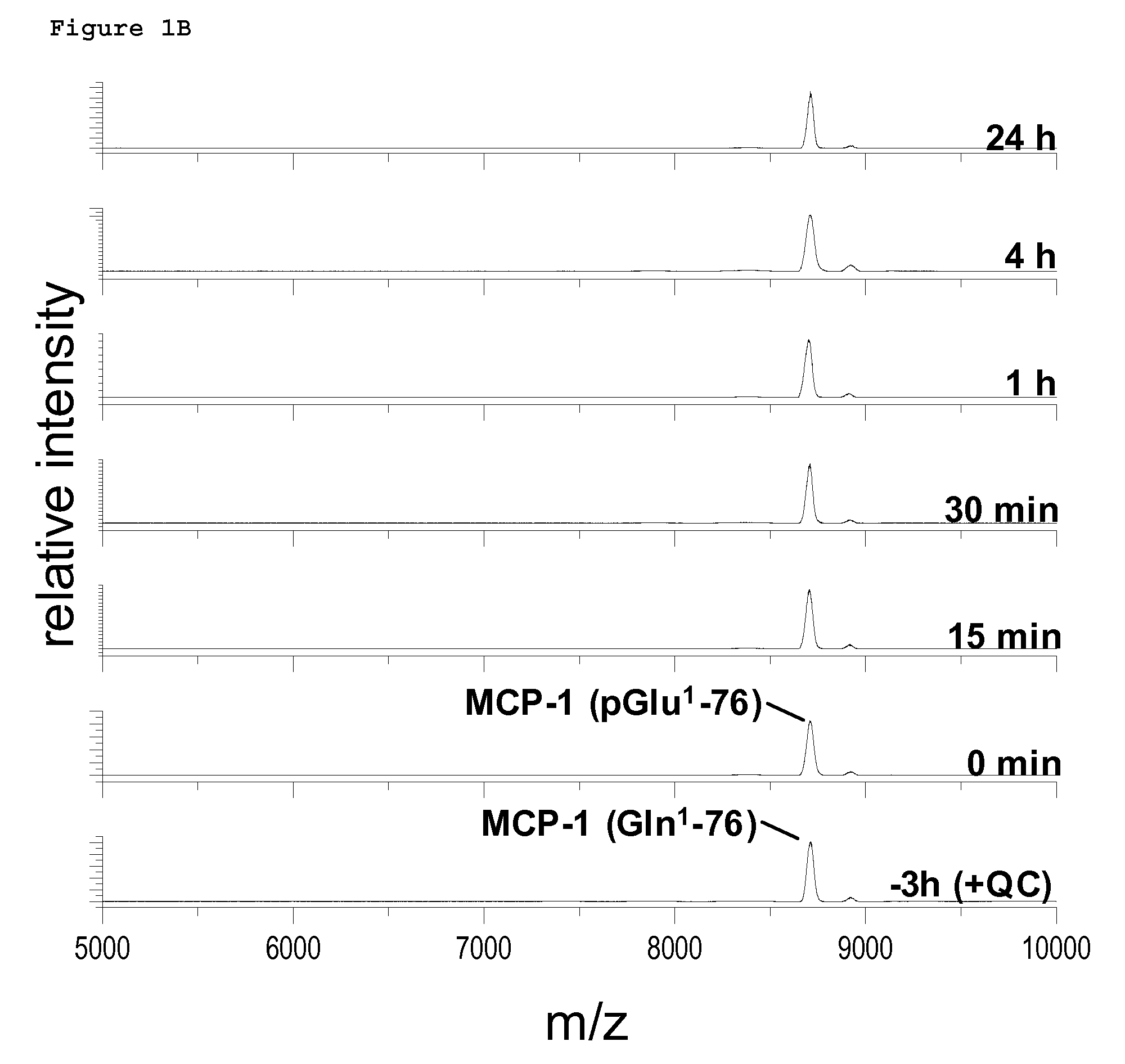
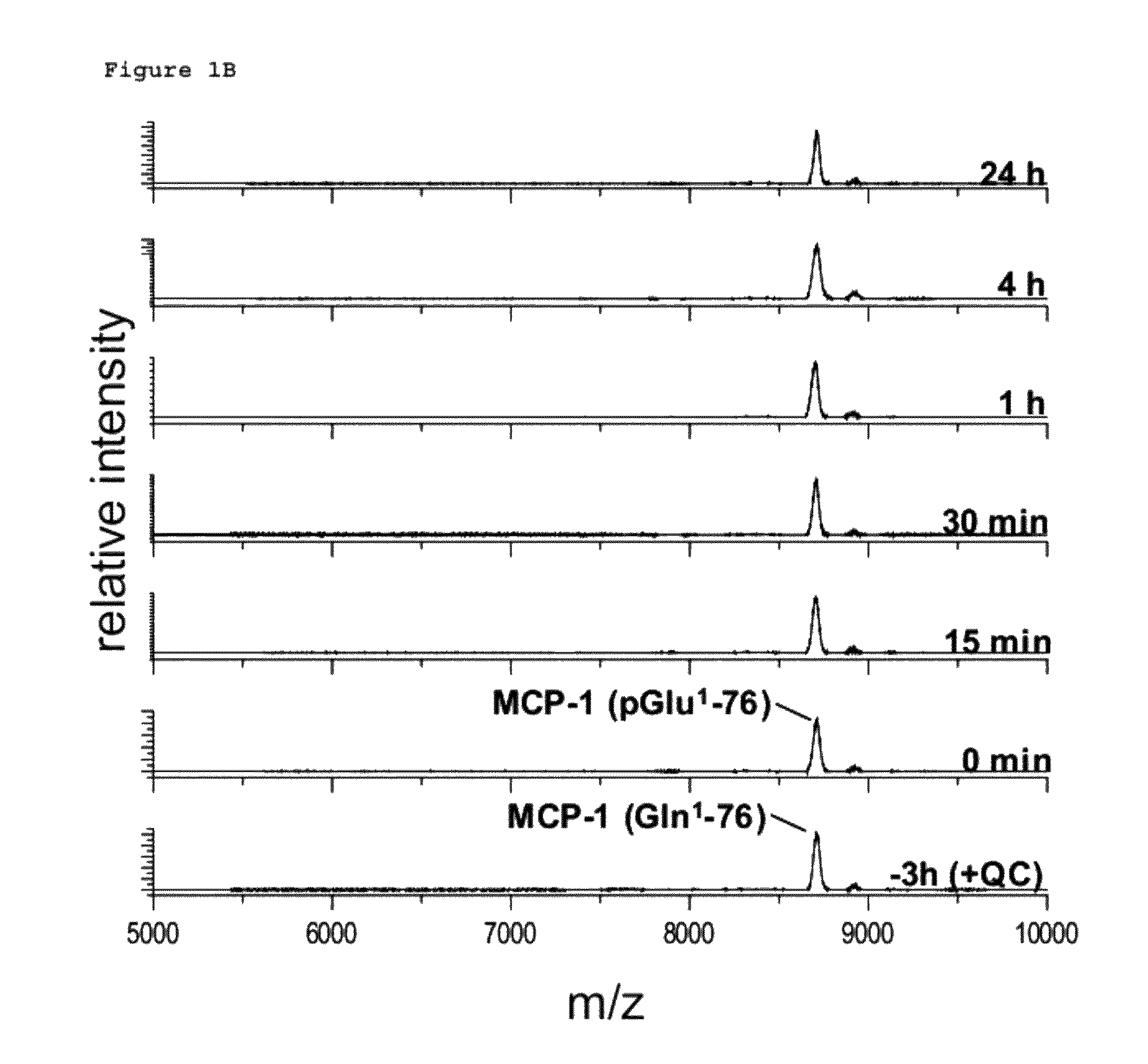
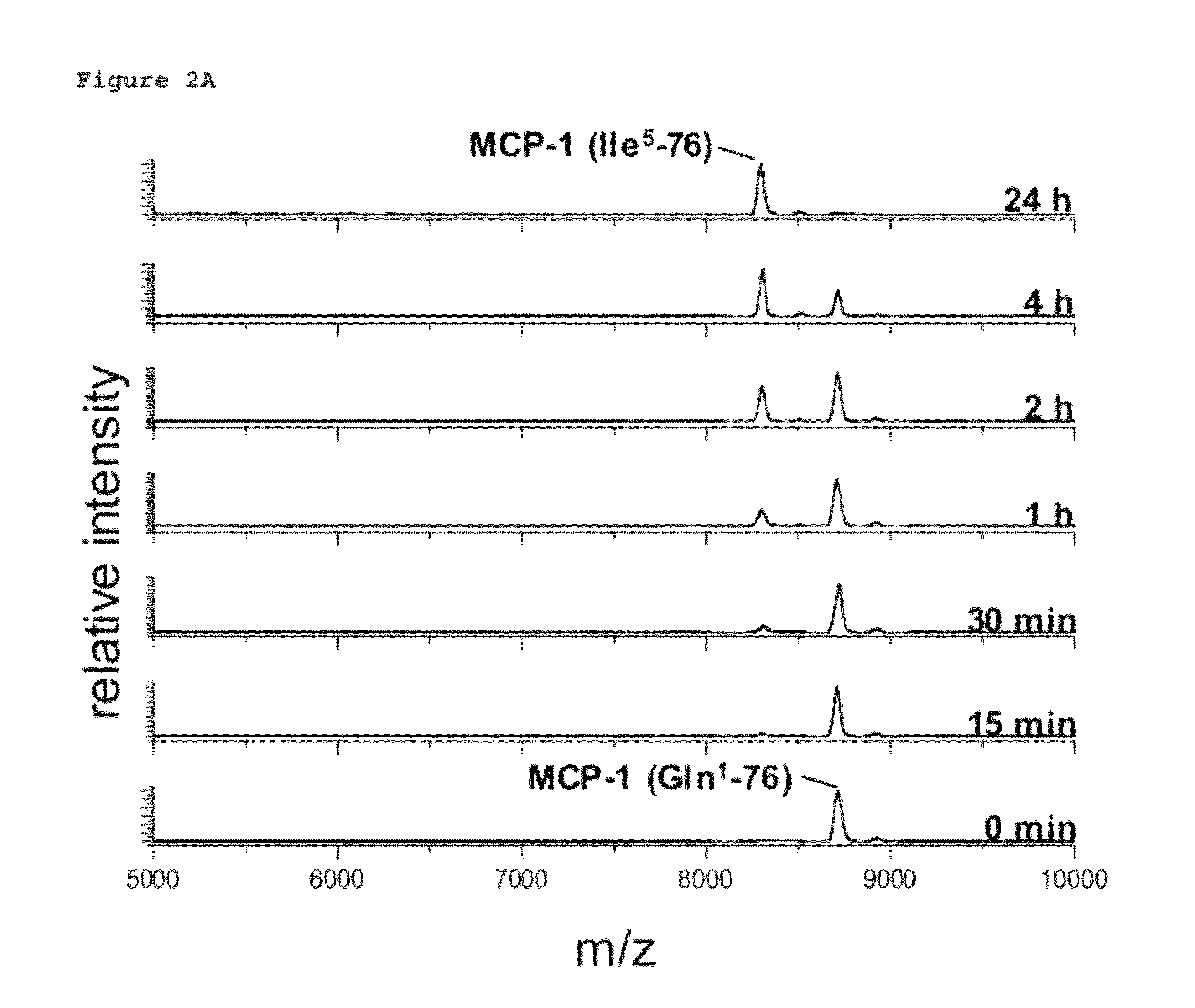
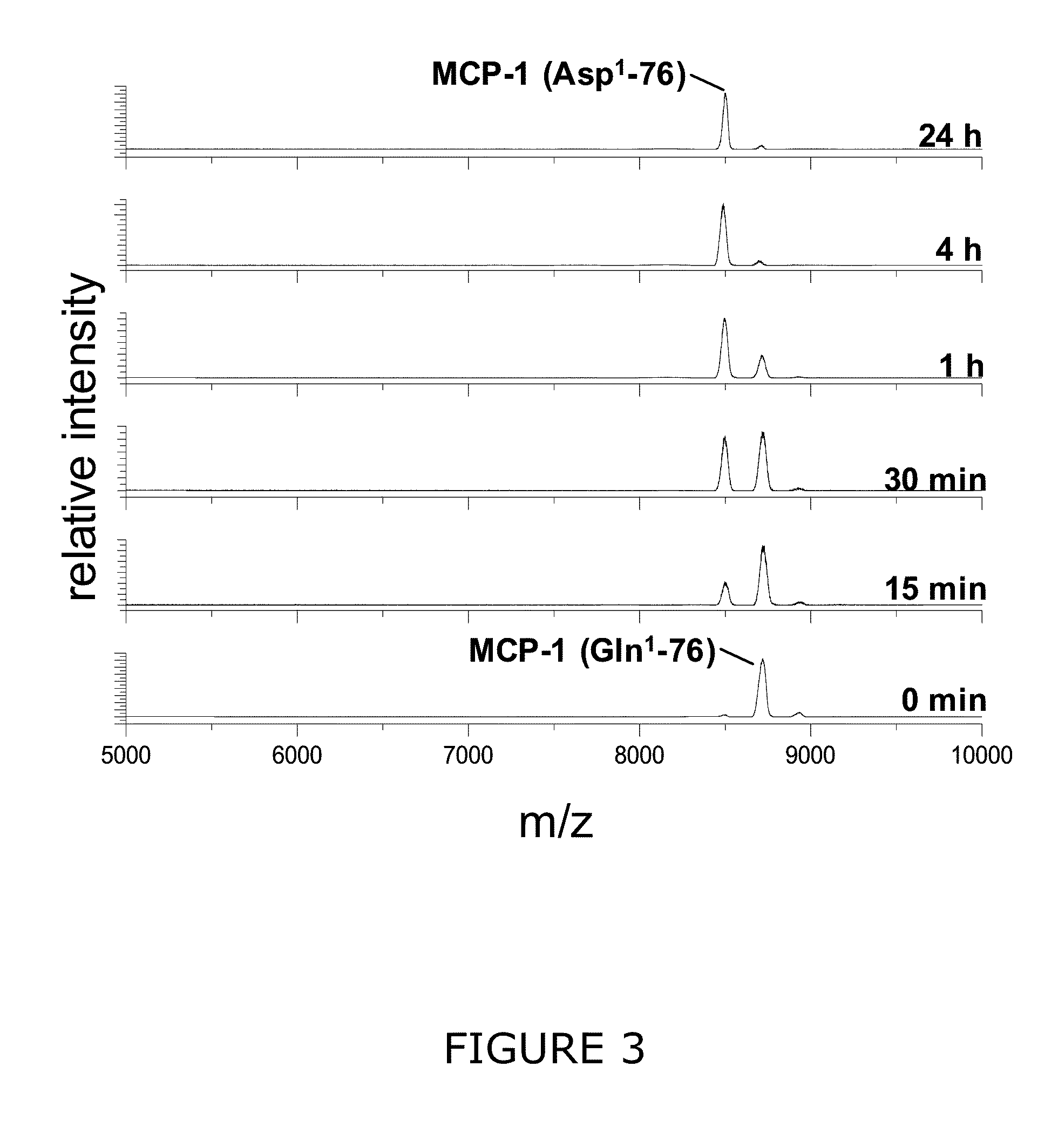
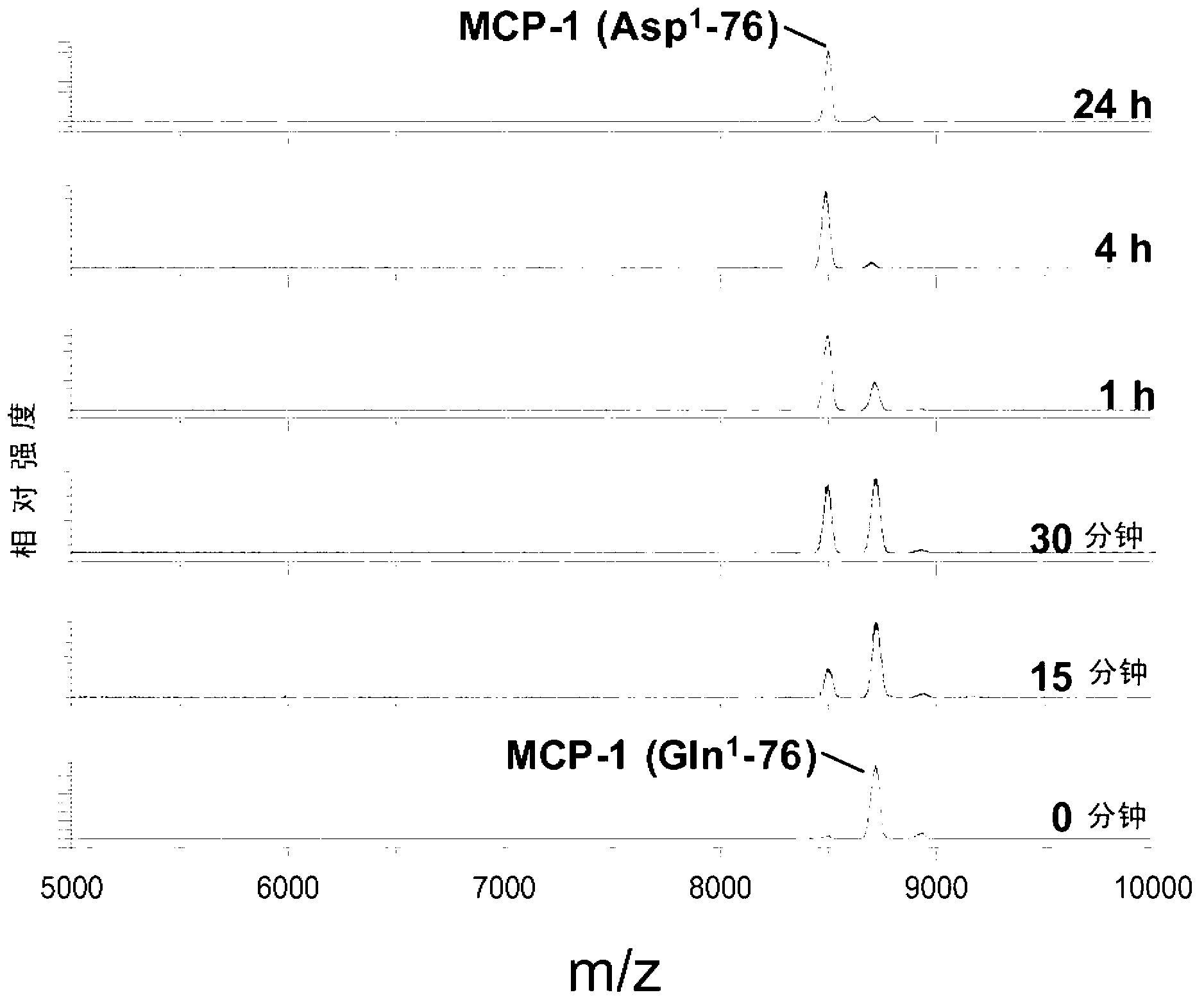
InactiveUS20110212853A1Applicability of MCP-Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningBiomarker (petroleum)Glutamine
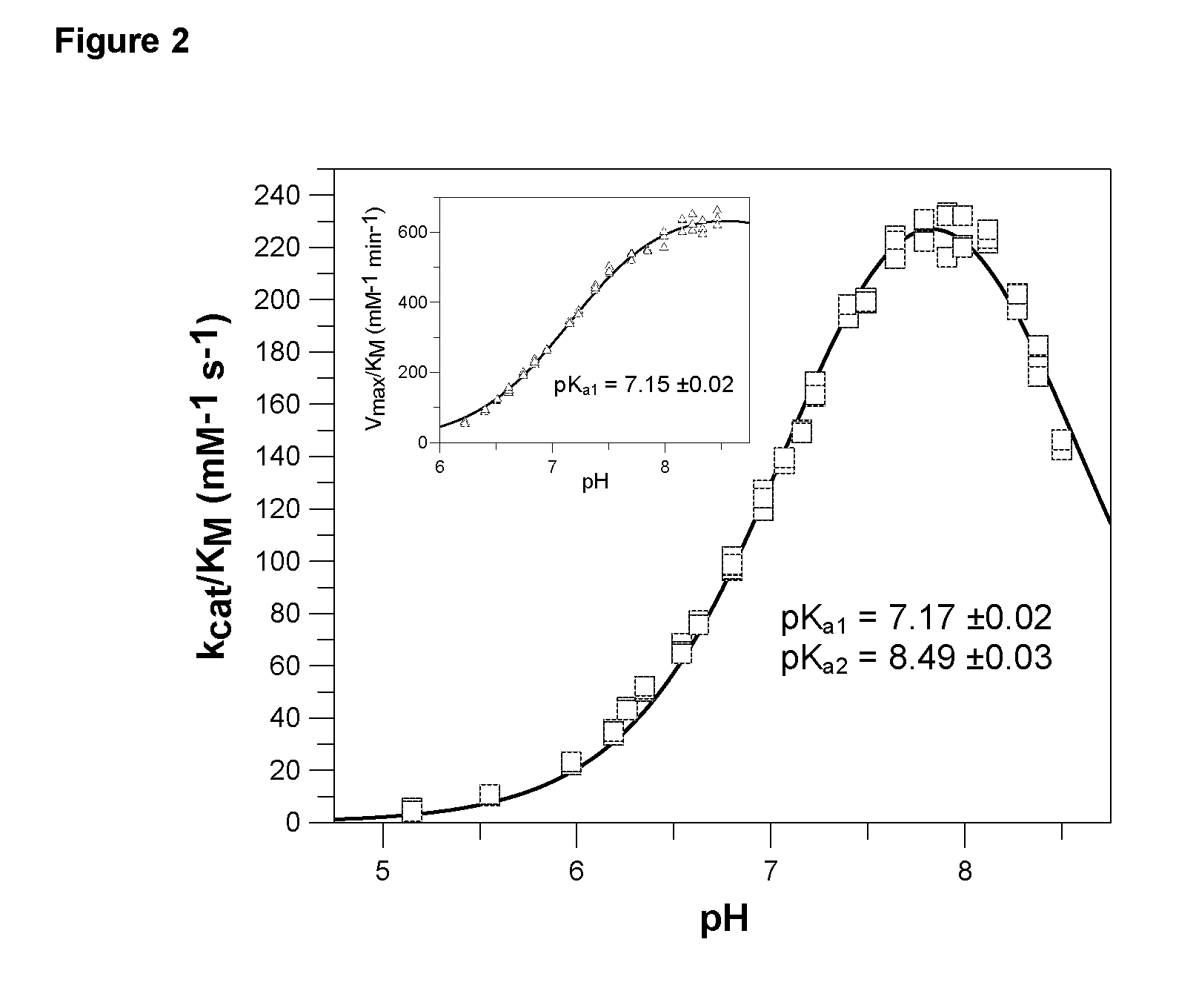
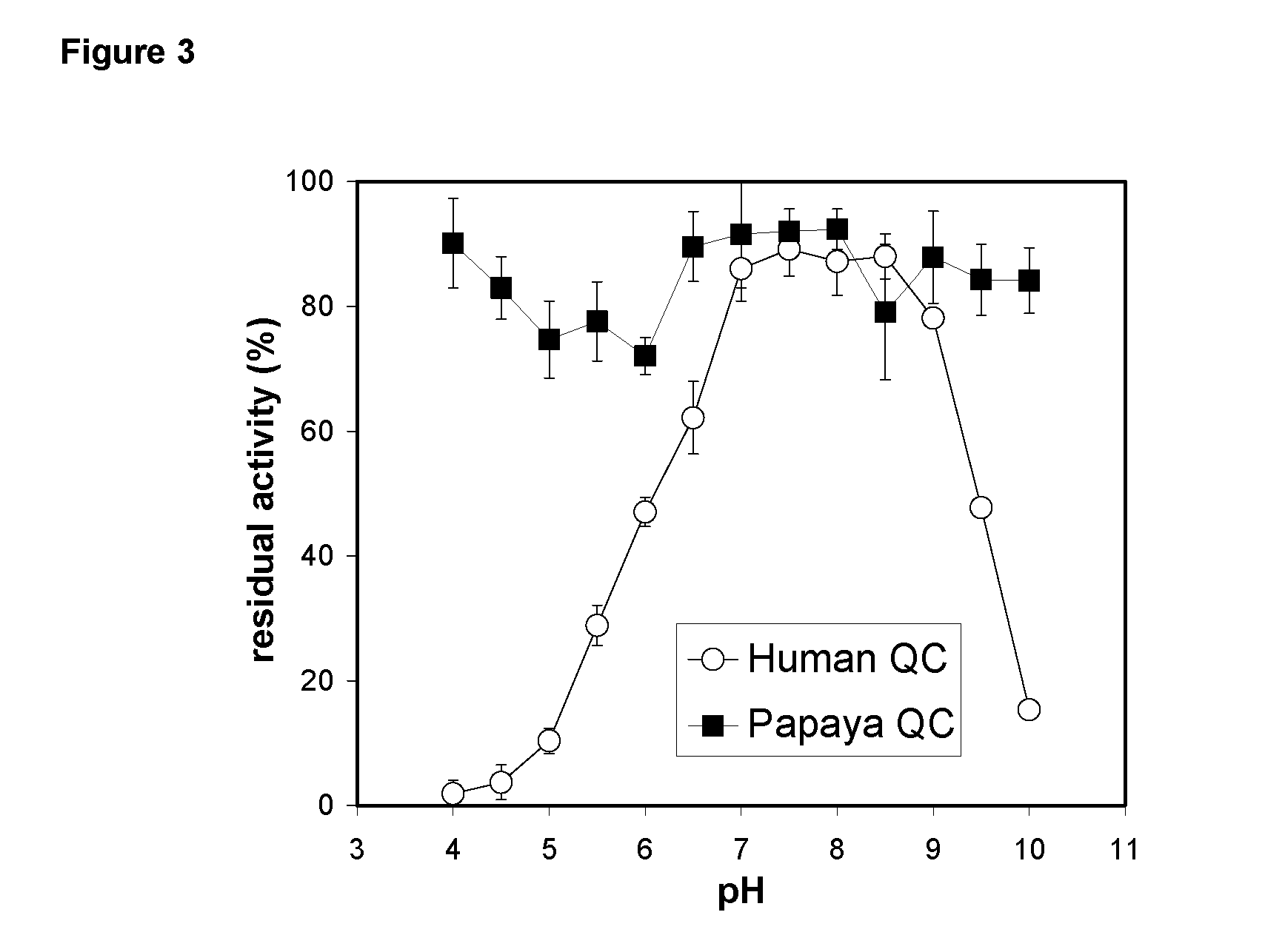
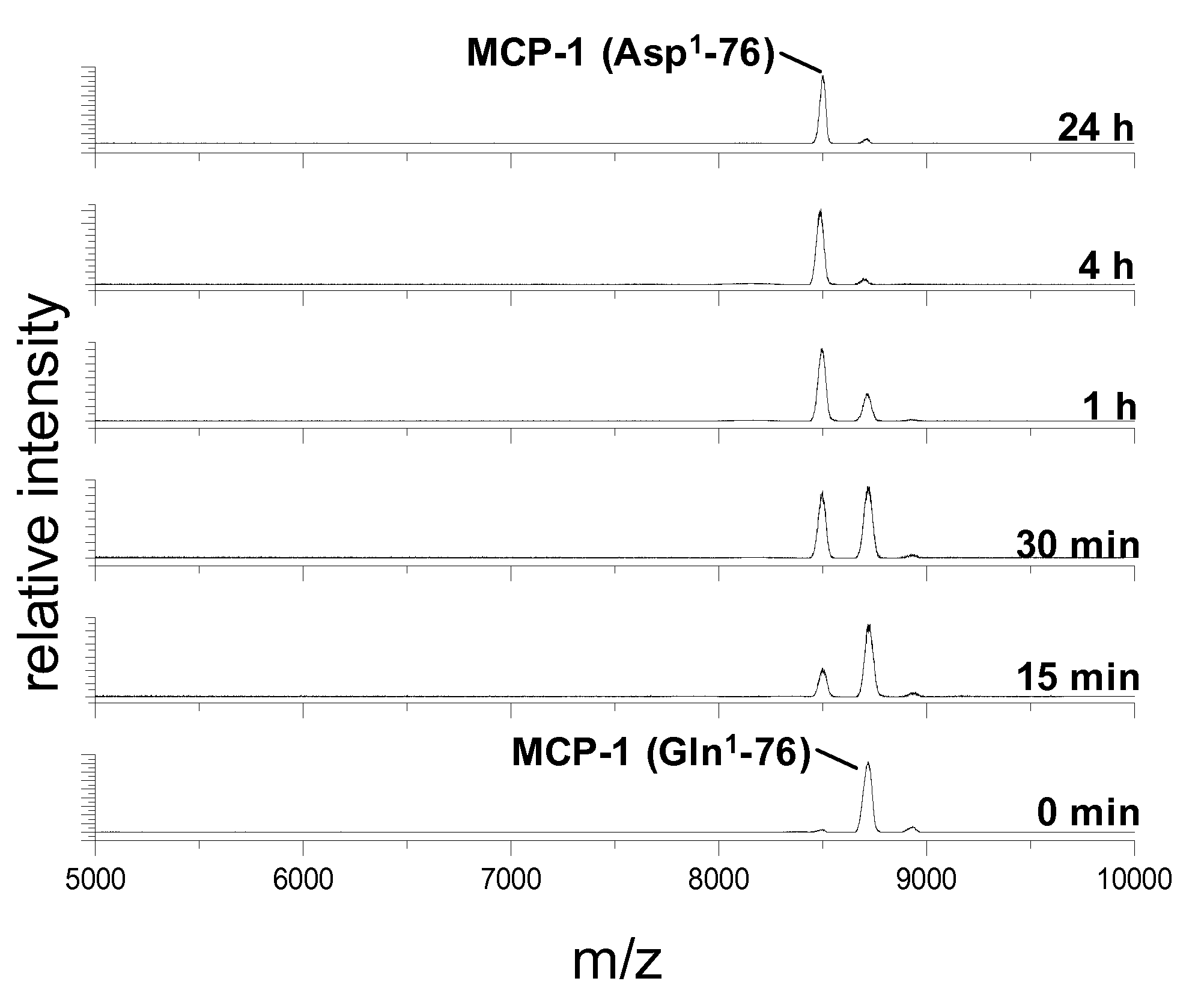
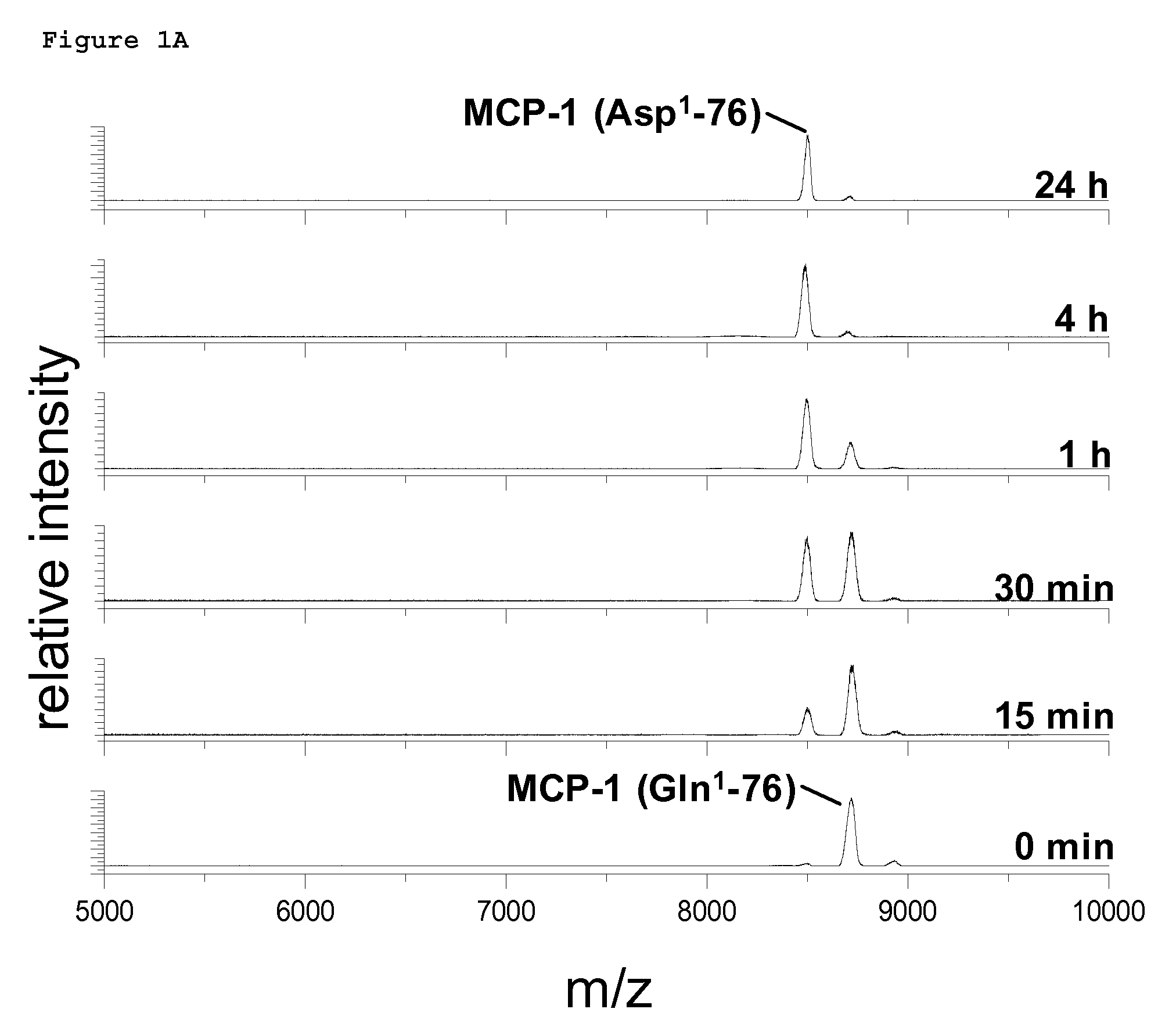
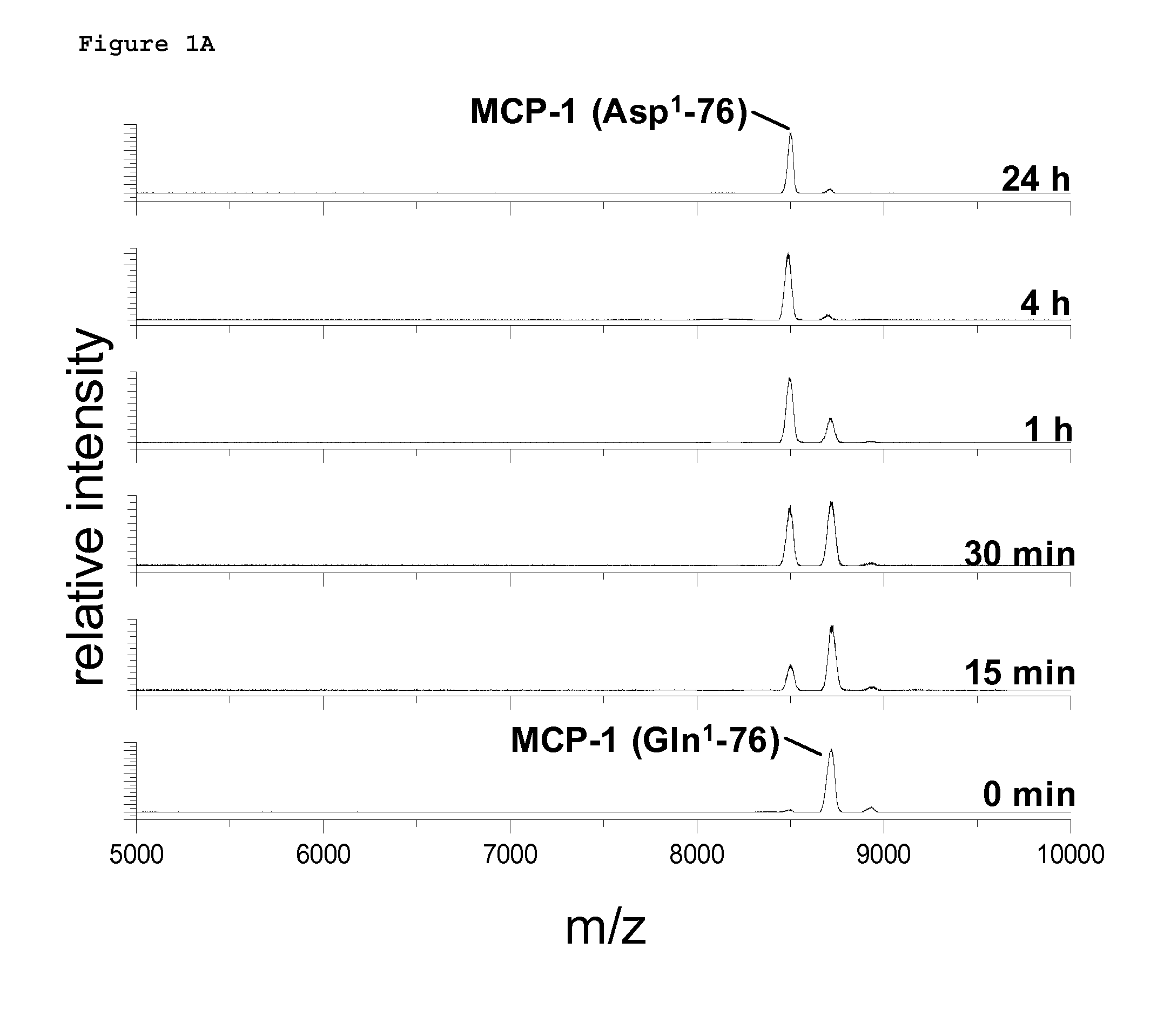
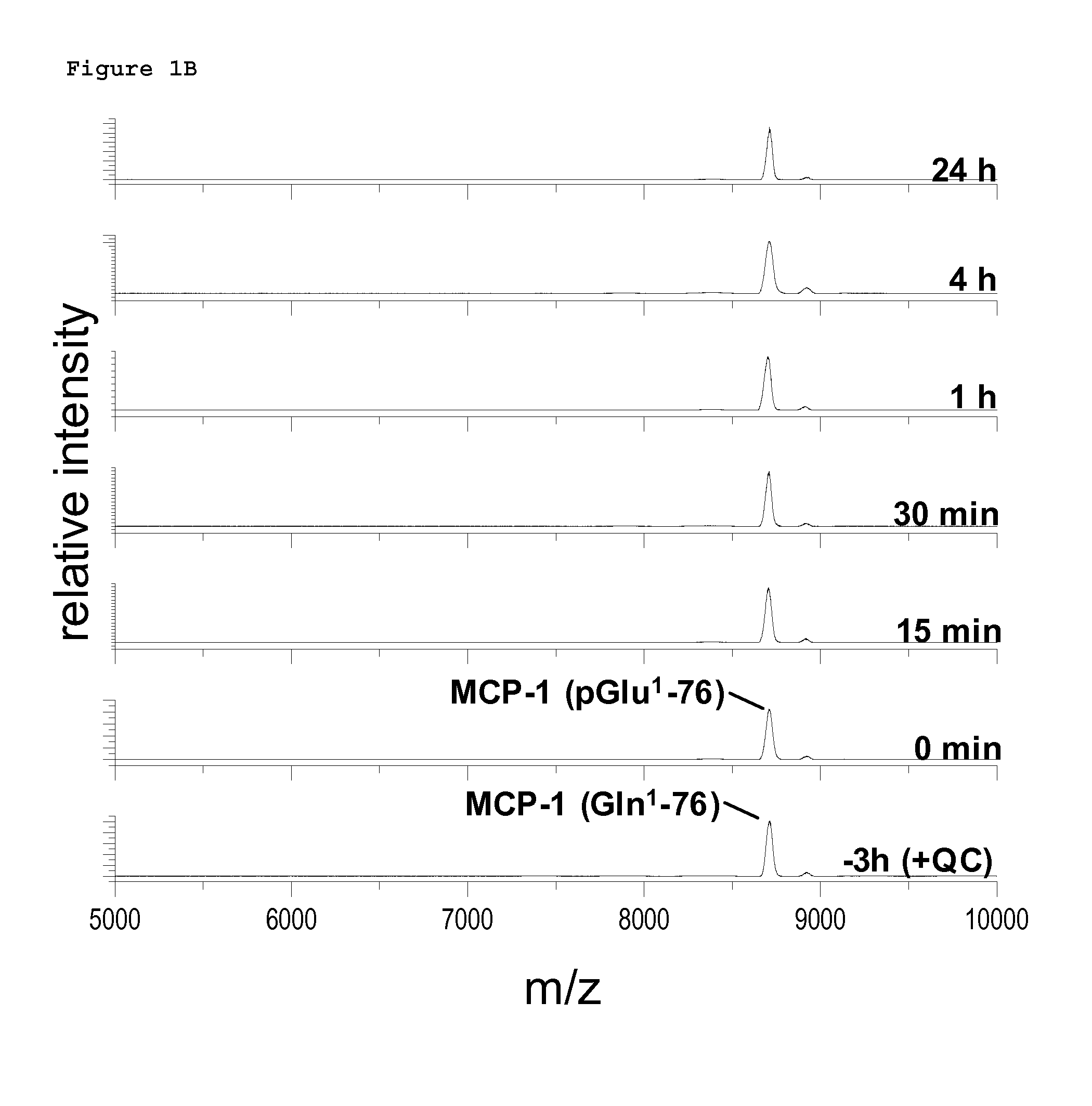
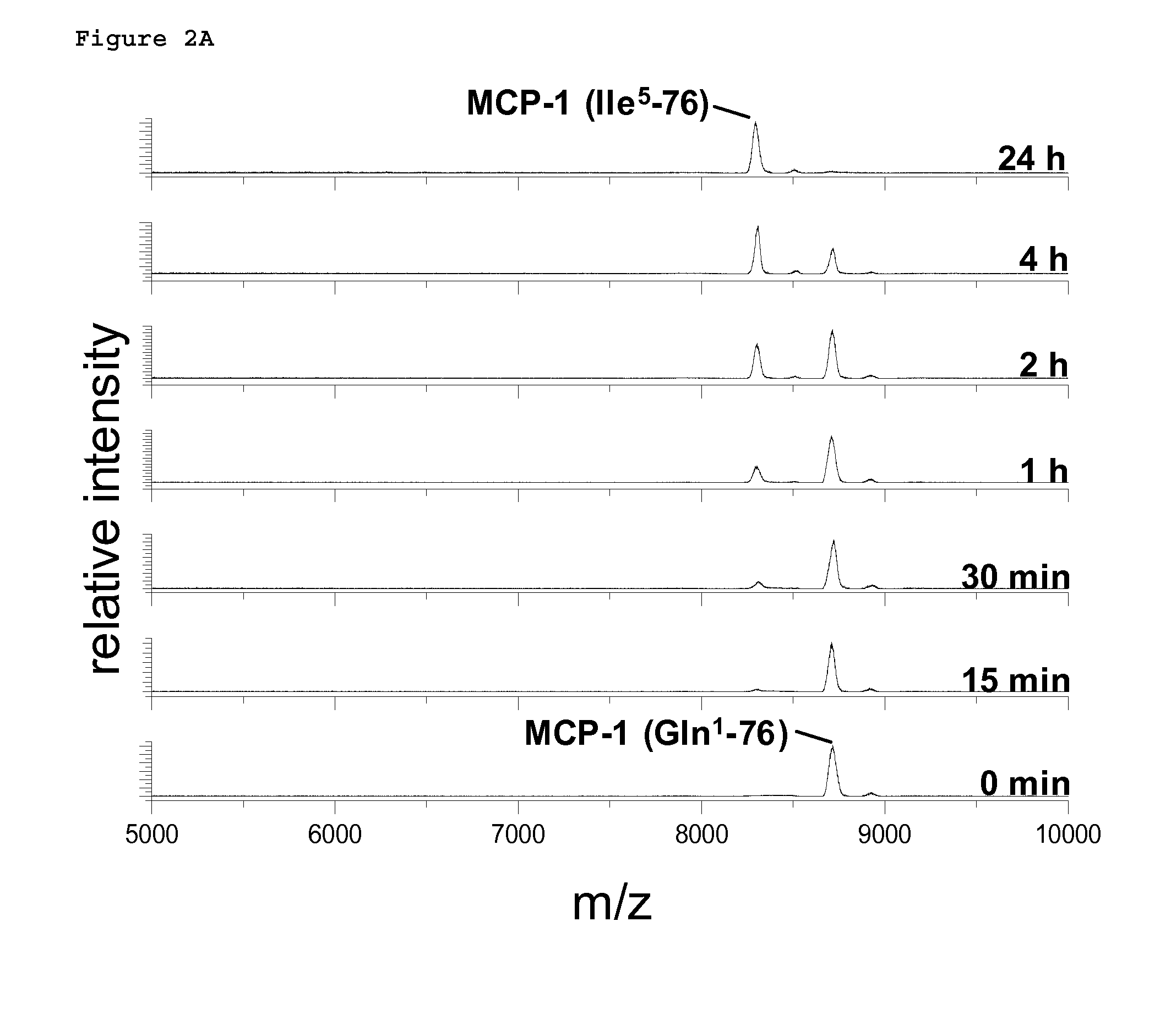
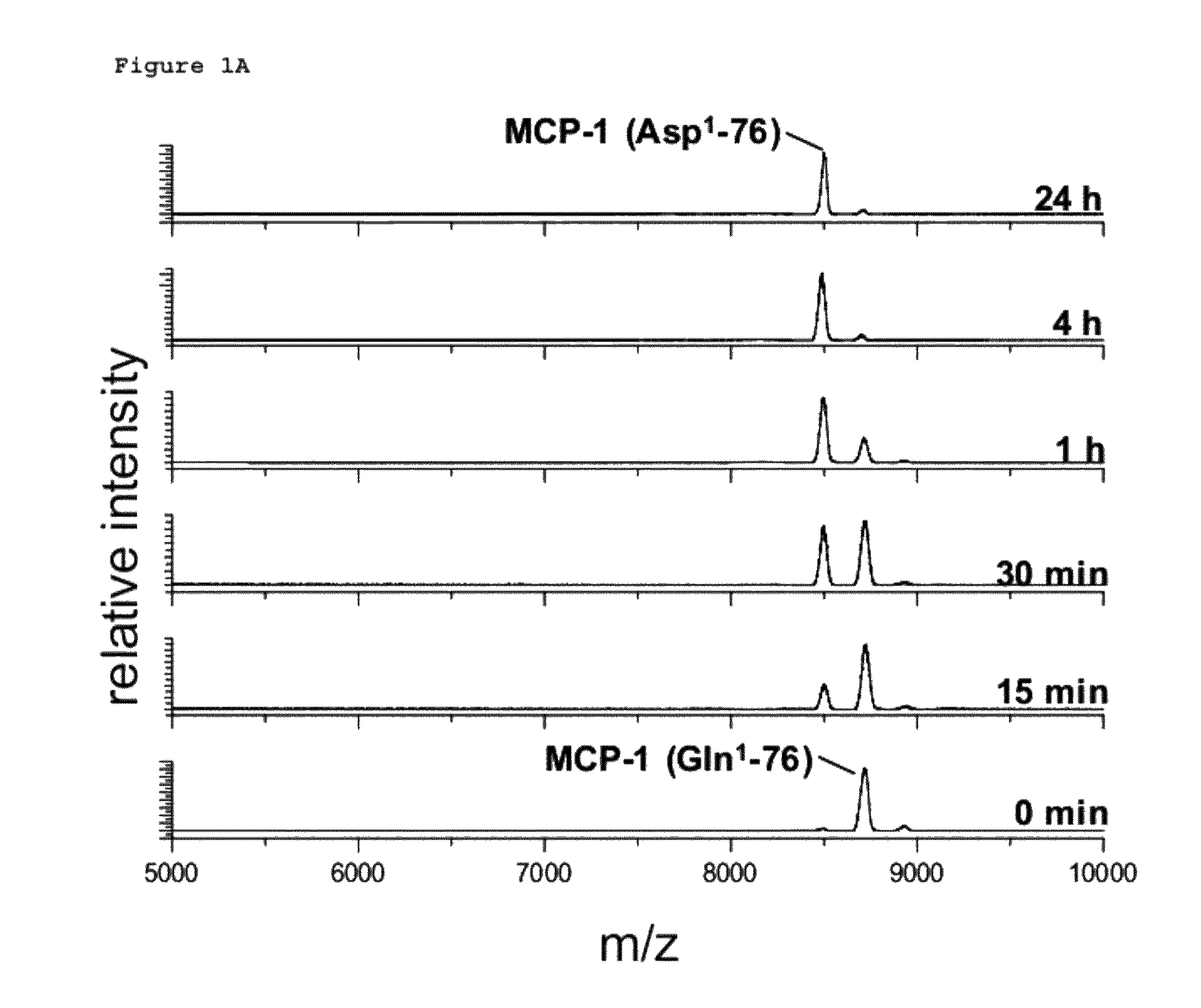
A method of monitoring treatment of an inflammatory disease or an inflammatory associated disease with the use of the ratio of N-terminal pyroglutamate modified MCP-1 (MCP-1 N1pE):total concentration of MCP-1 within a biological sample as a biomarker, and a method for determining the proportion of N-terminal pyroglutamate modified MCP-1 in relation to the total concentration of MCP-1 in biological samples. Also disclosed are a diagnostic kit and a method for screening a glutaminyl cyclase (QC) inhibitor or measuring the effectiveness of a glutaminyl cyclase (QC) inhibitor.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Medical use of inhibitors of glutaminyl and glutamate cyclases
The present invention provides novel physiological substrates of mammalian glutaminyl cyclase (QC, EC 2.3.2.5), new effectors of QC, methods for screeing for such effectors, and the use of such effectors and pharmaceutical compositions comprising such effectors for the treatment of conditions that can be treated by modulation of QC-activity. Preferred compositions additionally comprise inhibitors of DP IV or DP IV-like enzymes for the treatment or alleviation of conditions that can be treated by modulation of QC- and DP IV-activity.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Novel glutaminyl cyclase inhibitors and the use thereof in treatment of various diseases
Owner:OBSHCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOJ OTVETABTVENNOSTJU VALENTA INTELLEKT +1
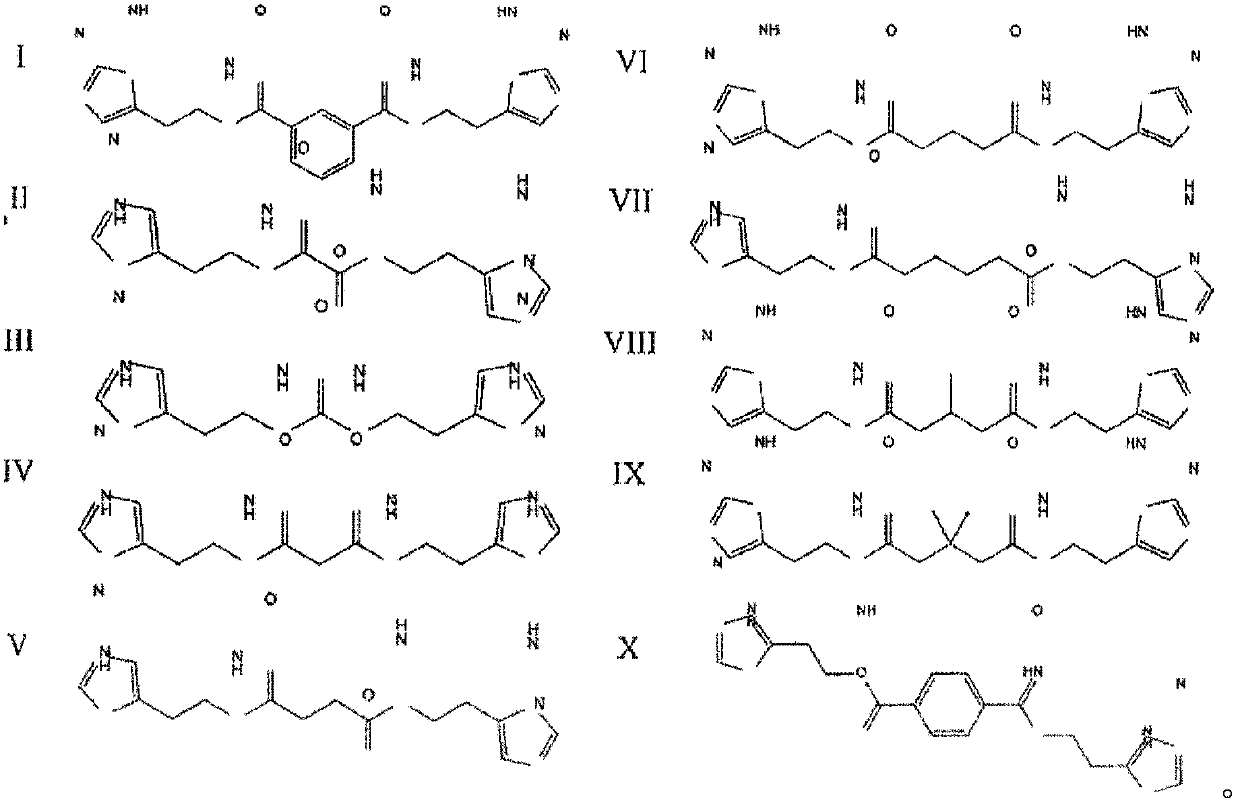
Synthesis method and application of multi-target A beta oligomerization inhibitor
ActiveCN106831713AHigh yieldSuitable for mass manufacturingNervous disorderOrganic chemistrySynthesis methodsDibromopropane
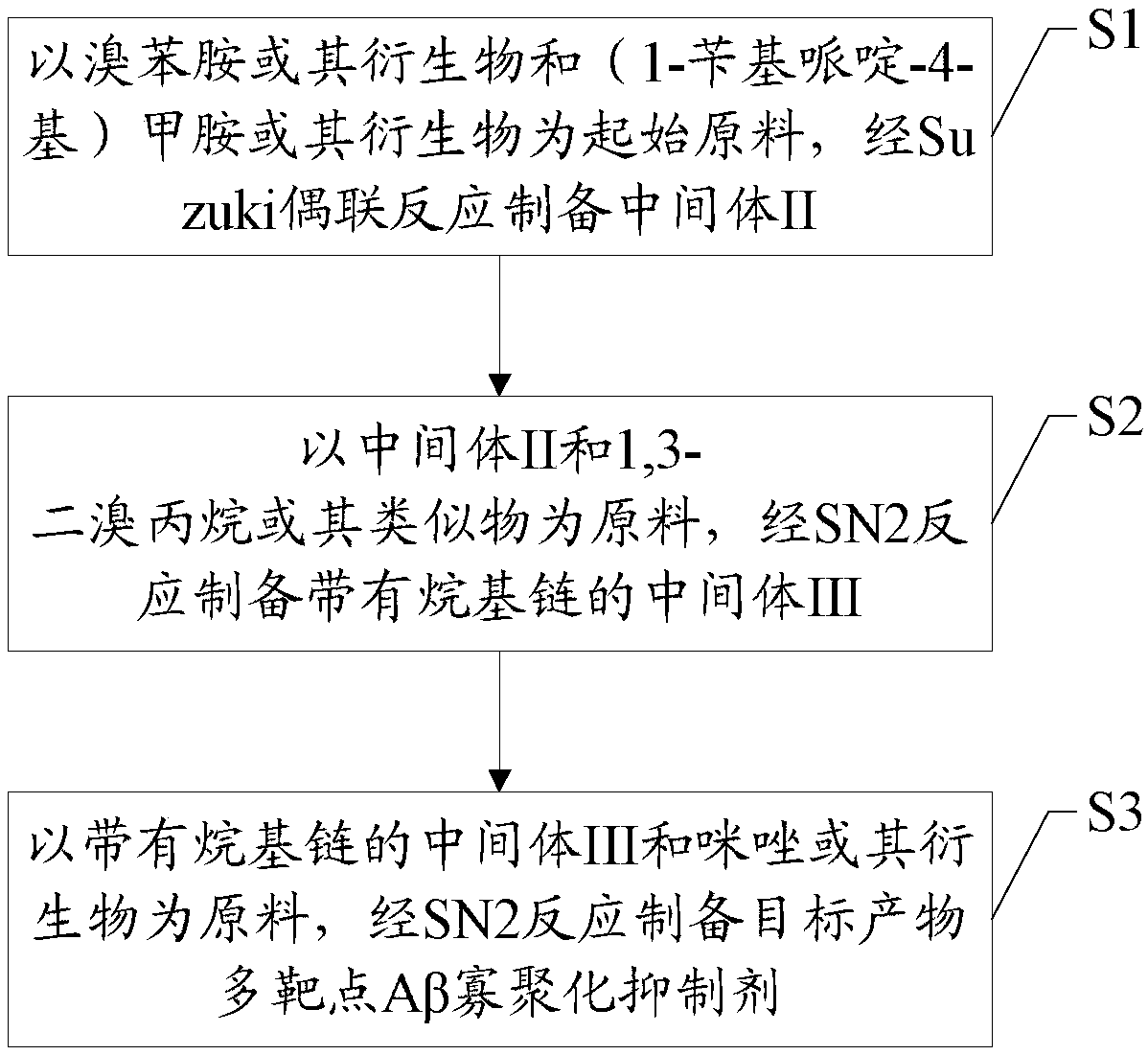
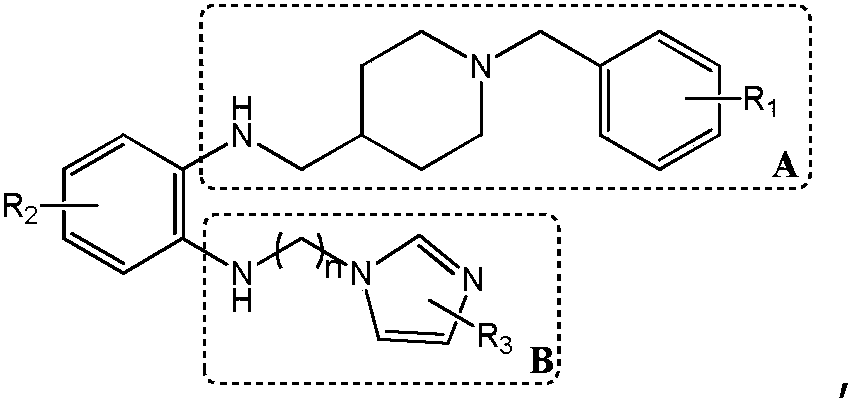
The invention discloses a synthesis method and application of a multi-target A beta oligomerization inhibitor. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: (1) taking bromaniline or derivatives thereof and (1-benzylpiperidine-4-yl)methylamine or derivatives thereof as starting raw materials, and carrying out Suzuki coupling reaction for preparing an intermediate II; (2) taking the intermediate II and 1,3-dibromopropane or other analogues as raw materials, and carrying out SN2 reaction for preparing an intermediate III with an alkyl chain; and (3) taking the intermediate III with the alkyl chain and imidazole or derivatives thereof as raw materials, and carrying out SN2 reaction for preparing the target product multi-target A beta oligomerization inhibitor. The synthesis method disclosed by the invention is simple and reliable in route, high in yield and more suitable for large-scale preparation. The multi-target A beta oligomerization inhibitor is applied to preparation of an A beta oligomerization inhibitor anti-AD medicine, a glutaminyl cyclase inhibitor anti-AD medicine and an acetylcholin esterase inhibitor anti-AD medicine and can be applied to kits of A beta oligomerization, glutaminyl cyclase and acetylcholin esterase.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
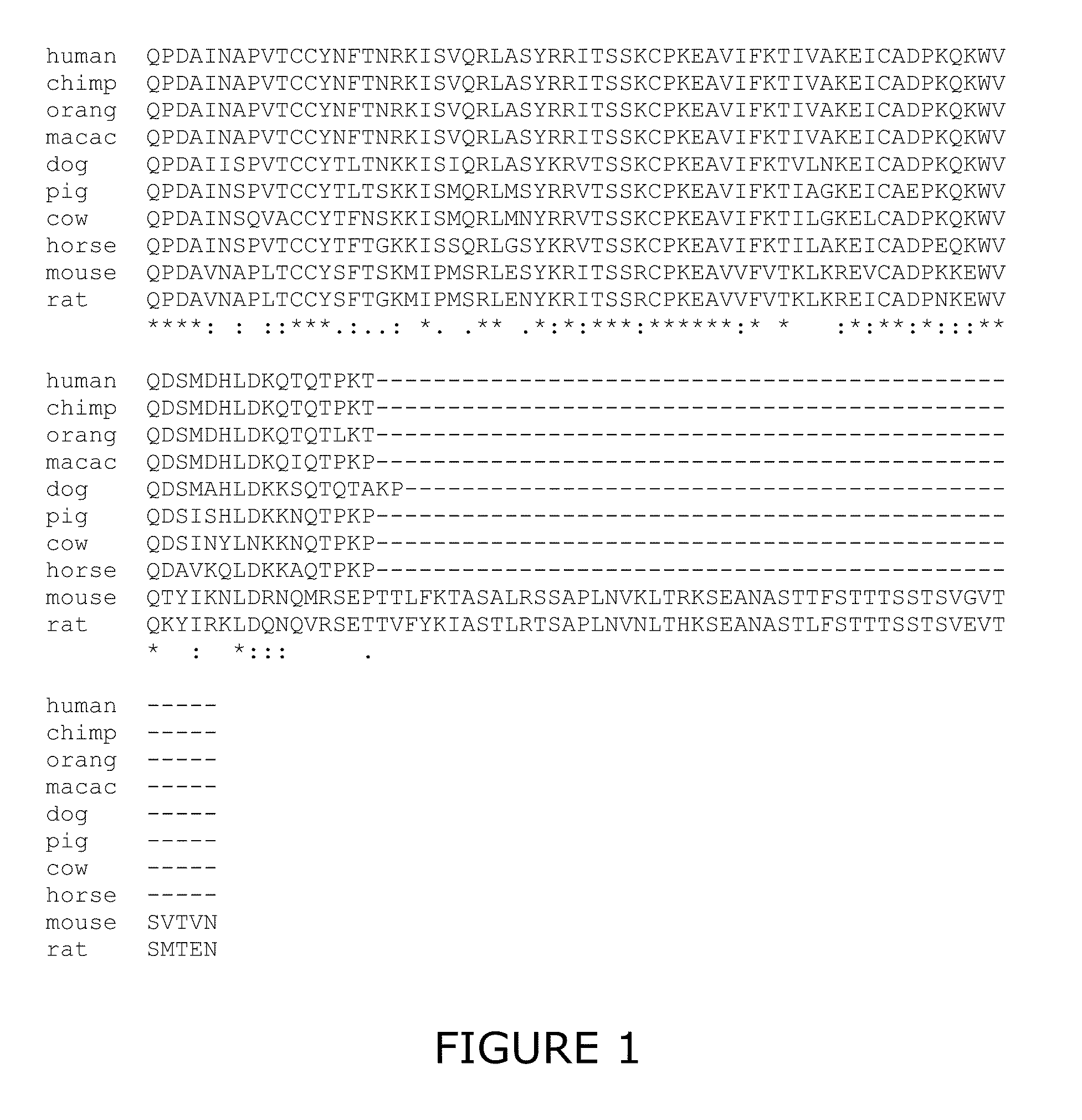
Glutaminyl cyclase as a diagnostic/prognostic indicator for neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS20150247180A1Easy to manageImprove current clinical diagnostic assessmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisNeuro-degenerative diseaseS syndrome
A method for predicting, diagnosing and prognosticating a neurodegenerative disease, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and neurodegeneration in Down's syndrome (NDS) using glutaminyl cyclase (QC) as a diagnostic / prognostic indicator. The use of antibodies binding to QC and kits for performing said diagnostic method are also provided.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Inhibitors
Novel heterocyclic derivatives of formula (I):or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate or polymorph thereof, including all tautomers and stereoisomers thereof, wherein Ra, n, R1 and R2 are as defined herein, as inhibitors of glutaminyl cyclase (QC, EC 2.3.2.5).
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Novel inhibitors
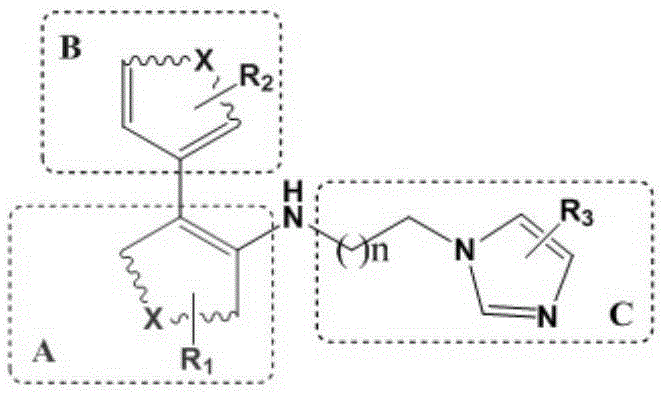
The invention relates to a compound of formula (I): A-B-D-E (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate or polymorph thereof, including all tautomers and stereoisomers thereof, wherein: A is selected from monocyclic and bicyclic heteroaryl, which may independently substituted by alkyl or amino; B is selected from alkyl, heteroalkyl, alkyl-amino, aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl and alkylene, wherein said groups may independently be substituted by alkyl; D is selected from aryl-amino, heteroaryl-amino, cycloalkyl-amino, heterocyclyl, heterocyclyl-amino, urea, thioamide, thiourea, sulfonamide, sulfoximine and sulfamoyl, wherein said aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl and heterocyclyl groups may independently be substituted; and E is selected from aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, wherein said aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl and heterocyclyl groups may independently be substituted. The compounds of formula (I) are inhibitors of glutaminyl cyclase (QC, EC 2.3.2.5). QC catalyzes the intramolecular cyclization of N-terminal glutamine residues into pyroglutamic acid (5-oxo-prolyl, pGlu*) under liberation of ammonia and the intramolecular cyclization of N-terminal glutamate residues into pyroglutamic acid under liberation of water.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Heterocyclic inhibitors of glutaminyl cyclase (QC, EC 2.3.2.5)
ActiveCN102791704ALasting effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsL-Pyroglutamic AcidAmmonia
The invention relates to novel heterocyclic derivatives as inhibitors of glutaminyl cyclase (QC, EC 2.3.2.5). QC catalyzes the intramolecular cyclization of N-terminal glutamine residues into pyroglutamic acid (5-oxo-prolyl, pGlu*) under liberation of ammonia and the intramolecular cyclization of N-terminal glutamate residues into pyroglutamic acid under liberation of water.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Novel inhibitors
ActiveCN105263927AGood pharmacokinetic propertiesOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderCyclaseLiberation
The invention relates to a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate or polymorph thereof, including all tautomers and stereoisomers thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, R4 and R5 are as defined herein, as inhibitors of glutaminyl cyclase (QC, EC 2.3.2.5). QC catalyzes the intramolecular cyclization of N-terminal glutamine residues into pyroglutamic acid (5-oxo-prolyl, pGlu*) under liberation of ammonia and the intramolecular cyclization of N-terminal glutamate residues into pyroglutamic acid under liberation of water.
Owner:维沃永治疗公众有限公司
Methods of diagnosing inflammatory diseases by determining pyroglutamate-modified mcp-1 and screening methods for inhibitors of glutaminyl cyclase
InactiveCN102947705AIndustrial applicabilityDisease diagnosisBiological testingGlutethimideScreening method
The invention relates to a method to monitor treatment of an inflammatory disease or an inflammatory associated disease with the use of the ratio of N-terminal pyroglutamate modified MCP-1 (MCP-1 N1pE) : total concentration of MCP-1 within a biological sample as a biomarker and further concerns a novel method to determine the proportion of N-terminal pyroglutamate modified MCP-1 in relation to the total concentration of MCP-1 in biological samples. The invention also provides a diagnostic kit and a method for screening a glutaminyl cyclase (QC) inhibitor or measuring the effectiveness of a glutaminyl cyclase (QC) inhibitor.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
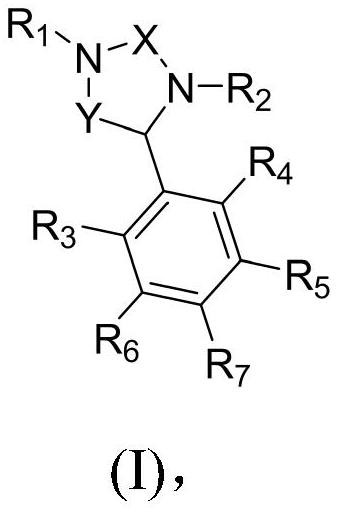
Inhibitors of glutaminyl cyclase
ActiveCN111315738BGood pharmacokinetic propertiesOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderCyclaseIsozyme
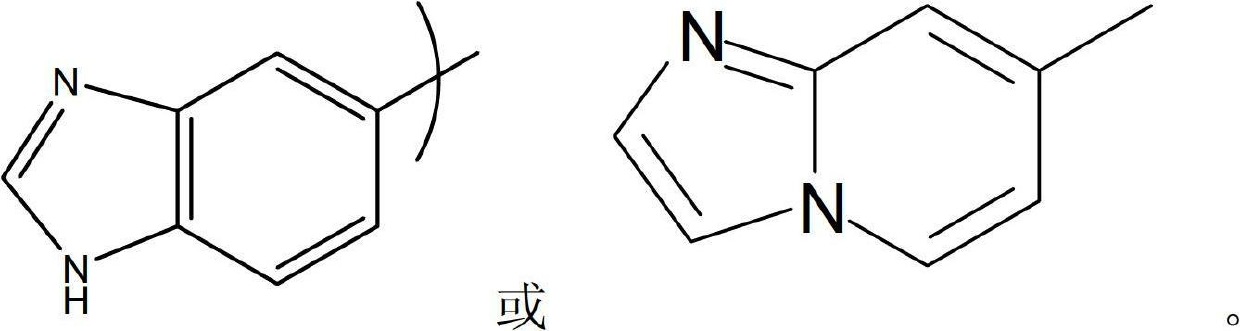
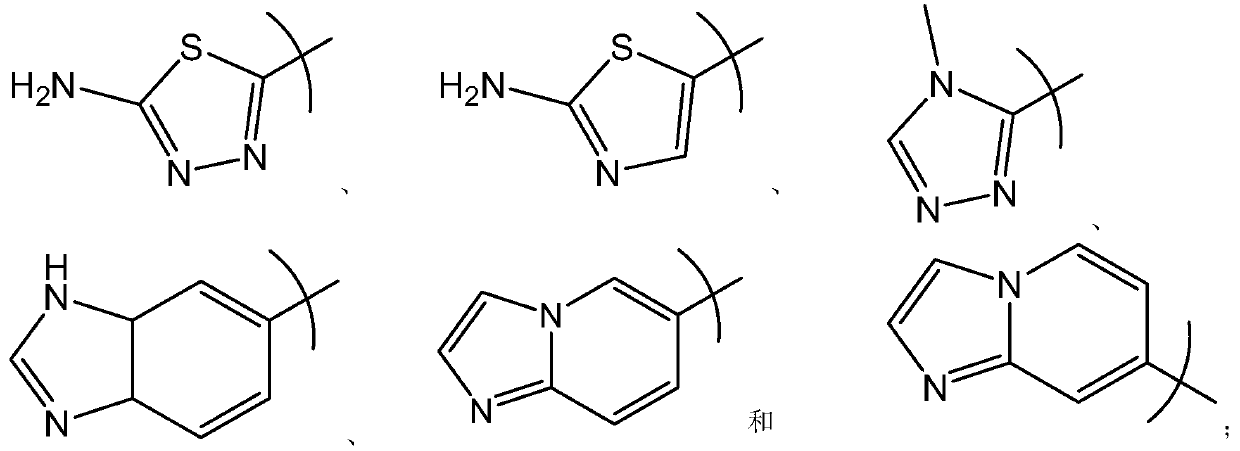
The present invention relates to a compound of formula (I), or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate or polymorph, including all tautomers and stereoisomers thereof, wherein: A is selected from 1H- Benzimidazolyl and heteroaryl of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, and R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 4 and R 5 As defined herein, it acts as an inhibitor of glutaminyl cyclase (QC, EC 2.3.2.5) and its isoenzyme glutaminyl peptide cyclotransferase-like protein (QPCTL). QC and QPCTL catalyze the intramolecular cyclization of N-terminal glutamine residues to pyroglutamic acid (5-oxo-prolyl, pGlu*) with the release of ammonia, and the release of N-terminal glutamic acid residues In the case of water, the intramolecular cyclization becomes pyroglutamic acid.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Synthesis method and application of a multi-target Aβ oligomerization inhibitor
ActiveCN106831713BHigh yieldSuitable for mass manufacturingNervous disorderOrganic chemistrySynthesis methodsDibromopropane
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
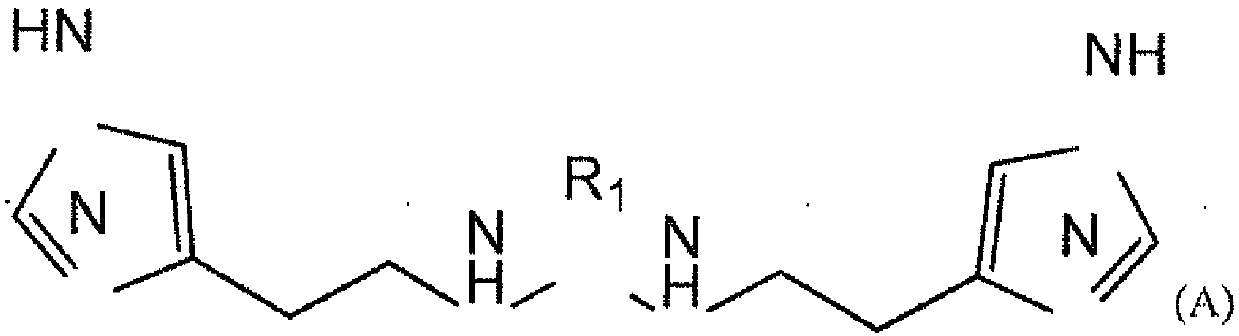
Novel zinc complex, production and use of same
The invention relates to a novel zinc complex of gamma-L-glutamyl histamine with a metal / ligand ratio of 1 / 1. In particular, the invention relates to a compound of formula (I). The complex according to the invention promotes the recovery of barrier functions of epithelial tissue and suppresses aberrant activity of immune system cells. The invention also relates to the production of the complex and the use of said zinc complex for the treatment of atopic dermatitis and other diseases associated with the disruption of barrier functions of epithelial tissue and the development of an aberrant inflammatory response. The invention also relates to the use of the obtained complex for inhibiting glutaminyl cyclase. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions containing a therapeutically effective quantity of the compound according to the invention.
Owner:OBSHCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOJ OTVETSTVENNOSTYU ZET TERAPEVTIKS
Medical use of inhibitors of glutaminyl and glutamate cyclases
The present invention provides novel physiological substrates of mammalian glutaminyl cyclase (QC, EC 2.3.2.5), new effectors of QC and the use of such effectors and pharmaceutical compositions comprising such effectors for the treatment of diseases that can be treated by modulation of QC-activity, e.g. diseases selected from the group consisting of duodenal cancer with or w / o Heliobacter pylori infections, colorectal cancer, Zolliger-Ellison syndrome, Familial British Dementia and Familial Danish Dementia.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Glutamine acyl cyclase isoenzyme inhibitor as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN114874186AIncrease structural diversityRaw materials are easy to getOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCyclaseDisease
The invention provides a glutamine acyl cyclase isoenzyme inhibitor as well as a preparation method and application thereof, the glutamine acyl cyclase isoenzyme inhibitor is a compound with a novel structural framework, and the preparation method of the novel inhibitor provided by the invention has the advantages that the raw materials are easy to obtain, and the preparation method is simple and feasible. According to the inhibitor provided by the invention, the molecular structure diversity of the glutamine acyl cyclase isoenzyme inhibitor is obviously expanded; the method can be widely applied to preparation of medicines for treating diseases related to high-specificity expression of the glutaminyl cyclase isoenzyme and preparation of kits for diagnosing the diseases related to high-specificity expression of the glutaminyl cyclase isoenzyme.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
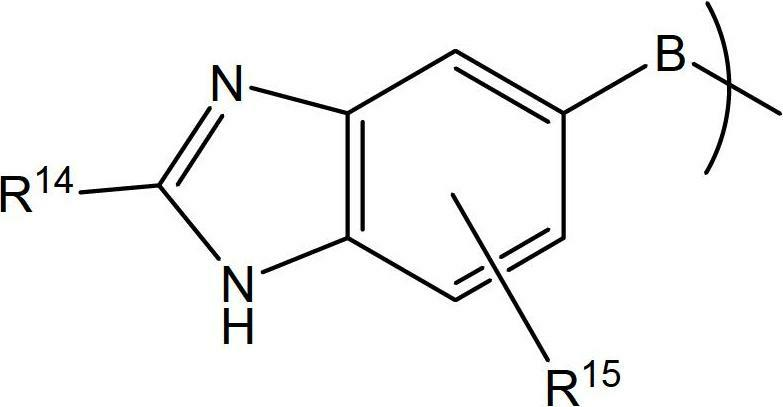
Benzimidazole compounds and use thereof for treating alzheimer's disease or huntington's disease
Benzimidazole compounds of formula (I), shown below, are disclosed. The compounds are potent human glutaminyl cyclase inhibitors. Also disclosed is a pharmaceutical composition containing one of these compounds and a pharmaceutical acceptable carrier, as well as a method of treating Alzheimer's disease or Huntington's disease by administering to a subject in need thereof an effective amount of such a compound.
Owner:台湾卫生研究院
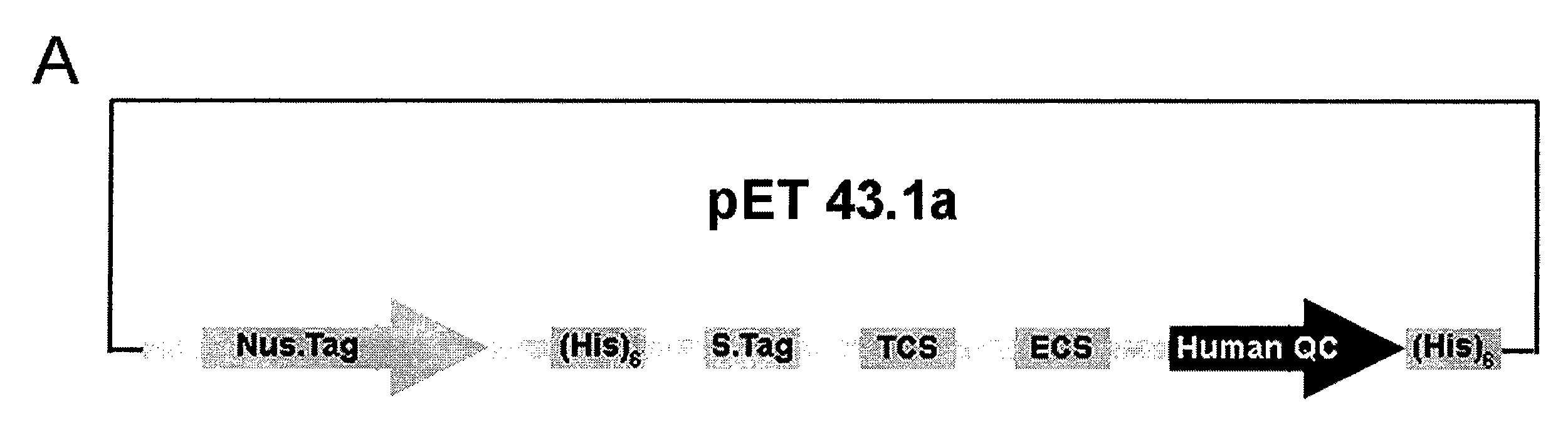
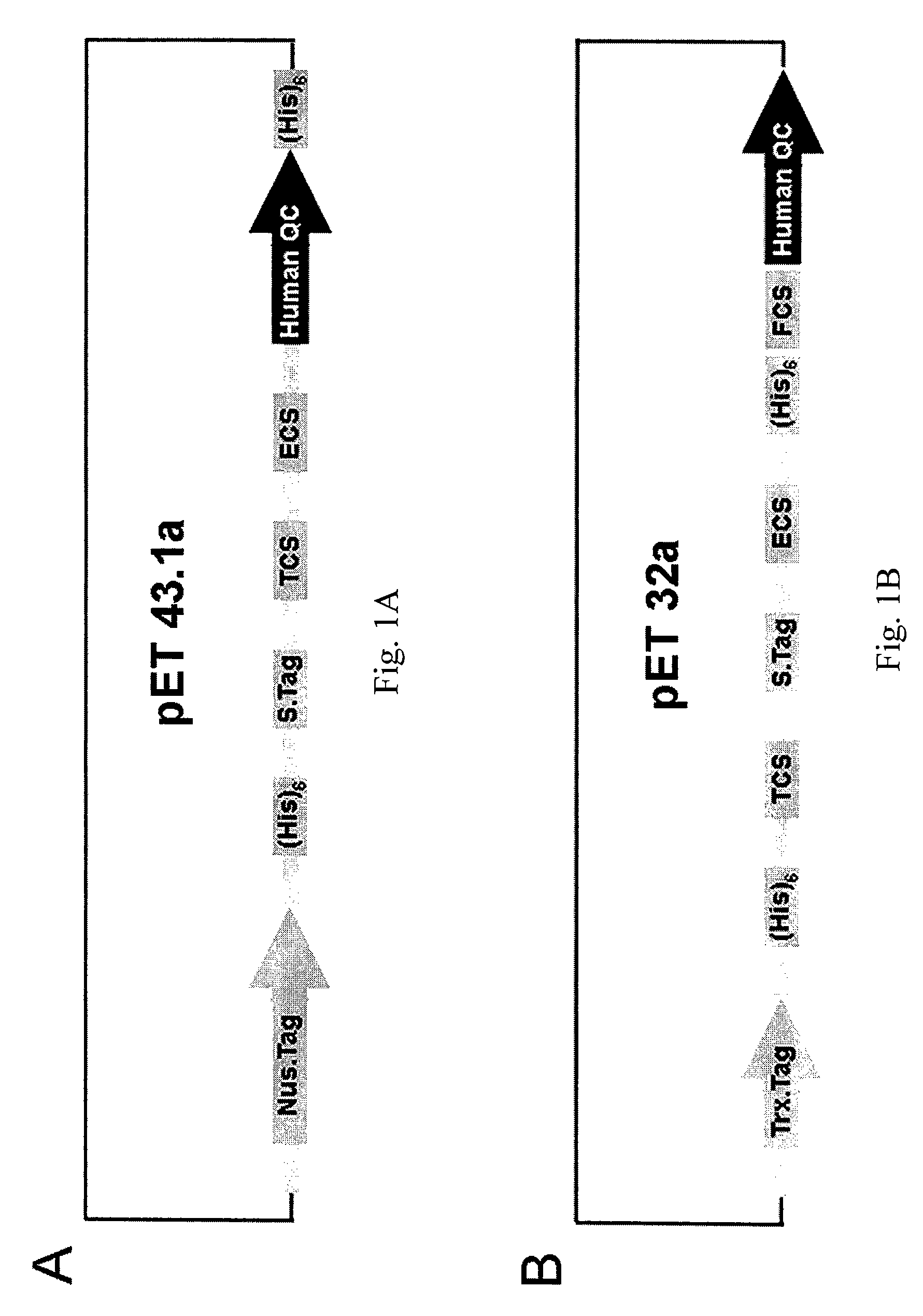
Express system of soluble glutaminyl cyclase
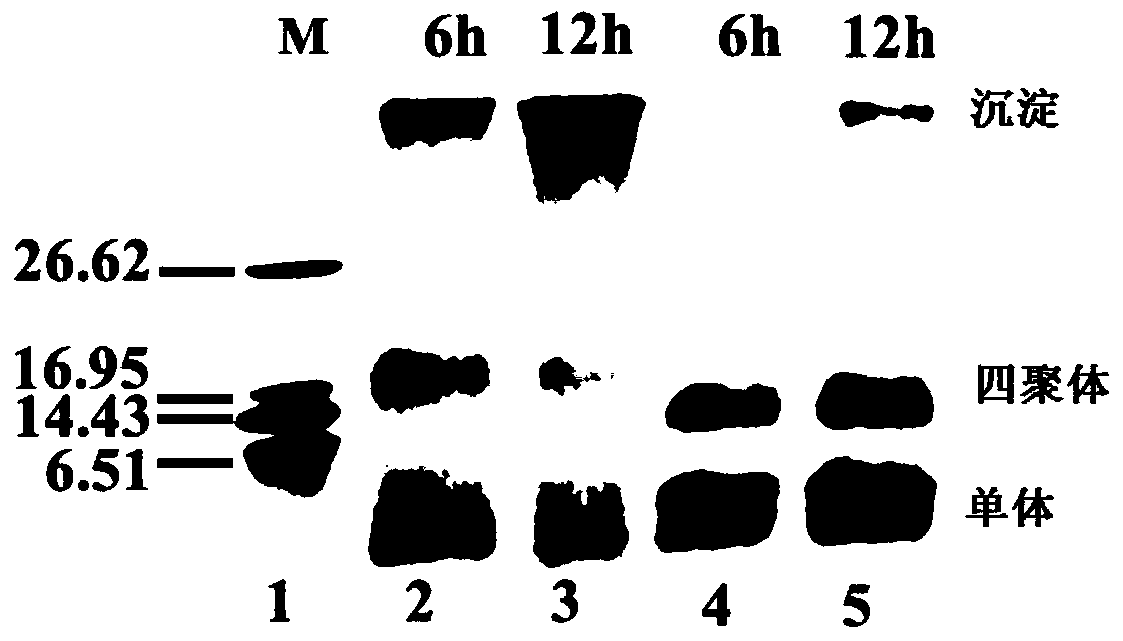
The present invention relates to a vector for expressing a soluble glutaminyl cyclase (QC) containing a sequence encoding QC, a fusion protein tag upstream of the sequence encoding QC, and a linker having at least one (His)x-tag between the sequence encoding QC and the fusion protein tag, wherein x is an integer of at least 6. Methods for expressing a soluble glutaminyl cyclase (QC) by the vector of the present invention are also provided.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com