Patents
Literature
45 results about "Peronospora effusa" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Peronospora effusa is an obligate pathogen that causes downy mildew on spinach and is considered the most economically important disease of spinach. The objective of the current research was to assess genetic diversity of known historical races and isolates collected in 2014 from production fields ...
Tobacco cultivar NC 2000
InactiveUS6965062B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationCultivarPeronospora tabacina
The present invention relates to a novel tobacco cultivar designated NC 2000, which is resistant to blue mold caused by the fungus Peronospora tabacina Adam. The invention provides seeds of the cultivar NC 2000, plants and parts thereof of the cultivar NC 2000, a tissue culture derived from the cultivar NC 2000, hybrids produced from cultivar NC 2000 and lines derived from cultivar NC 2000, as well as genetically modified forms of the foregoing plants and tissue culture. Also provided are methods of producing cultivar NC 2000 plants, cultivar NC 2000 hybrid plants, and tobacco lines derived from cultivar NC 2000.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Non r-gene mediated resistance
ActiveUS20170327839A1Increased durabilityStrong resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologySpinacia
The invention relates to plants and plant parts, in particular spinach plants (Spinacia oleracea L.), which are resistant to Peronospora farinosa f. sp. spinaciae. The invention also relates to seeds capable of producing Peronospora farinosa f sp. spinaciae resistant plants. The invention further relates to methods for obtaining said plants with altered genotypes and seeds thereof, which are resistant to Peronospora farinosa f sp. spinaciae.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Spinach plants that are resistant to downy mildew
InactiveUS20160177330A1Vector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyPeronospora effusa
The present invention relates to the field of spinach breeding, in particular to a new dominant resistance gene, designated RPF12, which confers resistance against all races of Peronospora farinosa and to spinach plants comprising said gene.
Owner:NUNHEMS BV
Spinach plants that are resistant to downy mildew
ActiveUS20170027126A1Confer resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyPeronospora effusa
The present invention relates to the field of spinach breeding, in particular to a new dominant resistance gene, designated RPF11, which confers resistance against races 7 to 14 of Peronospora farinosa and to spinach plants comprising said gene.
Owner:NUNHEMS BV
Spinach plants that are resistant to downy mildew
The present invention relates to the field of spinach breeding, in particular to a new dominant resistance gene, designated RPF11, which confers resistance against races 7 to 14 of Peronospora farinosa and to spinach plants comprising said gene.
Owner:NUNHEMS BV
Spinach plants that are resistant to downy mildew
ActiveUS20170027127A1Confer resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationSpinaciaGene
The present invention relates to the field of spinach breeding, in particular to a new dominant resistance gene, designated RPF12, which confers resistance against all races of Peronospora farinosa and to spinach plants comprising said gene.
Owner:NUNHEMS BV
Method for modifying the resistance profile of spinacia oleracea to downy mildew
ActiveUS20190127753A1Microbiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyPeronospora effusa
The present invention relates to a method for modifying the resistance profile of a spinach plant to Peronospora farinosa f. sp. spinaciae, comprising introducing a WOLF allele or a resistance-conferring part thereof into the genome of said spinach plant, or modifying an endogenous WOLF allele in the genome of said spinach plant. A WOLF allele encodes a CC-NBS-LRR protein that comprises in its amino acid sequence: the motif “MAEIGYSVC” at its N-terminus, and the motif “KWMCLR” for alpha-type WOLF proteins or “HVGCVVDR” for beta-type WOLF proteins. The invention relates to the WOLF alleles referred to in Table 3. The invention further provides a method for selecting a spinach plant comprising a novel WOLF gene that confers resistance to Peronospora farinosa f. sp. spinaciae in a spinach plant and a method for identifying a WOLF allele that confers resistance to one or more pathogenic races of Peronospora farinosa f. sp. spinaciae in a spinach plant and to primers for use in these methods.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
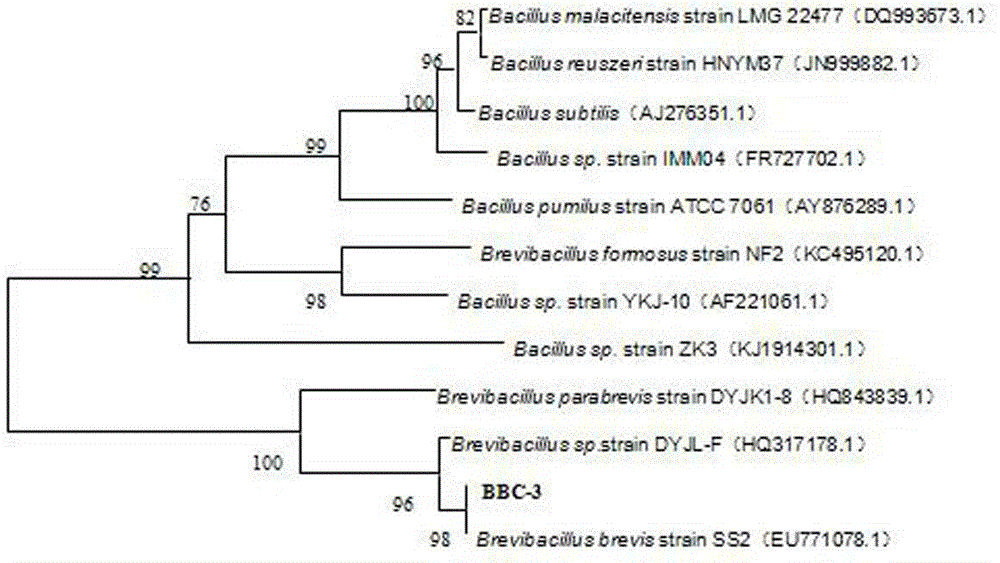
Brevibacillus brevis BBC-3 and application thereof as well as preparation method of microbial inoculum of brevibacillus brevis
ActiveCN104651260APromote vegetative growthSolve the problem of pesticide residuesBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyBrevibacillus brevis
The invention relates to an antagonistic bacterium for preventing the fungal diseases of broccoli as well as a preparation method and the application of a microbial preparation of the antagonistic bacterium, and belongs to the field of biological prevention and treatment of crop diseases. The invention provides a strain of brevibacillus brevis BBC-3 with the collection number CGMCC No. 9622, a production method of a microbial preparation containing the brevibacillus brevis, and also the application of the brevibacillus brevis BBC-3 or the microbial preparation in preventing and treating the fungal diseases of the broccoli. The brevibacillus brevis BBC-3 with the collection number CGMCC No. 9622 is obtained by virtue of preliminary screening and secondary screening, wherein a plate opposing test is performed for the preliminary screening and a liquid fermentation liquid is adopted for the secondary screening; the brevibacillus brevis BBC-3 is capable of effectively preventing and treating a plurality of fungal diseases of the broccoli, such as gray mold, downy mildew, stalk break, black rot and black spot, and has the prevention and treatment efficiency of above 70%; in addition, the brevibacillus brevis BBC-3 is good in environmental safety and has excellent development application prospect.
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF HEBEI ACAD OF SCI
Peronospora resistance in spinacia sp
The current invention concerns a spinach plant comprising resistance against Peronospora farinosa races 1-9, 11-15 and isolate UA1014APLP.
Owner:POP VRIEND RES
Plant-derived pesticide and production method thereof
InactiveCN104938538ANo pollution in the processGood control effectBiocideFungicidesNicotiana tabacumSclerotinia
The invention discloses plant-derived pesticide and a production method thereof. The plant-derived pesticide is prepared from Chinese herbal medicines such as licorice root, phellodendron bark, melia azedarach, cockscomb, radix ranunculi ternati, silktree flower, butterflybush flower, salvia chinensis, fenugreek seed and golden larch bark. A field test proves that the plant-derived pesticide has tobacco black shank prevention and treatment efficiency of 80% or more and has obvious effects better than that of metalaxyl with a concentration of 25%. The plant-derived pesticide has substantial prevention and treatment effects on a plurality of fungous diseases such as downy mildew, sclerotinia rot, powdery mildew, botrytis, anthracnose, epidemic disease, black shank and sheath blight of crops such as fruits, vegetables and paddy rice.
Owner:胡凡营
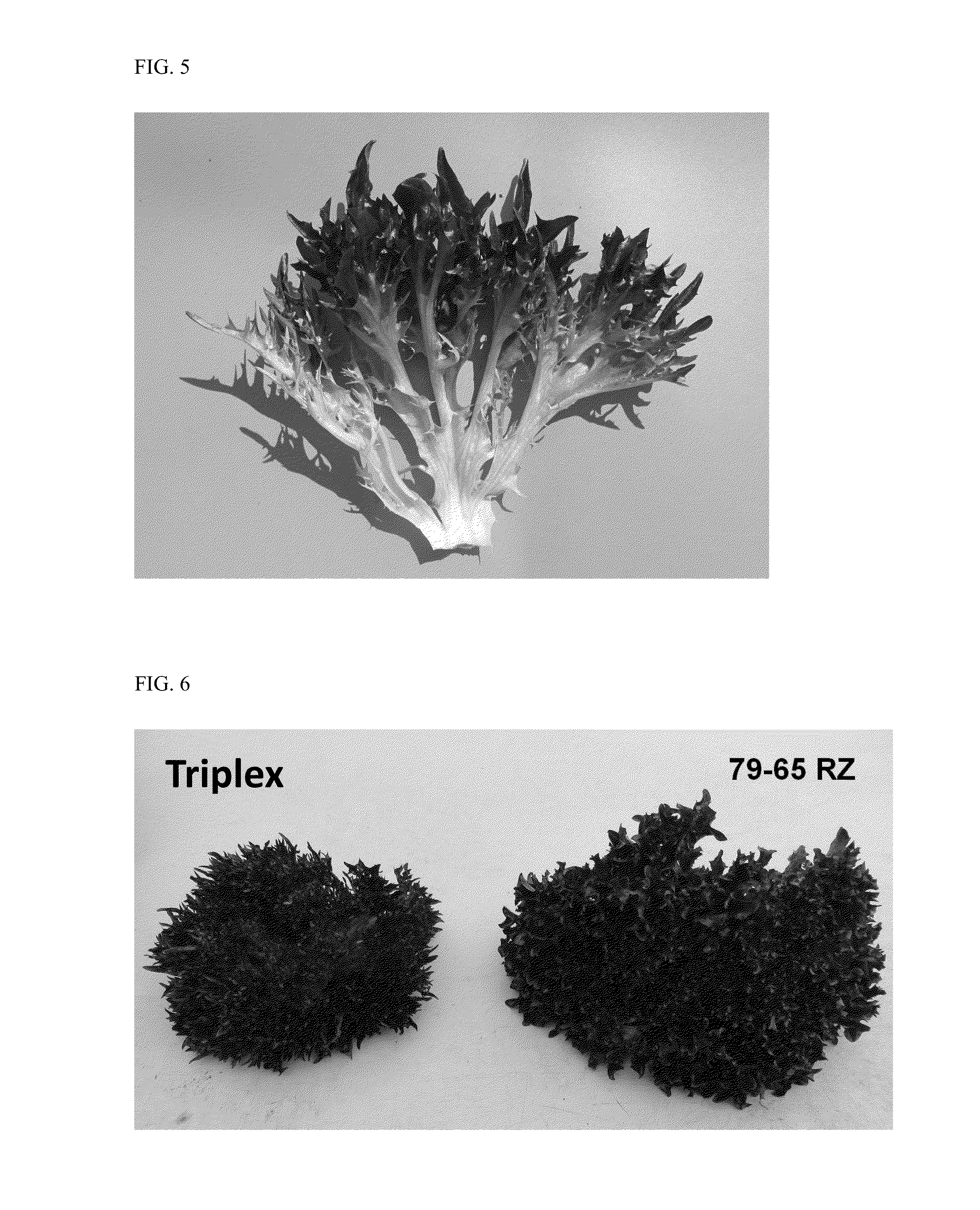
Lettuce variety 79-65 rz
ActiveUS20150135356A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningBremia lactucaePeronospora effusa
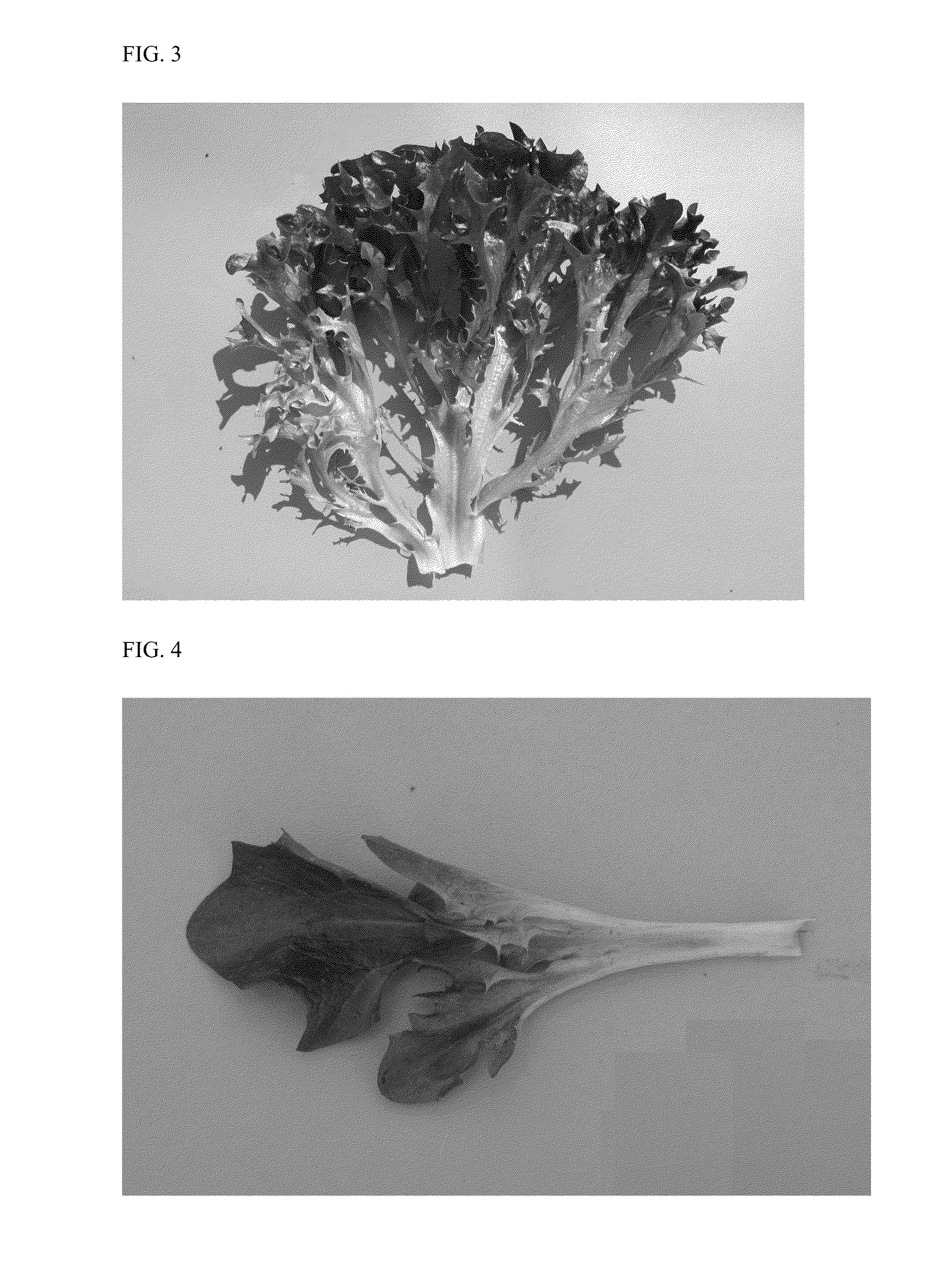
The present invention relates to a Lactuca sativa seed designated 79-65 RZ, which exhibits a combination of traits including resistance against downy mildew strains B1:1 to B1:31, CA-I to CA-VIII (Bremia lactucae), currant-lettuce aphid (Nasonovia ribisnigri) biotype Nr:0, and lettuce mosaic virus (LMV), as well as having intensely red, deeply incised, three-dimensional leaves, and a medium to small plant size. The present invention also relates to a Lactuca sativa plant produced by growing the 79-65 RZ seed. The invention further relates to methods for producing the lettuce cultivar, represented by lettuce variety 79-65 RZ.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Method for modifying the resistance profile of spinacia oleracea to downy mildew
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Peronospora resistance in spinacia oleracea
The present invention relates to an allele designated alpha-WOLF 15 which confers resistance to at least one Peronospora farinosa f. Sp. spinacea race, wherein the protein encoded by said allele is a CC-NBS-LRR protein that comprises in its amino acid sequence: a) the motif “MAEIGYSVC” at its N-terminus; and b) the motif “KWMCLR”; and wherein the LRR domain of the protein has in order of increased preference at least 92%, 93%, 94%, 95%, 96%, 97%, 98%, 99%, 100% sequence similarity to SEQ ID No:10. The allele when homozygously present in a spinach plant confers complete resistance to Peronospora farinosa f. Sp. spinacea races pfs:1, pfs:2, pfs:3, pfs:4 and pfs:5, pfs:6, pfs:8, pfs:9, pfs:11, pfs:12, pfs:13, pfs:14, pfs:15, pfs:16 and isolates UA1014 and US1508, and confers intermediate resistance to pfs:10, and does not confer resistance to pfs:7.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Method for modifying the resistance profile of spinacia oleracea to downy mildew
ActiveUS20190241905A1Microbiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyPeronospora effusa
The present invention relates to a method for modifying the resistance profile of a spinach plant to Peronospora farinosa f sp. spinaciae, comprising introducing a WOLF allele or a resistance-conferring part thereof into the genome of said spinach plant, or modifying an endogenous WOLF allele in the genome of said spinach plant. A WOLF allele encodes a CC-NBS-LRR protein that comprises in its amino acid sequence: the motif “MAEIGYSVC” at its N-terminus, and the motif “KWMCLR” for alpha-type WOLF proteins or “HVGCVVDR” for beta-type WOLF proteins. The invention relates to the WOLF alleles referred to in Table 3. The invention further provides a method for selecting a spinach plant comprising a novel WOLF gene that confers resistance to Peronospora farinosa f. sp. spinaciae in a spinach plant and a method for identifying a WOLF allele that confers resistance to one or more pathogenic races of Peronospora farinosa f sp. spinaciae in a spinach plant and to primers for use in these methods.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Peronospora resistance in Sinacia oleracea
The present invention relates to a spinach plant which may comprise a single dominant gene which confers resistance to Peronospora farinosa f. sp. spinaciae races Pfs1, Pfs2, Pfs3, Pfs4, Pfs5, Pfs6, Pfs9, Pfs11, Pfs12, Pfs13 and UA4410, and to isolate E1314-283, wherein the gene is obtainable by introgression from a plant grown from seeds of which a representative sample was deposited with the NCIMB under NCIMB accession numbers 41857, 41976, 41977, 41978, 41980, 41981, 41984, 42116. The invention further relates to progeny of the plant, to propagation material therefore, such as seed, and to food products which may comprise the spinach leaves.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Lettuce variety 79-504 rz
The present invention relates to a Lactuca sativa seed designated 79-504 RZ, which may exhibit a combination of traits including resistance against downy mildew strains Bl:1 to Bl:31, CA-I to CA-VIII (Bremia lactucae), currant-lettuce aphid (Nasonovia ribisnigri) biotype Nr:0, and lettuce mosaic virus (LMV), as well as an extraordinary high number of substantially equally sized leaves, which leaves are medium green, slightly to moderately blistered, and have a slightly to moderately undulated apical leaf margin, which is shallowly dentate. The present invention also relates to a Lactuca sativa plant produced by growing the 79-504 RZ seed. The invention further relates to methods for producing the lettuce cultivar, represented by lettuce variety 79-504 RZ.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Peronospora resistance in Spinacia oleracea
ActiveUS9615531B2Easy to introduceConfer resistanceVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationPeronosporaSpinacea oleracea
The present invention relates to a spinach plant which may comprise a single dominant gene which confers resistance to Peronospora farinosa f. sp. spinaciae races Pfs1, Pfs2, Pfs3, Pfs4, Pfs5, Pfs6, Pfs9, Pfs11, Pfs12, Pfs13 and UA4410, wherein the gene is obtainable by introgression from a plant grown from seeds of which a representative sample was deposited with the NCIMB under NCIMB accession number 41857. The invention further relates to progeny of the plant, to propagation material therefore, such as seed, and to food products which may comprise the spinach leaves.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Lettuce variety 79-05 rz
ActiveUS20150135357A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningBremia lactucaePeronospora effusa
The present invention relates to a Lactuca sativa seed designated 79-05 RZ, which may exhibit a combination of traits including resistance against downy mildew strains B1:1 to B1:31, CA-I to CA-VIII (Bremia lactucae), currant-lettuce aphid (Nasonovia ribisnigri) biotype Nr:0, and lettuce mosaic virus (LMV), as well as moderately glossy leaves with a medium to dark green leaf color. The present invention also relates to a Lactuca sativa plant produced by growing the 79-05 RZ seed. The invention further relates to methods for producing the lettuce cultivar, represented by lettuce variety 79-05 RZ.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Lettuce variety 79-05 RZ
ActiveUS9585361B2Microbiological testing/measurementAngiosperms/flowering plantsBremia lactucaePeronospora effusa
The present invention relates to a Lactuca sativa seed designated 79-05 RZ, which may exhibit a combination of traits including resistance against downy mildew strains Bl:1 to Bl:31, CA-I to CA-VIII (Bremia lactucae), currant-lettuce aphid (Nasonovia ribisnigri) biotype Nr:0, and lettuce mosaic virus (LMV), as well as moderately glossy leaves with a medium to dark green leaf color. The present invention also relates to a Lactuca sativa plant produced by growing the 79-05 RZ seed. The invention further relates to methods for producing the lettuce cultivar, represented by lettuce variety 79-05 RZ.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
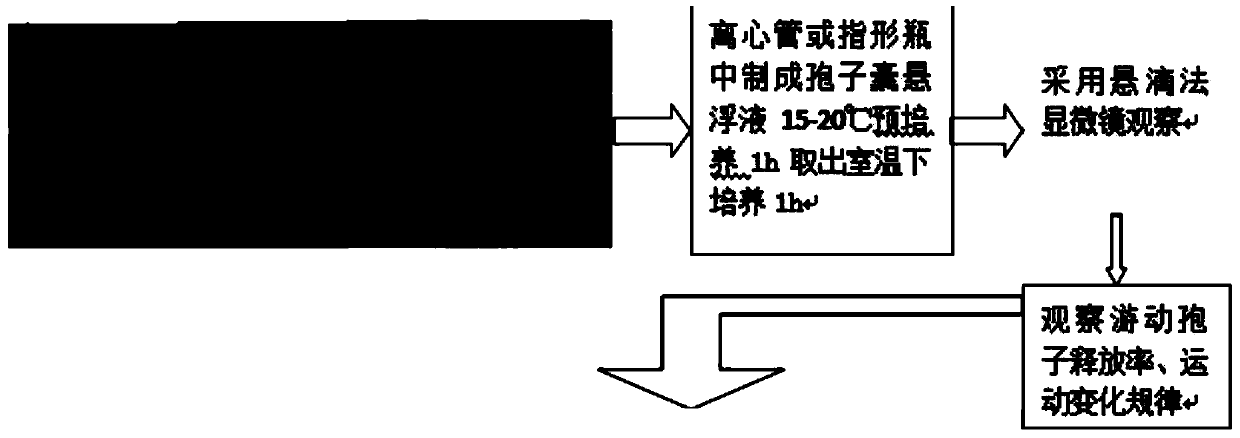
Downy mildew bacterium culture and observation method
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to a downy mildew bacterium culture and observation method. The method comprises the following steps: collecting downy mildew bacteria; preparing sporangium suspension liquid; and culturing the sporangium suspensions. Through repeated tests, a technology capable of inducing sporangium of cucumber downy mildew to germinate andrelease zoospore is obtained, the zoospore forms static spores through movement and morphological changes, the static spores germinate to form appressorium, and the appressorium germinates to generateinfection filaments. The technology can provide an effective technique for researchers to deeply research downy mildew biological basis, disease resistance identification, bactericide screening and the like. By means of the method, researchers can achieve quantitative statistics and monitoring of the number of zoospore of downy mildew, morphological changes and the number of formed infectors, andresearch of the action mechanism of the bactericide can also be achieved. Several development stages which must be experienced before downy mildew bacteria invade a host are clearly observed. The systematic observation method can provide first-hand data for prevention and treatment of the pathogenic bacteria on symptomatic drugs.
Owner:NINGXIA UNIVERSITY
Peronospora resistance in spinacia oleracea
The present invention relates to an allele designated alpha-WOLF 8 which confers resistance to at least one Peronospora farinosa f. Sp. spinacea race, wherein the protein encoded by said allele is a CC-NBS-LRR protein that may comprise in its amino acid sequence: a) the motif “MAEIGYSVC” at its N-terminus; and b) the motif “KWMCLR”; and wherein the LRR domain of the protein has in order of increased preference at least 92%, 93%, 94%, 95%, 96%, 97%, 98%, 99%, 100% sequence similarity to SEQ ID No:12. When the allele is homozygously present in a spinach plant confers complete resistance to Peronospora farinosa f. Sp. spinacea races pfs:1, pfs:2, pfs:6, pfs:8 and pfs:15, and confers intermediate resistance to pfs:5, pfs:10 and pfs:16, and does not confer resistance to pfs:3, pfs:4, pfs:7, pfs:9, pfs:11, pfs:12, pfs:13 and pfs:14.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Lettuce variety redglace
InactiveUS8785729B2Increase productionOther foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureBremia lactucaeLactuca ludoviciana
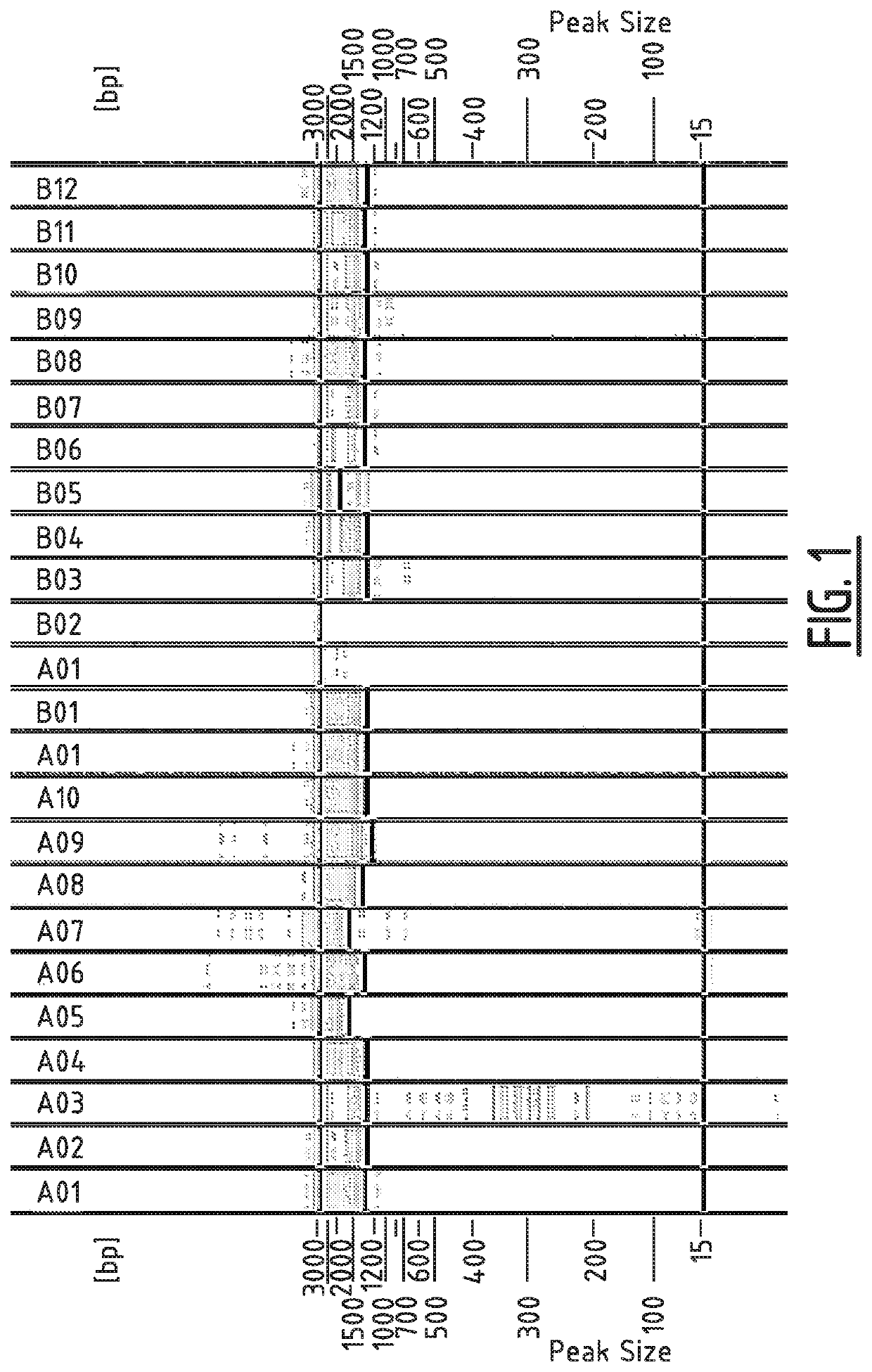
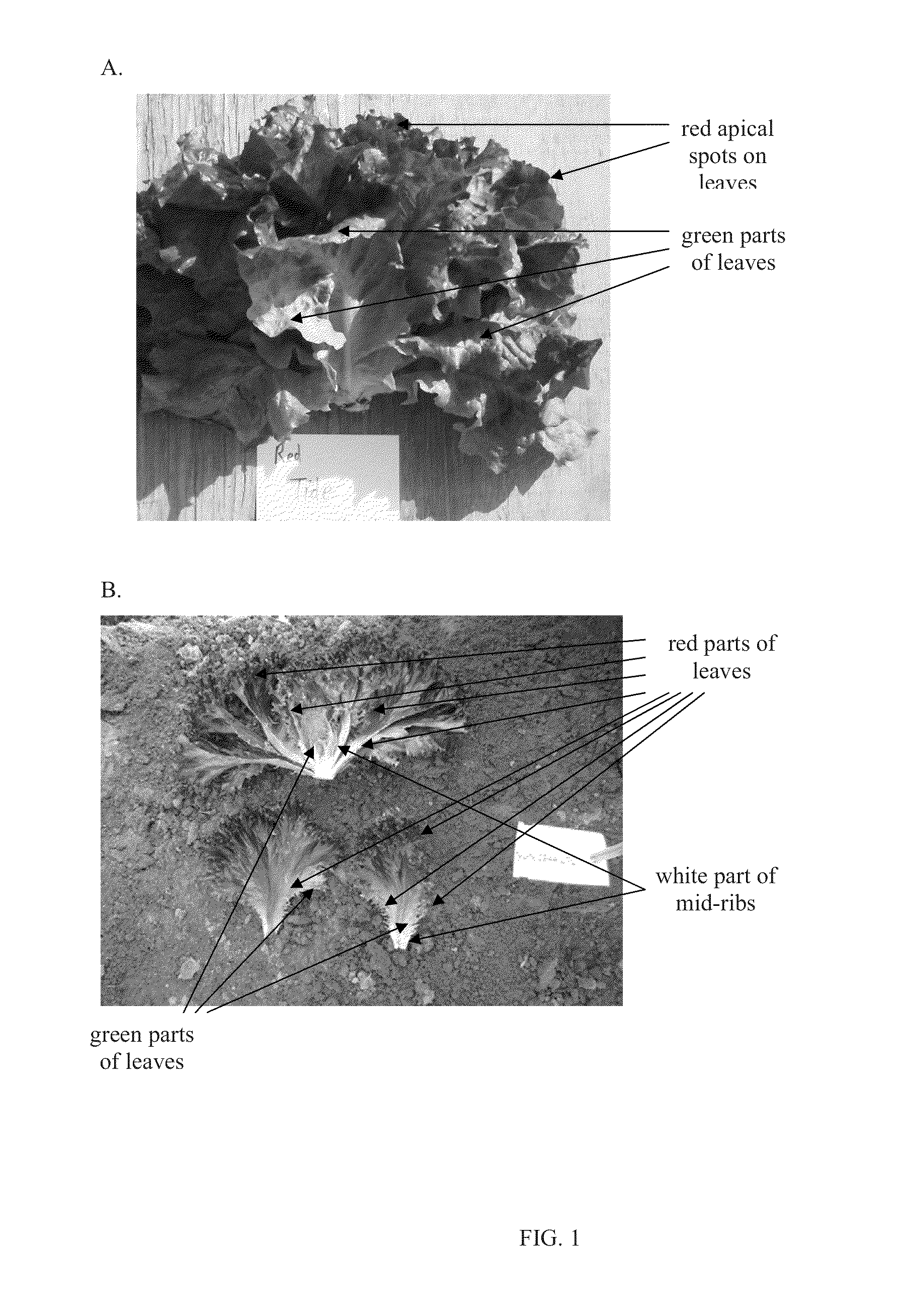
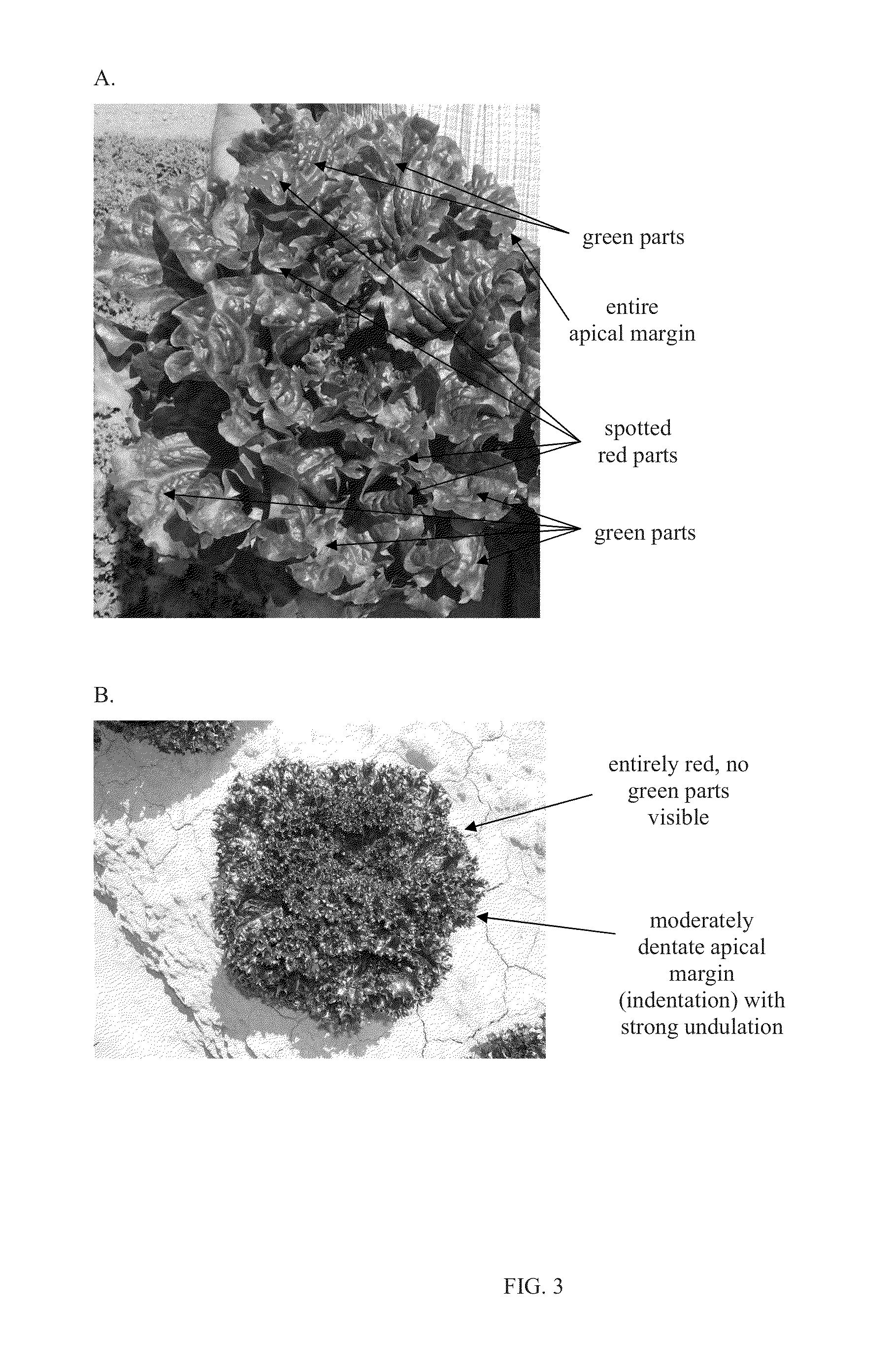
The present invention relates to a lettuce variety NUN 9044 LT (referred to as “REDGLACE”) having resistance against at least strains Bl: 1 to Bl: 26 of downy mildew (Bremia lactucae) and mature leaves which exhibit red color throughout their apical part. The invention further relates to methods for producing the new lettuce variety and representative seed having been deposited under Accession No. NCIMB 42228.
Owner:NUNHEMS BV
Peronospora resistance in spinacia oleracea
PendingUS20220135996A1Plant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionPeronospora effusaSpinacia
The present invention relates to an allele designated alpha-WOLF 26 which confers resistance to at least one Peronospora farinosa f. sp. spinacea race, wherein the protein encoded by said allele is a CC-NBS-LRR protein that may comprise in its amino acid sequence: a) the motif “MAEIGYSVC” SEQ ID NO: 1 at its N-terminus; and b) the motif “KWMCLR” SEQ ID NO: 2; and wherein the LRR domain of the protein has in order of increased preference at least 91%, 91.5%, 92%, 92.5%, 93%, 93.5%, 94%, 94.5%, 95%, 95.5%, 96%, 96.5%, 97%, 97.5%, 98%, 98.5%, 99%, 99.5%, 100% sequence identity to SEQ ID NO: 10. The allele when present in a spinach plant confers complete resistance to at least Peronospora farinosa f. sp. spinacea race Pfs:7, Pfs:10, Pfs:11, Pfs:12, Pfs:13, Pfs:14, Pfs:15, Pfs:16, Pfs:17, and does not confer resistance to downy mildew race Pfs:8 and Pfs:9.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
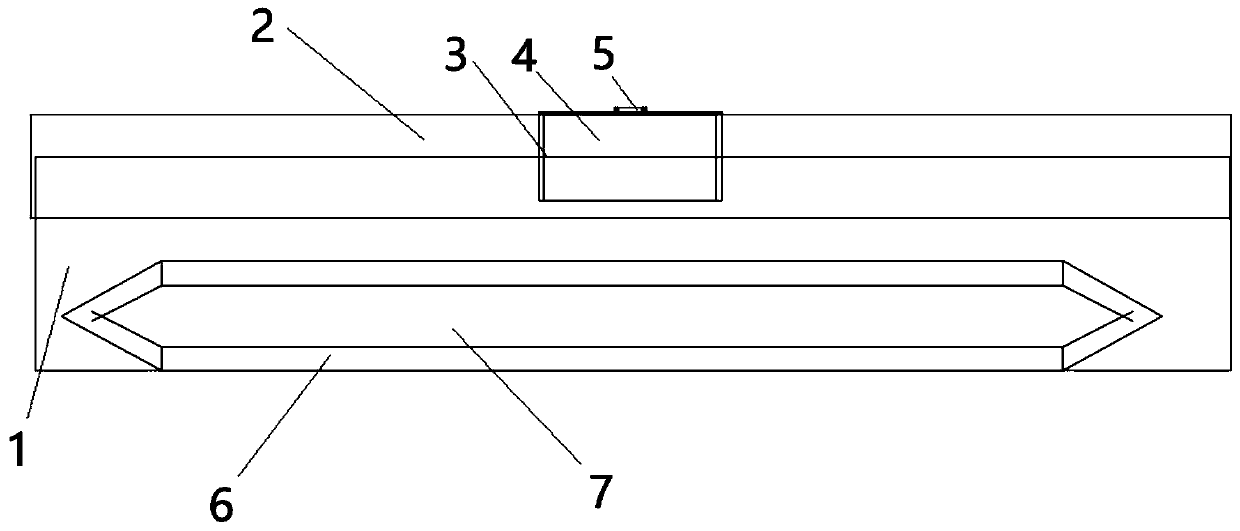
Lettuce variety 79-176 RZ
The present invention relates to a Lactuca sativa seed designated 79-176 RZ, which exhibits resistance against downy mildew strains B1:1-28 and Ca-V to Ca-VIII (Bremia lactucae), Nr:0-biotype of Nasonovia ribisnigri, and an extraordinary high number of leaves of substantially equal size. The present invention also relates to a Lactuca sativa plant produced by growing the 79-176 RZ seed. The invention further relates to methods for producing the lettuce cultivar, represented by lettuce variety 79-176 RZ.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Spinach plants that are resistant to downy mildew
ActiveUS20190185878A1Maximizing numberMinimize the numberVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsSpinaciaGene
The present invention relates to the field of spinach breeding, in particular to a new dominant resistance gene, designated RPF12, which confers resistance against all races of Peronospora farinosa and to spinach plants comprising said gene.
Owner:NUNHEMS BV
Hybrid spinach variety 51-337 RZ
The present invention relates to a Spinacia oleracea seed designated 51-337 RZ, which exhibits very slow bolting, dark green semi-savoy leaves, and resistance to downy mildew (Peronospora farinosa f.sp. spinaciae) races Pfs1 to Pfs10 and intermediate resistance to races Pfs 11 and 12. The present invention also relates to a Spinacia oleracea plant produced by growing the 51-337 RZ seed. The invention further relates to methods for producing the spinach cultivar, represented by spinach variety 51-337 RZ.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Peronospora resistance in spinacia oleracea
The present invention relates to an allele designated alpha-WOLF 15 which confers resistance to at least one Peronospora farinosa f. Sp. spinacea race, wherein the protein encoded by said allele is a CC-NBS-LRR protein that comprises in its amino acid sequence: a) the motif “MAEIGYSVC” (SEQ ID NO: 13) at its N-terminus; and b) the motif “KWMCLR” (SEQ ID NO: 14); and wherein the LRR domain of the protein has in order of increased preference at least 92%, 93%, 94%, 95%, 96%, 97%, 98%, 99%, 100% sequence similarity to SEQ ID NO: 10. The allele when homozygously present in a spinach plant confers complete resistance to Peronospora farinosa f. Sp. spinacea races pfs:1, pfs:2, pfs:3, pfs:4 and pfs:5, pfs:6, pfs:8, pfs:9, pfs:11, pfs:12, pfs:13, pfs:14, pfs:15, pfs:16 and isolates UA1014 and US1508, and confers intermediate resistance to pfs:10, and does not confer resistance to pfs:7.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Downy mildew resistant melon plants
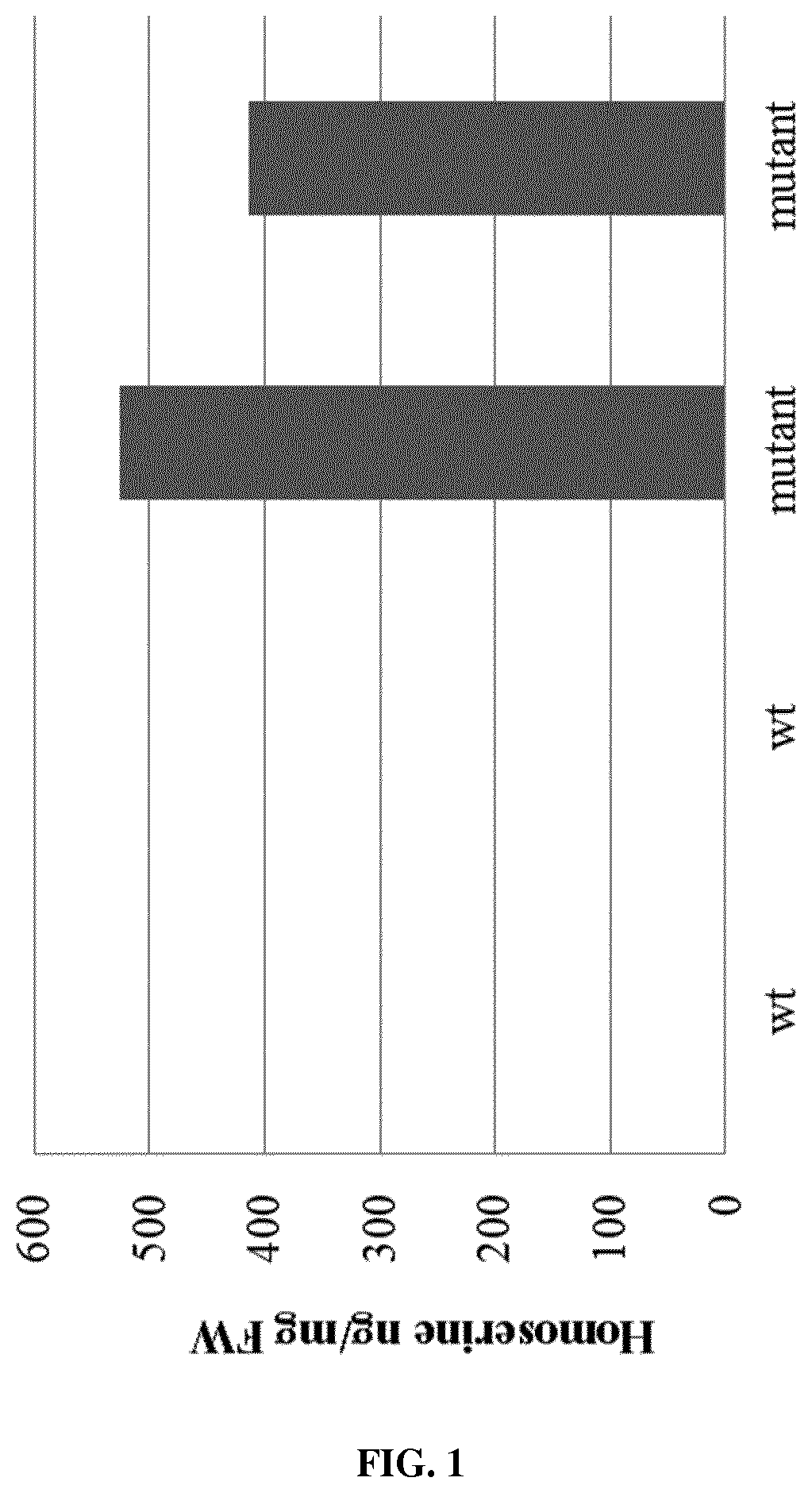
PendingUS20220228163A1Solve the lack of activityReduced activityTransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyHomoserine
The present disclosure relates to melon plants that are resistant to the plant disease downy mildew caused by the pathogen Pseudoperonospora cubensis. Specifically, the present disclosure relates to melon plants that are resistant to downy mildew disease including a mutated homoserine kinase gene encoding a mutated homoserine kinase protein. The present disclosure further relates to seeds, tissues, cells, or plant parts of the present melon plants, and to methods for identifying downy mildew resistant melon plants.
Owner:ENZA ZADEN BEHEER BV
Peronospora resistance in spinacia oleracea
The present invention relates to an allele designated alpha-WOLF 24 which confers resistance to at least one Peronospora farinosa f. sp. spinacea race, wherein the protein encoded by said allele is a CC-NBS-LRR protein that comprises in its amino acid sequence: a) the motif “MAEIGYSVC” SEQ ID NO: 1 at its N-terminus; and b) the motif “KWMCLR” SEQ ID NO: 2; and wherein the LRR domain of the protein has in order of increased preference at least 95%, 96%, 97%, 98%, 98.2%, 98.5%, 98.8%, 99%, 100% sequence similarity to SEQ ID NO: 10. The allele when present in a spinach plant confers complete resistance to at least Peronospora farinosa f. sp. spinacea race Pfs:1, Pfs:2, Pfs:5, Pfs:6, Pfs:7, Pfs:9, Pfs:11, Pfs:13, Pfs:15 and Pfs:17, and does not confer resistance to downy mildew race Pfs:16.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
The Application of Nucleus Penicillin as Agricultural Fungicide
The invention provides an agricultural fungicide, which is characterized in that it uses sclerotin or its salt as an active ingredient for preventing and treating sclerotinia Sclerotinia sclerotiorum , wheat snow mold leaf blight Monographella nivalis , Glycystia husk Gaeumannomyces graminis , Septoria tritici Septoria tritici , melon anthracnose Glomerella lagenarium , Peanut Mycosphaerella arachidis and downy mildew Plasmopara viticola caused by agricultural diseases.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com