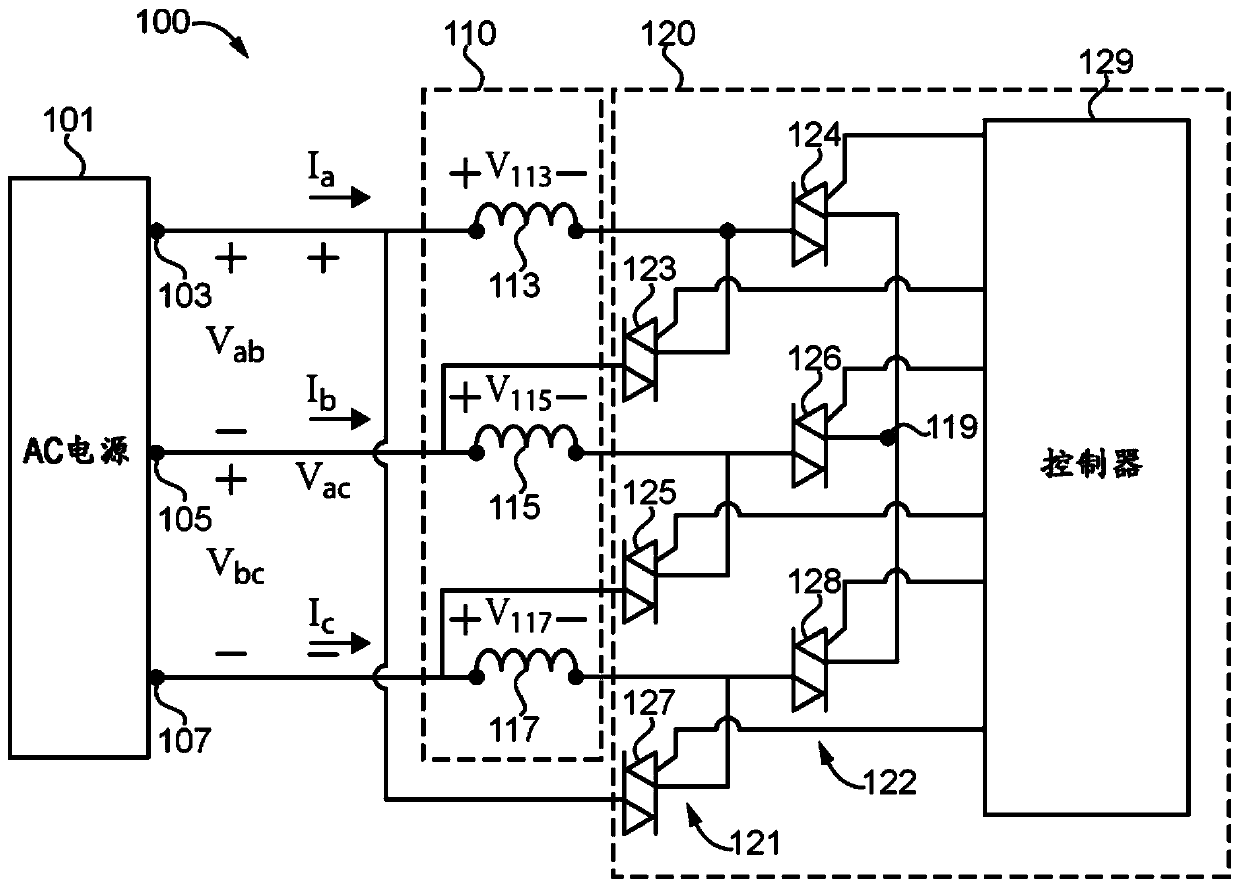
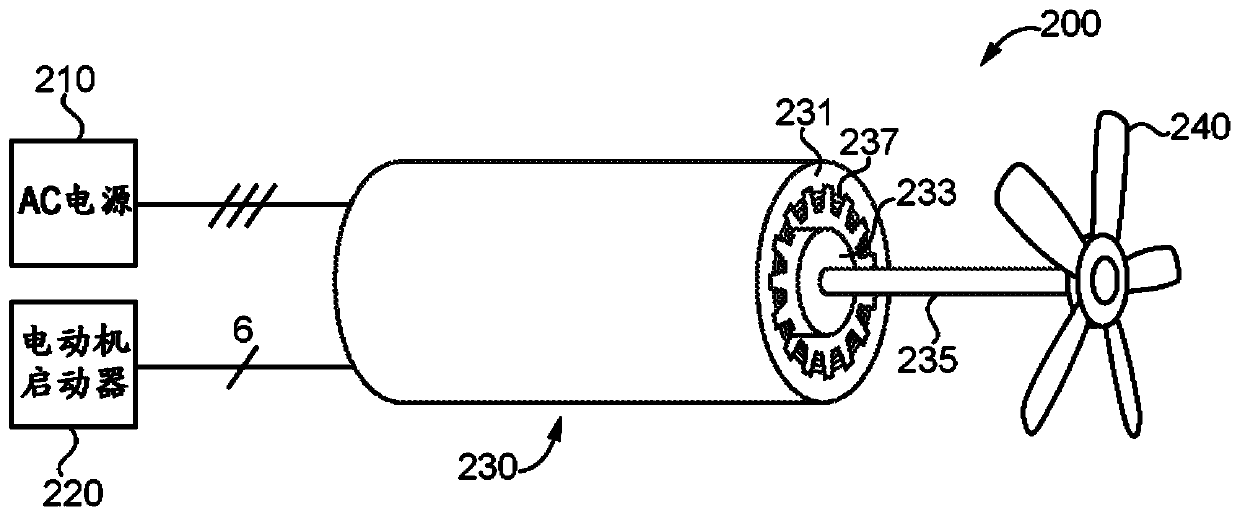
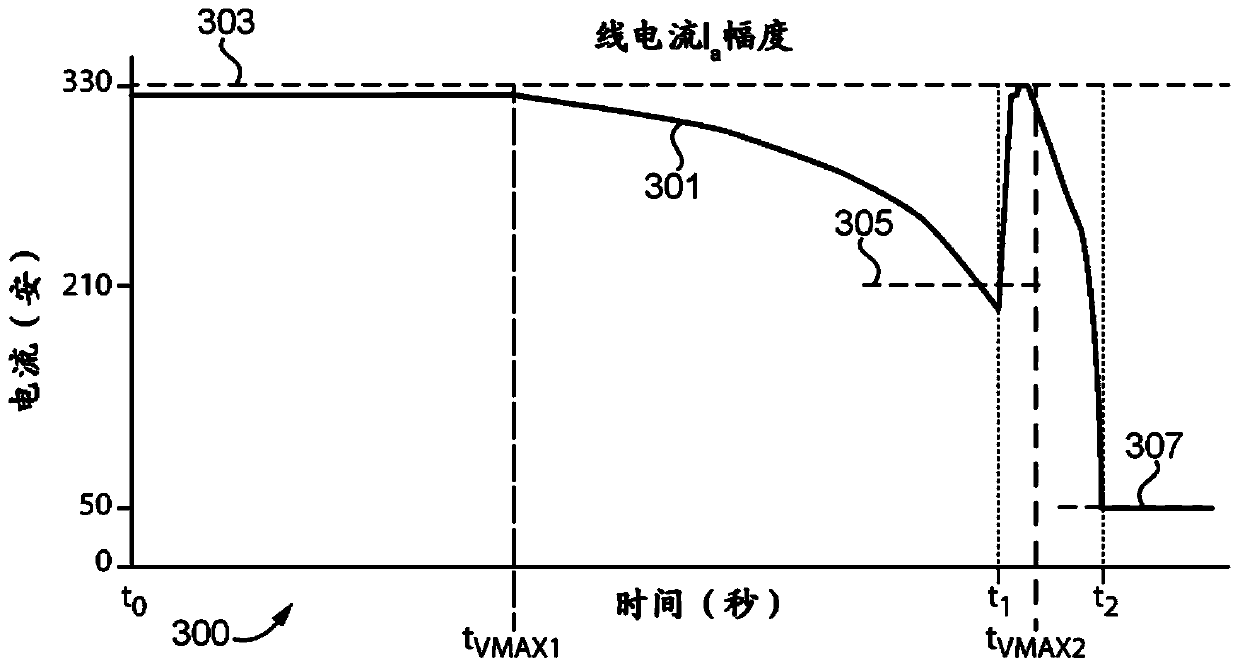
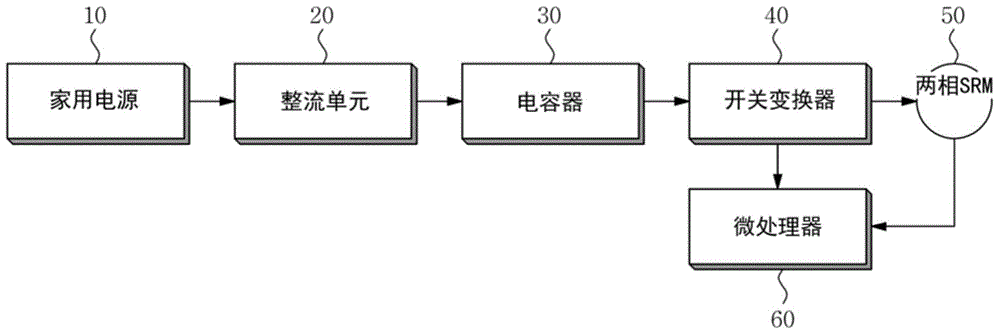
Patents
Literature
36results about "Reluctance motor starters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
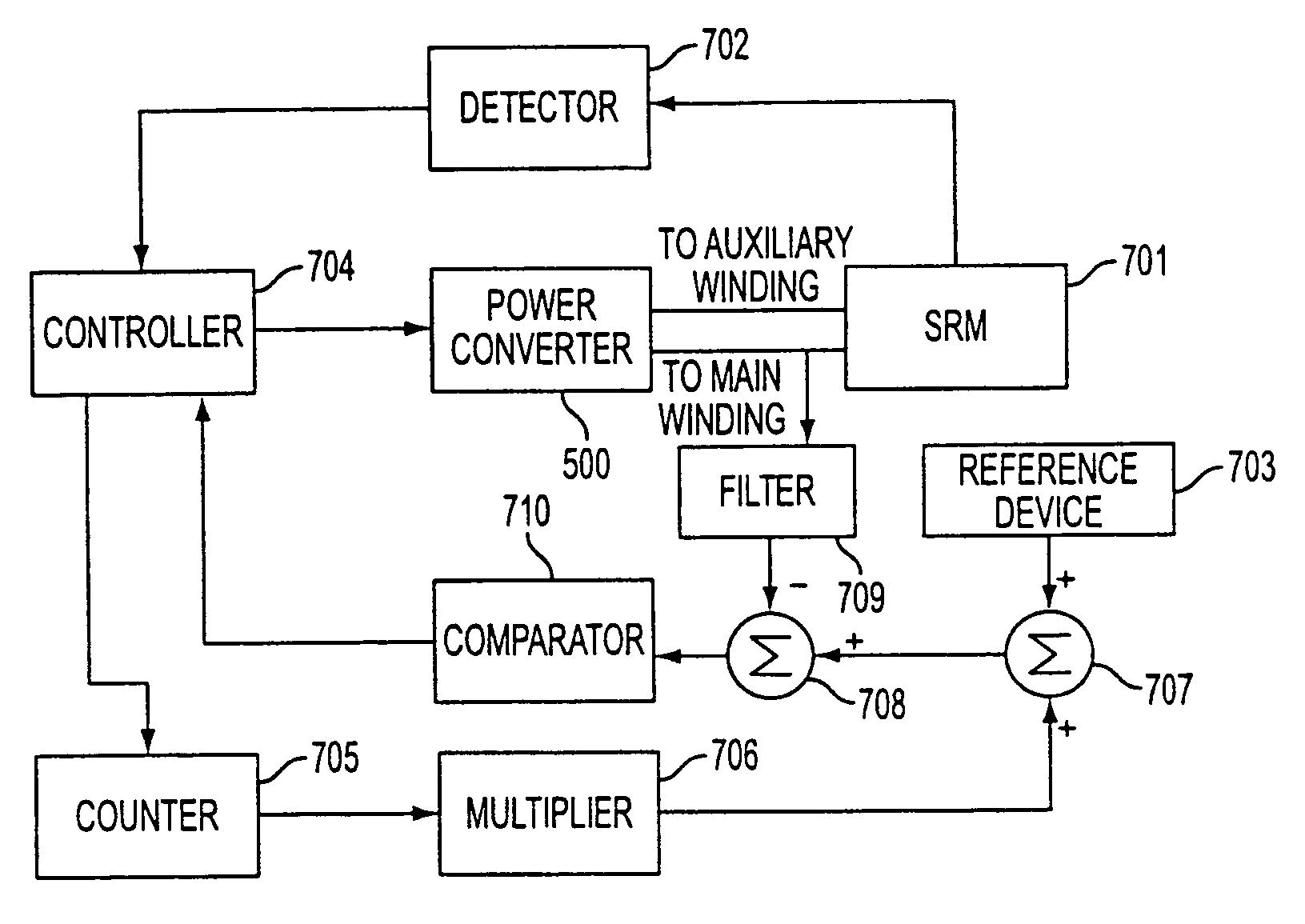
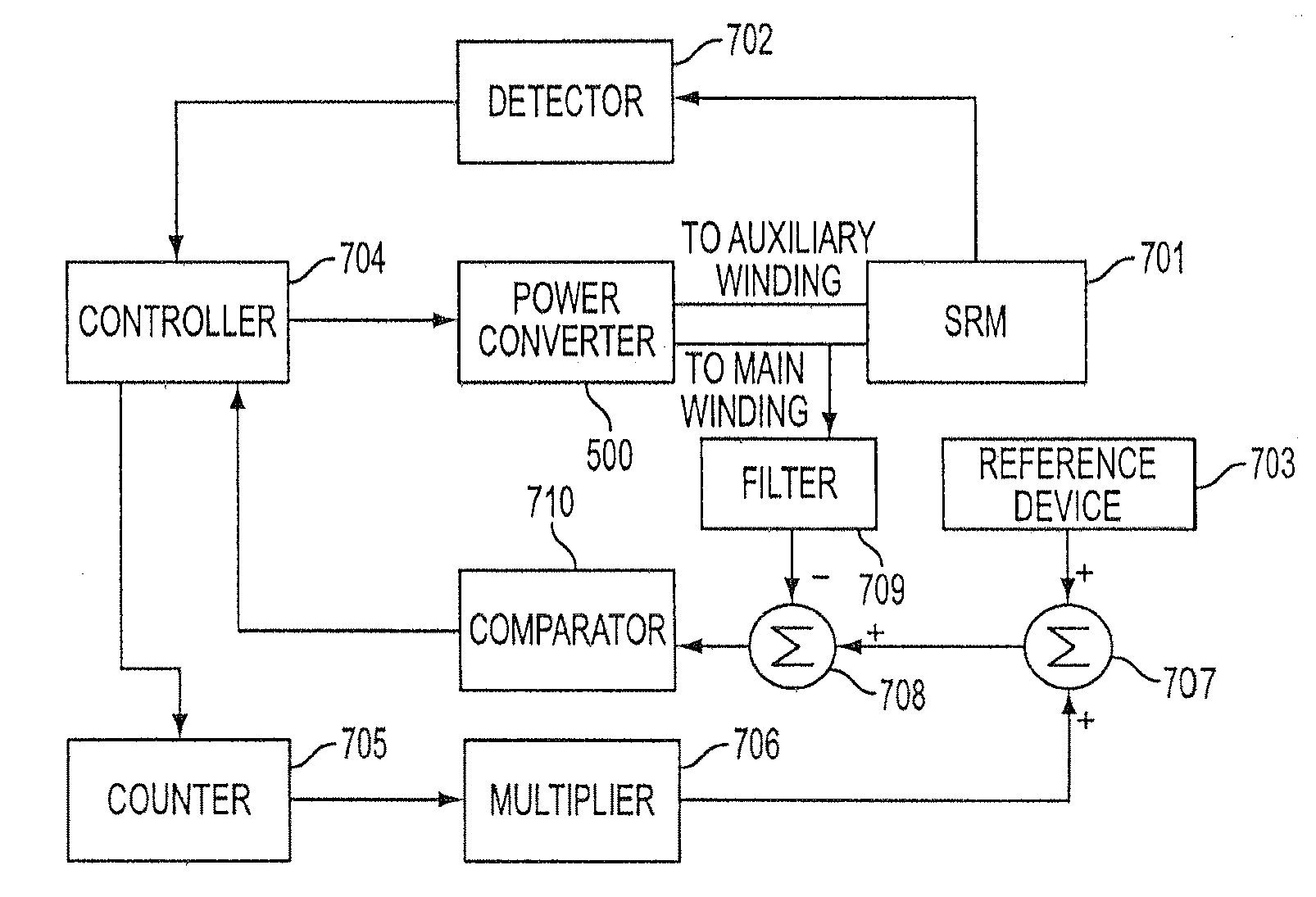
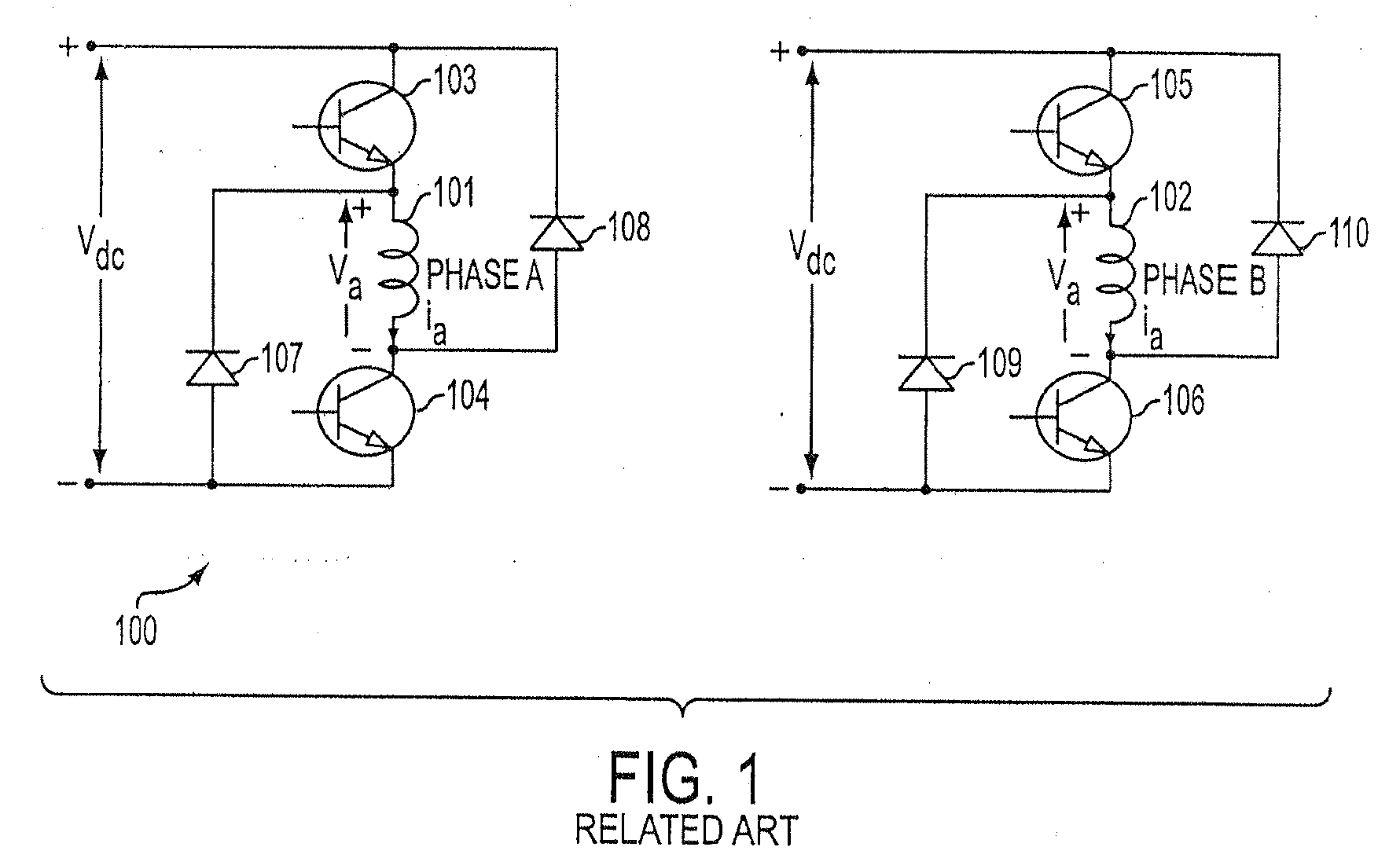
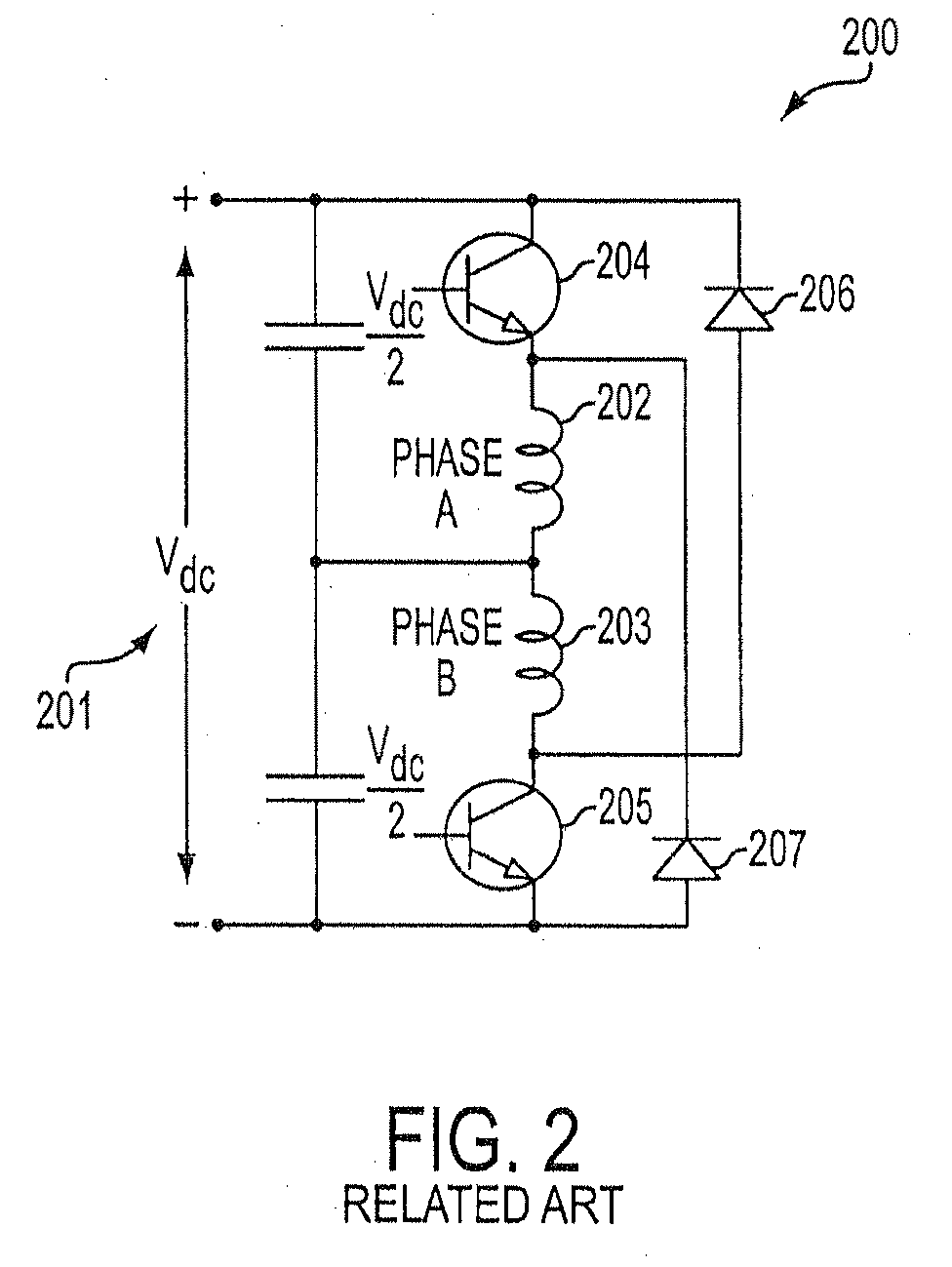
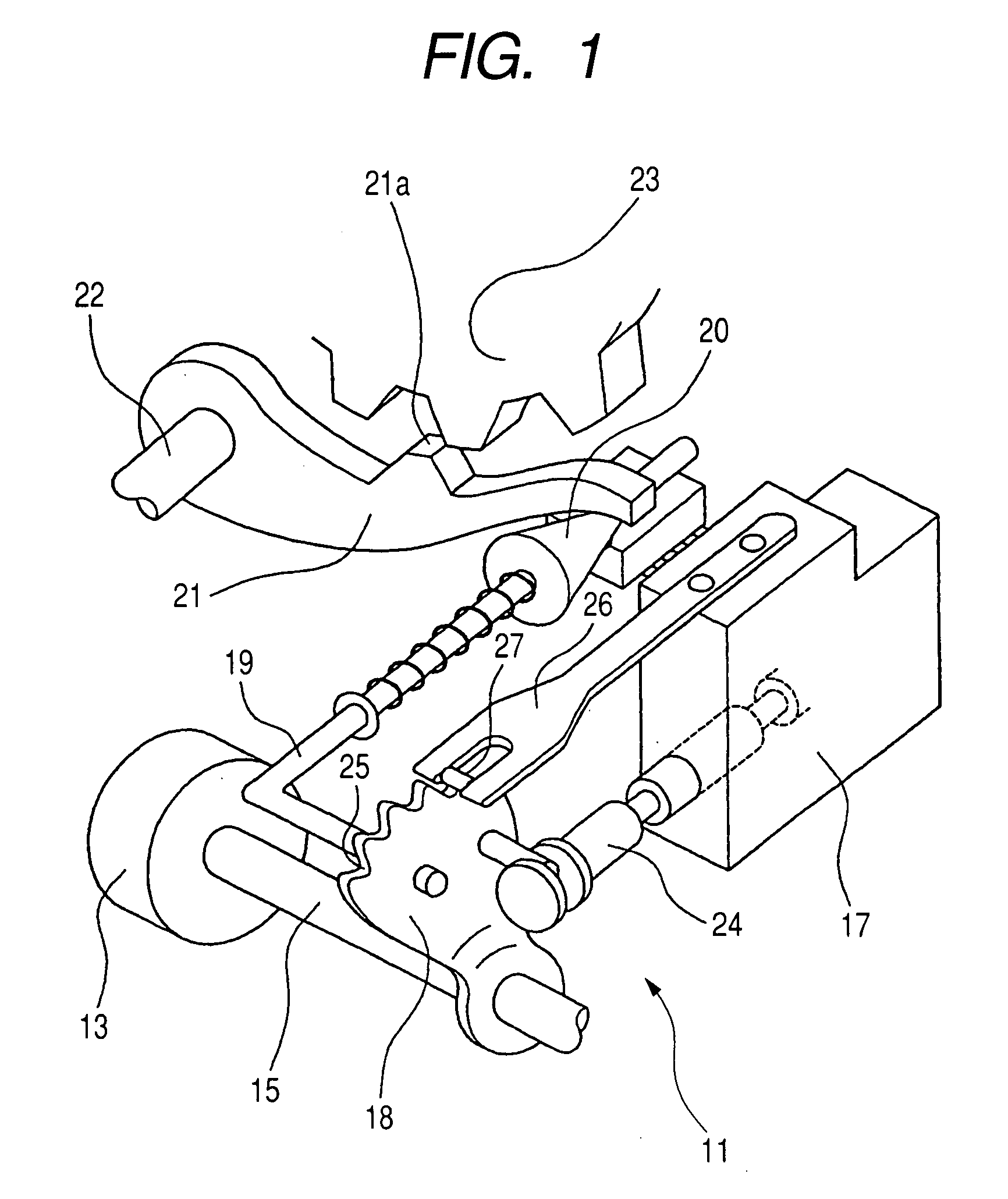
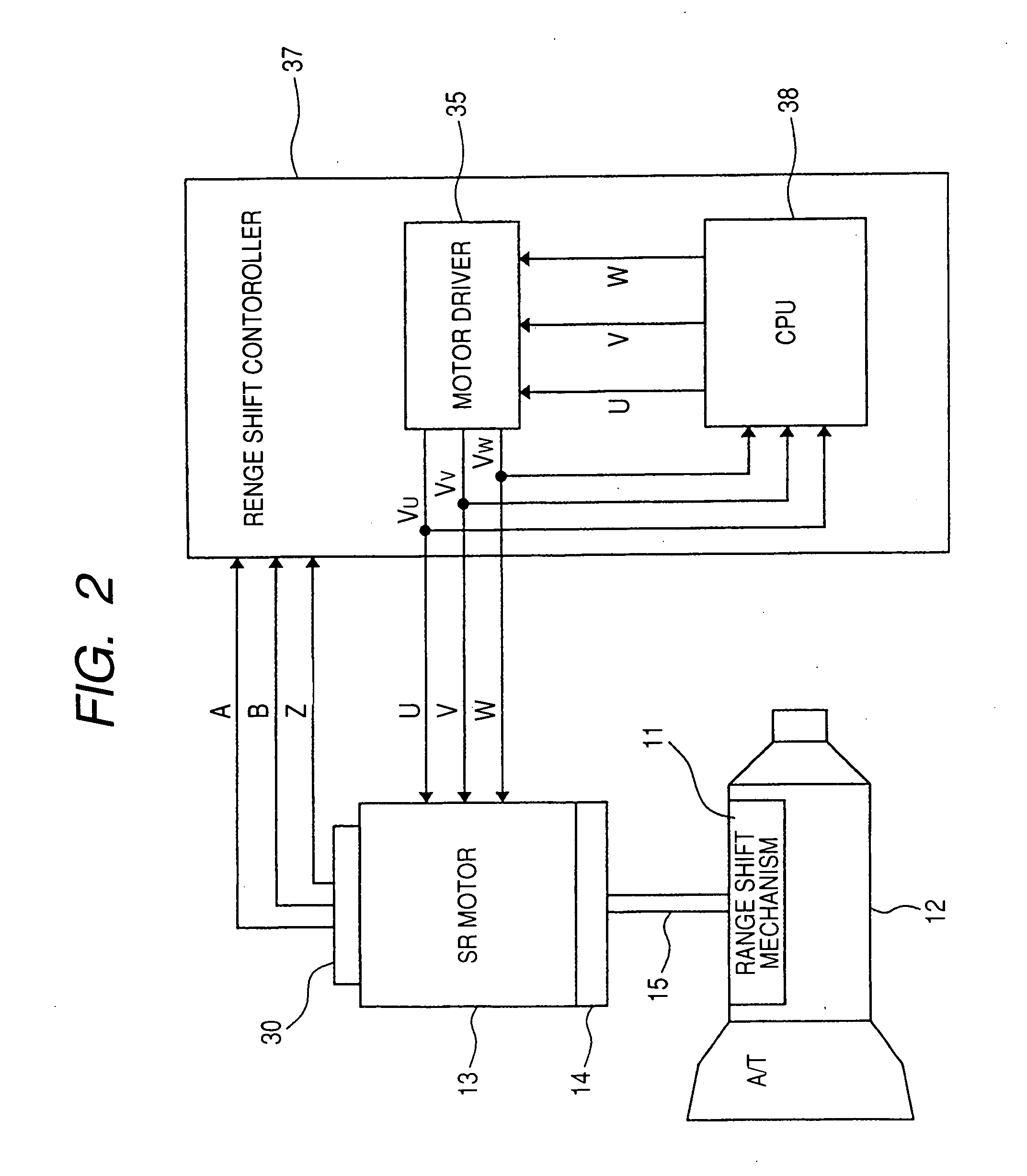
Method, apparatus, and system for drive control, power conversion, and start-up control in an SRM or PMBDCM drive system
InactiveUS7271564B2Low costReduce in quantityAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersFour quadrantsEngineering
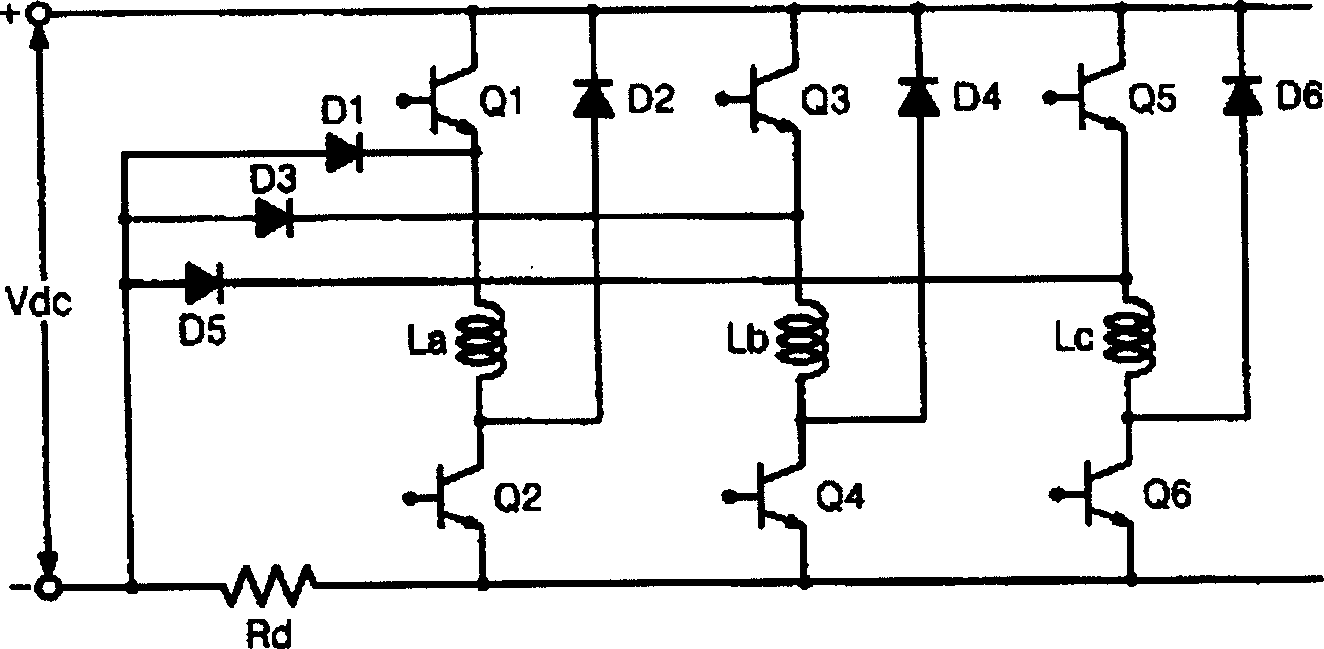
A power converter for a switched reluctance motor or a permanent magnet brushless direct current (dc) motor may include first and second partial circuits for forming multiple conduction circuits in cooperation with first and second phase windings of the motor. The controller also includes a switch operable to open and close a first conduction circuit, which includes the first phase winding, and to regulate energization of the first and second phase windings of the motor through opening and closing the first conduction circuit. Control of the switch provides four-quadrant operation of the motor through regulated energization of the first and second phase windings.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
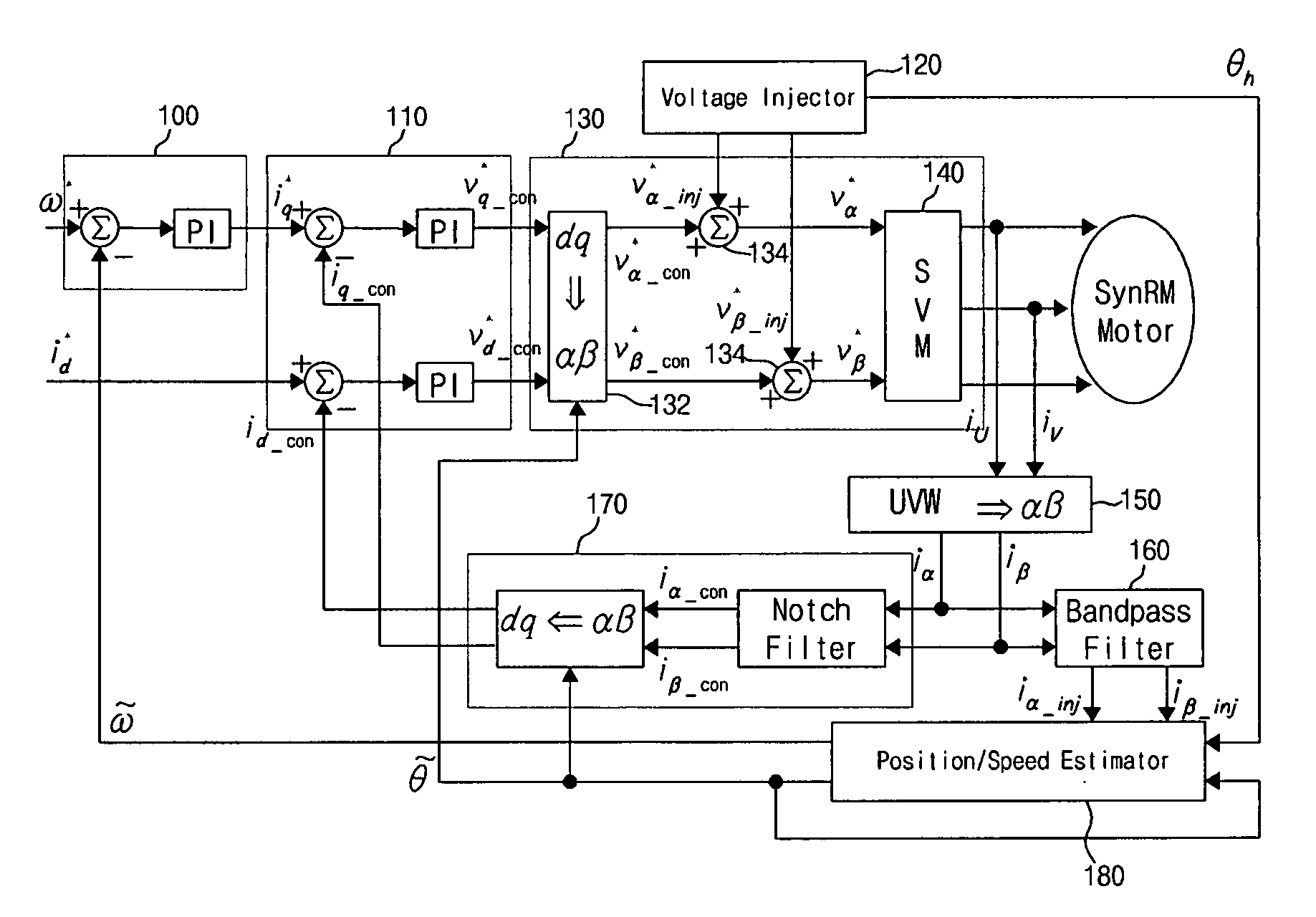
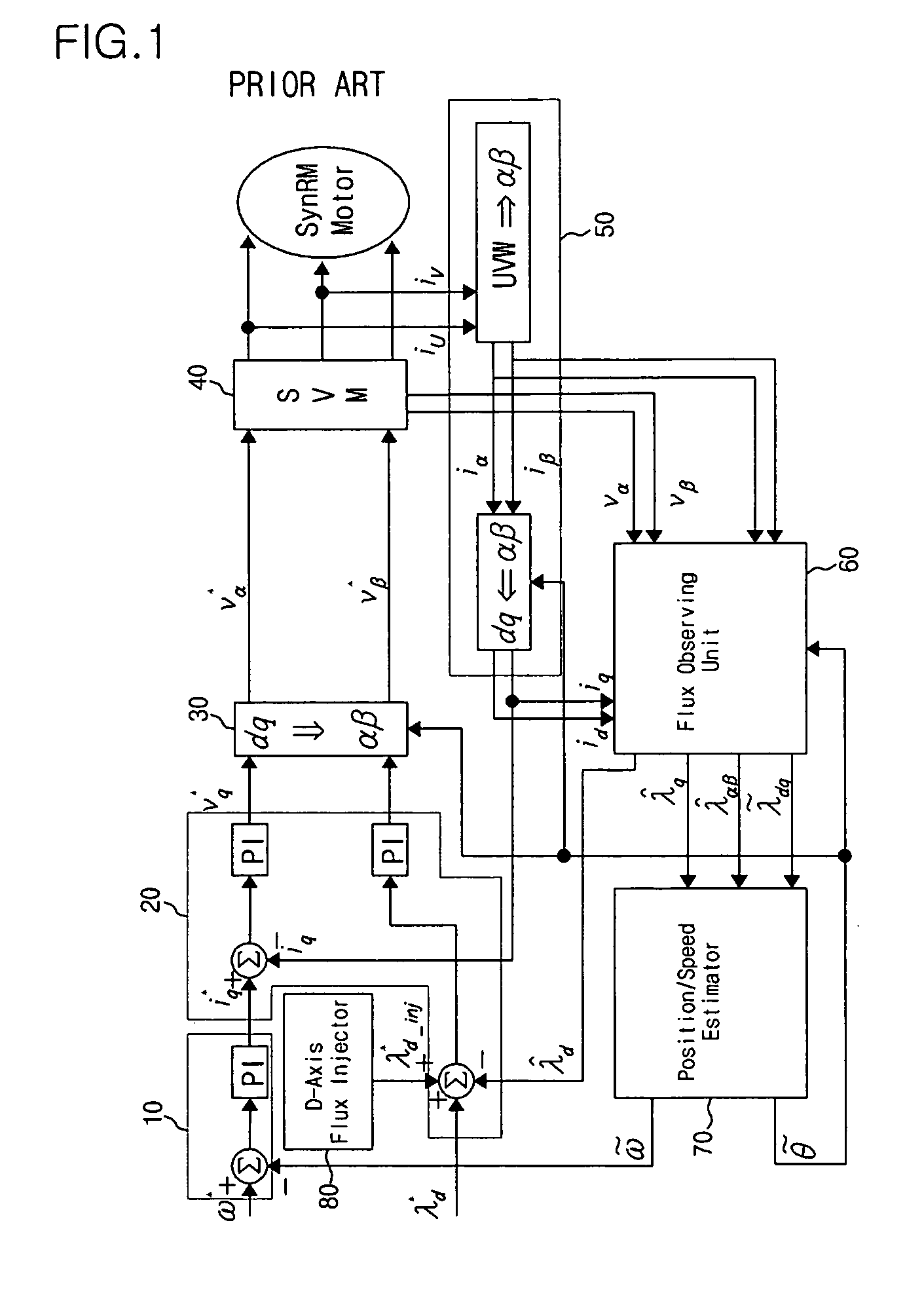
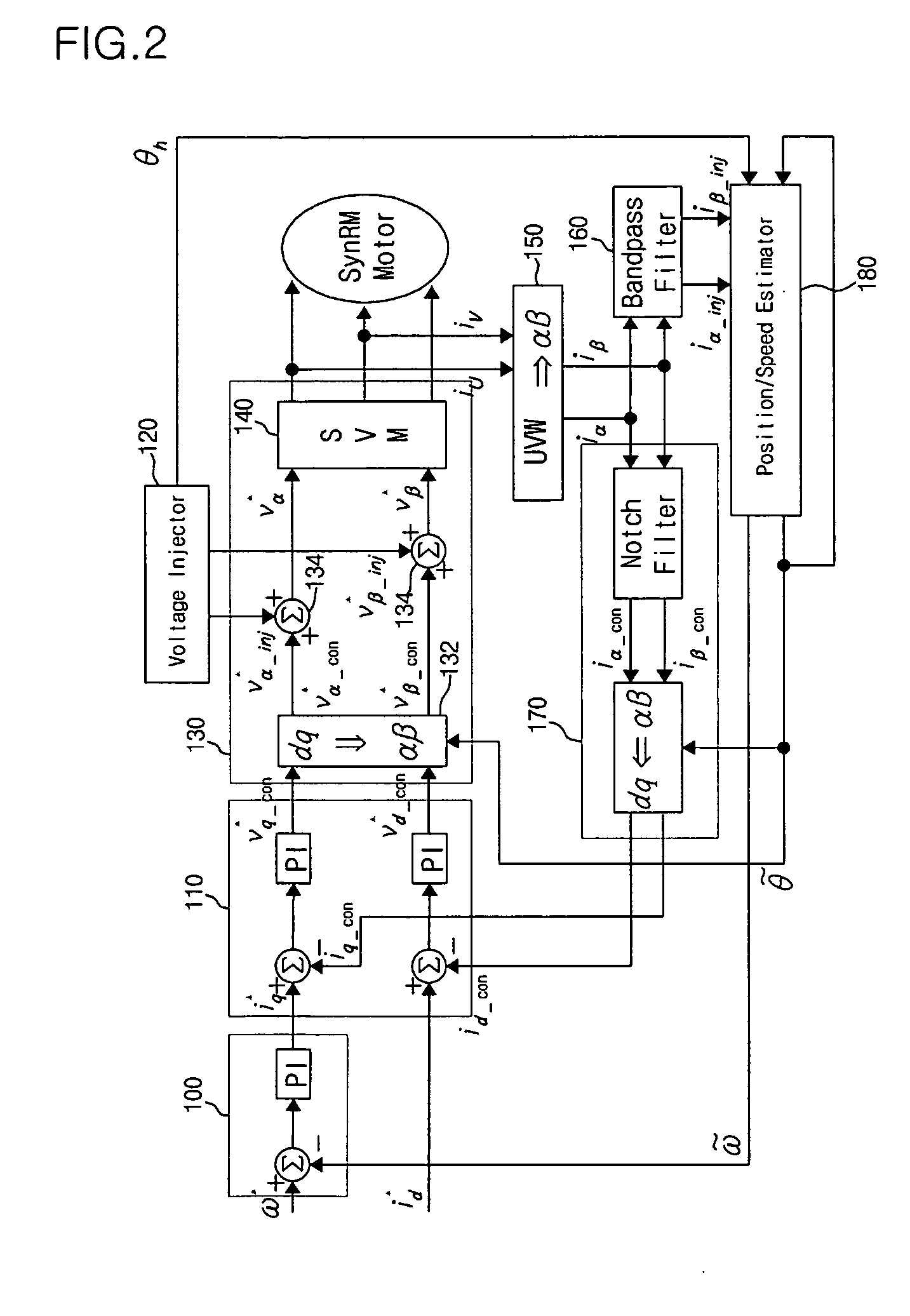
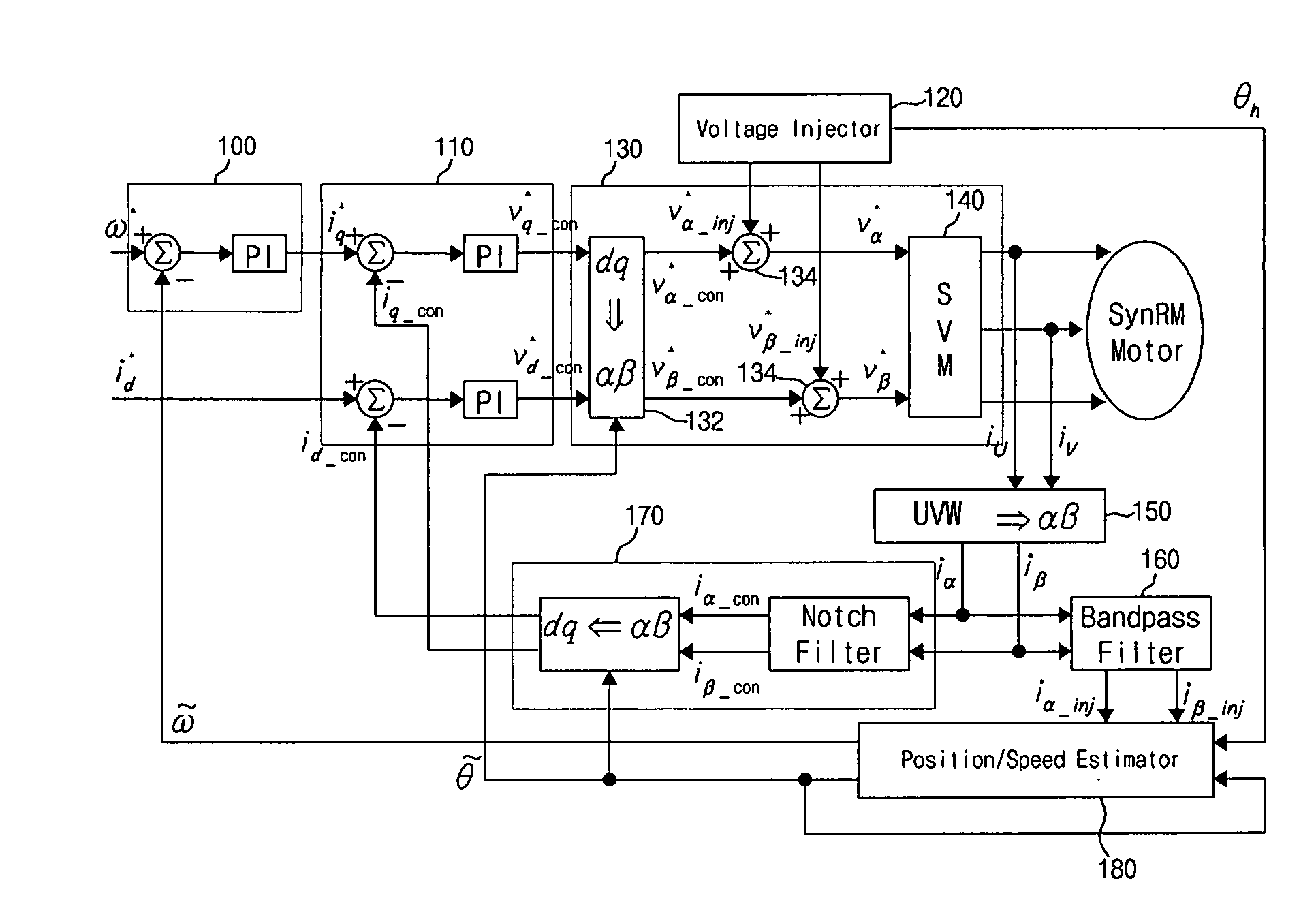
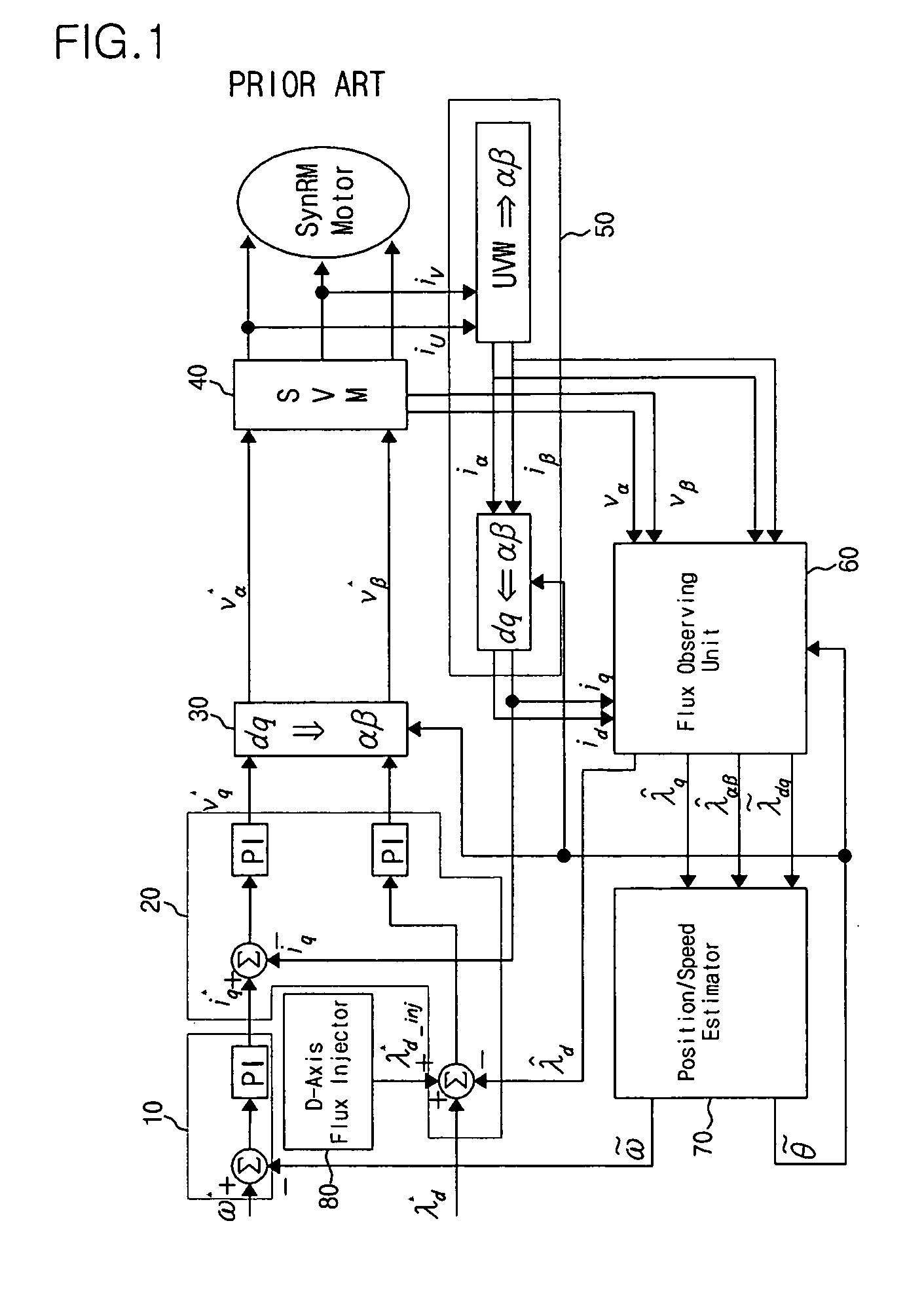
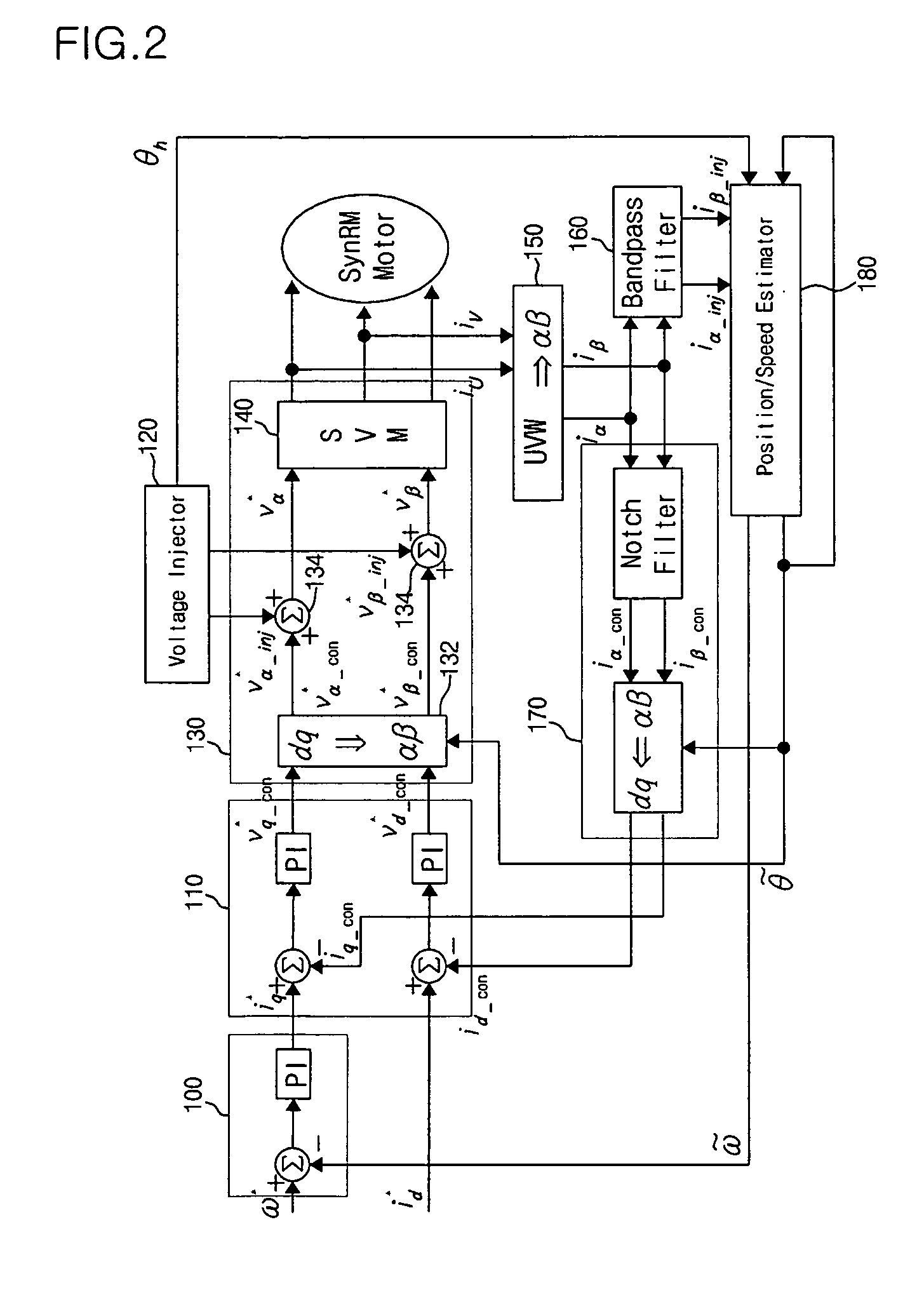
Method and device for controlling startup of motor
ActiveUS20060119305A1AC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlVoltage generatorSynchronous reluctance motor
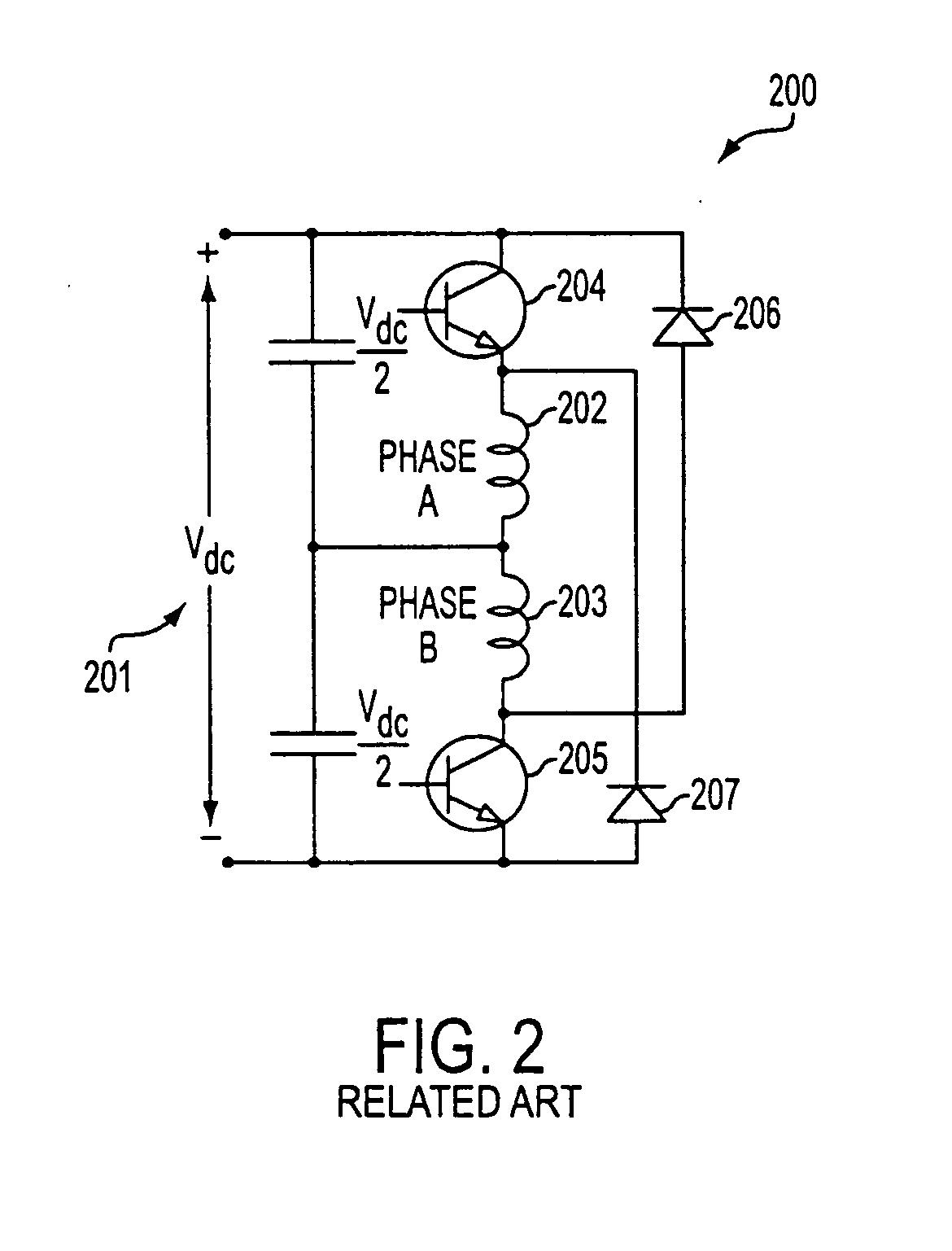
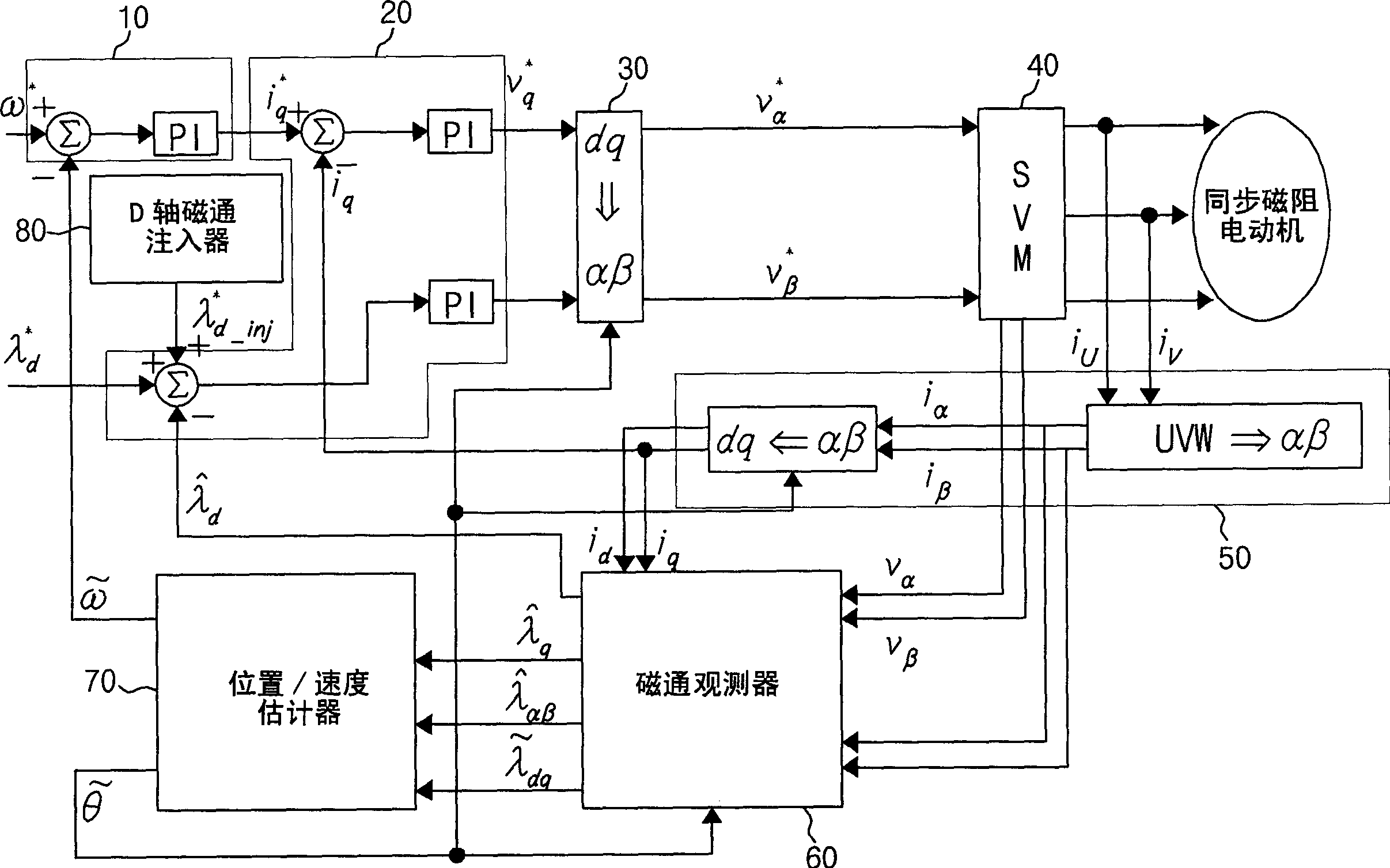
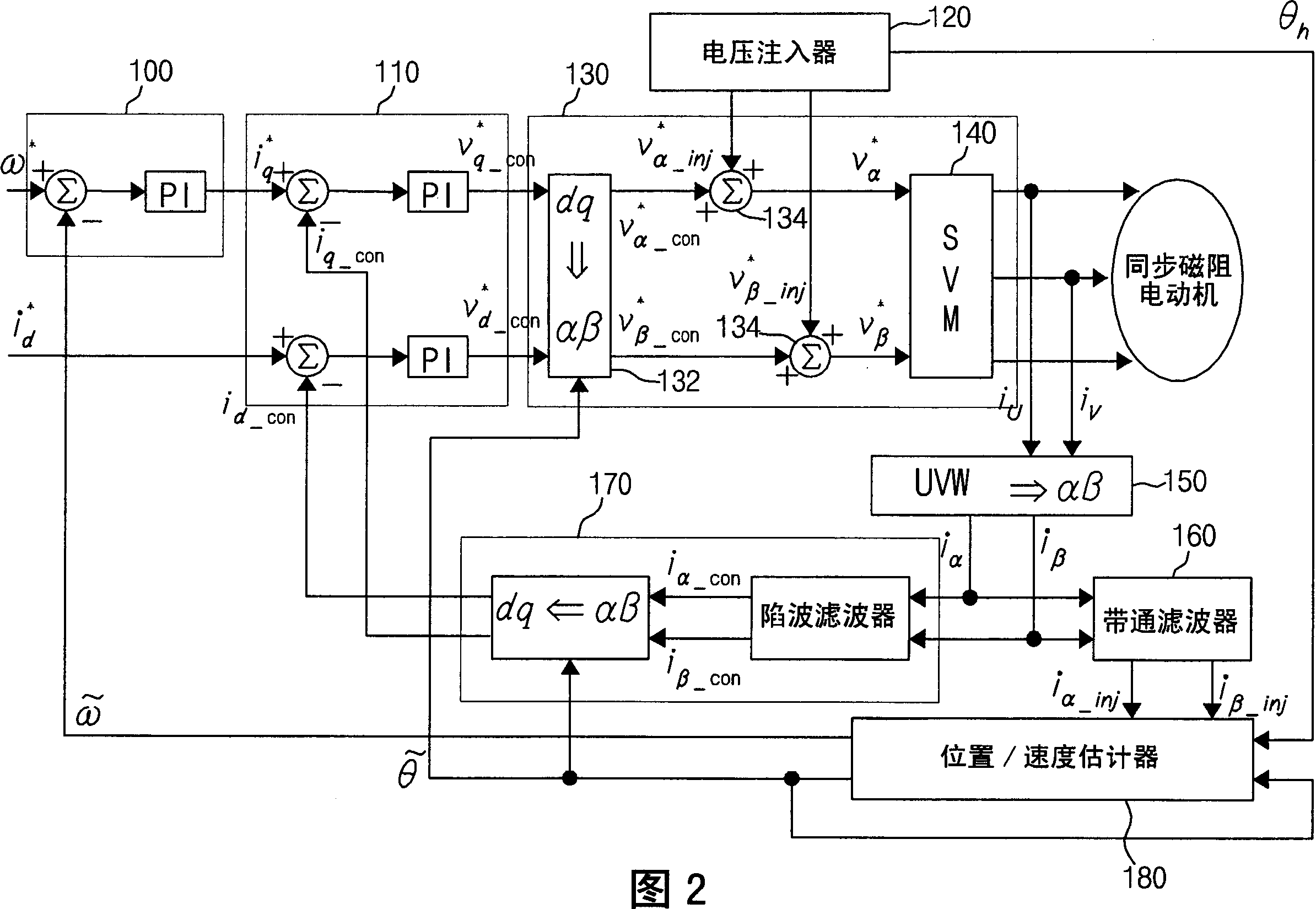
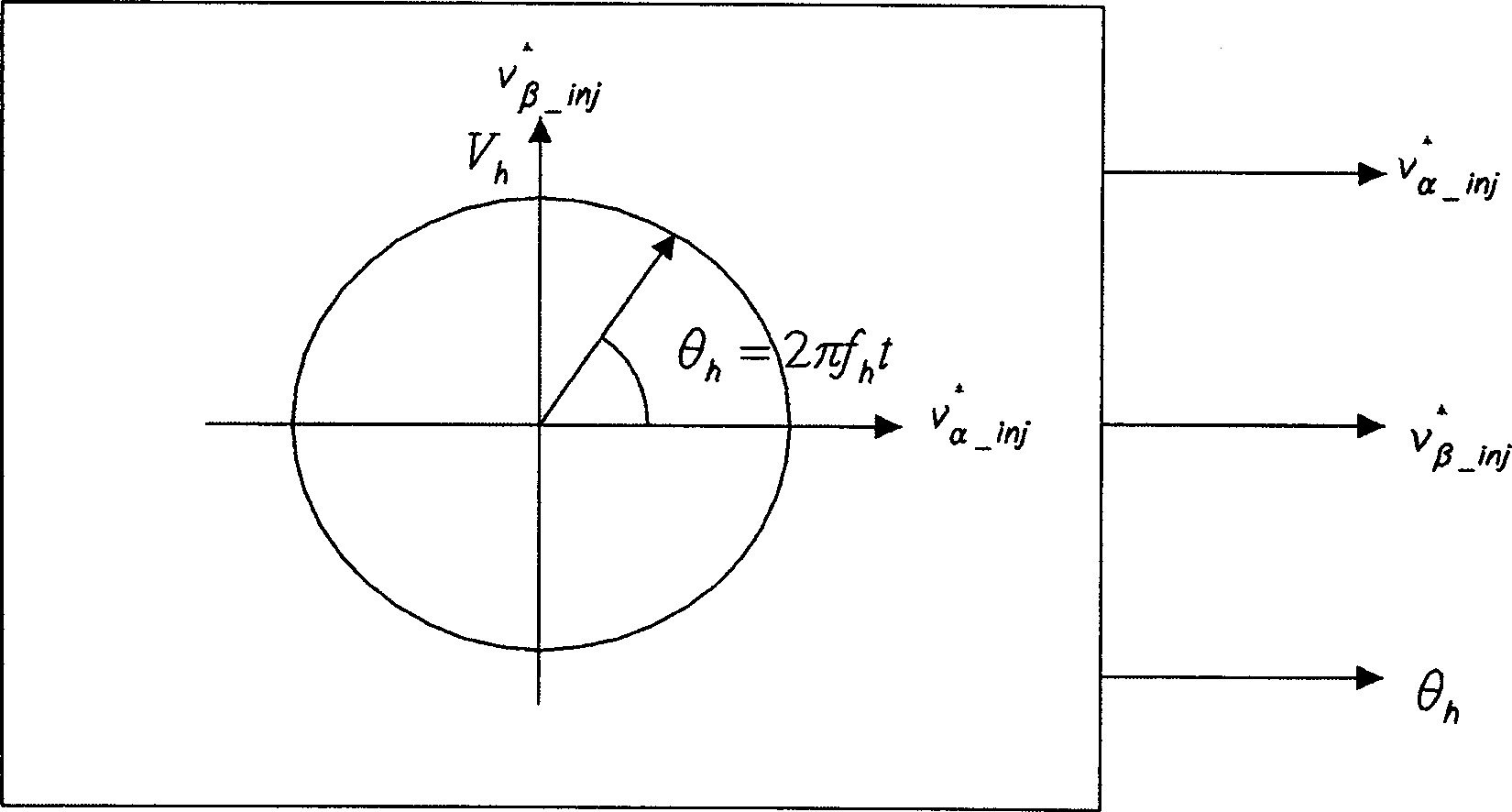
Disclosed is a method and device for controlling the startup of a synchronous reluctance motor. The device includes: a voltage injector which generates injection voltages to estimate an initial position of the rotor; a motor drive voltage generator which converts stationary-coordinate-system voltages including the injection voltages to three-phase motor drive voltages and applies the three-phase motor drive voltages to the motor; a current extractor which extracts response current components iα-inj, iβ-inj in respect to the injection voltages from two-phase stationary-coordinate-system currents converted from three-phase currents detected upon rotation of the motor; and a position / speed estimator which extracts response current components related to a rotor position from the response current components iα-inj, iβ-inj in respect to the injection voltages to calculate a rotor position error (e), and estimates the speed and position {tilde over (ω)},{tilde over (θ)} of the rotor from the calculated rotor position error (e).
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method, apparatus, and system for drive control, power conversion, and start-up control in an SRM or PMBDCM drive system
InactiveUS20050146304A1Small sizeLow costSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlFour quadrantsConductor Coil
A power converter for a switched reluctance motor or a permanent magnet brushless direct current (dc) motor may include first and second partial circuits for forming multiple conduction circuits in cooperation with first and second phase windings of the motor. The controller also includes a switch operable to open and close a first conduction circuit, which includes the first phase winding, and to regulate energization of the first and second phase windings of the motor through opening and closing the first conduction circuit. Control of the switch provides four-quadrant operation of the motor through regulated energization of the first and second phase windings.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
Method and device for controlling startup of motor
The invention discloses a method and a device for controlling the starting of a synchronous reluctance motor. The device comprises: a voltage injector, which generates an injected voltage to estimate the initial position of the rotor; a motor drive voltage generator, which transforms the stationary frame voltage including the injected voltage into a three-phase motor drive voltage and converts the three-phase motor a driving voltage is applied to the motor; a current extractor which extracts response current components iα-inj, iβ-inj corresponding to the injection voltage from the two-phase stationary coordinate system current transformed from the three-phase current detected according to the rotational speed of the motor ; and a position / speed estimator which extracts the response current component related to the rotor position from the response current components iα-inj, iβ-inj corresponding to the injected voltage to calculate the rotor position error (e), and based on the calculated The rotor position error (e) estimates the speed and position ω, θ of the rotor.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method, apparatus, and system for drive control, power conversion, and start-up control in an srm or pmbdcm drive system
InactiveUS20070273322A1Low costReduce in quantityAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersFour quadrantsEngineering
A power converter for a switched reluctance motor or a permanent magnet brushless direct current (dc) motor may include first and second partial circuits for forming multiple conduction circuits in cooperation with first and second phase windings of the motor. The controller also includes a switch operable to open and close a first conduction circuit, which includes the first phase winding, and to regulate energization of the first and second phase windings of the motor through opening and closing the first conduction circuit. Control of the switch provides four-quadrant operation of the motor through regulated energization of the first and second phase windings.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Method and device for controlling startup of motor
ActiveUS7271562B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlVoltage generatorSynchronous reluctance motor
Disclosed is a method and device for controlling the startup of a synchronous reluctance motor. The device includes: a voltage injector which generates injection voltages to estimate an initial position of the rotor; a motor drive voltage generator which converts stationary-coordinate-system voltages including the injection voltages to three-phase motor drive voltages and applies the three-phase motor drive voltages to the motor; a current extractor which extracts response current components iα-inj, iβ-inj in respect to the injection voltages from two-phase stationary-coordinate-system currents converted from three-phase currents detected upon rotation of the motor; and a position / speed estimator which extracts response current components related to a rotor position from the response current components iα-inj, iβ-inj in respect to the injection voltages to calculate a rotor position error (e), and estimates the speed and position {tilde over (ω)},{tilde over (θ)} of the rotor from the calculated rotor position error (e).
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
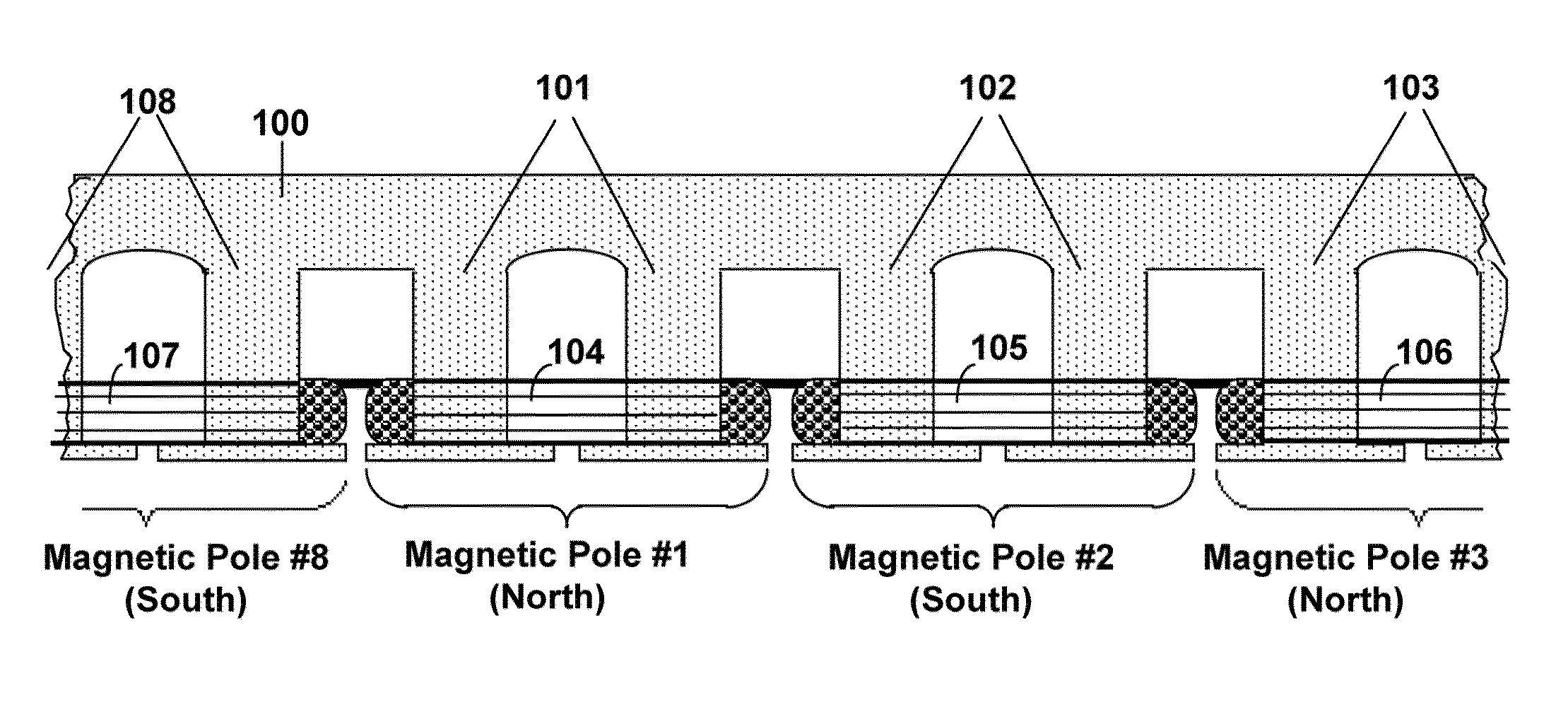
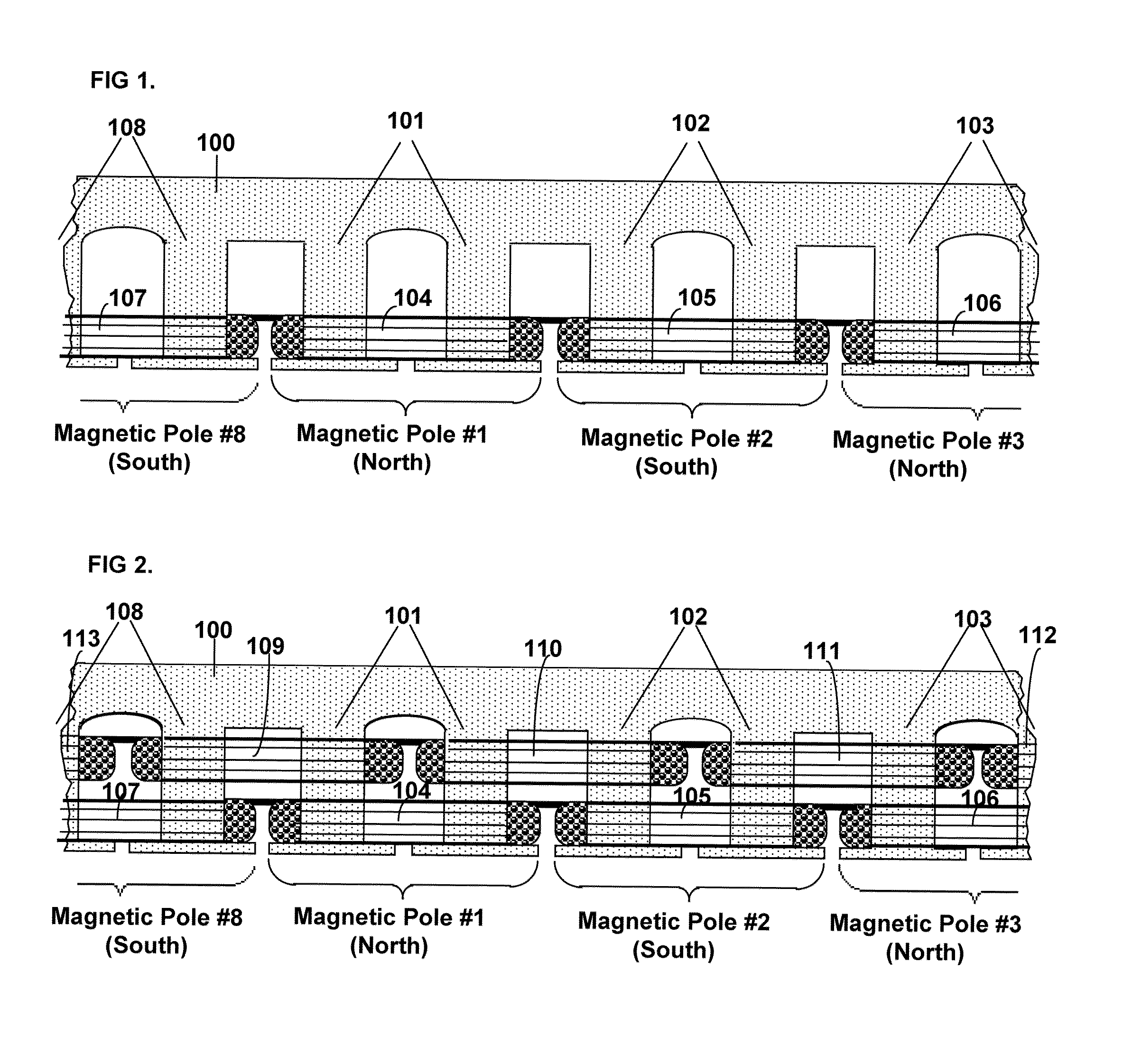
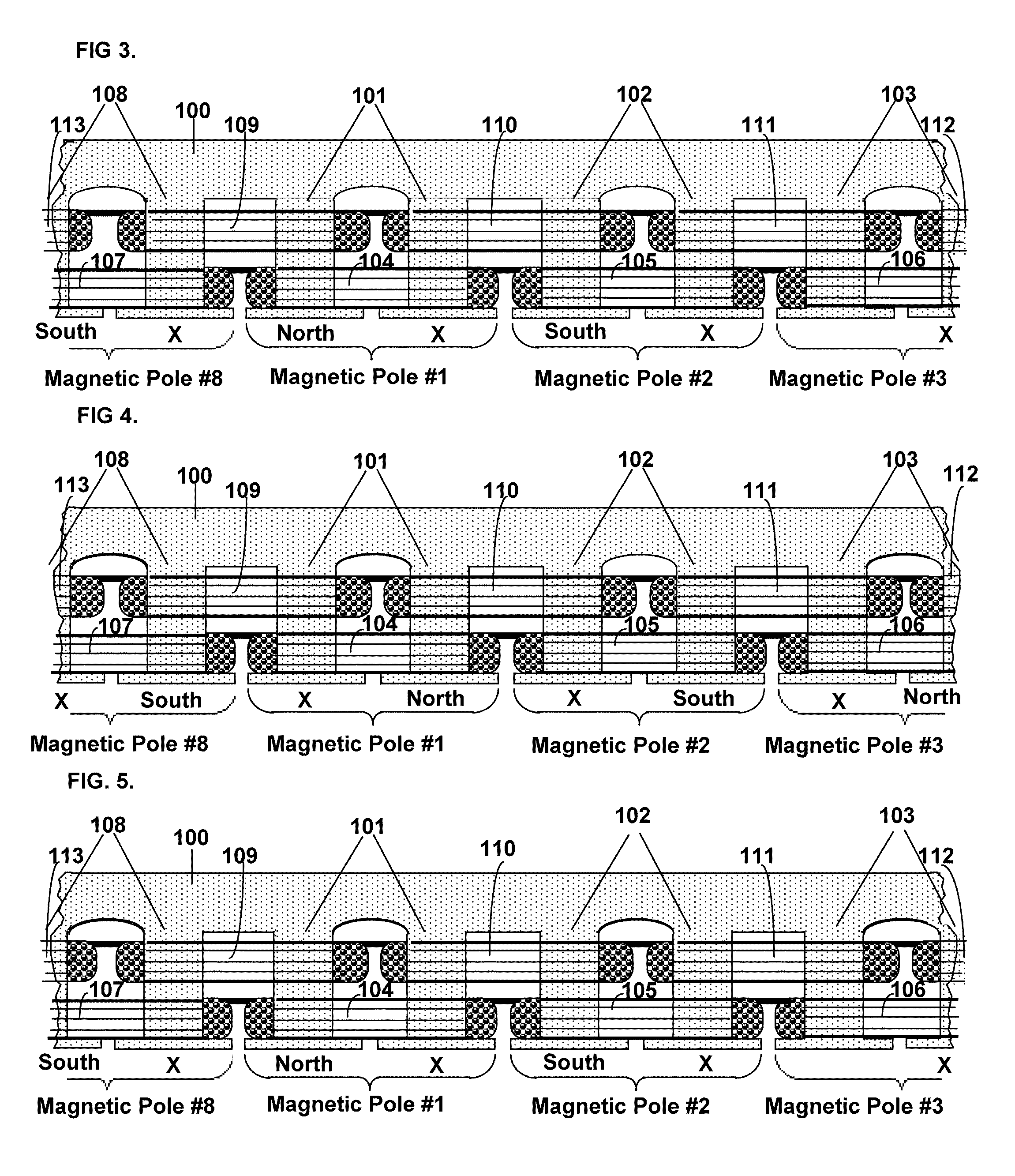
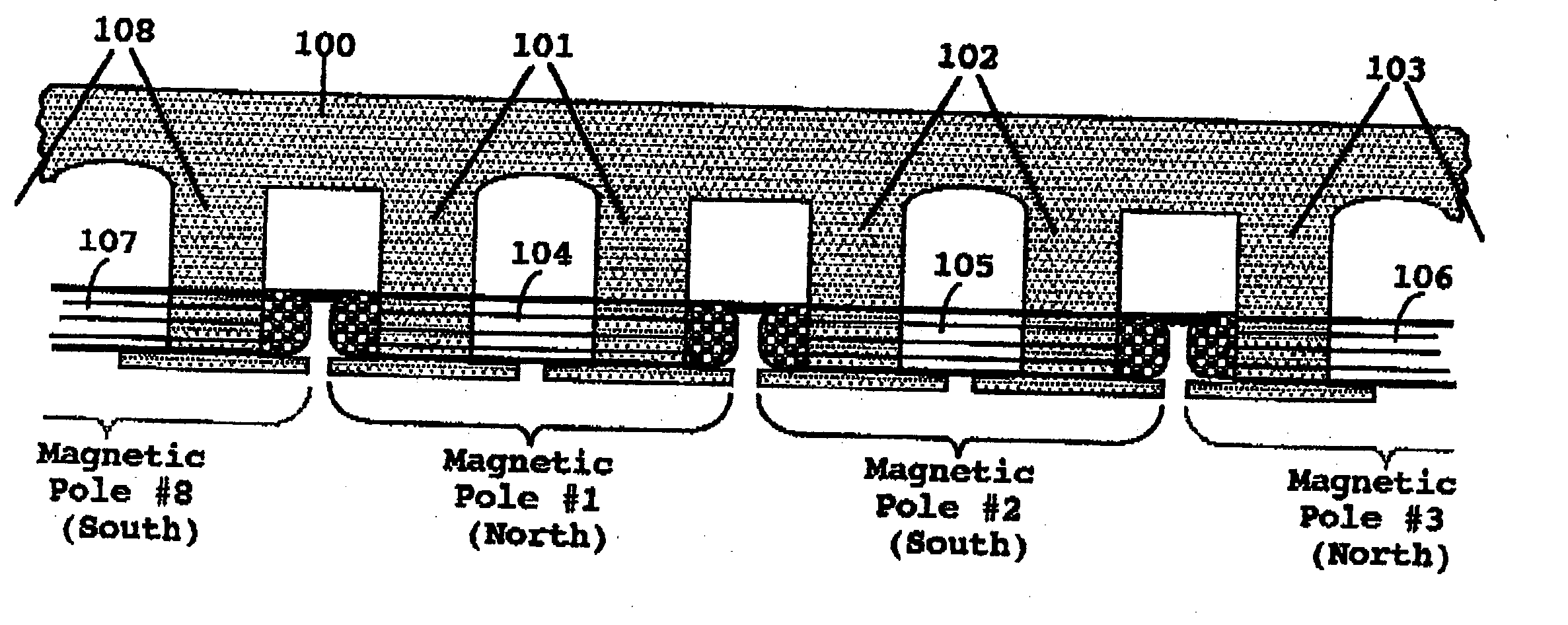
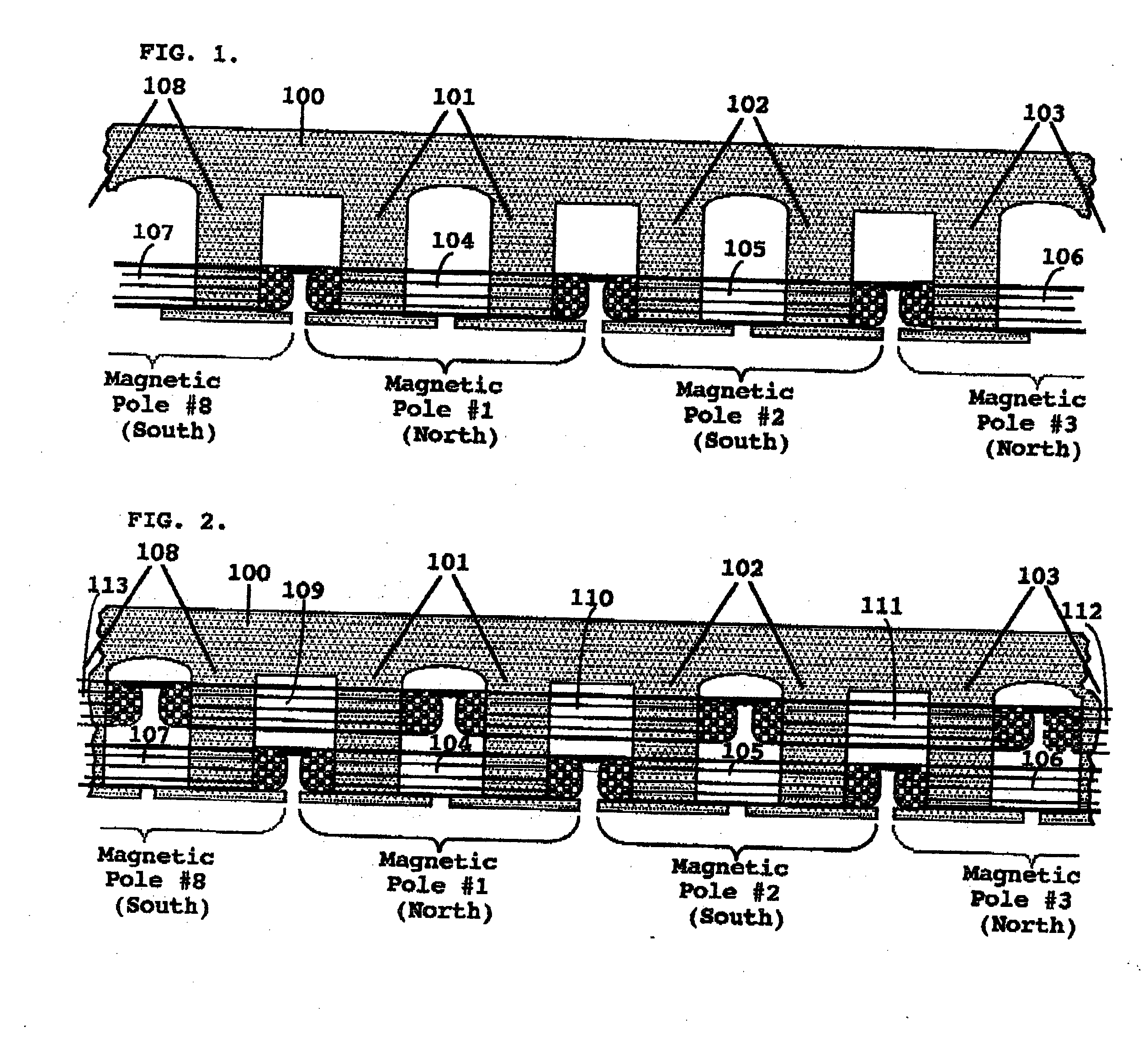
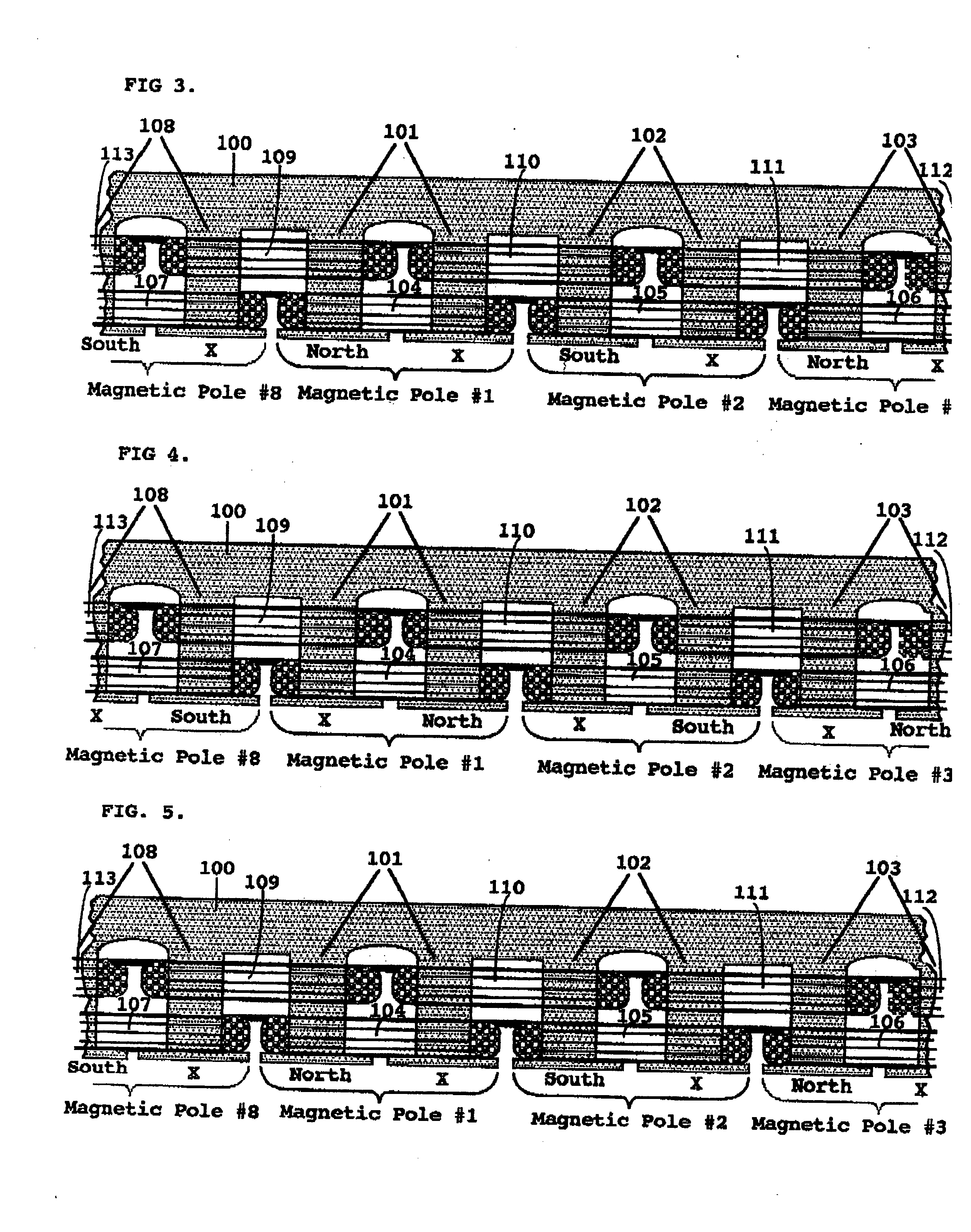
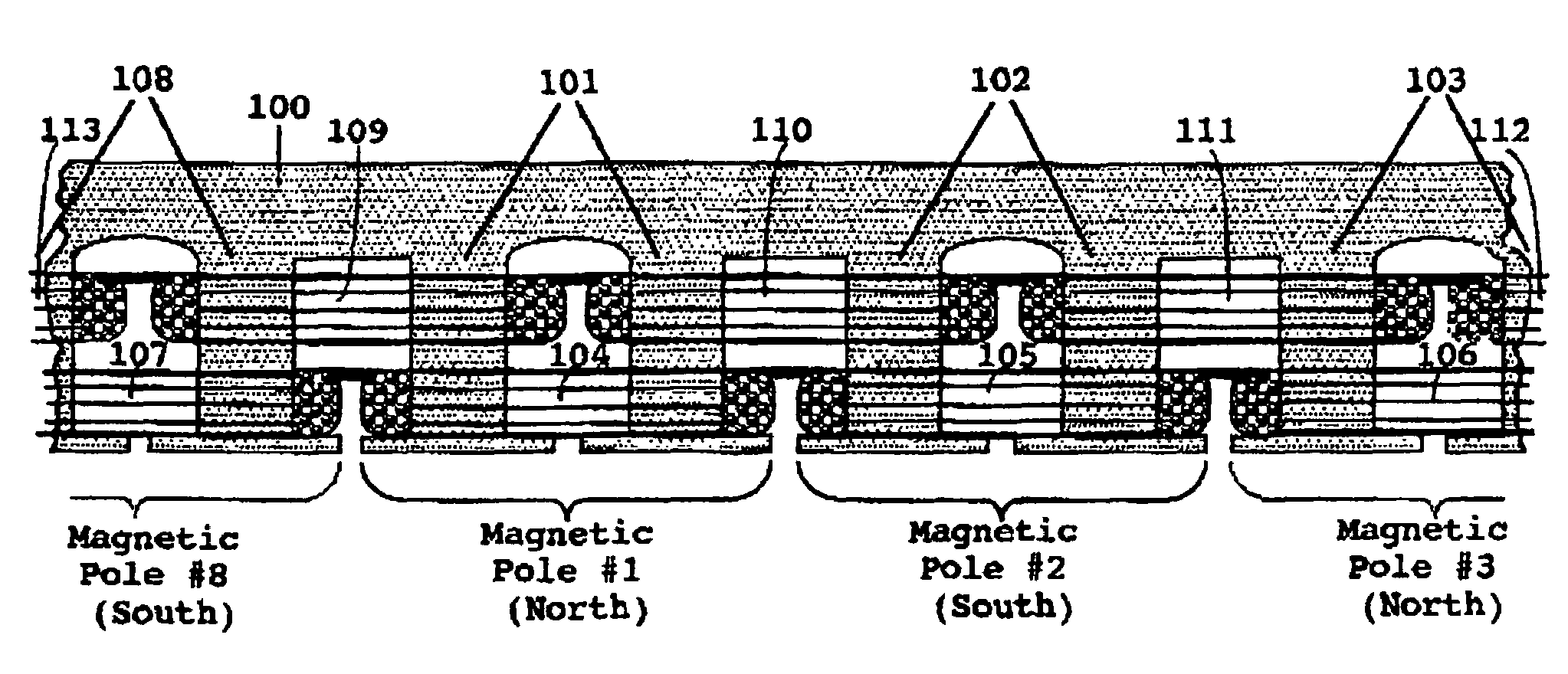
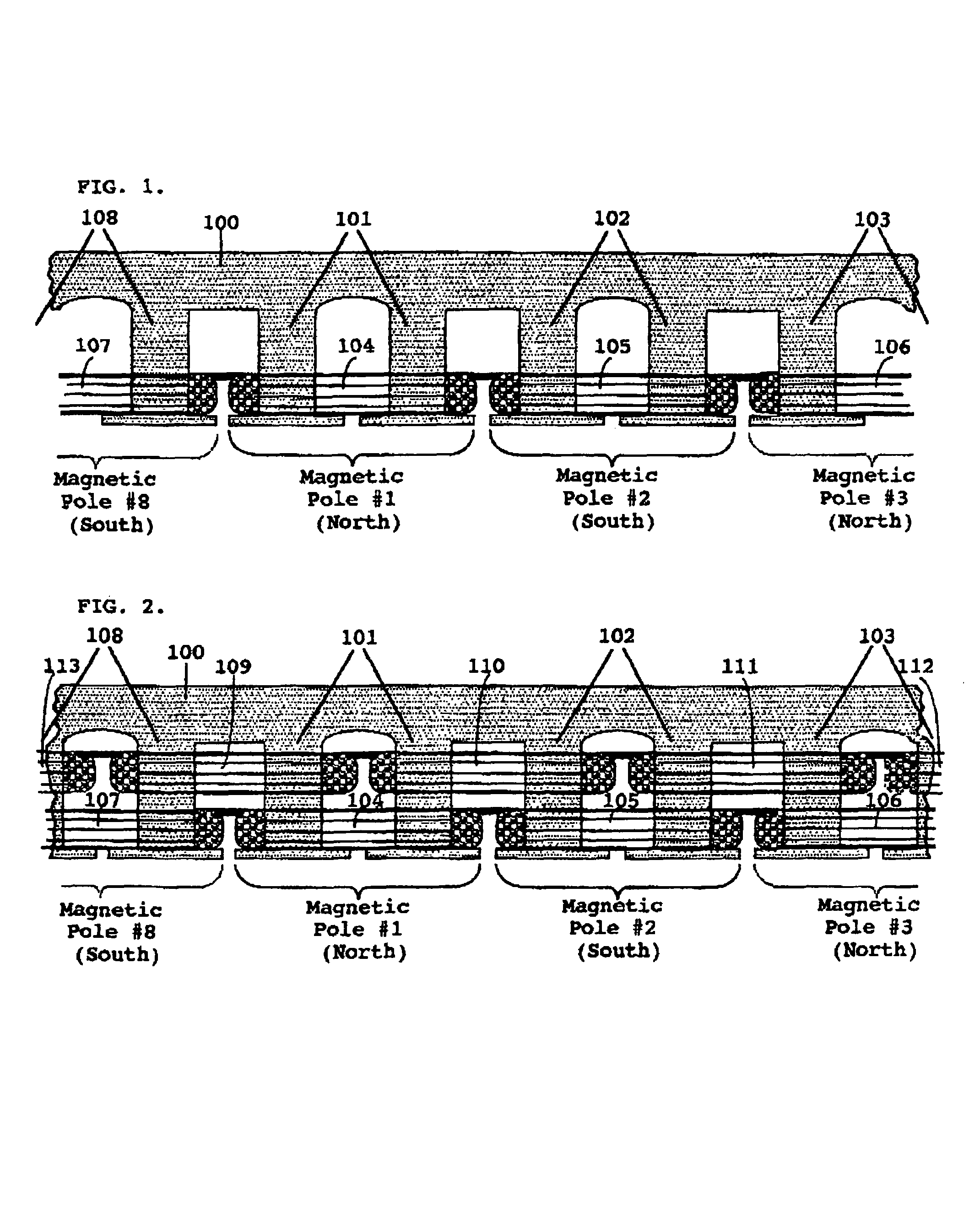
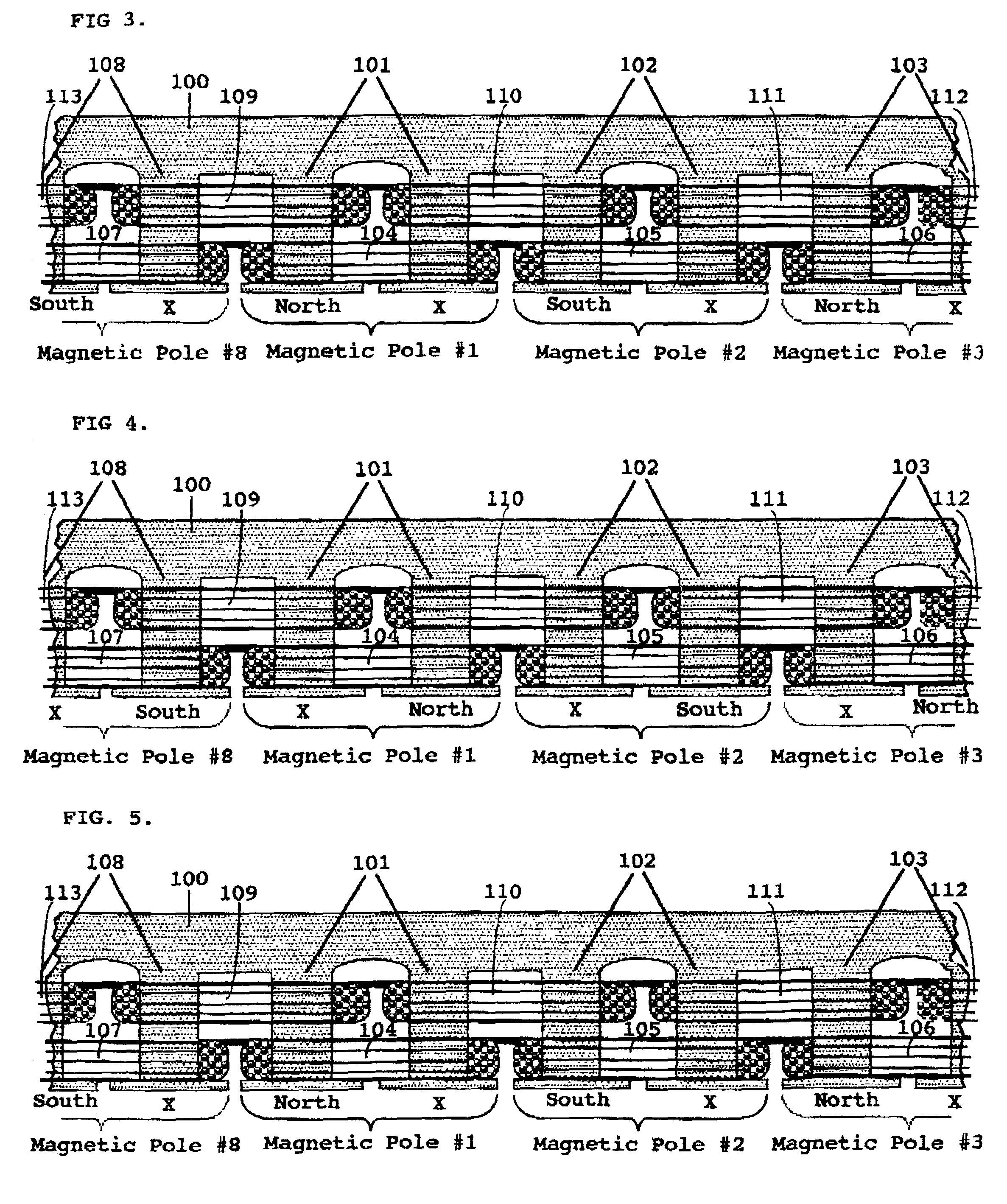
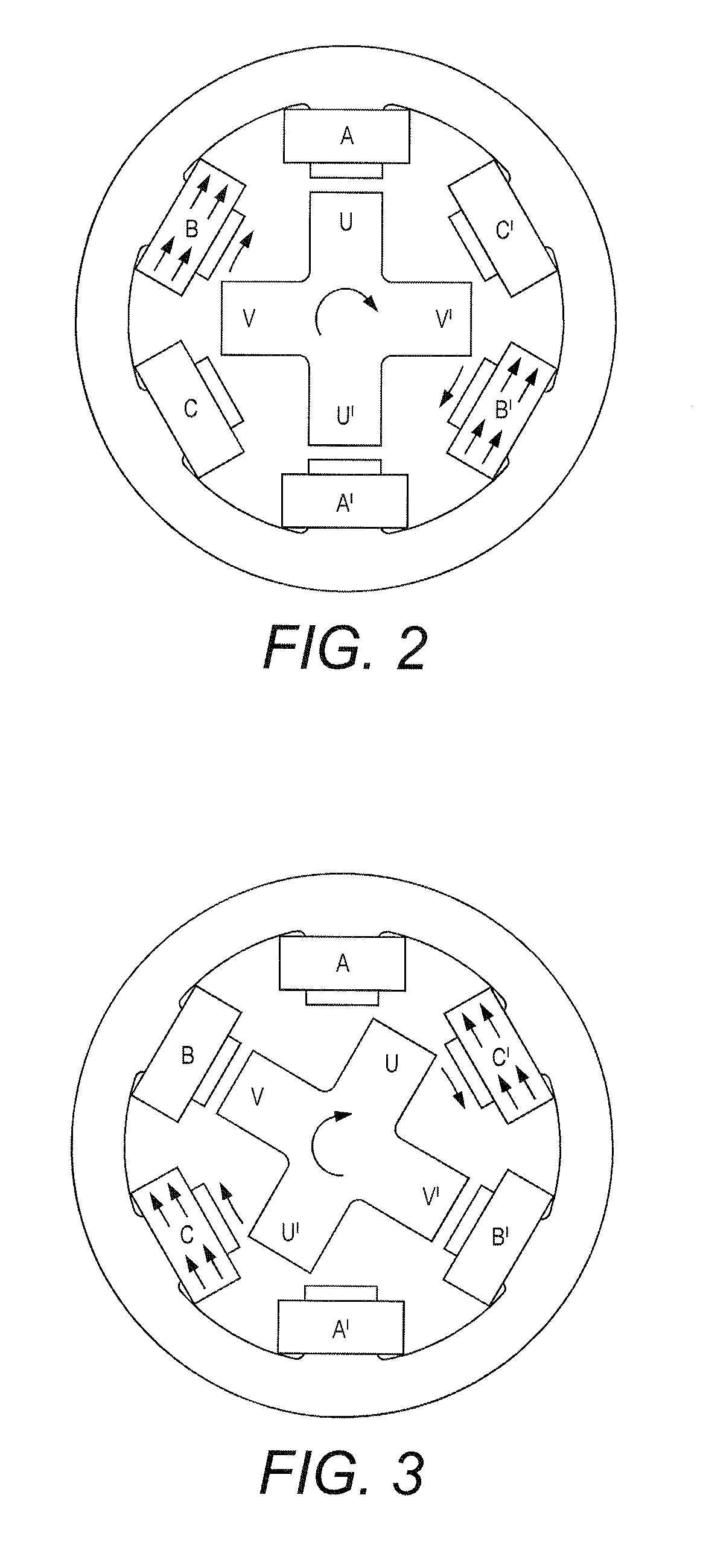
Starting system for salient-poled-rotor electric motor
InactiveUS7583000B2Torque between the rotor and the stator is substantially minimizedTorque between the rotor and the stator is substantially maximizedSynchronous generatorsWindingsMagnetic polesElectrical polarity
A starting system and method for starting a salient-poled-rotor electric motor having a stator with a plurality of spaced salient poles, a plurality of field coils of unchanging polarity, and a plurality of armature coils, wherein each field coil of the plurality of field coils at least partially overlaps an armature coil of the plurality of armature coils, and wherein variable excitement of the armature coils alternately creates a magnetic pole force in every other pole of the plurality of spaced salient poles of the stator. In such motors, the stator has a first position, wherein the rotor is in stasis with respect to the stator and torque between the rotor and the stator is substantially minimized, and a second position, wherein torque between the rotor and the stator is substantially maximized. A drive circuit provides current to the field coils and the armature coils. A start circuit is provided for regulating the drive circuit to vibrate the rotor to the second position. A current source is connectable to the drive circuit for variably exciting the armature coils to produce substantially continuous rotation of the rotor. A switch is provided for electrically engaging the start circuit with the drive circuit while the rotor moves from the first position to the second position, and for electrically engaging the current source with the drive circuit when the rotor reaches the second position.
Owner:TRI SEVEN RES
Starting system for salient-poled-rotor electric motor
InactiveUS20060273681A1Minimize torqueTorque between the rotor and the stator is substantially minimizedSynchronous generatorsWindingsMagnetic polesElectrical polarity
A starting system and method for starting a salient-poled-rotor electric motor having a stator with a plurality of spaced salient poles, a plurality of field coils of unchanging polarity, and a plurality of armature coils, wherein each field coil of the plurality of field coils at least partially overlaps an armature coil of the plurality of armature coils, and wherein variable excitement of the armature coils alternately creates a magnetic pole force in every other pole of the plurality of spaced salient poles of the stator. In such motors, the stator has a first position, wherein the rotor is in stasis with respect to the stator and torque between the rotor and the stator is substantially minimized, and a second position, wherein torque between the rotor and the stator is substantially maximized. A drive circuit provides current to the field coils and the armature coils. A start circuit is provided for regulating the drive circuit to vibrate the rotor to the second position. A current source is connectable to the drive circuit for variably exciting the armature coils to produce substantially continuous rotation of the rotor. A switch is provided for electrically engaging the start circuit with the drive circuit while the rotor moves from the first position to the second position, and for electrically engaging the current source with the drive circuit when the rotor reaches the second position.
Owner:TRI SEVEN RES
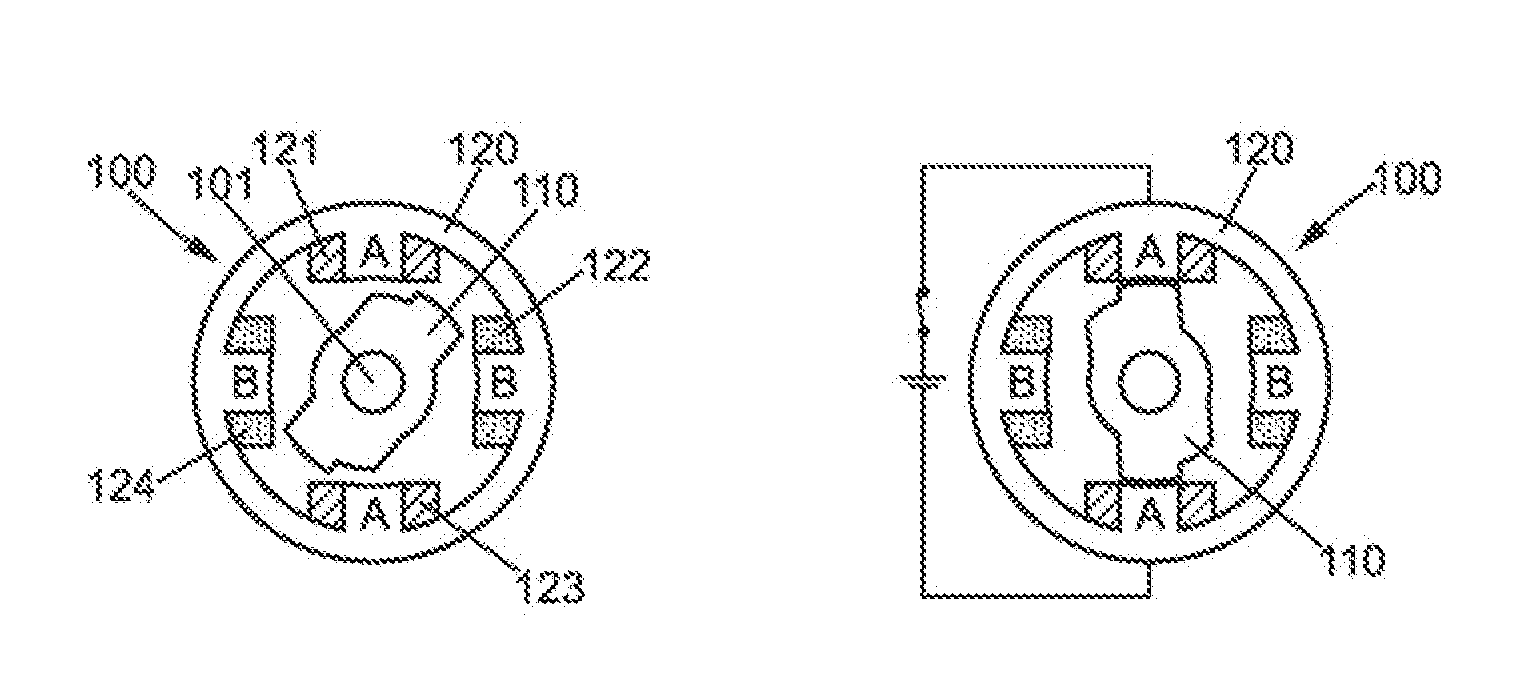
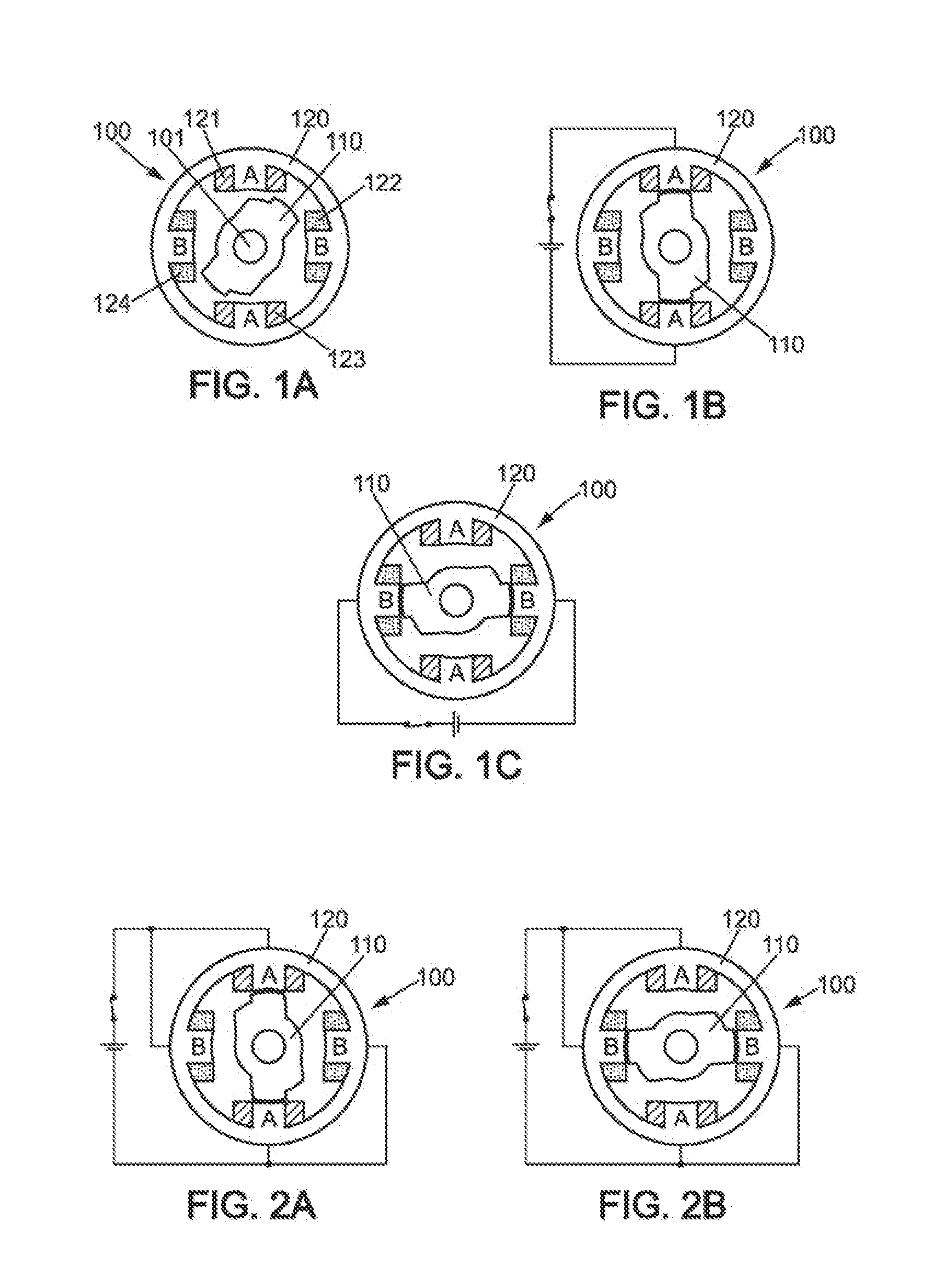
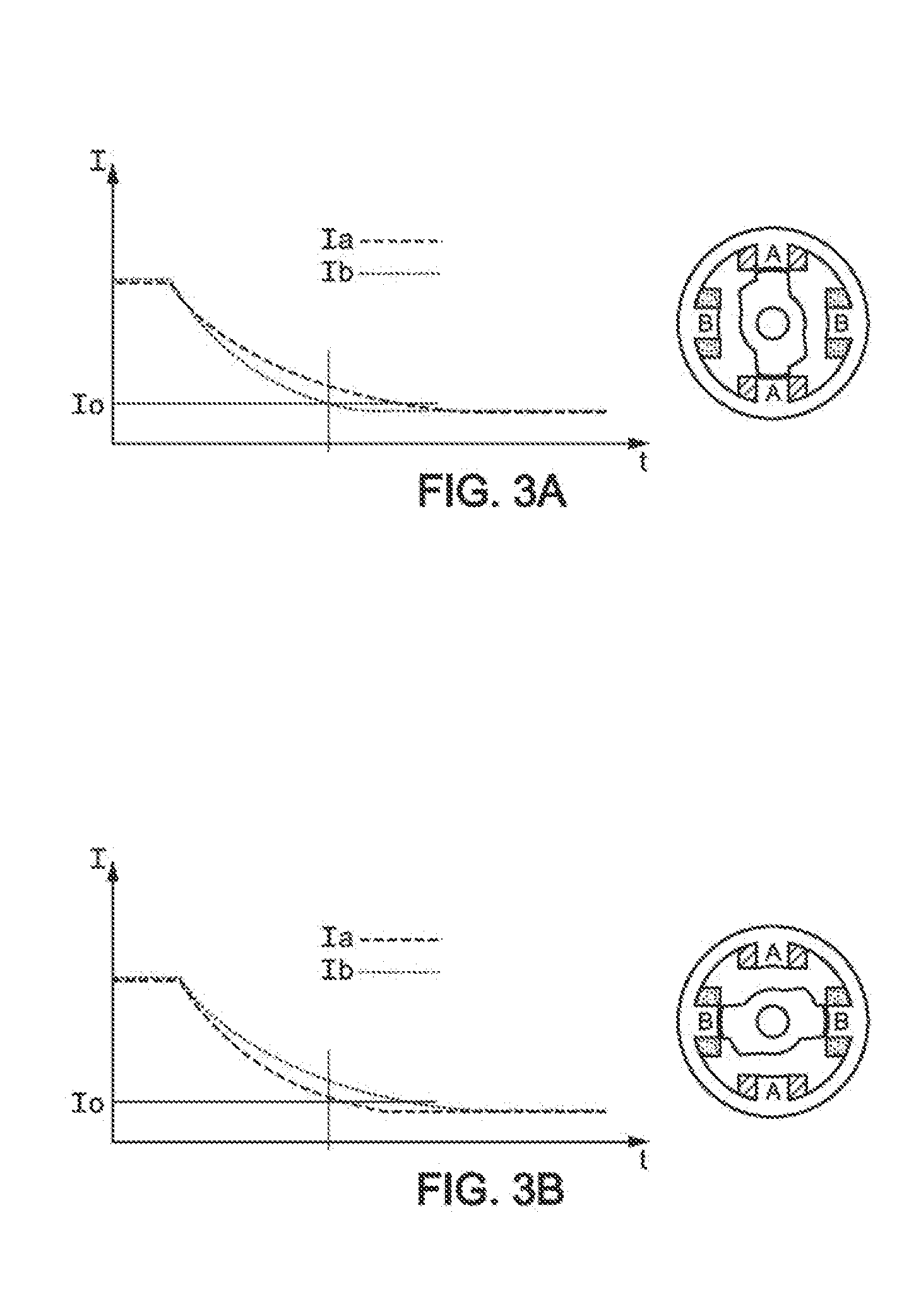
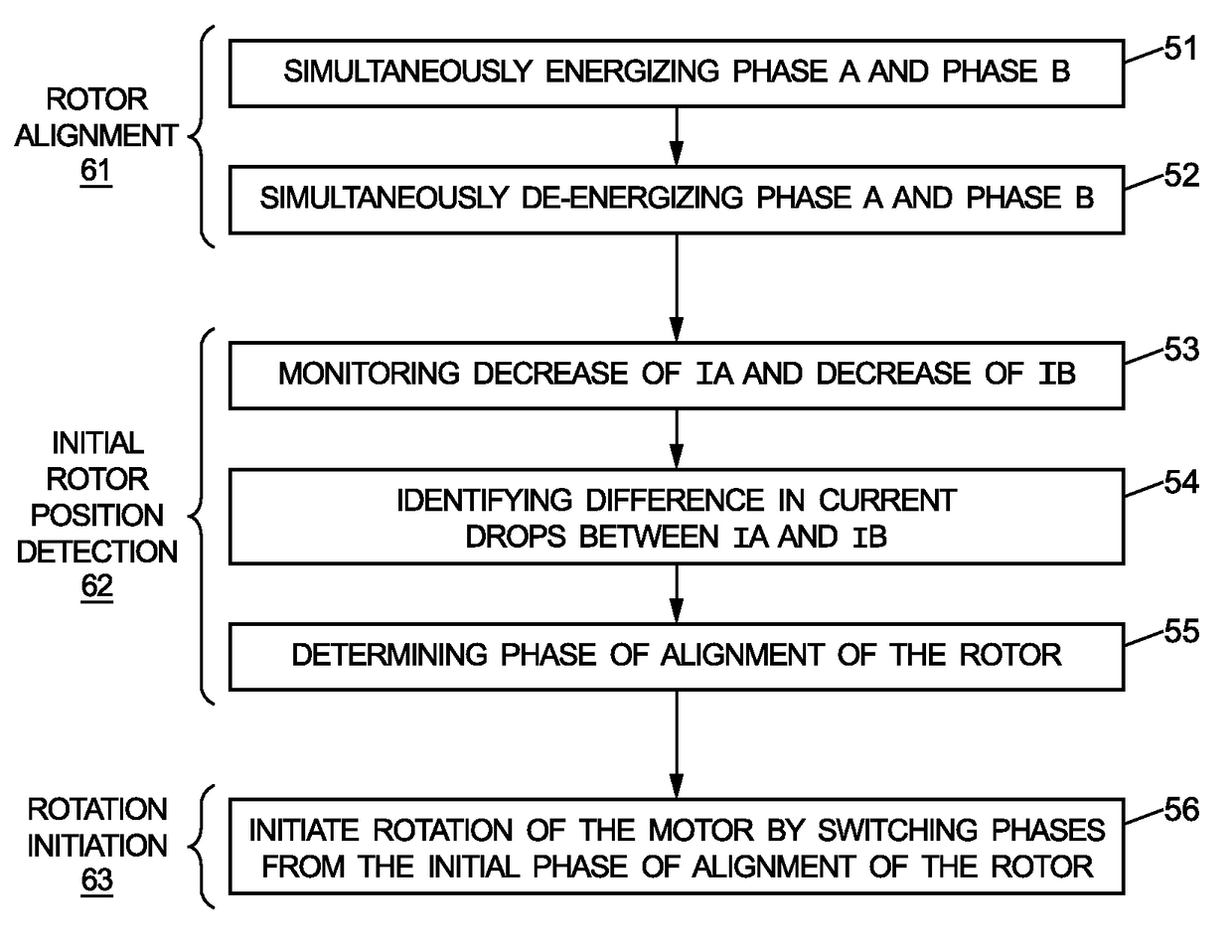
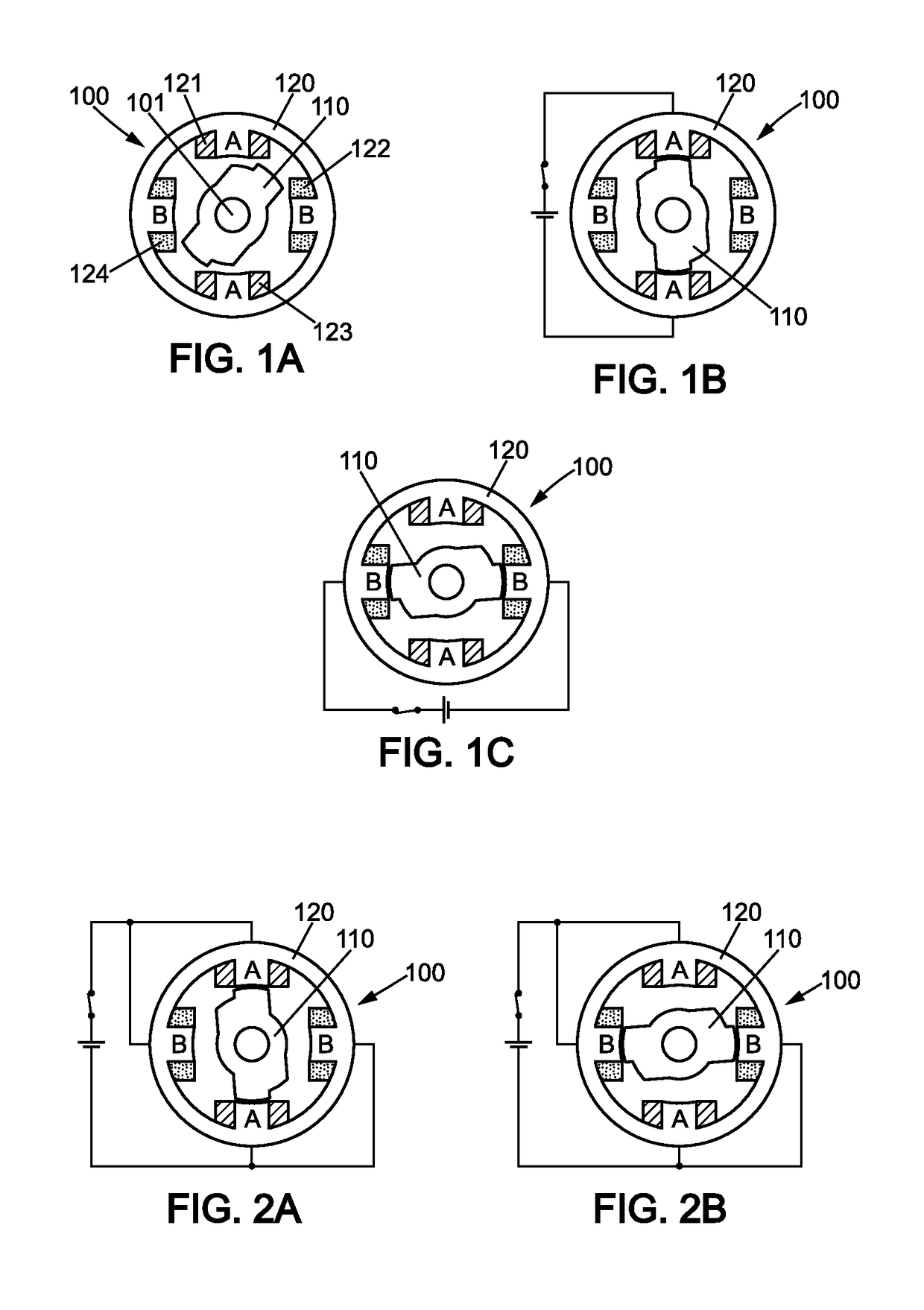
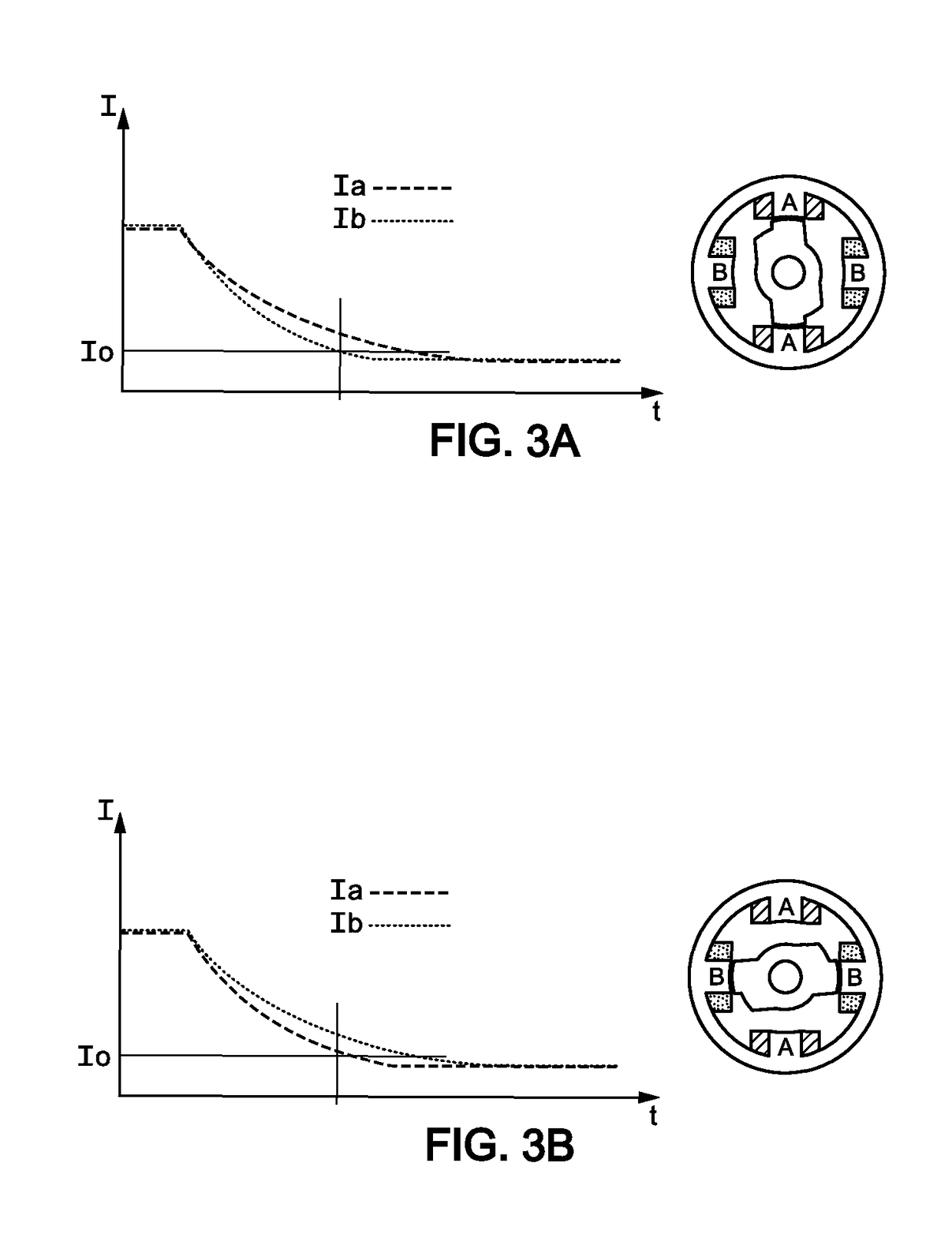
Method, computer program product and controller for starting-up a switched reluctance motor, and electrical apparatus implementing same
A method of starting-up a switched reluctance, SR, motor is provided. The method comprises simultaneously energizing a plurality of phases at a first time point with respective phase voltages that are substantially the same, until the motor rotor is stabilized in alignment with either one of the plurality of phases; simultaneously de-energizing the plurality of phases at a second time point that follows the first time point; monitoring a decrease of respective phase currents in the plurality of phases from a third time point that follows the second time point by a first predetermined time interval; determining a phase of alignment of the rotor using evaluation of the decrease of the phase currents following simultaneous de-energizing of the plurality of phases; and, initiating rotation of the rotor from the determined phase of alignment of the rotor.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Controller for ensuring start of operation of synchronous motor
InactiveUS20070296372A1Guaranteed smooth progressElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motorConductor Coil
A synchronous motor controller is provided which is designed to diagnose whether a failure is occurring or not in energizing one of phase windings of a synchronous motor which is required to be energized first to start the synchronous motor. When such a failure is found, the controller reverses the synchronous motor slightly to bring one of the phase windings which is possible to energize properly to a starting position where the energization of the phase windings is to be initiated to start the synchronous motor in a required direction, thereby ensuring the stability in starting the synchronous motor even if any of the phase windings is failing to be energized.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
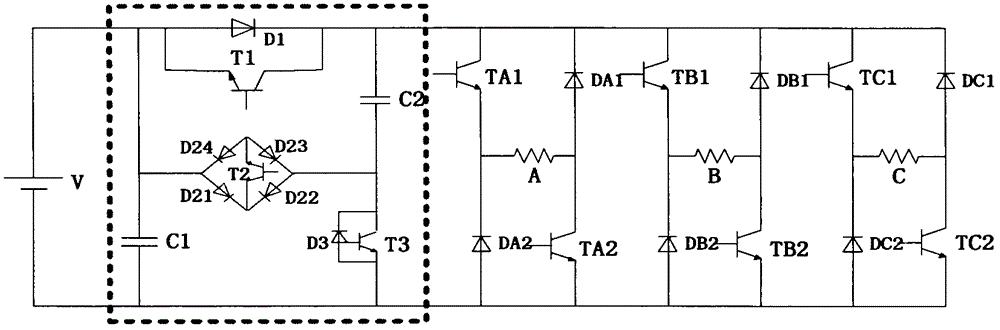
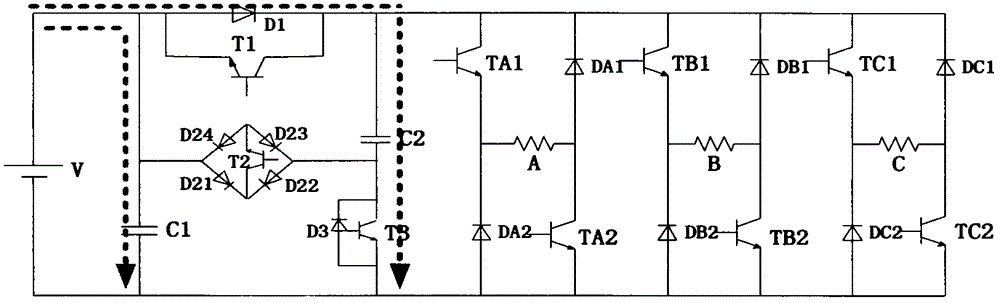
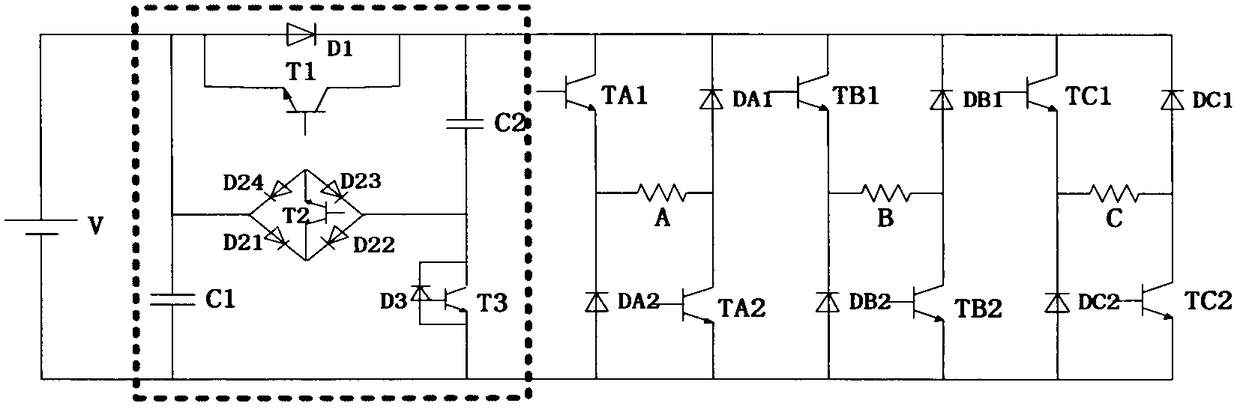
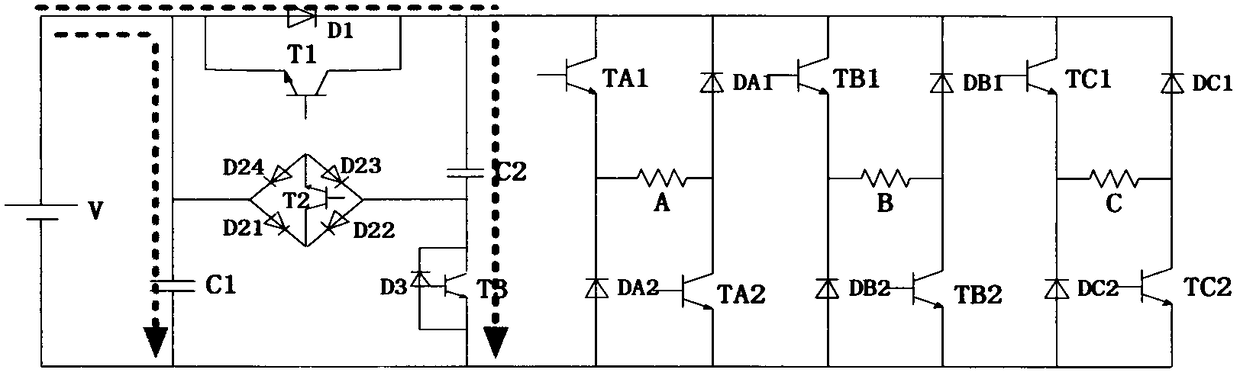
Multi-level power topology structure of switch reluctance motor
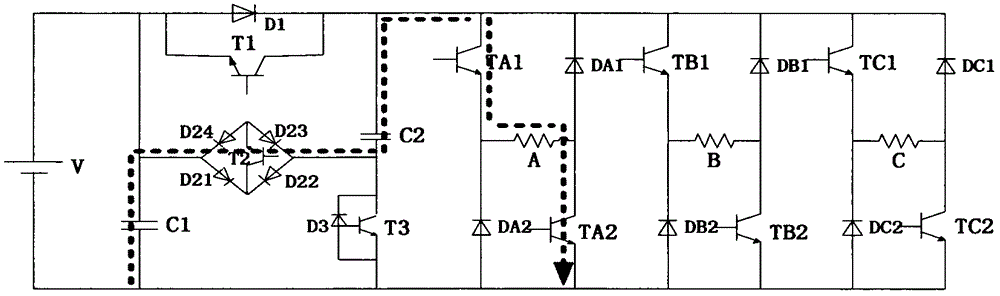
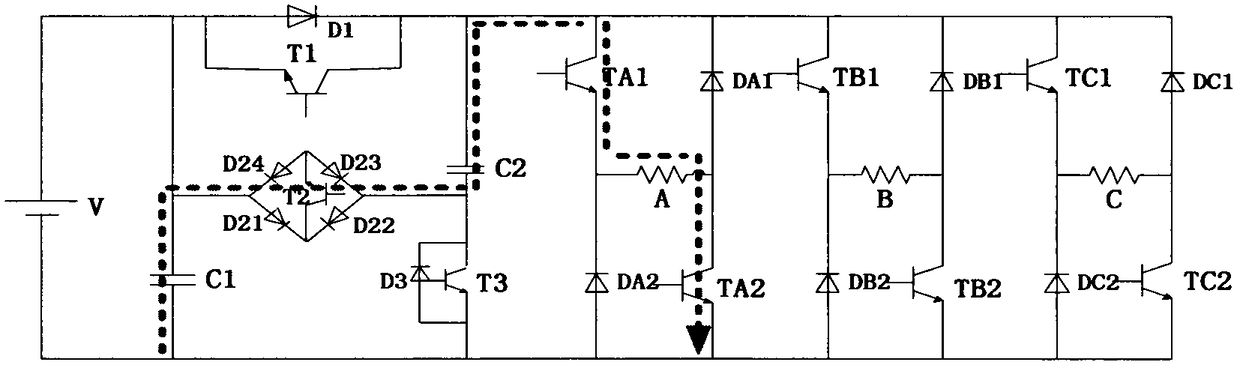
ActiveCN105743375AStart fastSolve the excitation current riseAc-dc conversionEnergy industryPower topologyExcitation current
The invention discloses a multi-level power topology structure of a switch reluctance motor. A boost circuit part is additionally arranged between a traditional asymmetric power conversion circuit and a DC power supply and comprises a capacitor C1, a boost capacitor C2, a switching tube T1 and a diode D1, a switching tube T3, a diode D3 and a bidirectional switch, wherein the switching tube T1 and the diode D1are reversely connected in parallel, the switching tube T3 and the diode D3 are reversely connected in parallel, and the bidirectional switch comprises a switching tube T2 and diodes D21, D22, D23 and D24. By controlling the switch-on and the switch-off of the switching tubes in the power topology, the switch reluctance motor can run by switching among five states of rapid excitation (+2), rapid demagnetization (-2), normal excitation (+1), normal demagnetization (-1) and follow current (0). The rapid excitation and the rapid demagnetization of the switch reluctance motor are achieved, the problems of slow excitation current rise and reduction, low system efficiency, low dynamic performance and the like during motor running are solved, and the multi-level power topology structure has high robustness, high reliability and intelligence and has huge application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
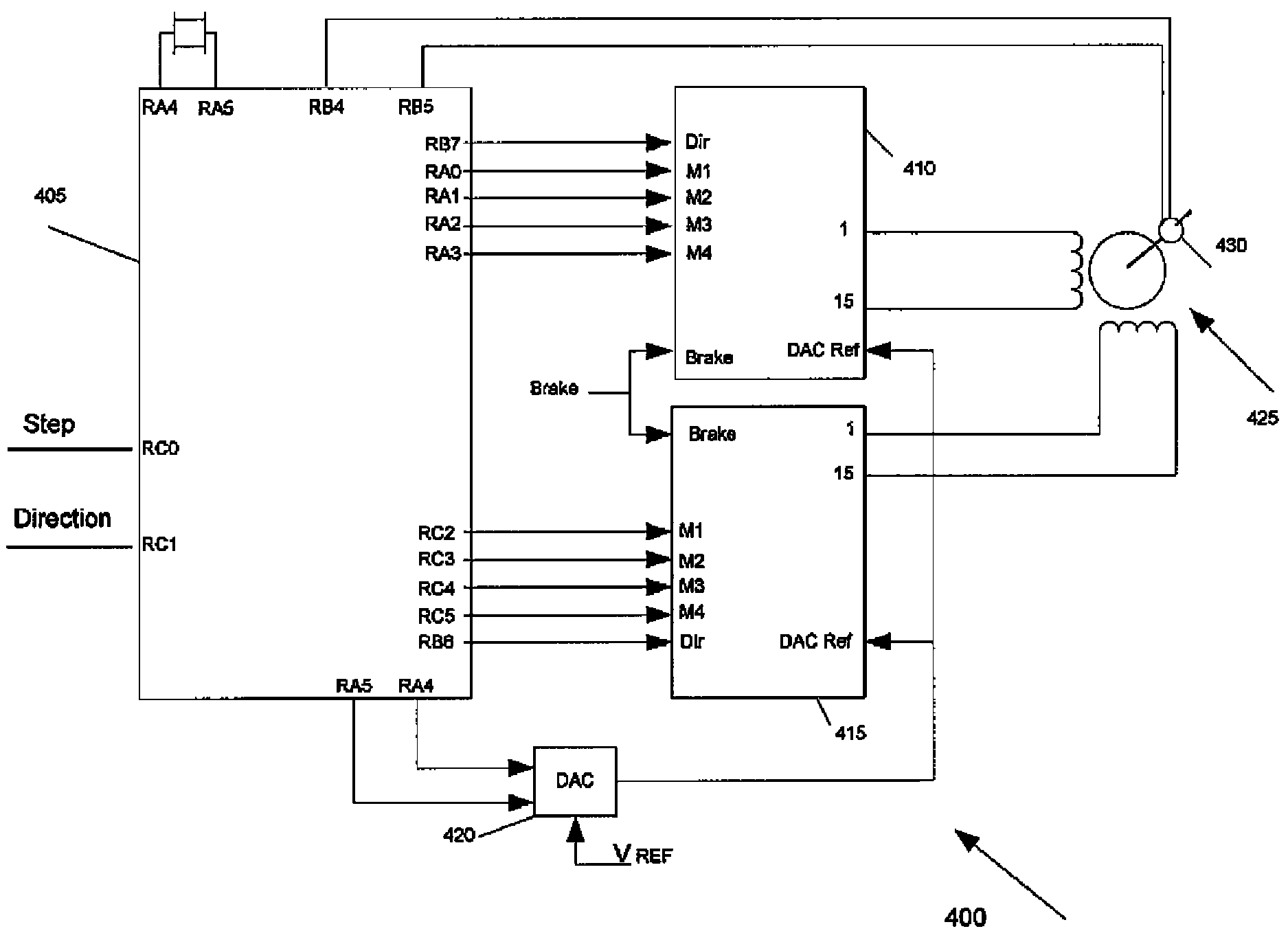
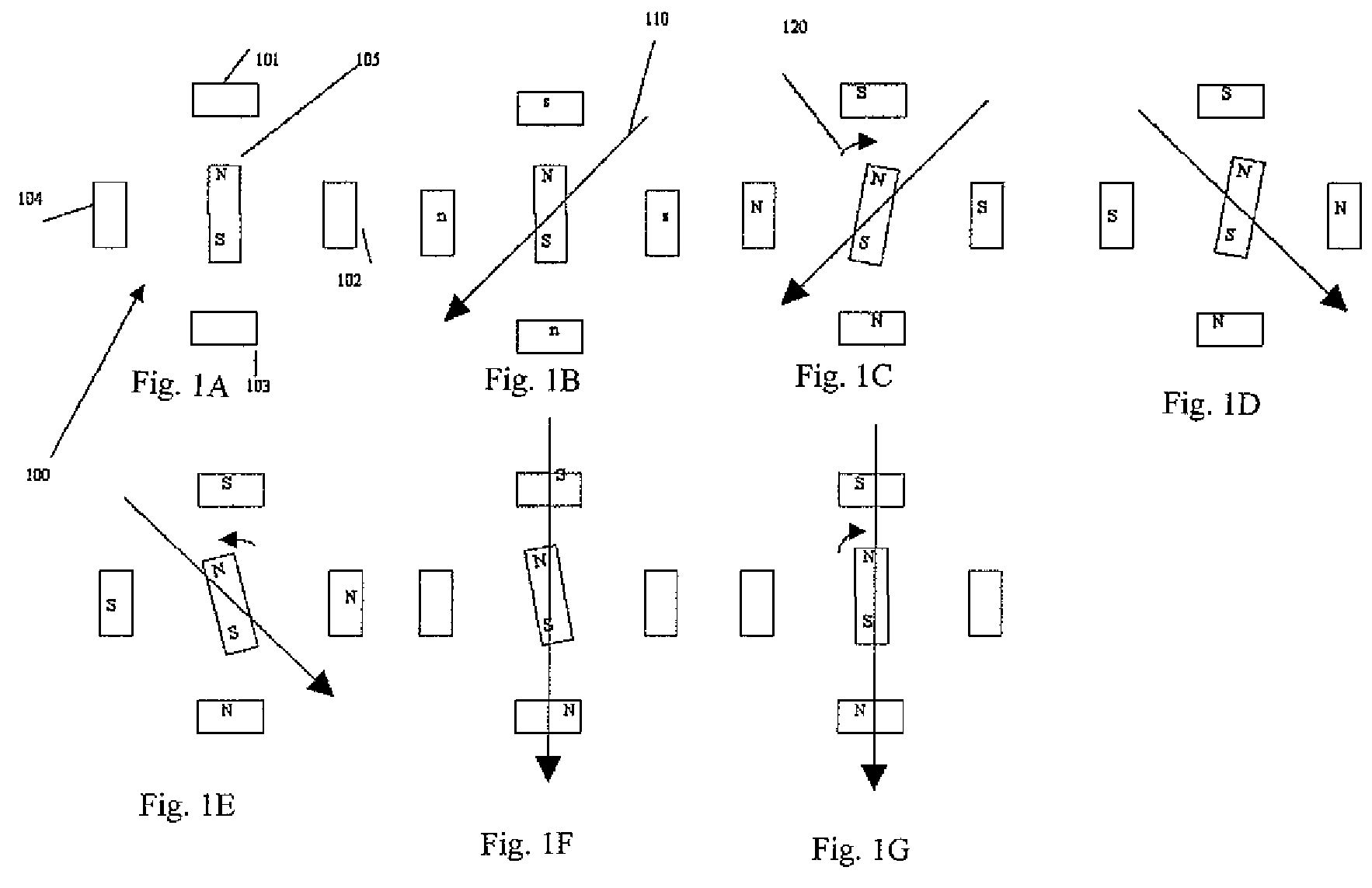
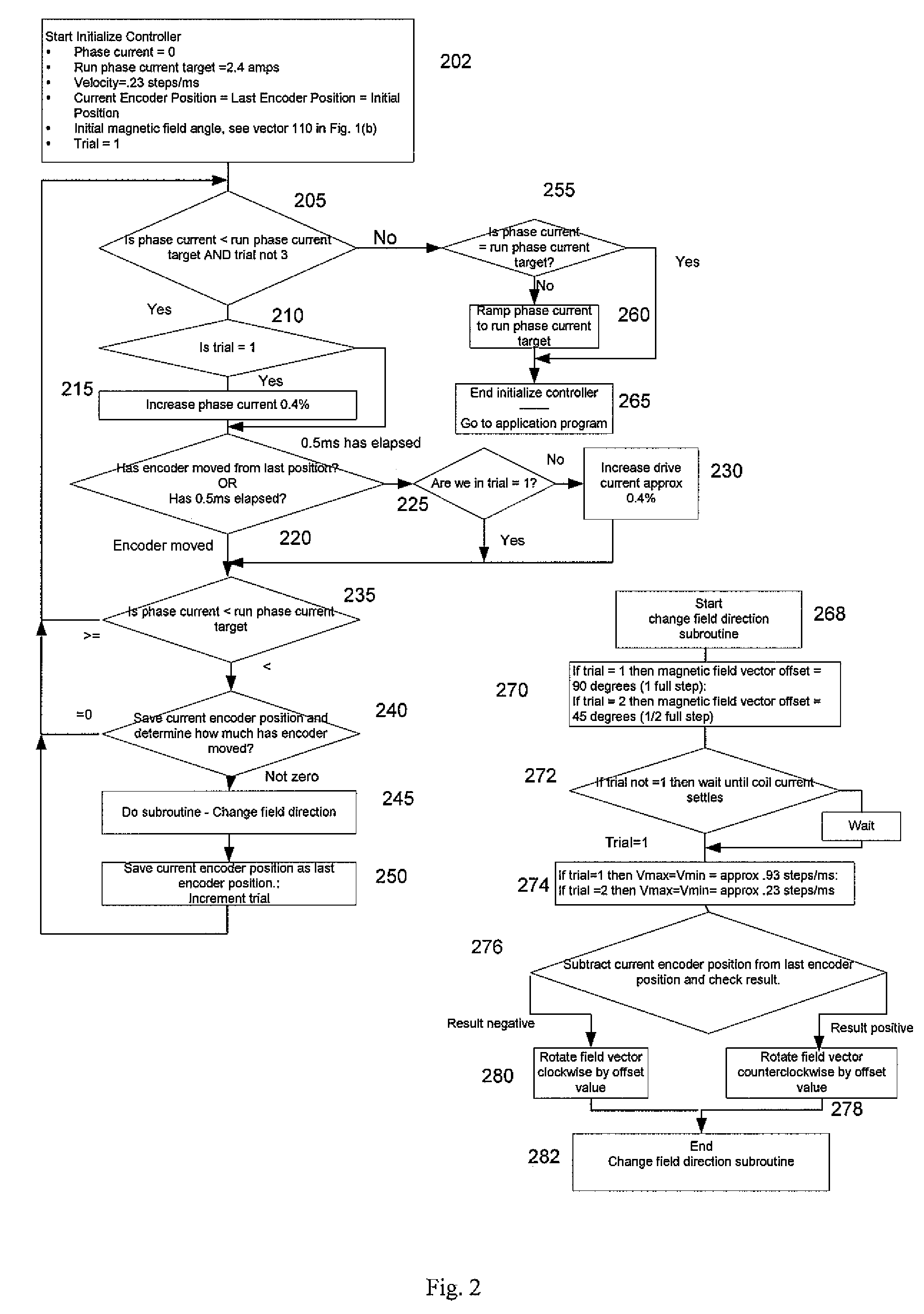
Apparatus and Method for Minimizing Undesirable Stepper Motor Rotor Motions
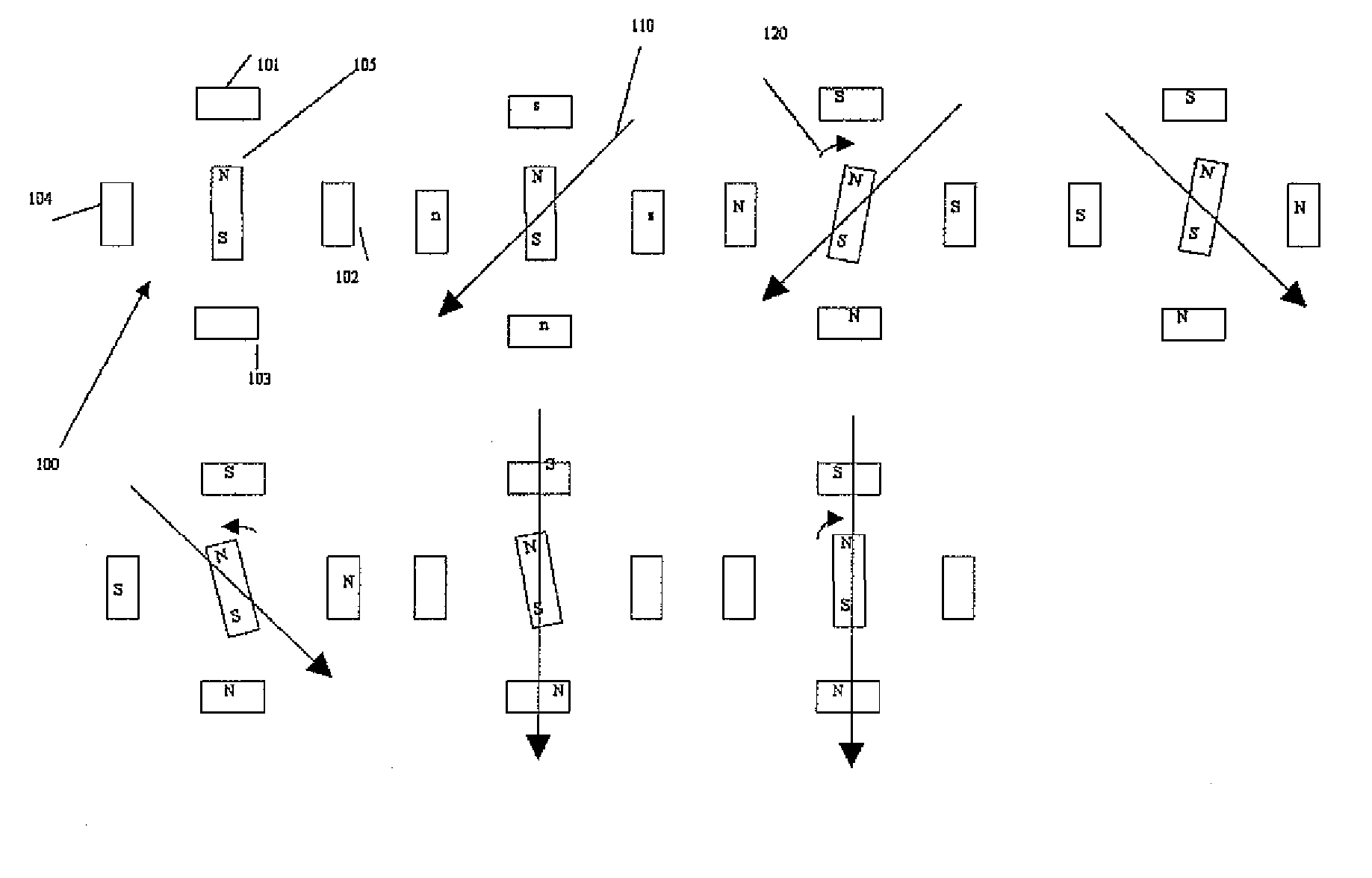
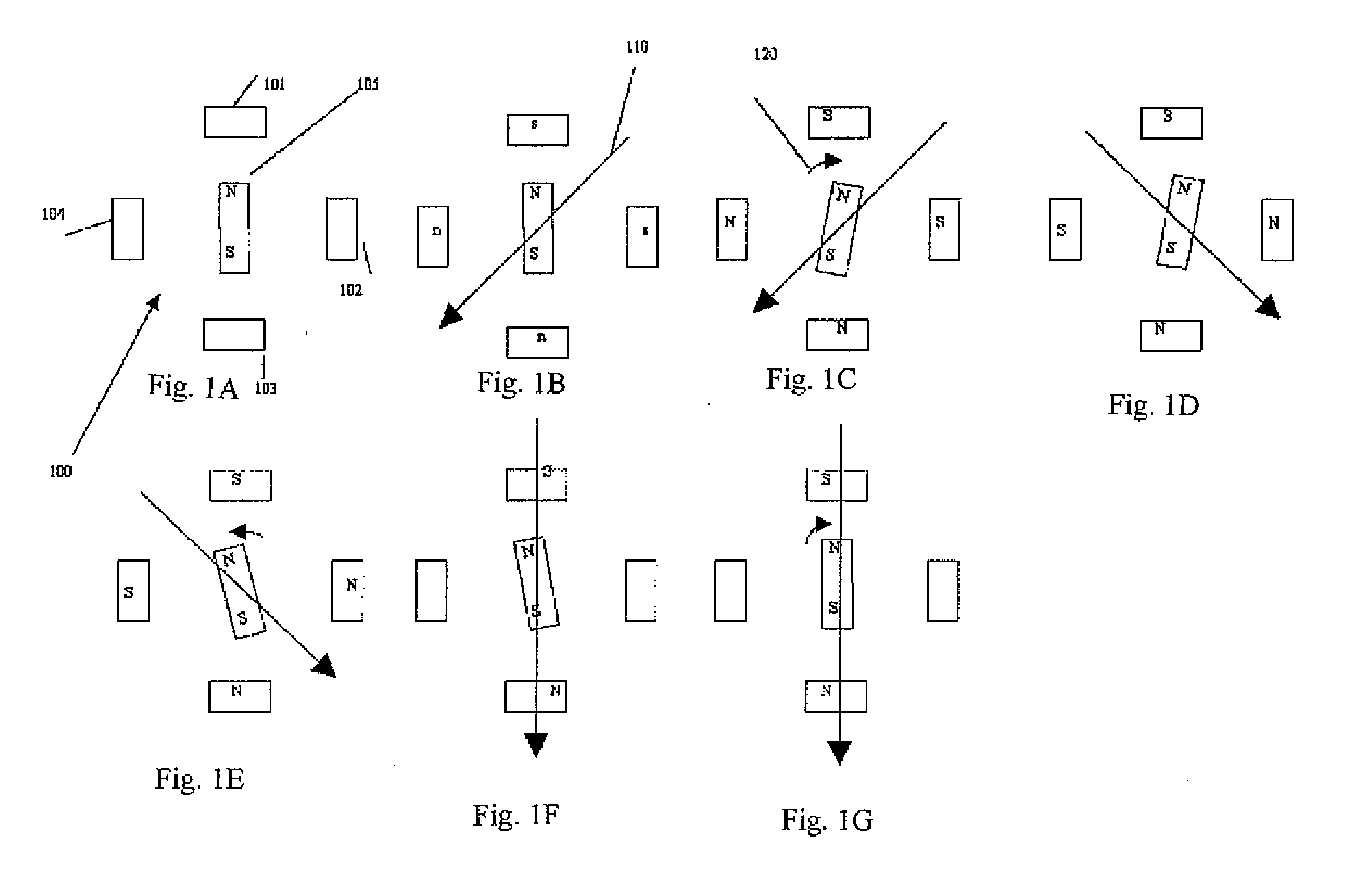
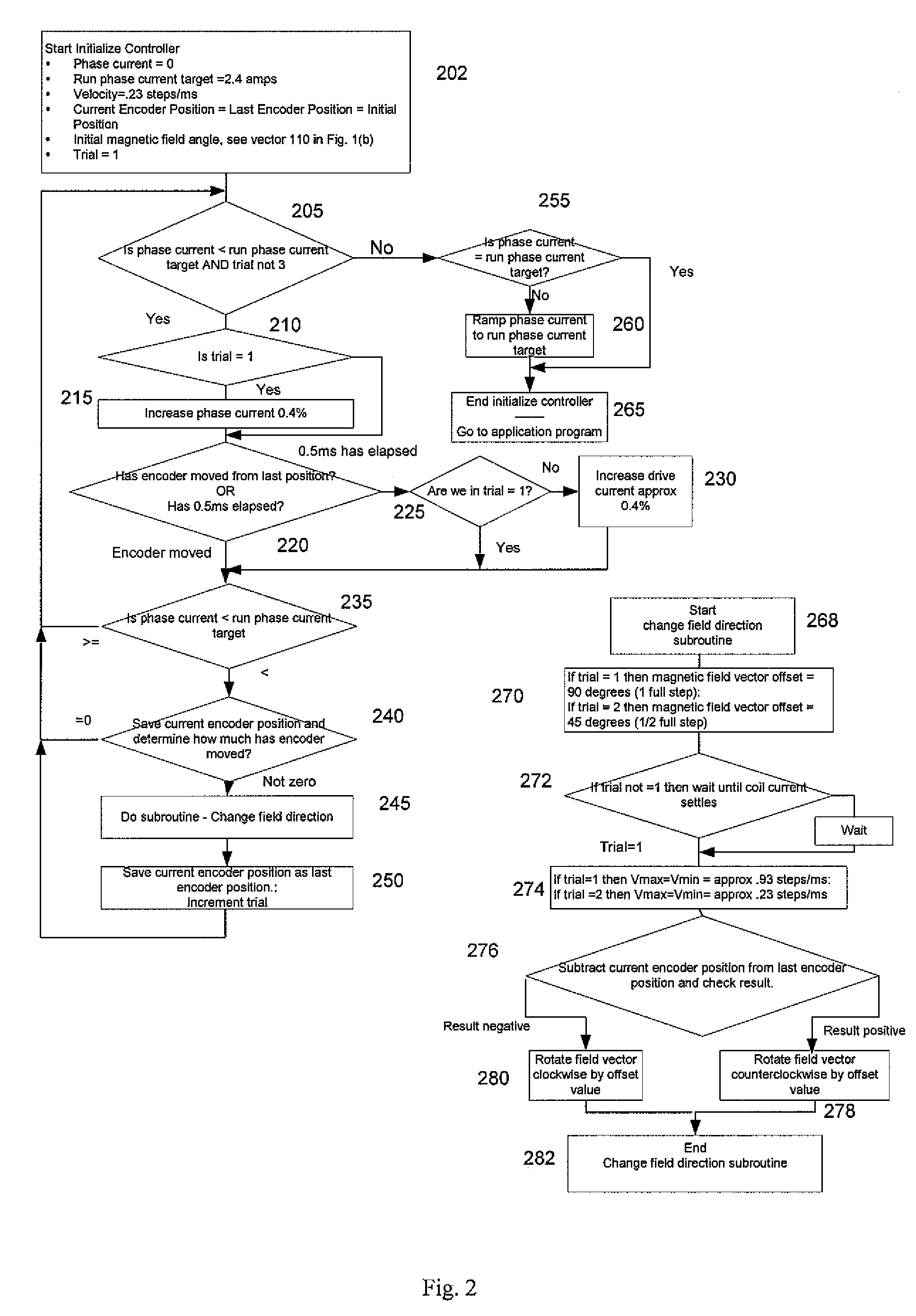
ActiveUS20100079102A1Reducing undesired motionReduce relative motionComputer controlSimulator controlMicrocontrollerElectric machine
An apparatus for reducing undesired motions during initialization of a stepper motor having a rotor and windings, the apparatus comprising a rotary encoder for sensing direction of rotor rotation; a microcontroller responsive to signals from the rotary encoder for generating bidirectional motor control waveforms having variable digital amplitude values; at least one motor driver for receiving the motor control waveforms and translating the waveforms to drive the motor windings; and wherein the translated waveforms urge the rotor in a first direction and then a second direction to locate a desired rotor position. A method of reducing undesired motions during initialization of a stepper motor having a rotary encoder coupled thereto comprises applying currents to the phase windings to form a magnetic field vector in a direction; sensing a direction of rotor rotation; changing at least one motor phase current to rotate the magnetic field vector in a direction opposite to the direction of first sensed rotor rotation by a first electrical angle; sensing a direction of rotor rotation; changing at least one motor phase current to rotate the magnetic field vector to a next position in a direction opposite to the second sensed rotor rotation by a second electrical angle; and ending initialization, whereby the rotor is aligned with the magnetic field vector in its next position.
Owner:NOVANTA CORP
Split-pole field-match motor
InactiveUS7276831B1Unnecessary useCost widerSynchronous generatorsWindingsMagnetic polesAlternating current
An electric motor having a plurality of rotor and stator poles, the poles of one element being alternately polarized and neutralized due to the use of direct current and alternating current windings on each pole. The poles of like current are connected in series, and the direct current poles are energized in synchronization with the alternating current poles.
Owner:TRI SEVEN RES
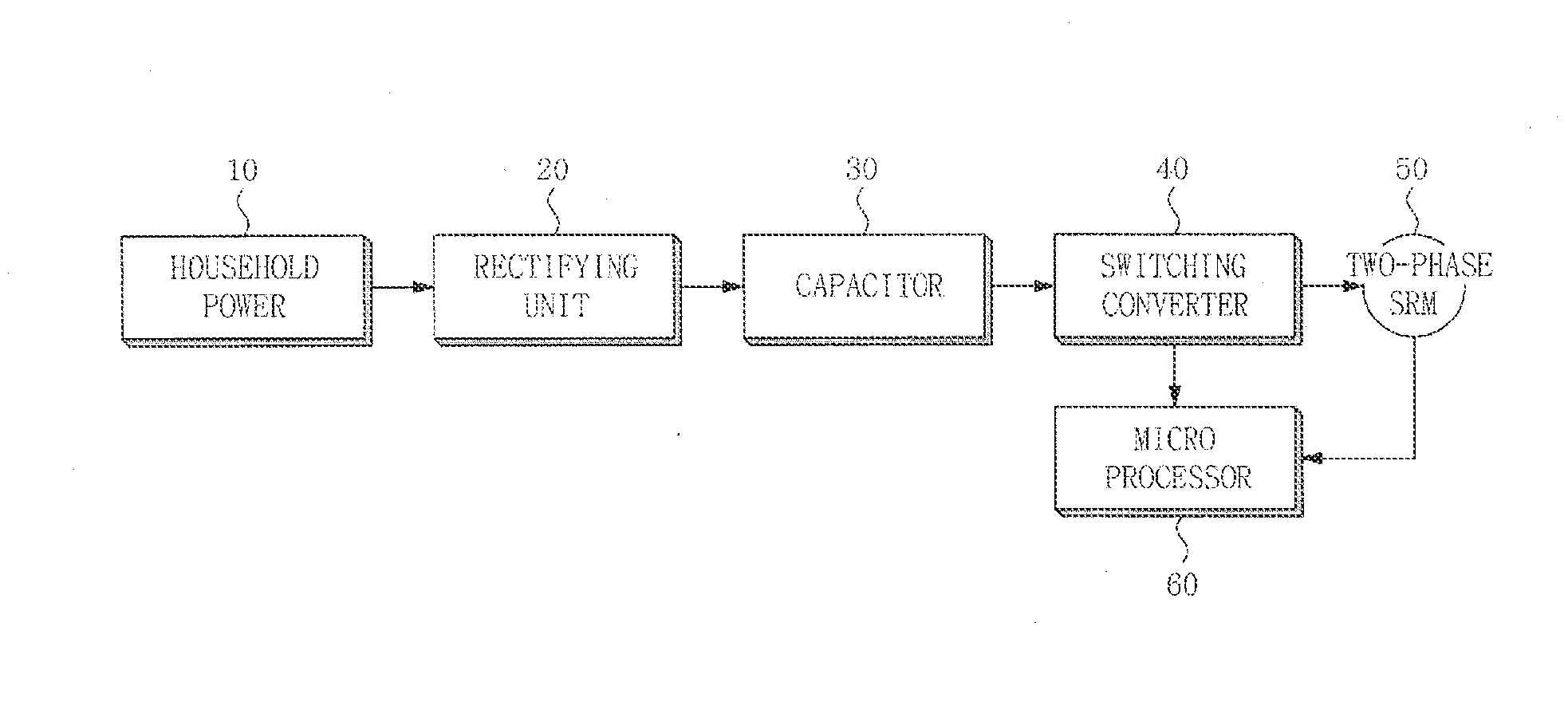
Motor acceleration apparatus and method
InactiveUS20150102751A1Avoid disturbanceDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlAlternating currentControl theory
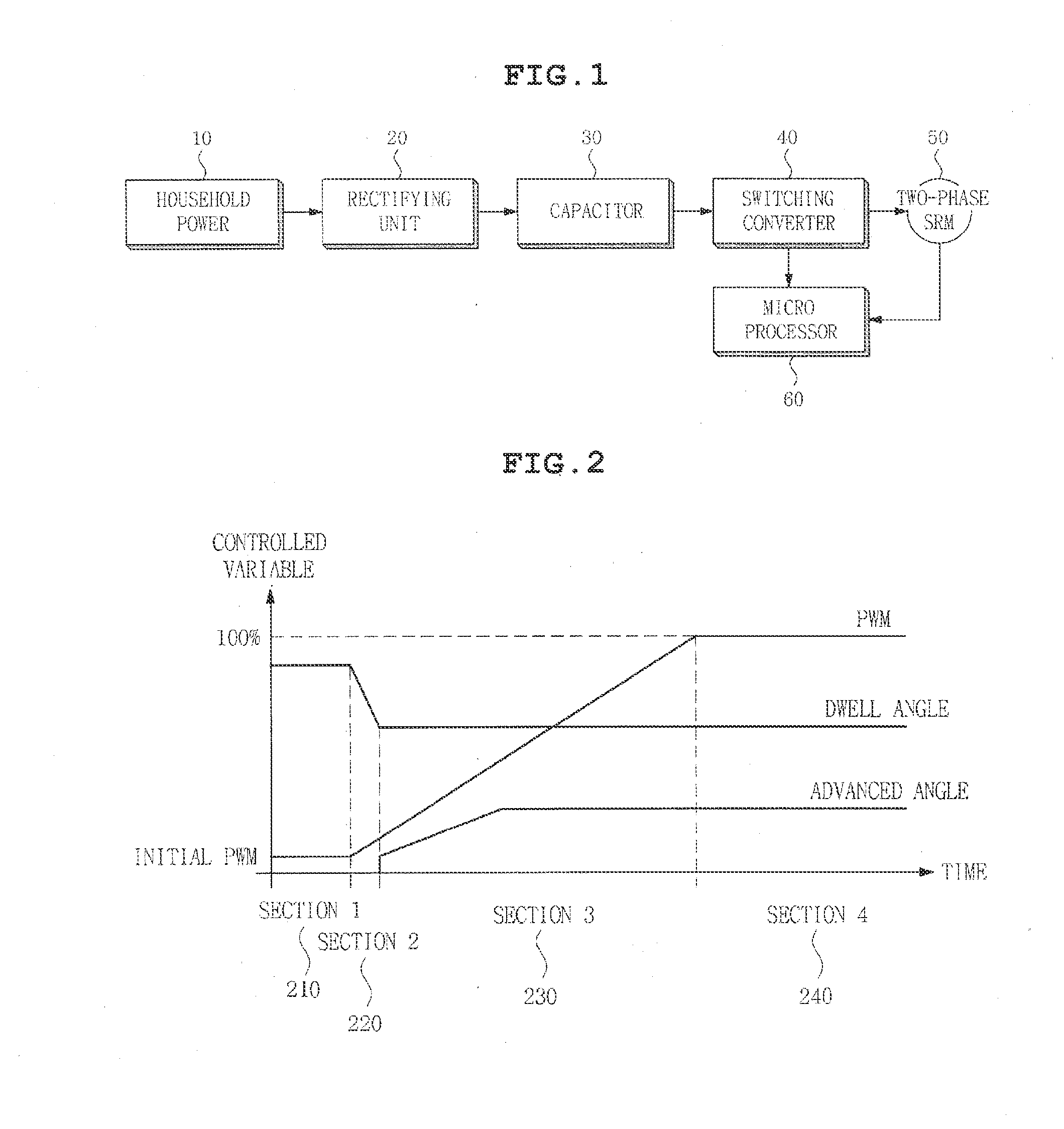
Embodiments of the invention provide a motor acceleration apparatus and a motor acceleration method. According to at least one embodiment, the motor acceleration apparatus includes a rectifier converting household power into direct current (DC) voltage to output the converted DC voltage, a switching converter switching the DC voltage output from the rectifier in an alternating current manner to drive a two-phase switched reluctance motor (SRM), and a microprocessor controlling the switching converter at the time of initial acceleration of the two-phase SRM, so that an initially set dwell angle is changed to a dwell angle in a normal operation state and starting an advanced-angle control.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Motor acceleration methods
InactiveUS20160336890A1Improve scalabilitySimple methodElectric devicesElectric machinesIntermediate stageImproved method
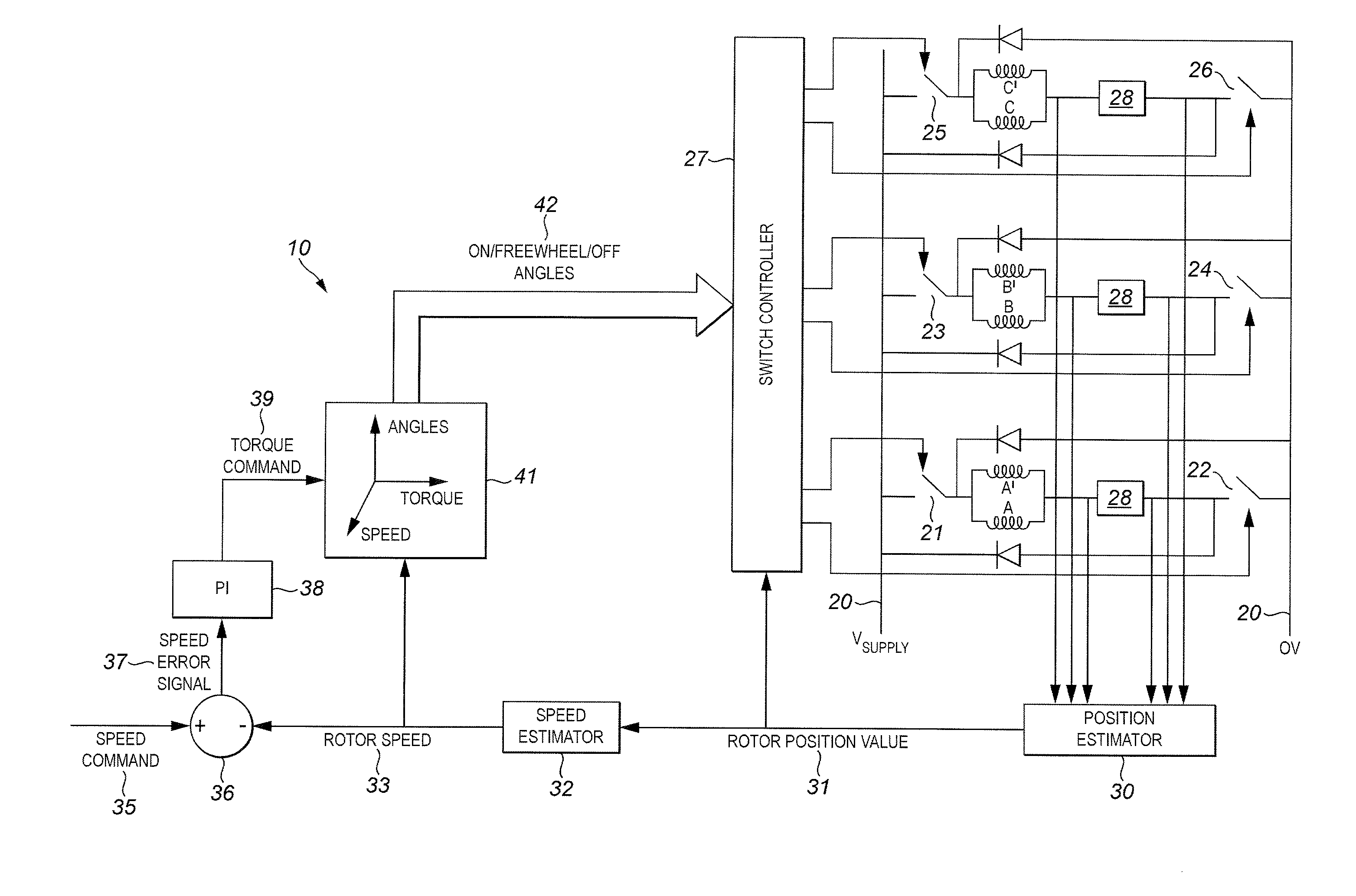
An improved method of starting a switched reluctance motor uses two neighbouring pairs of coils, both energised, to bring the rotor to its initial position. Then one of pairs of coils is turned off and the rotor is attracted by the other pair of coils to give it an initial rotational speed. An intermediate stage uses just one pair of coils of the motor to bring it up to operational speeds, after which the normal cycling of all the coils can be used.
Owner:VALEO AIR MANAGEMENT UK
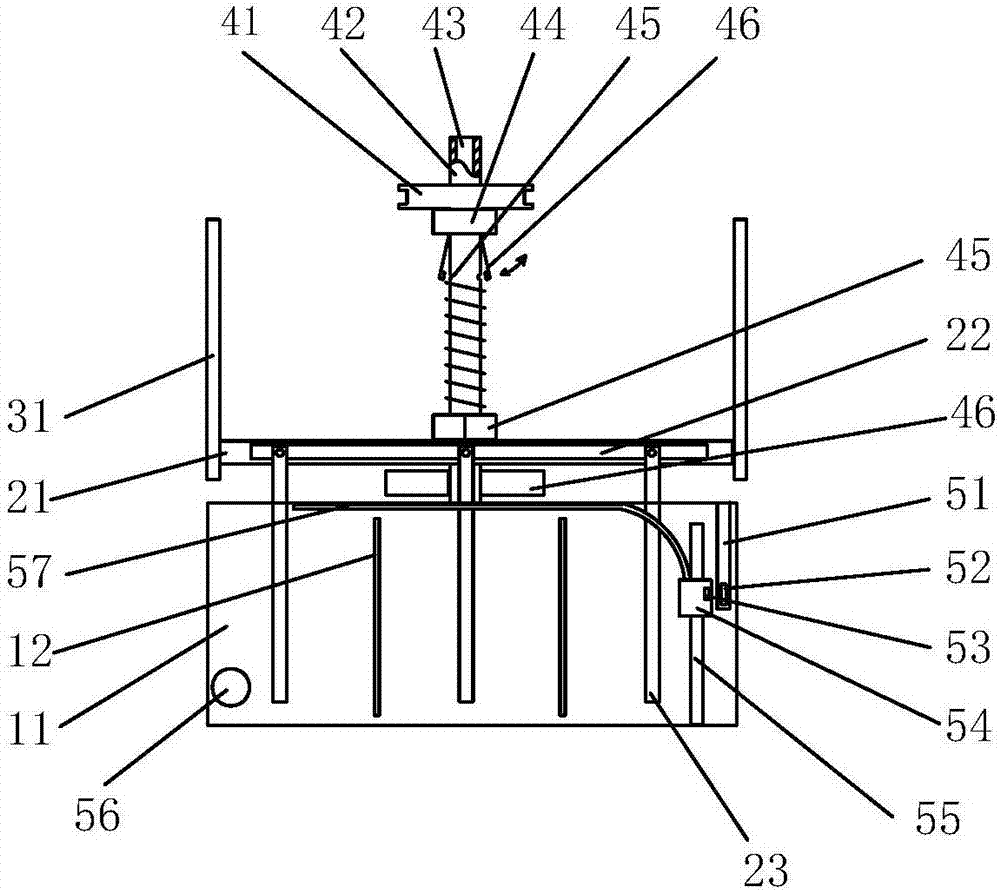
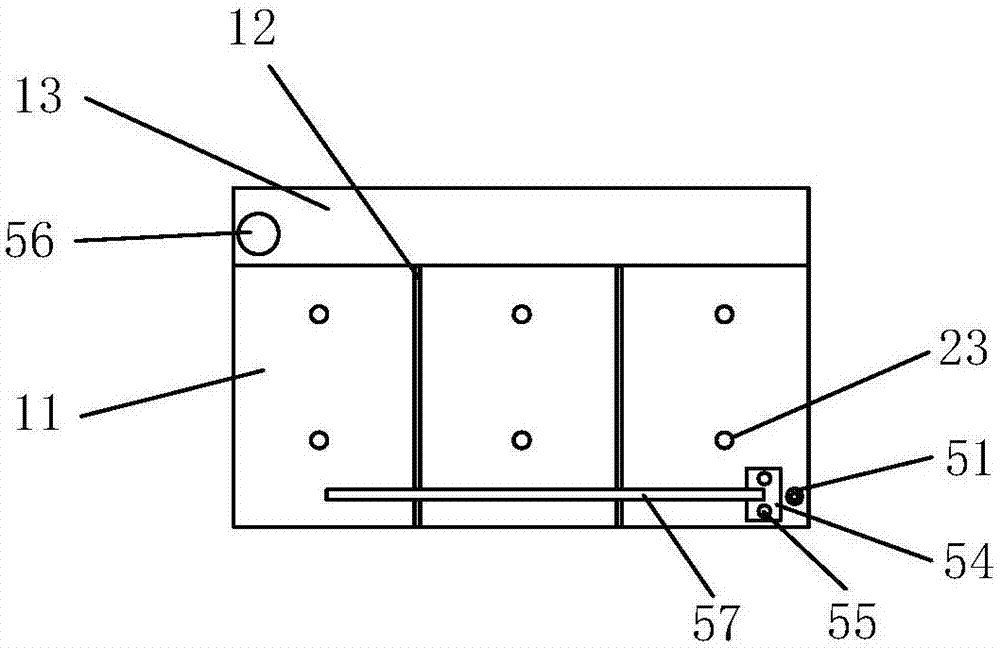
Rheostat structure based on electro-hydraulic starter rheostat
ActiveCN104270038AReduce the temperatureAutomatically add waterReluctance motor startersElectro hydraulicEngineering
The invention discloses a rheostat structure based on an electro-hydraulic starter rheostat. The rheostat structure comprises a water tank, three pairs of electrode bars inserted into the water tank and an electrode bar lifting structure capable of changing water resistance. A standby water tank, locating columns, a float, a magnetic material arranged on the float and a reed pipe are further included, the standby water tank is arranged adjacent to the water tank, the water tank and the adjacent water tank are separated only through a common plate, a water pump is arranged in the standby water tank, and the water pump can inject water of the standby water tank into the water tank through an inlet in the upper portion of the water tank. The locating columns are fixed in the water tank. The locating columns are sleeved with the float, and the float can vertically move along the water level. The reed pipe is arranged in a sealing pipe of the non-magnetic-conducting material. When the water level of the water tank is reduced, the reed pipe is triggered by the magnetic material to be closed, and the water pump works. A water tank cover is provided with holes allowing the electrode bars to be inserted, sealing rings and housings fixing the sealing rings on the inner face of the water tank cover, and the electrode bars are sleeved with the sealing rings. The rheostat structure has the advantages of reducing the temperature of the water tank, automatically adding water, preventing water losses, and prolonging the maintenance period.
Owner:南通曼淇威电气有限公司
Motor starter for synchronous machine
Embodiments of the invention relate to a motor starter for a synchronous machine. Systems, methods, techniques and apparatuses of motor starters are disclosed. One exemplary embodiment is a synchronous machine including a plurality of stator phase windings, a rotor, a motor starter, and a controller. The motor starter includes a plurality of wye semiconductor switches and a plurality of delta semiconductor switches. The controller is structured to operate the plurality of wye semiconductor switches and the plurality of delta semiconductor switches so as to couple the plurality of stator phasewindings in a delta configuration while an angular speed of the rotor is less than a synchronous speed, and structured to operate the plurality of wye semiconductor switches and the plurality of deltasemiconductor switches so as to couple the plurality of stator phase windings in a wye configuration in response to the angular speed of the rotor being equal to the synchronous speed.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Motor acceleration apparatus and method
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Method for controlling reluctance motor rotor alignment and driving circuit for realizing the method thereof
Disclosed is a method of controlling alignment of a rotor of an SRM with respect to a stator, the SRM including a stator having a plurality of diametrically opposed stator salient magnetic pole pairs around each which each of a plurality of phase coils is wound, and a rotor disposed about a shaft within the stator and having a plurality of diametrically opposed rotor salient pole pairs, comprising the steps of: applying a voltage pulse having an identical magnitude to each phase coil surrounding the plurality of pairs of stator salient magnetic poles in a plurality of respective motor phases of a stator of the SRM upon the initial starting of the SRM; detecting current flowing into the each phase coil in the plurality of respective motor phases in accordance to the application of the voltage pulse; comparing the respective magnitude values of the detected current in the respective motor phases with each other; and (d) bringing rotor salient pole pair of the rotor into alignment with a corresponding pair of stator salient poles of a motor phase with a phase coil into which current of the lowest level flows with the result of the comparison.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Switched reluctance motor starting methods
InactiveUS20160329839A1Improve scalabilityBalance current loadSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlEngineeringIntermediate stage
An improved method of starting a switched reluctance motor uses two neighbouring pairs of coils, both energised, to bring the rotor to its initial position. Then one of pairs of coils is turned off and the rotor is attracted by the other pair of coils to give it an initial rotational speed. An intermediate stage uses just one pair of coils of the motor to bring it up to operational speeds, after which the normal cycling of all the coils can be used.
Owner:VALEO AIR MANAGEMENT UK
Apparatus and method for driving 2-phase srm motor
InactiveUS20100156337A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersEngineeringMicroprocessor
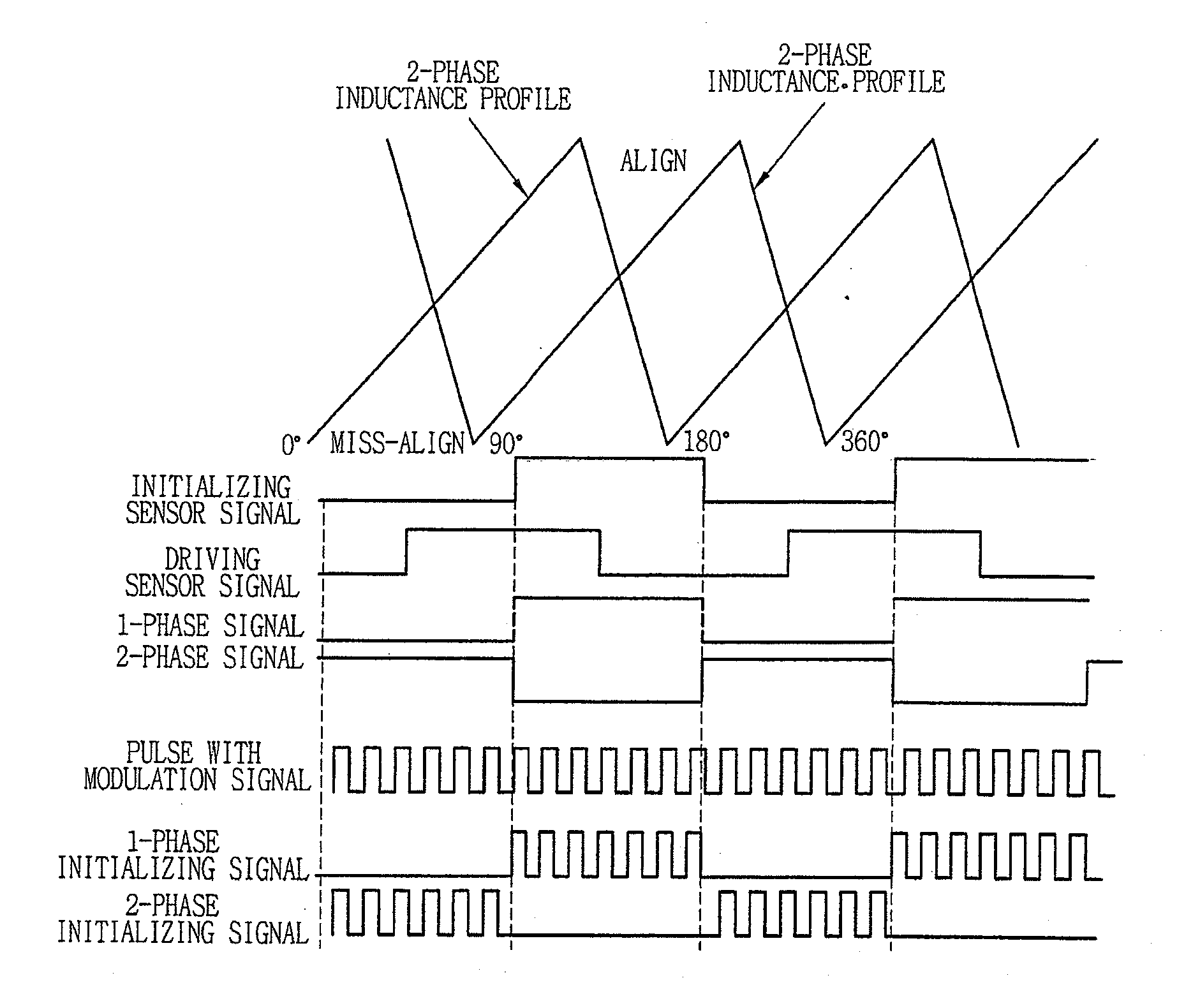
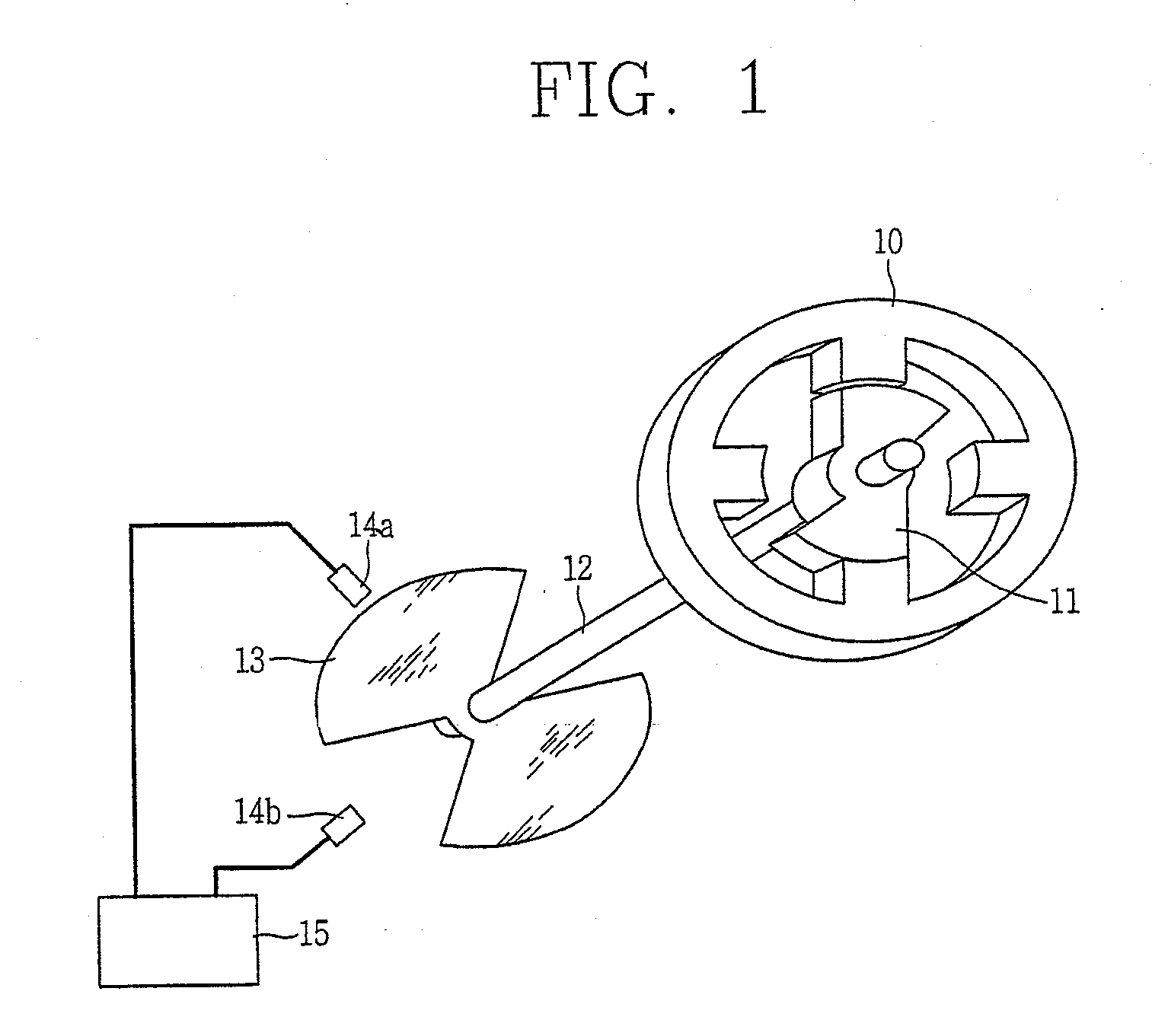
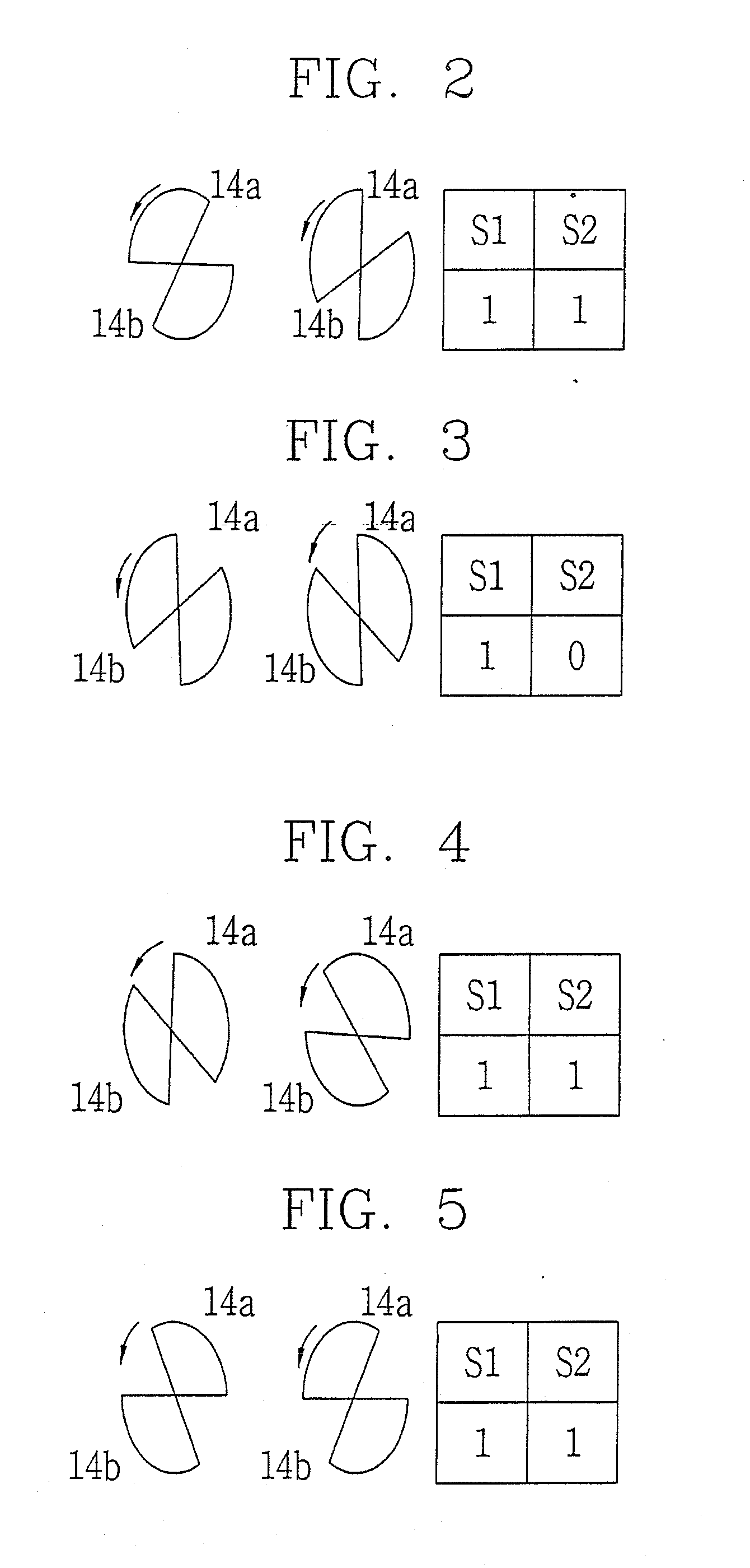
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for driving a 2-phase SRM. The method comprises initializing 2-phase based on a detected position of a rotor by an initializing sensor at the time of an initial driving, and normally driving 2-phase based on a detected position of the rotor by a driving sensor. Accordingly, a sufficient amount of torque is generated when the 2-phase SRM is driven at a high speed. The apparatus comprises an initializing sensor which detects each position of each phase of a 2-phase SRM, and generates an initializing sensor signal based on the detected result; a driving sensor which detects each position of each phase of the 2-phase SRM, and generates a driving sensor signal based on the detected result; and a microprocessor which initially drives the 2-phase SRM based on the initializing sensor signal at the time of an initial driving, and normally drives the 2-phase SRM based on the driving sensor signal at the time of a normal driving.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
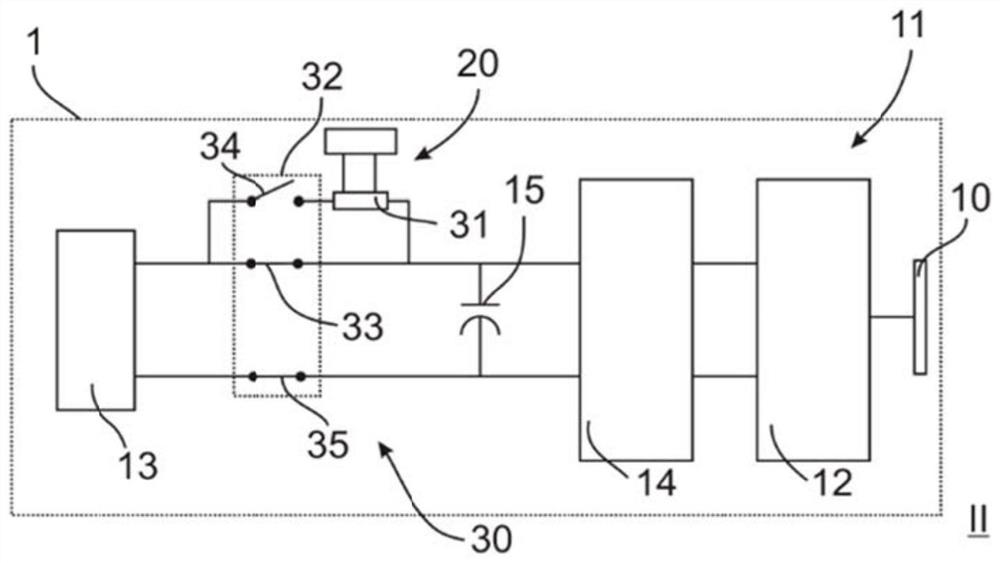
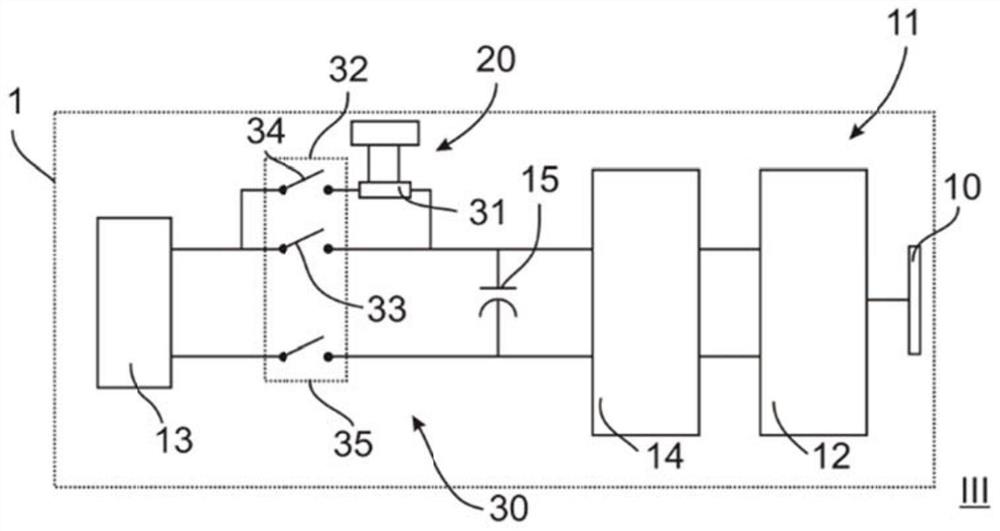
Domestic appliance and method for operating such a domestic appliance
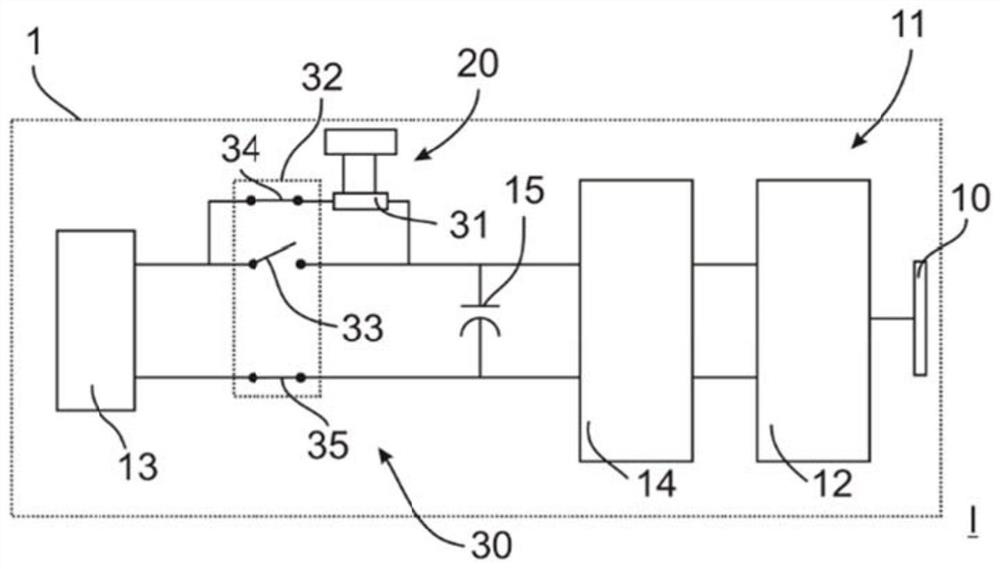
PendingCN111668822AOmit the weak pointSave costsBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric motor controlComputer hardwareHome appliance
The invention relates to a household appliance (1) having a movable first functional unit (10) for providing a first appliance function for a user, an electrically powered second functional unit (20)for providing a second appliance function for the user, and a drive device (11) for driving the first functional unit (10), a drive device comprises an electric motor (12), an interface (13) for supplying power to the electric motor (12), and a pre-connection circuit (30) arranged between the interface (13) and the electric motor (12), the pre-connection circuit (30) having a current-limiting element (31) for limiting a current (200).The invention also relates to a method (100) for operating a household appliance (1).
Owner:VORWERK & CO INTERHOLDING GMBH
A Multilevel Power Topology for Switched Reluctance Motor
ActiveCN105743375BStart fastImprove robustnessAc-dc conversionEnergy industryPower topologyExcitation current
The invention discloses a multi-level power topology structure of a switch reluctance motor. A boost circuit part is additionally arranged between a traditional asymmetric power conversion circuit and a DC power supply and comprises a capacitor C1, a boost capacitor C2, a switching tube T1 and a diode D1, a switching tube T3, a diode D3 and a bidirectional switch, wherein the switching tube T1 and the diode D1are reversely connected in parallel, the switching tube T3 and the diode D3 are reversely connected in parallel, and the bidirectional switch comprises a switching tube T2 and diodes D21, D22, D23 and D24. By controlling the switch-on and the switch-off of the switching tubes in the power topology, the switch reluctance motor can run by switching among five states of rapid excitation (+2), rapid demagnetization (-2), normal excitation (+1), normal demagnetization (-1) and follow current (0). The rapid excitation and the rapid demagnetization of the switch reluctance motor are achieved, the problems of slow excitation current rise and reduction, low system efficiency, low dynamic performance and the like during motor running are solved, and the multi-level power topology structure has high robustness, high reliability and intelligence and has huge application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method Of Operating Switched Reluctance Machine
A controller for a switched reluctance machine is operated to close a switch which would otherwise be open so as to connect a phase winding to the DC link to which the winding is connected during other parts of the electrical cycle. This produces a condition which allows the insulation of the system to be monitored by applying a voltage between the DC link and ground.
Owner:NIDEC SR DRIVES
Switched reluctance motor, starting method thereof and multifunctional food processor
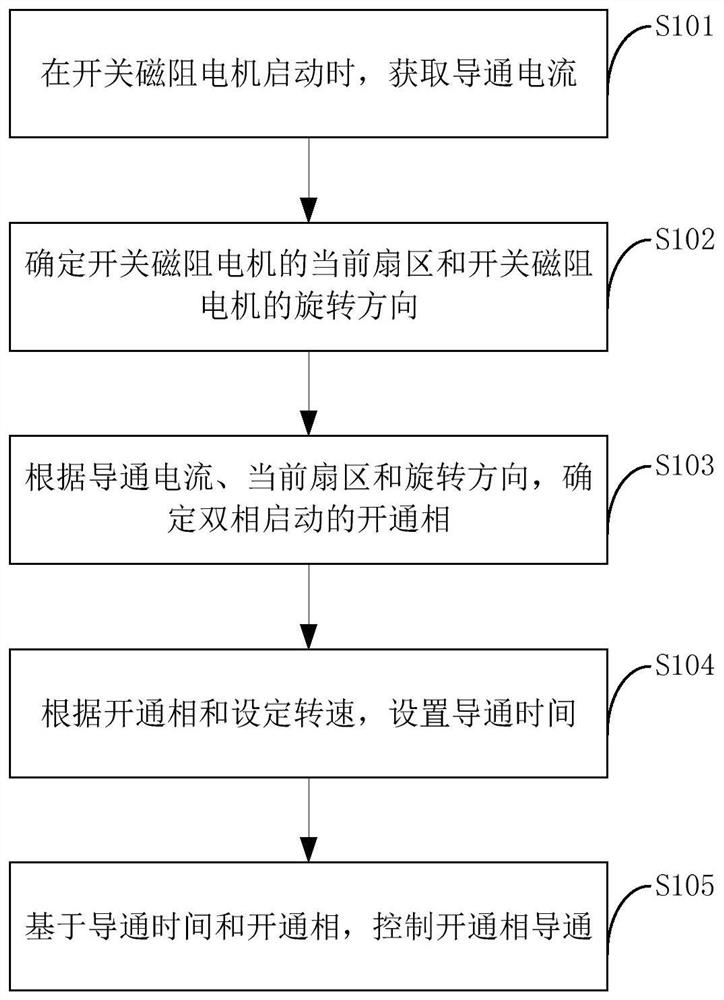
PendingCN113612410AIncrease starting torqueImprove startup performanceStarter detailsReluctance motor startersElectric machineControl engineering
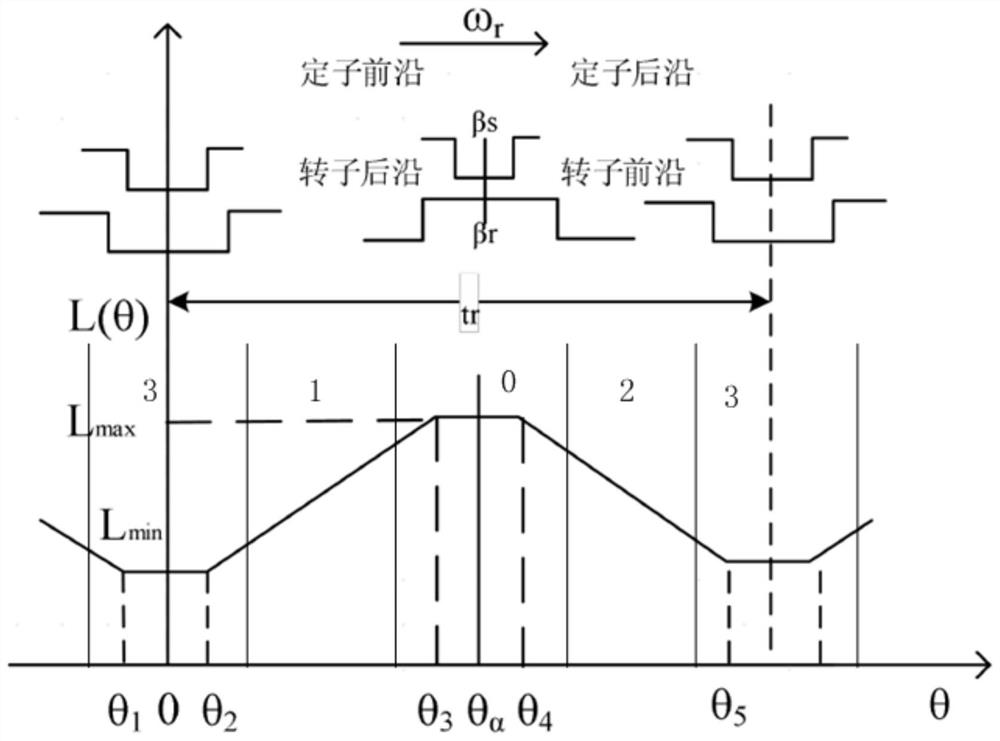
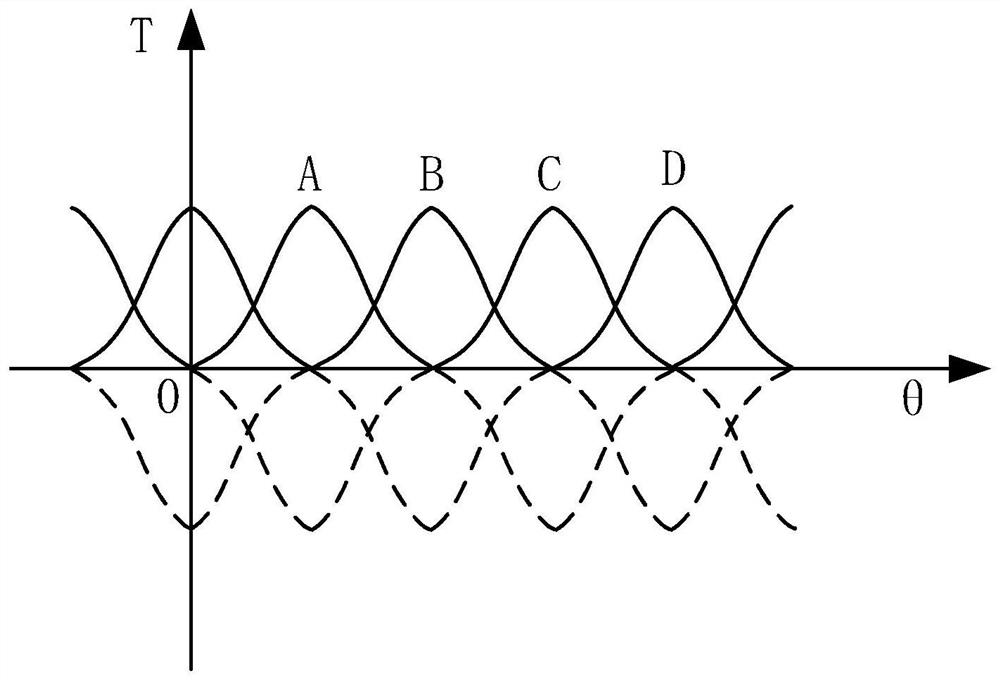
The invention relates to a switched reluctance motor and a starting method thereof, and a multifunctional food processer, and the starting method comprises the following steps: obtaining a conduction current when the switched reluctance motor is started; determining a current sector of the switched reluctance motor and a rotation direction of the switched reluctance motor; according to the breakover current, the current sector and the rotation direction, determining a breakover phase of double-phase starting; setting conduction time according to the opening phase and the set rotating speed; and controlling the turn-on phase to be turned on based on the turn-on time and the turn-on phase. According to the switched reluctance motor, the conducting current when the motor is started is detected, and the conducting two phases are determined by combining the position and the rotation direction of the motor, so that the position of the motor rotor is determined through the current to conduct the corresponding two phases, and the purpose of improving the starting torque of the switched reluctance motor is achieved; and the starting performance, the stability and the reliability of the switched reluctance motor are improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN TOPBAND CO LTD
Apparatus and method for minimizing undesirable stepper motor rotor motions
ActiveUS8344681B2Reduce relative motionReducing undesired motionComputer controlSimulator controlMicrocontrollerElectric machine
An apparatus for reducing undesired motions during initialization of a stepper motor having a rotor and windings, the apparatus comprising a rotary encoder for sensing direction of rotor rotation; a microcontroller responsive to signals from the rotary encoder for generating bidirectional motor control waveforms having variable digital amplitude values; at least one motor driver for receiving the motor control waveforms and translating the waveforms to drive the motor windings; and wherein the translated waveforms urge the rotor in a first direction and then a second direction to locate a desired rotor position. A method of reducing undesired motions during initialization of a stepper motor having a rotary encoder coupled thereto comprises applying currents to the phase windings to form a magnetic field vector in a direction; sensing a direction of rotor rotation; changing at least one motor phase current to rotate the magnetic field vector in a direction opposite to the direction of first sensed rotor rotation by a first electrical angle; sensing a direction of rotor rotation; changing at least one motor phase current to rotate the magnetic field vector to a next position in a direction opposite to the second sensed rotor rotation by a second electrical angle; and ending initialization, whereby the rotor is aligned with the magnetic field vector in its next position.
Owner:NOVANTA CORP
Motor control apparatus
ActiveUS10122305B2Low applicabilityEasy to learnWindingsAC motor accelaration/decelaration controlActuatorControl theory
A motor control apparatus which is applied to an actuator provided with a motor and an encoder, and drives the motor is provided. The motor control apparatus comprises: a controller that learns an initial position of a rotor, and also decides an energized phase; and a drive circuit that performs switching operation to energize an energized phase. The controller learns that, in learning the initial position, the initial position of the rotor is a two-phase facing position in which two adjacent salient poles of the rotor face salient poles of two energized phases of a stator, and the initial position of the rotor is a one-phase facing position in which one salient pole of the rotor faces a salient pole of one non-energized phase of the stator.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Switched reluctance motor starting methods
InactiveCN106464168ABalance current loadGuaranteed uptimeAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersIntermediate stageEngineering
An improved method of starting a switched reluctance motor uses two neighbouring pairs of coils, both energised, to bring the rotor to its initial position. Then one of pairs of coils is turned off and the rotor is attracted by the other pair of coils to give it an initial rotational speed. An intermediate stage uses just one pair of coils of the motor to bring it up to operational speeds, after which the normal cycling of all the coils can be used.
Owner:VALEO AIR MANAGEMENT UK
Rheostat structure based on electrohydraulic rheostat starter
ActiveCN104270038BReduce the temperatureAutomatically add waterReluctance motor startersElectro hydraulicEngineering
The invention discloses a rheostat structure based on an electro-hydraulic starter rheostat. The rheostat structure comprises a water tank, three pairs of electrode bars inserted into the water tank and an electrode bar lifting structure capable of changing water resistance. A standby water tank, locating columns, a float, a magnetic material arranged on the float and a reed pipe are further included, the standby water tank is arranged adjacent to the water tank, the water tank and the adjacent water tank are separated only through a common plate, a water pump is arranged in the standby water tank, and the water pump can inject water of the standby water tank into the water tank through an inlet in the upper portion of the water tank. The locating columns are fixed in the water tank. The locating columns are sleeved with the float, and the float can vertically move along the water level. The reed pipe is arranged in a sealing pipe of the non-magnetic-conducting material. When the water level of the water tank is reduced, the reed pipe is triggered by the magnetic material to be closed, and the water pump works. A water tank cover is provided with holes allowing the electrode bars to be inserted, sealing rings and housings fixing the sealing rings on the inner face of the water tank cover, and the electrode bars are sleeved with the sealing rings. The rheostat structure has the advantages of reducing the temperature of the water tank, automatically adding water, preventing water losses, and prolonging the maintenance period.
Owner:南通曼淇威电气有限公司
Method, computer program product and controller for starting-up a switched reluctance motor, and electrical apparatus implementing same
A method of starting-up a switched reluctance, SR, motor is provided. The method comprises simultaneously energizing a plurality of phases at a first time point with respective phase voltages that are substantially the same, until the motor rotor is stabilized in alignment with either one of the plurality of phases; simultaneously de-energizing the plurality of phases at a second time point that follows the first time point; monitoring a decrease of respective phase currents in the plurality of phases from a third time point that follows the second time point by a first predetermined time interval; determining a phase of alignment of the rotor using evaluation of the decrease of the phase currents following simultaneous de-energizing of the plurality of phases; and, initiating rotation of the rotor from the determined phase of alignment of the rotor.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com