Patents
Literature
30results about How to "Improve biaxial tensile properties" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
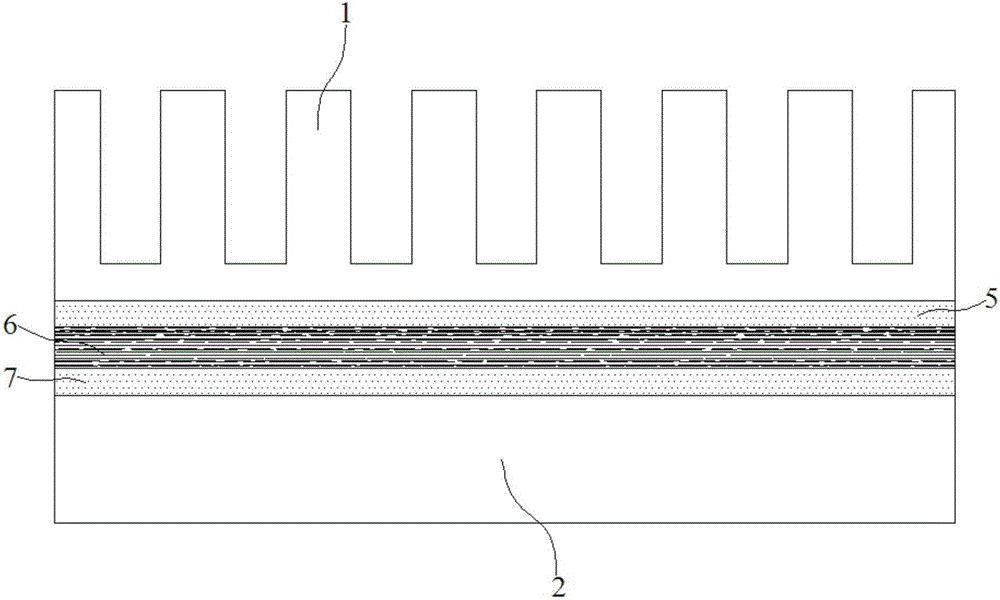
Heat conduction graphite flake and manufacturing process thereof
ActiveCN103787323AImprove biaxial tensile propertiesHigh thermal conductivityCarbon compoundsRadiationPolydimethylsiloxane
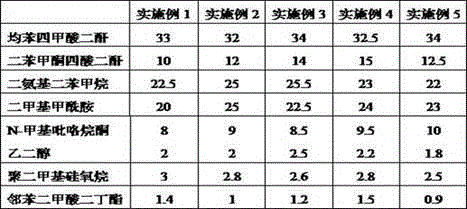
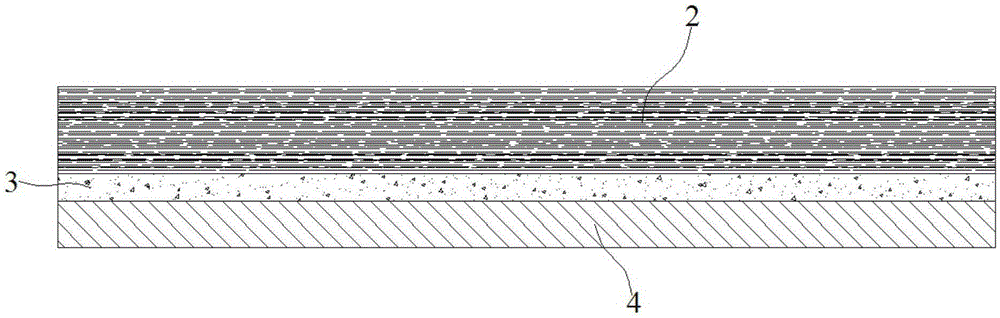
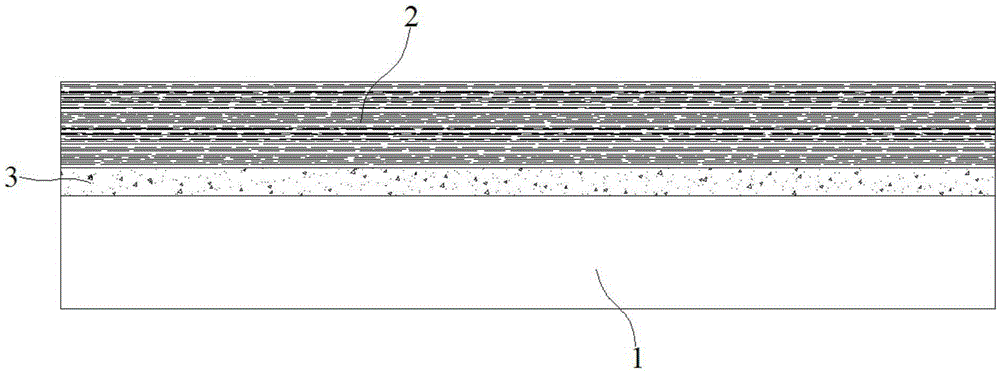
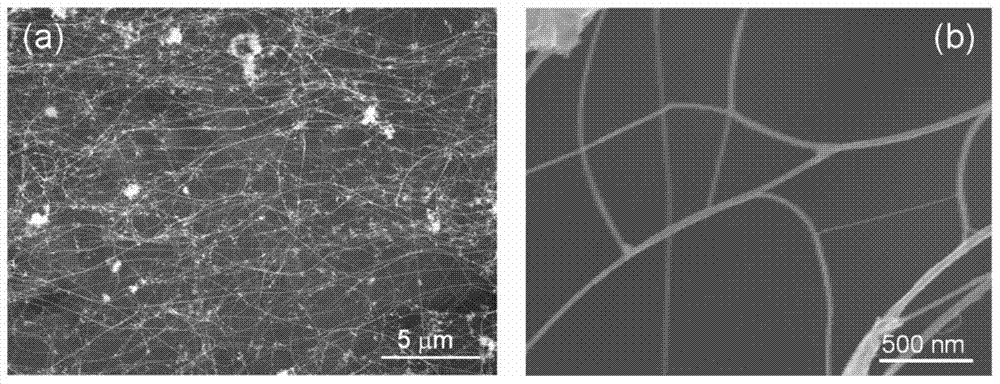
The invention discloses a heat conduction graphite flake, and a manufacturing process thereof. The heat conduction graphite flake comprises a polyimide film, a first coating layer and a second coating layer, wherein the first coating layer and the second coating layer are respectively arranged on the upper surface and the lower surface of the polyimide film; the first coating layer and the second coating layer are formed by sintering a graphite modifier; the graphite modifier comprises the following components in parts by weight: 20-25 parts of benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride, 14-16 parts of pyromellitic dianhydride, 22-26 parts of diaminodiphenyl methane, 25-35 parts of dimethylformamide, 1.8-2.5 parts of ethylene glycol, and 2.5-3 parts of polydimethylsiloxane. According to the heat conduction graphite flake, the heat conduction performance can be improved in the vertical direction and the horizontal direction, local overheat is avoided, the uniform heat conduction performance is achieved, and the stability and reliability of radiation performance of products are improved.
Owner:SUZHOU SIDIKE NEW MATERIALS SCI & TECH
Heat conduction graphite patch for microelectronic device
ActiveCN103763892AImprove biaxial tensile propertiesAvoid local overheatingLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsAdhesiveCarbonization
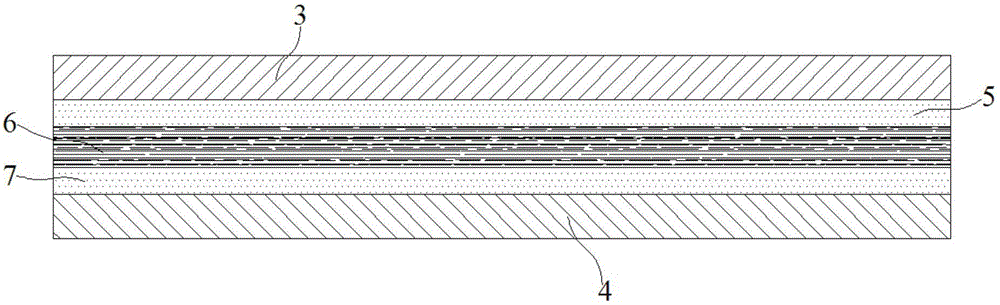
The invention discloses a heat conduction graphite patch for a microelectronic device. The heat conduction graphite patch comprises a first heat conduction adhesive layer, a graphite layer and a second heat conduction adhesive layer, the graphite layer is obtained through the following technique, and the technique comprises the following steps that the upper surface and the lower surface of a polyimide film after the first step are coated with graphite modifiers to obtain the processed polyimide film; the processed polyimide film is heated to 800 DEG C, heat preservation is carried out, and then the film is heated to 1200 DEG C to obtain a pre-burned carbonization film; a calender is adopted to calender the pre-burned carbonization film in the fourth step; the carbonization film is heated to 2400 DEG C, heat preservation is carried out, then the film is heated to 2900 DEG C, and therefore a mainly-burnt graphite film is obtained; the mainly-burnt graphite film obtained in the fifth step is calendered to obtain the graphite layer. The method avoids local overheating of adhesive tape, uniformity of heat conduction performance of the adhesive tape is achieved, the stability and reliability of heat dissipation performance of the patch are improved, and the cost of the patch is greatly reduced.
Owner:斯迪克新型材料(江苏)有限公司
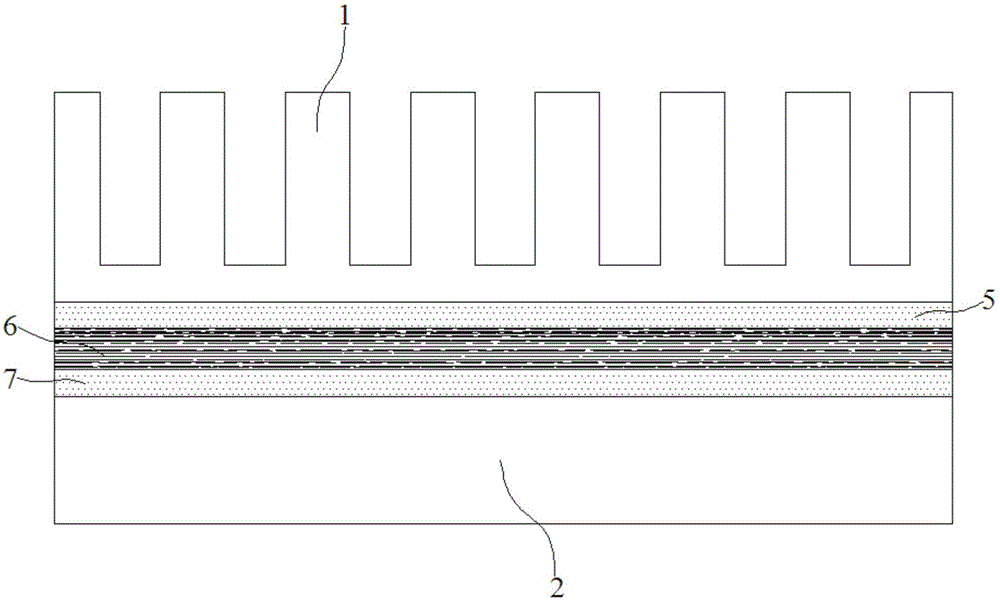
Heat conduction graphite paster for adhesive tape and preparing method of heat conduction graphite paster
ActiveCN103796493AAvoid local overheatingAchieve uniformityLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsAdhesiveDimethyl siloxane
The invention discloses a heat conduction graphite paster for adhesive tape and a preparing method of the heat conduction graphite paster. The surface of the heat conduction graphite paster is coated with a heat conduction adhesive layer, the heat conduction graphite paster is composed of a polyimide film, a first coating layer and a second coating layer, and the first coating layer and the second coating layer are located on the upper surface and the lower surface of the polyimide film respectively. The first coating layer and the second coating layer respectively comprise, by weight, 20-25 parts of benzophenone tetracid dianhydride, 12-18 parts of pyromellitic acid dianhydride, 20-28 parts of diaminodiphenylmethane, 20-25 parts of dimethyl formamide, 8-10 parts of N-methyl pyrrolidone, 1.5-2.5 parts of ethylene glycol, 2-3 parts of dimethyl silicone polymer and 0.8-1.5 parts of phthalic acid dibutyl ester. According to the heat conduction graphite paster, local overheating is avoided, the evenness of the heat conduction performance is achieved, the stability and reliability of the heat dissipation performance of the heat conduction graphite paster are improved, and the cost of the heat conduction graphite paster is reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU SIDIKE NEW MATERIALS SCI & TECH CO LTD
Manufacturing process of heat-conductive film used for cell phones
The invention discloses a manufacturing process of a heat-conductive film used for cell phones. The manufacturing process mainly includes the steps of: 1) pre-treating a thin film; 2) smearing a graphite modifier on the thin film; 3) pre-sintering the thin film; 4) calendering: calendering the pre-sintered carbonized film in the step 3) on a calender machine until the thickness of the film is 0.3-0.8 mm; 5) main sintering: heating the calendered polyimide thin film in the step 4) to 800-900 DEG C and maintaining the temperature for 30-60 min, and increasing the temperature to 900-1100 DEG C and maintaining the temperature for 10-30 min, and cooling the film to normal temperature to obtain the heat-conductive film. The manufacturing process is easy to carry out and is low in cost. The heat-conductive film is high in scraping strength and is high in heat conductivity. By uniformly smearing a layer of graphite modifier on both surfaces of the polyimide thin film, the heat conductive property in the vertical and horizontal directions is improved, so that heat dissipation uniformity of the film is achieved.
Owner:HEFEI DONGHENGRUI ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
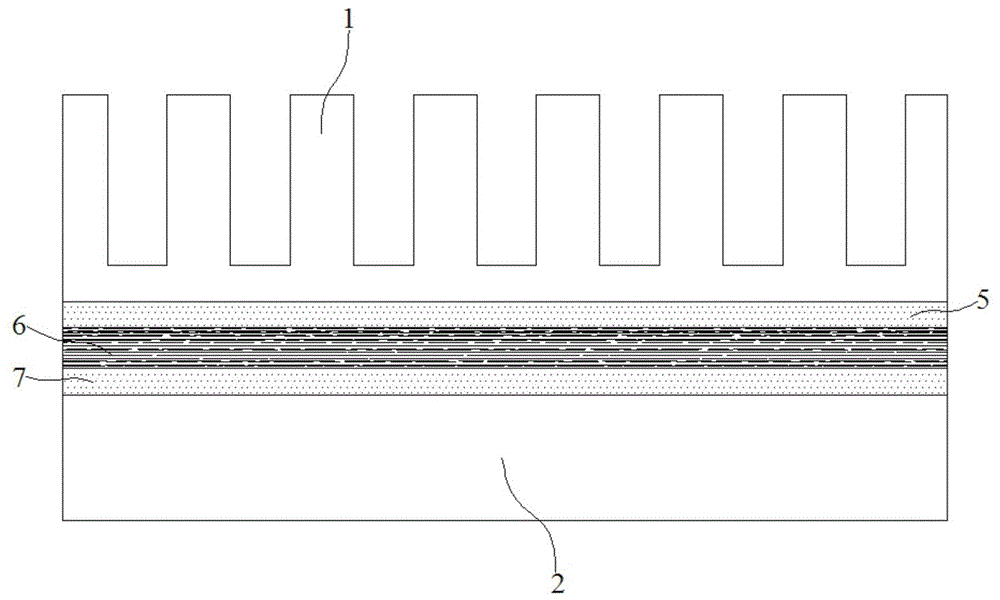
Heat-conduction double-sided bonded graphite flake
ActiveCN106304783AImprove biaxial tensile propertiesAvoid local overheatingLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsAdhesiveCarbonization
The invention discloses a heat-conduction double-sided bonded graphite flake. The heat-conduction double-sided bonded graphite flake is arranged between a heat dissipation part and a heating part in a close contact way and comprises a light-stripped PET film and a heavily-stripped PET film, a first heat-conduction adhesive layer, a graphite layer and a second heat-conduction adhesive layer are sequentially arranged between the light-stripped PET film and the heavily-stripped PET film, an upper surface and a lower surface of the graphite layer on a polyimide film are respectively coated with a layer of graphite modifier to obtain the processed polyimide film, and the graphite modifier comprises the following constituents based on part by weight: 22 parts of benzophenone dianhydride, 15.6 parts of pyromellitic dianhydride, 26 parts of diaminodiphenylmethane, 32 parts of dimethylformamide, 1.8 parts of ethylene glycol and 2.2 parts of polydimethylsiloxane. A calendaring machine is used for calendaring a pre-sintered carbonization film, and draped lines and volume shrinkage during graphitization sintering process are prevented.
Owner:斯迪克新型材料(江苏)有限公司
High-heat-conductivity-coefficient radiating patch
ActiveCN103805082BImprove biaxial tensile propertiesAvoid local overheatingCarbon compoundsFilm/foil adhesivesHeat conductingCarbonization
The invention discloses a high-heat-conductivity-coefficient radiating patch. The high-heat-conductivity-coefficient radiating patch is characterized in that a graphite layer is obtained by a following process method including the following steps: respectively coating a layer of graphite modifying agent on the upper and lower surfaces of a polyimide membrane so as to obtain the processed polyimide membrane, wherein the graphite modifying agent comprises the following components in parts by weight: 30-35 parts of benzenetetracarboxylic anhydride, 10-15 parts of benzophenone tetracarboxylic dianhydride, 22-26 parts of diaminodiphenylmethane, 20-25 parts of dimethylformamide, 8-10 parts of N-methyl pyrrolidone, 1.8-2.5 parts of ethylene glycol, 2.5-3 parts of polydimethylsiloxane and 0.8-1.5 parts of dibutyl phthalate; heating the processed polyimide membrane to be 790-810 DEG C, and heating the polyimide membrane to 1180-1250 DEG C so as to obtain a pre-fired carbonization membrane; calendering the pre-fired carbonization membrane by virtue of a calendar; heating the pre-fired carbonization membrane to 2850-2950 DEG C so as to obtain a mainly-fired graphite membrane. According to the high-heat-conductivity-coefficient radiating patch, the stability and reliability of the radiating performance of a product are improved when the uniformity of the heat-conducting performance is realized, and the cost of the product is greatly lowered.
Owner:斯迪克新型材料(江苏)有限公司
Tensile heat-radiating graphite patch
ActiveCN104812205AImprove biaxial tensile propertiesAvoid local overheatingLayered productsFilm/foil adhesivesAdhesiveRoom temperature
The invention discloses a tensile heat-radiating graphite patch. A release material layer is attached to a surface, away from a graphite layer, of a heat conduction adhesive layer. The graphite layer is prepared by the following process: respectively coating the upper and lower surfaces of a polyimide film with a layer of graphite modifier to obtain a polyimide film after processing, wherein the viscosity of the graphite modifier is 30000-48000CP; heating the polyimide film after processing from room temperature to 1180-1250 DEG C and cooling the polyimide film to obtain a pre-fired carbonized film; calendaring the pre-fired carbonized film in step 4 by a calendaring machine; heating the pre-fired carbonized film to 2850-2950 DEG C to obtain a fired graphite film; and calendaring the fired carbonized film obtained in step 4 to obtain the graphite layer. Uniform heat conduction performance is achieved, and meanwhile, the radiating performance, stability and reliability of products are improved, and the cost of products is greatly reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU SIDIKE NEW MATERIALS SCI & TECH CO LTD
High-compactability heat-conduction adhesive film
ActiveCN106118517AImprove biaxial tensile propertiesAvoid local overheatingCarbon compoundsFilm/foil adhesivesHeat conductingAdhesive
The invention discloses a high-compactability heat-conduction adhesive film. The heat-conduction adhesive film is jointed to the surface of a heating component, and comprises a graphite layer, a heat-conduction gluing layer locating on the surface of the graphite layer, and a release material layer. The graphite layer is obtained through the following technological method comprising the following steps of coating a layer of a graphite modifying agent on the upper surface and the lower surface of a polyimide thin film so as to obtain a treated polyimide thin film, wherein the graphite modifying agent is made from the following components in parts by weight: 28 parts of pyromellitic dianhydride, 13.5 parts of BTDA, 25 parts of diaminodiphenylmethane, 24 parts of dimethyl formamide, 9 parts of N-methylpyrrolidinone, 2.2 parts of glycol and 2.2 parts of polydimethylsiloxane; and raising the temperature of the treated polyimide thin film to 1200 DEG C, performing heat preservation, and performing cooling so as to obtain a prefiring carbonization film. According to the high-compactability heat-conduction adhesive film disclosed by the invention, puckers and volume shrinkage in the graphitization sintering process are avoided, the compactability and the crystalinity are improved, and the heat-conducting properties in a perpendicular direction and in a horizontal direction are further improved.
Owner:JIANGSU SIDIKE NEW MATERIALS SCI & TECH CO LTD
Heat conduction graphite sheet and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103770415BImprove biaxial tensile propertiesImprove thermal conductivityCarbon compoundsFilm/foil adhesivesPyrrolidinonesGraphite
Owner:斯迪克新型材料(江苏)有限公司
Graphite adhesion sheet capable of performing uniform heat conduction
InactiveCN106987215AImprove biaxial tensile propertiesAvoid local overheatingCarbon compoundsFilm/foil adhesivesThermal insulationRoom temperature
The present invention discloses a graphite adhesion sheet capable of performing uniform heat conduction. The graphite adhesion sheet comprises a graphite layer, a heat conduction adhesion layer positioned on the surface of the graphite layer, and a release material layer, wherein the release material layer is adhered on the heat conduction adhesion layer surface opposite to the graphite layer, and the graphite layer preparation method comprises: uniformly coating the upper surface and the lower surface of a polyimide film with a layer of a graphite modifier to obtain a treated polyimide film, heating the treated polyimide film to a temperature of 240-260 DEG C from a room temperature, carrying out thermal insulation, heating to a temperature of 480-520 DEG C, carrying out thermal insulation, heating to a temperature of 790-810 DEG C, heating to a temperature of 1180-1250 DEG C, cooling to obtain a pre-fired carbonized film, calendering the pre-fired carbonized film with a calendering machine, and calendering the obtained mainly-fired graphite film to obtain the graphite layer. According to the present invention, the uniformity of the heat conduction is achieved while the stability of the heat dissipating of the product is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU SIDIKE NEW MATERIALS SCI & TECH CO LTD
Preparation process for graphite heat conduction and dissipation patch
ActiveCN105873414AImprove biaxial tensile propertiesAvoid local overheatingLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsCarbonizationGraphite
The invention relates to a preparation process for a graphite heat conduction and dissipation patch. A first coating layer of the graphite heat conduction and dissipation patch is formed from a graphite modifier applied onto the upper surface of a polyimide thin film, and the graphite modifier comprises the following constituents by weight percent: benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride, pyromellitic dinahydride anhydride, diaminodiphenylmethane, dimethylformamide, N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, ethylene glycol, polydimethylsiloxane and dibutyl phthalate. The preparation process comprises the following steps of applying the graphite modifier onto the upper surface of the polyimide thin film to obtain the processed polyimide thin film; rising the temperature of a carbonization film to be 2,350-2,450 DEG C, carrying out heat preservation, rising the temperature again to be 2,850-2,950 DEG C, and cooling the carbonization film to obtain a graphite film mainly sintered. By the preparation process, local heating is prevented, the uniformity of heat conduction performance is achieved, meanwhile, the stability and the reliability of heat dissipation performance of a product are improved, and the product cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU SIDIKE NEW MATERIALS SCI & TECH CO LTD
Preparation technology of pressure sensitive adhesive tape for intelligent mobile phone
InactiveCN106118518AAvoid local overheatingAchieve uniformityCarbon compoundsFilm/foil adhesivesDispersion stabilityHeat conducting
The invention discloses a preparation technology of a pressure sensitive adhesive tape for an intelligent mobile phone. The preparation technology comprises the following steps of: step I, raising the temperature of a polyimide thin film from room temperature to 250 DEG C, performing heat preservation, raising the temperature to 400 DEG C, and then reducing the temperature to the room temperature; step II, coating a layer of a graphite modifying agent on the upper surface and the lower surface of the polyimide thin film obtained in the step I so as to obtain the treated polyimide thin film, wherein the stickiness of the graphite modifying agent is 30000-48000CP, and the graphite modifying agent is made from the following components in parts by weight: pyromellitic dianhydride, BTDA, diaminodiphenylmethane, dimethyl formamide, N-methylpyrrolidinone, glycol and polydimethylsiloxane; and step III, raising the temperature of the treated polyimide thin film to 800 DEG C, performing heat preservation, raising the temperature to 1200 DEG C, performing heat preservation, and then performing cooling so as to obtain a prefiring carbonization film. According to the preparation technology disclosed by the invention, the heat-conducting uniformity of the adhesive tape is realized, the heat dispersion stability and reliability of products are improved, and the cost of the products is greatly reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU SIDIKE NEW MATERIALS SCI & TECH CO LTD
Pressure Sensitive Tapes for Microelectronic Devices
ActiveCN103756588BAvoid local overheatingAchieve uniformityCarbon compoundsFilm/foil adhesivesHeat conductingCarbide
The invention discloses a pressure sensitive adhesive tape for a microelectronic device. The pressure sensitive adhesive tape is attached to the surface of a heating part, and a graphite layer is obtained through the following process methods: respectively coating a graphite modifier on the upper surface and the lower surface of a polyimide film to obtain a treated polyimide film, wherein the graphite modifier consists of the following components in parts by weight: 25-30 parts of benzenetetracarboxylic anhydride, 10-15 parts of benzophenonetetracarboxylic anhydride, 20-28 parts of diaminodiphenylmethane, 20-25 parts of dimethyl formamide, 8-10 parts of N-methyl pyrrolidone, 1.5-2.5 parts of ethylene glycol and 2-3 parts of polydimethylsiloxane; raising the temperature of the treated polyimide film to 800 DEG C, keeping the temperature, raising the temperature to 1,200 DEG C, and obtaining a pre-sintered carbide film; rolling the pre-sintered carbide film in the step 4 by adopting a roller mill. The uniformity of heat-conducting property of the adhesive tape is realized, the heat dissipation performance, stability and reliability of the product are improved, and the cost of the product is greatly lowered.
Owner:太仓斯迪克新材料科技有限公司
A kind of biaxially stretchable supercapacitor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104538202BImprove biaxial tensile propertiesExcellent tensile capacitor stabilityHybrid capacitor electrolytesHybrid capacitor electrodesCarbon nanotubeElectrolyte composition
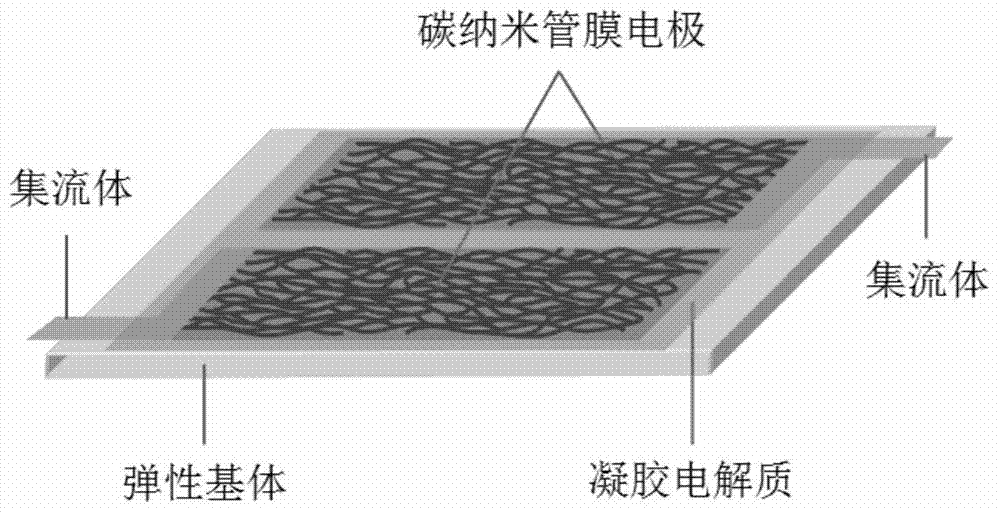
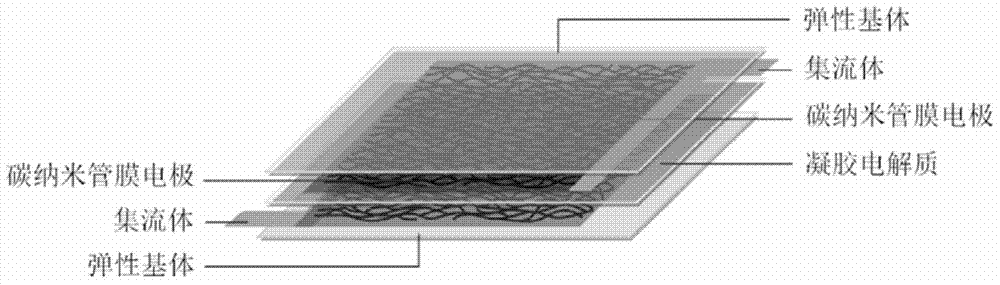
The invention discloses a two-way stretchable supercapacitor and a preparation method thereof. The supercapacitor is composed of carbon nanotube film electrodes, elastic polymer matrix and gel electrolyte, wherein the carbon nanotube film electrodes have an interconnected network structure. The carbon nanotube film electrode material is flexible, deformable and stretchable, and endows the supercapacitor with bidirectional stretchability. The bidirectionally stretchable supercapacitor provided by the present invention can be a planar structure or a sandwich sandwich structure. The supercapacitor prepared by the invention can be vertically stretched by 30%-100% in two directions in the plane, and maintain stable electrochemical performance, and the supercapacitor also has reciprocating stretching performance. The preparation method of the bidirectionally stretchable supercapacitor provided by the present invention is simple and easy to realize, and can realize mass production, and is used in various fields such as wearable electronics, electronic skin, and intelligent integrated devices.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Manufacturing Process for Graphite Heat Sinks
ActiveCN104812204BImprove biaxial tensile propertiesAvoid local overheatingLayered productsDigital data processing detailsRoom temperatureGraphite
Owner:斯迪克新型材料(江苏)有限公司
Heat transfer double-sided adhesive tape
InactiveCN106281087AAvoid local overheatingAchieve uniformityLamination ancillary operationsFilm/foil adhesivesPolyethylene terephthalateAdhesive
The invention discloses a heat transfer double-sided adhesive tape, namely a radiating double-sided adhesive film, which is attached between a radiating part and a heating component and comprises a light peelable PET (polyethylene terephthalate) film and a heavy peelable PET film; and a first heat transfer glue adhesive layer, a graphite layer and a second heat transfer adhesive layer are arranged sequentially between the light peelable PET film and the heavy peelable PET film; the graphite layer is made by a process including the steps of heating a polyimide film from room temperature to 250 DEG C, holding the temperature, heating to 400 DEG C, and cooling to room temperature; applying a layer of graphite modifier to each of the upper and lower surfaces of the polyimide film to obtain the processed polyimide film, wherein the graphite modifier is 30000-48000 CP in viscosity. Pinholes are filled during heating, crystallinity is improved, and non-uniformity due to excessive heat shrinkage is also overcome.
Owner:斯迪克新型材料(江苏)有限公司
Manufacturing technology of radiating fin for smart phone
ActiveCN107043108AImprove biaxial tensile propertiesAvoid local overheatingCarbon compoundsDigital data processing detailsManufacturing technologyGlycol synthesis
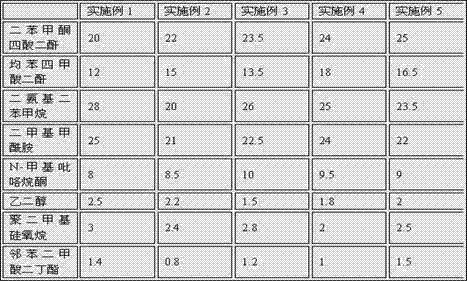
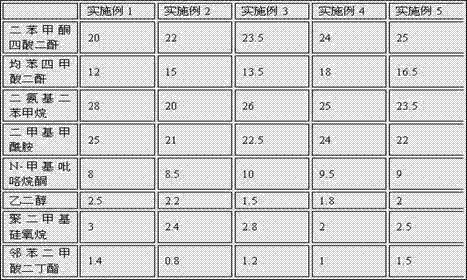
The invention discloses a manufacturing technology of a radiating fin for a smart phone. The radiating fin is obtained through the following step of (1) coating the upper surface and lower surface of a polyimide film with a graphite modifier separately to obtain a treated polyimide film, wherein the treated polyimide film comprises a polyimide film, a first coating layer and a second coating layer; and the graphite modifier is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 25 parts of diphenylketone tetrahydride, 16.5 parts of benzenetetracarboxylic anhydride, 23.5 parts of diaminodiphenylmethane, 22 parts of dimethylformamide, 9 parts of N-methyl pyrrolidone, 2 parts of ethylene glycol, 2.5 parts of polydimethylsiloxane and 1.5 parts of dibutyl phthalate. An azeotropic point and a smooth boiling point area are reduced, and the film-forming flatness and flexibility of a final product are improved.
Owner:斯迪克新型材料(江苏)有限公司
Heat conduction graphite flake and manufacturing process thereof
ActiveCN103787323BImprove biaxial tensile propertiesImprove thermal conductivityCarbon compoundsGraphitePyromellitic dianhydride
The invention discloses a heat conduction graphite flake, and a manufacturing process thereof. The heat conduction graphite flake comprises a polyimide film, a first coating layer and a second coating layer, wherein the first coating layer and the second coating layer are respectively arranged on the upper surface and the lower surface of the polyimide film; the first coating layer and the second coating layer are formed by sintering a graphite modifier; the graphite modifier comprises the following components in parts by weight: 20-25 parts of benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride, 14-16 parts of pyromellitic dianhydride, 22-26 parts of diaminodiphenyl methane, 25-35 parts of dimethylformamide, 1.8-2.5 parts of ethylene glycol, and 2.5-3 parts of polydimethylsiloxane. According to the heat conduction graphite flake, the heat conduction performance can be improved in the vertical direction and the horizontal direction, local overheat is avoided, the uniform heat conduction performance is achieved, and the stability and reliability of radiation performance of products are improved.
Owner:JIANGSU SIDIKE NEW MATERIALS SCI & TECH CO LTD
Efficient heat dissipation double-sided adhesion film
InactiveCN106987216AImprove biaxial tensile propertiesAvoid local overheatingFilm/foil adhesivesCoatingsThermal insulationRoom temperature
The present invention discloses an efficient heat dissipation double-sided adhesion film, which comprises a graphite layer, a heat conduction adhesion layer positioned on the surface of the graphite layer, and a release material layer, wherein the release material layer is adhered on the heat conduction adhesion layer surface opposite to the graphite layer, and the graphite layer preparation method comprises: uniformly coating the upper surface and the lower surface of a polyimide film with a layer of a graphite modifier to obtain a treated polyimide film, wherein the viscosity of the graphite modifier is 30000-48000 CP; heating the treated polyimide film to a temperature of 240-260 DEG C from a room temperature, carrying out thermal insulation, heating to a temperature of 480-520 DEG C, carrying out thermal insulation, heating to a temperature of 790-810 DEG C, and heating to a temperature of 1180-1250 DEG C; and cooling to obtain a pre-fired carbonized film. According to the present invention, the uniformity of the heat conduction is achieved while the stability and the reliability of the heat dissipating of the product is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU SIDIKE NEW MATERIALS SCI & TECH CO LTD
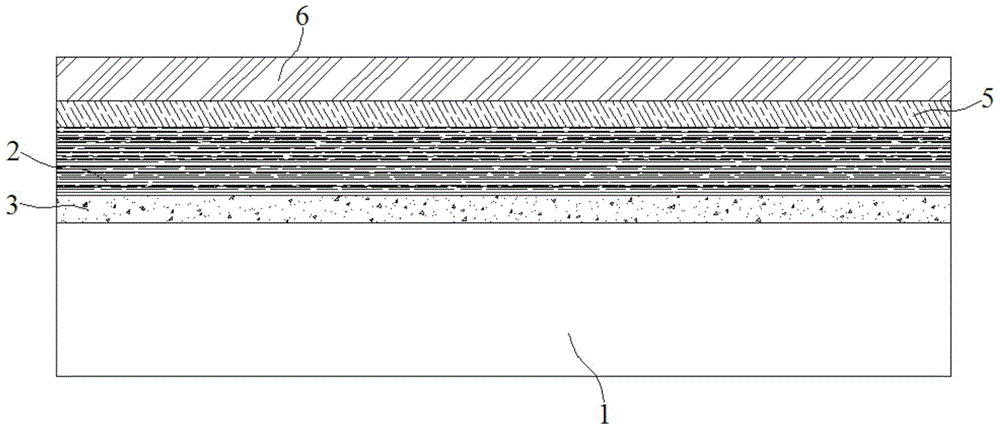
Film with high mechanical tensile property
InactiveCN104877586AImprove biaxial tensile propertiesAvoid local overheatingCarbon compoundsFilm/foil adhesivesPolyesterAdhesive
The invention discloses a high-reliability double-sided screen protector. The radiating double-sided screen protector is fitted between a radiating part and a heating part, a first heat conduction adhesive layer, a graphitic layer and a second heat conduction adhesive layer are sequentially arranged between a light peel-off type PET (polyester) film and a heavy peel-off type PET film, the graphitic layer is obtained according to the following process method comprising the step of coating a layer of graphite modifier on both the upper surface and the lower surface of a polyimide film to acquire the processed polyimide film, the graphite modifier comprises the following components in parts by weight: 20-25 parts of benzophenonetetracarboxylicdianhydride, 12-18 parts of pyromelliticdianhydride,20-28 parts of diaminodiphenylmethane, 30-35 parts of dimethylformamide, 1.5-2.5 parts of ethylene glycol, and 2-3 parts of polydimethylsiloxane. The heat conduction performances in both the vertical direction and the horizontal direction are improved, the local overheating of an adhesive tape is avoided, the stability and the reliability of the radiating performance of a product are improved, and the cost of the product is greatly lowered.
Owner:JIANGSU SIDIKE NEW MATERIALS SCI & TECH CO LTD
Pinhole-free type high-heat-conduction graphite adhesive tape
InactiveCN106118521AAvoid local overheatingAchieve uniformityCarbon compoundsFilm/foil adhesivesHeat conductingAdhesive
The invention discloses a pinhole-free type high-heat-conduction graphite adhesive tape. The pinhole-free type high-heat-conduction graphite adhesive tape is made through the following steps of coating a layer of a graphite modifying agent on the upper surface and the lower surface of a polyimide thin film so as to obtain a treated polyimide thin film, wherein the graphite modifying agent is made from the following components in parts by weight: pyromellitic dianhydride, BTDA, diaminodiphenylmethane, dimethyl formamide, N-methylpyrrolidinone, glycol and polydimethylsiloxane; raising the temperature of the treated polyimide thin film to 800 DEG C, performing heat preservation, raising the temperature to 1200 DEG C, performing heat preservation, and performing cooling so as to obtain a prefiring carbonization film; calendering the prefiring carbonization film through a calender; raising the temperature to 2900 DEG C, performing heat preservation, and then performing cooling so as to obtain a main firing graphite membrane; and calendering the main firing graphite film so as to obtain a graphite layer. According to the pinhole-free type high-heat-conduction graphite adhesive tape disclosed by the invention, the heat-conducting properties in a perpendicular direction and in a horizontal direction are improved, the heat-conducting uniformity is realized, and local superheating of the adhesive tape is avoided.
Owner:JIANGSU SIDIKE NEW MATERIALS SCI & TECH CO LTD
Preparation process of thermal double-sided adhesive tape
InactiveCN106318250AAvoid local overheatingImprove biaxial tensile propertiesLamination ancillary operationsCarbon compoundsPolyethylene terephthalate glycolPolyethylene terephthalate
The invention discloses a preparation process of a thermal double-sided adhesive tape. A thermal double-sided film is attached between a radiating part and a heating part and includes a light release PET (polyethylene terephthalate) film and a heavy release PET film, a first thermal adhesive layer, a graphite layer and a second thermal adhesive layer are arranged sequentially between the light release PET layer and the heavy release PET layer, and the graphite layer provides a graphite modifier layer for each of the upper and lower surfaces of polyimide film to obtain treated polyimide film, the graphite modifier has a viscosity of 30000-48000 CP, and the graphite modifier is made from, by weight, benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride, pyromellitic dianhydride, diaminodiphenylmethane, dimethylformamide, ethylene glycol, and polydimethylsiloxane. The adhesive tape is avoided being partially superheated, thermal transfer uniformity of the adhesive tape is achieved, and radiating property stability for the adhesive tape is improved.
Owner:STICK NEW MATERIALS JIANGSU CO LTD
Manufacturing process for high-thermal-conductivity graphite film
ActiveCN106304780AImprove biaxial tensile propertiesAvoid local overheatingLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsRoom temperatureGraphite
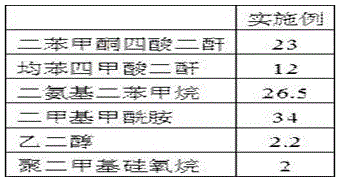
The invention discloses a manufacturing process for a high-thermal-conductivity graphite film. The manufacturing process comprises the following steps of heating a polyimide thin film from the room temperature to 250 DEG C at a heating speed of 4-6 DEG C / min, keeping the temperature for 0.9-1.1h, then heating to 400 DEG C at a heating speed of 2.5-3.5 DEG C / min, and keeping the temperature for 1h and then reducing to the room temperature; and coating the upper surface and the lower surface of the polyimide thin film obtained in the step one with a layer of graphite modifying agent to obtain a processed polyimide thin film, wherein the graphite modifying agent comprises the following components in parts by weight: 23 parts of benzophenone tetracid dianhydride, 12 parts of pyromellitic dianhydride, 26.5 parts of diaminodiphenylmethane, 34 parts of dimethyl formamide, 2.2 parts of ethylene glycol and 2 parts of polydimethylsiloxane. By adoption of the manufacturing process, pin holes in the heating process are filled, thereby improving degree of crystallinity, overcoming nonuniformity caused by overhigh thermal shrinkage, and improving the bidirectional tensile property of the graphite layer.
Owner:斯迪克新型材料(江苏)有限公司
Pressure-sensitive adhesive tape with heat uniformity and for smart phone
InactiveCN109280501AAvoid local overheatingAchieve uniformityCarbon compoundsFilm/foil adhesivesGraphiteEngineering
The invention provides a pressure-sensitive adhesive tape with heat uniformity and for a smart phone. The adhesive tape is a heat-dissipating double-sided film which is bonded between a heat-dissipating member and a heat-generating member. The heat-dissipating double-sided film comprises a light release PET film and a heavy release PET film, wherein a first heat-conductive adhesive layer, a graphite layer and a second heat-conductive adhesive layer are sequentially arranged between the light release PET film and the heavy release PET film. The pressure-sensitive adhesive tape of the inventionavoids local overheating of the adhesive tape, realizes the uniformity of the thermal conductivity of the adhesive tape, improves the stability and reliability of the heat dissipation performance of aproduct, and greatly reduces the cost of the product.
Owner:江苏博之高新材料科技有限公司
Thermally conductive graphite patch for adhesive tape and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103796493BAvoid local overheatingAchieve uniformityLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsAdhesiveDimethyl siloxane
The invention discloses a heat conduction graphite paster for adhesive tape and a preparing method of the heat conduction graphite paster. The surface of the heat conduction graphite paster is coated with a heat conduction adhesive layer, the heat conduction graphite paster is composed of a polyimide film, a first coating layer and a second coating layer, and the first coating layer and the second coating layer are located on the upper surface and the lower surface of the polyimide film respectively. The first coating layer and the second coating layer respectively comprise, by weight, 20-25 parts of benzophenone tetracid dianhydride, 12-18 parts of pyromellitic acid dianhydride, 20-28 parts of diaminodiphenylmethane, 20-25 parts of dimethyl formamide, 8-10 parts of N-methyl pyrrolidone, 1.5-2.5 parts of ethylene glycol, 2-3 parts of dimethyl silicone polymer and 0.8-1.5 parts of phthalic acid dibutyl ester. According to the heat conduction graphite paster, local overheating is avoided, the evenness of the heat conduction performance is achieved, the stability and reliability of the heat dissipation performance of the heat conduction graphite paster are improved, and the cost of the heat conduction graphite paster is reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU SIDIKE NEW MATERIALS SCI & TECH CO LTD
Thermally Conductive Graphite Chips for Microelectronics
ActiveCN103763892BImprove biaxial tensile propertiesAvoid local overheatingLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsAdhesiveCarbonization
The invention discloses a heat conduction graphite patch for a microelectronic device. The heat conduction graphite patch comprises a first heat conduction adhesive layer, a graphite layer and a second heat conduction adhesive layer, the graphite layer is obtained through the following technique, and the technique comprises the following steps that the upper surface and the lower surface of a polyimide film after the first step are coated with graphite modifiers to obtain the processed polyimide film; the processed polyimide film is heated to 800 DEG C, heat preservation is carried out, and then the film is heated to 1200 DEG C to obtain a pre-burned carbonization film; a calender is adopted to calender the pre-burned carbonization film in the fourth step; the carbonization film is heated to 2400 DEG C, heat preservation is carried out, then the film is heated to 2900 DEG C, and therefore a mainly-burnt graphite film is obtained; the mainly-burnt graphite film obtained in the fifth step is calendered to obtain the graphite layer. The method avoids local overheating of adhesive tape, uniformity of heat conduction performance of the adhesive tape is achieved, the stability and reliability of heat dissipation performance of the patch are improved, and the cost of the patch is greatly reduced.
Owner:STICK NEW MATERIALS JIANGSU CO LTD
Manufacturing process of heat-dissipating fin
InactiveCN107043255AImprove biaxial tensile propertiesAvoid local overheatingDigital data processing detailsPress rollersHeat conductingPyrrolidinones
The invention discloses a manufacturing process of a heat-dissipating fin. The manufacturing process comprises the following steps of: separately coating a graphite modifier on the upper and lower surfaces of a polyimide film, wherein the treated polyimide film is composed of a polyimide film, a first coating and a second coating, and the graphite modifier is composed of the following components: benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride, benzenetetracarboxylic anhydride, diaminodiphenylmethane, dimethylformamide, N-methyl pyrrolidinone, ethylene glycol, polydimethylsiloxane and dibutyl phthalate; heating the treated polyimide film from room temperature to 1200 DEG C to obtain a pre-sintered carbonized film; and heating the carbonized film to 2850-2950 DEG C and cooling the film to obtain the sintered graphite film. The stability and reliability of the heat-dissipating property of a product are improved while the uniformity of the heat-conducting property is realized.
Owner:斯迪克新型材料(江苏)有限公司
Manufacturing method of radiating fins for notebook computers
InactiveCN107043258AImprove biaxial tensile propertiesAvoid local overheatingDigital data processing detailsPress rollersRoom temperatureGraphite
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of radiating fins for notebook computers. The radiating fins are prepared by the following steps: respectively applying a graphite modifier onto the upper and lower surfaces of a polyimide film to obtain a treated polyimide film, so that the treated polyimide film consists of a polyimide film, a first coating layer and a second coating layer; under inert-gas protection, heating the treated polyimide film from room temperature to 240DEG C-260DEG C, then heating the treated polyimide film to 480DEG C-500DEG C after heat preservation, then heating the treated polyimide film to 780DEG C-820DEG C after heat preservation, then heating the treated polyimide film to 1200DEG C after heat preservation, and cooling the treated polyimide film, thereby obtaining a pre-burnt carbonized film; and heating the carbonized film to 2350DEG C-2450DEG C, conducting heat preservation, then heating the carbonized film to 2850DEG C-2950DEG C, and cooling the carbonized film, thereby obtaining the burnt graphite film. The manufacturing method improves the crystallinity, simultaneously overcomes the nonuniformity caused by excessive thermal shrinkage, and improves the two-way tensile property of a graphite layer.
Owner:斯迪克新型材料(江苏)有限公司
High-compactness and heat dissipating double-sided adhesion film
InactiveCN106987213AImprove biaxial tensile propertiesAvoid local overheatingFilm/foil adhesivesCoatingsRoom temperatureGraphite
The present invention discloses a high-compactness and heat dissipating double-sided adhesion film, wherein a release material layer is adhered on a heat conduction adhesion layer surface opposite to a graphite layer, and the graphite layer preparation method comprises: uniformly coating the upper surface and the lower surface of a polyimide film with a layer of a graphite modifier to obtain a treated polyimide film, wherein the viscosity of the graphite modifier is 30000-48000 CP; heating the treated polyimide film to a temperature of 1180-1250 DEG C from a room temperature, and cooling to obtain a pre-fired carbonized film; calendering the pre-fired carbonized film with a calendering machine; heating to a temperature of 2850-2950 DEG C to obtain a mainly-fired graphite film; and calendering the obtained mainly-fired graphite film to obtain the graphite layer. According to the present invention, the volume shrinkage during the wrinkling and graphitization sintering process is avoided, the compactness and the crystallinity are increased, and the heat conduction performances in the vertical direction and the horizontal direction are further improved.
Owner:JIANGSU SIDIKE NEW MATERIALS SCI & TECH CO LTD
Production method of high-density radiating fins
InactiveCN107573072AImprove biaxial tensile propertiesAvoid local overheatingDigital data processing detailsPress rollersPyromellitic dianhydrideDimethyl siloxane
The invention provides a production method of high-density radiating fins. The production method comprises the following steps: applying a graphite modifier to an upper surface and a lower surface ofa polyimide film, wherein the treated polyimide film is composed of a polyimide film, a first coating layer and a second coating layer, and the graphite modifier comprises the following components inparts by weight: benzophenone tetracarboxylic dianhydride, pyromellitic dianhydride, diaminodiphenylmethane, dimethylformamide, N-methylpyrrolidone, ethylene glycol, polydimethylsiloxane and dibutyl phthalate; heating up the treated polyimide film from a room temperature to 1200 DEG C to obtain a pre-fired carbonized film; heating up the carbonized film to 2850-2950 DEG C, and then cooling to obtain a primarily fired graphite film. The production method provided by the invention realizes uniformity of thermal conductivity and also improves heat dissipation performance of products.
Owner:TAICANG SIDIKE NEW MATERIALS SCI & TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com