Method for separating rare earth, iron, copper, cobalt and tungsten from alloy
A technology of alloys and rare earths, which is applied in the field of waste metal recycling, can solve problems such as pollution, operator influence, and high power consumption, and achieve the effects of simple process flow, low equipment requirements, and high recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
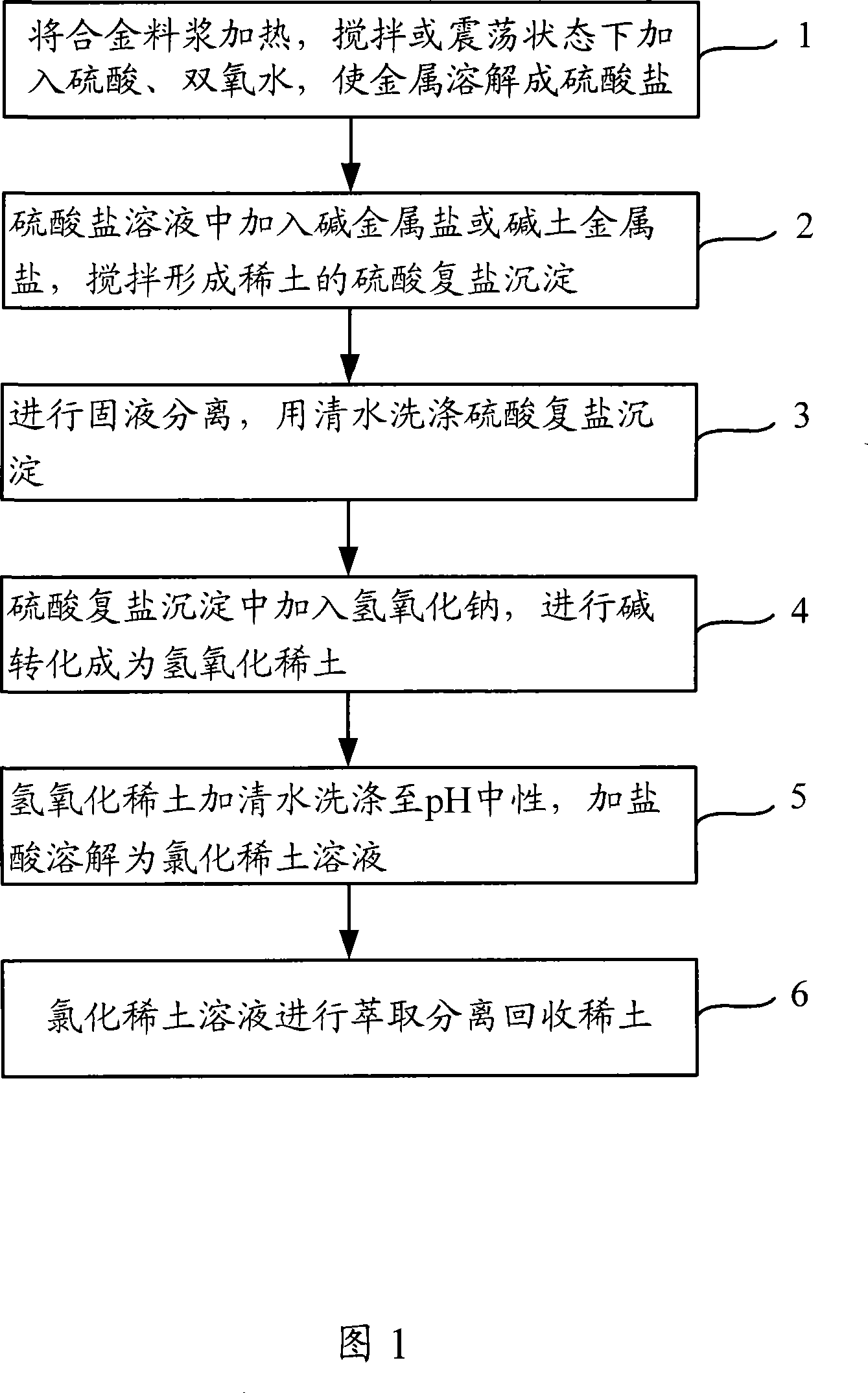
[0086] 1 kg of NdFeB waste is separated and recycled. The main components of the waste metal are neodymium Nd and iron Fe, and contain a small amount of Co. The specific process of its treatment is as follows: after crushing the waste, put it in a container, add 500ml of water and stir, slowly add 6mol / L [H + ] 7L of sulfuric acid, 1Kg of 30wt% hydrogen peroxide, heated to 80°C to dissolve, and filtered to separate the solid and liquid. At this time, the solution contained RE ions, Fe ions and Co ions, heated the solution to 90°C, and added NaCl700g to generate a rare earth sulfate double salt precipitation. Add 4Kg of 30wt% liquid caustic soda to the filtered and washed precipitate, heat to 110°C for 4 hours, filter and wash, and dissolve in hydrochloric acid to obtain a rare earth chloride solution. The sulfate solution containing iron and cobalt is added with sodium carbonate to adjust the pH to 3 and precipitate to obtain ferric hydroxide to realize the separation and rec...
Embodiment 2
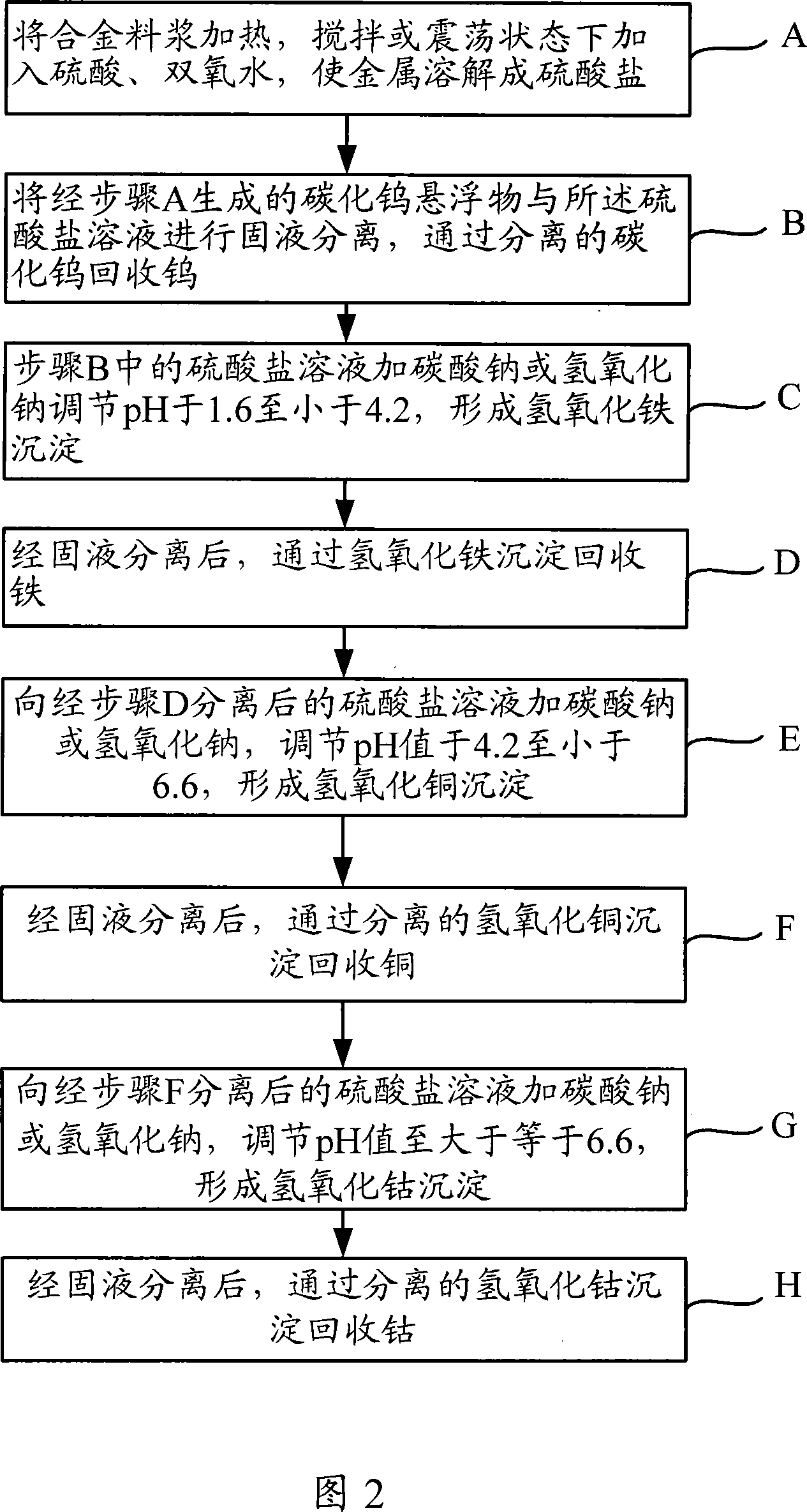
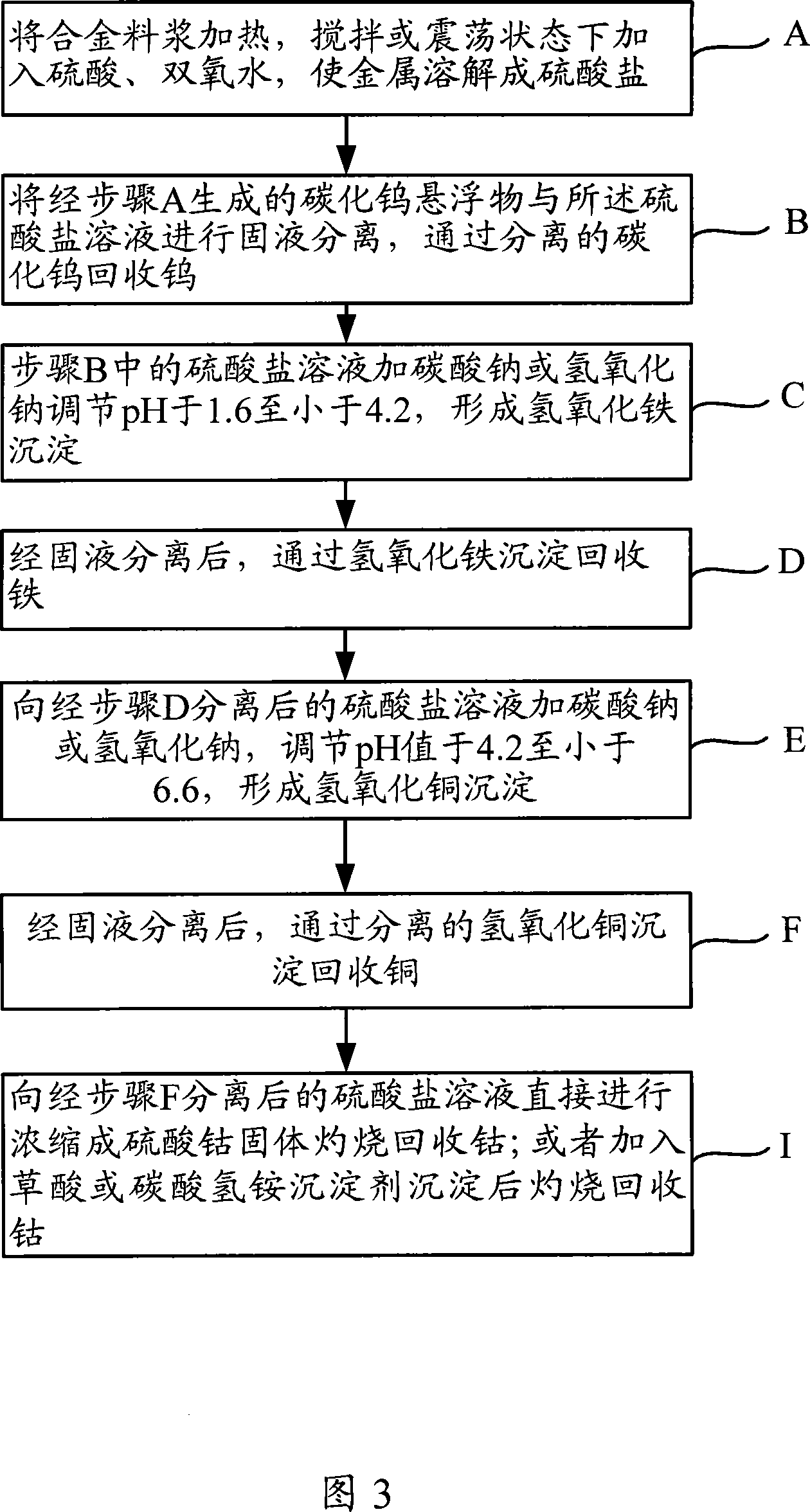
[0088] 1 kg of cemented carbide waste is separated and recycled. The main components of the cemented carbide waste are tungsten W, iron Fe, and cobalt Co. The specific process of its treatment is: after crushing the waste, put it in a container, slowly add 4L of 20wt% sulfuric acid, 500ml of 30wt% hydrogen peroxide, plug the container tightly, place it on a shaker and shake it at room temperature for 30 hours, and the tungsten carbide is suspended in the In the solution, tungsten can be recovered and utilized after centrifugal separation, washing and drying. The solution part is the sulfate of iron and cobalt. Sodium carbonate is added to adjust the pH to 2, and ferric hydroxide is precipitated, and iron is recovered through ferric hydroxide. Cobalt sulfate is precipitated and burned with oxalic acid to obtain cobalt oxide, and cobalt is recovered through cobalt oxide.
Embodiment 3
[0090] 1 kg of alloy waste from a cobalt salt factory, the main components are iron Fe, cobalt Co and copper Cu. After the alloy waste is broken, put it in an enamel reaction kettle, add water and stir, slowly add 6mol / L sulfuric acid, 30wt% hydrogen peroxide, keep the temperature at 90-95°C, and the reaction time is 12 hours. The concentration of the main chemical components in the leachate is For: Co45g / L, Cu20g / L, Fe30g / L. Heating the leaching solution to 85°C, adding 20wt% sodium carbonate solution for neutralization, controlling the pH value in the range of 3.2-3.4, when the Fe in the feed solution is less than 0.5g / L, filter and wash the iron hydroxide precipitate, and remove it from hydrogen Iron recovery from iron oxide precipitation. After removing iron, heat the feed liquid to 80°C, add 20wt% sodium carbonate solution, adjust the pH value of the feed liquid to 4.2-4.4, form and precipitate copper hydroxide, and the feed liquid is mainly cobalt, which can be used to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com