Bacillus subtilis HL-1 and application thereof in respect of soil phosphate dissolving
A technology of Bacillus subtilis and inoculum, applied in the application, soil conditioning materials, bacteria and other directions, can solve the problems of less than 20% utilization rate in the current season, waste of resources, etc., and achieves the advantages of promoting recycling, saving resources and simple preparation process. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1 Isolation, purification and identification of Bacillus subtilis HL-1
[0037] (1) Separation
[0038] Prepare insoluble inorganic phosphorus medium: glucose 10.0g, ammonium sulfate 0.5g, sodium chloride 0.3g, potassium chloride 0.3g, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.03g, manganese sulfate tetrahydrate 0.03g, yeast extract 0.4g, phosphoric acid Calcium 5g, distilled water 1L, pH value 7.0~7.5.
[0039] Take the soil collected on Huolu Mountain, Tianhe District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province as the screening soil sample, accurately weigh 10.0g of the soil sample to be tested by the flat plate coating method, and put it into a 250mL triangular flask filled with 90mL sterile water (with glass beads) , shake the shaker for 30 minutes to fully disperse the microorganisms, let it stand for 20~30s, and take the supernatant for 10-fold decreasing dilution, using 10 3 ~10 5 Dilution: Use a pipette gun to pipette 0.1mL of the dilution respectively, spread it on the i...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2 Characterization
[0044] (1) Morphological characteristics of bacteria
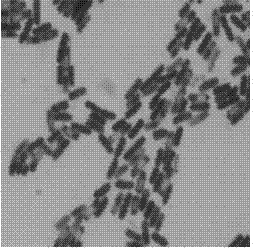
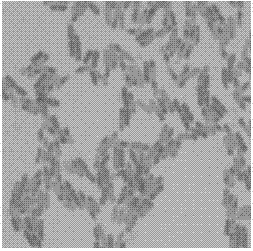
[0045] Gram-positive bacteria with spores that do not expand after spore formation. The bacteria are rod-shaped, non-capsulated, motile, and aerobic. Gram staining effect see figure 1 , the cells were stained blue-purple, and the spores were not colored. Spore staining effect see figure 2 , the thallus is yellow-brown, and the spores are light blue.
[0046] (2) Colony Morphological Characteristics
[0047] The colonies formed on the nutrient agar medium were round, yellowish, rough and opaque, with irregular edges.
[0048] (3) Physiological and biochemical characteristics
[0049] According to the Biolog microbial identification instrument, the utilization of 31 different carbon sources by this strain under aerobic conditions was analyzed, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0050] Features result Features result water + Methyl D-glucoside + ...
Embodiment 3
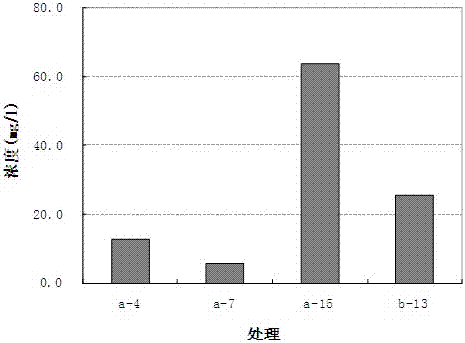
[0054] Growth characteristics of embodiment 3 HL-1 bacteria under different carbon source environments
[0055] Beef extract peptone medium: 5g beef extract, 5g peptone, 5g sodium chloride, 1000ml water, pH 7.1~7.4.
[0056] Corn flour, wheat bran, glucose, peanut bran, sucrose, rice bran and plant starch were used as carbon sources, respectively, with a concentration of 20 g / L, to replace beef extract in the beef extract-peptone medium, and other components remained unchanged. Boil the above seven kinds of medium for 10 minutes, cool down to room temperature naturally, adjust the pH value to 7.1~7.5 with 1mol / L NaOH or HCl, and prepare the fermentation medium. In 250mL Erlenmeyer flasks, 45mL of each group's culture medium was dispensed, sterilized, and each group's culture medium was repeated three times. According to the inoculation amount of 10%, HL-1 bacteria were inoculated into the above-mentioned sterilized fermentation medium, cultured at a temperature of 33°C and a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com