Borate silicate aluminate glass bead, and preparation method thereof
A borosilicate aluminate and glass microsphere technology, applied in glass manufacturing equipment, glass molding, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problem of low compressive strength of hollow glass microspheres, unstable product quality, uneven bubble size, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of high uniformity of compressive strength, high yield and short melting time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Embodiment 1 A kind of preparation method of borosilicate glass microsphere
[0056] Include the following steps:
[0057] (1) Weigh raw materials
[0058] Weigh 2.6Kg of white carbon black, 0.9Kg of boric acid, 2Kg of calcium carbonate, 1.6Kg of sodium nitrate, 2.5Kg of aluminum nitrate, and 0.4kg of magnesium nitrate.
[0059] (2) Melting
[0060]Put the mixed raw materials into a glass melting furnace and melt at 900°C for 30 minutes.
[0061] (3) Water quenching
[0062] Then the molten glass is quenched with water.
[0063] (4) wet grinding
[0064] Pass the water-quenched cullet and water through a sand mill and ball mill to grind to 5-80 microns, D50=35-40 microns.
[0065] (5) spray drying
[0066] The precursor glass powder was obtained by spray drying.
[0067] (6) Pressure treatment
[0068] The dried precursor glass powder was first treated at 0.5MPa for 30 minutes, then increased to 1MPa for 5 minutes, and then reduced to -0.1Mpa at a speed of 0.1M...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Embodiment 2 A kind of preparation method of alumino-borosilicate glass beads
[0078] Include the following steps:
[0079] (1) Weigh raw materials
[0080] Weigh 2.7 Kg of white carbon black, 0.9 Kg of boric acid, 2 Kg of calcium nitrate, 1.8 Kg of sodium nitrate, 0.2 Kg of magnesium nitrate, 2.8 kg of aluminum nitrate, and 0.1 Kg of aluminum silicate.
[0081] (2) Melting
[0082] Put the mixed raw materials into a glass melting furnace and melt at 1000°C for 30 minutes.
[0083] (3) Water quenching
[0084] Then the molten glass is quenched with water.
[0085] (4) wet grinding
[0086] Pass the water-quenched cullet and water through a sand mill and ball mill to grind to 5-80 microns, D50=35-40 microns.
[0087] (5) spray drying
[0088] Afterwards, the precursor glass powder is obtained by spray drying.
[0089] (6) Pressure treatment
[0090] The dried precursor glass powder was first treated at 0.5MPa for 30 minutes, then increased to 1MPa for 5 minutes...
Embodiment 3
[0100] Embodiment 3 Raw material ratio optimization experiment
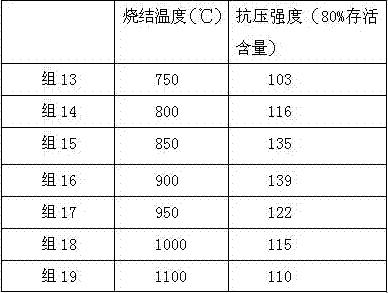
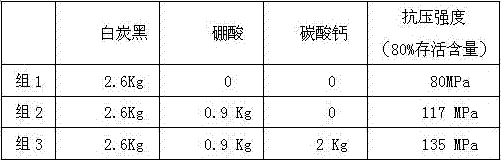
[0101] On the basis of Example 1, only the mass ratio of white carbon black, boric acid, and calcium carbonate was changed to prepare glass microspheres, and the compressive strength (80% survival content) was measured. See Table 1 for details.
[0102]
[0103] Boric acid and calcium carbonate are added to the raw materials to prepare and sinter to obtain boron oxide and calcium oxide respectively; the raw material white carbon black finally obtains silicon dioxide. It can be seen from Table 1 that boron oxide, calcium oxide and silicon dioxide can play a synergistic effect. Together increase the compressive strength of glass beads.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| D50 | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com