System and process for fluorine-circulation magnesium removal of sulfate solution
The technology of zinc sulfate solution and sulfate is applied in the field of sulfate solution fluorine cycle demagnesization process and system, which can solve the problems of intractability, high zinc content in magnesium sulfate crystals, and inability to use, so as to reduce processing costs and facilitate batch production. , the effect of eliminating environmental risks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
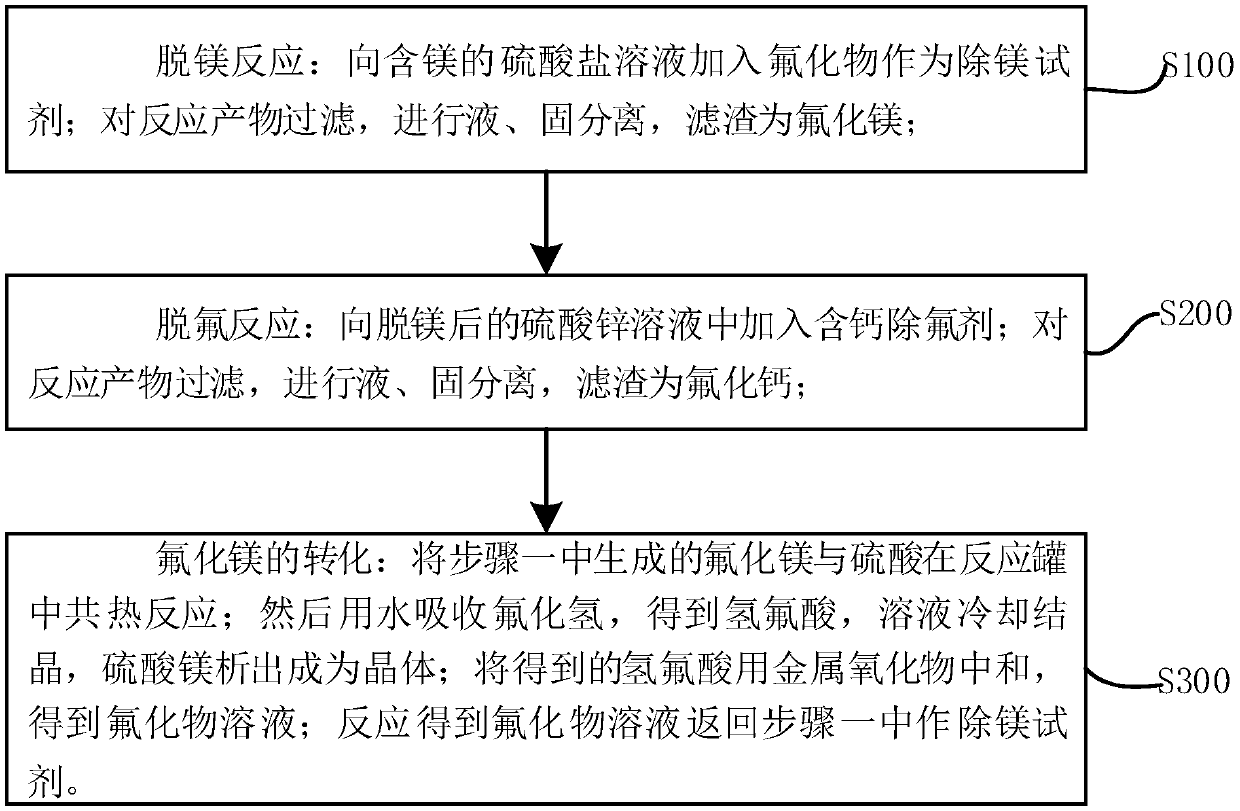
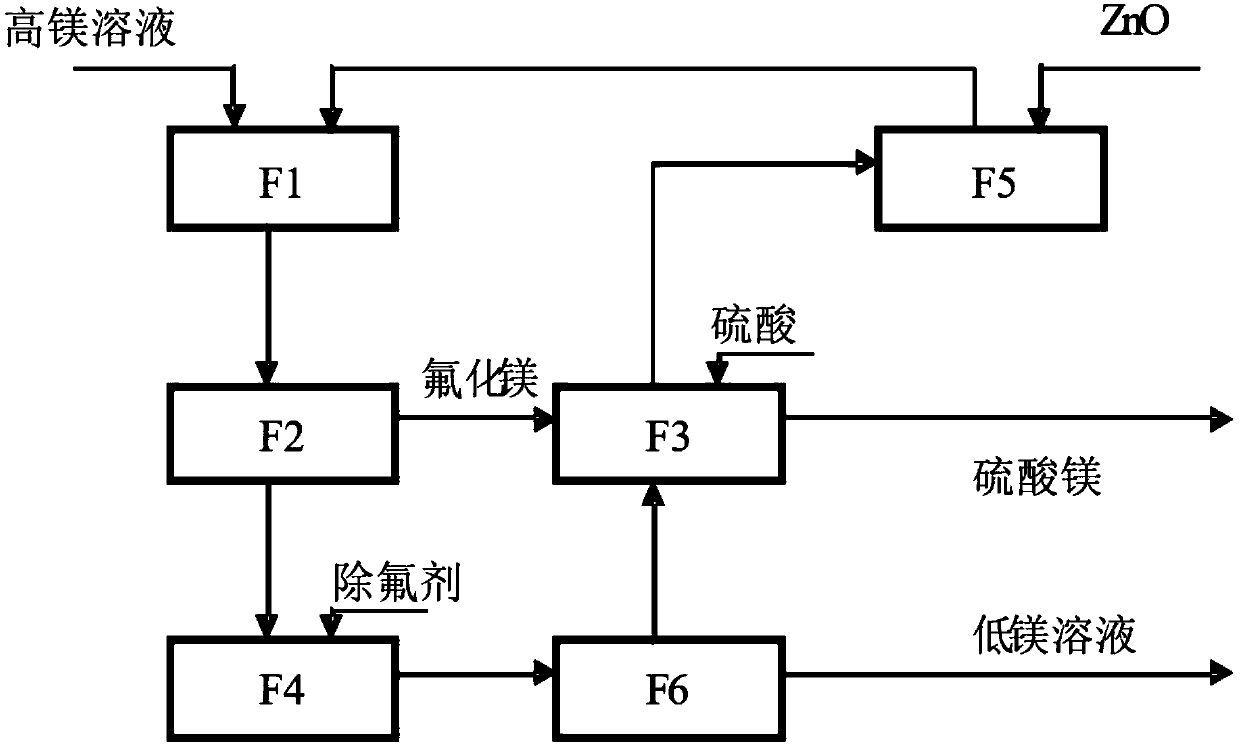
[0043] The present invention relates to the removal process of magnesium ion in a set of complete sulfate (especially zinc sulfate, manganese sulfate) solution, its flow process sees figure 1 , is an independent fluorine circulation process for removing magnesium, which makes magnesium be removed by crystallization of magnesium sulfate. Its technical scheme is as follows, including three processes:
[0044]①The first process of the process is magnesium removal: at 20°C, the solubility of zinc fluoride is 1.6g / 100ml, the solubility of zinc sulfate is 53.8g / 100ml; the solubility of manganese fluoride is 10.6g / 100ml, the solubility of manganese sulfate It is 62.9g / 100ml, while at normal temperature, the solubility of magnesium sulfate is 33.7g / 100ml, and the solubility product of magnesium fluoride is very small, only 6.4×10 -9 , taking advantage of these properties, the addition of zinc fluoride to a magnesium-containing zinc sulfate solution produces the following reaction:
...
Embodiment 2
[0062] The present invention relates to the removal process of magnesium ion in a set of complete sulfate (especially zinc sulfate, manganese sulfate) solution, its flow process sees figure 1 , is an independent fluorine circulation process for removing magnesium, which makes magnesium be removed by crystallization of magnesium sulfate. Its technical scheme is as follows, including three processes:
[0063] ①The first process of the process is magnesium removal:
[0064] The addition of manganese fluoride to a magnesium-containing manganese sulfate solution produces the following reaction:
[0065] Mg 2+ +SO 4 2- +Mn 2+ +2F - =Mn 2+ +SO 4 2- +MgF 2 ↓
[0066] The process determines the reaction conditions: temperature 50 ° C, stirring speed 40 rpm, time 45 minutes;
[0067] Filter the reaction product with a filter for liquid and solid separation, the filter residue is magnesium fluoride, the solution Mg 2+ Reduced to <1g / l, realizing the removal of magnesium in th...
Embodiment 3
[0081] The present invention relates to a set of complete sulfate (especially zinc sulfate, manganese sulfate) solution magnesium ion removal process, its flow process see figure 1 , is an independent fluorine circulation process for removing magnesium, which makes magnesium be removed by crystallization of magnesium sulfate. Its technical scheme is as follows, including three processes:
[0082] 1. The first step of the process is magnesium removal: adding sodium fluoride to magnesium-containing sodium sulfate solution will produce a reaction:
[0083] Mg 2+ +SO 4 2- +2Na + +2F - = 2Na + +SO 4 2- +MgF 2 ↓
[0084] The process determines the reaction conditions: the temperature is 80°C, the stirring speed is 90 rpm, and the time is 90 minutes;
[0085] Filter the reaction product with a filter for liquid and solid separation, the filter residue is magnesium fluoride, the solution Mg 2+ Reduced to <1g / l, realizing the removal of magnesium in the solution;
[0086] ②...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com