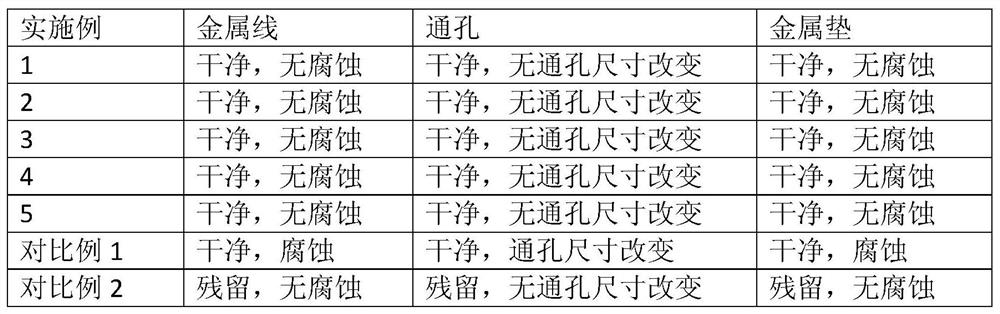
The above-mentioned residues after etching usually contain highly insoluble metal residues, which are difficult to remove by common chemical stripping solvents. At the same time, during the
ashing process, the above-mentioned metal residues will be further oxidized, making it more difficult to remove. Therefore, a stripping solution is required. The stripping solution can remove the residues generated on various substrates during the etching process, and the stripping solution cannot corrode these substrate materials such as aluminum and
copper, aluminum and
copper /
silicon / copper,
titanium,
titanium nitride,
titanium /
tungsten,
Tungsten,
silicon oxide, polysilicon, etc., the stripper can also remove unashed photoresist residues;
[0004] At present, typical Al-based stripping solutions mainly include the following types:
hydroxylamine-based stripping solutions,
fluorine-based stripping solutions, semi-aqueous amine-based stripping solutions (without
hydroxylamine) and water-based cleaning agents, EKC265, EKC270 and EKC270T, ACT915, ACT927, ACT930, and ACT940 are typical
hydroxylamine-based stripping solutions, and are currently the most commonly used Al-based back-end stripping solutions. The composition of hydroxylamine-based stripping solutions mainly includes organic amines, hydroxylamine, water, corrosion inhibitors and stabilizers. The typical patents corresponding to hydroxylamine stripping fluid include US5279771, US5911835, US6187730, US5988186, US5419779, EP0656405A2, US6951710, etc. The
advantage of hydroxylamine stripping fluid is that it can effectively remove various insoluble inorganic residues and organic residues, but the
operating temperature of hydroxylamine cleaning agents is usually at 65 o Above C, and hydroxylamine is very unstable, and there is a danger of explosion at a higher
operating temperature. At the same time, a higher
operating temperature will cause rapid
decomposition of the
system composition and volatilization of water, making the bath life of the hydroxylamine stripping solution (life time) is usually only about 1000 minutes, and continuous replenishment is required to maintain the life of the bath. In addition, after the
wafer is treated with hydroxylamine stripping solution, IPA or NMP
organic solvent is required as an intermediate rinse, and then rinsed with deionized water to avoid damage to the
crystal. The metal on the surface of the element causes corrosion, which also increases the cost of wafer manufacturing;
[0005] Typical
fluorine-containing stripping solutions mainly include ELM C30, ACT@NE series, EKC6800 series, and ideal clean960 (SP), etc. The composition of
fluorine-containing stripping solutions mainly includes
fluoride, organic stripping
solvent, water, and metal corrosion inhibitors And buffer solutions, etc. Typical patents for fluorine-containing stripping solutions include US5279771, US5630904, WO2012171324, US20020037820, US2003022800A, US20130237469A, US2003148910A1, etc. Currently, fluorine-containing stripping solutions still cannot control the corrosion of substrate materials well. Even after cleaning, it is easy to change the characteristic size of the channel. On the other hand, the fluorine-containing stripping liquid is not compatible with the
quartz substrate. The higher the operating temperature, the more serious the corrosion of the
quartz substrate. However, the current
wet cleaning of some
semiconductor companies The equipment is made of
quartz, which limits the widespread use of fluorine-containing stripping fluids;
[0006]
Hydroxylamine-based strippers and fluorine-based strippers are the two most commonly used strippers for Al-based post-cleaning. In addition, there are semi-aqueous amine-based cleaners (without hydroxylamine) and water-based strippers. Typical semi-aqueous amine stripping solutions include ALEG310, ALEG380, ST26S and ACT970, etc. Typical patents for semi-aqueous amine stripping solutions include US2003130146, WO2006023061A, etc. The composition mainly includes organic amines, organic stripping solvents, water and metal corrosion Inhibitors, etc., semi-aqueous amine cleaning agents have a wide
operating temperature range, usually at 50-90 o C Compared with hydroxylamine cleaning agents, these cleaning agents are less effective in removing inorganic metal residues, especially titanium-rich metal residues, and are currently not widely used;
[0007] Low-temperature,
environmentally friendly, water-based strippers that can be directly washed with water are the future development direction of
semiconductor strippers. Although patents US6585825, US2006293208 and US2006016785 report water-based formulations for removing photoresists and photoresist residues after etching, there are obviously problems that cannot It can control the corrosion of metal and non-metal substrates well at the same time, and it is easy to cause the change of channel feature size and weak cleaning ability after cleaning
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More