Patents
Literature
67 results about "Machine condition monitoring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
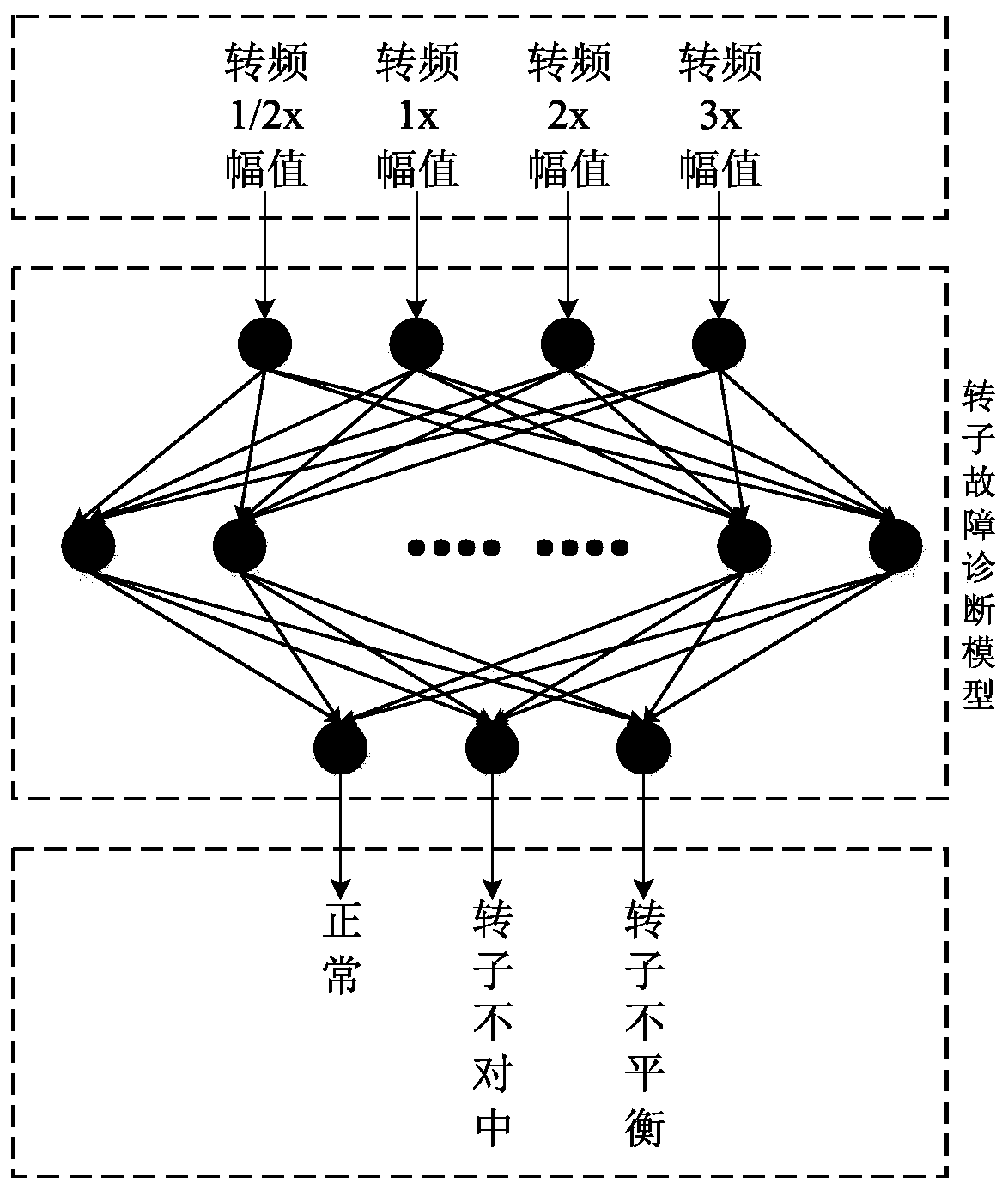
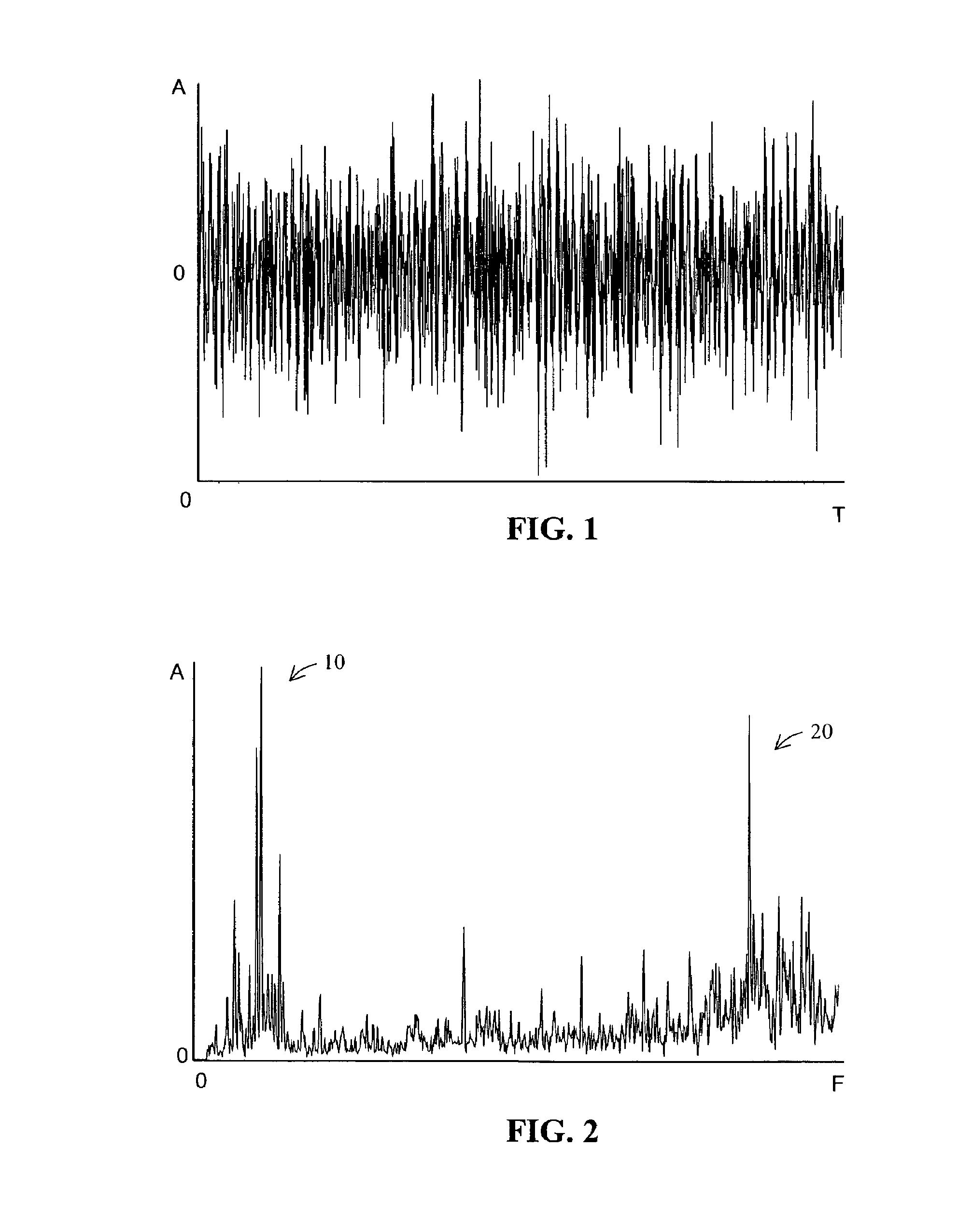
Machine condition monitoring is the process of monitoring the condition of a machine with the intent to predict mechanical wear and failure. Vibration, noise, and temperature measurements are often used as key indicators of the state of the machine.
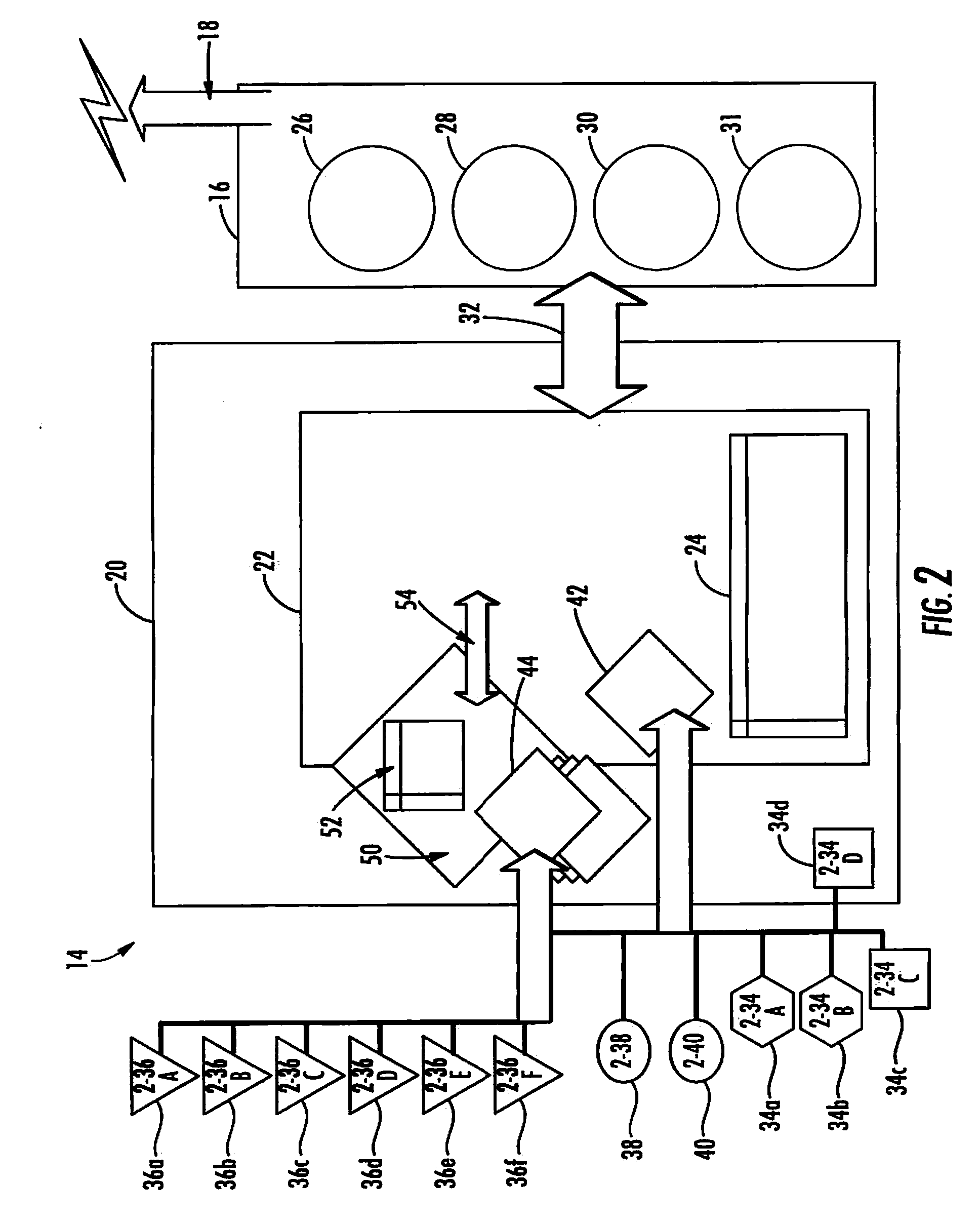
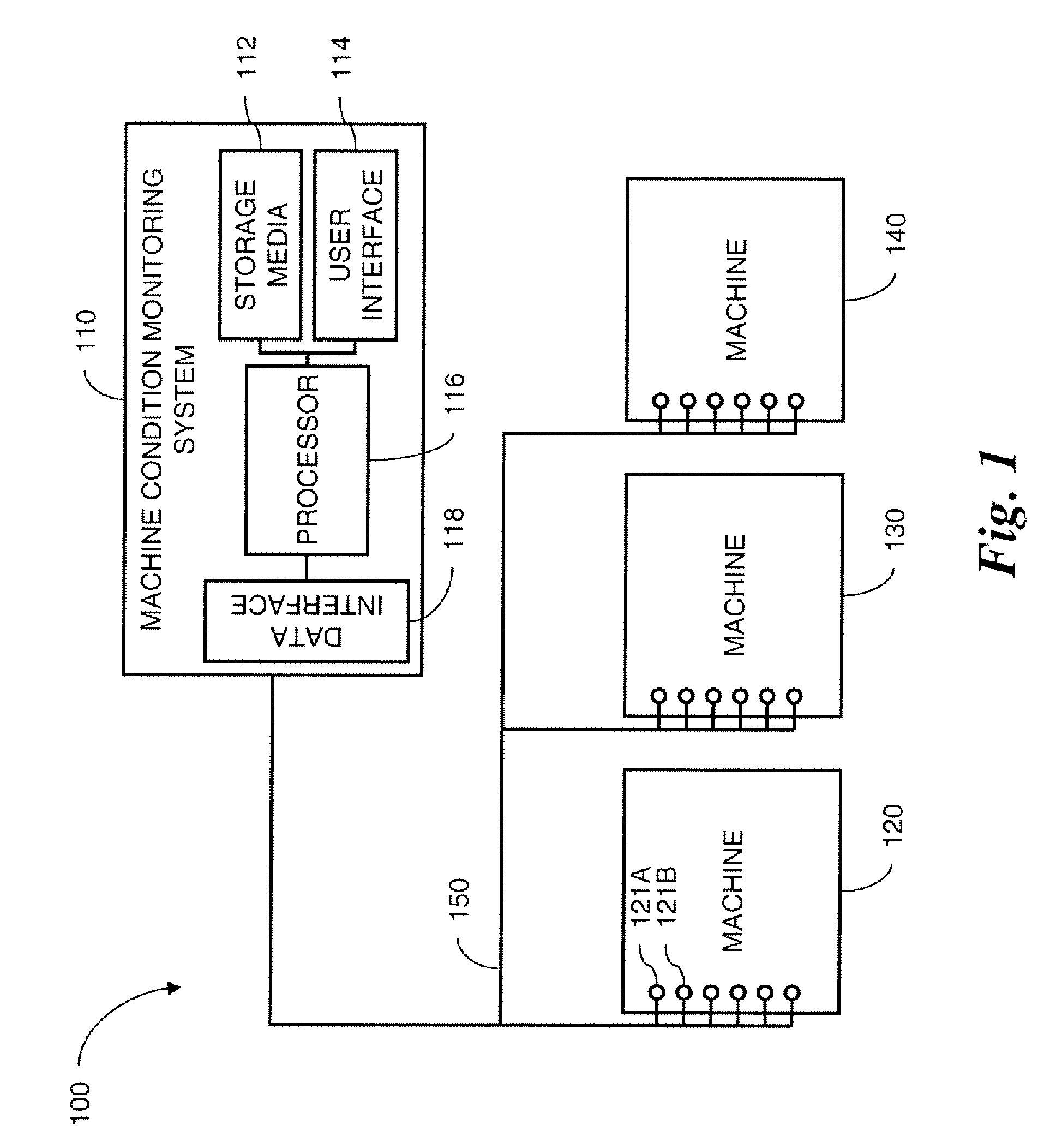
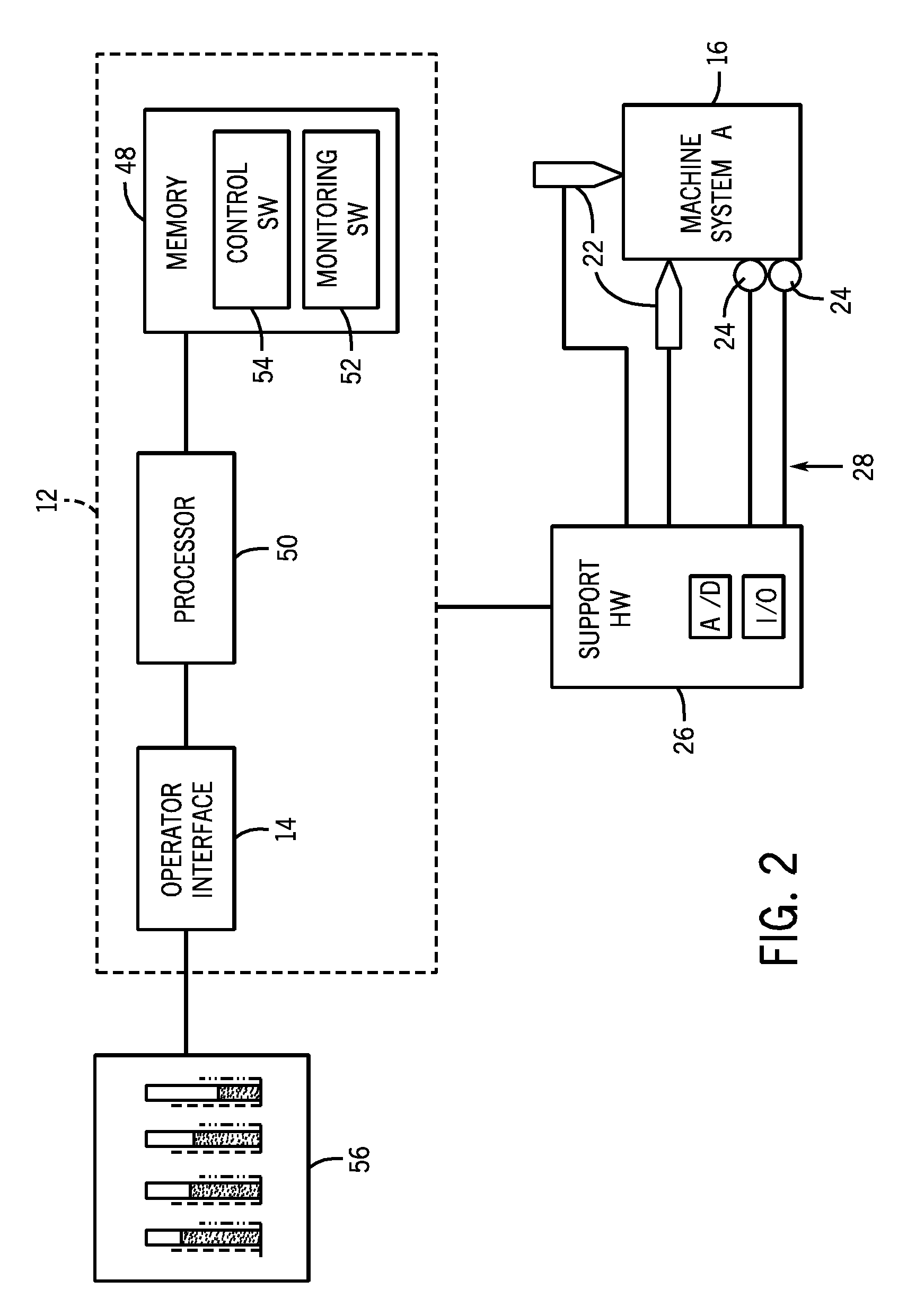
Machine condition measurement system with haptic feedback
ActiveUS20170004697A1Input/output for user-computer interactionTactile signalling systemsEngineeringAnkle
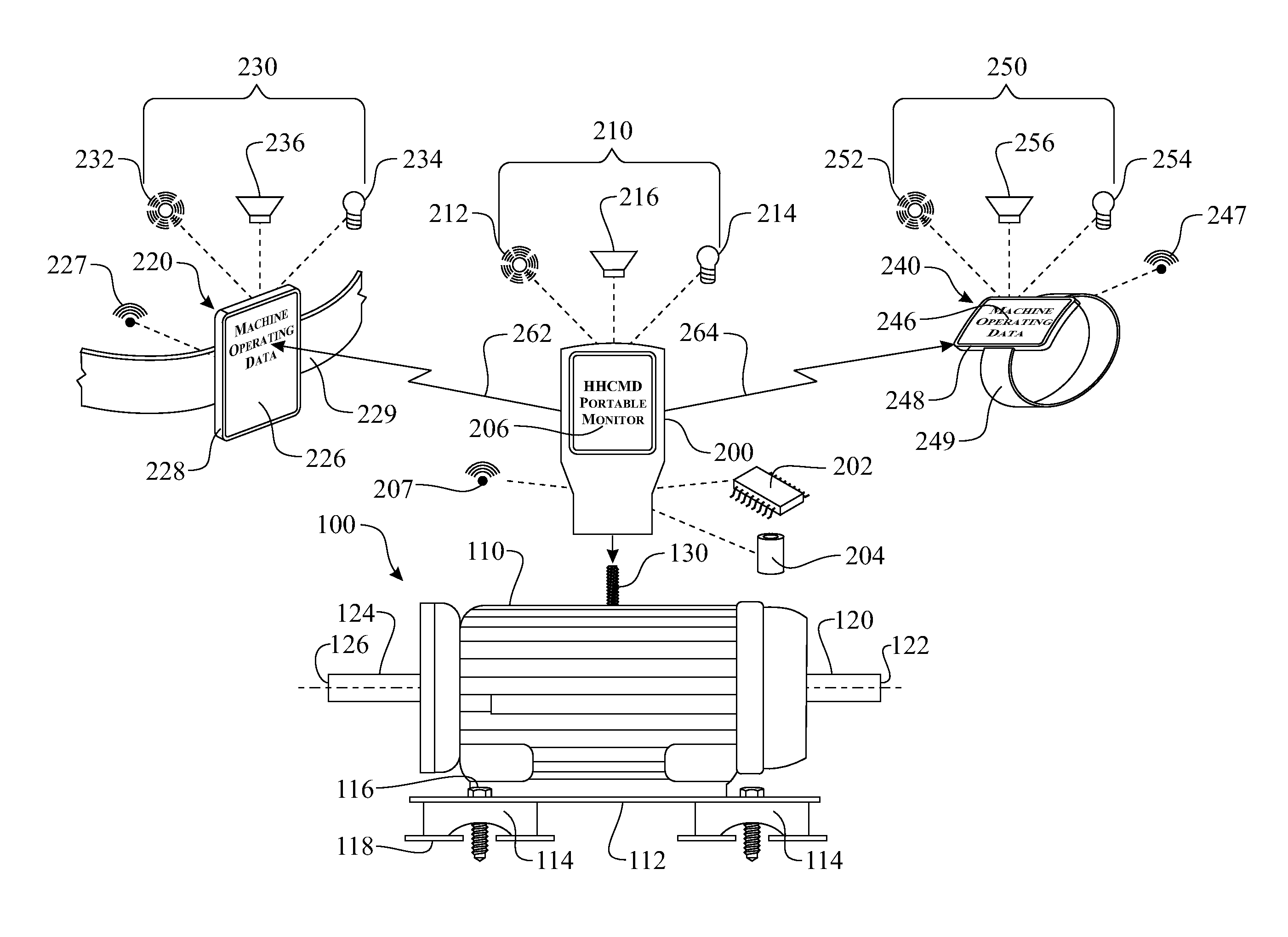
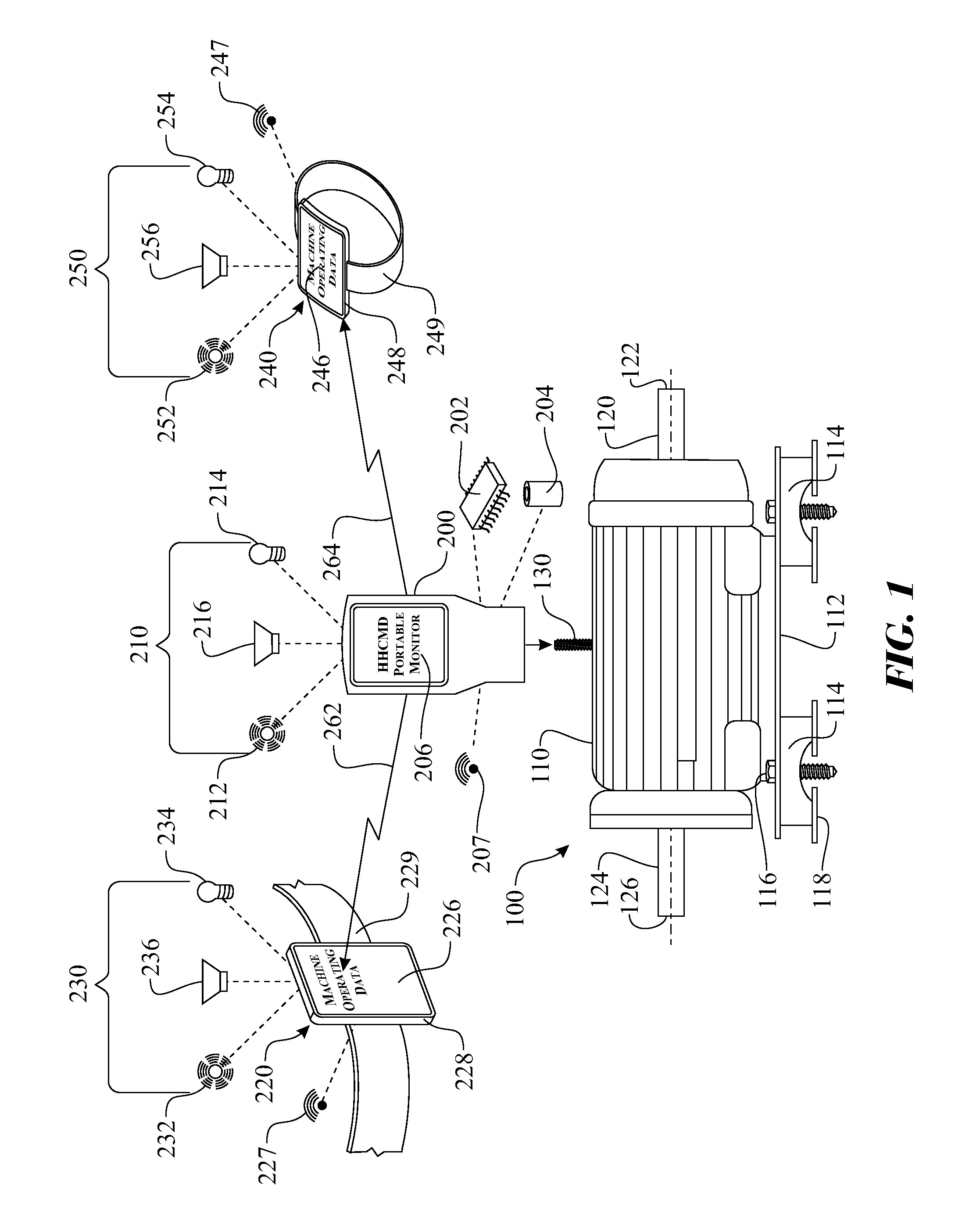
A machine condition monitoring system employing a haptic feedback device. The haptic feedback device can be employed to notify an operator of an acquisition of a machine parameter measurement. The haptic feedback device can be integrated into a control unit of a condition monitoring device and / or a remote condition monitoring status receiving device. The haptic feedback device containing notification apparatus can be worn by the operator, thus providing immediate notification without requiring the Operator's undivided attention. The notification apparatus can be worn on the operator's waist, wrist, upper arm, ankle, neck, etc. The notification apparatus can also be stored within a pocket of a garment worn by the operator.
Owner:AB SKF
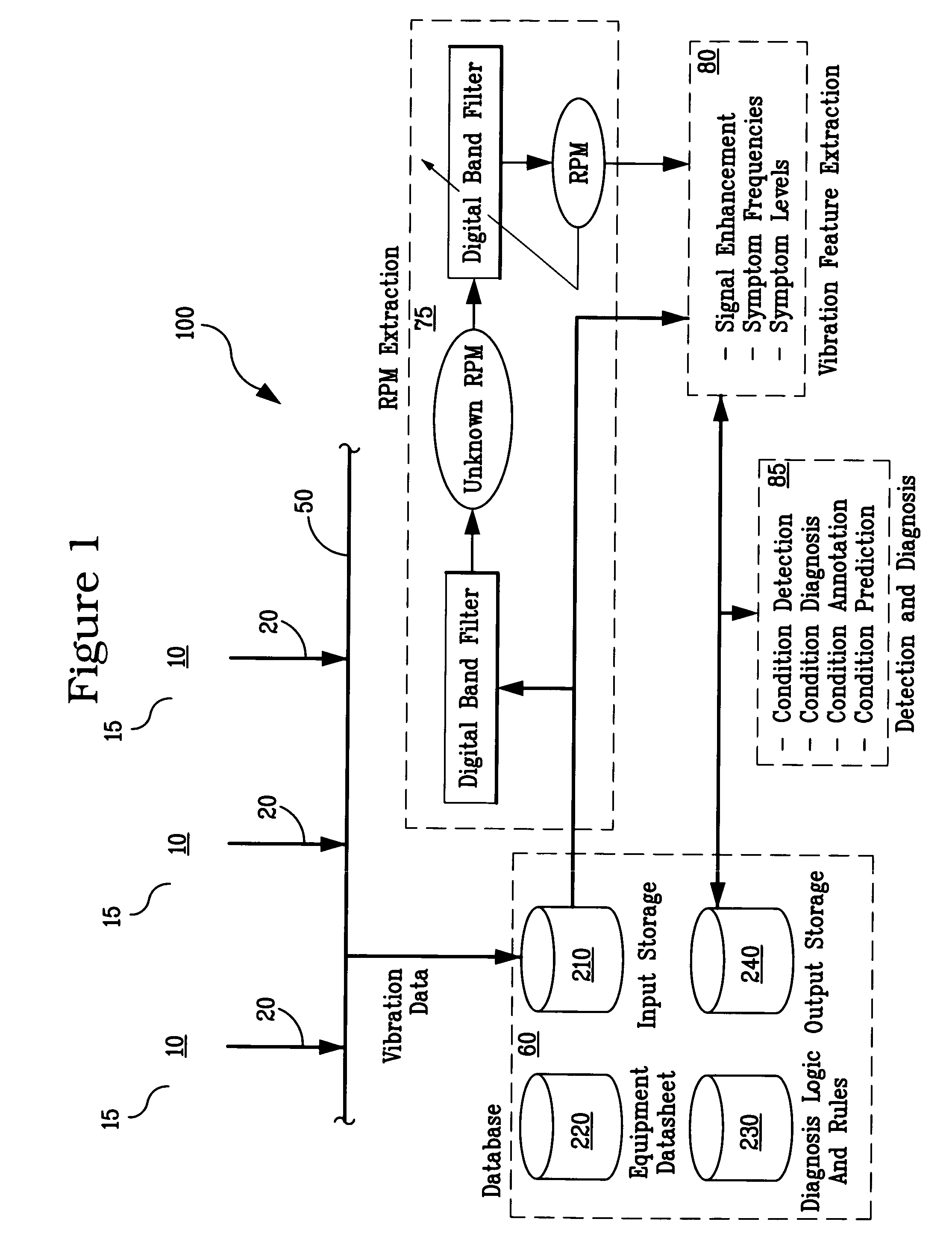
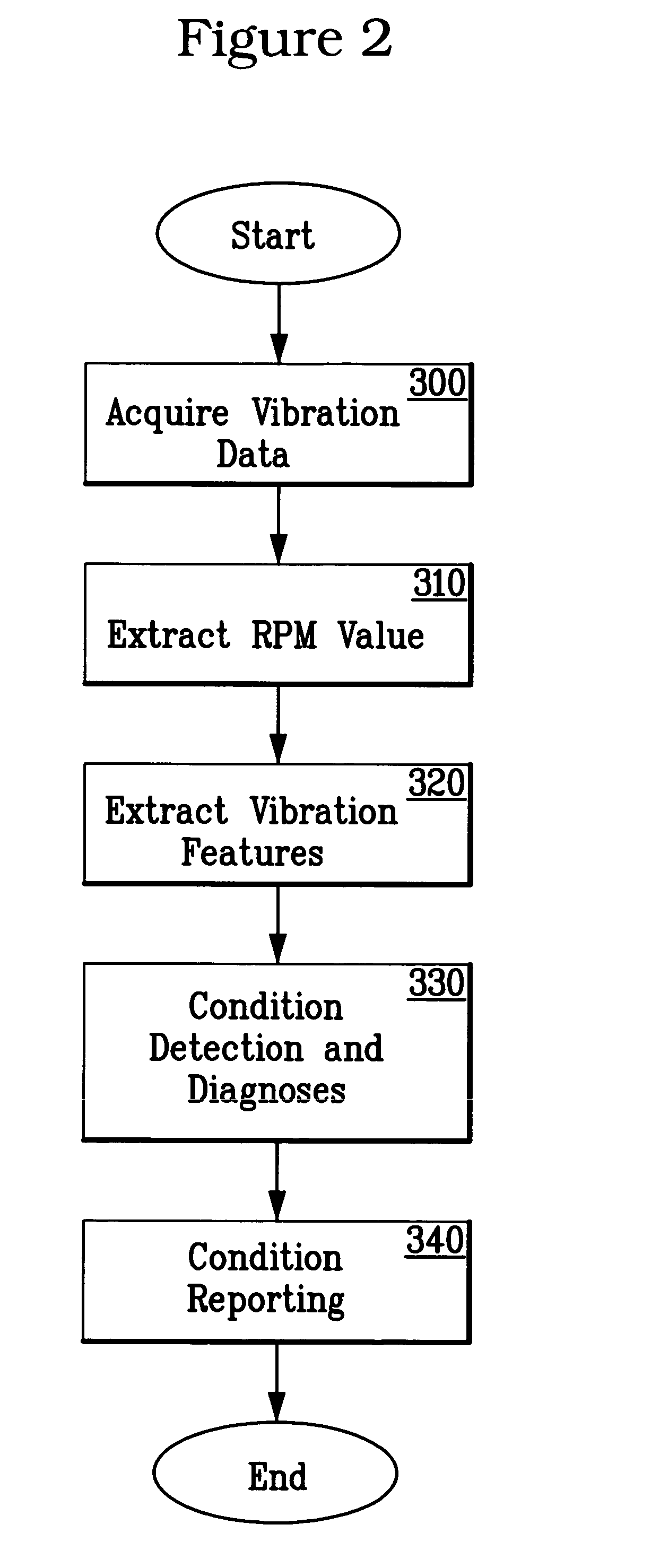
System and methodology for vibration analysis and condition monitoring
InactiveUS7133801B2Accurate speedImplemented quickly and inexpensivelyDigital computer detailsDevices using electric/magnetic meansTransducerSample sequence
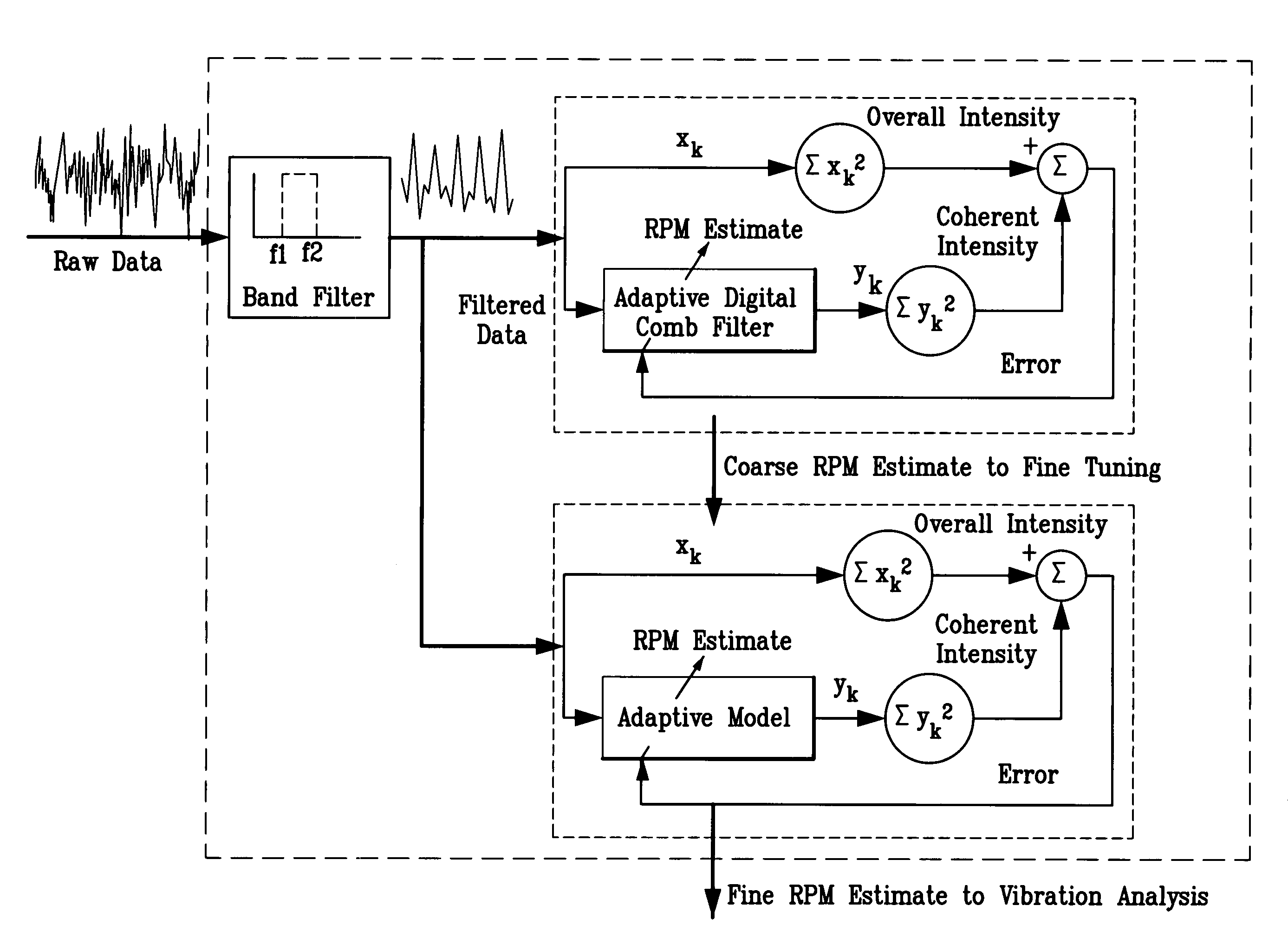
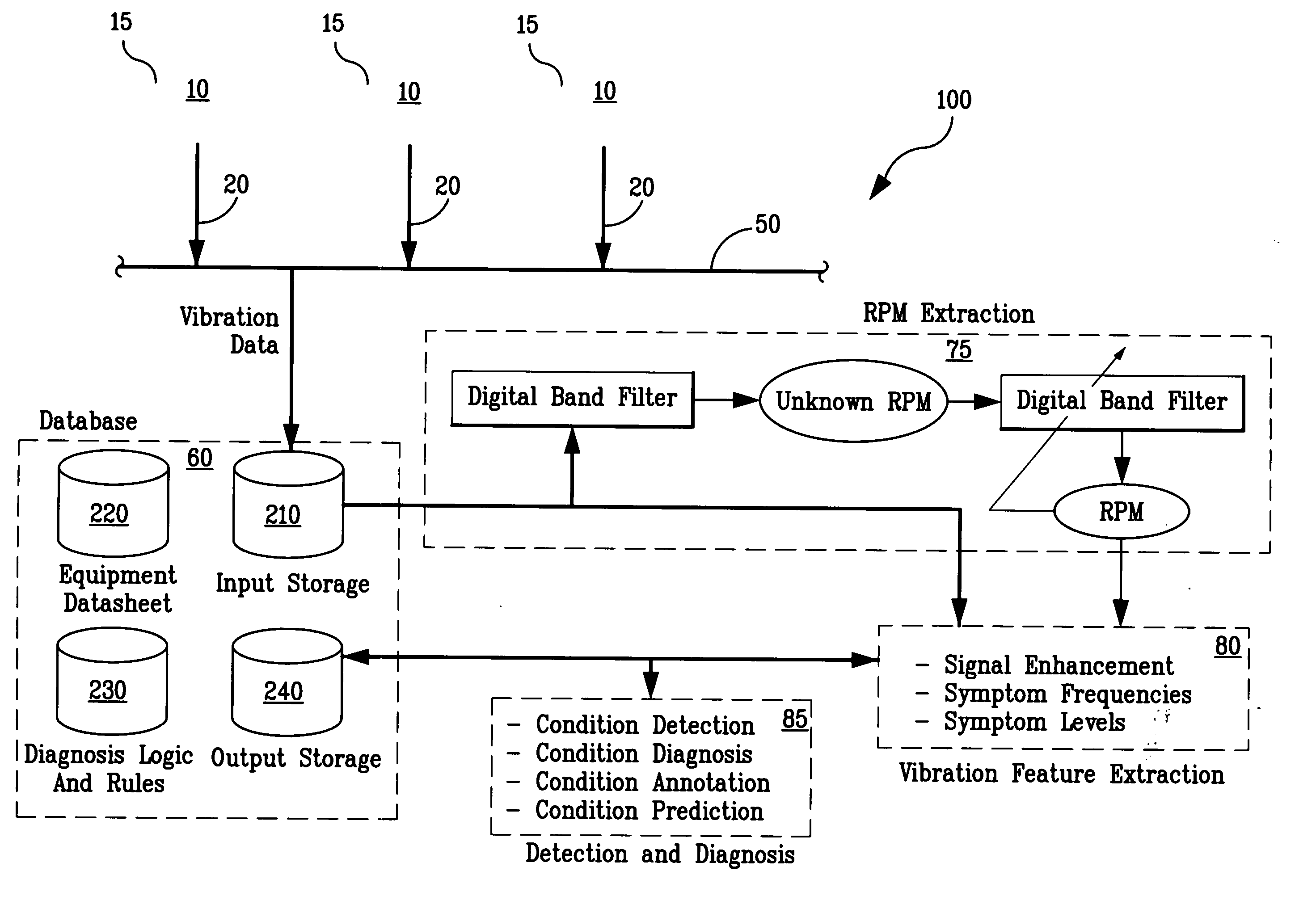
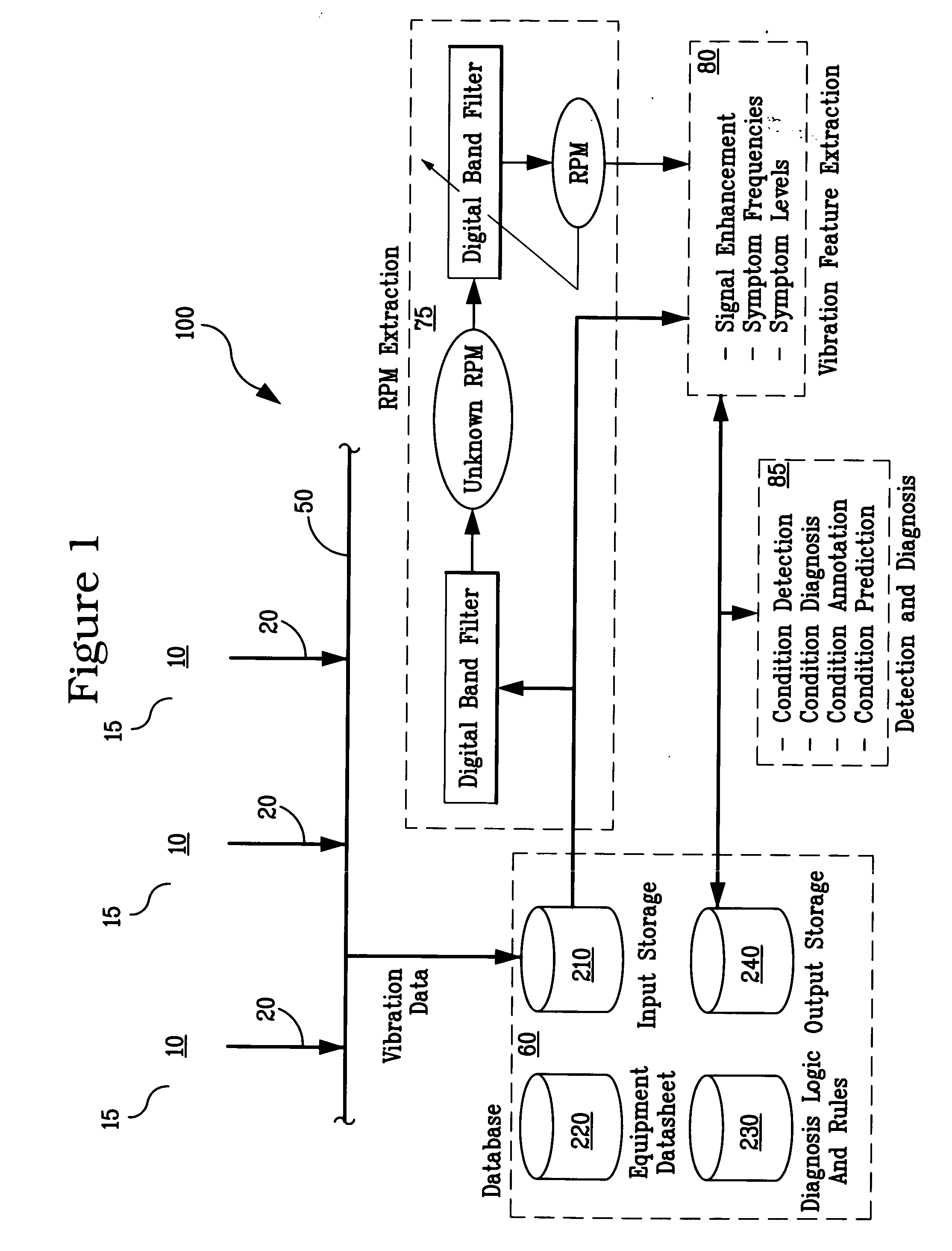
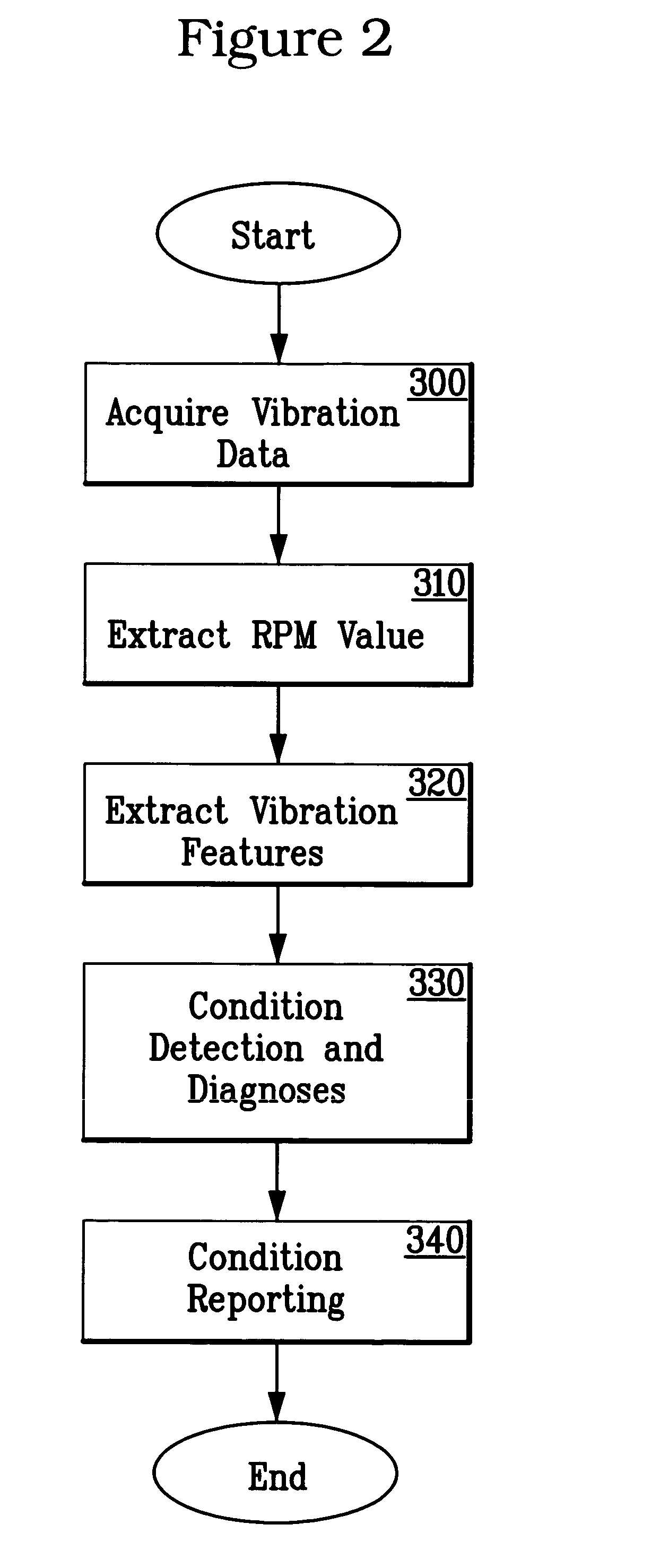
A system and methodology for continuous condition monitoring of rotating equipment. Employ adaptive signal processing techniques to determine the RPM of a rotating machine from time-based vibration data. RPM is determined based upon the input of a digitized time-based sample sequence of vibration data acquired directly from a vibration transducer for on-line real-time measurement of the machine RPM. Once RPM is determined, online vibration analysis for a given RPM or set of RPMs may be performed. The present invention extracts characteristic vibration features from vibration data and uses these extracted values to provide condition detection and diagnoses of machine faults.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
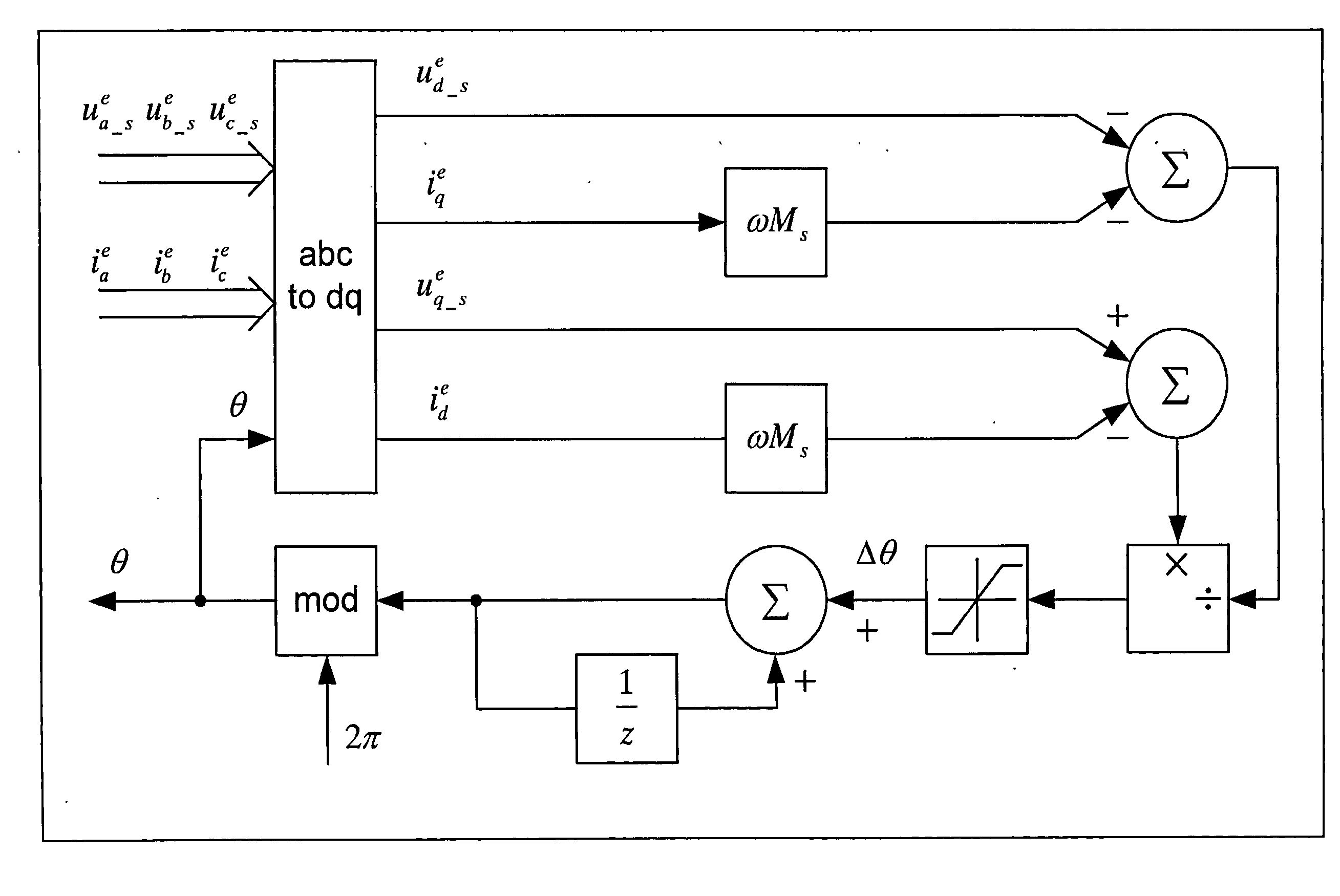
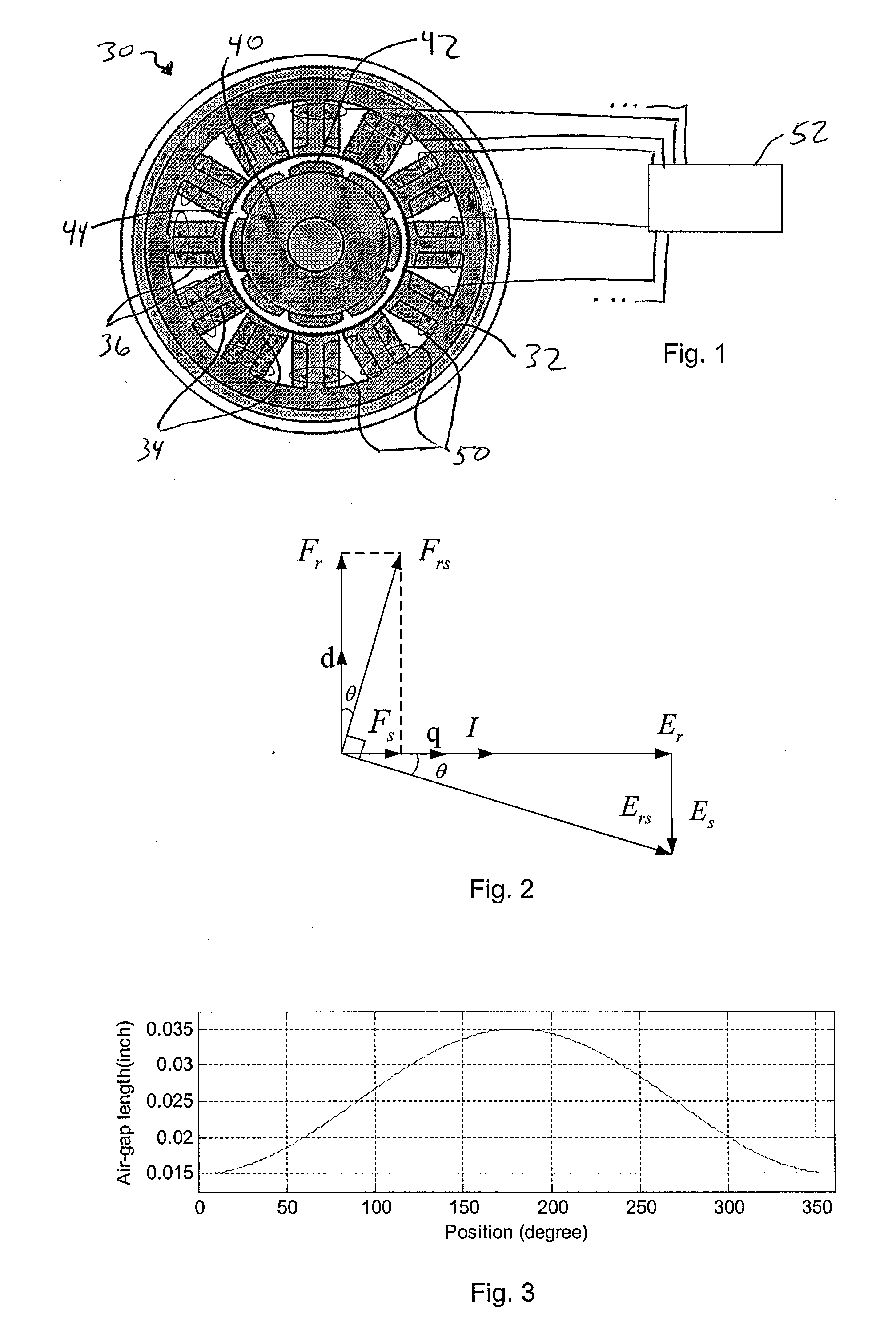
Apparatus and method for permanent magnet electric machine condition monitoring
InactiveUS20130033215A1Improve diagnostic reliabilityImprove reliabilityMotor/generator/converter stoppersElectric motor controlElectric machineRotor flux
An apparatus and method for determining a condition of an electric machine. Search coils are wound around stator teeth and the induced voltage is used to decouple stator and rotor fluxes. The decoupled fluxes allow for machine condition monitoring and fault diagnosis.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
System and methodology for vibration analysis and condition monitoring
InactiveUS20050209814A1Accurate speedImplemented quickly and inexpensivelyDigital computer detailsDevices using electric/magnetic meansTransducerSample sequence
A system and methodology for the continuous condition monitoring of rotating equipment. The present invention comprises a method that employs adaptive signal processing techniques to determine the RPM of a rotating machine from the time-based vibration data. According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, RPM is determined based upon the input of a digitized time-based sample sequence of vibration data acquired directly from a vibration transducer mounted on the machine for on-line real-time measurement of the machine RPM. Alternatively, the input to the “virtual RPM sensor” could come from a database or file where the sample sequences of the vibration signal are stored for off-line measurement of the machine RPM. Once RPM is determined, online vibration analysis for a given RPM or set of RPMs may be performed. The present invention extracts characteristic vibration features from vibration data and uses these extracted values to provide condition detection and diagnoses of machine faults.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
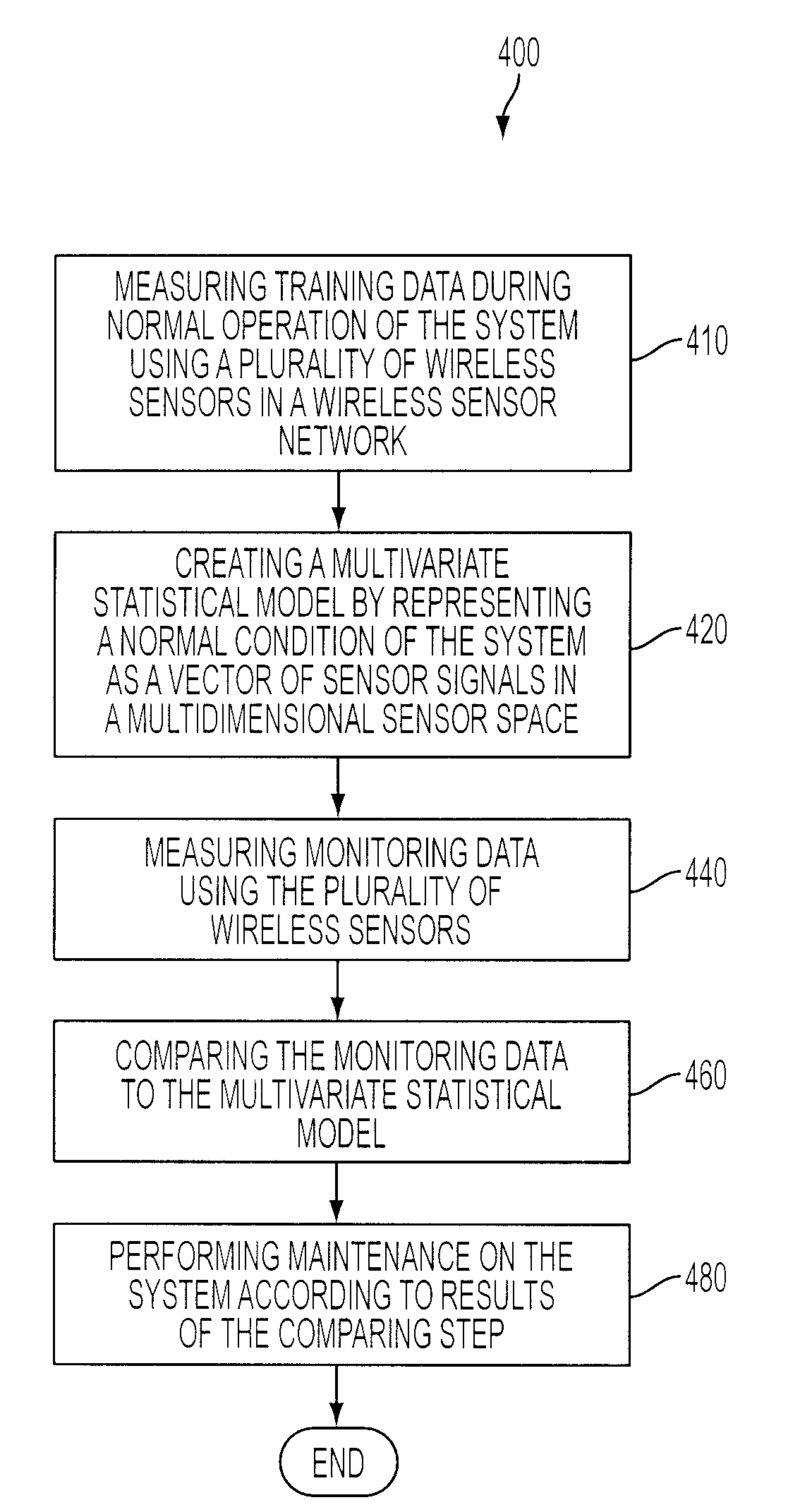
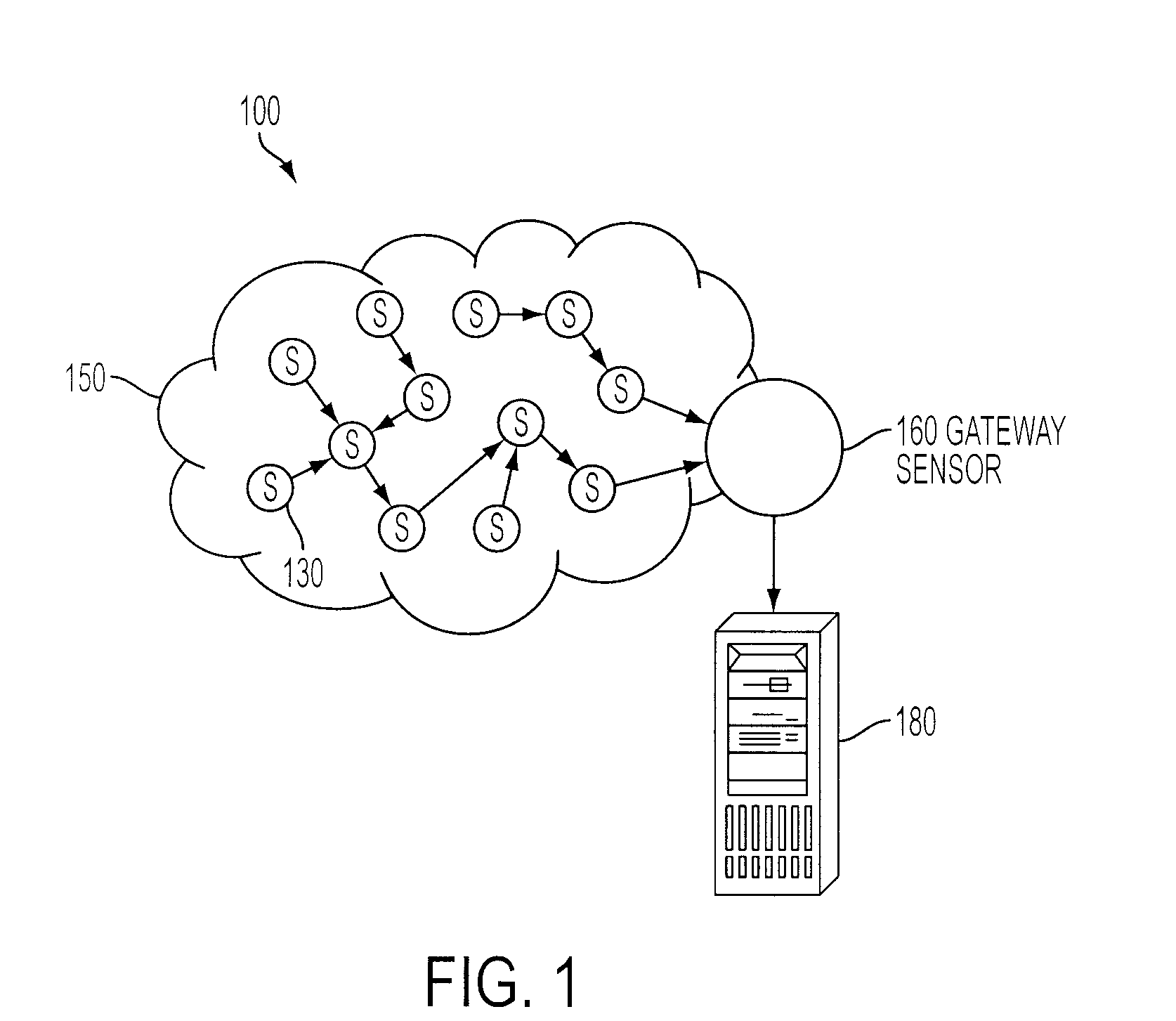
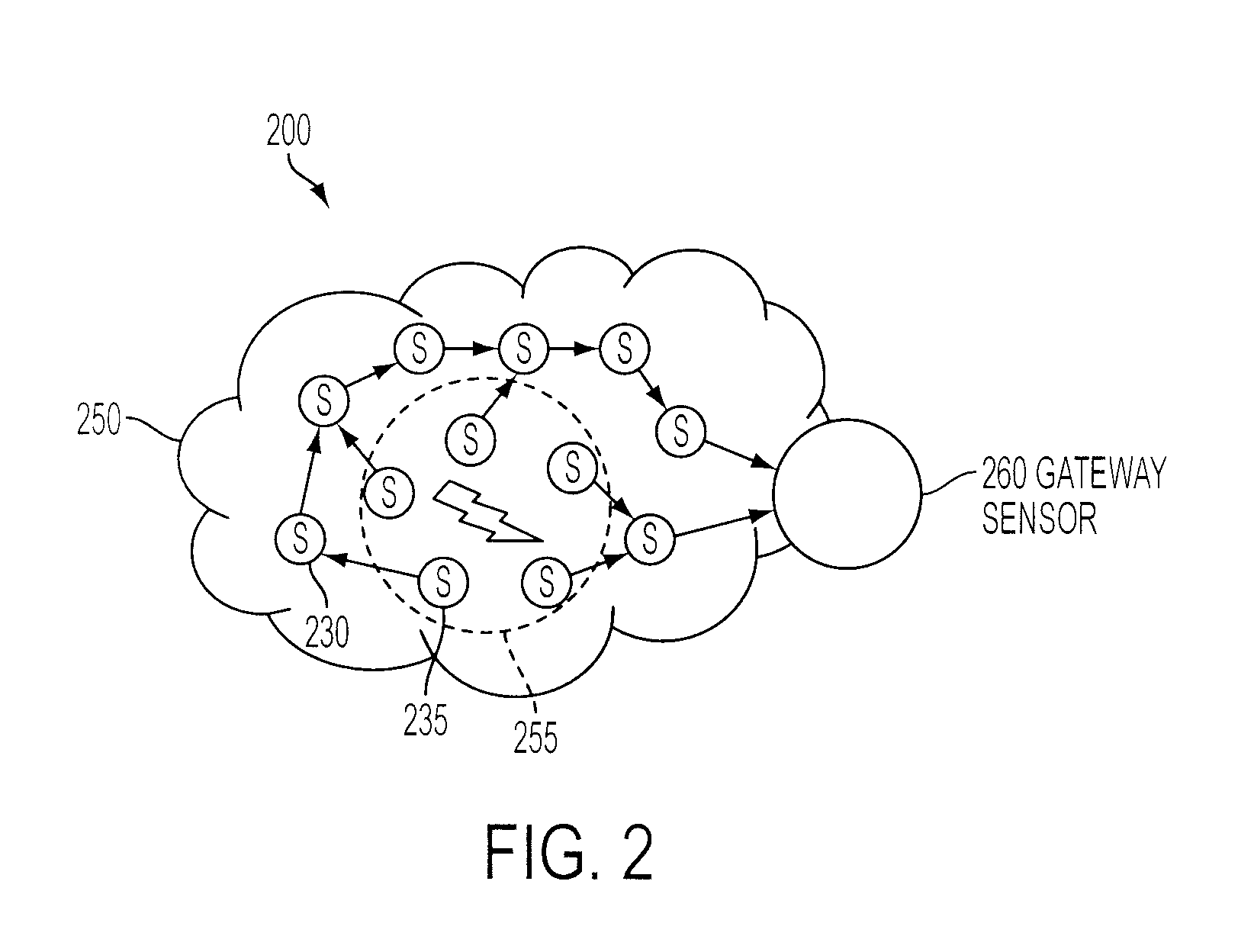
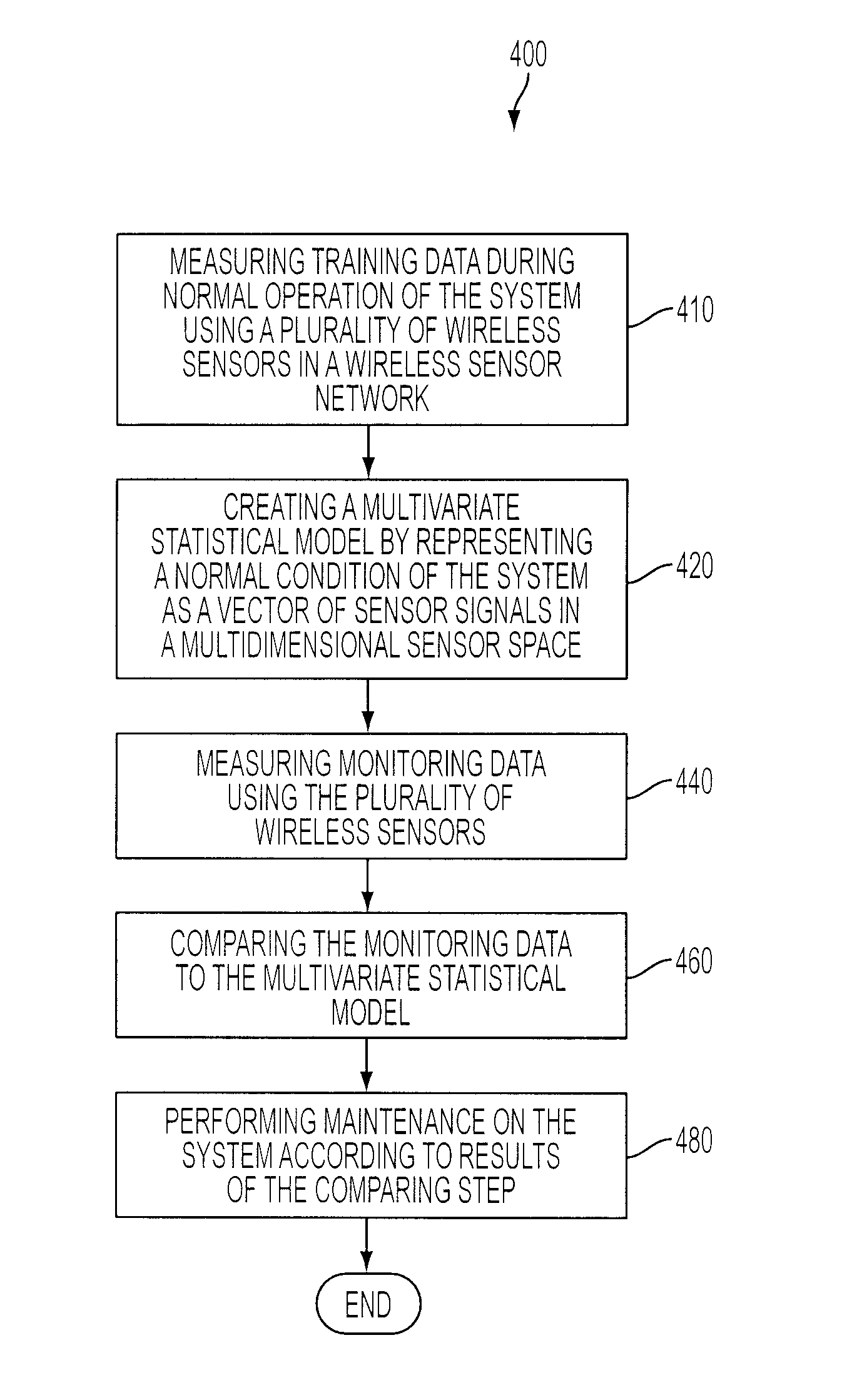
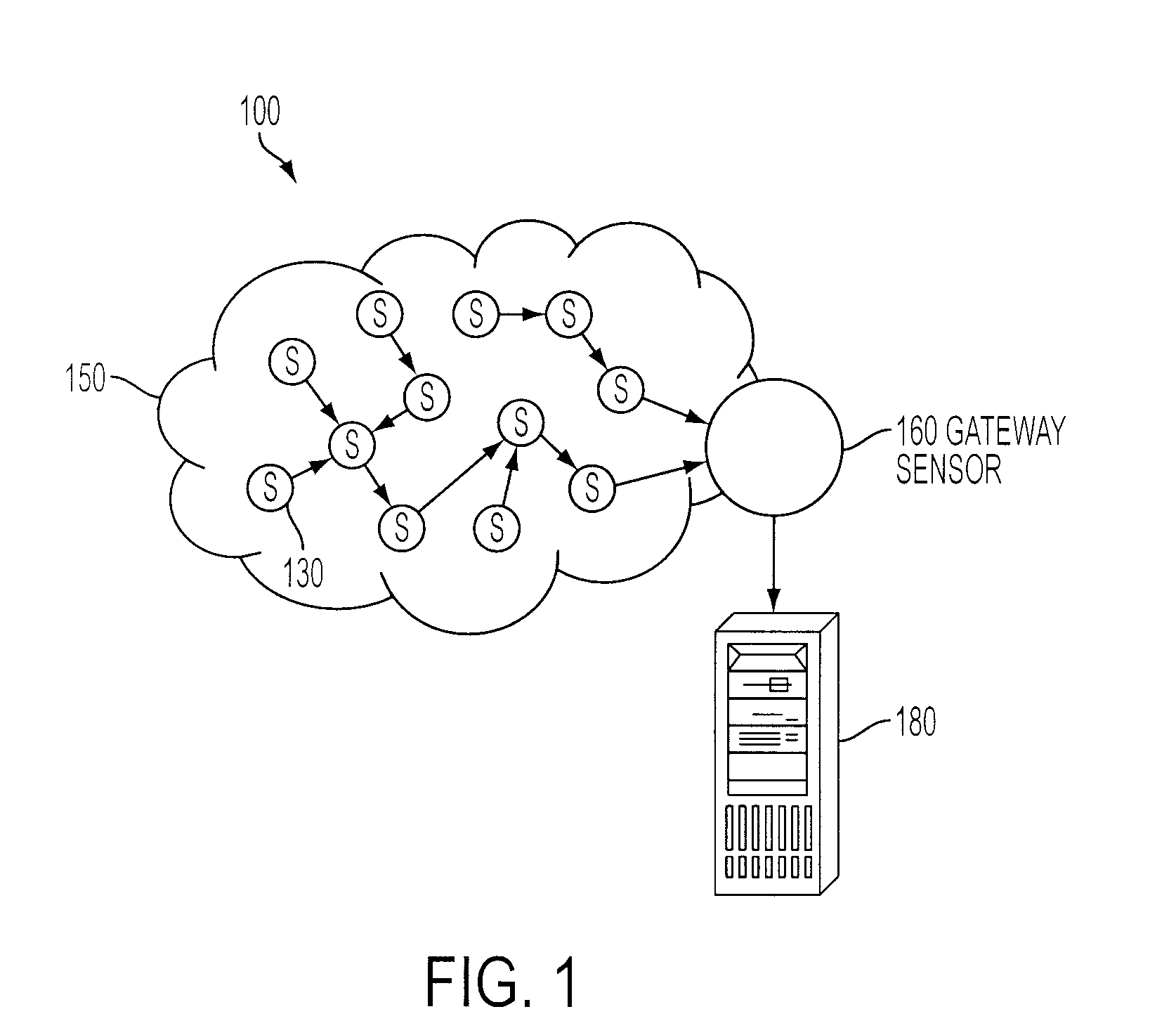
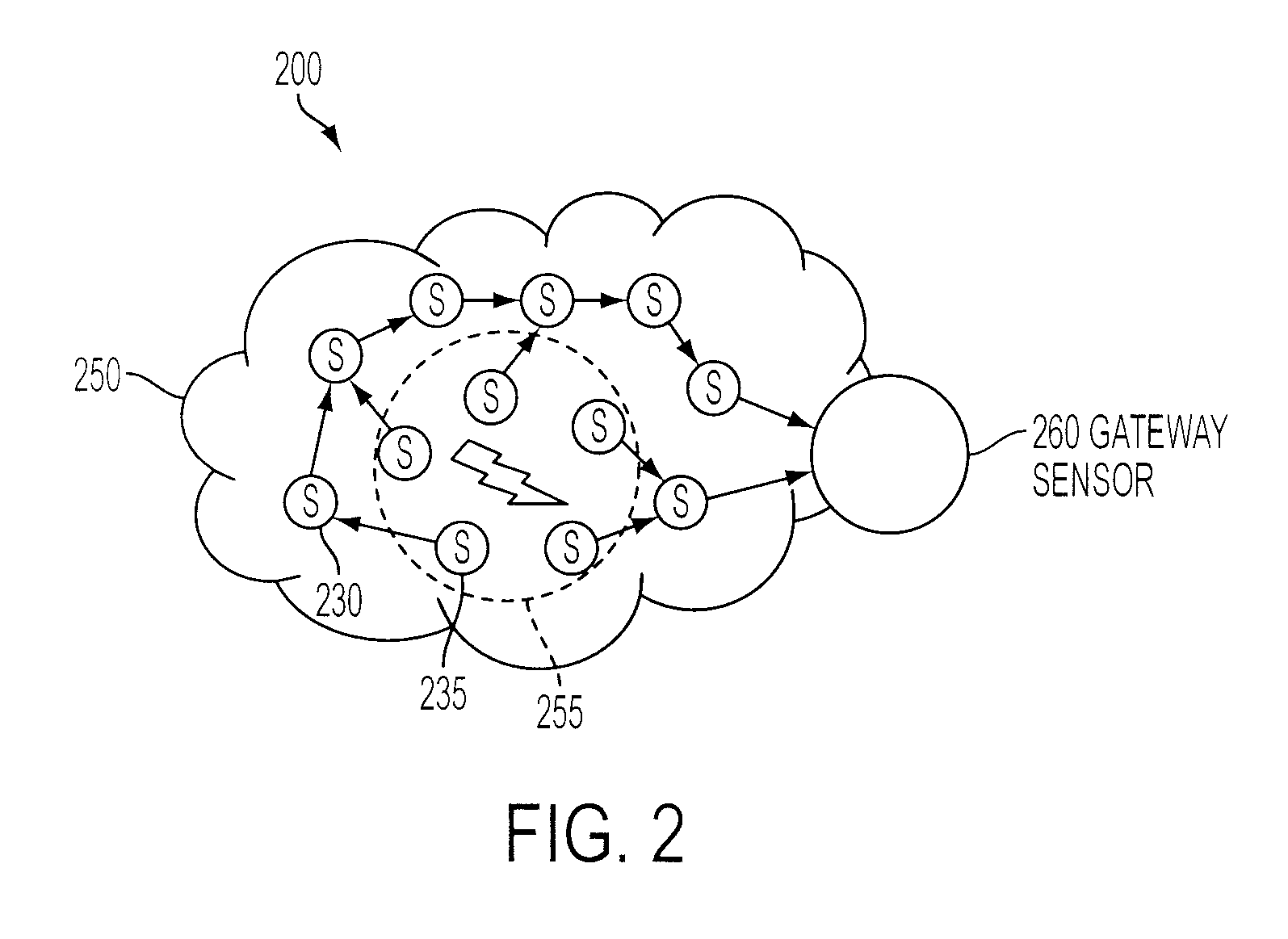
Multivariate Analysis of Wireless Sensor Network Data for Machine Condition Monitoring
ActiveUS20090119243A1Probabilistic networksFuzzy logic based systemsLine sensorDiagnostic Radiology Modality
Machine condition monitoring on a system utilizes a wireless sensor network to gather data from a large number of sensors. The data is processed using a multivariate statistical model to determine whether the system has deviated from a normal condition. The wireless sensor network permits the acquisition of a large number of distributed data points from plural system modalities, which, in turn, yields enhanced prediction accuracy and a reduction in false alarms.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
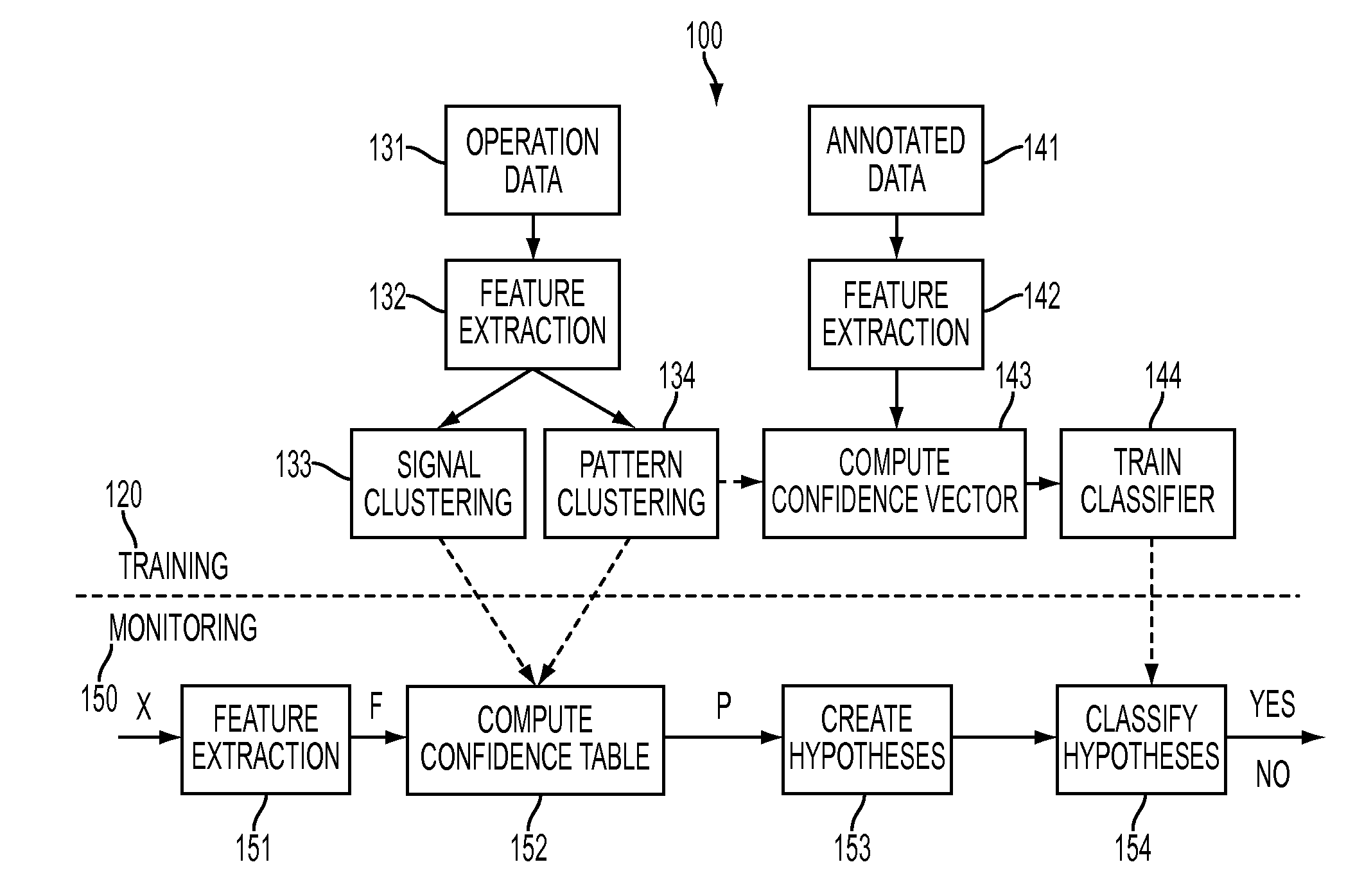
Generalized pattern recognition for fault diagnosis in machine condition monitoring
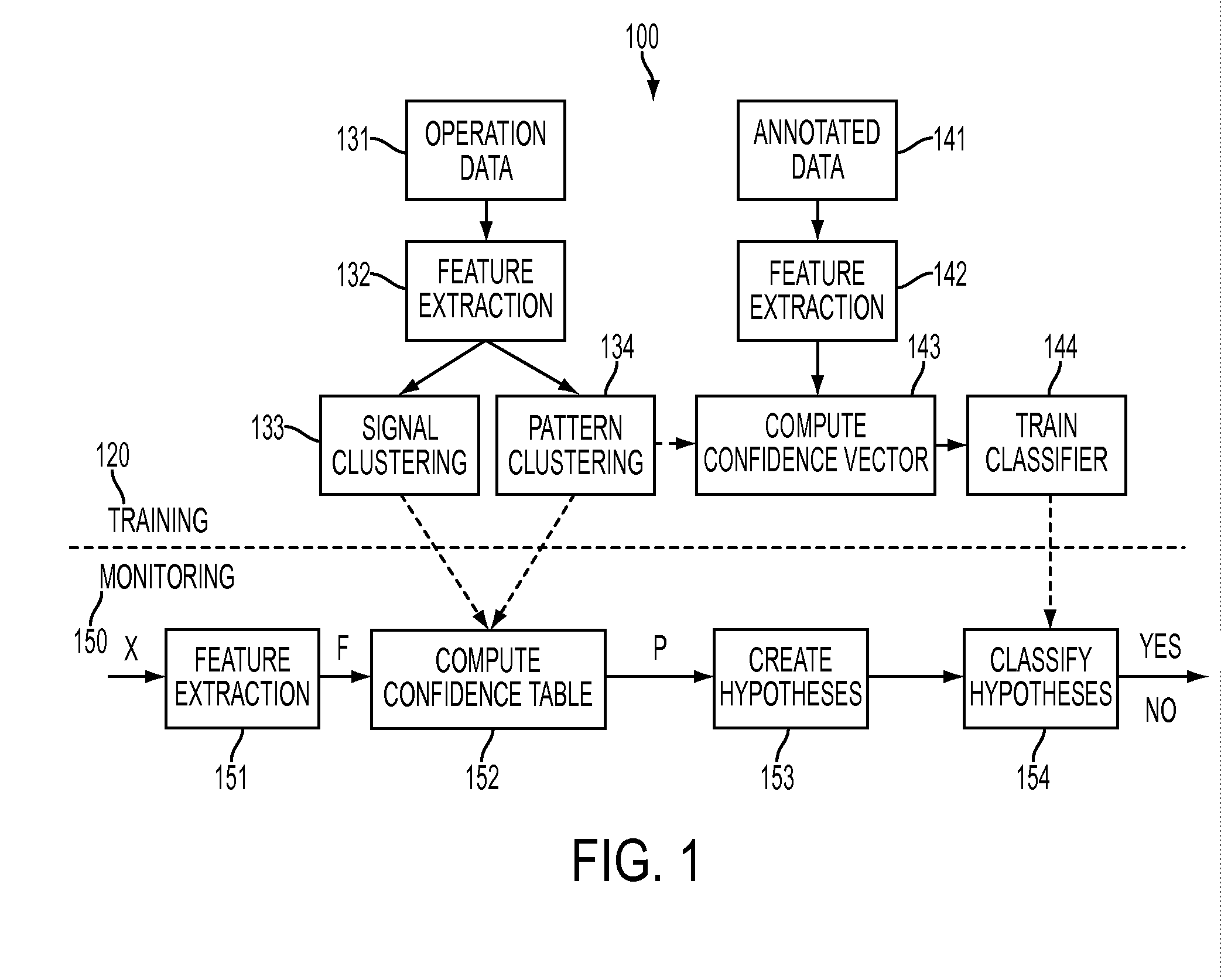
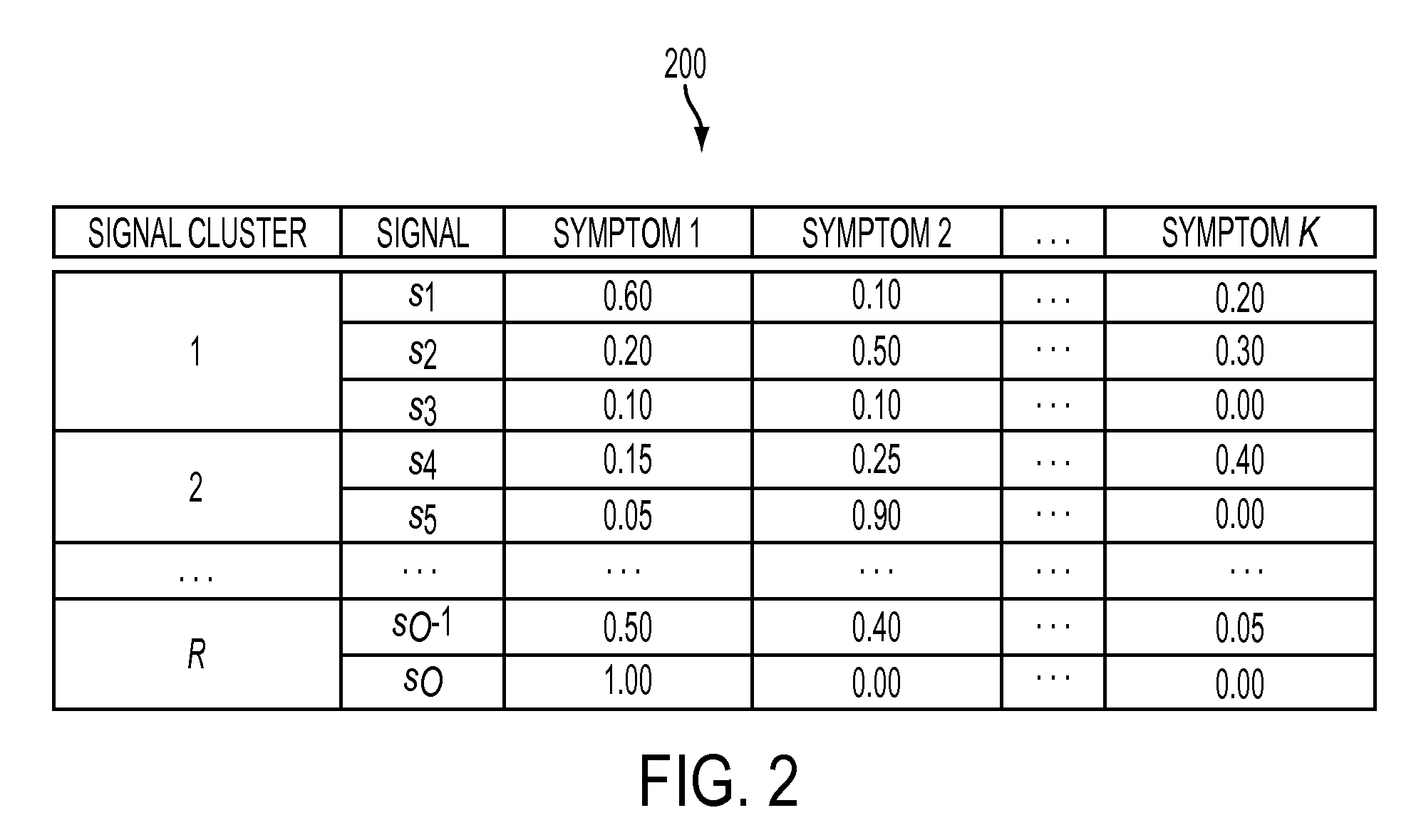
ActiveUS20130332773A1Error detection/correctionTesting/monitoring control systemsPattern recognitionMachine condition monitoring
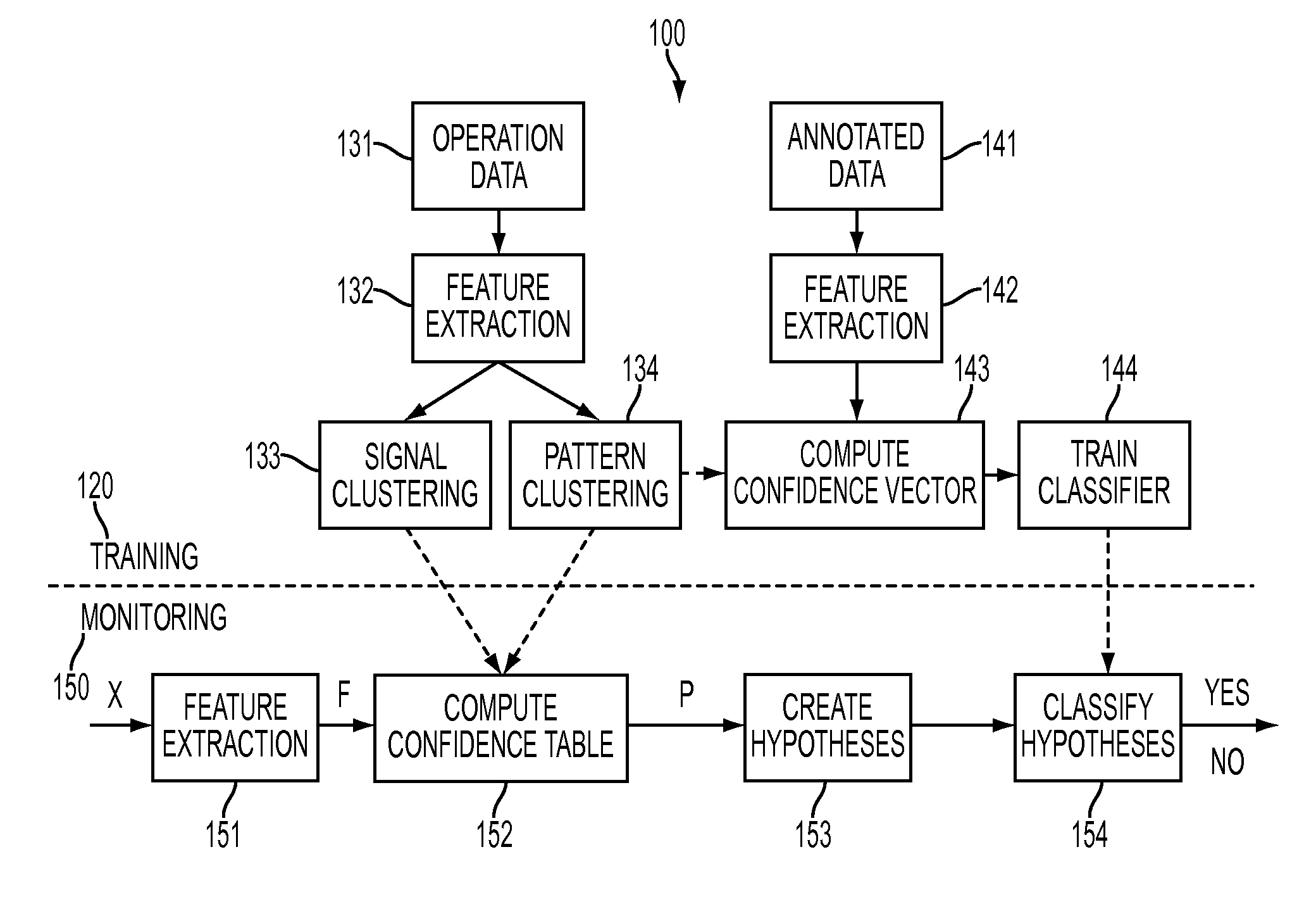
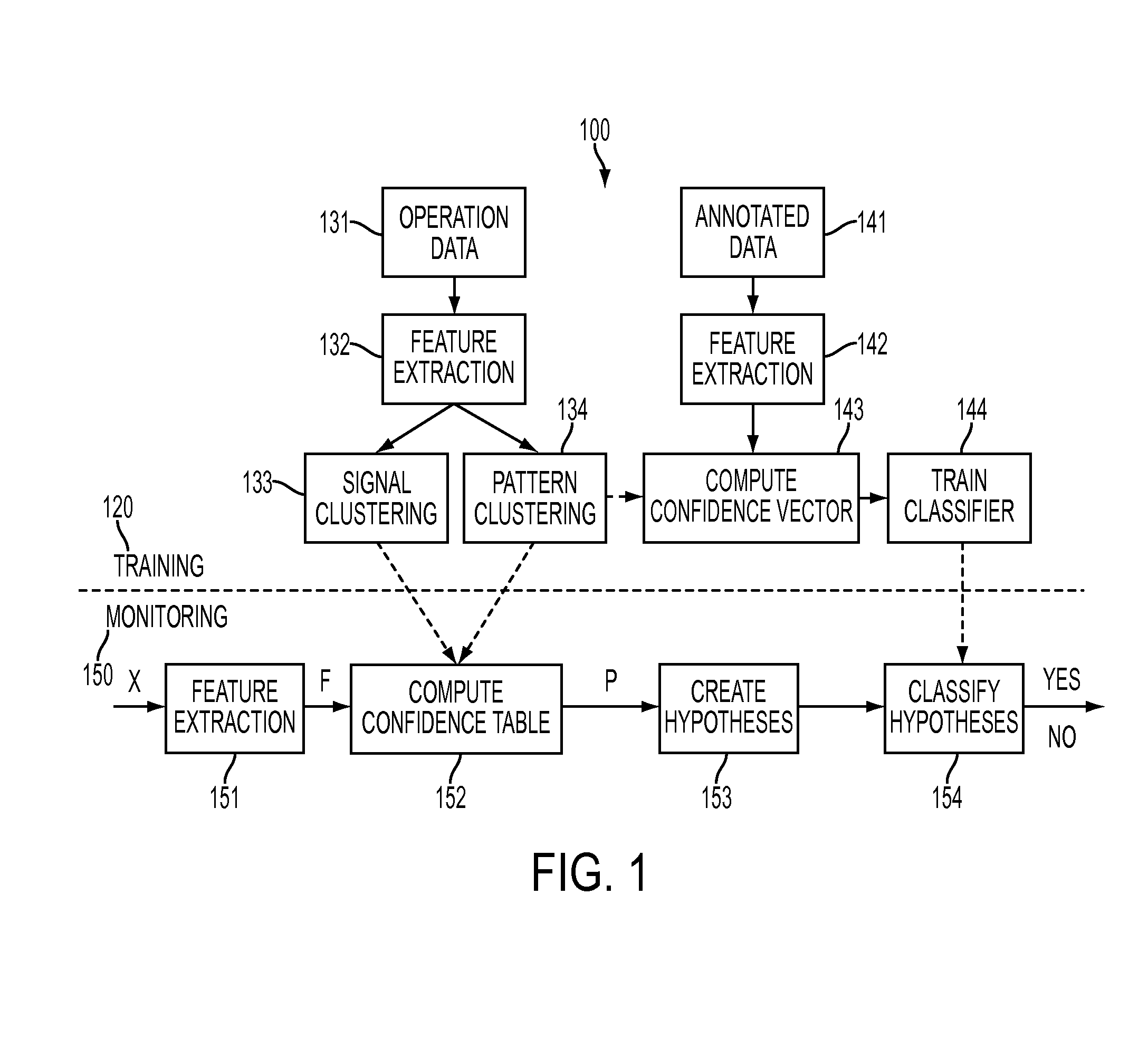
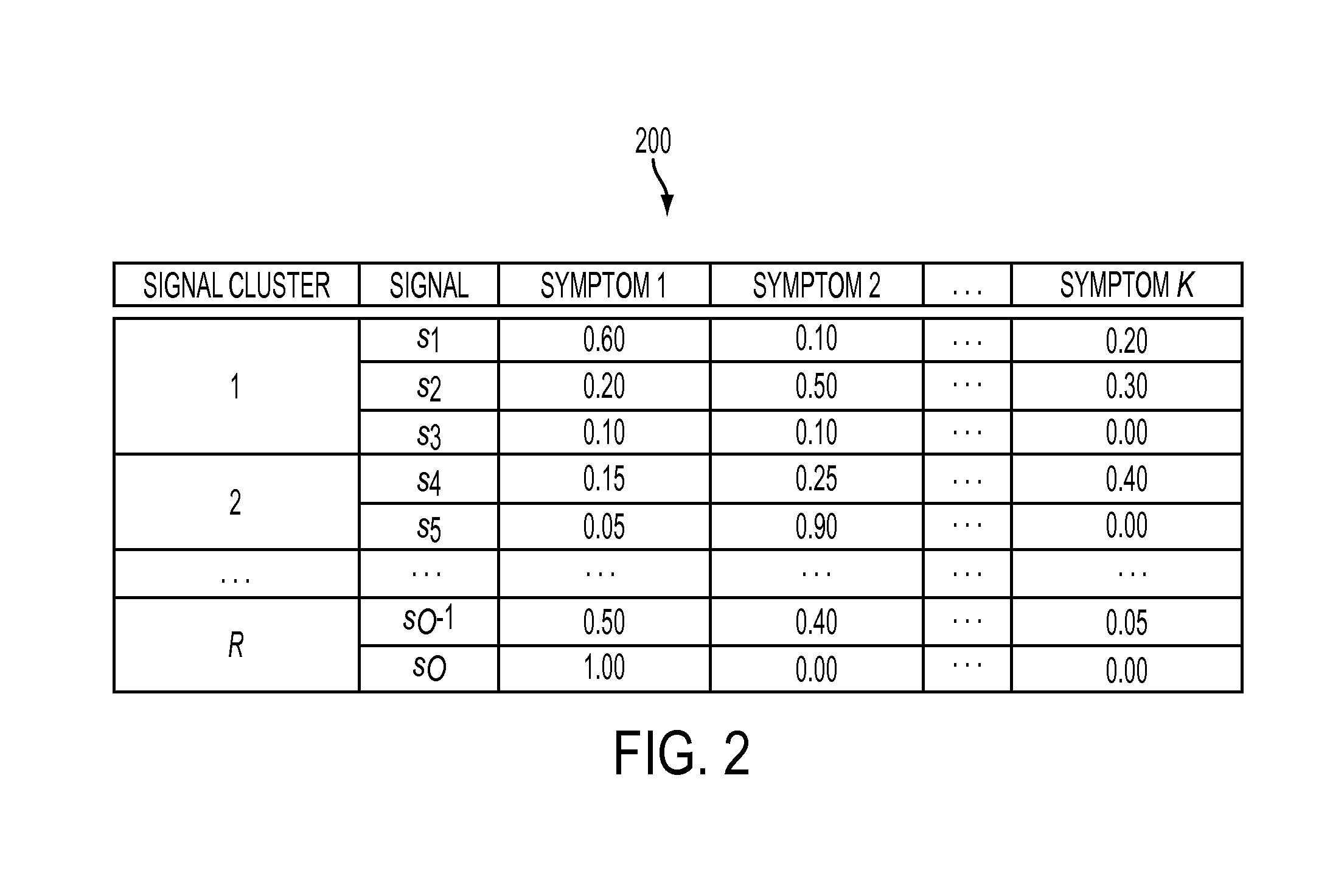
A generalized pattern recognition is used to identify faults in machine condition monitoring. Pattern clusters are identified in operating data. A classifier is trained using the pattern clusters in addition to annotated training data. The operating data is also used to cluster the signals in the operating data into signal clusters. Monitored data samples are then classified by evaluating confidence vectors that include substitutions of signals contained in the training data by signals in the same signal clusters as the signals contained in the training data.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Machine condition indication system
ActiveUS20080106424A1Programme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsState parameterIndustrial communication
A machine condition monitor resides in close proximity to a machine train, such as an AC inductive electric motor coupled to a driven unit such as a centrifugal pump or fan. A plurality of sensing devices are connected to the machine and the machine condition monitor. Machine state and condition parameters sensed by these devices are utilized by the machine condition monitor to derive machine condition values for each component and for the machine train as a whole. These derived condition values are transmitted via an industrial communications network to a control center where they can be trended and monitored. With no particular knowledge of machine analysis techniques or severity of specific machine faults, and no special training, Operators and Production Planners can use the condition values to plan production schedules, adjust process parameters, and request appropriate maintenance action.
Owner:COMPUTATIONAL SYST
Supervised fault learning using rule-generated samples for machine condition monitoring
InactiveUS20120304008A1Error detection/correctionTesting/monitoring control systemsFeature vectorDecision boundary
A machine fault diagnosis system is provided. The system combines a rule-based predictive maintenance strategy with a machine learning system. A simple set of rules defined manually by human experts is used to generate artificial training feature vectors to portray machine fault conditions for which only a few real data points are available. Those artificial training feature vectors are combined with real training feature vectors and the combined set is used to train a supervised pattern recognition algorithm such as support vector machines. The resulting decision boundary closely approximates the underlying real separation boundary between the fault and normal conditions.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Multivariate analysis of wireless sensor network data for machine condition monitoring
ActiveUS8112381B2Probabilistic networksFuzzy logic based systemsMultivariate statisticalWireless sensor networking
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
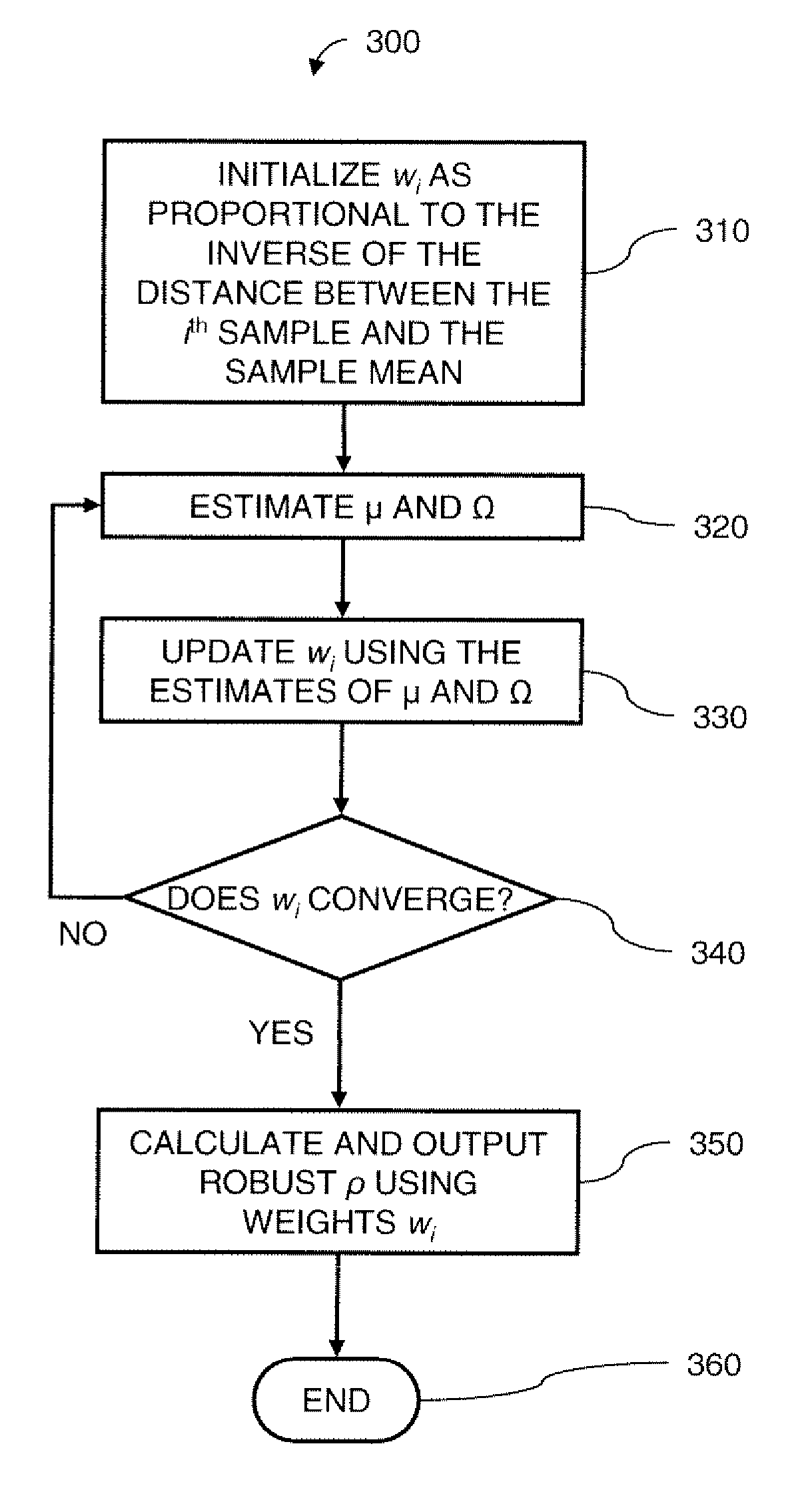
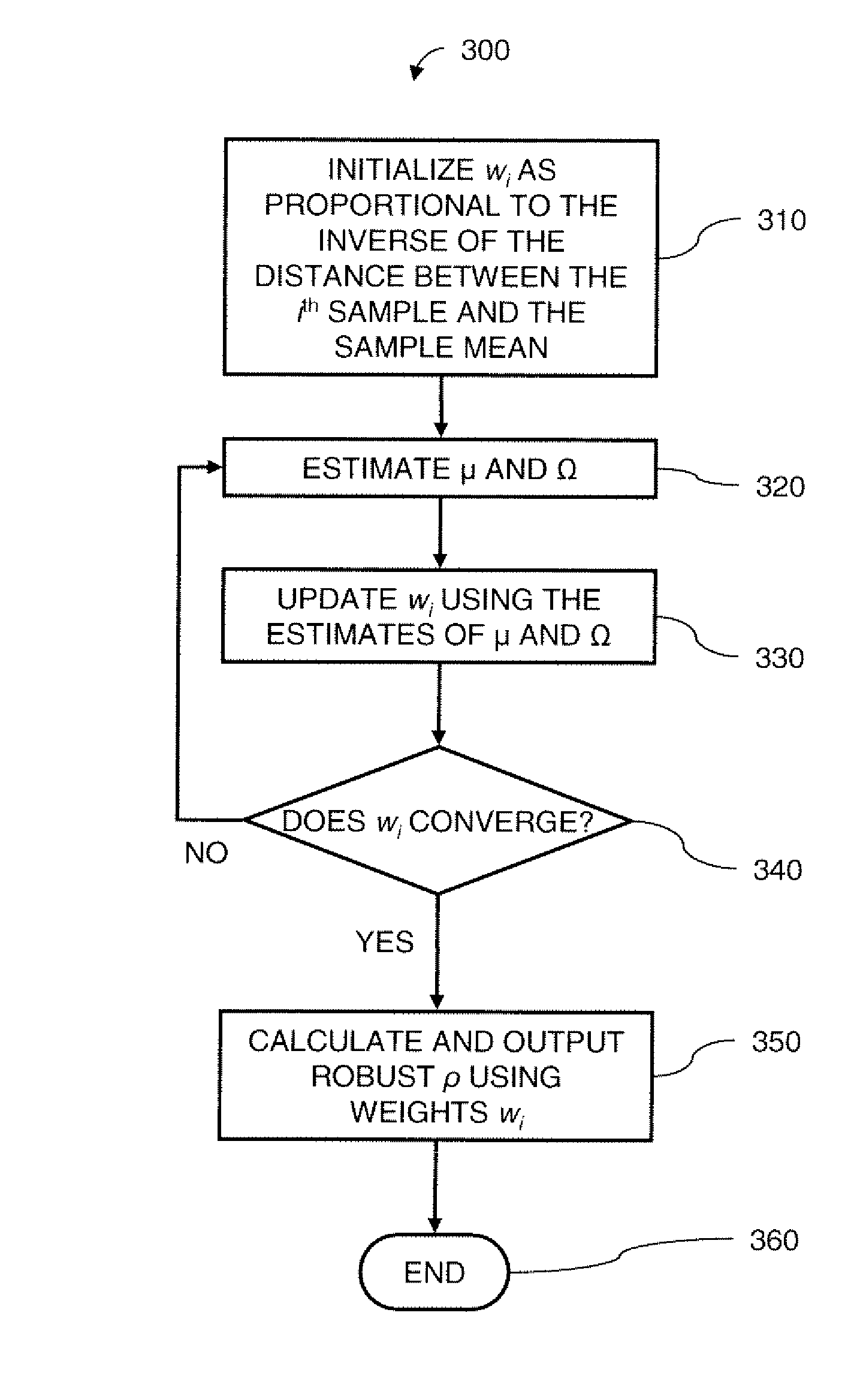
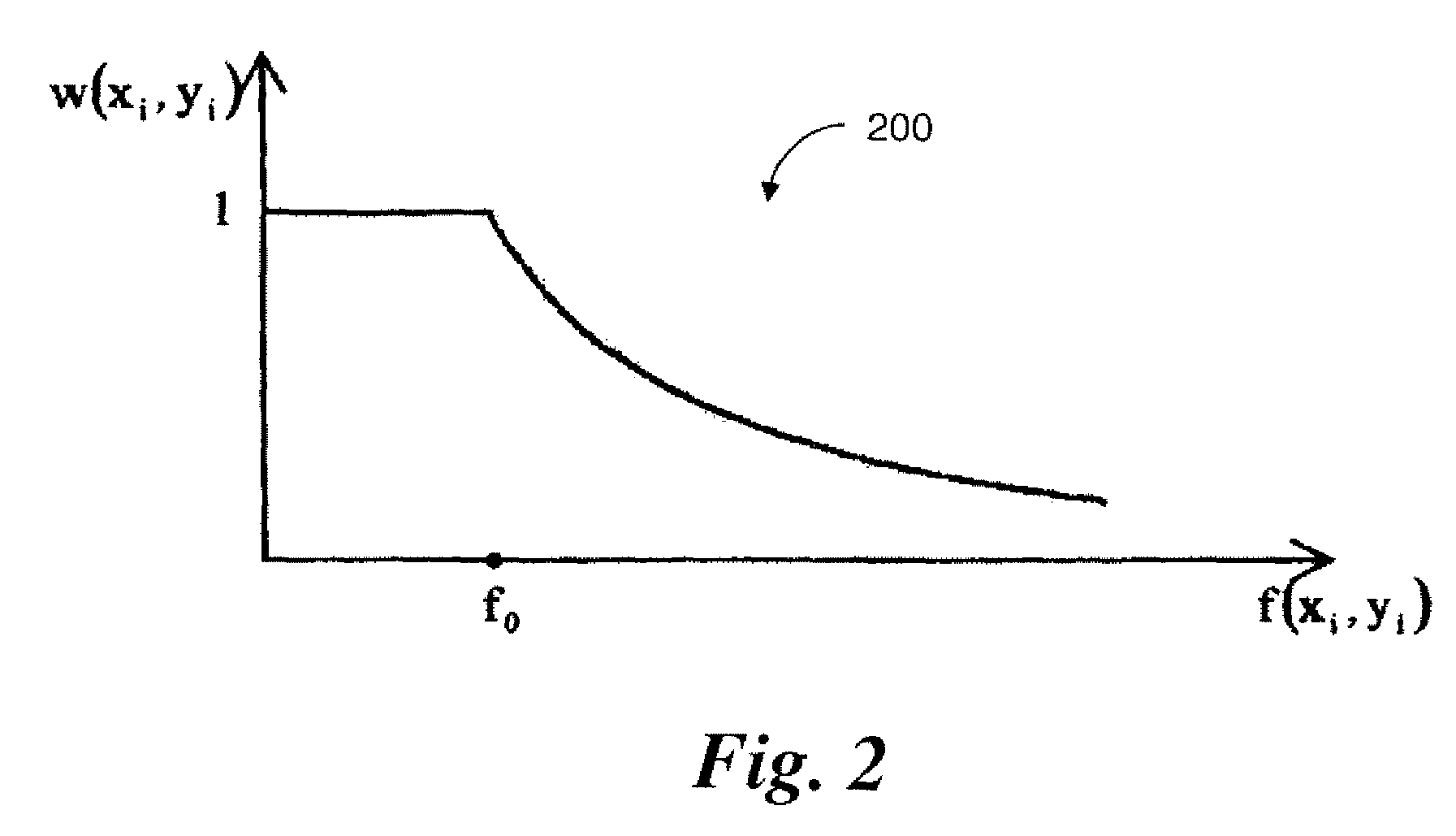
Robust Sensor Correlation Analysis For Machine Condition Monitoring
InactiveUS20070162241A1Easy to getProgramme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsCorrelation coefficientMahalanobis distance
A method for monitoring machine conditions is based on machine learning through the use of a statistical model. A correlation coefficient is calculated using weights assigned to each sample that indicate the likelihood that that sample is an outlier. The resulting correlation coefficient is more robust against outliers. The calculation of the weight is based on the Mahalanobis distance from the sample to the sample mean. Additionally, hierarchical clustering is applied to intuitively reveal group information among sensors. By specifying a similarity threshold, the user can easily obtain desired clustering results.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
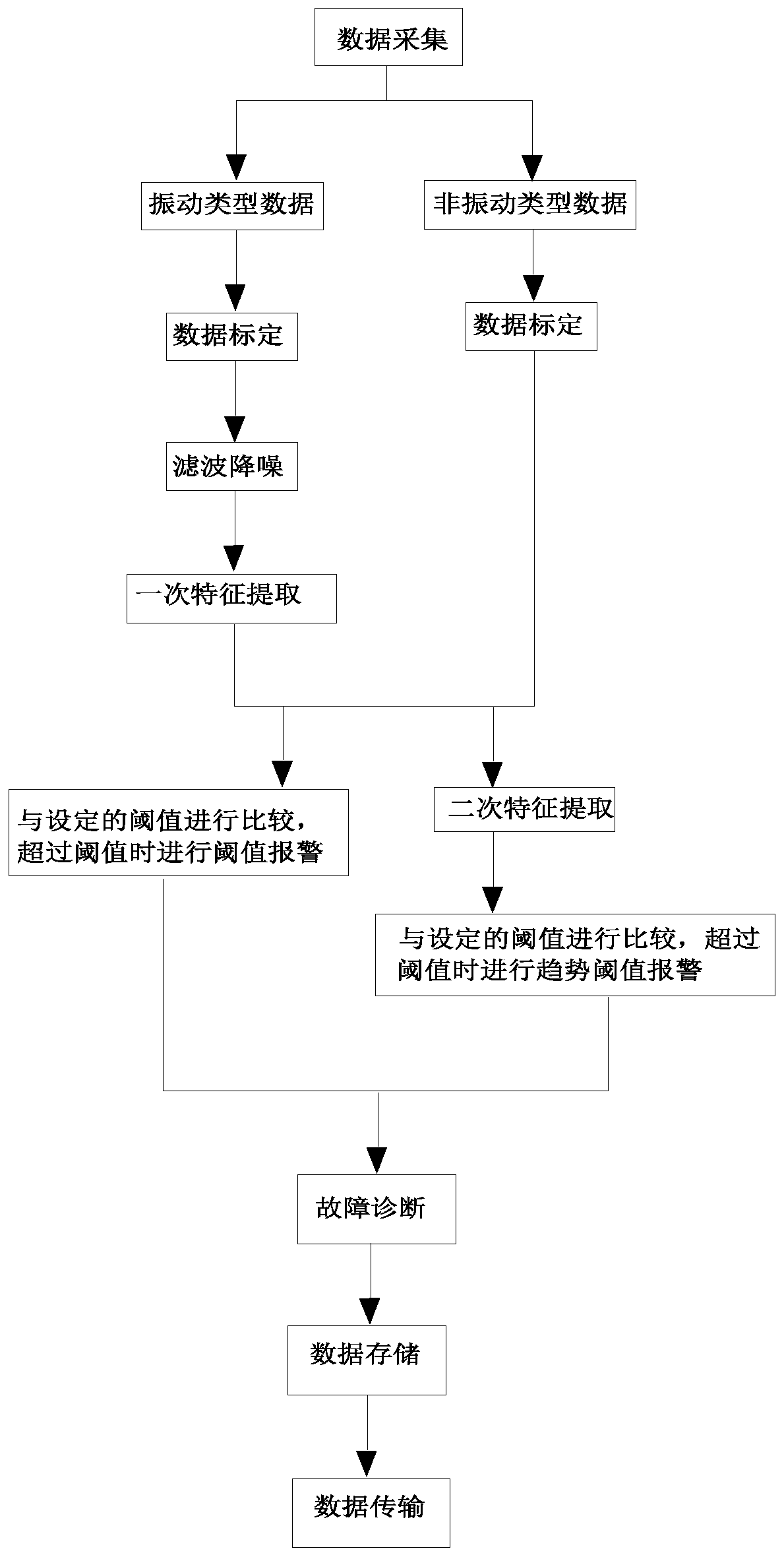
Mechanical equipment operating state monitoring method and system used for edge calculation side
ActiveCN109901537AEasy to monitorRealize online real-time status monitoringTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlTime conditionFeature extraction
The invention discloses a mechanical equipment operating state monitoring method and system used for an edge calculation side. Equipment operation condition data is collected, which includes vibrationtype and non-vibration type data. According to a unit component type, characteristic extraction is performed on vibration data, which includes one extraction of a corresponding characteristic value of the vibration type data, and also includes secondary extraction of the corresponding characteristic value of the vibration type data and the non-vibration type data. Threshold judgment of the data is possessed, and a data change trend can be acquired, which includes a change slope, a magnitude of jump, and the magnitude of the change. Whether there are slow rise, slow decline, and sudden changeconditions in mechanical settings can be accurately determined. Data types are enriched and data monitoring quality is improved. Online real-time condition monitoring of equipment and automatic earlywarning of an operating condition are realized, and effective and real-time data is provided for a subsequent system.
Owner:北京大通惠德科技有限公司
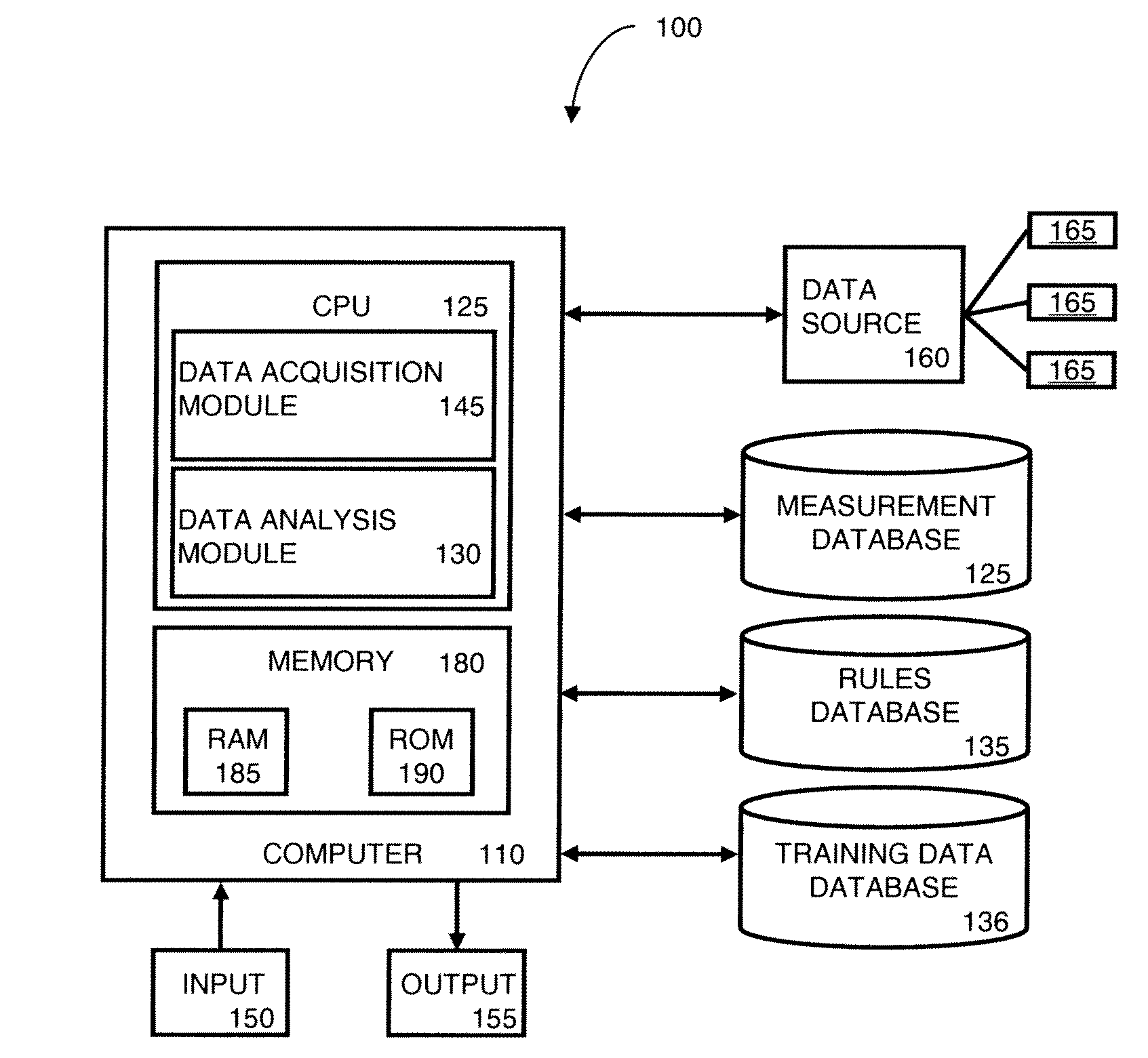
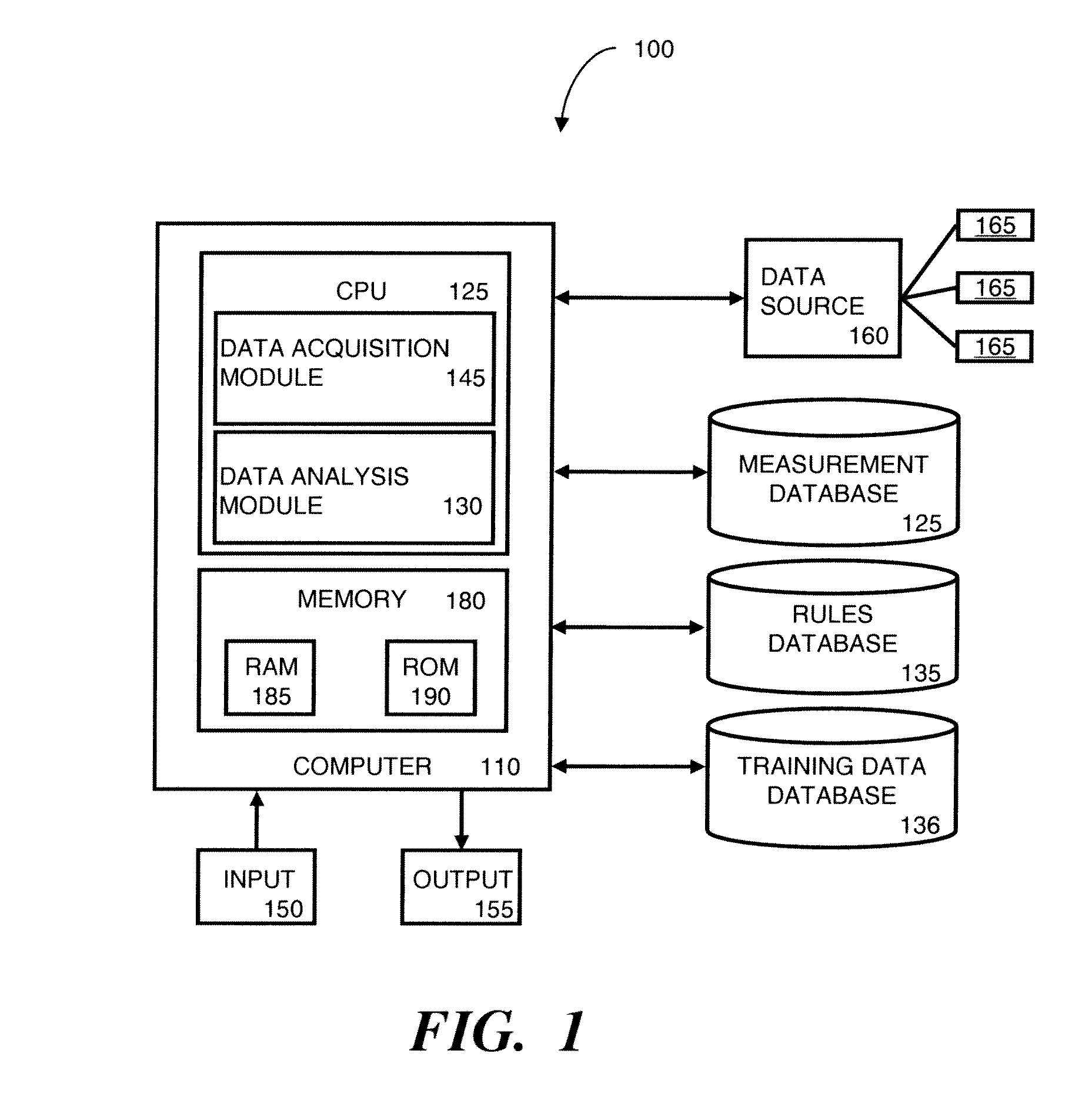
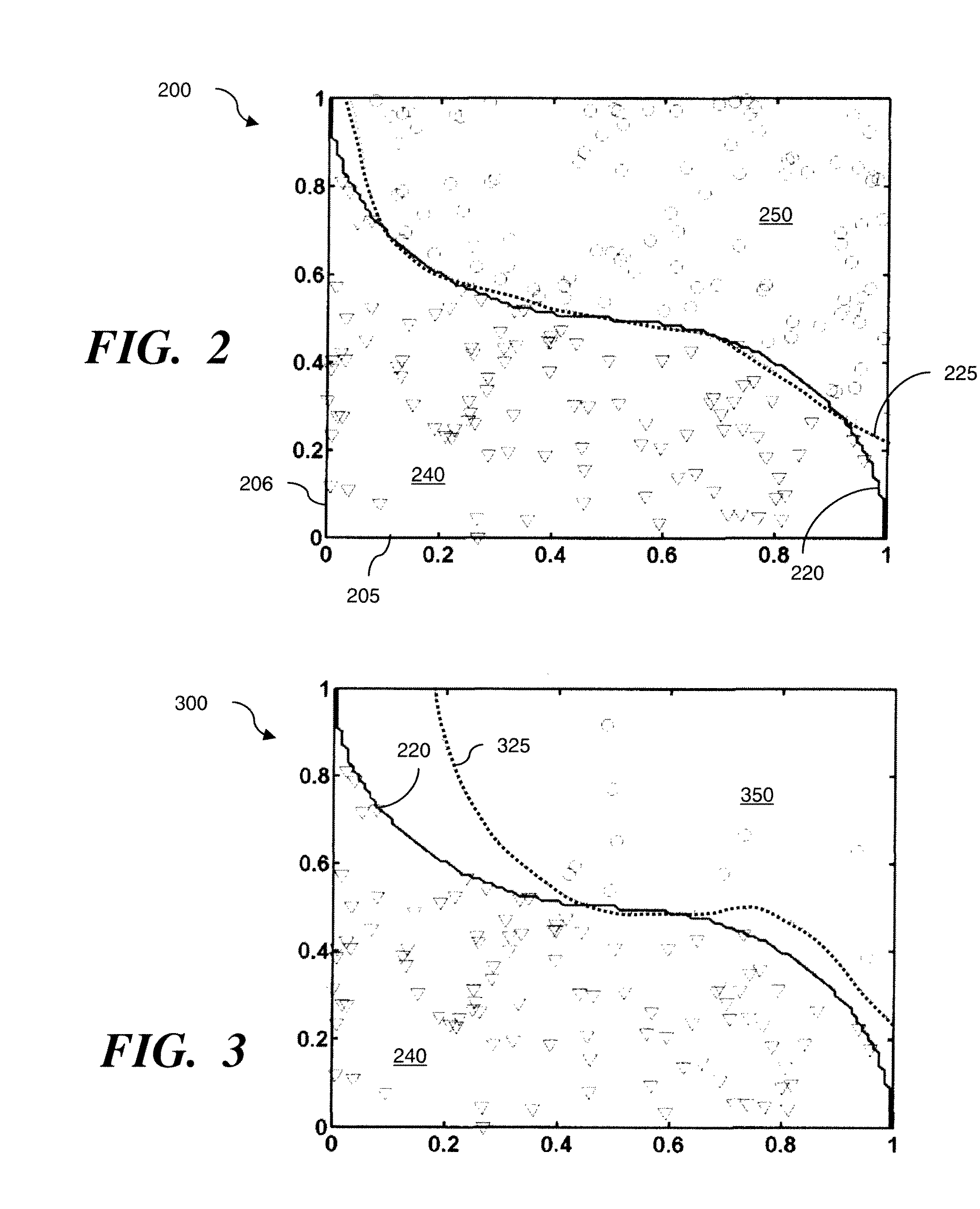
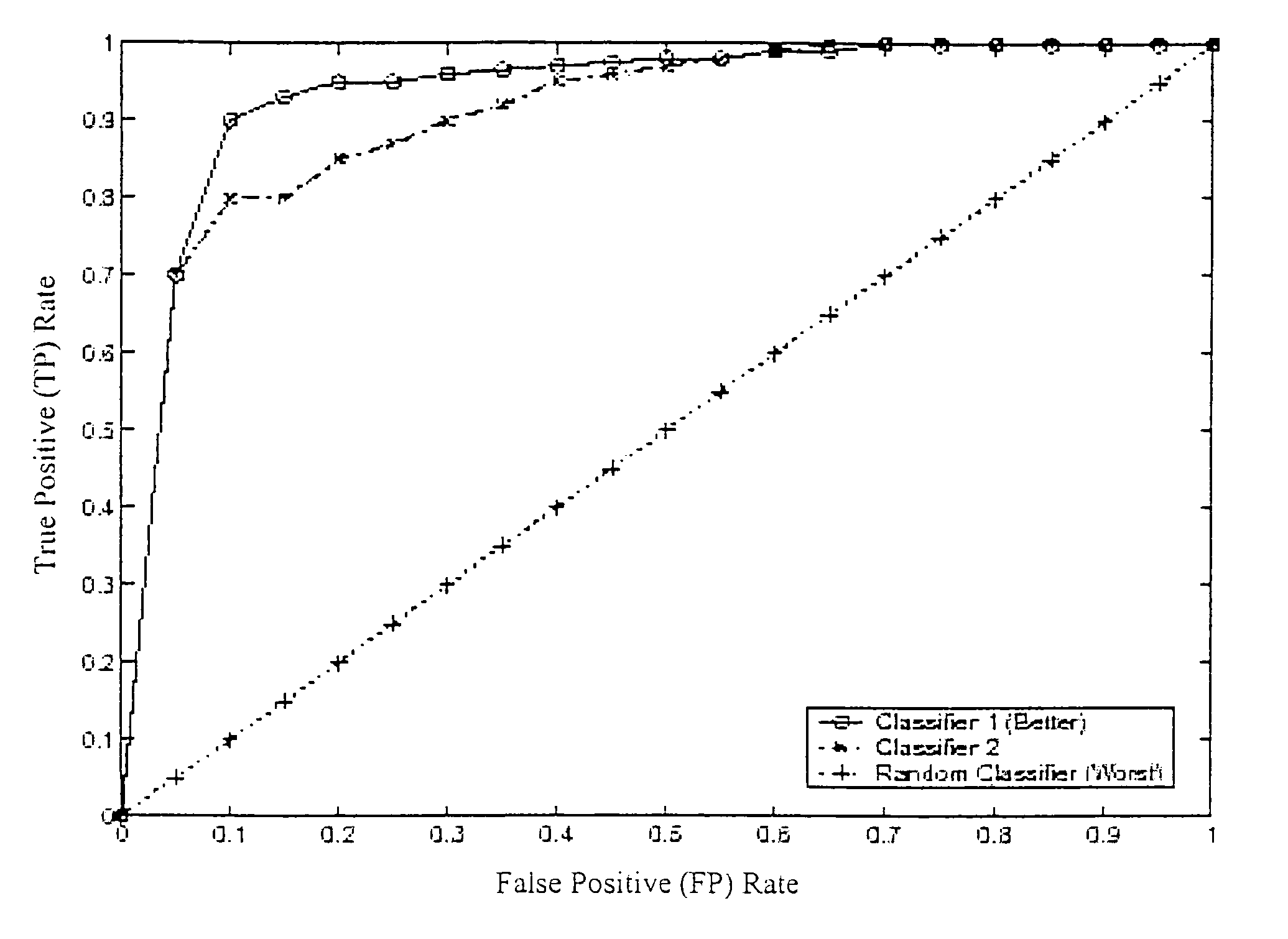
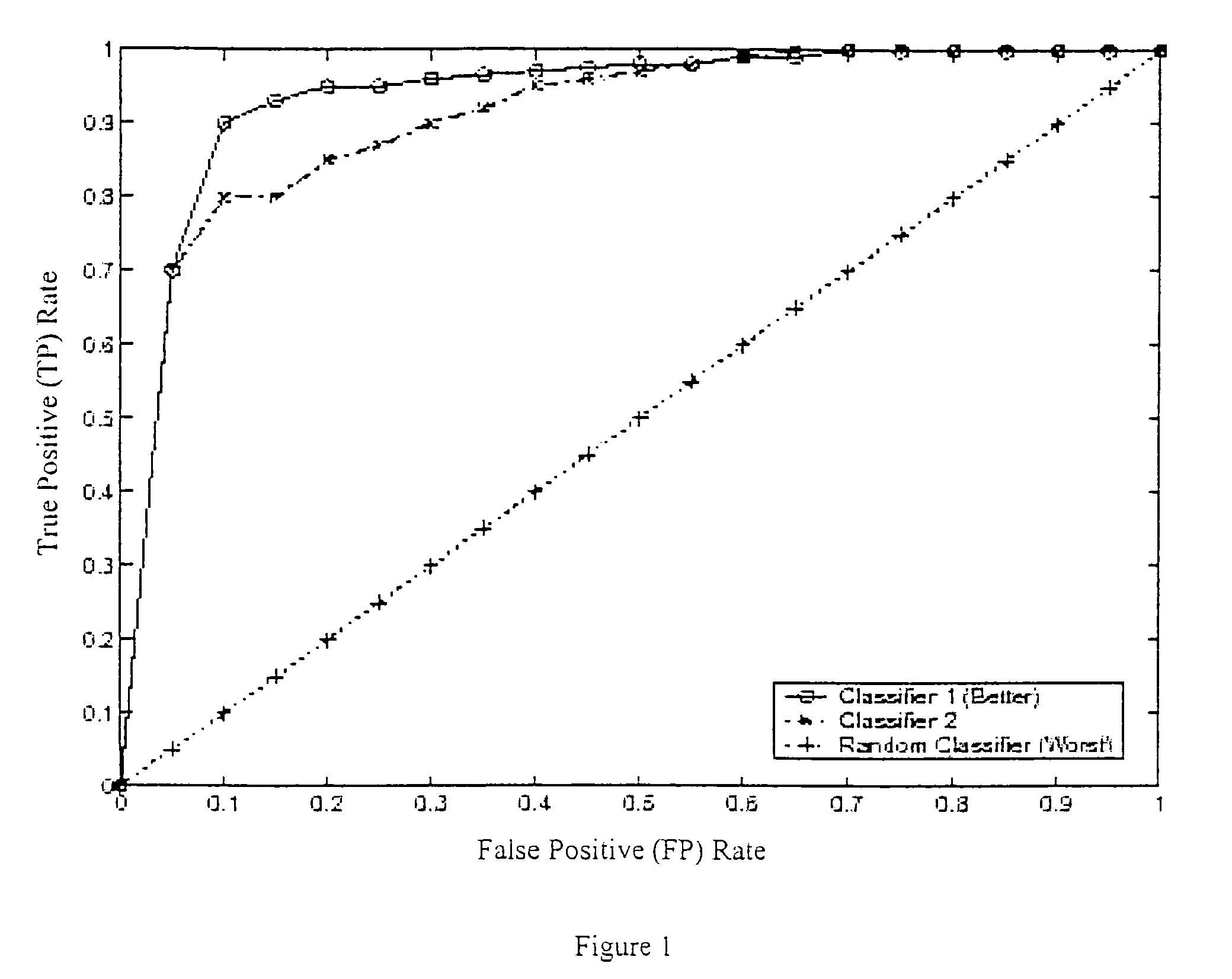
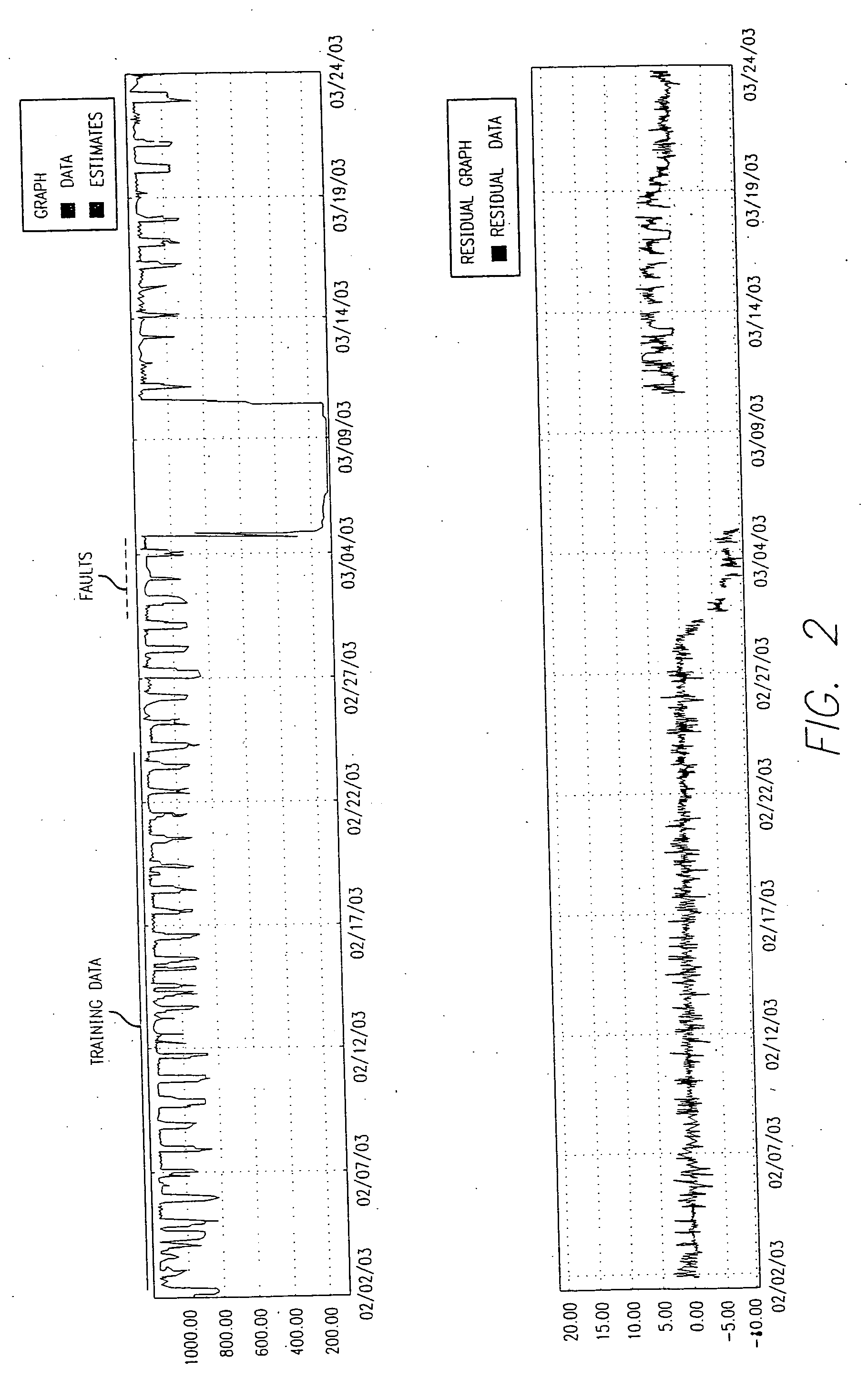
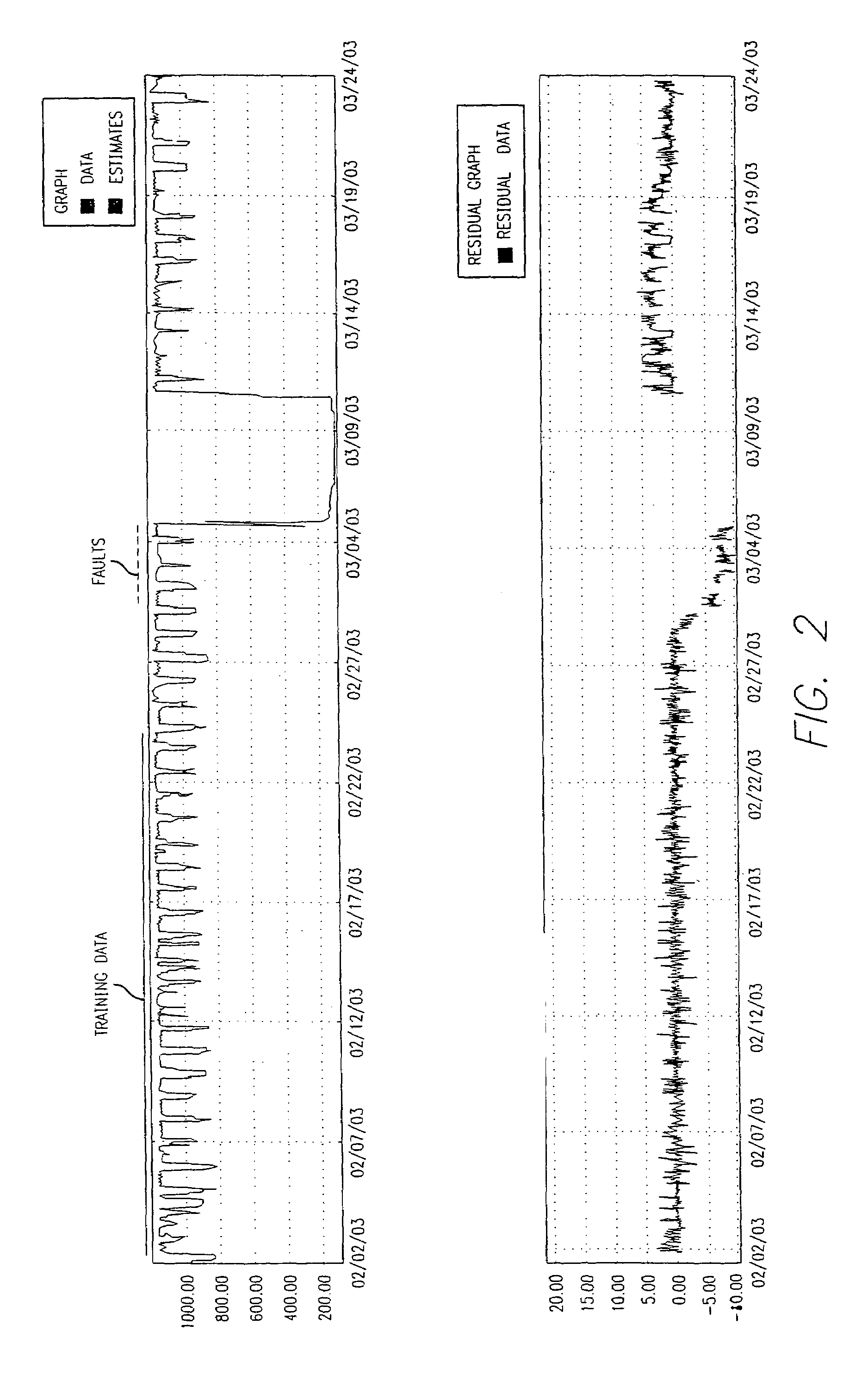
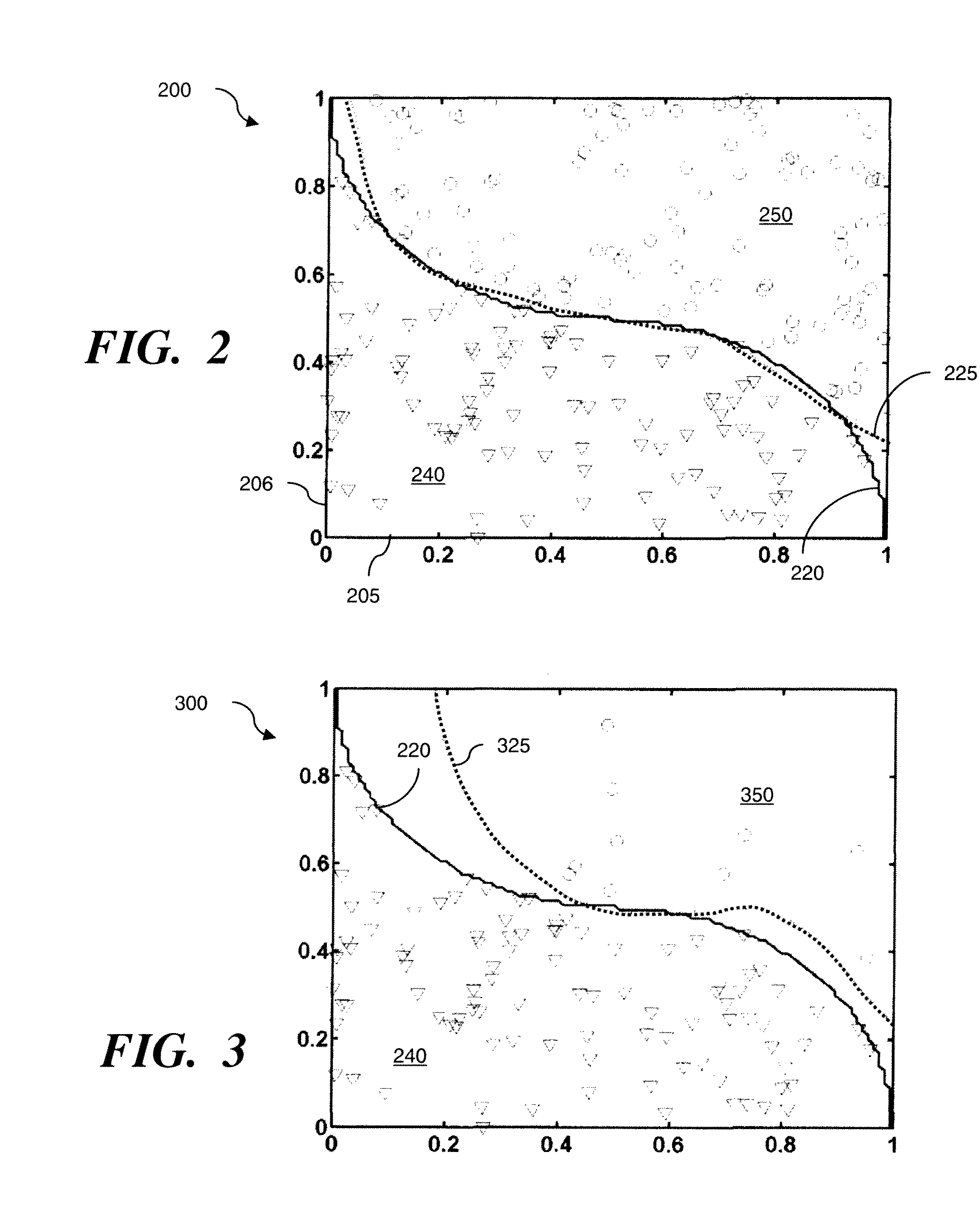
Method to use a receiver operator characteristics curve for model comparison in machine condition monitoring
InactiveUS7552035B2Testing/monitoring control systemsDigital computer detailsPower stationReceiver operating characteristic
A method to use a receiver operator characteristics curve for model comparison in machine condition monitoring. The method and systems of using this method may be used to evaluate different monitoring models. These models may be used to monitor a variety of different systems such as power plant systems or magnetic resonance imaging systems. The methods use training data and designate one or more points in the data as a false negative, thereby permitting a receiver operator characteristics analysis to be performed. Multiple receiver operator characteristics analyses may be performed either on different models or on different points within a single model, thereby permitting the receiver operator characteristics analyses to be used to select a beneficial model for monitoring a particular system.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
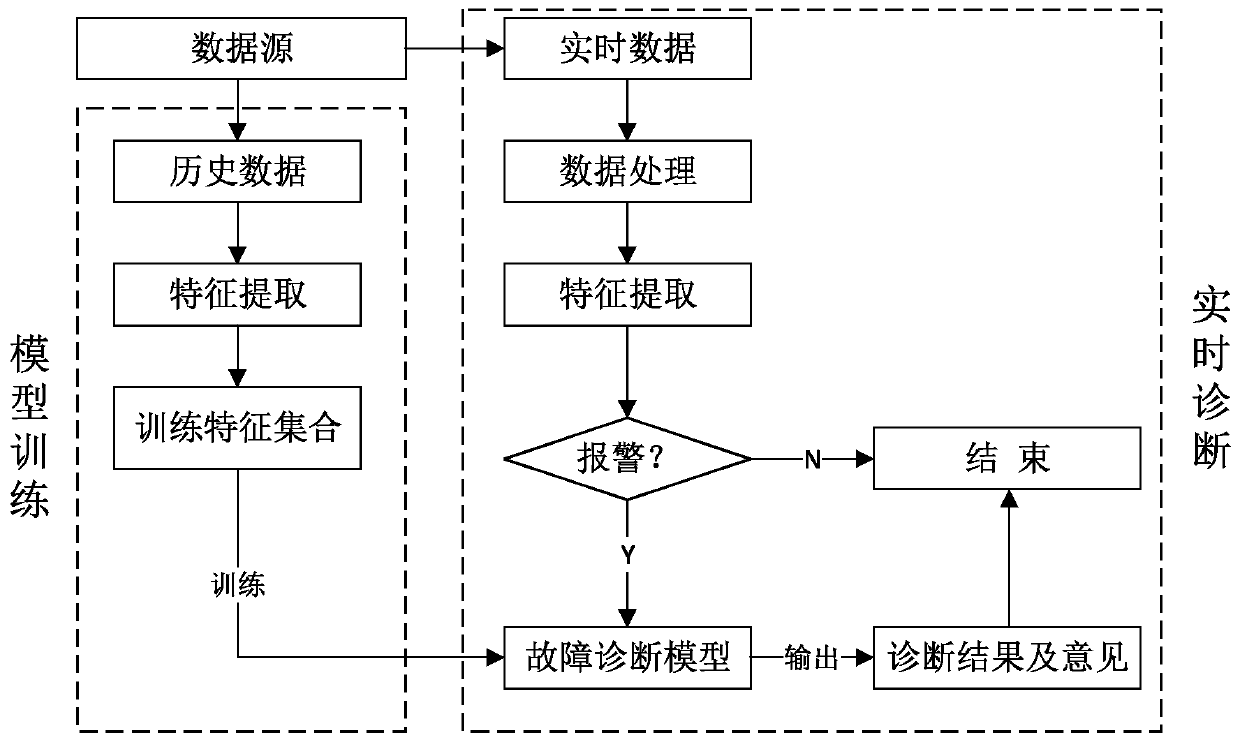
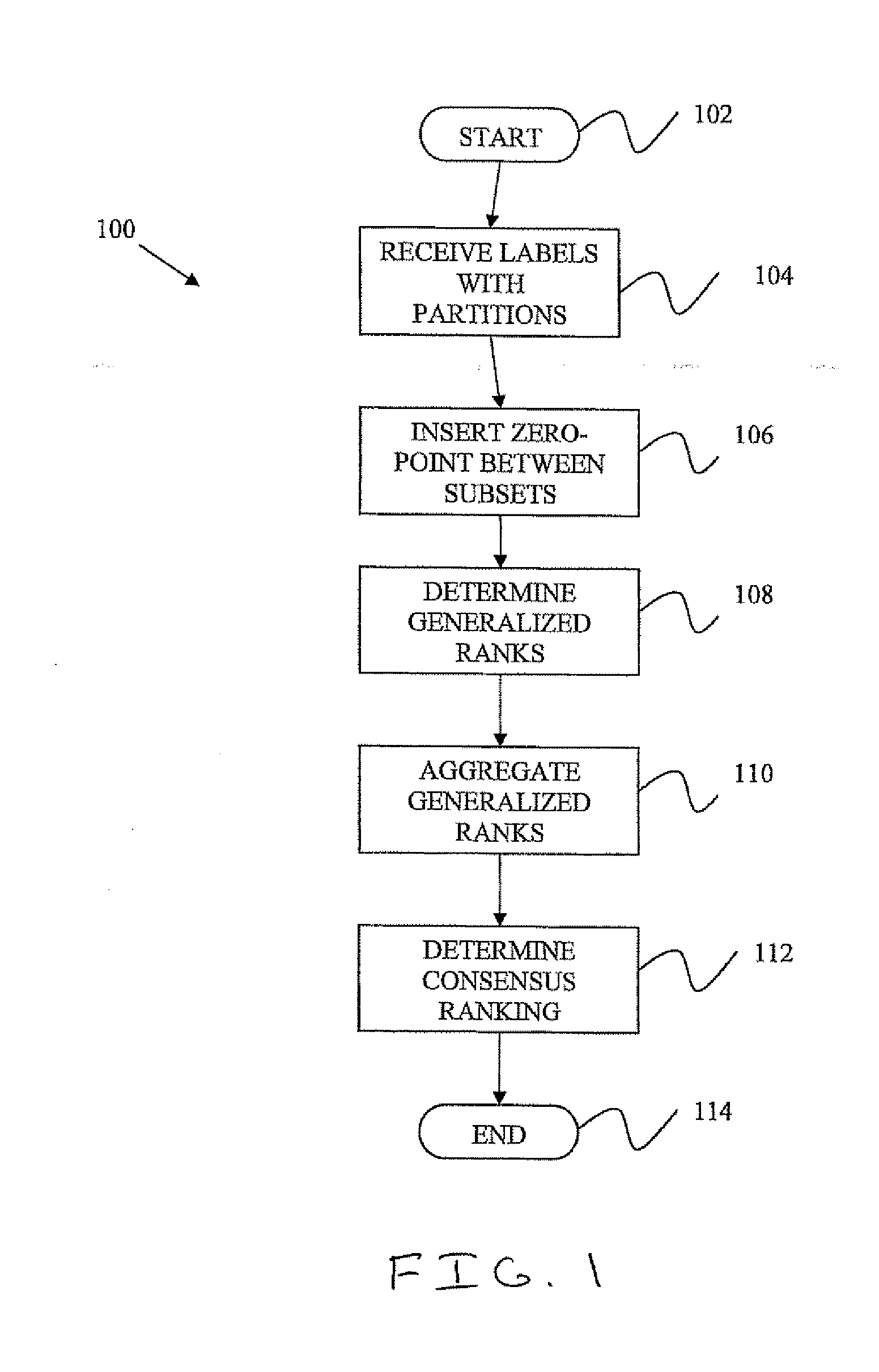
System and Method for Case-Based Multilabel Classification and Ranking
InactiveUS20080010226A1Testing/monitoring control systemsDigital computer detailsState dependentMulti-label classification
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for determining and utilizing case-based ranking methods, such as methods for machine condition monitoring. Specifically, the present invention provides a method for identifying and prioritizing labeled data. The method allows a monitored system to be associated with a calibrated and ordered set of states. Further, in machine condition monitoring, the machine condition is associated with the entire set of states in a particular order with one or more relevance zero-points That is, a ranked set of calibrated data describing machine conditions is augmented with an annotation indicating a cut-off between relevant and non-relevant data.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
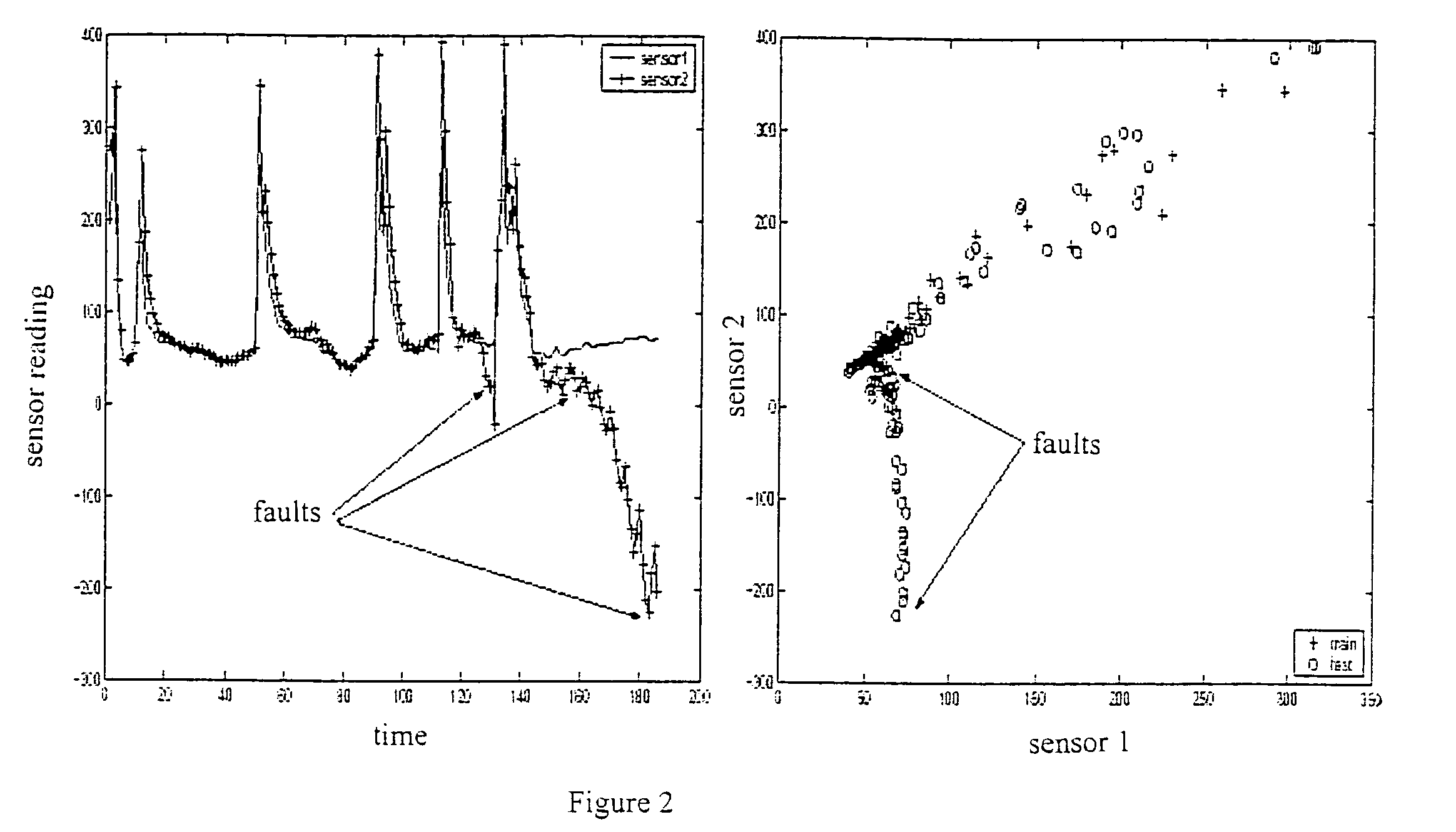
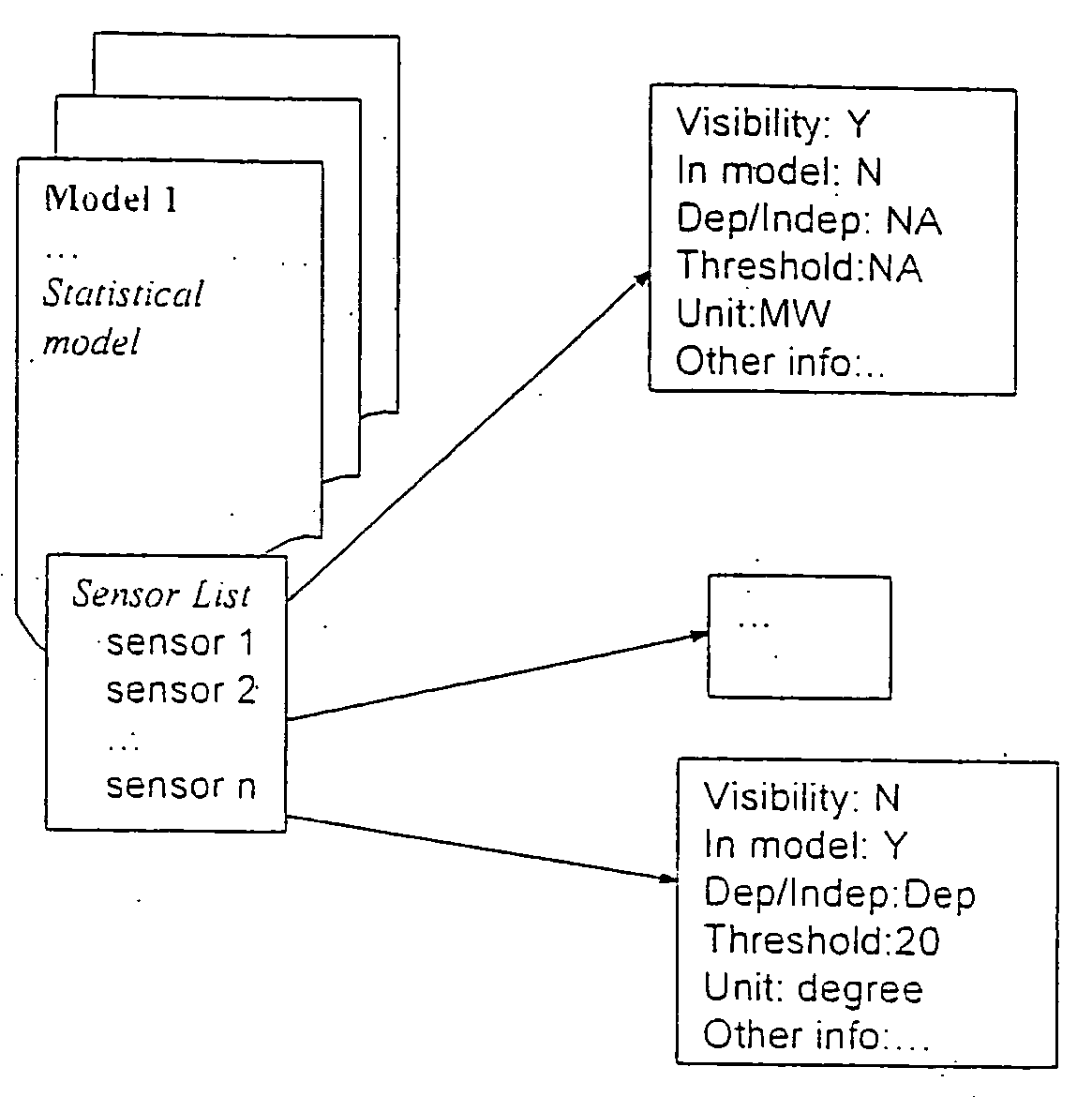
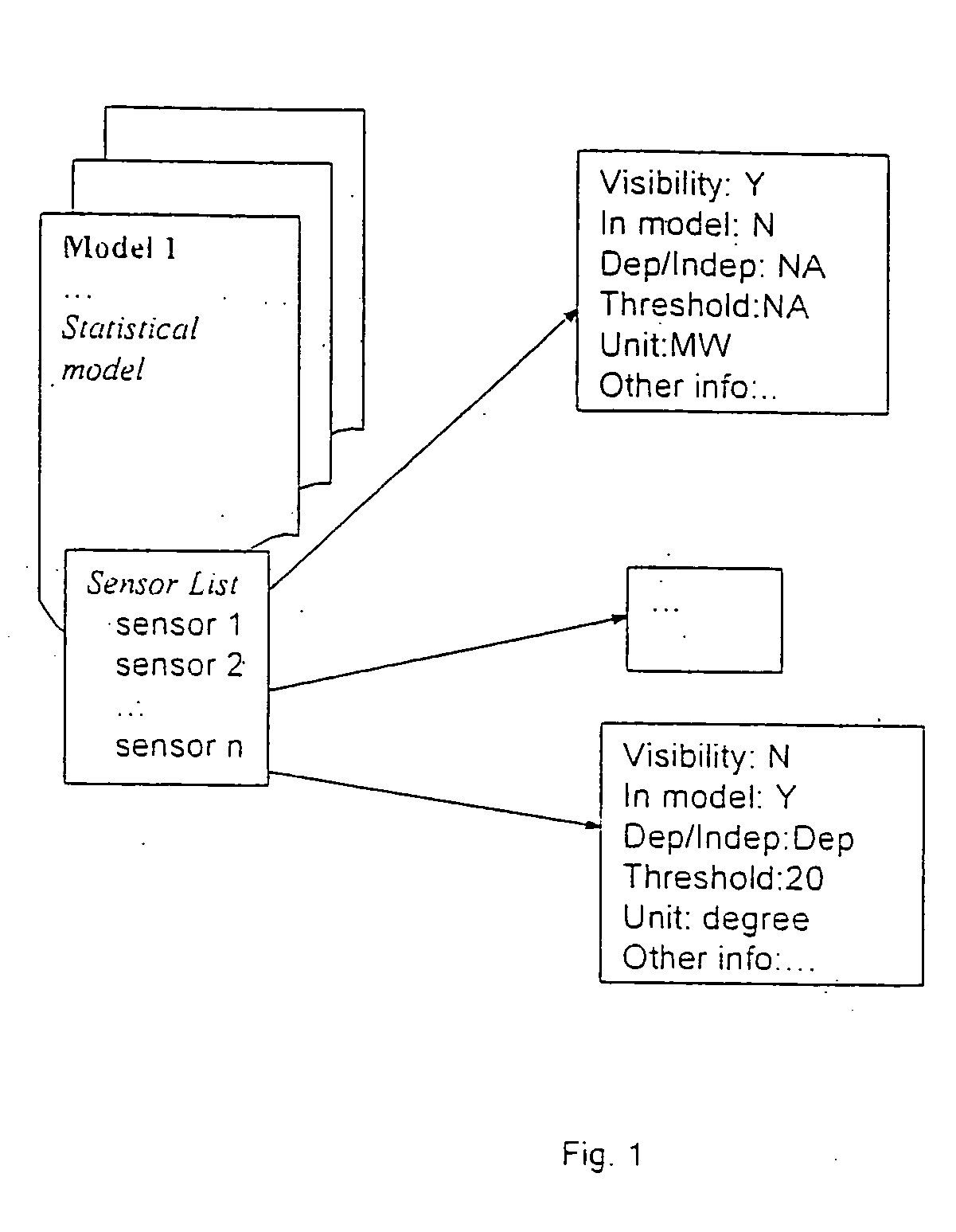
Tool for sensor management and fault visualization in machine condition monitoring
ActiveUS20050062599A1Effective toolElectrical testingElectric testing/monitoringPower stationMonitoring system
A tool for sensor management and fault visualization in machine condition monitoring. The method and system are able to monitor a plurality of sensors at one time. The sensors may be used in a power plant system monitoring system. The method and system may display a fault status for each sensor in the plurality of sensors in a single display, wherein the fault status for each sensor is displayed over time. The method and system also provide a mechanism that permits a user to examine details of each sensor in the plurality of sensors at any given time. In addition, the method and system are capable of categorizing each fault in the fault status using one or more properties or categorizing criteria. The method and system also permit sensors to be tested such that different operating models may be examined by utilizing different sensors.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
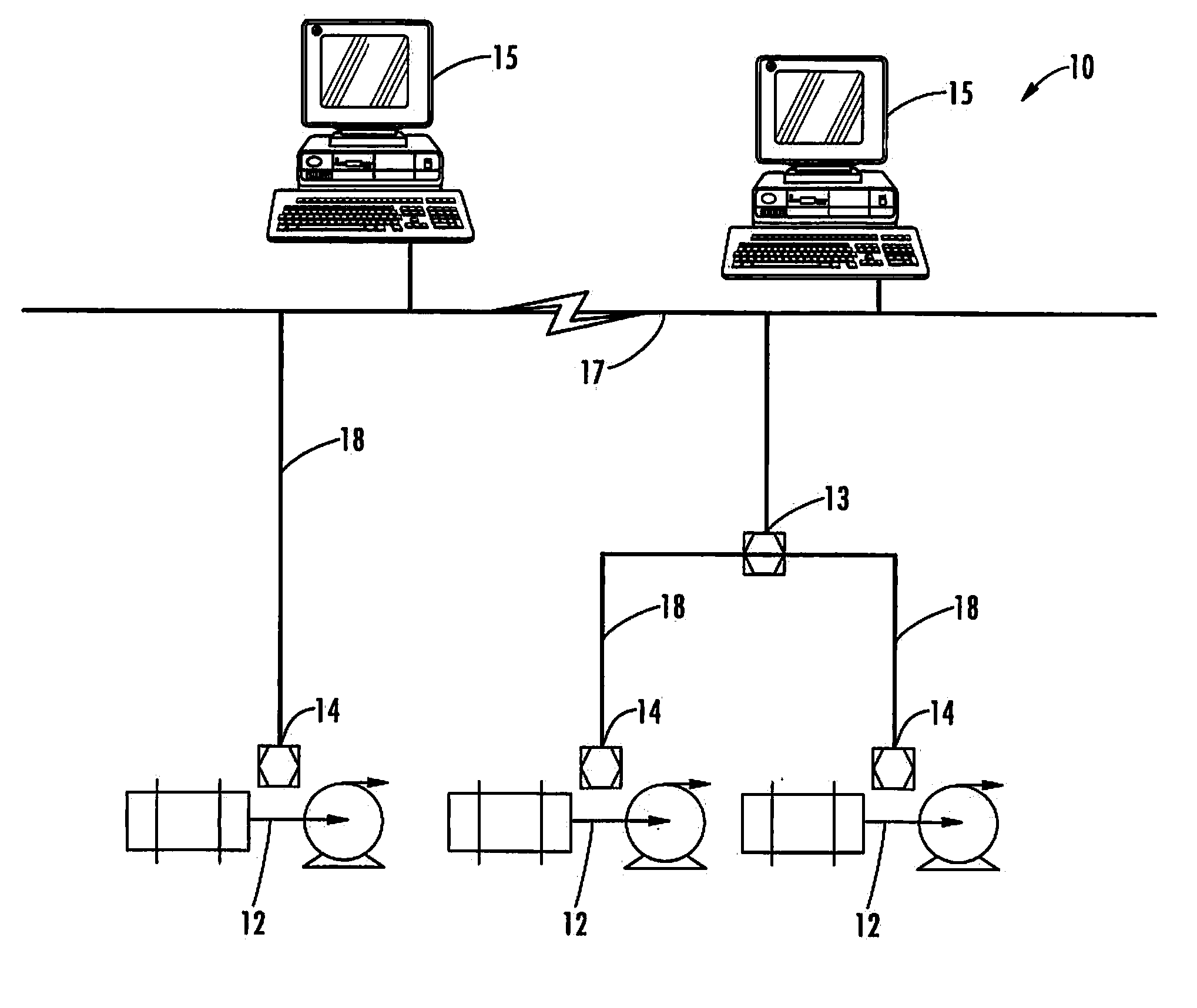
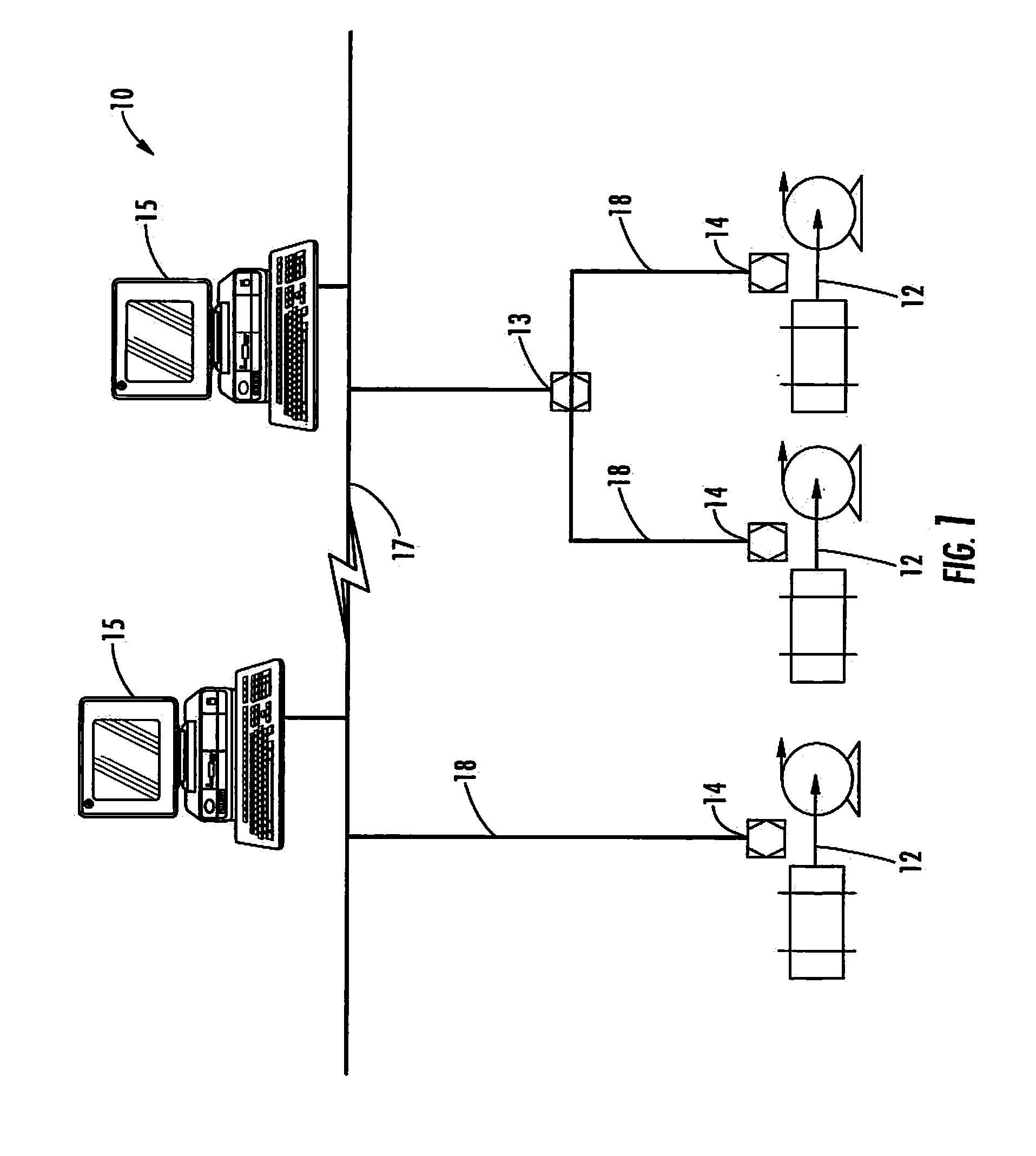
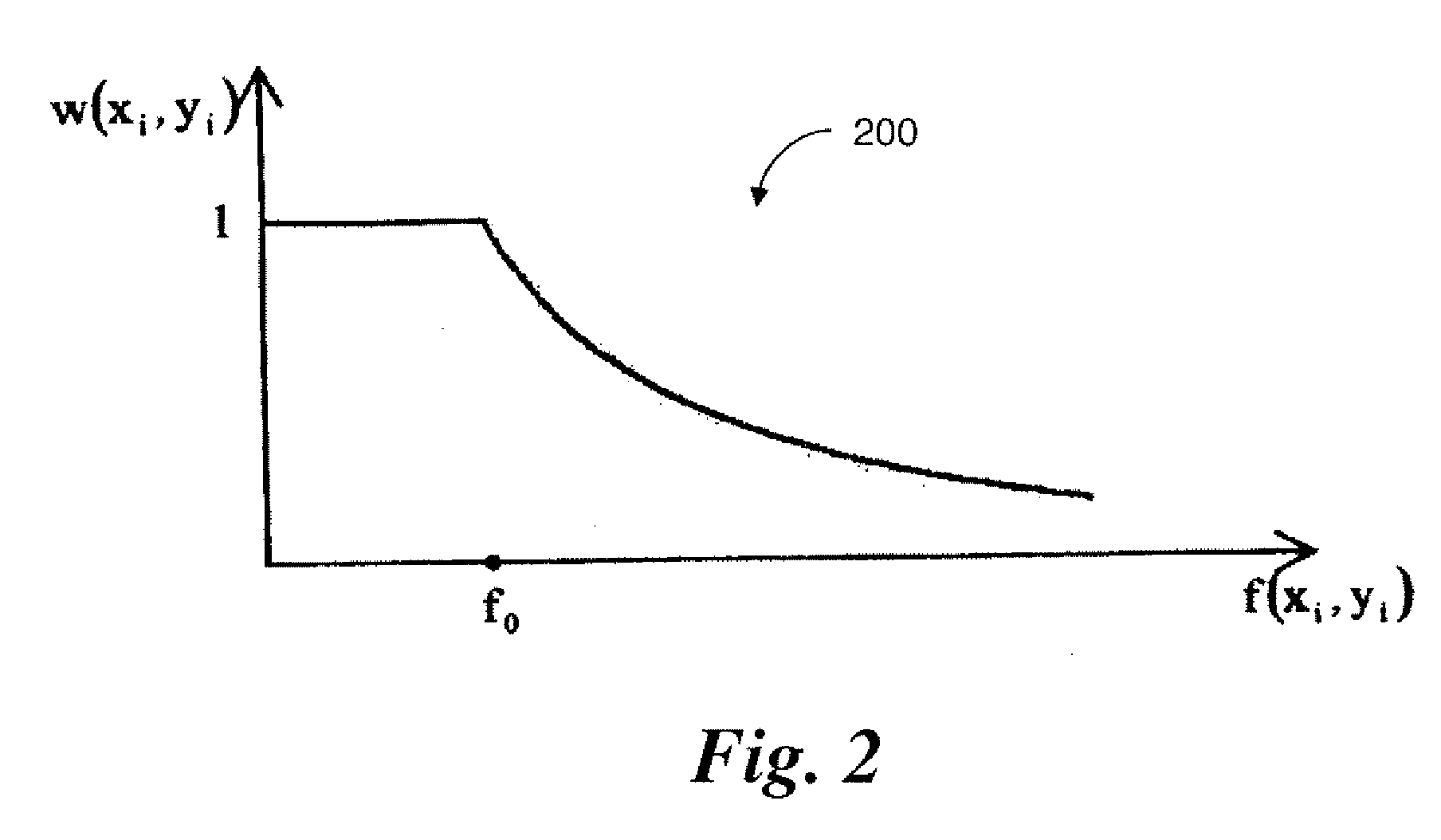
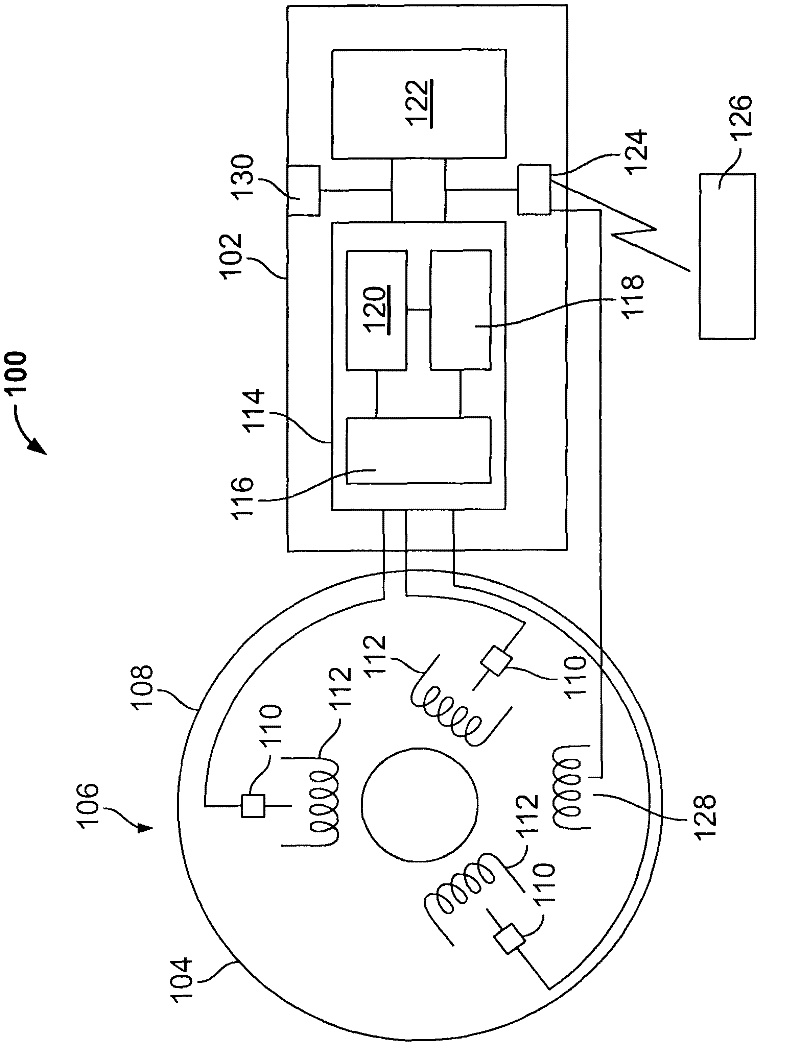
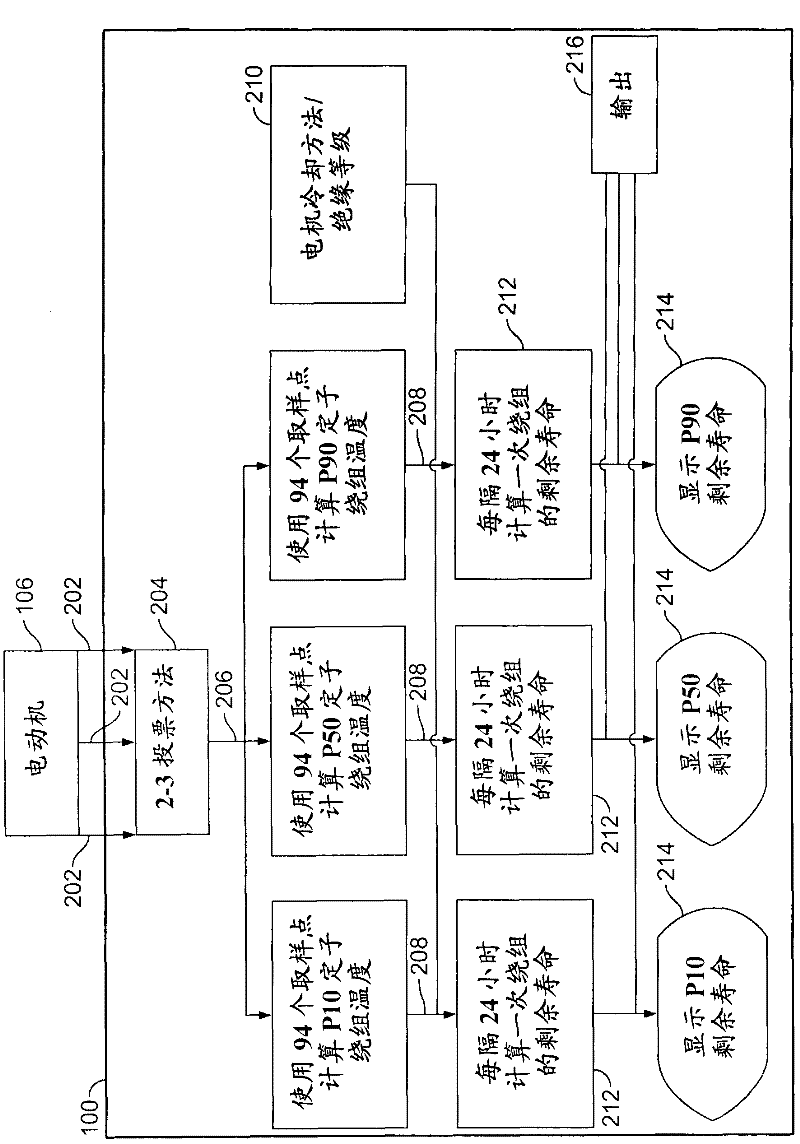
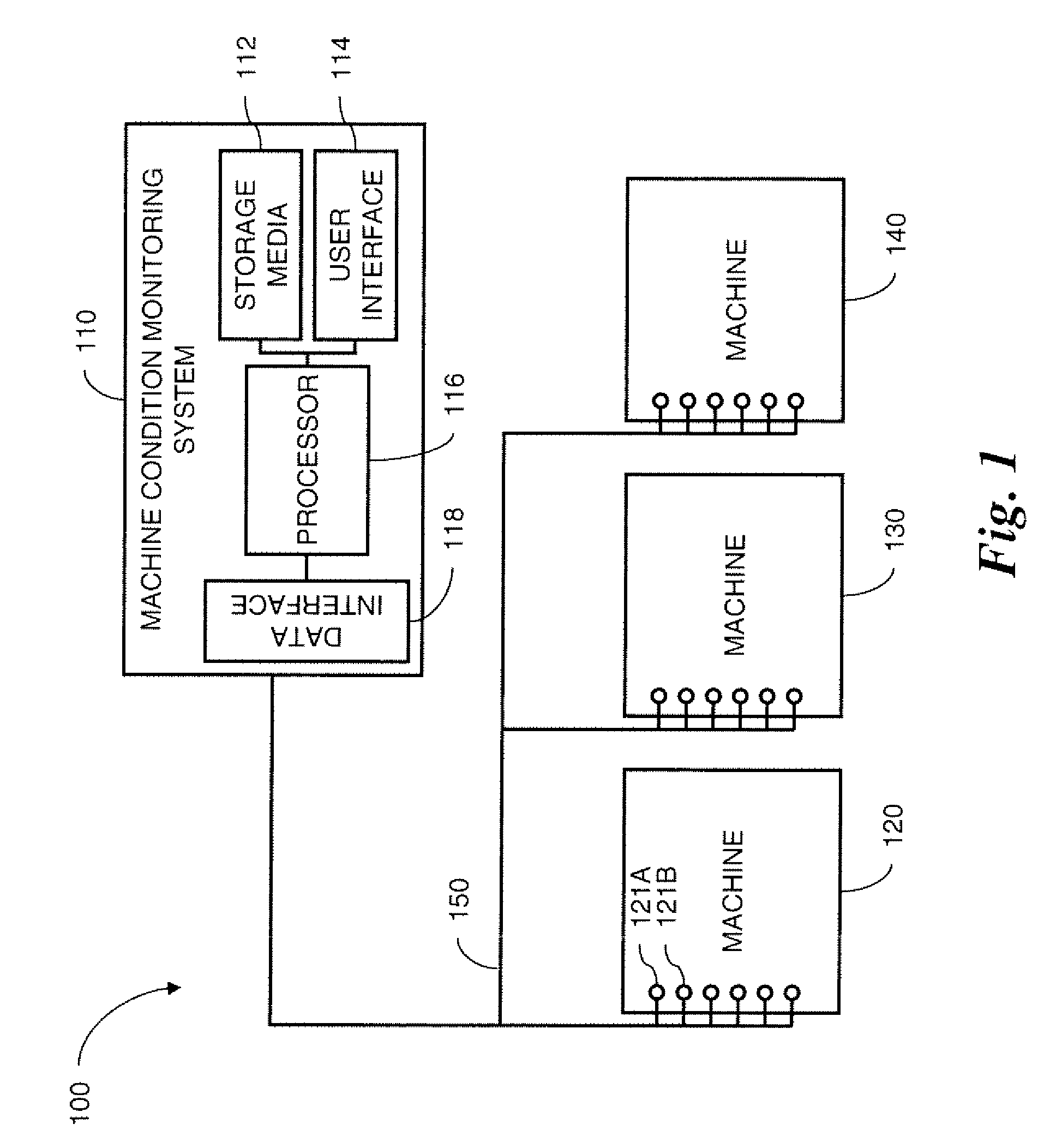
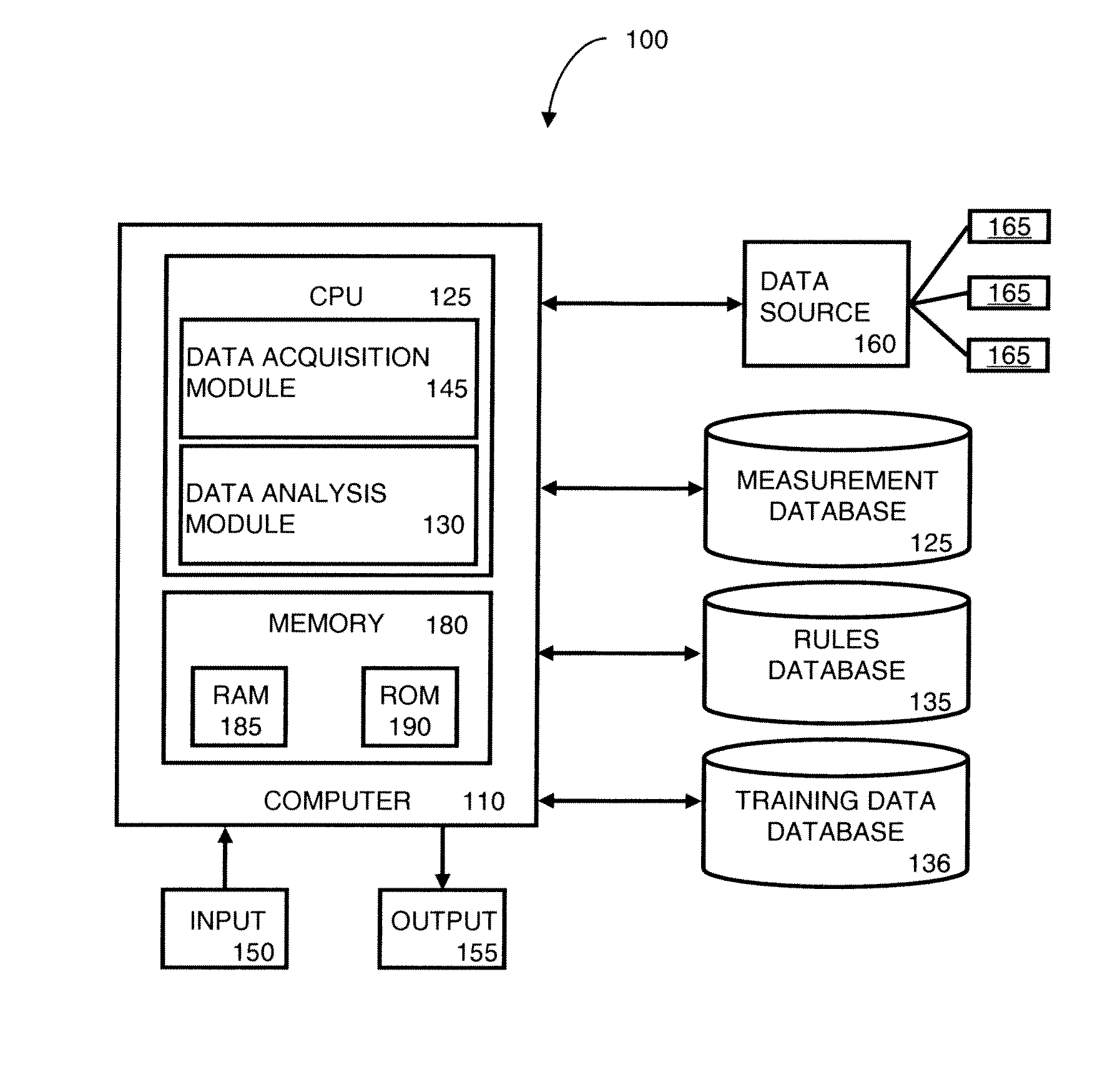
Method and system for machine condition monitoring
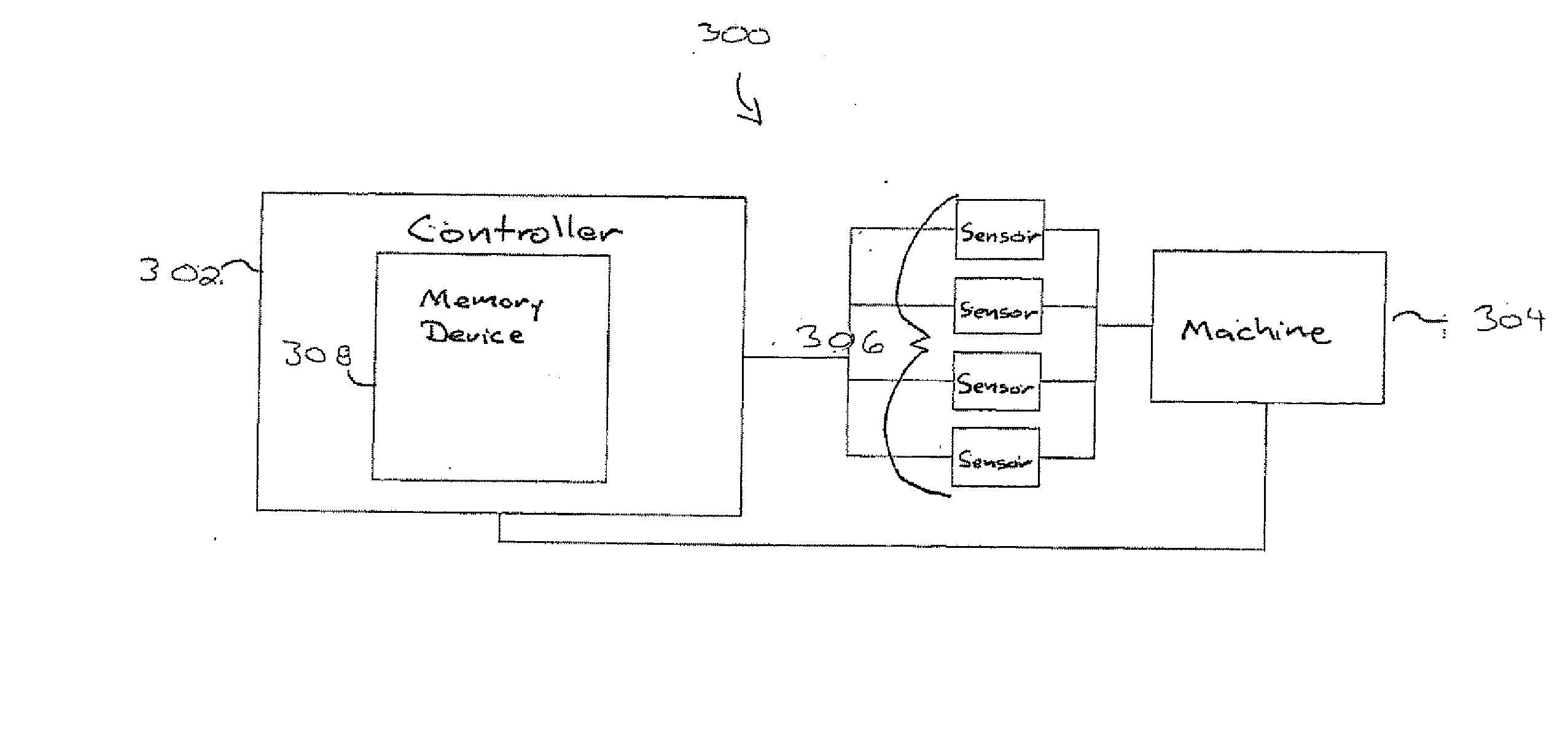
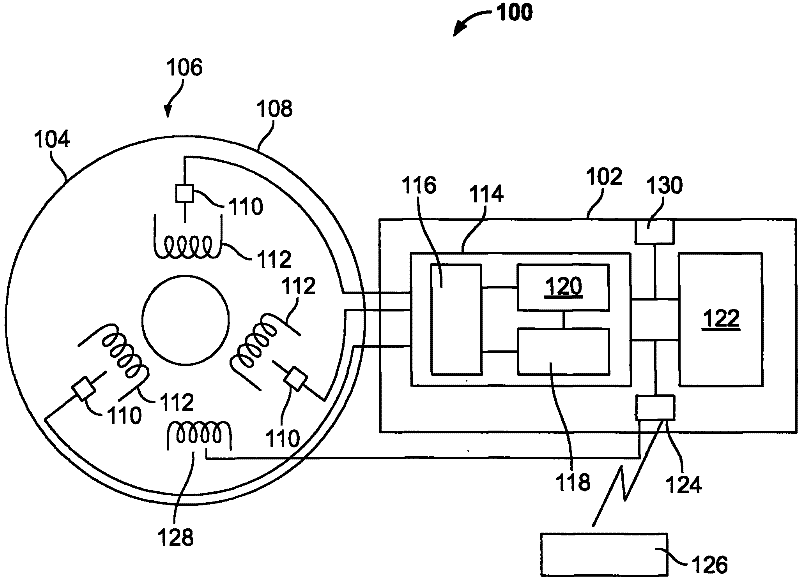
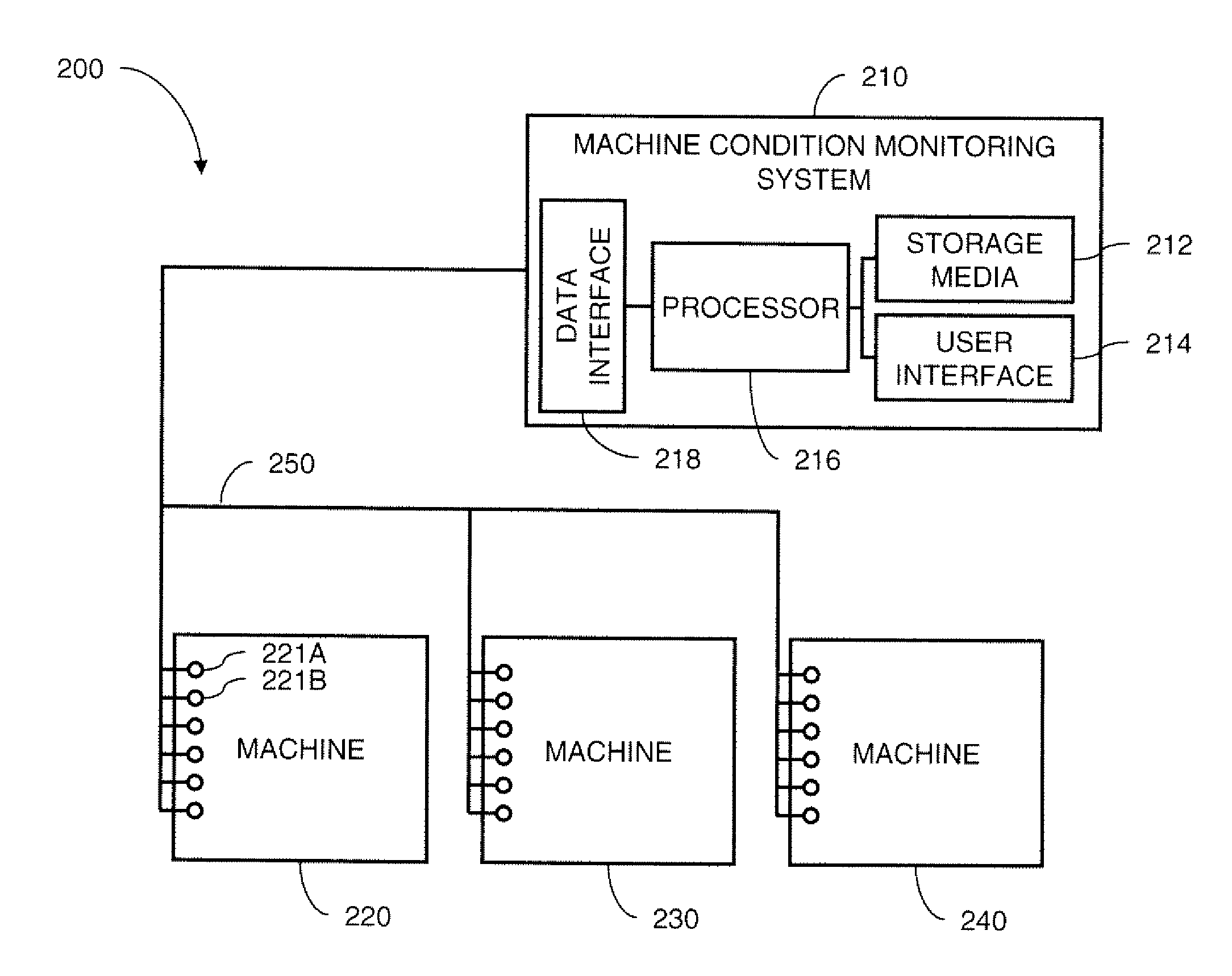
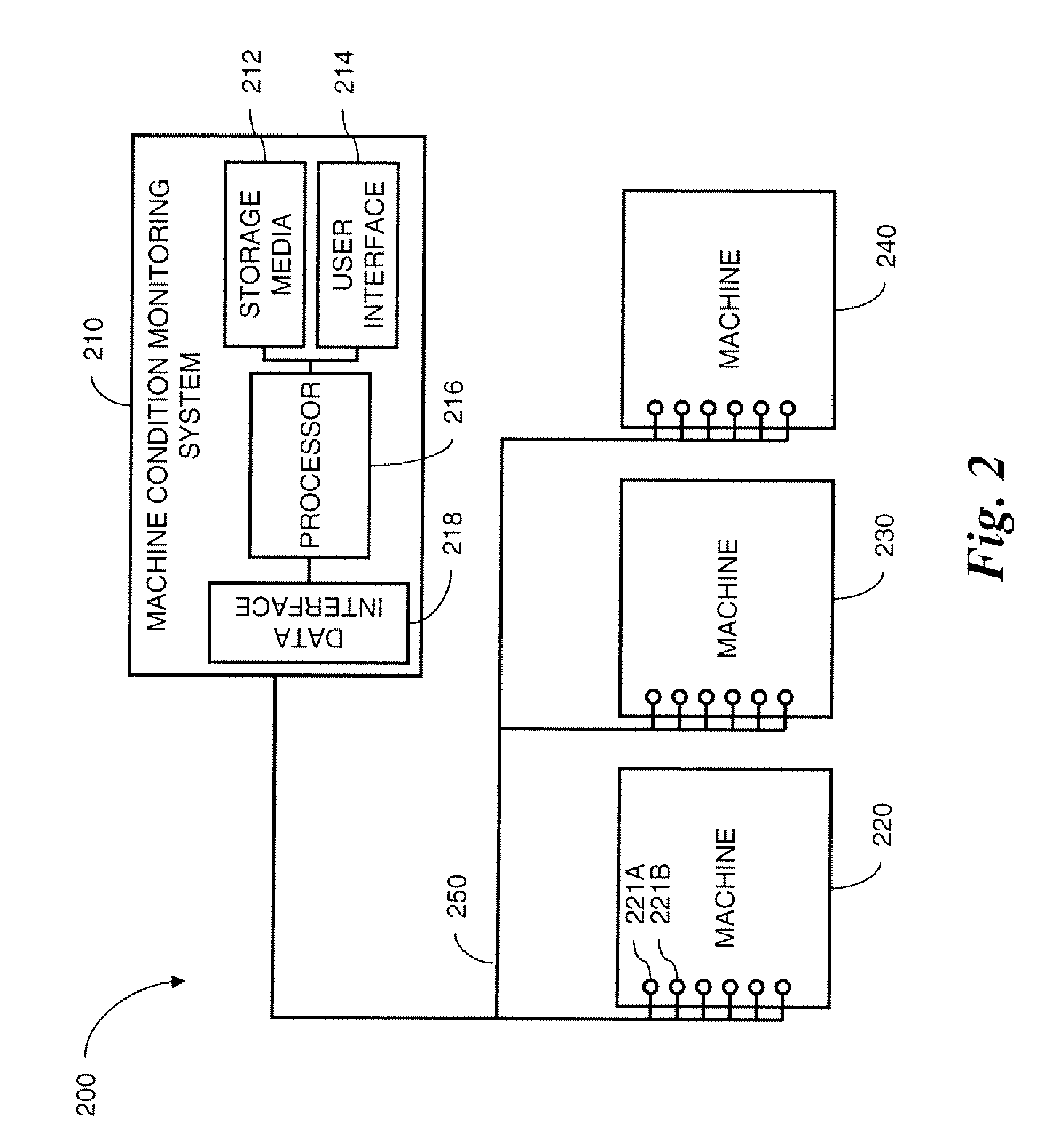
InactiveCN102539180AProgramme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsMonitoring systemDisplay device
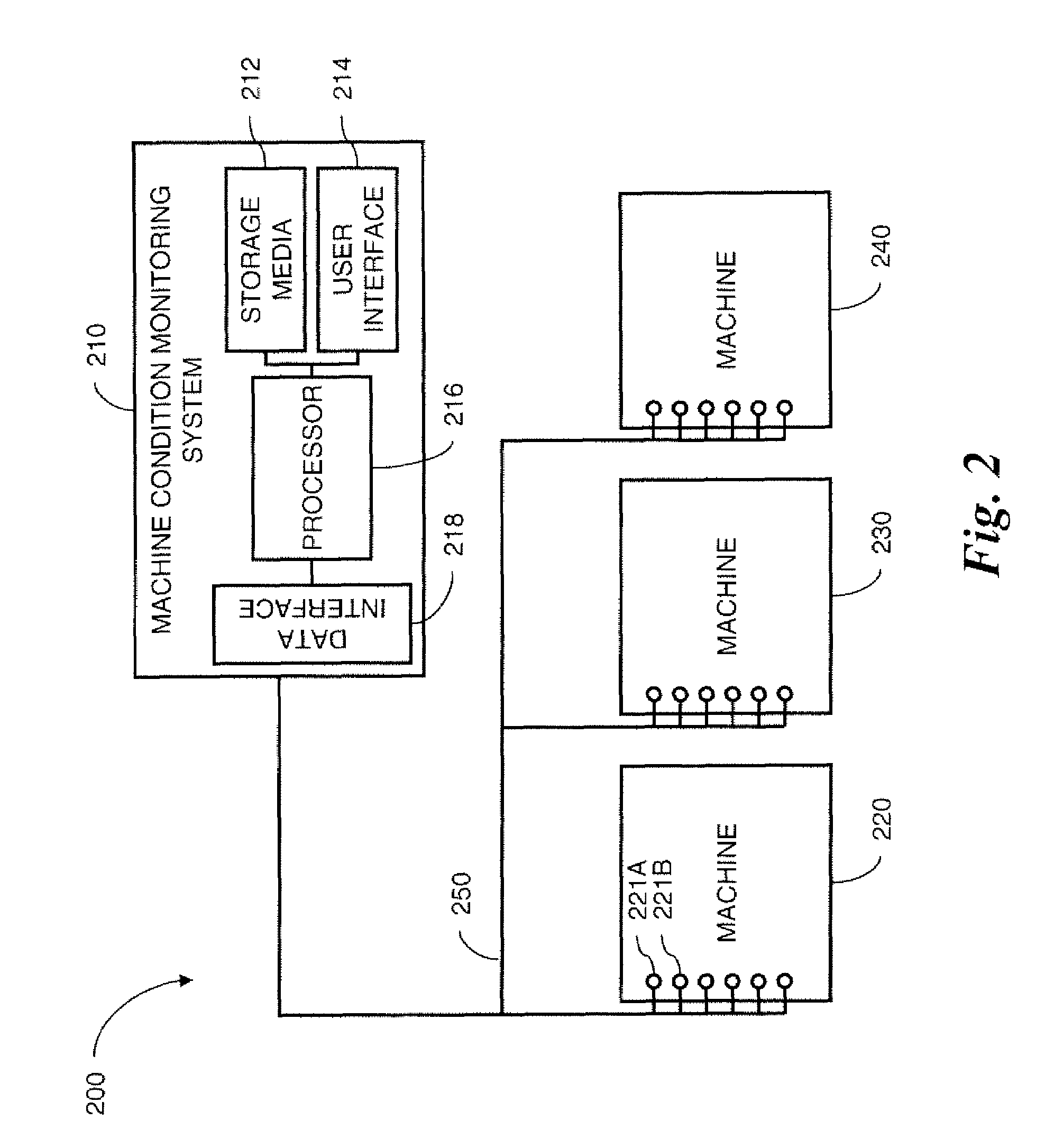
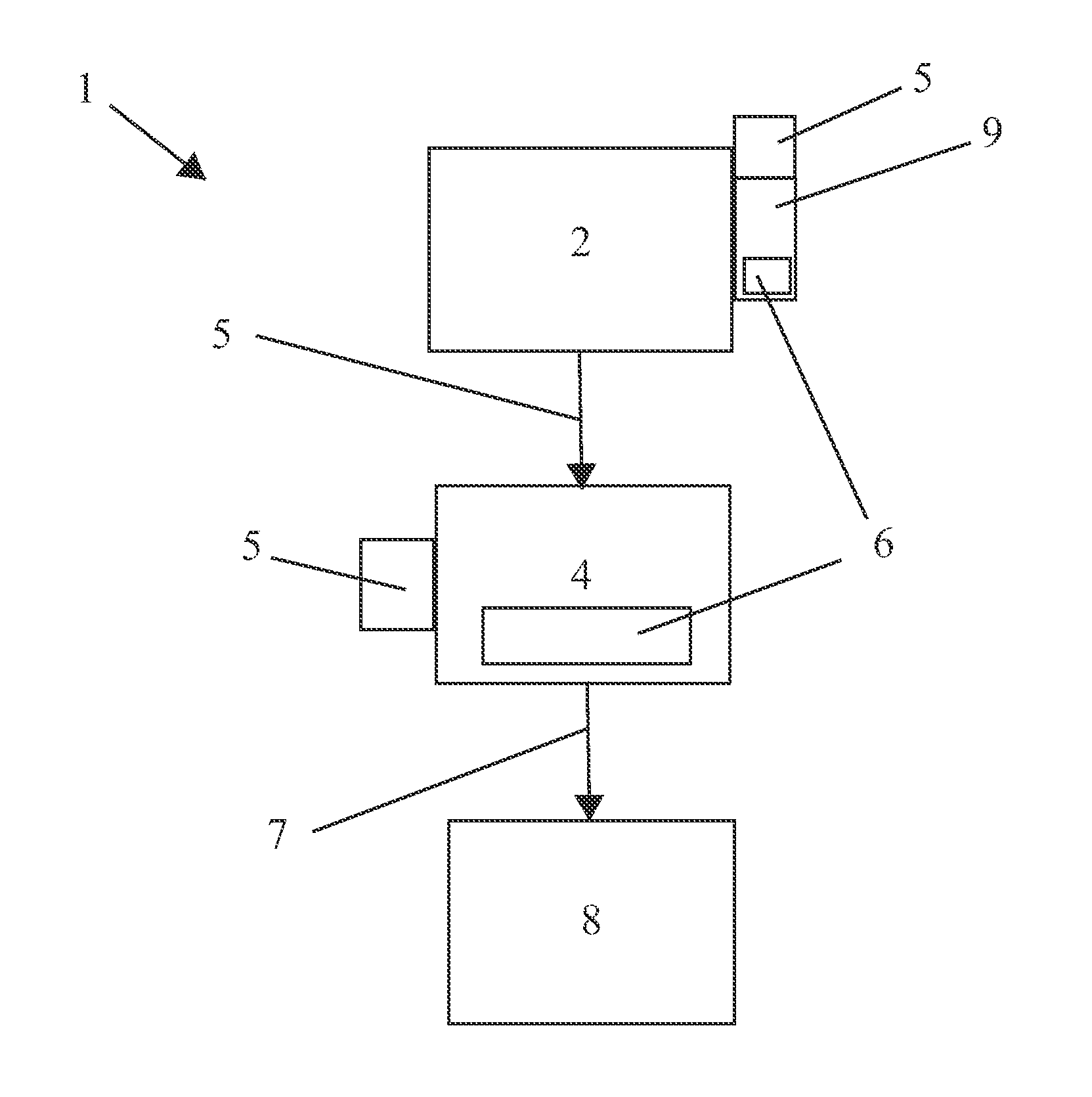
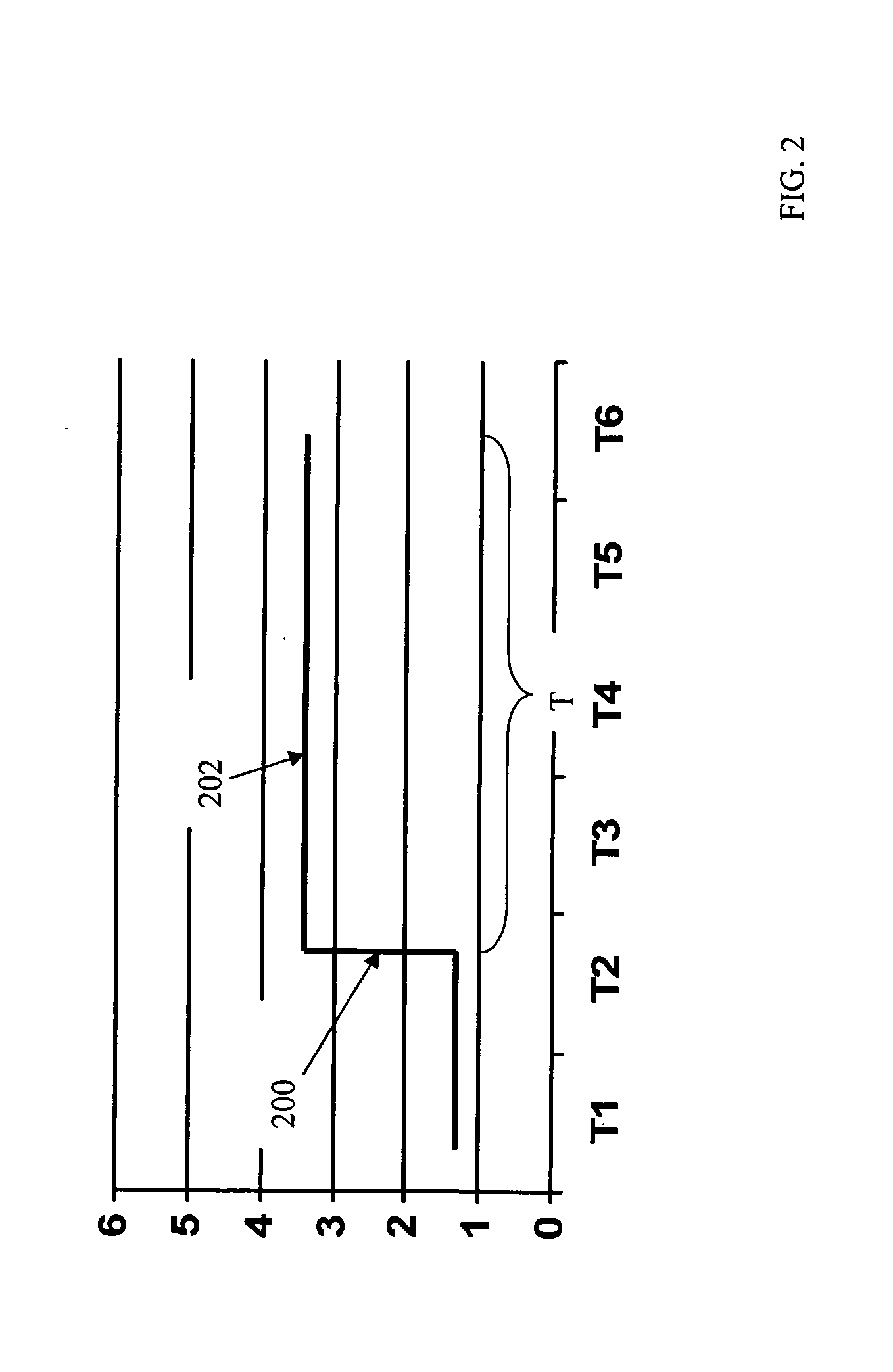
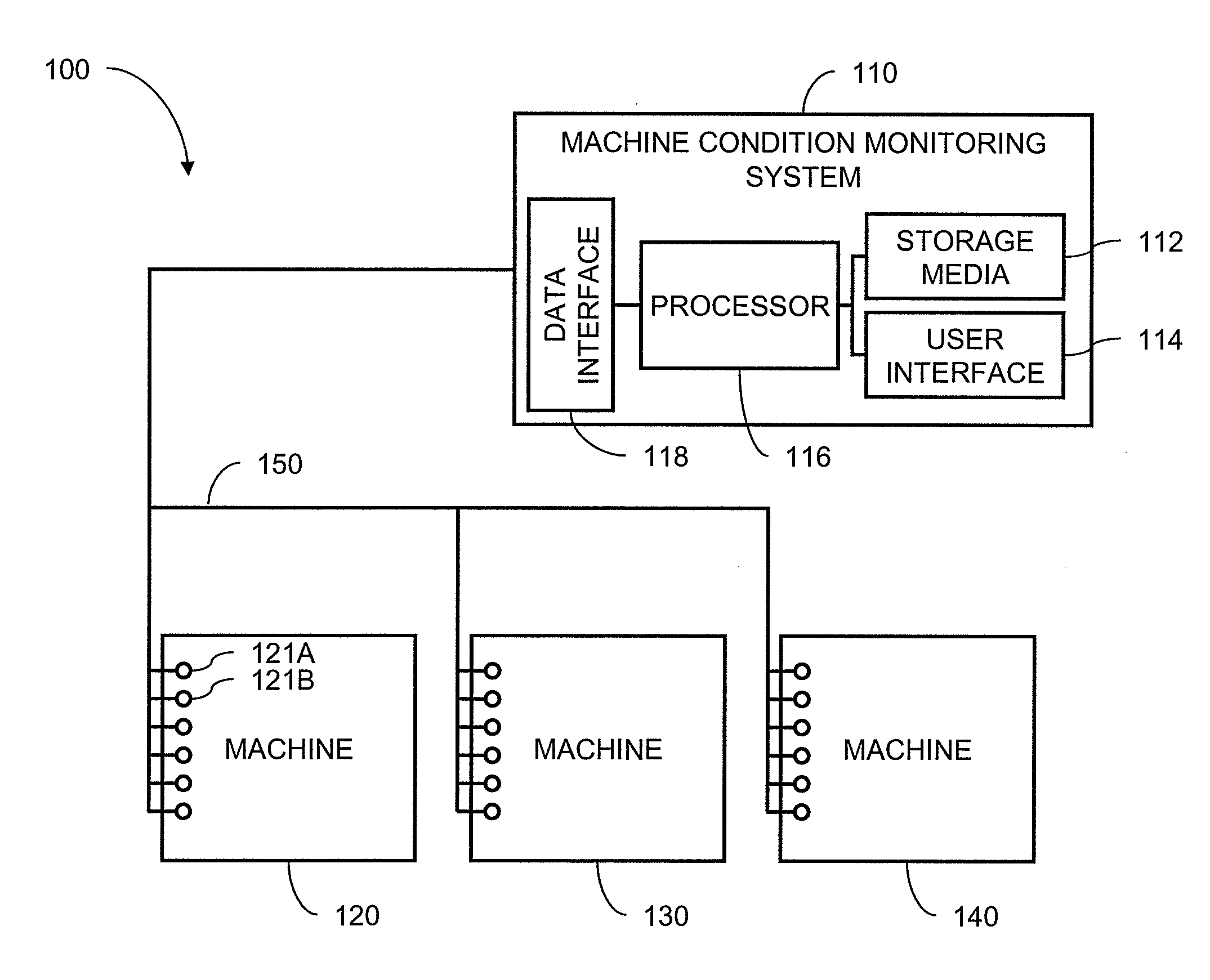
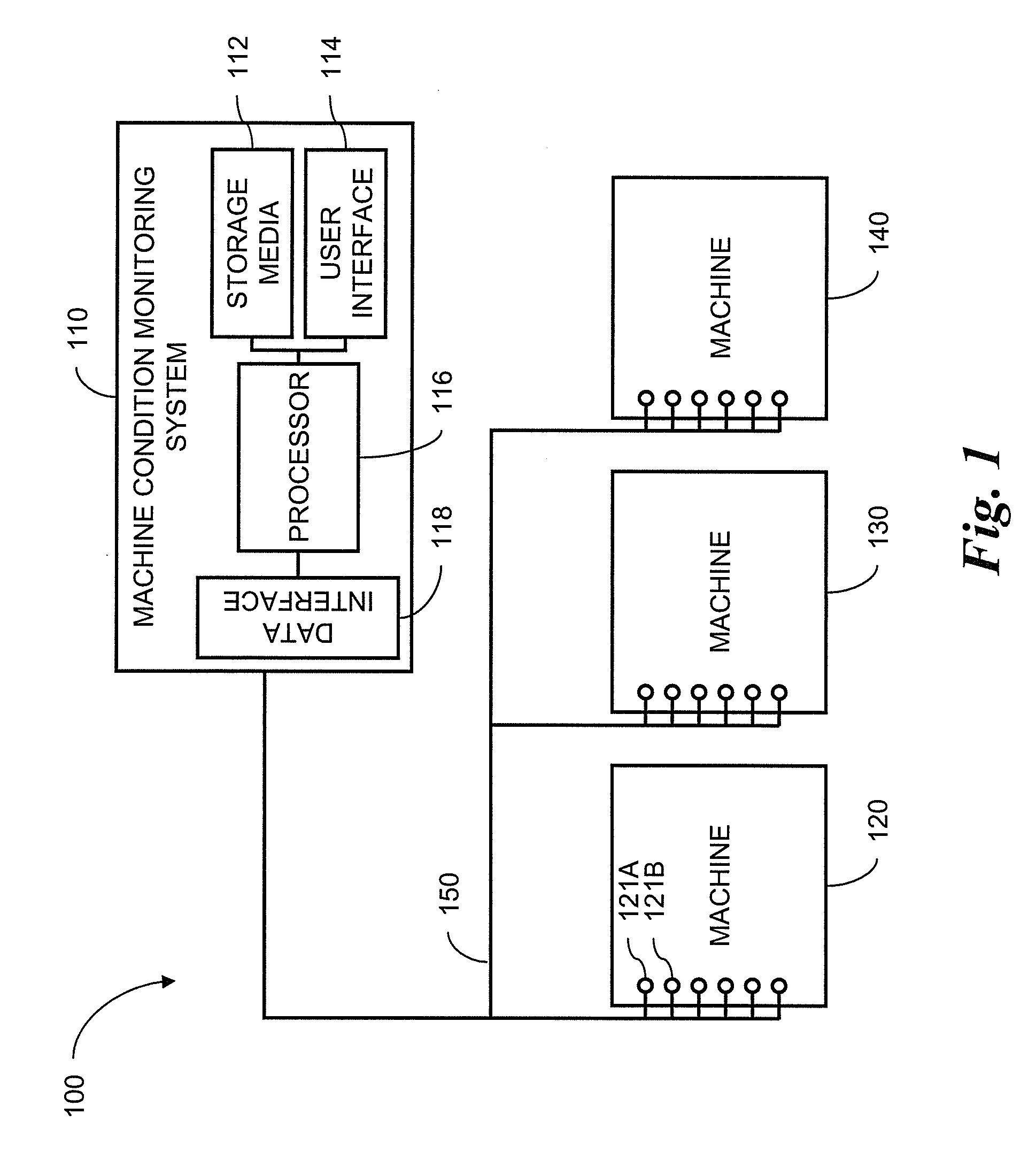
A machine monitoring system (100) is provided. The system includes a housing (102) mounted to a surface (108) of a machine (106), a plurality of sensors (110) configured to monitor a parameter of the machine and generate respective output signals (202), the parameter indicative of a condition of the machine, a voting module (116) positioned within the housing and configured to receive the respective output signals and generate a corrected output (206) based on the respective output signals, a memory device (118) positioned within the housing and including a store location configured to store manual input functions (210) relating to a construction of the machine, a life calculator (120) positioned within the housing and communicatively coupled to the voting module and the memory device, the life calculator configured to determine a life remaining in the machine using the corrected output and the manual input functions, and a display (122) positioned within the housing and configured to display (214) the life remaining in the machine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
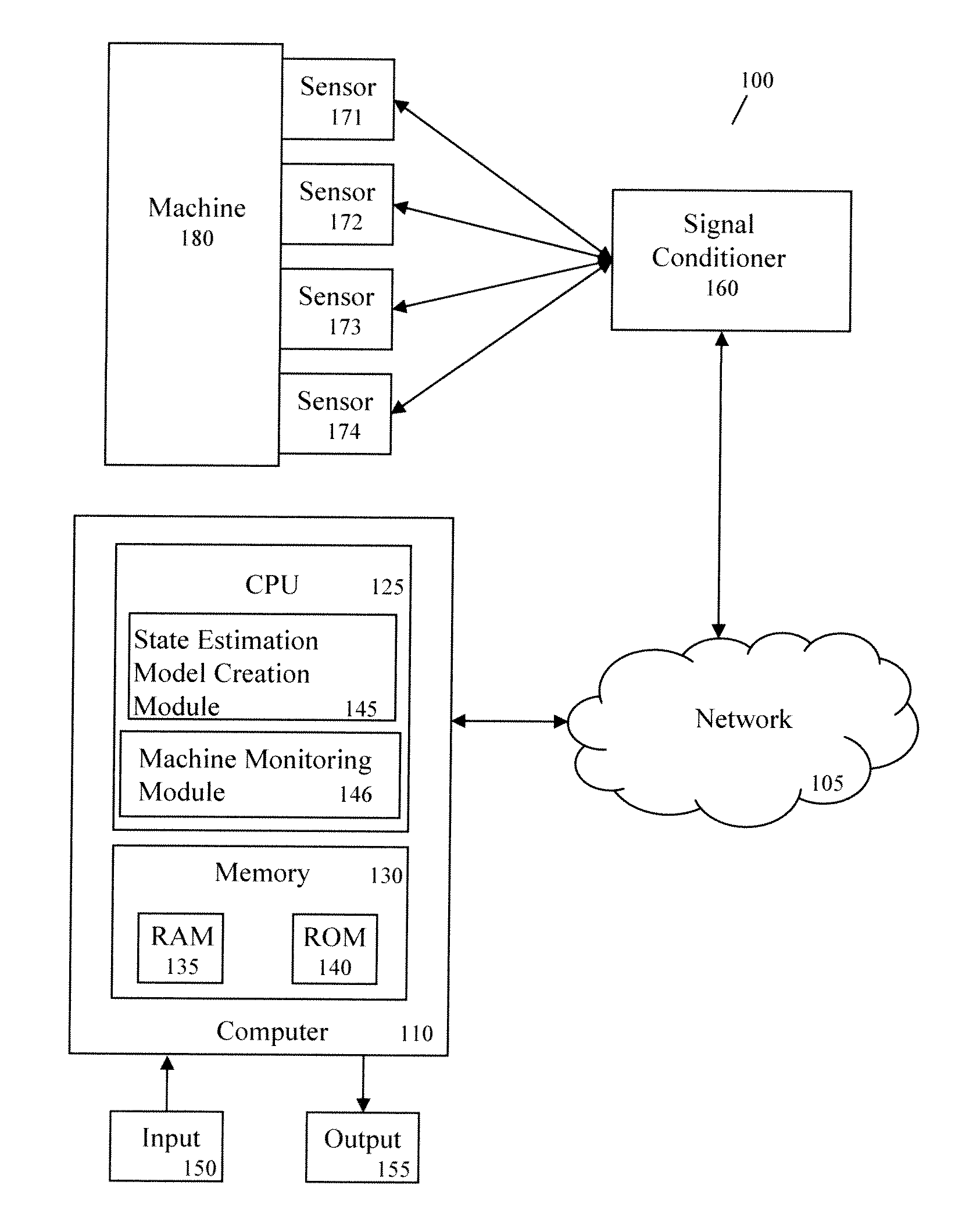
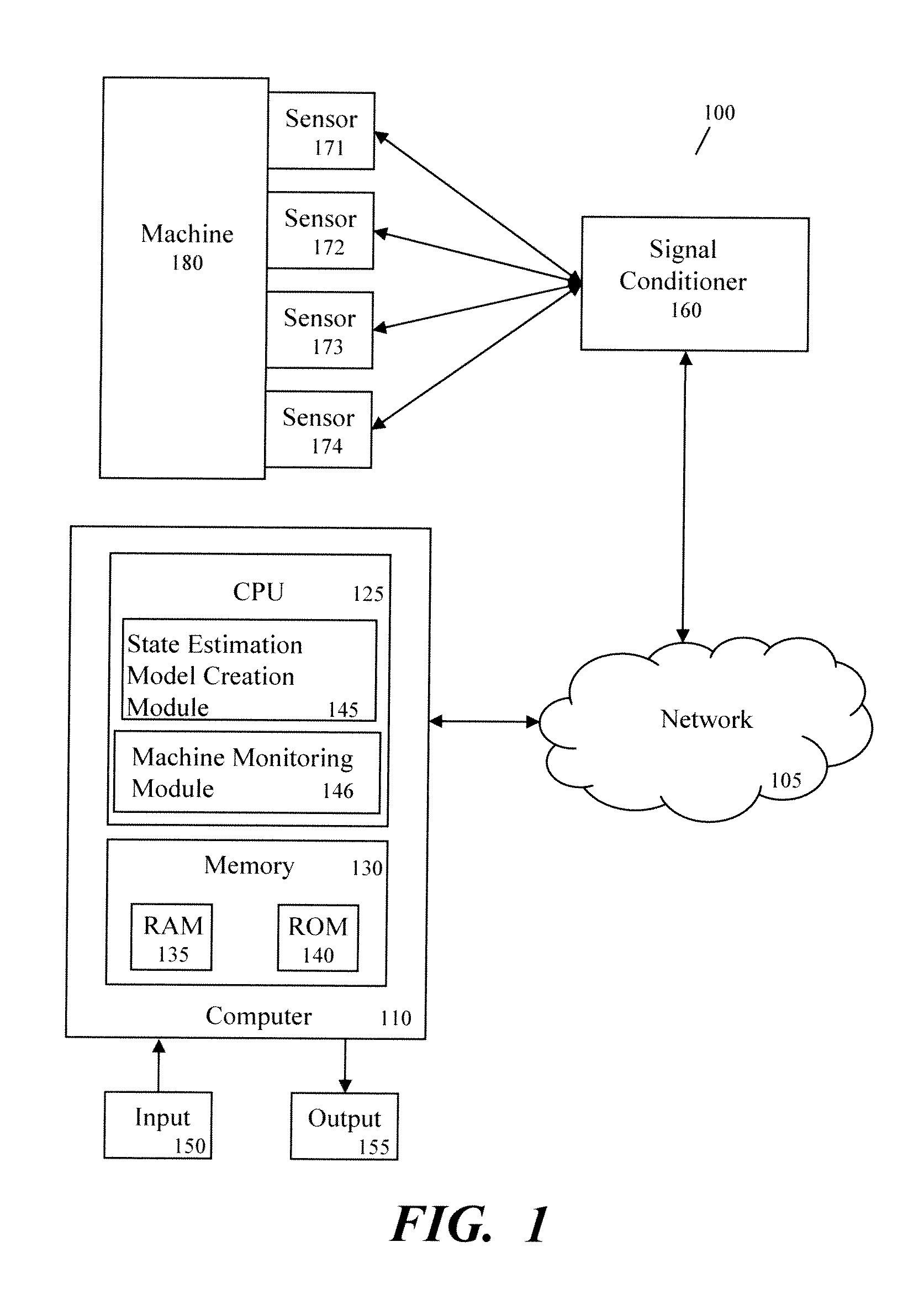
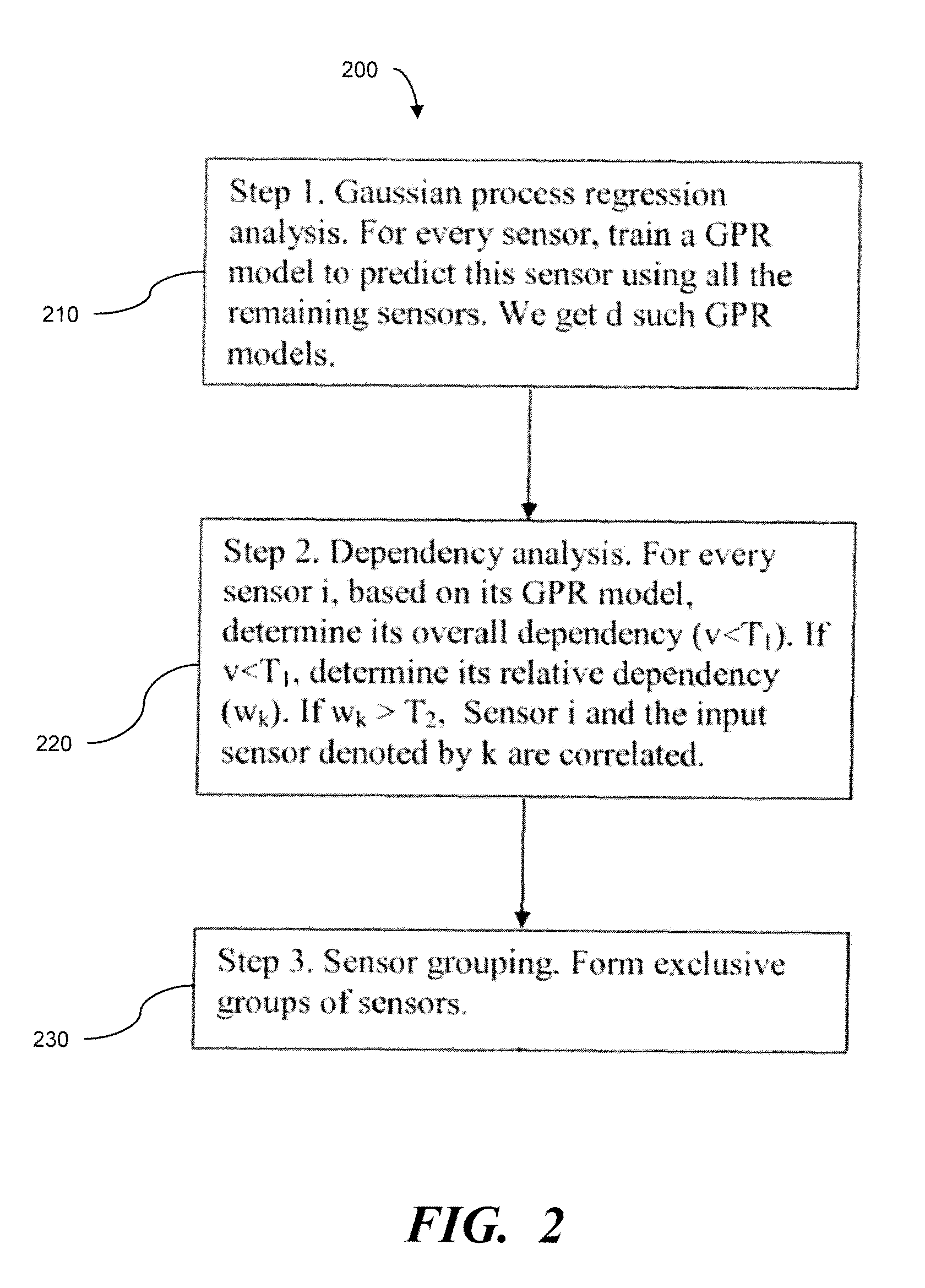
Method And Apparatus For Creating State Estimation Models In Machine Condition Monitoring
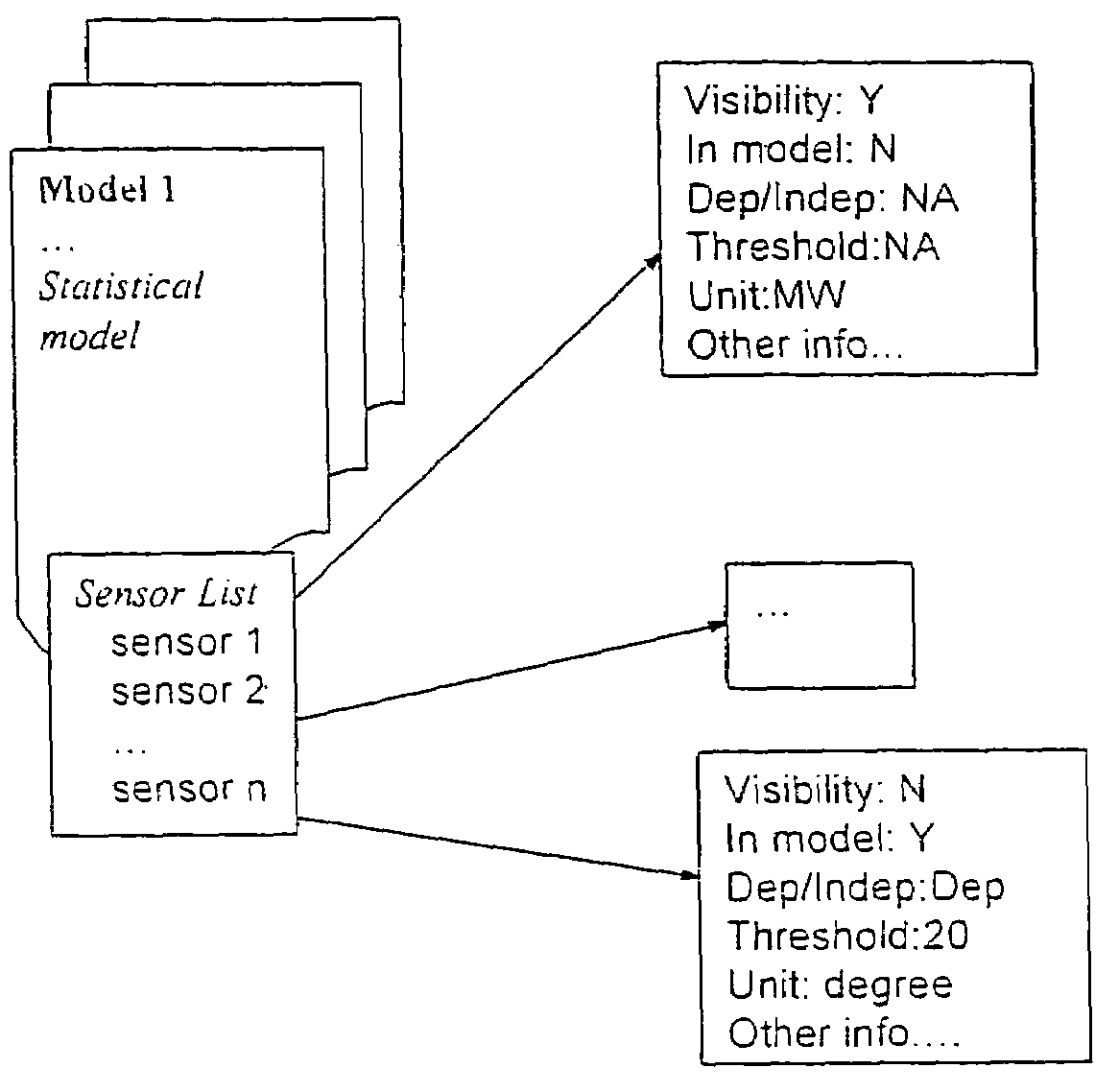
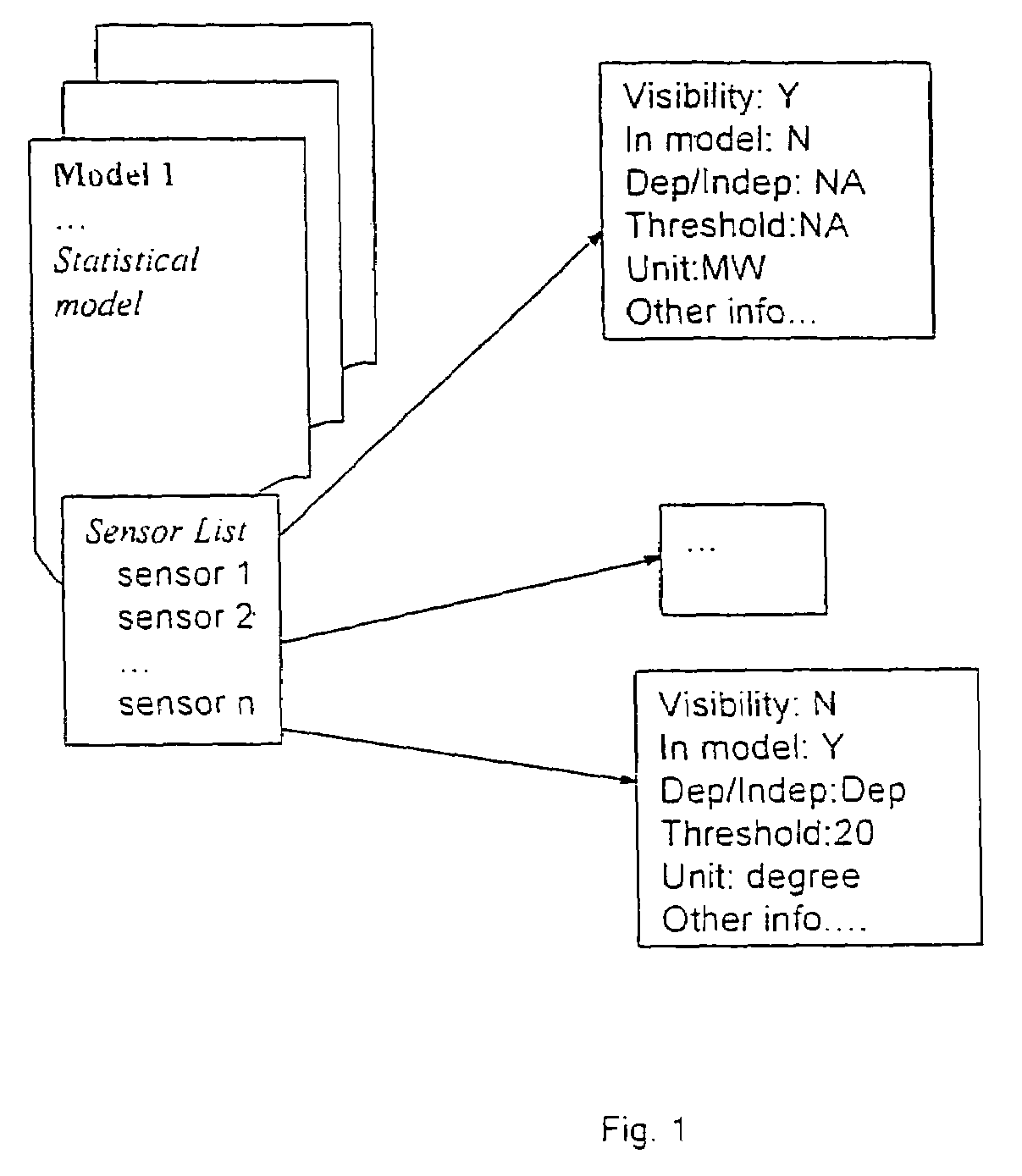
In a machine condition monitoring technique, related sensors are grouped together in clusters to improve the performance of state estimation models. To form the clusters, the entire set of sensors is first analyzed using a Gaussian process regression (GPR) to make a prediction of each sensor from the others in the set. A dependency analysis of the GPR then uses thresholds to determine which sensors are related. Related sensors are then placed together in clusters. State estimation models utilizing the clusters of sensors may then be trained.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
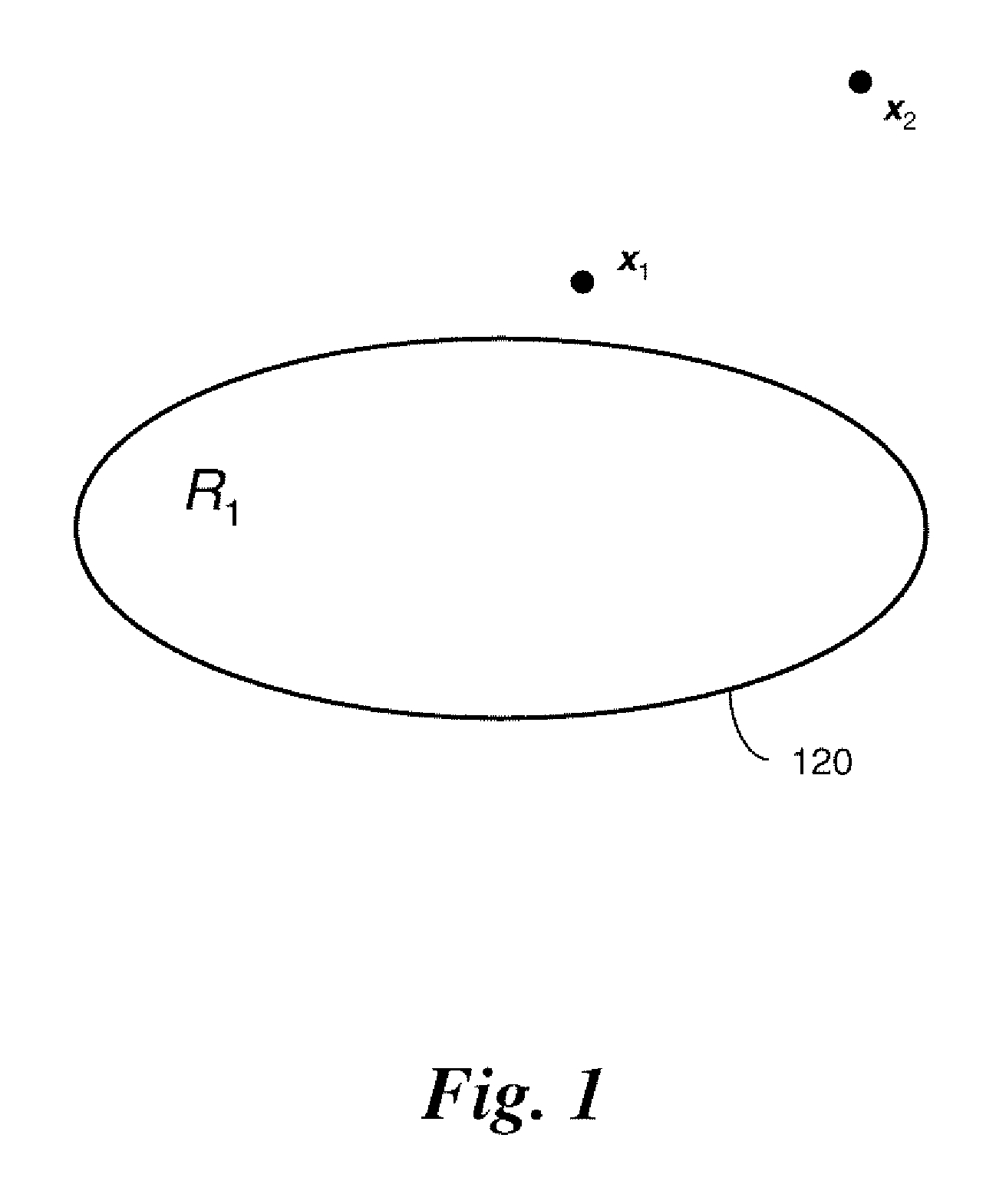
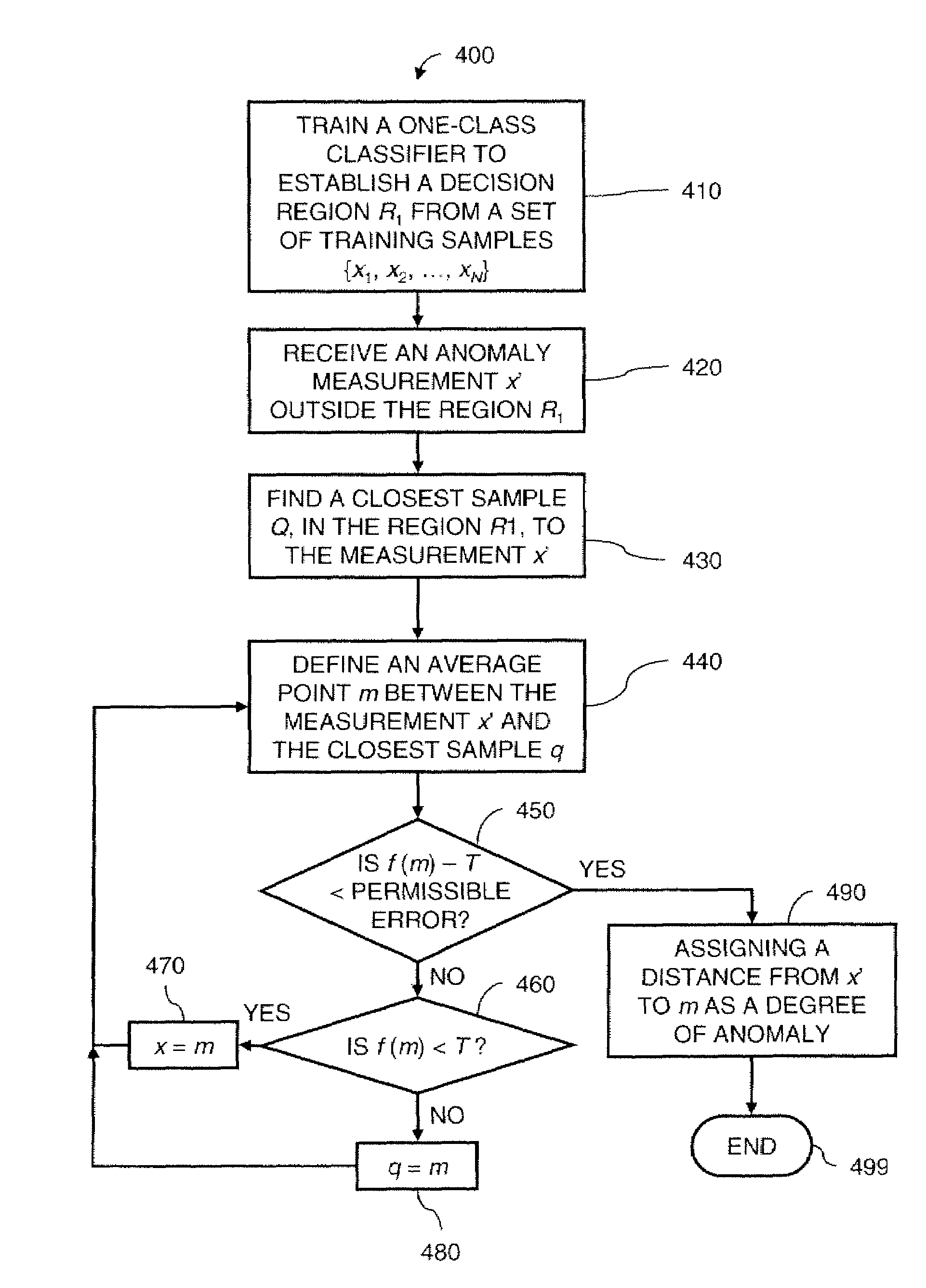
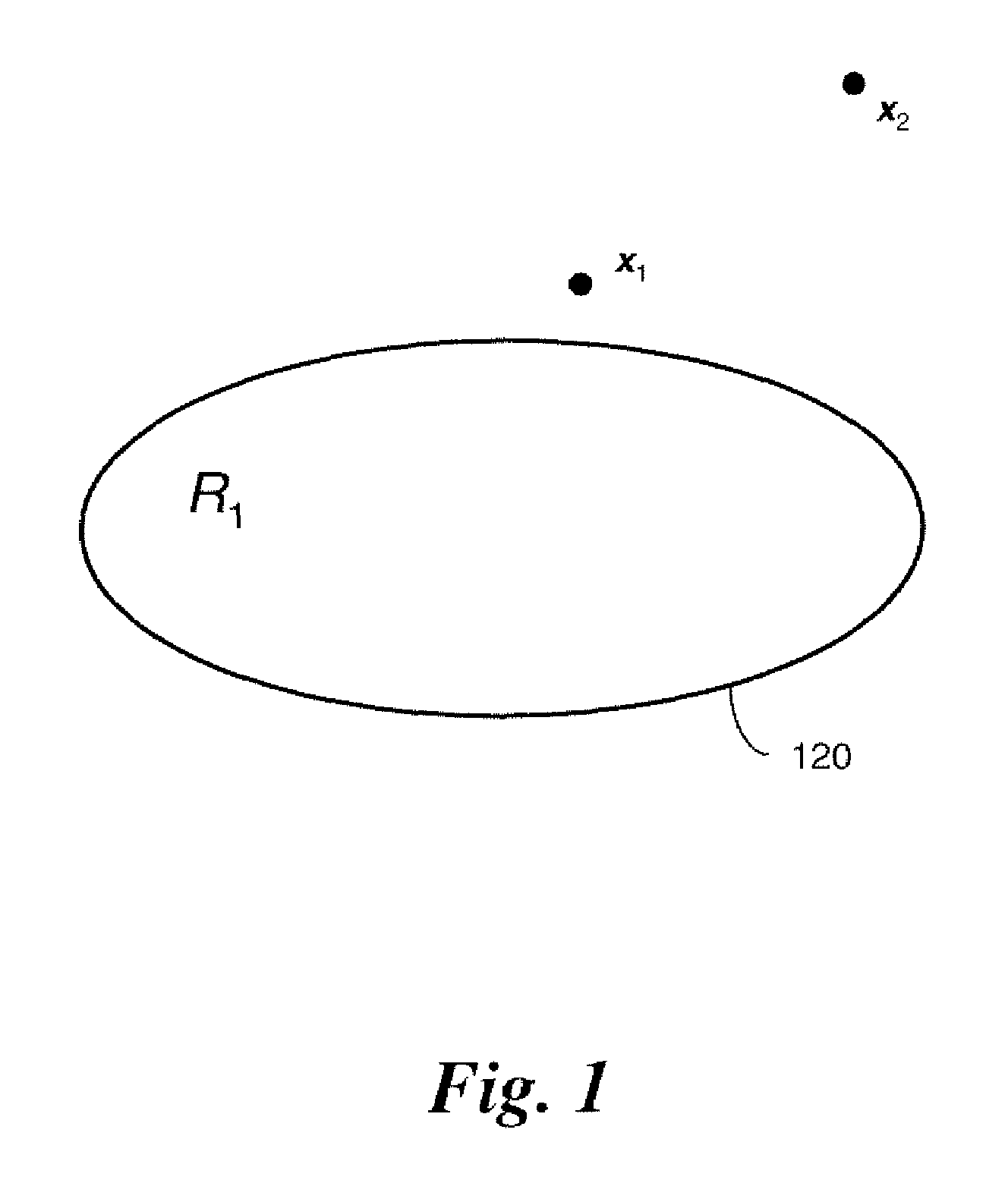
Evaluating Anomaly For One Class Classifiers In Machine Condition Monitoring
ActiveUS20070143038A1Small sample sizeReduce in quantityProgramme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsOne-class classificationMachine condition monitoring
A method for monitoring machine conditions provides additional information using a one-class classifier in which an evaluation function is learned. In the method, a distance is determined from an anomaly measurement x to at boundary of a region R1 containing all acceptable measurements. The distance is used as a measure of the extent of the anomaly. The distance is found by searching along a line from the anomaly to a closest acceptable measurement within the region R1.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method and equipment for cleaning and maintaining rolls
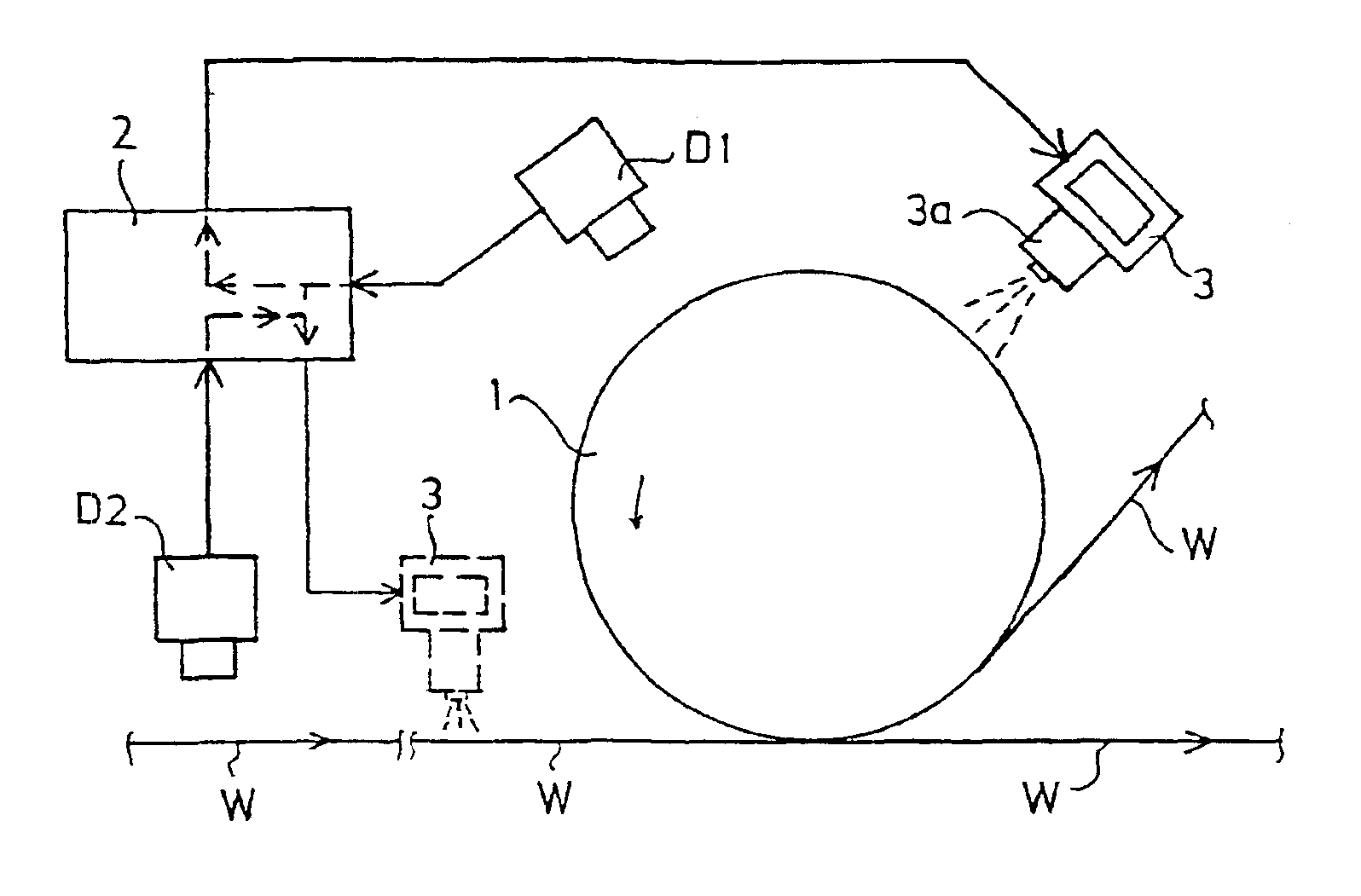
InactiveUS6905573B2Effective maintenanceRapid localizationSuction cleanersBrushesCardboardControl system
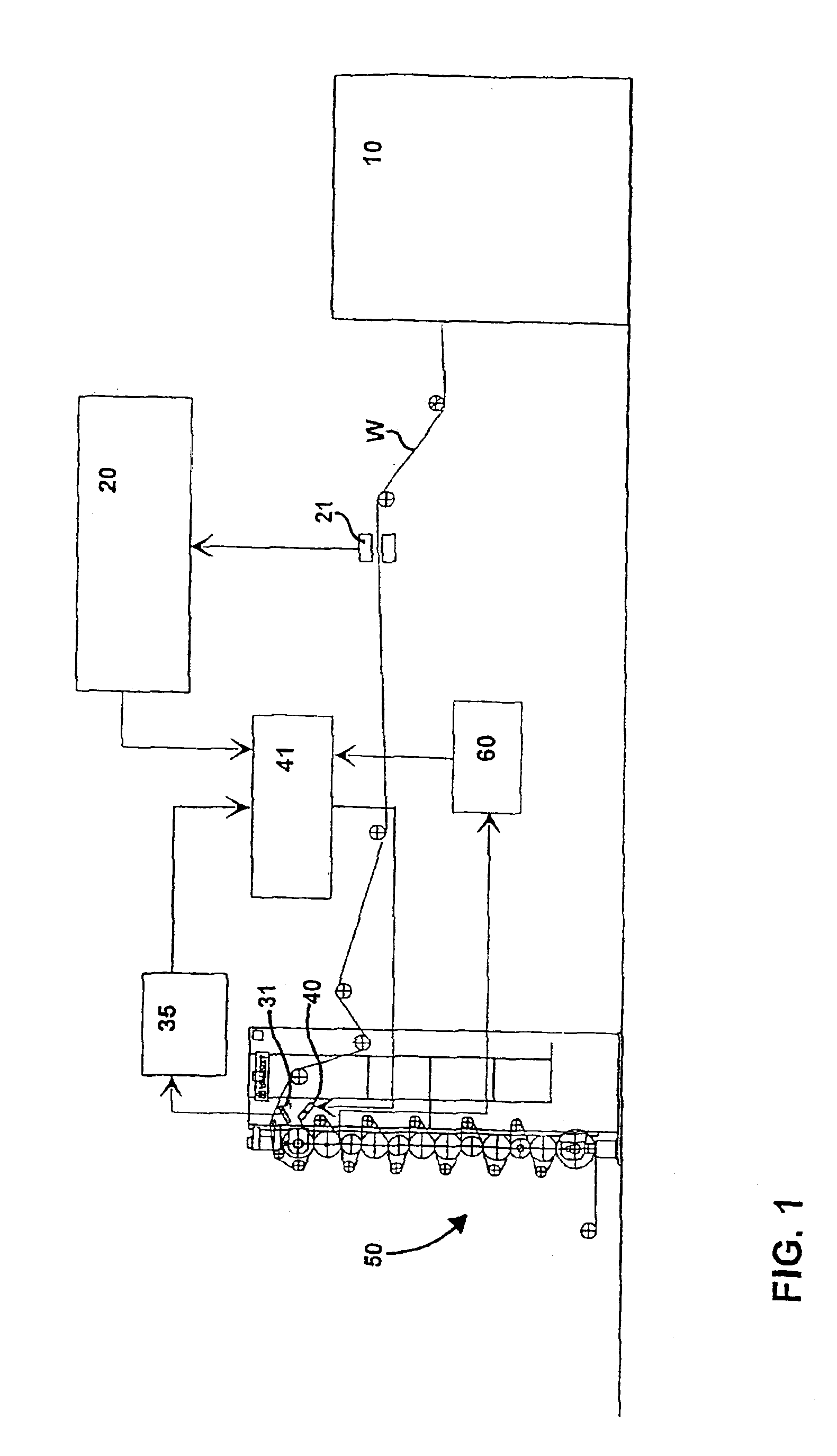
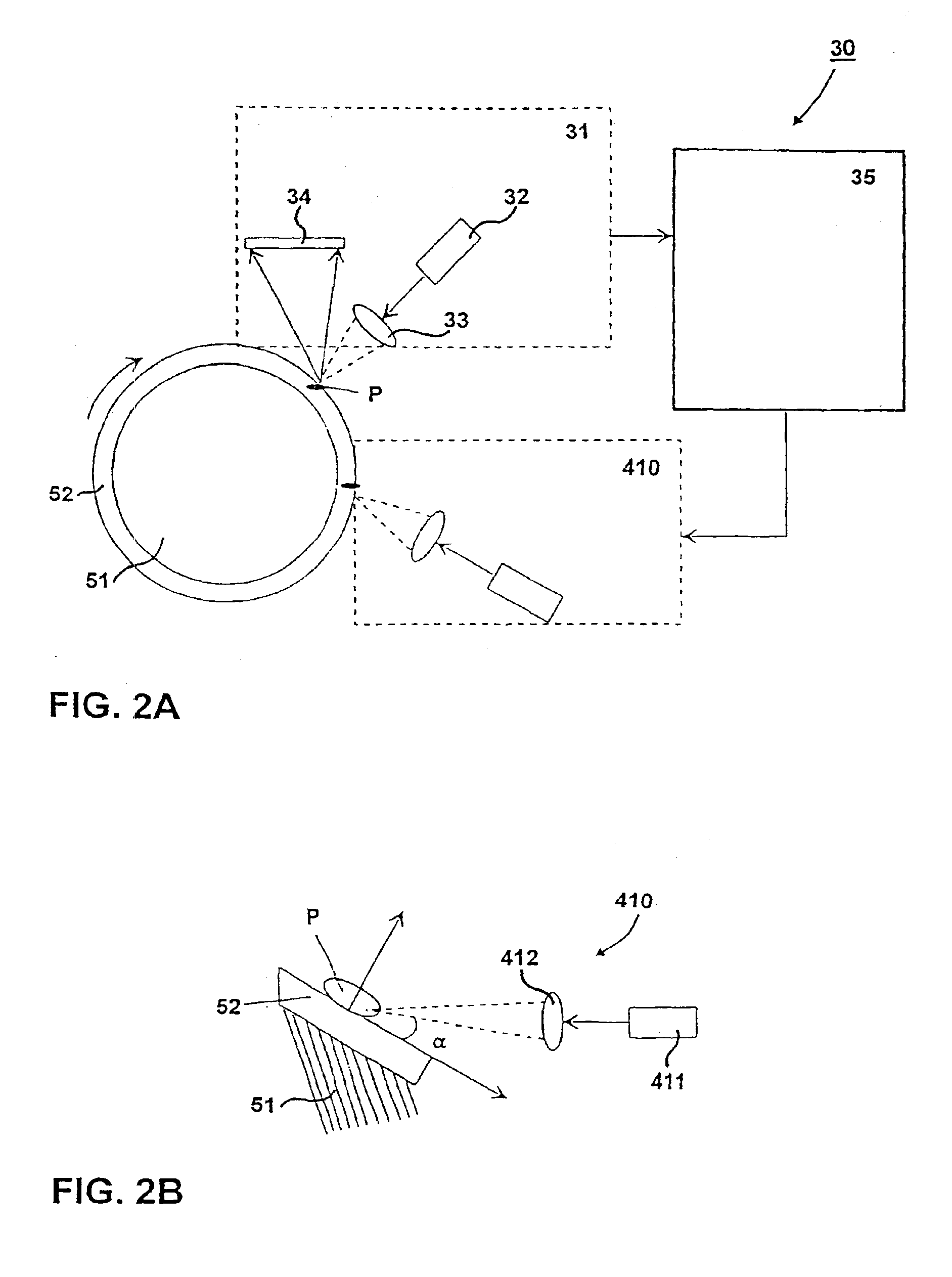
The surface of a web is monitored by a fault detection system (20), a machine condition monitoring system, a quality measurement system, a web moisture measurement and / or a web temperature measurement and the soiled part of the surface of the roll is detected and localized by means of a soiling monitoring apparatus (31, 35; 60). A control system (41) controls a cleaning device (40) to remove the detected soiling. As a web (W) travels in a paper or board production or finishing process or in finishing machinery the web and / or the surface of the roll is monitored and after a detected deviation the surface thereof is momentarily spread with a liquid while machinery is running at the same time as the web (W) travels over said roll surface.
Owner:VALMET TECH INC
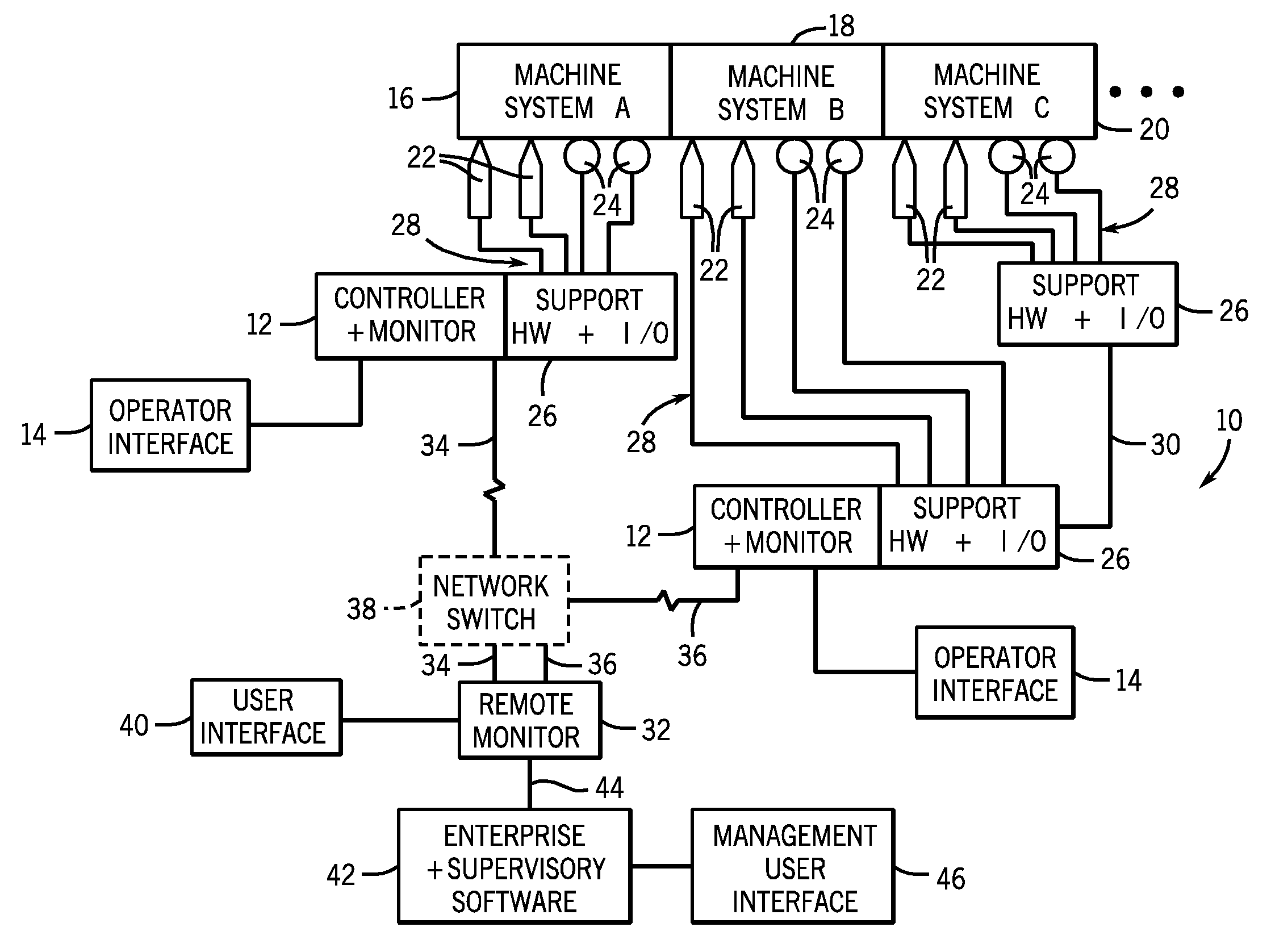
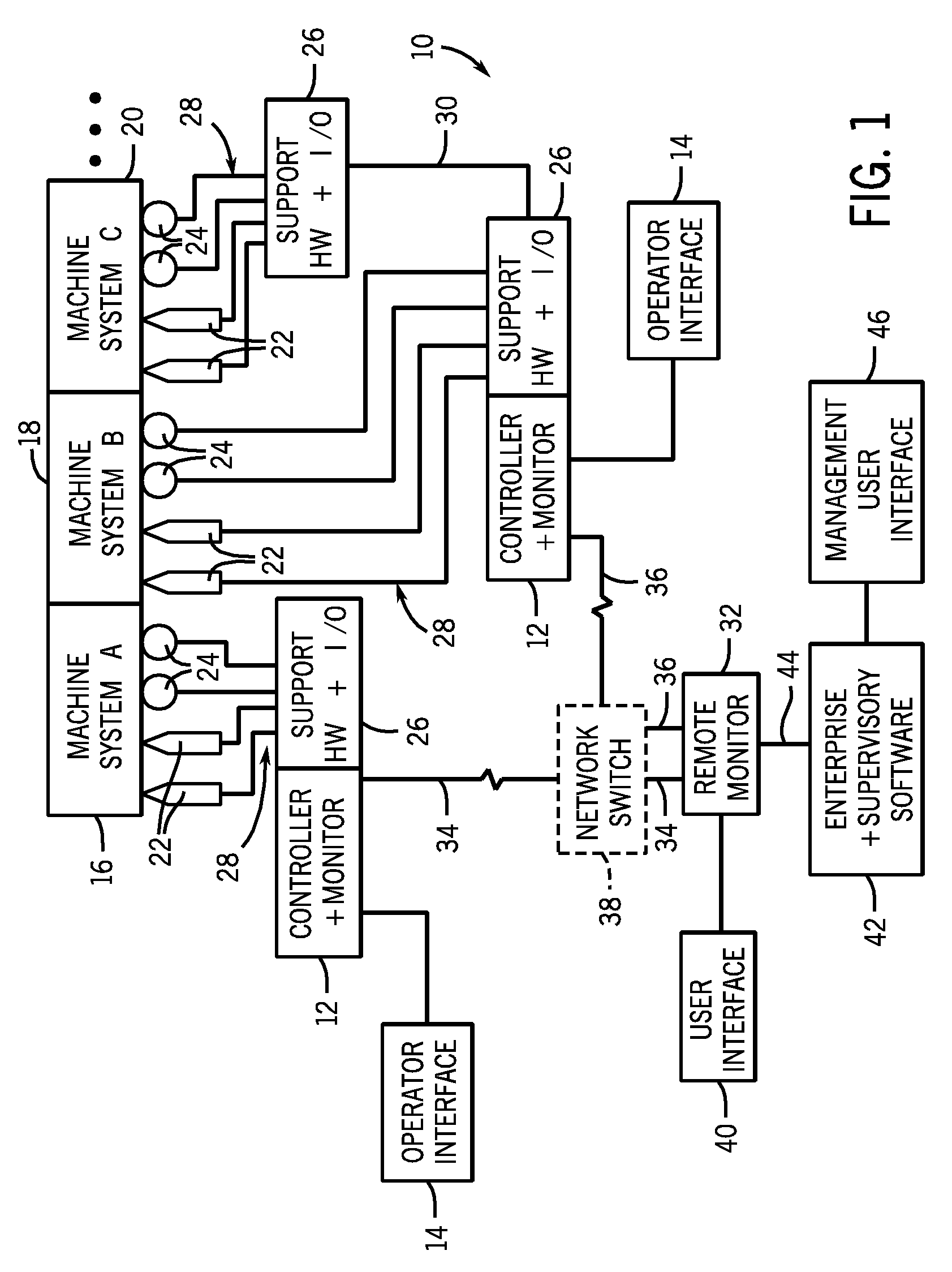
Modular condition monitoring integration for control systems
ActiveUS20100082273A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementFlow propertiesControl systemModularity
A system, in one embodiment, includes a controller configured to receive sensor signals from a machine system and to control operation of the machine system via actuators. The embodiment also includes function blocks stored and operational in the controller and configured to receive machine condition monitoring information and to calculate vibration parameters based upon the machine condition monitoring information. In another embodiment, the system includes a controller that includes computer code configured to control operation of a machine system via actuators based upon sensor signals. Moreover, the embodiment includes computer code configured to perform vibration monitoring of the machine system, including function blocks configured to receive vibration data and to calculate vibration parameters based upon the vibration data.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Robust sensor correlation analysis for machine condition monitoring
InactiveUS7769561B2Easy to getProgramme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsCorrelation coefficientMahalanobis distance
A method for monitoring machine conditions is based on machine learning through the use of a statistical model. A correlation coefficient is calculated using weights assigned to each sample that indicate the likelihood that that sample is an outlier. The resulting correlation coefficient is more robust against outliers. The calculation of the weight is based on the Mahalanobis distance from the sample to the sample mean. Additionally, hierarchical clustering is applied to intuitively reveal group information among sensors. By specifying a similarity threshold, the user can easily obtain desired clustering results.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
System and method for conditional multi-output regression for machine condition monitoring
InactiveUS20120084042A1MaximizingMeasurement devicesSimulator controlTraining phaseMonitoring system
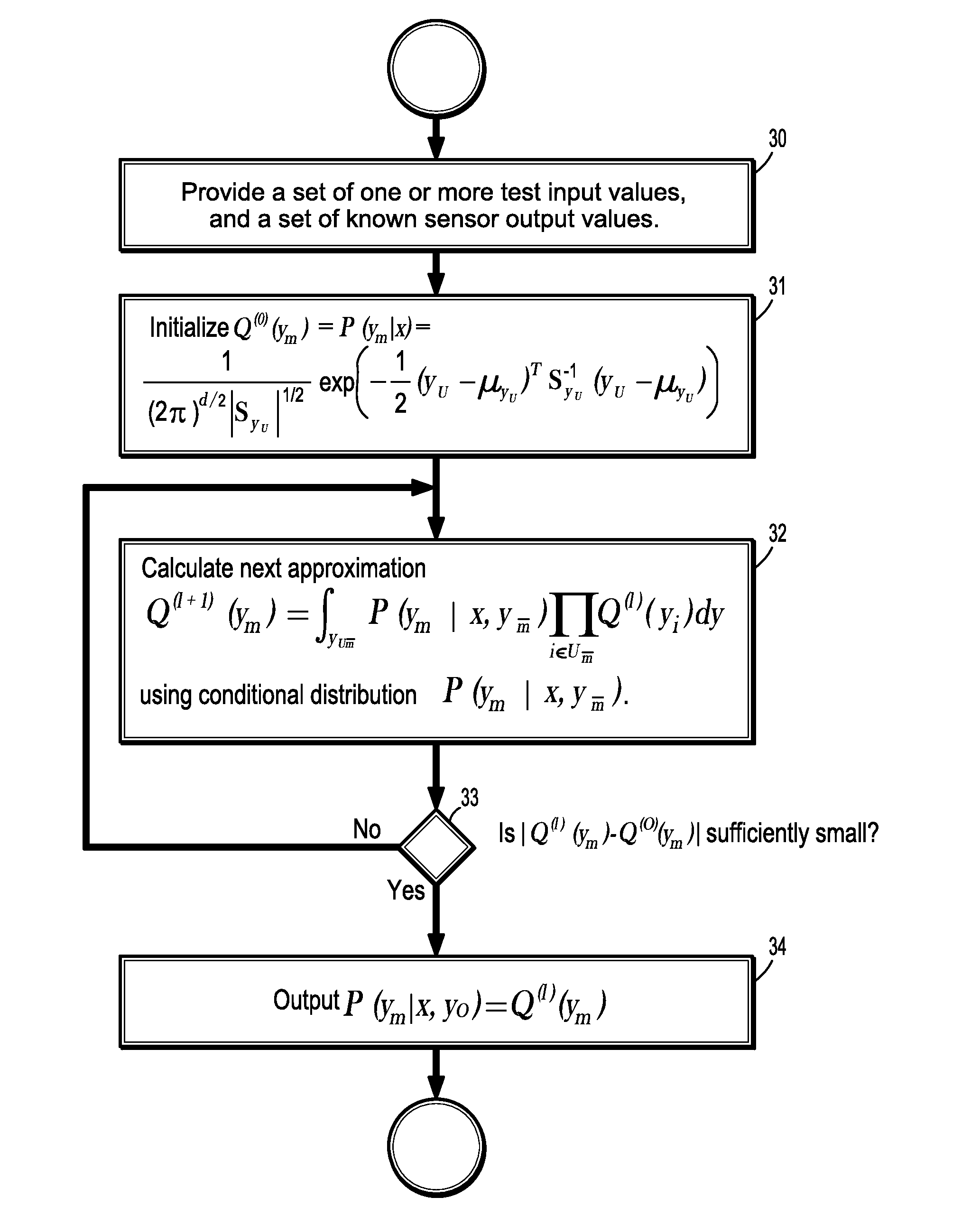
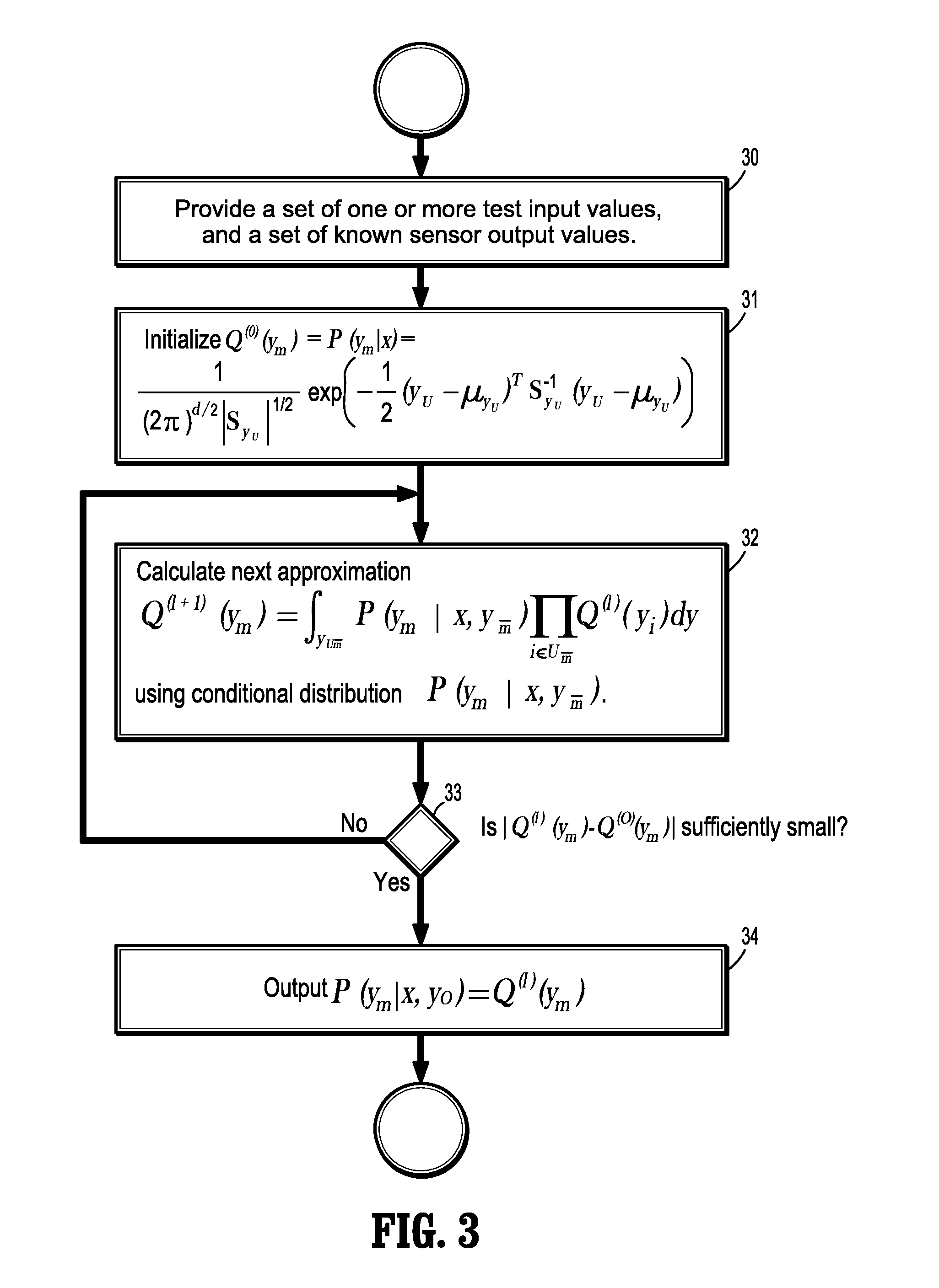
A method for predicting sensor output values of a sensor monitoring system, includes providing a set test input values to a system of sensors, and one or more known sensor output values from the sensor system, where other sensor output values are unknown, calculating, for each unknown sensor output value, a predictive Gaussian distribution function from the test input values and the known output sensor values, and predicting each unknown output ym by integrating over a product of the predictive Gaussian distribution function and a conditional Gaussian distribution of the unknown output sensor values with respect to the test input values and other unknown output sensor values. A mean and covariance of the predictive Gaussian distribution function are determined from a training phase, and a hyperparameter of the conditional Gaussian distribution are determined by another training phase.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
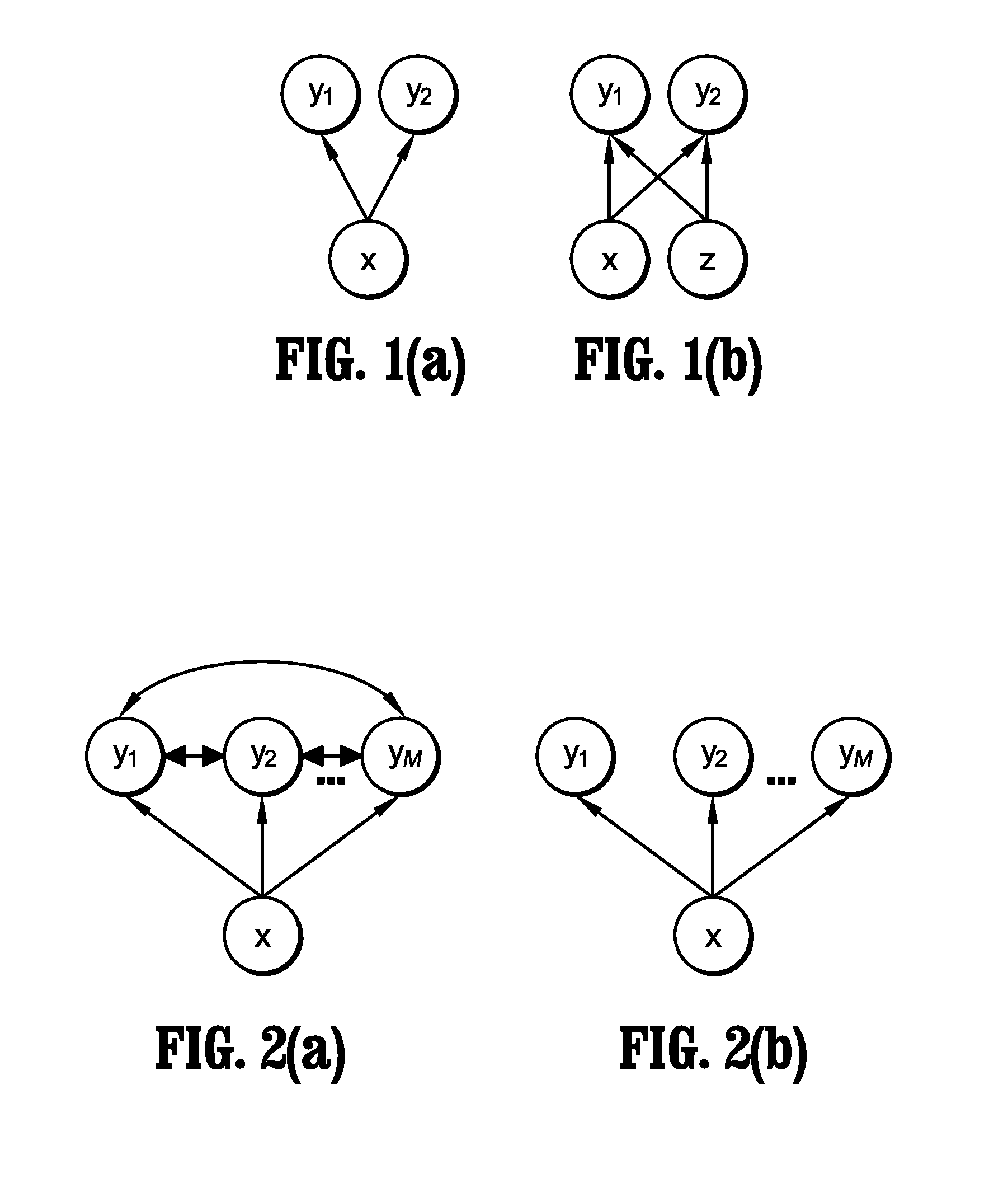
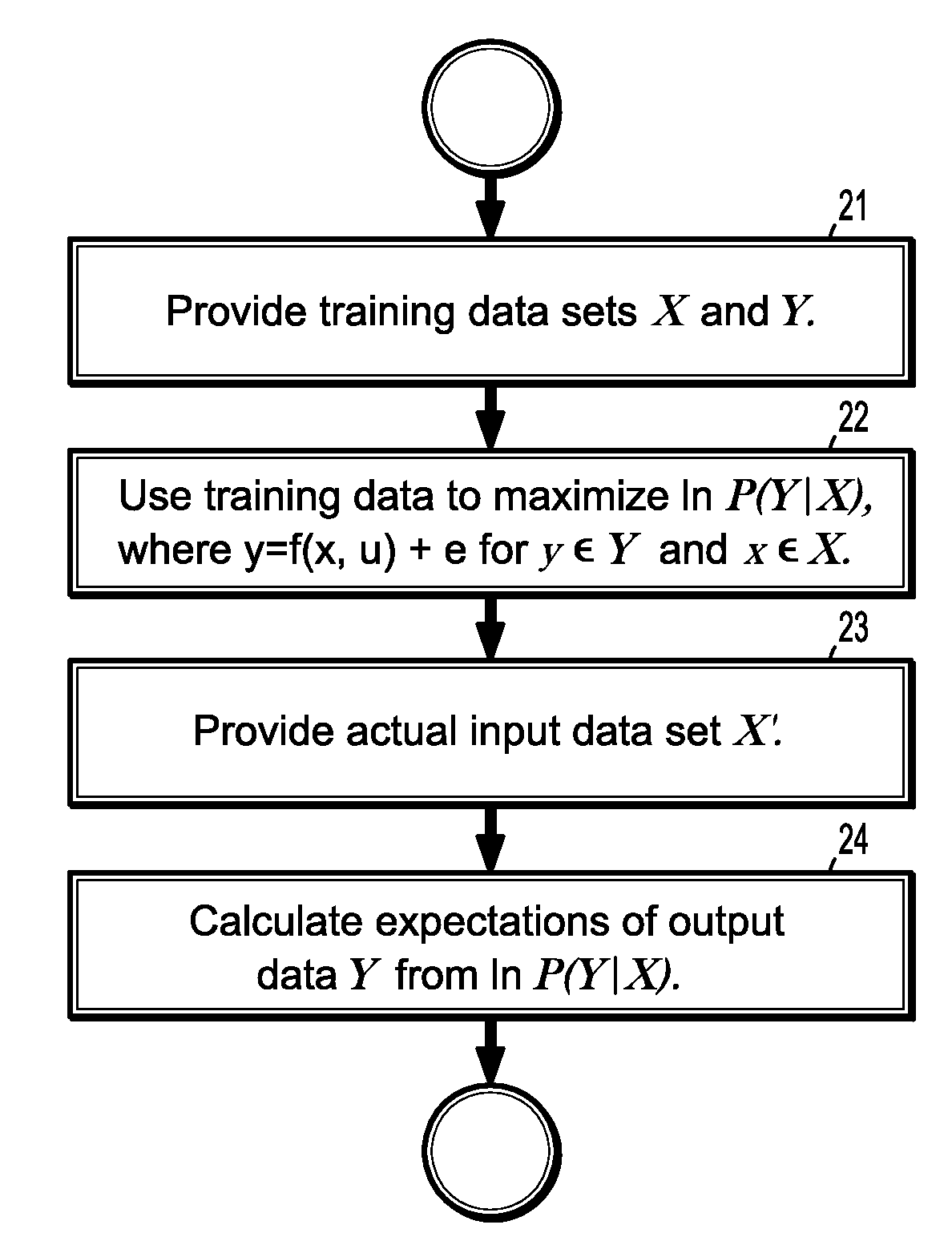
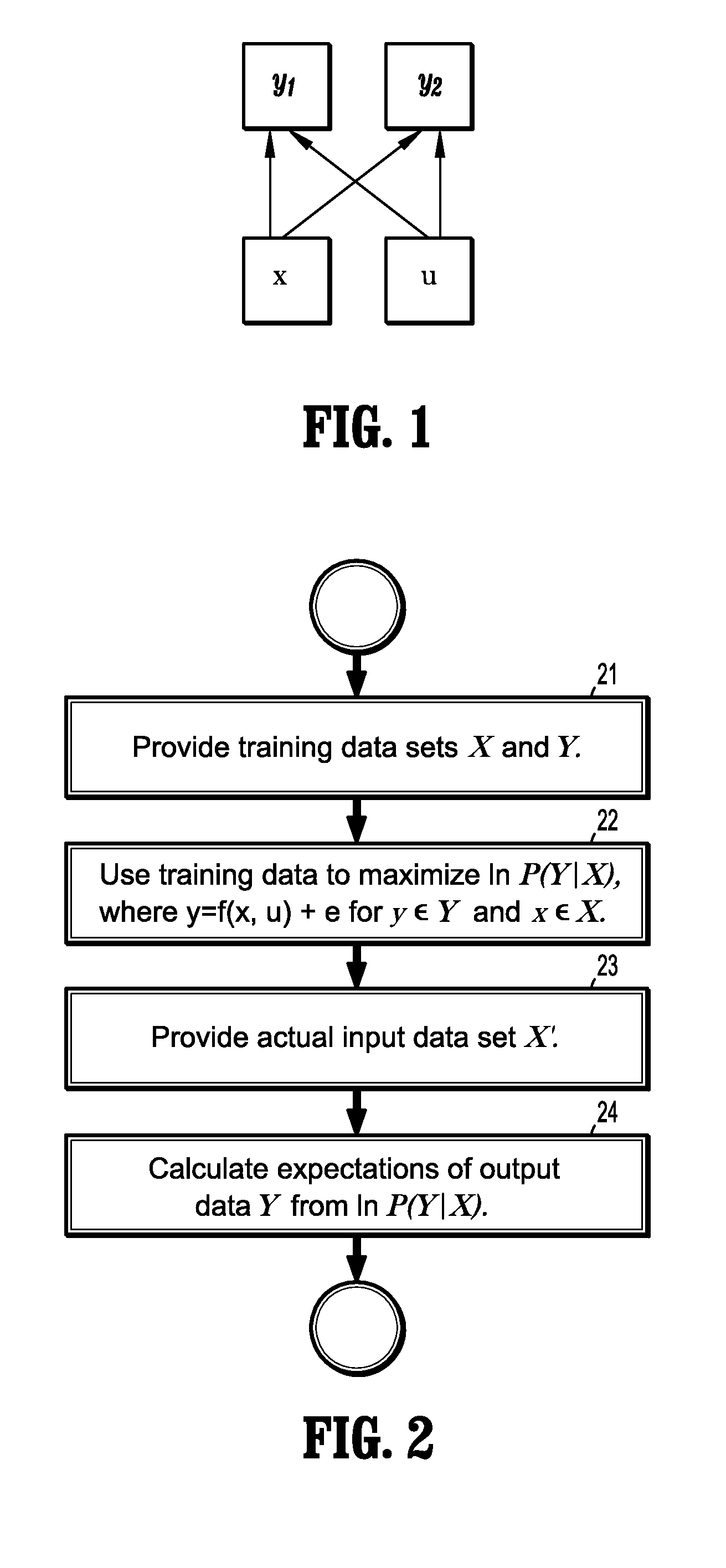
System and method for modeling conditional dependence for anomaly detection in machine condition monitoring
InactiveUS20120072173A1Simulator controlTesting/monitoring control systemsAnomaly detectionMonitoring system
A method for predicting sensor output values of a machine sensor monitoring system includes providing a set of input sensor data X and a set of output sensor data Y for a plurality of sensors the monitor the performance of a machine, learning a functional relationship that maps the input sensor data to the output sensor data by maximizing a logarithm of a marginalized conditional probability function P(Y|X) where a dependence of the output sensor data Y with respect to unknown hidden machine inputs u has been marginalized, providing another set of input sensor data X′, and calculating expected values of the output sensor data Y′ using the input sensor data X′ and the marginalized conditional probability function P(Y|X′), where the calculated expectation values reflect the dependence of the output sensor data Y″ with respect to the unknown hidden machine inputs u.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Evaluating anomaly for one class classifiers in machine condition monitoring
ActiveUS7567878B2Reduce in quantityProgramme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsOne-class classificationMachine condition monitoring
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Generalized pattern recognition for fault diagnosis in machine condition monitoring
ActiveUS8886574B2Electric testing/monitoringDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionMachine condition monitoring
A generalized pattern recognition is used to identify faults in machine condition monitoring. Pattern clusters are identified in operating data. A classifier is trained using the pattern clusters in addition to annotated training data. The operating data is also used to cluster the signals in the operating data into signal clusters. Monitored data samples are then classified by evaluating confidence vectors that include substitutions of signals contained in the training data by signals in the same signal clusters as the signals contained in the training data.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Tool for sensor management and fault visualization in machine condition monitoring
ActiveUS7183905B2Effective toolElectrical testingElectric testing/monitoringPower stationDisplay device
A tool for sensor management and fault visualization in machine condition monitoring. The method and system are able to monitor a plurality of sensors at one time. The sensors may be used in a power plant system monitoring system. The method and system may display a fault status for each sensor in the plurality of sensors in a single display, wherein the fault status for each sensor is displayed over time. The method and system also provide a mechanism that permits a user to examine details of each sensor in the plurality of sensors at any given time. In addition, the method and system are capable of categorizing each fault in the fault status using one or more properties or categorizing criteria. The method and system also permit sensors to be tested such that different operating models may be examined by utilizing different sensors.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Systems and Methods for Energy Efficient Machine Condition Monitoring of Fans, Motors, Pumps, Compressors and Other Equipment
ActiveUS20140195197A1Reduce amountReduce power consumptionVibration measurement in solidsPower managementData compressionPower equipment
Methods and systems to achieve highly efficient rotational machine integrity determinations in which at least one sensor (106) senses indicia (105) such as time-varying rotational indicia from a rotational motive apparatus (103) and a processor (108) may provide many different functions including but not limited to operational function energy apportioning decisional processing, data compression, intelligent hierarchical data ranking, differential data processing, or the like perhaps to generate information (109) such as a rotational integrity abridgment transmissor to which an abridgment transmissor electromagnetic signal (112) may be created and perhaps even transmitted from a rotational motive apparatus to facilitate a machine integrity determination.
Owner:AB SKF
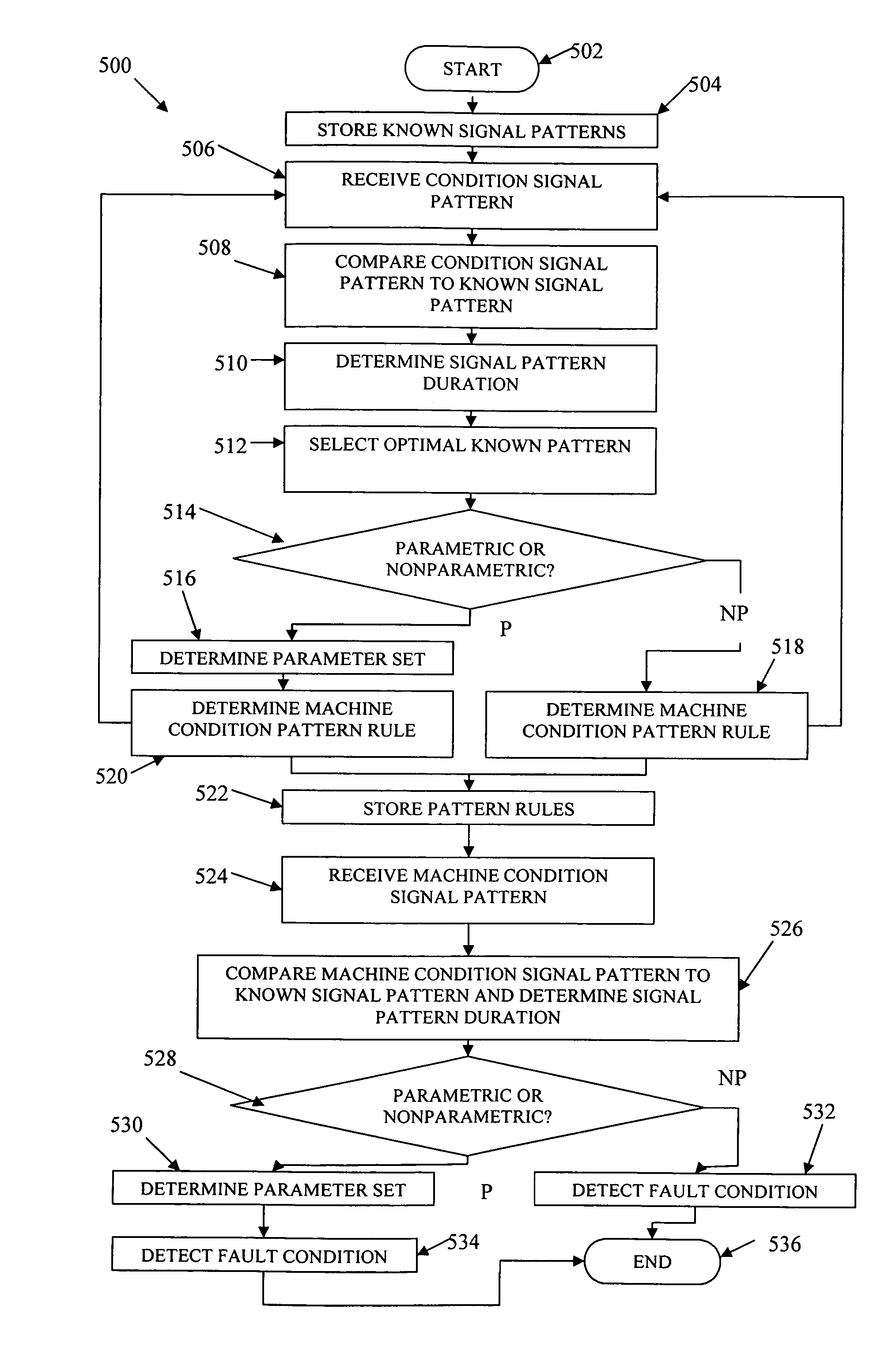
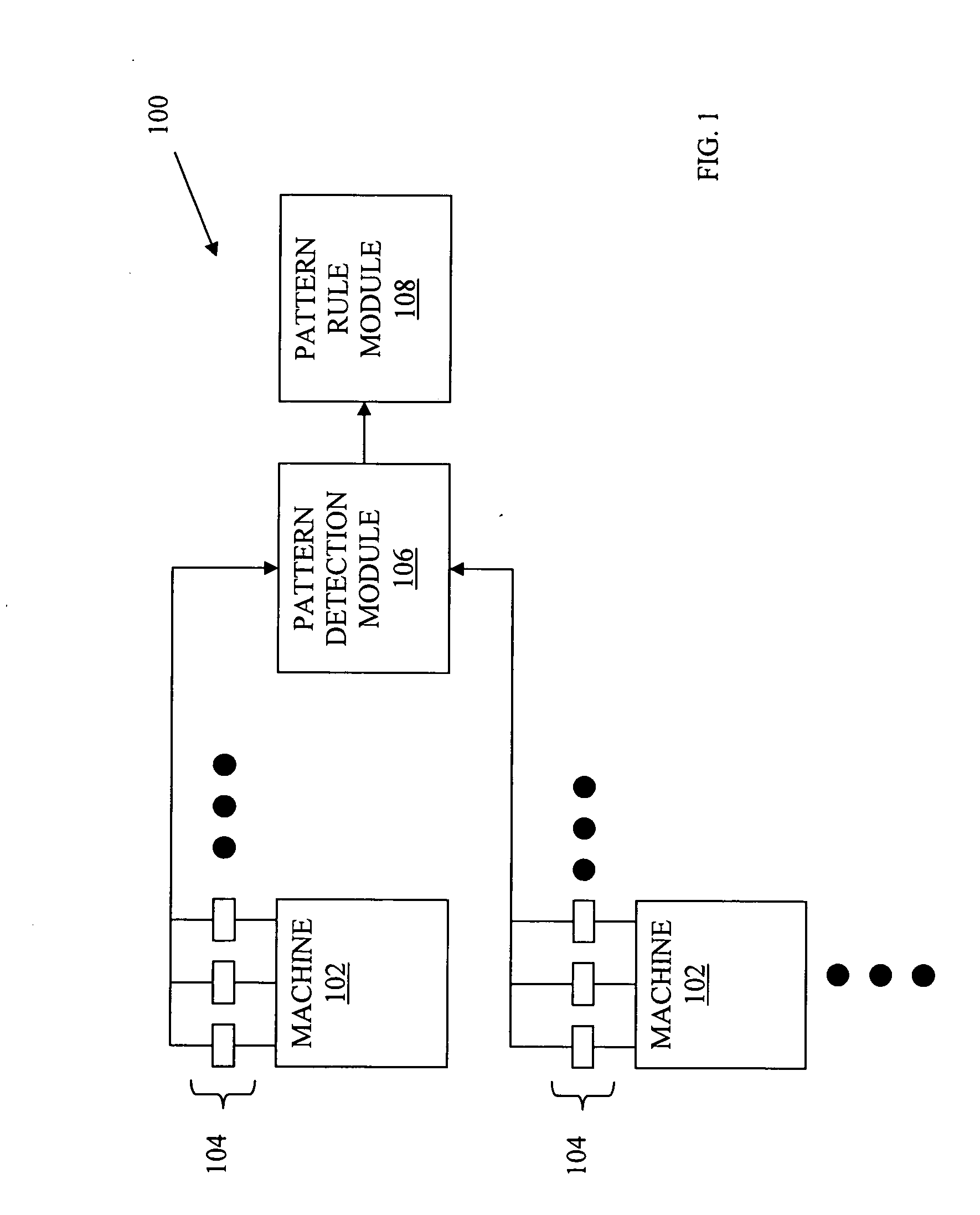
Machine condition monitoring using pattern rules
Pattern rules are created by comparing a condition signal pattern to a plurality of known signal patterns and determining a machine condition pattern rule based at least in part on the comparison of the condition signal pattern to one of the plurality of known signal patterns. A matching score based on the comparison of the condition signal pattern to one of the plurality of known signal patterns as well as a signal pattern duration is determined. The machine condition pattern rule is then defined for nonparametric condition signal patterns as a multipartite threshold rule with a first threshold based on the determined matching score and a second threshold based on the determined signal duration. For parametric signal patterns, one or more parameters of the signal pattern are determined and the machine condition pattern rule is further defined with a third threshold based on the determined one or more parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
Use of Sequential Clustering for Instance Selection in Machine Condition Monitoring
A method is provided for selecting a representative set of training data for training a statistical model in a machine condition monitoring system. The method reduces the time required to choose representative samples from a large data set by using a nearest-neighbor sequential clustering technique in combination with a kd-tree. A distance threshold is used to limit the geometric size the clusters. Each node of the kd-tree is assigned a representative sample from the training data, and similar samples are subsequently discarded.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP +1
Supervised fault learning using rule-generated samples for machine condition monitoring
InactiveUS8868985B2Error detection/correctionElectric testing/monitoringFeature vectorDecision boundary
A machine fault diagnosis system is provided. The system combines a rule-based predictive maintenance strategy with a machine learning system. A simple set of rules defined manually by human experts is used to generate artificial training feature vectors to portray machine fault conditions for which only a few real data points are available. Those artificial training feature vectors are combined with real training feature vectors and the combined set is used to train a supervised pattern recognition algorithm such as support vector machines. The resulting decision boundary closely approximates the underlying real separation boundary between the fault and normal conditions.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
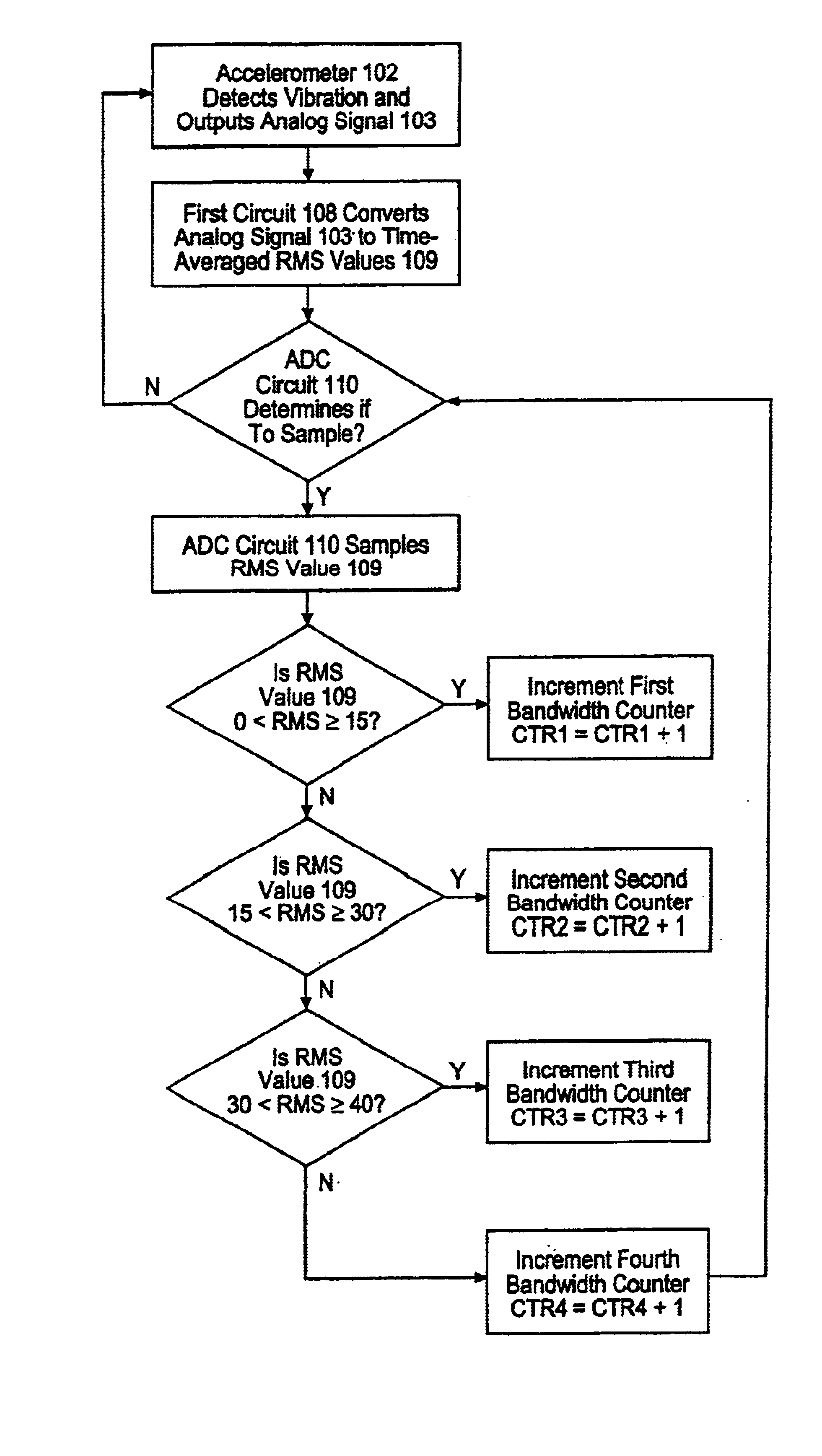
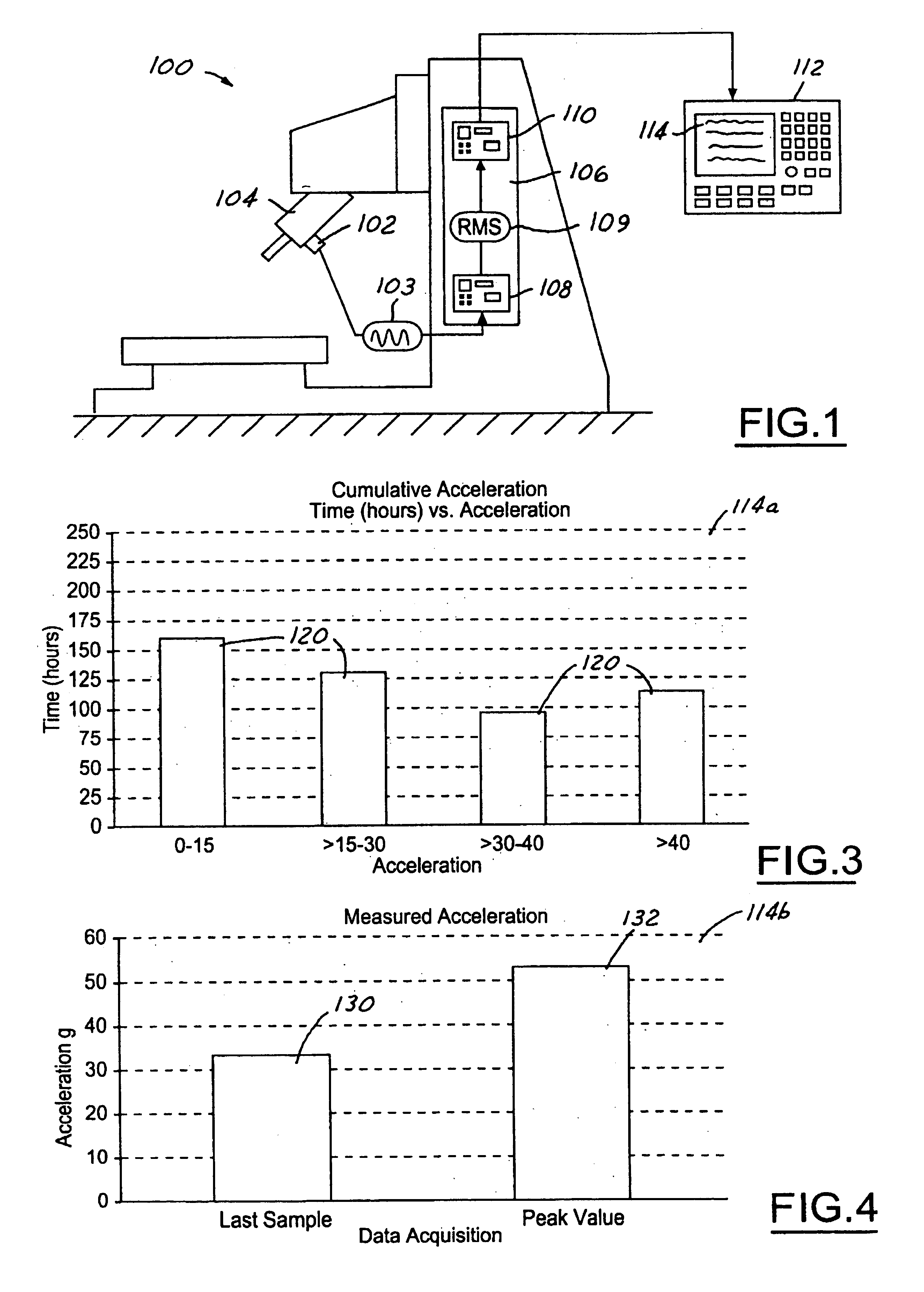
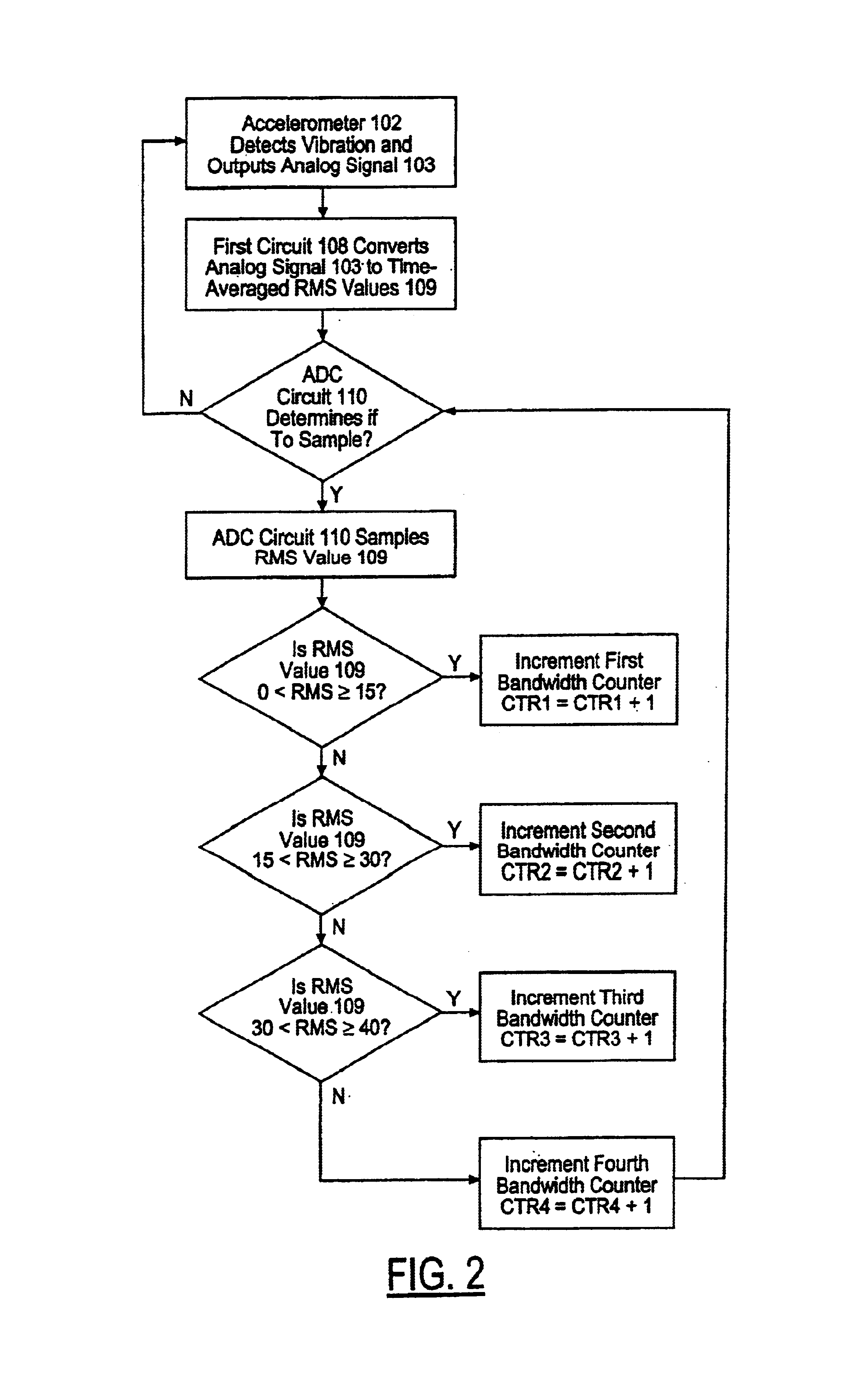
Control embedded machine condition monitor
Analog signals are generated in response to one or more operating parameters of a machine such as vibration and used to provide a log of the operating history of the machine. The analog signals are converted into root mean square (rms) values which are periodically sampled. The sampled signals are sorted into predefined rms value bands. Each occurrence of a signal in an rms value band is used to increment a counter in order to keep track of the number of occurrences of signals in a particular rms value band. The number of accumulated signals in each of the rms value bands provides an indication of the usage and condition of the machine.
Owner:WELLS FARGO BANK NAT ASSOC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com