Carrier protein of bacterial polysaccharide conjugate vaccine and application thereof
A fusion protein and polysaccharide technology, applied in the direction of anti-bacterial immunoglobulin, anti-bacterial drugs, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of limited immunogenicity and low polysaccharide protein
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
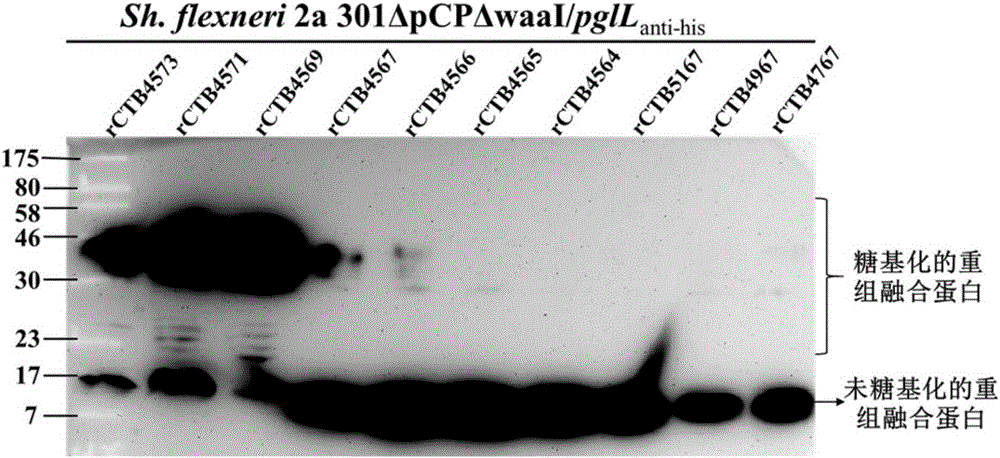
[0123] Example 1. Preparation and Application of Shigella flexneri O Polysaccharide-Recombinant Cholera Toxin B Subunit Fusion Protein Conjugate
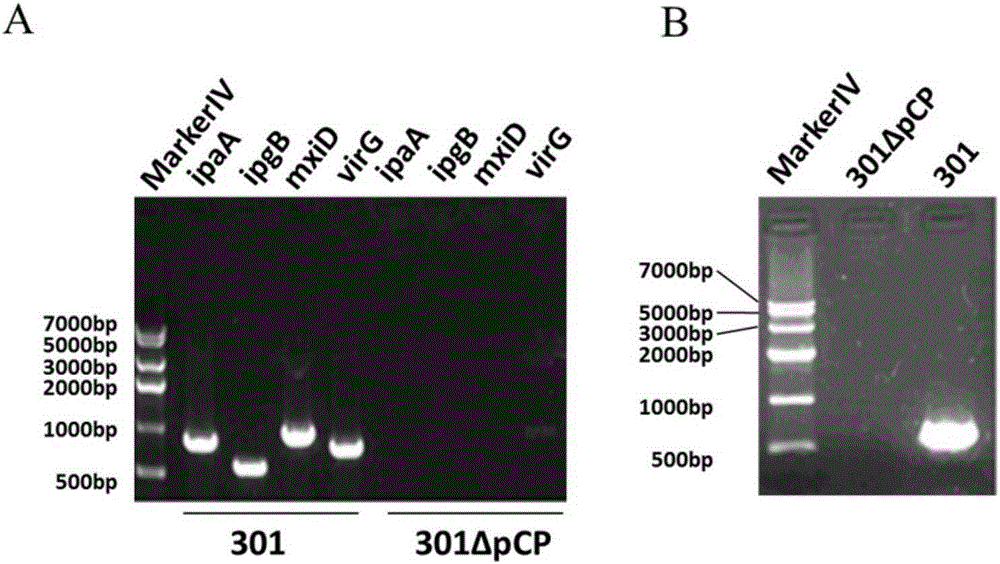
[0124] Shigella spp., commonly known as Shigella spp., is a highly contagious Gram-negative enteropathogenic bacterium, which mainly invades human colonic epithelial cells and finally locates in the large intestine, causing typical bacillary dysentery ( fever, abdominal pain, tenesmus, fecal pus and blood), and the large virulence plasmid is the most important factor of its pathogenicity. The large virulence plasmid contains about 32 genes related to virulence, mainly including System-related mxi-spa gene, virulence genes such as ipaBCD and ipgC closely related to bacterial invasion of epithelial cells. In order to develop it as a safe host bacterium, the large plasmid pCP encoding the virulence factor must be removed first, and on this basis, the O antigen ligase gene waaI is deficient, thereby developing a host bacterium suitable ...
Embodiment 2
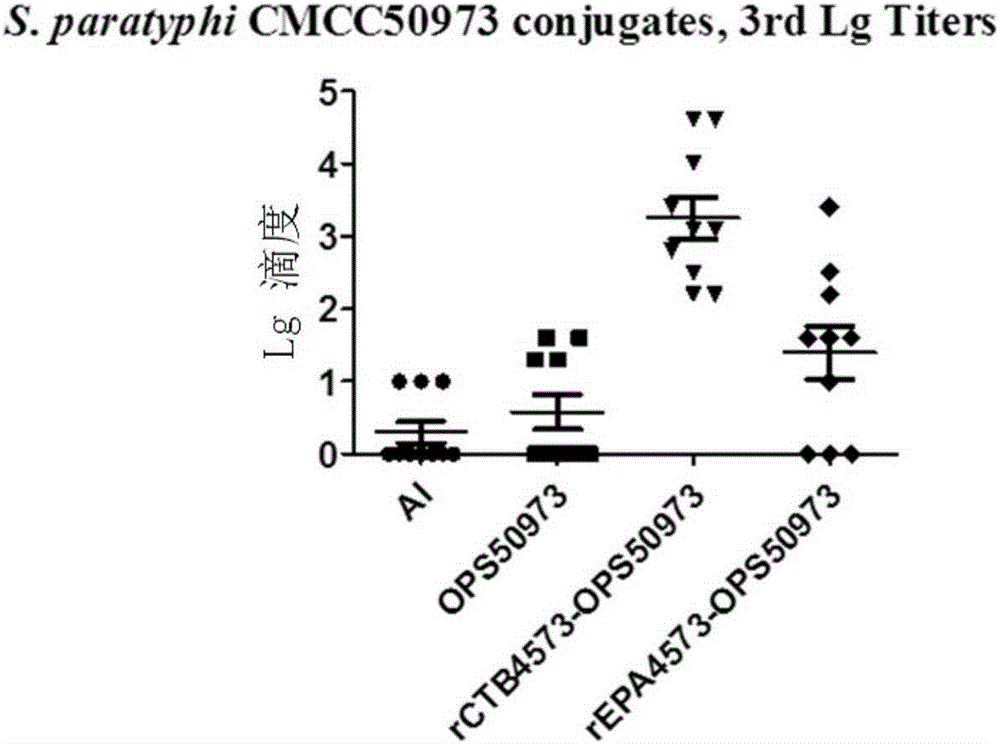
[0273] Example 2. Preparation and Application of Salmonella Paratyphi A O Polysaccharide-Recombinant Cholera Toxin B Subunit Fusion Protein Conjugate
[0274] A. Exploring the construction of recombinant bacteria to extend the sugar chain of Salmonella paratyphi A O antigen
[0275] 1. Knockout of the O antigen chain length control enzyme gene cld of Salmonella paratyphi A CMCC50973 strain
[0276] 1. Preparation of linear targeting DNA fragment 1
[0277] 1) Design of PCR primers
[0278] According to the S. paratyphi ATCC9150 genome sequence (CP000026) published by GeneBack, a targeting fragment of the cld gene (position 887812 to 888789) was designed to knock out the cld gene of Salmonella paratyphi A CMCC50973. Cut off 500bp at the upstream and downstream of the cld gene as the homology arm, amplify the target fragment of the chloramphenicol resistance gene containing 500bp homologous sequence and FRT site at both ends by PCR, and identify it with 50973cldup 5' and 50973...
Embodiment 3
[0417] Example 3. Preparation and Application of Escherichia coli O157 O Polysaccharide-Recombinant Cholera Toxin B Subunit Fusion Protein Conjugate
[0418] When exogenous polysaccharides are used to modify recombinant fusion proteins, bacteria that are double-deficient in O-antigen ligase gene and host O antigen synthesis should be used as the host. None of the polysaccharides can be used by the host LPS synthesis pathway, and the host's O antigen synthesis defect ensures that the glycosylation modification system only uses exogenous polysaccharides to modify the recombinant fusion protein, and does not appear to be modified by the host's own O antigen polysaccharides. pollution phenomenon. The host bacteria co-express the recombinant fusion protein gene, Neisseria meningitidis O-oligosaccharide transferase PglL gene, and exogenous polysaccharide synthesis gene cluster. Under the catalysis of oligosaccharide transferase PglL, the exogenous polysaccharide is transferred to th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com