Fluorescent probe for bacteria resistant to carbapenem antibiotics and its synthesis method and application
A technology of carbapenems and fluorescent probes, applied in the field of compound preparation, can solve the problem of inability to distinguish between β-lactamase and carbapenemase, fluorescent probes do not explain optical properties, different selectivity and detection sensitivity, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of simple and convenient application, high accuracy and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
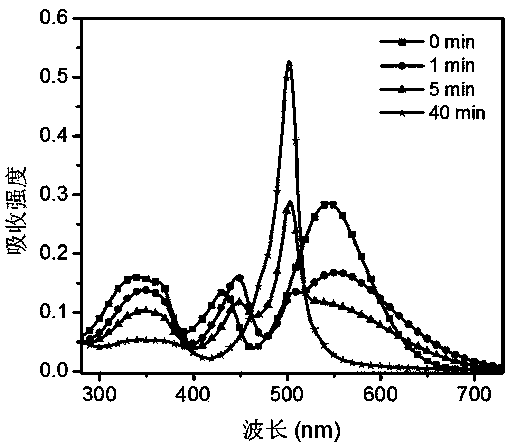
[0072] Embodiment 1 (see figure 1 )
[0073] A method for synthesizing a fluorescent probe resistant to carbapenem antibiotics bacteria, the preparation method of its compound 3 is:
[0074] Compound 1 [0.39 mmol (mmol), 189 mg (mg)] and compound 2 (0.3 mmol, 135 mg) were placed in a reaction flask, and N,N-dimethylformamide 1.2 mL and triethylamine 0.3 mL were added; After degassing the resulting mixture through three cycles of freeze-true-dissolution, 0.03 mmol (6.7 mg) of palladium acetate and 0.045 mmol (13.7 mg) of tris(o-methylphenyl)phosphine were added, followed by degassing twice.
[0075] The reaction system was reacted at 80° C. for 16 h under a nitrogen atmosphere. After cooling, ethyl acetate was added to dilute the reaction system. The ethyl acetate phase was washed with water and saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated.
[0076] The resulting mixture was purified by silica gel column chromatography using petroleum ether and ethyl...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Embodiment 2 (see figure 1 )
[0081] A method for synthesizing a fluorescent probe resistant to carbapenem antibiotics bacteria, the preparation method of its compound 4 is:
[0082] A total of 57 mg (0.07 mmol) of compound 3 prepared in Example 1 was dissolved in 0.7 ml of N-methylpyrrolidone / N,N-dimethylformamide, N-methylpyrrolidone and N,N-dimethylformamide The volume ratio of amides is 1:3;
[0083] After that, 15.9 mg (0.28 mmol) of ammonium bifluoride was added and reacted at room temperature (25°C) for 36 h;
[0084] After the reaction was completed, ethyl acetate was added to dilute the reaction system, the ethyl acetate phase was washed with water and saturated brine respectively, dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate, and then concentrated;
[0085] The resulting mixture was purified by silica gel column chromatography using petroleum ether and ethyl acetate as mobile phases to obtain 39.6 mg of compound 4 with a yield of 79%.
[0086] Its synthetic route ...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Embodiment 3 (see figure 1 )
[0090] A kind of synthetic method of the fluorescent probe of carbapenem-resistant antibiotic bacteria, the preparation method of its fluorescent probe (CVB-1) is:
[0091] A total of 13.9mg (0.02mmol) of compound 4 obtained in Example 2 was dissolved in 0.5ml of tetrahydrofuran, and 0.3mL of 0.35M phosphate buffer (PB) with a pH of 6.0 and 26.2mg (0.02mmol) of activated zinc powder were added, React at 20°C for 1h;
[0092] The reaction solution was filtered, washed with chromatographic acetonitrile, purified with a reversed-phase C18 preparative column, and freeze-dried to obtain a black-purple compound, namely the fluorescent probe (CVB-1).
[0093] The synthesis route and structural formula of the fluorescent probe (CVB-1) are:
[0094]
[0095] Spectral features are: 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ7.63(d,J=16.9Hz,1H),7.50–7.44(m,2H),7.32–7.26(m,2H),6.46(d,J=16.9Hz,1H),6.00(s,1H ),4.30–4.19(m,1H),4.15(d,J=8.9Hz,1H),3.47–3.37(m,1H),...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com