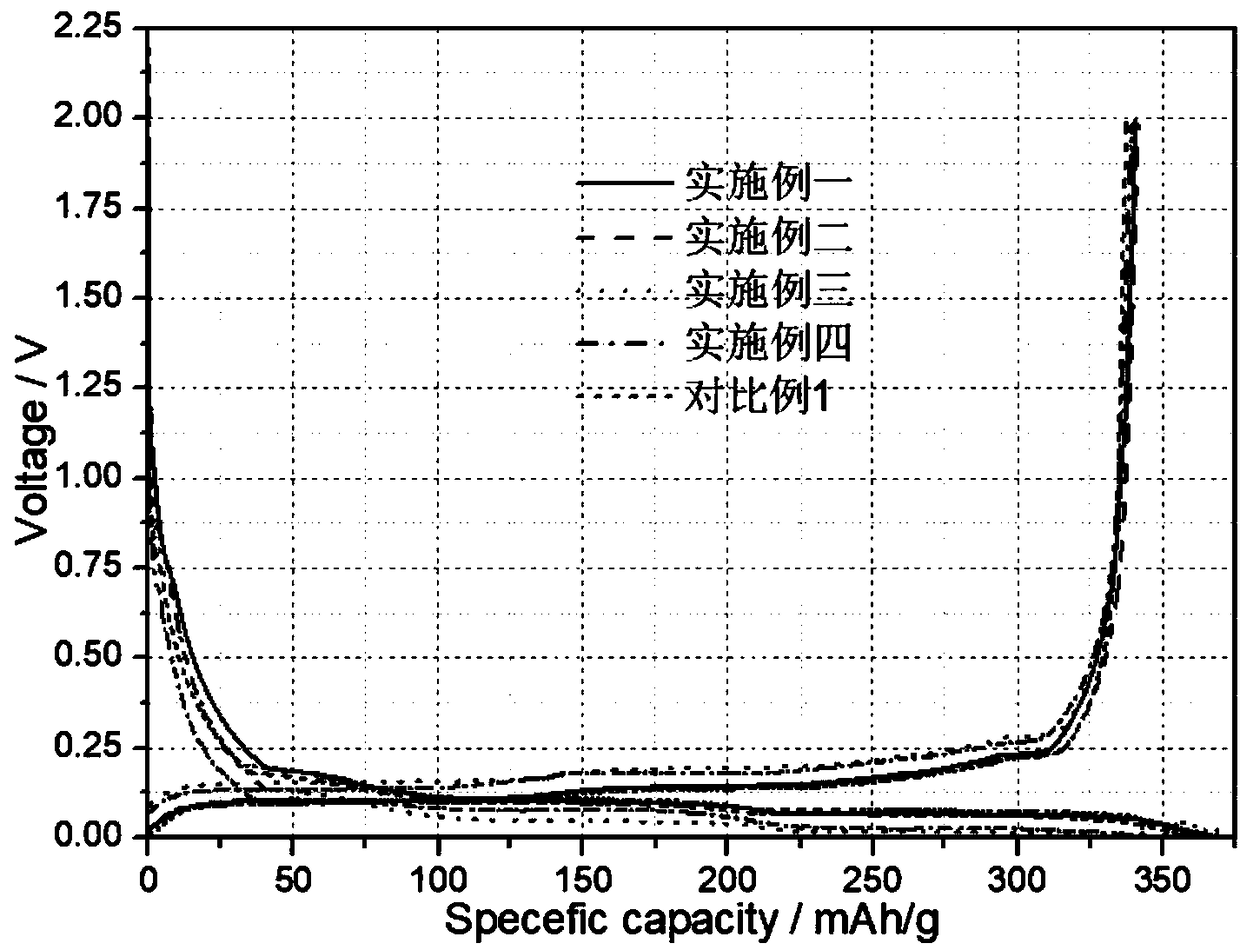
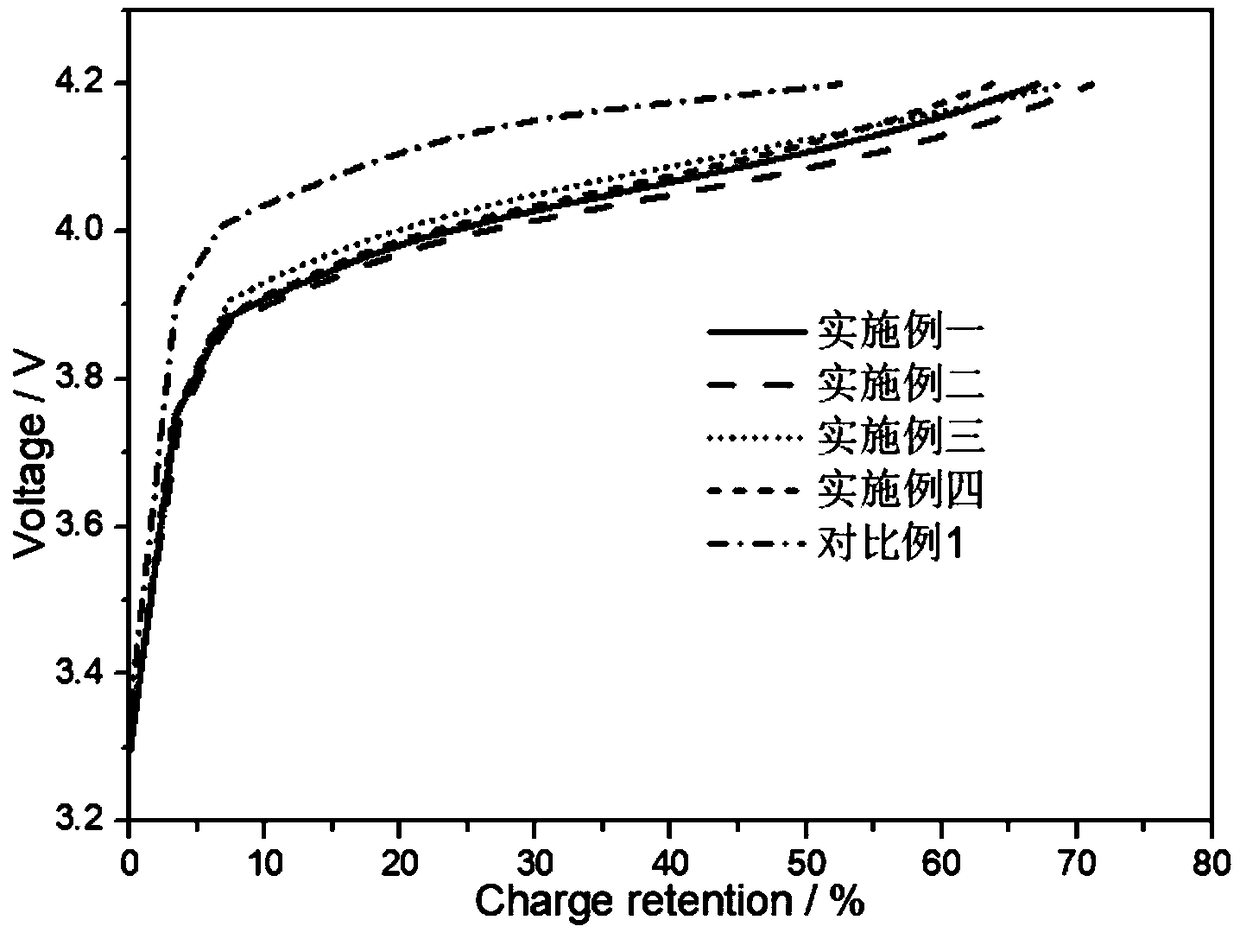
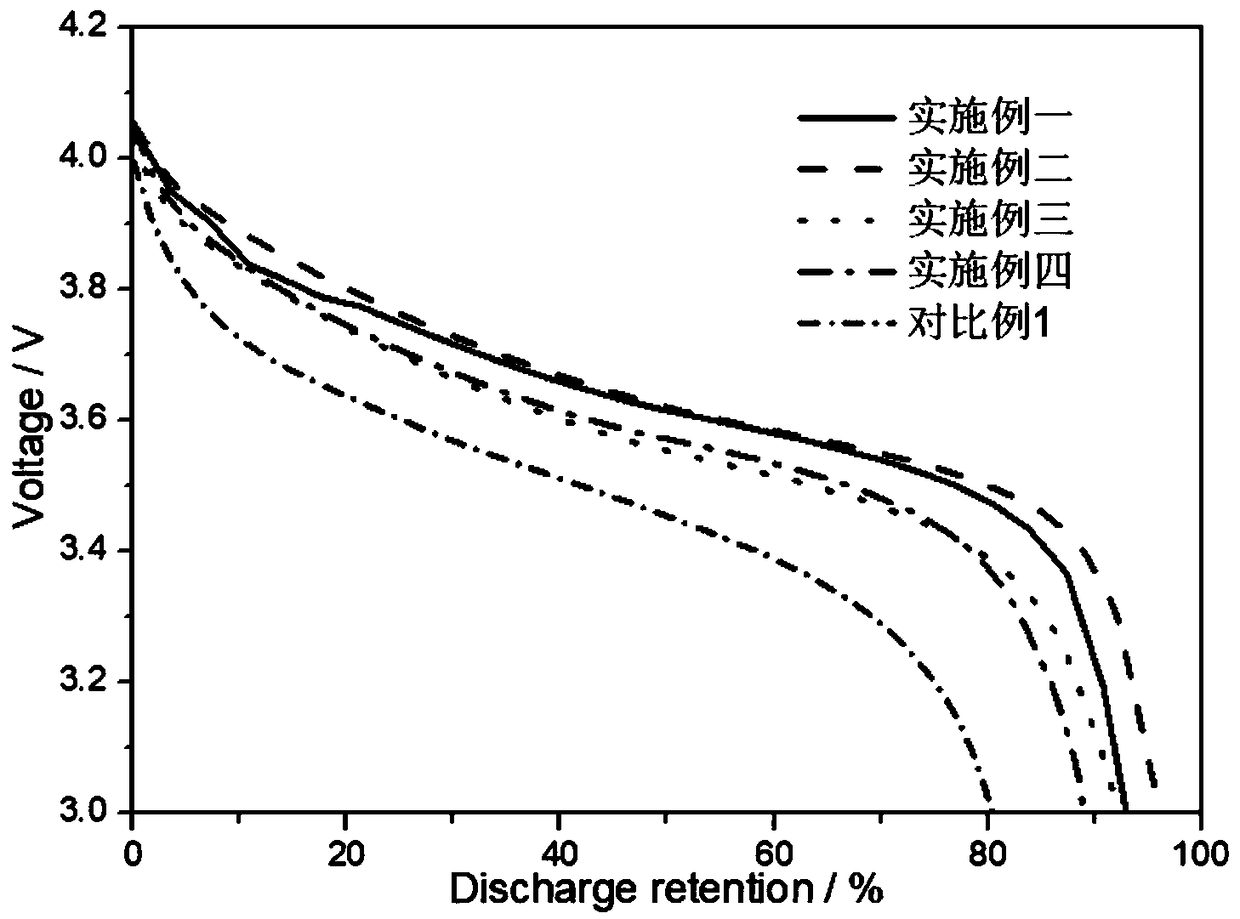
A boron doping modified hard carbon coating negative electrode material with high rate performance and a liquid phase preparation method thereof
A negative electrode material, boron doping technology, applied in the direction of battery electrodes, electrical components, electrochemical generators, etc., can solve the problems that it is difficult to meet the high rate charge and discharge, the general rate performance of graphite materials, and difficult large-scale application, etc., to achieve Less pollution, increased layer spacing, and economical raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0044] The liquid-phase preparation method of above-mentioned negative electrode material, comprises the following steps:
[0045] 1) taking the powder of the negative electrode substrate, adding a hard carbon carbon source and a boron compound to the powder to obtain a mixed powder;
[0046] 2) Transfer the mixed powder into a container, add a solvent, stir and disperse evenly to obtain a slurry;
[0047] 3) drying and granulating the slurry to obtain granules;
[0048] 4) Put the particulate matter into the carbonization equipment, under protective atmosphere, heat to 600-1350°C, preferably 1000-1200°C, keep it warm, take it out after natural cooling, and obtain the negative electrode material;
[0049] 5) Sieving the negative electrode material to obtain a finished product.
[0050] Preferably, in step 2), the solvent is at least one of water, ethanol and ethylene glycol.
[0051] As a preference, in step 2), the stirring time is 0.5-12h, wherein the preferred time is 1-...
Embodiment 1
[0055] Example 1: Boron-doped modified high-rate negative electrode material with 0.5% sodium tetraphenylborate and 3% petroleum resin carbon source
[0056] Take 1g of sodium tetraphenylborate (the median particle size is 3 microns) and 6g of petroleum resin (the median particle size is 7 microns) and add 200g of graphite negative electrode material (the median particle size is 8.60 microns), transfer it to a beaker, and add 200mL Deionized water, stirred for one hour, mixed evenly, and then granulated by spray drying, the granulated material was transferred to a tubular carbonization furnace, heated to 1000°C under a nitrogen atmosphere, heated for 5 hours, and cooled naturally After sieving with a 325-mesh sieve, a boron-doped modified high-rate negative electrode material coated with 0.5% of non-metallic boron doped with 3% of hard carbon is obtained. The prepared product was uniformly mixed with SP, CMC, and SBR according to the ratio of 95.2:1:1.9:1.9, and after beating,...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2: Boron-doped modified high-rate negative electrode material with 2.5% sodium tetraphenylborate dopant and 8% petroleum resin carbon source.
[0059] Get 16g petroleum resin (median particle diameter is 10 microns), 5g sodium tetraphenylborate (median particle diameter is 5 microns) and 200g graphite negative electrode material (median particle diameter is 8.60 microns), transfer in the beaker, add 200mL Deionized water, stirred for an hour, mixed evenly, and then granulated by spray drying, the granulated material was transferred to a tubular carbonization furnace, and heated to 1200°C in a nitrogen atmosphere, heated for 10 hours, and cooled naturally. Obtain the negative electrode material. Pass the fluorine gas through the cooling medium containing calcium chloride and ice and the filter layer of sodium fluoride at 100 °C in sequence, then pass it into the reaction furnace, add the negative electrode material into the reaction furnace, and react at 425 °C f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Median particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Median particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com