Biological bamboo cellulose extraction method
A bamboo cellulose and extraction method technology, applied in the field of biotechnology and cellulose extraction, can solve the problems of steam explosion method, environmental pollution, high equipment requirements, etc., and achieve the effect of simple process, small environmental pollution and simple steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
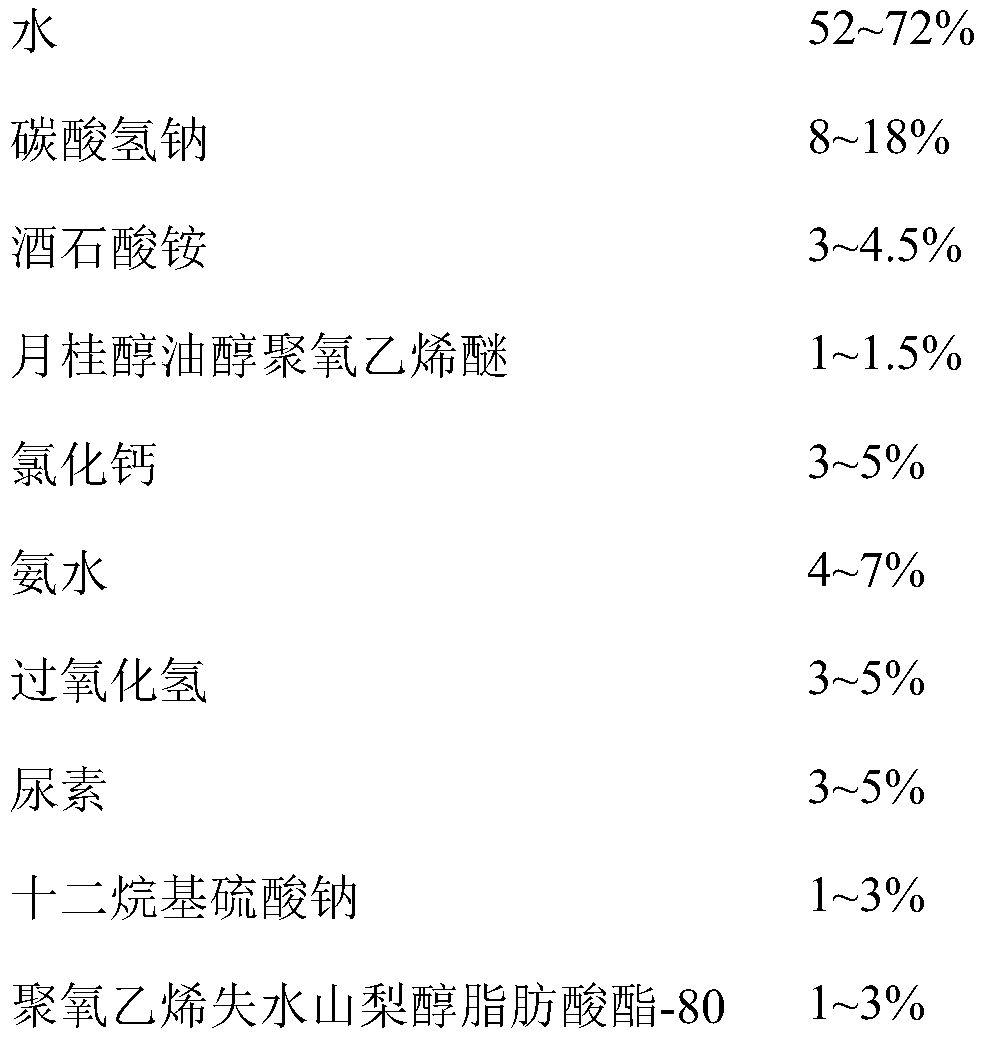
[0037] According to the following formula mass ratio, the following components are dissolved in water to make 5L cellulose extractant;
[0038]
[0039]
[0040] According to the components of Aspergillus aculeatus culture medium, 30 g of sucrose, 15 g of agar, 0.01 g of ferrous sulfate, 0.5 g of potassium chloride, and 3 g of sodium nitrate were dissolved in distilled water to prepare 1 L of culture medium, and the pH value was adjusted to 7.0. Put the prepared medium into a shaker flask and sterilize at 0.15Mpa at 120°C for 15 minutes; after the sterilization is complete, inoculate Aspergillus aculeatus into the medium, shake at 140r / min, and culture at 36°C for 15 hours , prepared into a shake flask bacterial solution. Take 120g of sucrose, 2g of magnesium sulfate, 6g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 3g of ammonium sulfate, 1g of potassium chloride, 3g of potassium nitrate, 1g of calcium chloride, 8g of yeast extract, and 5.4g of naringin according to the compositio...
Embodiment 2
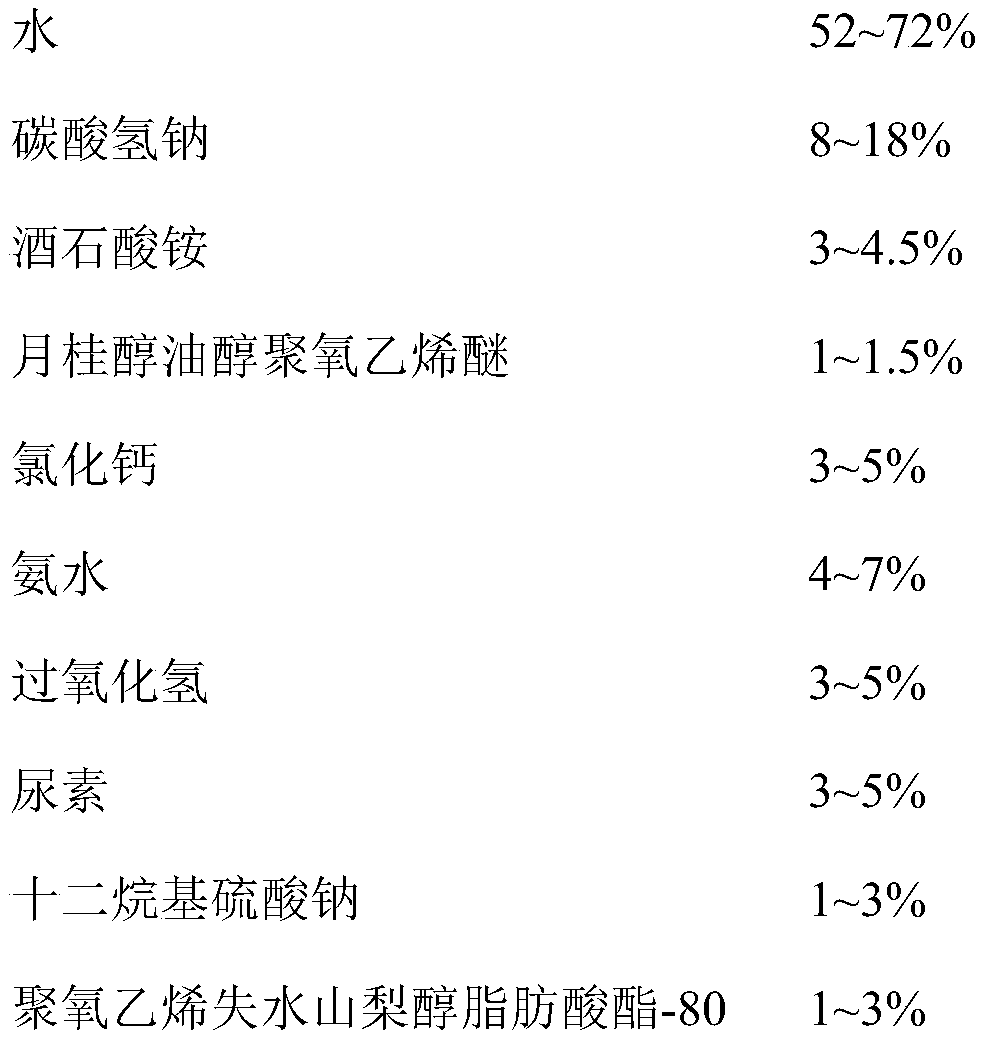
[0045] According to the following formula mass ratio, the following components are dissolved in water to make 10L cellulose extractant;
[0046]
[0047] According to the components of Aspergillus aculeatus culture medium, take 40 g of sucrose, 18 g of agar, 0.02 g of ferrous sulfate, 0.6 g of potassium chloride, and 4 g of sodium nitrate in distilled water to prepare 1 L of culture medium, and adjust the pH to 7.0. Put the culture medium into a shake flask and sterilize it at 0.15Mpa at 120°C for 20 minutes; inoculate Aspergillus aculeatus into the culture medium, shake it at 140r / min at 36°C for 15 hours, and prepare the shake flask bacterial liquid . Take 240g of sucrose, 3g of magnesium sulfate, 12g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 6g of ammonium sulfate, 1.5g of potassium chloride, 4.5g of potassium nitrate, 1.5g of calcium chloride, 21g of yeast extract, and 9g of naringin according to the components of the fermentation medium. Dissolve in distilled water to config...
Embodiment 3
[0052] According to the following formula mass ratio, the following components are dissolved in water to make 15L cellulose extractant;
[0053]
[0054] According to the components of Aspergillus aculeatus culture medium, 50 g of sucrose, 20 g of agar, 0.03 g of ferrous sulfate, 0.8 g of potassium chloride, and 5 g of sodium nitrate were dissolved in distilled water to prepare 1 L of culture medium, and the pH value was adjusted to 7.0. Put the medium into a shaker flask and sterilize at 0.15Mpa at 120°C for 15 minutes; inoculate Aspergillus aculeatus into the sterilized medium, shake it at 140r / min at 36°C for 15 hours, and prepare Shake flask broth. According to the composition of the fermentation medium, take 480g of sucrose, 4g of magnesium sulfate, 20g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 12g of ammonium sulfate, 2g of potassium chloride, 6g of potassium nitrate, 2g of calcium chloride, 40g of yeast extract, and 12g / L of naringin. Prepare 4L of fermentation medium in d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com