Preparation method and application of a flower-shaped iron ferric oxide-molybdenum disulfide-manganese dioxide nanocomposite
A technology of ferric oxide and nanocomposites, which is applied in the direction of iron oxide/iron hydroxide, molybdenum sulfide, ferrous oxide, etc., can solve the problems of small specific surface area and low activity of molybdenum disulfide, and achieve high The effect of electrocatalytic performance, low cost, and excellent performance of nitrite
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] (1) Weigh 30 grams of ferric chloride hexahydrate and 15 grams of iron sulfide in 250 ml of deionized water, respectively, introduce nitrogen for 20 minutes and stir until transparent;
[0070] (2) Stir the mixed solution obtained in step (1) at 60°C for 5 minutes, add ammonia water, and age at 70°C for 30 minutes to obtain ferric oxide;
[0071] (3) Weigh 0.3g of sodium molybdate and 0.4g of thiourea respectively in deionized water and stir well;
[0072] (4) Weigh 0.4g of the obtained ferric oxide and add it to step (3), stir at room temperature for 40 minutes, transfer to the autoclave, and react at 200 ° C for 24 hours;
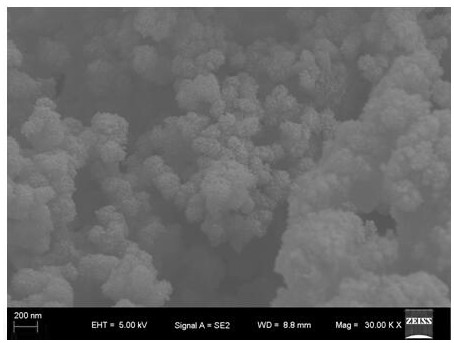
[0073] (5) After centrifuging the reaction product of step (4) to remove moisture, first wash with ethanol to remove unreacted organic matter, then wash with deionized water to remove unreacted inorganic ions, and place the washed reaction product in an oven drying at 70 °C in the middle to obtain the triiron tetroxide-molybdenum disulfide nanocom...
Embodiment 2
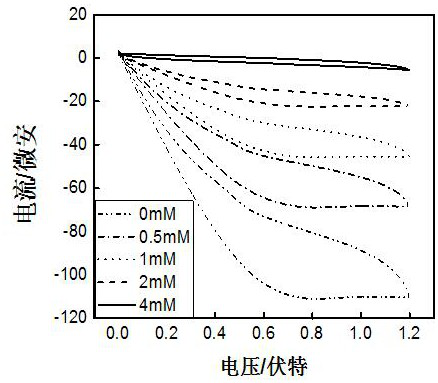
[0083] The three-electrode system prepared in Example 1 was placed in a solution containing no and 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 mmol dm -3 0.1 mol dm of sodium nitrite -3 The catalytic performance of ferric oxide-molybdenum disulfide-manganese dioxide complexes for nitrite was determined by cyclic voltammetry in phosphate buffer solution. The cyclic voltammogram is shown in figure 2 shown.
[0084] figure 2 Modified glassy carbon electrodes for ferric oxide-molybdenum disulfide-manganese dioxide composites without and with 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 mmol dm -3 0.1 mol dm of sodium nitrite -3 Cyclic voltammogram in phosphate buffered solution. It can be seen from the figure that when the composite modified glassy carbon electrode was moved from the phosphate buffer solution to the solution containing sodium nitrite, an oxidation peak appeared near 0.7V, and the peak appeared with the increase of nitrite concentration. the current increases. This result indicates that the nitrite undergoes a ...
Embodiment 3
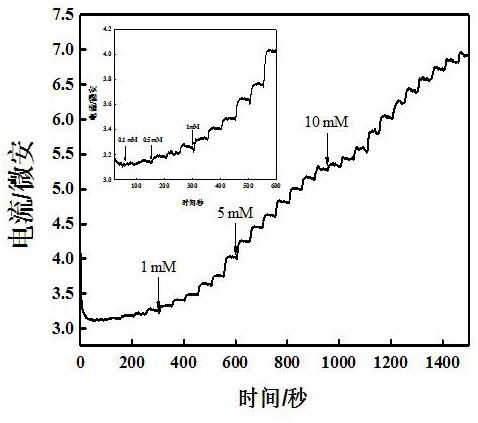
[0087] The three-electrode system prepared in Example 1 was placed in 0.1 mol dm -3 In the phosphate buffer solution, sodium nitrite solutions of different concentrations were added dropwise, and the response current values corresponding to different concentrations of sodium nitrite solutions were measured by the potentiostatic method, and the linear relationship between the nitrite concentration and the response current was obtained ( image 3 );
[0088] from image 3 It can be seen from: Fe3O4-molybdenum disulfide-manganese dioxide composite modified glassy carbon electrode pair 0.1mmol dm -3 nitrite can respond. Figure 4 is true image 3 A plot of nitrite concentration versus response current. As can be seen from the graph: at 5.0 to 3400µmol dm -3 A good linear relationship is maintained within the range of .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com