Process method for treating hot-dip galvanizing waste hydrochloric acid
A process method and waste hydrochloric acid technology are applied in the field of industrial waste resource treatment, which can solve the problems of wasting enterprise costs, unfavorable small and medium-sized enterprises to promote the use of hot-dip galvanizing waste hydrochloric acid treatment, and environmental pollution, so as to avoid the increase of waste water treatment volume Large, conducive to the protection of the ecological environment, the effect of low operational risk factor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
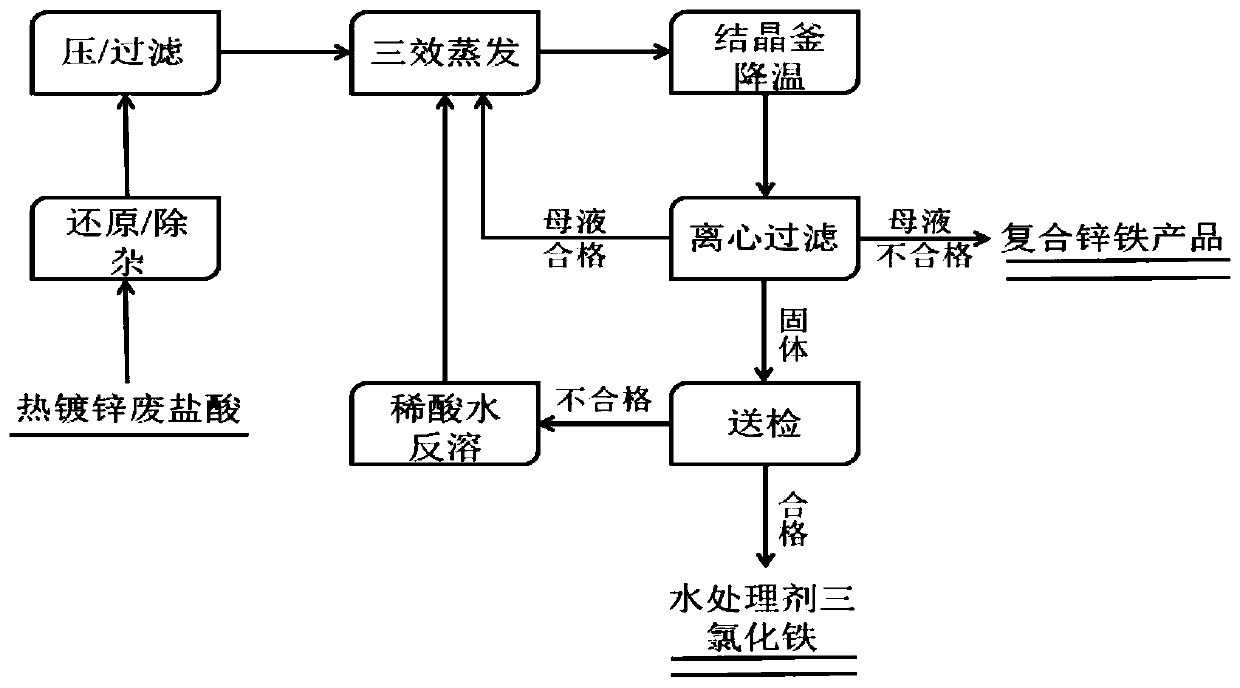
[0037] (1) Beat the hot-dip galvanizing waste hydrochloric acid with a zinc content of 9985ppm into the stirring tank, add excess coil iron, stir for 30 minutes, and then feed the three-effect evaporation after passing through a 300μm pore size filter.
[0038] (2) When the specific gravity of the evaporated material liquid reaches 1.45, start to discharge the material to the crystallization kettle, and the crystallization kettle is covered with cooling water.
[0039] (3) When the feed liquid temperature in the crystallization tank was down to 45°C, it began to discharge to the centrifuge, and a primary crystallization and mother liquor of ferrous chloride were obtained. After testing, the zinc content of the primary crystallization was 2085ppm, and the zinc content of the mother liquor was 2085ppm. 33125ppm.
[0040] (4) the primary crystallization in step (3) is dissolved in 0.16% evaporative condensed water with an acid content (in HCl, the same below), and the gained soluti...
Embodiment 2
[0048] (1) Beat hot-dip galvanizing waste hydrochloric acid with a zinc content of 4820ppm into the stirring tank, add excess iron sheet, stir for 30 minutes, and then feed the three-effect evaporation after passing through a 100μm pore size filter.
[0049] (2) When the specific gravity of the evaporated material liquid reaches 1.49, start to discharge the material to the crystallization kettle, and the crystallization kettle is covered with cooling water.
[0050] (3) When the feed liquid temperature in the crystallization tank was down to 23°C, it began to discharge to the centrifuge, and the primary crystallization and mother liquor of ferrous chloride were obtained. After testing, the zinc content of the primary crystallization was 945ppm, and the zinc content of the mother liquor was 945ppm. 14500ppm.
[0051] (4) the primary crystallization in step (3) is dissolved in 5.34% evaporative condensed water with acid content (in terms of HCl, the same below), and the gained s...
Embodiment 3
[0056] (1) Beat hot-dip galvanizing waste hydrochloric acid with a zinc content of 6640ppm into the mixing tank, add excess iron sheet, stir for 30 minutes, and then filter through a 1300-mesh filter cloth press to feed the three-effect evaporation.
[0057] (2) When the liquid-solid-liquid ratio (volume ratio) of the evaporated material reaches 25%, start discharging to the crystallization kettle, and the crystallization kettle is covered with cooling water.
[0058] (3) When the feed liquid temperature in the crystallization tank was down to 32°C, it began to discharge to the centrifuge, and the primary crystallization and mother liquor of ferrous chloride were obtained. After testing, the zinc content of the primary crystallization was 1867ppm, and the zinc content of the mother liquor was 1867ppm. 21290ppm.
[0059] (4) the primary crystallization in step (3) is dissolved in 8.90% evaporative condensed water with an acid content (in terms of HCl, the same below), and the g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com