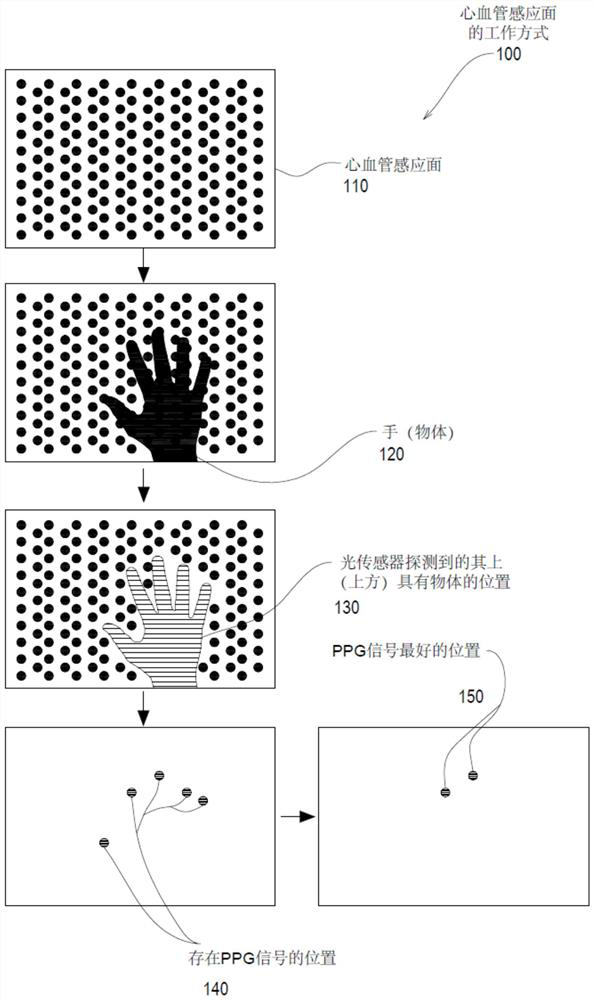
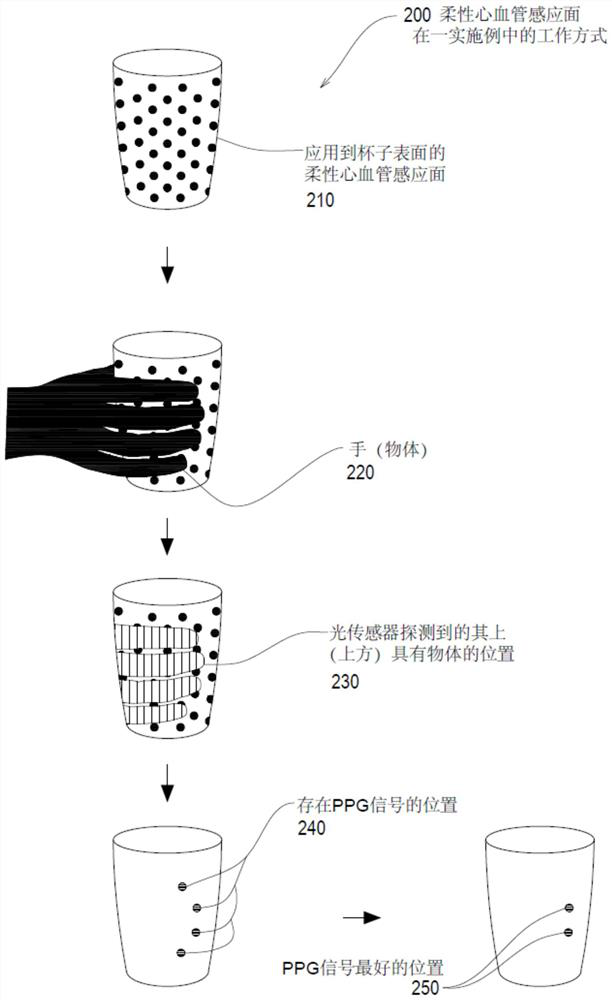
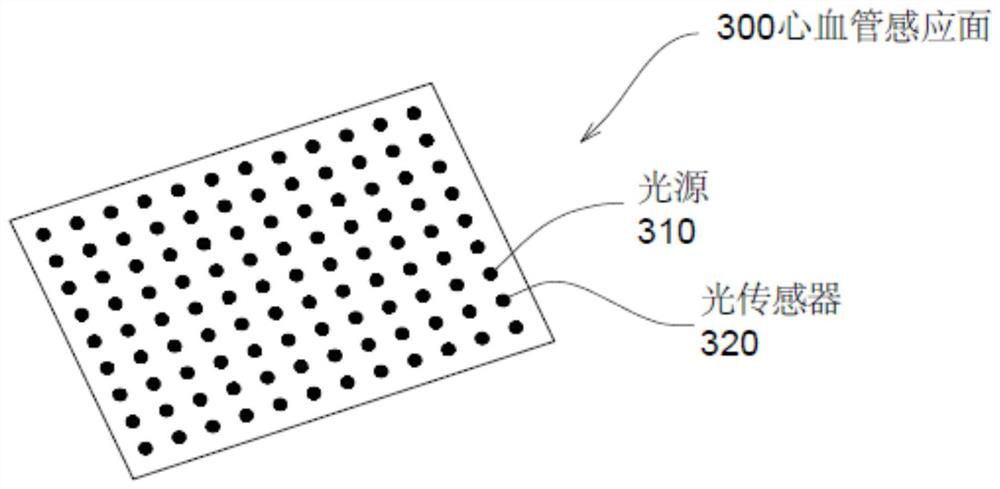
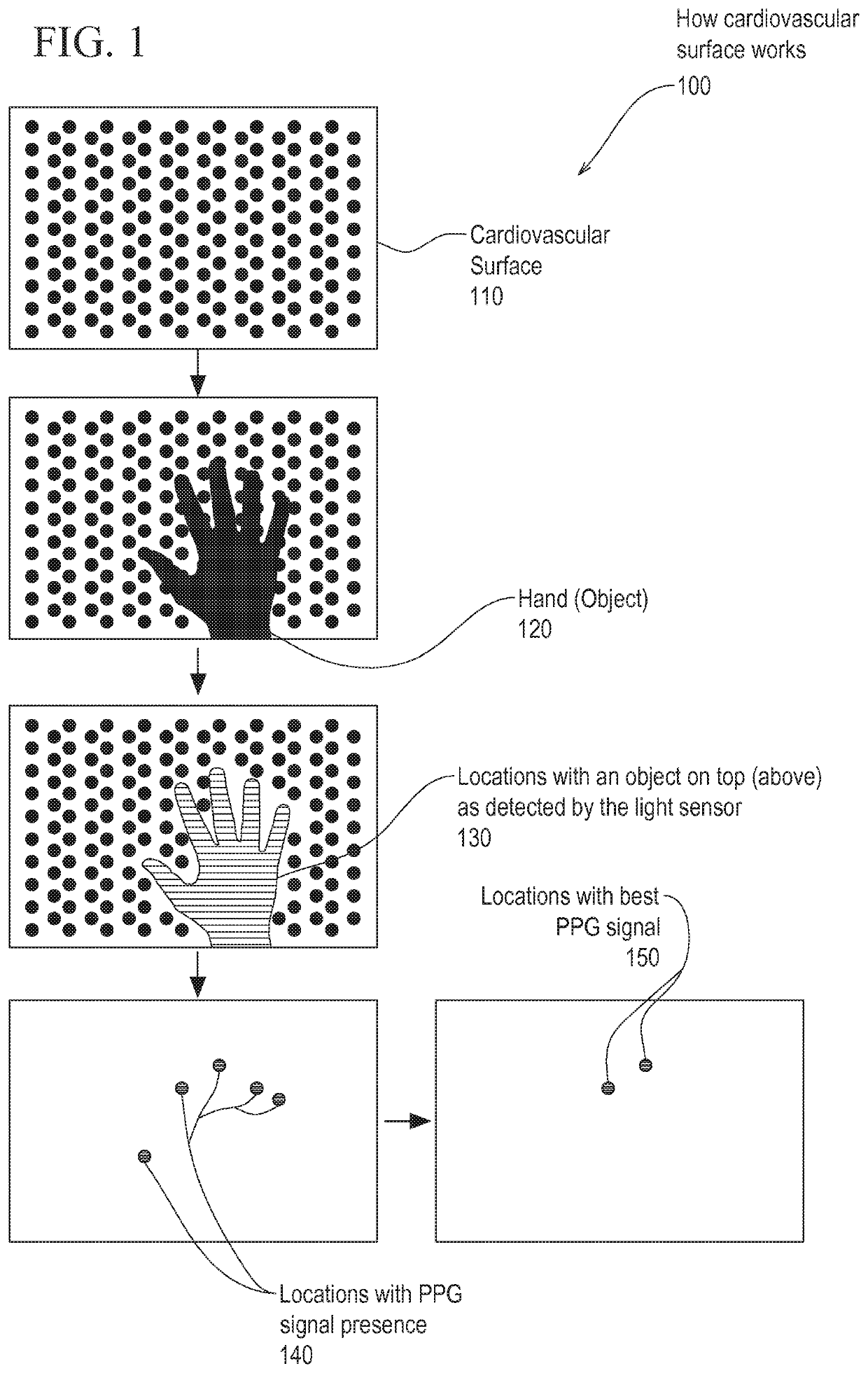
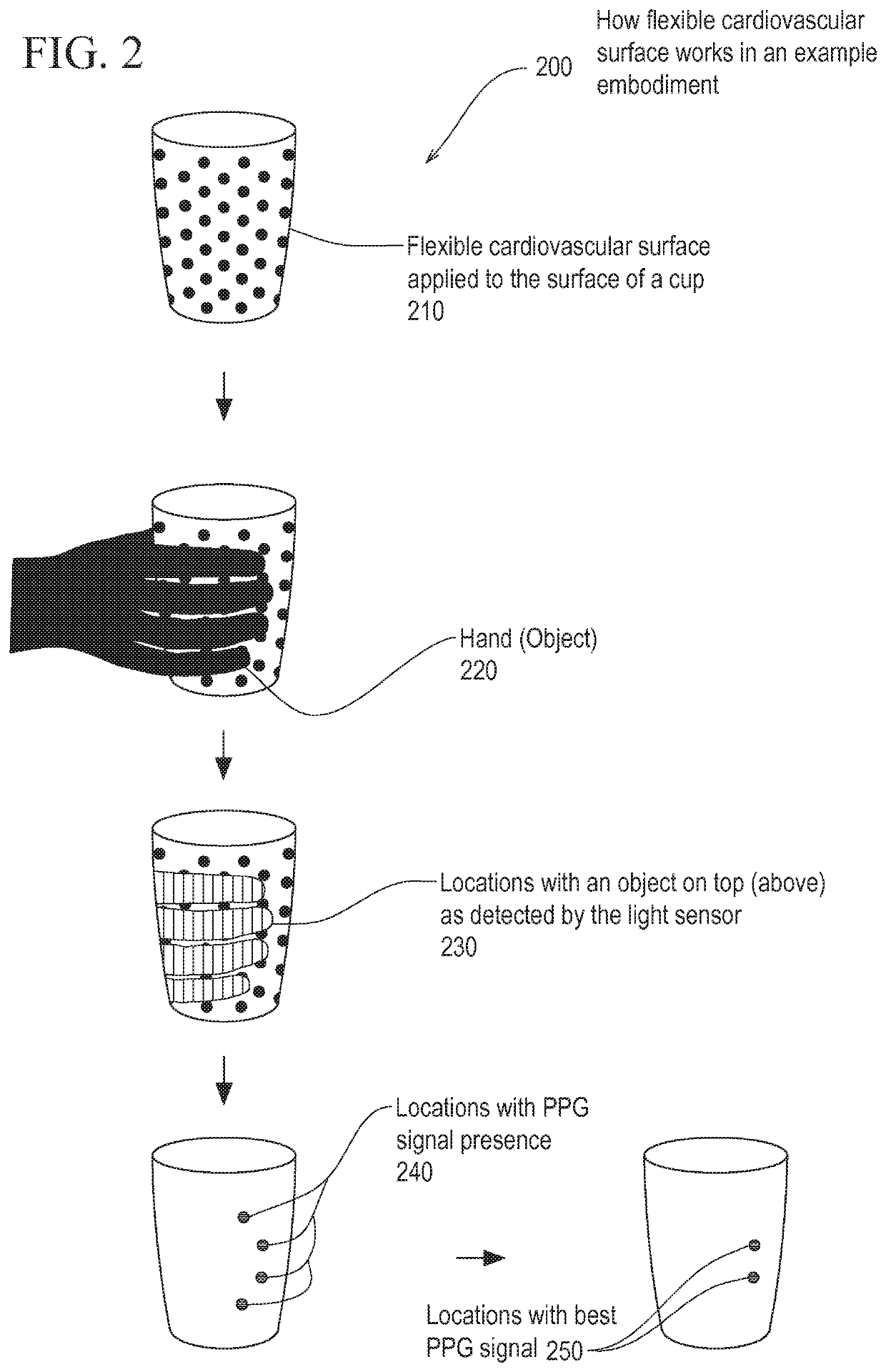
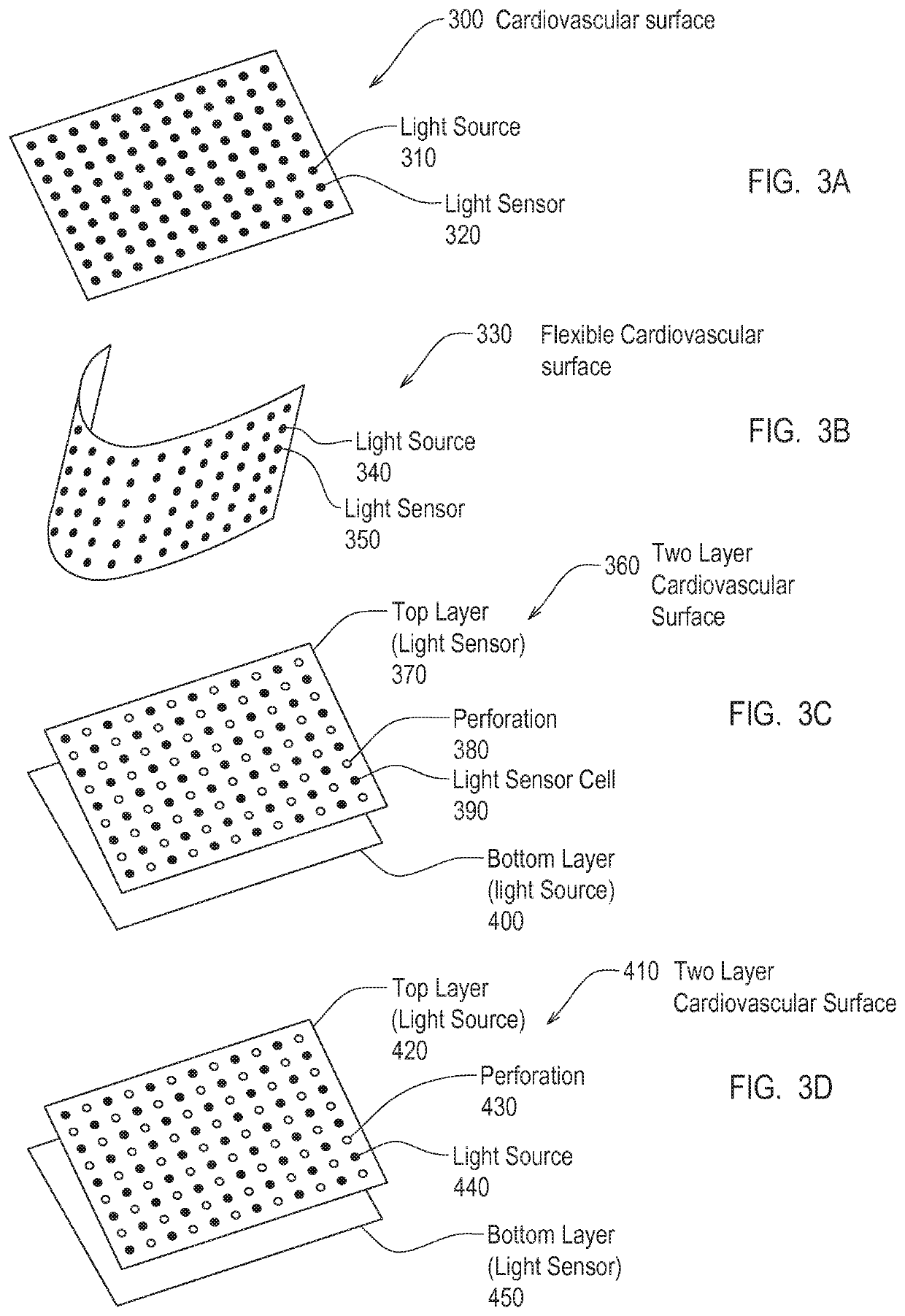
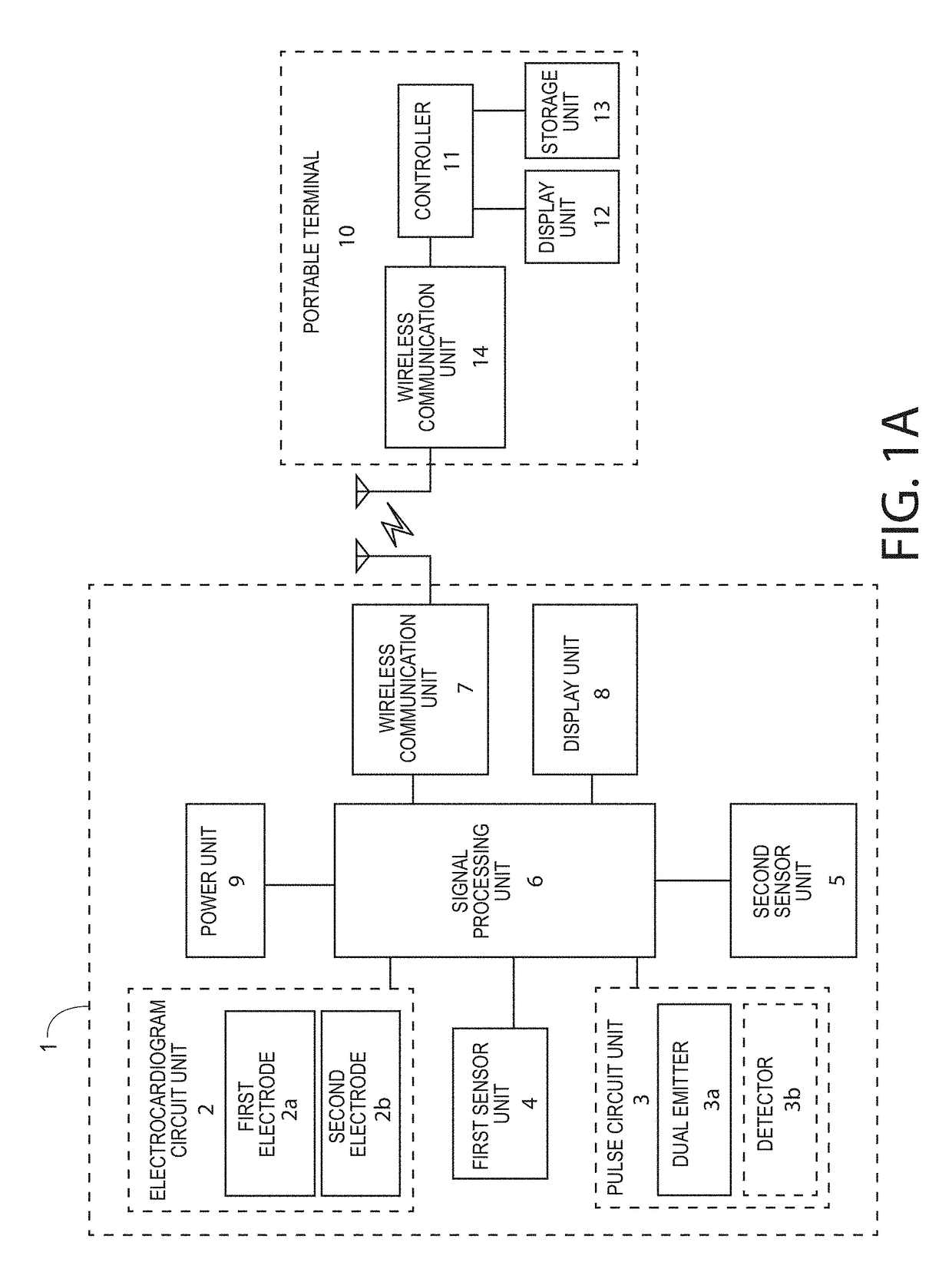
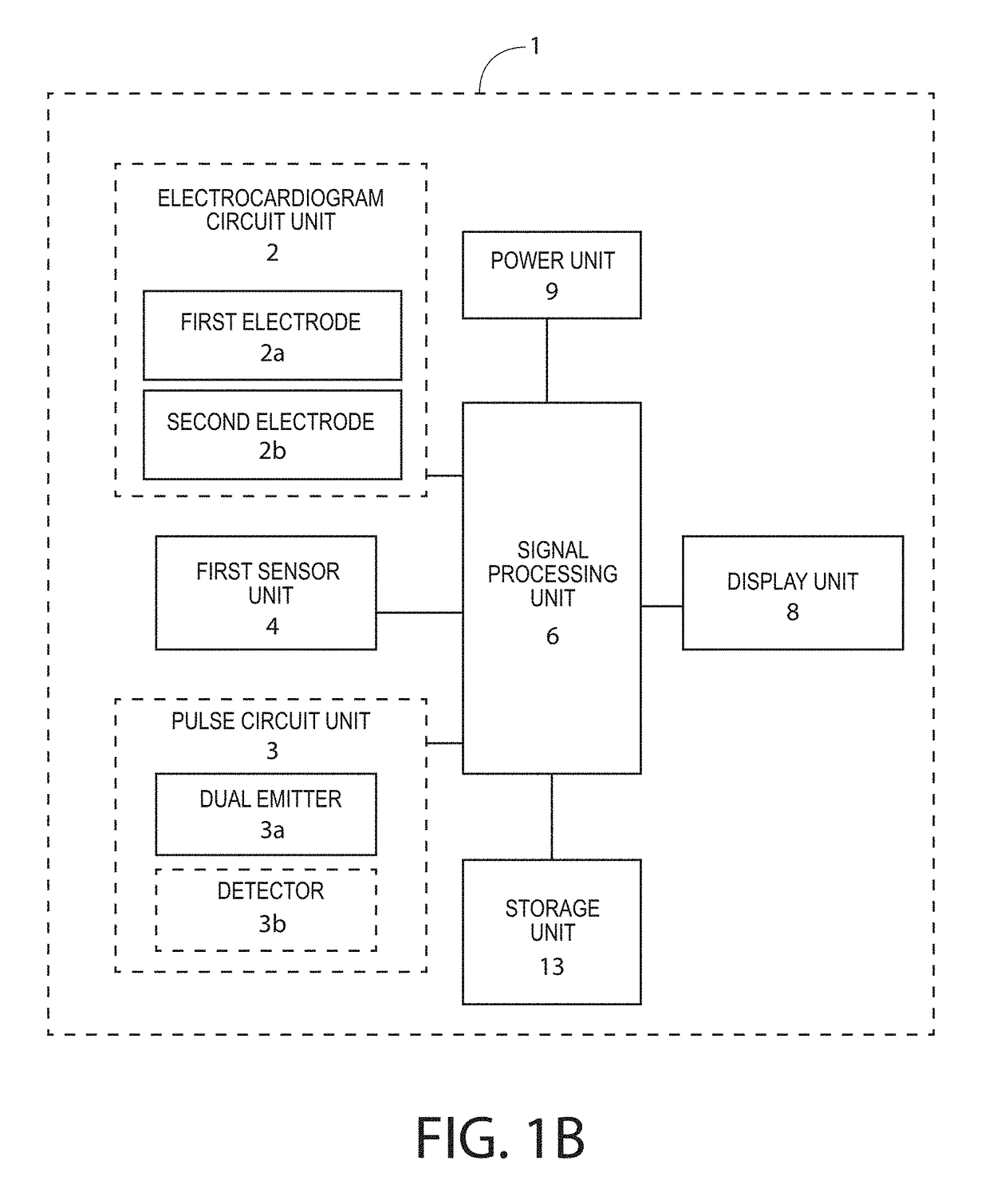
Patents
Literature
45 results about "Cardiovascular monitoring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
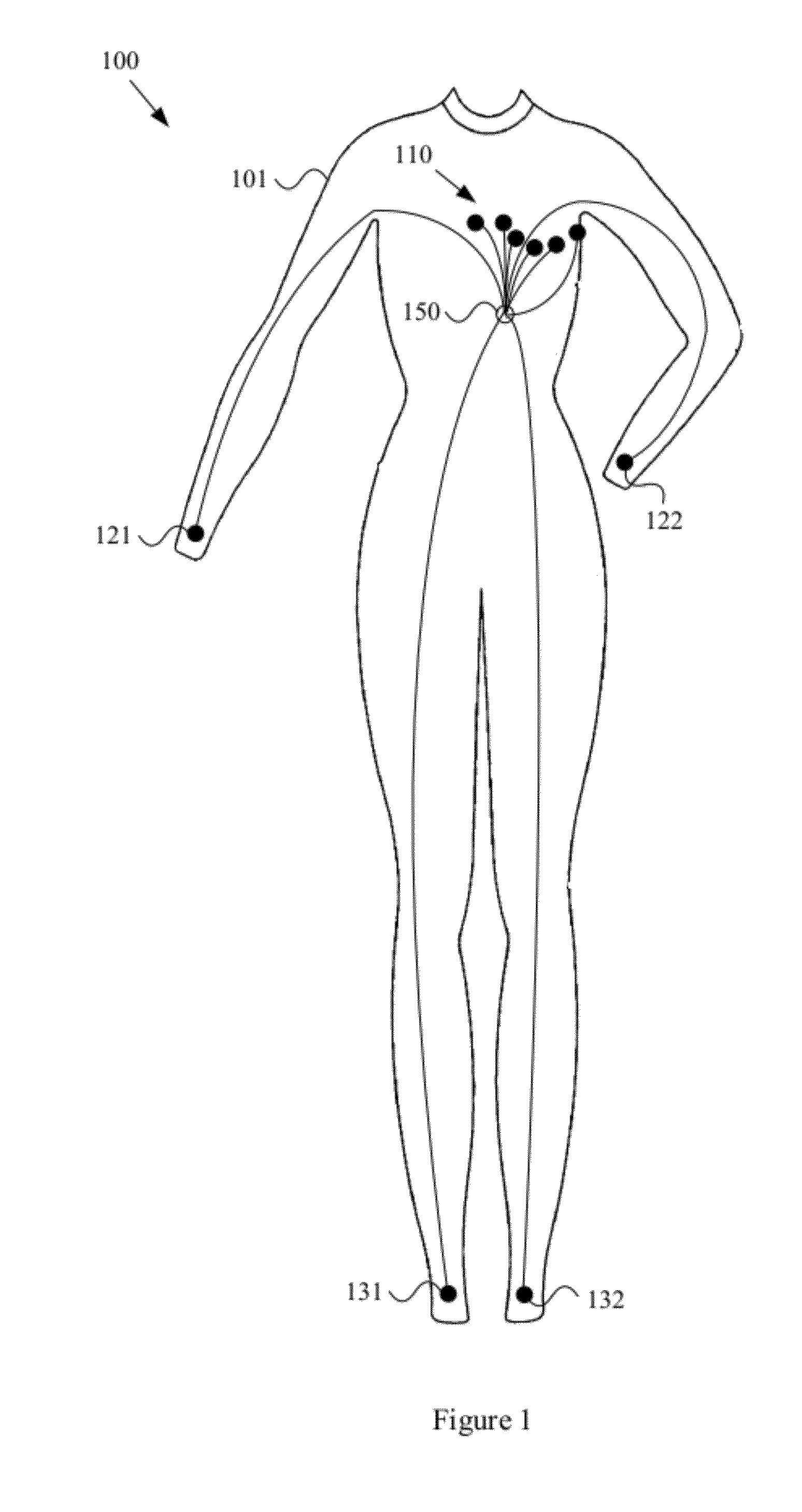
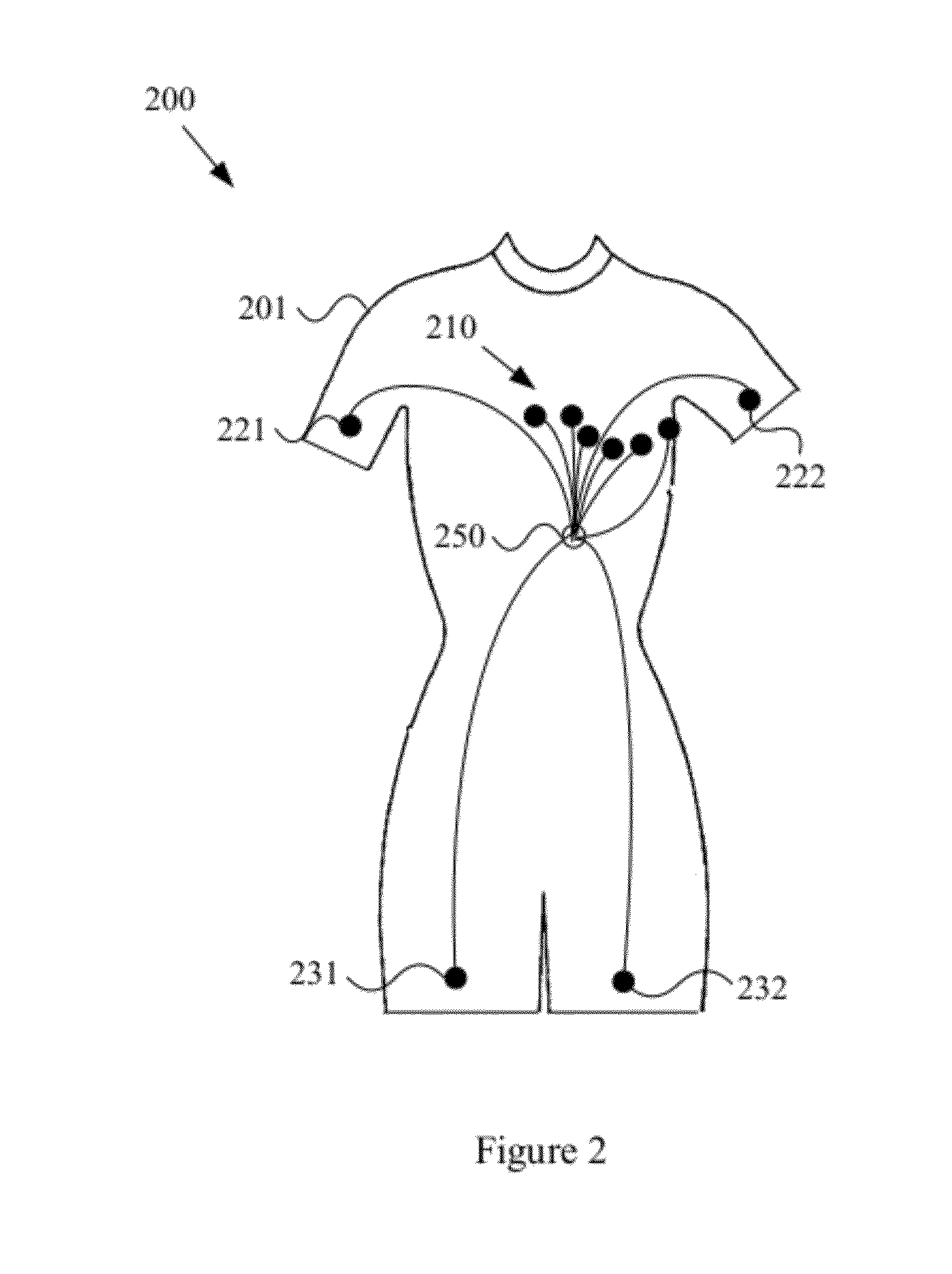
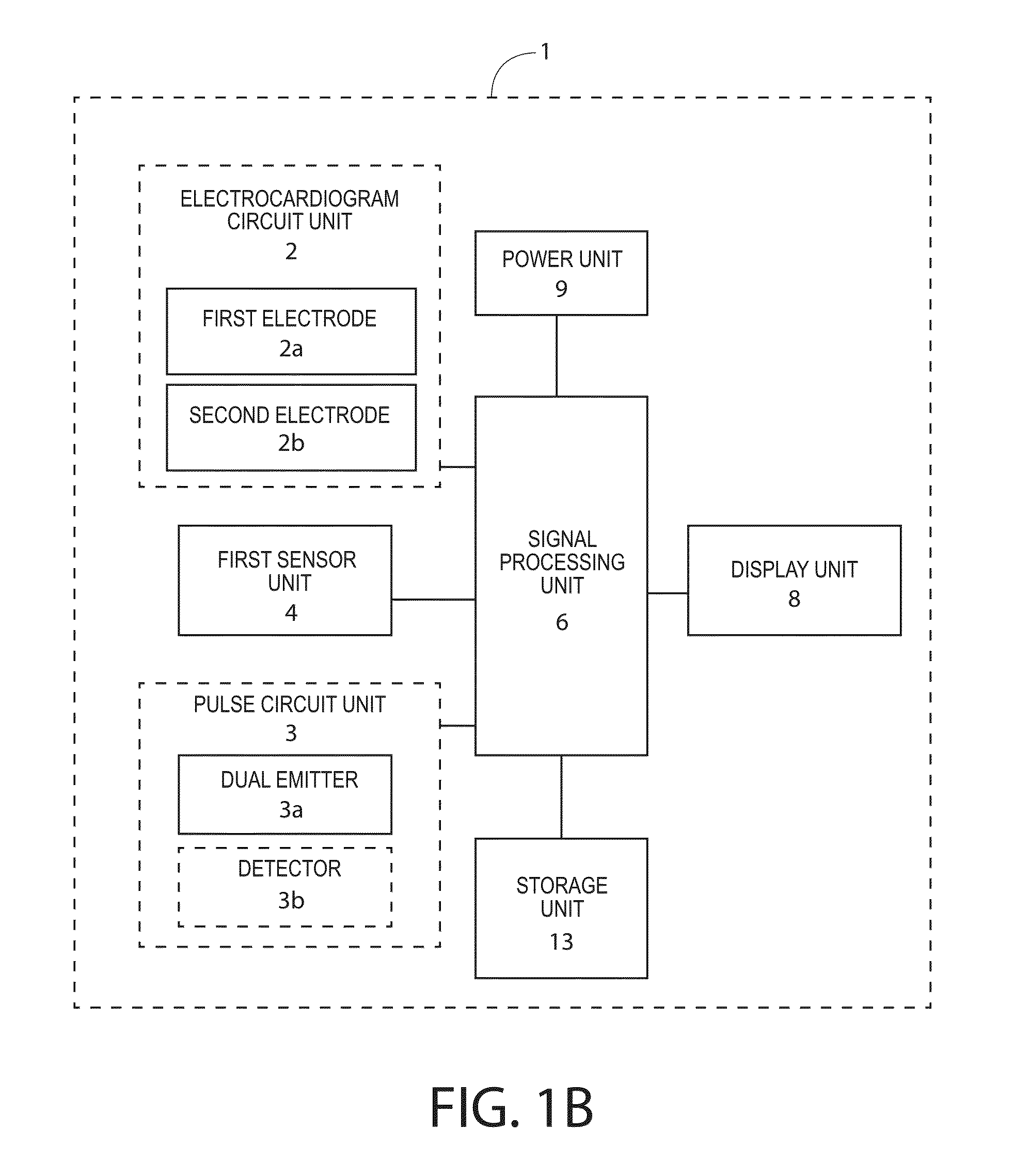
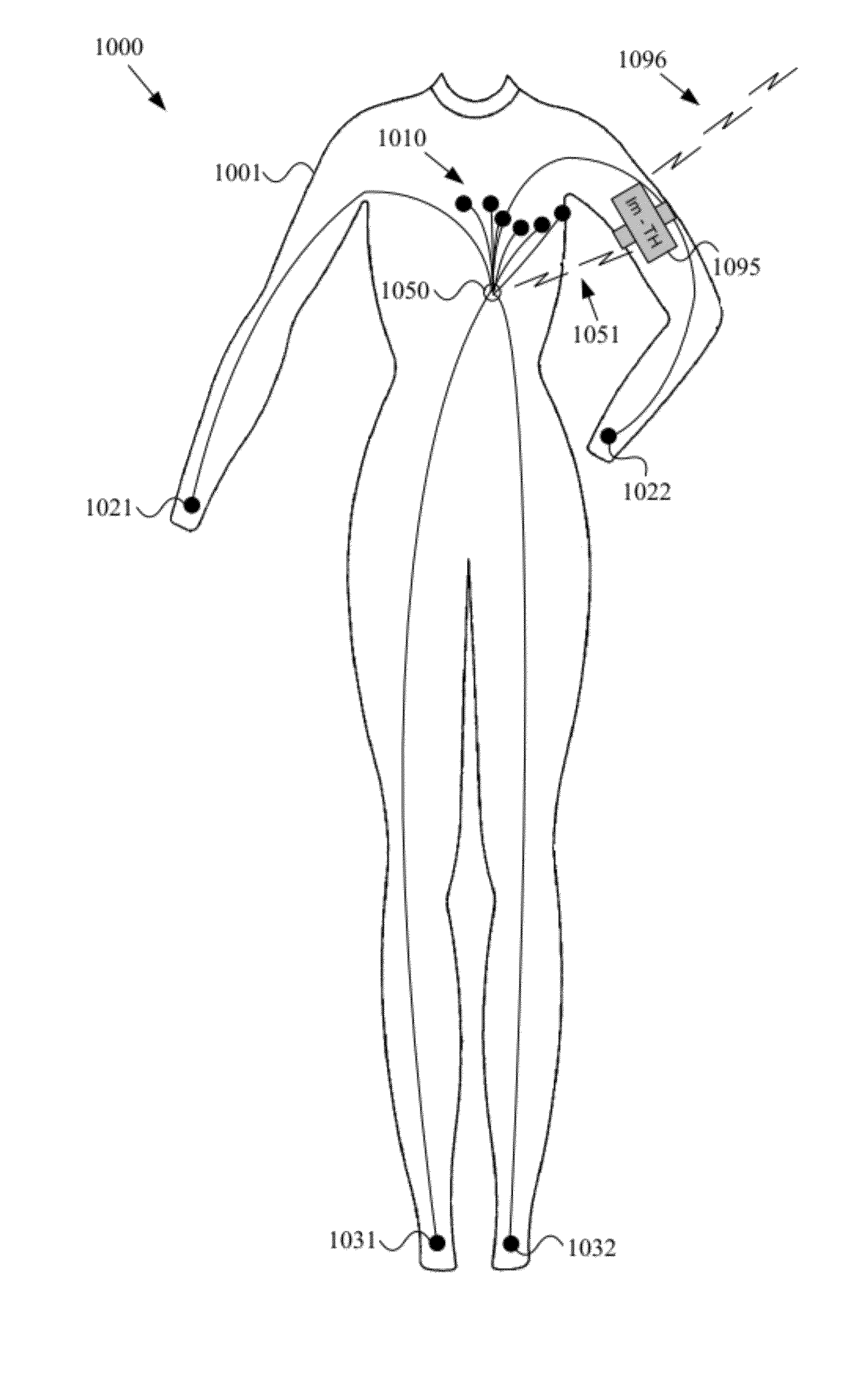
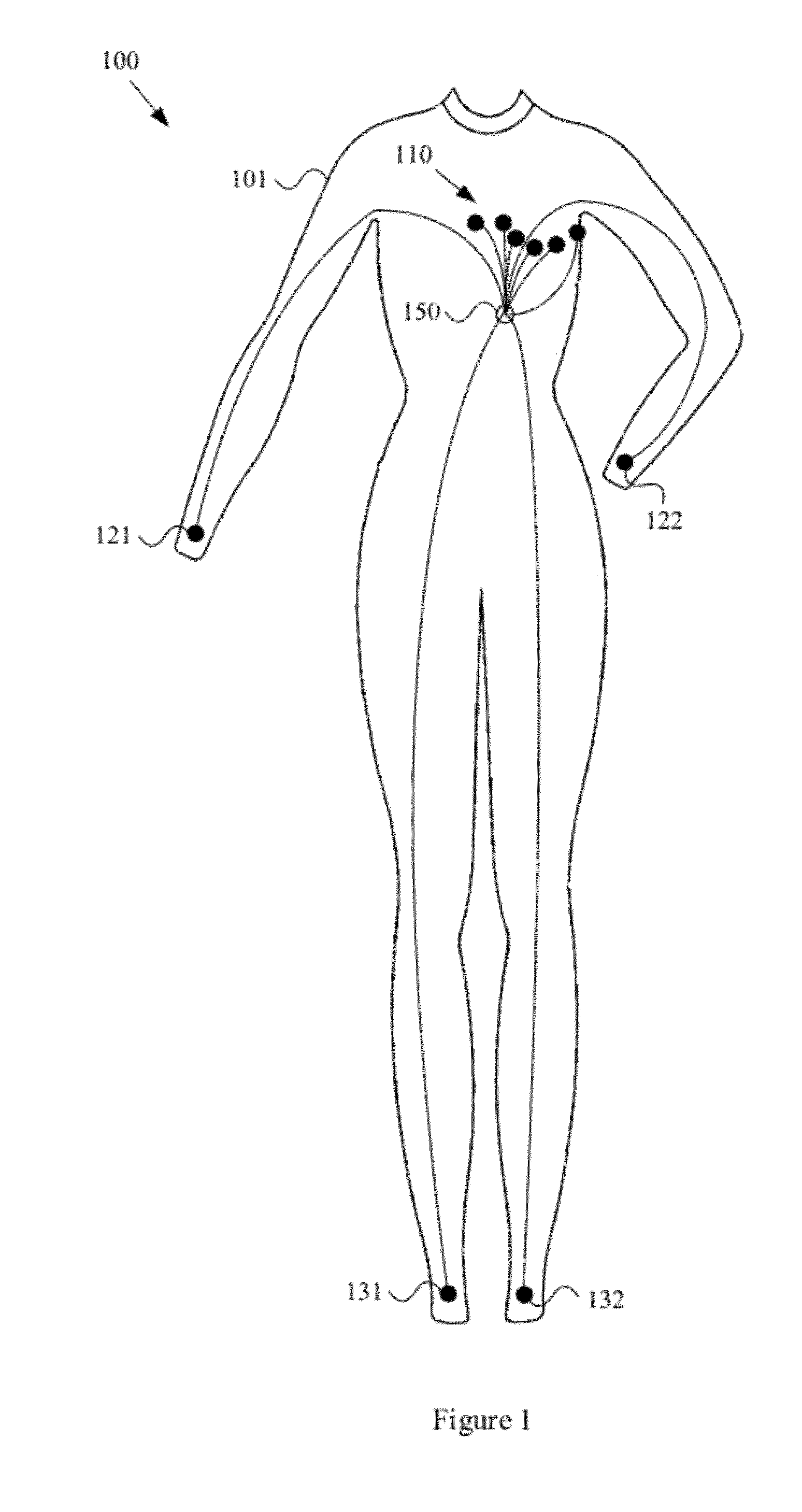
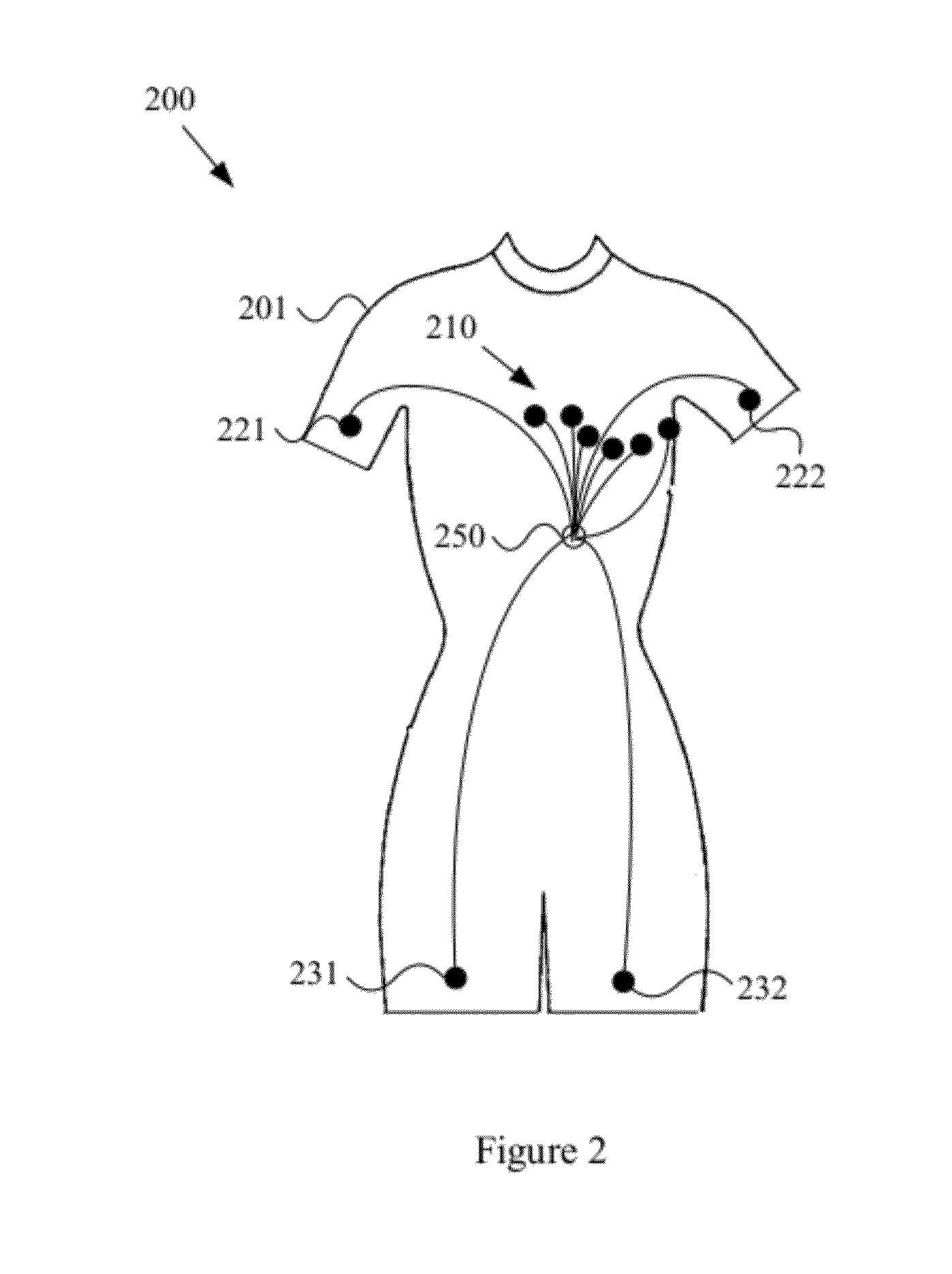
Wearable items providing physiological, environmental and situational parameter monitoring
A garment and / or garment system with health-monitoring (e.g., cardiovascular monitoring) capability, substantially as shown in and / or described in connection with at least one of the figures, as set forth more completely in the claims.
Owner:MARKEL GAL
Noninvasive cardiovascular monitoring methods and devices
InactiveUS20050096557A1Facilitate signal acquisitionElectrocardiographySensorsPhysiologic StatesDevice Monitor
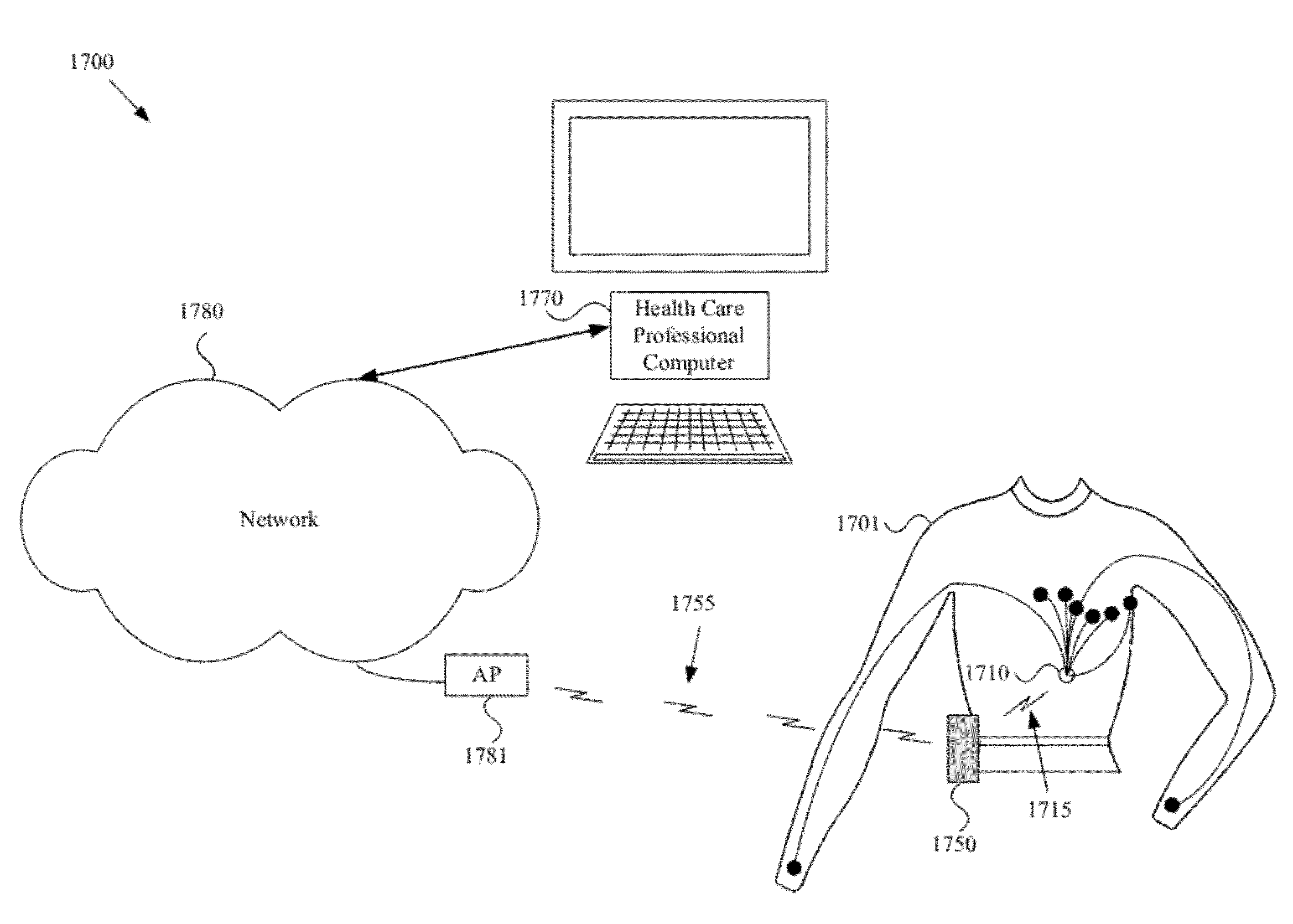
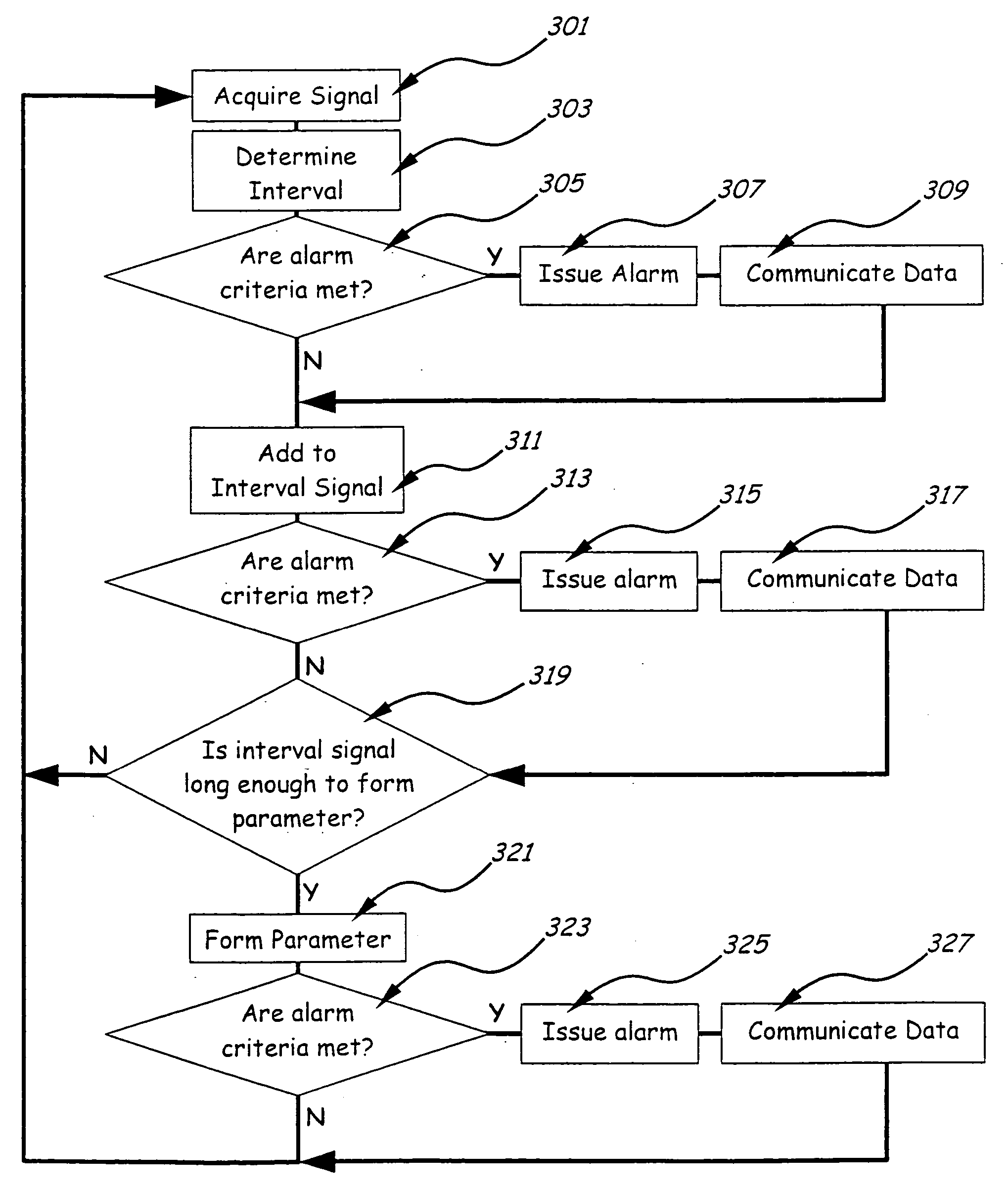
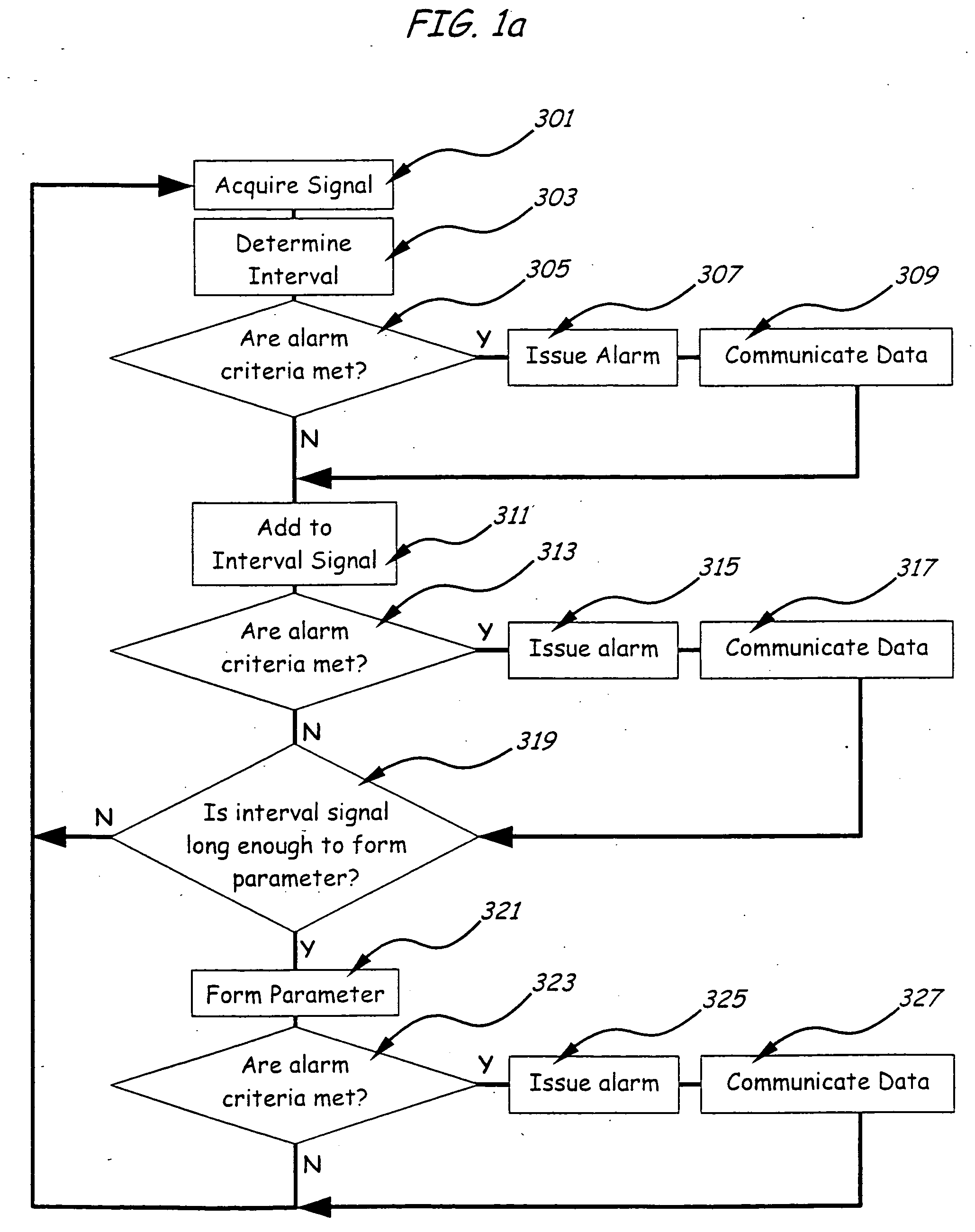
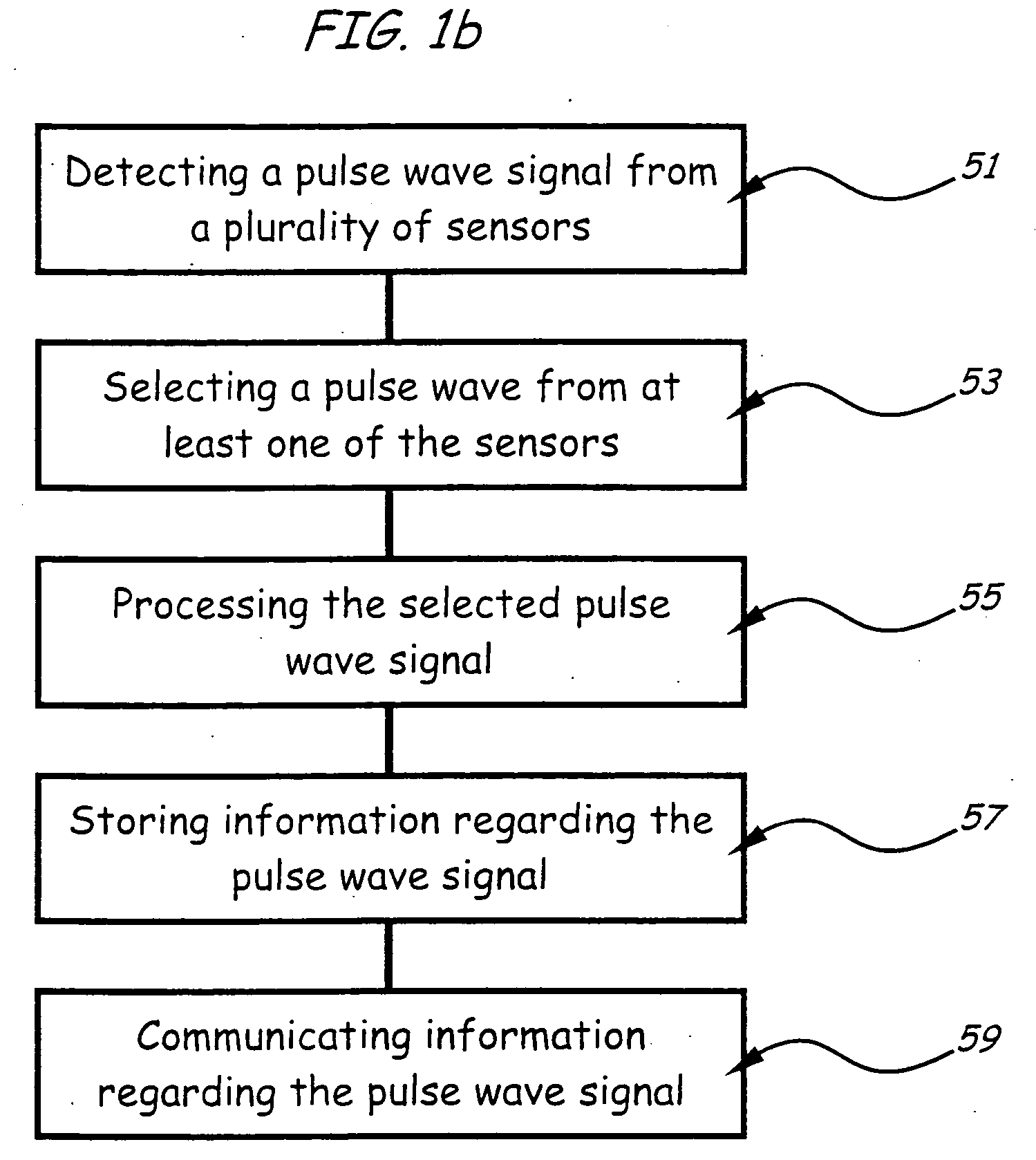
Monitoring the physiologic status of a human or animal subject includes detecting a blood vessel signal with a sensor. A physiologic time interval can be determined, and information related to the physiologic status of the subject can be analyzed and communicated.
Owner:VOSBURGH FREDERICK +2
Mobile communication device and other devices with cardiovascular monitoring capability
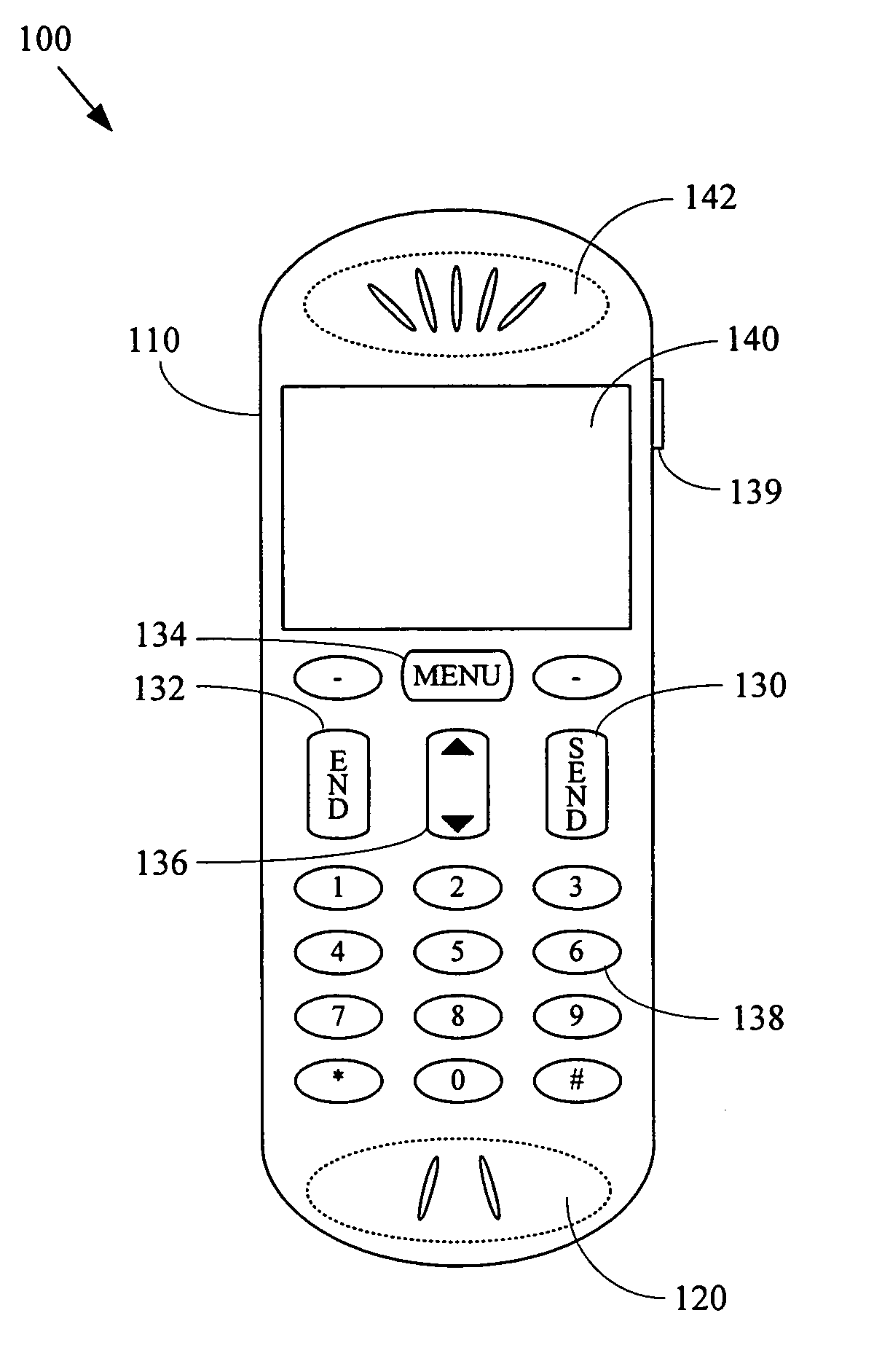
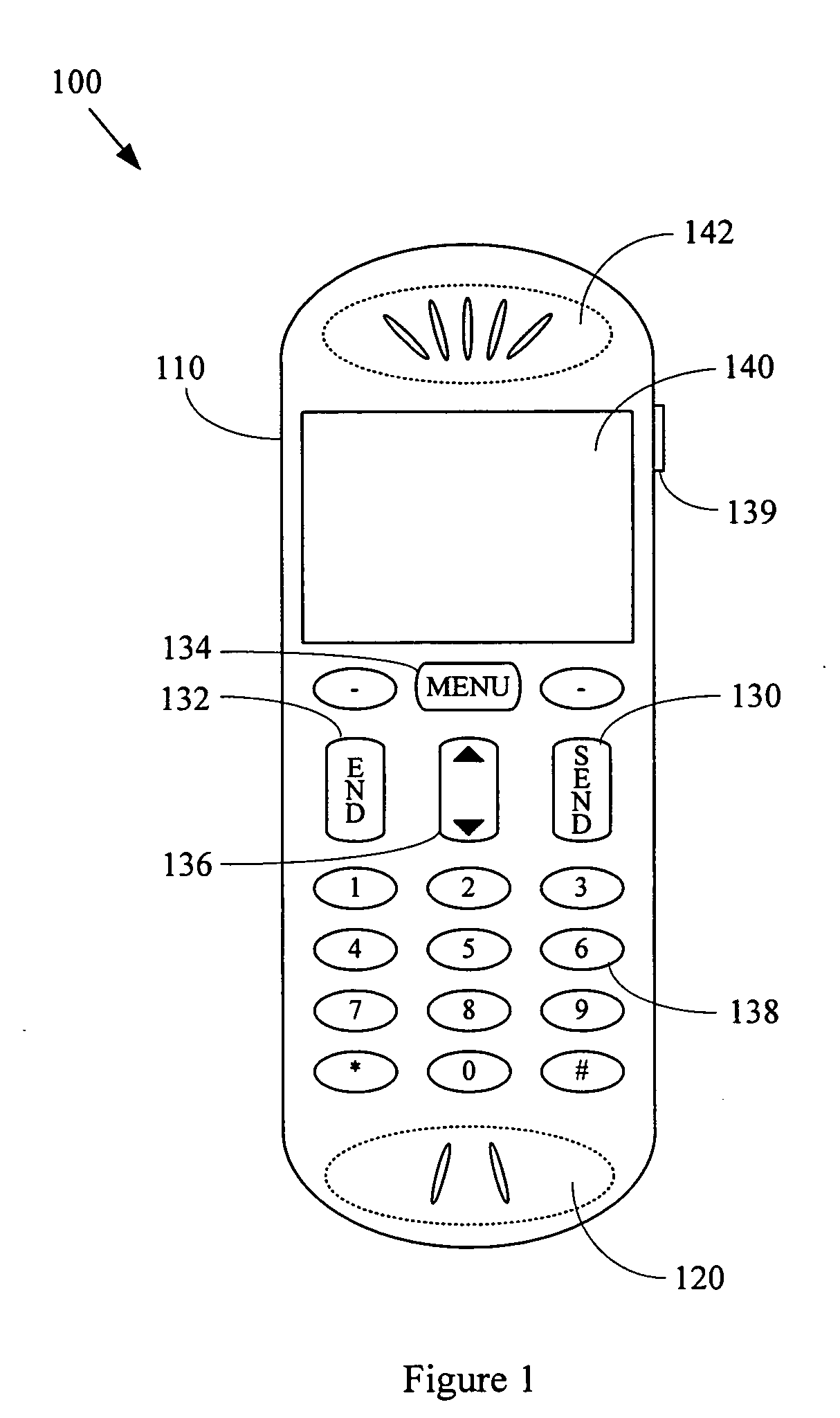
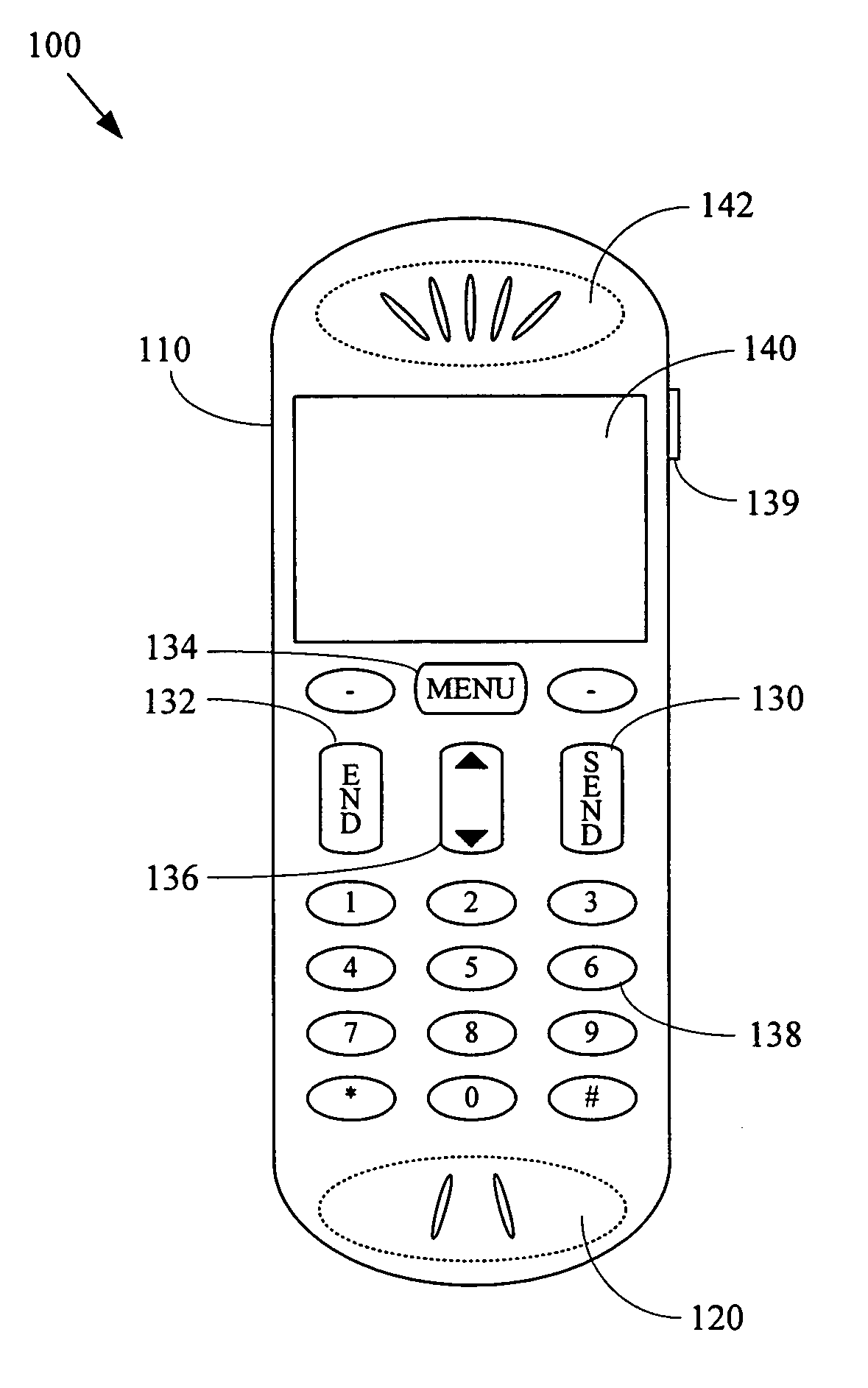
A general-purpose mobile communication device, general-purpose computer user-interface device, and other non-health-related electronic devices with cardiovascular monitoring capability. Various aspects of the present invention may comprise a general-purpose mobile communication device (e.g., a cellular telephone, portable email device, personal digital assistant, etc.) comprising a communication interface module adapted to communicate with a general-purpose communication network, and at least one module operational to acquire cardiac information from a user of the general-purpose mobile communication device. The general-purpose communication device may, for example, comprise a cardiac sensor (e.g., electrodes) disposed on the mobile communication device, which may be utilized to acquire cardiac information during use of the mobile communication device. Various aspects of the present invention may also comprise a non-health related electronic device (e.g., a general-purpose mobile communication device, general-purpose user-interface device for a general-purpose computer, gaming controller, etc.) that, during normal non-health-related utilization, acquire, analyze and / or communicate user health-related information.
Owner:MARKEL GAL
System and apparatus for providing diagnosis and personalized abnormalities alerts and for providing adaptive responses in clinical trials
InactiveUS8838217B2ElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsHolter ElectrocardiographyClinical trial
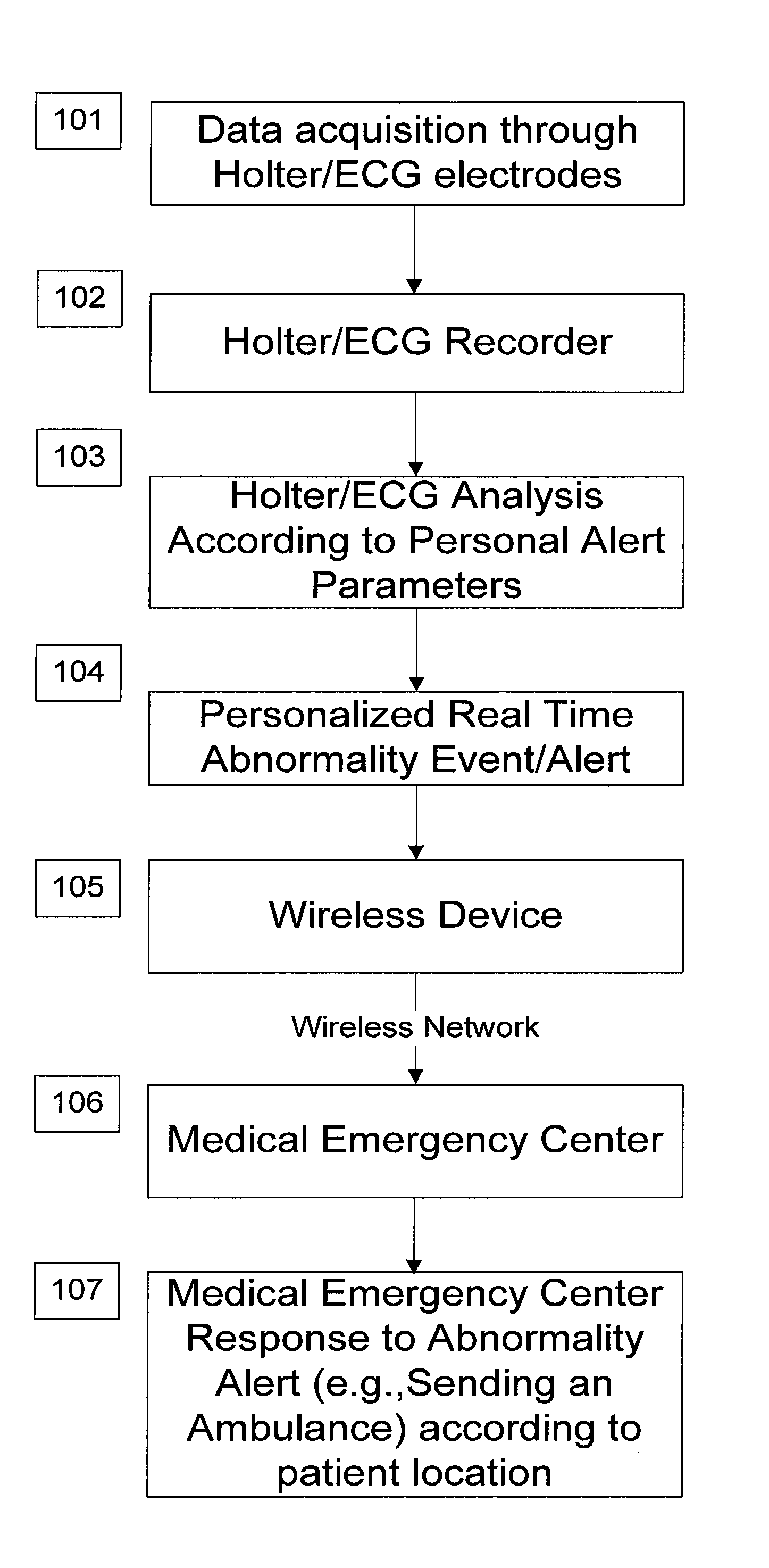
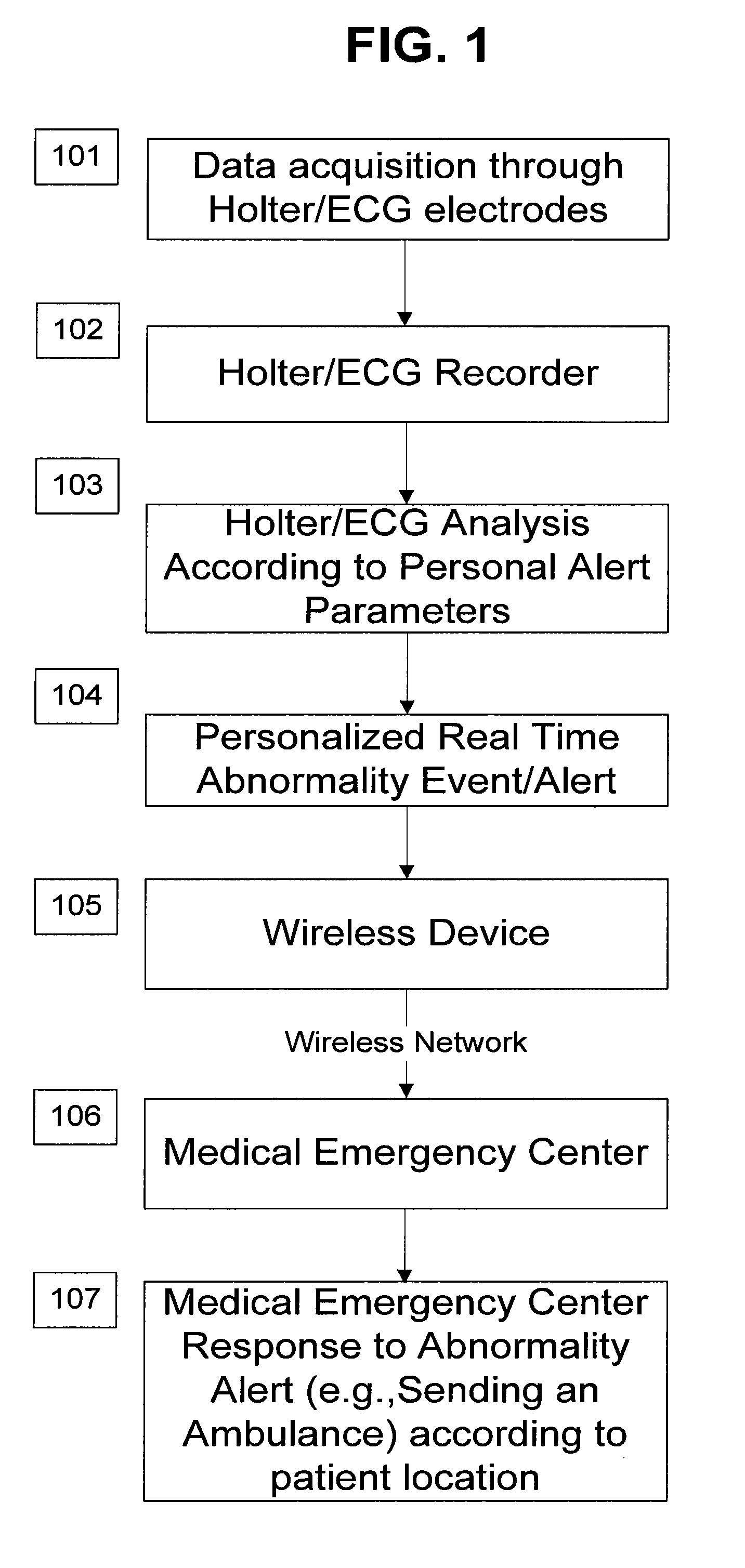
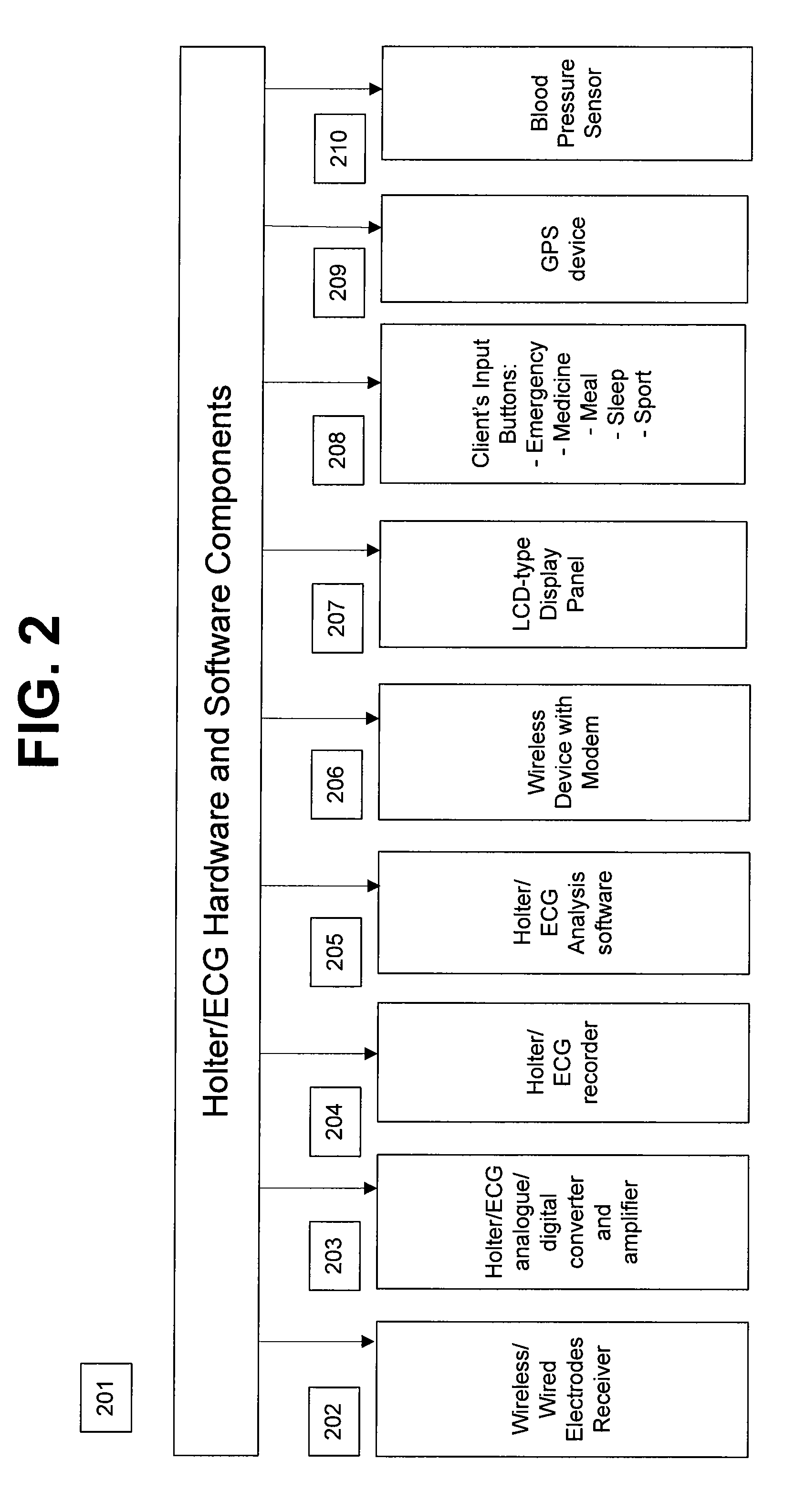
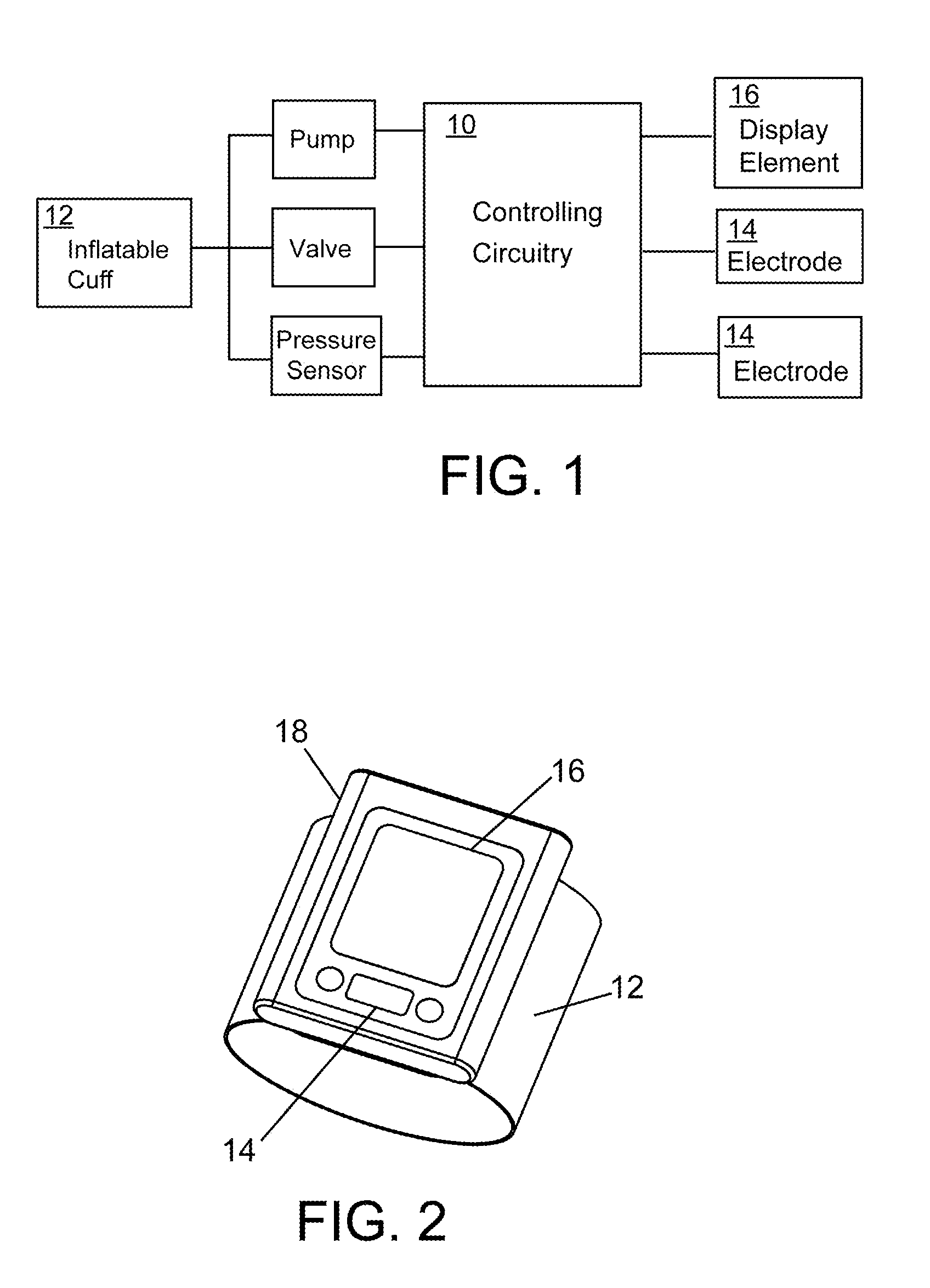
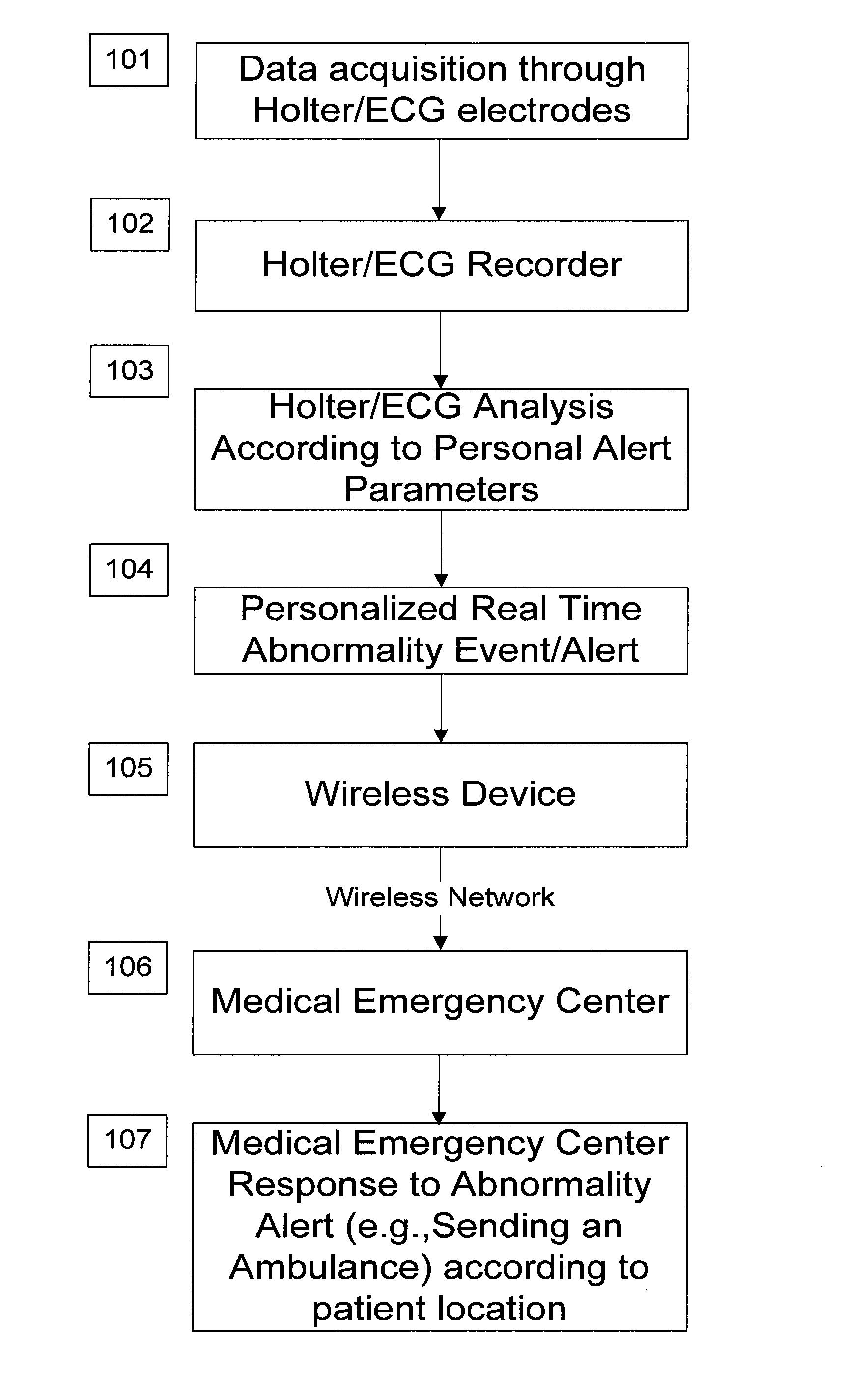
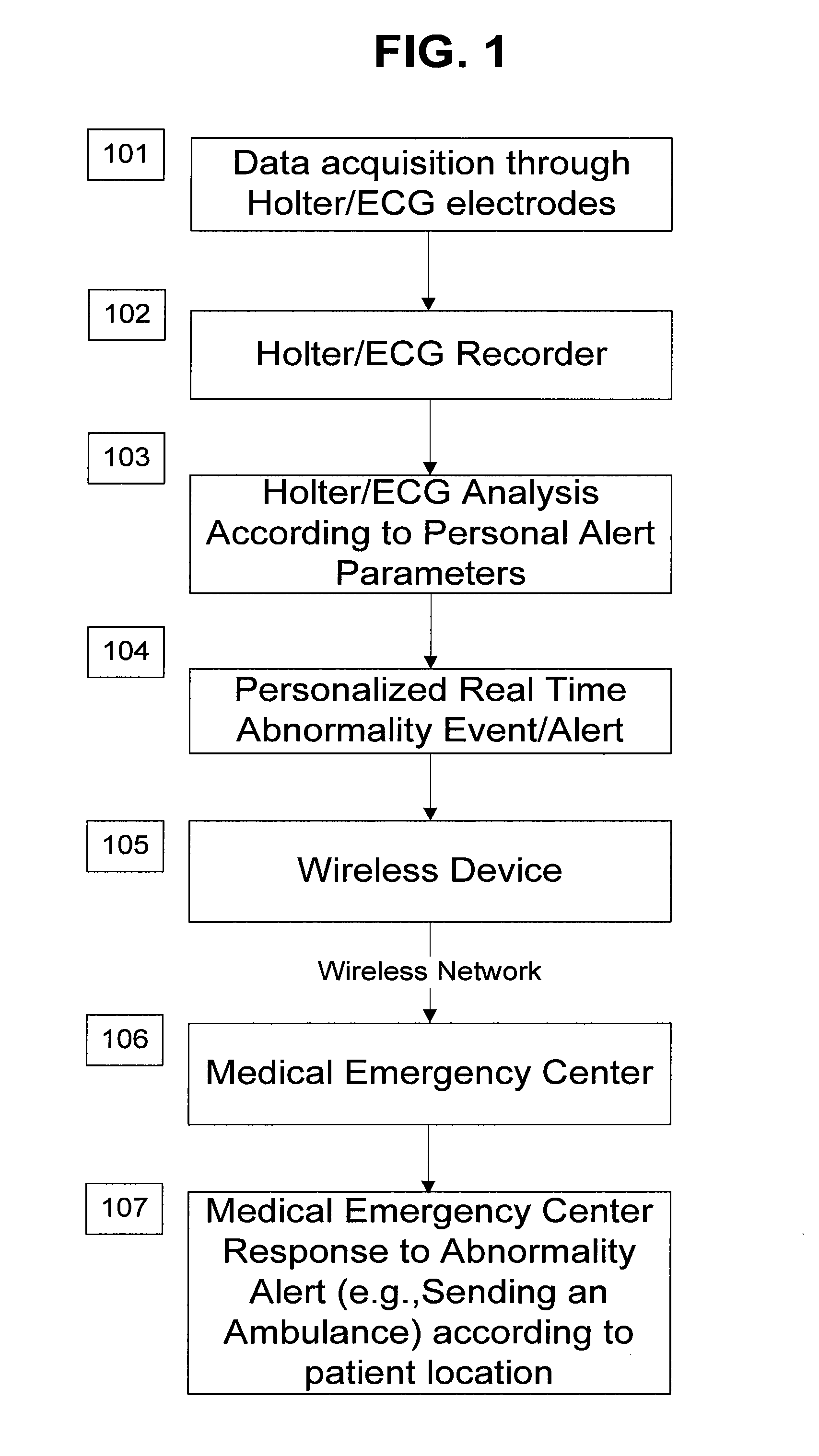
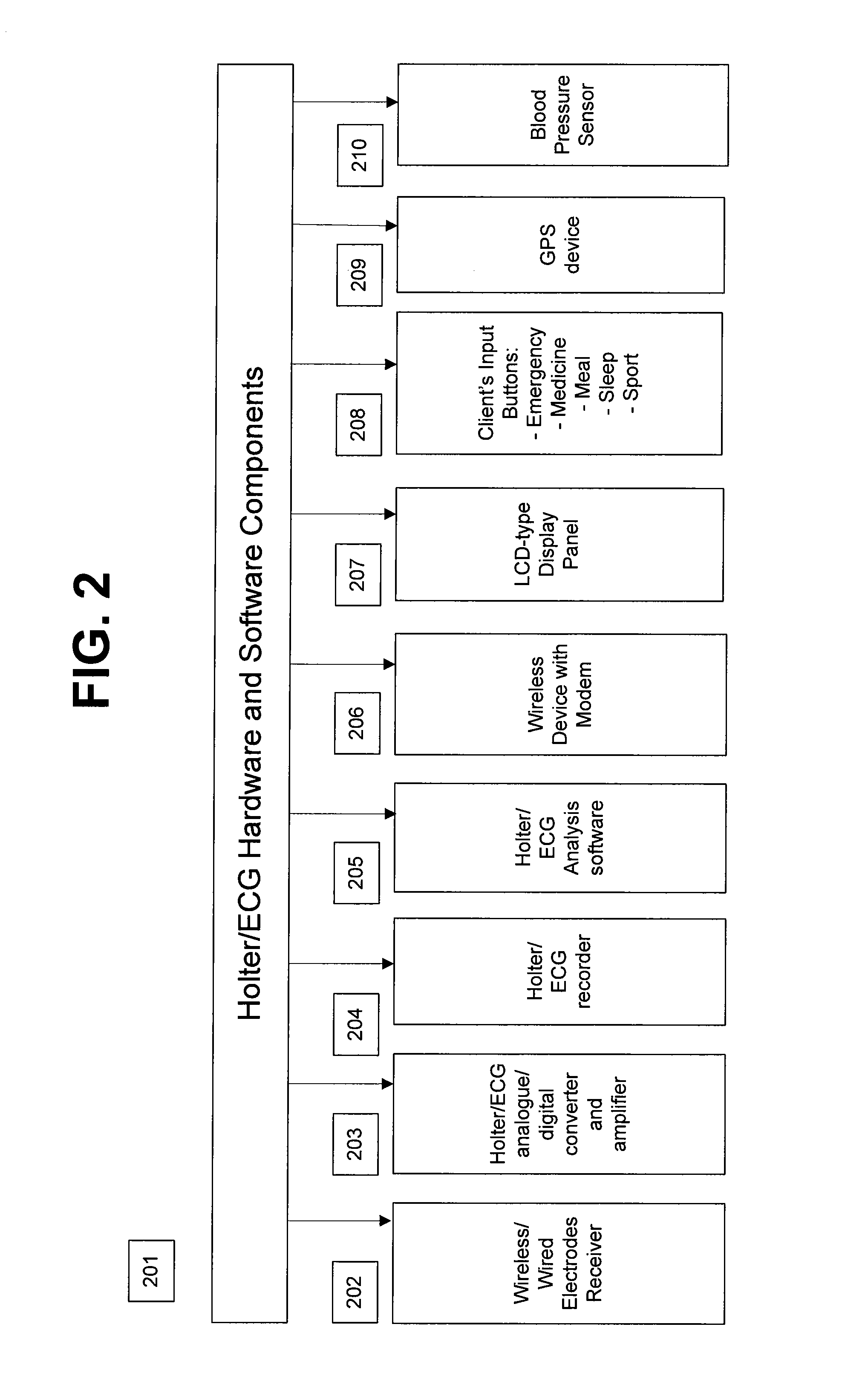
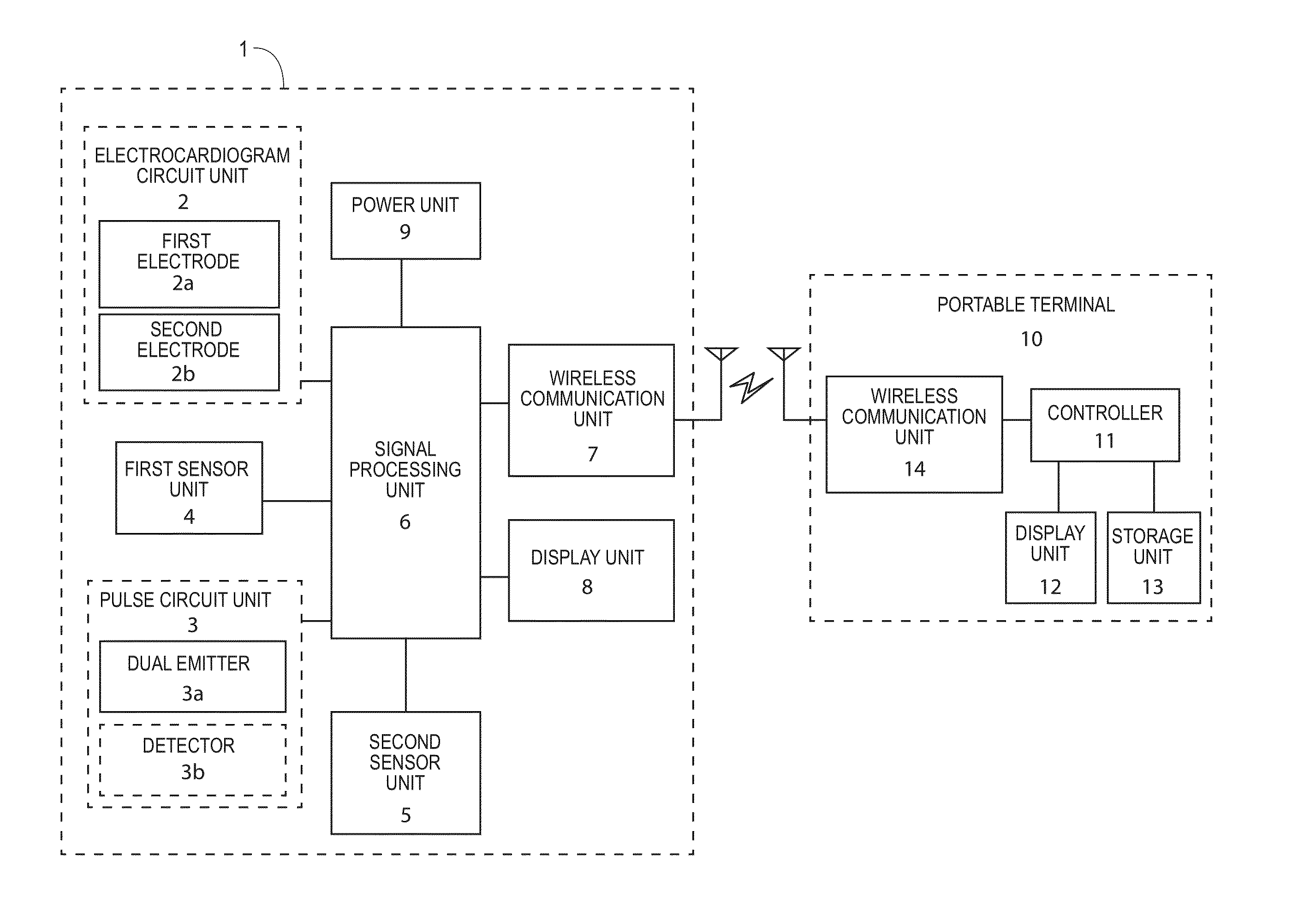
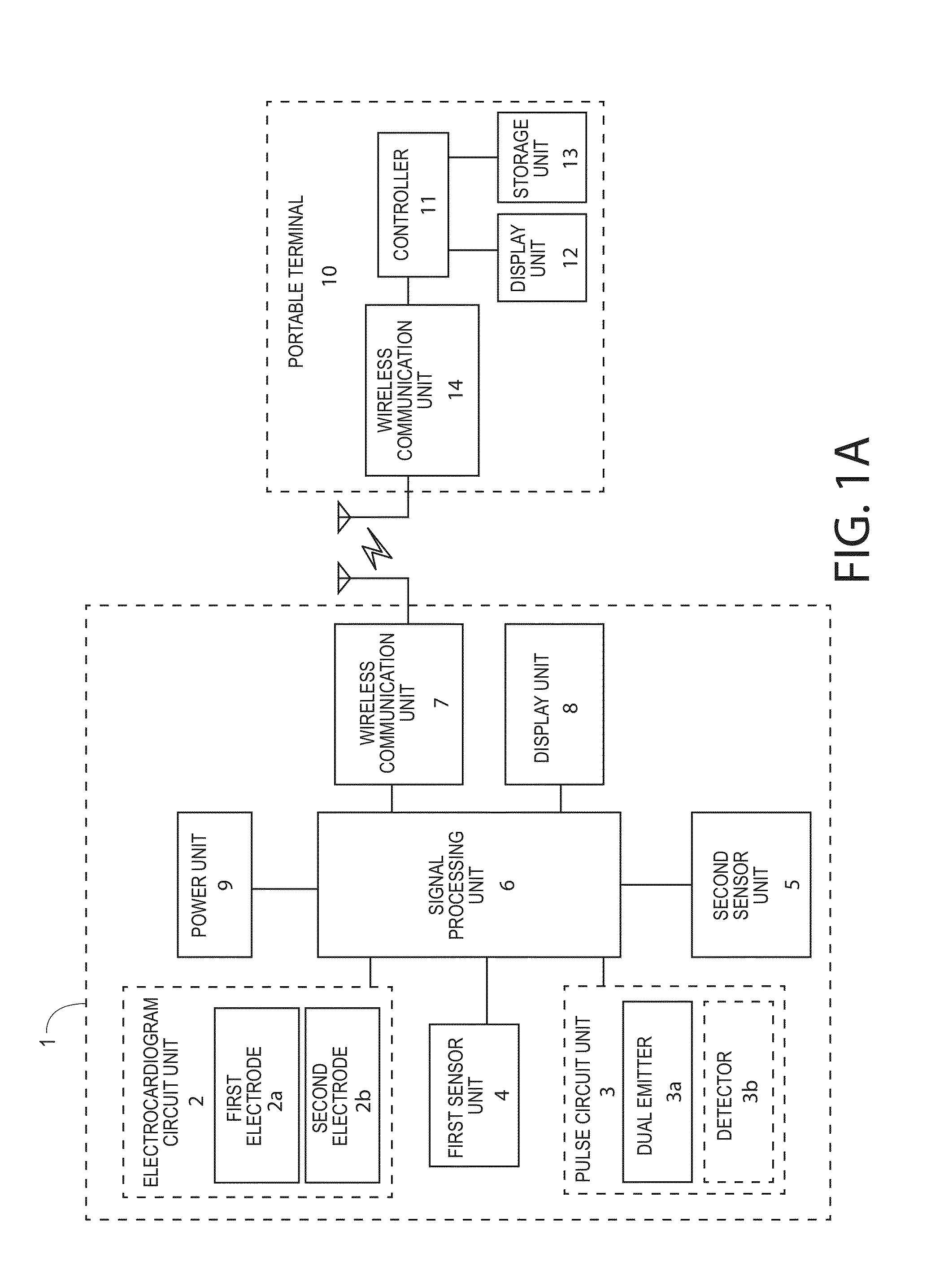
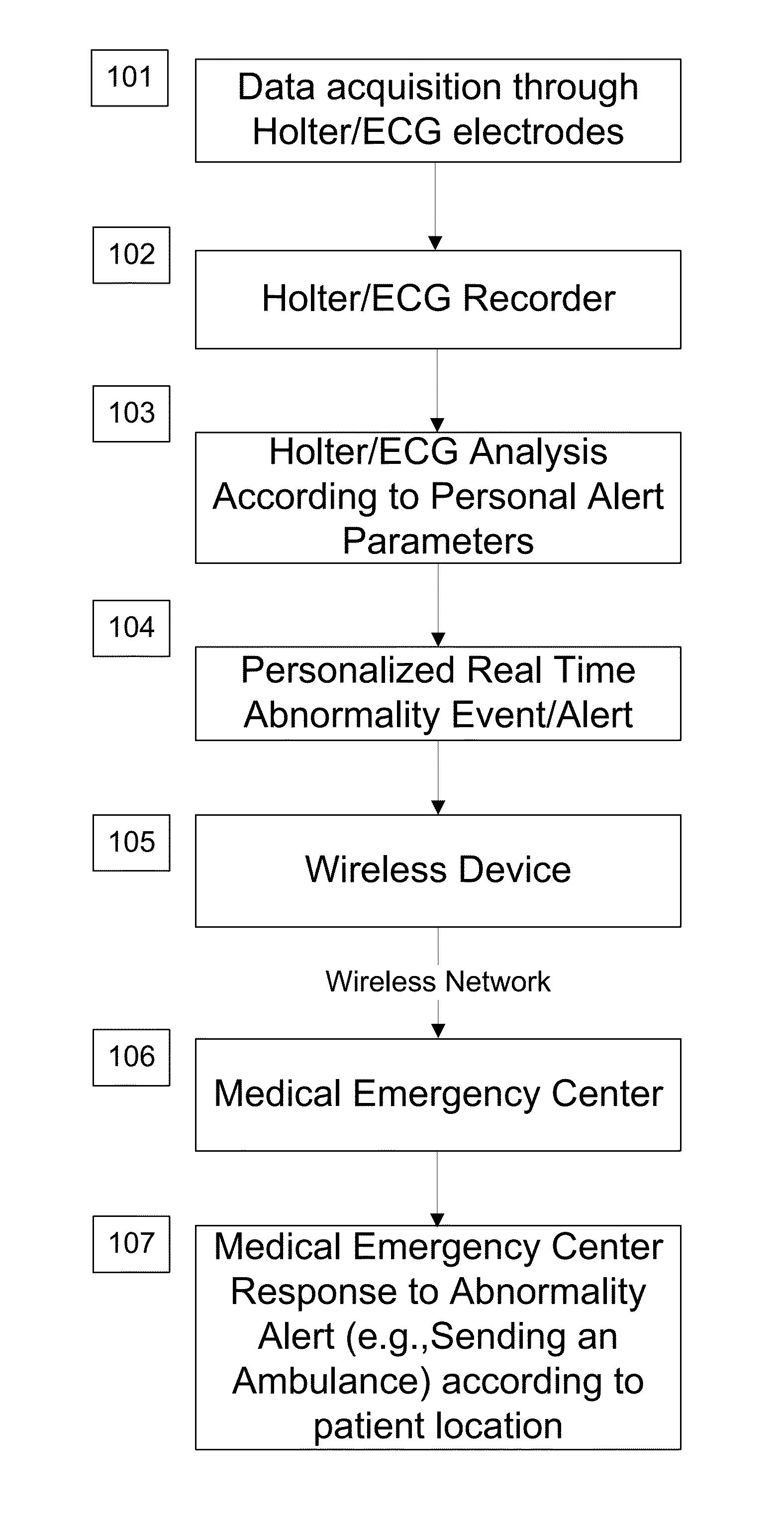
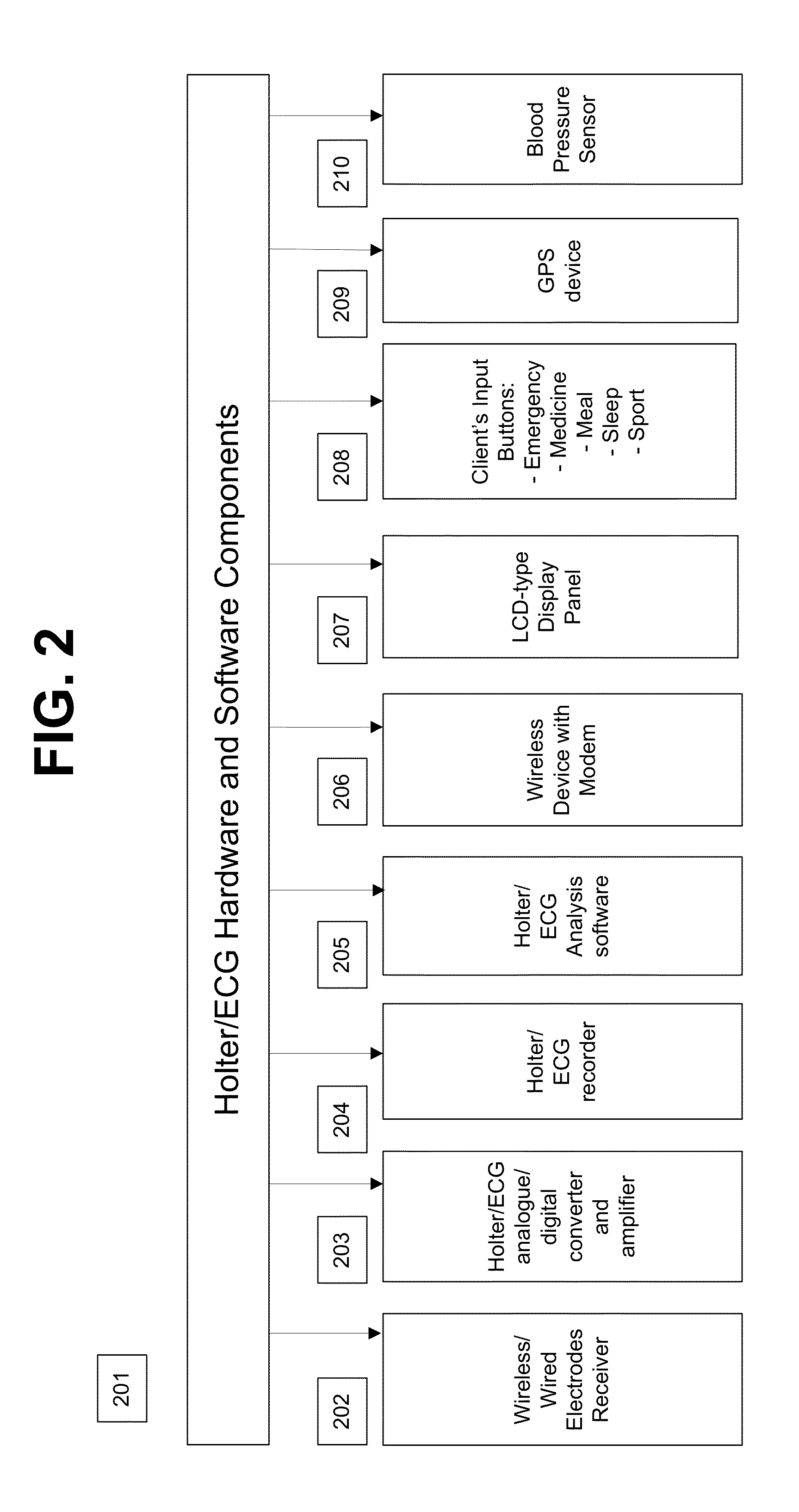
A personalized real-time automated cardiovascular monitoring system monitors abnormalities in a patient's cardiovascular activity data through the use of individually adjusted electrocardiogram Holter apparatus (Holter / ECG device) that provides an automatic medical diagnosis of cardiac abnormalities and generates abnormality alert signals representative of certain abnormalities in patient's cardiac activities. The signals are transmitted using a wireless network to a medical dispatcher center. A response is generated according to the abnormality detected. Individual parameters indicative of patient's cardio activities are personalized to allow for adjustments of chronic patients. A base Holter / ECG unit, includes the wireless / electric electrodes and their respective wireless / electric connections, and a Holter / ECG recording unit affixed to the base unit. Automatic real-time medical response may be provided based on automatic cardiac abnormality alert detection from the Holter / ECG data.
Owner:MAKOR ISSUES & RIGHTS
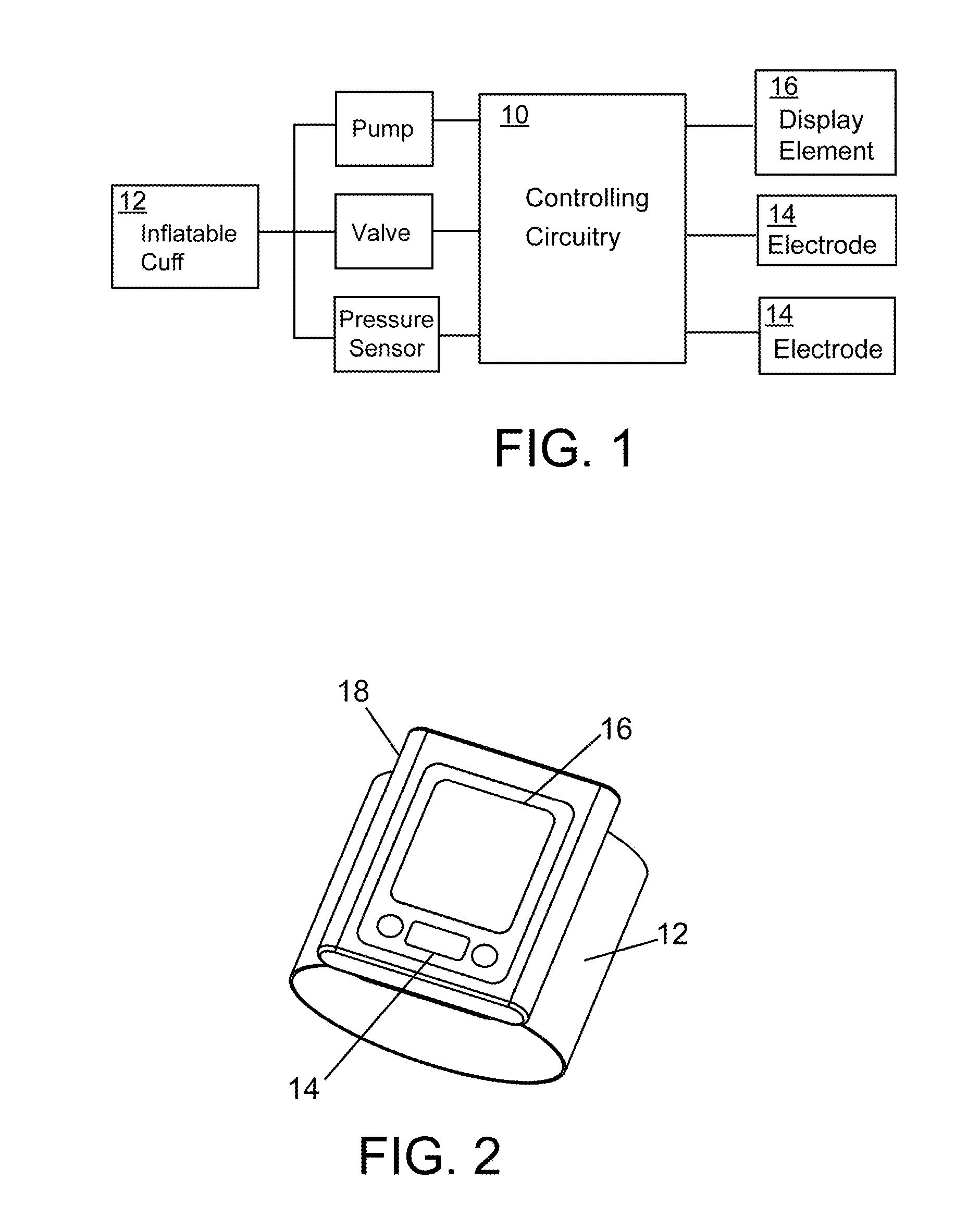
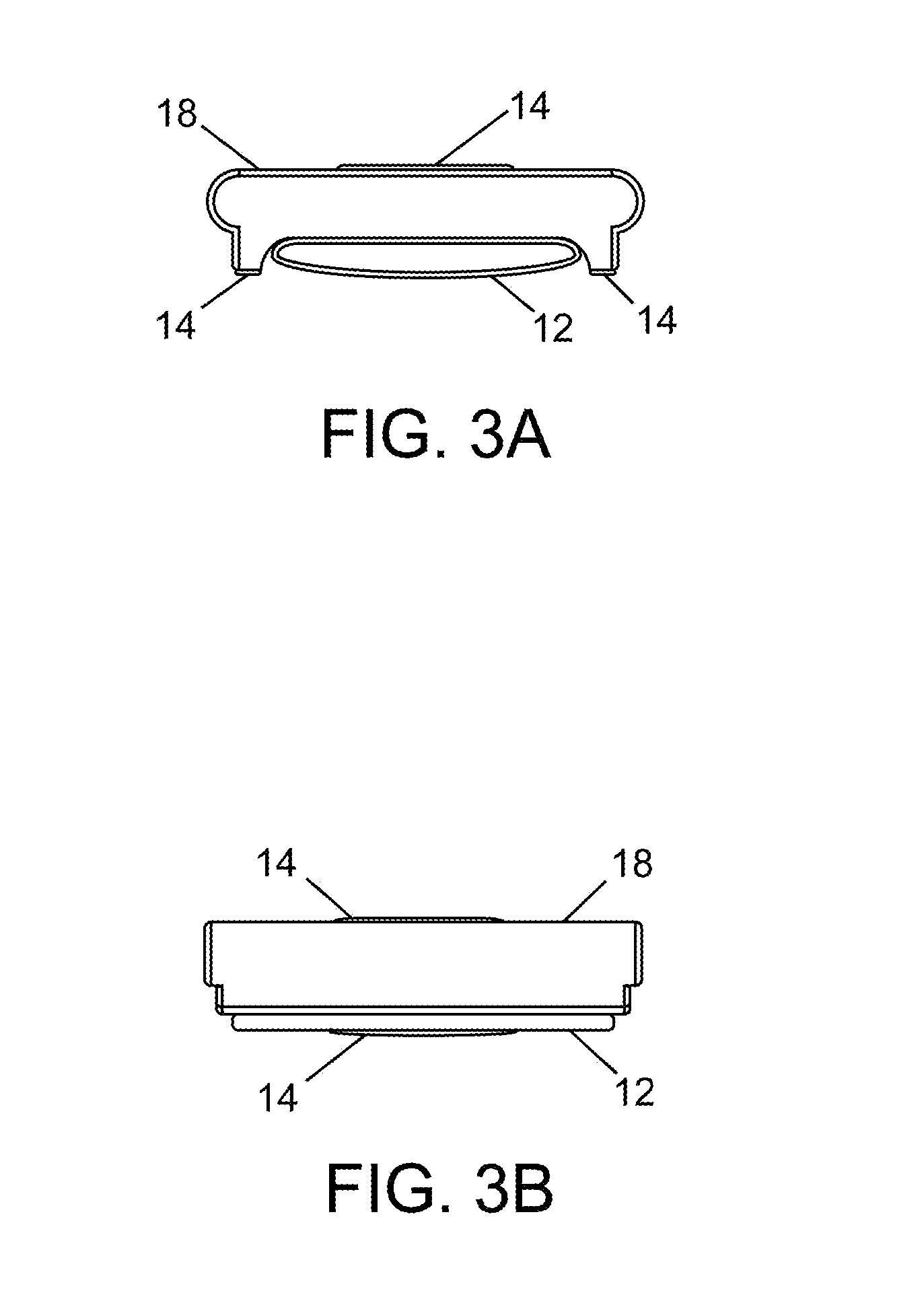
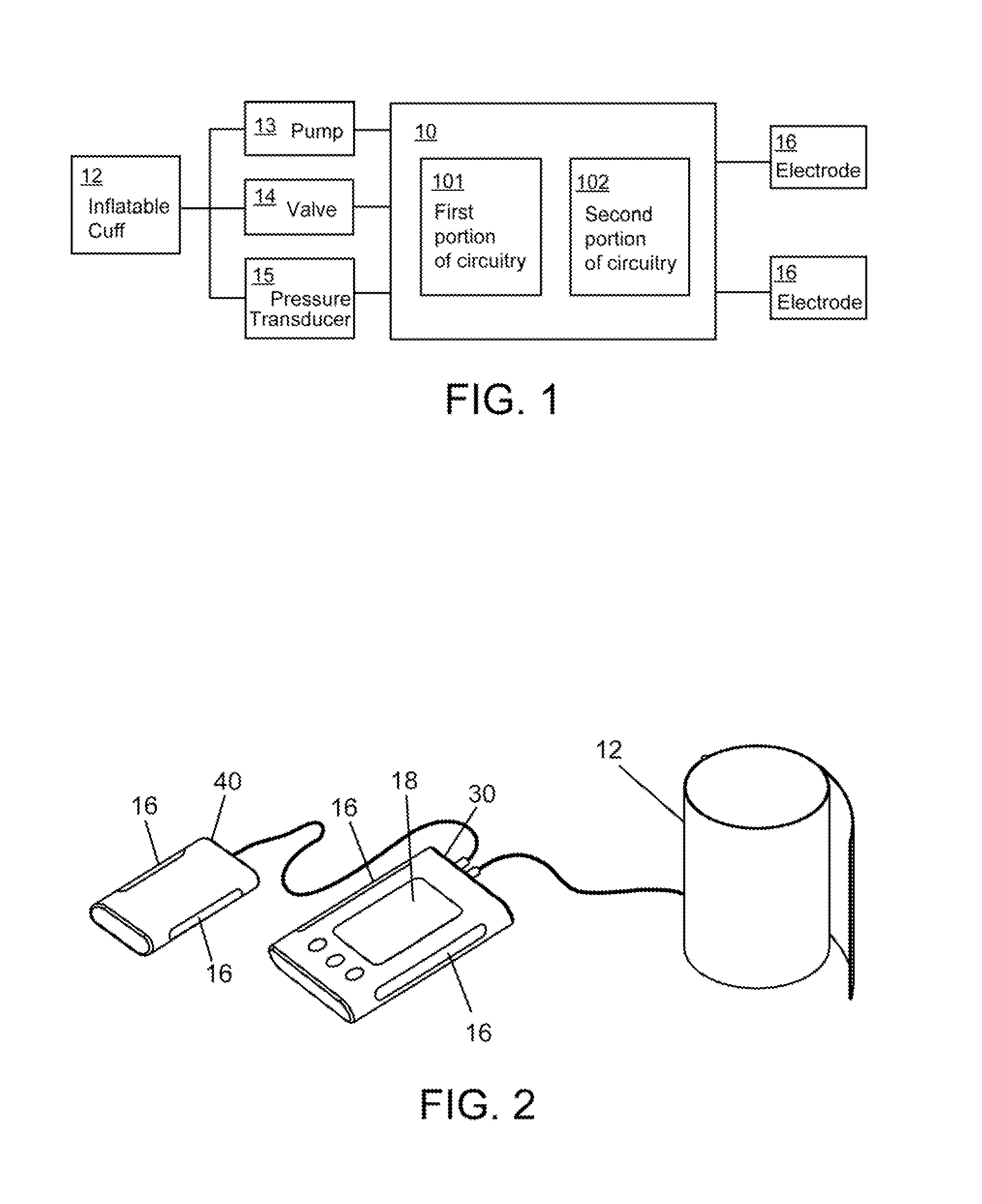
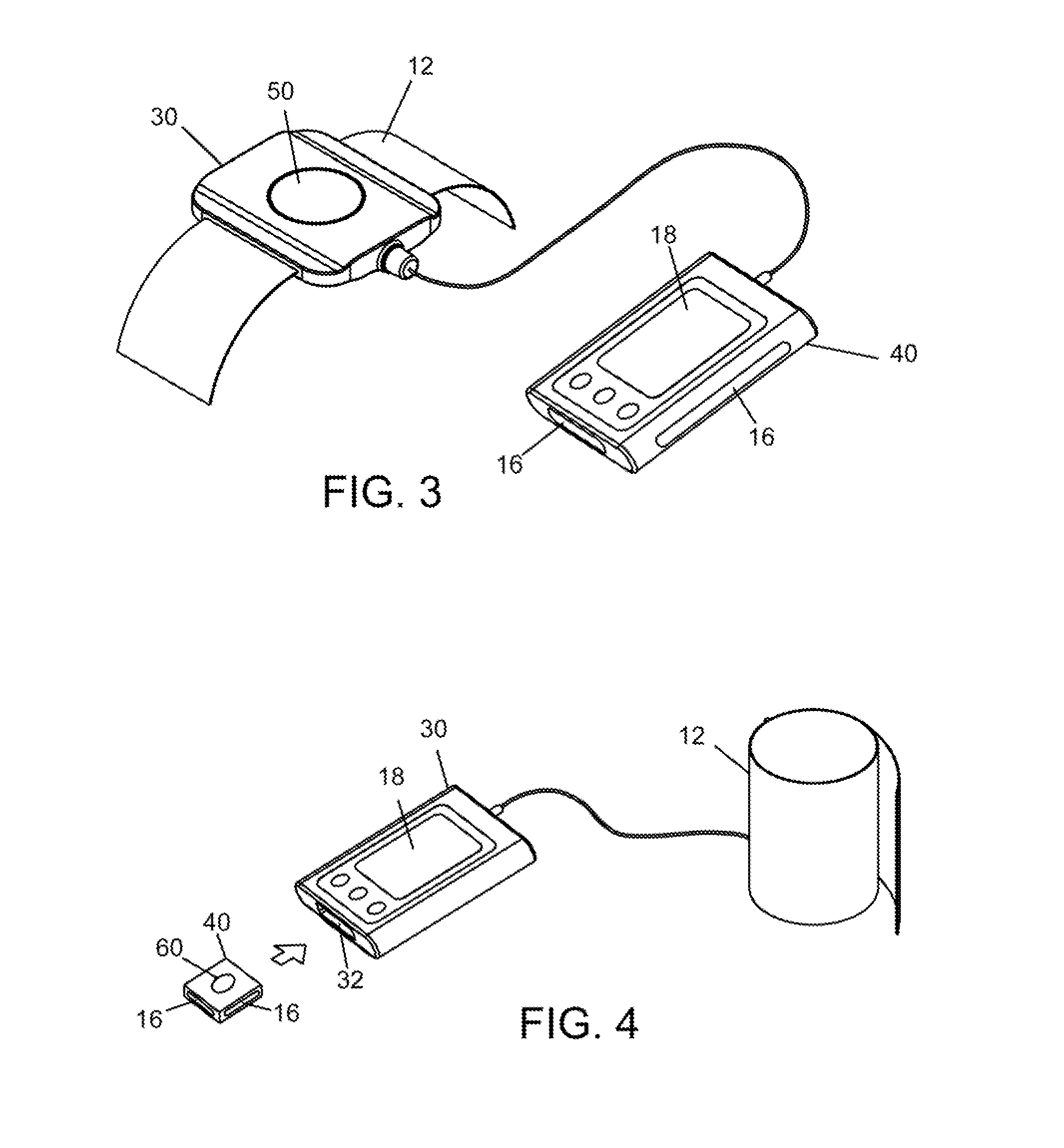
Cardiovascular monitoring device
InactiveUS20160235325A1Improve measurement resultsFunction increaseElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsBlood pressure monitorsCuff
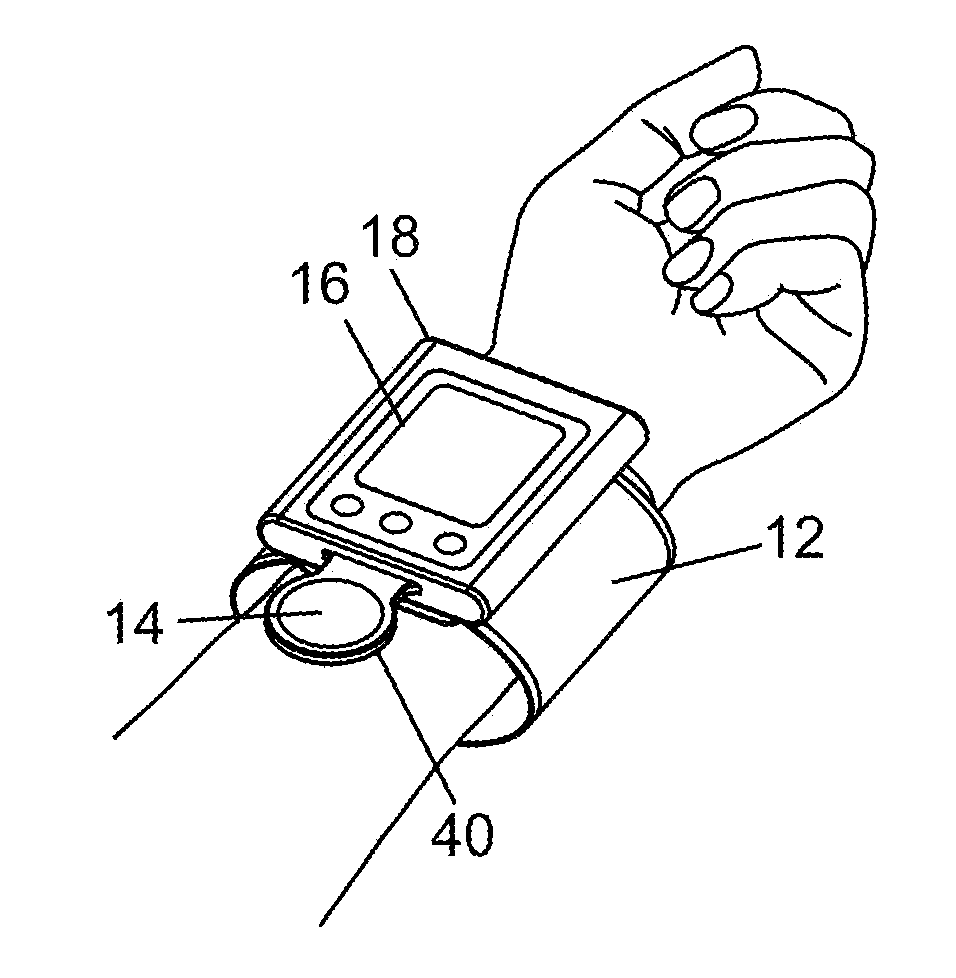
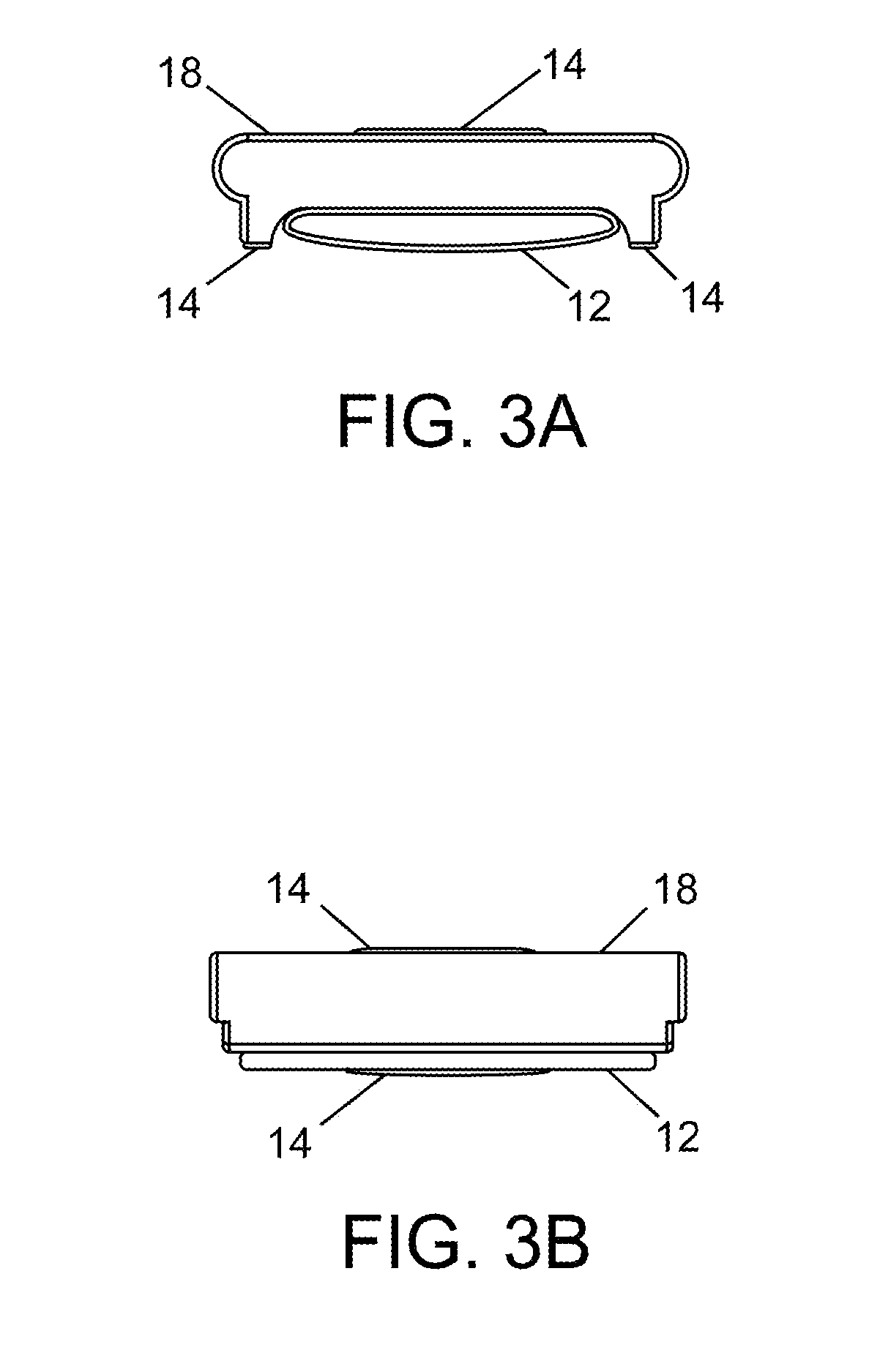
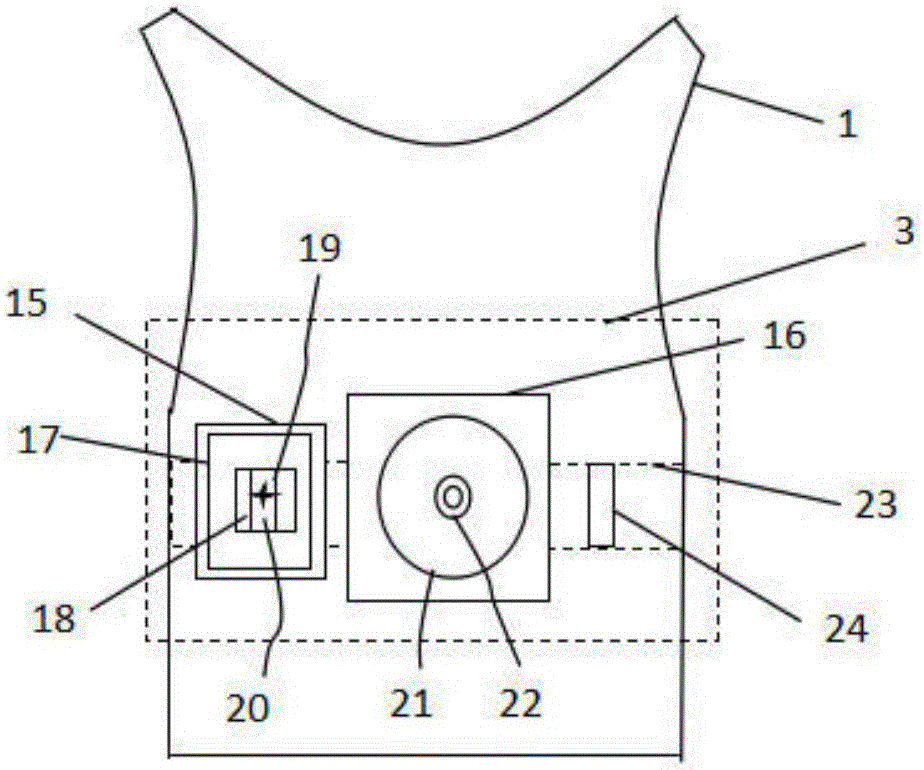
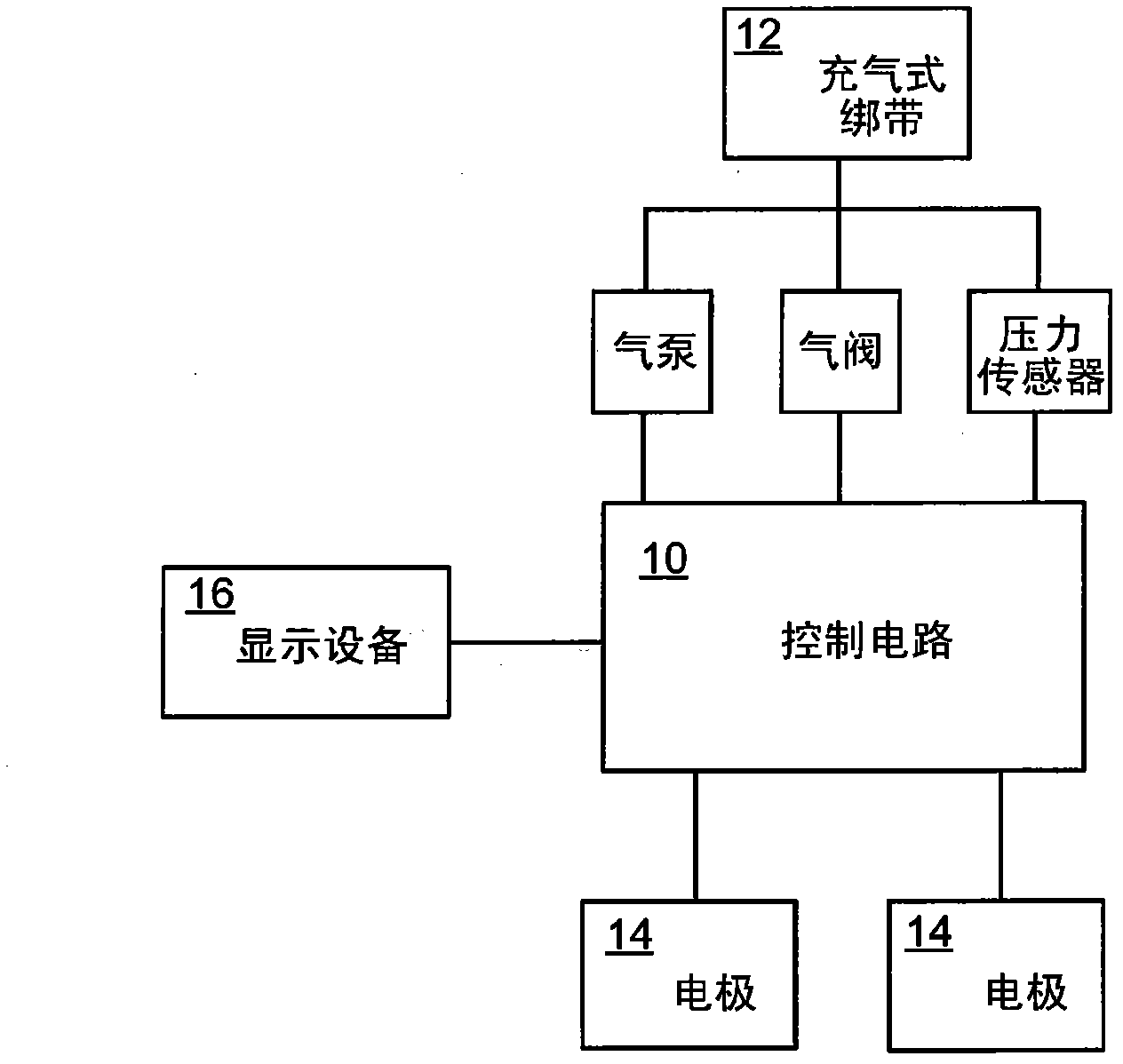
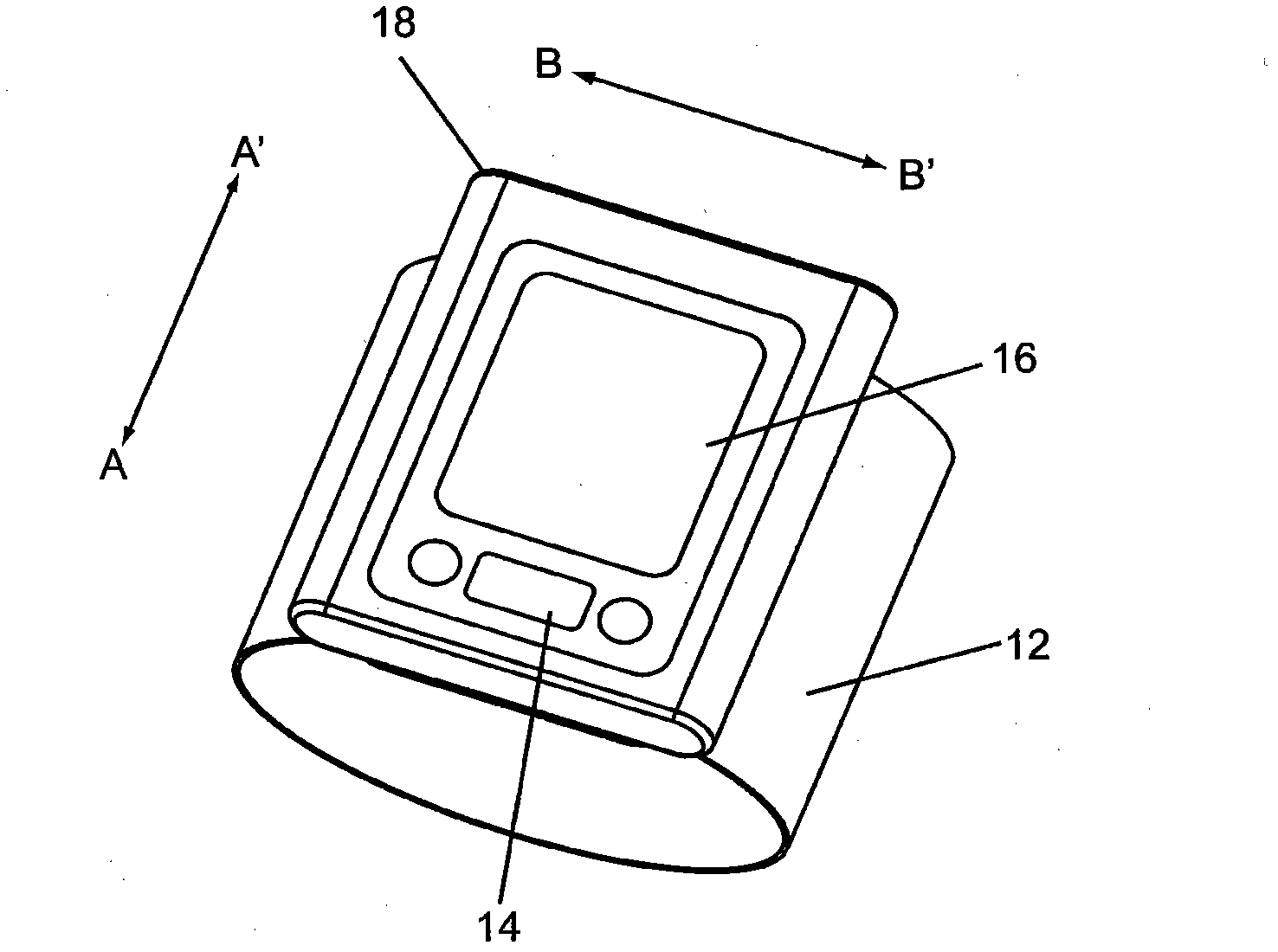
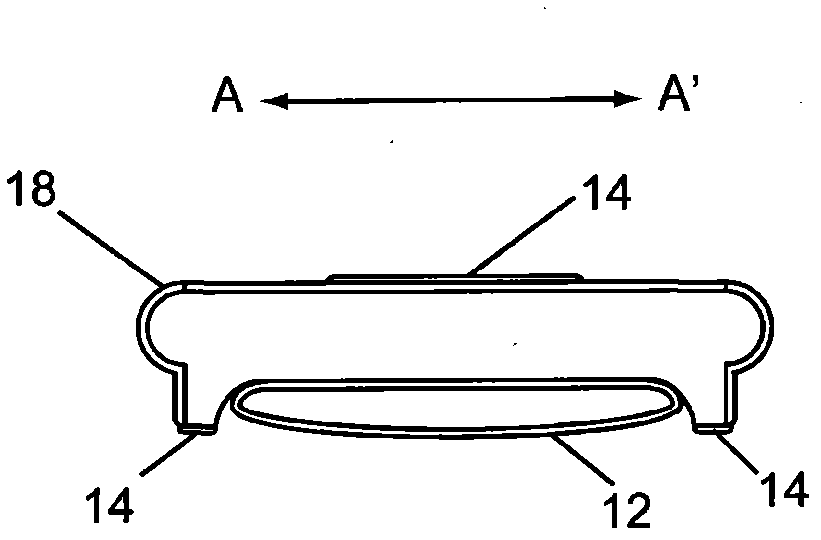
The present invention is related to a cardiovascular monitoring device including an inflatable cuff for surrounding a limb of a user, at least a first and a second electrodes, a controlling circuitry with a processor accommodated in a housing, and a display element. The controlling circuitry is configured to perform a blood pressure measurement through controlling a pressure inside the inflatable cuff, and perform an electrocardiogram measurement by using the electrodes. The processor is also configured to provide a diastolic blood pressure and a systolic blood pressure when the blood pressure measurement is performed, and to provide a heart rhythm information when the electrocardiogram measurement is performed. Further, for achieving a better and more stable contact between the electrodes and the user's skin, the present invention provides an improved structure with electrodes arranged thereon based on the conventional blood pressure monitor.
Owner:MD BIOMEDICAL
System and apparatus for providing diagnosis and personalized abnormalities alerts and for providing adaptive responses in clinical trials
A personalized real-time automated cardiovascular monitoring system monitors abnormalities in a patient's cardiovascular activity data through the use of individually adjusted electrocardiogram Holter apparatus (Holter / ECG device) that provides an automatic medical diagnosis of cardiac abnormalities and generates abnormality alert signals representative of certain abnormalities in patient's cardiac activities. The signals are transmitted using a wireless network through a bi-directional wireless protocol to a medical dispatcher center. A response is generated according to the abnormality detected. Individual parameters indicative of patient's cardio activities are personalized to allow for adjustments of chronic patients. A base Holter / ECG unit, includes the wireless / electric electrodes and their respective wireless / electric connections, and a Holter / ECG recording unit affixed to the base unit. The Holter / ECG apparatus can be integrated as a chip into a wireless device, such device being in a wireless phone network. Automatic real-time medical response may be provided to detection of risks of adverse effects resulting from use of at least one medication, based on automatic cardiac abnormality alert detection from the Holter / ECG data.
Owner:MAKOR ISSUES & RIGHTS
Cardiovascular monitoring device
ActiveUS20160081572A1ElectrocardiographyDiagnostics using lightBlood pressure cuffsBlood pressure kit
Portable physiological measuring devices and methods are disclosed. Embodiments may provide measurement of blood pressure without traditional blood pressure cuffs. Further, disclosed embodiments may gather pulse oximetry (SpO2), heart rate and body temperature measurements simultaneously. A user's blood pressure index and other vital physiological results may be displayed on a portable physiological measuring apparatus or a portable terminal. Embodiments may provide a portable physiological measuring method and apparatus that displays results on a displayed screen.
Owner:MOCACARE
Wearable items providing physiological, environmental and situational parameter monitoring
A garment and / or garment system with health-monitoring (e.g., cardiovascular monitoring) capability, substantially as shown in and / or described in connection with at least one of the figures, as set forth more completely in the claims.
Owner:MARKEL GAL
Portable cuff wearing type health monitoring device and application method thereof
InactiveCN104173035ARealize synchronized measurementsReduce volumeEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsEcg signalData information
The invention relates to the technical field of medical parameter monitoring devices for human physiology, in particular to a portable cuff wearing type health monitoring device and an application method thereof, and provides a portable cuff wearing type health monitoring device with small size and integrated functions. According to the device, the pulse wave and electrocardiosignals are measured synchronously, acquired signals are subjected to data analysis by a single chip microcomputer, then related parameters such as the heart rate, the heart rate variability, the oxygen saturation, the pulse transit time and noninvasive continuous blood pressure data information which are required for cardiovascular monitoring are acquired, and the data information acquired through analysis of the single chip microcomputer is displayed on a display screen.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Portable device for heart and blood vessel health monitoring
InactiveCN106419877AGuaranteed timelinessFast signal transmission rateOrganic active ingredientsElectrotherapyCompression deviceCardiovascular health
The invention discloses a portable device for heart and blood vessel health monitoring. The portable device comprises a shell, a heart and blood vessel monitoring assembly, a heart and blood vessel nursing assembly and a control assembly. The appearance of the shell is in a vest shape, and the heart and blood vessel monitoring assembly is located at the position in front of the left side of the shell and provided with a hematomanometer, an electrocardiogram instrument, a thermometer and an alarm. The heart and blood vessel nursing assembly is provided with a fumigator and a mechanical external chest compression device. The fumigator is provided with a heater, a magnetizer, an injector and a medicine bag. The mechanical external chest compression device is provided with an air bag, a piston and a bandage. The control assembly comprises two parts, one part is located in the shell, and the other part is a remote controller. The monitoring device is high in precision and convenient to use and carry, and has high economic value.
Owner:马延军
Cardiovascular monitoring device
ActiveCN102631190AAccurate measurementContact stabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalDisplay device
The invention relates to a cardiovascular monitoring device which can measure blood pressure and an electrocardio signal at the same time. The cardiovascular monitoring device comprises an inflatable band used for surrounding limbs of a user, at least one first electrode and one second electrode, a control circuit contained in a shell and a display device used for displaying information of blood pressure measurement and / or electrocardio signal measurement, wherein the control circuit can execute the blood pressure measurement by controlling pressure in the band and can execute the electrocardio signal measurement by virtue of the electrodes; and meanwhile, special design on positions and types of the electrodes as well as a contact type between the electrodes and the skin of the user is provided by the invention to realize stable contact between the electrodes and the skin of the user.
Owner:MD BIOMEDICAL +1
System and apparatus for providing diagnosis and personalized abnormalities alerts and for providing adaptive responses in clinical trials
InactiveUS20140221858A1ElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsPersonalizationStatistical analysis
A personalized real-time automated cardiovascular monitoring system monitors abnormalities in a patient's cardiovascular activity data through the use of individually adjusted electrocardiogram Holter apparatus (Holter / ECG device) that provides an automatic medical diagnosis of cardiac abnormalities and generates abnormality alert signals representative of certain abnormalities in patient's cardiac activities. The signals are transmitted using a wireless network through a bi-directional wireless protocol. Individual parameters indicative of patient's cardio activities are personalized to allow for adjustments of chronic patients. A base Holter / ECG unit, includes the wireless / electric electrodes and their respective wireless / electric connections, and a Holter / ECG recording unit affixed to the base unit. Data is collected and subjected to statistical analysis.
Owner:MAKOR ISSUES & RIGHTS
Cardiovascular disease surveillance platform construction method
InactiveCN108201439AReach timely rescueReduce emergency department stressDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSystem architecture designBluetooth
The invention discloses a cardiovascular disease surveillance platform construction method. The method comprises the following steps of step one, the architecture design of a remote cardiovascular disease surveillance system; step two, a RFID and wireless sensor network fusion technology; and step three, the design and implementation of health surveillance. According to the cardiovascular diseasesurveillance platform construction method, cardiovascular monitoring equipment collects electrocardio, body temperatures, blood glucose and blood oxygen physiological parameters of a patient, data issent to a surveillance software of a family or community through a Bluetooth or a wireless sensor network, then a community surveillance system compares and analyzes the local background data, the system feeds back a corresponding health advice to the patient, notifies the patient and a community medical institution for abnormal data by a mode of grading alarm to achieve the function of timely rescuing the patient, thereby the timeliness and the early warning reaction capacity are improved, the pressure of hospital emergency is effectively reduced, the patient can enjoy the convenience of family practice, and the medical expense is reduced.
Owner:HARBIN GUANGKAI TECH DEV
Multifunctional cardiovascular monitoring system
InactiveCN109350026AEasy to wearEasy to useEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsDiseaseVascular disease
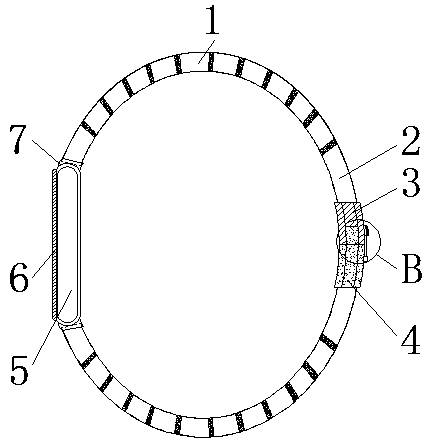
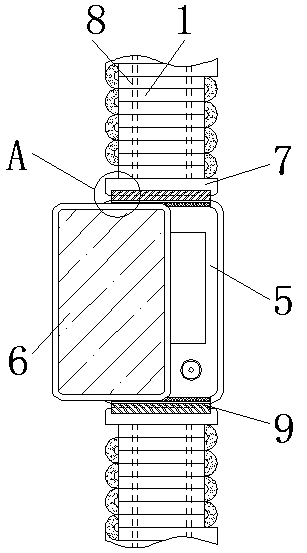
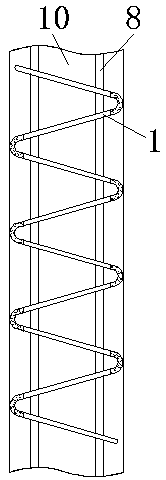
The invention relates to a multifunctional cardiovascular monitoring system, comprising moving rings; connection rods are arranged on the left and right of each moving ring; the connection rods are made of rubber; a connection ring is connected to one side of each moving ring; a first fastener is connected to one side of each connection ring; a second fastener is connected to one side of each first fastener. The multifunctional cardiovascular monitoring system has the advantages that the moving rings are connected to the two sides of a pressure detection display screen of a carry-on band for detection of vascular diseases via connectors, the moving rings can expand, two connection rods are inserted in each moving ring, the connection rods are made of rubber, and therefore, the diameter ofthe carry-on band can be adjusted through the connection rods and the moving rings, the size of the band can be adjusted according to conditions, it is convenient to wear the band, and the band is suitable for a single person to carry on; the moving rings and the pressure detection display screen can be split so that both using and storage are facilitated.
Owner:郑曼
Mobile communication device and other devices with cardiovascular monitoring capability
A general-purpose mobile communication device, general-purpose computer user-interface device, and other non-health-related electronic devices with cardiovascular monitoring capability. Various aspects of the present invention may comprise a general-purpose mobile communication device (e.g., a cellular telephone, portable email device, personal digital assistant, etc.) comprising a communication interface module adapted to communicate with a general-purpose communication network, and at least one module operational to acquire cardiac information from a user of the general-purpose mobile communication device. The general-purpose communication device may, for example, comprise a cardiac sensor (e.g., electrodes) disposed on the mobile communication device, which may be utilized to acquire cardiac information during use of the mobile communication device. Various aspects of the present invention may also comprise a non-health related electronic device (e.g., a general-purpose mobile communication device, general-purpose user-interface device for a general-purpose computer, gaming controller, etc.) that, during normal non-health-related utilization, acquire, analyze and / or communicate user health-related information.
Owner:MARKEL GAL
Cardiovascular monitoring device
InactiveUS20160235307A1Improve measurement resultsFunction increaseElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsCardiovascular monitoringControl circuit
The present invention is related to a cardiovascular monitoring device including an inflatable cuff for surrounding a limb of a user, at least a first and a second electrodes, a controlling circuitry with a processor accommodated in a housing, and a display element. The controlling circuitry is configured to perform a blood pressure measurement through controlling a pressure inside the inflatable cuff, and perform an electrocardiogram measurement by using the electrodes. The processor is also configured to provide a diastolic blood pressure and a systolic blood pressure when the blood pressure measurement is performed, and to provide a heart rhythm information when the electrocardiogram measurement is performed. Further, for achieving a better and more stable contact between the electrodes and the user's skin, the present invention provides an improved structure with electrodes arranged thereon based on the conventional blood pressure monitor.
Owner:CHOU
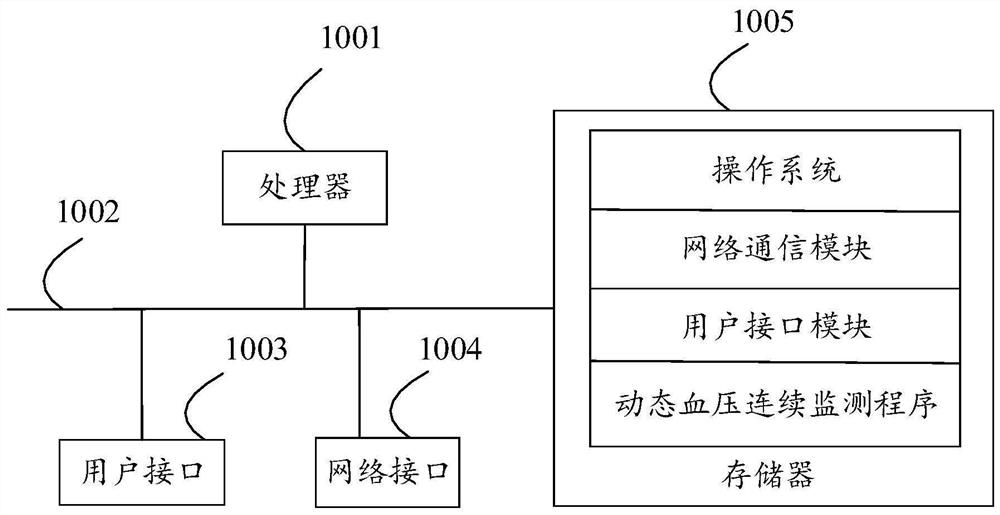
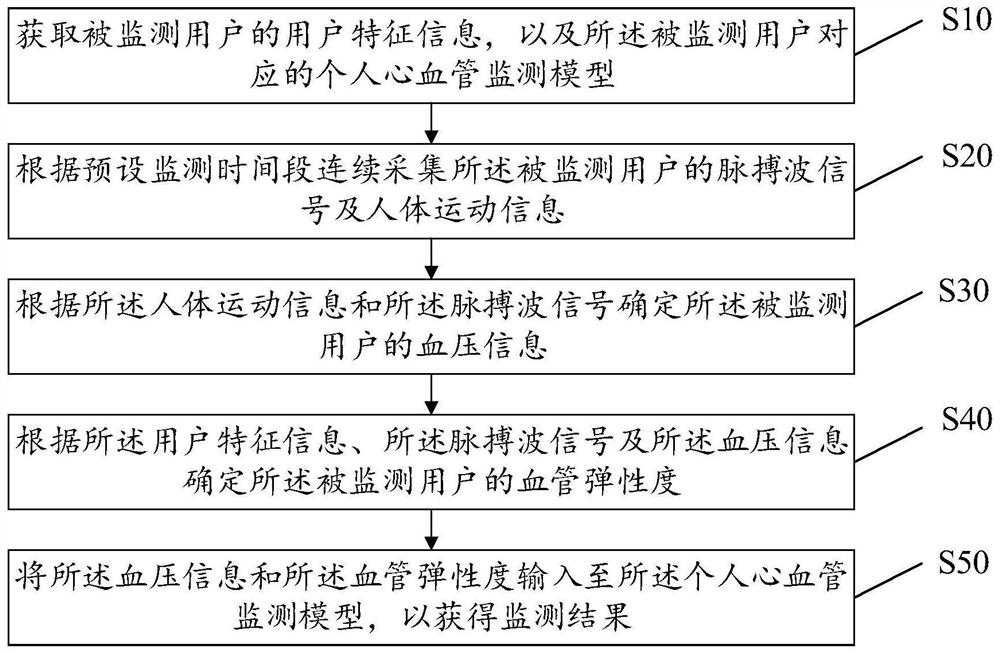
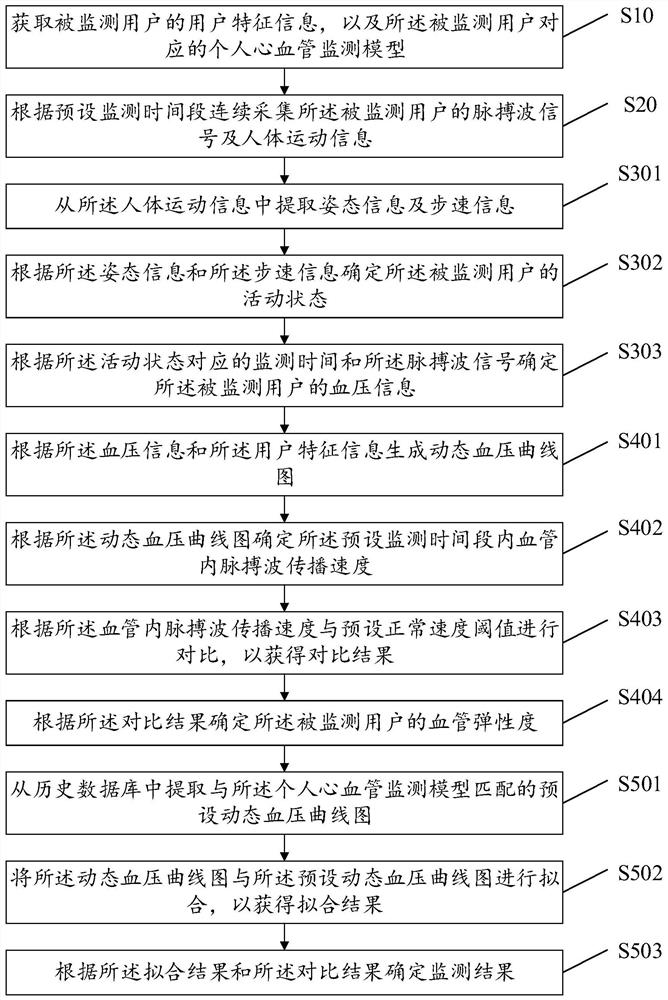
Dynamic blood pressure continuous monitoring device, storage medium and system
InactiveCN113499047AImprove accuracyRealize real-time tracking and monitoringEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterBlood pressure ambulatoryDynamic monitoring
The invention discloses an ambulatory blood pressure continuous monitoring device, a storage medium and a system. The pulse wave signal and the human body motion information of the monitored user are continuously collected in the preset monitoring time period, the blood pressure information is determined according to the human body motion information and the pulse wave signal, and the vascular elasticity of the monitored user is determined according to the user feature information, the pulse wave signal and the blood pressure information, and the blood pressure information and the vascular elasticity are inputted into a personal cardiovascular monitoring model to obtain a monitoring result. The blood pressure information is determined according to the pulse wave signal and the human body motion information of the monitored user, and the vascular elasticity is determined according to the blood pressure information, the pulse wave signal and the user feature information. In the prior art, an existing dynamic monitoring mode is static fragment monitoring and cannot continuously monitor for 24 hours, so the accuracy of dynamic monitoring data is lower. The physiological parameters of the monitored user are tracked and monitored in real time, so the data accuracy is improved.
Owner:湖北智奥物联网科技有限公司
Cardiovascular monitoring device
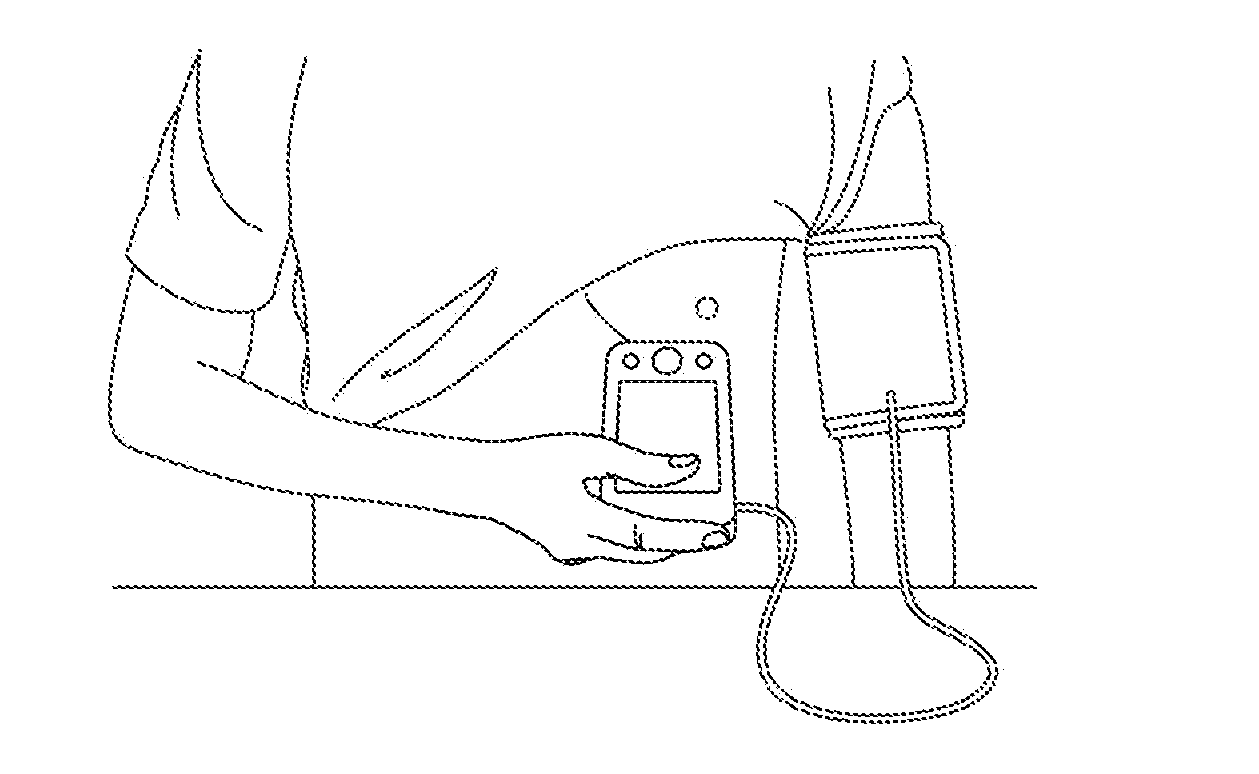
InactiveUS20130345575A1Increase flexibilityImprove operational convenienceEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterBlood pressure kitBlood pressure
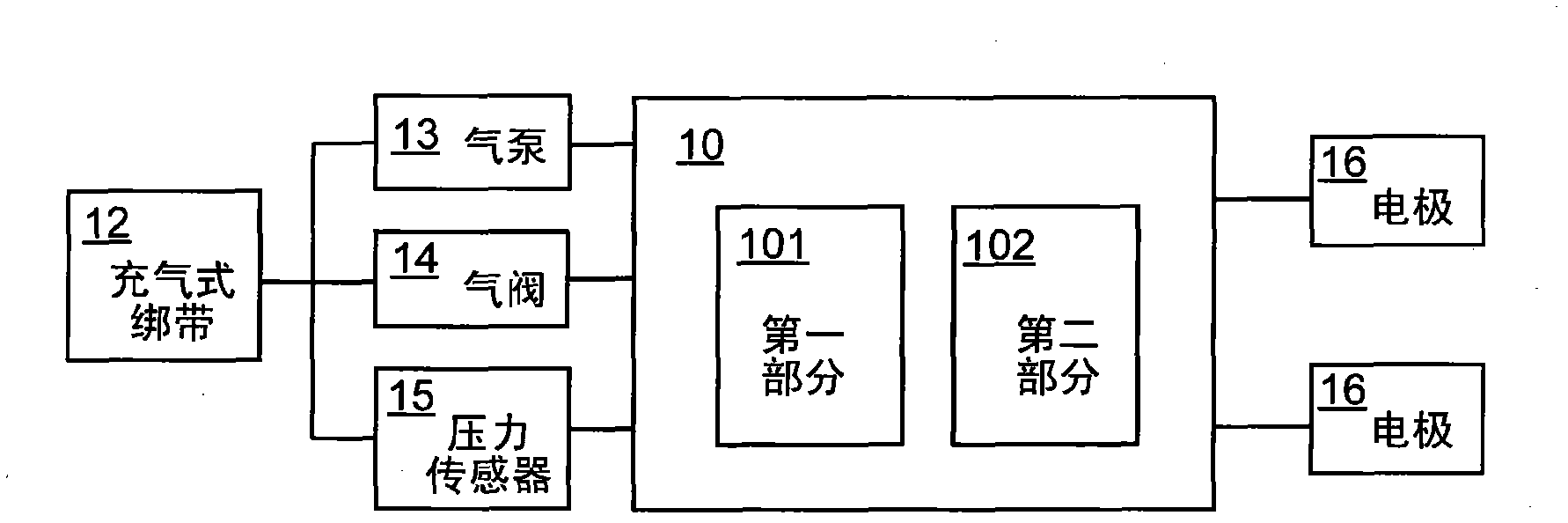
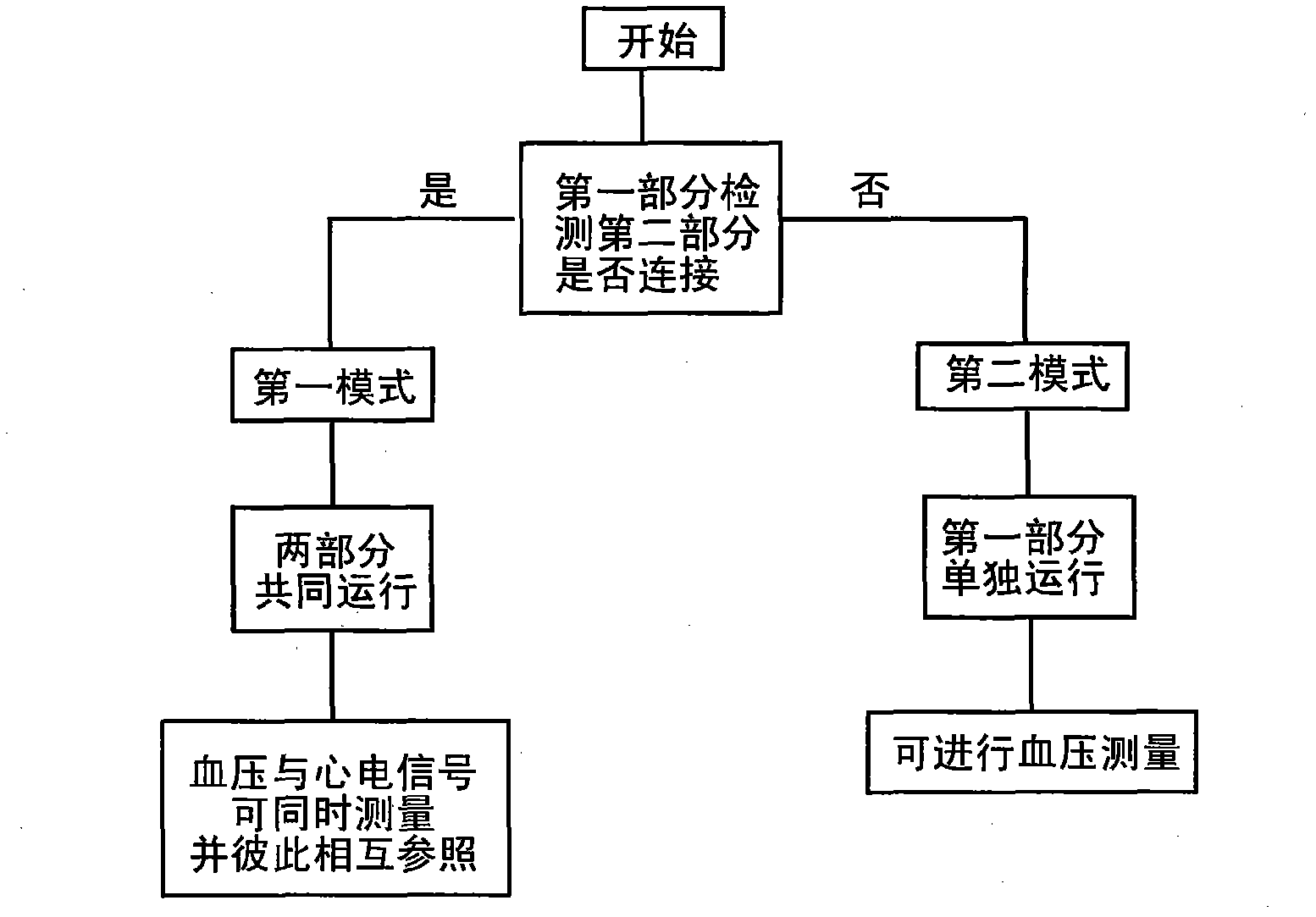
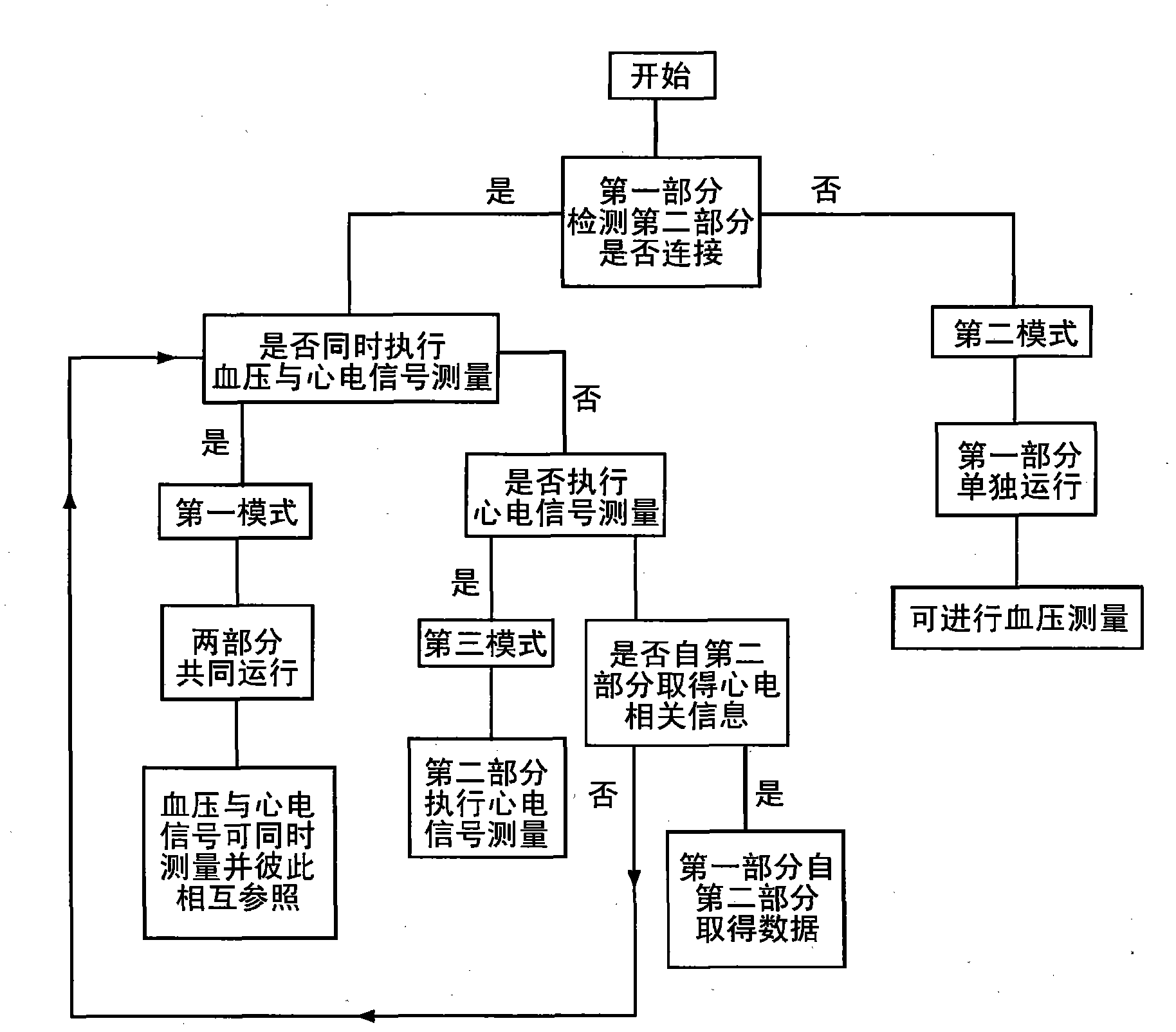
The present invention relates a cardiovascular monitoring device including a first housing and a second housing, a circuitry with at least a processor, distributed in the first and second housings to form a first unit and a second unit, for providing functions of blood pressure and electrocardiogram measurements, an inflatable cuff connected with the first housing for being used during blood pressure measurement, and at least two electrodes, at least one of which is a dry electrode and mounted on the second housing for contacting the user's hand. The processor can detect an activation of the functions of blood pressure and electrocardiogram measurements, and based on a detecting result, trigger the device to enter different operation modes. The processor can further provide diastolic and systolic blood pressures when the blood pressure measurement function is activated, and provide a heart rhythm information when the electrocardiogram measurement function is activated.
Owner:CHOU
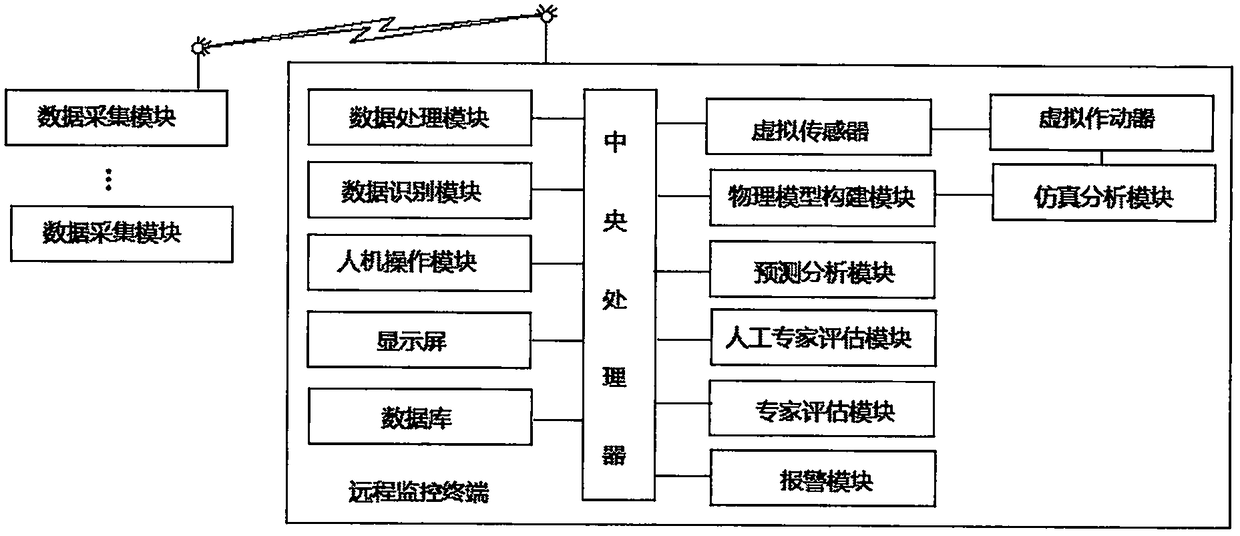
Multifunctional cardiovascular monitoring system
InactiveCN108095735ARealize monitoringTimely processingDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsPhysical modelData acquisition
The invention discloses a multifunctional cardiovascular monitoring system which comprises data acquisition modules and a remote monitoring terminal. The remote monitoring terminal is used for receiving data acquired by the data acquisition modules, and processing, storing and analyzing the data; the remote monitoring terminal particularly comprises a man-machine operation module, a data processing module, a physical model building module, a virtual actuator, a virtual sensor, a simulation analysis module, an expert evaluation module, a prediction analysis module, an artificial expert evaluation module, an alarm module and a central processing unit. The multifunctional cardiovascular monitoring system has the advantages that detection results of diversified facilities and dictated symptomsof patients are perfectly fused with one another, the physical model building module is designed, cardiovascular simulation models of the patients can be built, accordingly, cardiovascular conditionsof the patients can be vividly presented in the front of doctors and can be analyzed by the doctors from multiple angles according to requirements, and simulation analysis can be carried out on diversified therapeutic schemes; the multifunctional cardiovascular monitoring system has a cardiovascular development condition prediction function.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System and Method for Cardiovascular Monitoring and Reporting
PendingUS20210045647A1Convenient and accurateReduce the valueMedical communicationElectrocardiographyCardiac functioningEmergency medicine
Owner:MINDMICS INC
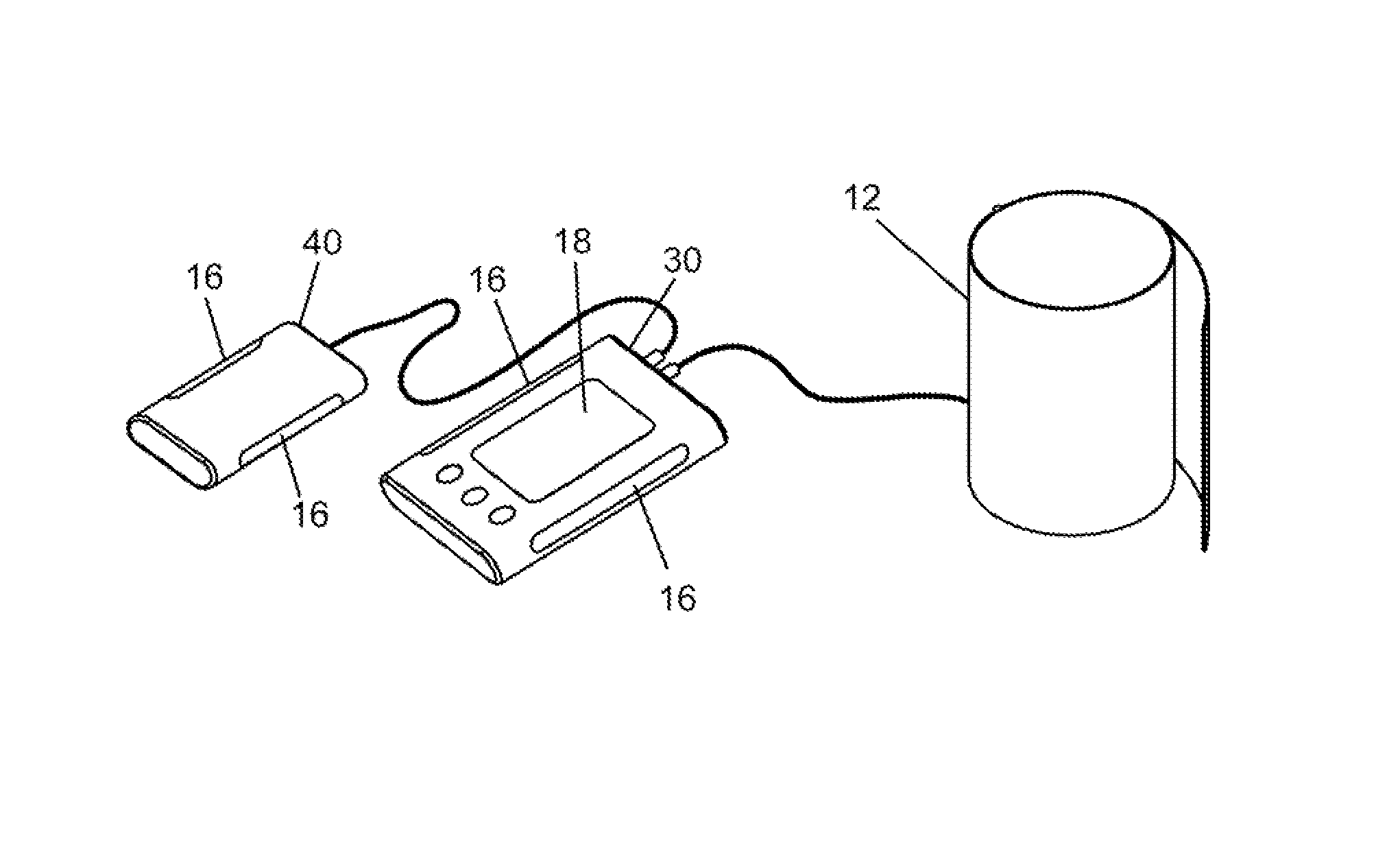
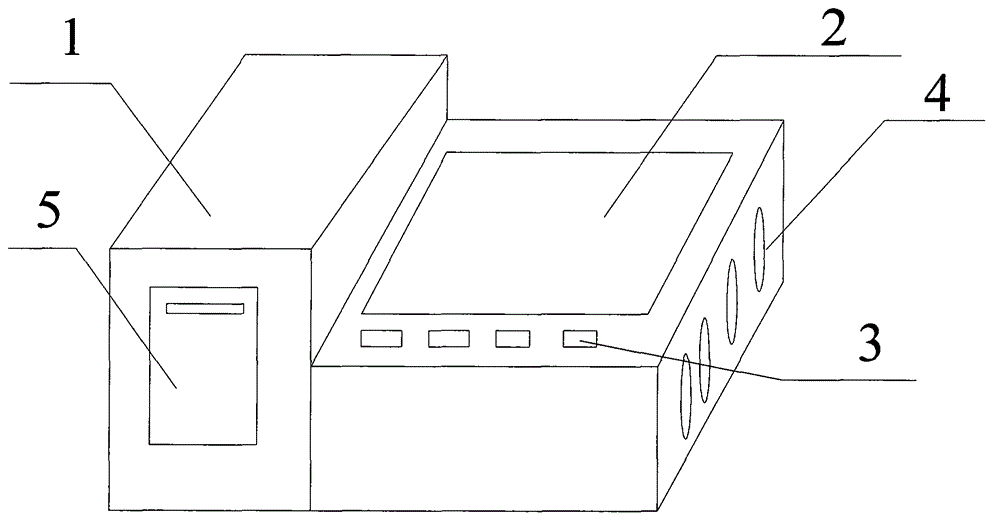
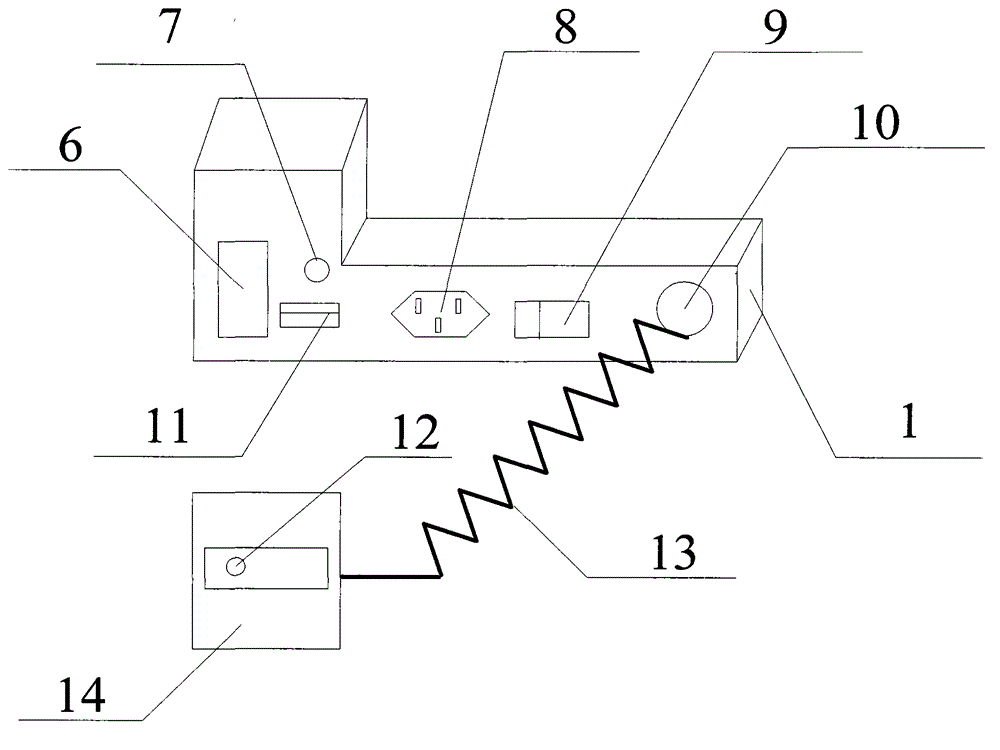
Portable integrated angiocarpy monitor
InactiveCN104688216AEasy to carryHigh degree of integrationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringPower switchingCuff
The invention discloses a portable integrated angiocarpy monitor which comprises a host, a display screen, control keys, heat dissipation holes, a printer, a lithium battery, a power light, a power socket, a power switch, a sensor interface, a USB interface, a pulse sensor, a signal wire and a cuff, wherein the printer is arranged on the left side of the host; the heat dissipation holes are formed in the side of the host; the display screen is arranged on the right side of the host; the control keys are arranged below the display screen; the lithium battery is arranged in the host; the USB interface is arranged on the rear left side of the host; the power light is arranged at the upper part of the USB interface; the sensor interface is formed in the lower right side of the host. Through the arrangement of the host, the display screen, the printer, the sensor interface, the USB interface, the pulse sensor and the signal wire, the portable integrated angiocarpy monitor is convenient to carry when a house call is made, high in integration degree, convenient to operate and beneficial for household application and popularization.
Owner:张峰
Cardiovascular monitoring device
InactiveCN102631193ASimple blood pressureSimple ECG measurementEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsEcg signalBlood pressure
Owner:MD BIOMEDICAL +1
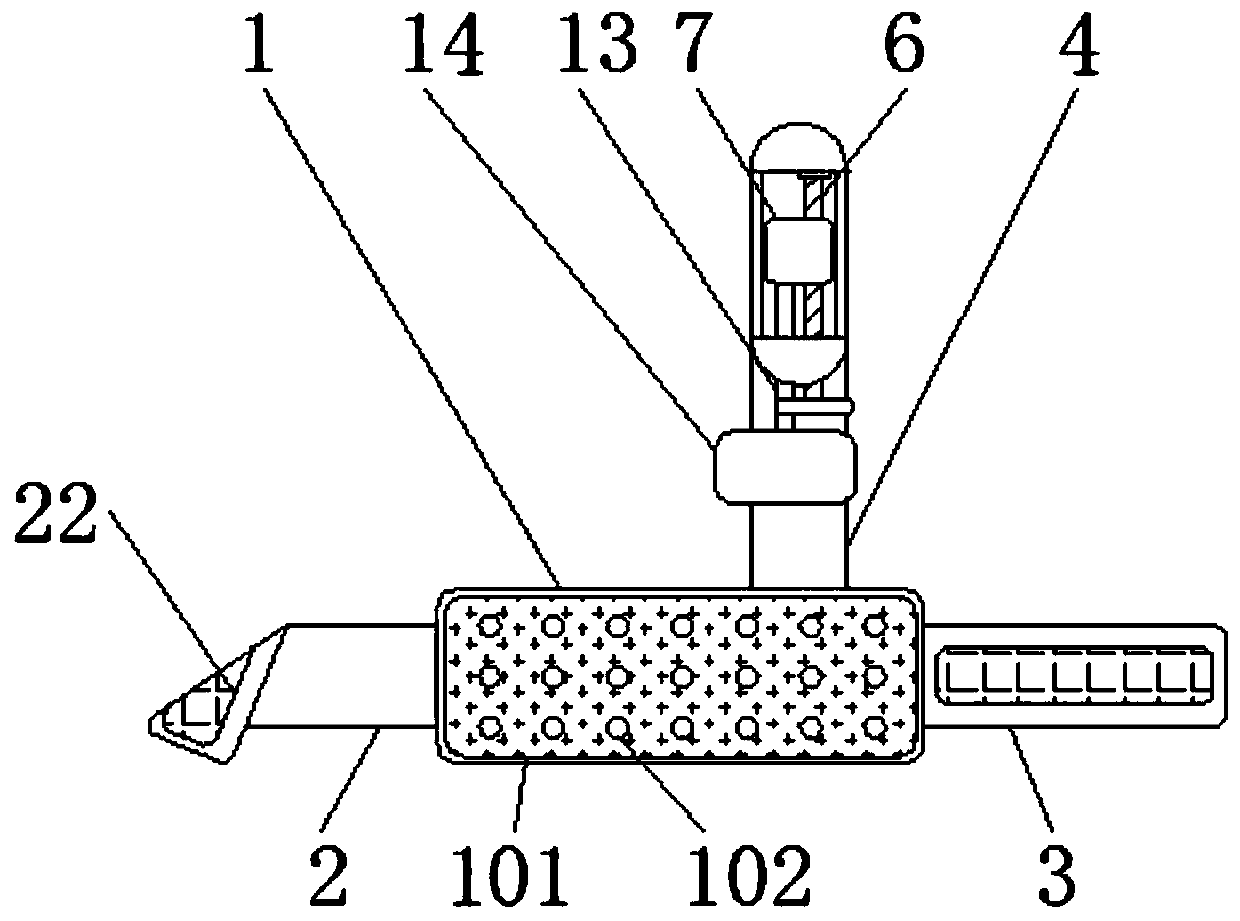
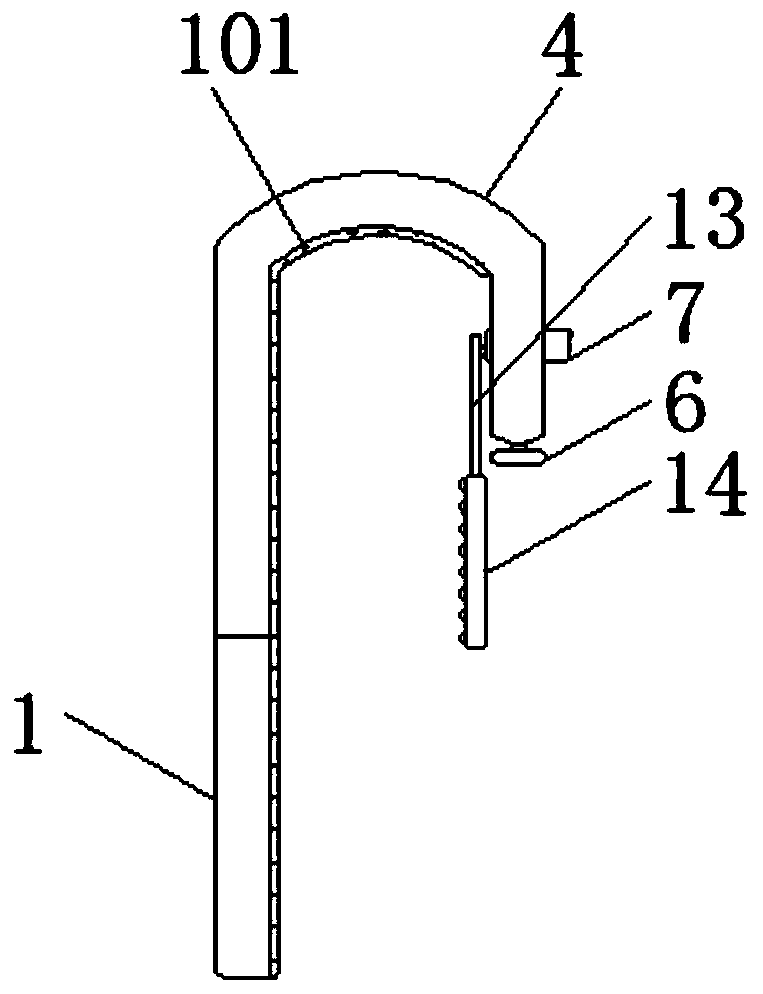
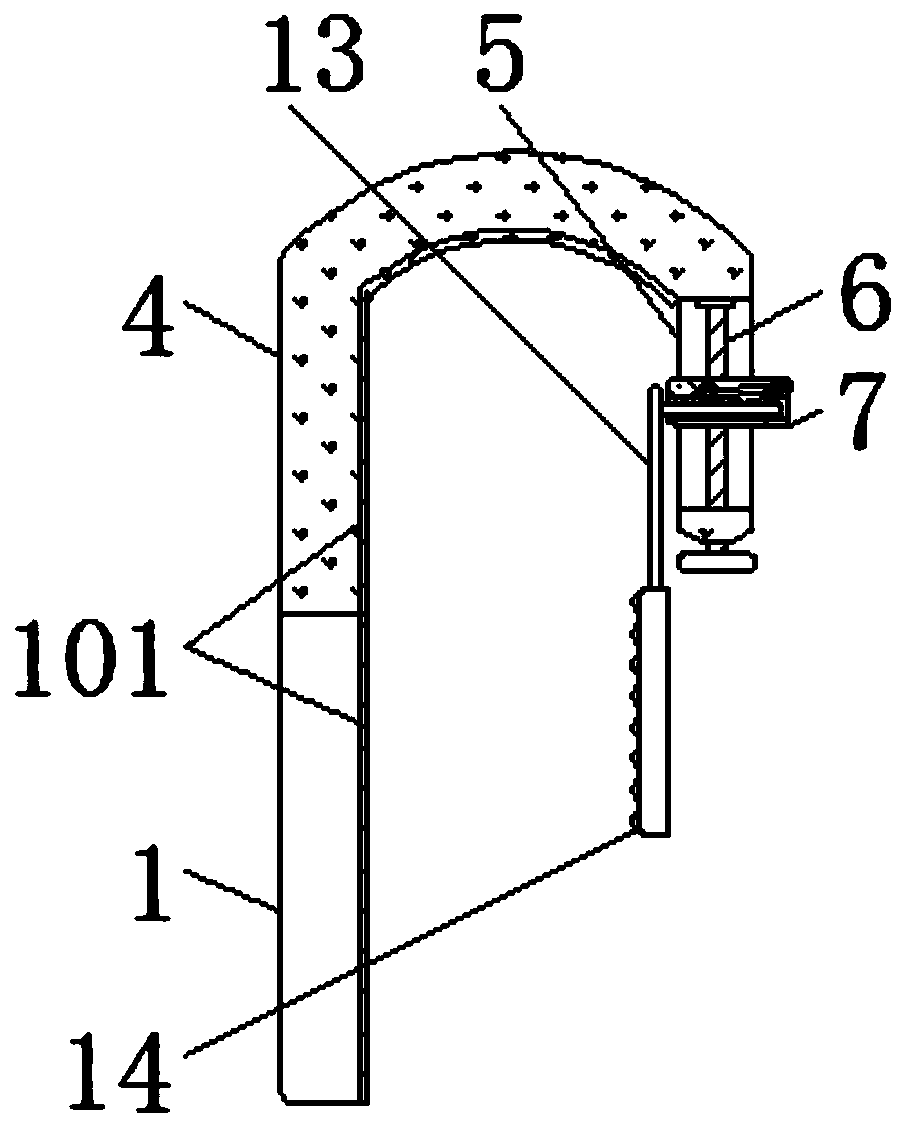
Cardiovascular monitoring wearable device and use method thereof
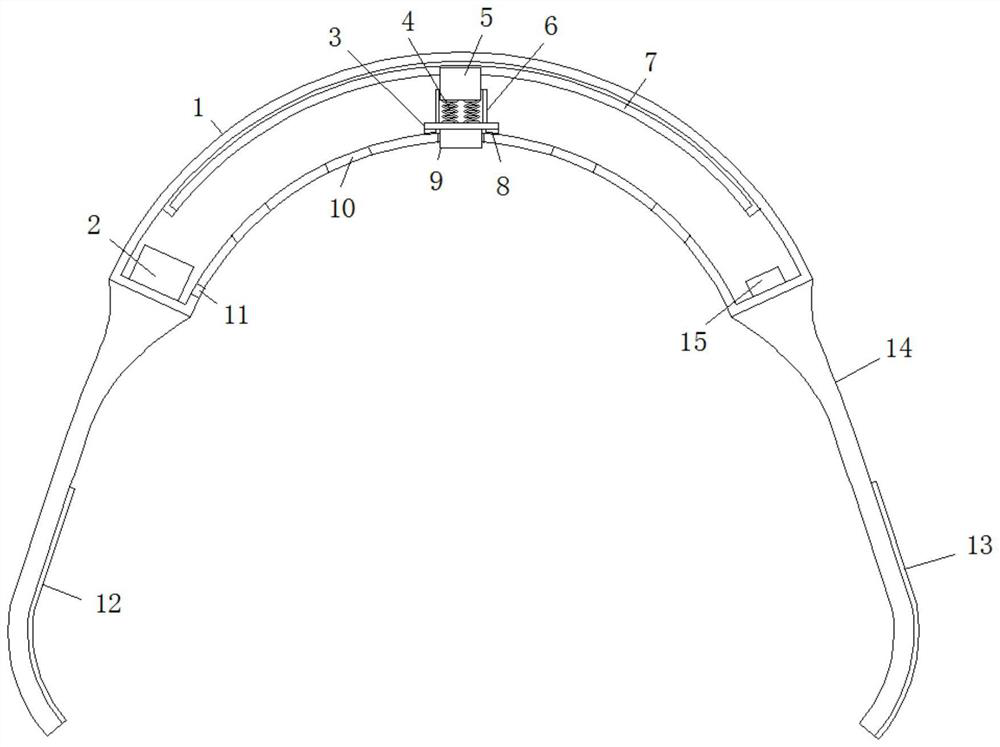
InactiveCN113440146AIncrease diversityTo achieve the purpose of fire warningEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsEngineeringData memory
The invention discloses a cardiovascular monitoring wearable device and a use method thereof. The cardiovascular monitoring wearable device comprises a hollow flexible plate, wherein a plurality of preformed holes distributed at equal intervals are formed on the bottom of the hollow flexible plate; a sliding seat is fixedly connected to the top of an inner cavity of the hollow flexible plate; a sliding rod is slidably connected to the inner side of the sliding seat; the bottom of the sliding rod is movably connected with a sleeve through a spring; the bottom of the sleeve is fixedly connected with a supporting plate; and the bottom of the supporting plate is fixedly connected with a blood pressure and heart rate sensor, a blood oxygen concentration sensor and an electrocardiosignal sensor in sequence from front to back. The cardiovascular monitoring wearable device is provided with the sliding seat, the sliding rod, a moving block, a sliding groove, the spring, the sleeve, the supporting plate, the blood pressure and heart rate sensor, the blood oxygen concentration sensor, the electrocardiosignal sensor, the preformed holes, a data memory, a positioner, a temperature and humidity sensor, a smoke sensor and a 4G communication module, so that the functional diversity of the device is effectively improved, and therefore, great convenience is brought to use of people.
Owner:THE FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF NANTONG
Multifunctional cardiovascular monitoring system
InactiveCN105496370AIntelligent and humanized monitoringEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterControl systemCardiovascular disease monitoring
The invention discloses a multifunctional cardiovascular monitoring system comprising a wearable part and a control system part. The wearable part is formed by a first light sensor, a second light sensor, a contact sensor, a signal conversion module, a left elastic wrist band, a right wrist band of a wireless signal transmission module and an elastic band covered in a neck part; the control system part is formed by a data calculation chip, a data processing chip, a first data storage chip and a second data storage chip as well as a wireless signal receiving module. By the use of the intelligent data processing and storage chip integration, the cardiovascular monitoring control system can actively monitor various types of storage of data and give personalized prevention and treatment advice for individual conditions, so cardiovascular disease monitoring work can be more intelligent and humanized.
Owner:GUANGDONG CARDIOVASCULAR INSITITUTE +1
Bed-based ballistocardiogram apparatus and method
PendingUS20210298683A1Maximize probabilityNursing bedsSensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationNormal density
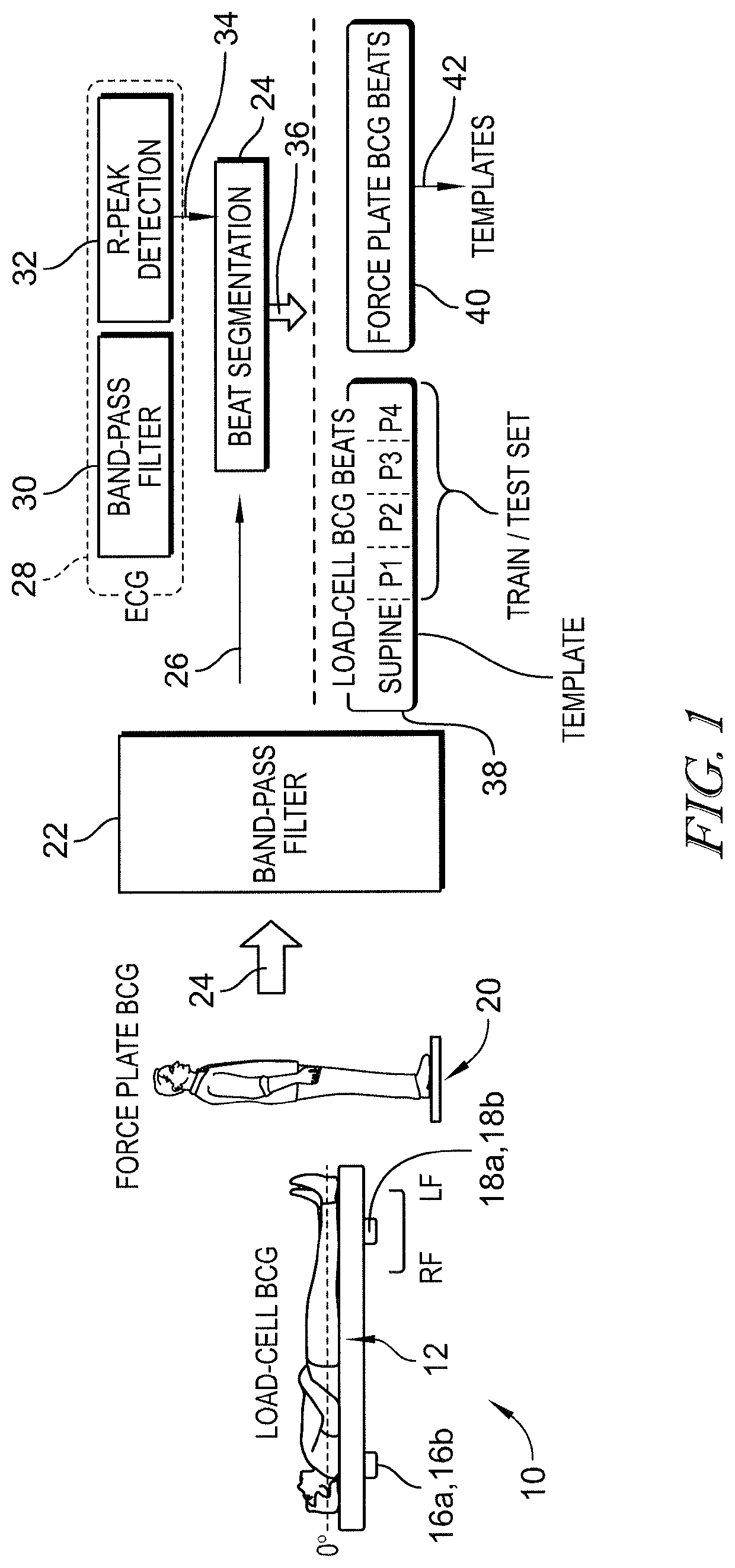
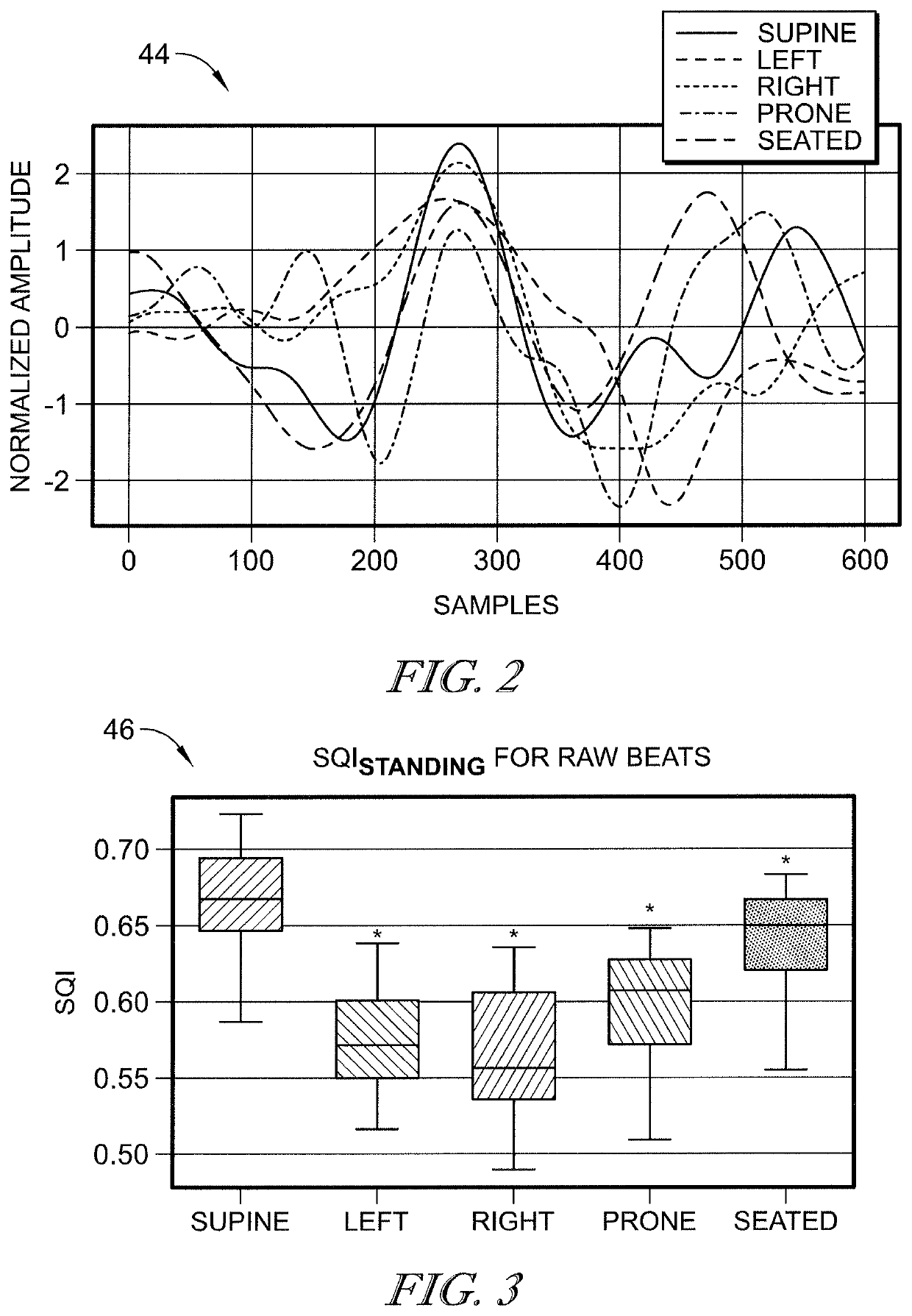
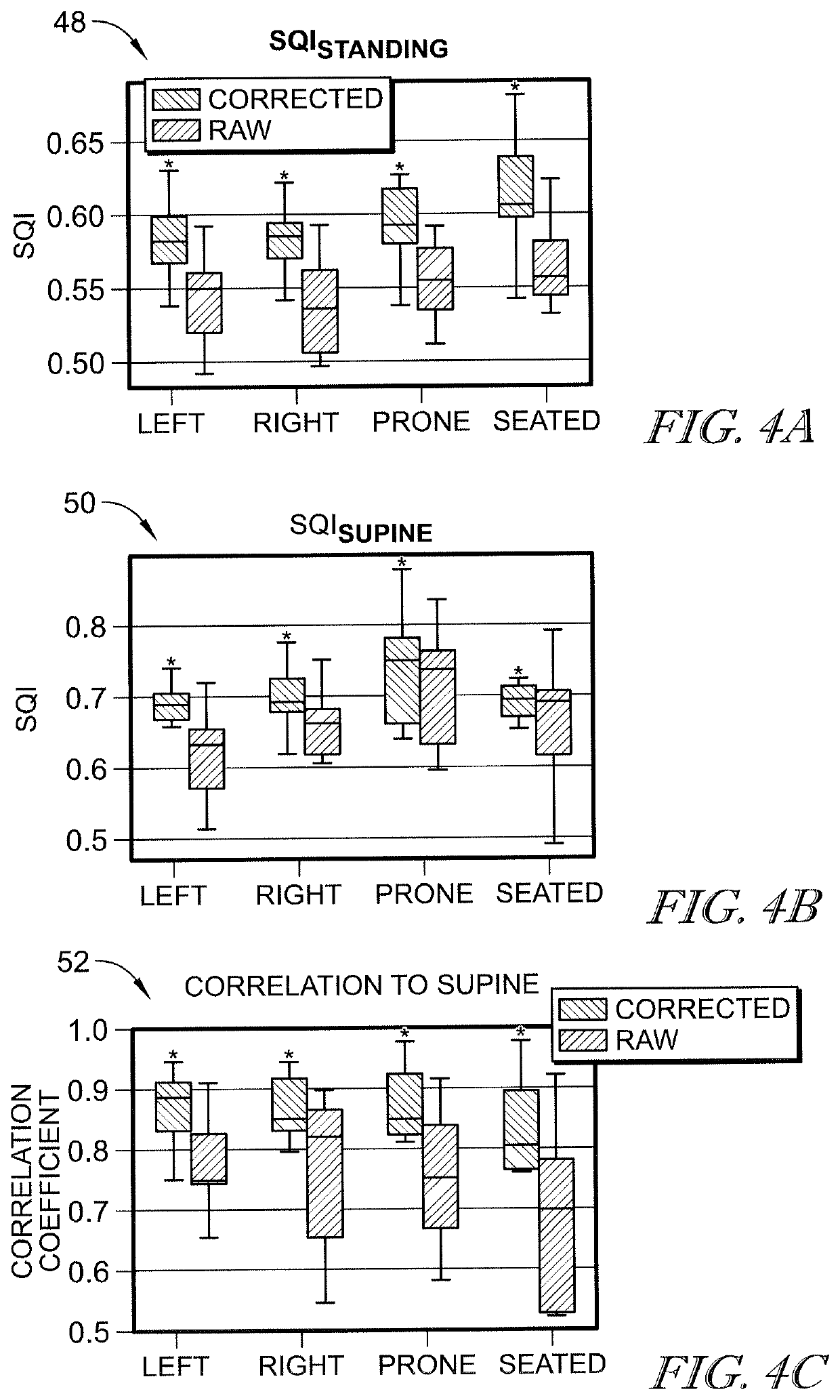
A ballistocardiogram (BCG), a measurement of cardiogenic whole body movements, is a technique that enables non-invasive cardiovascular monitoring. A main challenge of the BCG signal is that its morphology and amplitude are sensitive to the posture and / or position of the subject during the recording period. The effects of posture on the BCG measured from a subject standing on a weighing scale have been investigated in the literature, but the effects of body posture and / or position on BCG signals measured from a subject lying in a bed have not been quantified. A contemplated method for bed-based BCG recordings includes (1) creating templates for standing BCG signals obtained from subjects in a prior study, and (2) quantifying the distance between these templates and BCG waveforms obtained in different body positions on the bed for a new set of subjects. In addition, an array processing technique is presented, which includes the application of Gaussian weights on a joint probability density function (PDF) and the similarity score called the q-value to assess those PDFs. The Gaussian curve weights the joint probability according to the reference value obtained from the previous inter-beat-interval (IBI) estimations. The PDFs are selected and combined according to their reliability measured by q-values. This array processing significantly reduces the FIR estimation error by comparing the performance of selective channel combinations to the existing multi-channel algorithm.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
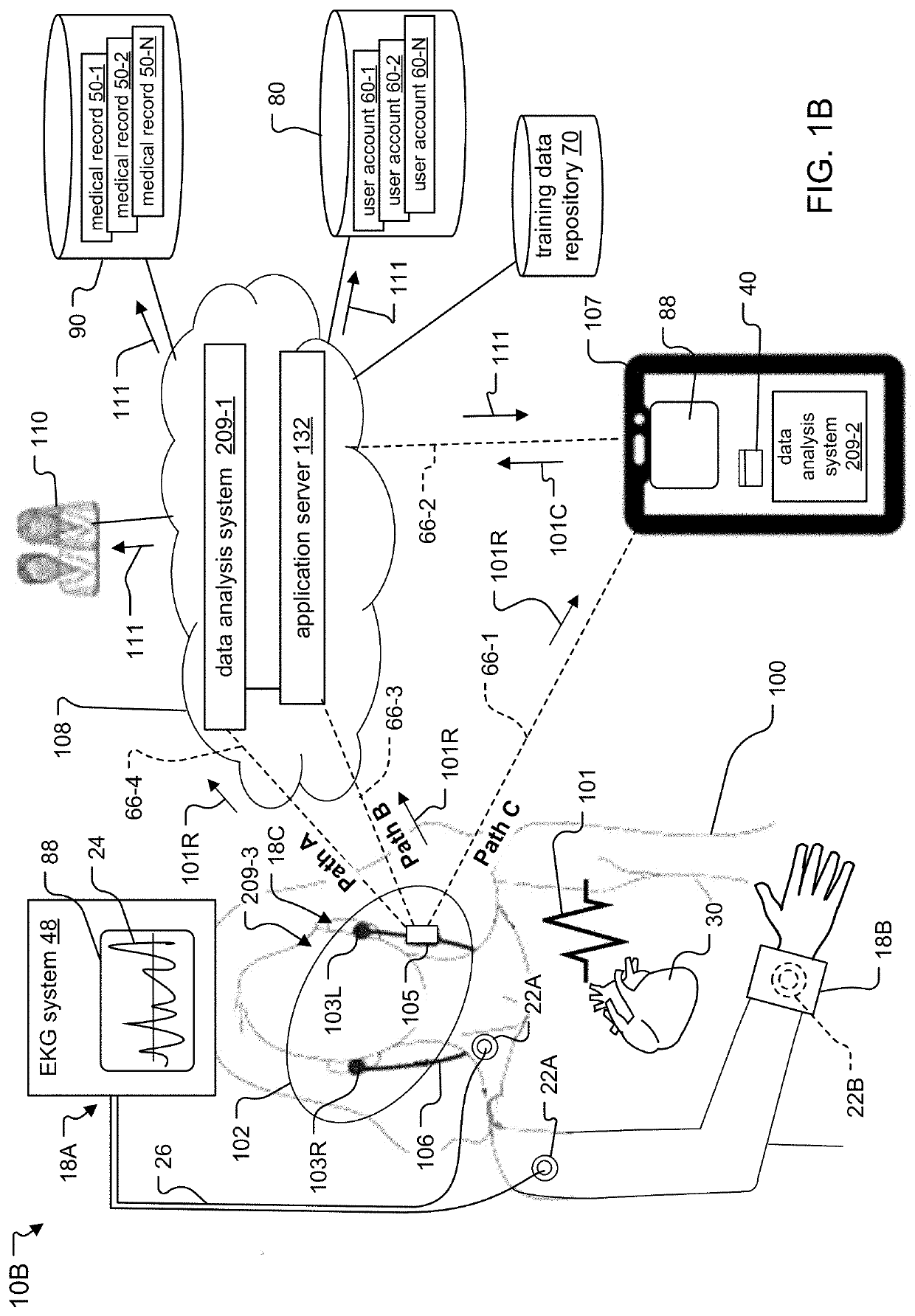
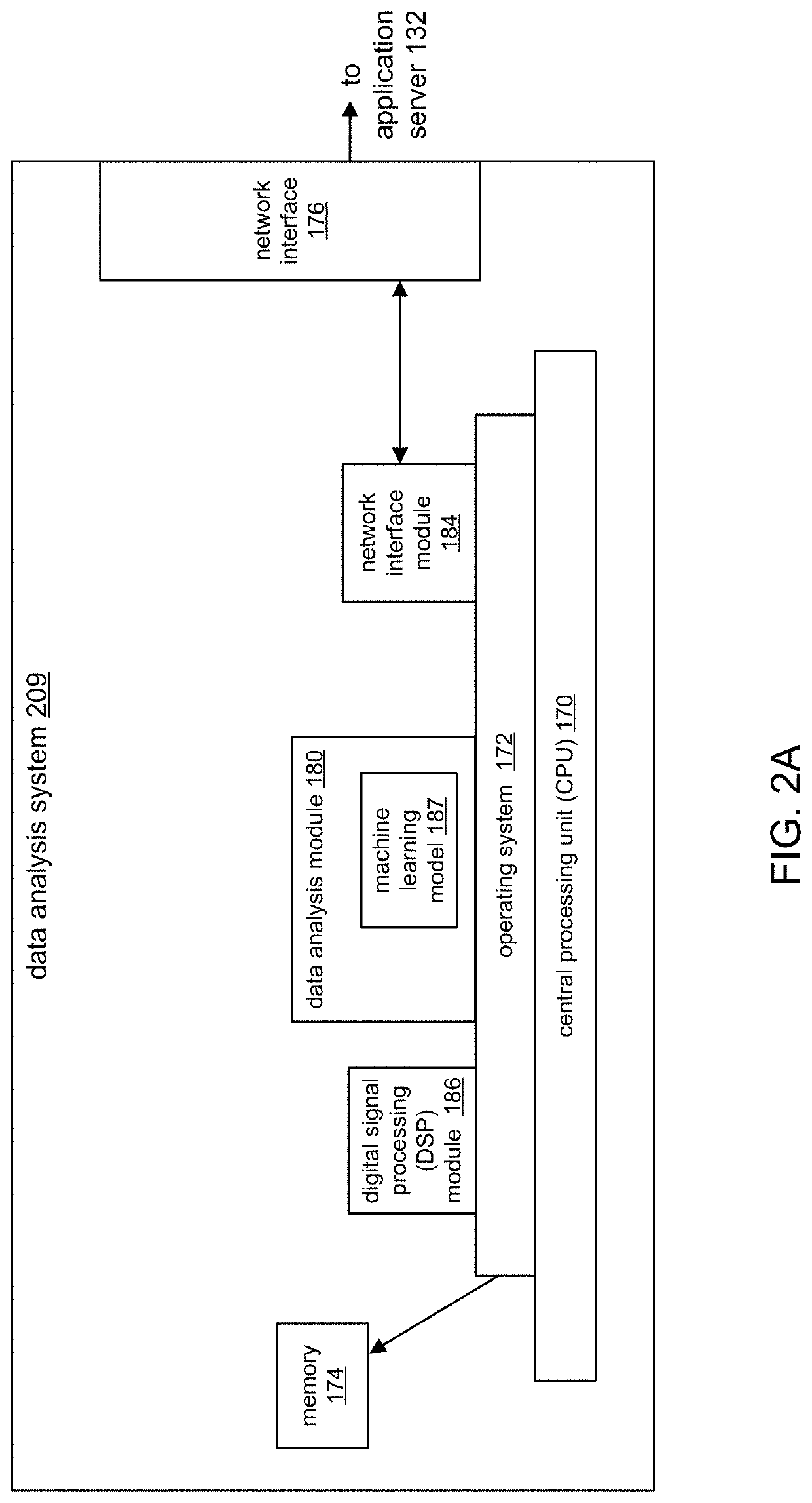
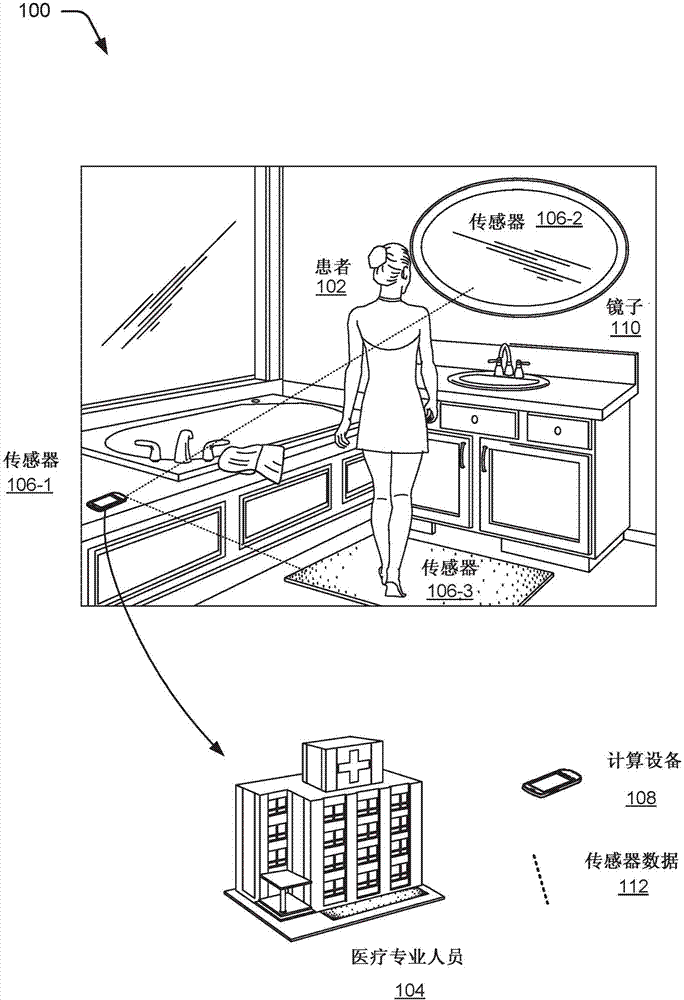
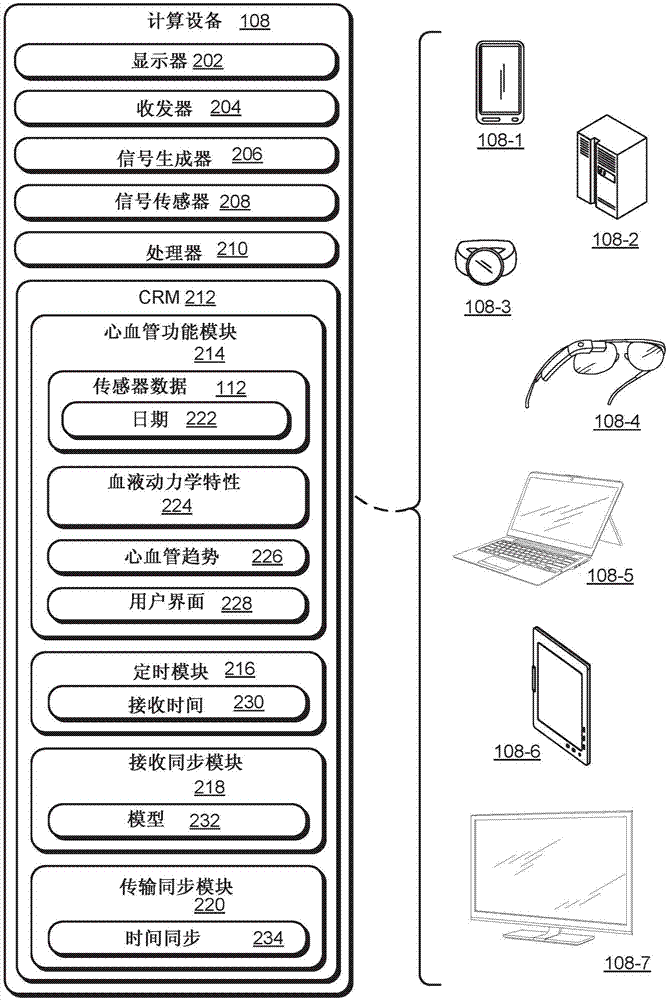
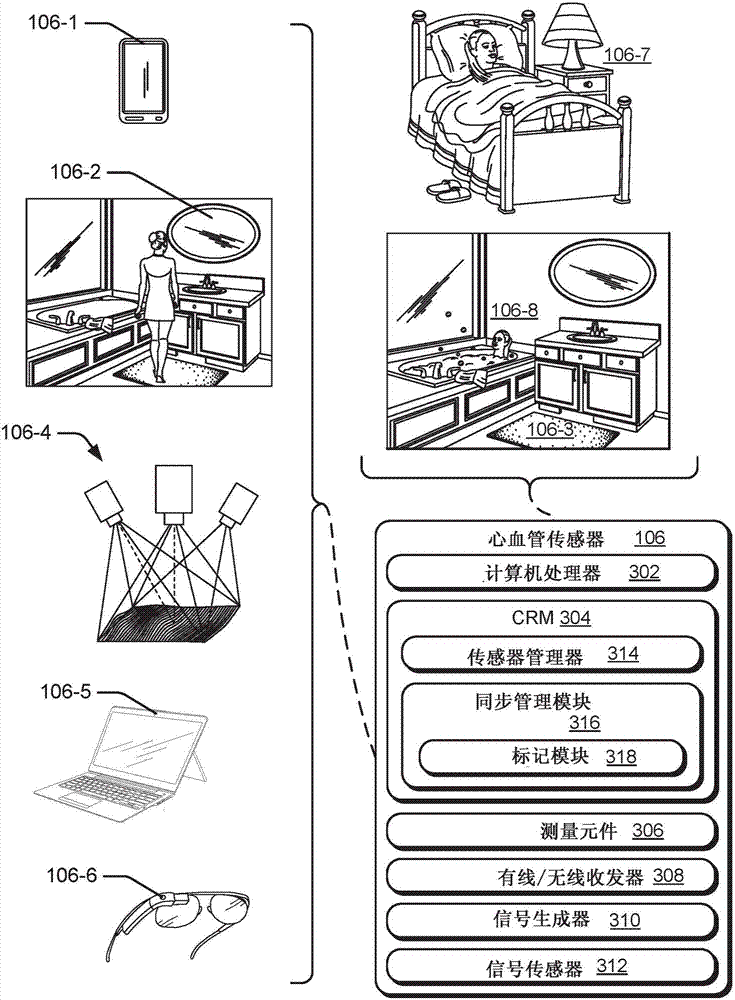
Synchronizing cardiovascular sensors for cardiovascular monitoring
This document describes synchronizing cardiovascular sensors for cardiovascular monitoring, such as through sensing relevant hemodynamics understood by pulse transit times, blood pressures, pulse-wave velocities, and, in more breadth, electrical conduction properties, cardiac rhythms, thoracic impedance, ballistocardiograms and pressure-volume loops. The techniques disclosed in this document use various cardiovascular sensors to sense hemodynamics, such as skin color and skin and other organ displacement. These cardiovascular sensors require little if any risk to the patient and are simple and easy for the patient to use.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Cardiovascular monitoring wearable equipment
ActiveCN111466896AAvoid affecting daily lifeEasy to wearCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringThoracic structureEngineering
The invention discloses cardiovascular monitoring wearable equipment. The cardiovascular monitoring wearable equipment comprises a first fixing strap, a screw rod and a cardiovascular detection module, wherein the first fixing strap is connected with the left side of a support pad, the right side of the support pad is connected with a second fixing strap, the outer sides of the second fixing strapand the first fixing strap are sewn with powerful Velcro, a support frame is fixedly installed on the upper side of the support pad, an adjustment groove is formed inside the support frame, the screwrod is in bearing connection with the inside of the adjustment groove, and the outer side of the screw rod is in threaded connection with an adjustment seat. In the cardiovascular monitoring wearableequipment, the rotation of the screw rod can drive the adjustment seat to move vertically to adjust a height position of the adjustment seat, thereby a height position of the cardiovascular detectionmodule is adjusted, and the cardiovascular detection module is pushed to drive the adjustment rod to fit in a position of the middle part of the thoracic cavity to ensure that the cardiovascular detection module is closely fitted to the position of the middle part of the thoracic cavity, so that the stable cardiovascular monitoring is performed, and the accuracy of monitoring data is ensured.
Owner:西安市第一医院
Cardiovascular health monitoring device
PendingCN111954488ADiagnostics using lightEvaluation of blood vesselsLight sensingEmergency medicine
Provided is a cardiovascular monitoring device. The device comprises a photoplethysmography (PPG) sensor (510), having at least one light emitting element (310) and at least one light sensing element(320) for obtaining at least one PPG signal from a patient; and a controller comprising: a determination module (550) for determining whether a signal obtained by a particular light sensing element issuitable for deriving information relevant to a patient's cardiovascular system; and a processing module (540) for processing a signal that is determined to be suitable for deriving information relevant to the patient cardiovascular system to derive information relevant to the patient cardiovascular system.
Owner:生物隐形有限公司
Cardiovascular health monitoring
PendingUS20210093211A1Good avenue for monitoring cardiovascular healthImprove processing efficiencyDiagnostics using lightEvaluation of blood vesselsLight sensingEmergency medicine
A cardiovascular monitoring apparatus, the apparatus comprising: a photoplethysmography (PPG) sensor (510), having at least one light emitting element (310) and at least one light sensing element (320), for obtaining at least one PPG signal from a patient; and a controller comprising: a determination module (550) for determining whether a signal obtained by a particular light sensing element is suitable for deriving information relevant to a patient's cardiovascular system; and a processing module (540) for processing a signal that is determined to be suitable for deriving information relevant to the patient's cardiovascular system to derive information relevant to the patient's cardiovascular system.
Owner:BIOSTEALTH LTD
Cardiovascular monitoring device
ActiveUS10213123B2ElectrocardiographyDiagnostics using lightBlood pressure cuffsBody temperature measurement
Portable physiological measuring devices and methods are disclosed. Embodiments may provide measurement of blood pressure without traditional blood pressure cuffs. Further, disclosed embodiments may gather pulse oximetry (SpO2), heart rate and body temperature measurements simultaneously. A user's blood pressure index and other vital physiological results may be displayed on a portable physiological measuring apparatus or a portable terminal. Embodiments may provide a portable physiological measuring method and apparatus that displays results on a displayed screen.
Owner:MOCACARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com