Patents
Literature
43 results about "Context dynamics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
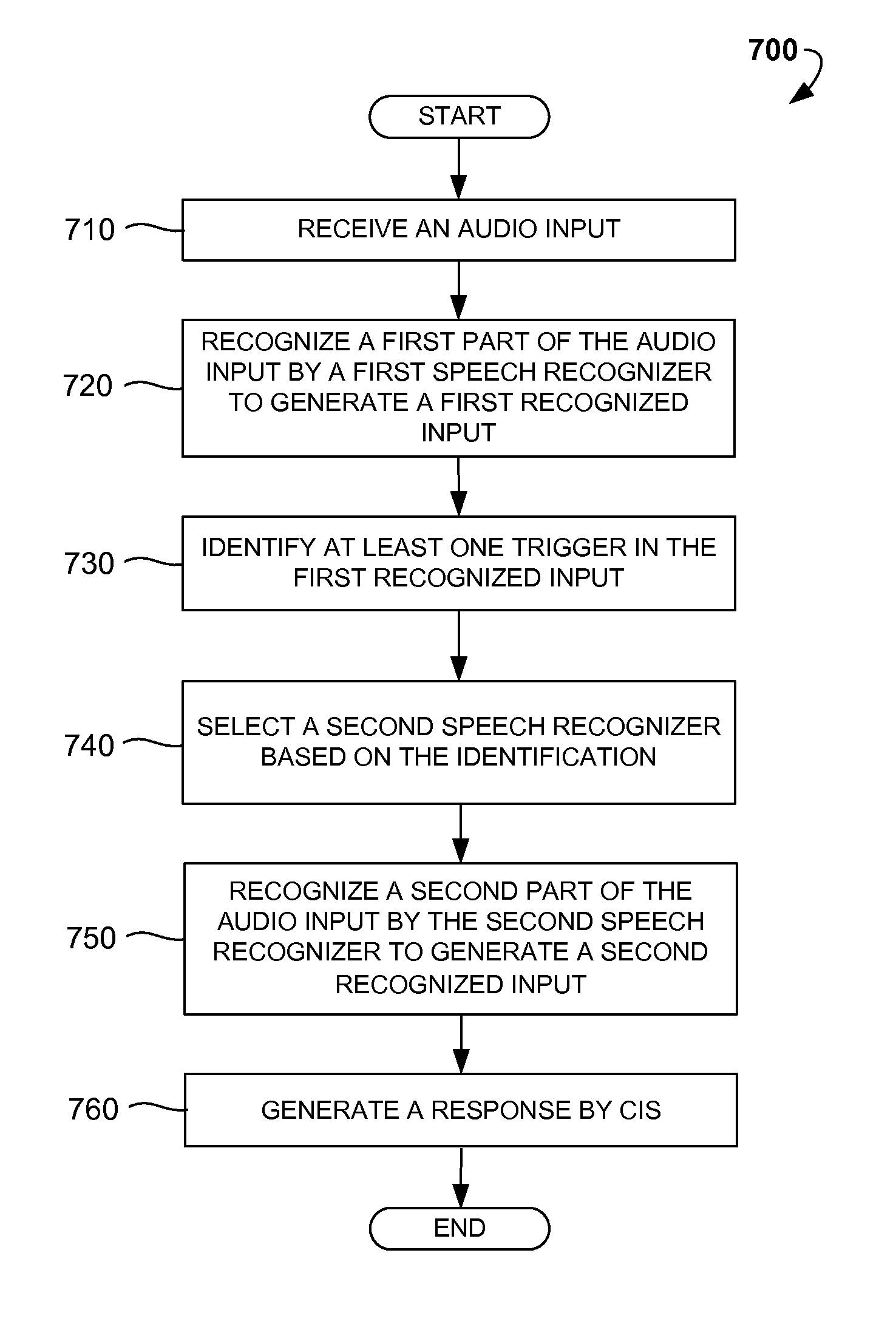
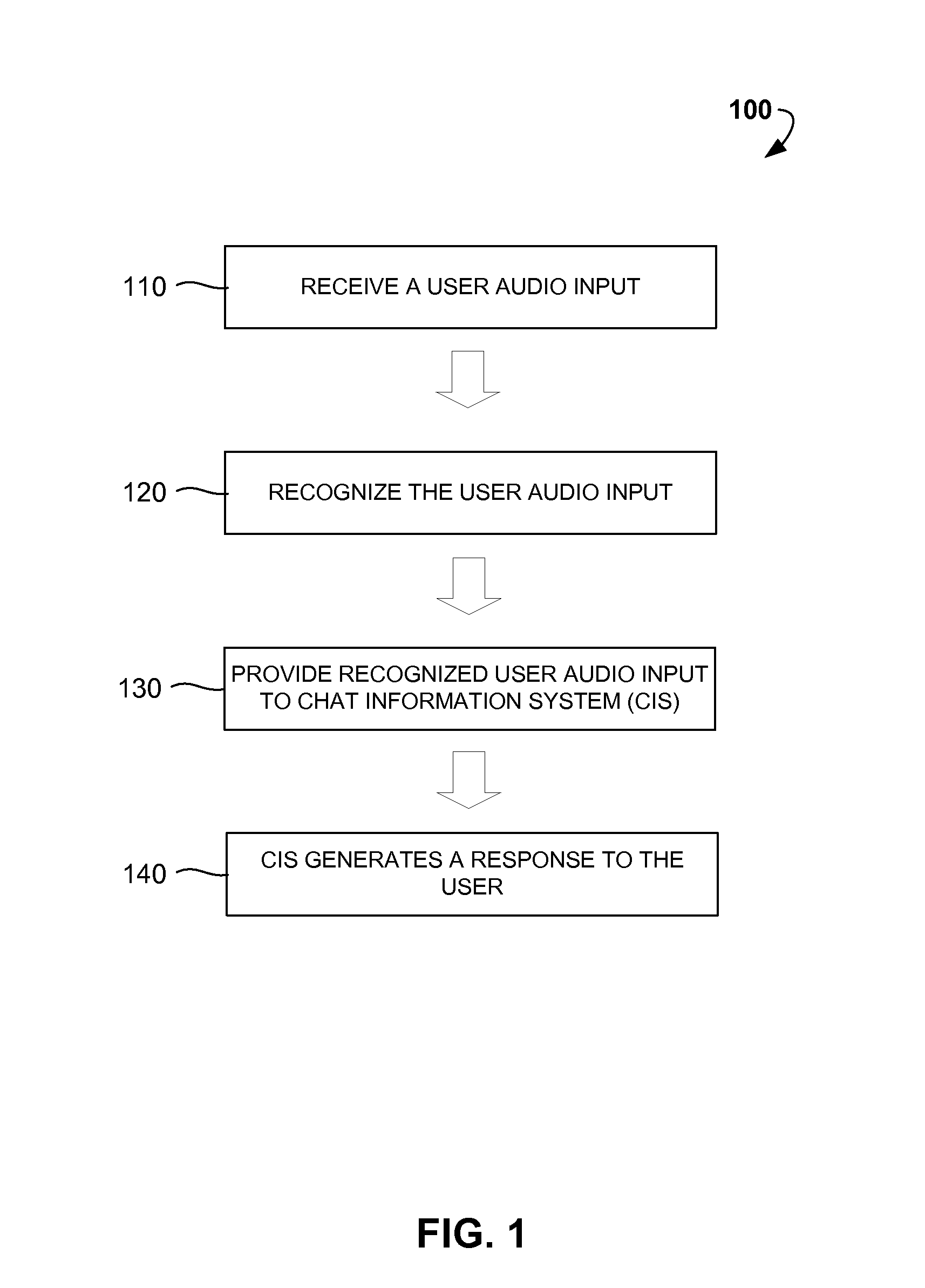
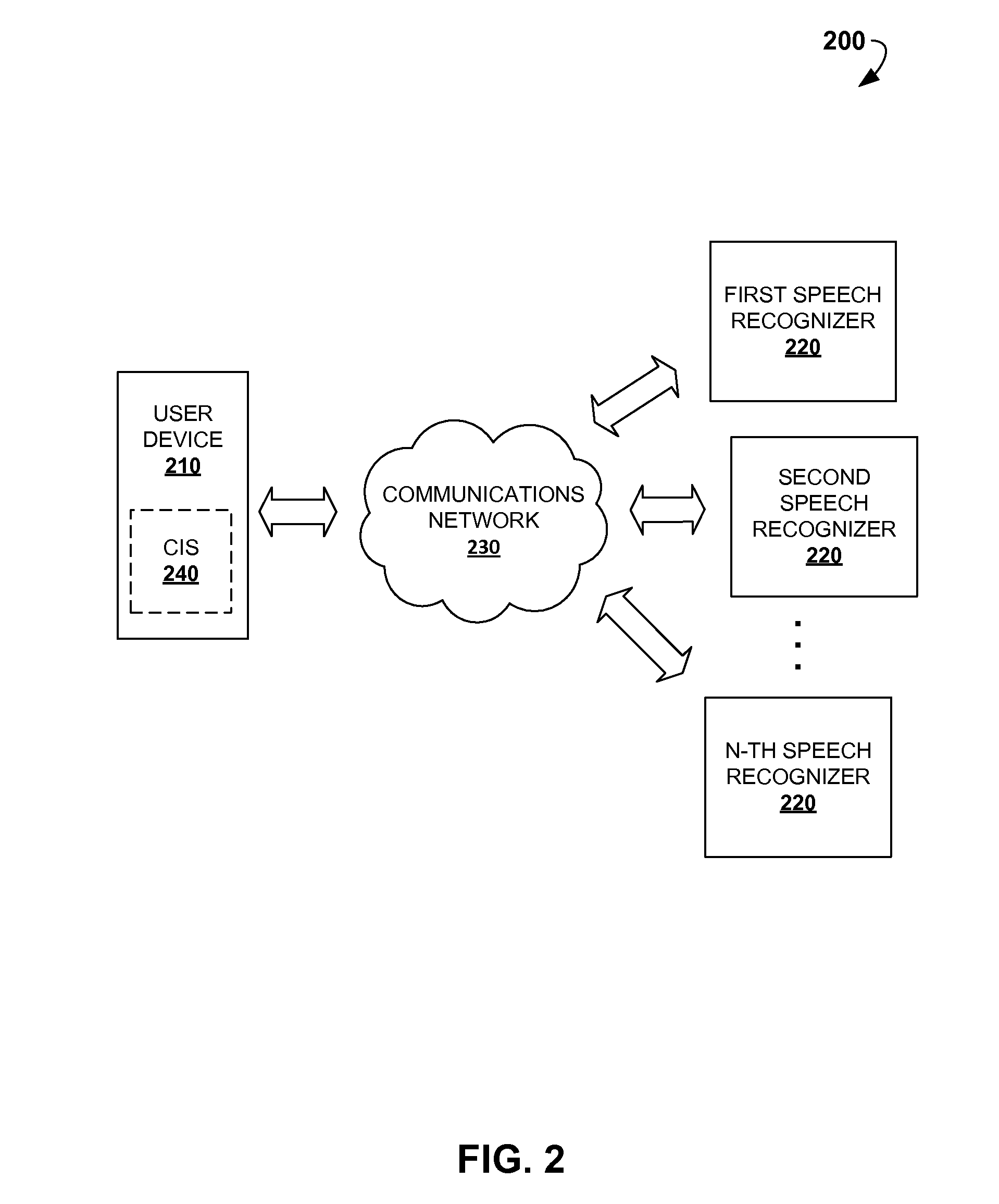
Selective speech recognition for chat and digital personal assistant systems
ActiveUS20160260434A1Simple technologyImprove accuracySpeech recognitionAddress bookMultiple criteria
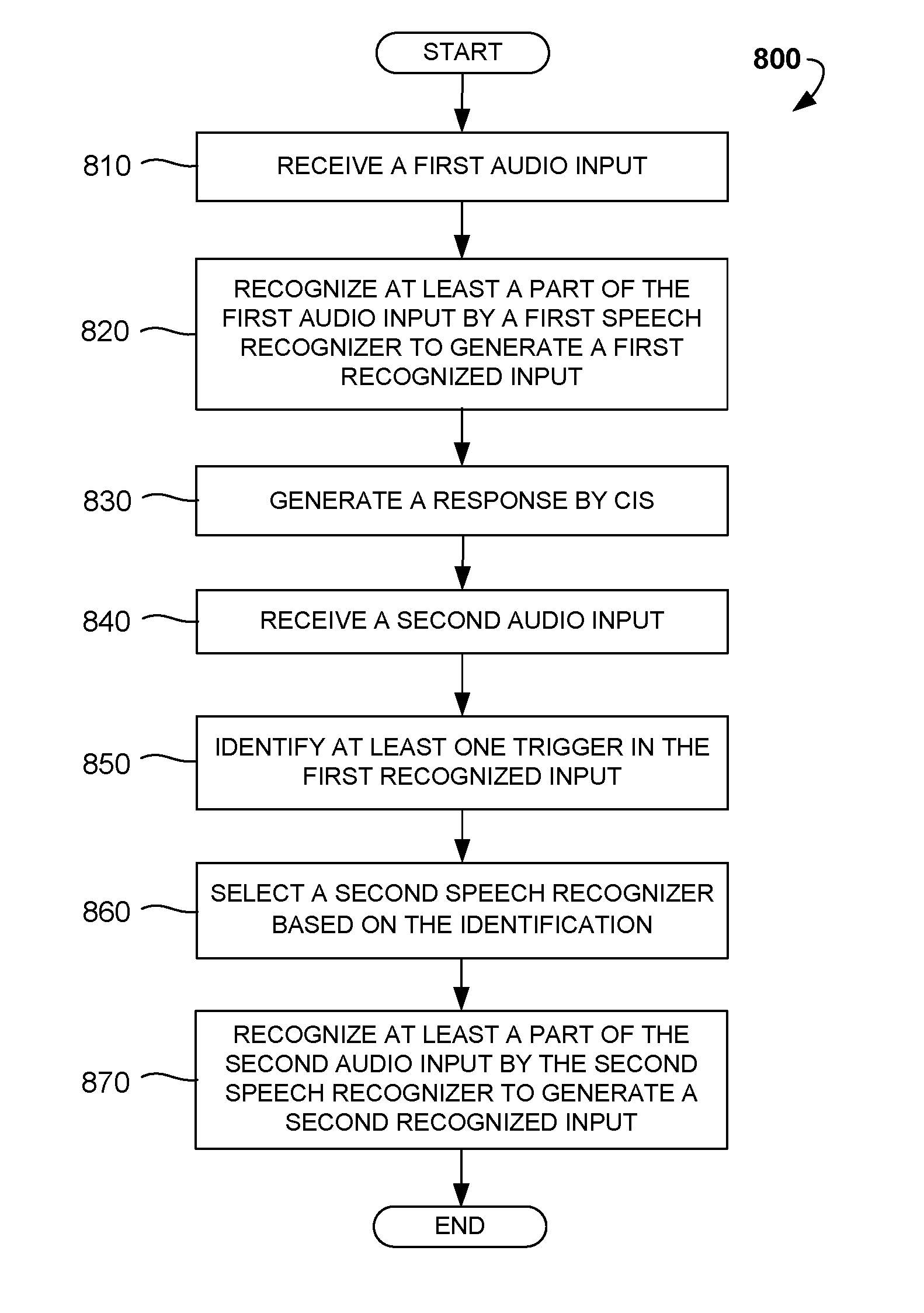
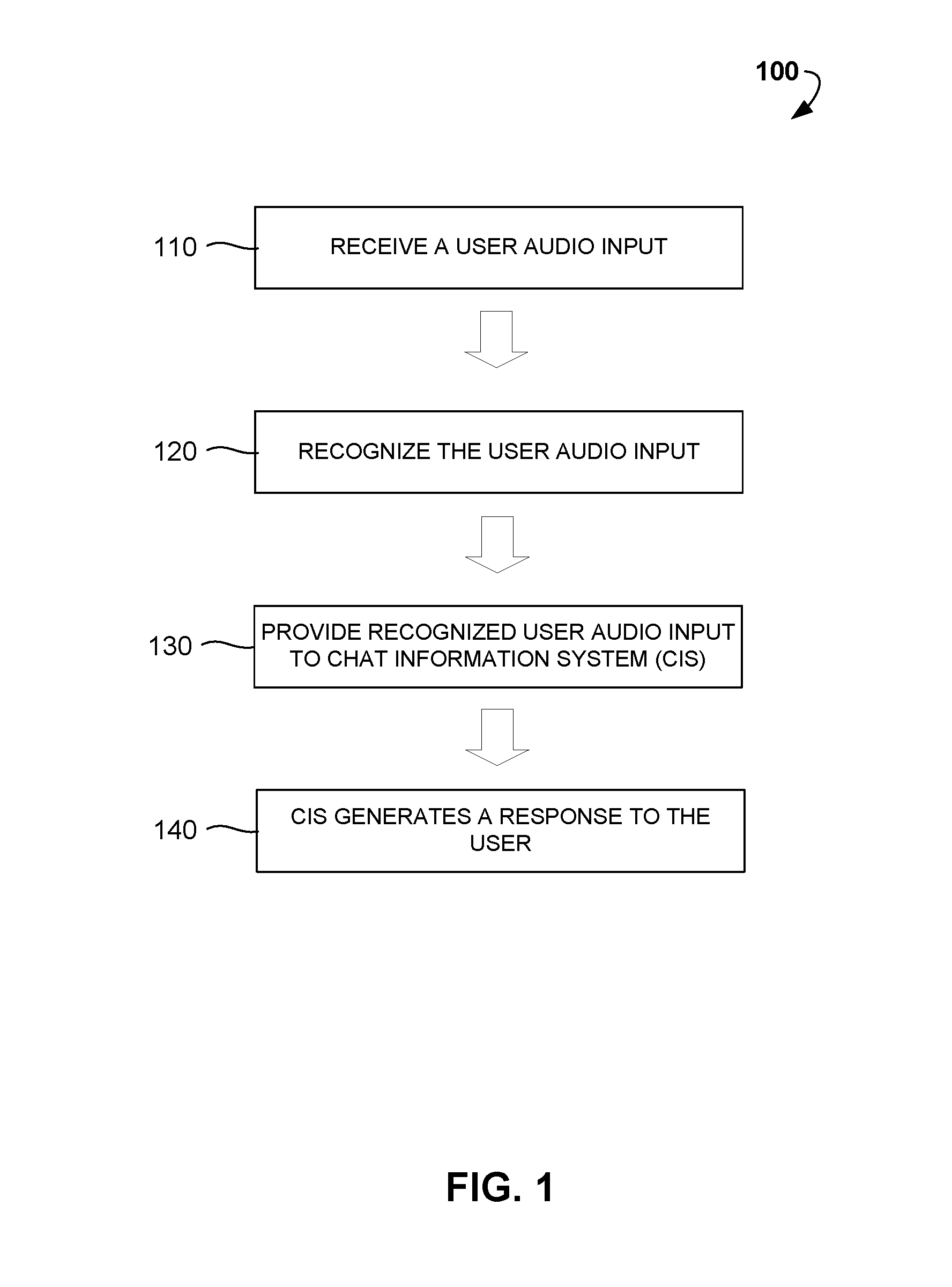
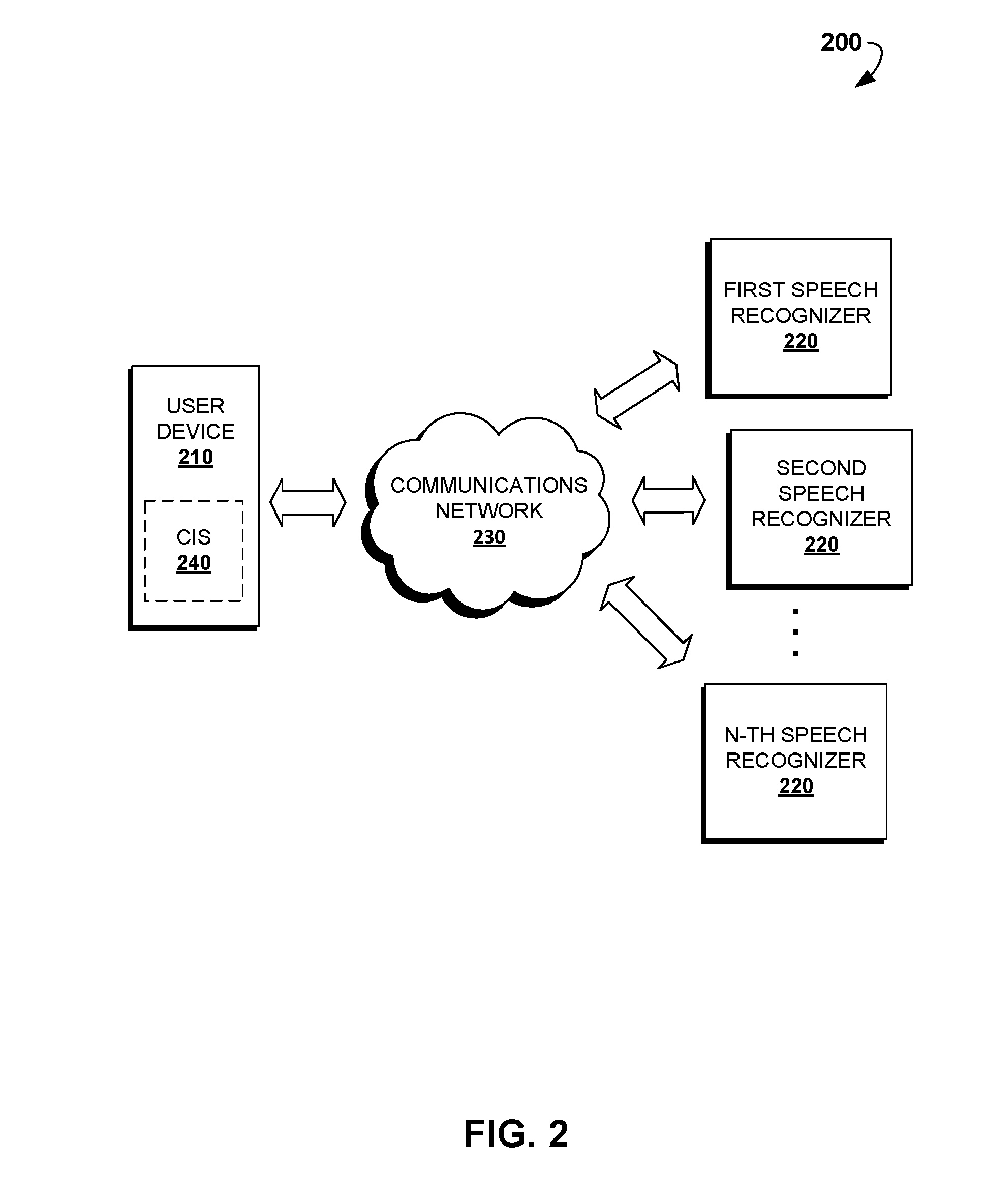
Disclosed are computer-implemented methods and systems for dynamic selection of speech recognition systems for the use in Chat Information Systems (CIS) based on multiple criteria and context of human-machine interaction. Specifically, once a first user audio input is received, it is analyzed so as to locate specific triggers, determine the context of the interaction or predict the subsequent user audio inputs. Based on at least one of these criteria, one of a free-diction recognizer, pattern-based recognizer, address book based recognizer or dynamically created recognizer is selected for recognizing the subsequent user audio input. The methods described herein increase the accuracy of automatic recognition of user voice commands, thereby enhancing overall user experience of using CIS, chat agents and similar digital personal assistant systems.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
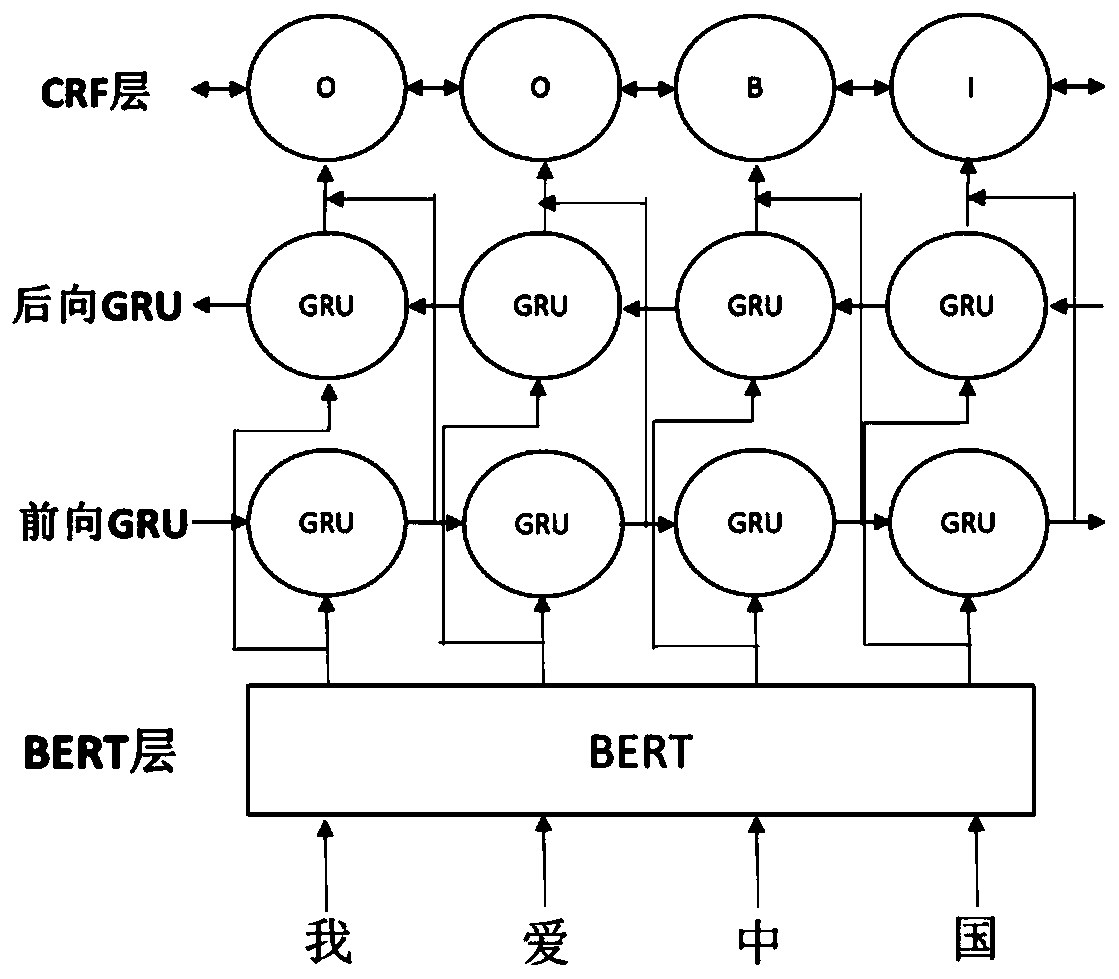
Chinese named entity recognition method based on BERT-BiGRU-CRF
ActiveCN110083831AHigh precisionEffectively represent ambiguitySemantic analysisEnergy efficient computingSemantic vectorPattern recognition
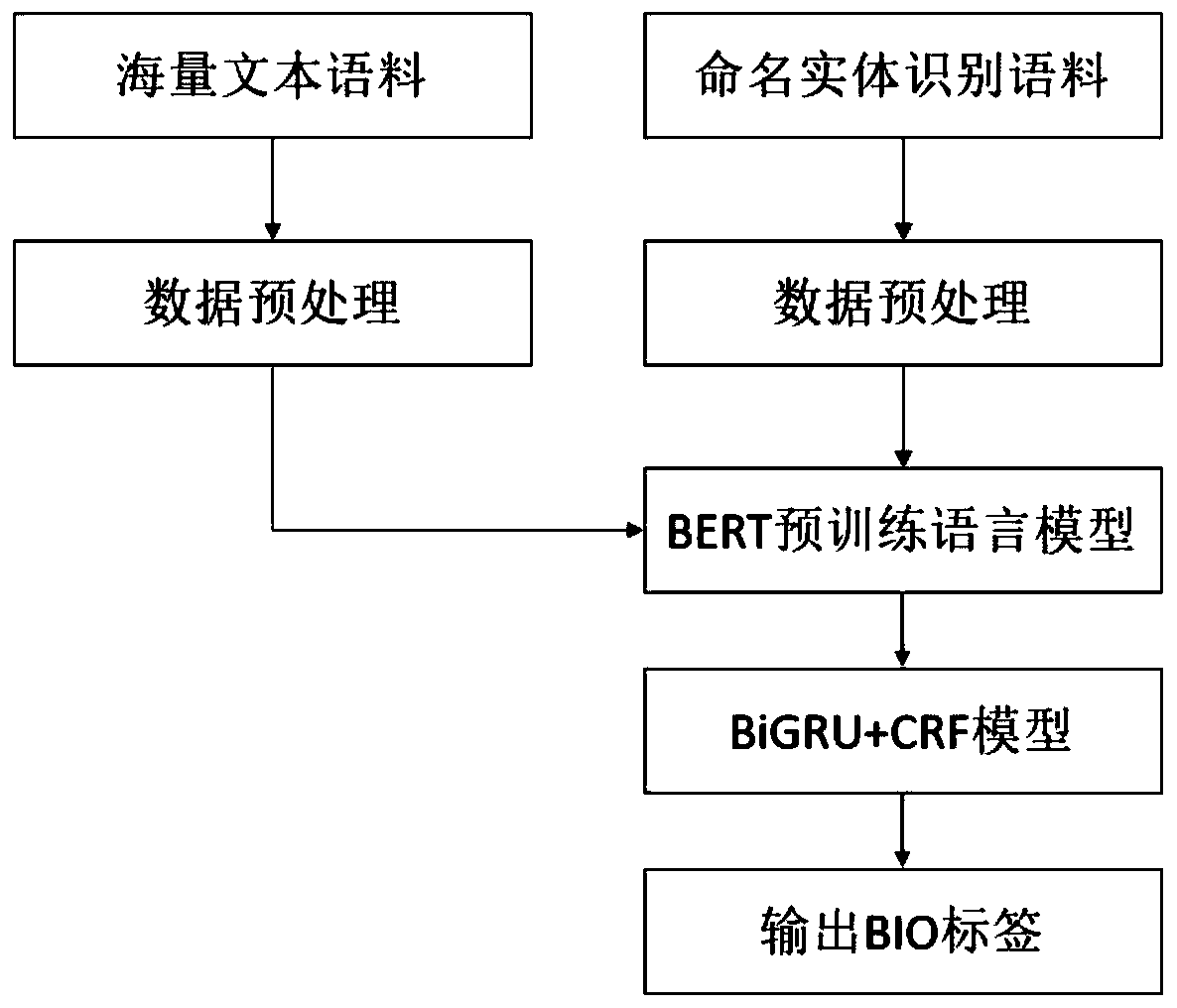
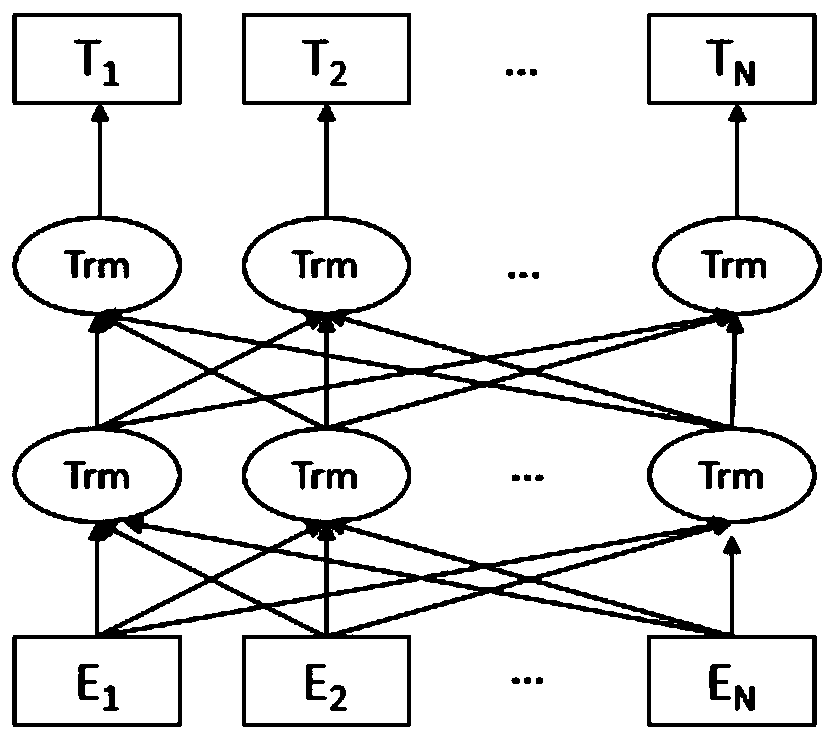
The invention discloses a Chinese named entity recognition method based on BERT-BiGRU-CRF. The method comprises three stages: in the first stage, preprocessing mass text corpora, and pre-training a BERT language model; in the second stage, preprocessing the named entity recognition corpus, and encoding the named entity recognition corpus through the trained BERT language model; and at the third stage, inputting the encoded corpus into a BiGRU+CRF model for training, and performing named entity recognition on the to-be-recognized statement by using the trained model. Construction of the Chinesenamed entity recognition method based on BERT-BiGRU-CRF is carried out, semantic representation of characters is enhanced through a BERT pre-training language model, semantic vectors are dynamicallygenerated according to contexts of the characters, and the ambiguity of the characters is effectively represented. Compared with a method based on fine tuning of a language model, the method has the advantages that training parameters are reduced, and the training time is saved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
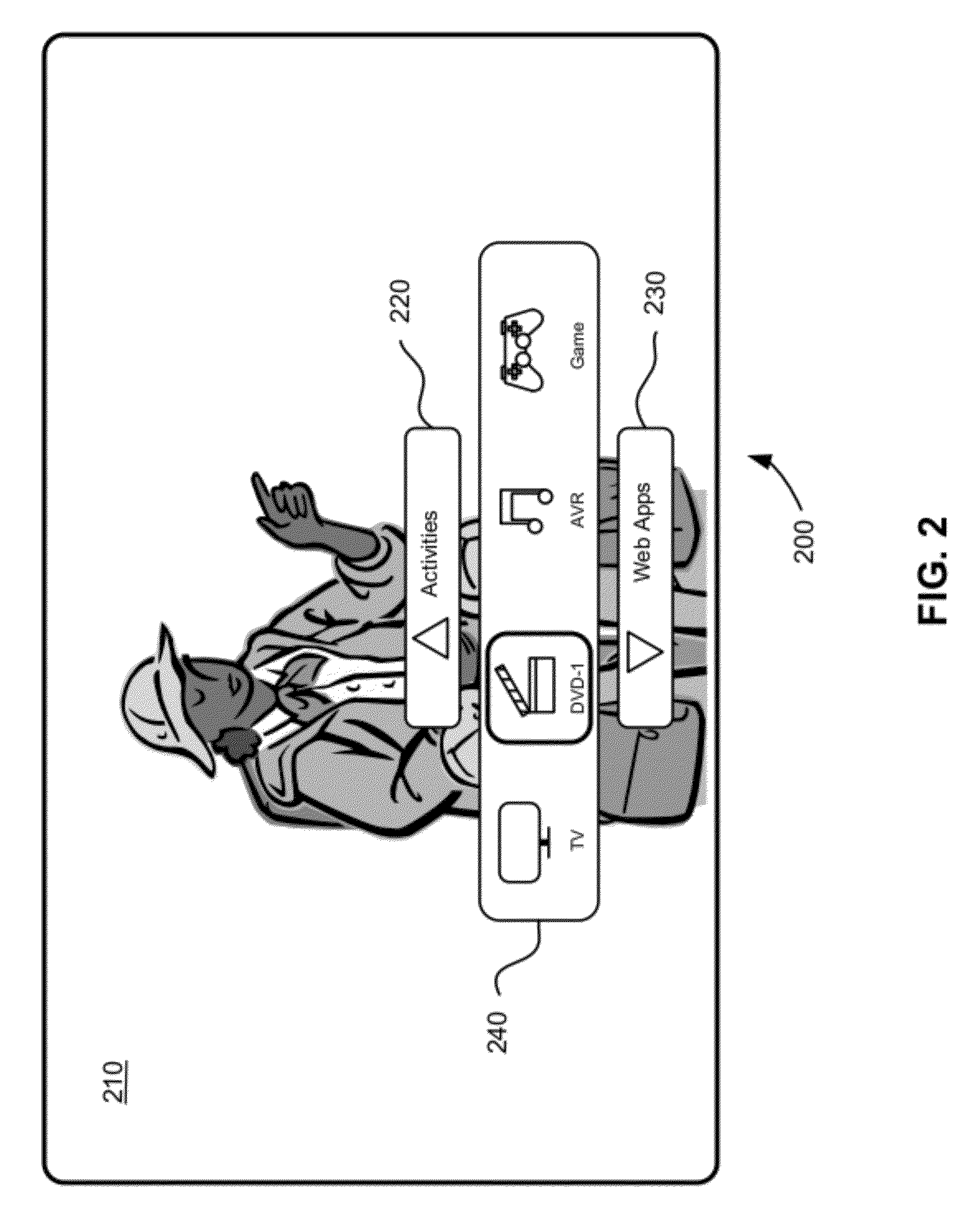
Remote control system for connected devices
ActiveUS20120274863A1Minimal costReduce complexityTelevision system detailsMultimedia data retrievalControl systemRemote control
Systems and methods utilize a display to provide universal remote control functionality. A menu of options appears on a display of a display device. A user can navigate the various options to control devices that are separate from the display device. The menu may be dynamically configured according to the context in which the display device is being used. The menu may be activated using a remote control device or other device and the menu may include options for controlling one or more devices that are absent from the remote control device.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
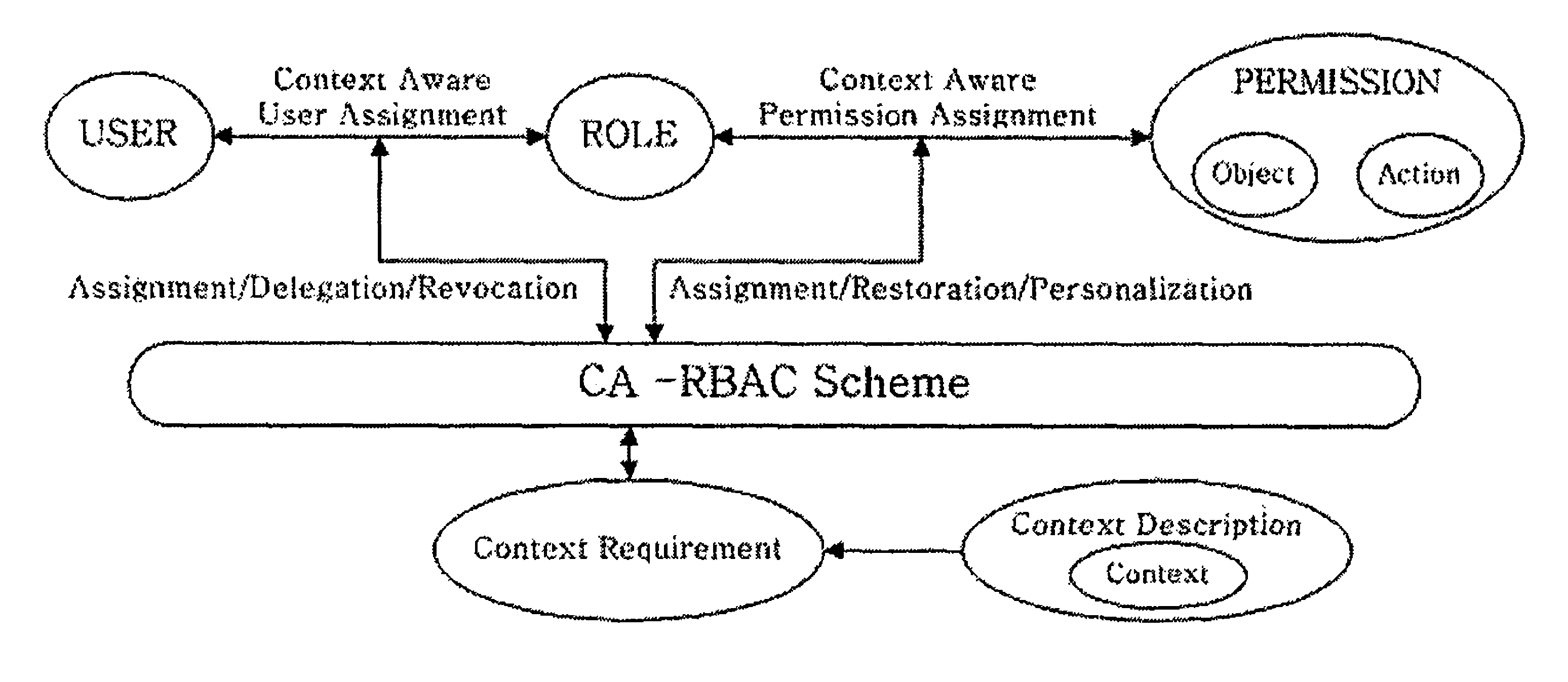
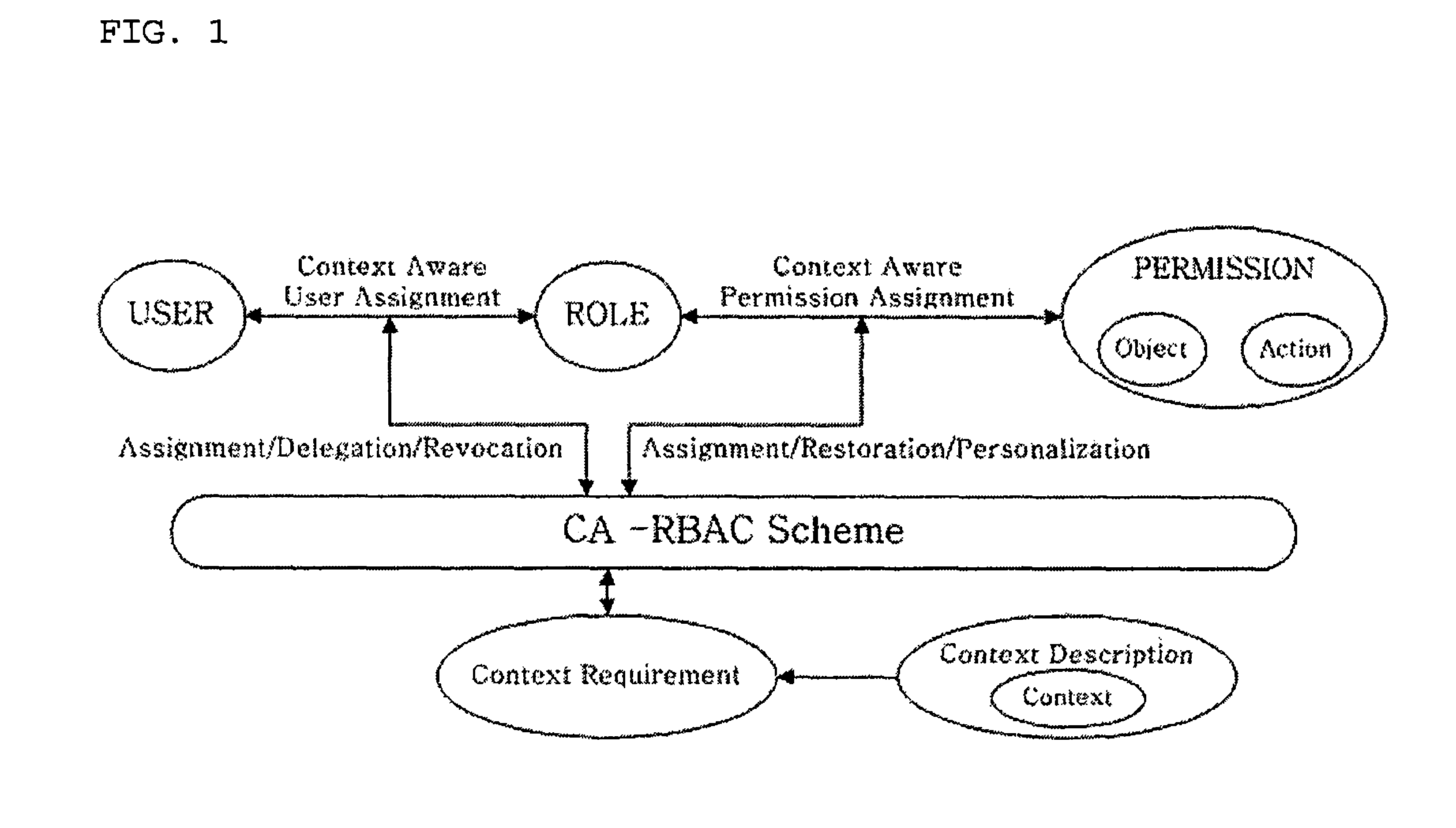
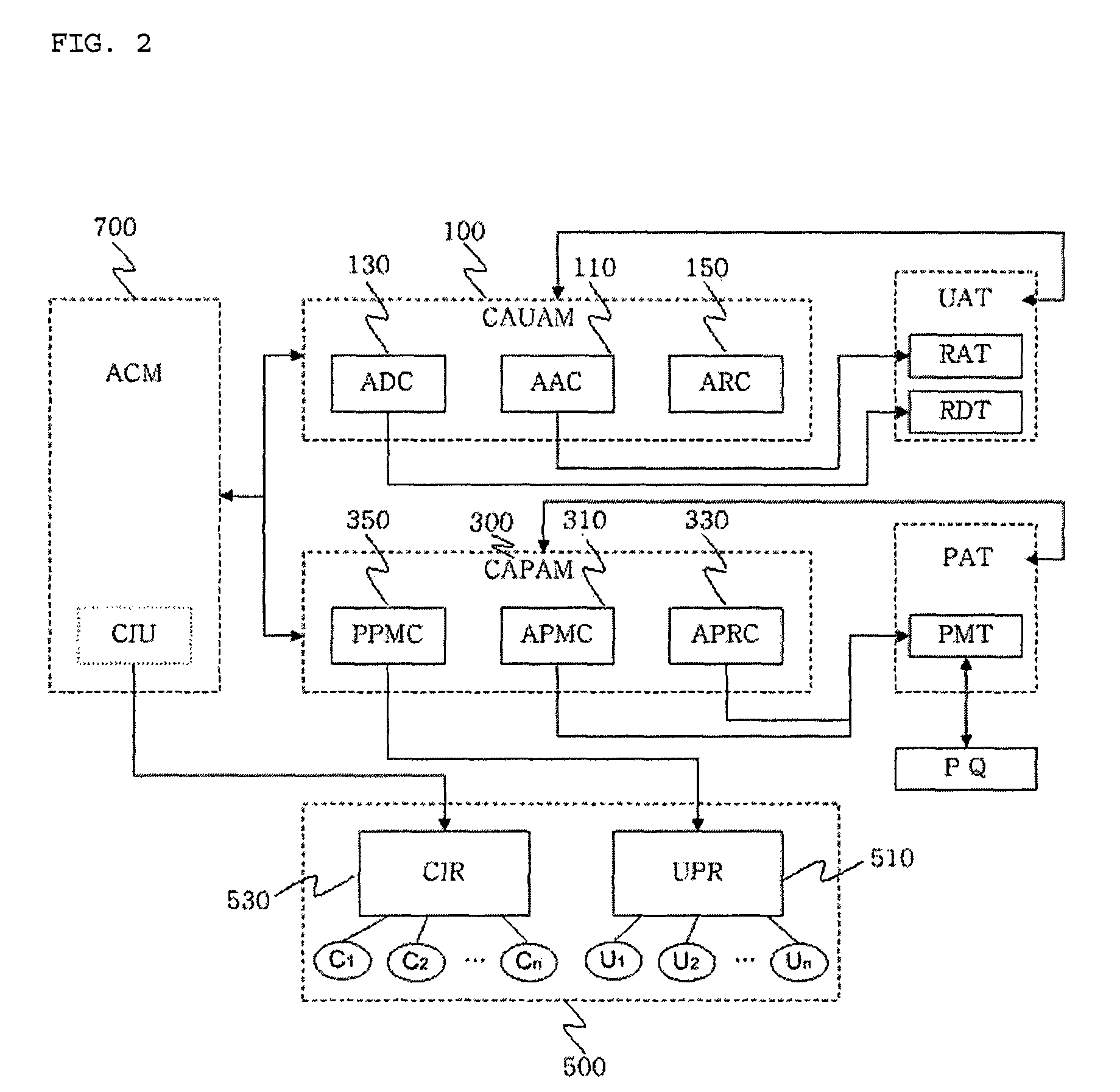
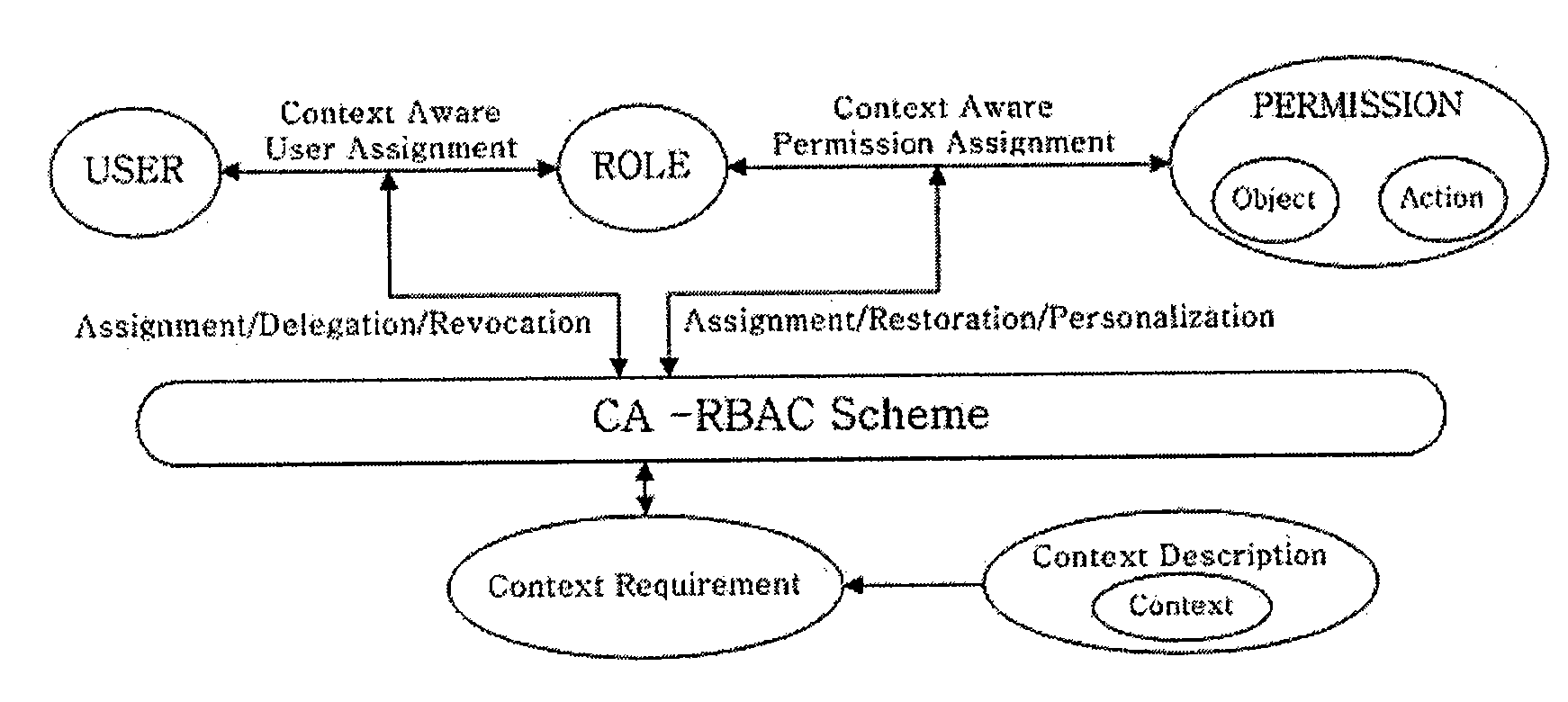
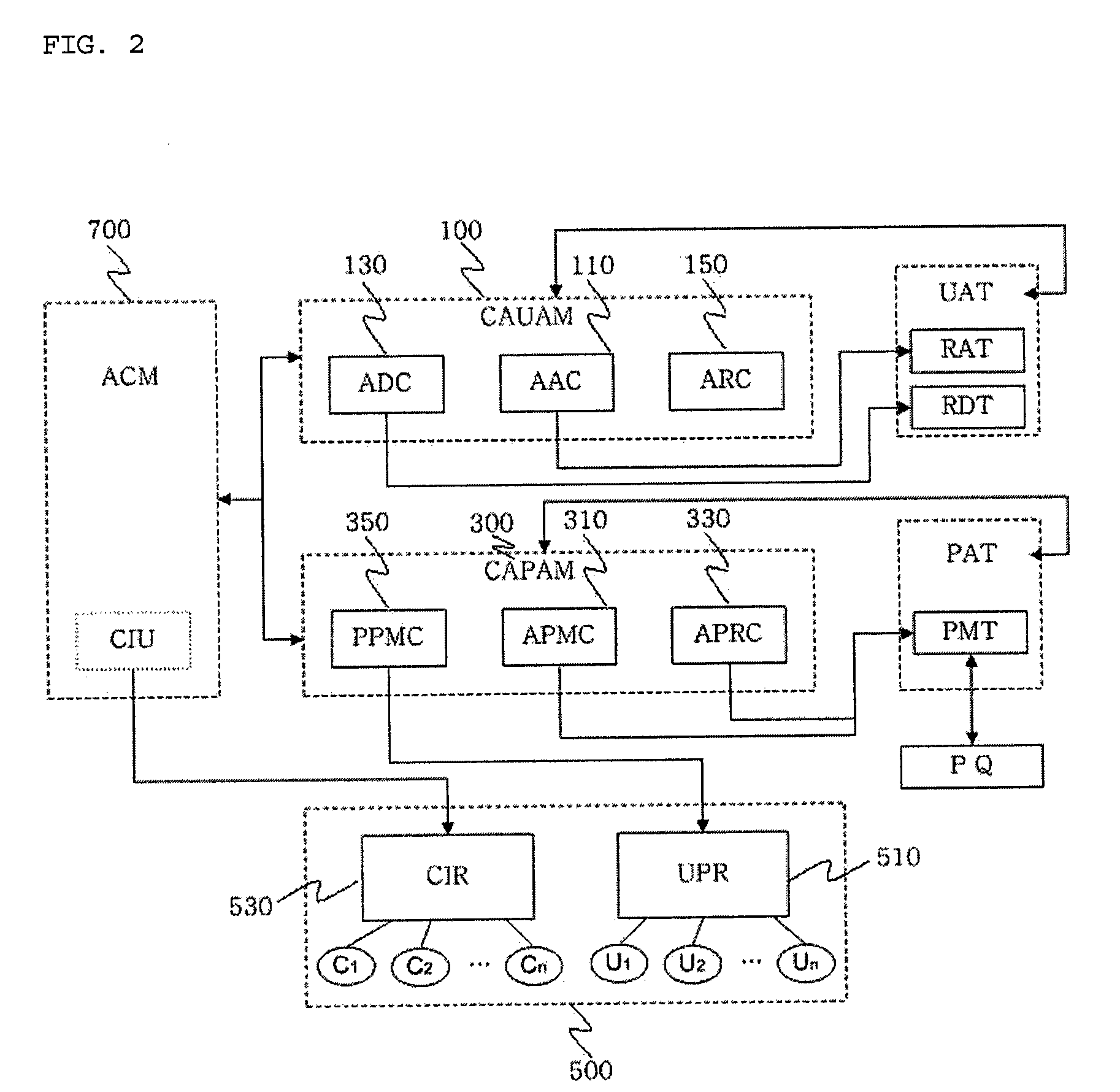
Context-aware role-based access control system and control method thereof
ActiveUS8387117B2Efficient expressionEffective controlDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPersonalizationInformation repository
A context-aware role-based access control system and a control method thereof. The context-aware role-based access control system includes: a context-aware user assignment manager (CAUAM) for performing a role assignment function, a role delegation function, or a role revocation function for a user according to a context of the user, based on a preset context request condition; a context-aware permission assignment manager (CAPAM) for performing a permission modification, a permission restoration, and a personalized permission modification for a permission, which the role has, according to changes in the context of the user; an information repository for storing a user profile and context information; and an access control manager (ACM) for controlling the context-aware user assignment manager, the context-aware permission assignment manager, and the information repository, and processing an access control request. Accordingly, more efficient access control can be achieved in ubiquitous environments where the context of the user dynamically changes.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
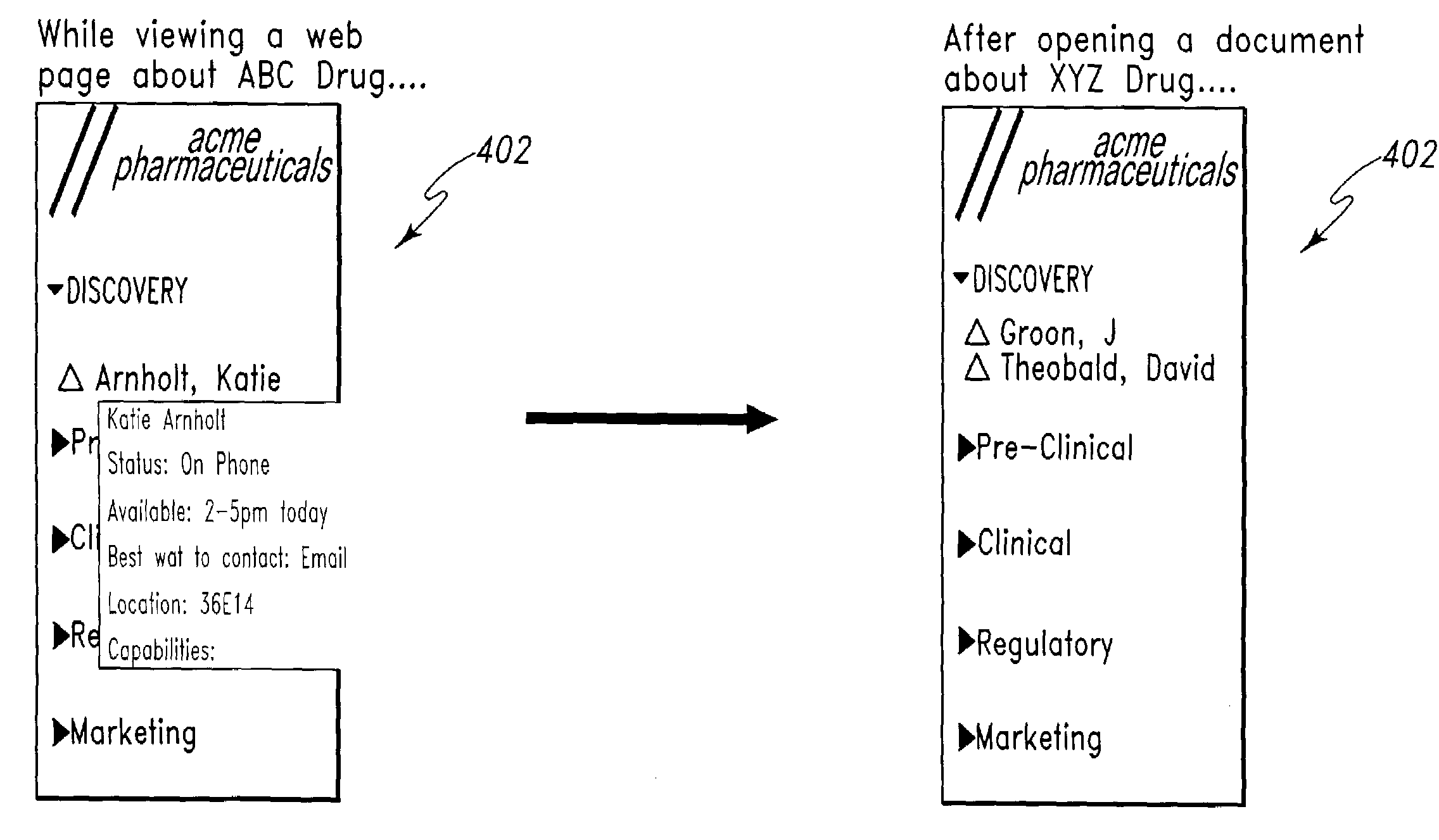
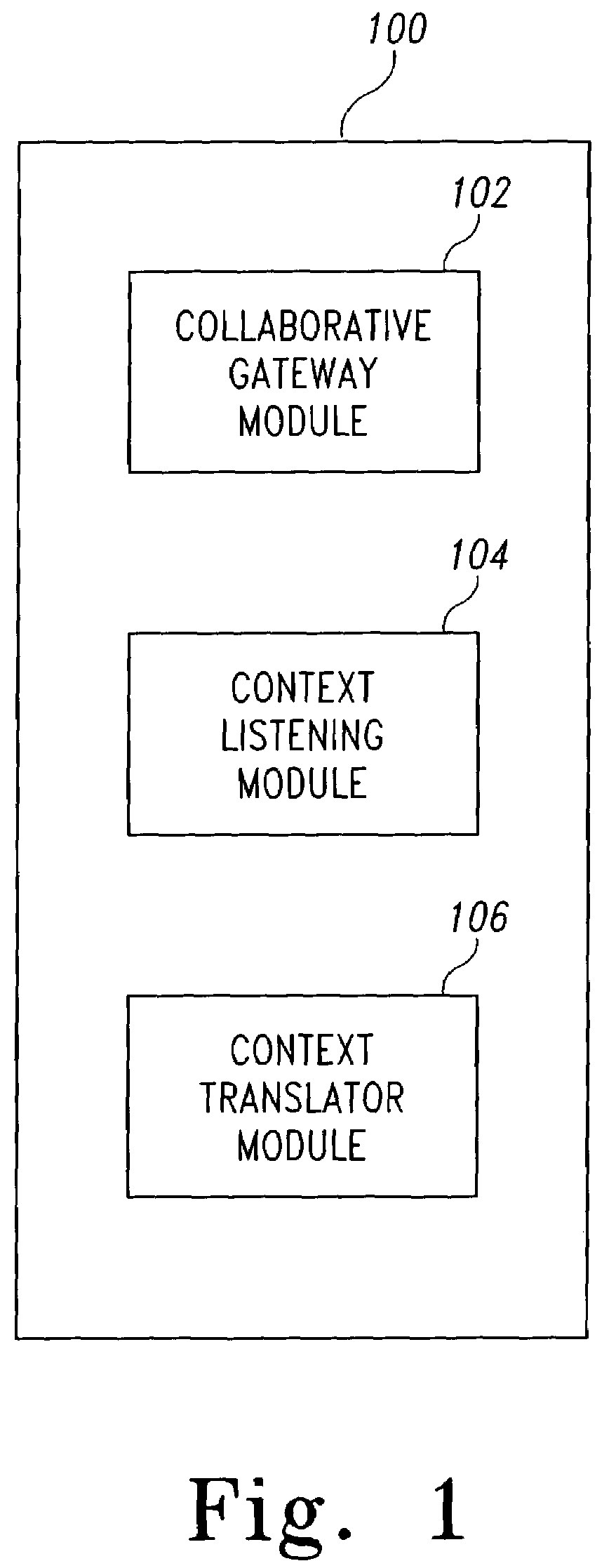
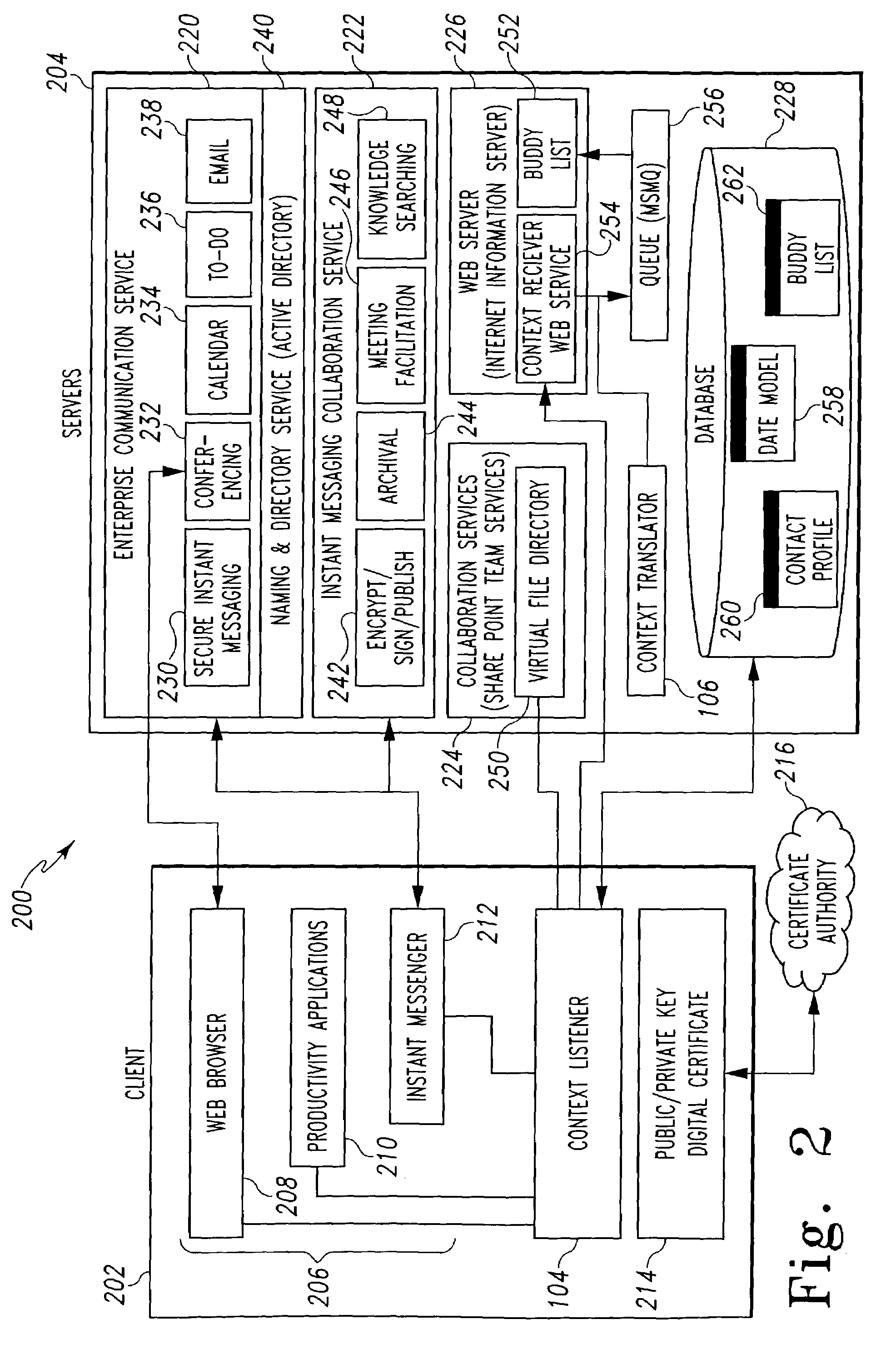
Dynamic collaboration assistant
ActiveUS7543237B2Office automationInput/output processes for data processingApplication softwareWorld Wide Web
A dynamic collaboration assistant application for use in a computing system including a terminal connected to a server. The dynamic collaboration assistant application includes a collaborative gateway application for generating a collaborative gateway GUI on the terminal. A context listener module located on the terminal is used to continuously monitor a context in which a user is using the terminal. A context translator module analyzes the context message and dynamically adjusts the display of the plurality of collaboration applications in the collaborative gateway GUI as a function of the context in which the user is using the terminal.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
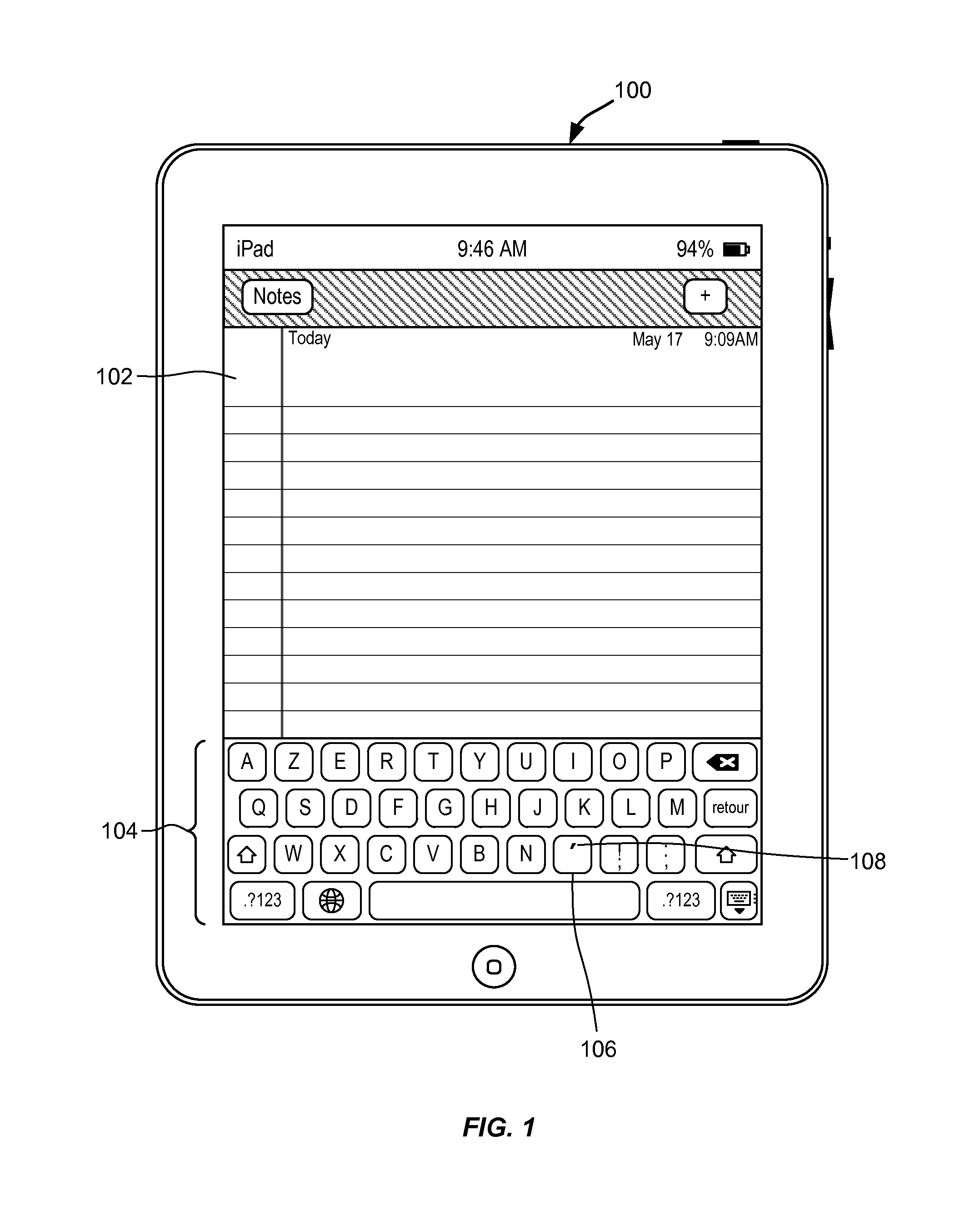
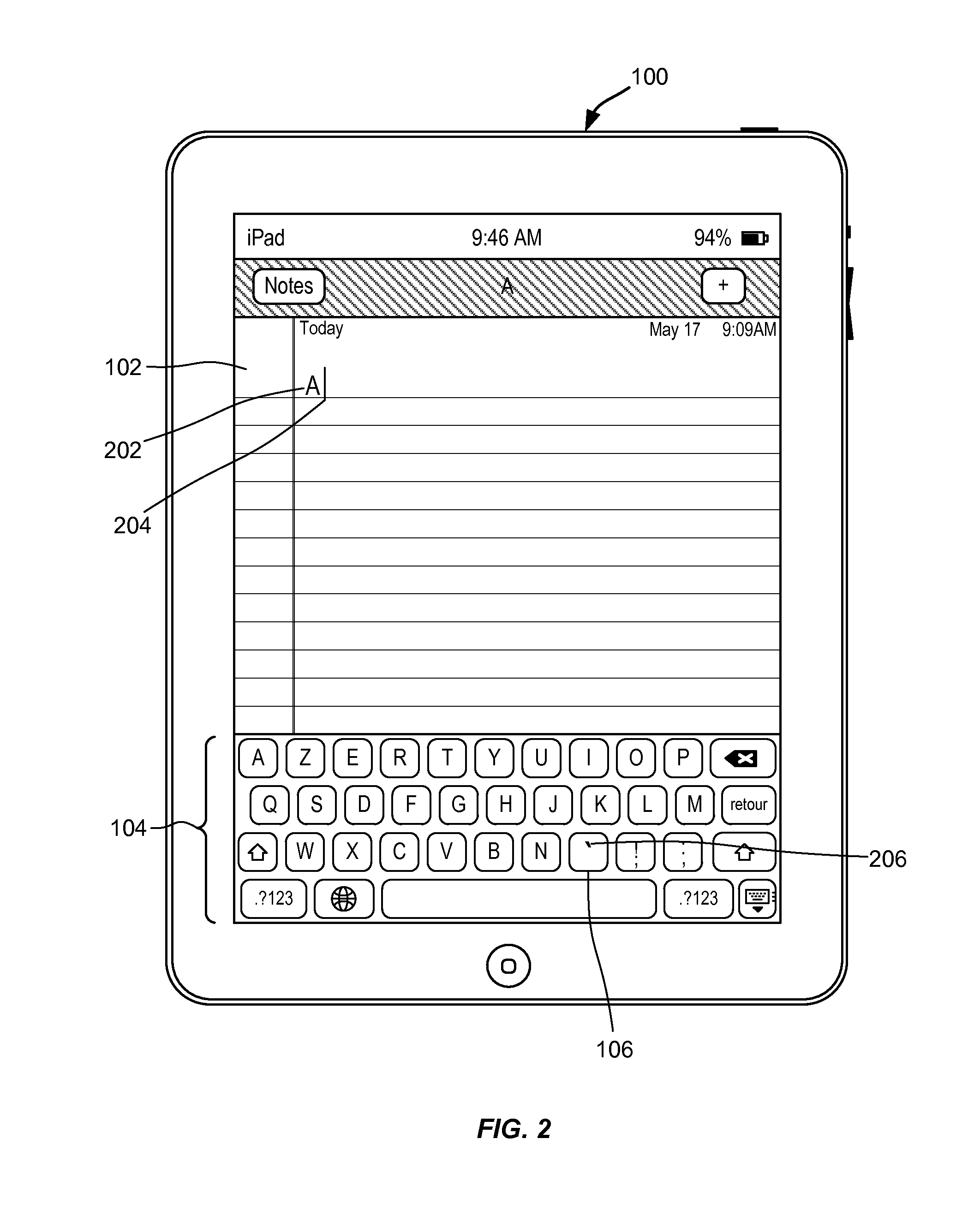
Dynamically changing a character associated with a key of a keyboard
InactiveUS20130321267A1Sure easyInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsContext basedHuman–computer interaction
A software keyboard is provided with a dedicated key (dynamic character key) for inputting a character, where the character associated with the key is determined based upon a context and may dynamically change according to the context. For example, a first character may be dynamically determined and associated with the dedicated key for a first context and a second character, possibly different from the first character, may be selected and associated with the dedicated key for a different context. The character that is associated with the dynamic character key may also be displayed on the dynamic character key. In some embodiments, the character associated with the dynamic character key may be a non-alphanumeric character such as a diacritical mark, a punctuation mark, and the like.
Owner:APPLE INC
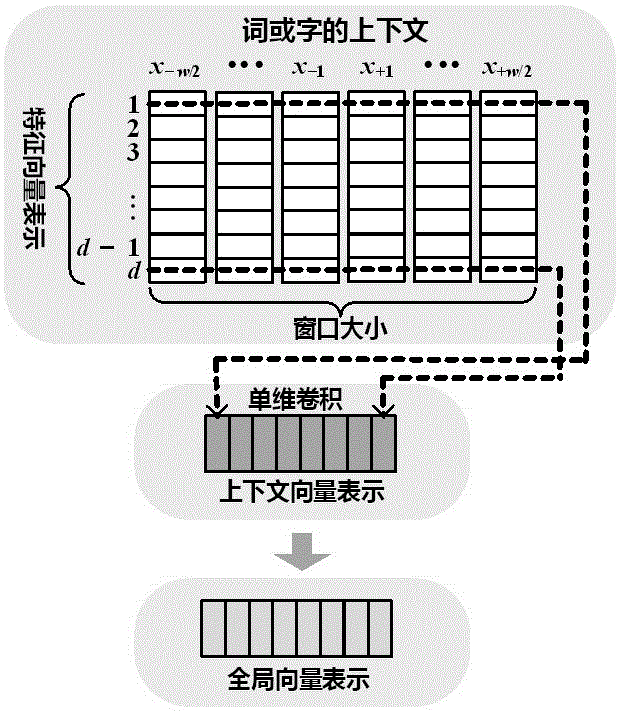
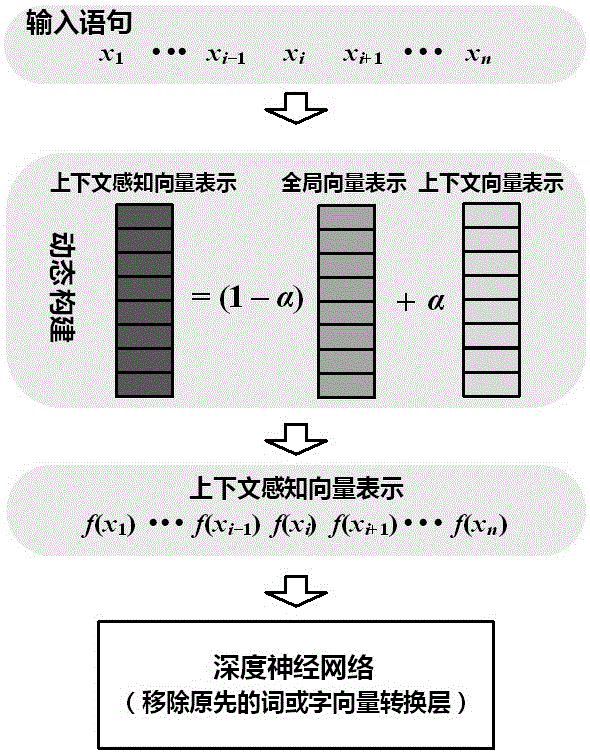
Construction and utilization method for context-aware dynamic word or character vector on the basis of deep learning
The invention belongs to the technical field of the natural language processing of computers, in particular to a construction and utilization method for a context-aware dynamic word or character vector on the basis of deep learning. The dynamic construction method for the context-aware dynamic word or character vector on the basis of the deep learning comprises the following steps of: in massive texts, through an unsupervised learning method, simultaneously learning a global feature vector of a word or character and the feature vector representation of the global feature vector when a specific context appears, and combining the global feature vector with the context feature vector, and dynamically generating word or character vector representation. By use of the method, the word or character vector dynamically constructed on the basis of the context can be applied to a natural language processing system. The method is mainly used for solving a problem that the word or character vector expresses different meanings in different contexts, i.e. the problem that one word or one character has multiple meanings can be solved. The dynamic word or character vector can be used for obviously improving the performance of various natural language processing tasks of different languages, wherein the tasks comprise Chinese word segmentation, part-of-speech tagging, naming recognition, grammatical analysis, semantic role tagging, sentiment analysis, text classification, machine translation and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Context-aware role-based access control system and control method thereof
ActiveUS20100100941A1Efficient expressionEffective controlDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPersonalizationInformation repository
A context-aware role-based access control system and a control method thereof. The context-aware role-based access control system includes: a context-aware user assignment manager (CAUAM) for performing a role assignment function, a role delegation function, or a role revocation function for a user according to a context of the user, based on a preset context request condition; a context-aware permission assignment manager (CAPAM) for performing a permission modification, a permission restoration, and a personalized permission modification for a permission, which the role has, according to changes in the context of the user; an information repository for storing a user profile and context information; and an access control manager (ACM) for controlling the context-aware user assignment manager, the context-aware permission assignment manager, and the information repository, and processing an access control request. Accordingly, more efficient access control can be achieved in ubiquitous environments where the context of the user dynamically changes.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
Selective speech recognition for chat and digital personal assistant systems
ActiveUS20160027440A1Simple technologyImprove accuracySpeech recognitionAddress bookSpeech identification
Disclosed are computer-implemented methods and systems for dynamic selection of speech recognition systems for the use in Chat Information Systems (CIS) based on multiple criteria and context of human-machine interaction. Specifically, once a first user audio input is received, it is analyzed so as to locate specific triggers, determine the context of the interaction or predict the subsequent user audio inputs. Based on at least one of these criteria, one of a free-diction recognizer, pattern-based recognizer, address book based recognizer or dynamically created recognizer is selected for recognizing the subsequent user audio input. The methods described herein increase the accuracy of automatic recognition of user voice commands, thereby enhancing overall user experience of using CIS, chat agents and similar digital personal assistant systems.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Dynamic chart control that triggers dynamic contextual actions
A system and method are described herein that provide for dynamically controlling a chart visualized in a user interface by turning business objects visualized in the chart into clickable action buttons to trigger corresponding business actions. Business objects are retrieved from a backend server and displayed as visual representations in a chart rendered in a calendar application user interface. A user clicking or tapping a visual representation in the chart triggers a corresponding predefined action that has been customized in the connected system or backend server and is dynamically assigned to the chart control based on the business context of the calendar application.
Owner:SAP AG
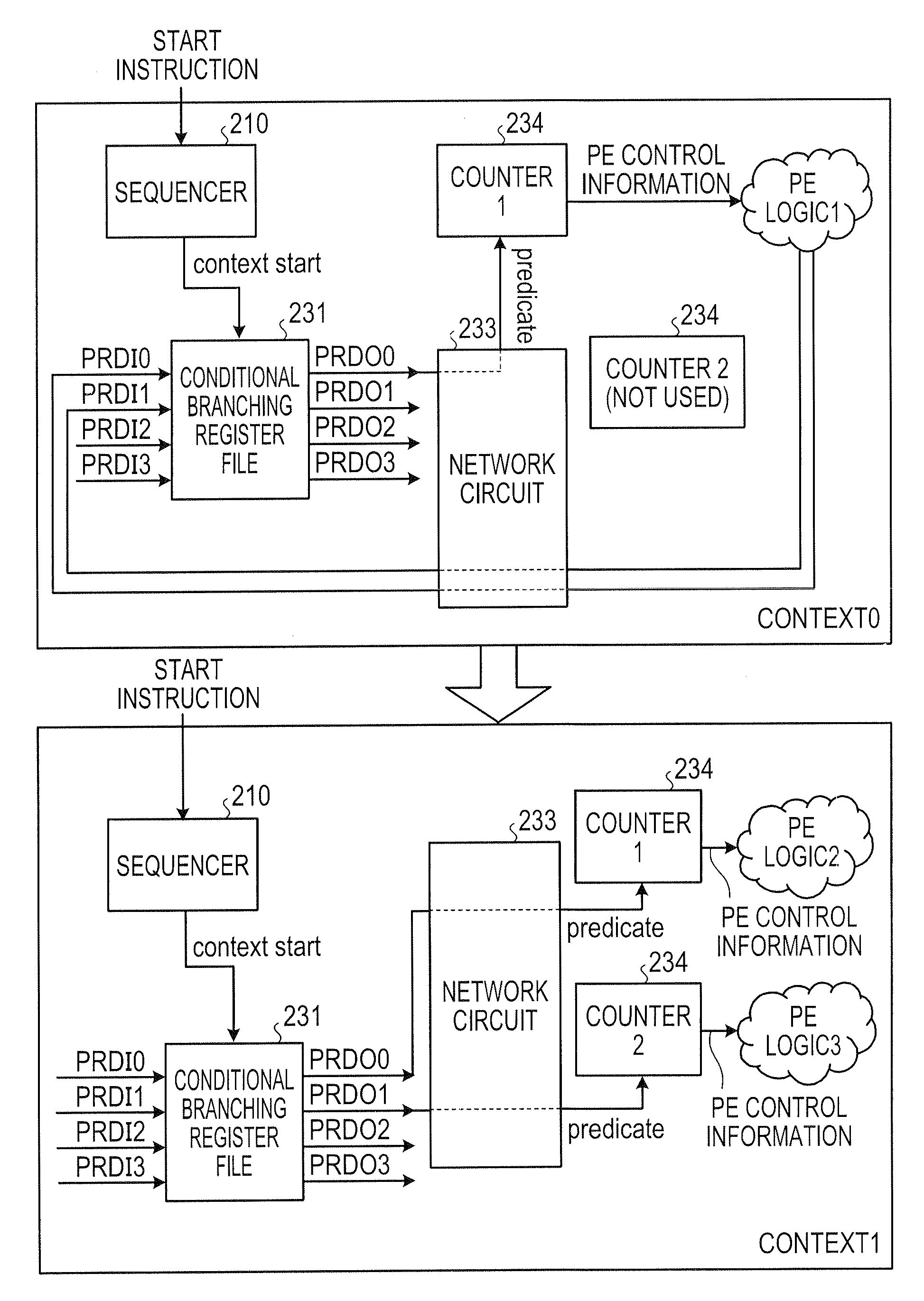
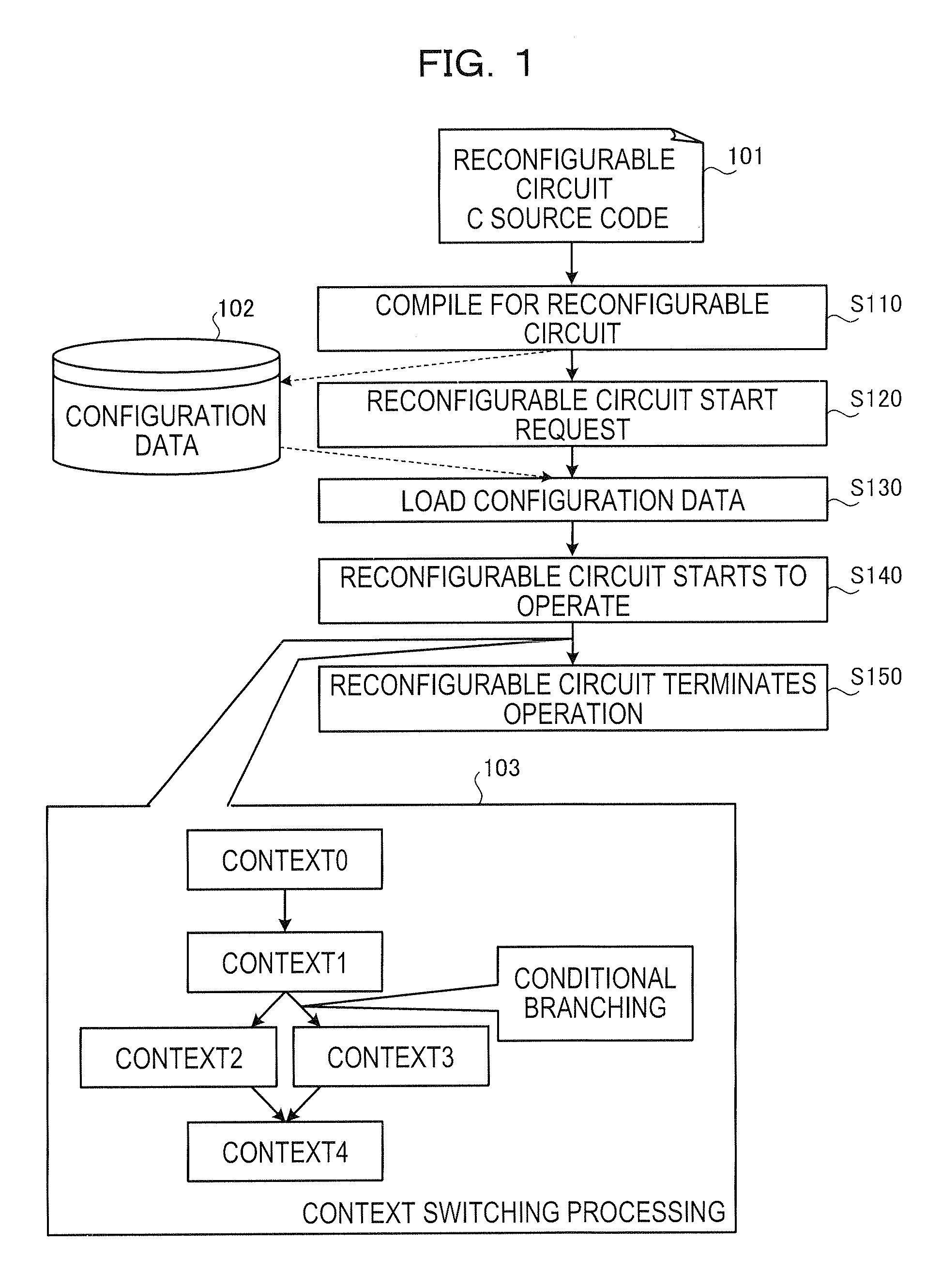
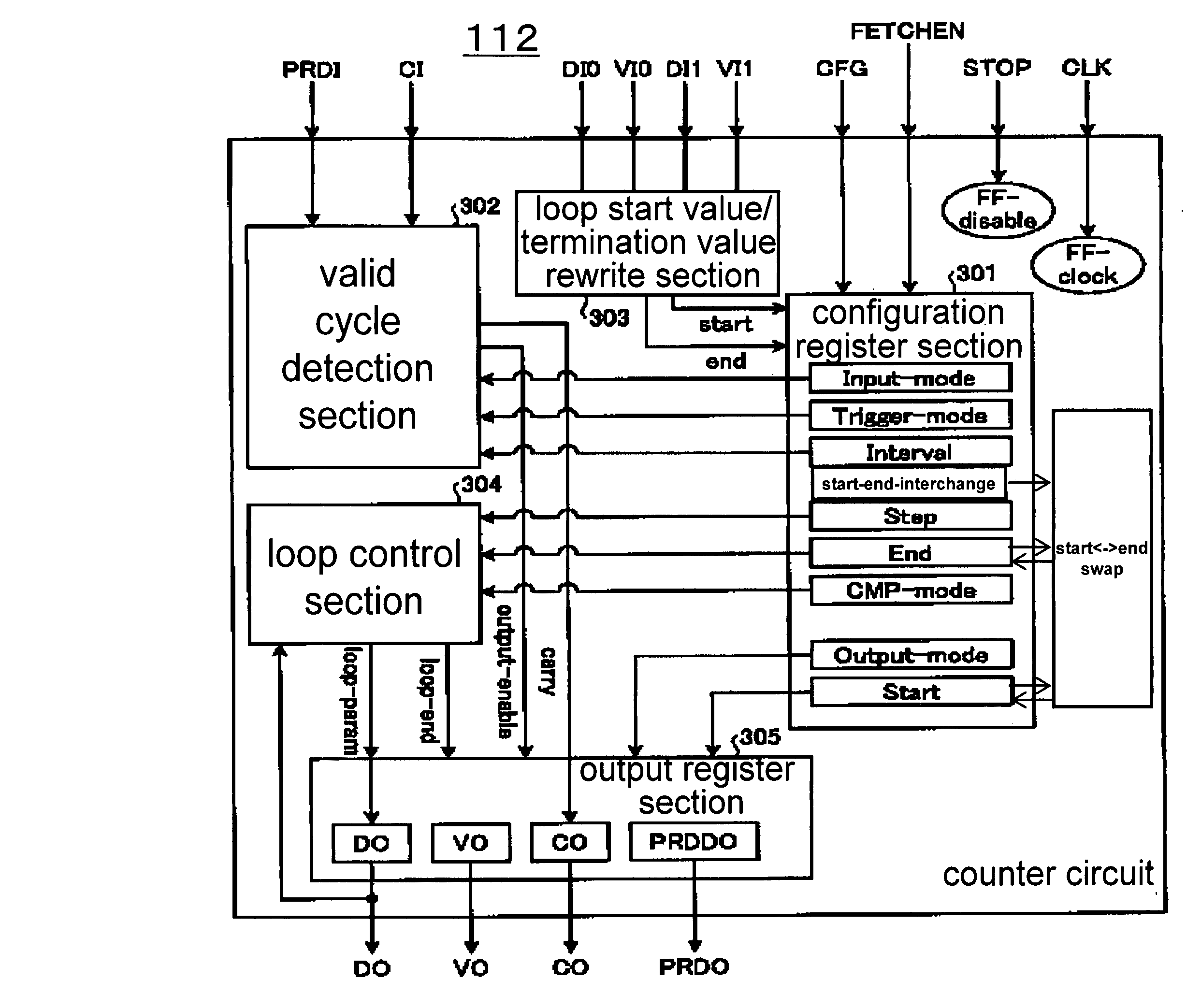
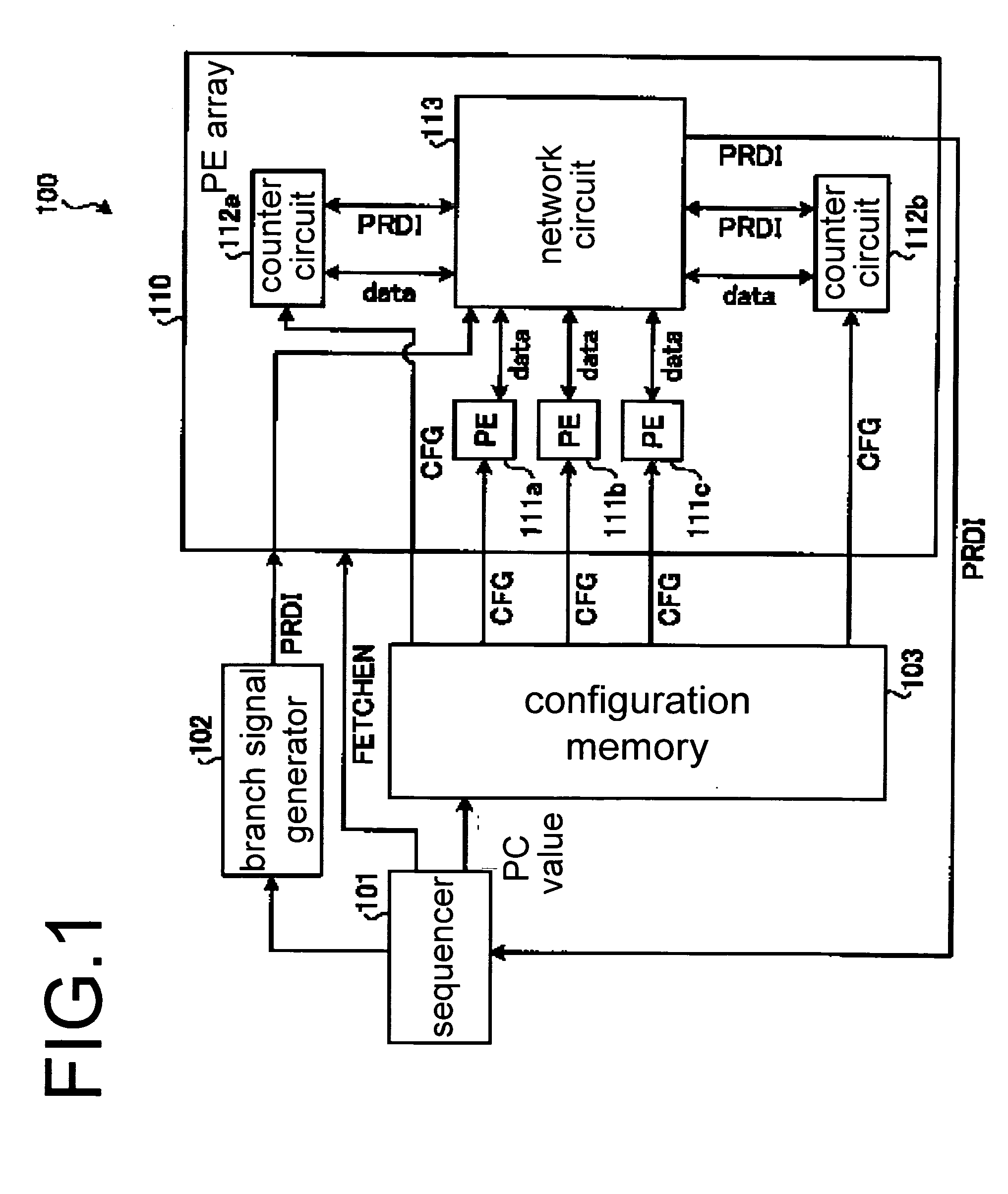
Counter control circuit, dynamic reconfigurable circuit, and loop processing control method
InactiveUS20090193239A1Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionProcessing elementControl circuit
A counter control circuit that controls the operation of a counter arranged in a dynamic reconfigurable circuit executing an arbitrary instruction by dynamically switching an aggregation of reconfigurable processing elements (hereinafter referred to as “PEs”) according to a context reciting a processing content of the PE and a connection content between the PEs, the counter control circuit including: keeping means for keeping an operation instruction signal when the PE executing a conditional branching computation outputs, in a context being adapted to the dynamic reconfigurable circuit, the operation instruction signal of the counter for a subsequent context; output means for outputting the operation instruction signal kept in the keeping means to the counter; and control means for causing the output means to output the operation instruction signal when the context being adapted to the dynamic reconfigurable circuit is switched to the subsequent context.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Dynamic aggression management of cellular connectivity
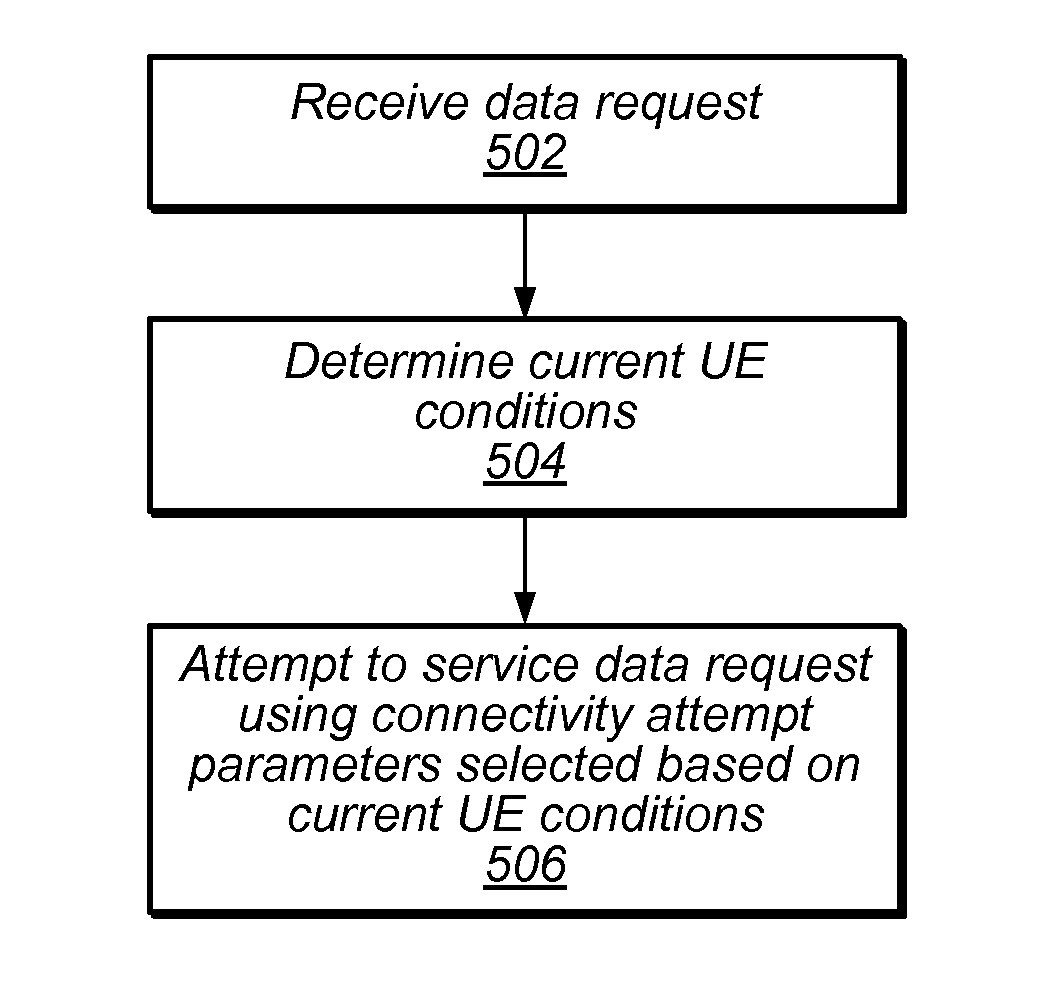
ActiveUS9414298B1Less aggressiveMore aggressivePower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunicationsActivity level
This disclosure relates to techniques for dynamic selection of connection attempt throttling algorithms based on user context. According to some embodiments, a wireless device may monitor certain current conditions of the UE, such as battery level, user activity level, motion level, and / or other conditions. Depending at least in part on the current conditions of the UE, cellular connection attempt parameters may be selected. In some conditions the cellular connection attempt parameters may be selected such as to allow more aggressive pursuit of cellular connectivity, while in other conditions the cellular connection attempt parameters may be selected such as to allow less aggressive pursuit of cellular connectivity.
Owner:APPLE INC
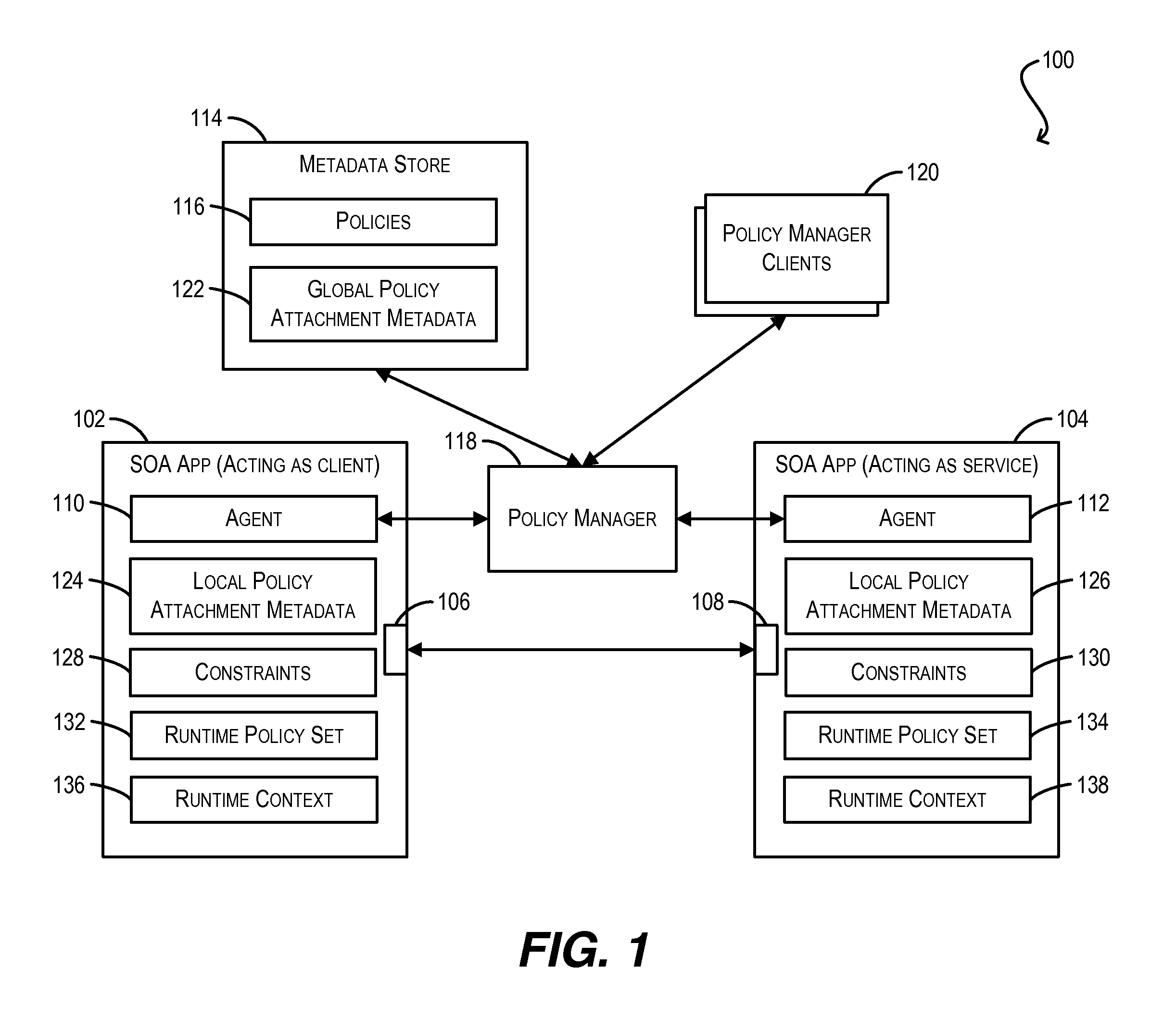
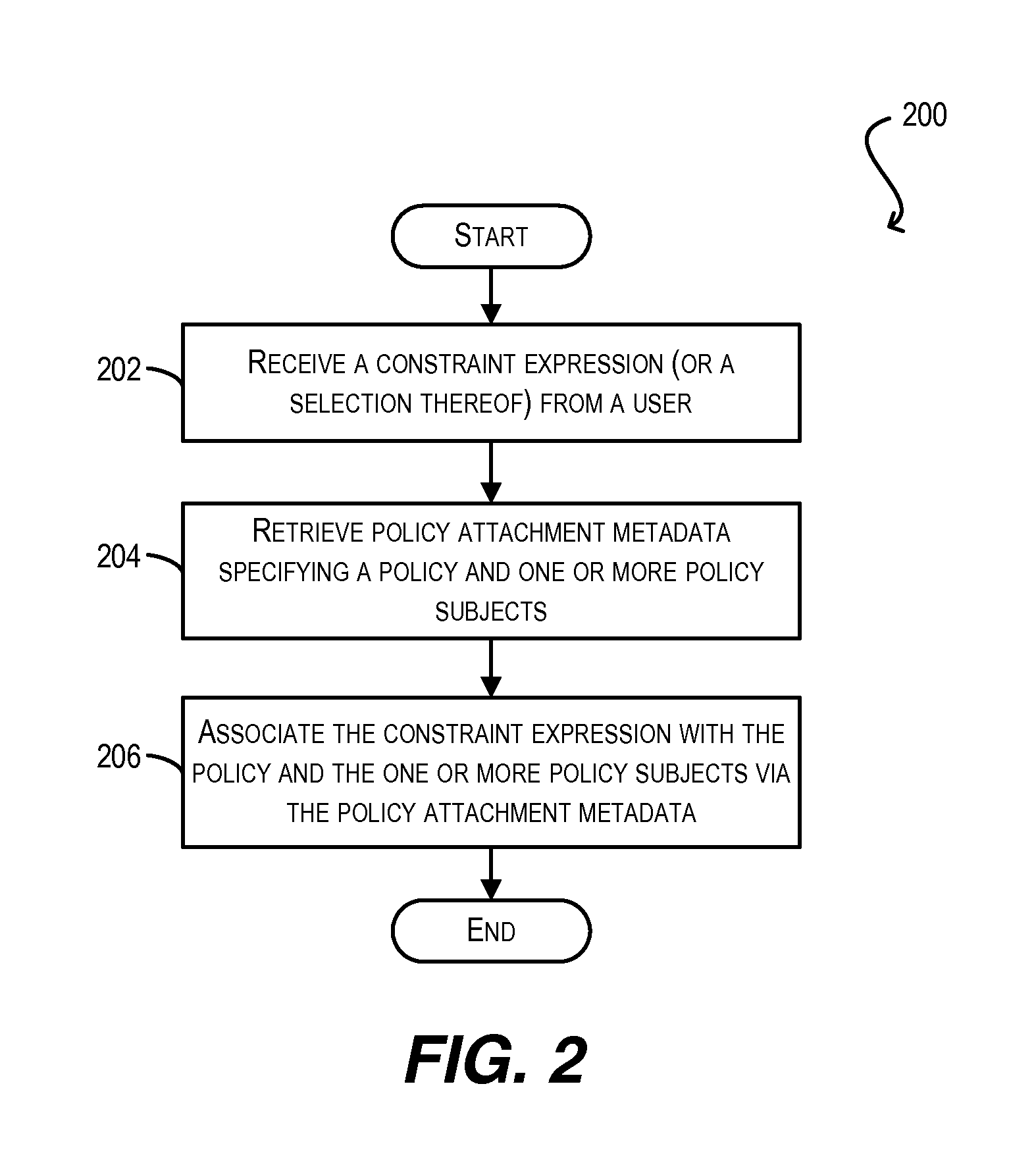
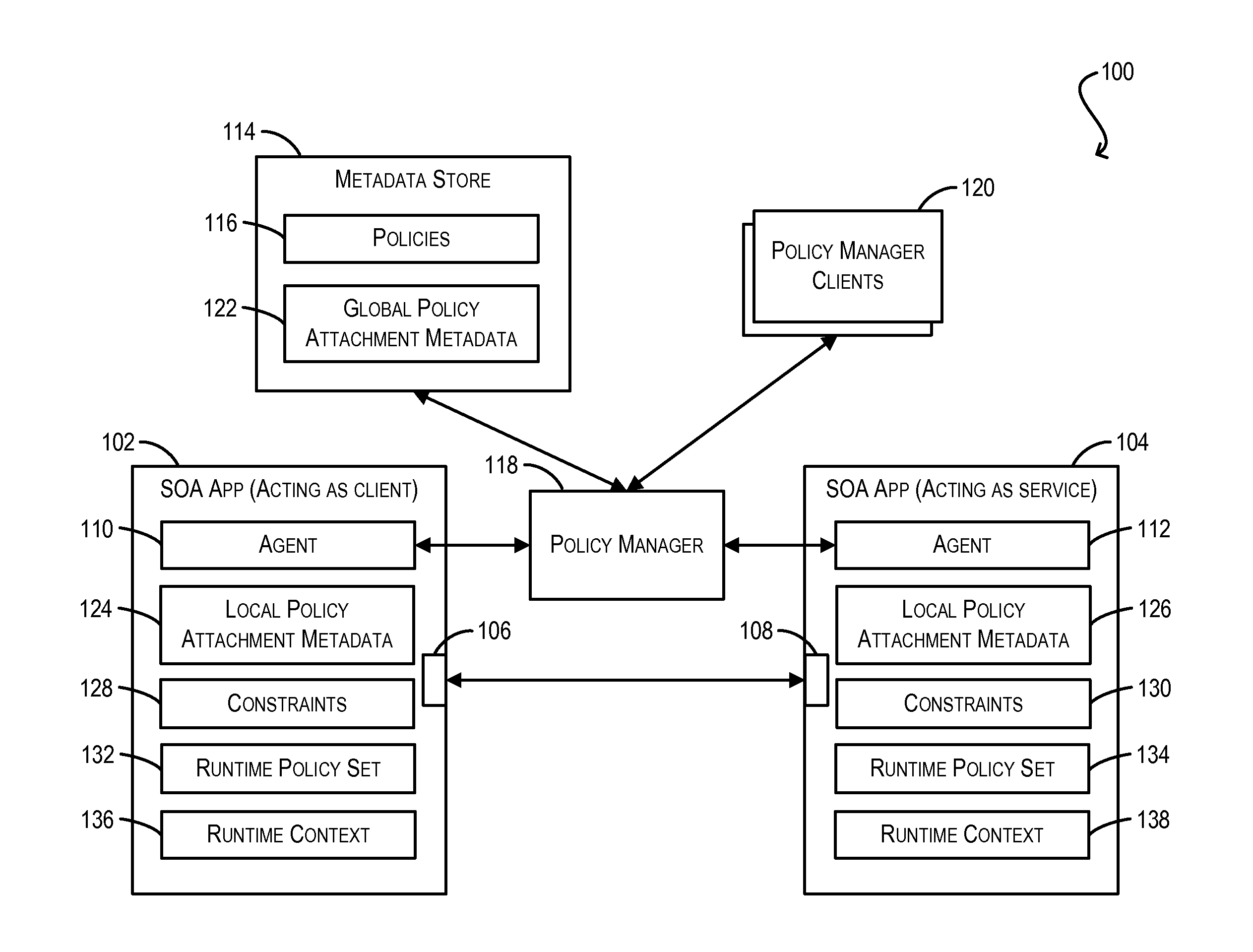
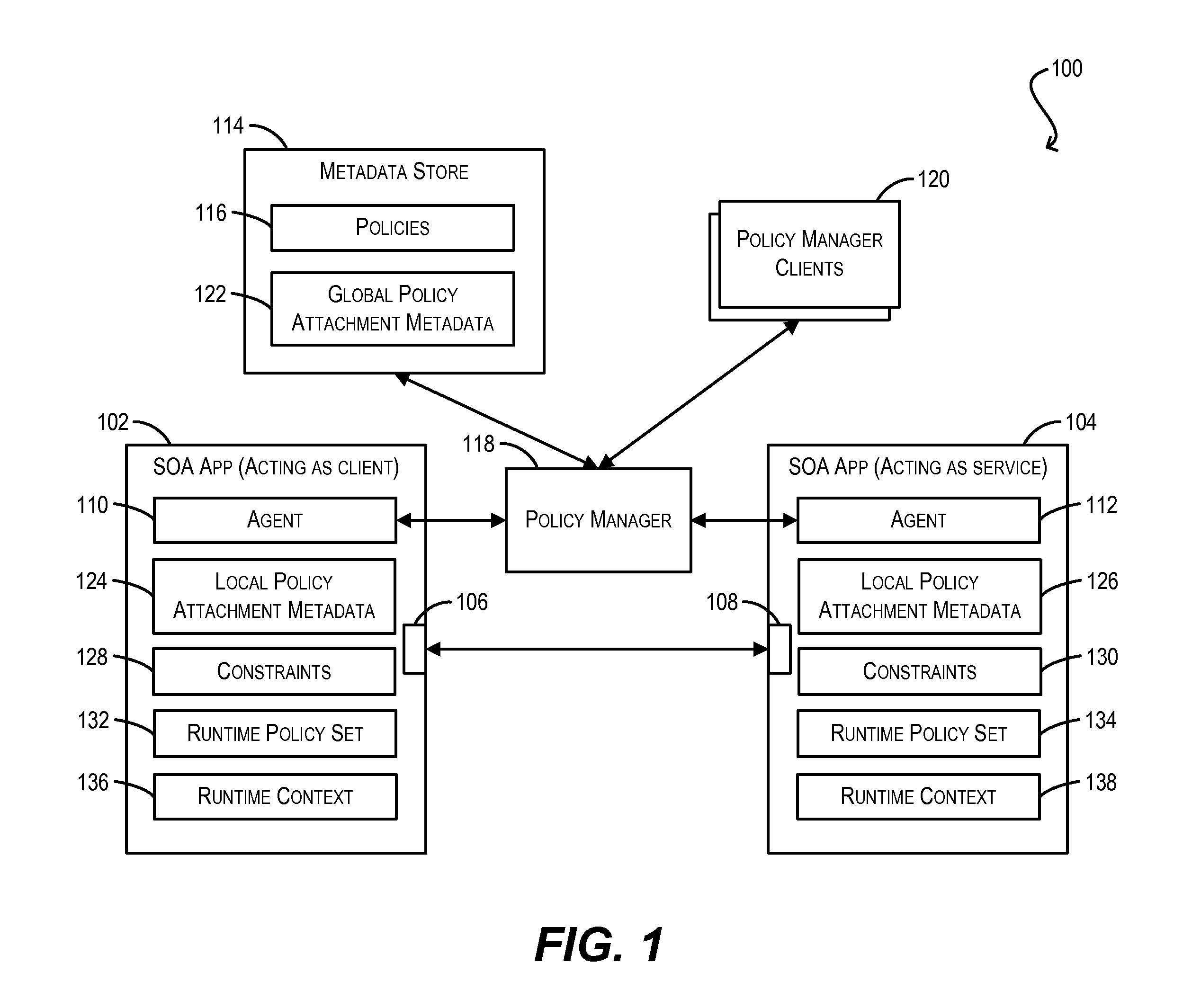
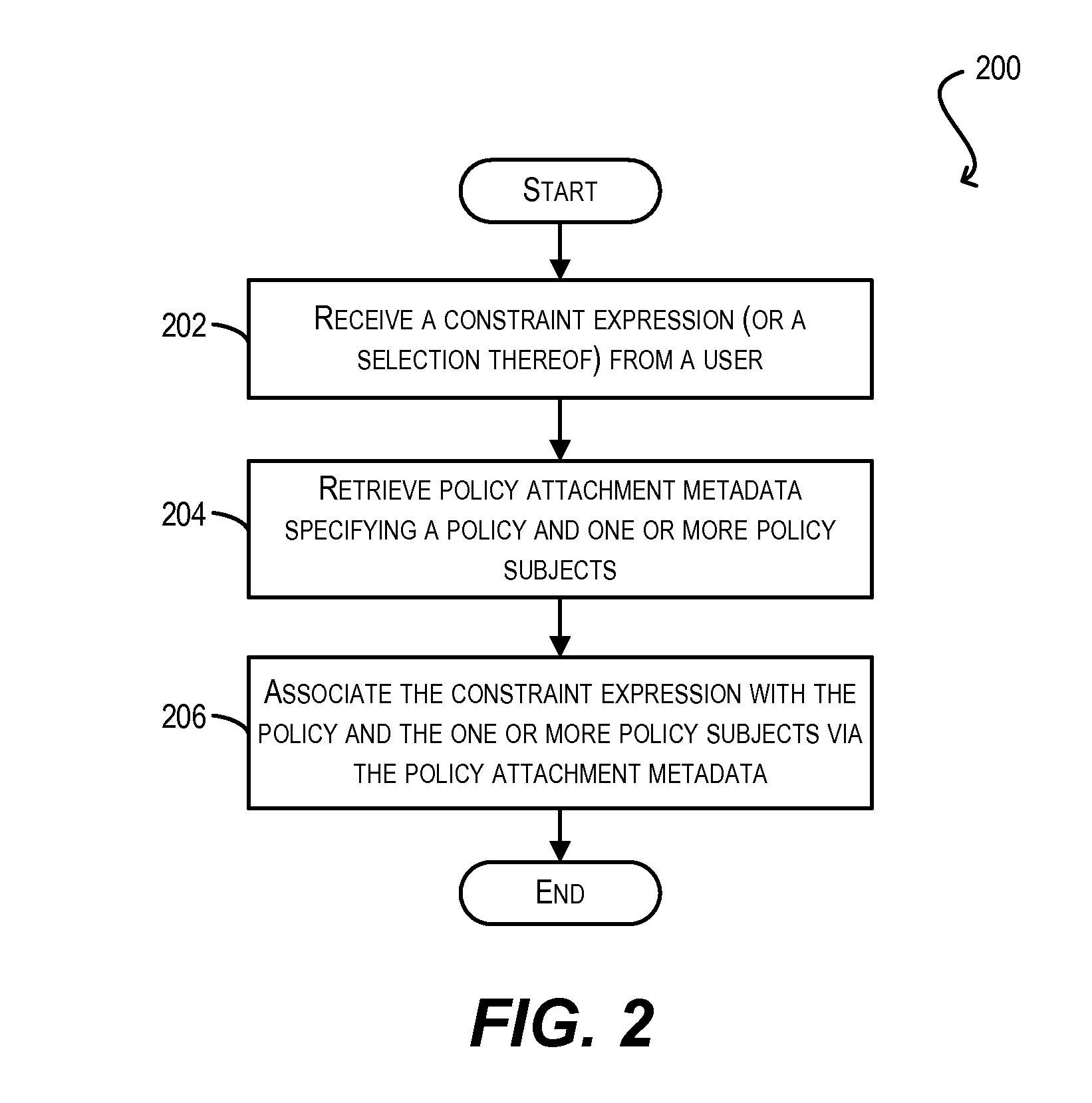
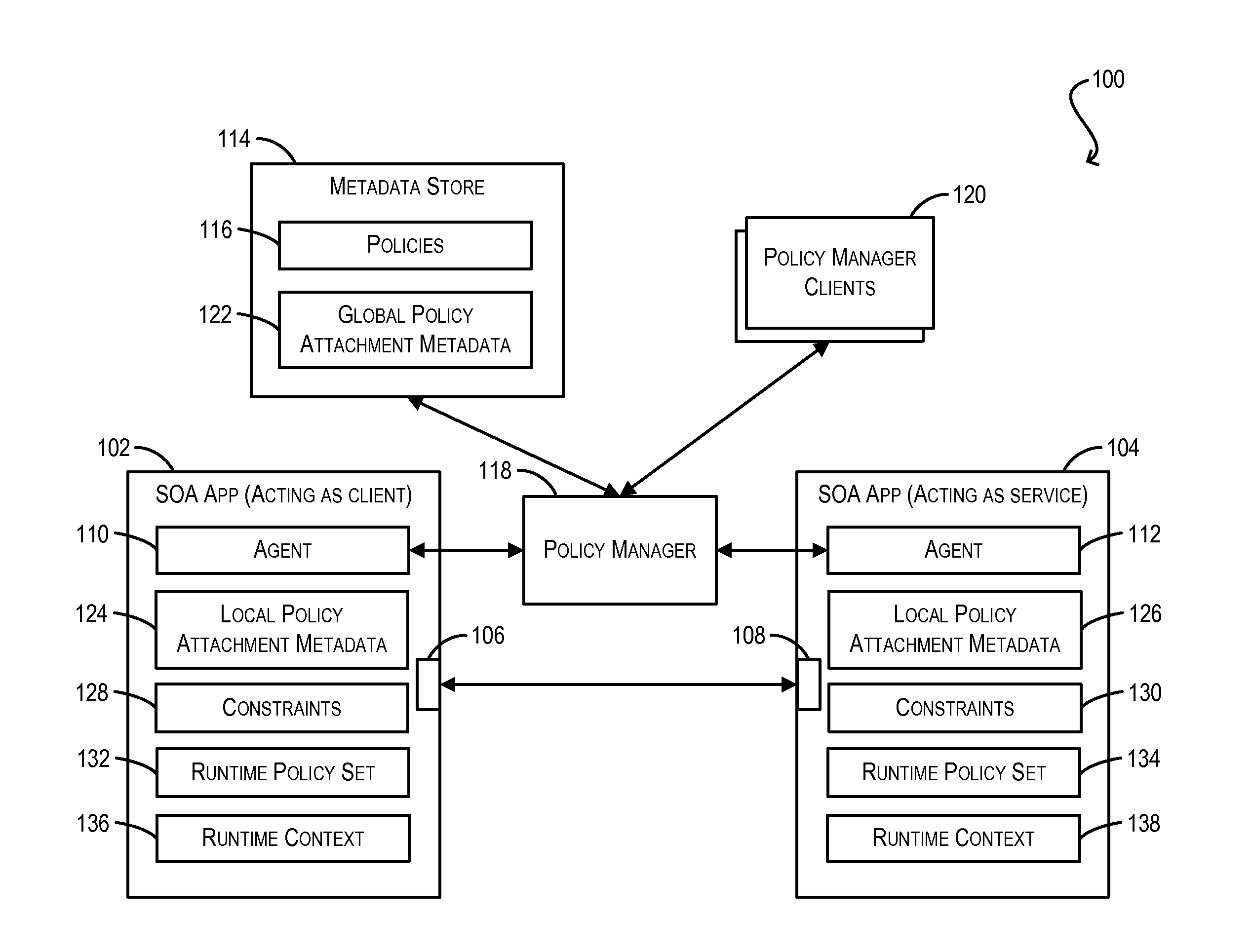
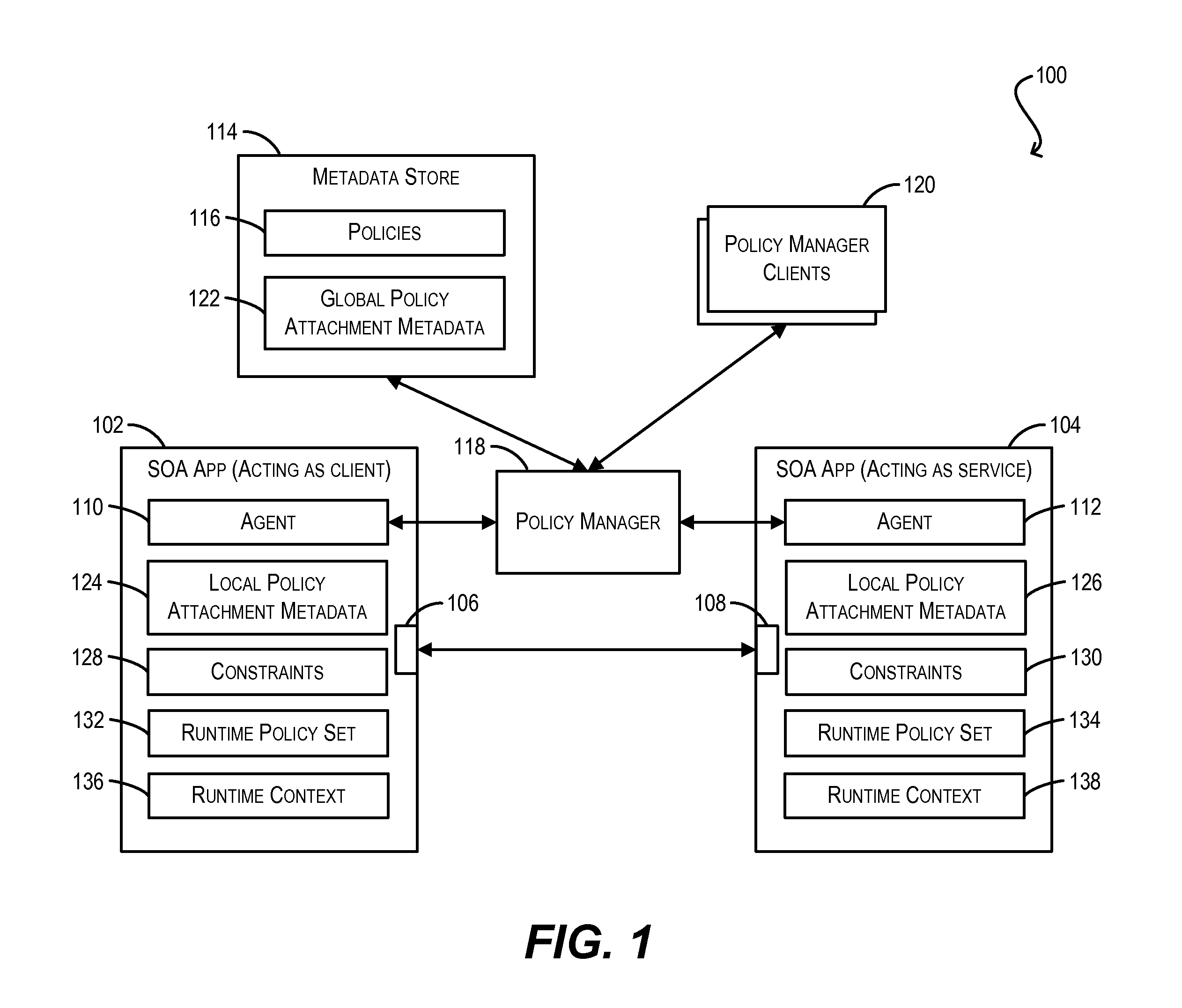
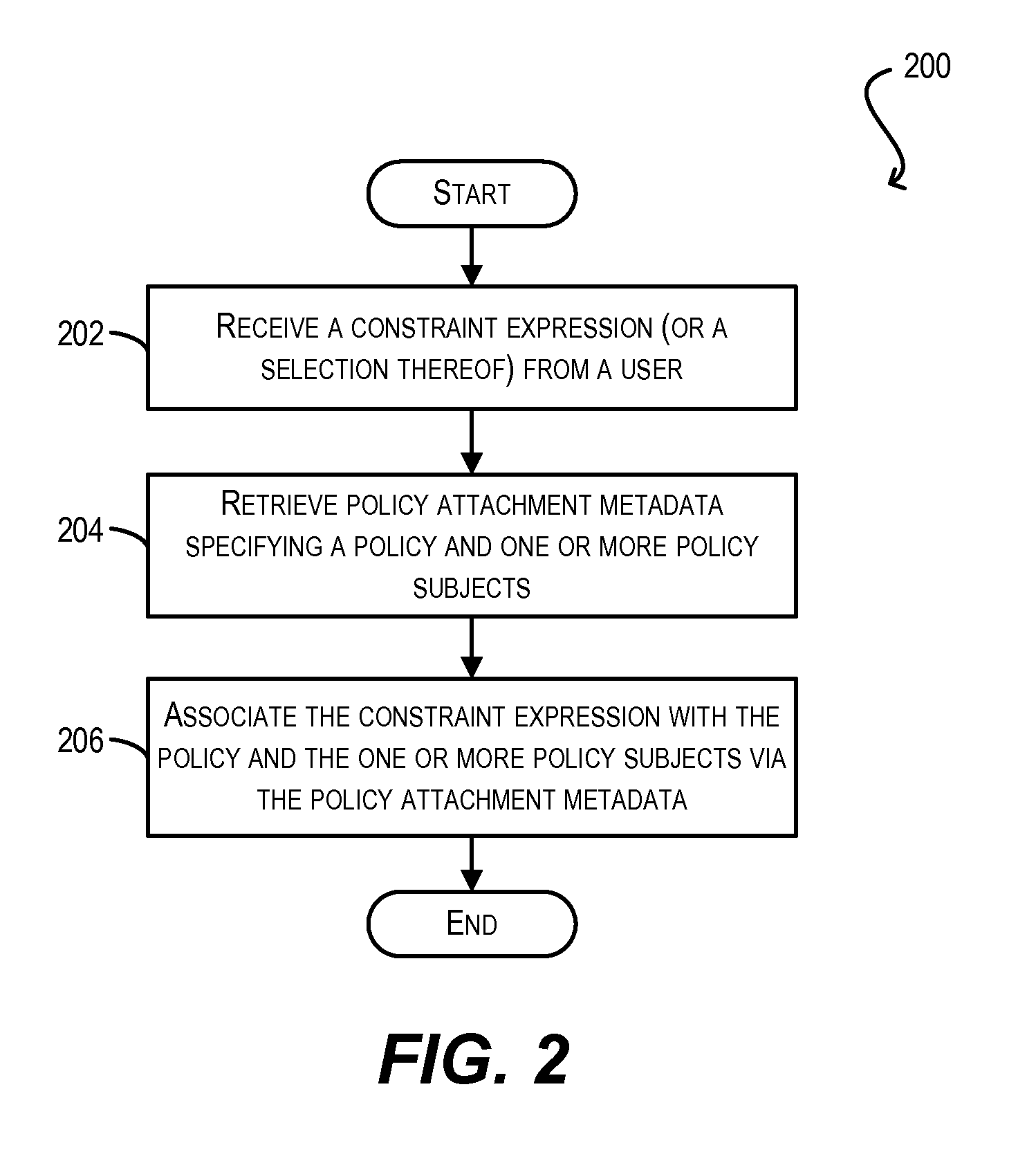
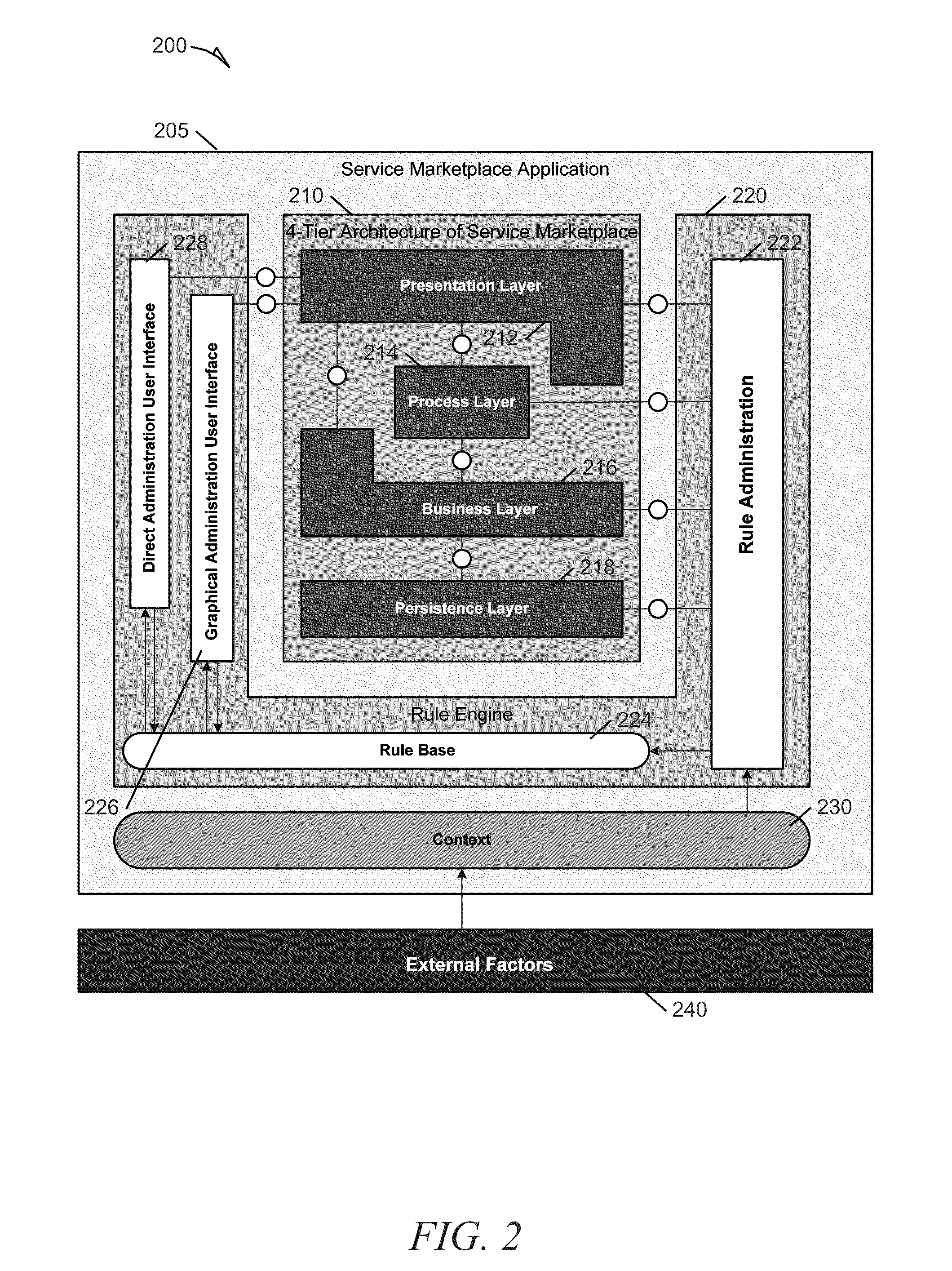
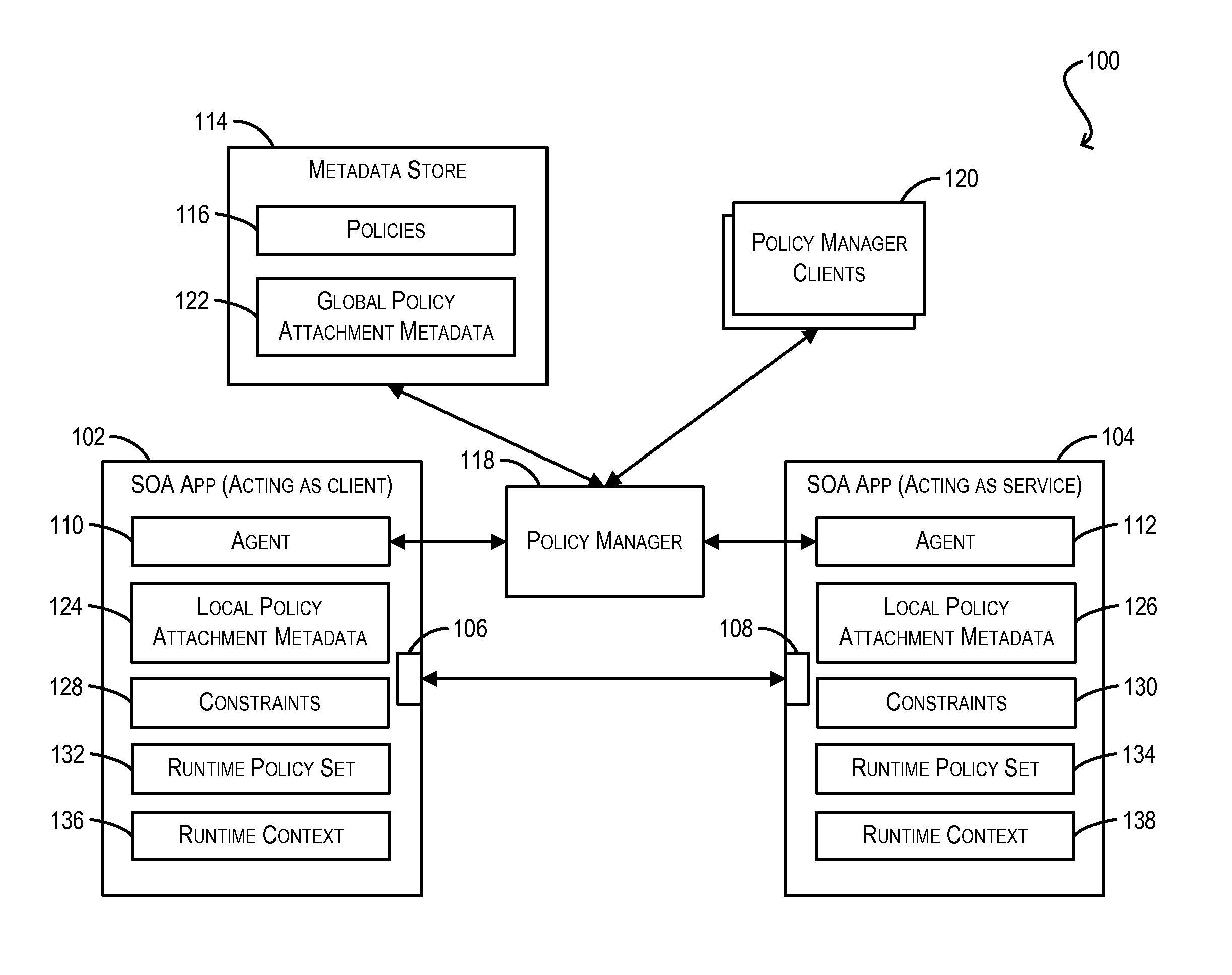
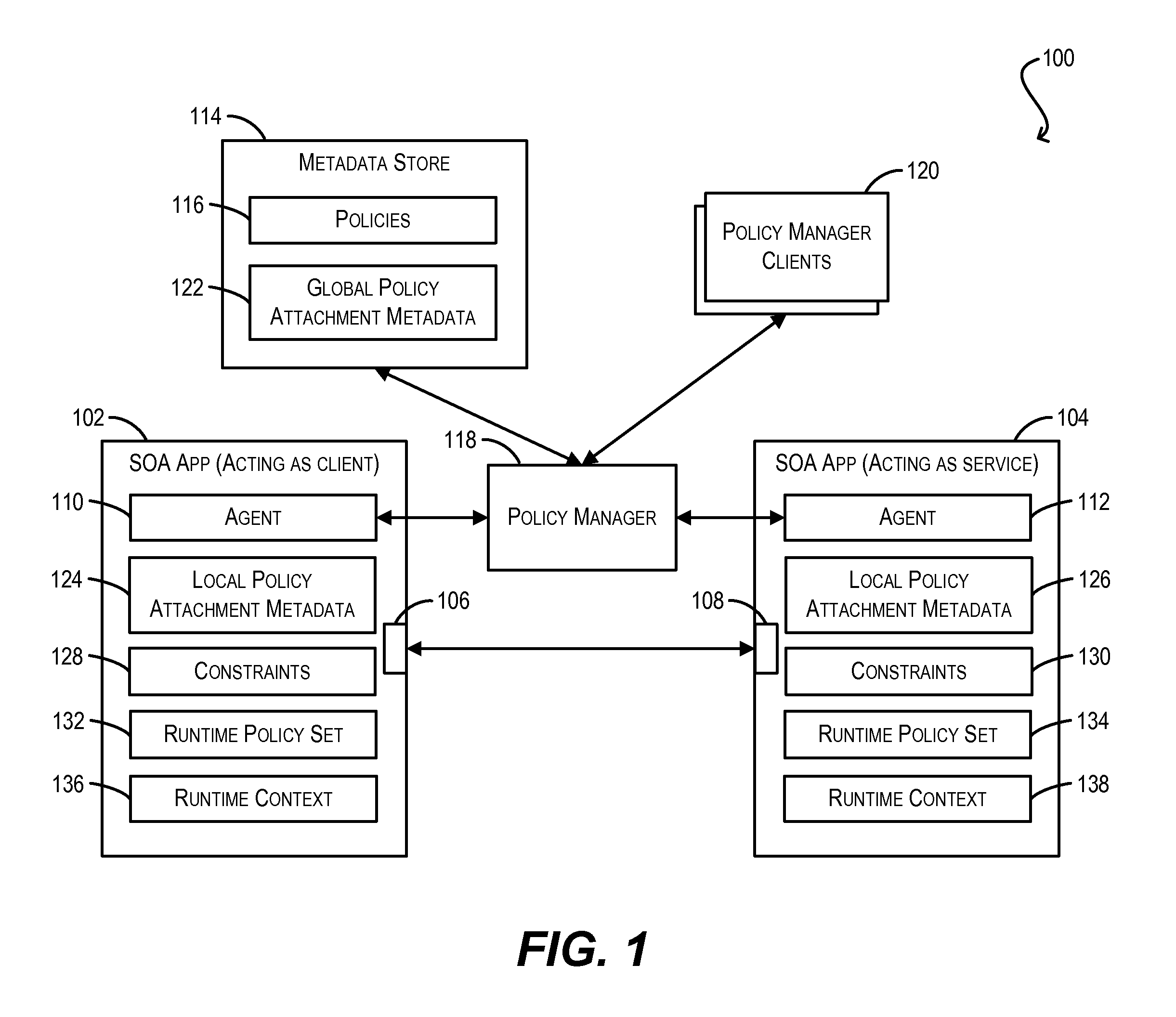
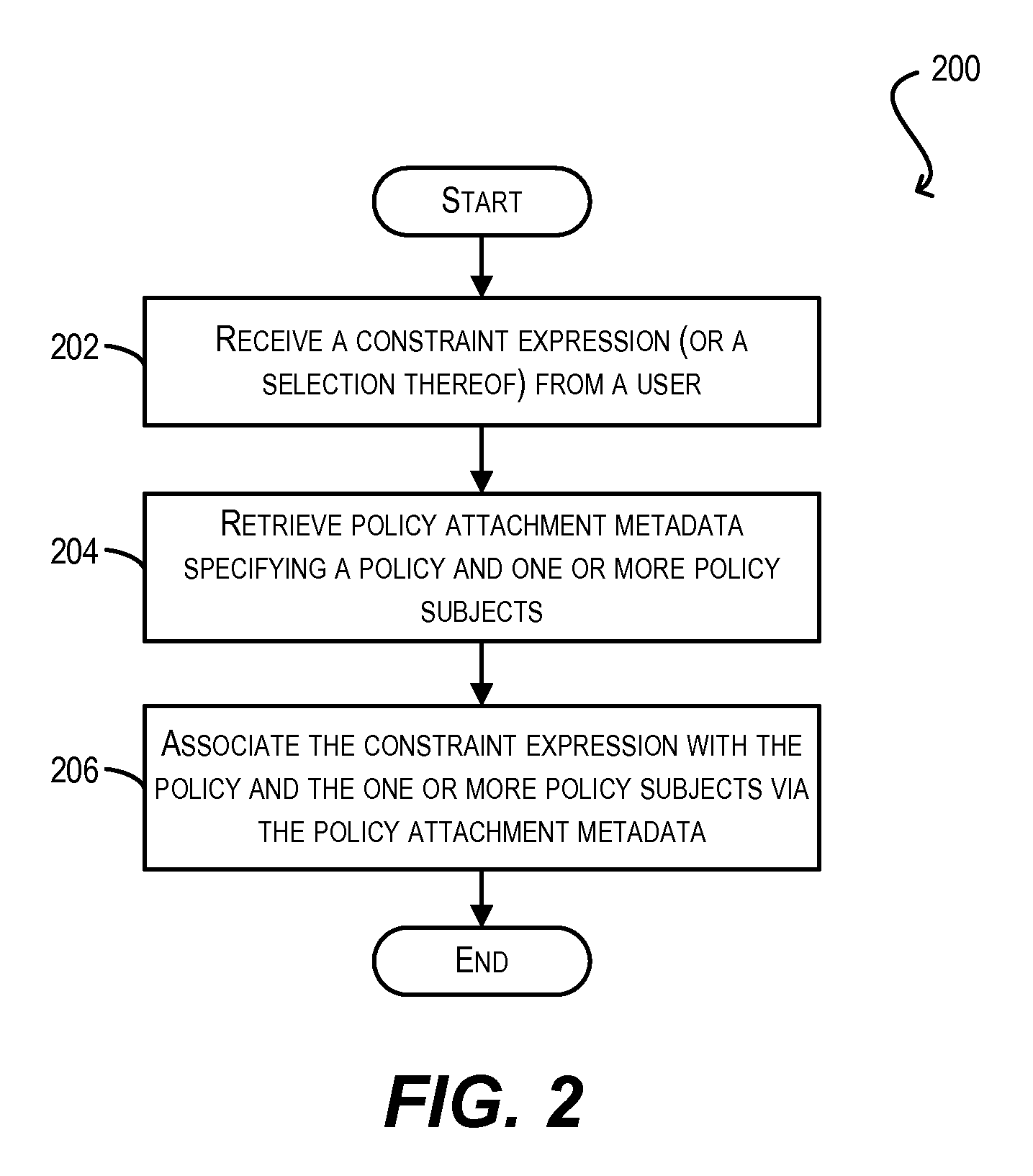
Constraint definition for conditional policy attachments
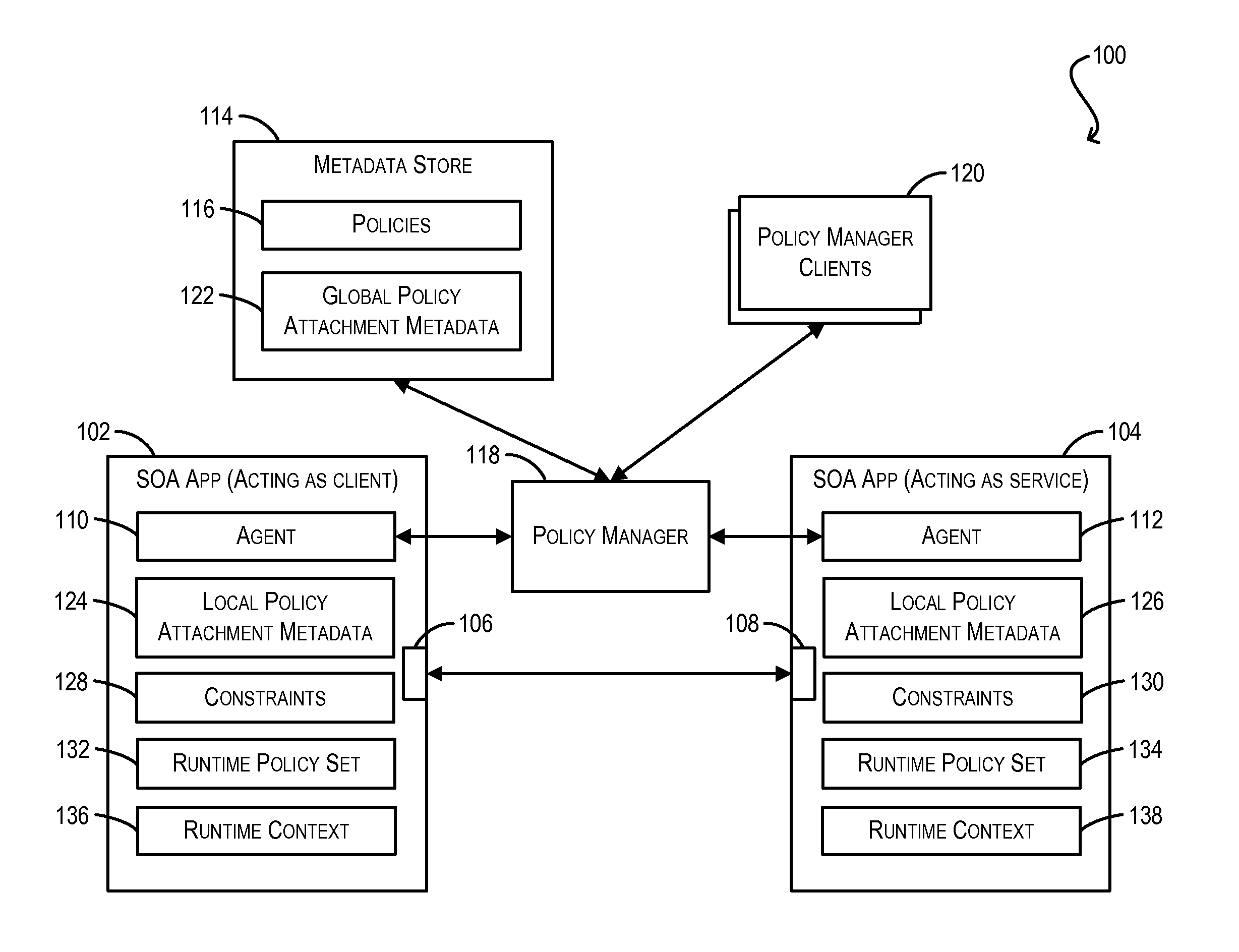
ActiveUS20130086626A1Raise priorityDigital computer detailsComputer security arrangementsWeb serviceClient-side
Framework for conditionally attaching web service policies to a policy subject (e.g., a web service client or service endpoint) at subject runtime. In one set of embodiments, a constraint expression can be defined that specifies one or more runtime conditions under which a policy should be attached to a policy subject. The constraint expression can be associated with the policy and the policy subject via policy attachment metadata. The constraint expression can then be evaluated at runtime of the policy subject to determine whether attachment of the policy to the policy subject should occur. If the evaluation indicates that the policy should be attached, the attached policy can be processed at the policy subject (e.g., enforced or advertised) as appropriate. Using these techniques, the policy subject can be configured to dynamically exhibit different behaviors based on its runtime context.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
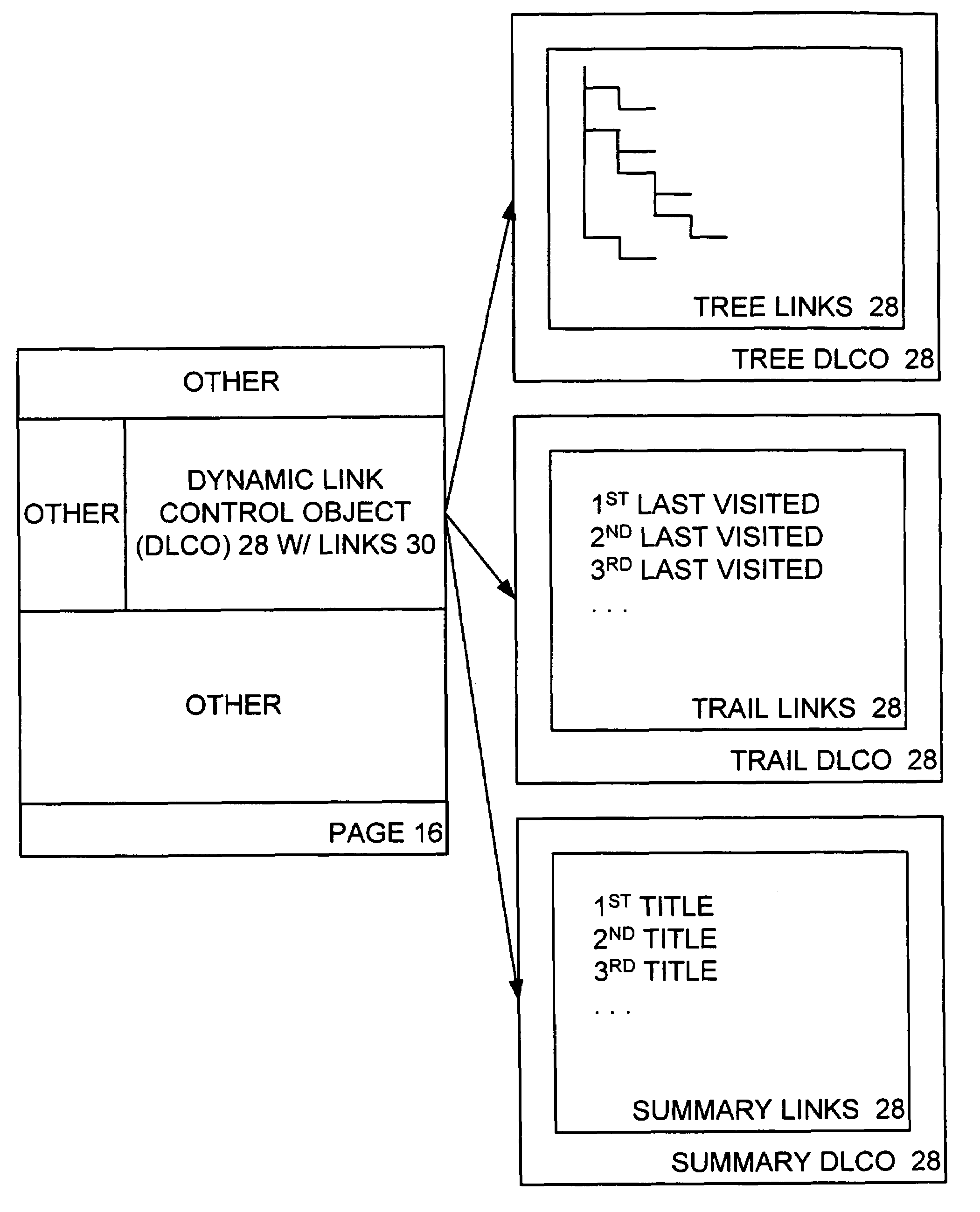
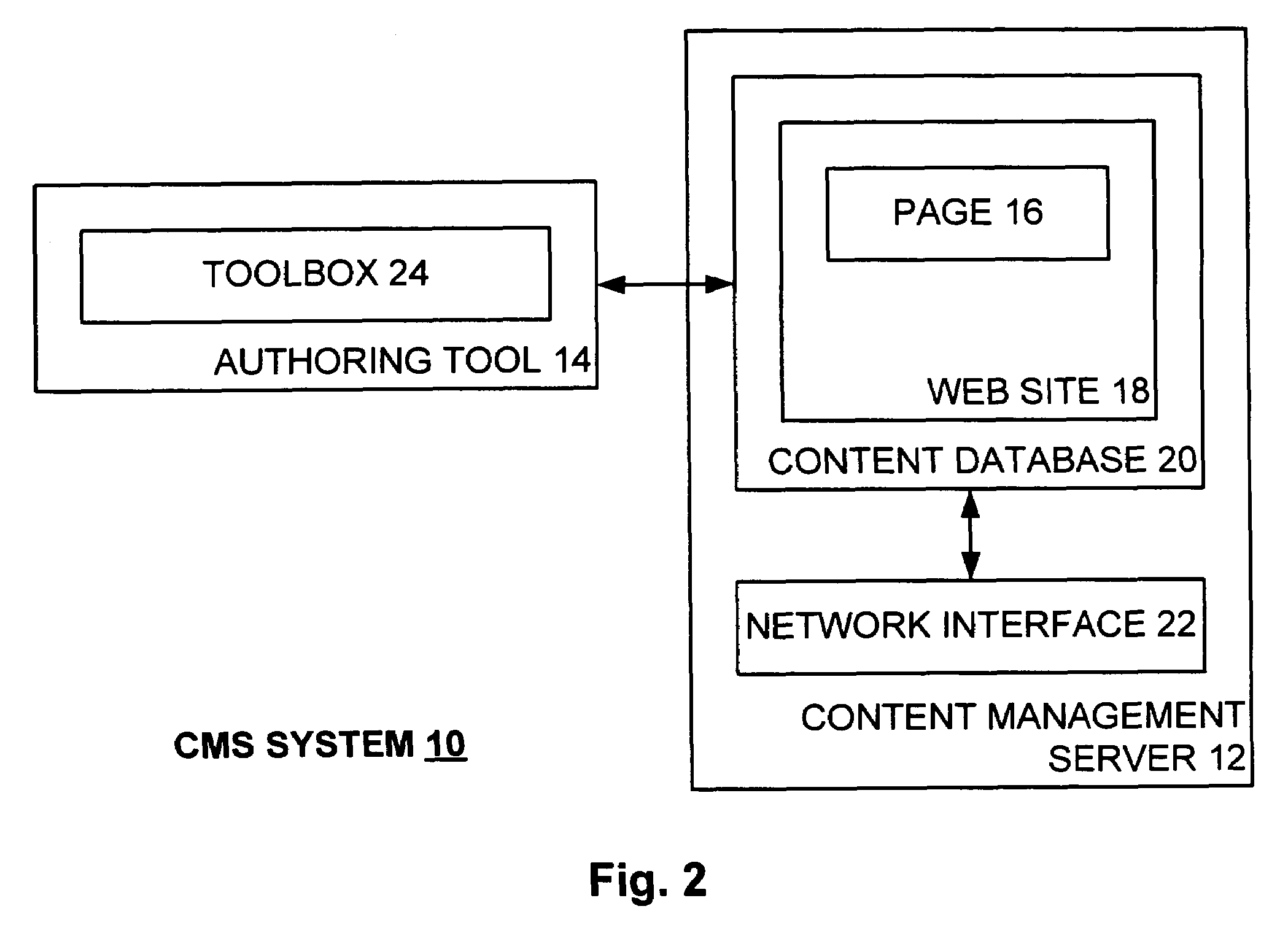
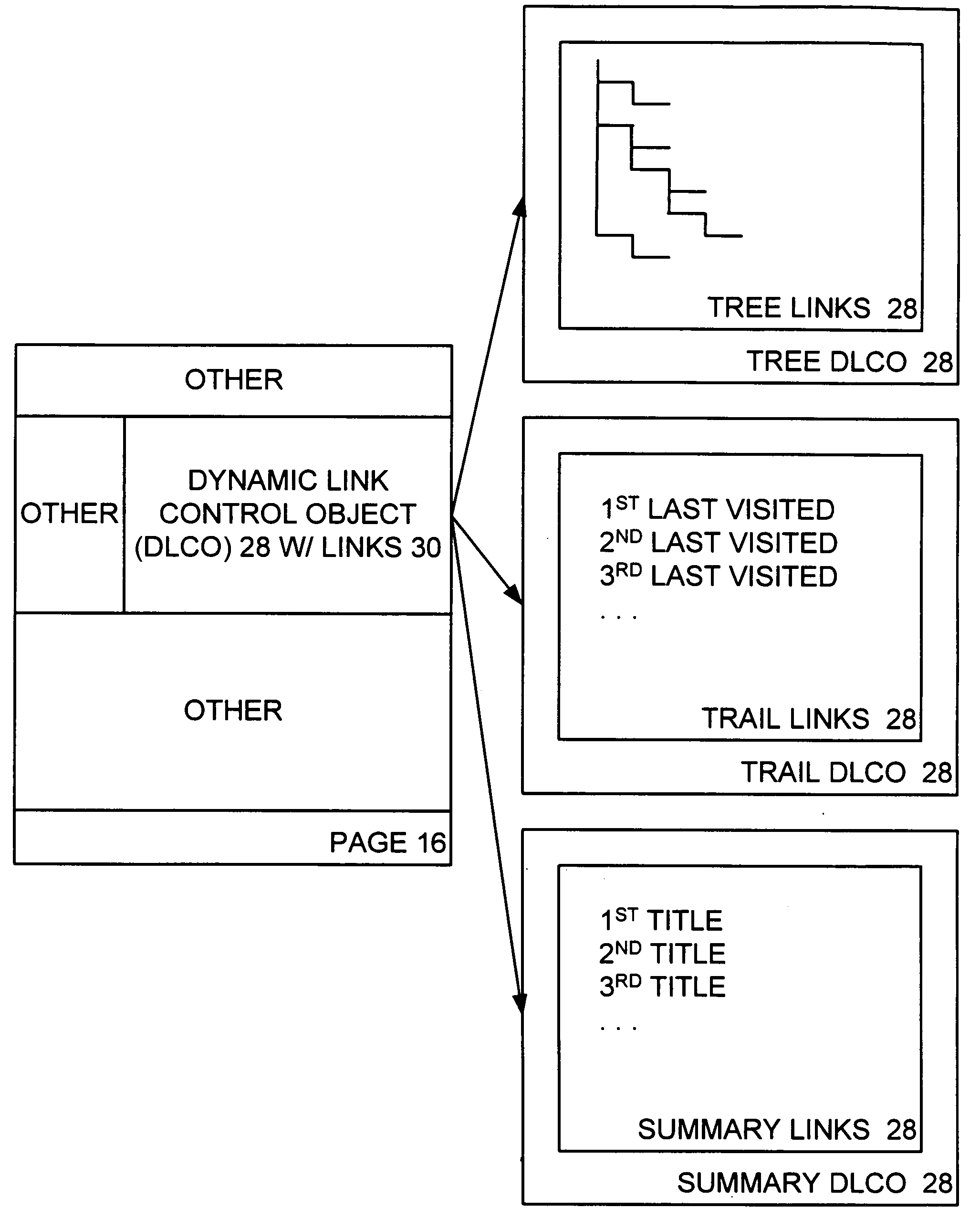
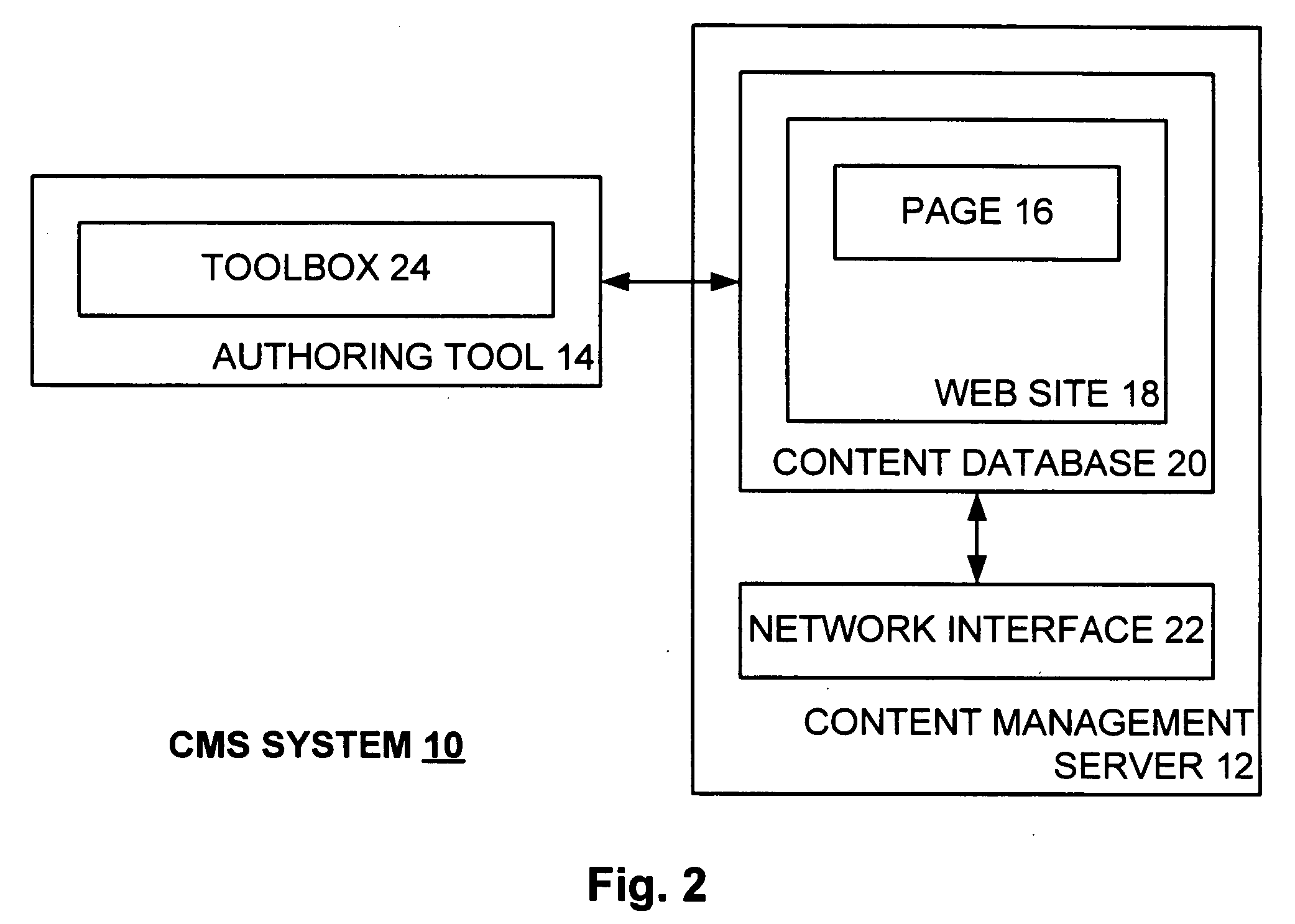
Dynamic link control object for dynamically presenting link options in connection with a content management server system
A dynamic link control object (DLCO) is positioned on a page of a web site. The web site is hosted by a content management server (CMS) that stores the page with the DLCO therein and serves same to a requestor thereof. The page as served to the requestor has a context associated therewith. The DLCO on the page as viewed by the requester displays navigation links associated with the page, where the displayed navigation links dynamically vary according to the context of the page. Thus, the DLCO on a first page with a first context may display different links as compared to the DLCO on a second page with a second context. A designer designing a page creates particular types of links on such page by placing the DLCO on the page without specifically defining each link.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
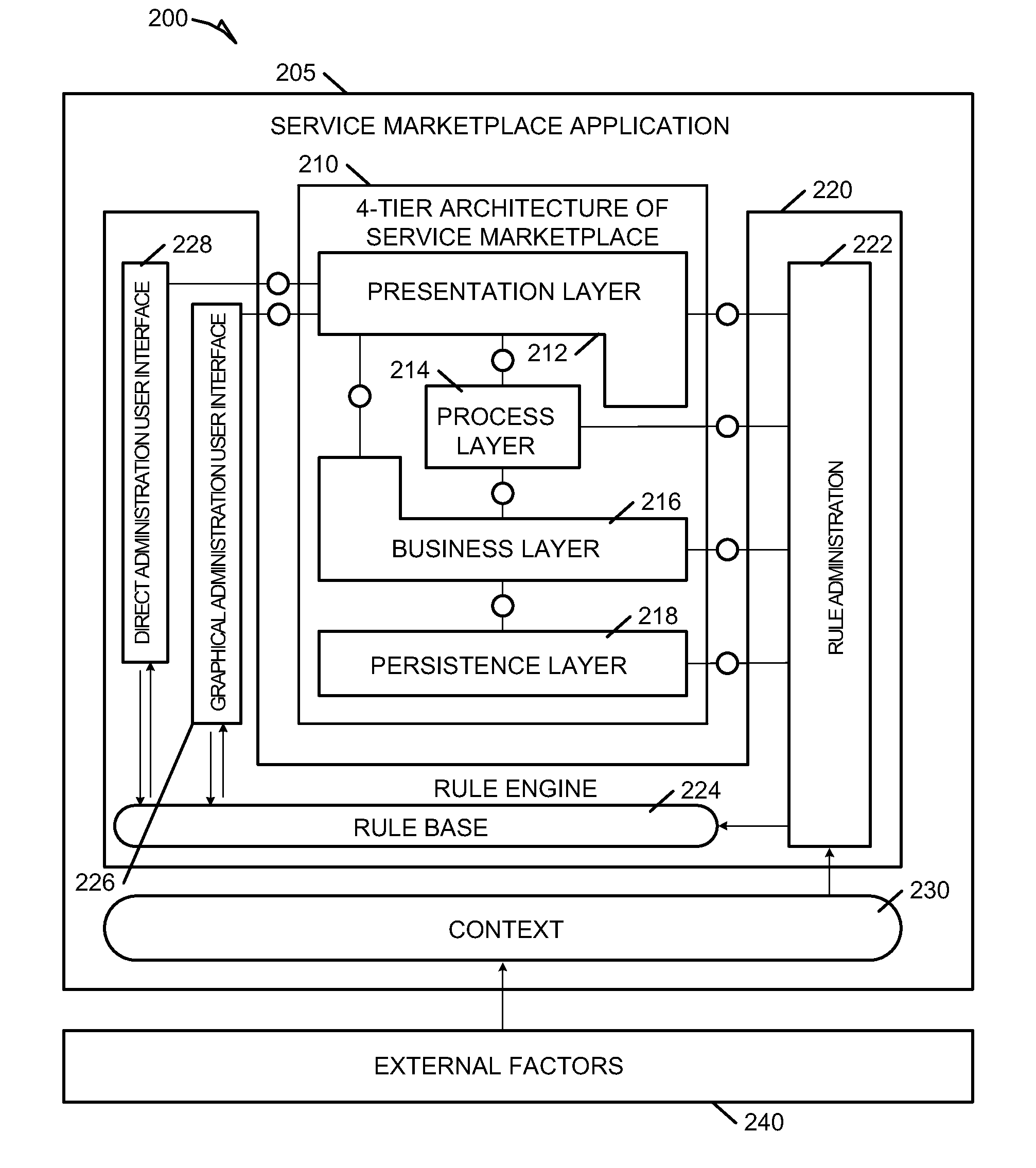
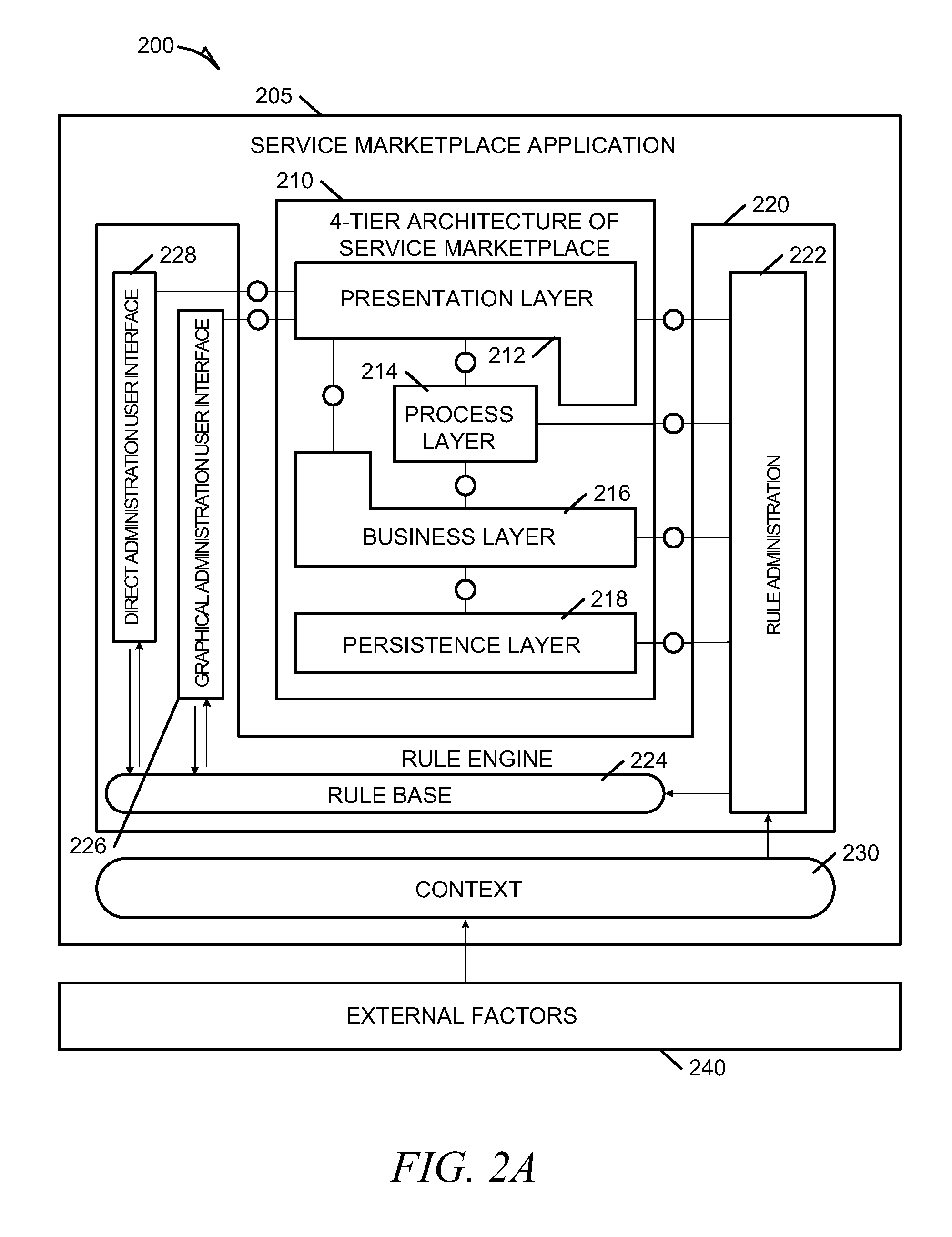
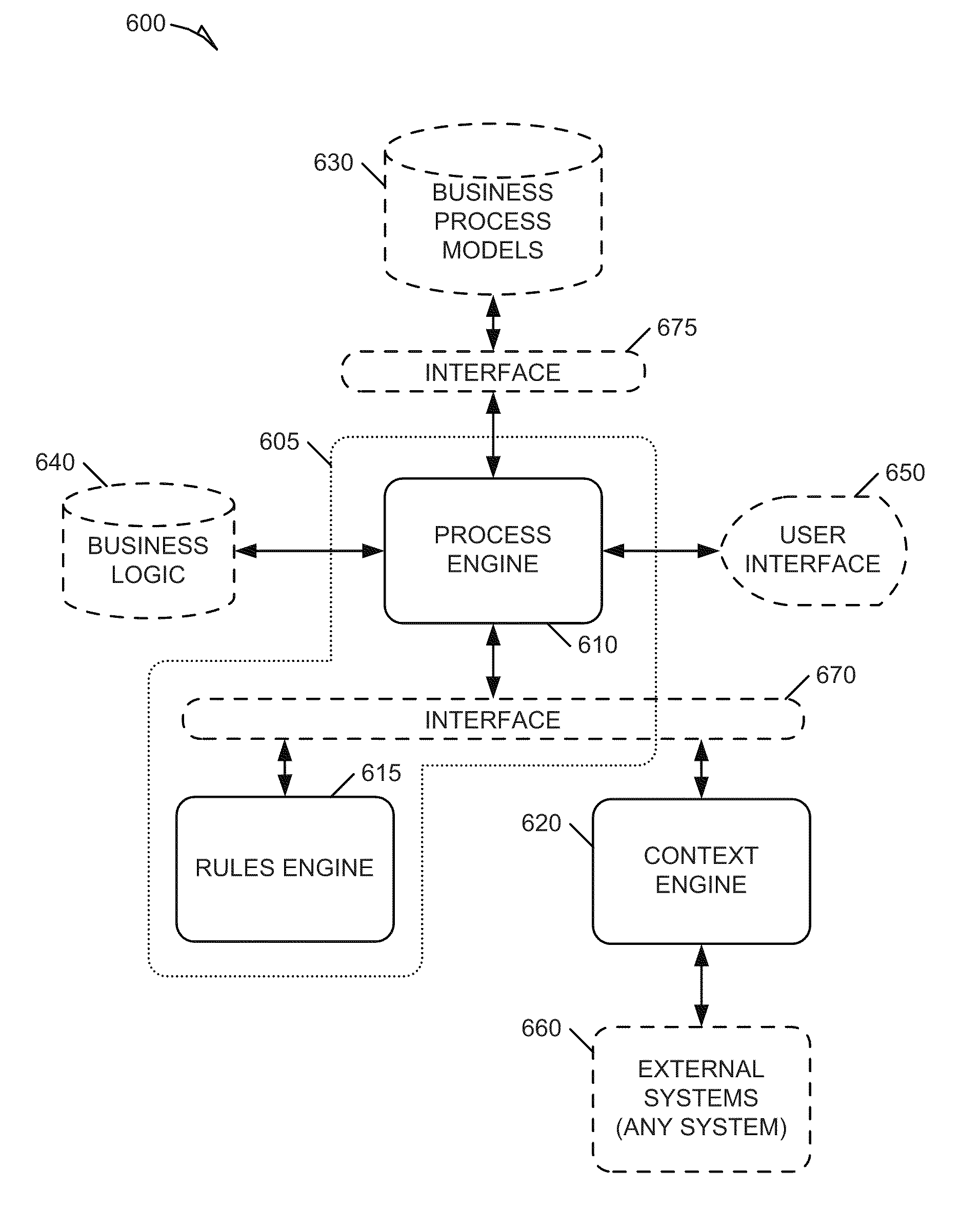
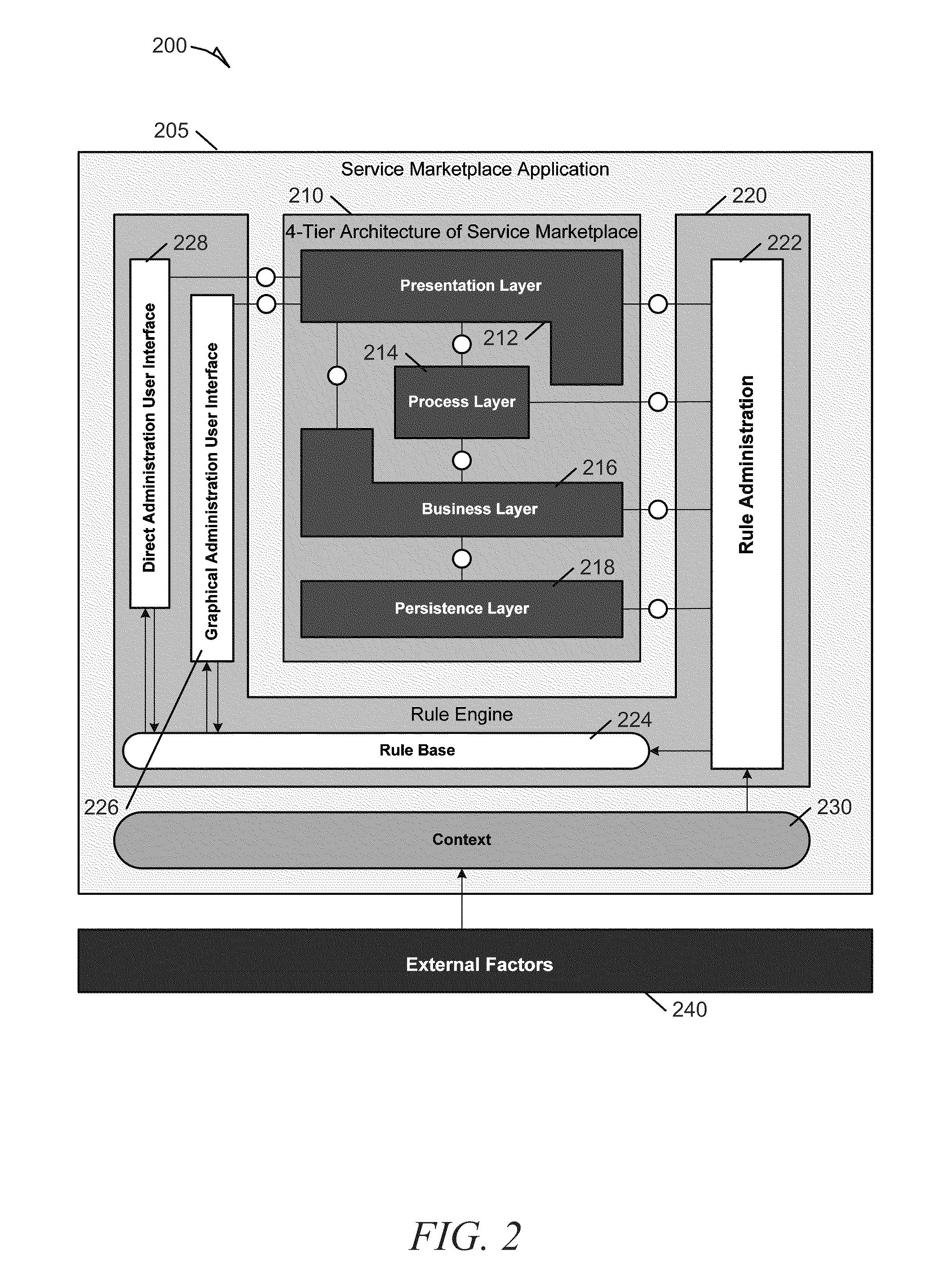
Systems and methods for dynamic process model reconfiguration based on process execution context
Methods and systems to dynamically reconfigure an instance of a process model based on process execution context are described. In one example, a system includes a context engine, a rules engine, and a business process engine. The context engine maintains context information related to a business process model. The context information is dynamically updated continuously. The rules engine produces decisions based on information from the context engine. The rules engine evaluates decision points within an instance of the business process model using a relevant context obtained from the context engine. The rule engine also receives changes in context dynamically from the context engine, and re-evaluates decision points based on the context changes. The business process engine executes the instance of the business process model and can dynamically alter the instance during execution based on decisions generated by the rules engine.
Owner:SAP AG
Enforcement of conditional policy attachments
Framework for conditionally attaching web service policies to a policy subject (e.g., a web service client or service endpoint) at subject runtime. In one set of embodiments, a constraint expression can be defined that specifies one or more runtime conditions under which a policy should be attached to a policy subject. The constraint expression can be associated with the policy and the policy subject via policy attachment metadata. The constraint expression can then be evaluated at runtime of the policy subject to determine whether attachment of the policy to the policy subject should occur. If the evaluation indicates that the policy should be attached, the attached policy can be processed at the policy subject (e.g., enforced or advertised) as appropriate. Using these techniques, the policy subject can be configured to dynamically exhibit different behaviors based on its runtime context.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
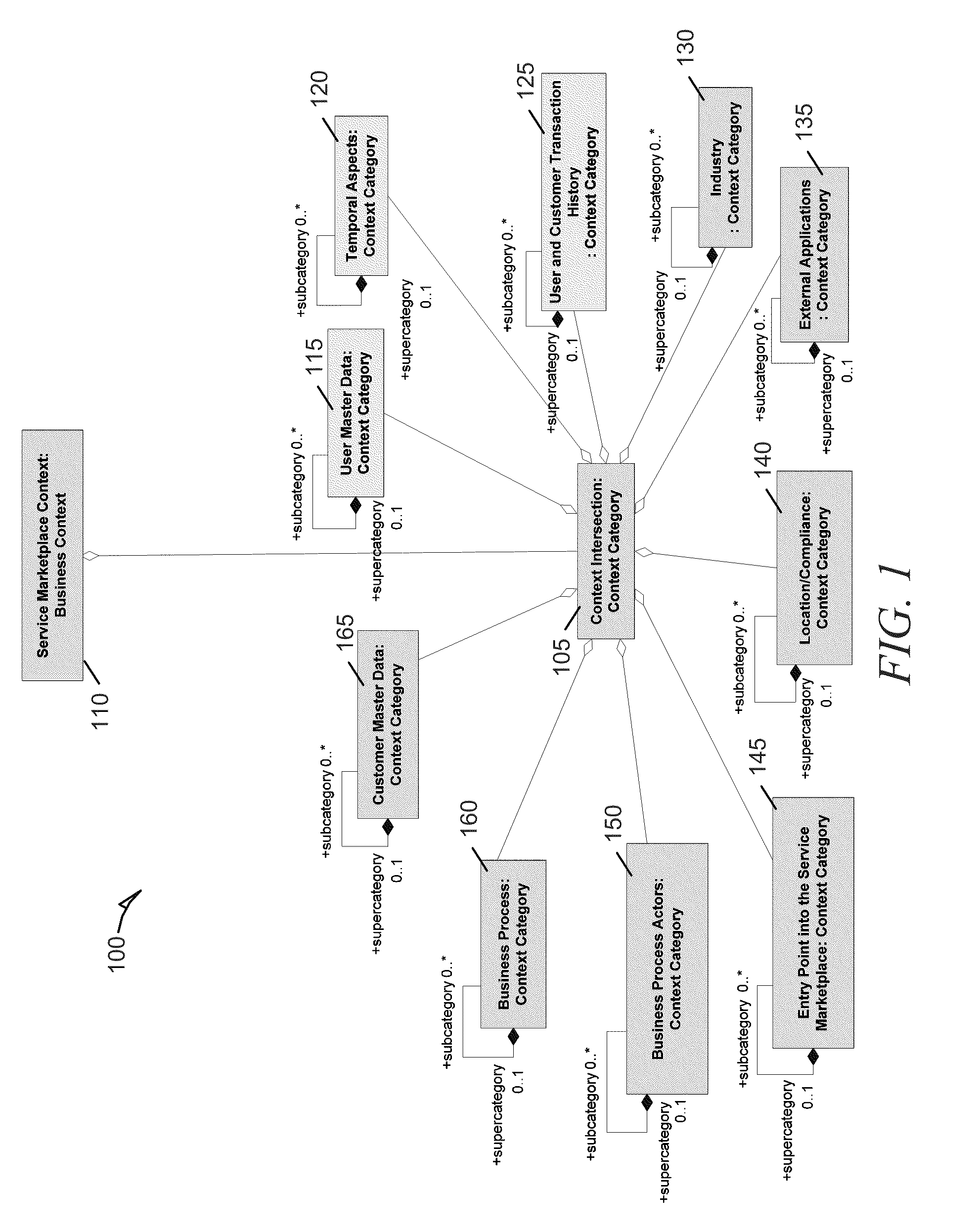
Systems and methods for dynamic process model configuration based on process execution context
ActiveUS8346520B2ResourcesAnalogue processes for specific applicationsComputer scienceContext dynamics
Methods and systems to dynamically configure a process model based on process execution context are described. In one example embodiment, a system to dynamically configure a process model can include a context engine, a rules engine, and a business process engine. The context engine can maintain context information related to an executable business process model. The context information is dynamically extensible during execution of the executable business process model. The rules engine can obtain a relevant context form the context information. The relevant context can be associated with a step and a rule to control the step within the executable business process model. The business process engine can execute the executable business process model and can dynamically configure the executable business process model during execution based on application of the relevant context by the rules engine.
Owner:SAP AG
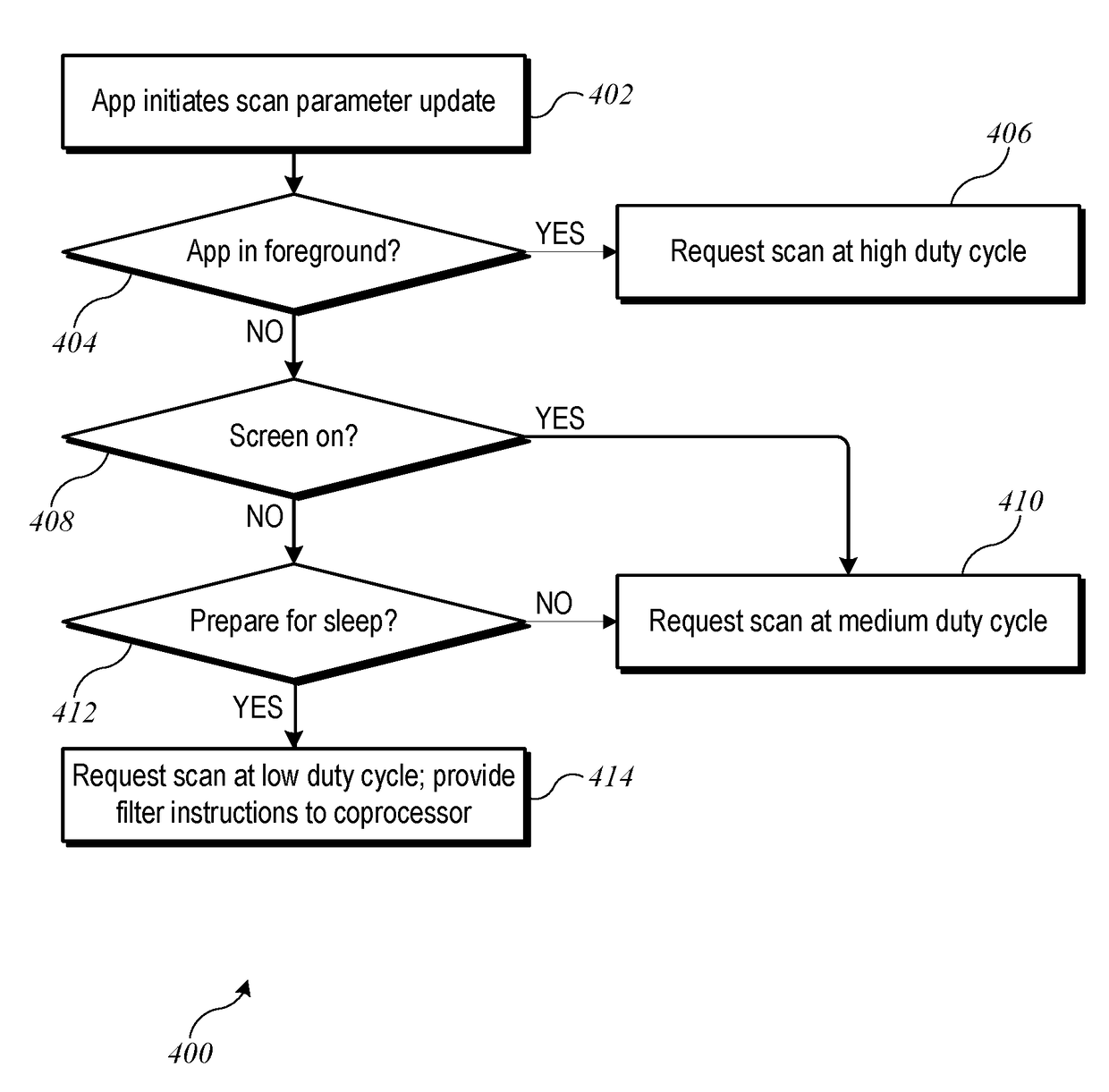
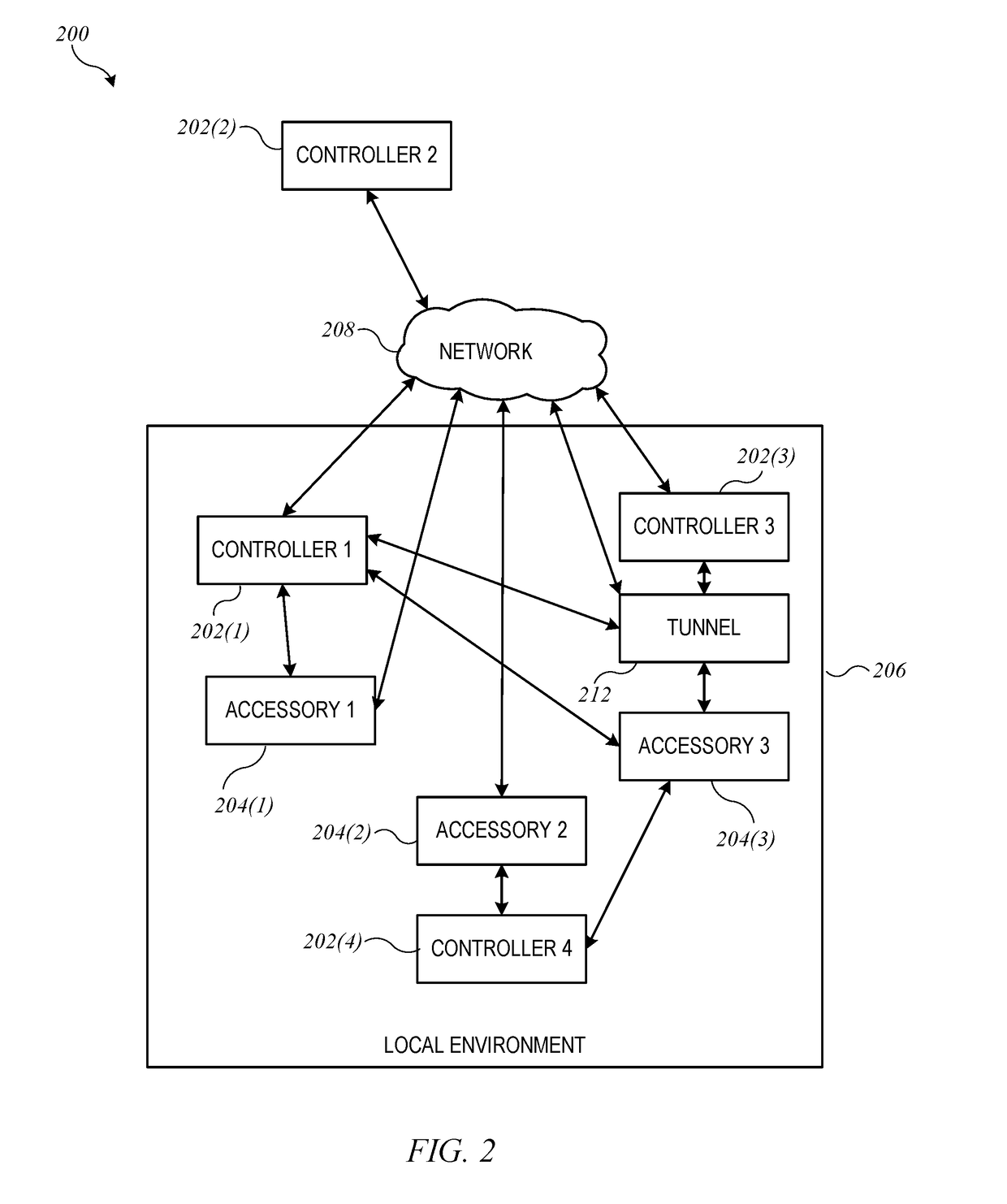
Dynamic connection path detection and selection for wireless controllers and accessories
InactiveUS20170201942A1Reduce power consumptionAvoiding excessive delayPower managementSubstation equipmentWireless controlReachability
Controllers can communicate with accessories using various paths, such as a wireless communication path. A controller can maintain reachability information for each accessory indicating the path(s) via which the accessory is currently reachable. Maintaining the reachability information can include scanning to detect broadcasts from the accessories and updating the reachability information based on the results of scanning. Scanning parameters such as scan interval and scan duration can be selected dynamically based on the current operating context of the controller (e.g., where the controller is located, what processes are active on the controller, what other devices have been detected within communication range of the controller).
Owner:APPLE INC
Advertisement of conditional policy attachments
Framework for conditionally attaching web service policies to a policy subject (e.g., a web service client or service endpoint) at subject runtime. In one set of embodiments, a constraint expression can be defined that specifies one or more runtime conditions under which a policy should be attached to a policy subject. The constraint expression can be associated with the policy and the policy subject via policy attachment metadata. The constraint expression can then be evaluated at runtime of the policy subject to determine whether attachment of the policy to the policy subject should occur. If the evaluation indicates that the policy should be attached, the attached policy can be processed at the policy subject (e.g., enforced or advertised) as appropriate. Using these techniques, the policy subject can be configured to dynamically exhibit different behaviors based on its runtime context.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Dynamic link control object for dynamically presenting link options in connection with a content management server system
InactiveUS20050177676A1Satisfies needWeb data navigationSpecial data processing applicationsWeb siteContent management
A dynamic link control object (DLCO) is positioned on a page of a web site. The web site is hosted by a content management server (CMS) that stores the page with the DLCO therein and serves same to a requestor thereof. The page as served to the requestor has a context associated therewith. The DLCO on the page as viewed by the requester displays navigation links associated with the page, where the displayed navigation links dynamically vary according to the context of the page. Thus, the DLCO on a first page with a first context may display different links as compared to the DLCO on a second page with a second context. A designer designing a page creates particular types of links on such page by placing the DLCO on the page without specifically defining each link.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Dual pointer management method using cooperating input sources and efficient dynamic coordinate remapping
InactiveUS20100328206A1Convenient and efficient interactionMore intuitiveCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingComputer scienceContext dynamics
The pointer management technology establishes a protocol and method for dual pointer management in both absolute input mode and relative input mode. The method defines a set of properties / constraints for contextual dynamic remapping between input sensor coordinates and target screen coordinates. The remapping of the left pointer (respectively the right pointer) depends on the position of the right pointer (respectively the left pointer) in the target screen space. This inter-dependence enables a more flexible and more powerful interaction as it exploits the contextual layout to re-estimate the remapping transformations at each instant.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Systems and methods for dynamic process model configuration based on process execution context
ActiveUS20110066456A1ResourcesAnalogue processes for specific applicationsComputer scienceContext dynamics
Methods and systems to dynamically configure a process model based on process execution context are described. In one example embodiment, a system to dynamically configure a process model can include a context engine, a rules engine, and a business process engine. The context engine can maintain context information related to an executable business process model. The context information is dynamically extensible during execution of the executable business process model. The rules engine can obtain a relevant context form the context information. The relevant context can be associated with a step and a rule to control the step within the executable business process model. The business process engine can execute the executable business process model and can dynamically configure the executable business process model during execution based on application of the relevant context by the rules engine.
Owner:SAP AG
Enforcement of conditional policy attachments
Framework for conditionally attaching web service policies to a policy subject (e.g., a web service client or service endpoint) at subject runtime. In one set of embodiments, a constraint expression can be defined that specifies one or more runtime conditions under which a policy should be attached to a policy subject. The constraint expression can be associated with the policy and the policy subject via policy attachment metadata. The constraint expression can then be evaluated at runtime of the policy subject to determine whether attachment of the policy to the policy subject should occur. If the evaluation indicates that the policy should be attached, the attached policy can be processed at the policy subject (e.g., enforced or advertised) as appropriate. Using these techniques, the policy subject can be configured to dynamically exhibit different behaviors based on its runtime context.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
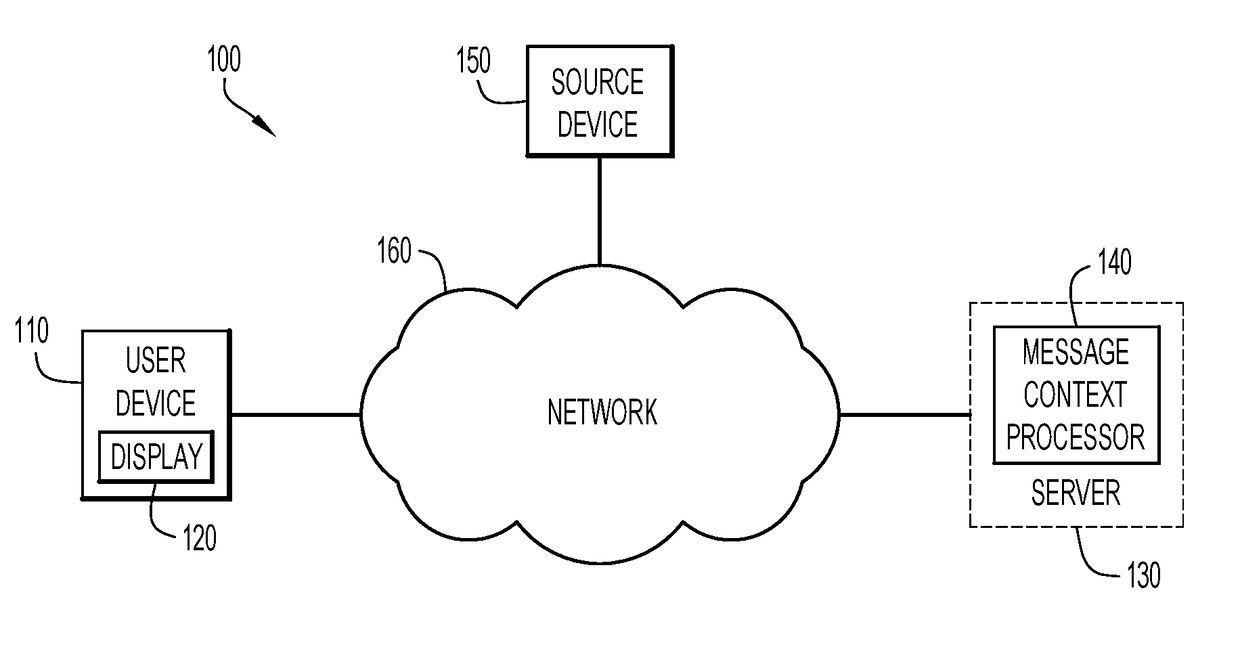
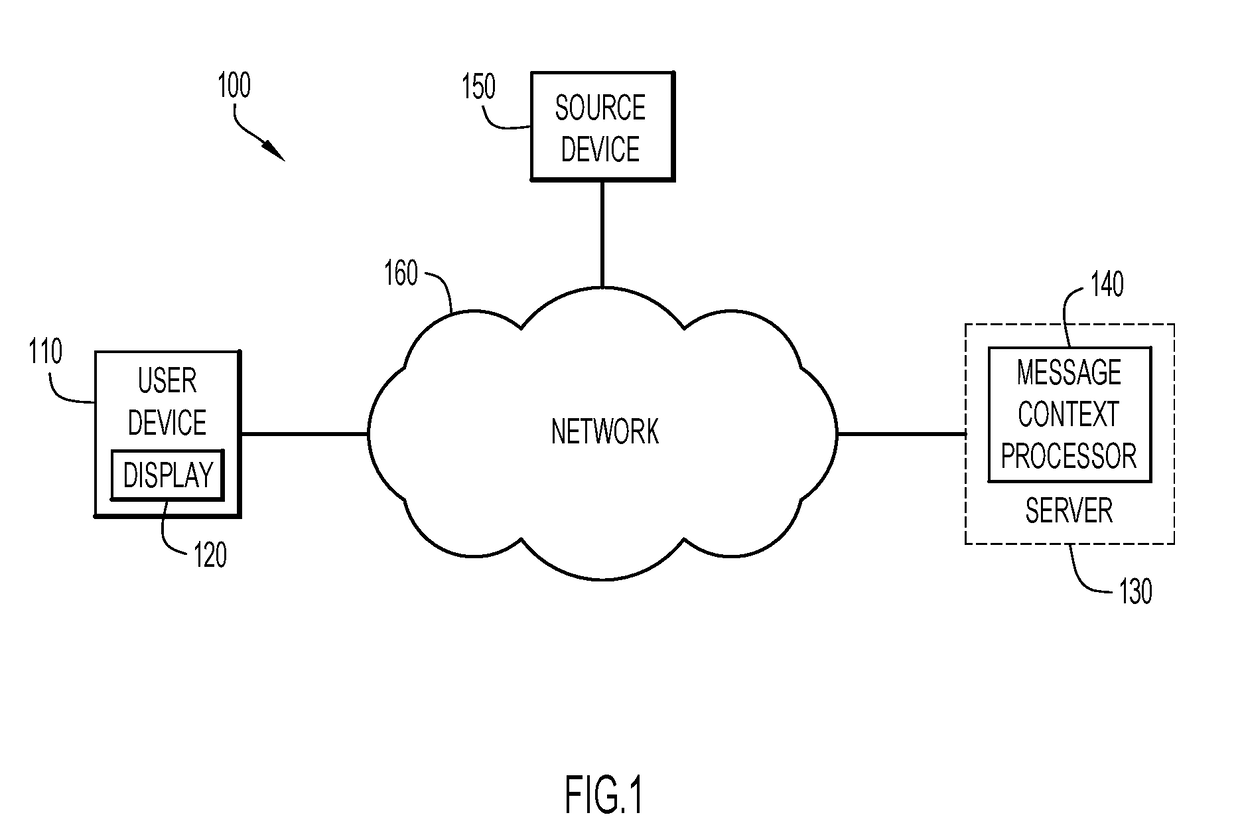
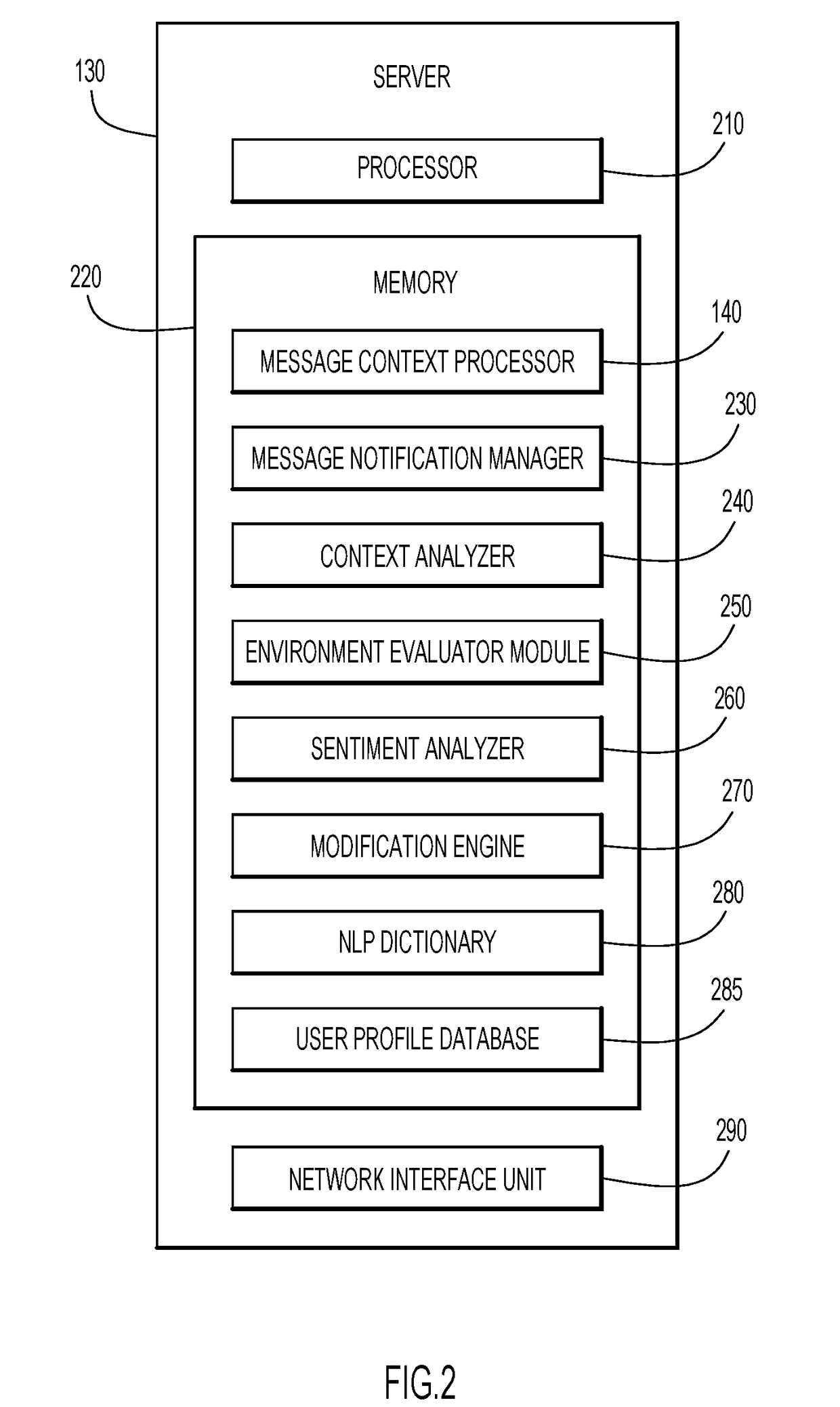
Automated message modification based on user context
According to an embodiment of the present invention, a system dynamically modifies an incoming message based on the context of the message and the user receiving the message. Initially, a server receives an incoming message directed to a user of a digital device, and analyzes the incoming message to determine a message content associated with the message and a user context based on one or more environmental parameters associated with the user. A processor in the server determines whether the incoming message should be modified based on the message content and user context, and, in response, generates a modified message for display to the user in accordance with the message content and the user context. Embodiments of the present invention further include a method and computer program product for dynamically modifying a message based on the context of the user in substantially the same manner described above.
Owner:IBM CORP
Middleware platform
ActiveUS7676594B2Network traffic/resource managementDigital computer detailsTelecommunicationsMiddleware
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
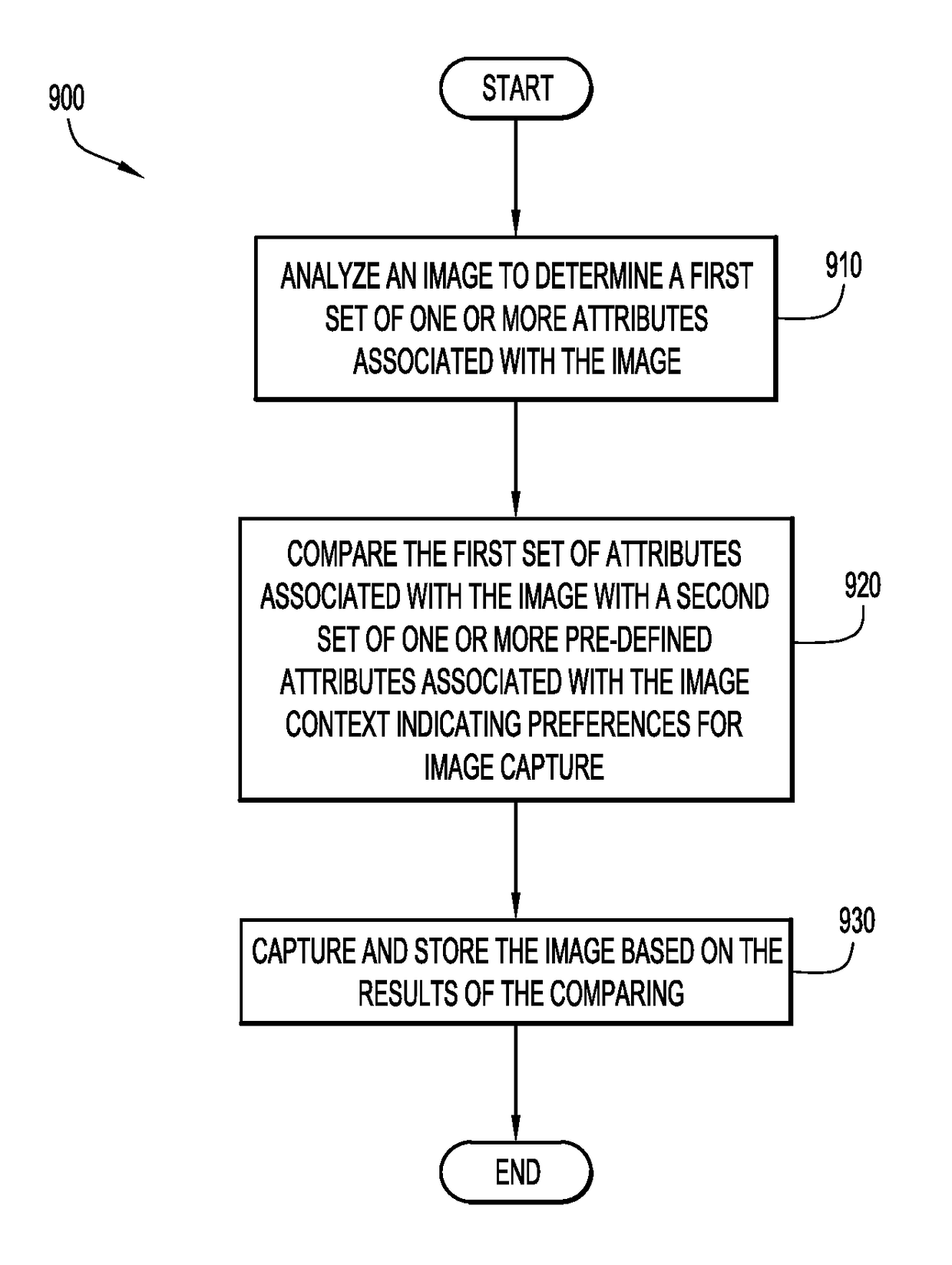
Automated image capture based on image context
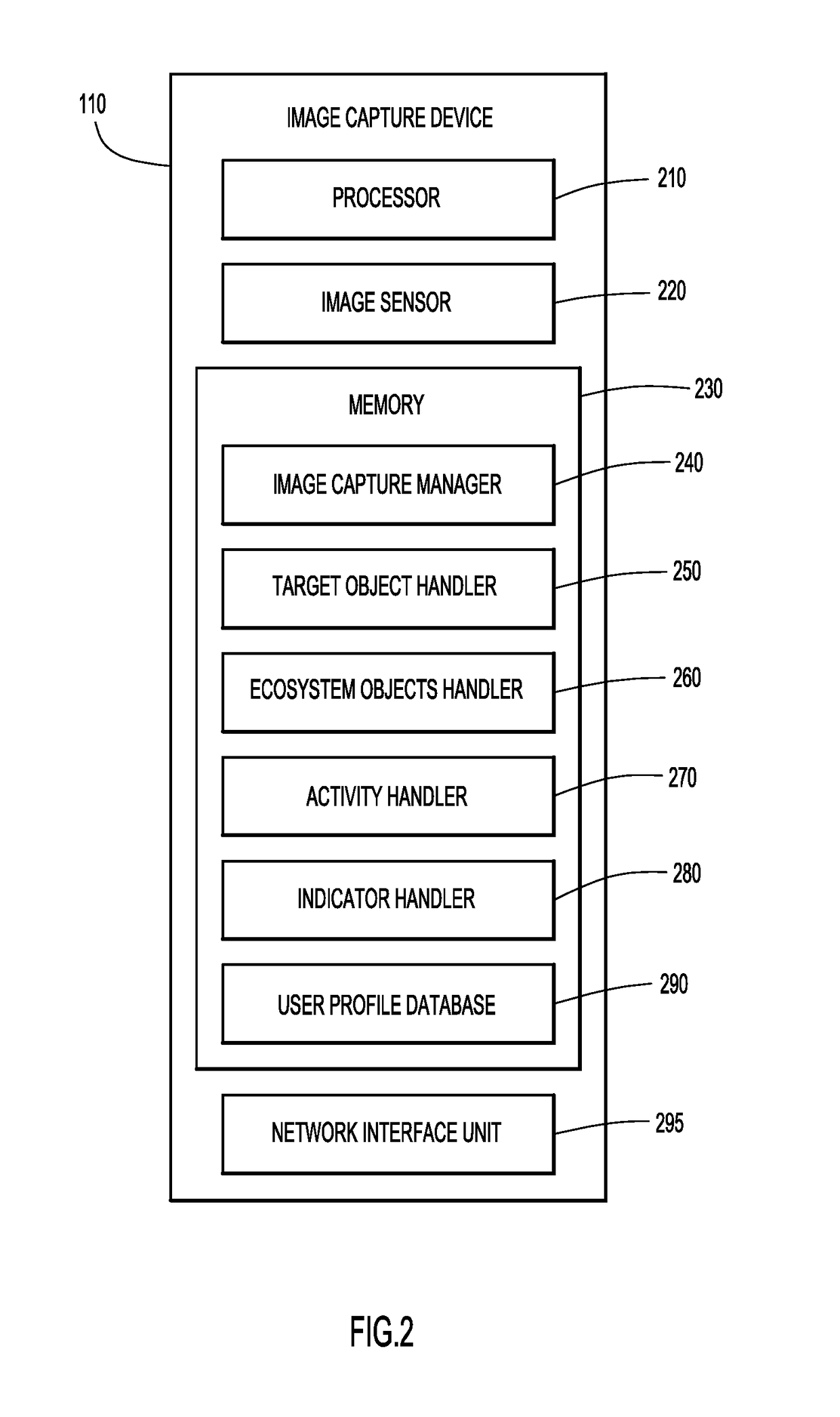
ActiveUS20180160036A1Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionContext dynamicsImage capture
According to an embodiment of the present invention, a system dynamically captures and stores an image based on the context of the image being captured. Initially, an image capture device receives and analyzes an image to determine a first set of one or more attributes associated with the image. A processor compares the first set of attributes associated with the image with a second set of one or more pre-defined attributes associated with an image context indicating preferences for image capture, and, based on the results of the comparing, instructs the image capture device to store the image. Embodiments of the present invention further include a method and computer program product for capturing an image based on the context of the image in substantially the same manner described above.
Owner:IBM CORP
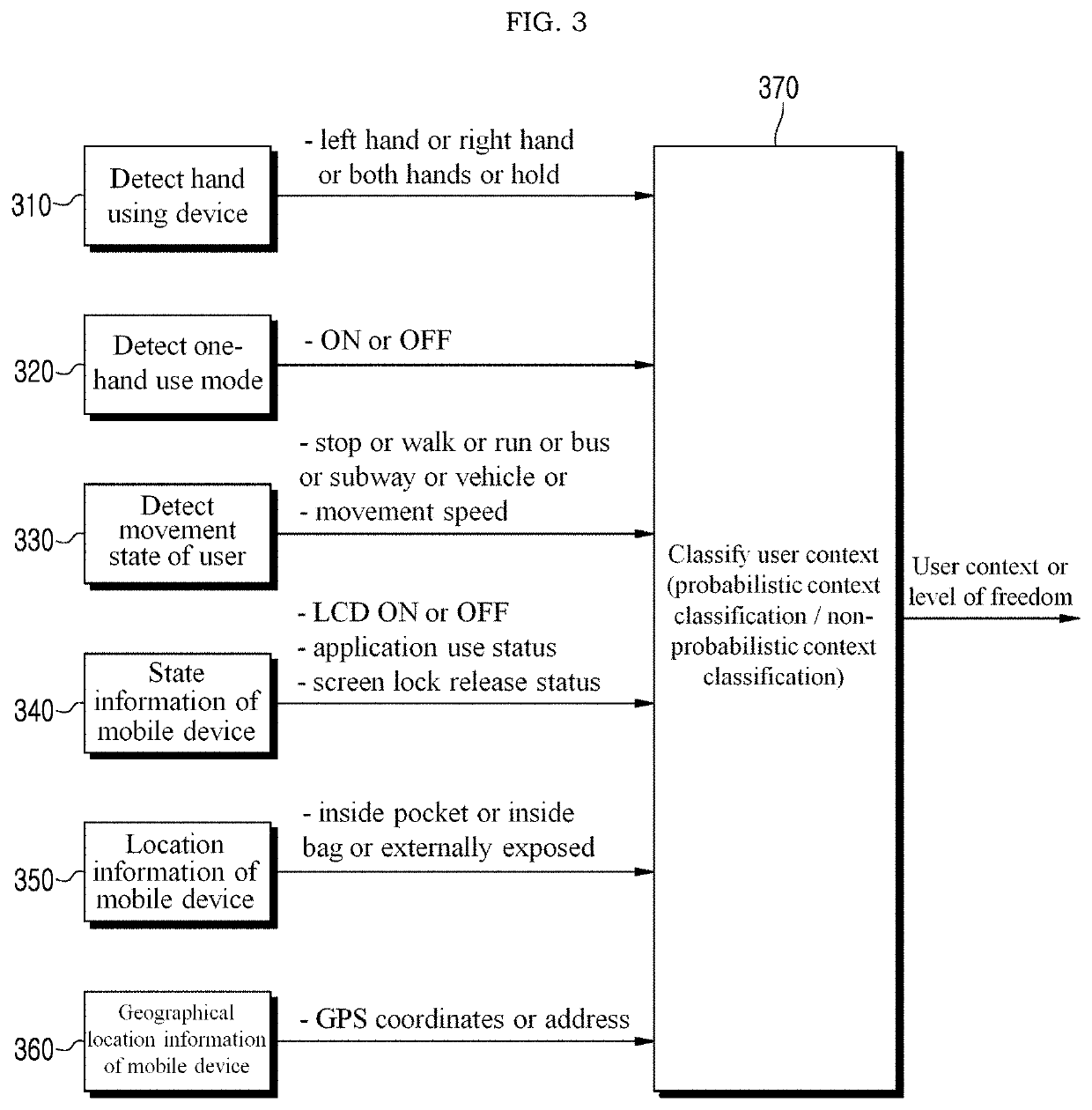
User context recognition in messaging service environment and interaction with messaging service based on user context recognition
Disclosed is technique for a user context detection and interaction with a messaging service based on a user context in a messaging service environment. An interaction method of a mobile device may include acquiring information associated with a context of at least one of a mobile device and a user of the mobile device under control of an application installed and executed on the mobile device in association with a messaging service, determining a context of the user based on the acquired information, verifying a function to be provided to the user through the messaging service based on the determined context of the user, dynamically determining a configuration of a user interface based on the determined context of the user, and providing the function through the user interface of which the configuration is dynamically determined.
Owner:LINE PLUS
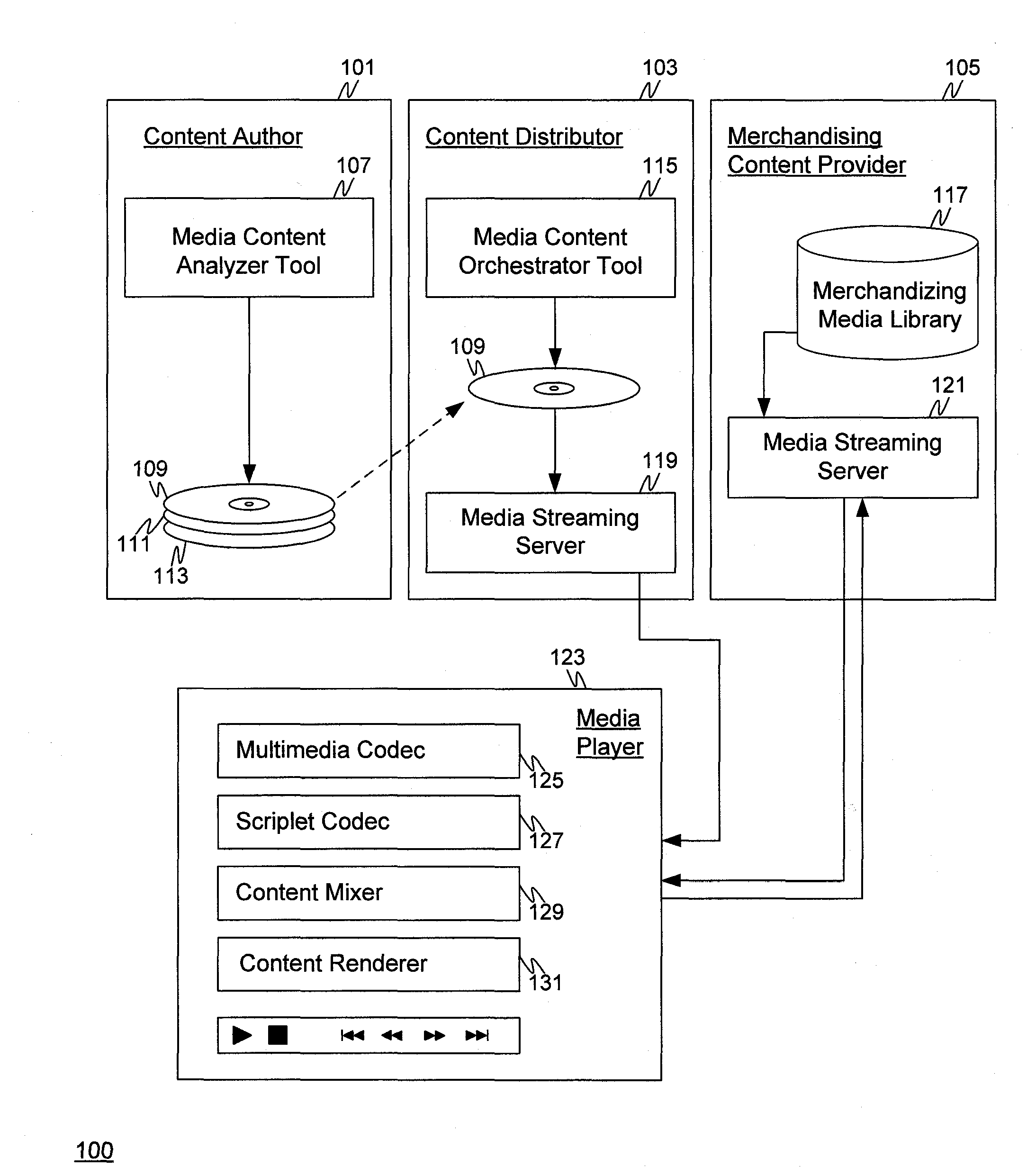
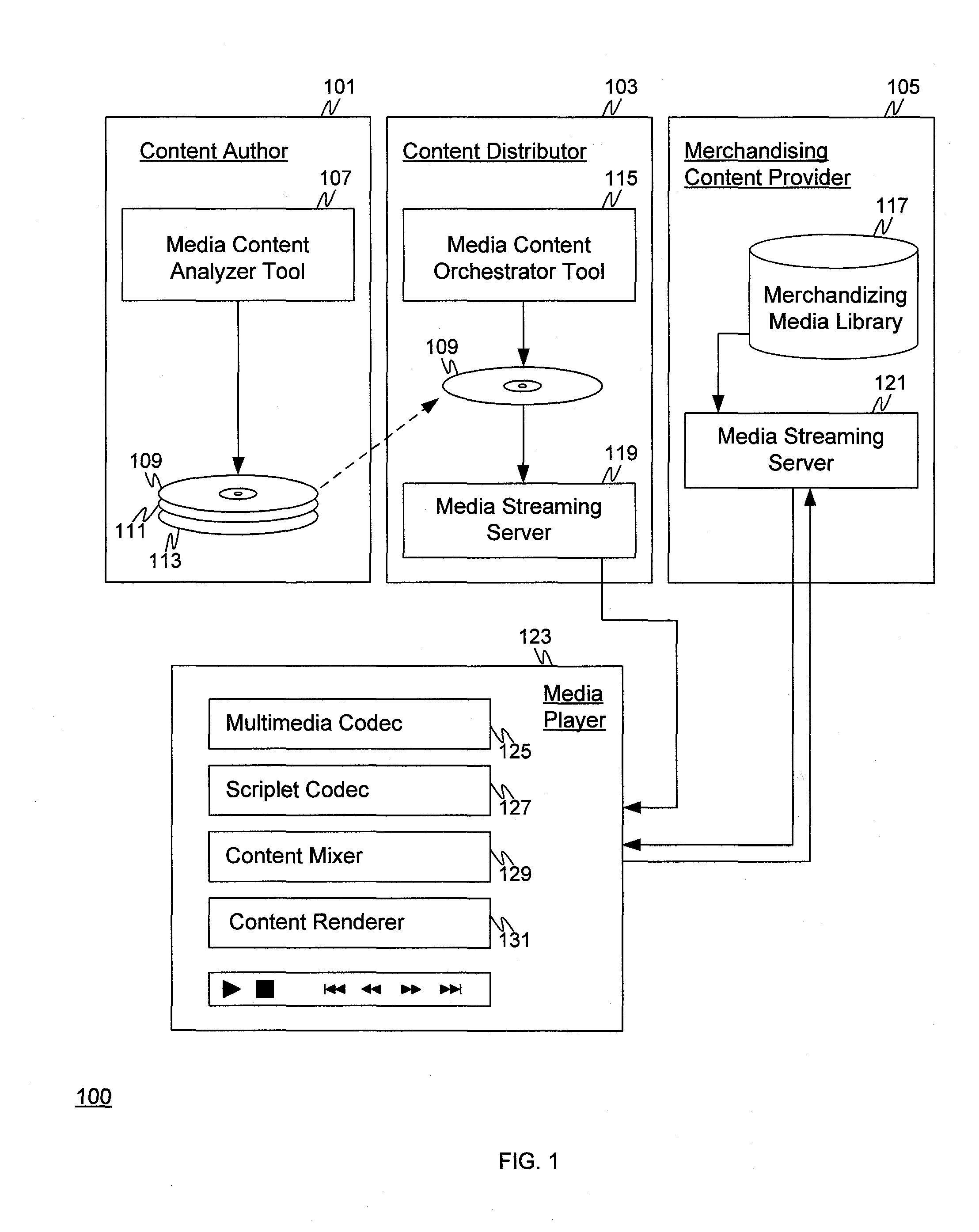
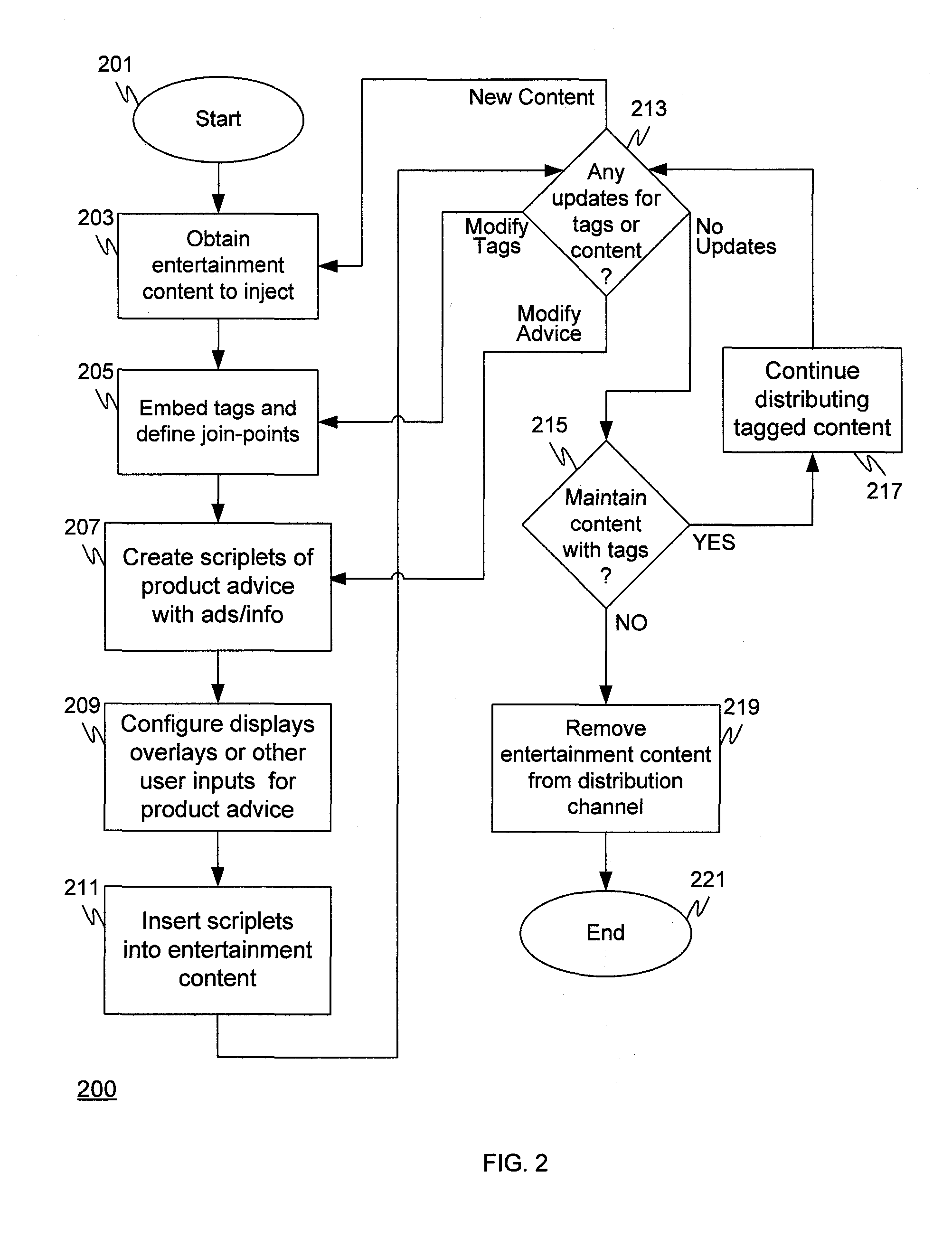
Systems and Method for Dynamic Content Injection Using Aspect Oriented Media Programming
InactiveUS20110066614A1Overcomes drawbackDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsAnalysis toolsContext dynamics
A system for injecting business content dynamically based on the context of the user. A media content analysis tool may be used to analyze existing media to identify features and insert tags based on the content and / or time. A media content orchestrator may be used to author scriplets containing product advice for the media stream to insert and associate scriplets to tags in the media stream. The media player, equipped with a codec for the new media format, performs functions such as browsing product information, places orders, or the like.
Owner:IBM CORP
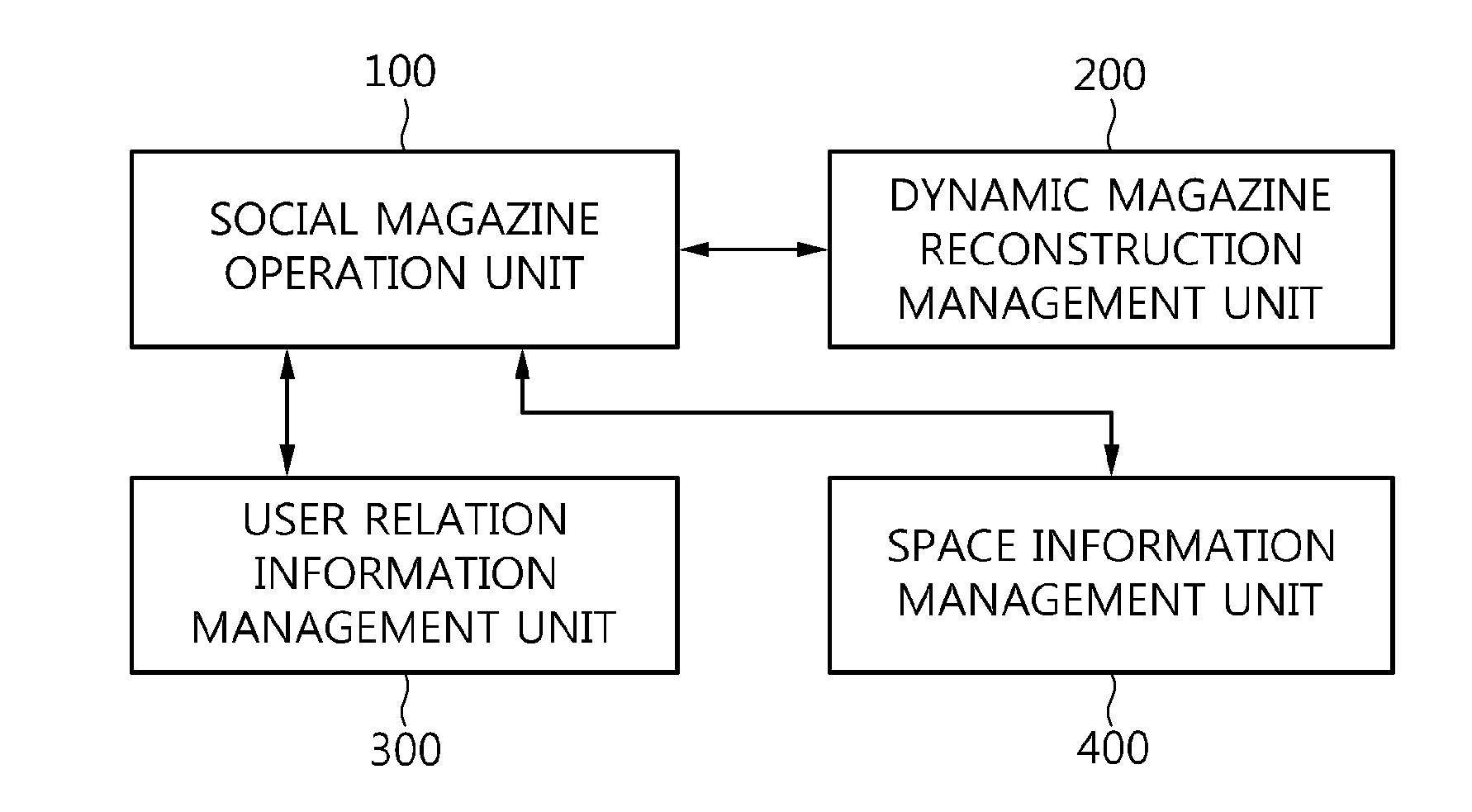
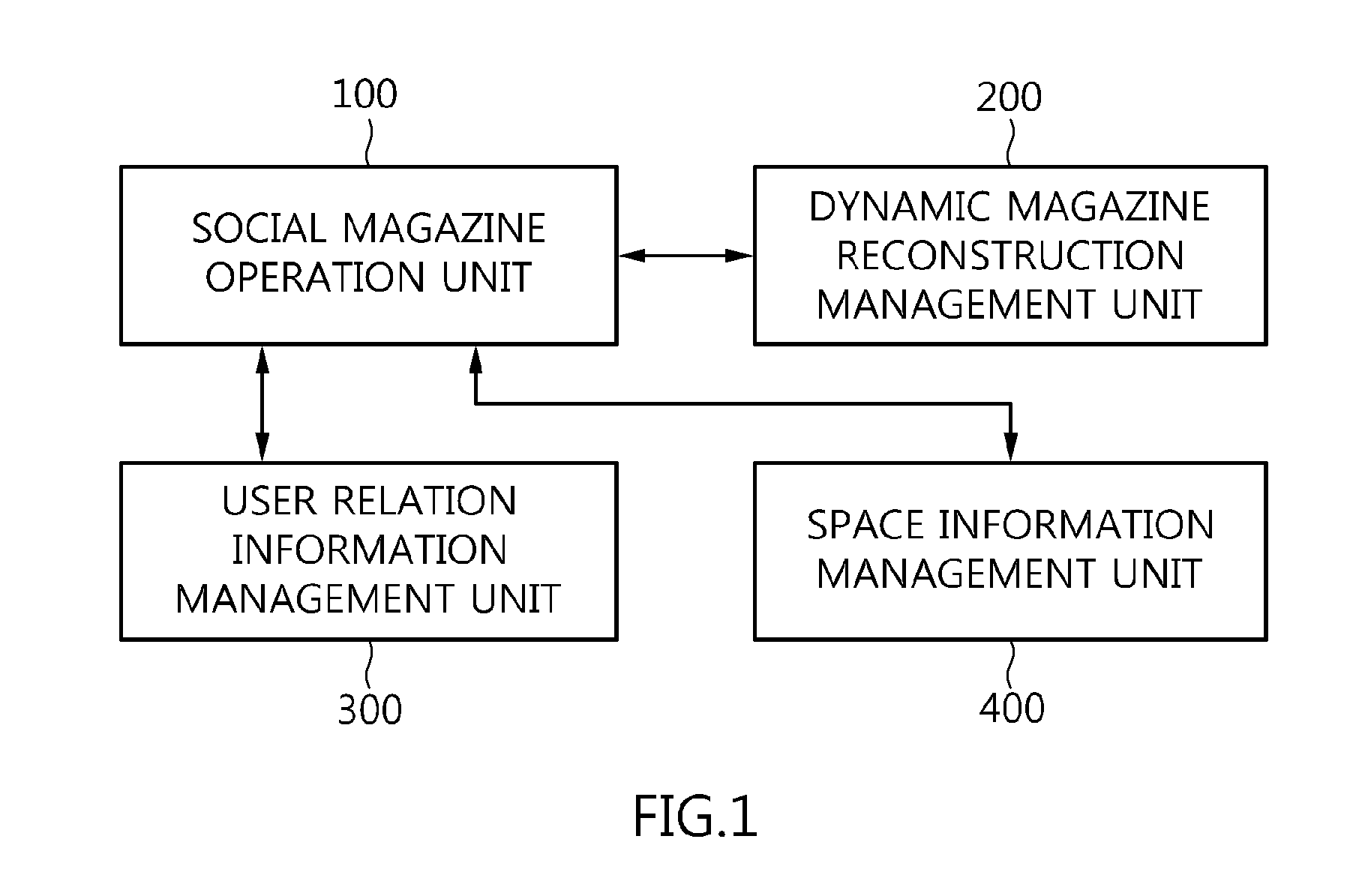
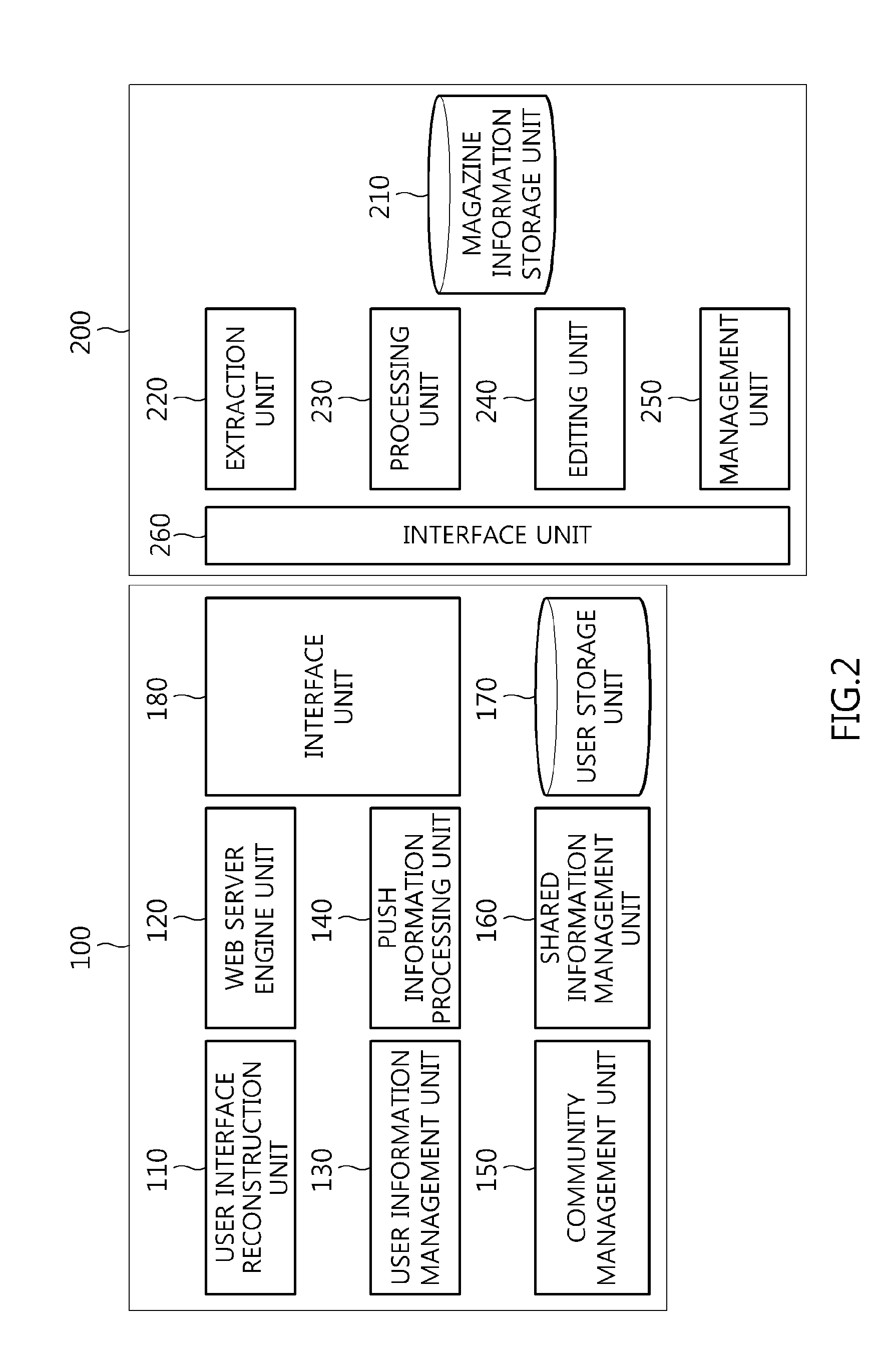
Apparatus and method for providing social magazine information
InactiveUS20130198282A1Electrolysis componentsMultiple digital computer combinationsSocial informationContext dynamics
Disclosed herein is an apparatus and method for providing social magazine information. The method is configured such that an apparatus operating in conjunction with at least one user terminal provides social magazine information to a corresponding user terminal. In the method, a social magazine is dynamically reconstructed according to a context of a user of each user terminal. Customized information corresponding to the user terminal is provided based on the reconstructed social magazine. A community is formed among user terminals which share the reconstructed social magazine, and social magazine information is shared through the formed community.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
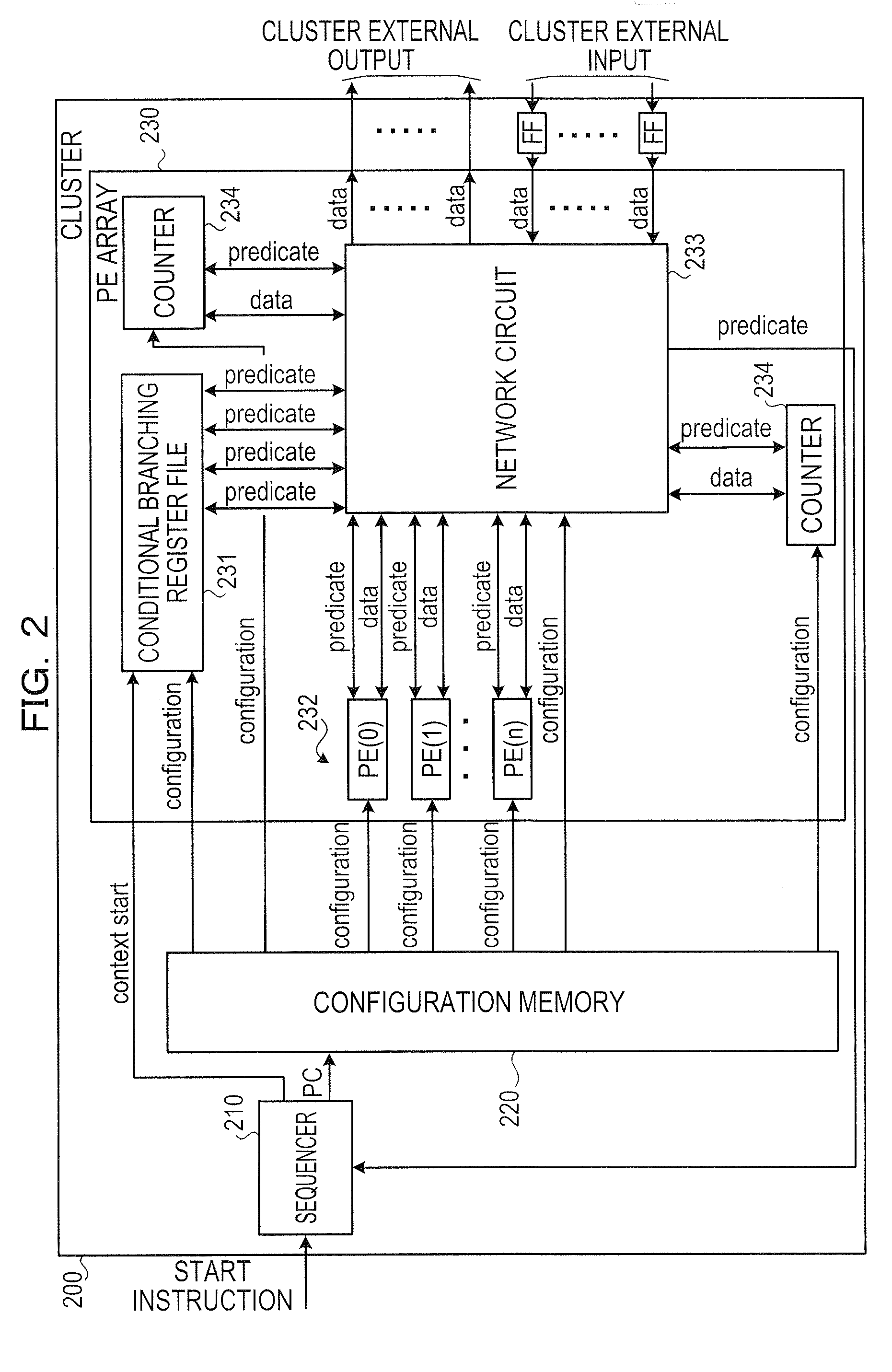
Counter circuit, dynamic reconfigurable circuitry, and loop processing control method
InactiveUS20090083527A1General purpose stored program computerSpecific program execution arrangementsLoop controlProcessor register
A dynamic reconfigurable circuit that implements optional processing by dynamically switching a processing content of a reconfigurable processing element (PE) and a connection content between the PEs in accordance with a context, includes: a configuration register section for setting a content of loop processing on the basis of the context, the loop processing content including an output source of an output signal from each of a set of the reconfigured PEs, an output destination of the output signal, and a condition for outputting the output signal to the output destination; and at least one counter circuit including a loop control section and an output register section that implement the set loop processing, that count the number of implementations of the loop processing implemented by the loop control section, and that output the output signal to the output destination based on the counted number of implementations and the condition.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com