Patents
Literature
36 results about "Normal priority" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Priority-based virus scanning with priorities based at least in part on heuristic prediction of scanning risk
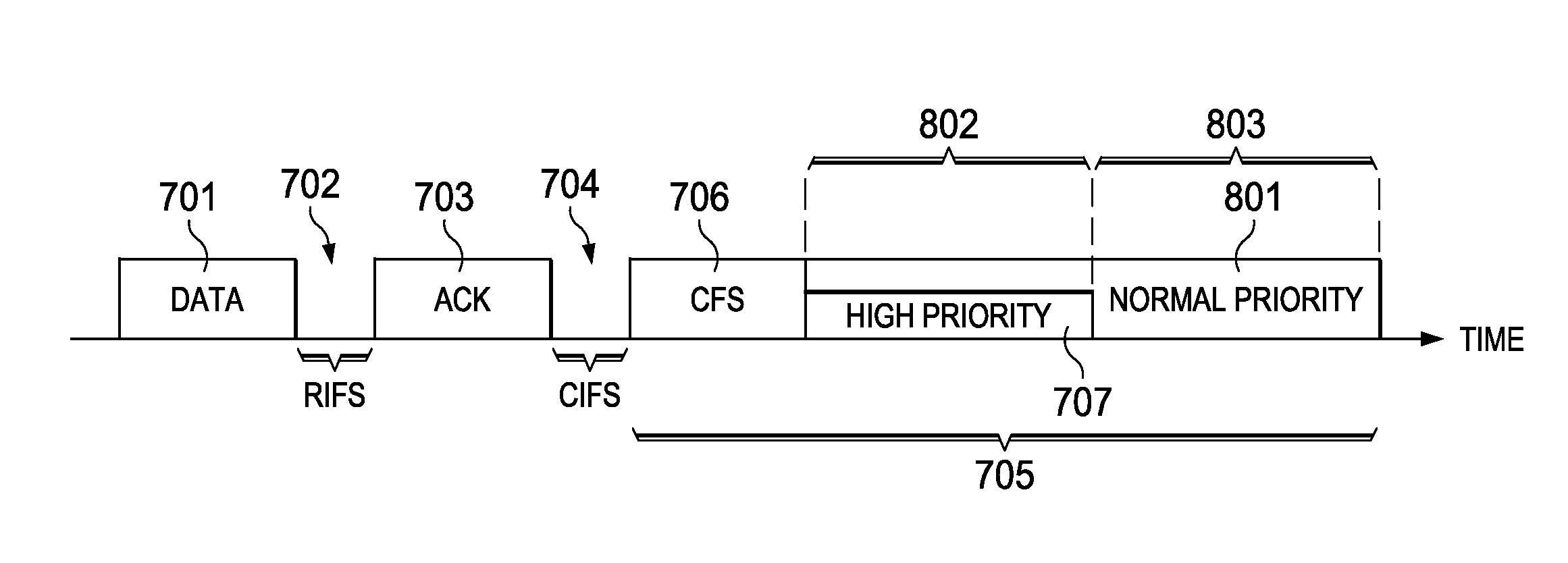
Anti-virus scanners can be deliberately disabled, inadvertently disabled, or simply slowed down to a point where the scanner becomes ineffective and the primary function of the scanning host device is disrupted when a suitably complex file is received by the scanning system for scanning. Archive files pose particular problems for scanners, since archives may contain very complex data structures, and require time consuming analysis. Virus scanners typically scan each element of an archive. Some virus scanners decompress each archive component for scanning. Virus developers have taken advantage of this scanning approach by creating complex archives designed to overwhelm a scanner, leaving a system unprotected or in a denial of service state. To counter such measures, when an archive (or other file) is passed to a scanner, various heuristics are applied to the archive so as to determine a risk-based scanning priority for the archive. Priorities can include normal priority, low priority for archives having suspicious characteristics, and discard without scanning for archives appearing to be constructed so as to overwhelm a scanner. Normal priority scans can occur immediately, while low priority scans can be relegated to only occurring while the scanning system is otherwise idle.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
Access control method and device
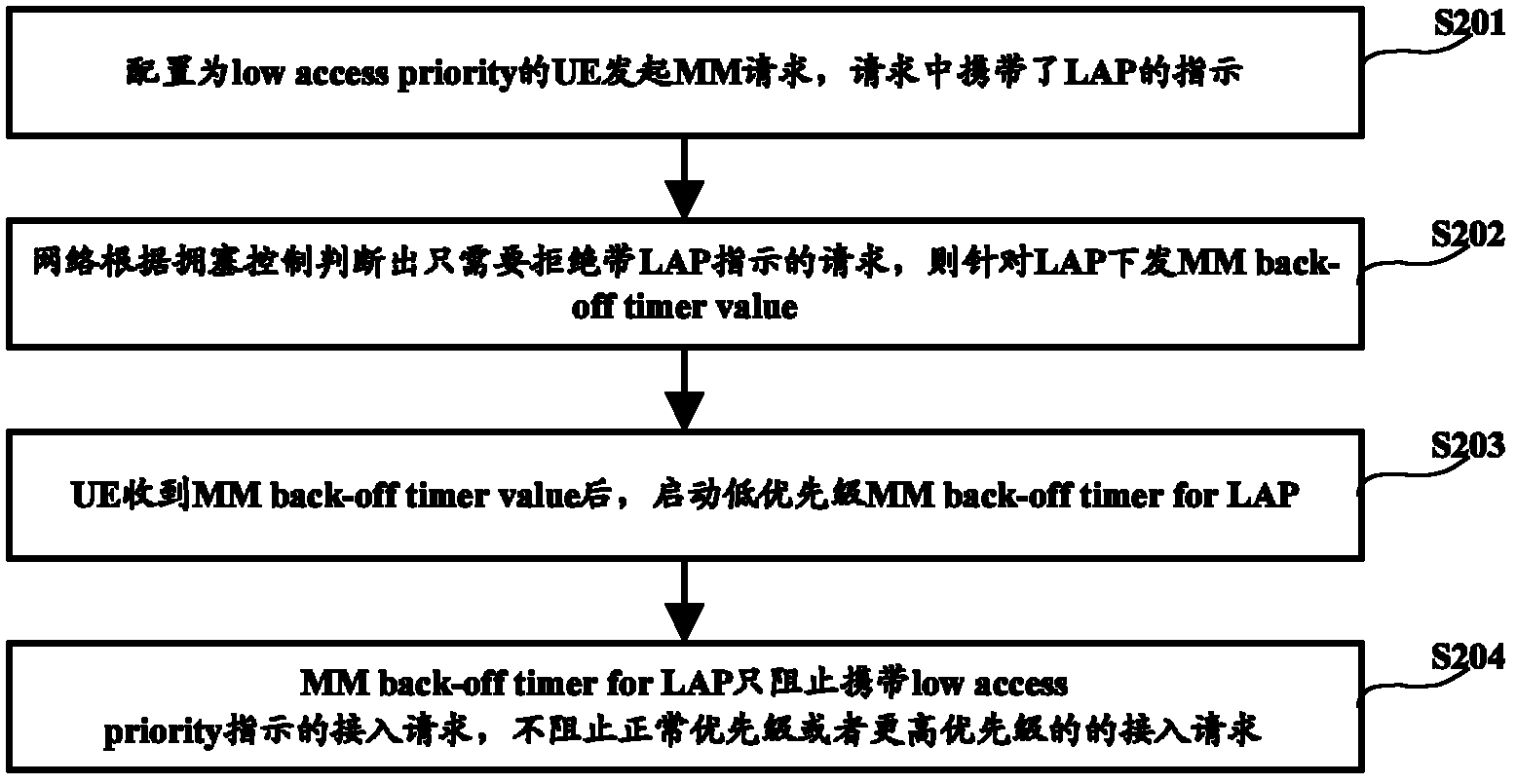
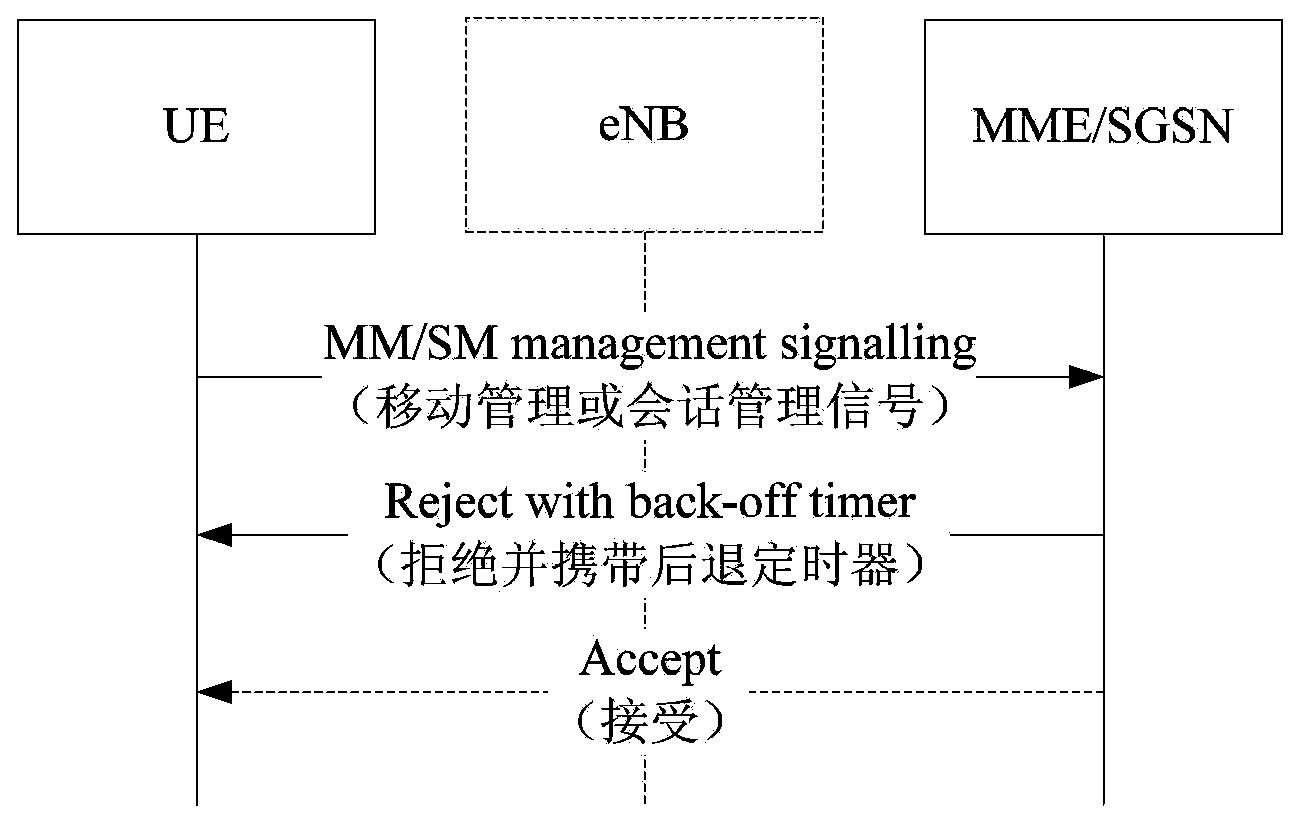
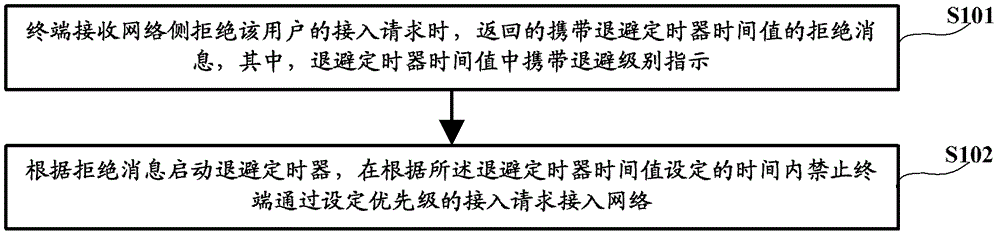
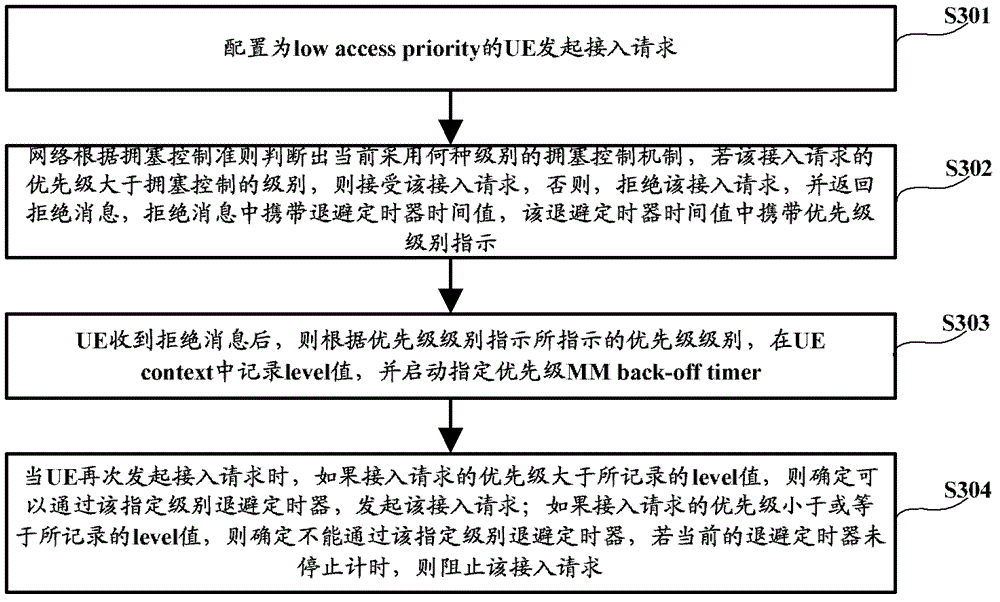
The invention discloses an access control method and device, relating to a communication technology. The method comprises the steps of: after receiving a rejection message returned by a network side, starting a backoff timer, wherein the rejection message carries a backoff level indication; and prohibiting a terminal from accessing a network through an access request with set priority within set time. Because of no rejection of all priorities of access requests, when a user accesses the network according to an access request with a normal priority or access request with higher priority, the accessing can not be prohibited by the backoff timer with lower priority, thus accessing with normal priority can be initiated after the terminal with low access priority is rejected from being accessed.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
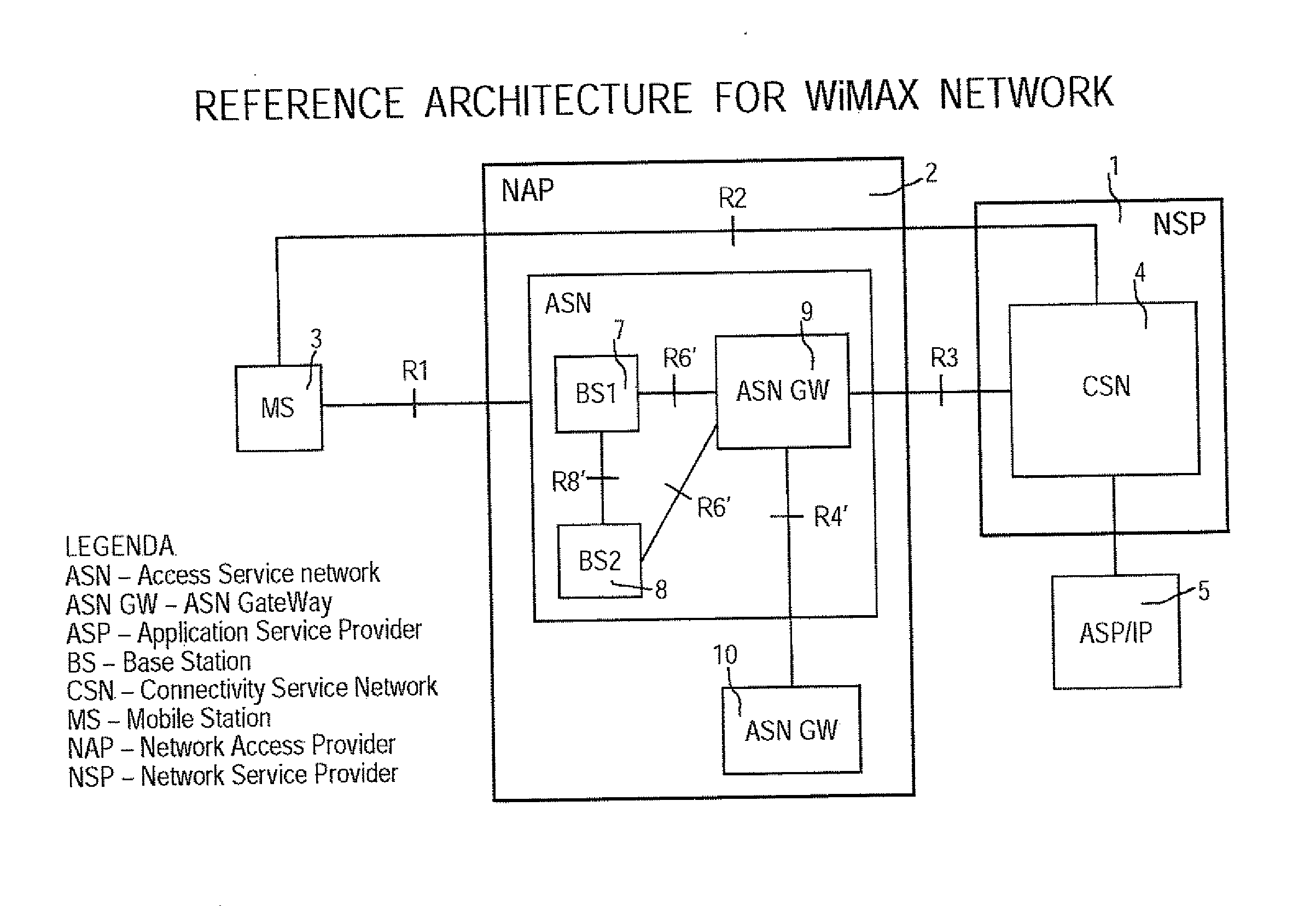
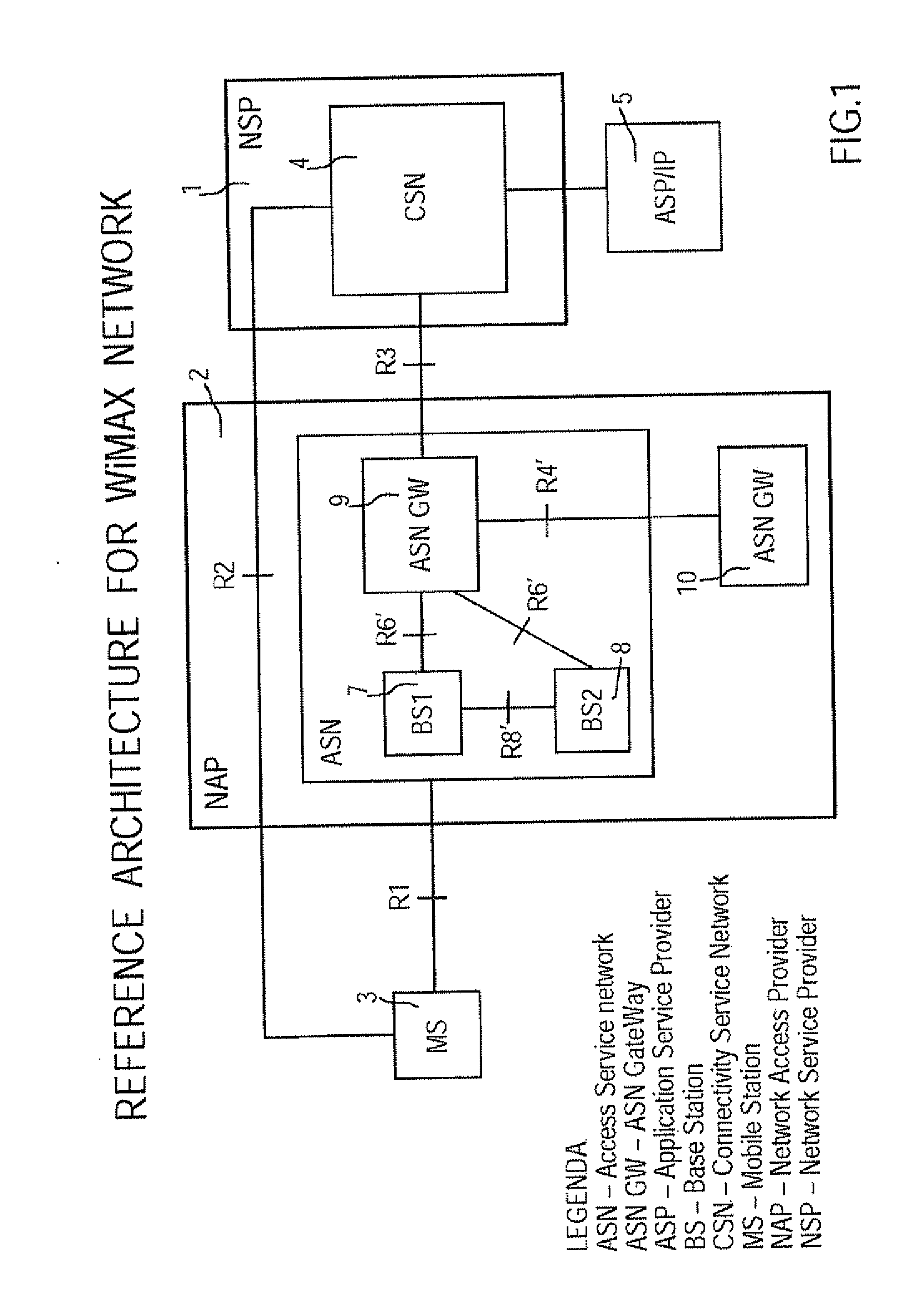
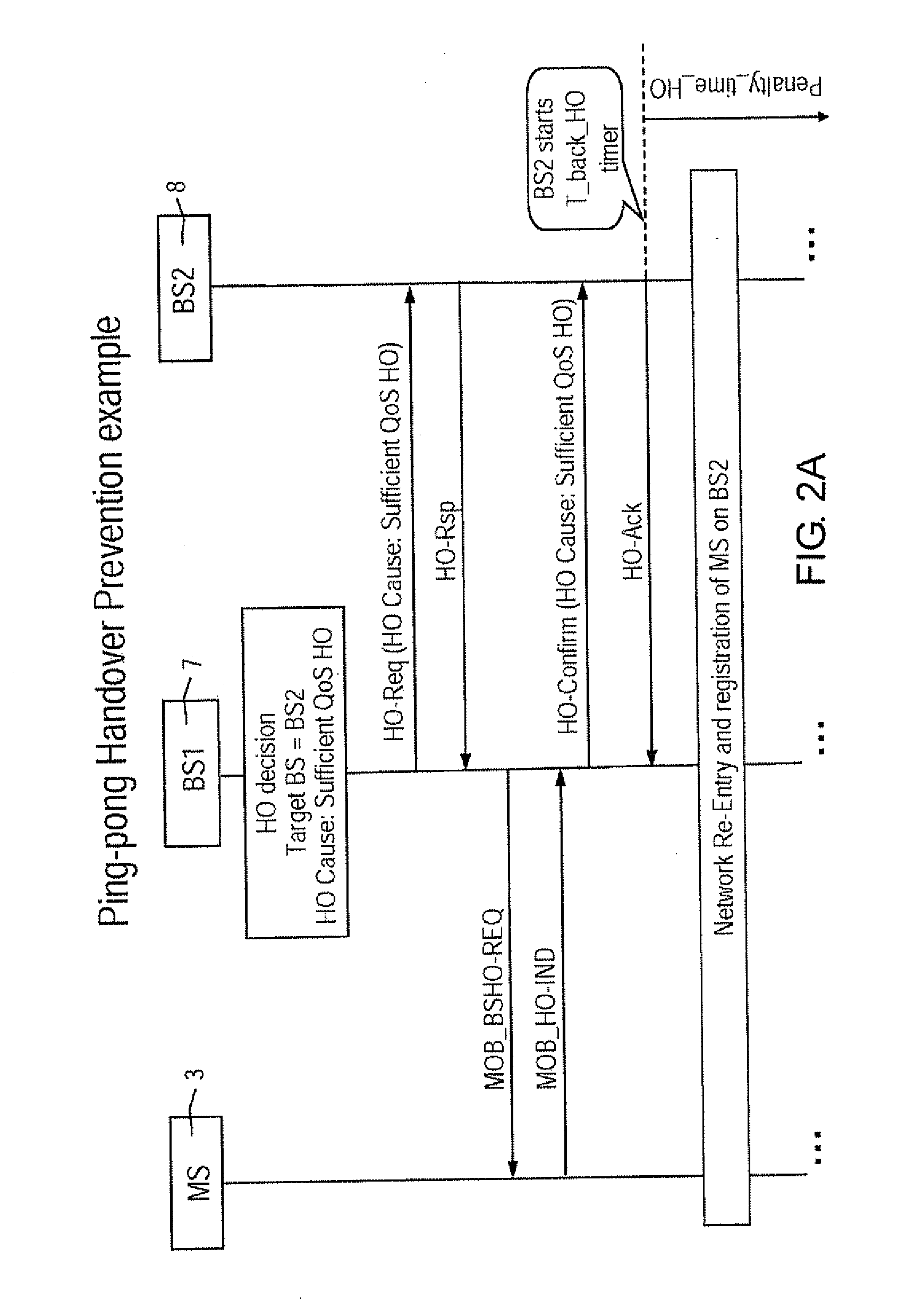
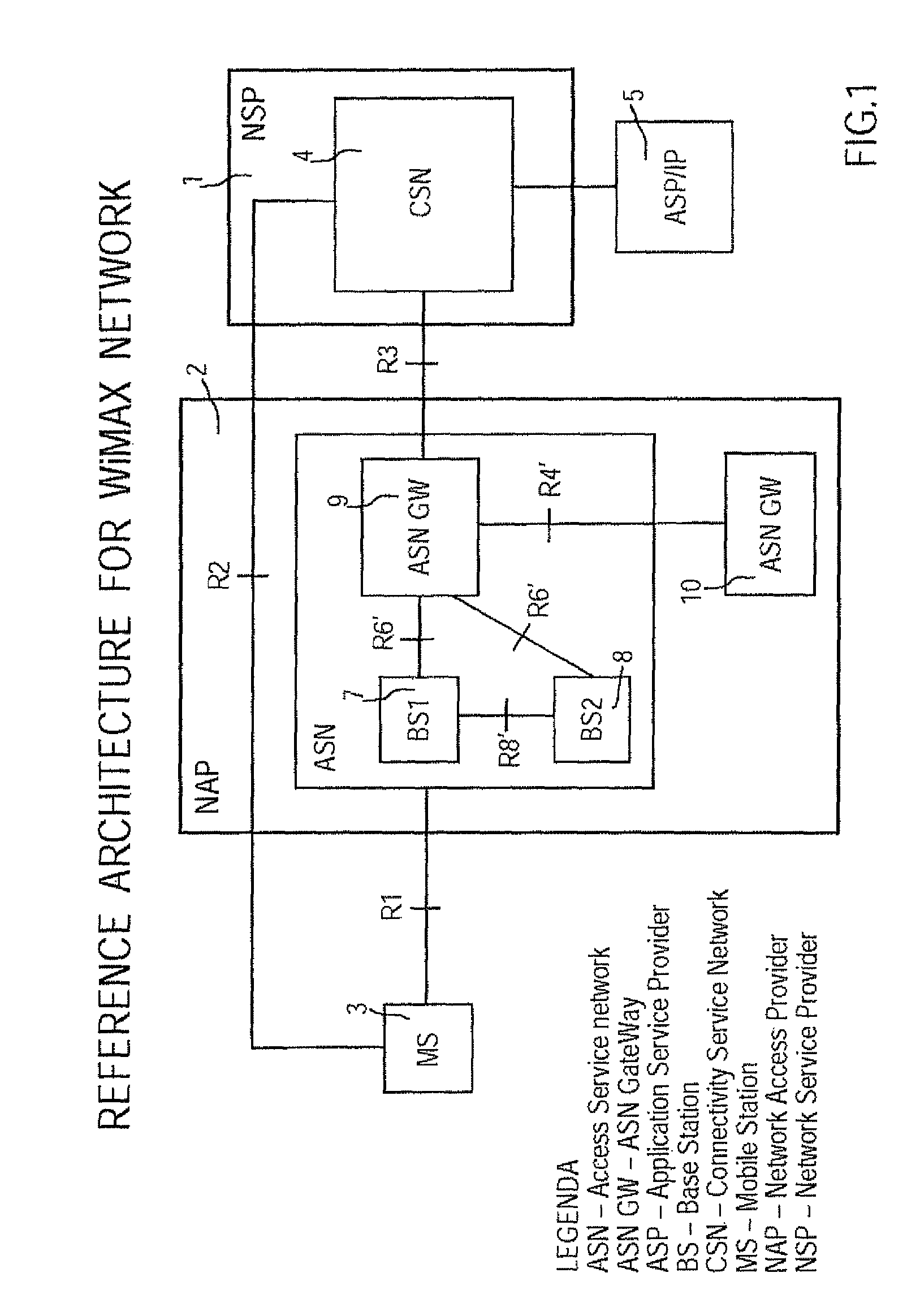
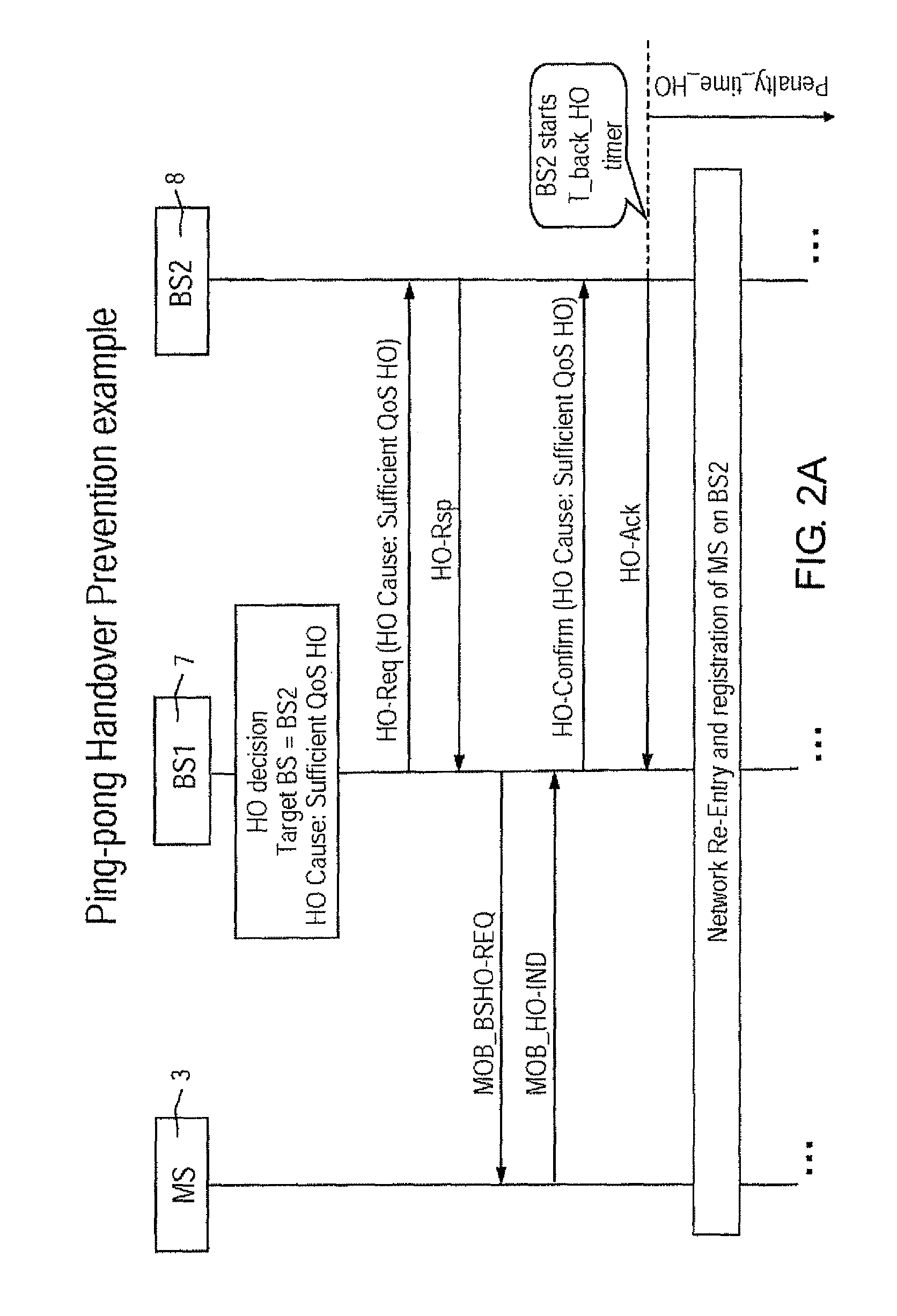
Method for preventing pin-pong handover effect in mobile wimax networks
ActiveUS20090274118A1Reduce noise levelHarmful oscillationWireless commuication servicesNormal priorityMobile device
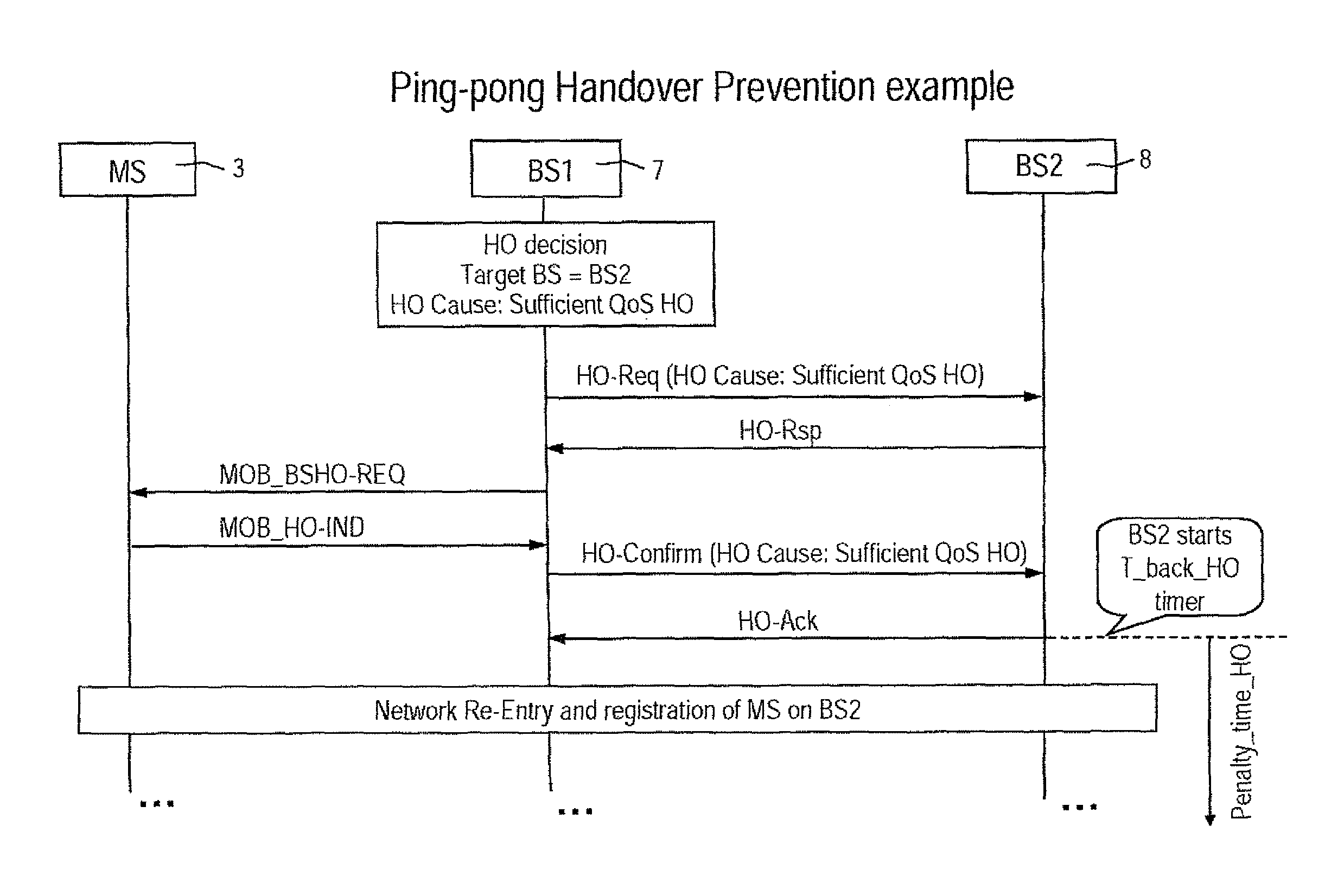
To prevent a handover ping-pong effect between base-station in WiMAX-compliant networks, a priority level is firstly assigned to the trigger causes for handover, and the prioritized causes are coded. Then codes are subdivided into a first class of unrestricted handovers and a second class of handover subjected to restriction. The first class includes the highest priority handovers. The second class includes a given subset of handovers with a high or normal priority intended for optimizing resources. Outside this subset the second class also includes handovers for power budget having a normal priority level. When an outgoing handover is decided, the actual serving BS either permits or selectively suppresses the Handover Request to the target BS when the latter is corresponding to the preceding serving BS for that mobile. The selection mechanism operates on the second class of restricted handovers, during a penalty time triggered by the occurrence of handover causes included in the given subset of the second class.
Owner:RPX CORP
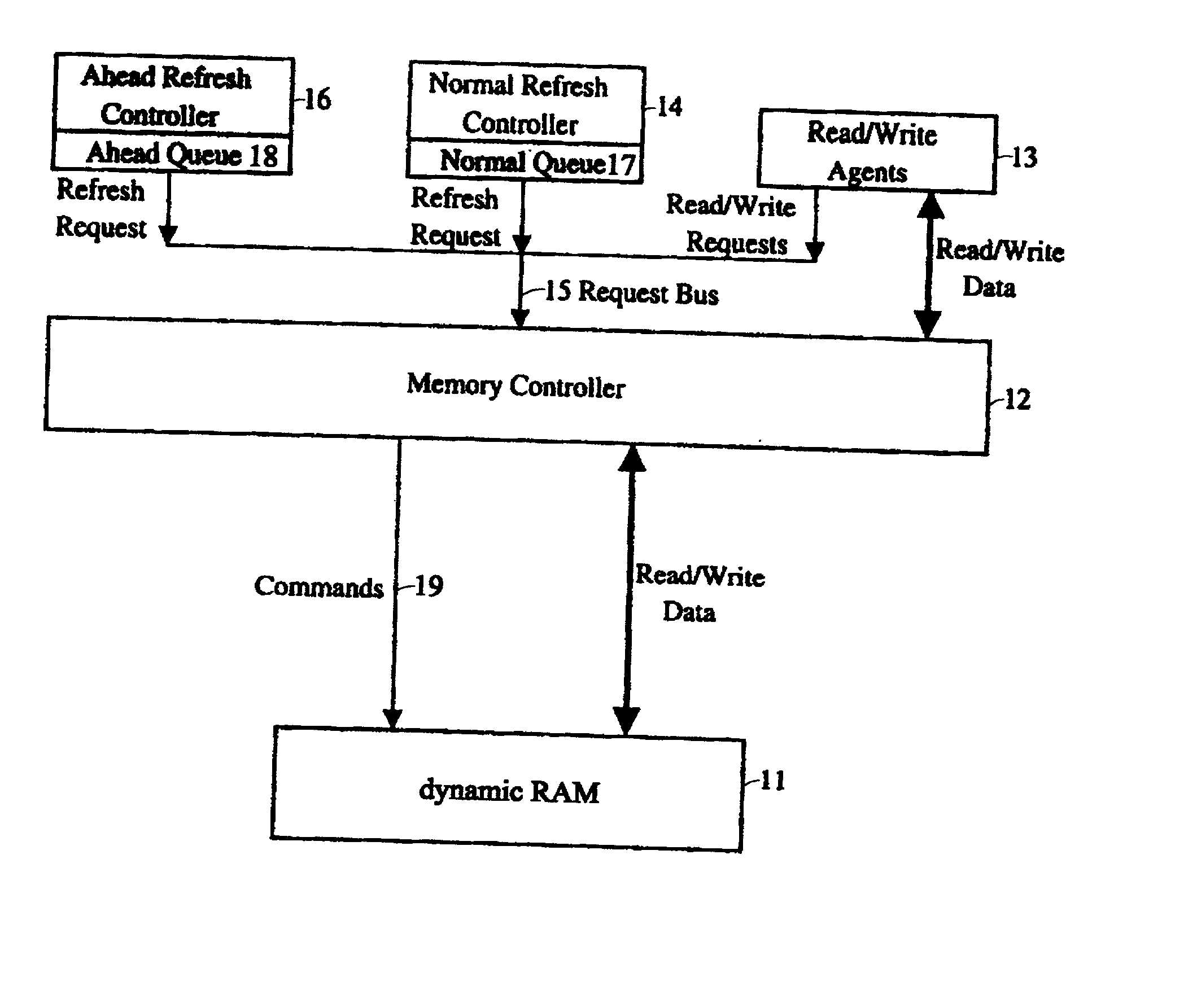
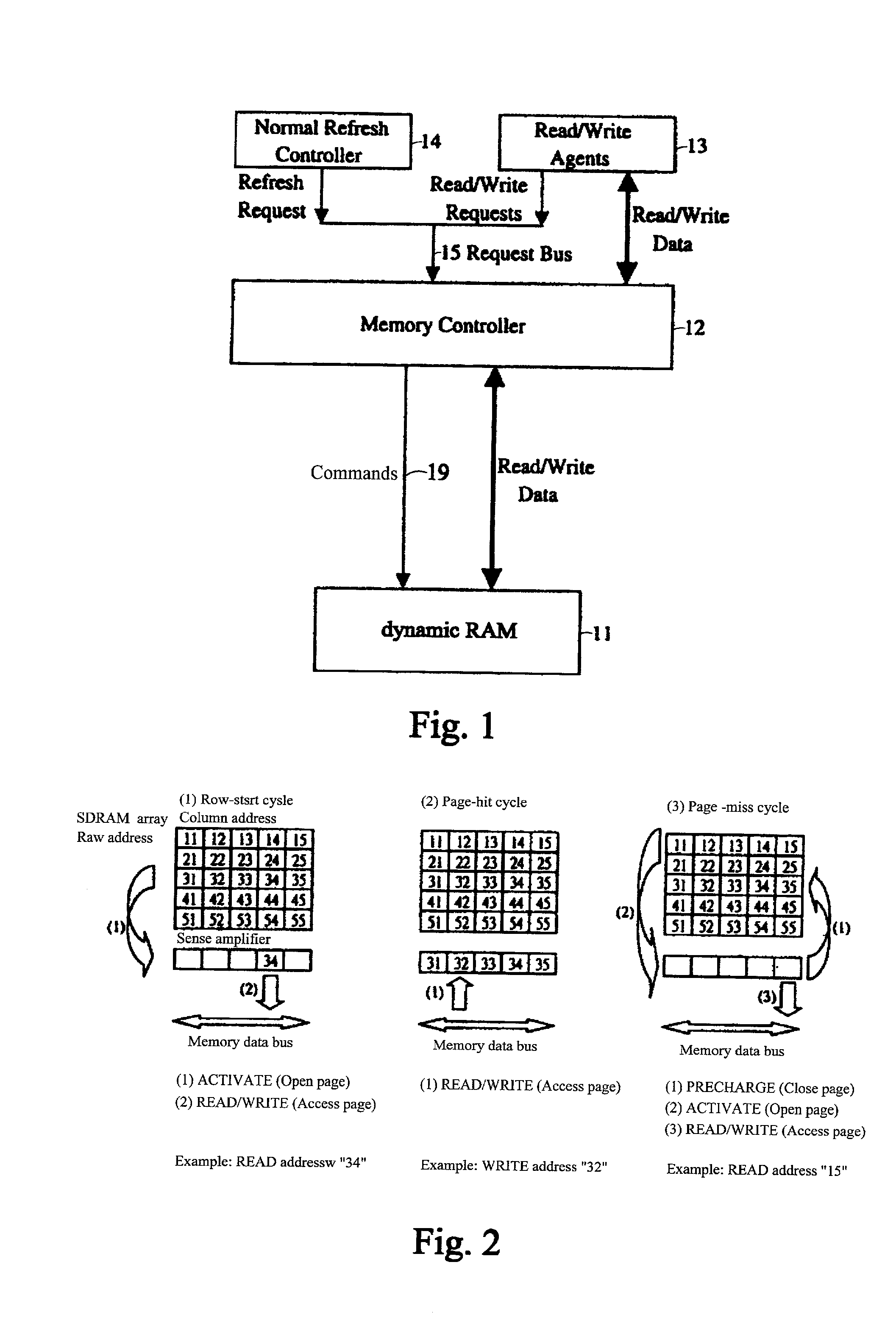
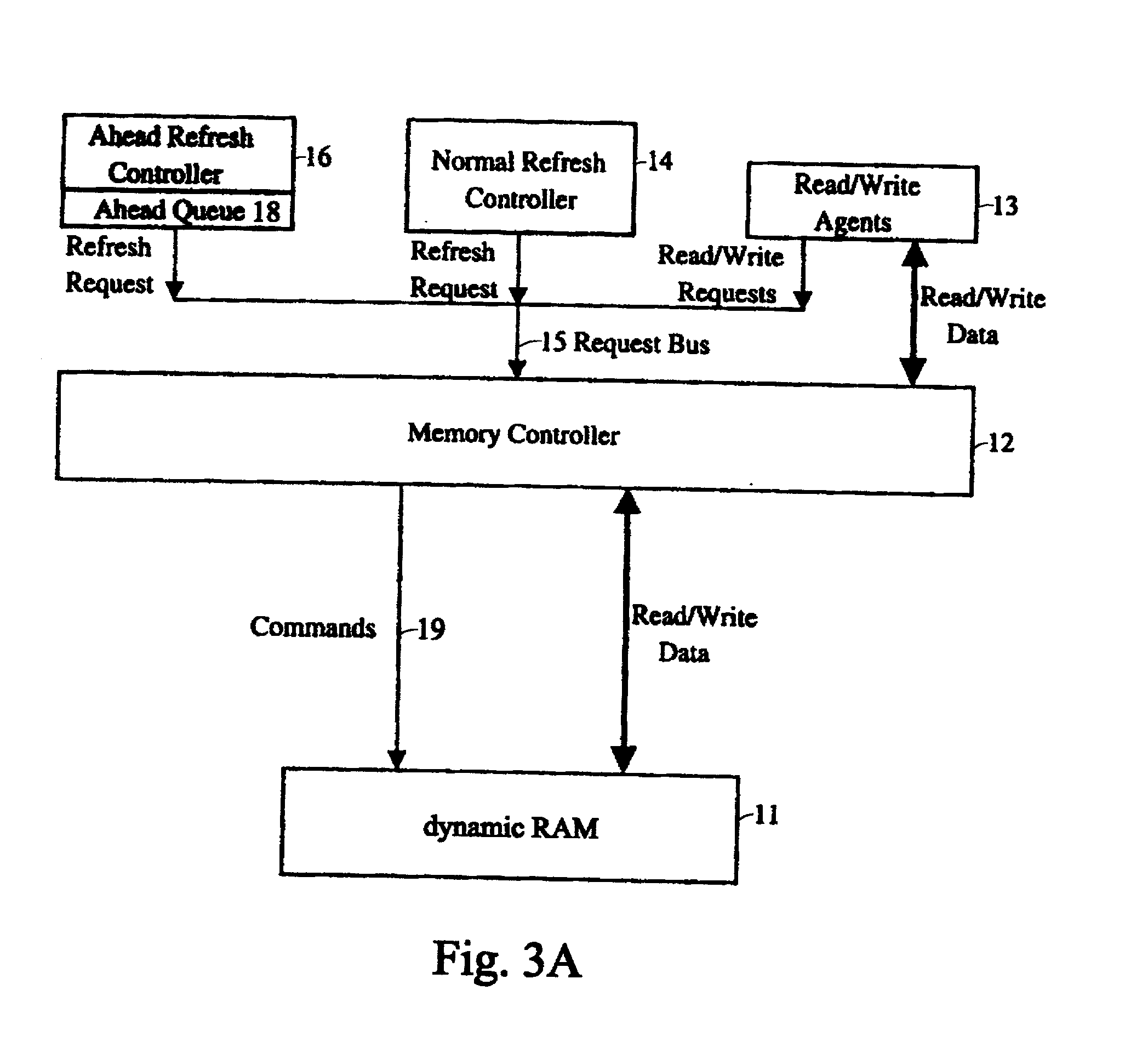
Method and apparatus of event-driven based refresh for high performance memory controller
A method and apparatus for refreshing dynamic memory is provided. The apparatus includes an ahead refresh controller having an ahead queue for refreshing dynamic random access memory (DRAM) when the memory request bus is idle. In such a way that no dynamic RAM bandwidth is wasted. The apparatus also comprises a normal refresh controller having a normal queue. Giving the normal refresh request in the normal priority unless the normal queue is full. The present invention allows the refresh cycles to gather on the basis of events to minimize the overheads. In other words, even when the system is running in peak performance, the normal refresh controller can largely compact the refresh cycles by means of the normal queue to decrease occurrence of interruption.
Owner:SILICON INTEGRATED SYSTEMS
Dynamic priority adjustment in a real time streaming engine
InactiveUS6876647B2Low priorityOptimize the numberData switching by path configurationHybrid transportData streamNormal priority
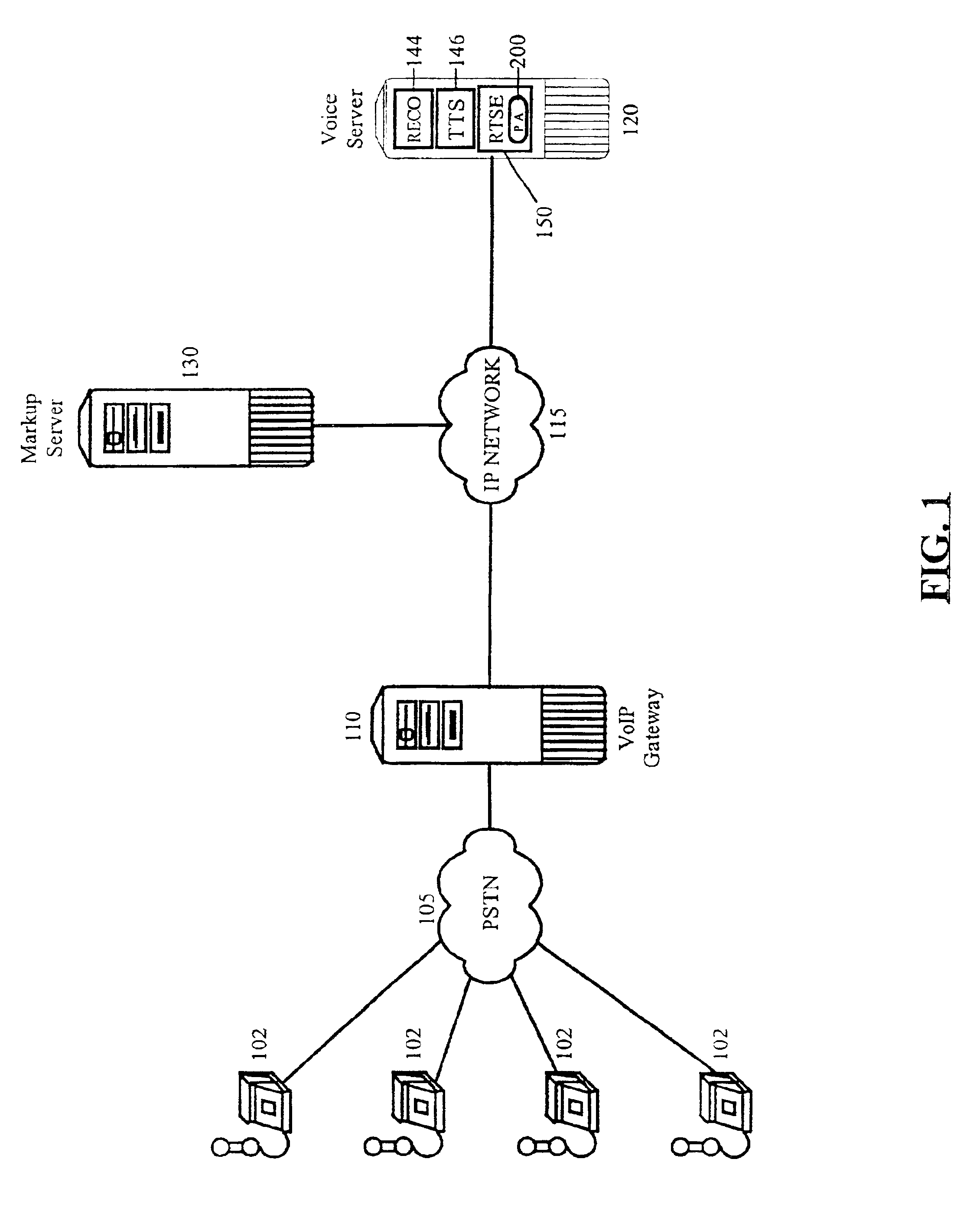
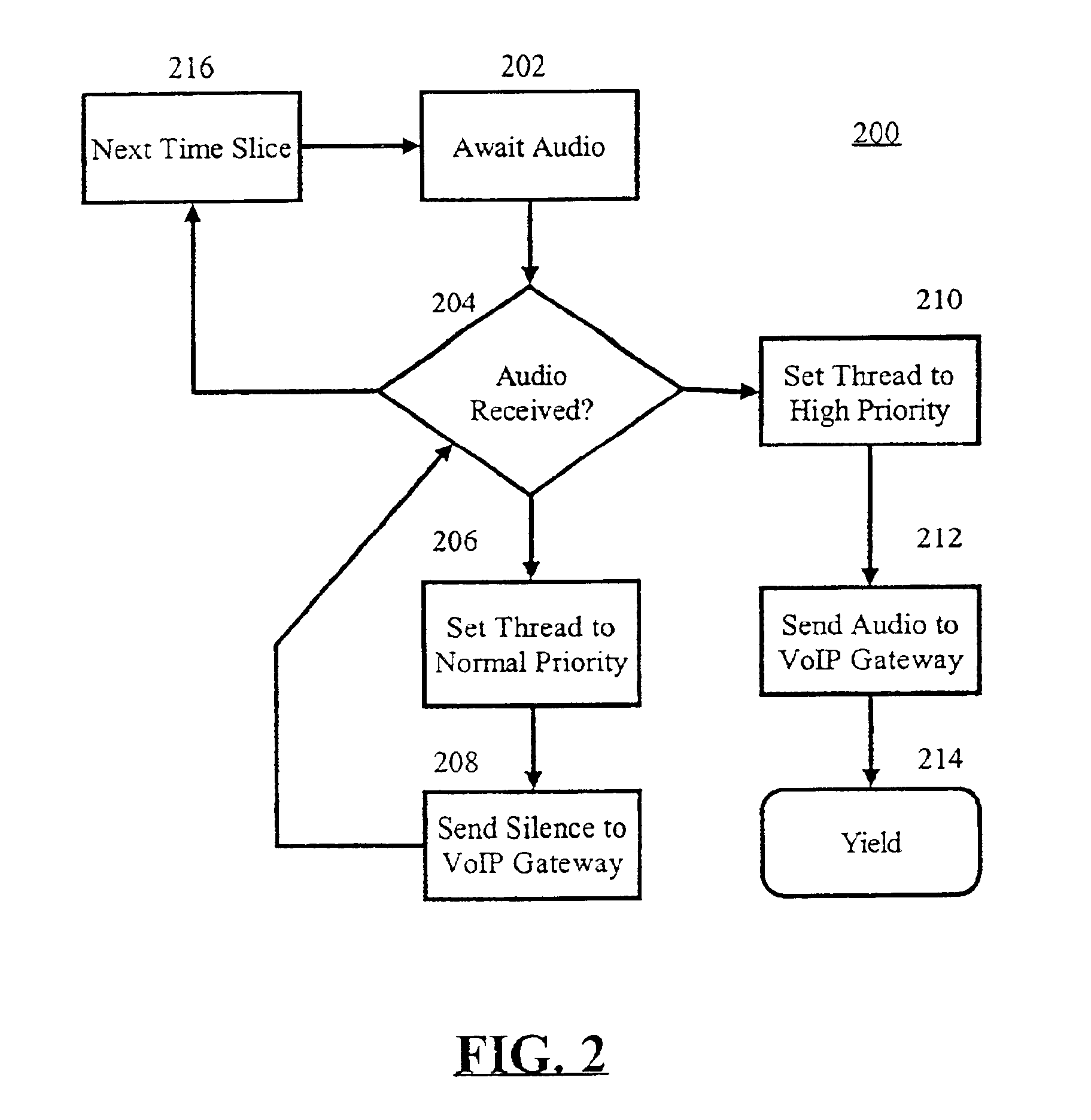
A voice data streaming method can include establishing a voice call connection with a VoIP gateway; receiving audio data from a network source; assigning a high priority to a thread of execution in which the received audio data can be streamed to the VoIP gateway; and, reducing the high priority to a normal priority when the received audio data has been completely streamed to the VoIP gateway. Notably, the step of receiving audio data from a network source can include receiving a recorded audio prompt from the network source. Similarly, the step of receiving audio data from a network source can include receiving synthesized audio from a text-to-speech (TTS) engine. The method also can include the step of streaming silence data in the thread of execution after the high priority has been reduced to the normal priority. Finally, the method can include the step of packetizing the audio data for transmission over a packet-switched network; and, streaming the packetized audio data in the high priority thread of execution according to RTP.
Owner:IBM CORP
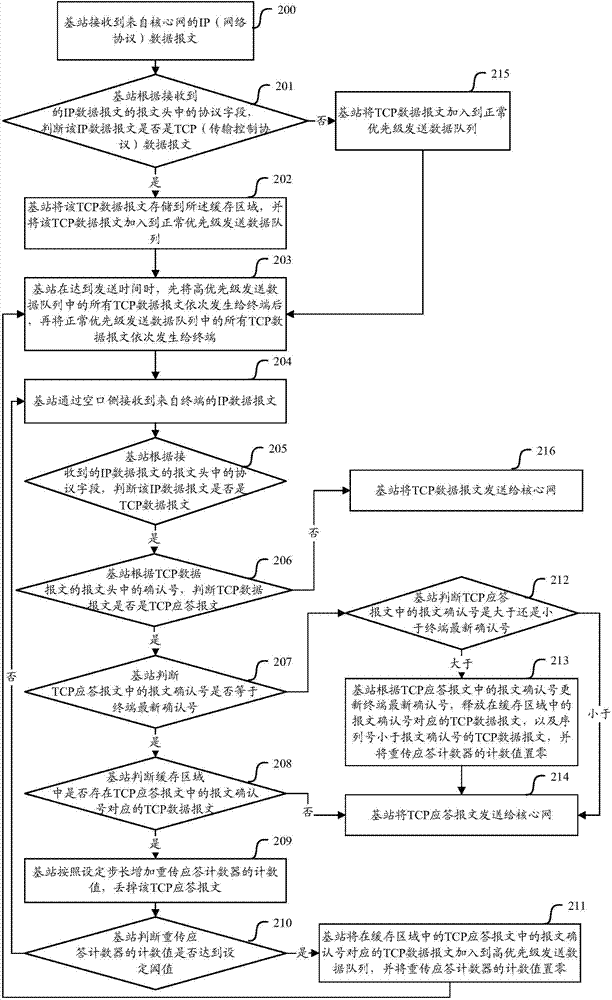
Method and equipment for retransmitting TCP (transmission control protocol) data messages
InactiveCN104780028AImprove timelinessError prevention/detection by using return channelNormal priorityCore network
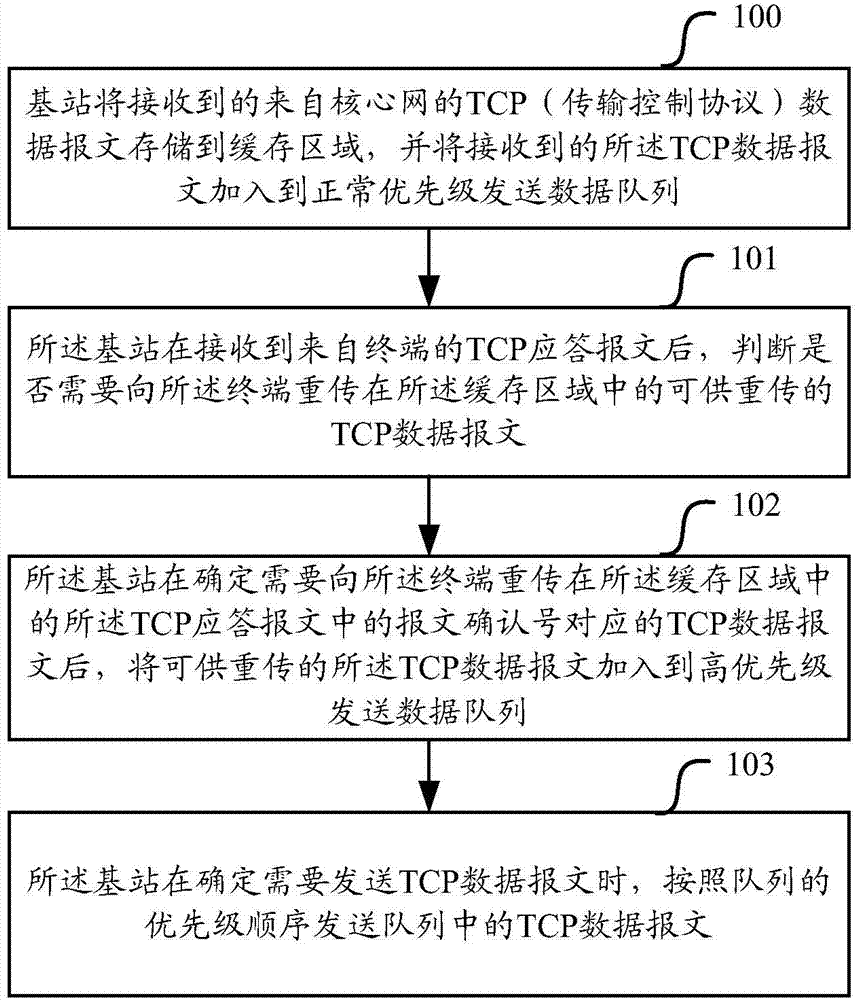
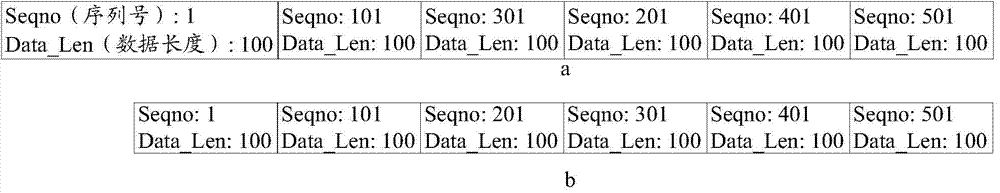
An embodiment of the invention provides a method and equipment for retransmitting TCP (transmission control protocol) data messages and aims to solve the problem that a method for retransmitting TCP data messages through a core network is not high in retransmission timeliness rate in the prior art. The method comprises steps as follows: a base station stores the received TCP data messages from the core network in a cache zone and adds the TCP data messages to a normal priority sending data queue; the base station judges whether to retransmit the TCP data messages which can be retransmitted and are stored in the cache zone to a terminal or not after receiving TCP response messages from the terminal; the base station adds the TCP data messages which can be retransmitted to a high priority sending data queue after determining that retransmission is required; the base station sends the TCP data messages according to the priority sequence of queues when determining that the TCP data messages are required to the retransmitted. With the adoption of the method, the base station retransmits the TCP data messages which can be retransmitted to the terminal according to the priority sequence, and the retransmission timeliness rate is increased.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM SYST CHINA LTD +3
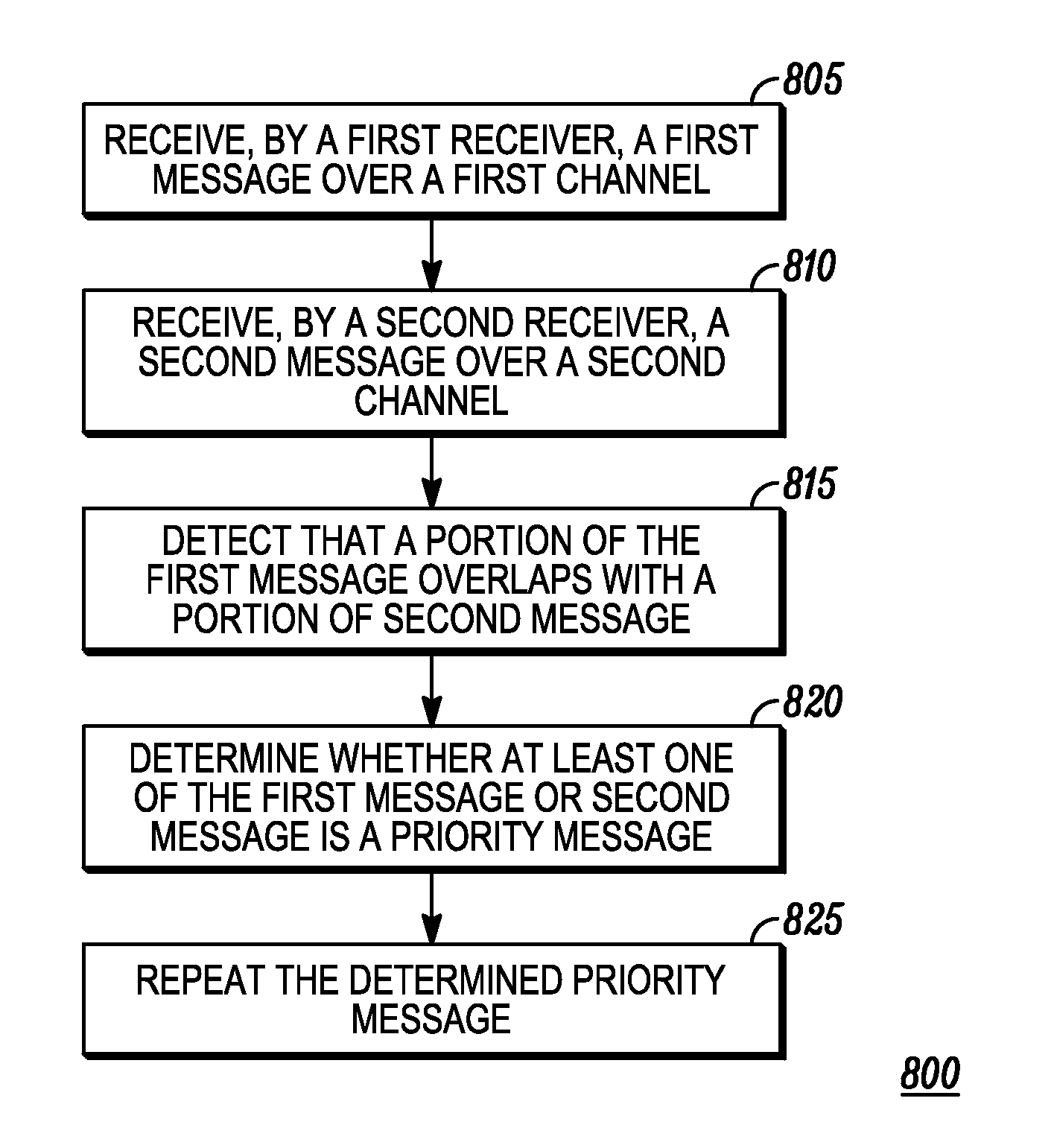
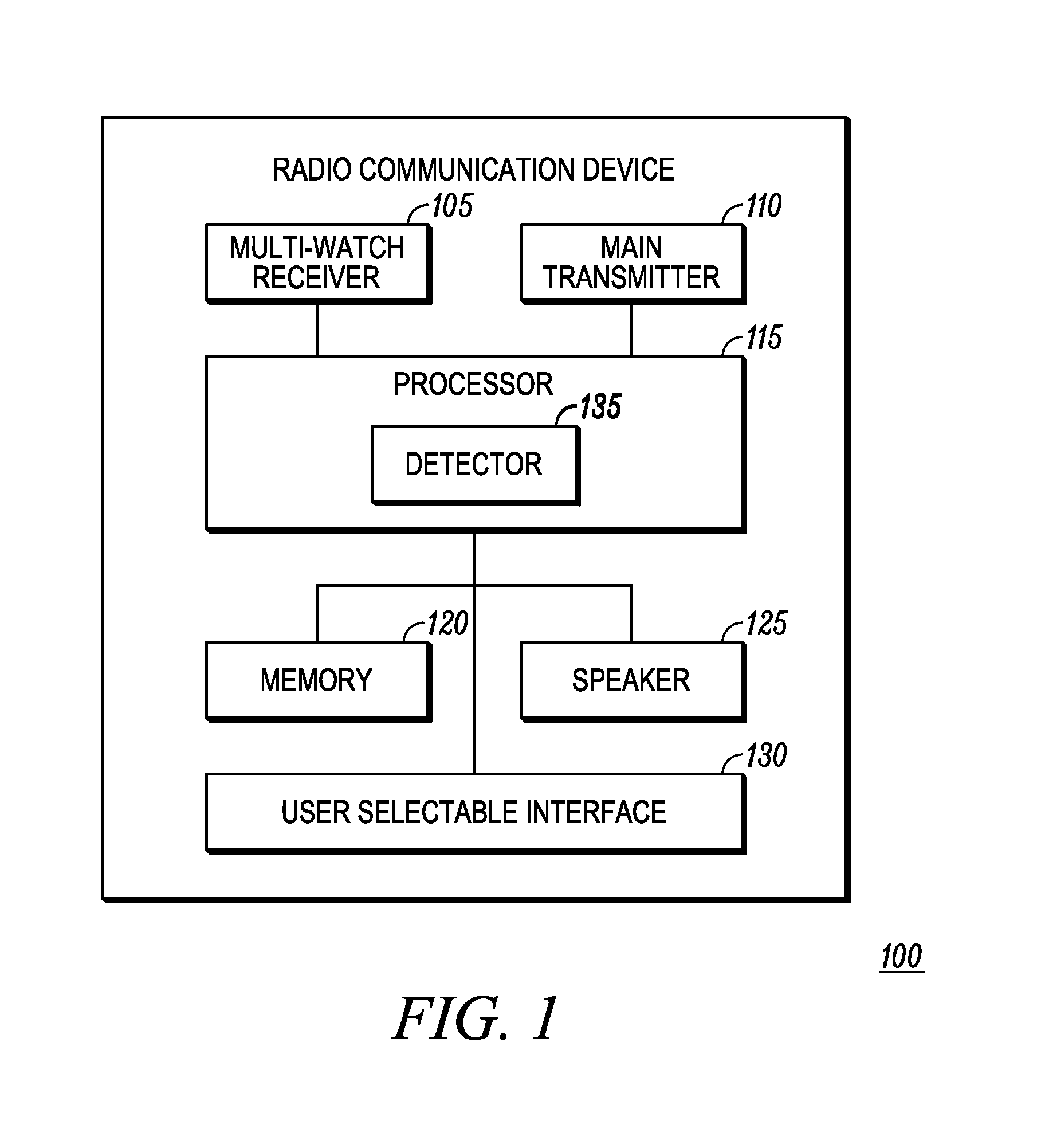
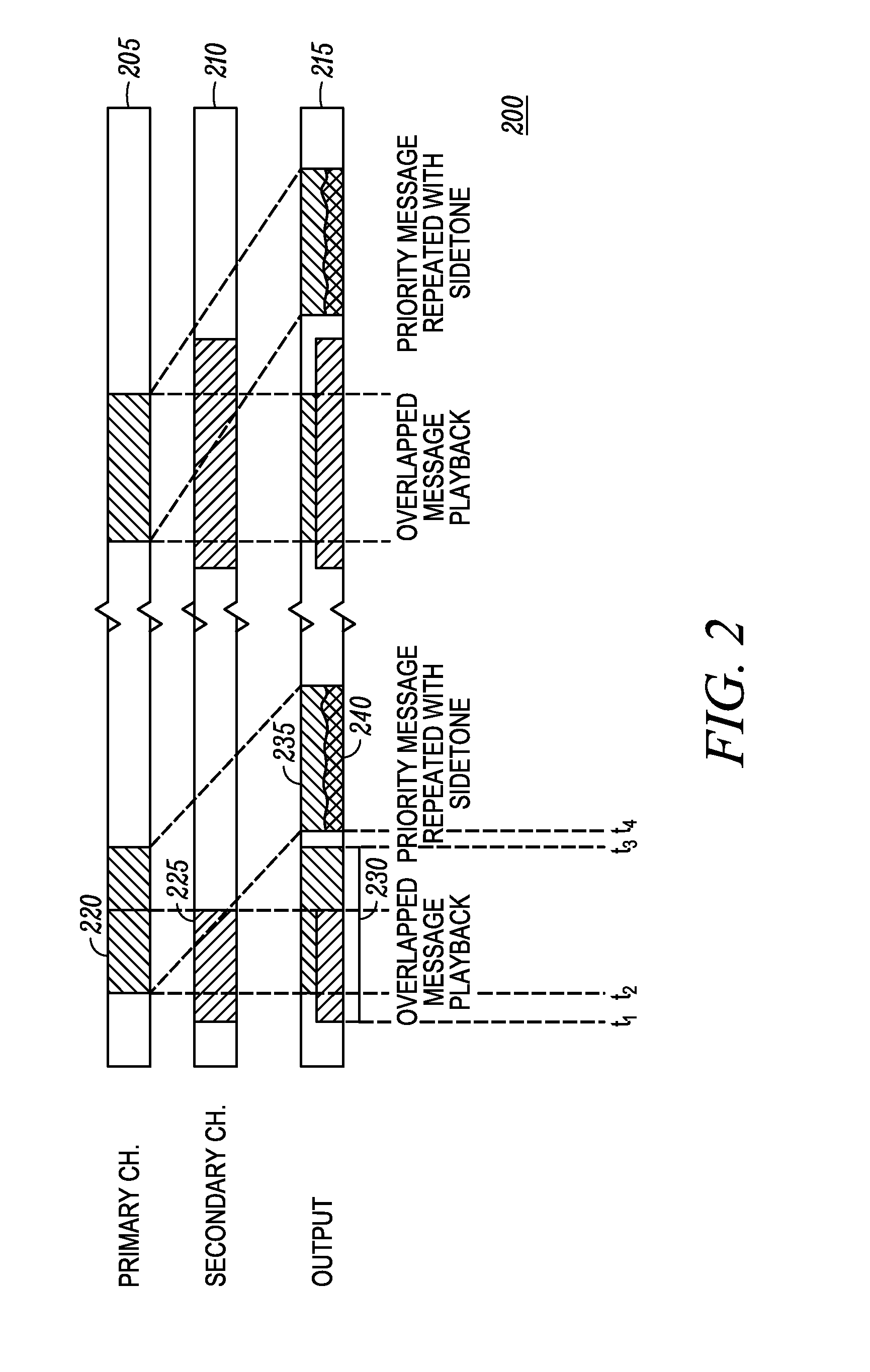
Intelligibility of overlapping audio
ActiveUS20150147990A1Spatial transmit diversitySpecial service for subscribersTelecommunicationsNormal priority
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
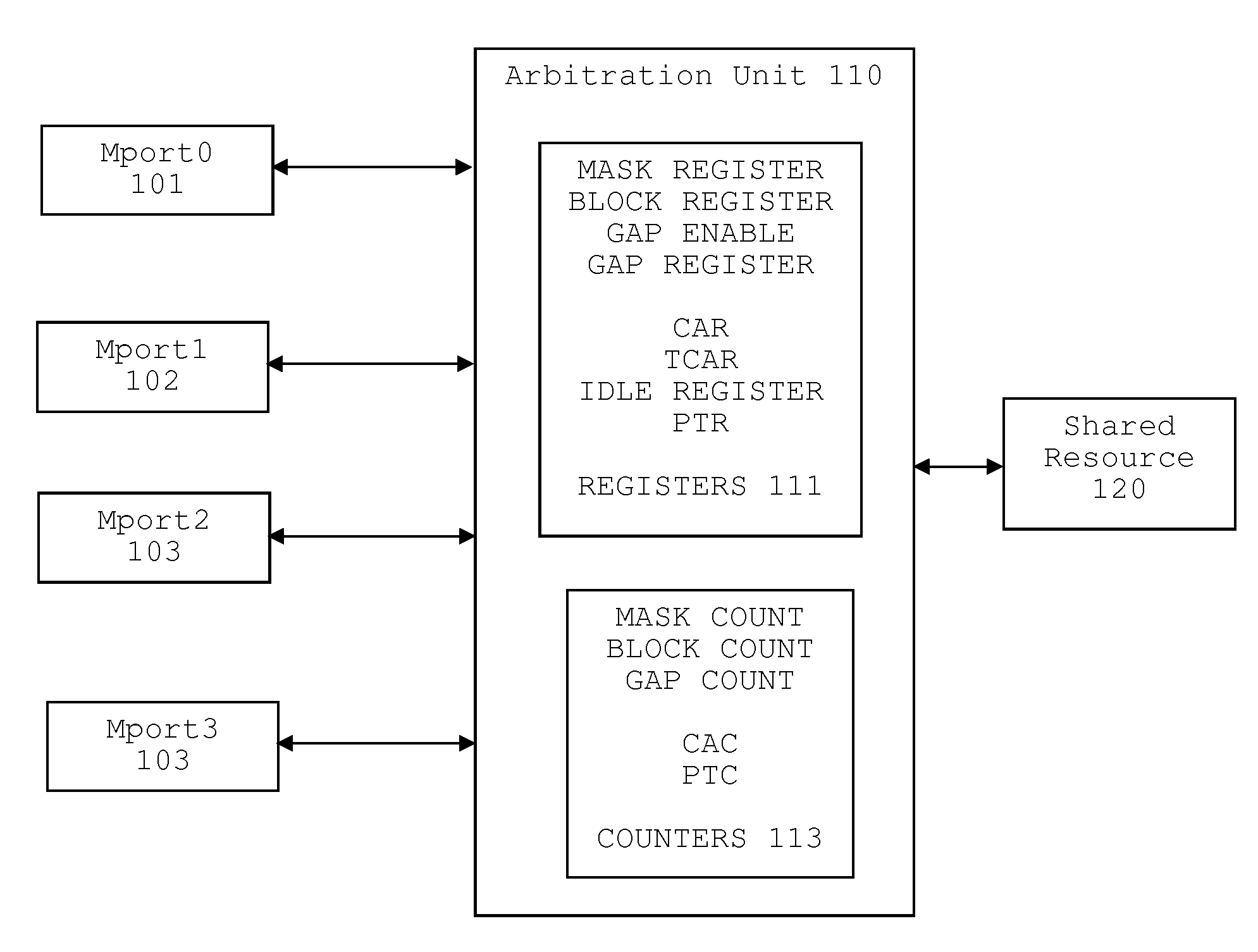
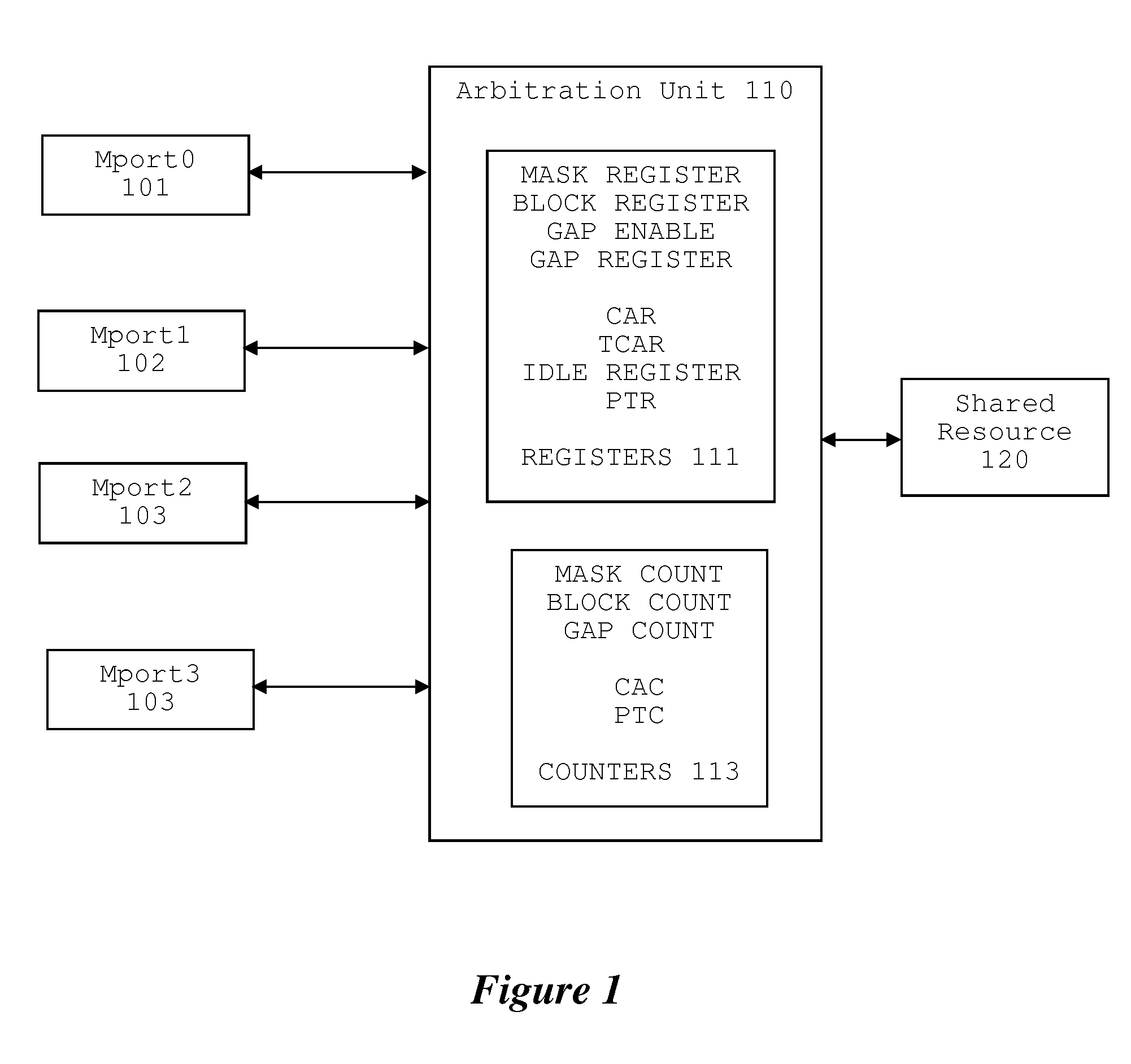
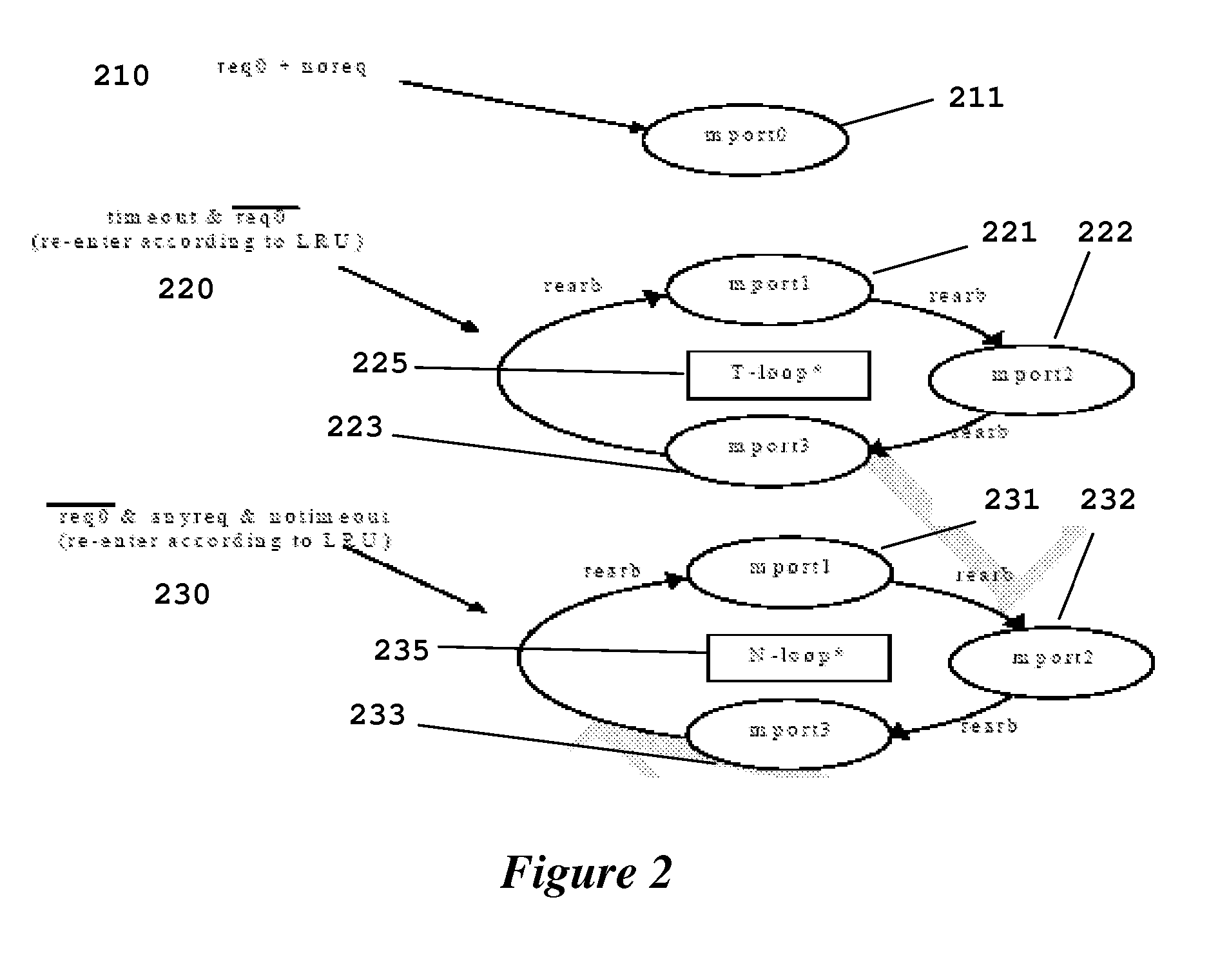
Software Programmable Dynamic Arbitration Scheme
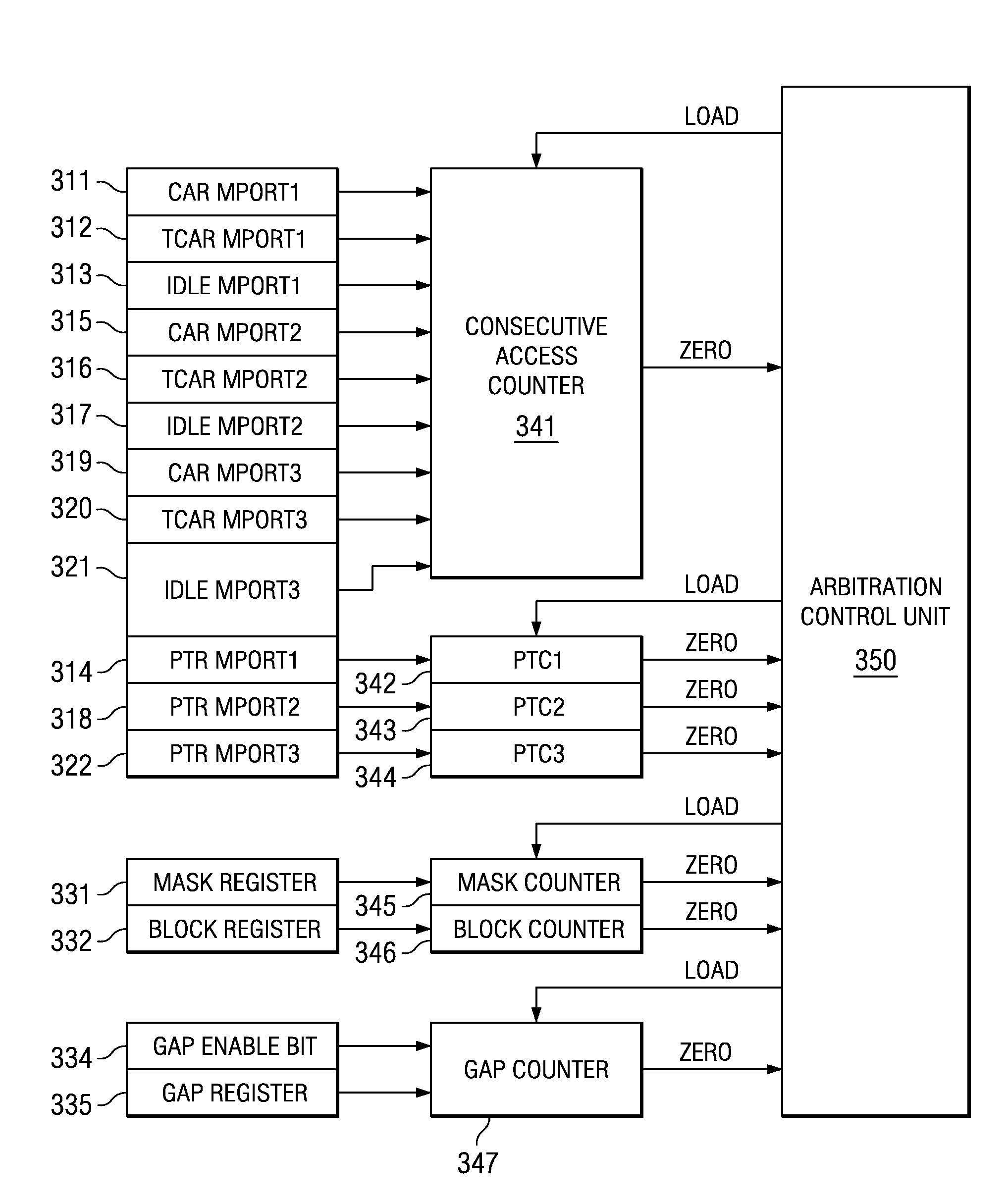
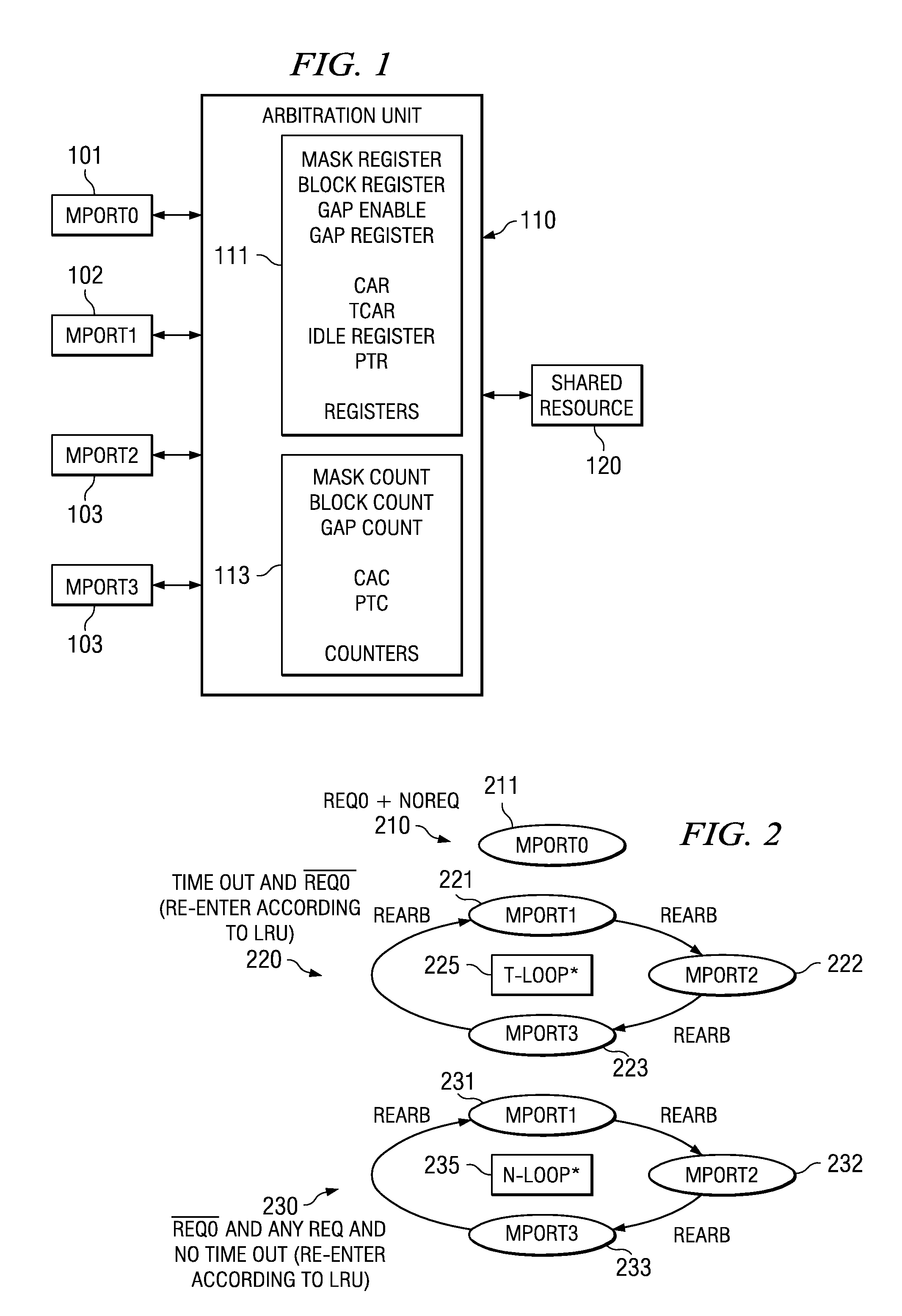
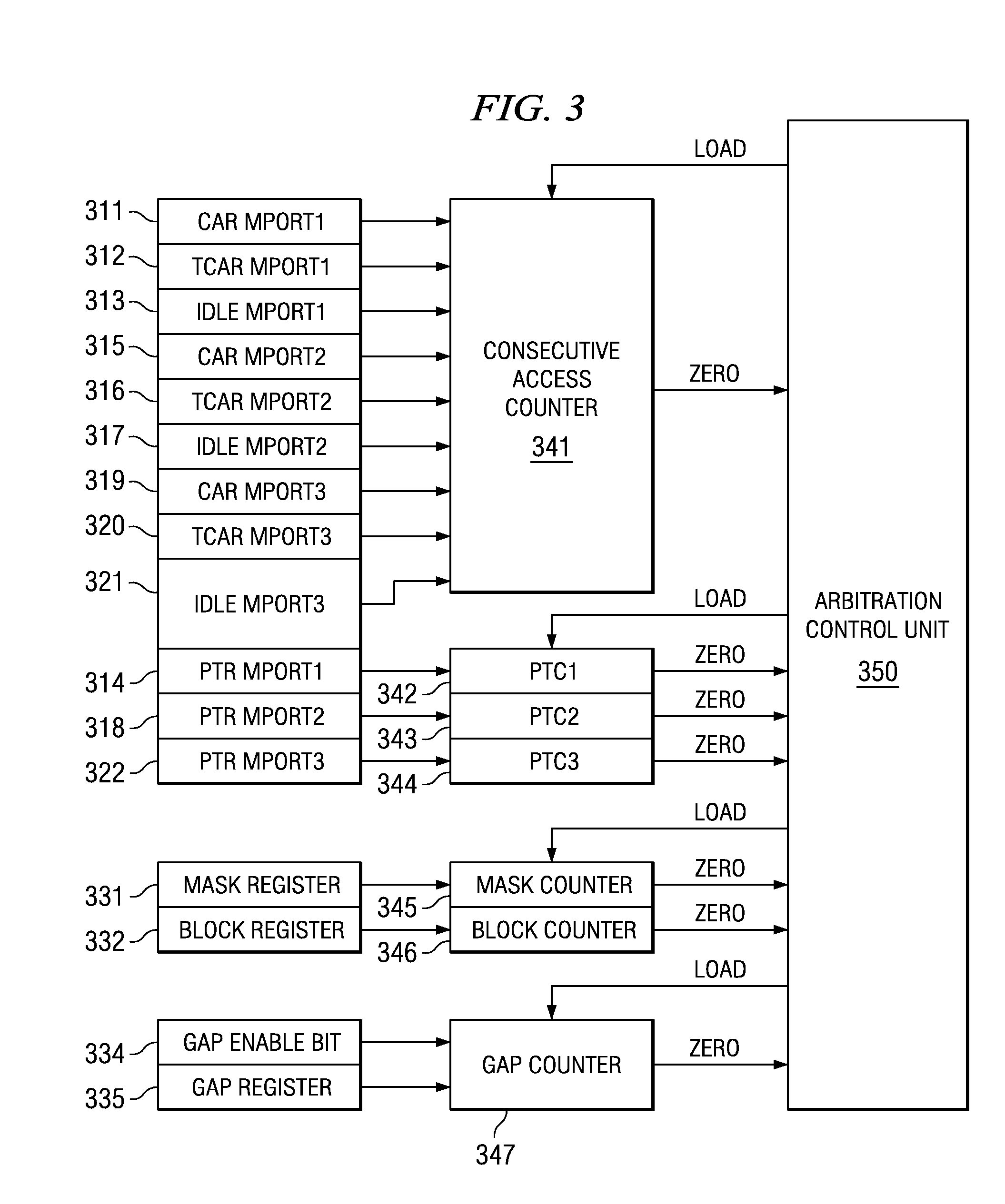
A method for arbitration among a plurality of requesting devices for a shared resource in which one device is an ultra high priority device grants access to one requesting device at a time. The ultra high priority device is granted access if it requests access interrupting access by another device. The ultra high priority device is limited to a selectable number of accesses and thereafter is masked for a selectable interval. This interval permits access may by other devices. Each of the other devices is also limited to a selectable number of accesses followed by re-arbitration. The other devices can have a normal priority or a time out priority if a request hasn't been granted in a selectable amount of time.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
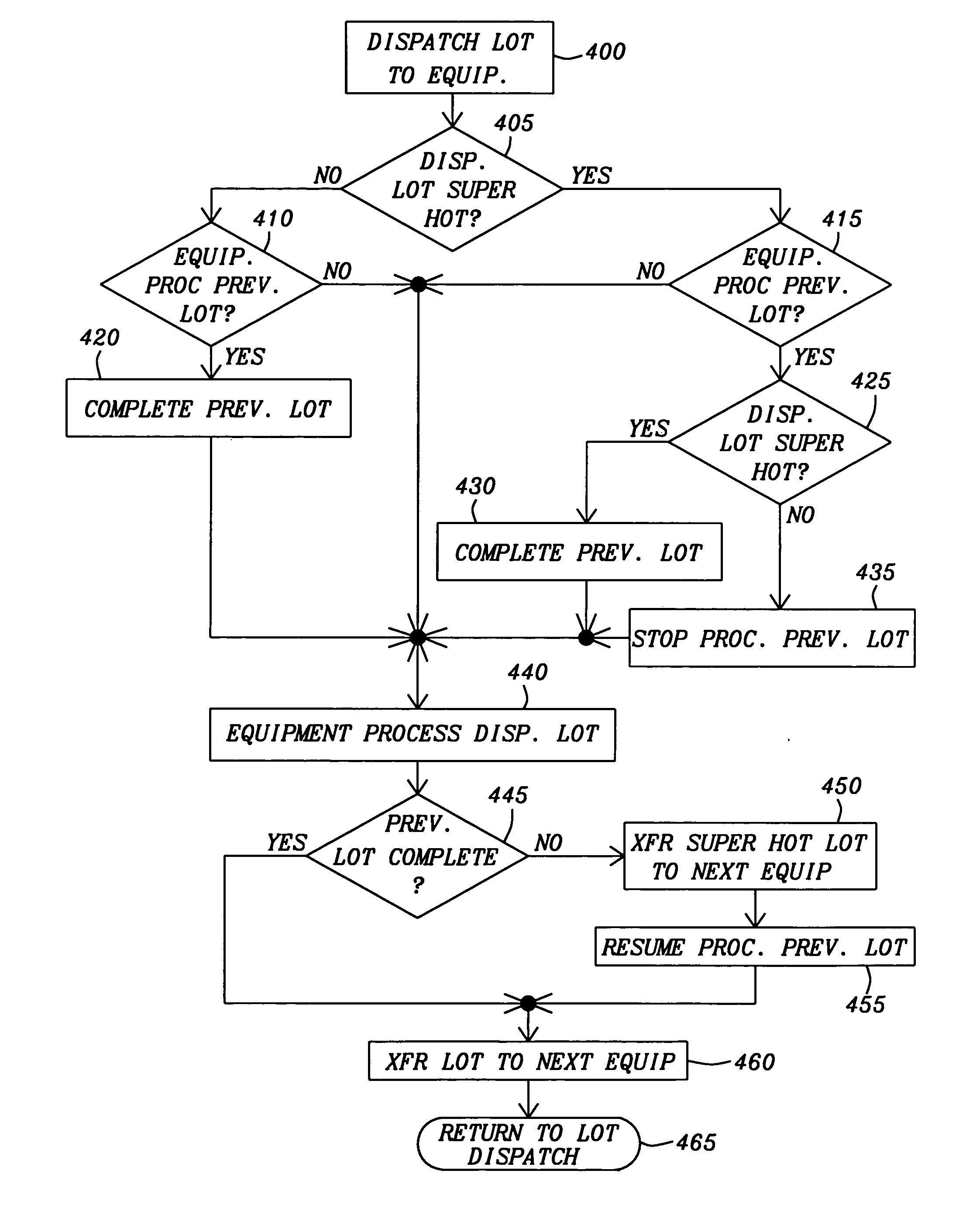
Scheduling system and method for avoiding low equipment utilization
InactiveUS20050203655A1Minimize low utilization rateProgramme controlResourcesSequence controlProcess equipment
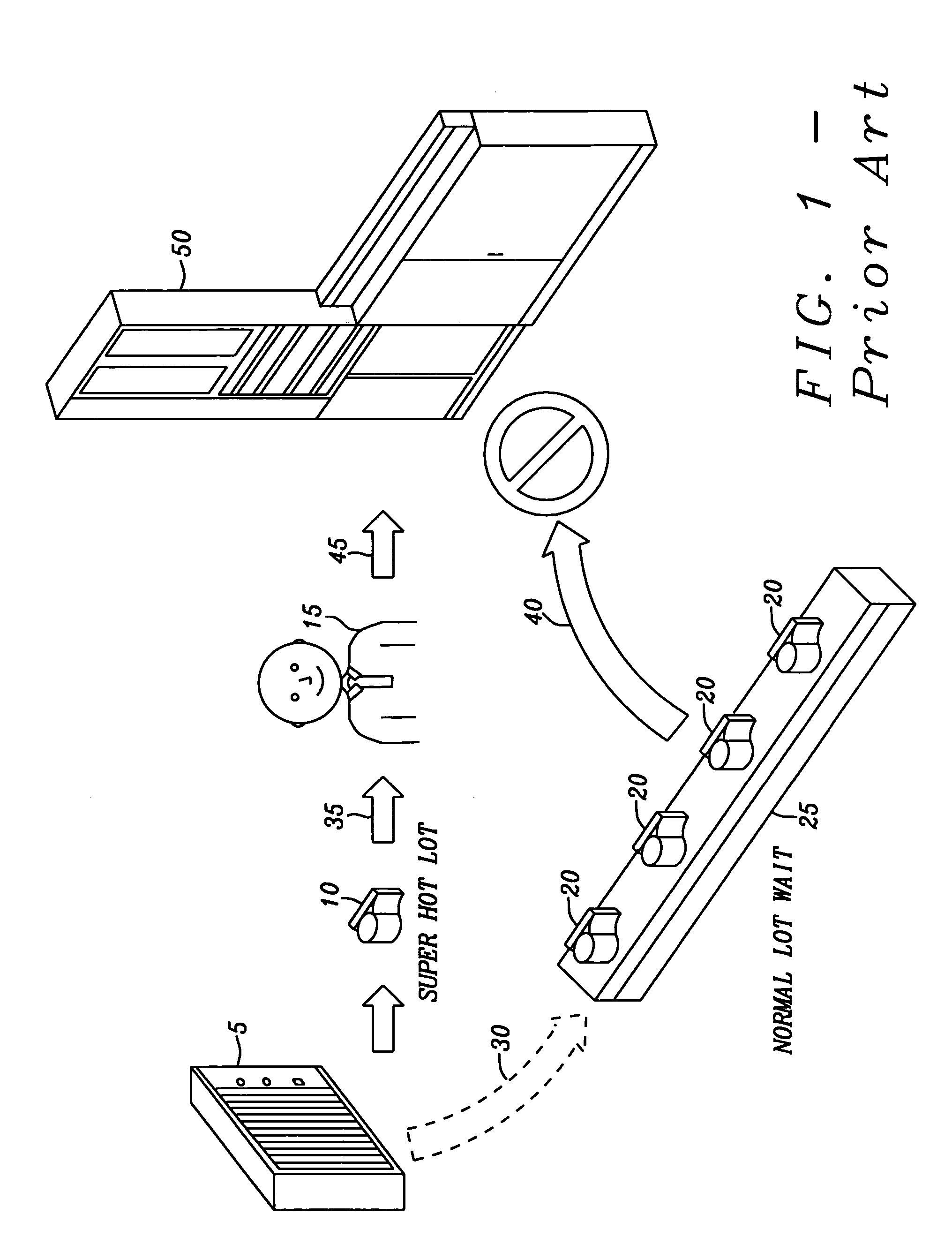
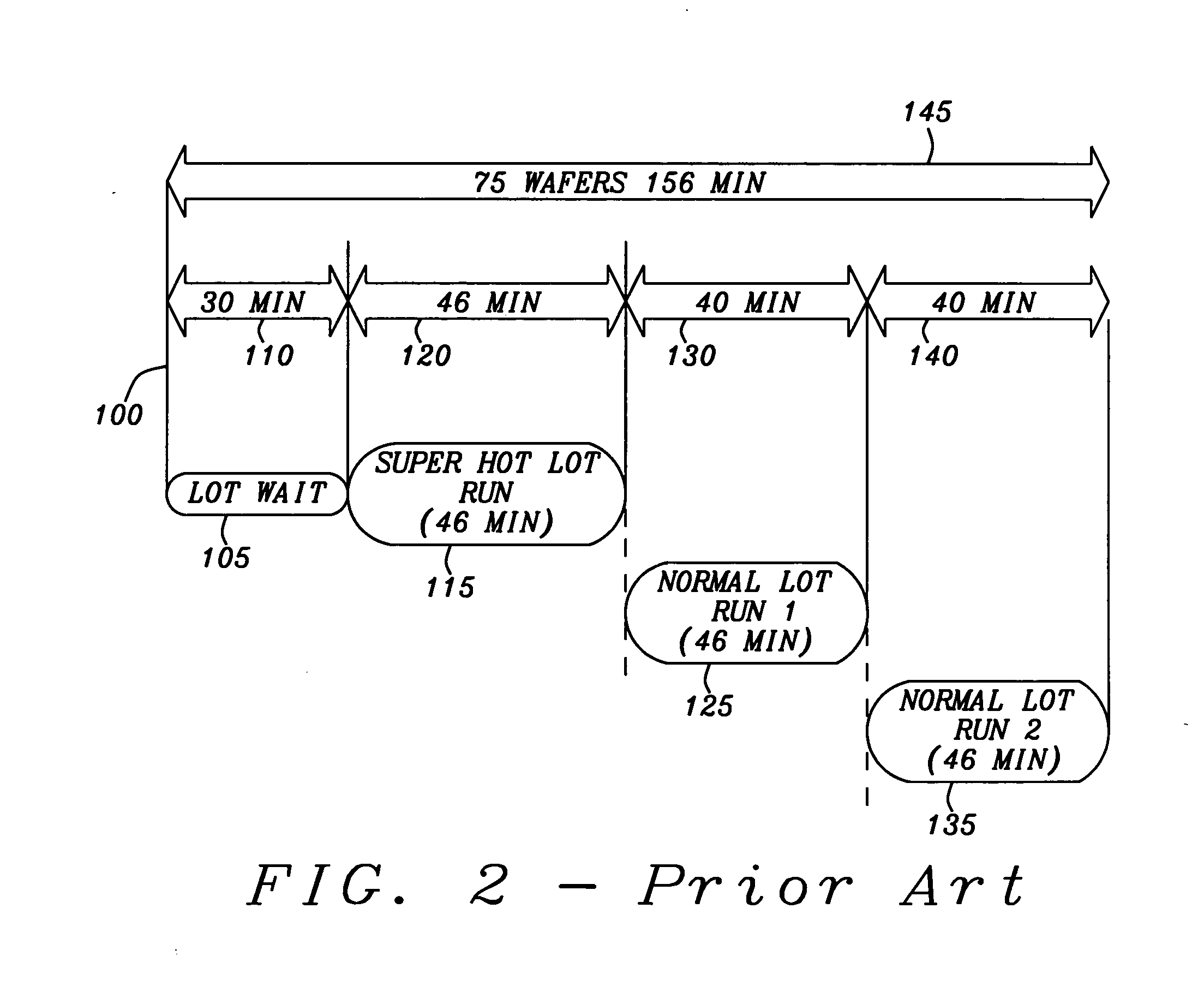
A manufacturing equipment scheduler controls the run sequences of product lots to minimize low utilization rates of units of manufacturing equipment within a manufacturing facility. The manufacturing equipment scheduling system includes a product lot sequence controller that receives priority information of the product lots dispatched for fabrication The product lot sequence controller determines a priority of a currently dispatched product lot. If the current product lot has a high priority, the product lot sequence controller then determines if a previous product lot remains in a selected unit of processing equipment and has a normal priority. If the previous product lot has a normal priority, the product lot is removed from the selected unit of processing equipment and the product lot with the high priority is processed. Upon completion of processing the current product lot with high priority, processing for the previous product lot is continued.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
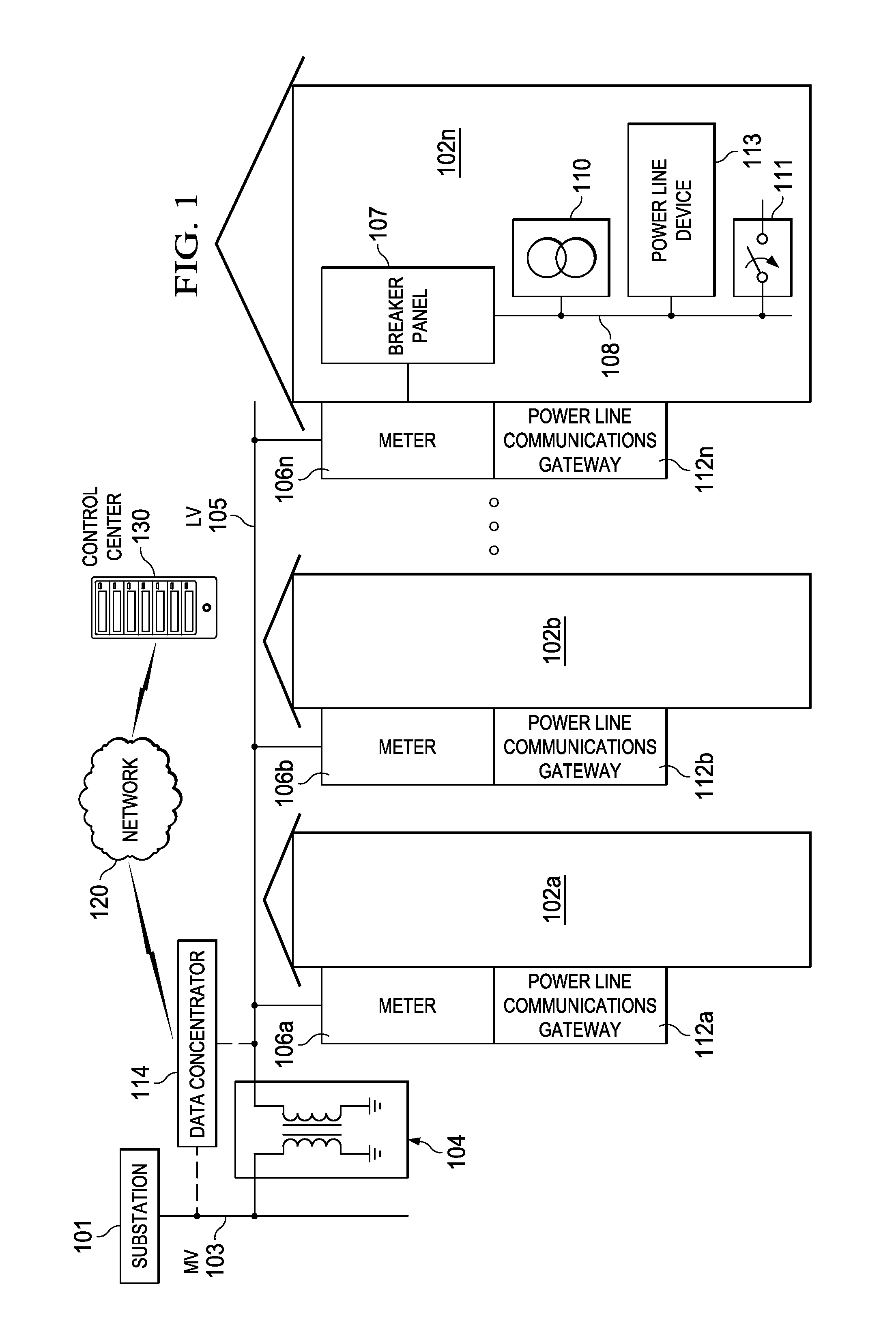
Overlapping priority contention windows power line communications networks
ActiveUS20150180680A1Small impactIncrease window sizePower distribution line transmissionRemote meteringNormal priorityIdle channel
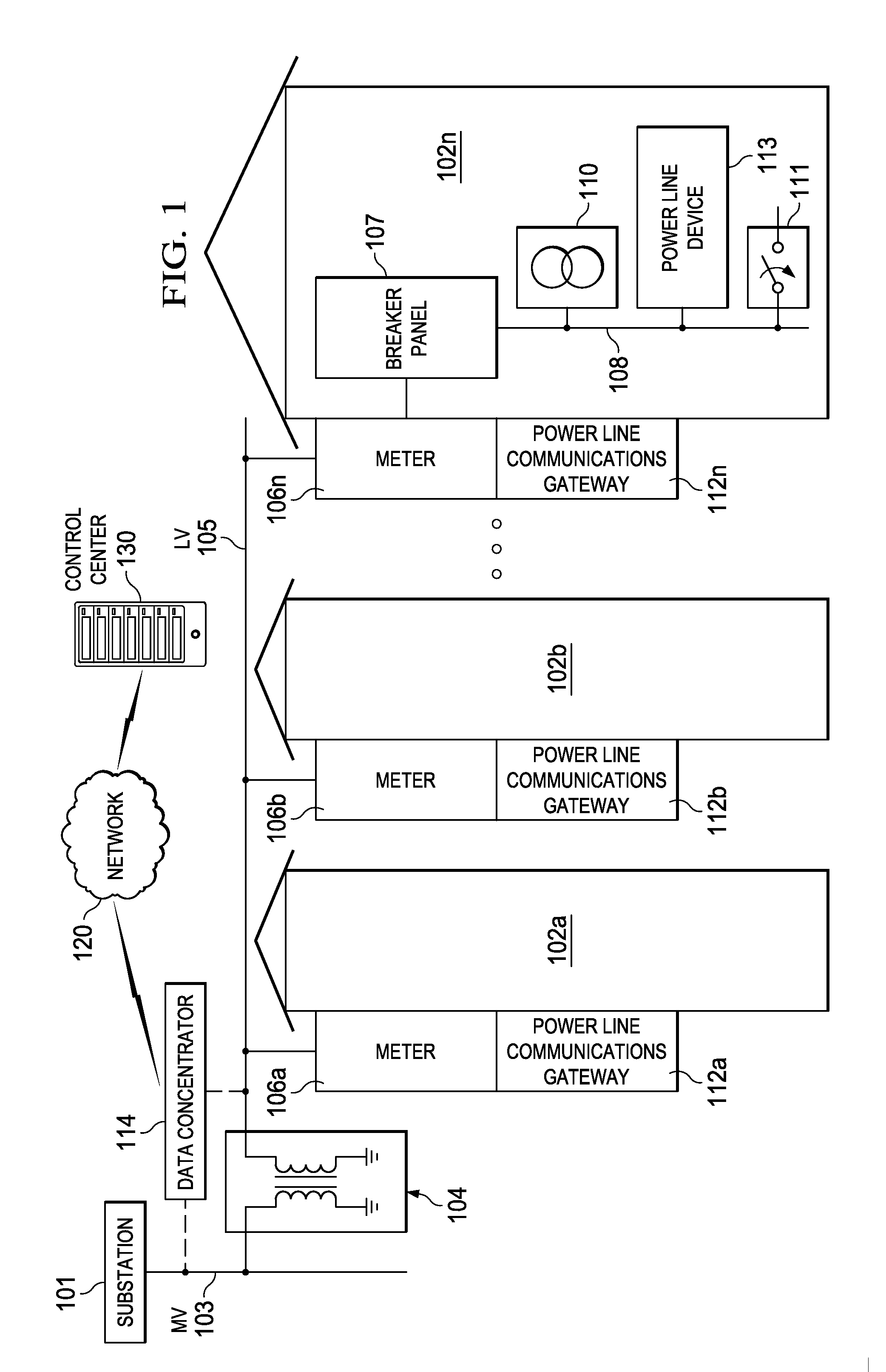
Embodiments of a power line communication (PLC) transmitter device for overlapping priority contention windows are presented. A processor is configured to perform a physical channel sense operation to detect an idle channel on a PLC network. A transmitter transmits a normal priority data packet on the channel during a high priority contention window. In another embodiment, a Normal Priority Contention Window (NPCW) is allowed to overlap with a High Priority Contention Window (HPCW). The minimum contention window for the normal priority frames (i.e., NPCW) is equal to or longer than the contention window for high priority frames (i.e., HPCW). By making the NPCW longer than the HPCW, the high priority frames will have a better chance than normal priority frames to get access to the channel on transmission reattempts.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and device for setting priority of data transmission
ActiveUS20150009988A1Network traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationNormal priorityData transmission
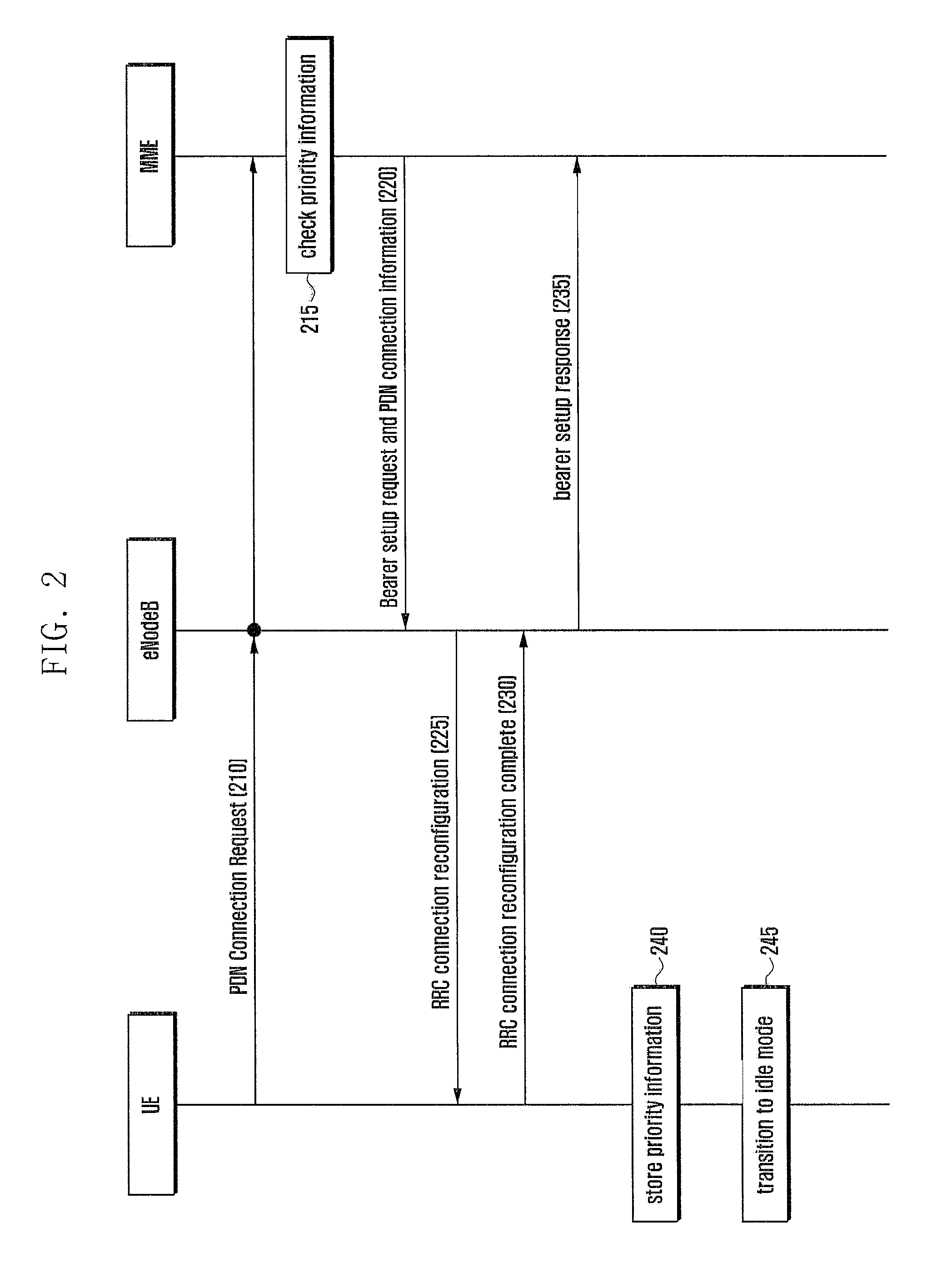
A method and a device for setting priority of data transmission are provided. A terminal, which is set to transmit low priority data to a network, transmits a connection request to the network in order to transmit normal-priority data, and receives and stores priority information on data transmission from the network.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Overload control method for Internet of things
InactiveCN102170662AImprove effectivenessDecongestionNetwork traffic/resource managementTraffic capacityGeneral Packet Radio Service
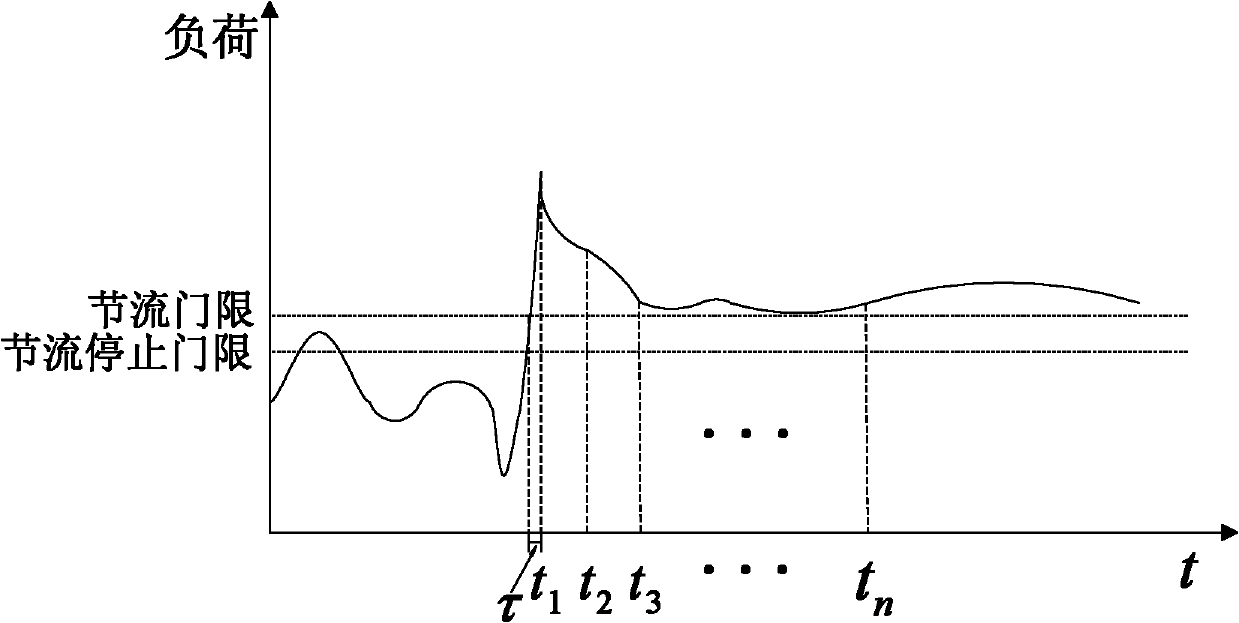
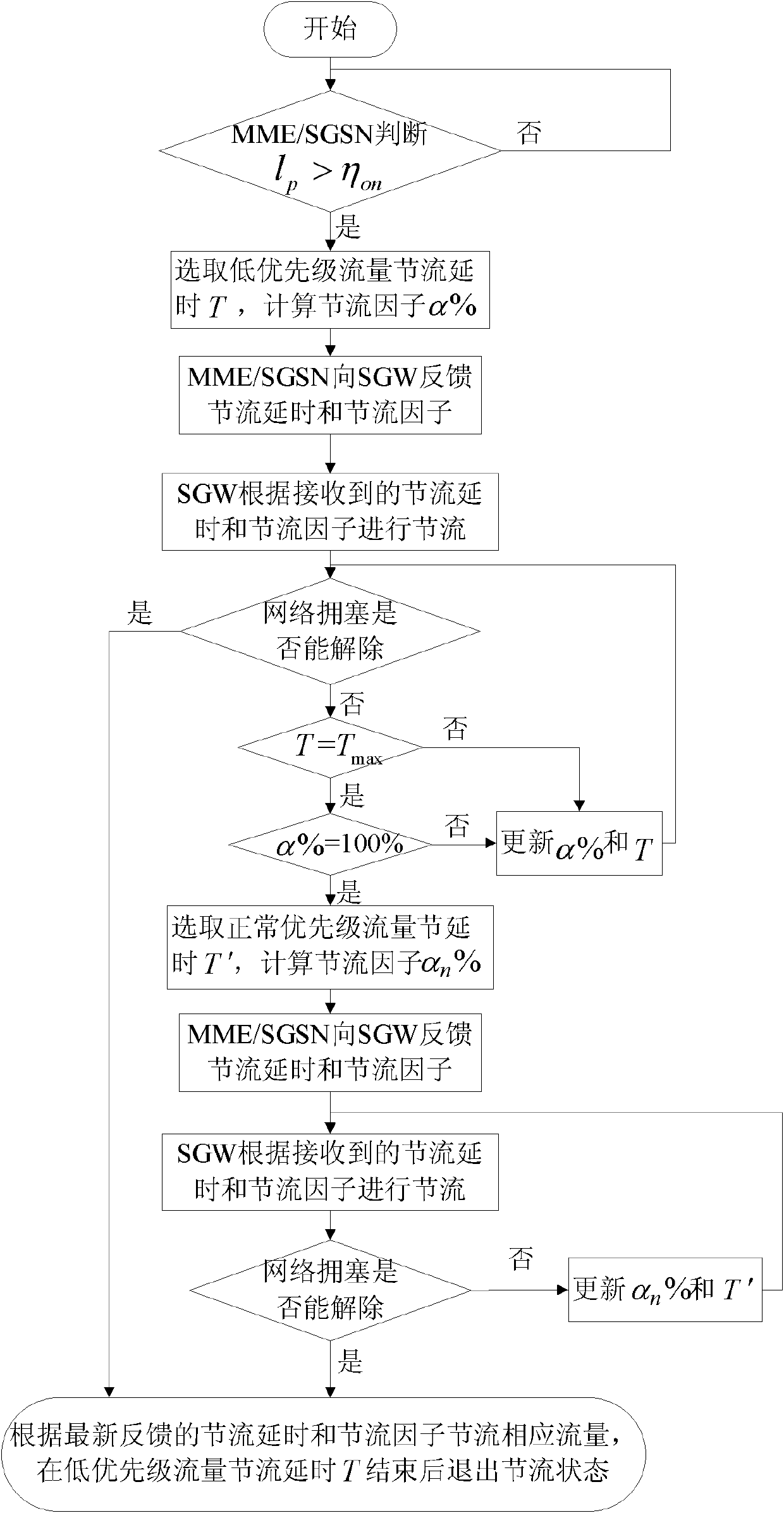
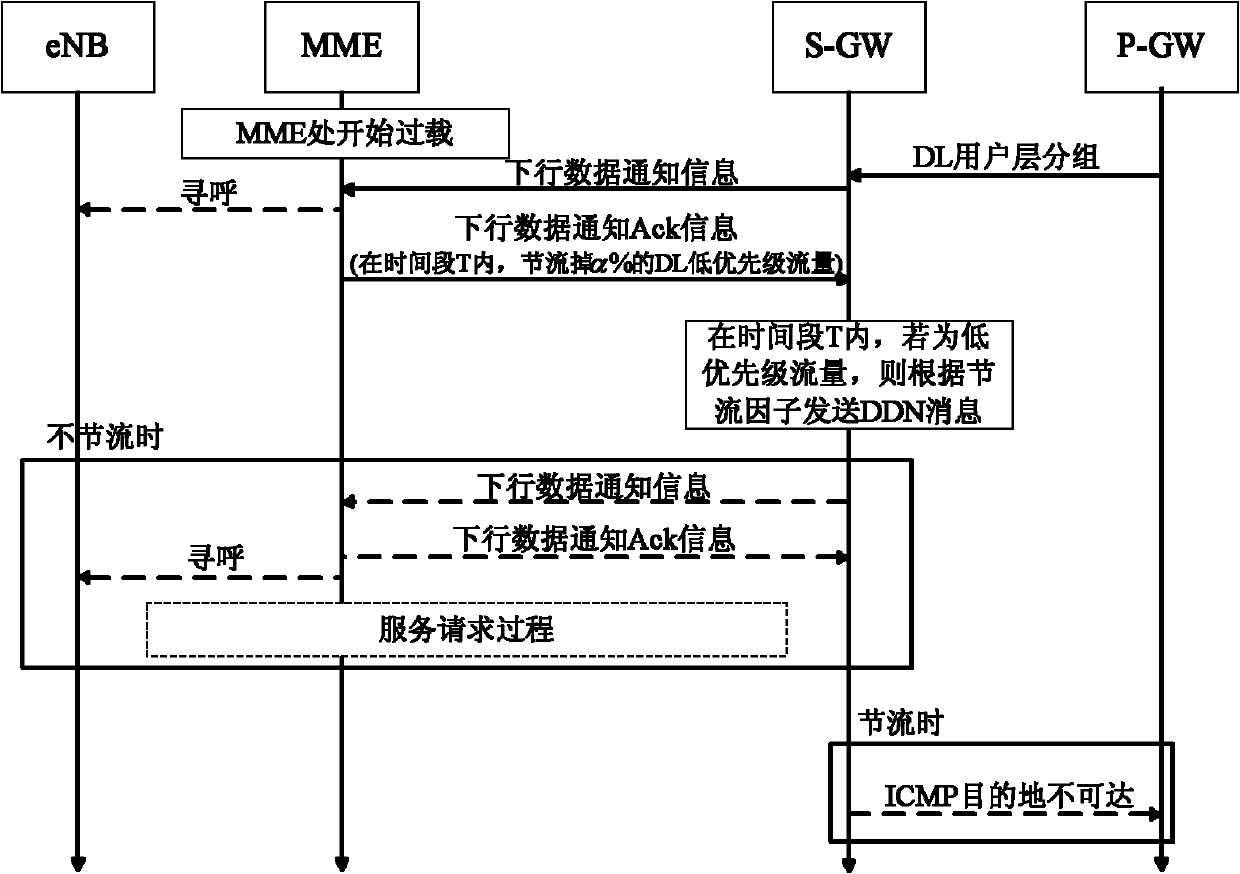
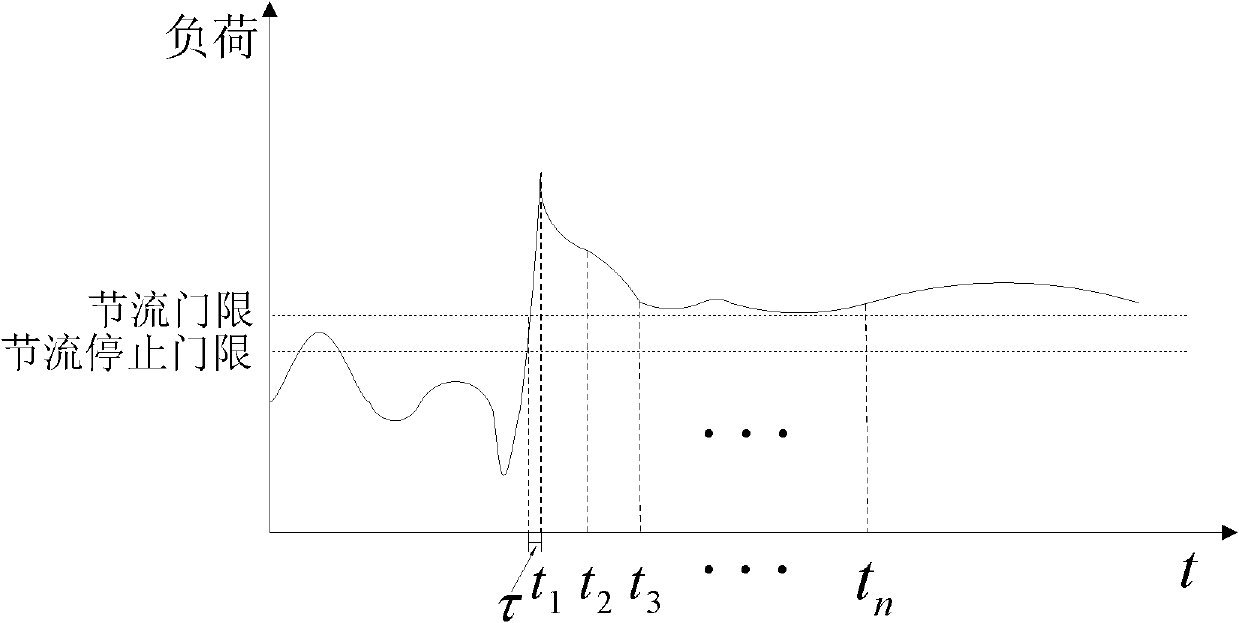
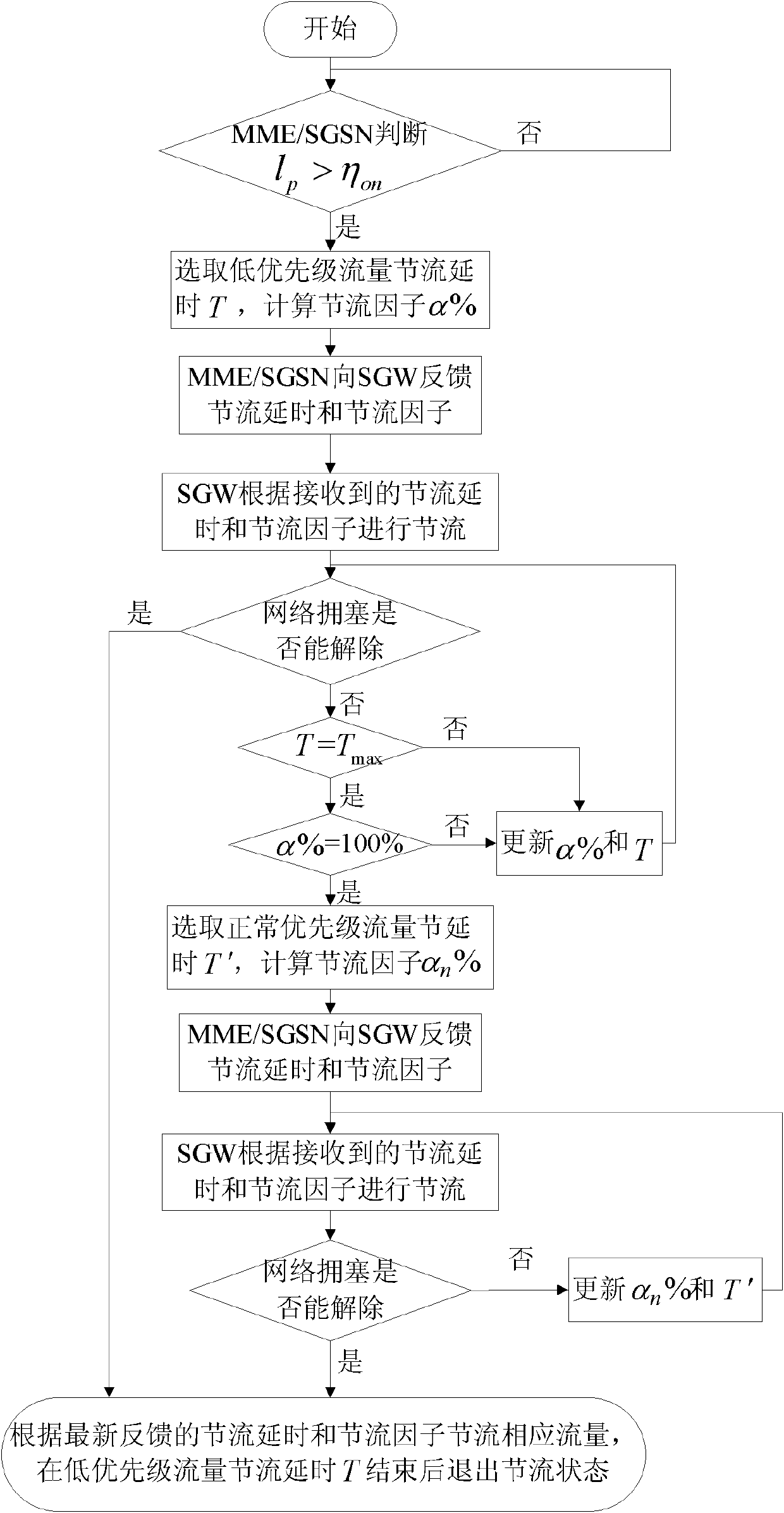
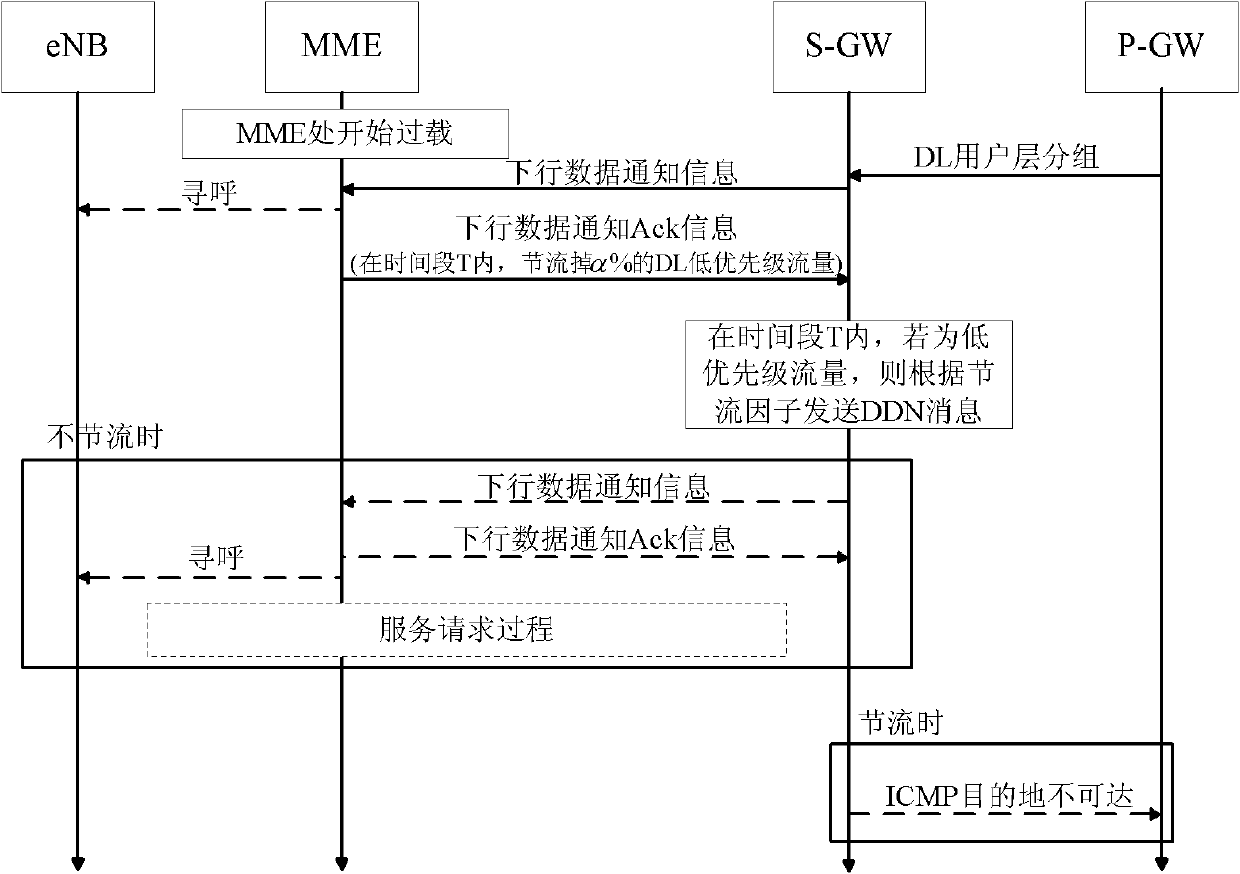
The invention discloses an overload control method for the Internet of things, which mainly aims to solve the problem that network congestion cannot be relieved when the proportion of low-priority traffic is low in a conventional downlink throttling method for the Internet of things. The method comprises that: a mobility management entity (MME) or a serving general packet radio service (GPRS) supporting node (SGSN) monitors a real-time load value of a network, and judges whether throttling is required or not; if the network is in a congested state, a serving gateway (SGW) starts performing throttling on the low-priority traffic, and simultaneously the MME or SGSN judges whether the network congestion can be relieved only by performing the throttling on the low-priority traffic or not according to a throttling effect; and if the network congestion cannot be relieved only by performing the throttling on the low-priority traffic, the SGW starts performing the throttling on normal-priority traffic, and quits a throttling state after throttling delay is finished. By the method, the applicability and efficiency of the conventional scheme are enhanced by expanding downlink throttled traffic, and the problems of function failures of the conventional scheme when the proportion of the low-priority traffic is low can be effectively solved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
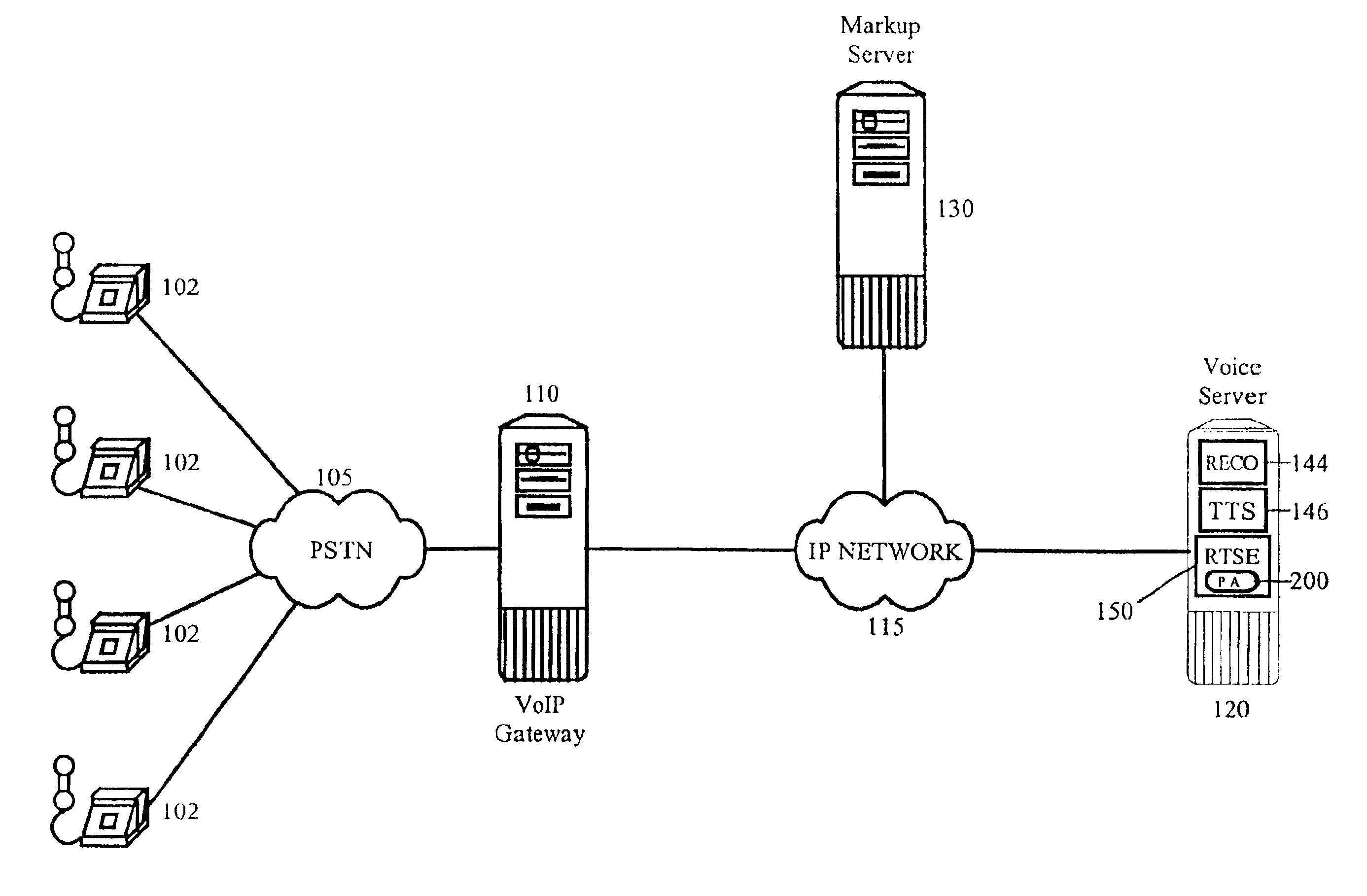
Media broadcast over an internet protocol (IP) network
InactiveCN101248617ANo waste of bandwidthReal-time processingSpecial service provision for substationInternet protocol suiteCommunications system
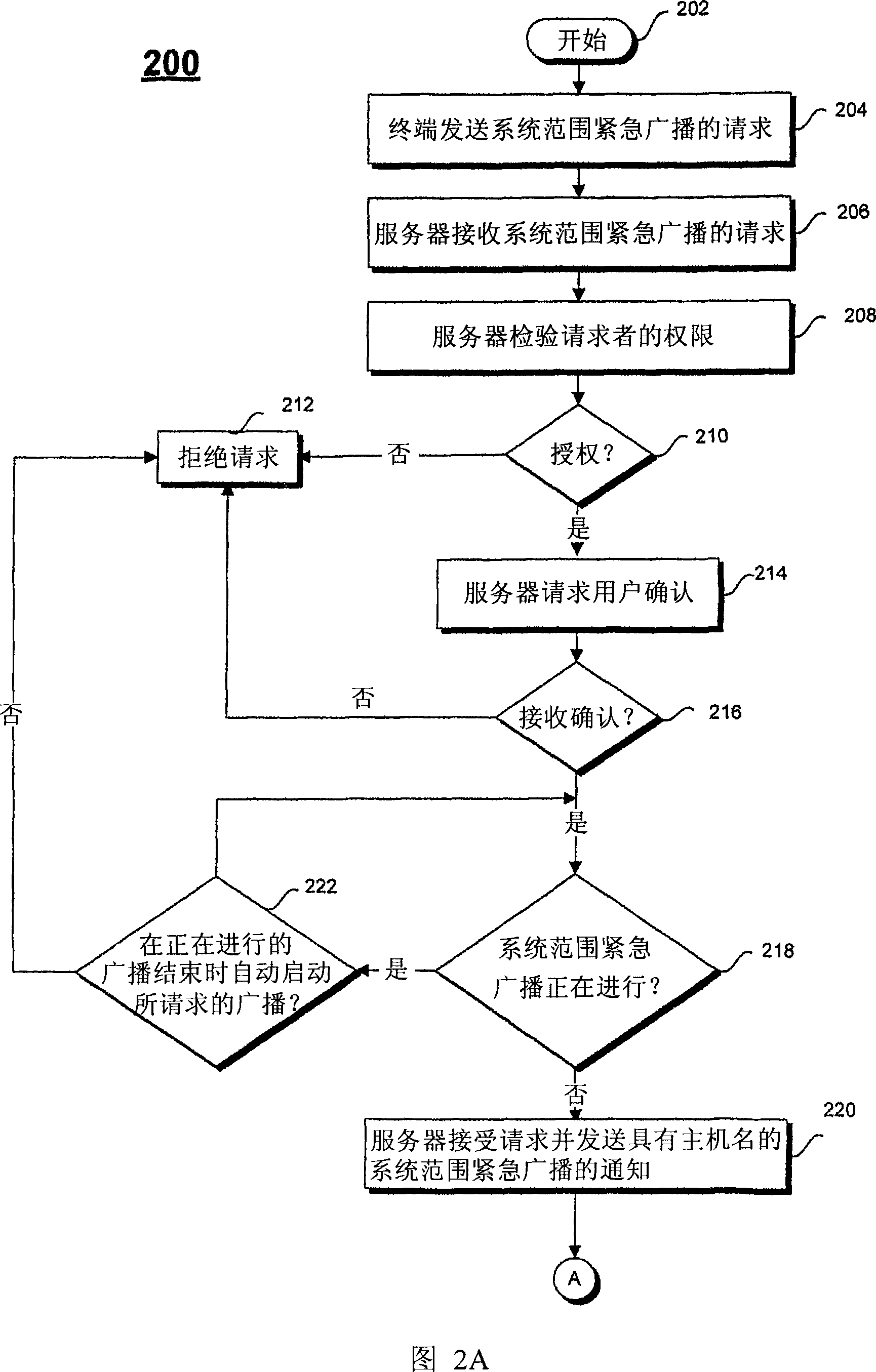
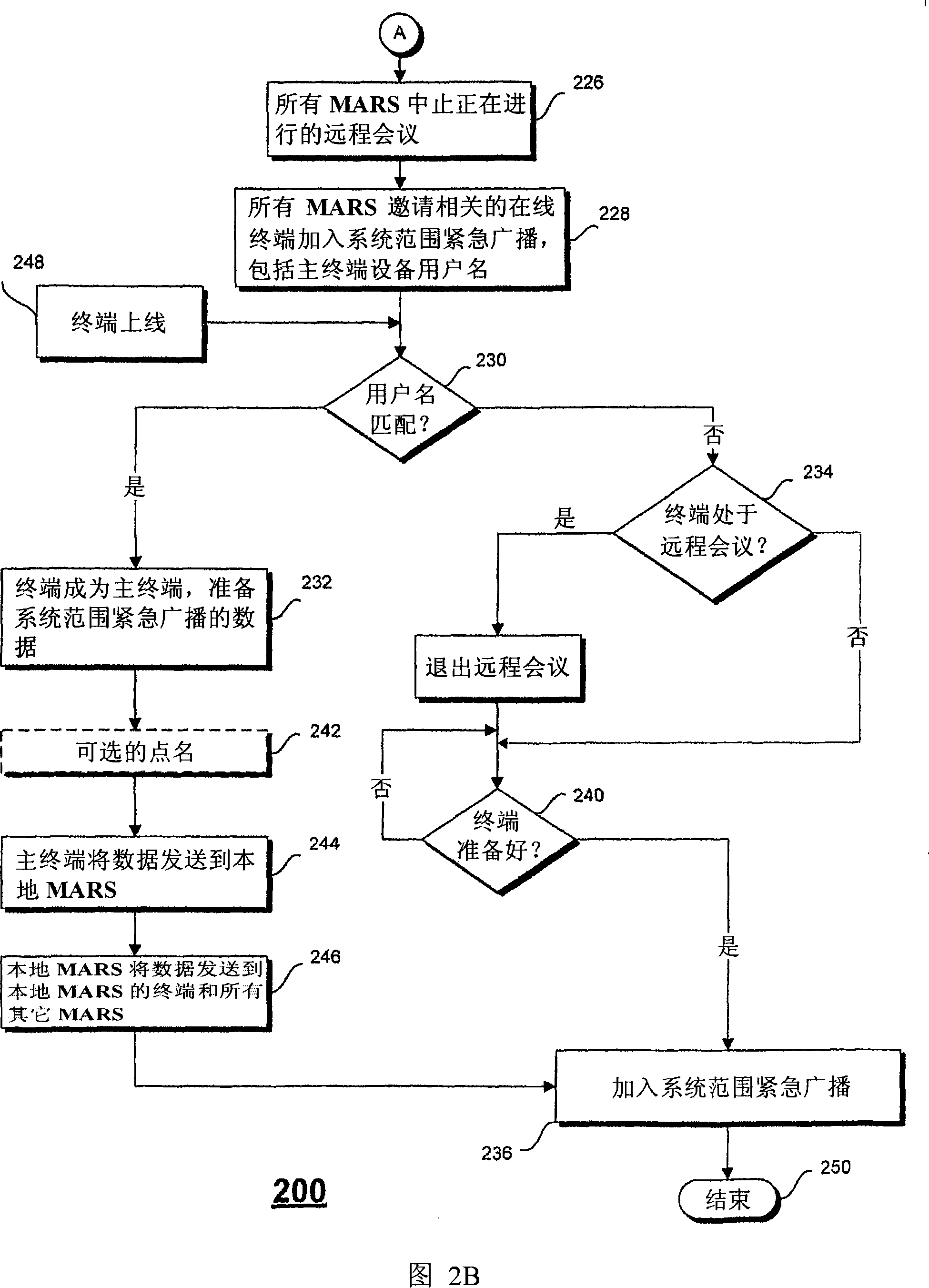
A multimedia communication system in an Internet Protocol (IP) network includes broadcast capabilities. A system-wide emergency broadcast initiated by a user with the appropriate authority interrupts all teleconferences in progress. A group-wide high priority broadcast initiated by a user with the appropriate authority may interrupt some teleconferences in progress in the selected or other group(s). A group-wide normal priority broadcast allows all teleconferences to remain in progress and user may choose to join or not join the broadcast when the in-progress teleconference has ended.
Owner:友谊系统有限公司
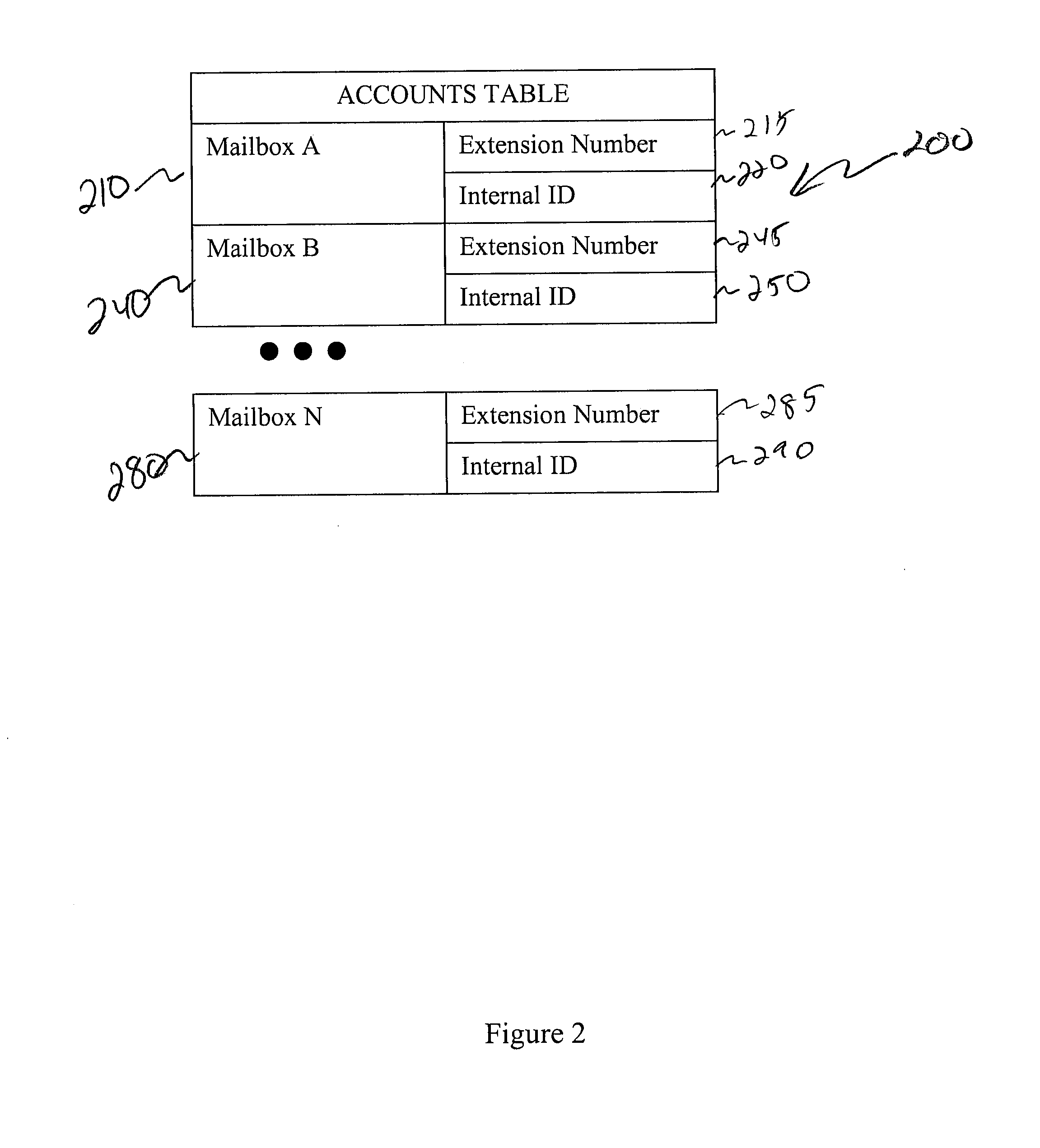
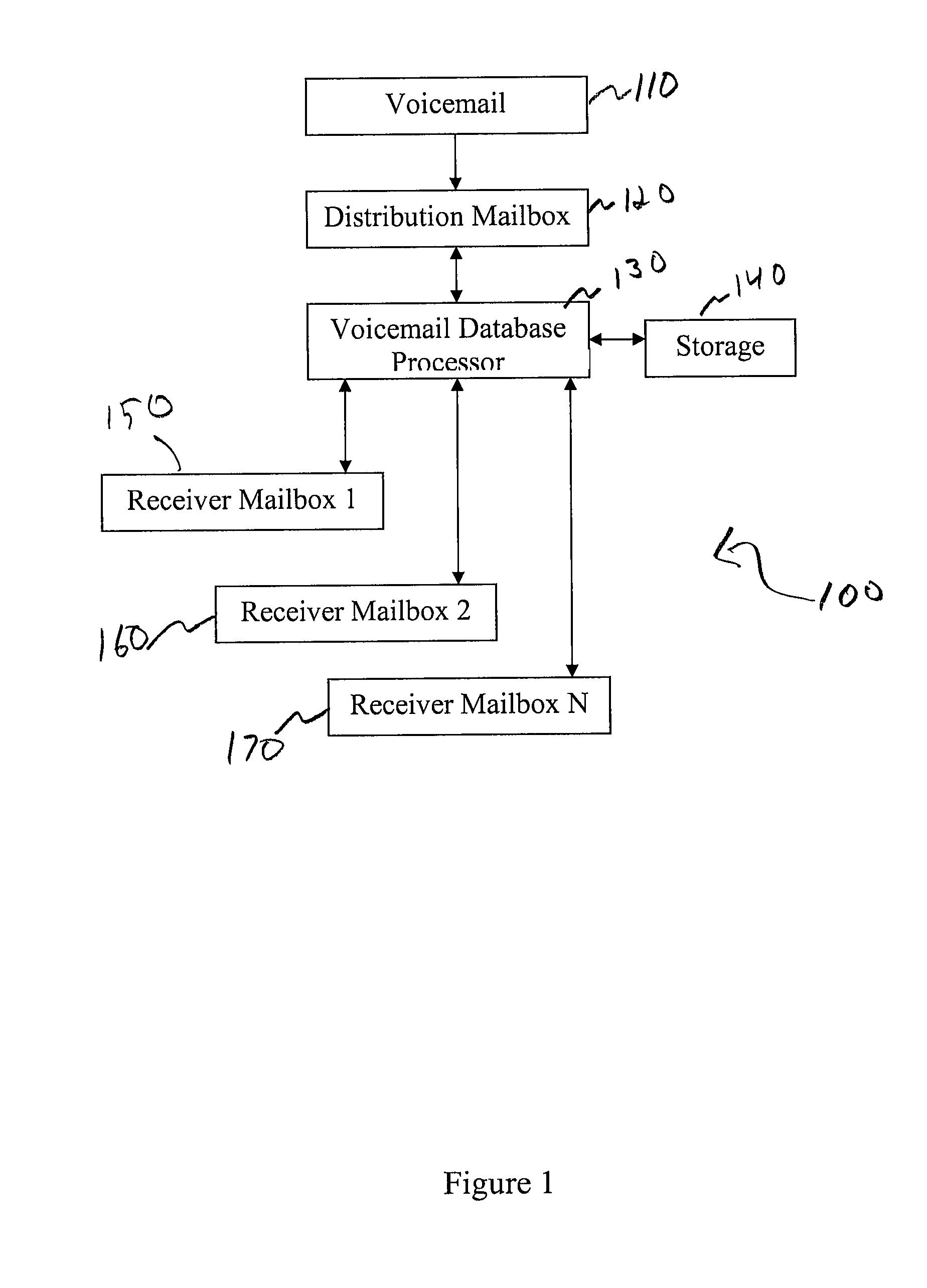
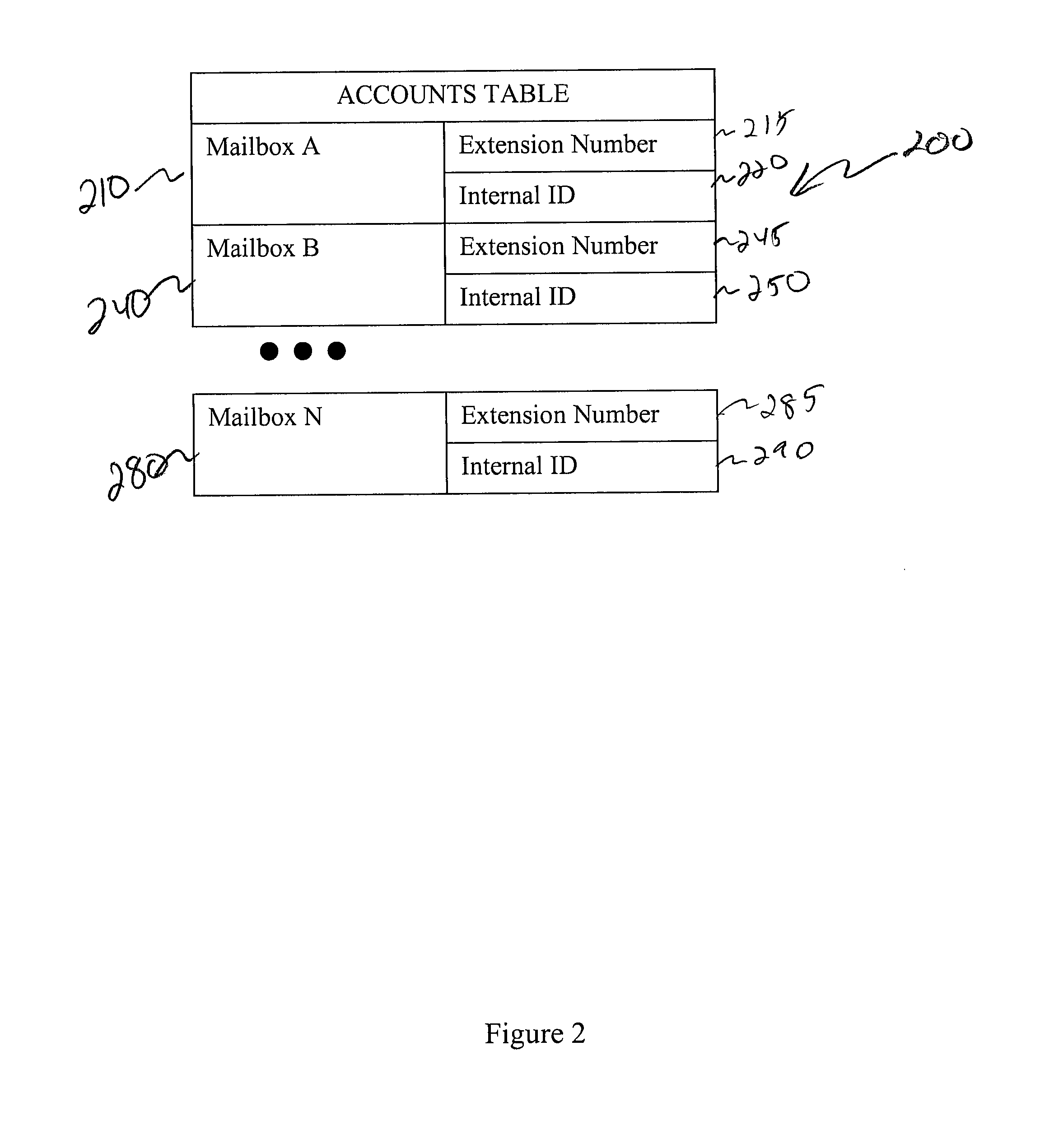
Enhanced Voicemail System and Method
ActiveUS20090262910A1Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingAutomatic exchangesNormal prioritySpeech sound
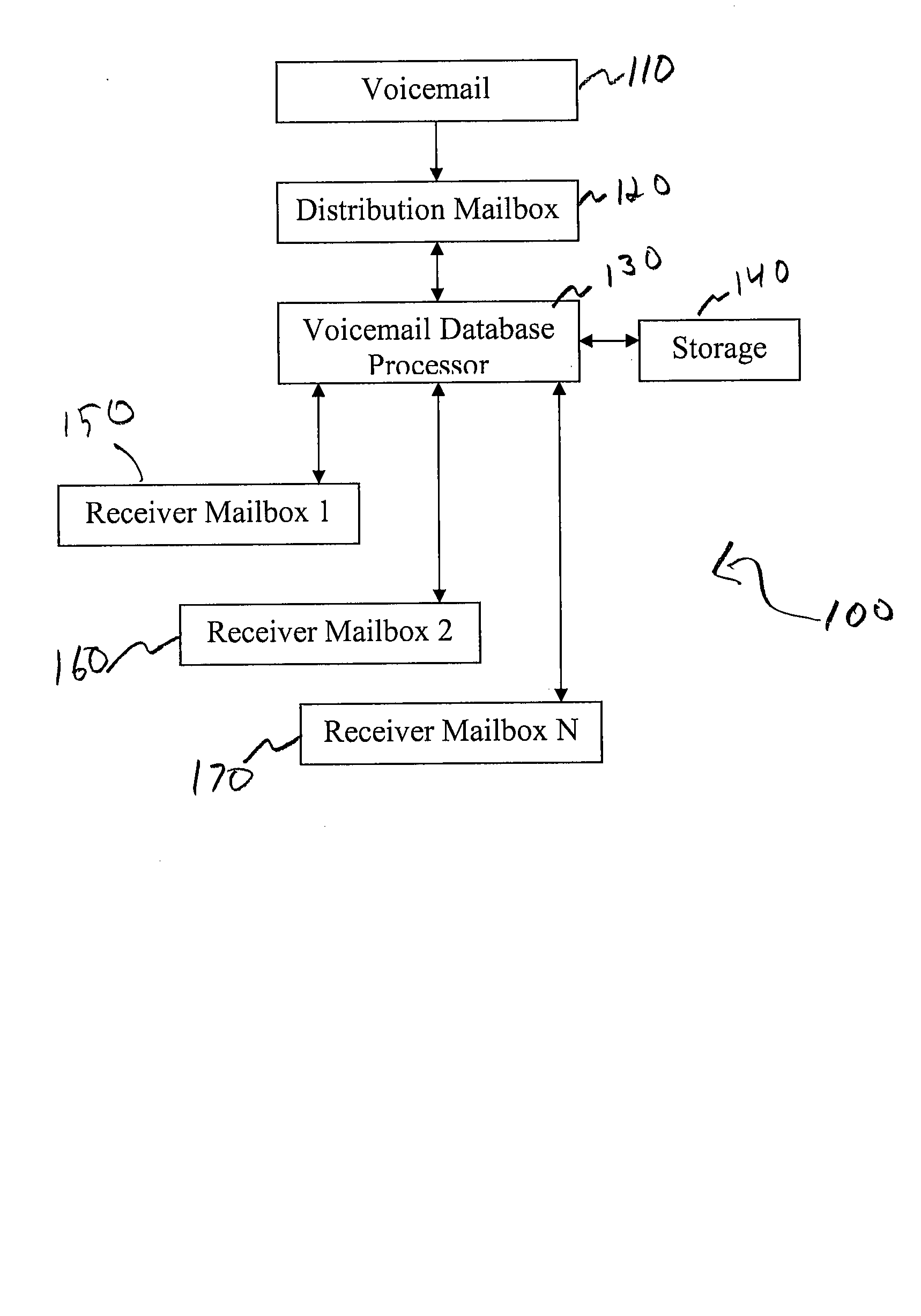
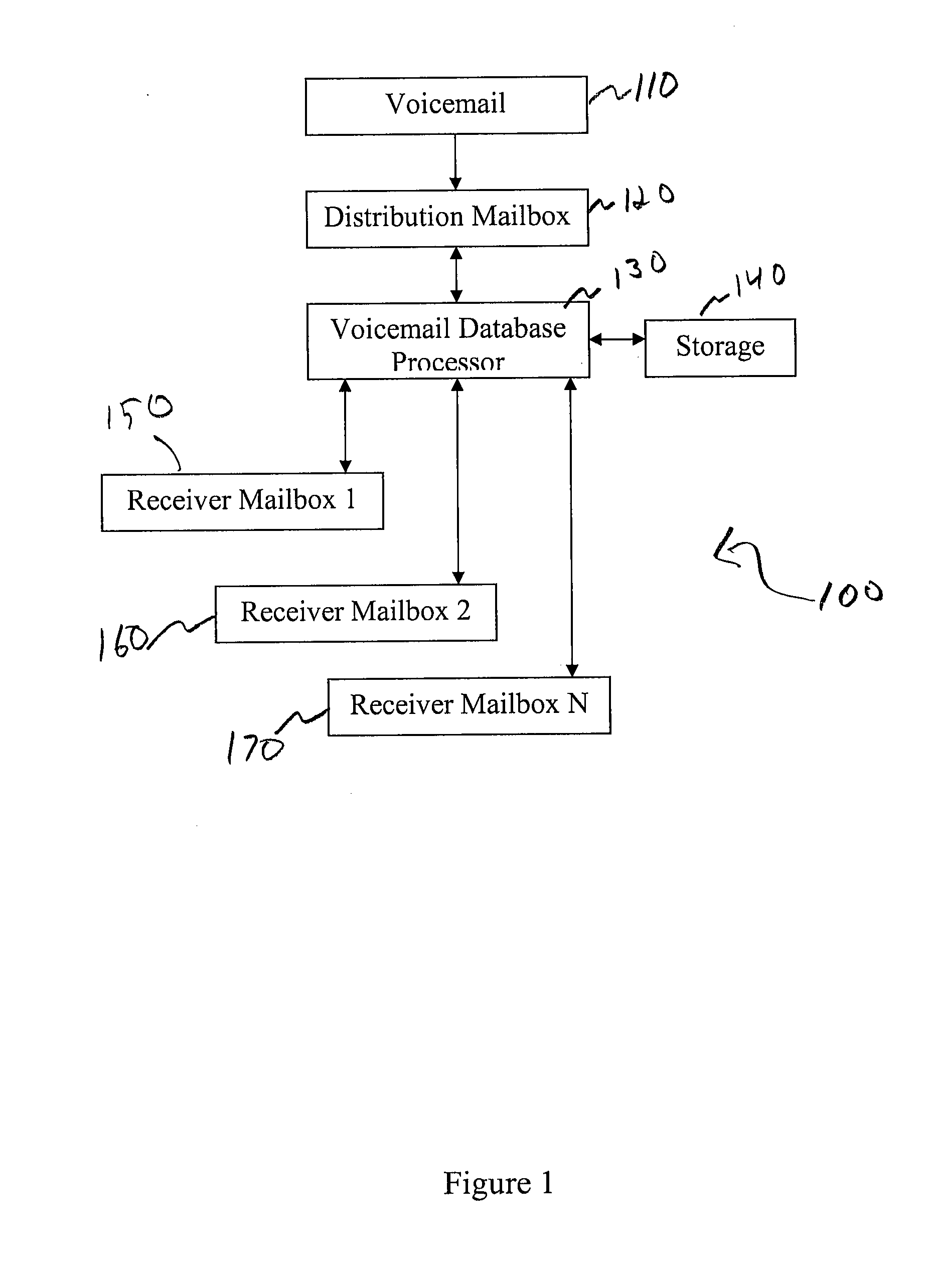
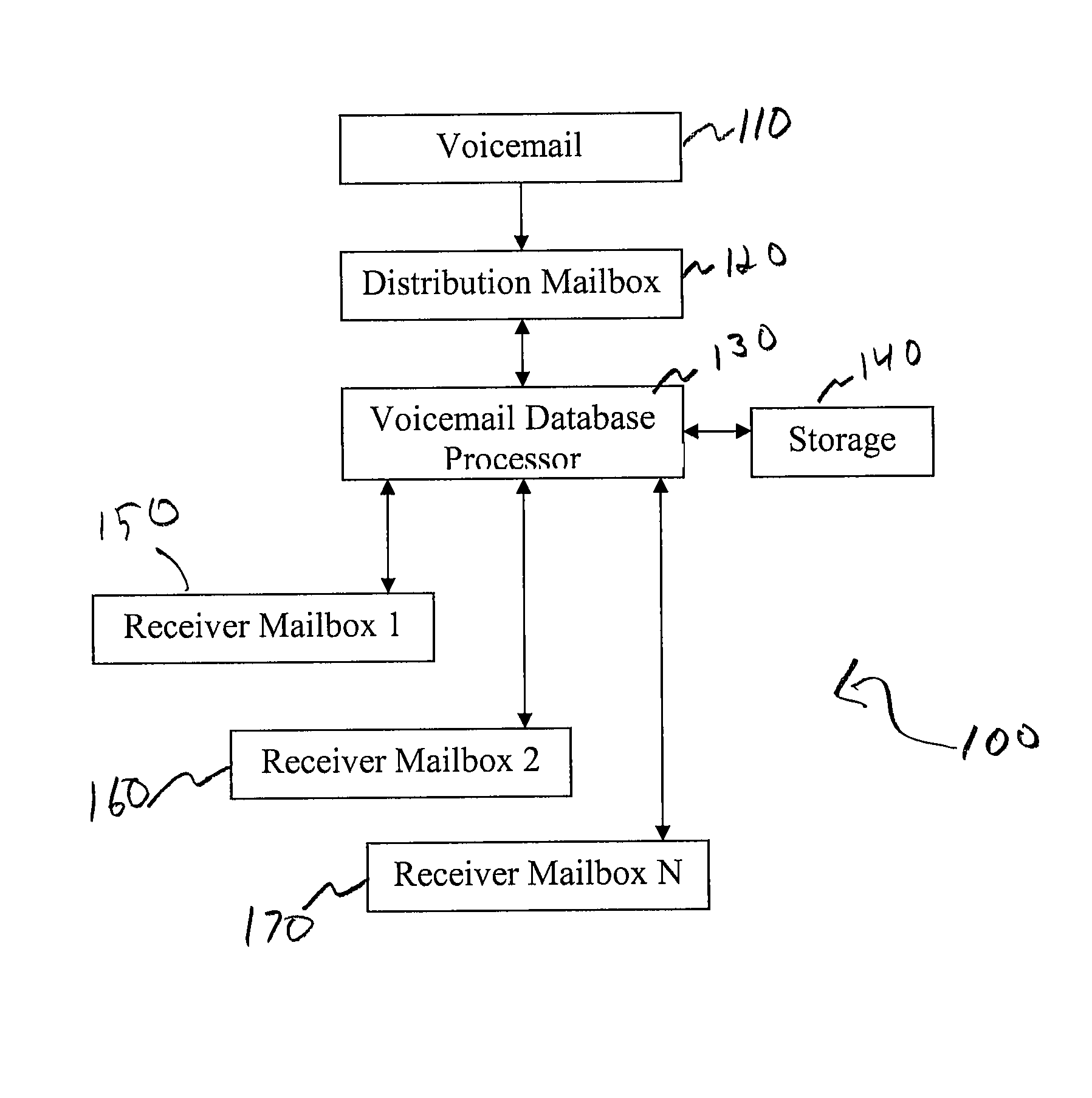
A system for processing voicemail is provided that includes a voicemail database processor establishing one ore more of an accounts table, a messages table, a distribution list table, a distribution lists members tables, and a delete request table. In operation a message navigation menu is provided to a user to allow the user to move back and forth a specified number of voicemails, change between urgent and normal priority voicemails, retrieve messages only from a specific mailbox or from outside the system, or initiate an improved deletion operation.
Owner:SCOPES PHILIP M
Device and Method of Handling Measurement Configuration
A communication device for handling a measurement configuration comprises a storage unit for storing instructions and a processing means coupled to the storage unit. The instructions comprise receiving a measurement configuration comprising a first carrier frequency and a low priority for the first carrier frequency from a network; changing the low priority of the first carrier frequency to a normal priority in response to a radio resource control (RRC) procedure; and performing a measurement on the first carrier frequency according to the measurement configuration comprising the first carrier frequency with the normal priority. The processing means is configured to execute the instructions stored in the storage unit.
Owner:HTC CORP
Software programmable dynamic arbitration scheme
A method for arbitration among a plurality of requesting devices for a shared resource in which one device is an ultra high priority device grants access to one requesting device at a time. The ultra high priority device is granted access if it requests access interrupting access by another device. The ultra high priority device is limited to a selectable number of accesses and thereafter is masked for a selectable interval. This interval permits access may by other devices. Each of the other devices is also limited to a selectable number of accesses followed by re-arbitration. The other devices can have a normal priority or a time out priority if a request hasn't been granted in a selectable amount of time.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
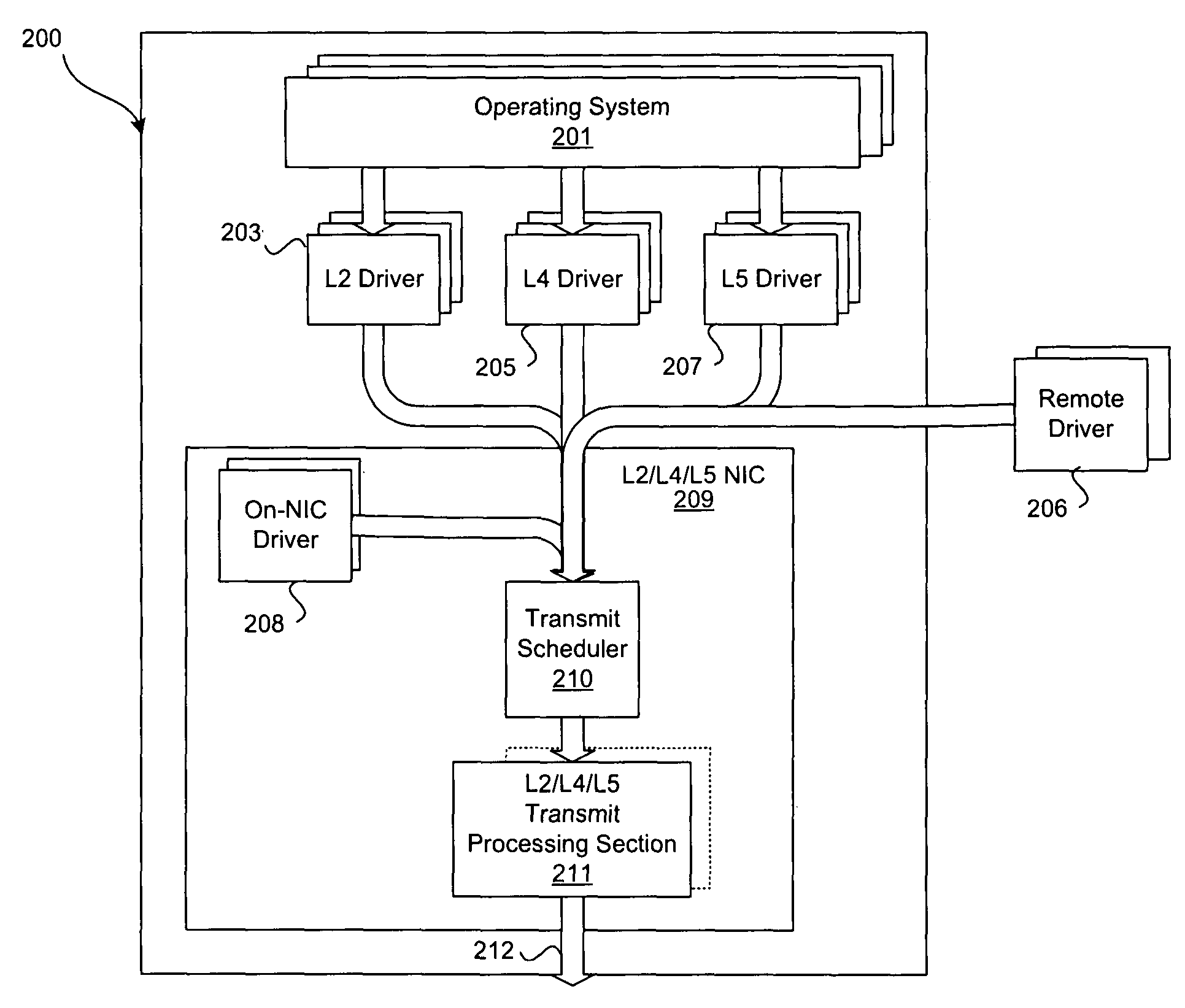
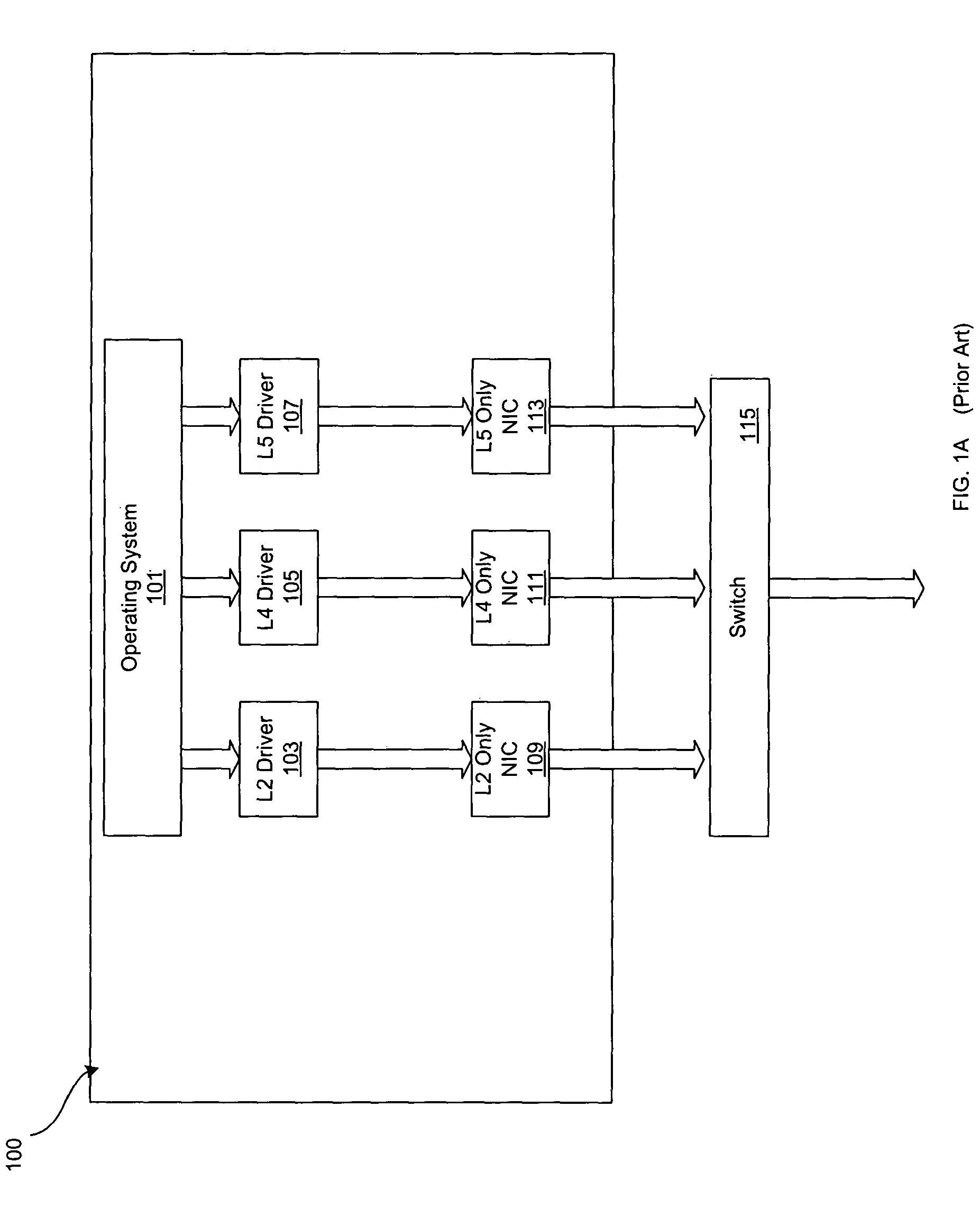
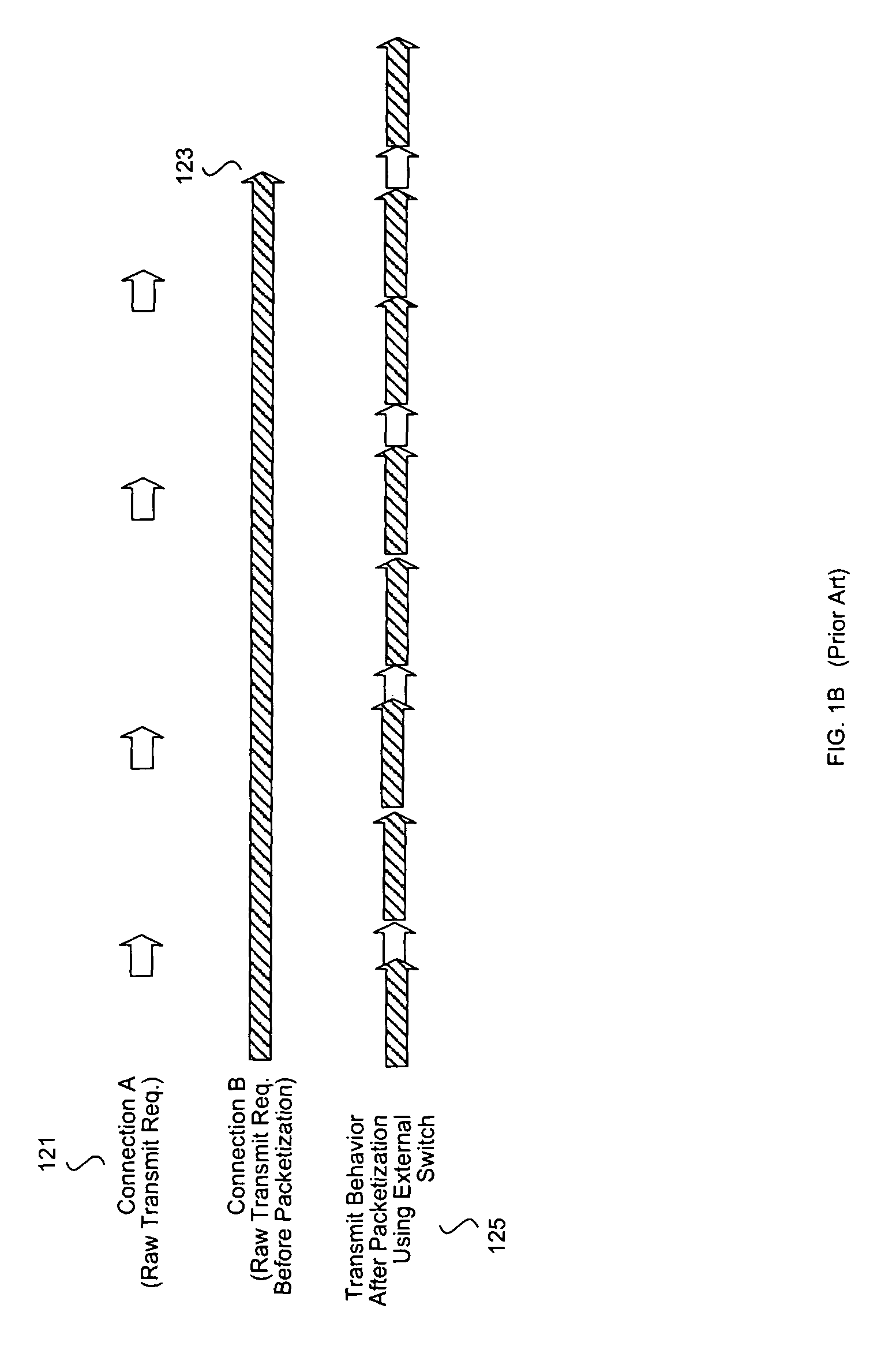
Method and system for transmit scheduling for multi-layer network interface controller (NIC) operation
Certain embodiments of the invention may be found in a method and system for multi-layer network interface controller (NIC) operation. An aspect of the invention may utilize a two (2) level work-conserving scheduling system for network interface controller operation and may comprise tracking for all L4 / L5 offload connections with active transmit requirements as well as layer 2 (L2) level transmit requirements. The first level may comprise a round-robin scheme that may be utilized to select the next high priority, normal priority, and layer 2 (L2) transmit requirement independently. The send level arbitration may comprise a work-conserving programmable weighted round-robin priority scheme that may be utilized to select amongst the transmit tasks selected by the first level priority scheme.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
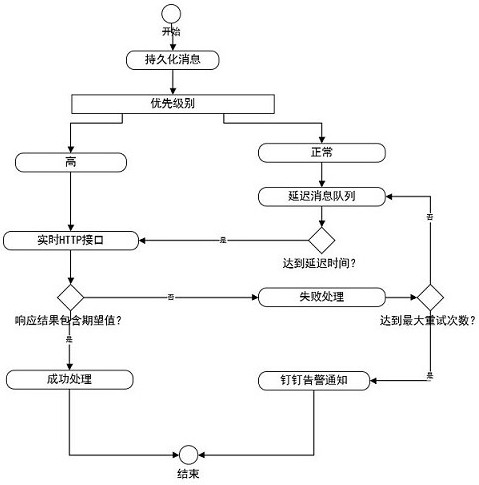
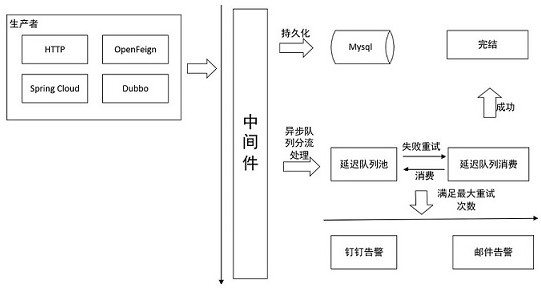
Distributed message asynchronous notification middleware implementation method and system
PendingCN112988428AReduce waiting timeGuaranteed closed loopInterprogram communicationCommunications softwareEngineering
The invention provides a distributed message asynchronous notification middleware implementation method and system, and the method comprises the steps: receiving an HTTP request, carrying out the persistence of the HTTP request into a database, and carrying out the classification according to the priority level; processing the requests with high priorities in real time; pushing the data with the normal priority level to a delay queue pool to wait for a fixed time and then processing the data; judging whether the processed response message contains the set expected content or not; if the response message contains the expected content, updating the information state to be successful, and ending the task; if the response message does not contain the expected content, calculating the number of failures and judging whether the number of failures reaches the maximum number of retry times set by configuration or not; if the failure frequency is smaller than the maximum retry frequency, pushing the corresponding request message to the delay queue pool, and repeating waiting processing; and if the failure times are greater than the maximum retry times, calling communication software to carry out abnormal alarm notification, and ending the task. The distributed system asynchronous notification message traceability and abnormity alarm are realized, and the service closed loop is ensured.
Owner:南京蜂泰互联网科技有限公司
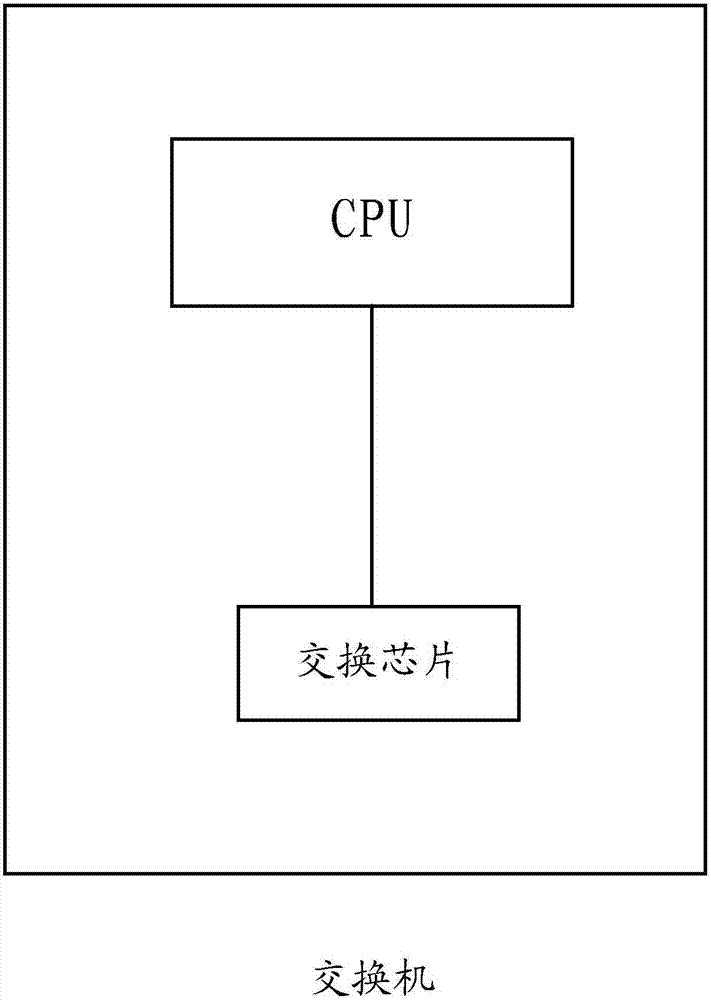
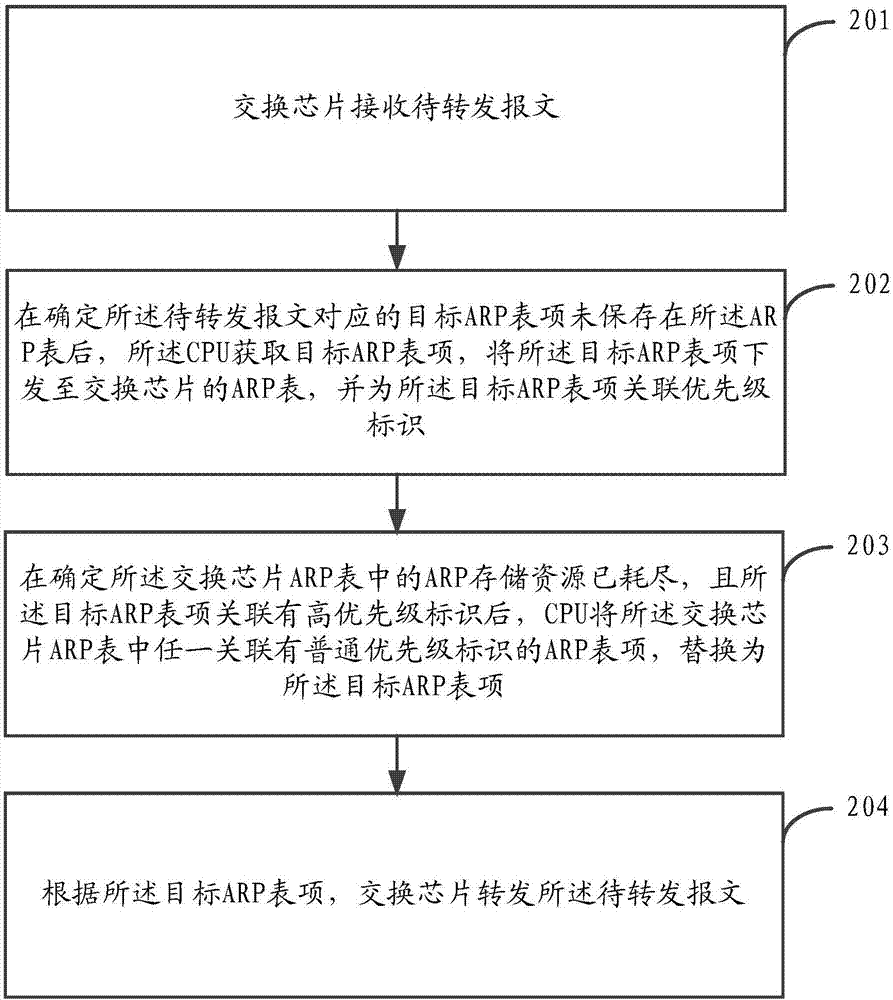
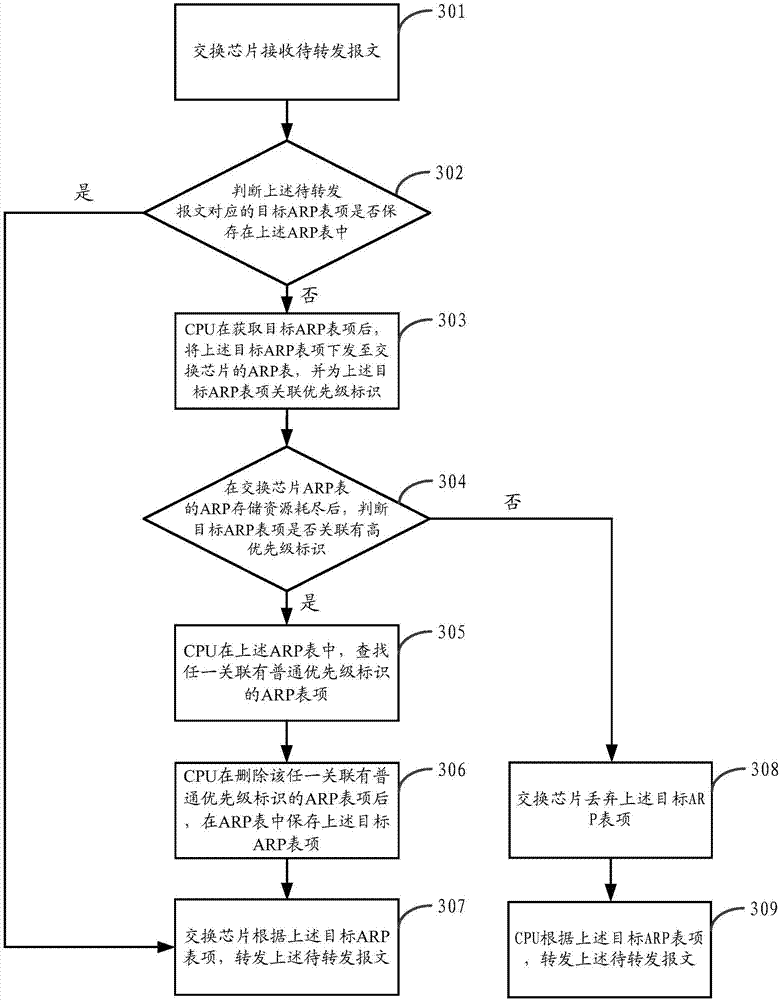
Message forwarding method and system
ActiveCN107070797AAvoid delayAvoid interruptionData switching networksNormal priorityOperating system
The invention provides a message forwarding method and system. The method is applied to a switch, and comprises the following steps: a switch chip receives a message to be forwarded; after determining that a target ARP table item corresponding to the message to be forwarded is not stored in an ARP table, a CPU acquires the target ARP table item, associates a priority identifier for the target ARP table item, and issues the target ARP table item to a switch chip ARP table; when ARP storage resources in the switch chip ARP table are exhausted and the target ARP table item is associated with a high priority identifier, the CPU replaces any ARP table item that is associated with a normal priority identifier in the switch chip ARP table as the target ARP table item; and the switch chip forwards the message to be forwarded according to the target ARP table item. By adopting the message forwarding method and system provided by the invention, the ARP table items of the switch chip are associated with different priority identifiers, the ARP table items with low priority are replaced by the ARP table items with high priority, and thus the switch chip can store the three layers of forwarded ARP table items when the ARP storage resources are exhausted, and network delay or interruption caused by excessive usage of the CPU when forwarding the three layers of messages can be avoided.
Owner:HANGZHOU DPTECH TECH
Method of determining database search path
InactiveUS7191173B2Improve reliabilityReliable dataData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalNormal priorityData mining
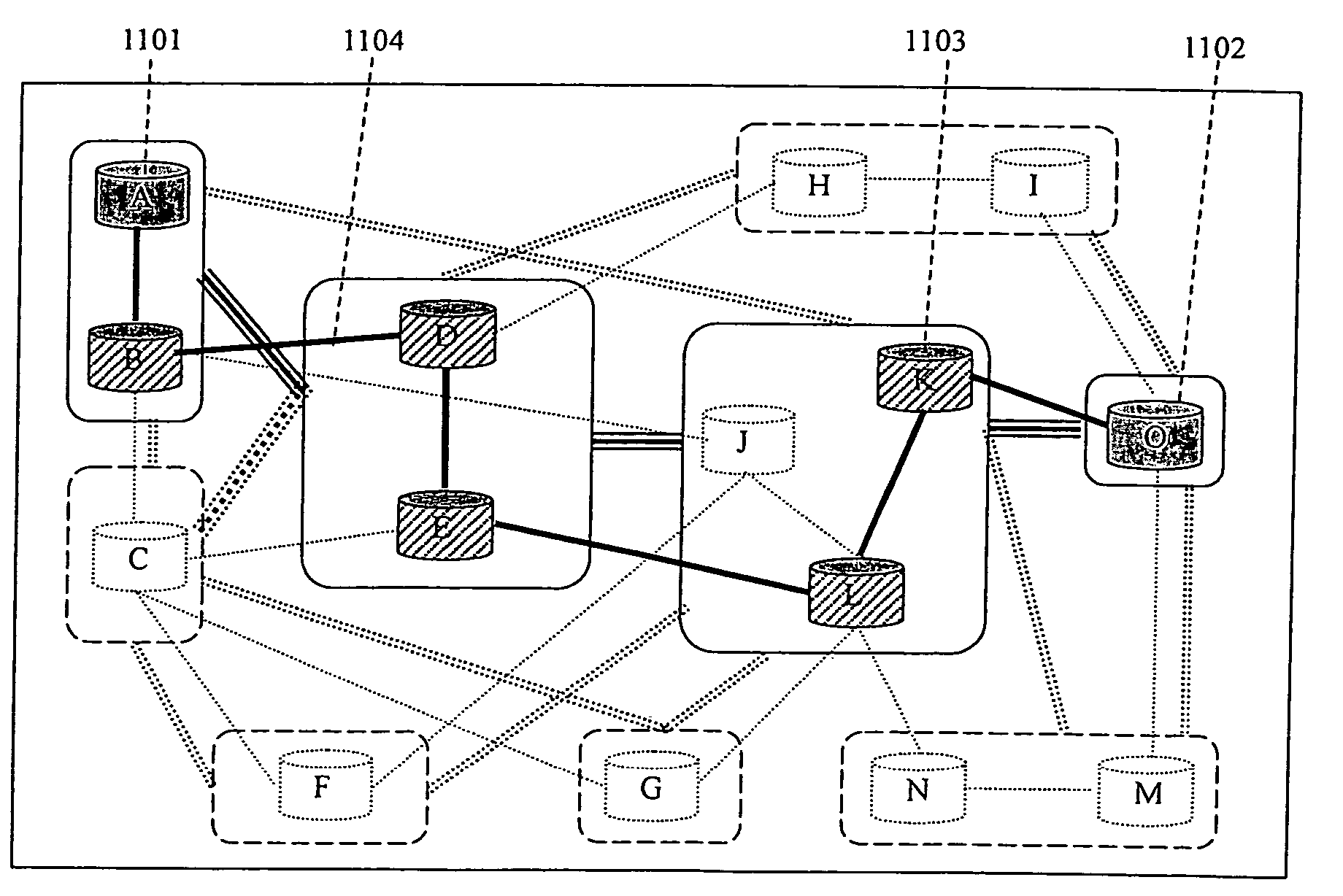
A plurality of database search path candidates are automatically determined and provided. Databases containing information with similar characteristics are divided into groups (hereafter referred to as a “category group”), and a correlation diagram is created based on links between those category groups. In the diagram, high priority is given to links between category groups constituting a path that has to be passed through due to relevance between the characteristic of databases, and normal priority is given to other links. When a path search is carried out in this diagram, an important path is selected regardless of attributes such as distance between databases or time by carrying out a first path search along the high priority path between category groups.
Owner:HITACHI SOFTWARE ENG
Overlapping priority contention windows for G3 power line communications networks
ActiveUS9001844B2Small impactIncrease window sizePower distribution line transmissionRemote meteringNormal priorityPower-line communication
Embodiments of methods and systems for overlapping priority contention windows in G3-PLC networks are presented. In one embodiment, a Normal Priority Contention Window (NPCW) is allowed to overlap with a High Priority Contention Window (HPCW). The minimum contention window for the normal priority frames (i.e., NPCW) is equal to or longer than the contention window for high priority frames (i.e., HPCW). By making the NPCW longer than the HPCW, the high priority frames will have a better chance than normal priority frames to get access to the channel on transmission reattempts.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
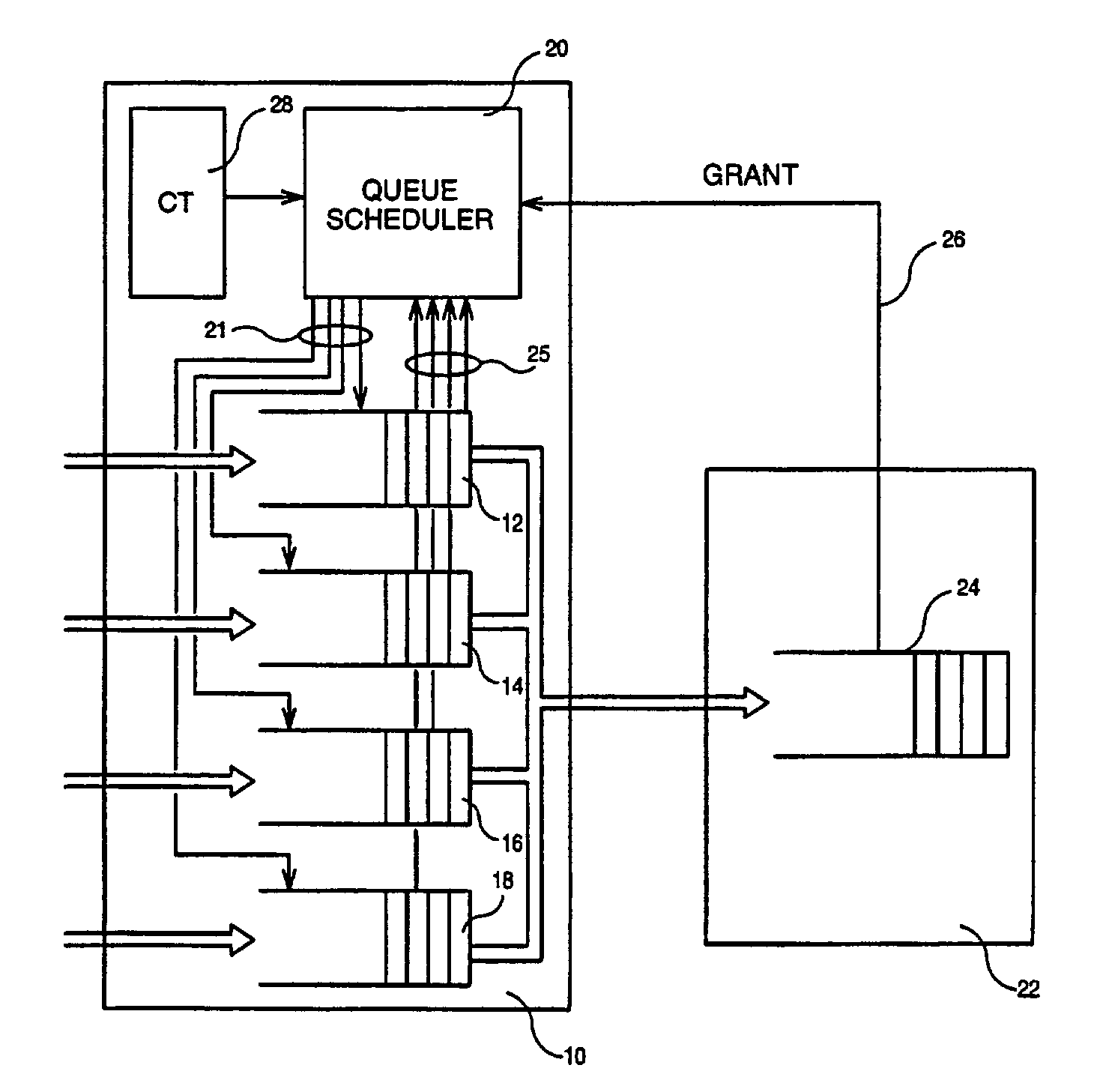
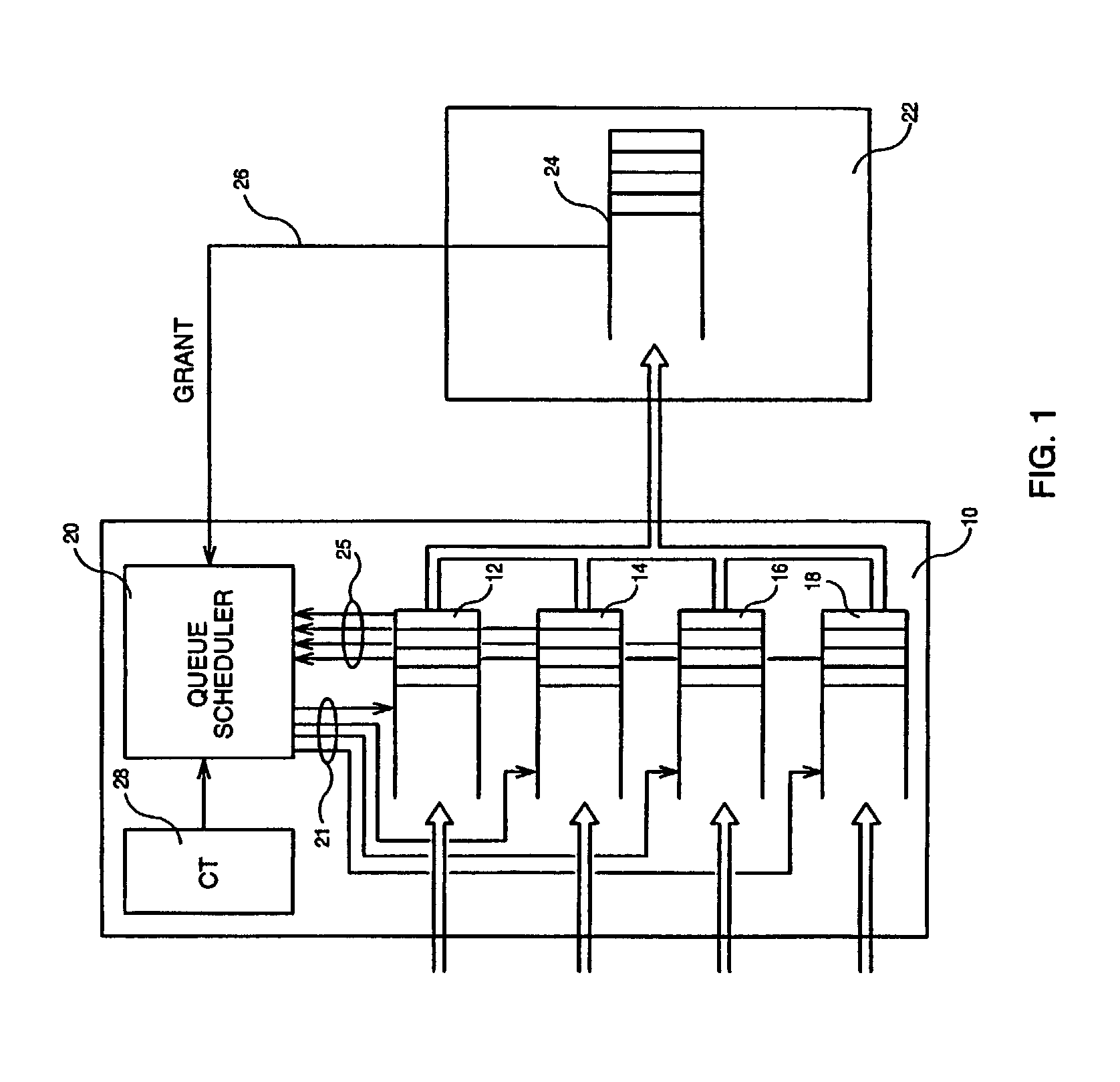
Queue scheduling mechanism in a data packet transmission system
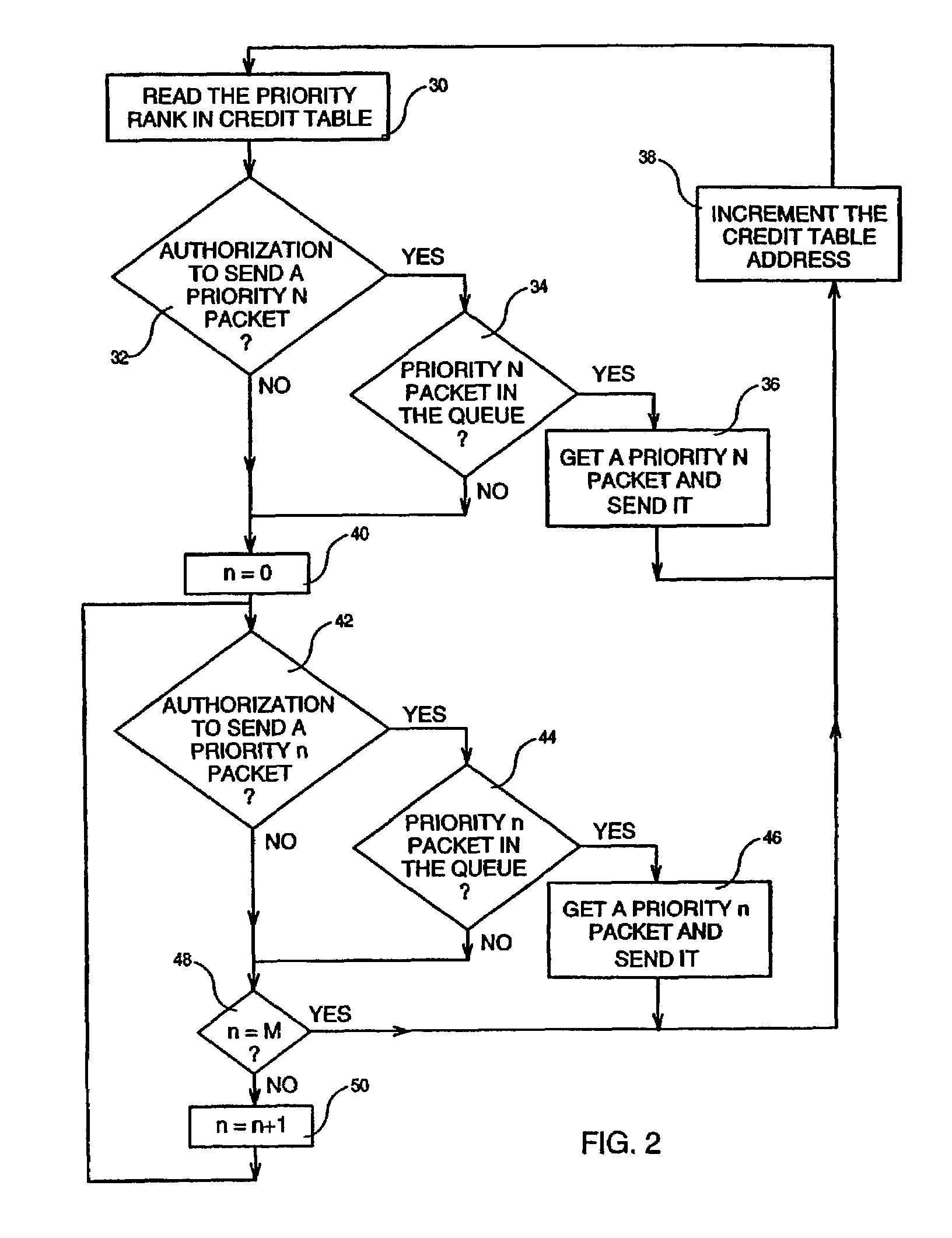
InactiveUS7382792B2Avoids low priorityMinimum bandwidthNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationNormal priorityData transmission
A queue scheduling mechanism in a data packet transmission system, the data packet transmission system including a transmission device for transmitting data packets, a reception device for receiving the data packets, a set of queue devices respectively associated with a set of priorities each defined by a priority rank for storing each data packet transmitted by the transmission device into the queue device corresponding to its priority rank, and a queue scheduler for reading, at each packet cycle, a packet in one of the queue devices determined by a normal priority preemption algorithm. The queue scheduling mechanism includes a credit device that provides at each packet cycle a value N defining the priority rank to be considered by the queue scheduler whereby a data packet is read by the queue scheduler from the queue device corresponding to the priority N instead of the queue device determined by the normal priority preemption algorithm.
Owner:IBM CORP
Sending method, device and user equipment
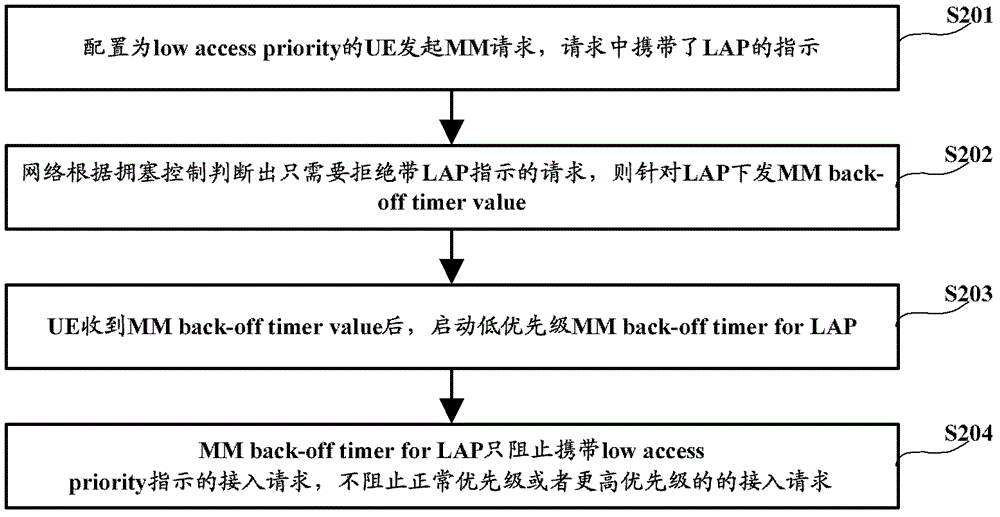
The invention discloses a request sending method, a device and user equipment; the method comprises the steps of: storing priority of a retreat timer, wherein the priority of the retreat timer refers to the priority of a first request when the retreat timer is started; sending a second request to a network side according to the priority of the retreat timer. When a low priority request of the user equipment is rejected by the network side and the retreat timer is started, a normal priority request cannot be started; the method and equipment of the invention can solve the said problems, so the user equipment can send requests to the network side according to the priority of the retreat timer.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Access control method and device
The present invention relates to the communications technologies. Disclosed are an access control method and apparatus. After a rejection message that is returned by a network side and carries a back-off level indication is received, a back-off timer is started, and a terminal is forbidden in a set time from accessing the network through an access request of a set priority. Since access requests of all priorities are not rejected, when a user accesses the network through an access request of a normal priority or an access request of a higher priority, the user is not forbidden by a back-off timer that rejects a low priority, so that it is implemented that a terminal with a low access priority can initiate normal priority access after being denied for accessing.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Method for preventing ping-pong handover effect in mobile WiMAX networks
ActiveUS8379597B2Large resource wasting is avoidedImprove transmission qualityWireless commuication servicesNormal priorityPower budget
To prevent a handover ping-pong effect between base-station in WiMAX-compliant networks, a priority level is assigned to the trigger causes for handover, and the prioritized causes are coded. Then codes are subdivided into a first class of unrestricted handovers and a second class of restricted handovers. The first class includes the highest priority handovers. The second class includes a subset of handovers with a high or normal priority intended for optimizing resources. Outside this subset the second class also includes handovers for power budget having a normal priority level. When an outgoing handover is decided, the actual serving BS permits or selectively suppresses the Handover Request to the target BS when the latter corresponds to the preceding serving BS for that mobile. The selection mechanism operates on the second class of restricted handovers, during a penalty time triggered by the occurrence of handover causes included in the second class subset.
Owner:RPX CORP
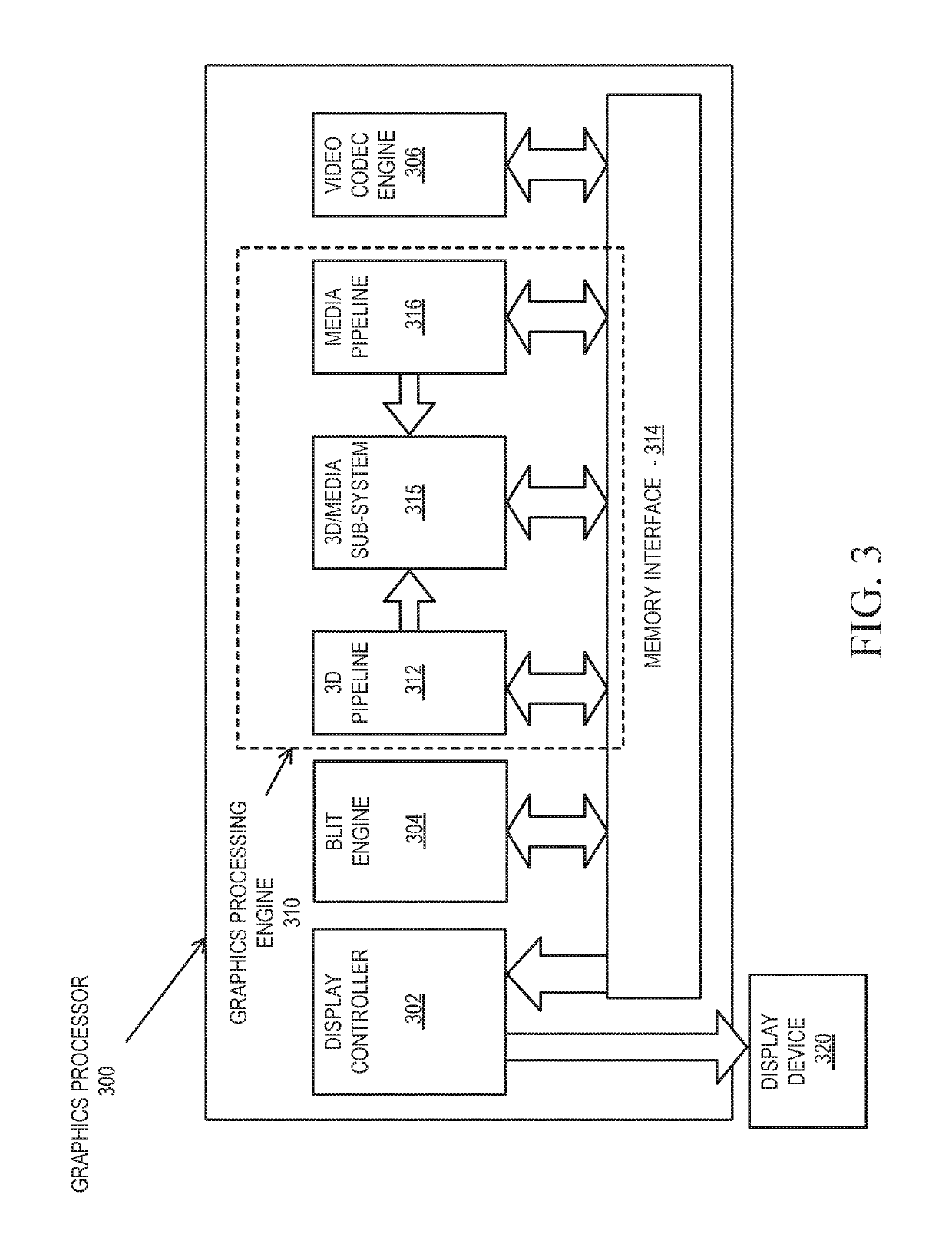
GPU minimum latency dispatch for short-duration tasks
Graphics processing systems and methods are described. For example, one embodiment of a graphics processing apparatus comprises a graphics processing unit (GPU), the GPU including a high priority command streamer to dispatch high priority commands from an application, a normal priority command streamer to receive normal priority commands through a command path, one or more execution units, and a thread dispatcher. The thread dispatcher to dispatch normal priority commands to the one or more executions units, determine the high priority command streamer includes at least one command, cause the one or more execution units to save their states, and dispatch at least one command from the high priority queue to the one or more execution units.
Owner:INTEL CORP
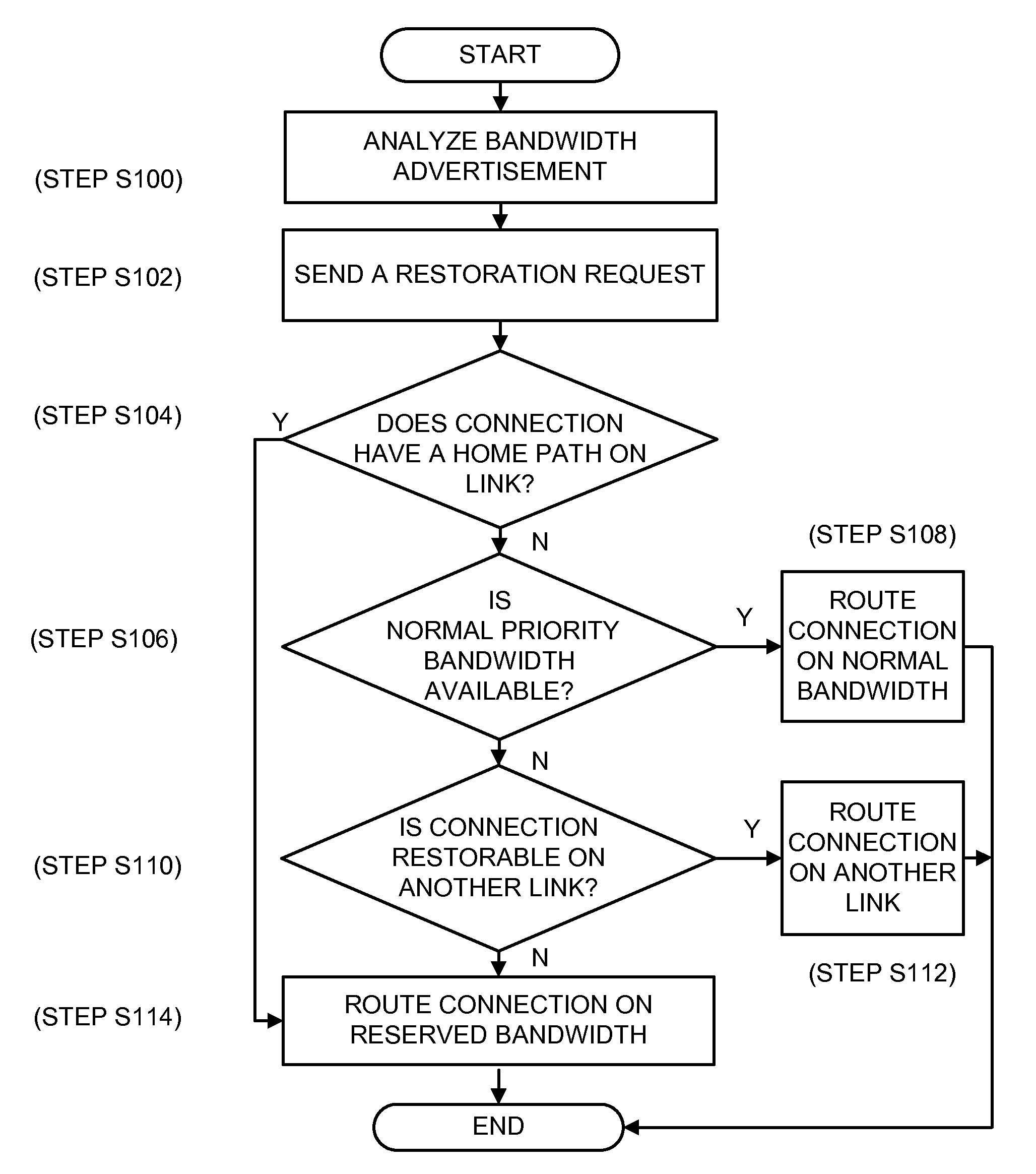
Retention of a sub-network connection home path
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method and system for reserving a connection's home path resources and restoring the connection on a link that includes a reserved priority bandwidth. A bandwidth advertisement indicating that the reserved priority bandwidth is available is analyzed and a restoration request requesting to route the connection on the link is sent. The reserved priority bandwidth is used to route the connection when the connection has a reserved home path on the link. When the connection has a reserved home path not on the link, a determination is made as to whether a normal priority bandwidth on the link is available and whether the connection is unrestorable on another link. The reserved priority bandwidth is used to temporarily route the connection when normal priority bandwidth on the link is unavailable and the connection is unrestorable on another link.
Owner:CIENA
Overload control method for Internet of things
InactiveCN102170662BImprove effectivenessDecongestionNetwork traffic/resource managementGeneral Packet Radio ServiceOverload control
The invention discloses an overload control method for the Internet of things, which mainly aims to solve the problem that network congestion cannot be relieved when the proportion of low-priority traffic is low in a conventional downlink throttling method for the Internet of things. The method comprises that: a mobility management entity (MME) or a serving general packet radio service (GPRS) supporting node (SGSN) monitors a real-time load value of a network, and judges whether throttling is required or not; if the network is in a congested state, a serving gateway (SGW) starts performing throttling on the low-priority traffic, and simultaneously the MME or SGSN judges whether the network congestion can be relieved only by performing the throttling on the low-priority traffic or not according to a throttling effect; and if the network congestion cannot be relieved only by performing the throttling on the low-priority traffic, the SGW starts performing the throttling on normal-priority traffic, and quits a throttling state after throttling delay is finished. By the method, the applicability and efficiency of the conventional scheme are enhanced by expanding downlink throttled traffic, and the problems of function failures of the conventional scheme when the proportion of the low-priority traffic is low can be effectively solved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Enhanced voicemail system and method
ActiveUS8369497B2Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingAutomatic exchangesNormal prioritySpeech sound
A system for processing voicemail is provided that includes a voicemail database processor establishing one or more of an accounts table, a messages table, a distribution list table, a distribution lists members tables, and a delete request table. In operation a message navigation menu is provided to a user to allow the user to move back and forth a specified number of voicemails, change between urgent and normal priority voicemails, retrieve messages only from a specific mailbox or from outside the system, or initiate an improved deletion operation.
Owner:SCOPES PHILIP M
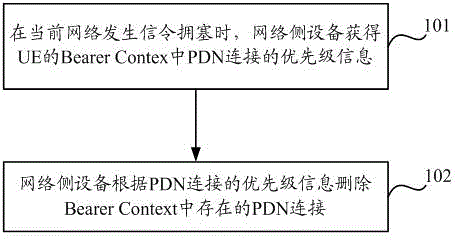
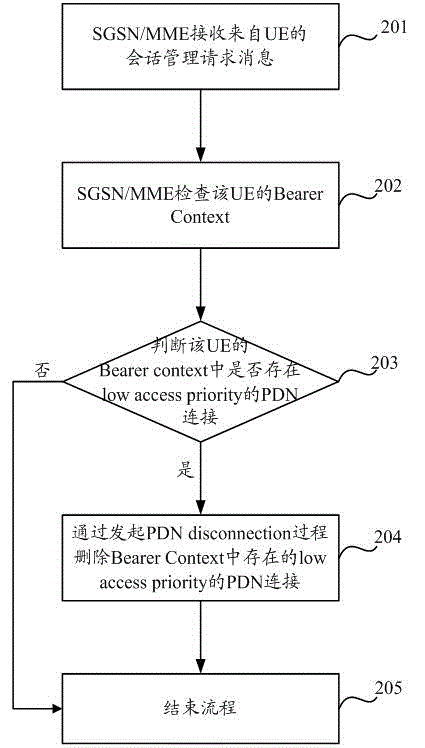
A method and device for deleting a pdn connection
ActiveCN102625475BEasy to useNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementTelecommunicationsNormal priority
Disclosed are a PDN connection deleting method and device. The method comprises: when a current network generates signalling congestion, a network-side device obtaining priority information about a PDN connection in a bearer context of UE, the priority information about the PDN connection being determined by an indication as to whether the PDN connection has a low access priority; and the network-side device deleting the PDN connection existing in the bearer context according to the priority information about the PDN connection. When the degree of network congestion is lower, the embodiments of the present invention can ensure that a PDN connection of which the priority is higher than the low access priority and a PDN connection of an emergency service can coexist, thereby ensuring that UE can simultaneously obtain a normal priority service and an emergency service as far as possible, and improving the user usage experience.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com