Patents
Literature
41 results about "Object-relational database" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
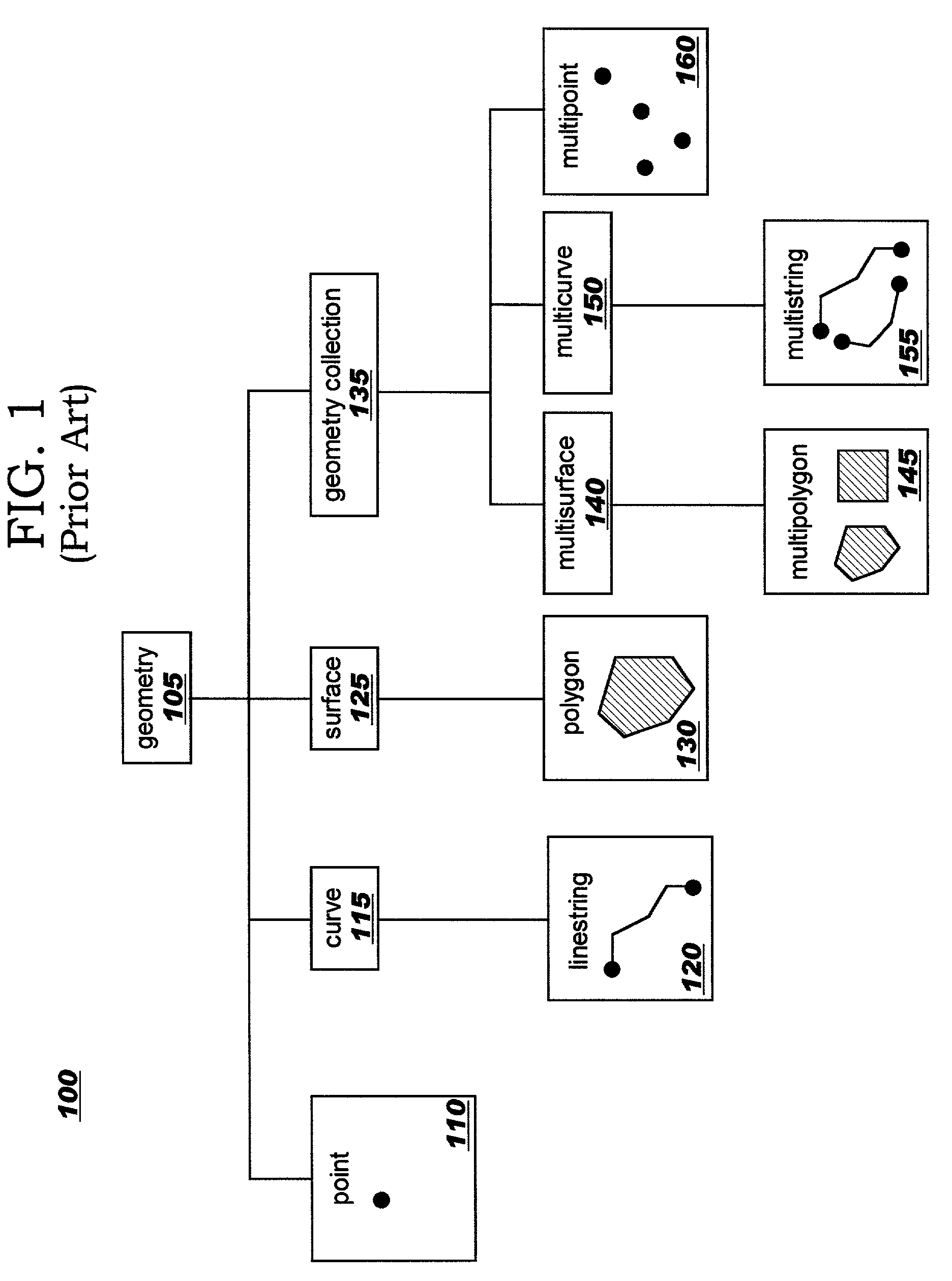
An object-relational database (ORD), or object-relational database management system (ORDBMS), is a database management system (DBMS) similar to a relational database, but with an object-oriented database model: objects, classes and inheritance are directly supported in database schemas and in the query language. In addition, just as with pure relational systems, it supports extension of the data model with custom data types and methods.
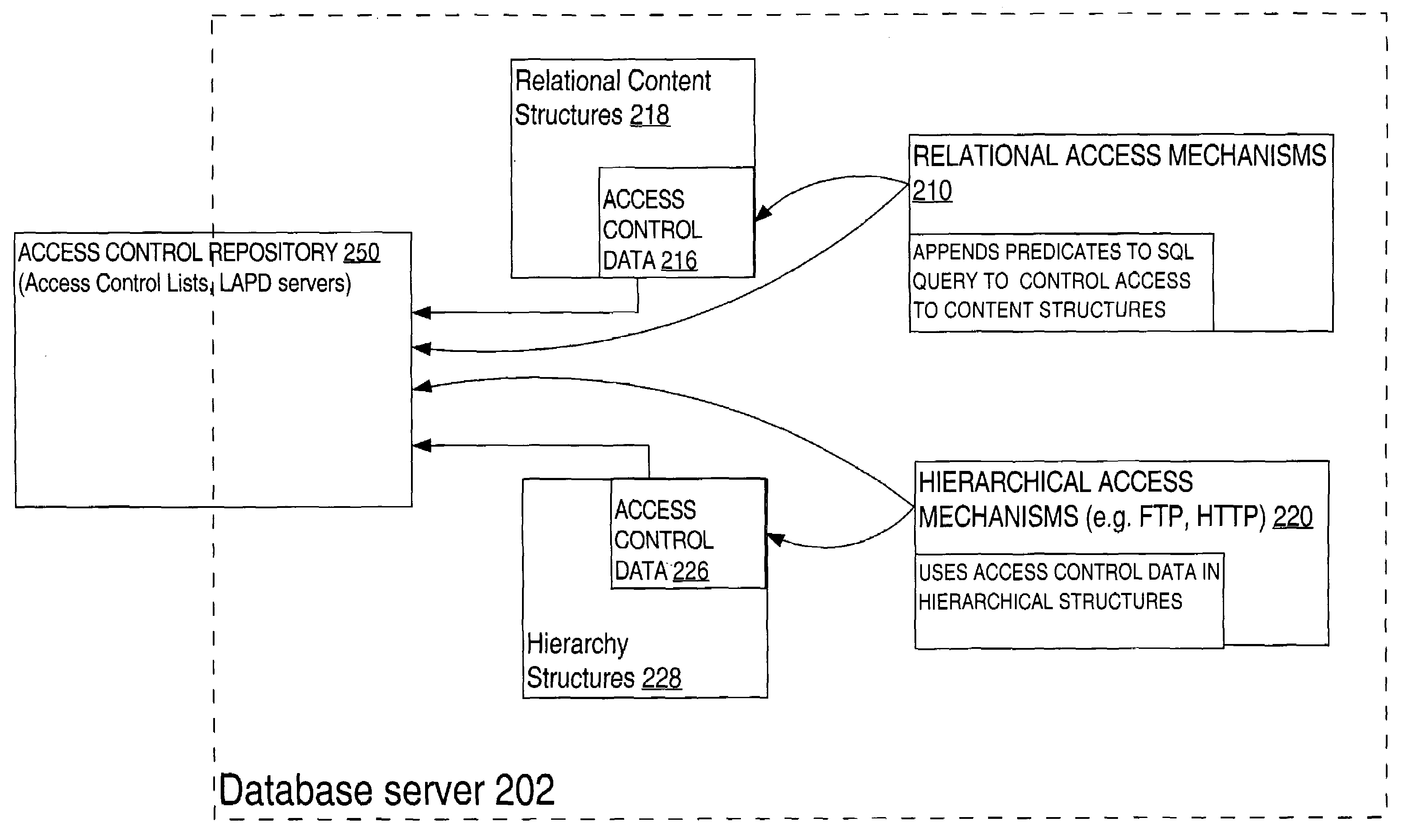
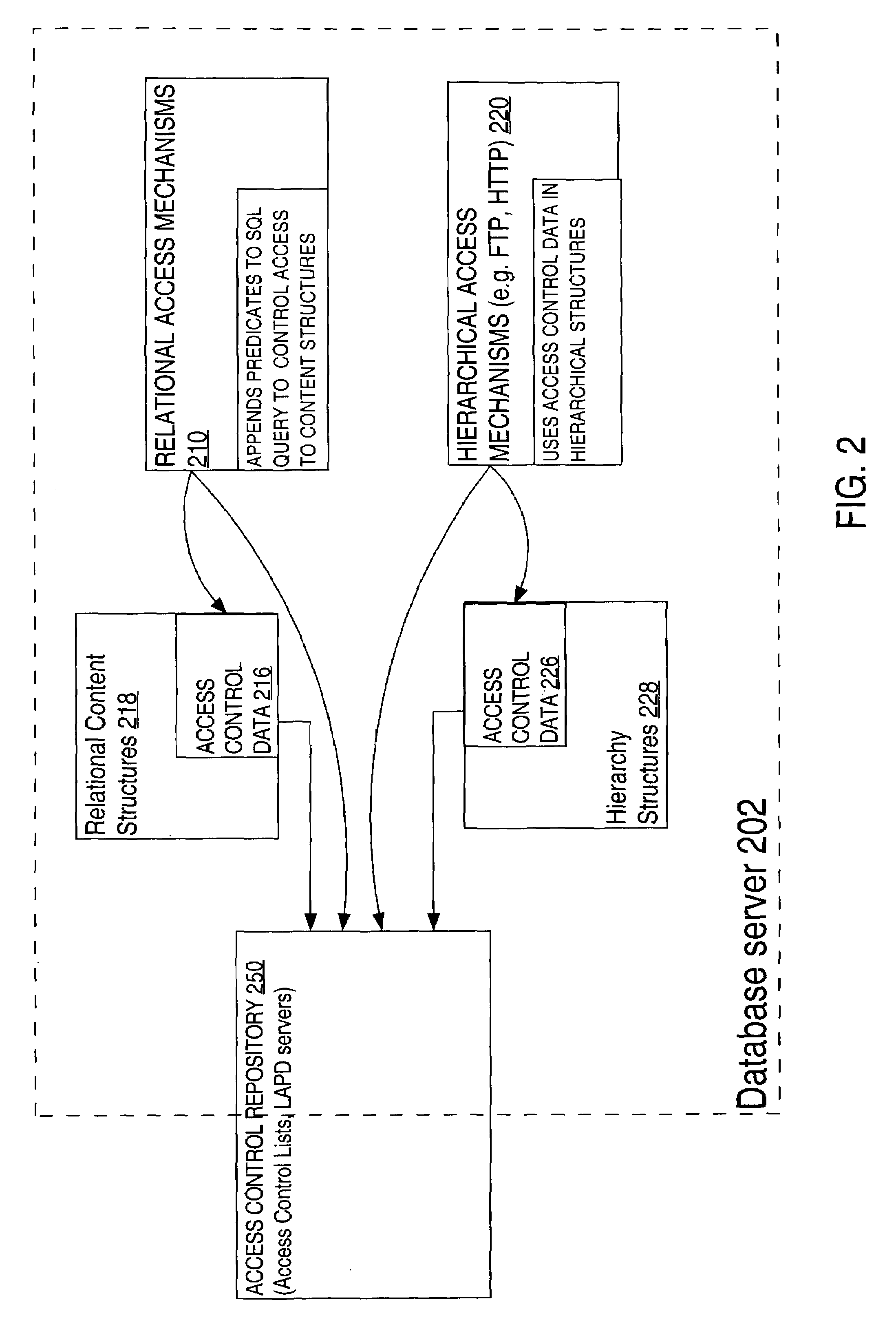
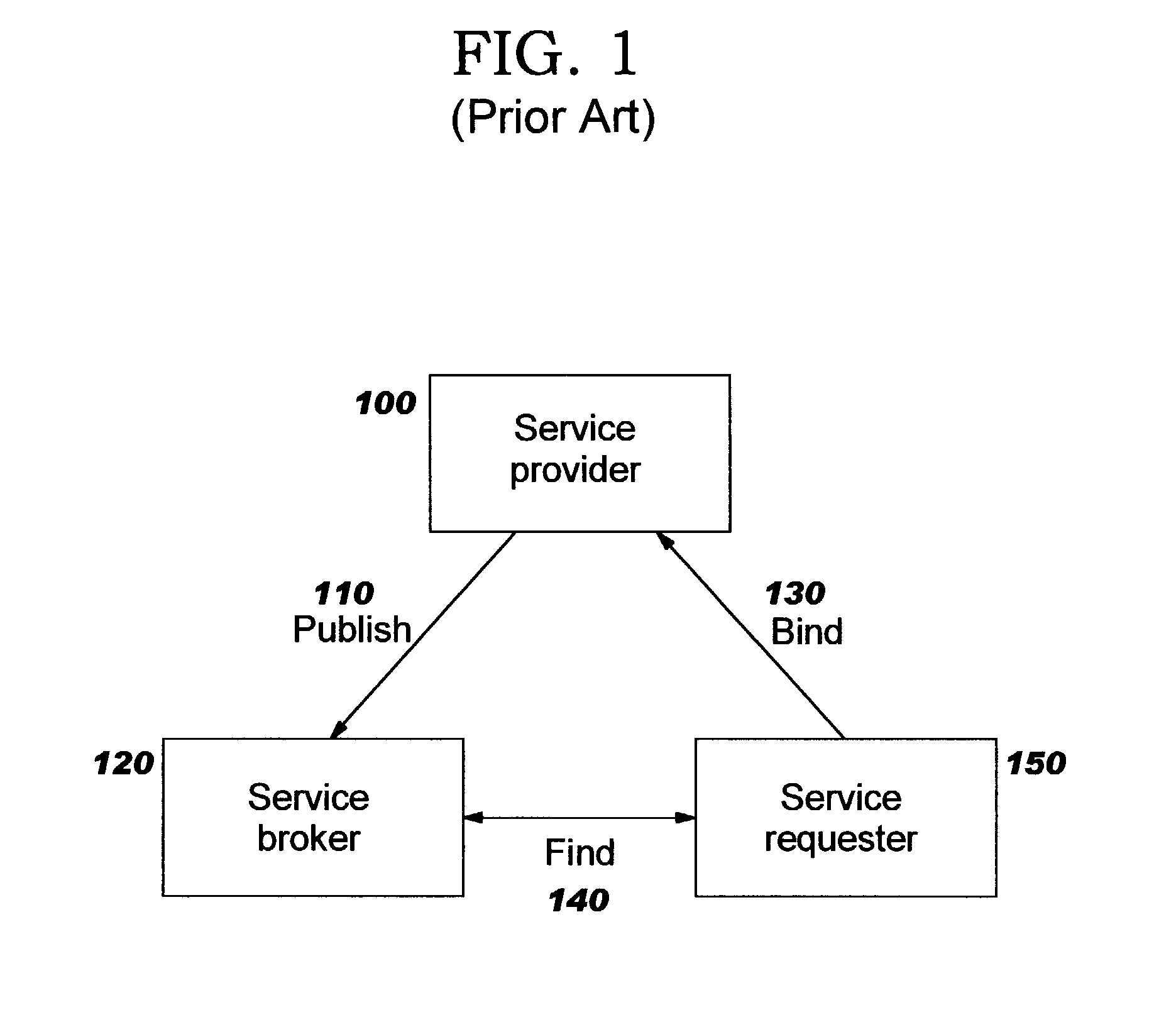
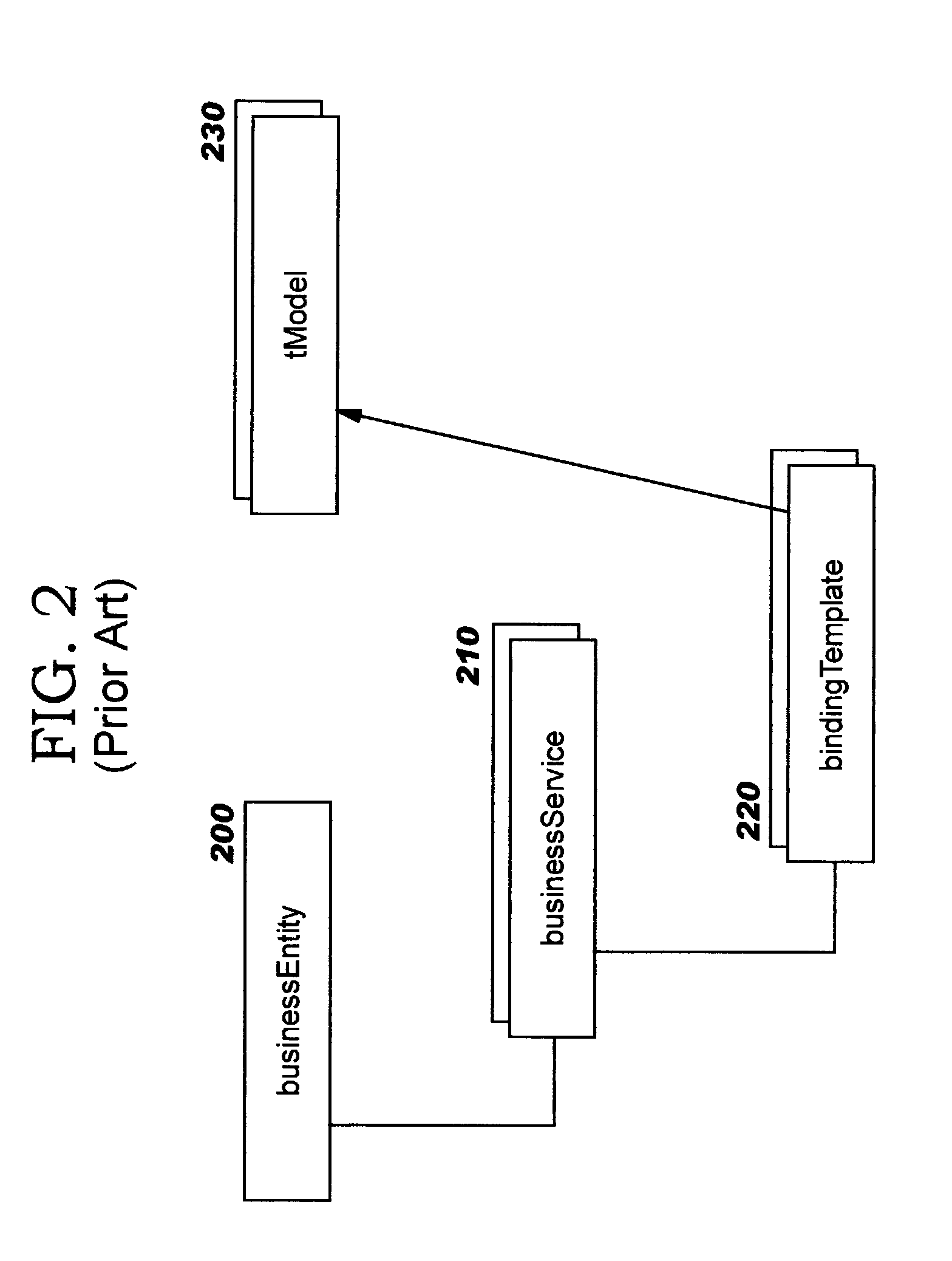
Mechanism for uniform access control in a database system
ActiveUS7051039B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData controlDatabase server
Techniques are provided for facilitating uniform access control to data managed by a database server that can emulate hierarchically organized systems, whether the data is accessed through hierarchical or relational access mechanisms. A database server that can emulate hierarchically organized systems uses separate relational or object-relational database tables to store the content of the resources that belong to a hierarchy (the “content structures”) and information that captures the hierarchy (the “hierarchy structures”). Both types of structures contain access control data that define consistent user access privileges. To determine access privileges for a user requesting access to data in the database, access control information is accessed in the hierarchy structures when the request is made through the hierarchical access mechanism, or accessed in the content structures when the request is made through a relational access mechanism. Access control is consistent between the hierarchical or relational access mechanisms because access through either is governed by user access data that reflects the same privileges.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
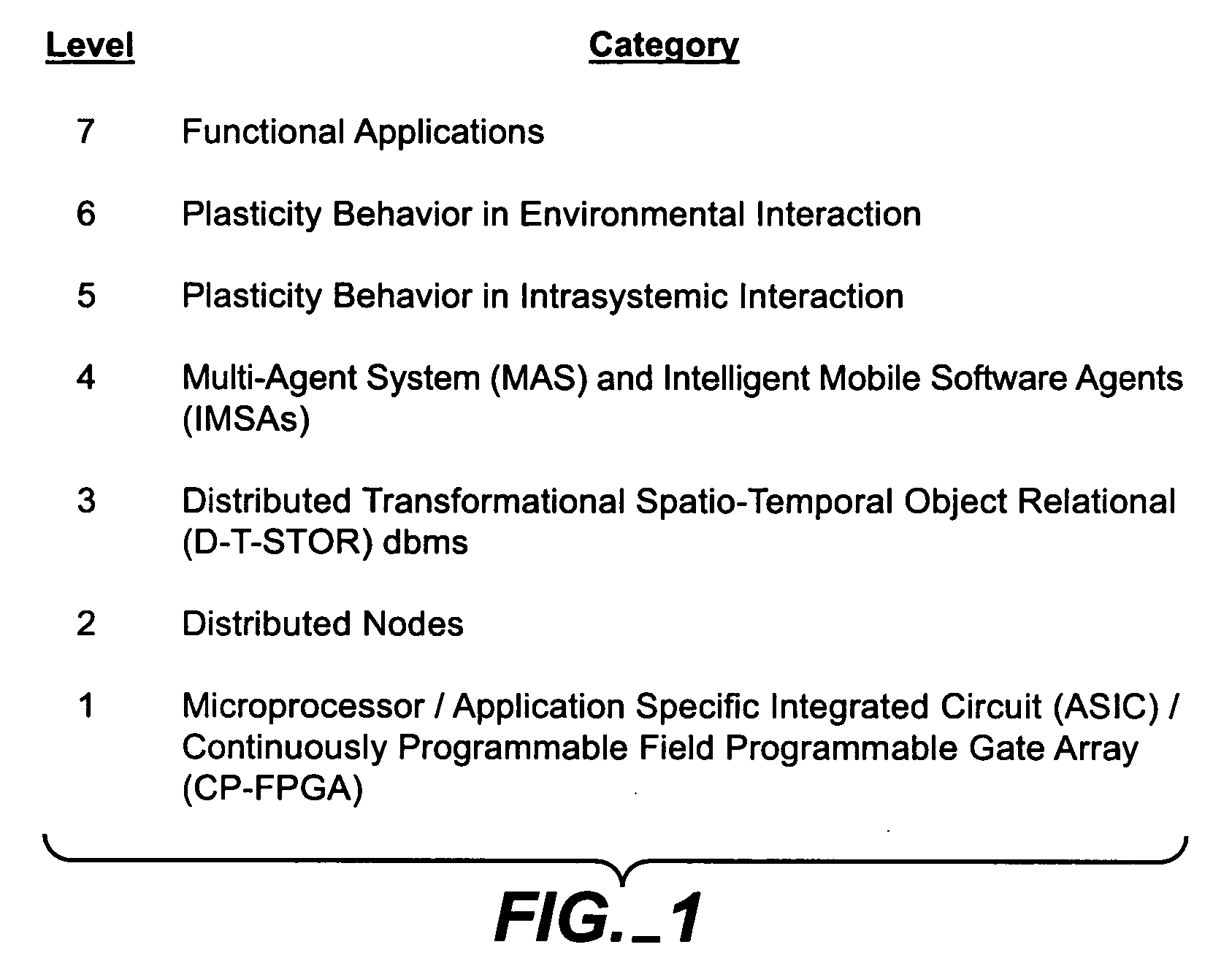
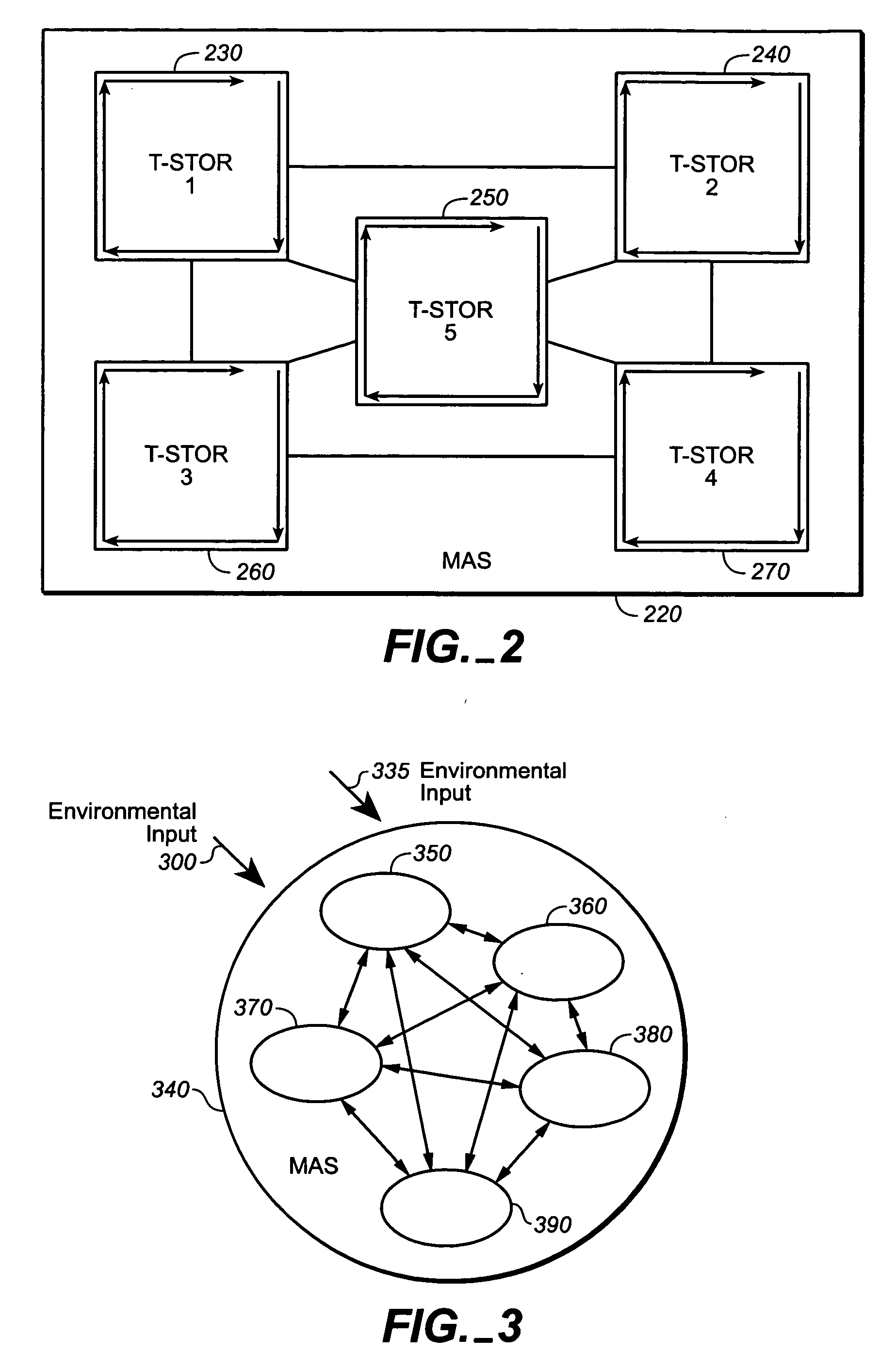
Dynamic adaptive distributed computer system
InactiveUS20050177593A1Most efficientOptimizes adaptive self-organizing operationDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsSearch analyticsComplex system
A system, methods and apparatus are described involving the self-organizing dynamics of networks of distributed computers. The system is comprised of complex networks of databases. The system presents a novel database architecture called the distributed transformational spatio-temporal object relational (T-STOR) database management system (dbms). Data is continuously input, analyzed, organized, reorganized and used for specific commercial and industrial applications. The system uses intelligent mobile software agents in a multi-agent system in order to learn, anticipate, and adapt and to perform numerous functions, including search, analysis, collaboration, negotiation, decision making and structural transformation. The system links together numerous complex systems involving distributed networks to present a novel model for dynamic adaptive computing systems, which includes plasticity of collective behavior and self-organizing behavior in intelligent system structures.
Owner:SOLOMON NEAL
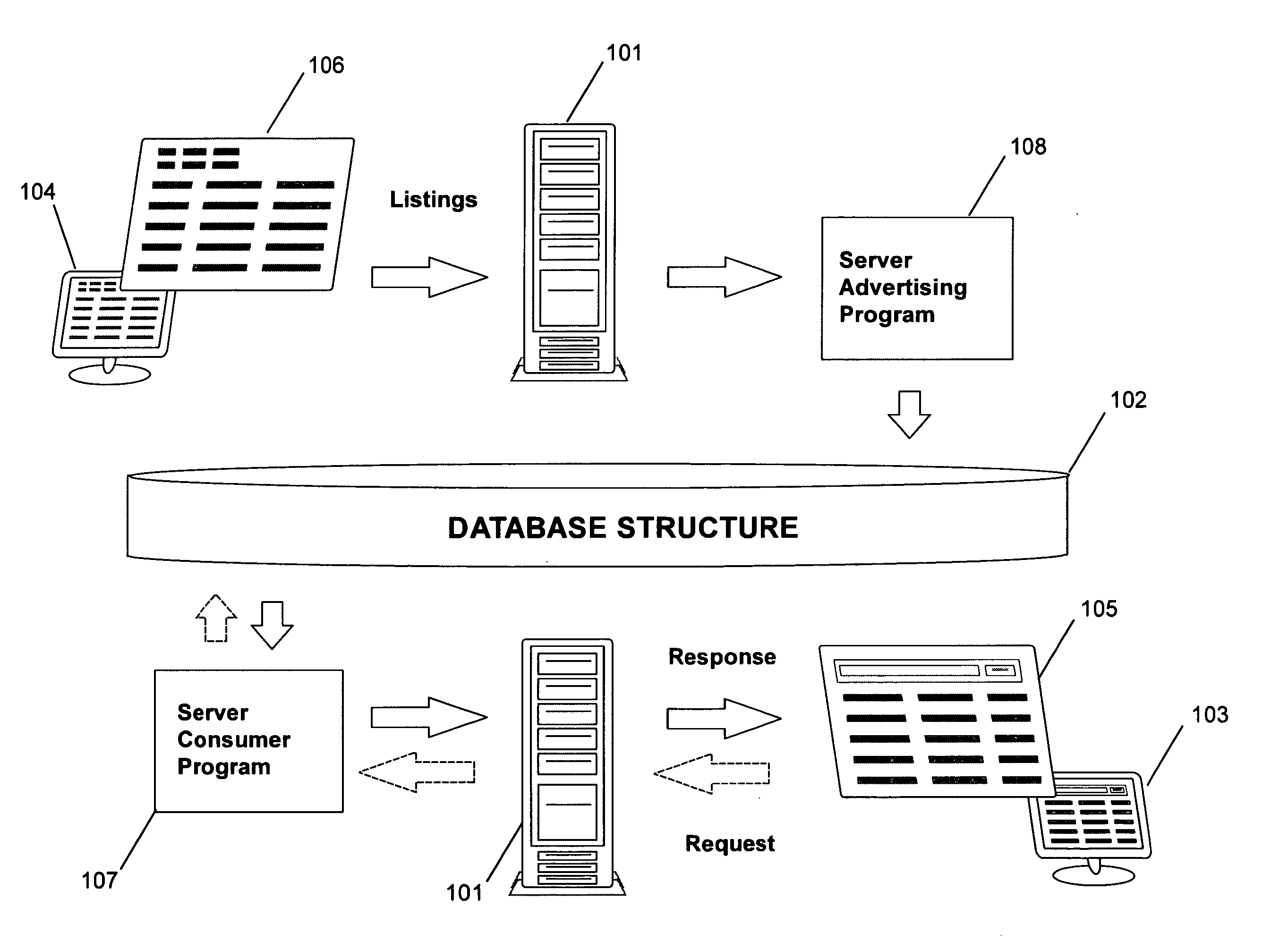
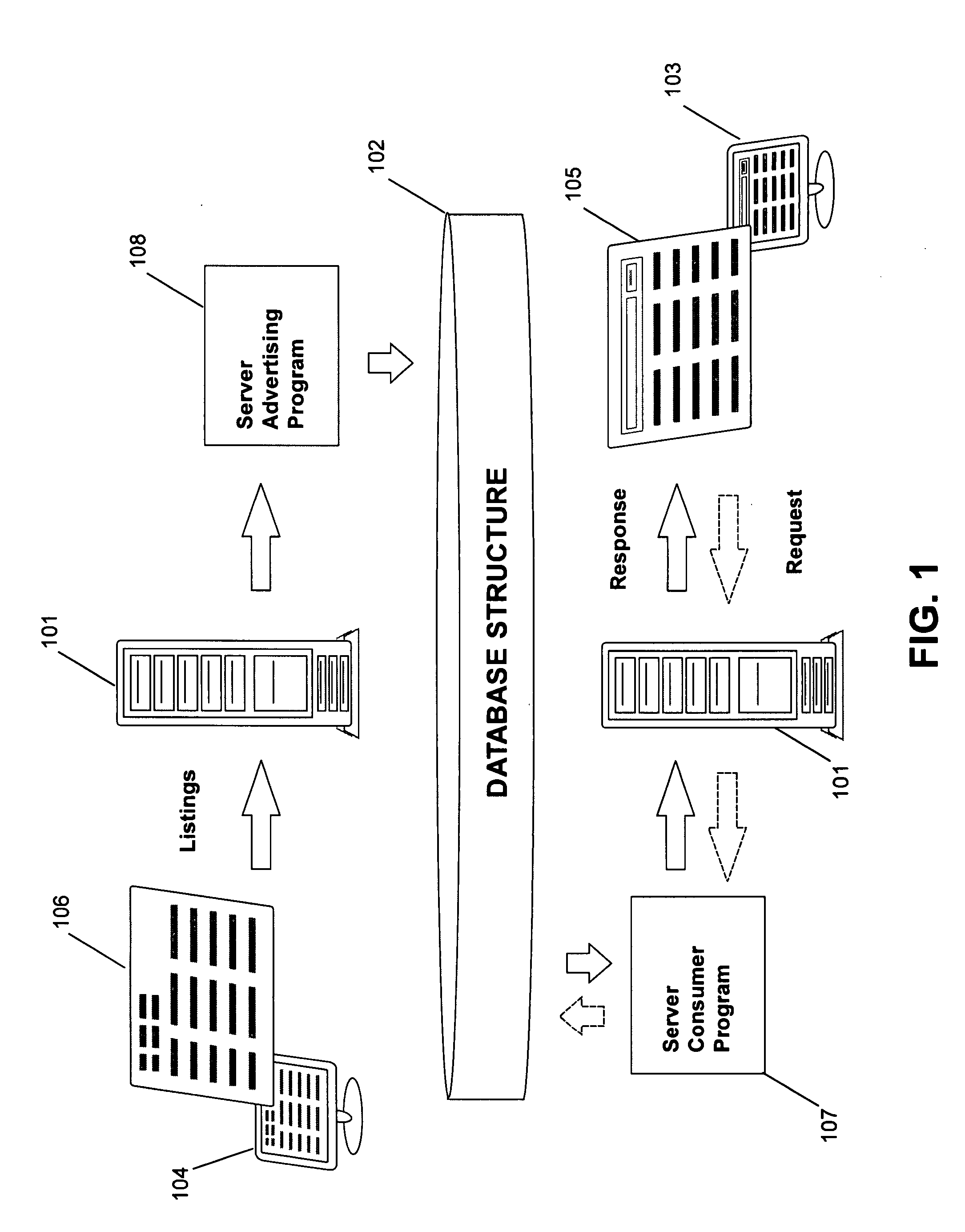
Network information distribution system and a method of advertising and search for supply and demand of products/goods/services in any geographical location
The proposed system and method embodiments allow placing advertisements and searching for items within a network (Internet, intranets, etc.), particularly encompass server advertiser and consumer programs associated with database means, provide for multi-language, multi-currency, multi-items entry, multi-location, geographical-category and catalog-category resolution, multi-parameters setting, and other types of support. The method may include combinations of a normalized category suggestion, user feedback category / listing suggestion, custom-made category creation, and regular keyword search modes for placement and search phases. The user feedback suggestion is provided by the system memorizing previous user-approved linkages between entered keyterms and respective categories or listings, and then proposing them to current users entering similar keyterms. The normalized category suggestion is generated by the system storing records preferably based on a normalized data hierarchy. The custom-made categories may be converted into relational, object-relational, or object-oriented database records. Such modes facilitate placement and search for users of different skills levels.
Owner:SEE VISIONS
Decentralized database optimizations
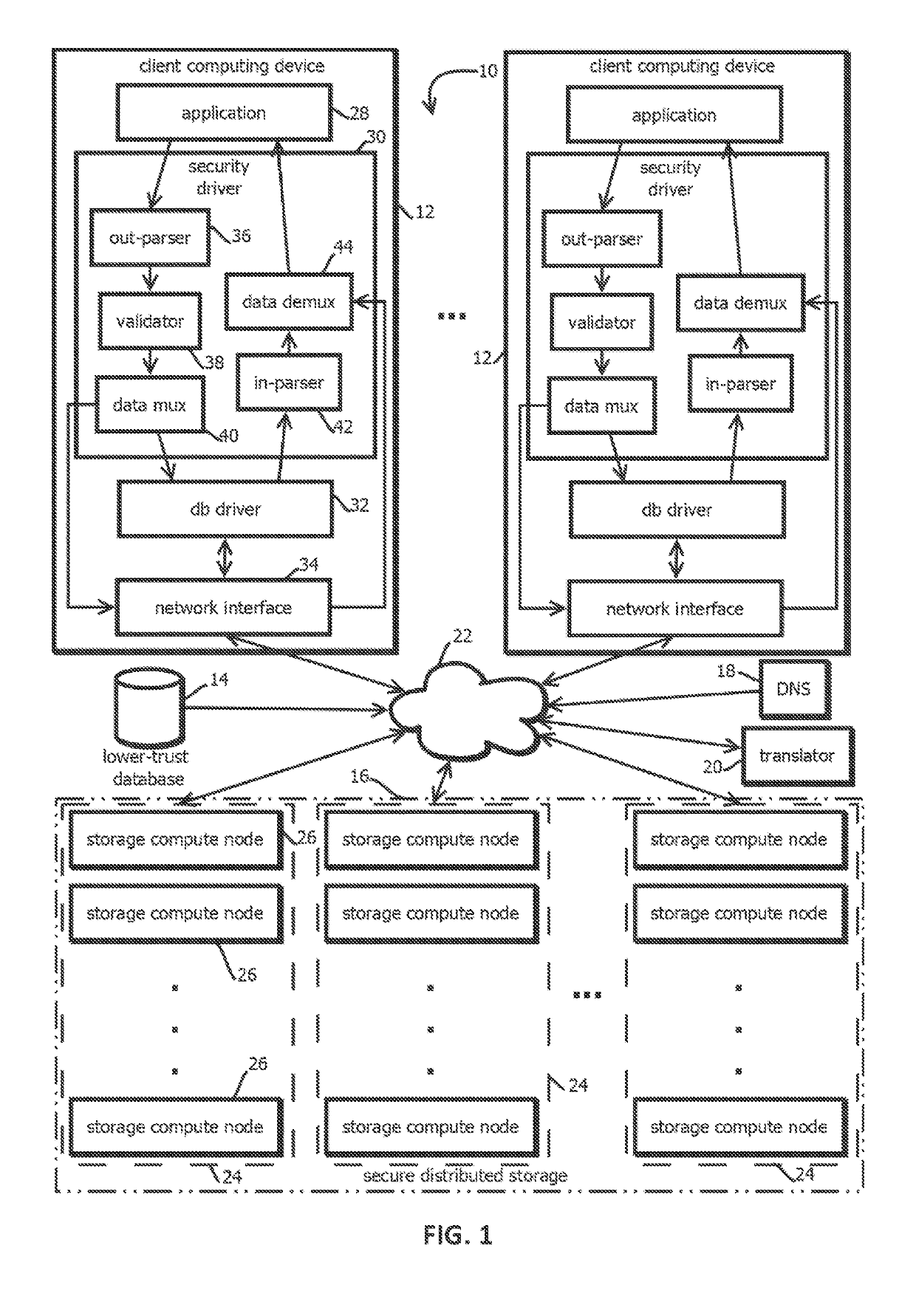
ActiveUS20190288850A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationRelational databaseData storing
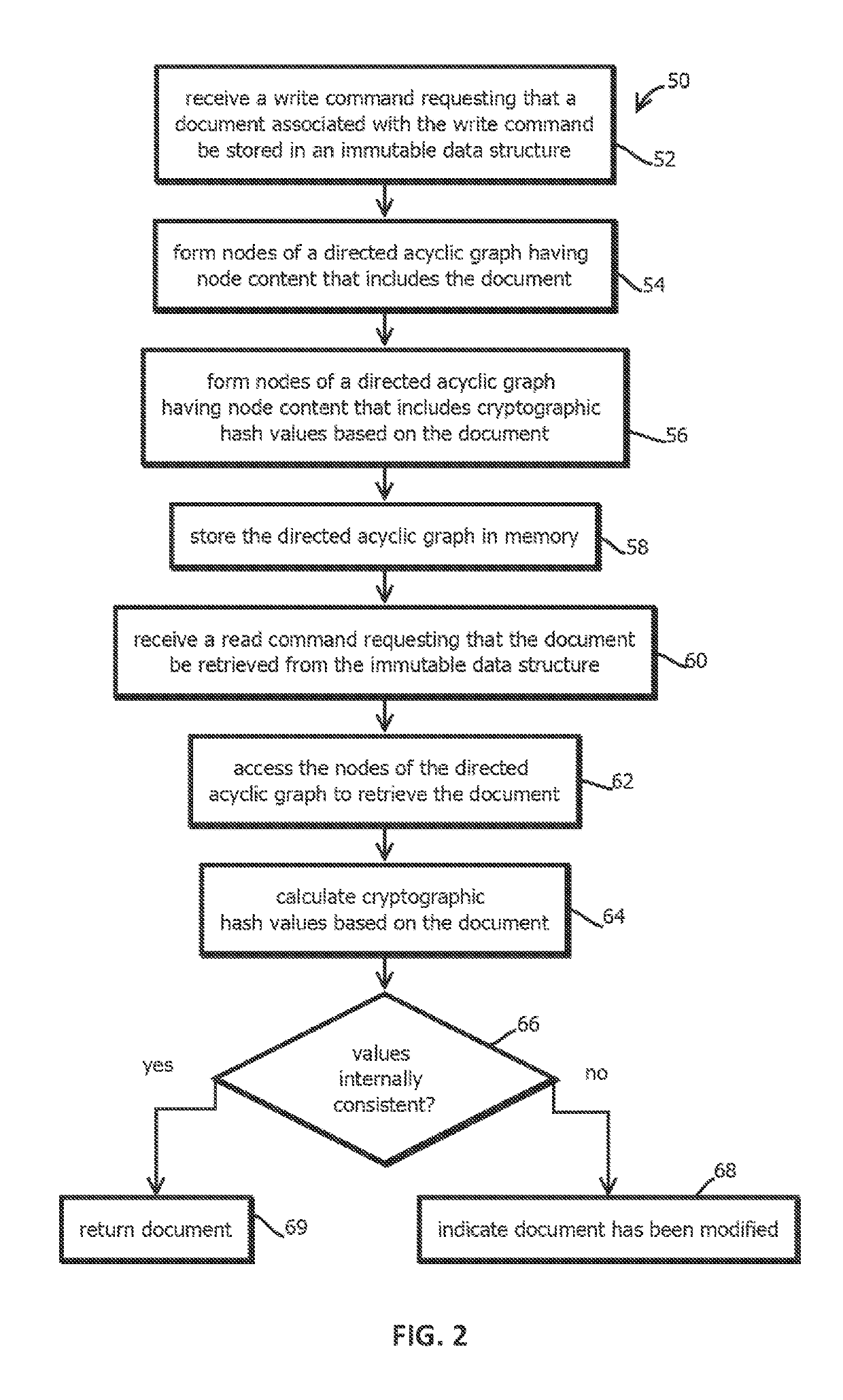
Techniques for managing data stored within a database, such as a decentralized database are provided. Some techniques involve managing some data within a lower-trust database and some other data within a higher-trust database. A higher-trust database may be a decentralize database including a blockchain. A lower-trust database may store references to data within the blockchain, and optionally other data in association with those references. Disclosed techniques include WHERE clause query handling in databases with reference values, replacement of distinct data in a relational database with a distinct reference to that data, number line storing for secure indexing, APIs for databases, and consensus operations for private blockchain networks.
Owner:ALTR SOLUTIONS INC
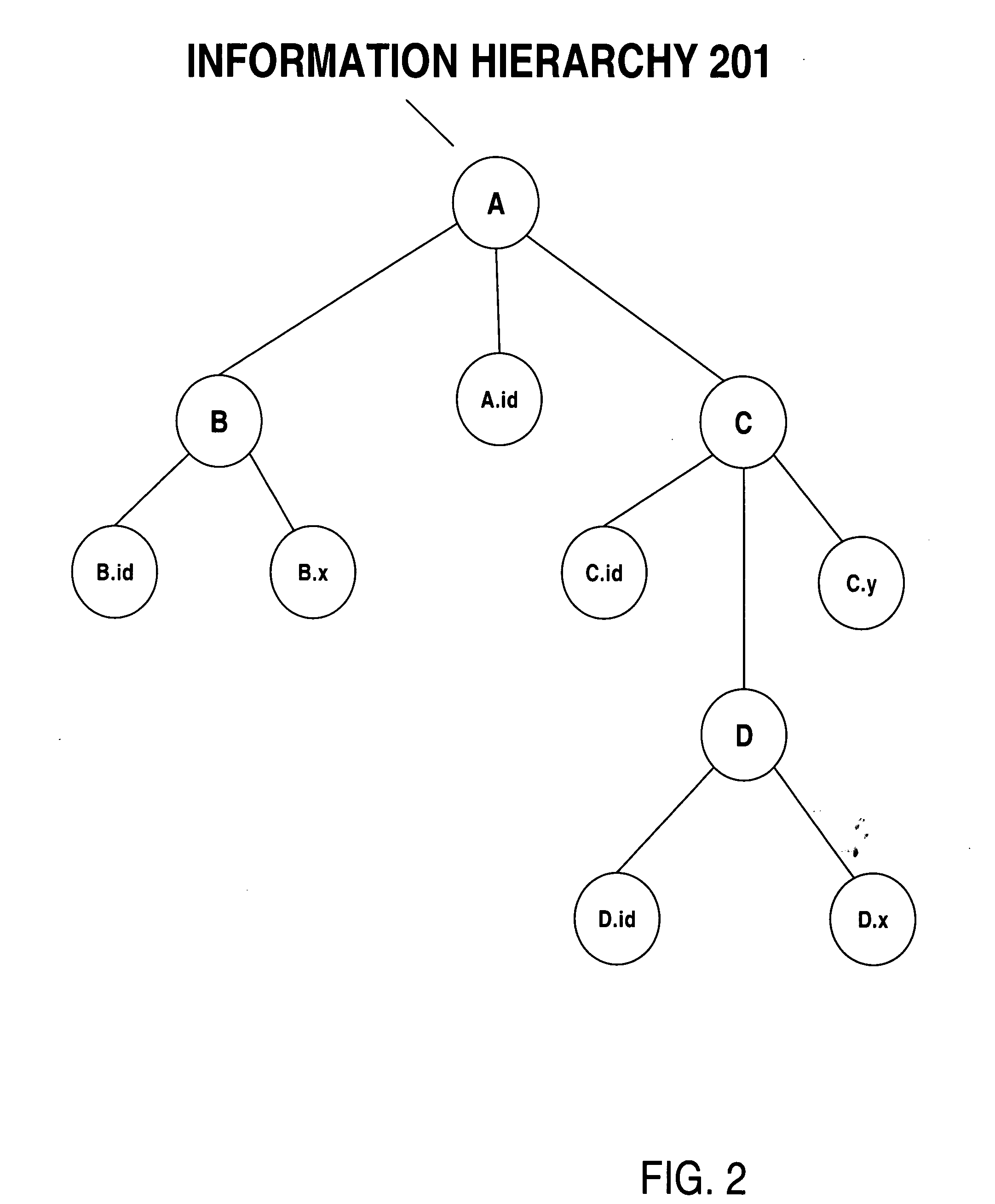
Storing XML documents efficiently in an RDBMS
ActiveUS20050055343A1Digital data processing detailsUnstructured textual data retrievalRelational databasePattern matching
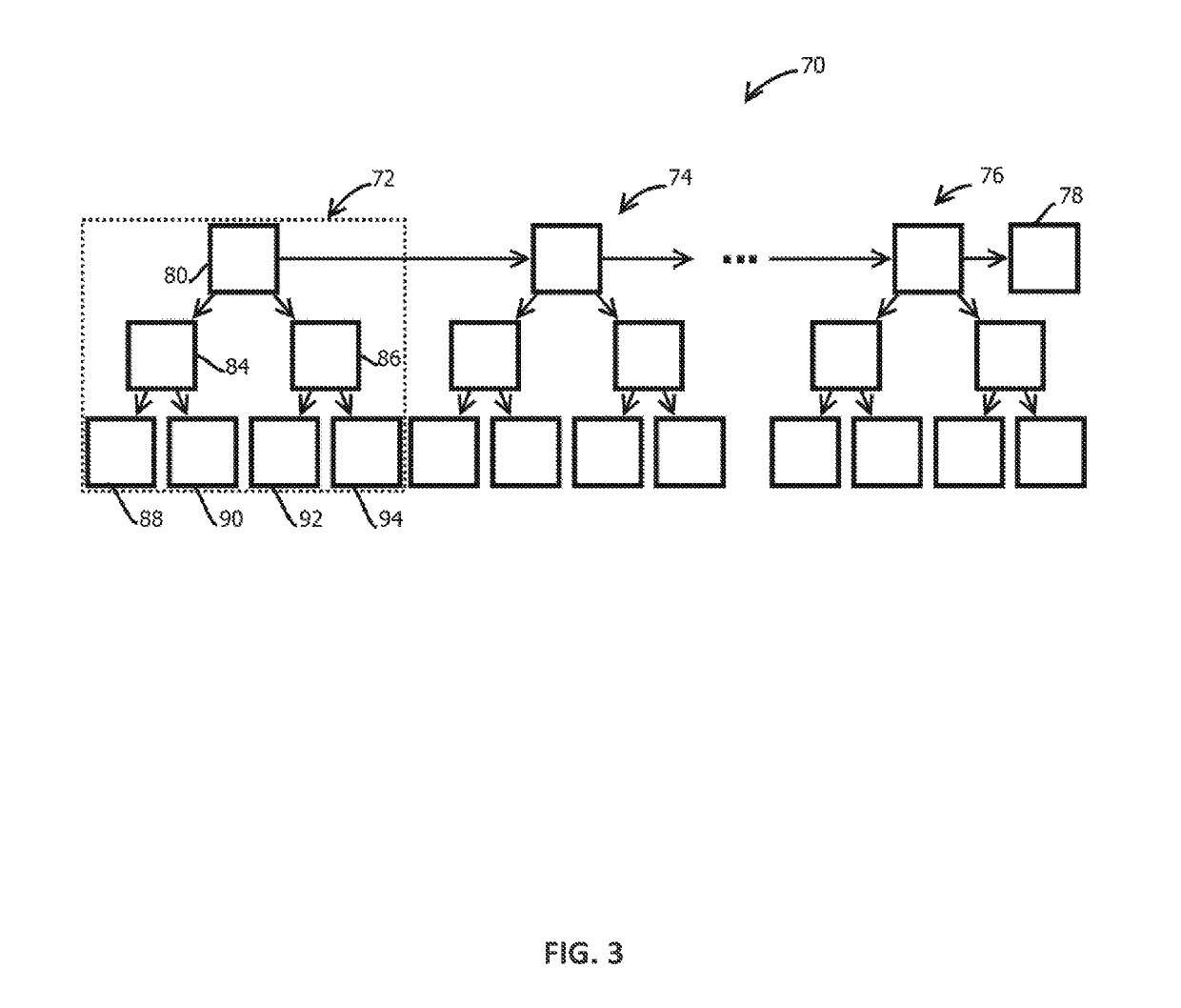
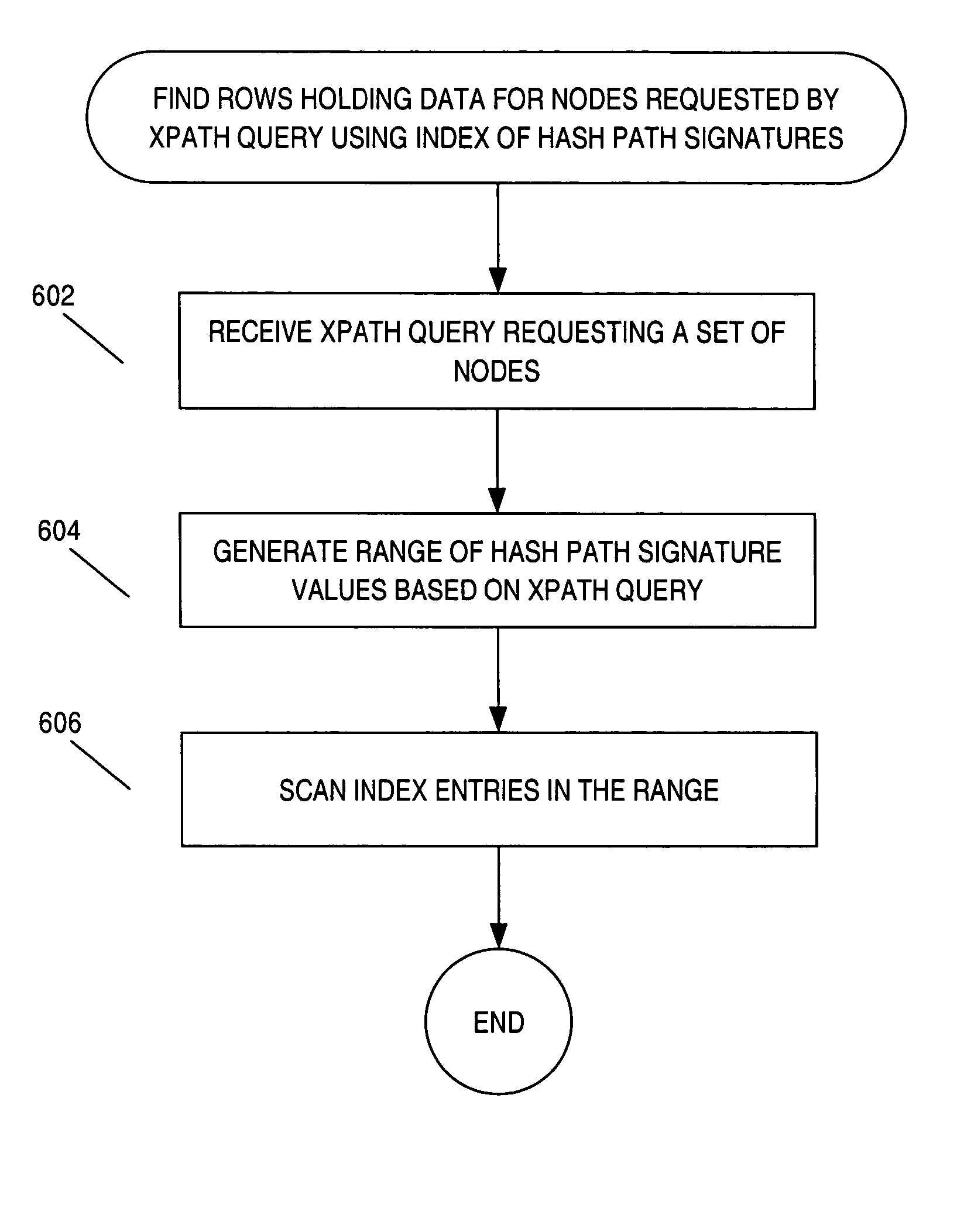
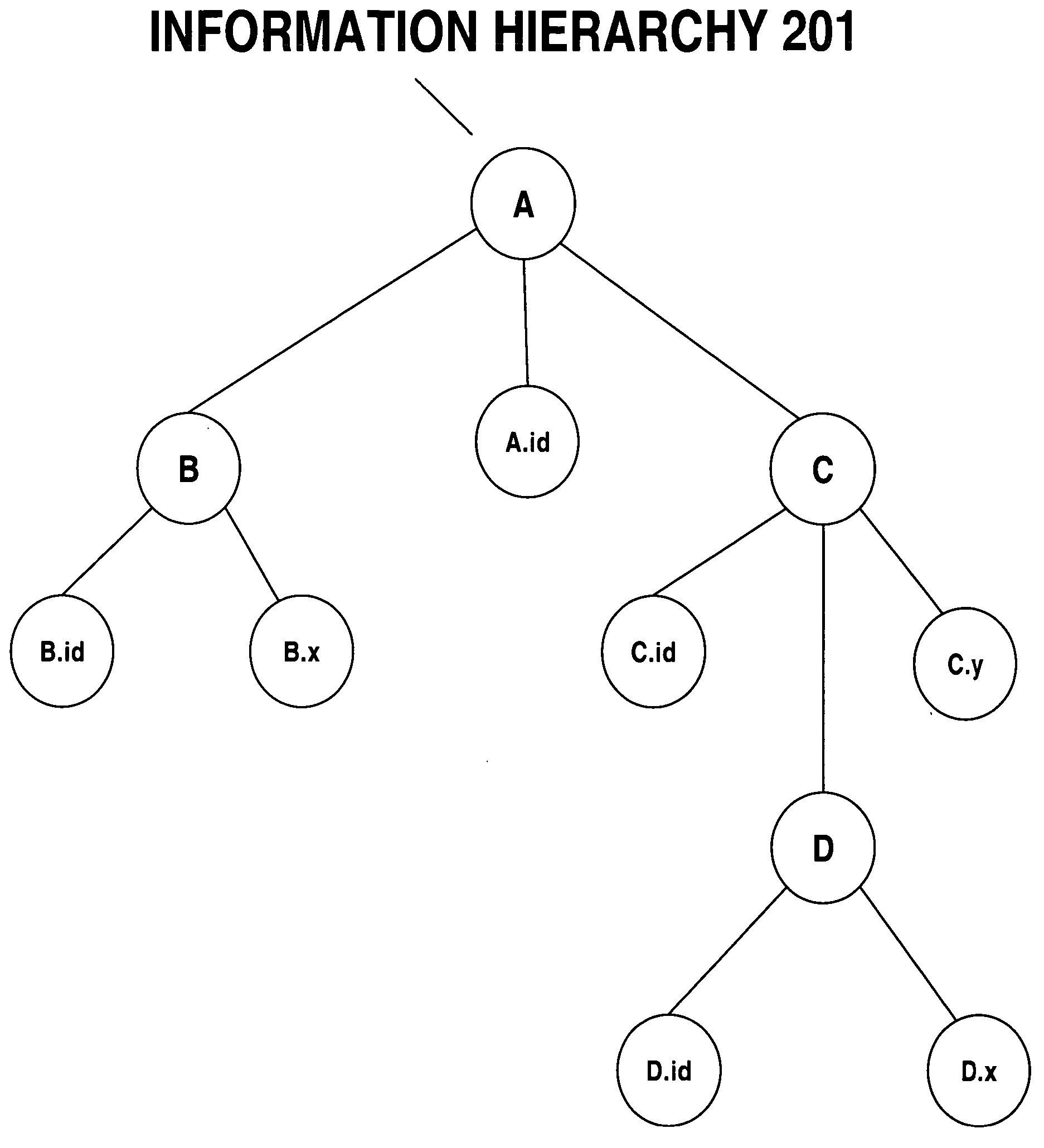
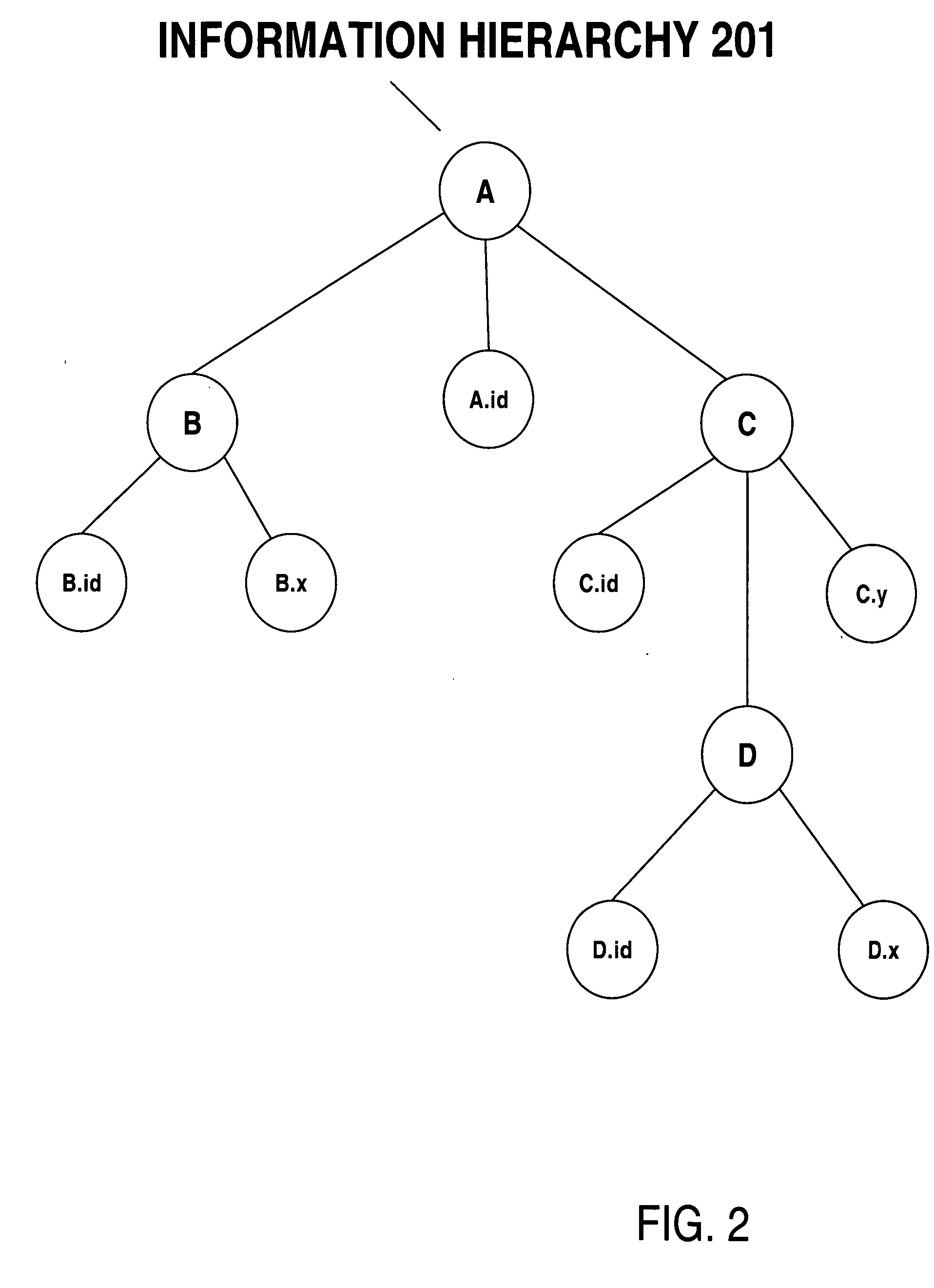
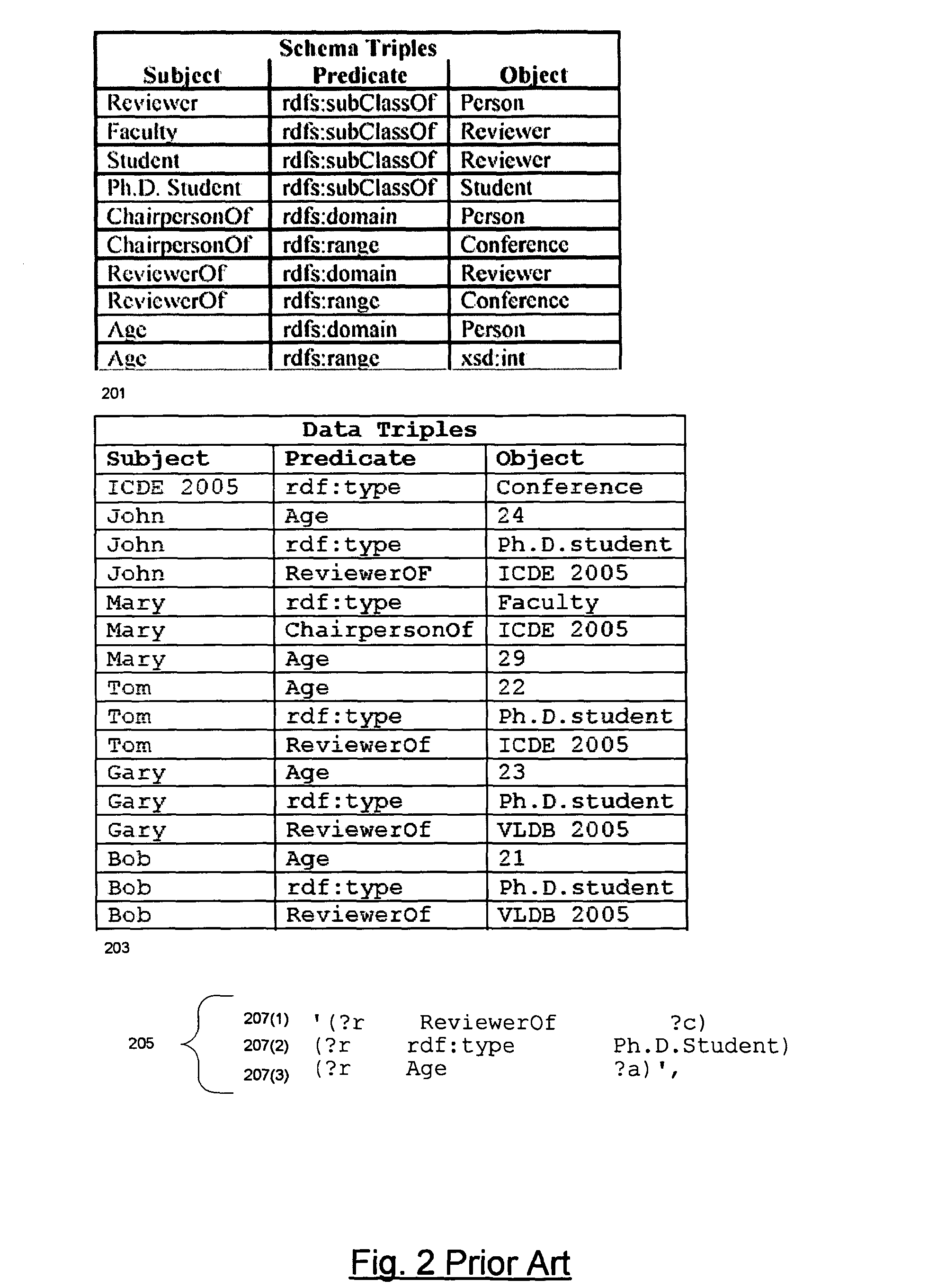
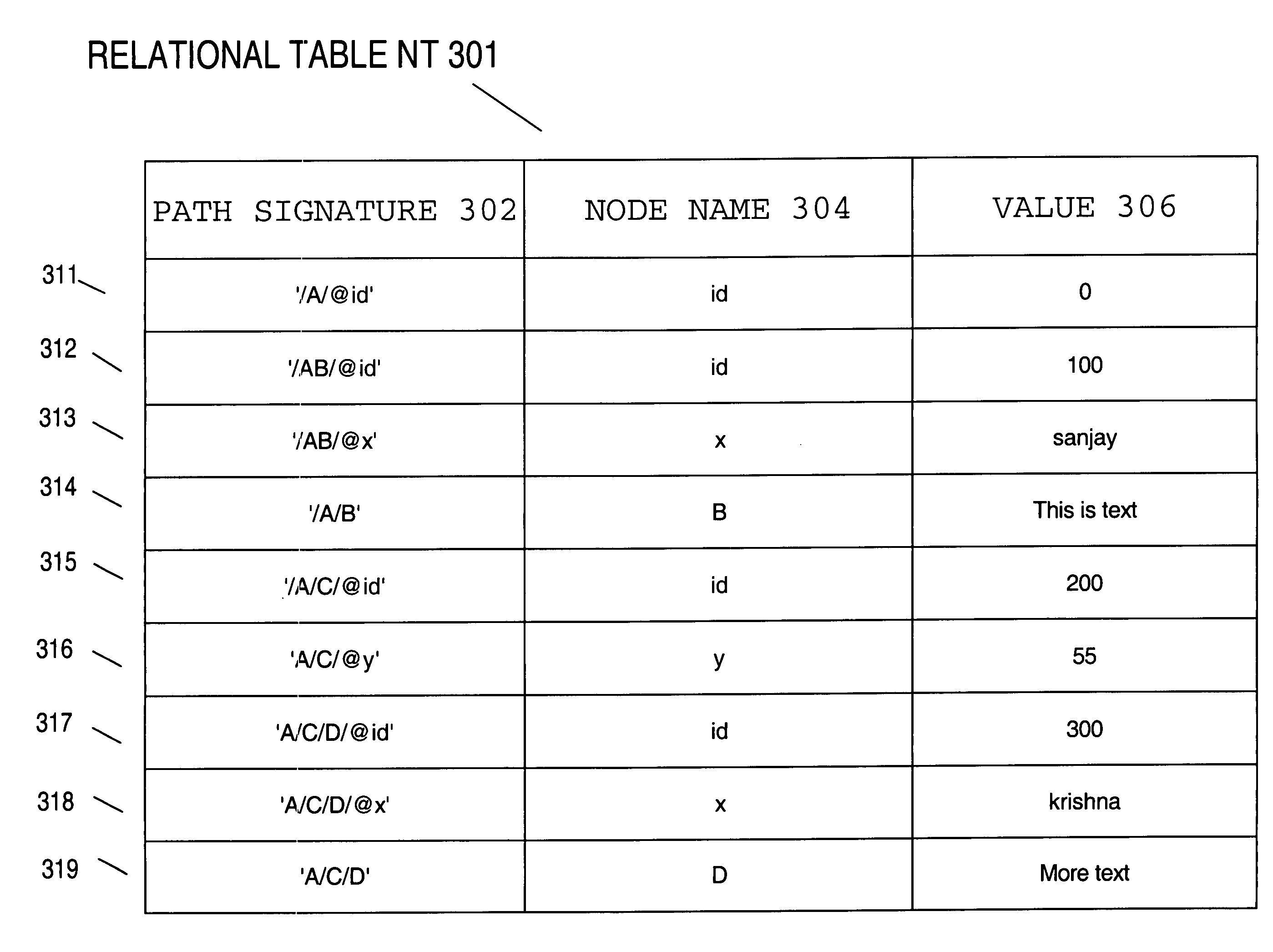
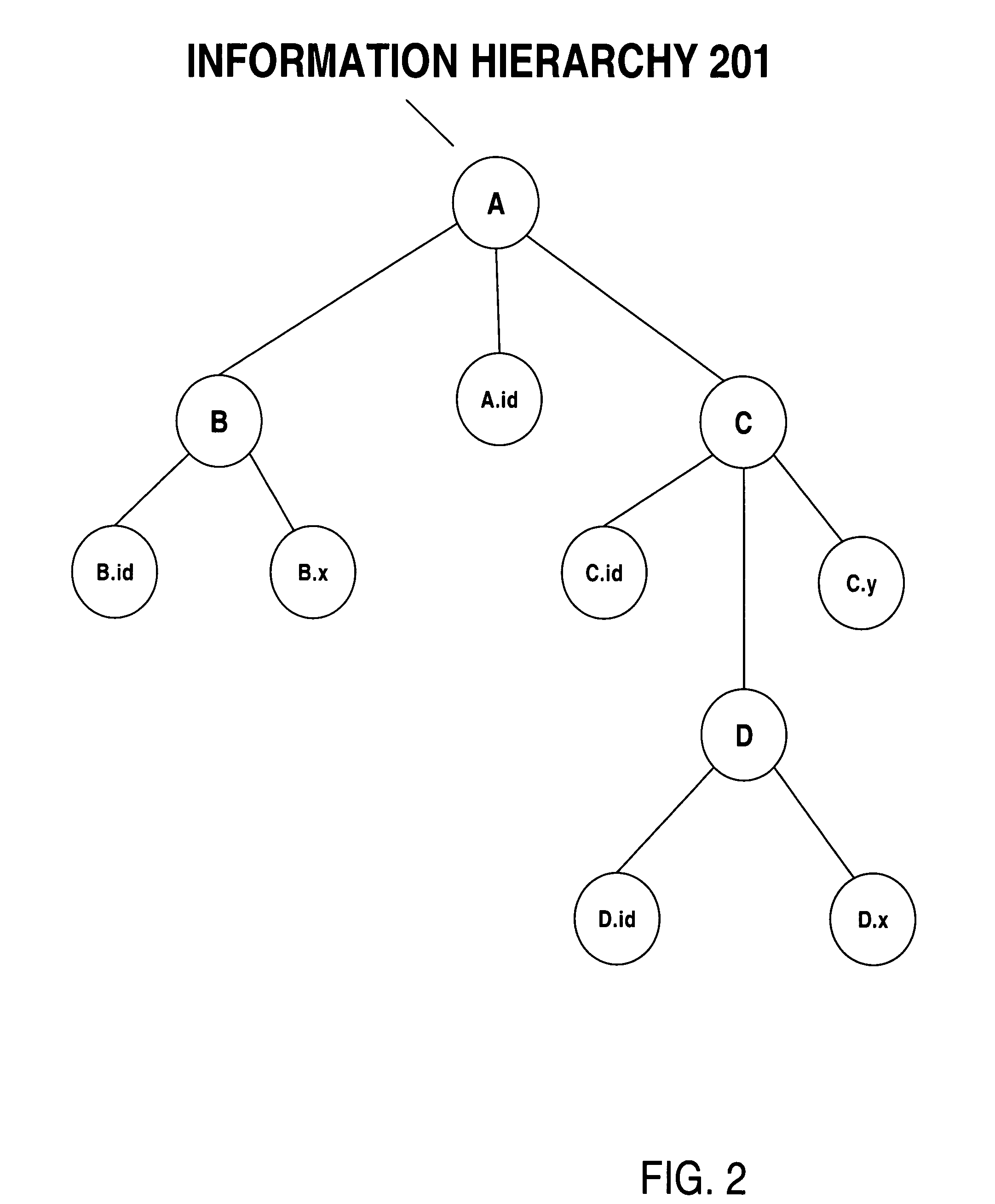
Information hierarchies are efficiently stored and accessed in a relational or object-relational database system. A path signature, similar to a pathname, is stored in a database system in association with data for the node identified by the pathname. For example, a path signature identifying an element is stored in a row that holds data for the element. To retrieve data for a hierarchical query that identifies the data requested using, for example, an XPATH string, a string pattern is generated that is matched by path signatures identified by the XPATH string. Pattern matching is then used to select rows associated with matching path signatures, and data from the selected rows is used to compute the XPATH query. Furthermore, hash values representing path signatures are generated in a way that preserves the ordering of data in an information hierarchy. The hash values can be indexed to provide quick access.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
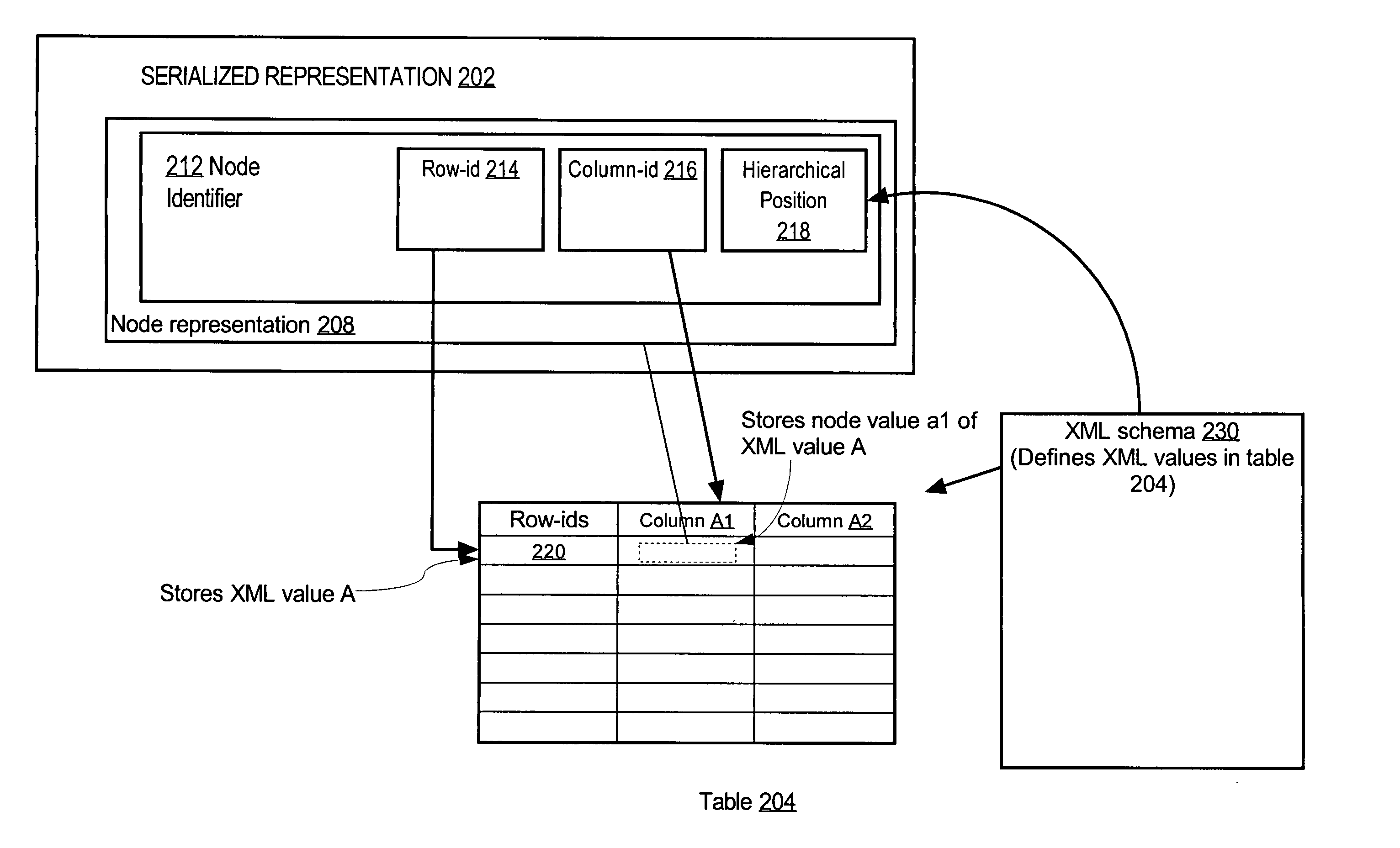
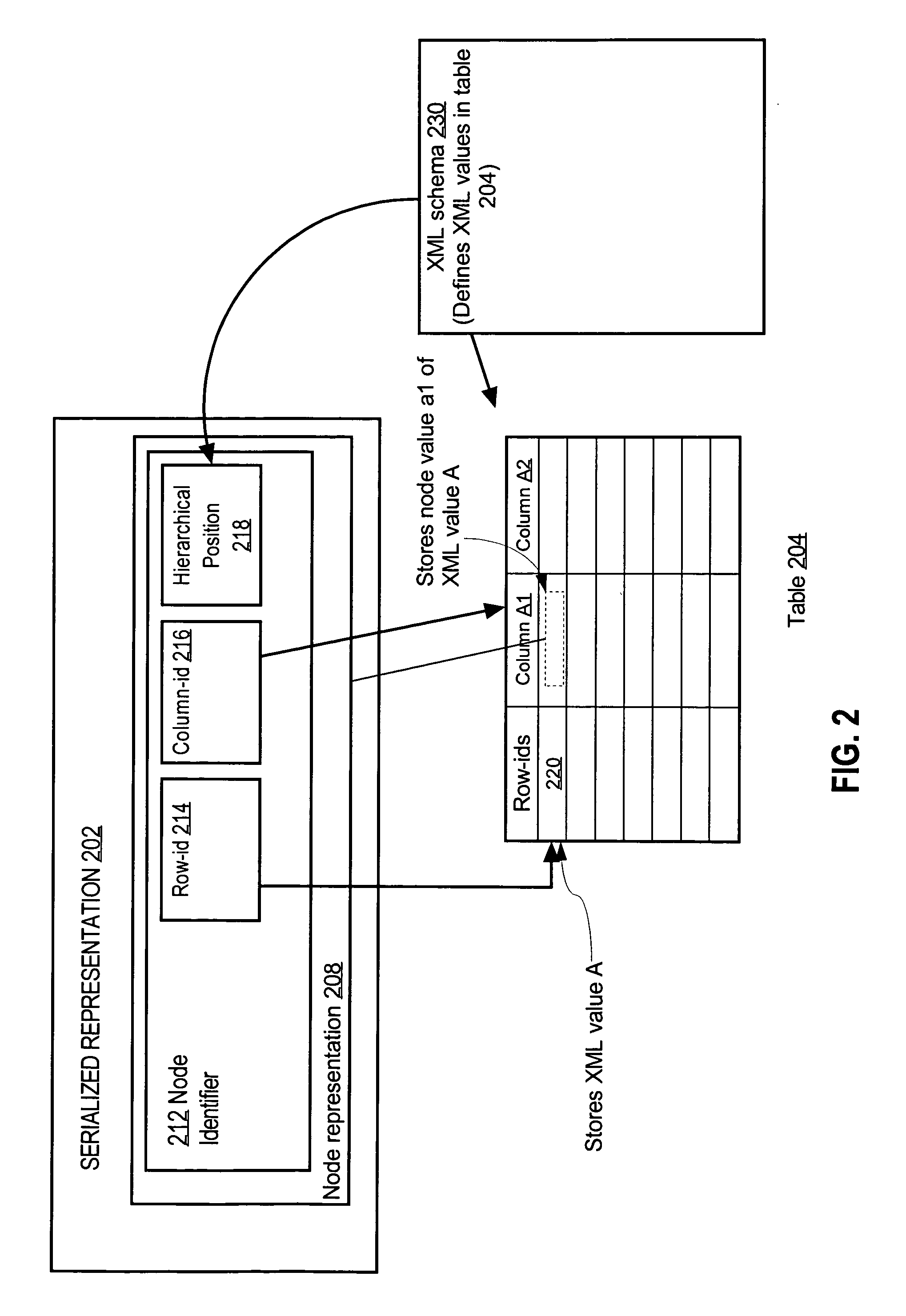
Providing XML node identity based operations in a value based SQL system
InactiveUS20050289175A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsSerializationByte
Object-relational database systems process XML values in a way that preserves node identities of nodes in the XML values and perform node-id based operations more efficiently or even in circumstances where such operations were not performed. An object-relational database system represents an XML value as a serialized stream of bytes, herein referred to as a serialized image. A serialized image may represent an XML value of the XMLType that is stored and / or generated by an object-relational database system. The serialized image contains one or more node identifiers that identify nodes within the XML value. The serialized image may also contain a pointer to an in-memory representation of the XML value, allowing the in-memory representation to be accessed via the pointer without having re-create the in-memory representation.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
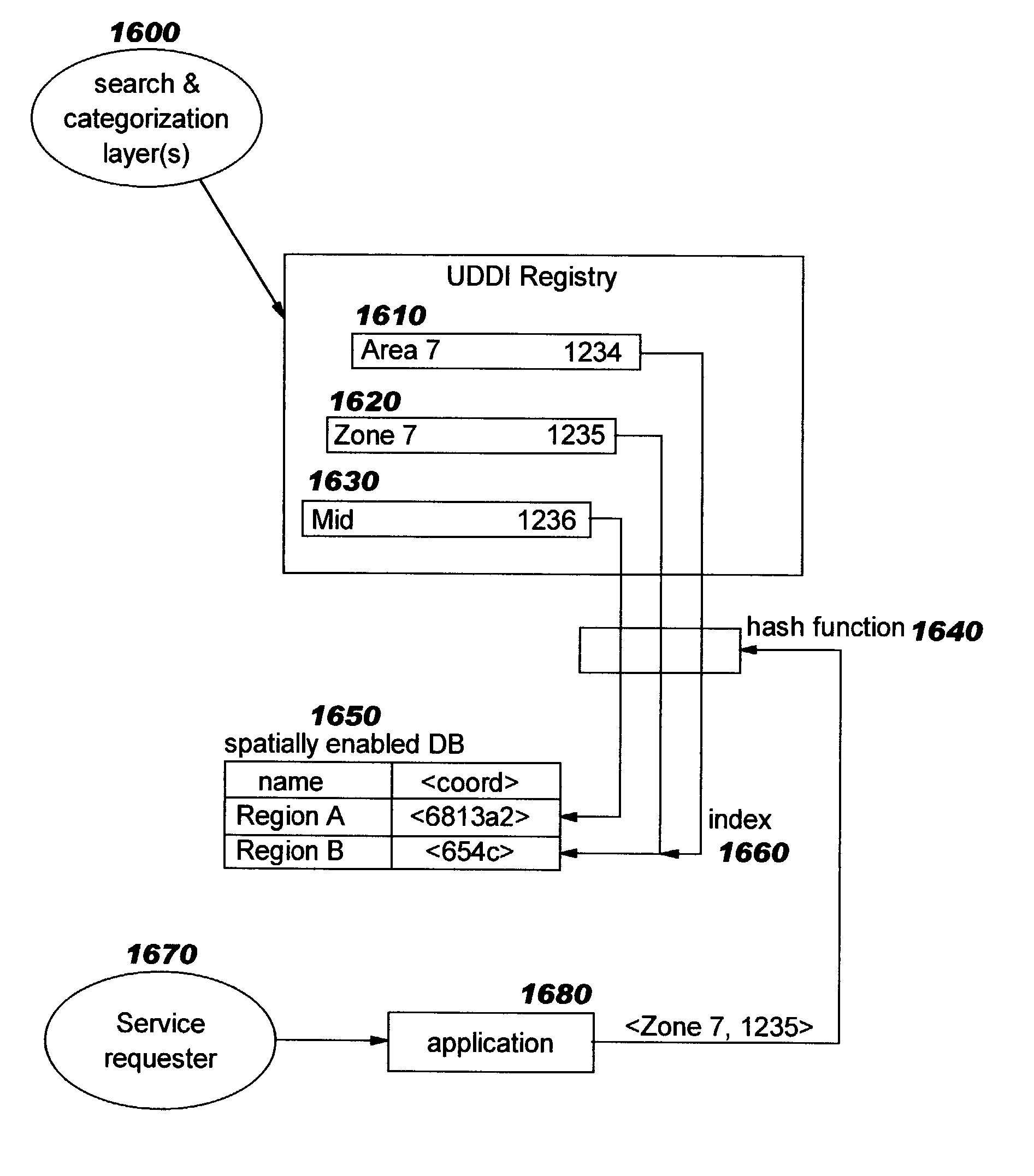
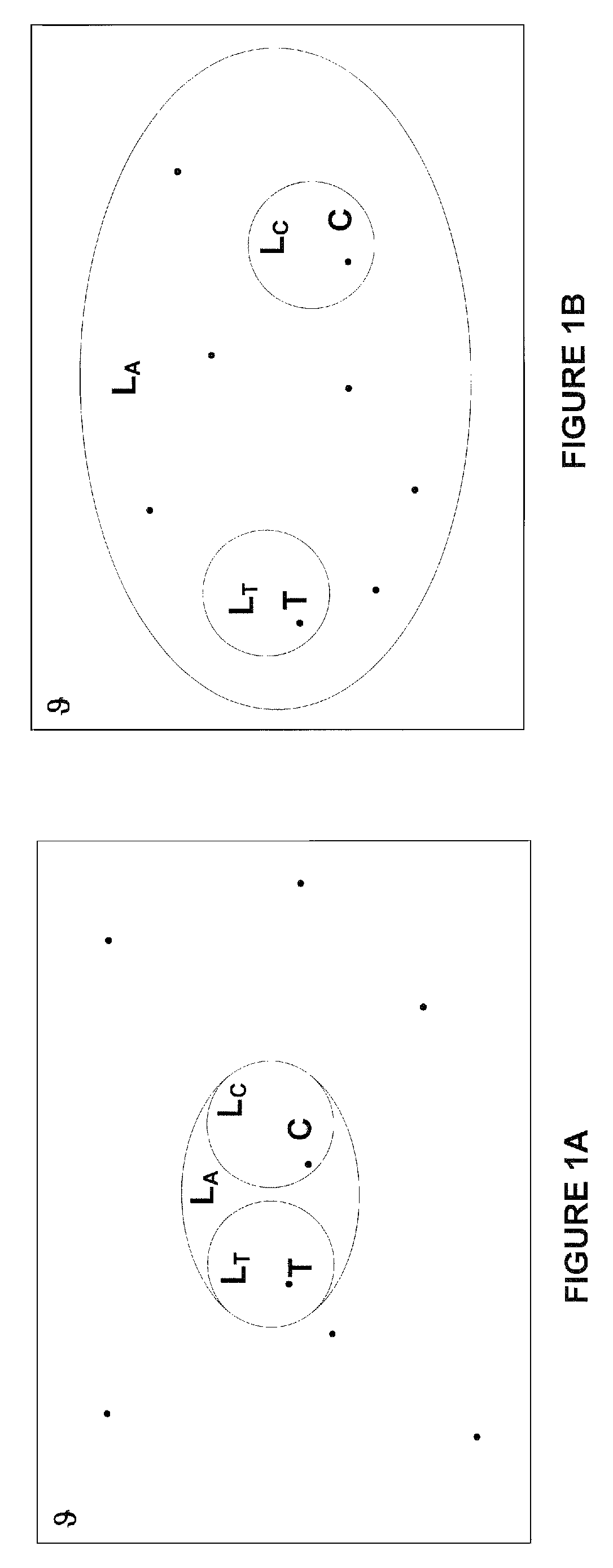
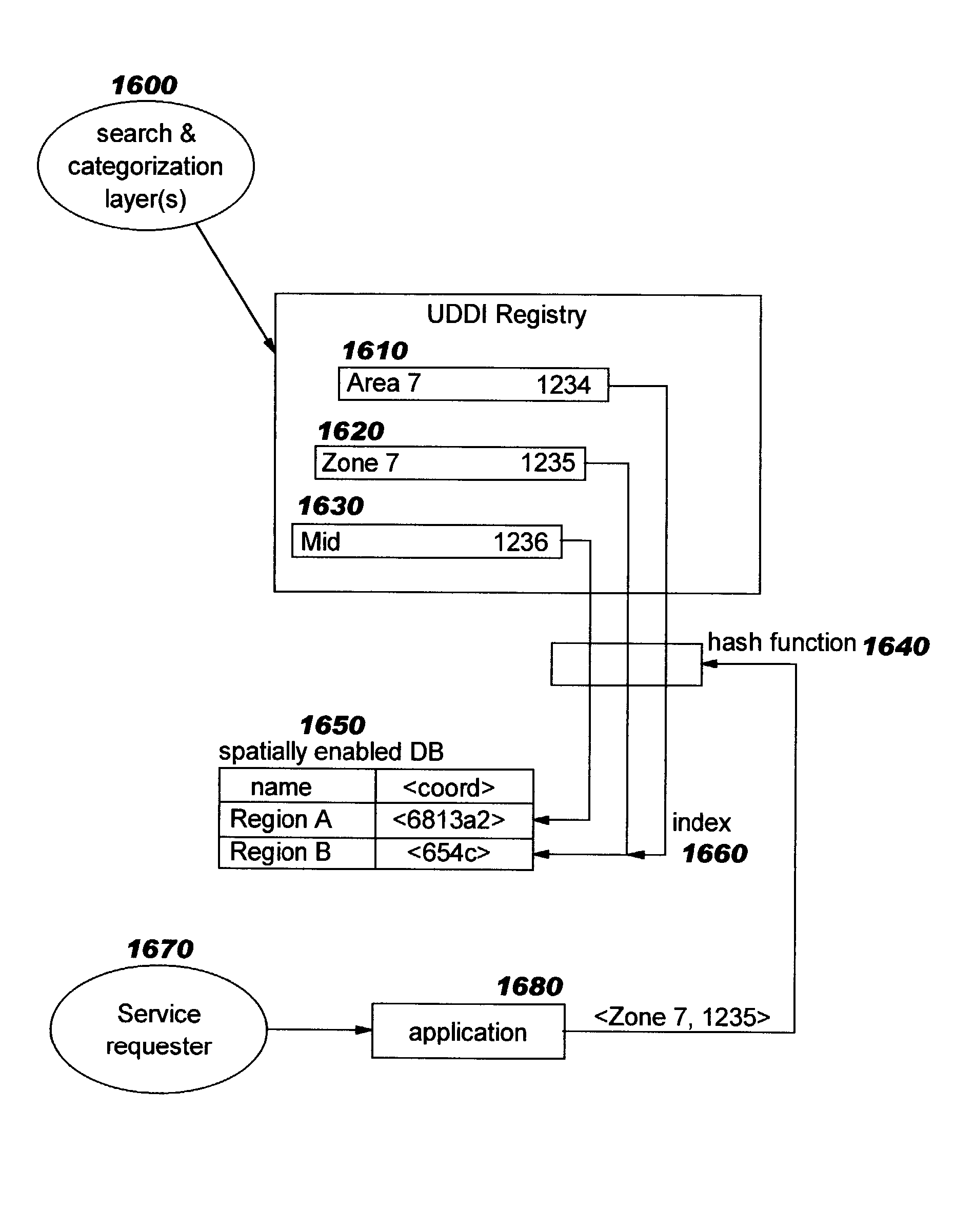
Implementing geographical taxonomy within network-accessible service registries using spatial extensions
ActiveUS6976027B2Improved categorization techniqueFine granularityData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData miningWindows Registry
Techniques are disclosed for using geographical taxonomy data in network-accessible registries (such as the Universal Description, Discovery, and Integration, or “UDDI”, registry), where this taxonomy data leverages spatial extenders within spatially-enabled databases. Built-in functions of a spatially-enabled object relational database system can then be used for entries in the network-accessible registry.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
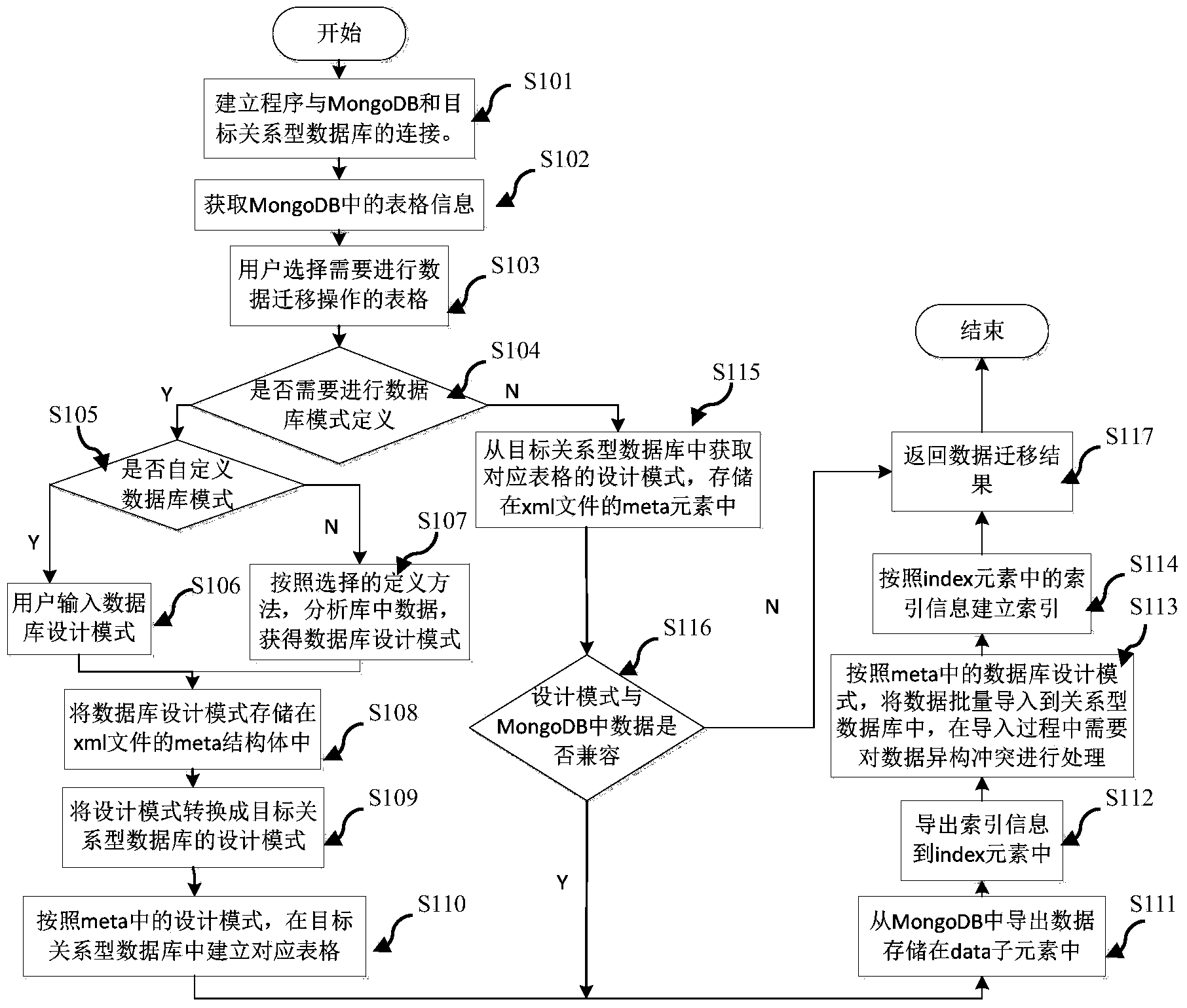
Method for migrating data from non-relational database to relational database
ActiveCN103530327AAddressing anti-paradigm designSolving schemalessRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsRelational databaseData type
The invention relates to a method for migrating data from a non-relational database to a relational database. The method comprises the following steps: connecting the non-relational database needing data migration, and obtaining table information in the database; selecting a table needing data migration and a database mode definition method, wherein the selectable database mode definition method comprises user definition, union set compatibility, intersection compatibility, and first article data; guiding the information from the non-relational database to a defined xml document; converting the database design mode of the non-relational database to a design mode of the corresponding relational database; connecting the corresponding relational database, and setting up a corresponding data table according to the database design mode in the xml document; setting up a corresponding index according to index information in the index element. The method for migrating data solves the problems of a denormalization design, non-modeling and special data types when data are migrated from the non-relational database (such as a MonogDB) to the relational database.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Object graph faulting and trimming in an object-relational database system
ActiveUS7165075B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsRelational databaseSerialization
A method and system for storing and retrieving data in an object-relational database system includes receiving a query which results in a request to load a first object. The method also includes identifying relationship types of other objects having a relationship with the first object. Then, the first object and those of the other objects which have a composition relationship with the first object are eager loaded. Those of the other objects which have an association relationship with the first object are marked as fault on demand. Preventing re-faulting of the same object in the same object graph, and trimming of graphs for serialization are also provided.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Techniques for peer-to-peer replication of objects in a relational database
InactiveUS6889229B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalRelational databaseDistributed database
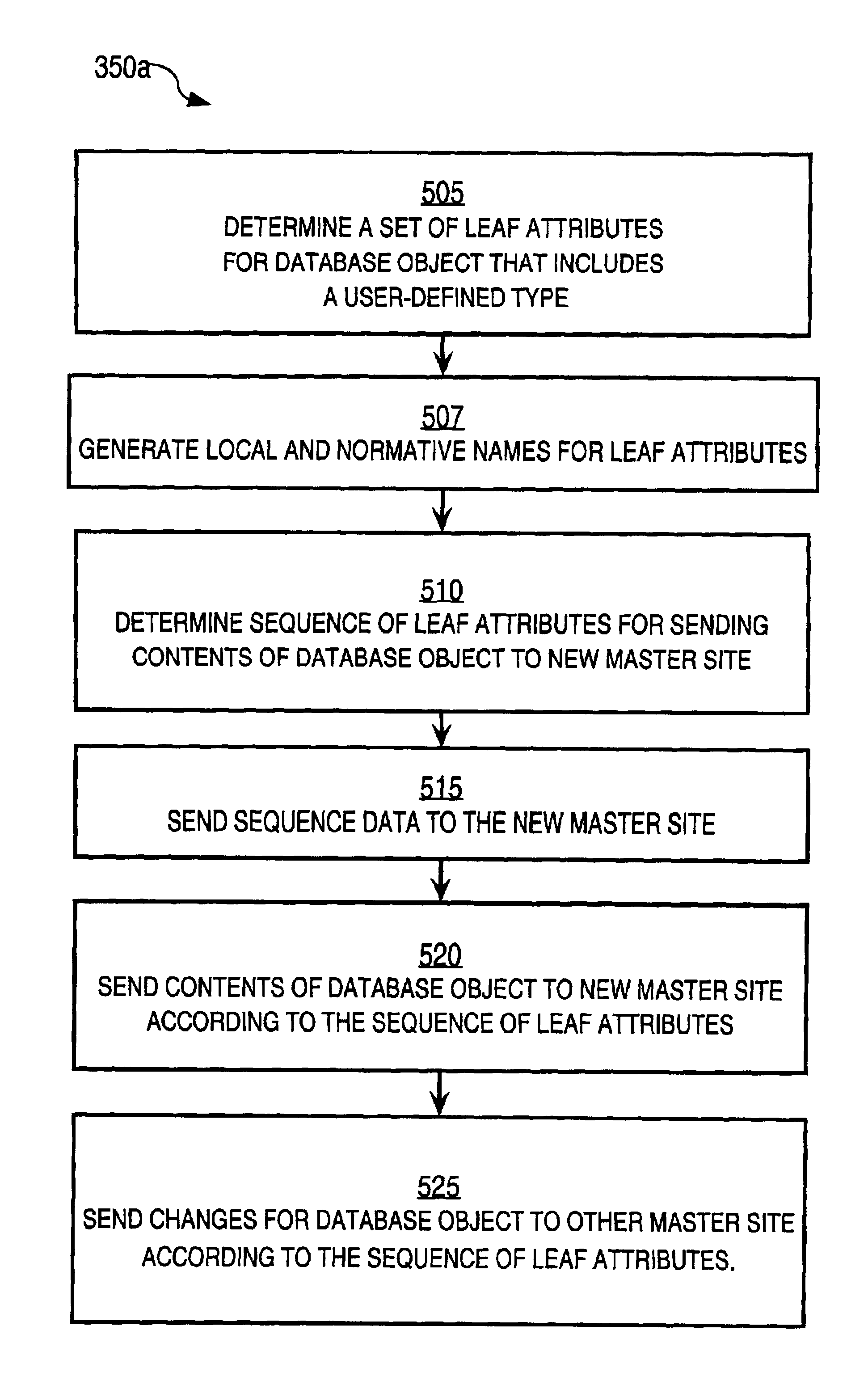
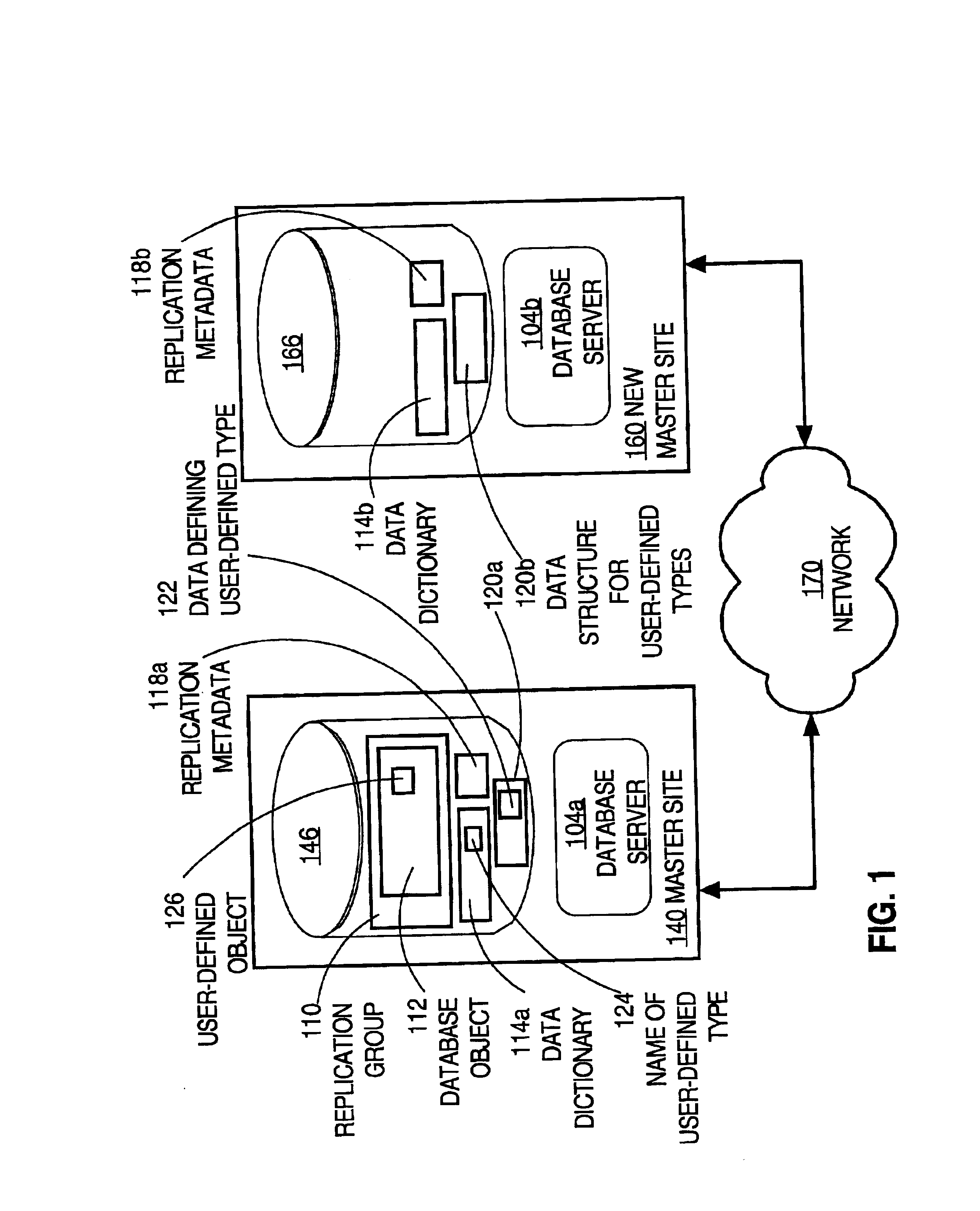
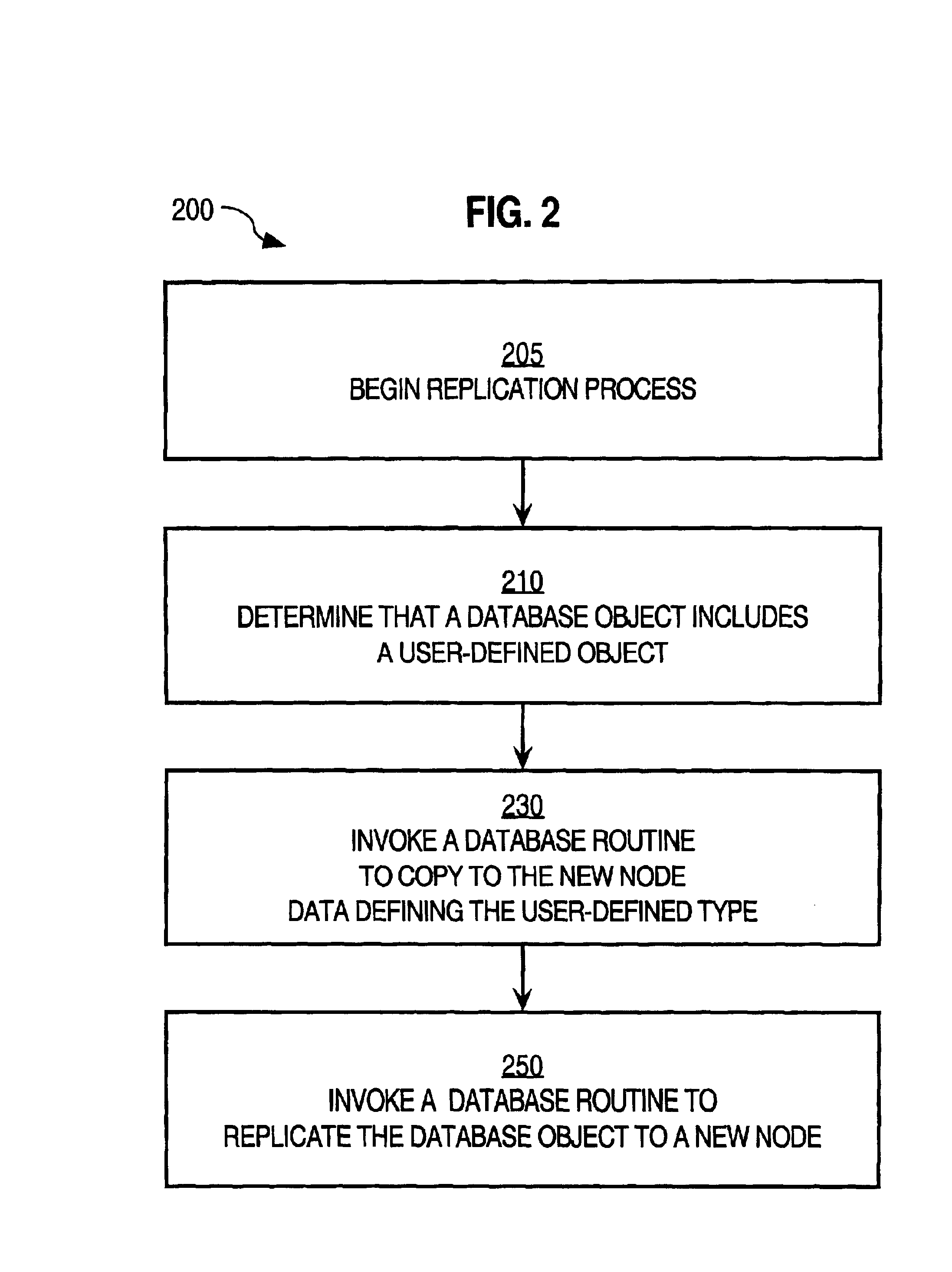
Techniques for replicating a database object of a relational database managed by a database system from a first node on a network to a second node on the network include determining that the database object on the first node includes a user-defined object. A first routine of the database system is invoked. The first routine performs the step of copying the database object to the second node of the network. The first routine copies a name of a user-defined defined type of the user-defined object from the first node to the second node. The first routine also copies a first definition of the user-defined type from the first node to the second node. The first routine then copies a second definition of the database object from the first node to the second node. The second definition includes the name of the user-defined type. These techniques provide the benefits of peer-to-peer replication in a distributed database to users of object-relational databases that including user-defined objects.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Computer program products, systems and methods for information discovery and relational analyses
The present invention is a system, method for accessing domains of information to identify heretofore unknown relationships between disparate sources of data to seek and obtain knowledge, the invention includes a source of data with one or more domains of information, an Object-Relationship Database for integrating objects from one or more domains of information and a knowledge discovery engine where relationships between two or more objects are identified, retrieved, grouped, ranked, filtered and numerically evaluated.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Indexing XML documents efficiently
ActiveUS20050055334A1Unstructured textual data retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsPattern matchingTheoretical computer science
Information hierarchies are efficiently stored and accessed in a relational or object-relational database system. A path signature, similar to a pathname, is stored in a database system in association with data for the node identified by the pathname. For example, a path signature identifying an element is stored in a row that holds data for the element. To retrieve data for a hierarchical query that identifies the data requested using, for example, an XPATH string, a string pattern is generated that is matched by path signatures identified by the XPATH string. Pattern matching is then used to select rows associated with matching path signatures, and data from the selected rows is used to compute the XPATH query. Furthermore, hash values representing path signatures are generated in a way that preserves the ordering of data in an information hierarchy. The hash values can be indexed to provide quick access.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
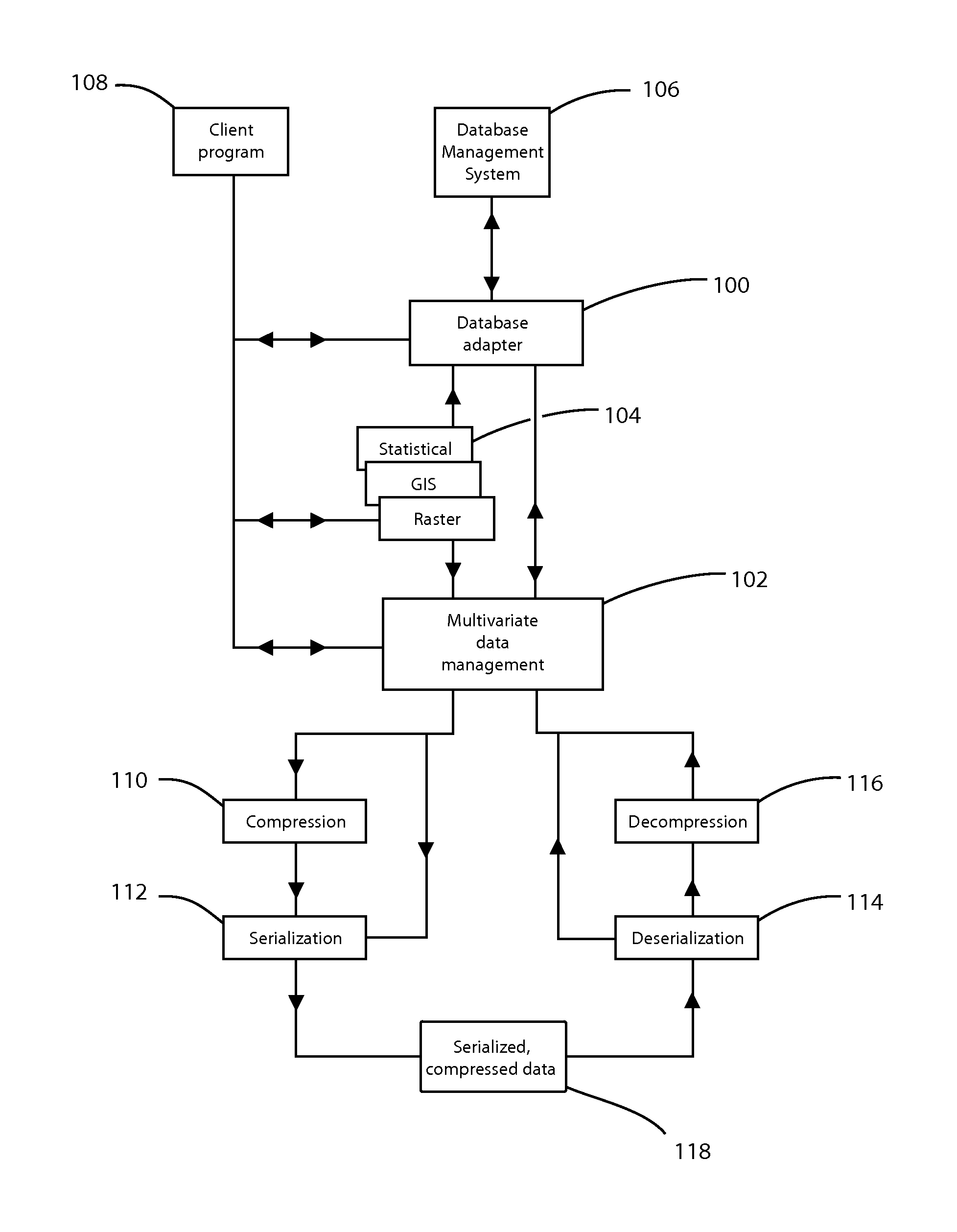
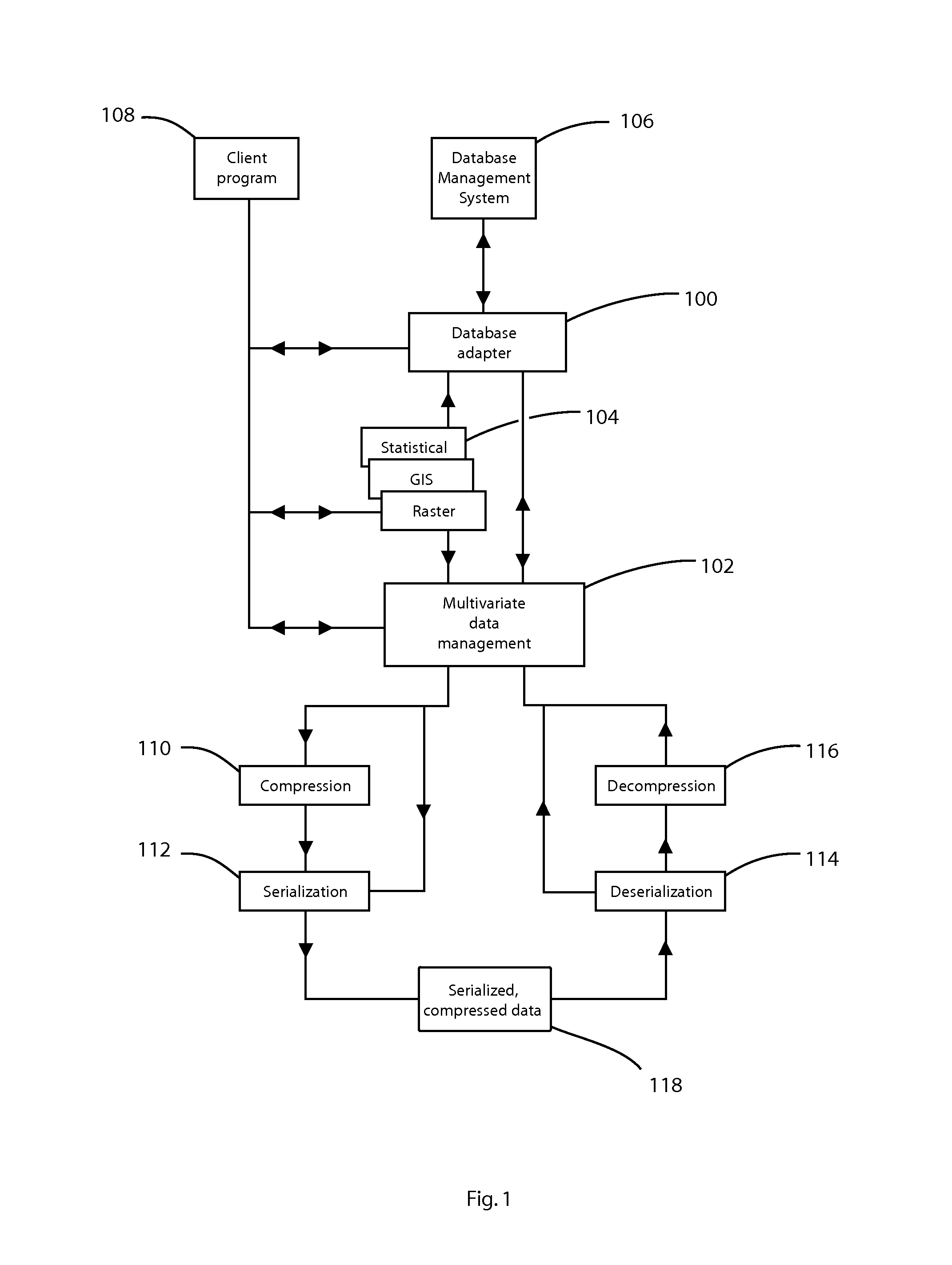
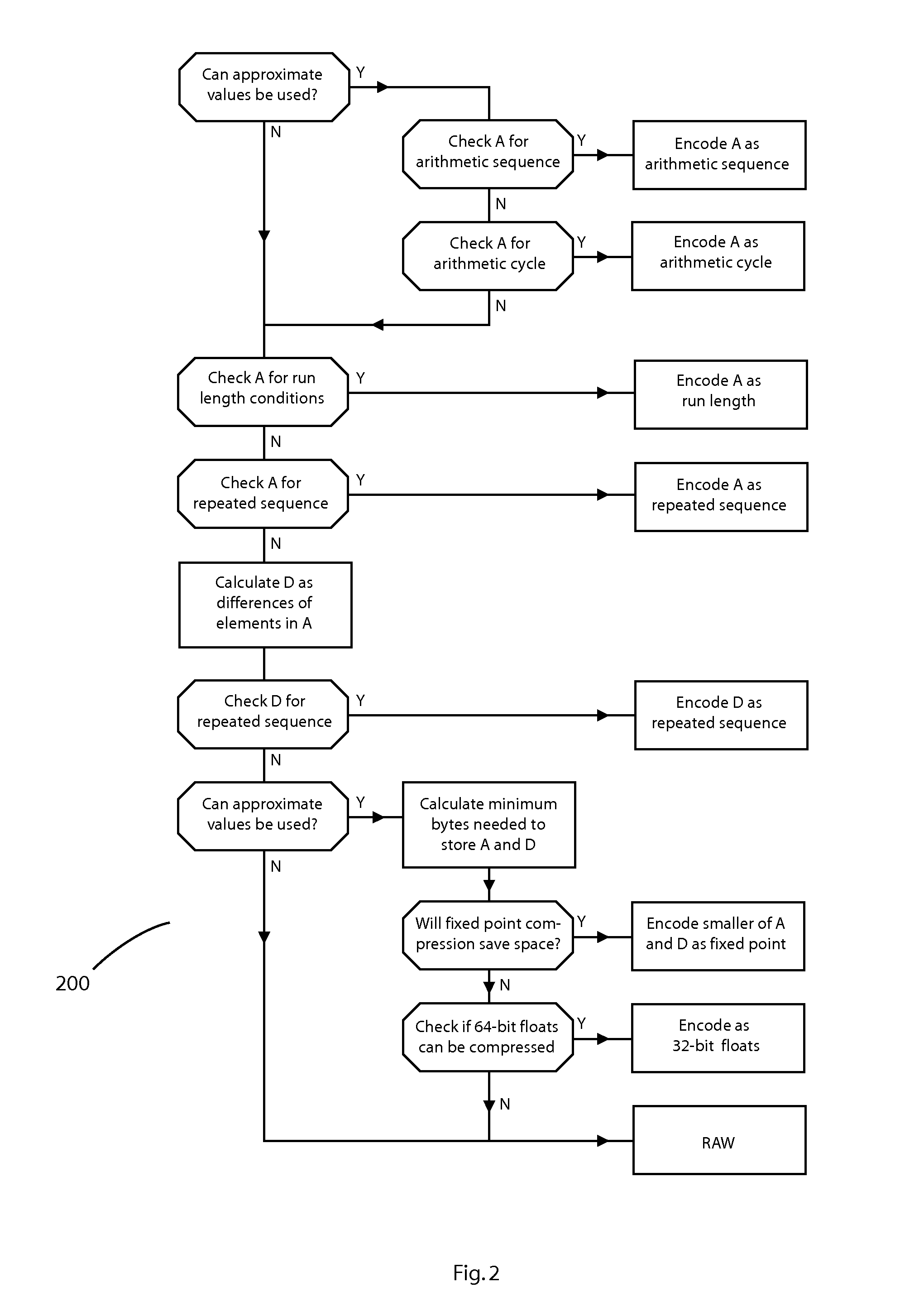
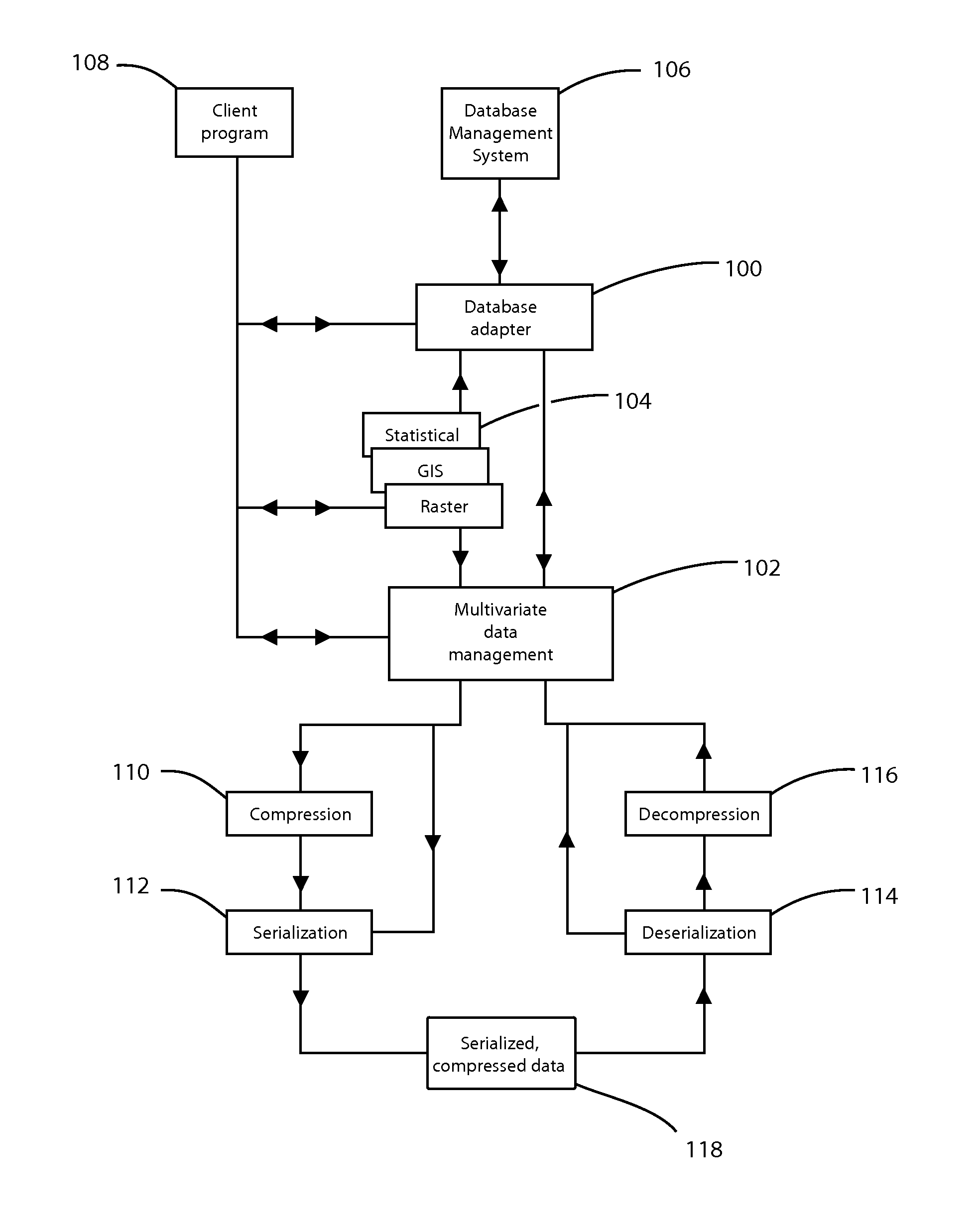
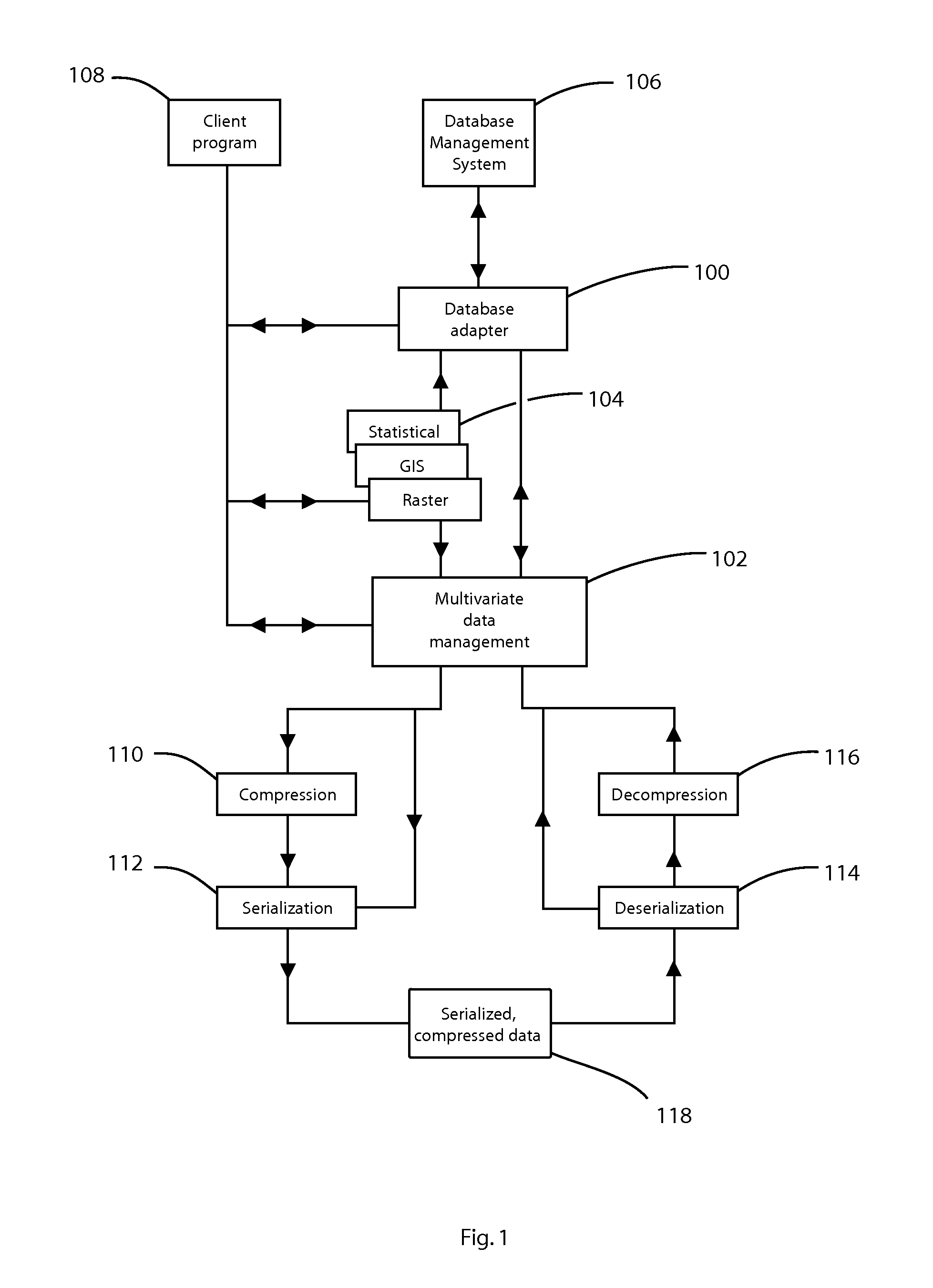
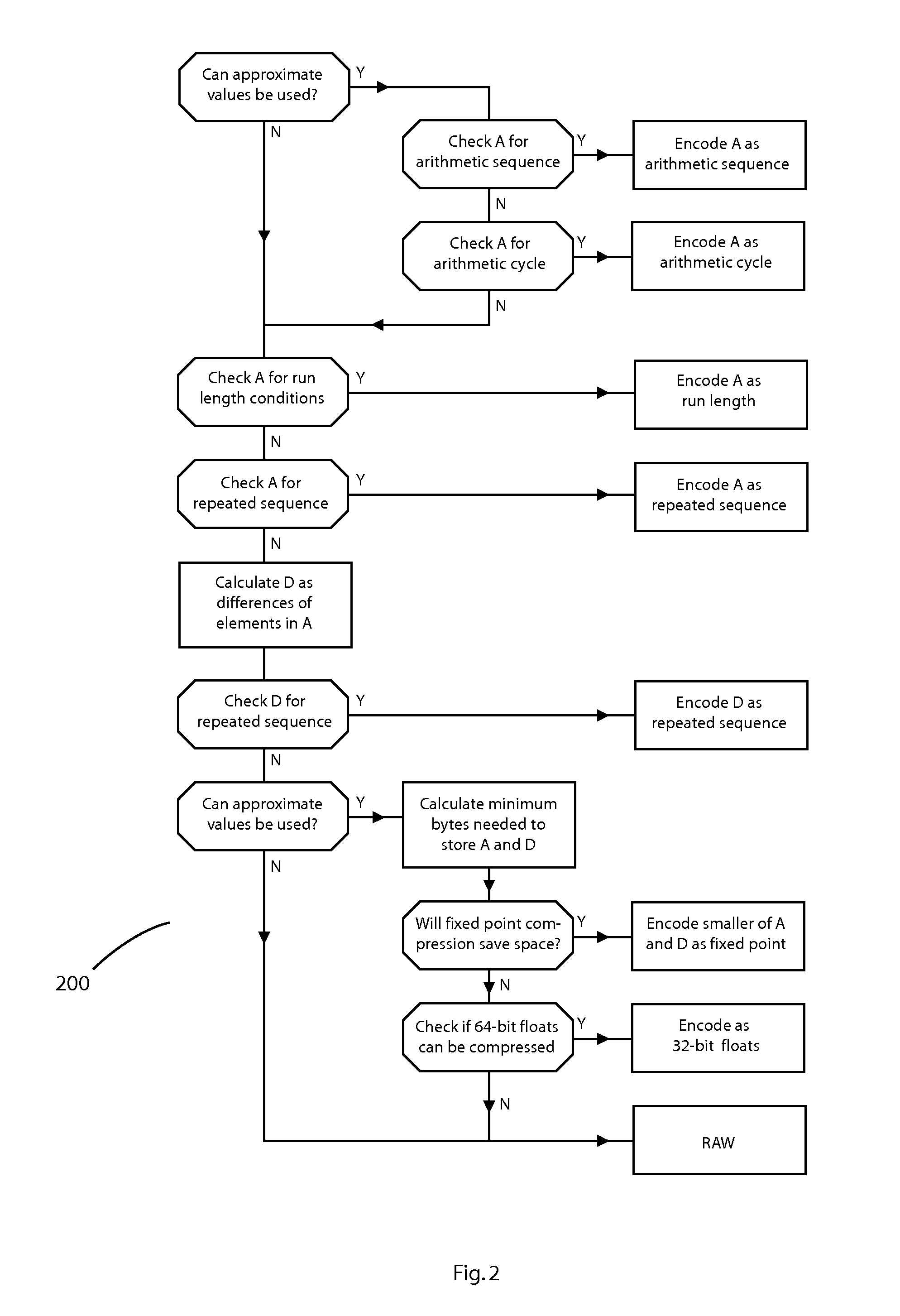
Database adapter for relational datasets
InactiveUS20080021914A1Simplify updateSimplify insertionDigital data information retrievalCode conversionData setRelational database
The invention is a database adapter providing improved methods for storing and retrieving relational data. Suitable source data is structured as a table with a fixed number of columns of predetermined types and a variable number of rows. The invention reduces the space and time used to store data and the time taken to retrieve stored data. The invention is best implemented inside Object Relational Database Systems, but can also be implemented in any database that can execute routines written in programming languages such as C#, C or Java. Functionally, the invention combines the concept of nested tables with fast compression techniques so that nested tables are practical for solving a wide class of problems.
Owner:BARRODALE COMPUTING SERVICES
Computer-based method for finding similar objects using a taxonomy
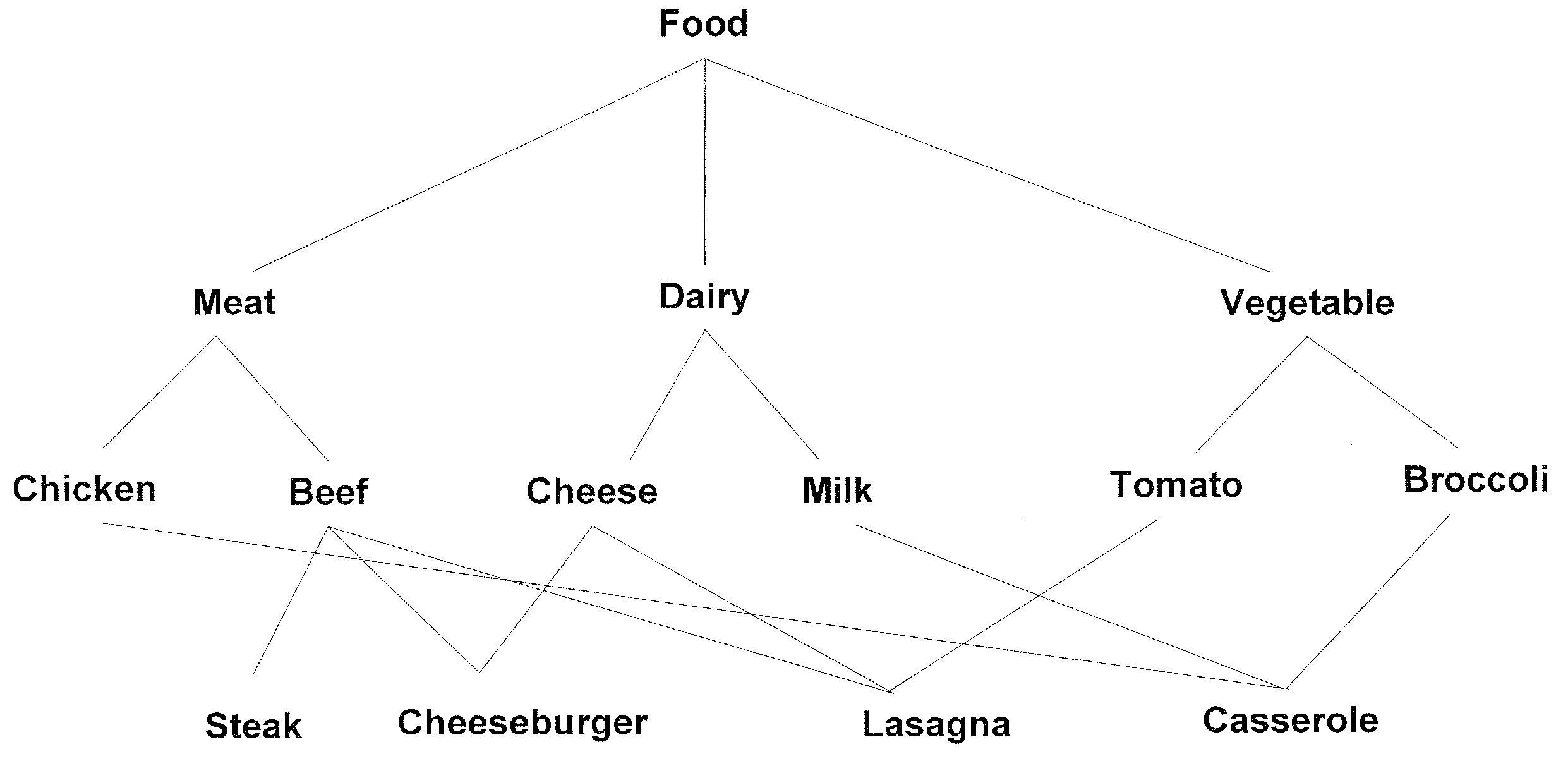
InactiveUS7533096B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalAs DirectedAmbiguity
A generalized axiomatic definition of information-theoretic similarity is provided for taxonomies that are structured as directed acyclic graph form which multiple terns may be used to describe an object. The definition is adaptable in the presence of ambiguity, as introduced by an evolving taxonomy or classifiers with imperfect knowledge, and two new similarity measures are introduced based on the definitions. A pragmatic implementation is also provided for similarity measures that arc tightly integrated with an object-relational database and scales to large taxonomies and large datasets.
Owner:IBM CORP
Implementing geographical taxonomy within network-accesible service registries using spatial extensions
ActiveUS20040039738A1Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsData miningWindows Registry
Techniques are disclosed for using geographical taxonomy data in network-accessible registries (such as the Universal Description, Discovery, and Integration, or "UDDI", registry), where this taxonomy data leverages spatial extenders within spatially-enabled databases. Built-in functions of a spatially-enabled object relational database system can then be used for entries in the network-accessible registry.
Owner:IBM CORP
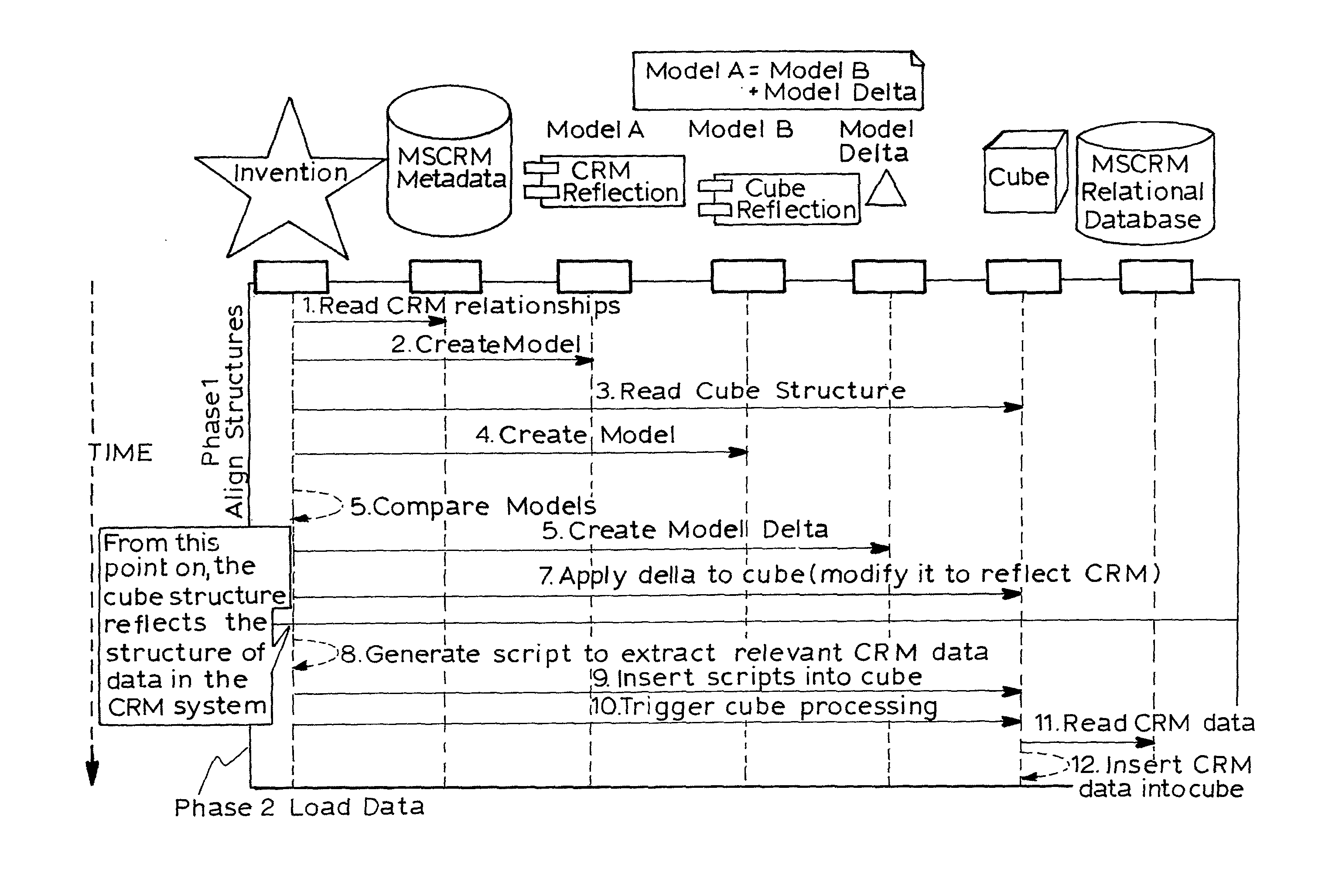
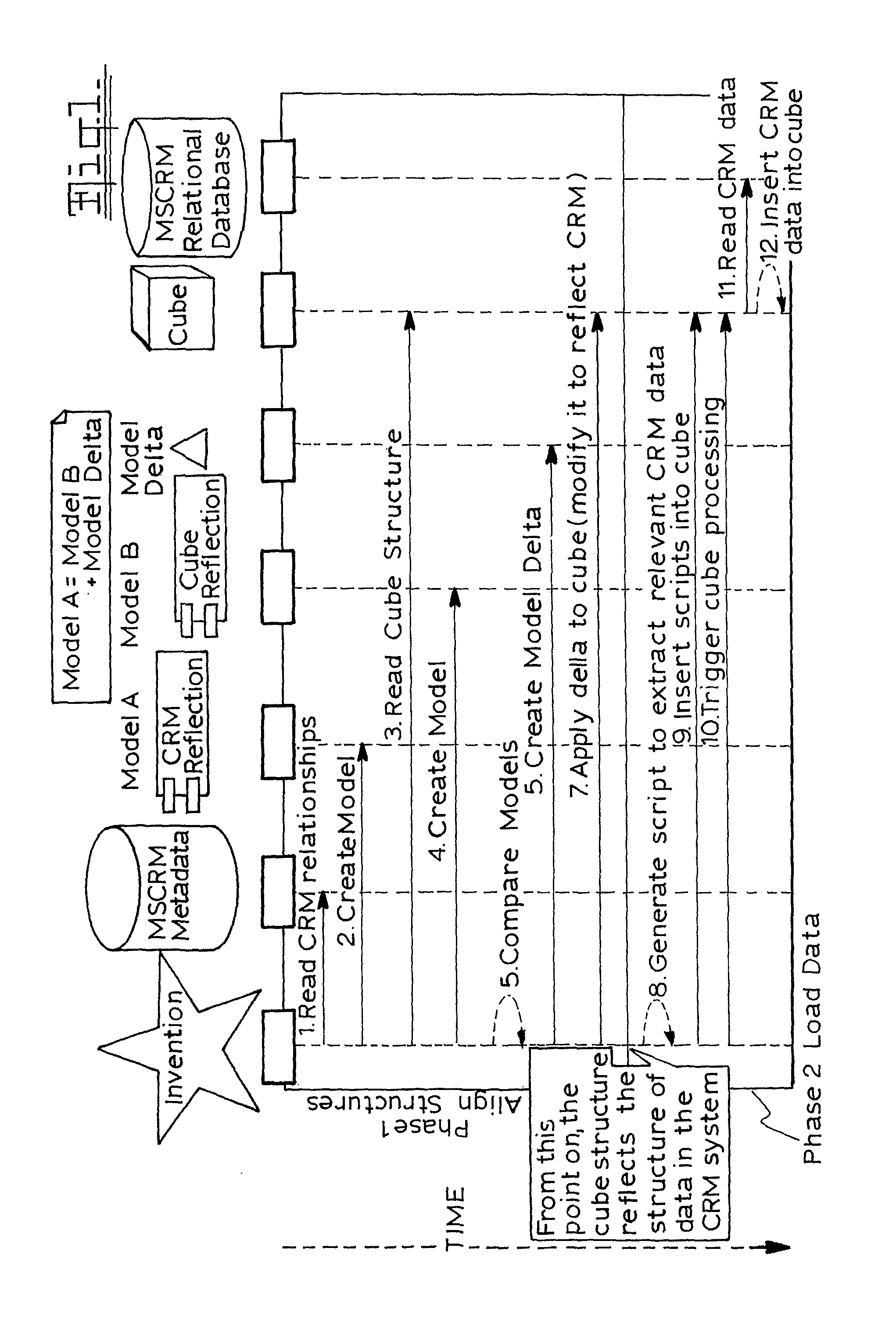
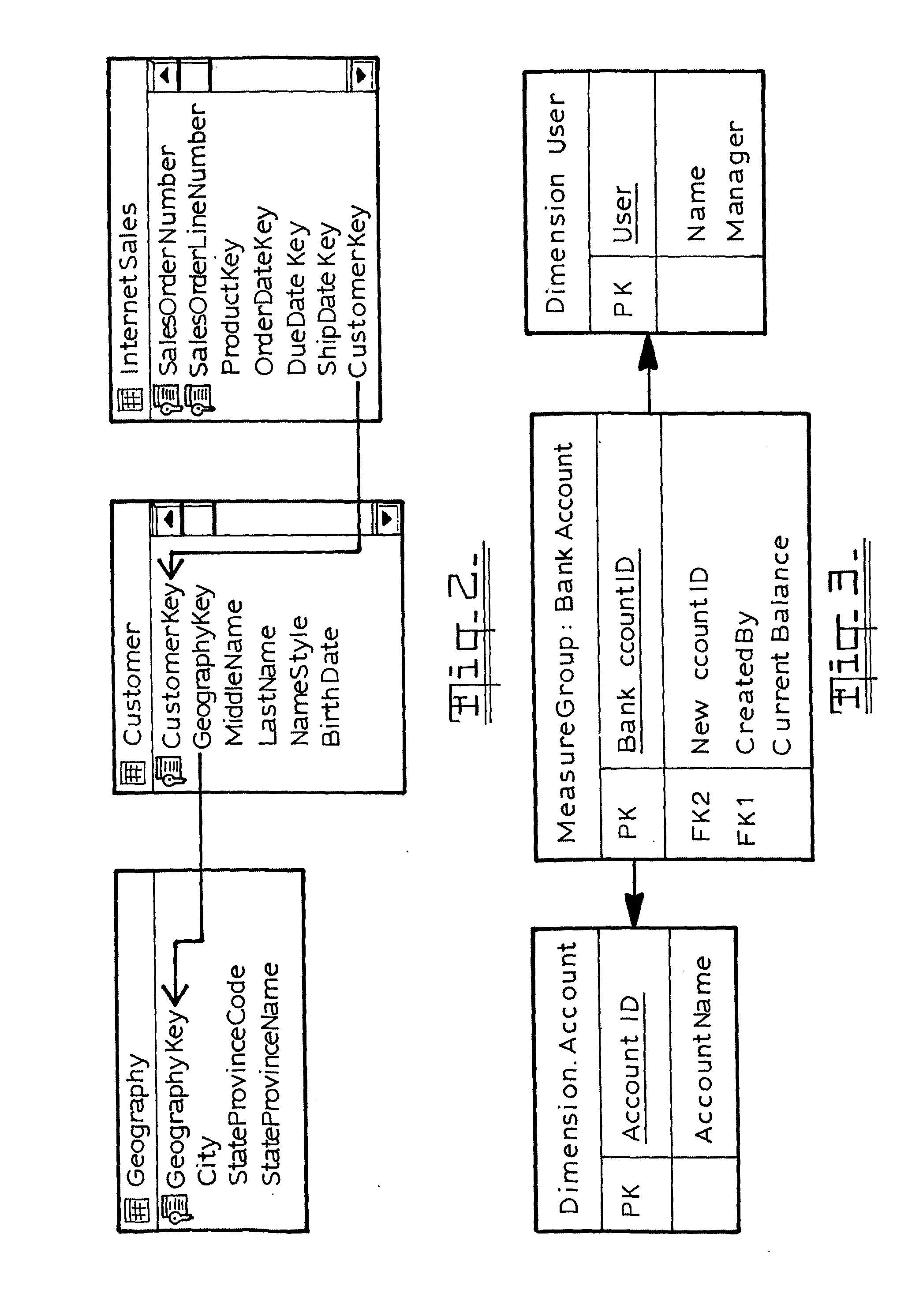
Synchronization of relational databases with olap cubes
InactiveUS20110231359A1Digital data processing detailsMulti-dimensional databasesData setRelational database
A method of synchronizing a source system that stores its records in a relational database and defines its own application level security with an OLAP cube, in which the structure of the relational database and cube is modelled to an intermediate representation for the purpose of comparing both structures; the differences between the two models are identified and used to modify the structure of the cube; the modified structure of the cube is used to generate a script for retrieving data from the relational database for insertion into the cube, after which the script is run and the data is inserted into the modified cube. A unique identifier is used for each item in the base system and each system is tagged with the same identifier in the cube.
Owner:ZAP HLDG LTD
Operators for accessing hierarchical data in a relational system
ActiveUS7028037B1Efficient managementData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsRelational systemData storing
Techniques and systems are provided for efficiently managing hierarchical relational data stored in object-relational database system by extending the syntax of the database language supported by the database system (e.g. SQL) to incorporate several new “hierarchical” operators. These operators are evaluated based on the hierarchical relationship defined for hierarchical relational data. The operators maybe incorporated in SQL queries along with relational operators.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
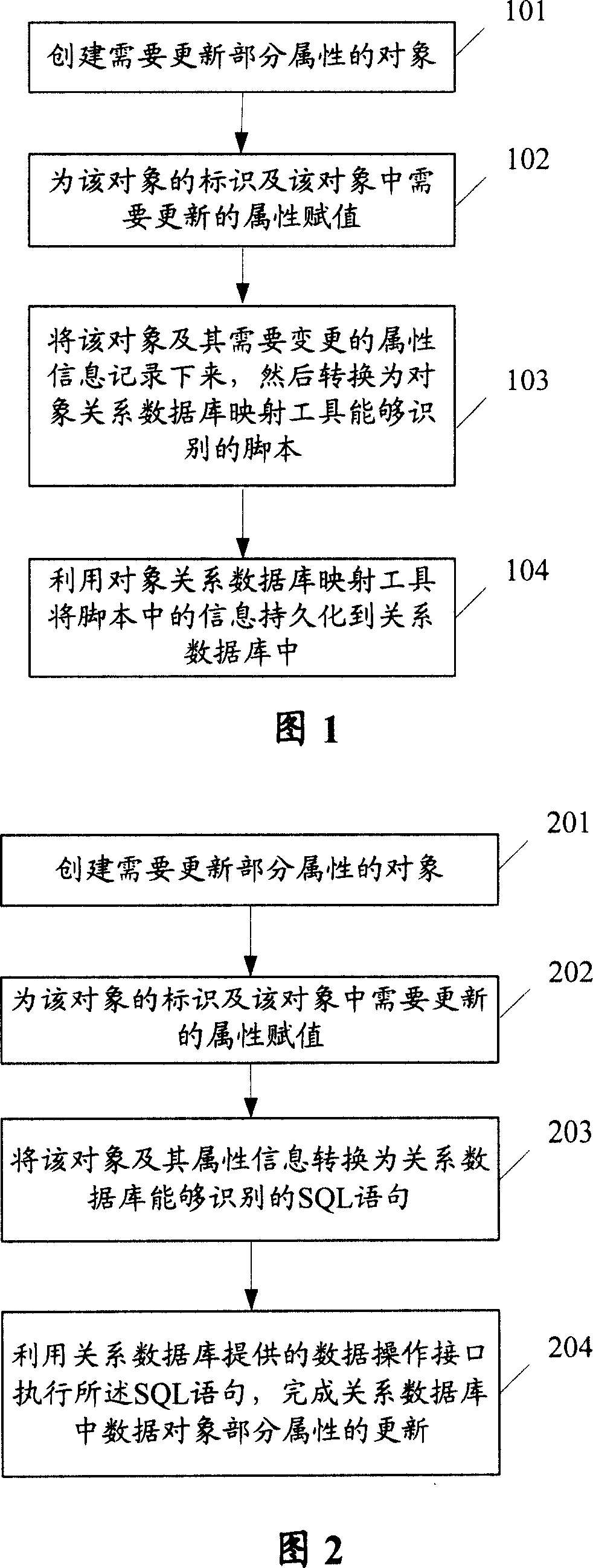
Method and apparatus for updating object local attribute to related data bank
InactiveCN101021877AAvoid influenceSpecial data processing applicationsRelational databaseObject Attribute
This invention discloses a method and a device for updating partial attributes of an object to a relation database including: setting up objects necessary for updating partial attributes, assigning the ID of the object and attribute needing to be updated, converting said object and its attribute information to a script identified by the mapping tool of the object relation database to be used to perdure the information in the script to said relation database. The device includes: an object relation database mapping unit, an object generation unit and an object information converting unit.
Owner:山东众友建筑工程有限公司郓城潘渡分公司
Integrating RDF data into a relational database system
ActiveUS8719250B2Database management systemsDigital data processing detailsRDF SchemaRelational database
The TABLE function mechanism available in a RDBMS is used to integrate RDF models into SQL queries. The table function invocation takes parameters including an RDF pattern, an RDF model, and an RDF rule base and returns result rows to the SQL query that contain RDF triples resulting from the application of the pattern to the triples of the model and the triples inferred by applying the rule base to the model. The RDBMS includes relational representations of the triples and the rules. Optimizations include indexes and materialized views of the representations of the triples, precomputed inferred triples, and a method associated with the TABLE function that rewrites the part of the SQL query that contains the TABLE function invocation as an equivalent SQL string. The latter technique is generally applicable to TABLE functions.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Storing XML documents efficiently in an RDBMS
ActiveUS8229932B2Digital data processing detailsUnstructured textual data retrievalPattern matchingTheoretical computer science
Information hierarchies are efficiently stored and accessed in a relational or object-relational database system. A path signature, similar to a pathname, is stored in a database system in association with data for the node identified by the pathname. For example, a path signature identifying an element is stored in a row that holds data for the element. To retrieve data for a hierarchical query that identifies the data requested using, for example, an XPATH string, a string pattern is generated that is matched by path signatures identified by the XPATH string. Pattern matching is then used to select rows associated with matching path signatures, and data from the selected rows is used to compute the XPATH query. Furthermore, hash values representing path signatures are generated in a way that preserves the ordering of data in an information hierarchy. The hash values can be indexed to provide quick access.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Programmatically calculating paths from a spatially-enabled database
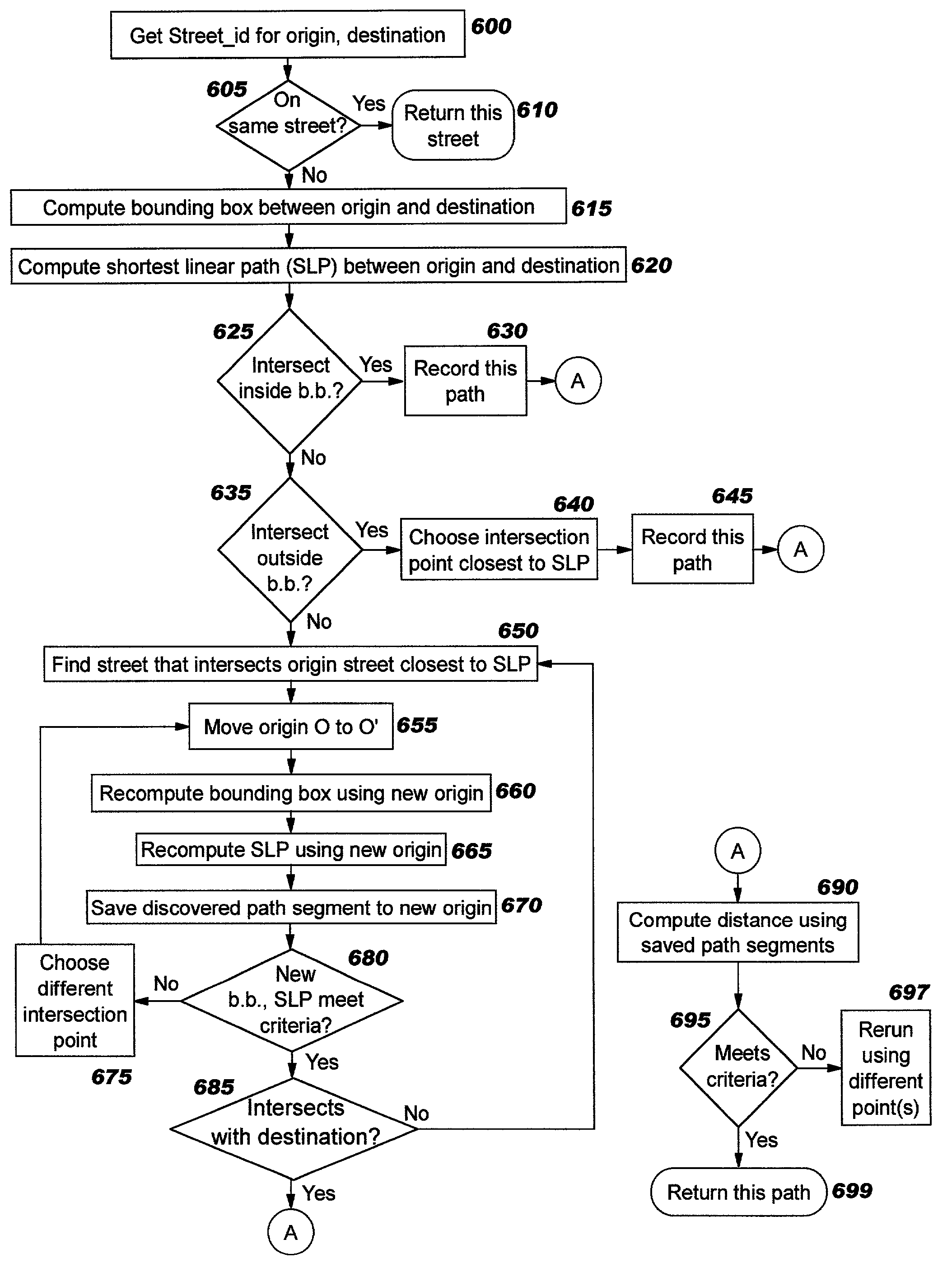
InactiveUS20040204838A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlDirected graphRelational database
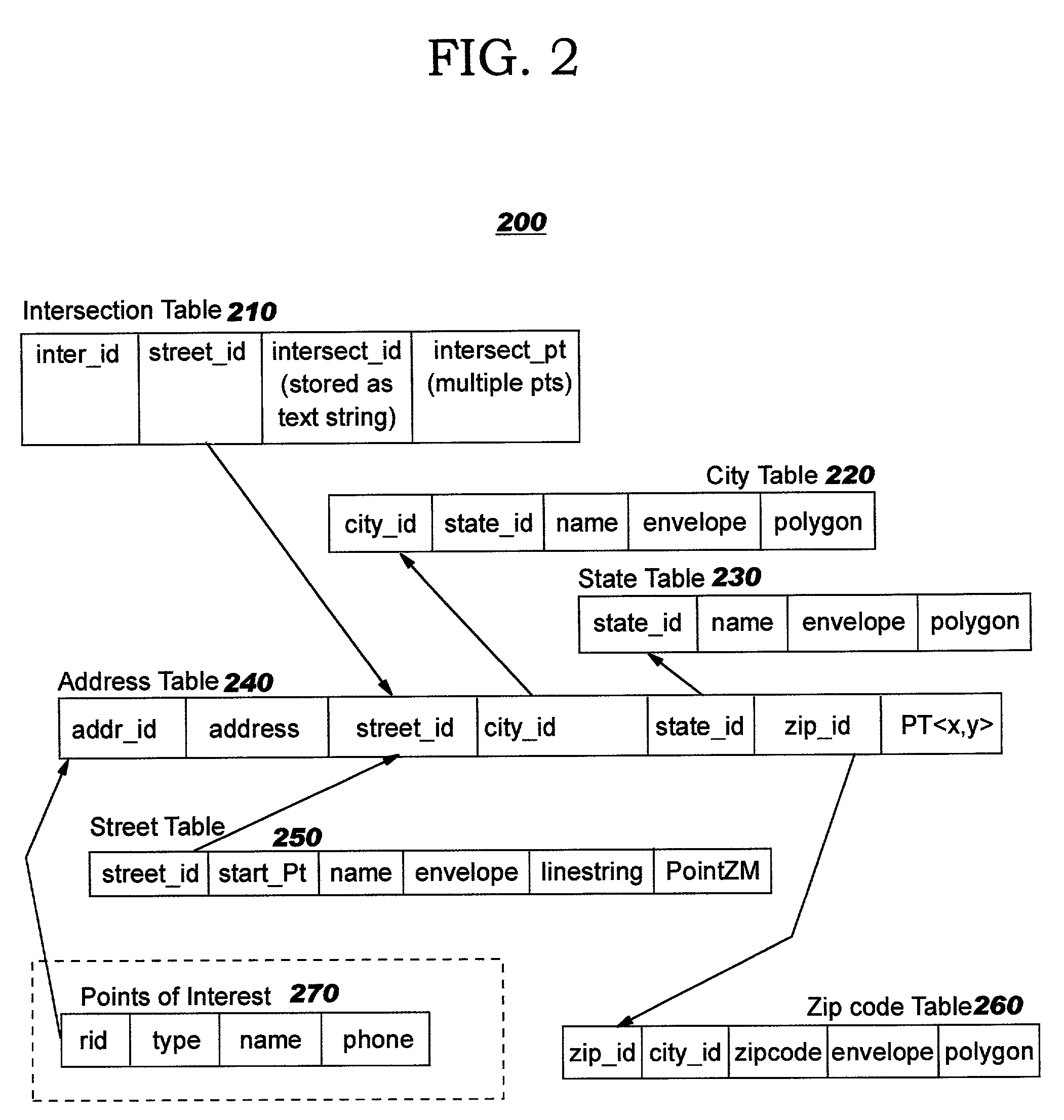
Techniques are disclosed for programmatically calculating directions (or other types of paths between points) without reliance on proprietary file formats or binary shape files, and without requiring application programmers to write code that performs complex manipulations of directed graphs. Preferred embodiments leverage built-in functions of a spatially-enabled object relational database system. Information about intersections between streets is used in a novel manner to compute paths between points. The intersection information is preferably obtained from precomputed information stored in a spatially-enabled relational database table.
Owner:IBM CORP
Processing method and system of XML (Extensive Markup Language) document data
InactiveCN105117447AEasy to handleImprove processing efficiencySemi-structured data indexingSemi-structured data queryingRelational databaseDocument preparation
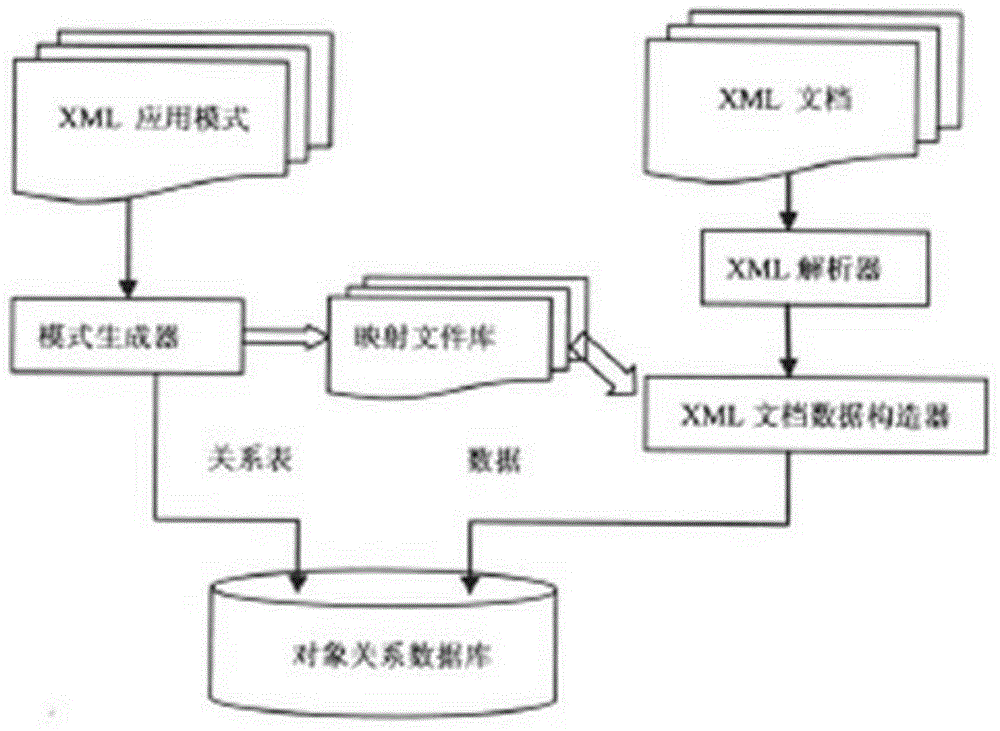
The invention provides a processing method of XML (Extensive Markup Language) document data. The processing method comprises the following steps: firstly, according to a mapping file corresponding to a target XML document, establishing a relational mapping table in an object-relational database, then, processing the XML document, classifying the target XML document according to an XML application mode, and putting the target XML document under the application mode corresponding to the target XML document; utilizing the mapping file corresponding to the application mode to carry out data analysis on the target XML document; and storing the analyzed data corresponding to the mapping file into the relational mapping table. The mapping file accurately describes the corresponding relationship between the XML application mode and a database mode, the technology of the relational database is combined with the object oriented technology, the data analysis of the XML document can be carried out only by the mapping file, the processing method is a general method for processing the XML document data, and data processing efficiency is improved.
Owner:INSPUR BEIJING ELECTRONICS INFORMATION IND
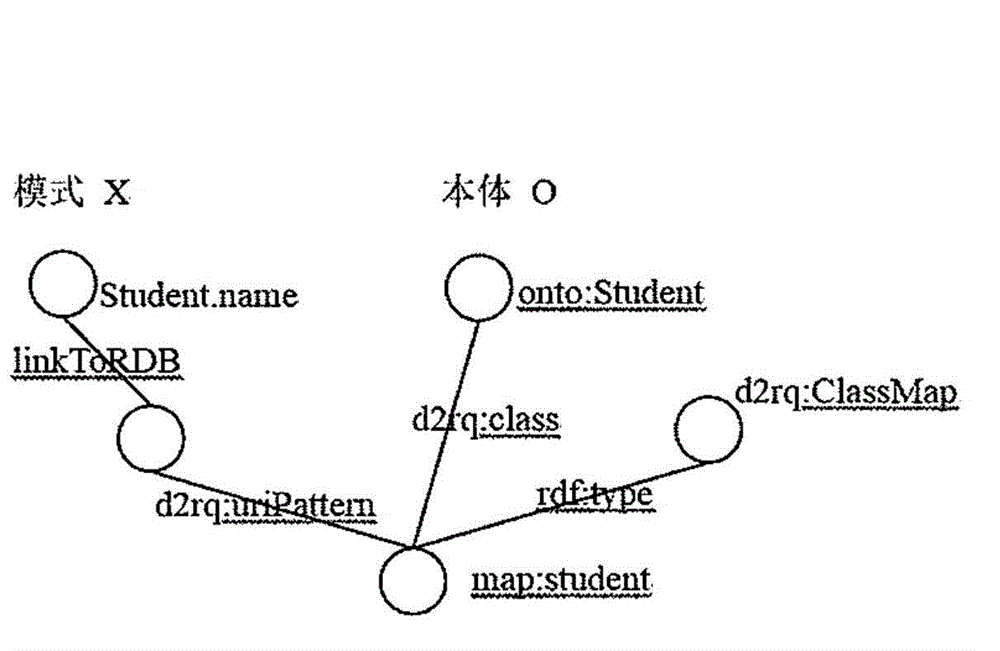
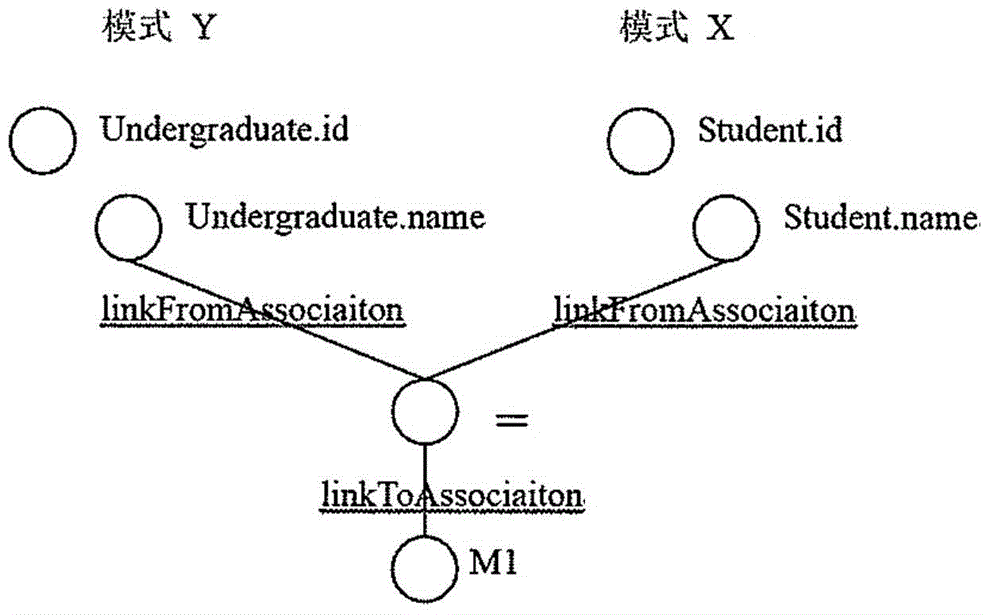
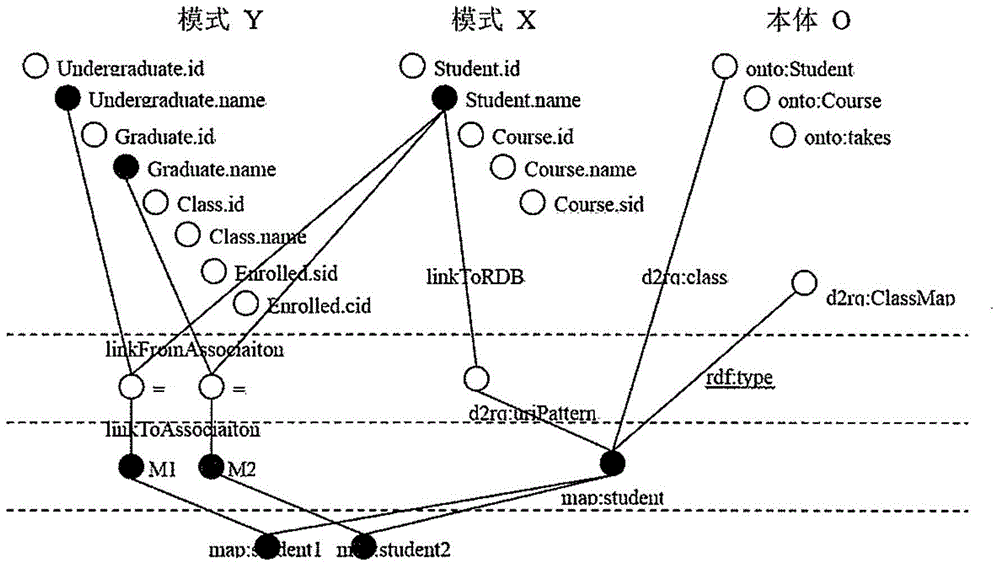
Method and system used for automatically generating semantic mapping for relational databases
ActiveCN105138526AImproving the efficiency of generating semantic mapsRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsSchema mappingRelational database
A method for automatically generating a semantic mapping for a relational database RDB includes obtaining a first semantic mapping from a first RDB to an ontology of linked data; obtaining a schema mapping from the first RDB to a second RDB; and generating a second semantic mapping from the second RDB to the ontology of the linked data based on the first semantic mapping and the schema mapping.
Owner:IBM CORP
Database adapter for relational datasets
InactiveUS8077059B2Easy to insertIncrease storage overheadCode conversionRelational databasesData setRelational database
The invention is a database adapter providing improved methods for storing and retrieving relational data. Suitable source data is structured as a table with a fixed number of columns of predetermined types and a variable number of rows. The invention reduces the space and time used to store data and the time taken to retrieve stored data. The invention is best implemented inside Object Relational Database Systems, but can also be implemented in any database that can execute routines written in programming languages such as C#, C or Java. Functionally, the invention combines the concept of nested tables with fast compression techniques so that nested tables are practical for solving a wide class of problems.
Owner:BARRODALE COMPUTING SERVICES
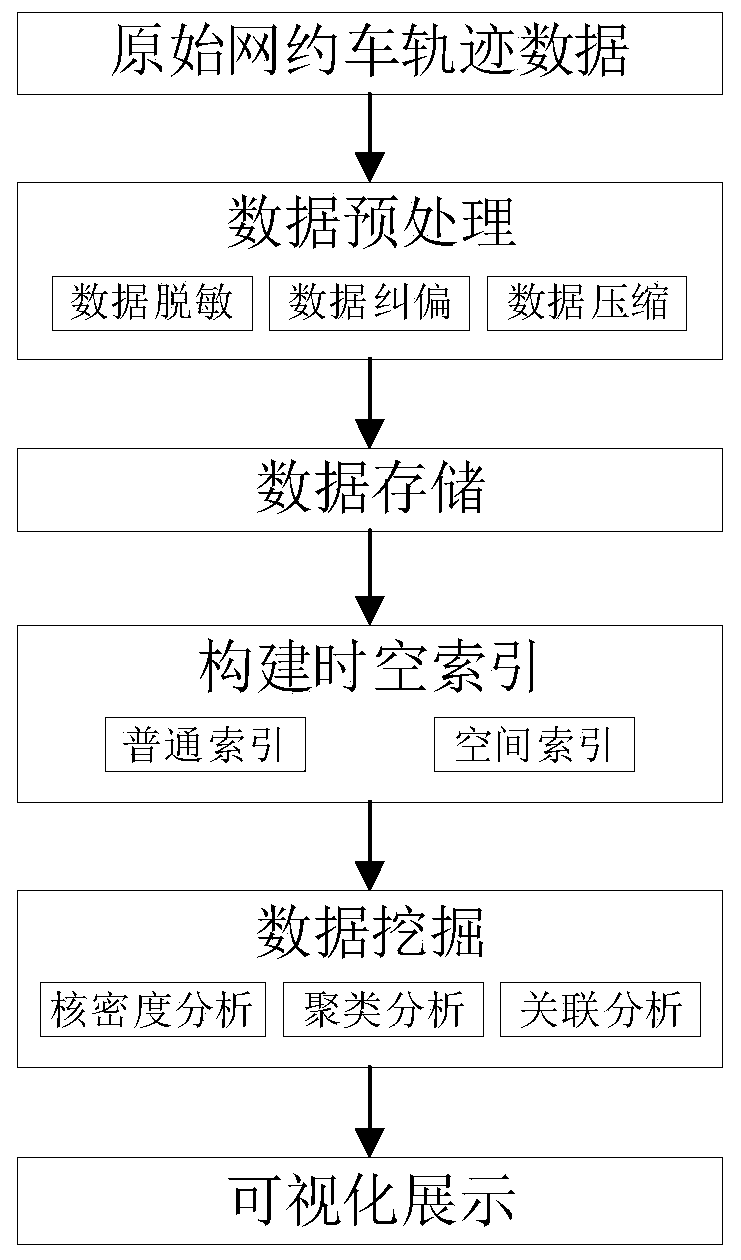
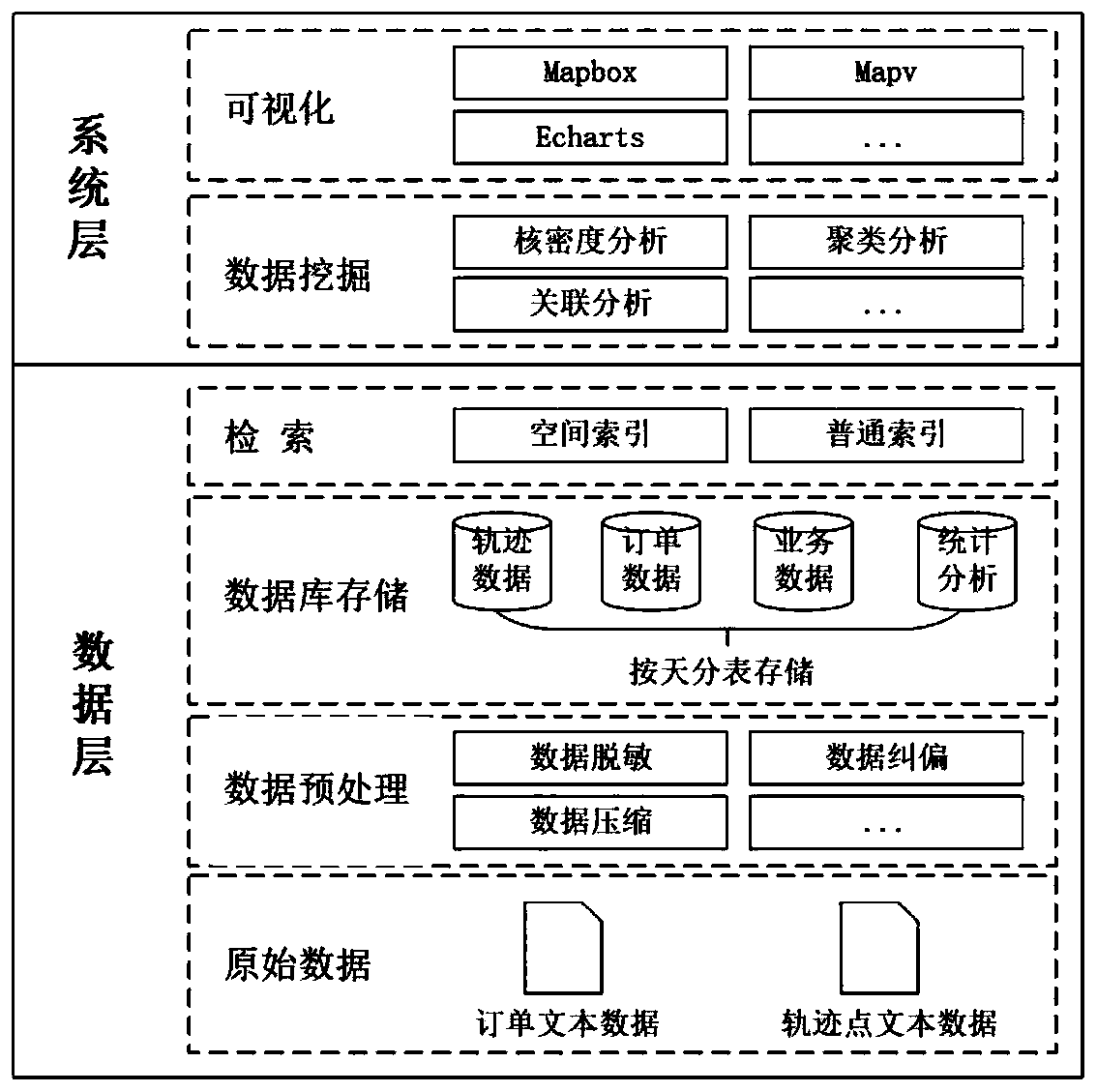
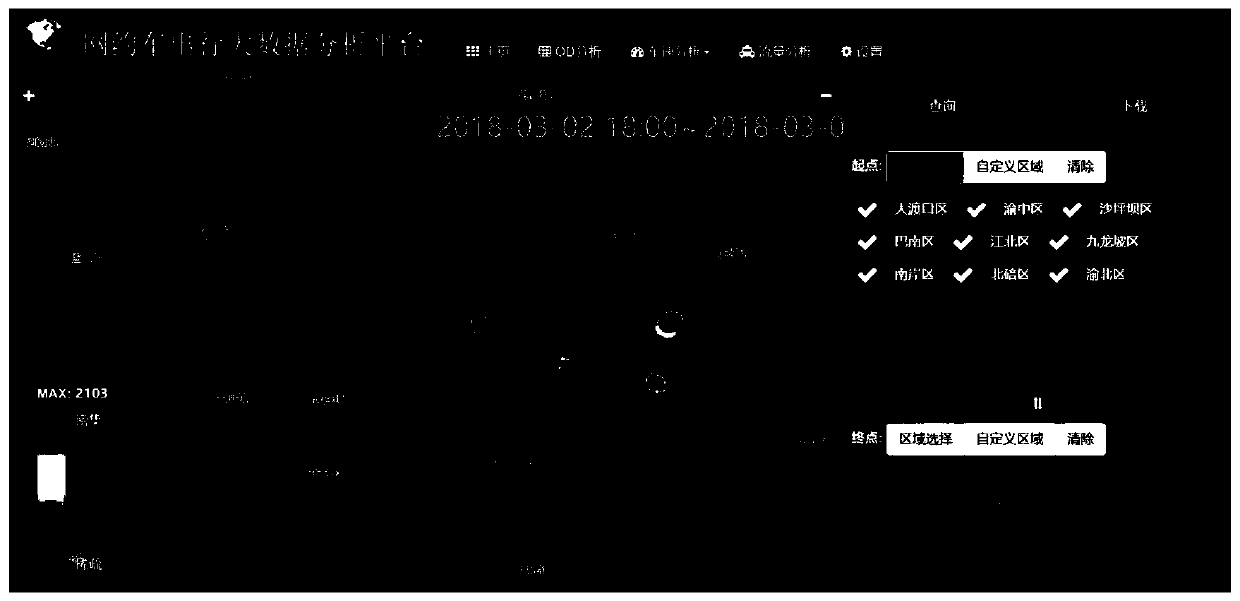
Trajectory data analysis and visualization method and system based on online car-hailing travel
InactiveCN110716935AThe method flow is simpleEasy to operateData processing applicationsVisual data miningRelational databaseTrajectory data mining
The invention discloses a trajectory data analysis and visualization method and system based on online car-hailing travel. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing original online car-hailing trajectory data; storing the preprocessed online car-hailing trajectory data into an object-relational database in a day division table manner, and constructing a space-time index; carrying outdata mining on the stored online car-hailing trajectory data by adopting a data analysis method to realize OD analysis, vehicle speed analysis and vehicle flow analysis of the online car-hailing trajectory data; and visually displaying the obtained data mining result. The method has the remarkable effects that the data volume, the processing speed and the usability and applicability of the miningtechnology are comprehensively considered, a set of simple, operable and easy-to-master track data mining method under multi-technology integration is constructed, and the method is used for mining small and medium-scale track data.
Owner:CHONGQING GEOMATICS & REMOTE SENSING CENT
A method for updating a relational database to a non-relational database based on an ETL tool
InactiveCN109241156AImprove portabilityImprove reusabilityDatabase management systemsSemi-structured data queryingRelational databaseStream data
The invention relates to a method for updating a relational database to a non-relational database based on an ETL tool. The method comprises the following steps: collecting source data of each platform through a collector of the ETL tool, thereby obtaining target data; updating a relational database to a non-relational database. Storing the collected target data into a relational database; extracting target data from a relational database as data to be processed, and taking the data to be processed as intermediate state data in a format of binary Avro data; converting the data to be processedin binary Avro data format into the data to be processed in JSON format; the data to be processed in JSON format is temporarily stored in the local disk in the form of FlowFile stream data to obtain the temporarily stored data to be processed; the temporary data to be processed is stored in the non-relational database through the ETL tool. The method of the invention has the advantages of high configurability and strong process controllability, can accurately locate the link where the error occurs, and saves the time for searching the error.
Owner:ANHUI SUN CREATE ELECTRONICS
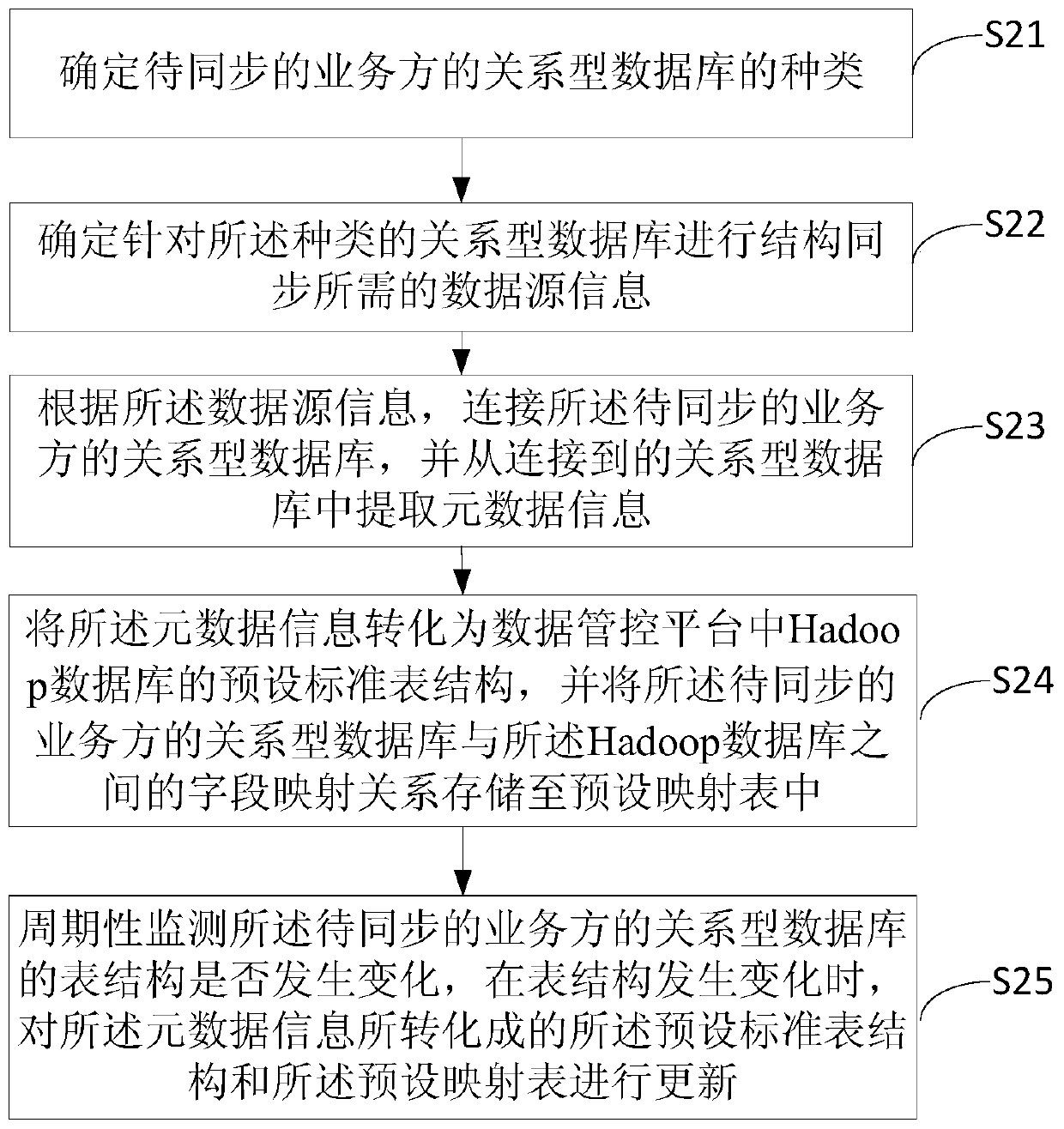
Structure synchronization method and device from relational database to Hadoop database
PendingCN110245145AConvenient operation and maintenance managementReduce workloadDatabase updatingDatabase distribution/replicationRelational databaseStructure of Management Information
The invention relates to a structure synchronization method and device from a relational database to a Hadoop database, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of determining the type of the relational database of a service party to be synchronized; determining data source information; connecting a relational database of a service party to be synchronized, and extracting metadata information from the connected relational database; converting the metadata information into a preset standard table structure of a Hadoop database in a data management and control platform, and storing a field mapping relation between a relational database of a business party to be synchronized and the Hadoop database into a preset mapping table; periodically monitoring whether the table structure of the relational database of the service party to be synchronized changes or not, and if the table structure changes, updating the preset standard table structure converted from the metadata information and the preset mapping table. The table knots of the relational database can be synchronized to the preset standard table structure of the Hadoop database, namely, the table knots are synchronized to the unified standard table structure, and operation and maintenance management is facilitated.
Owner:ONE CONNECT SMART TECH CO LTD SHENZHEN
Method and apparatus to facilitate transactional consistency for references in object-relational databases
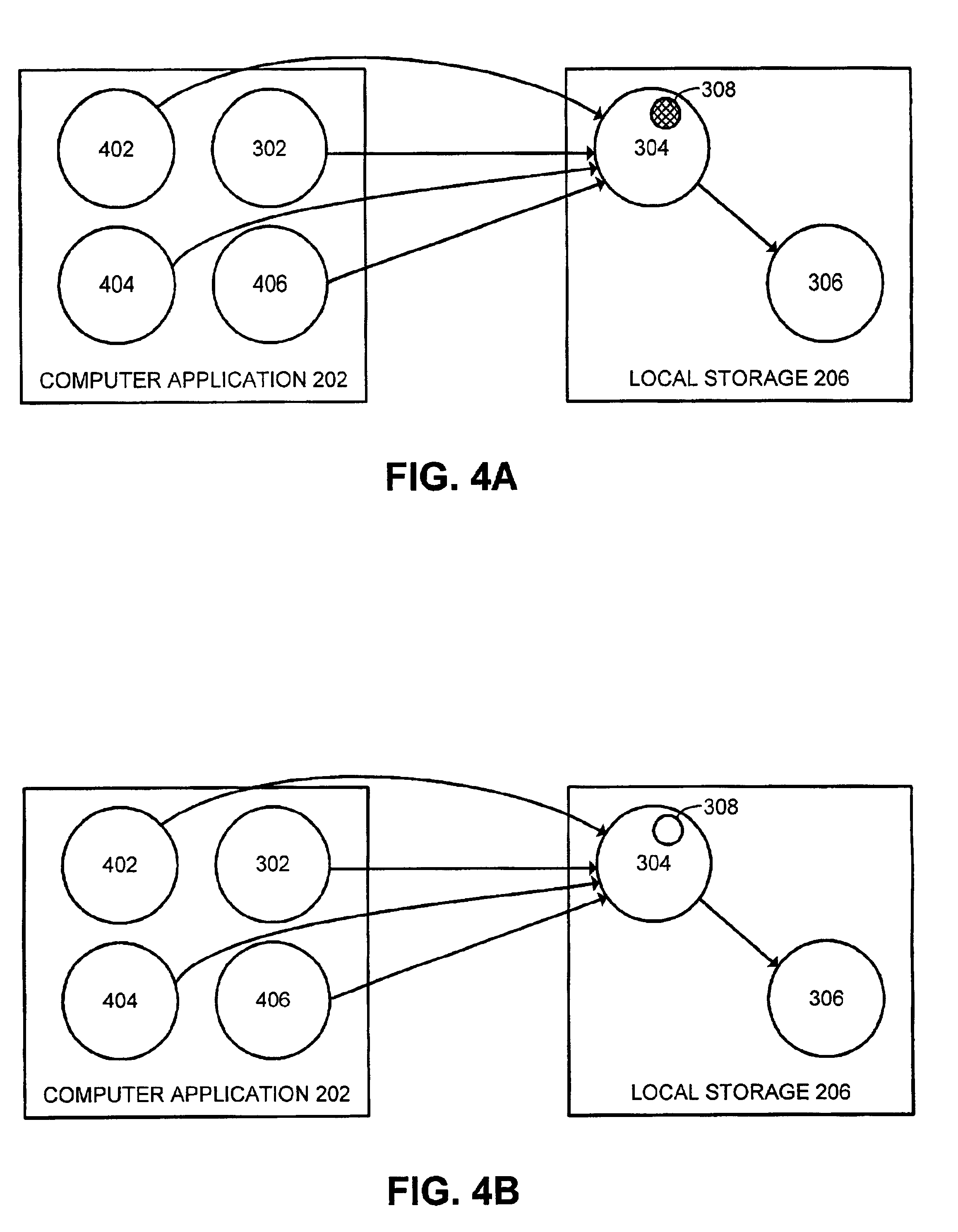
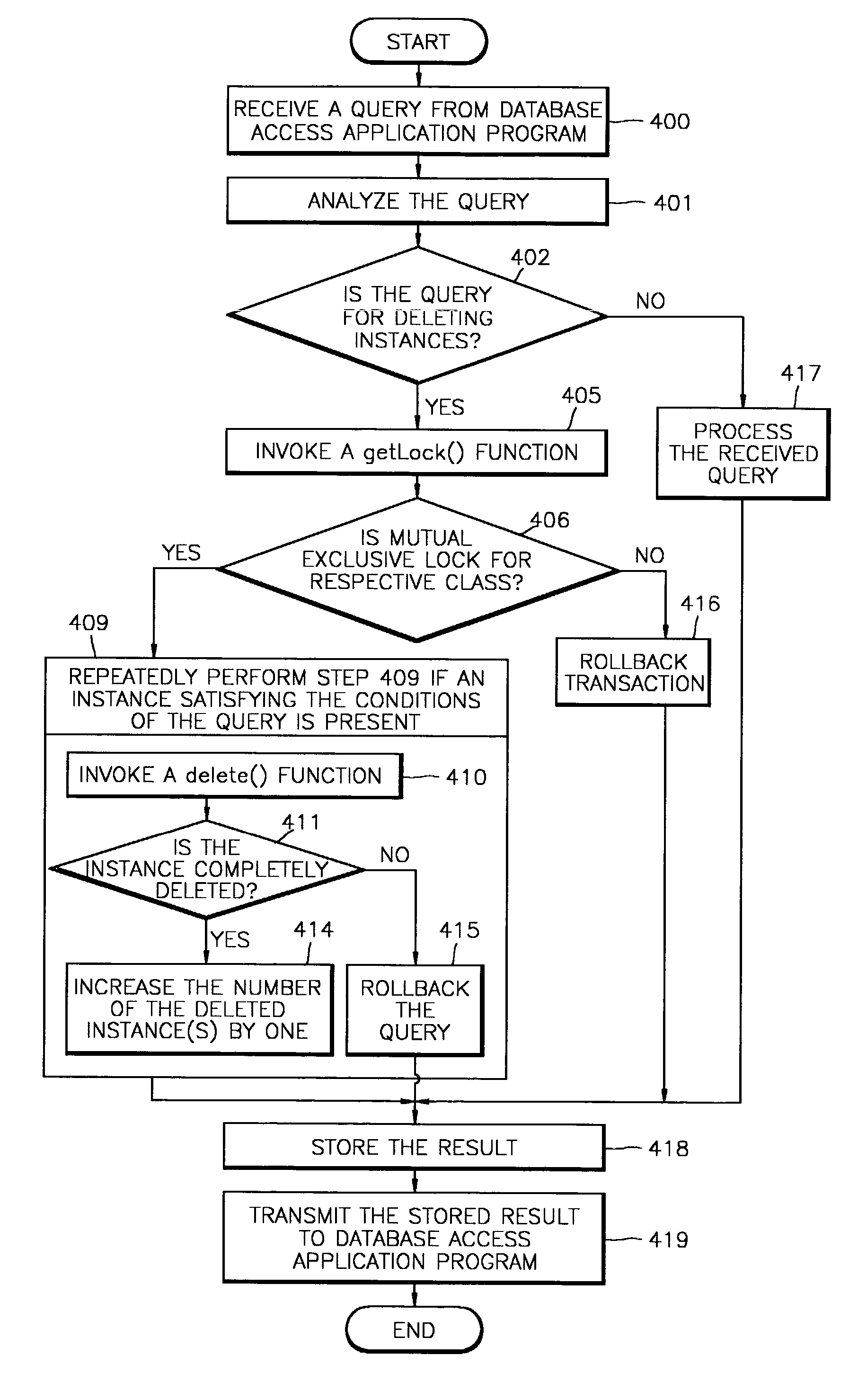
InactiveUS6877014B1Facilitates transactional consistencyData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalRelational databaseObject description
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that facilitates transactional consistency for references in an object-relational database. The system operates by first receiving a reference to an object located in the object-relational database. Next, the system creates a reference object within local storage that includes an object descriptor to indicate whether the object has been loaded into local storage. The reference is stored in this reference object. A pointer within an application program can then point to the reference object, so that the application program can use the pointer to access the object.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Object-relational database management system and method for deleting class instance for the same
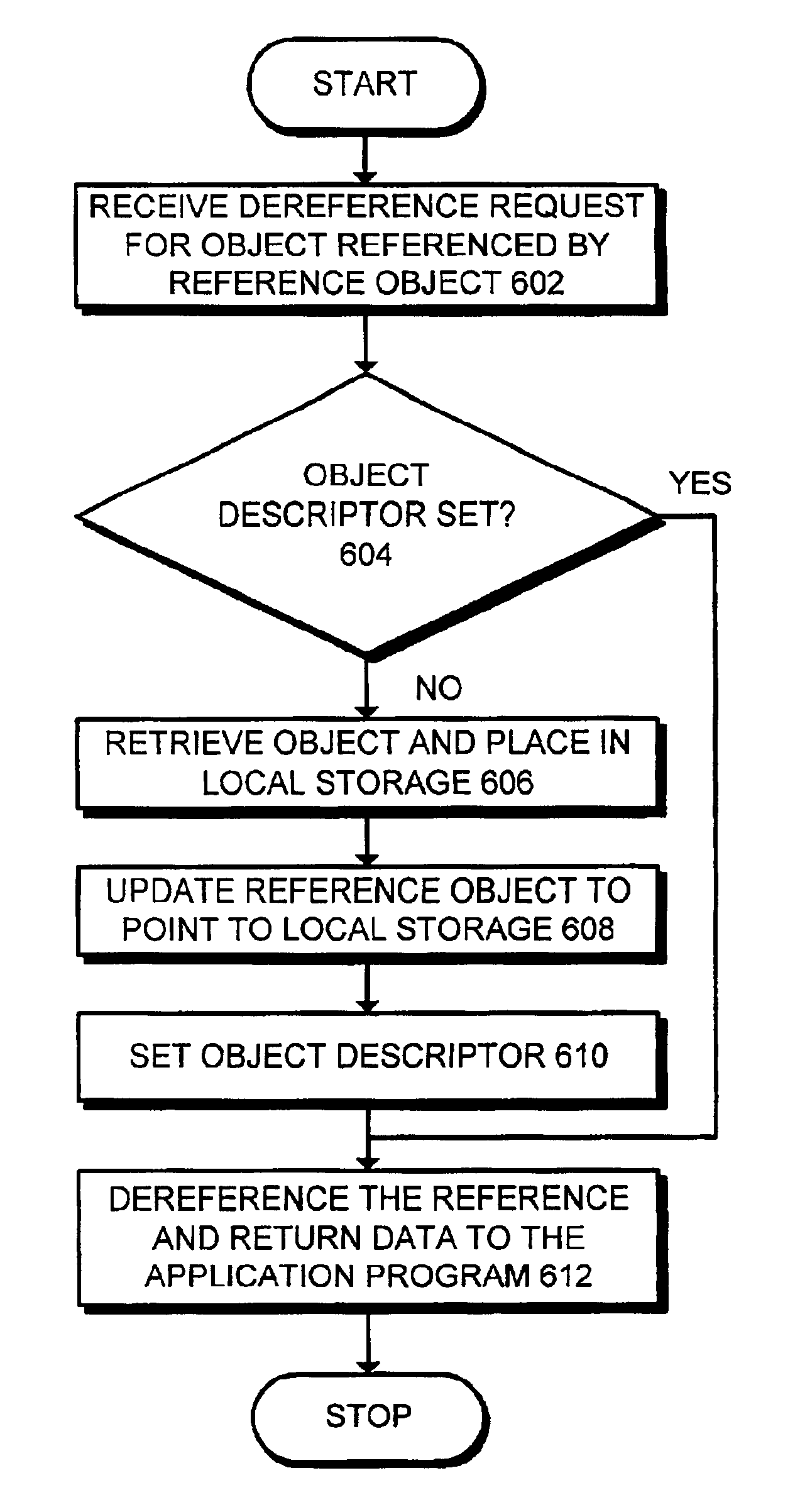
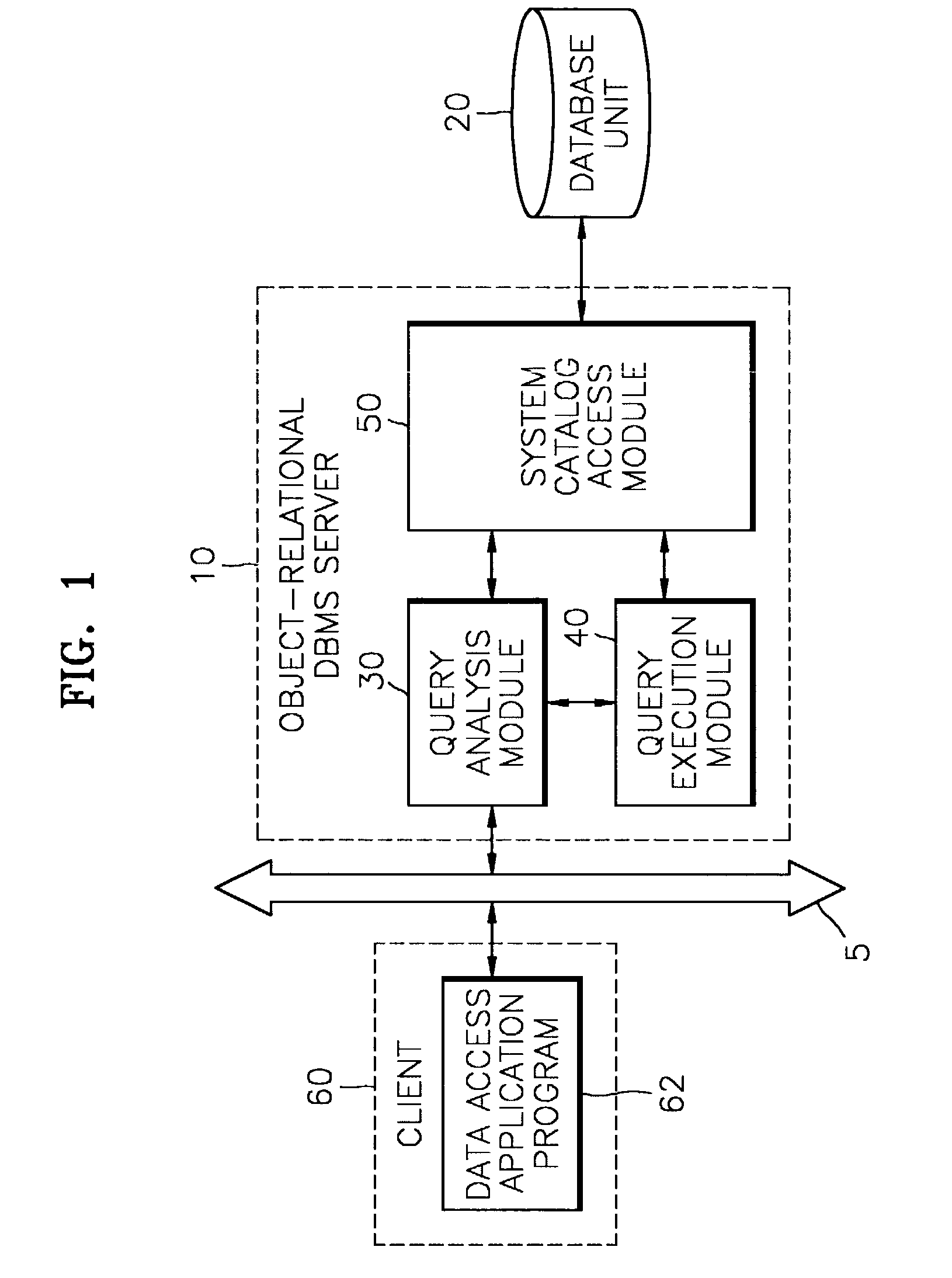
ActiveUS7076490B2Deteriorating consistencyData processing applicationsProgram synchronisationProgramming languageRelational database management system
Provided are a main-memory resident object-relational database management system (ORDBMS) and a method of deleting a class instance using the ORDBMS. The method includes obtaining a mutual exclusive lock for a class to be deleted as per the query and a child class inheriting from the class when a query of deleting an instance is input from a database access application program, and deleting the instance from the class and at least one instance related to the instance from its child class using OID reference.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
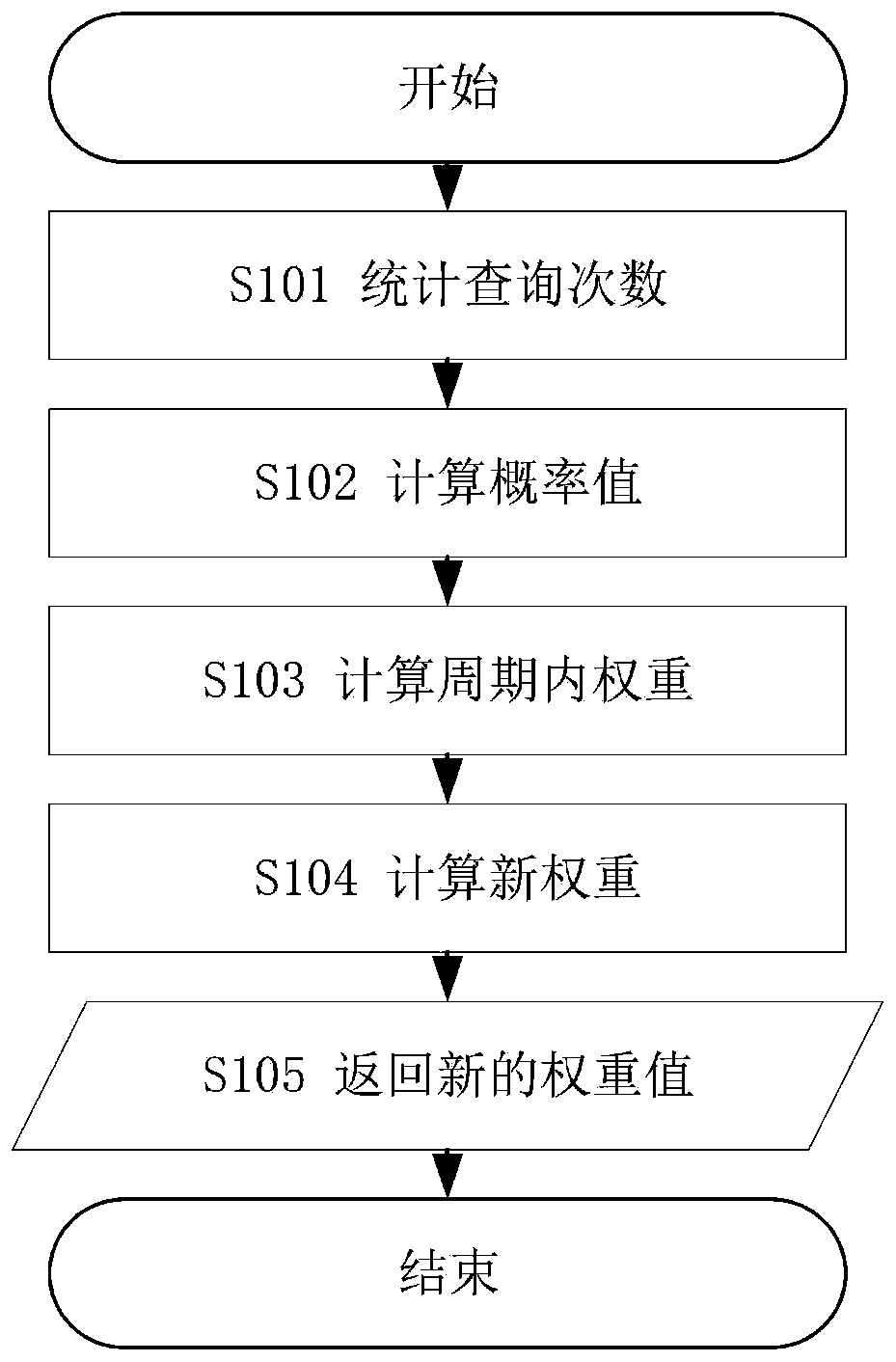
Dynamic hybrid indexing method for non-relational database
ActiveCN110069500ASave space storage lossImprove conditional query efficiencyEnergy efficient computingSpecial data processing applicationsRelational databaseBig data
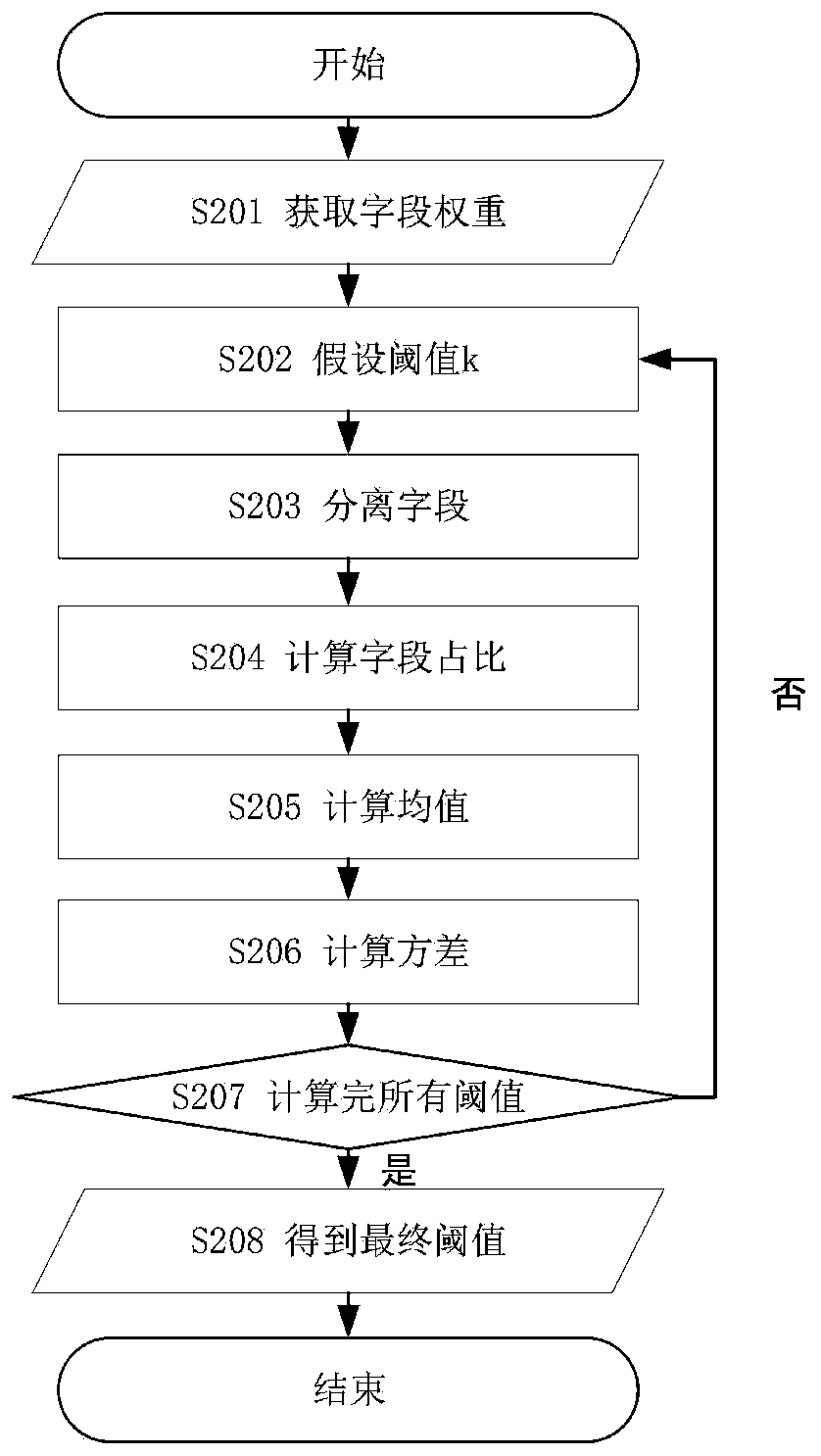
The invention relates to a dynamic hybrid indexing method for a non-relational database, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of establishing a non-primary key indexing structure of a key value pair non-relational database; defining the weight of the non-primary key field, and updating the weight value of the non-primary key field by taking the field as the frequency of the query condition and the historical weight of the field within one period; dynamically dividing index types; and carrying out hybrid indexing. According to the mixed indexing method of the key value pairnon-relational database provided by the invention, the conditional query efficiency of the non-primary key field can be effectively improved. The method overcomes the defect that the key value pair non-relational data does not support the non-primary key field and does not support the index query, and establishes the mixed index of the non-primary key field. In terms of big data storage, the function of quick query is achieved, and unnecessary storage expenditure is saved.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com