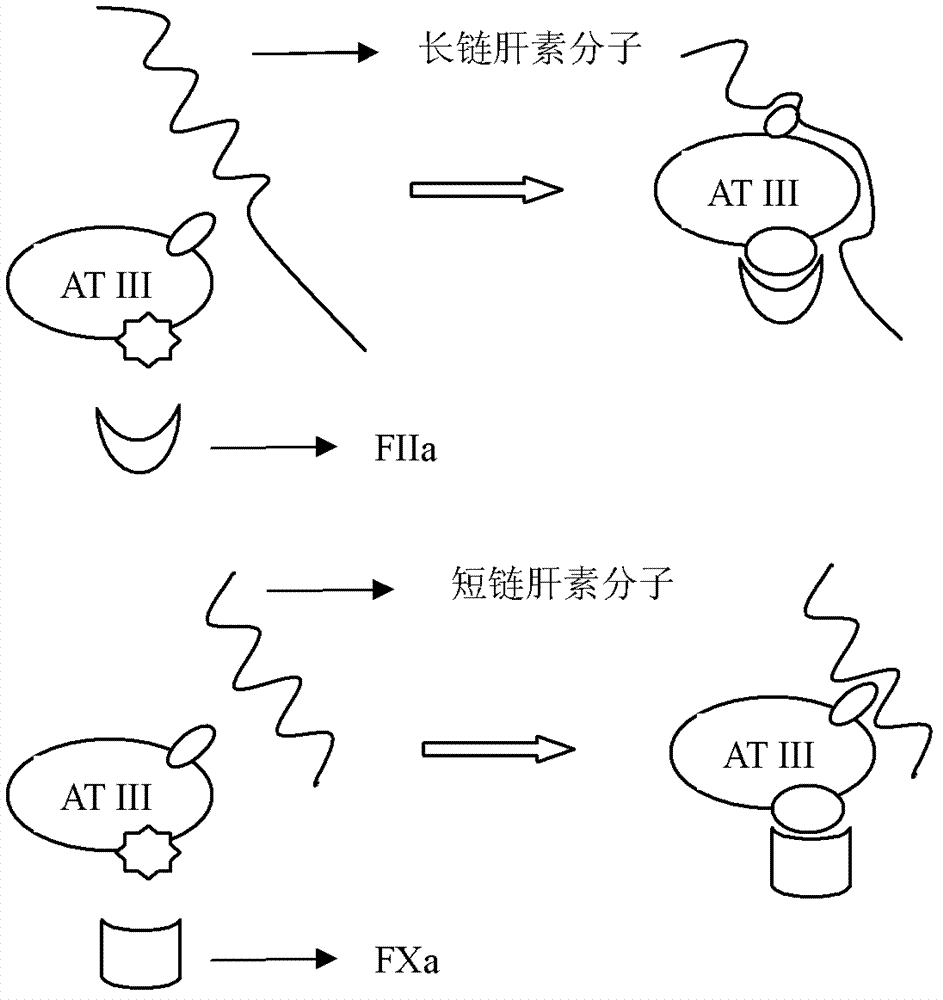
Dentritic heparin nano-material modified biological type artificial blood vessel
A nano-material and dendritic technology, which is applied to the types of packaging items, anti-coagulation treatment, special packaging items, etc., can solve the problem that the regeneration and remodeling process is difficult to occur, the amount of heparin modification is difficult to control, and the surface properties cannot meet the requirements of biological materials. Capacitance and tissue regeneration needs and other issues to achieve the effect of enhancing activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Embodiment 1, the preparation of heparin oligosaccharide
[0075] 1. Preparation of 3-5K and 5-10K heparin by enzymatic degradation
[0076] Heparin extracted from porcine small intestinal mucosa is degraded by type I heparanase for a certain period of time, and then ultrafiltered and dialyzed with an ultrafiltration membrane with strong molecular weight selectivity to obtain:
[0077] (1) Prepare 0.1M Tris-hydrochloric acid buffer solution, and adjust the pH between 7.00±0.02.
[0078] (2) Weigh 806.9 mg of heparin powder (white), and sterilize it by ultraviolet light for 30±1 minutes in a biological safety cabinet. This was added to 16.0 ml of Tris buffer filtered through a 220 micron pore filter. (take a sample and measure the pH value of the system with a pH meter, it is 7.08).
[0079] (3) Filter the bacteria with a filter membrane again. Add 100 μl of 100 units (sigma unit, about 1 / 600th international unit) heparinase-Tris buffer solution, perform aseptic enzy...
Embodiment 2
[0082] Example 2, Synthesis of Hydrazide CysPAMAM (CysPAMAM-HYD) and Heparin Modified Hydrazide CysPAMAM
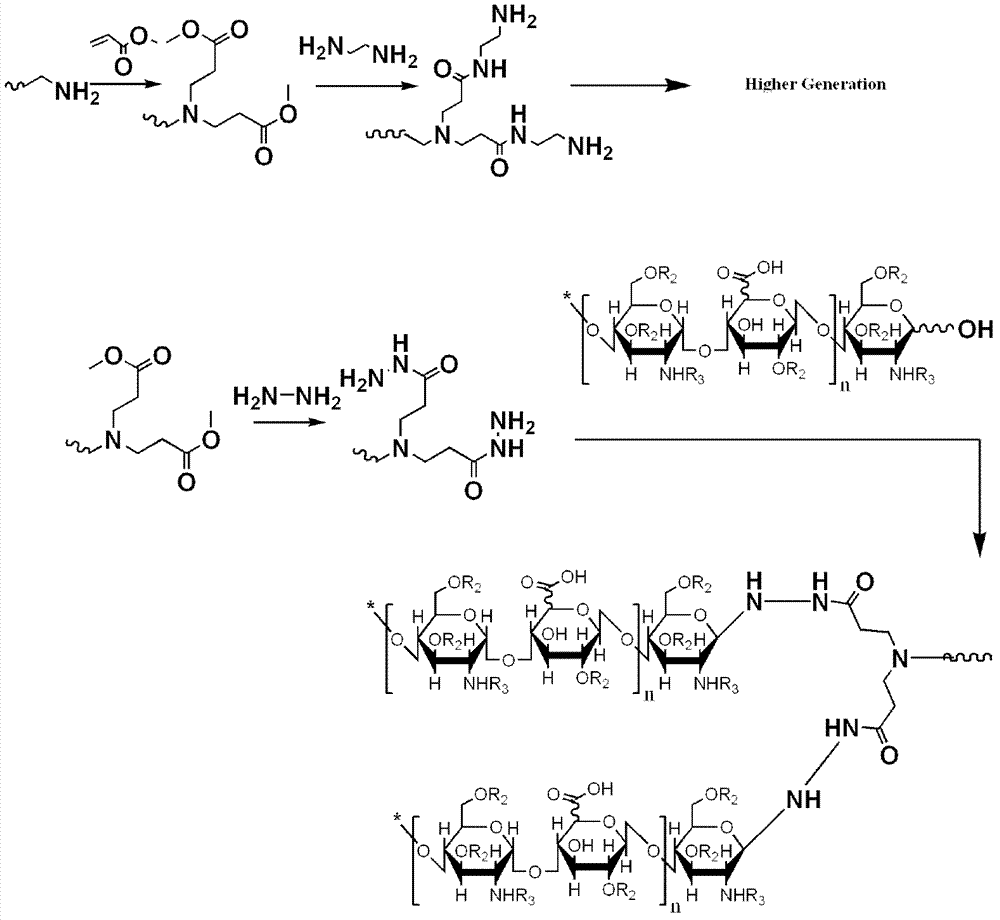
[0083] The principle is as follows: first prepare cystamine-core polyamidoamine (CysPAMAM) with all hydrazide end groups, and then covalently react the reducing end of heparin retaining the hemiacetal structure with the hydrazide group, without catalyst action, in a mild Heparin oligosaccharides were modified to CysPAMAM-HYD by terminal groups under certain conditions. The reaction process is shown in figure 2 .
[0084] 1. Synthesis of CysPAMAM-HYD:
[0085] (1) Preparation of G0.5 CysPAMAM and G2.5 CysPAMAM:
[0086] Under stirring in an ice bath, slowly add methyl acrylate to the cystamine-methanol solution with a concentration of 50 mg / ml, and react in a water bath at 37°C for 48 hours (the molar ratio of cystamine to methyl acrylate is 1:20, methyl acrylate Excess ester), then the solvent and unreacted methyl acrylate were removed by suspension evaporation at 65°...
Embodiment 3
[0126] Embodiment 3, dendritic heparin-PAMAM complex chemical component analysis
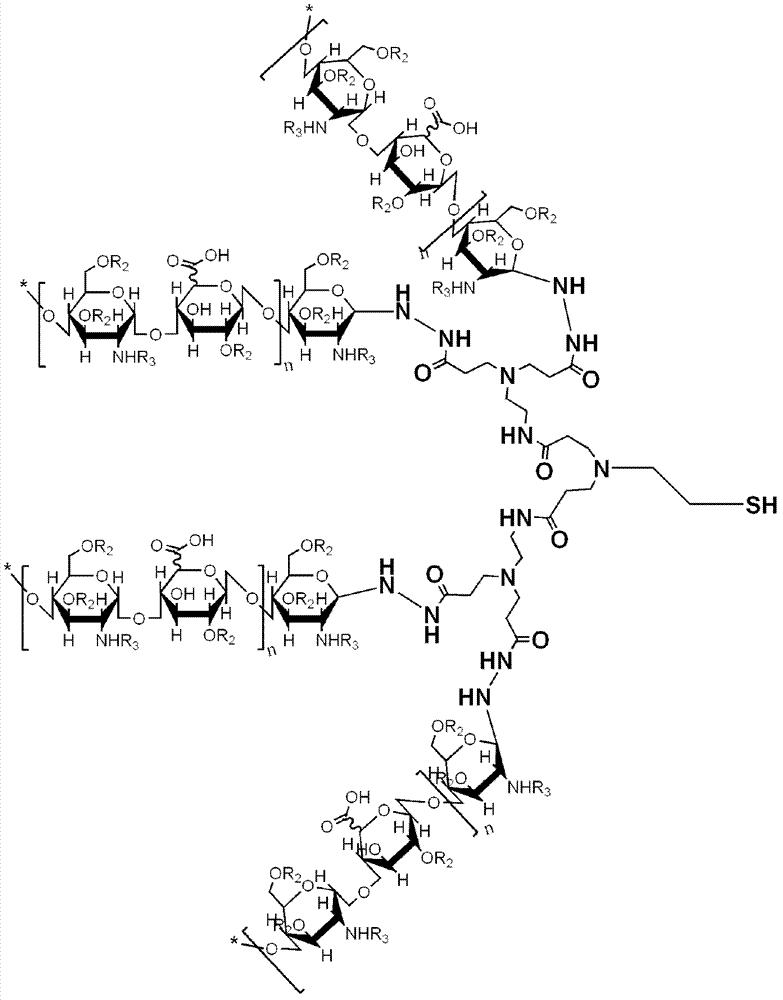
[0127] The structural formula of heparin oligosaccharide-modified hydrazide CysPAMAM (Heparin / CysPAMAM-HYD G0.5) is shown in formula III:
[0128]
[0129]
[0130] Through nuclear magnetic resonance analysis, it can be seen from the structure of heparin after synthesis (shown in formula III) that there are 12 Hs on the disaccharide repeating unit, and there are Hs (peaks) adjacent to the carbonyl on the CysPAMAM-HYD skeleton molecule, which are integrated Regions do not overlap and can be used for quantification. Therefore by adding δ2.750-2.800 (-CH in the CysPAMAM-HYD moiety 2 -C=O-, G0.5 is 24H, G2.5 is 120H) multiple peak calibration is 1.00, all the other are from the peak between δ3.0-6.5 (remove the hydrogen peak on the water molecule of 4.70-4.90 and The same calibration G0.5 that overlaps with it on PAMAM is 8 H of 0.33 units, and G2.5 is 56 H of 0.47). The sum of the remaining...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com