High-yield culture medium for producing pleomycin E from deep-sea streptomyces gene engineering mutant strain and large-scale fermentation process of high-yield culture medium
A technology of genetically engineered strains and elamycin, applied in genetic engineering, microorganism-based methods, fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of low yield of elamycin E, restricting the research on biological activity of elamycin E system, etc. , to achieve the effect of being conducive to popularization and application, high flux of secondary metabolic pathways, and increasing titer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Example 1 Construction of SCSIO ZH16ΔilaR strain
[0063] The S.atratus SCSIO ZH16ΔilaR strain of the present invention is obtained by using the gene knockout plasmid PKCCas9dilaR to knock out the ilaR gene in S.atratus SCSIO ZH16 based on the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology. Specific steps are as follows:
[0064] First, the PKCCas9dO plasmid cut with the restriction enzymes SpeI and HindIII was ligated with the 1173 bp upstream fragment and the 1109 bp downstream fragment of the guide RNA assembled at the 190th base region of the ilaR gene by the method of restriction endonucleases SpeI and HindIII, and then transformed into The PKCCas9dilaR recombinant plasmid was obtained from E.coil DH5α. The sequence of the guide RNA is shown in SEQ ID NO.1.
[0065] Guide RNA:
[0066] ATTCCAAGGACGACGGAAAGTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGCAAGTTAAAATAAGGCTAGTCCGTTATCAACTTGAAAAAGTGGCACCGAGTCGGTGC, SEQ ID NO. 1.
[0067] The upstream fragment containing the guide RNA is based on the Strept...
Embodiment 2
[0081] 1. Optimization of carbon and nitrogen sources
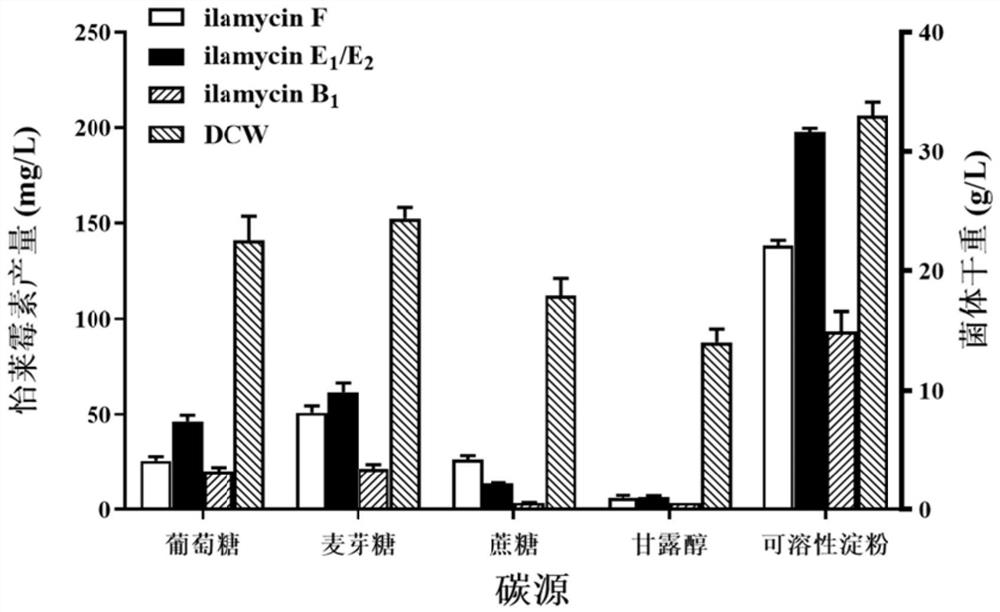
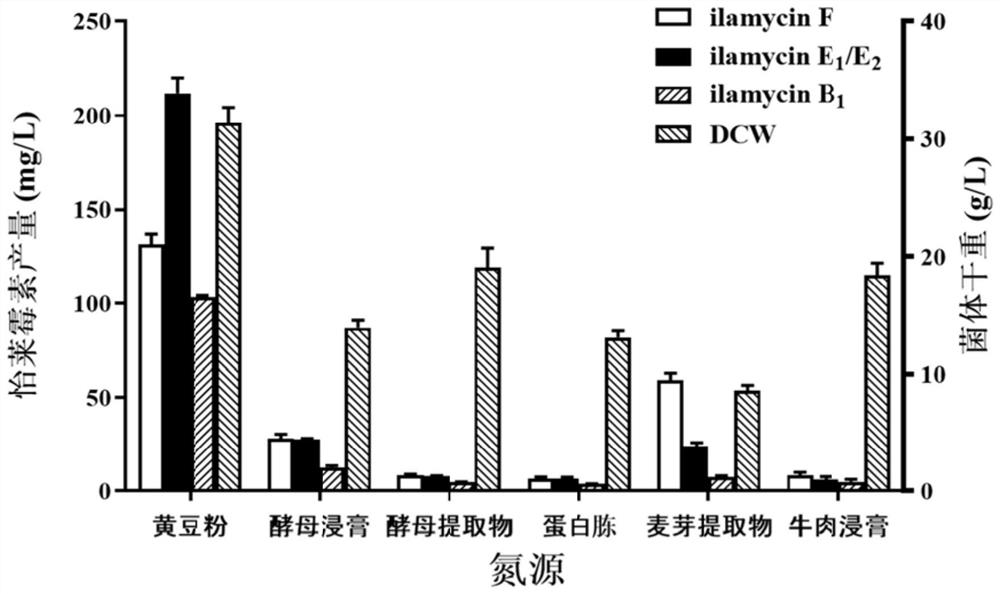
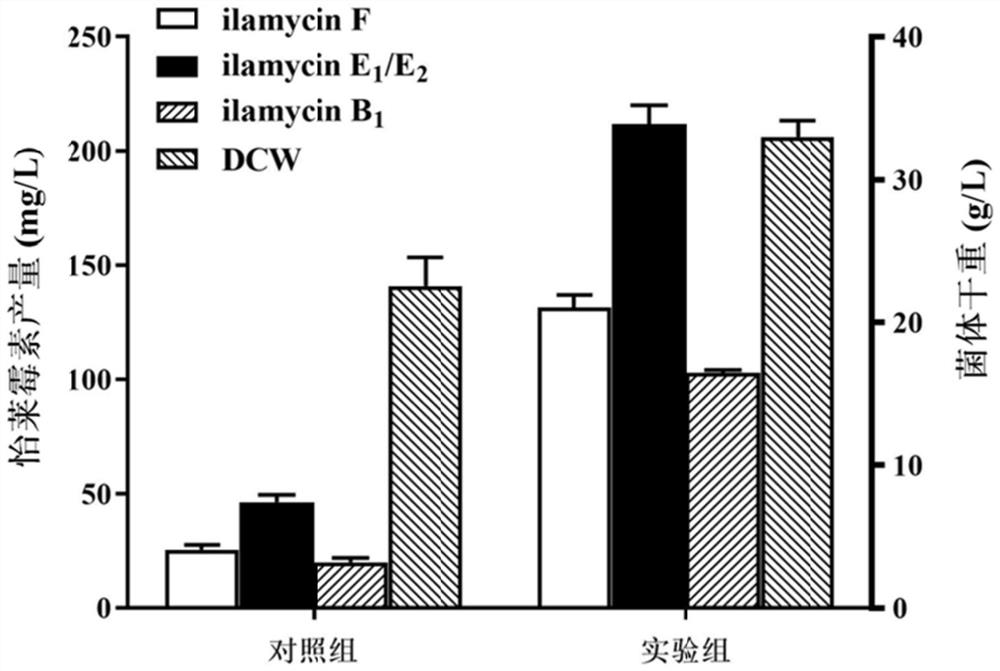
[0082] By screening more than 20 kinds of medium, the medium formula was determined to be 120g of glucose, 20g of soybean powder, 2.4g of corn steep liquor, 6g of sodium chloride, 9.6g of sodium nitrate, 6.4g of ammonium sulfate, 0.24g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, and 9.6g of calcium carbonate. g. The glucose in the basal fermentation medium was replaced by maltose, sucrose, mannitol and soluble starch, respectively. The mass fraction of each carbon source was the same, and the other components were unchanged. Soybean powder was replaced with yeast extract, yeast extract powder, peptone, malt extract, and beef extract respectively. The mass fraction of each nitrogen source was the same, and other components were unchanged. The experimental results are as Figure 1 to Figure 2 shown. figure 1 and figure 2 The results showed that the optimal carbon source was soluble starch, and the optimal nitrogen source was so...
Embodiment 3
[0094] Example 3 Experimental design, data analysis and detection results
[0095] The Plackett-Burman experimental design can analyze the significance of the response values of multiple different factors to find the medium components that are most important for fermentation titer or cell growth, and take the highest (+1) for each factor. and low (-1) two levels, through the statistical analysis between the difference between the two levels of each factor and the overall difference to determine the significance of each factor to the corresponding variable. Through the design of Design Expert 12 data processing software, 8 influencing factors are selected in this experiment, and the PB experimental design table with N=12 is selected. The factors and levels represented by each parameter are shown in the table (see Table 1 and Table 2). X in Table 1 1 , X 2 , X 3 , X 4 , X 5 , X 6 , X 7 , X 8 Respectively represent soluble starch, soybean flour, corn steep liquor, sodi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com