Materials and methods for preventing and treating microbe-mediated epithelial disorders
a technology of epithelial disorders and materials, applied in the direction of immunological disorders, antibacterial agents, antibody medical ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of imposing a burden on healthcare systems worldwide, affecting the health of man and animals, and conventional therapeutic approaches to the prevention or treatment of microbe-mediated epithelial disorders such as gut-derived sepsis have met with incomplete success, etc., to achieve cost-effective, suppress virulence expression, and protect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
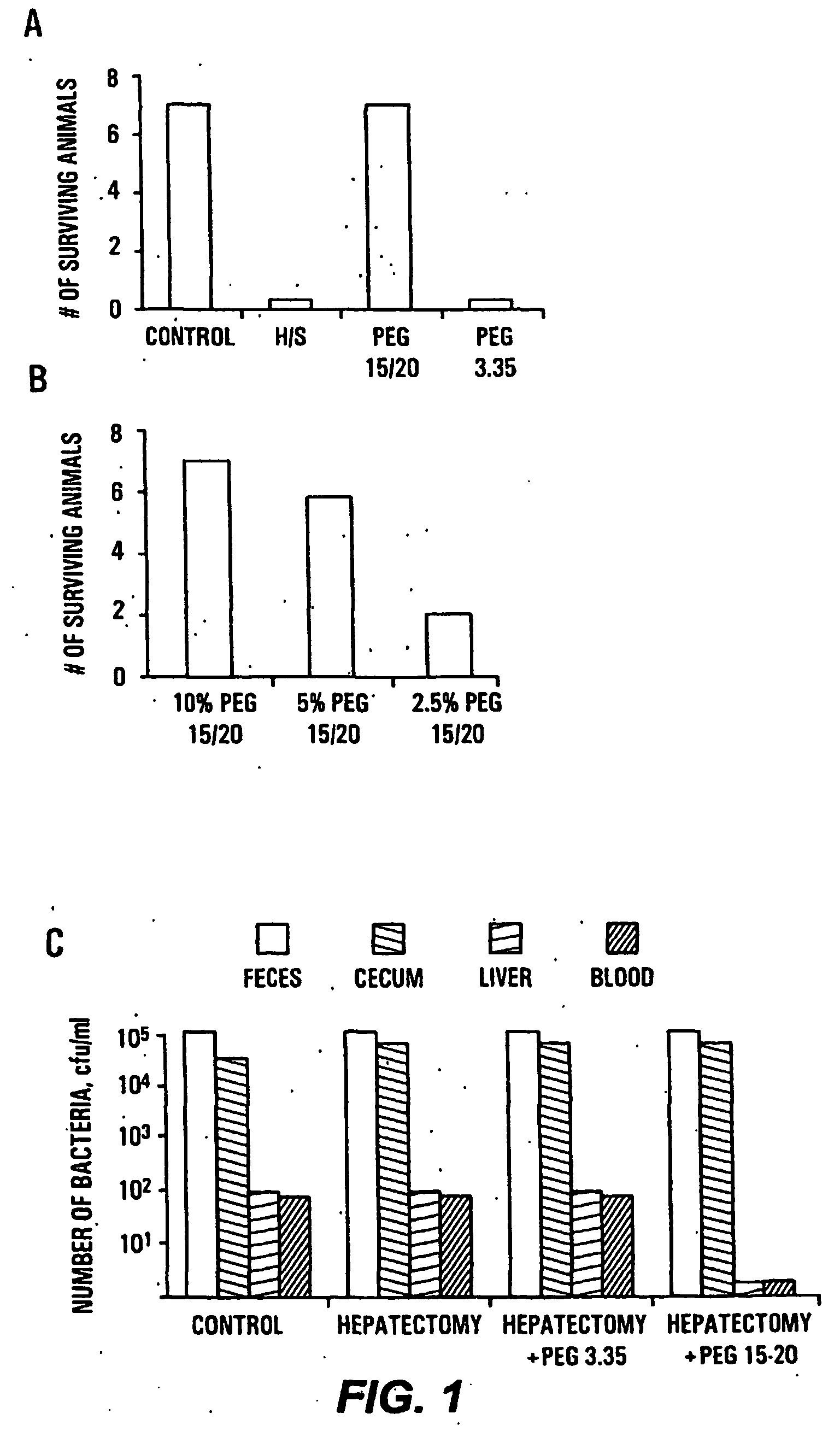
HMW PEG Protects against Gut-Derived Sepsis Following 30% Hepatectomy
[0068] Male Balb / c mice were anesthetized and subjected to hepatectomy using a conventional protocol. A 30% bloodless excision of the liver along the floppy left lobe was performed. Control mice underwent manipulation of the liver without hepatectomy. The experimental and control groups each contained seven mice. In all mice, a volume of 200 μl of 107 cfu / ml of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA27853 was injected into the base of the cecum by direct needle puncture diluted in either saline, PEG 3.350 or PEG 15-20 (PEGs). The relatively low molecular weight PEGs are commercially available; PEG 15-20, having an average molecular weight of 15,000 to 20,000 daltons, is a combination of PEG 7-8 and PEG 8-10 covalently joined to a phenol ring. The PEG 7-8 has an average molecular weight of 7,000 to 8,000 daltons and the PEG 8-10 has an average molecular weight of 8,000 to 10,000 daltons. One of skill in the art will realize that...
example 2
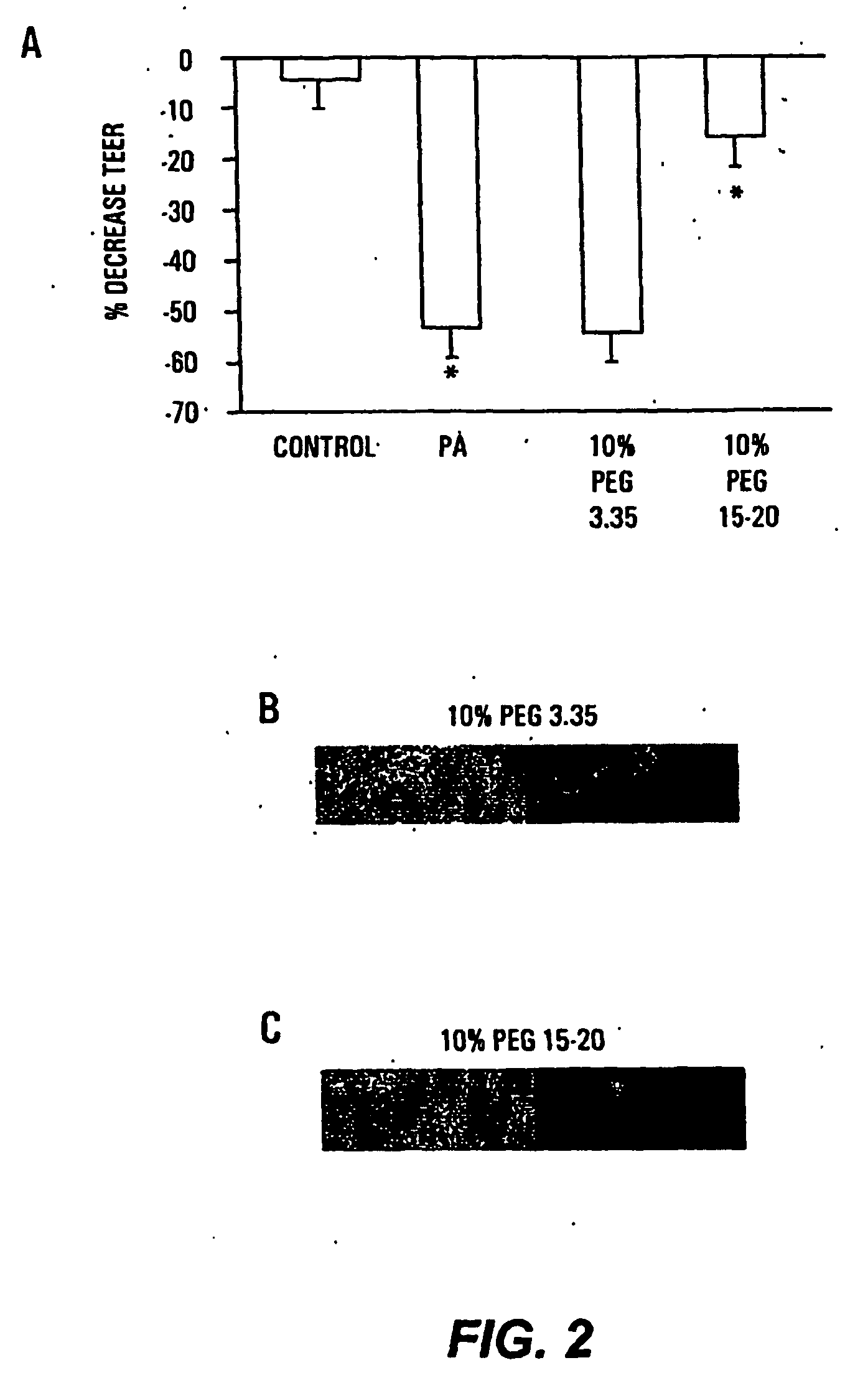
HMW PEG Prevents Pathogen Adherence to Intestinal Epithelia
[0073] Tight junctions are dynamic elements of the epithelial cell cytoskeleton that play a key role in the barrier function of the mammalian intestinal tract. P. aeruginosa results in a profound alteration in tight junctional permeability as measured by the transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) of both Caco-2 cells and T-84 cells. Caco-2 cells are well-characterized human colon epithelial cells that maintain a stable TEER in culture, and this cell line provides a recognized in vitro model of the in vivo behavior of intestinal pathogens. To determine the protective effect of PEG on P. aeruginosa PA27853-induced decreases in TEER of cultured Caco-2 monolayers, 1×107 cfu / ml of PA27853 was apically inoculated onto two Caco-2 cell monolayers in the presence of 10% PEG 3.35 or 10% PEG 15-20. TEER was serially measured for 8 hours and the maximal fall in TEER recorded.
[0074] Only PEG 15-20 protected significantly against ...
example 3
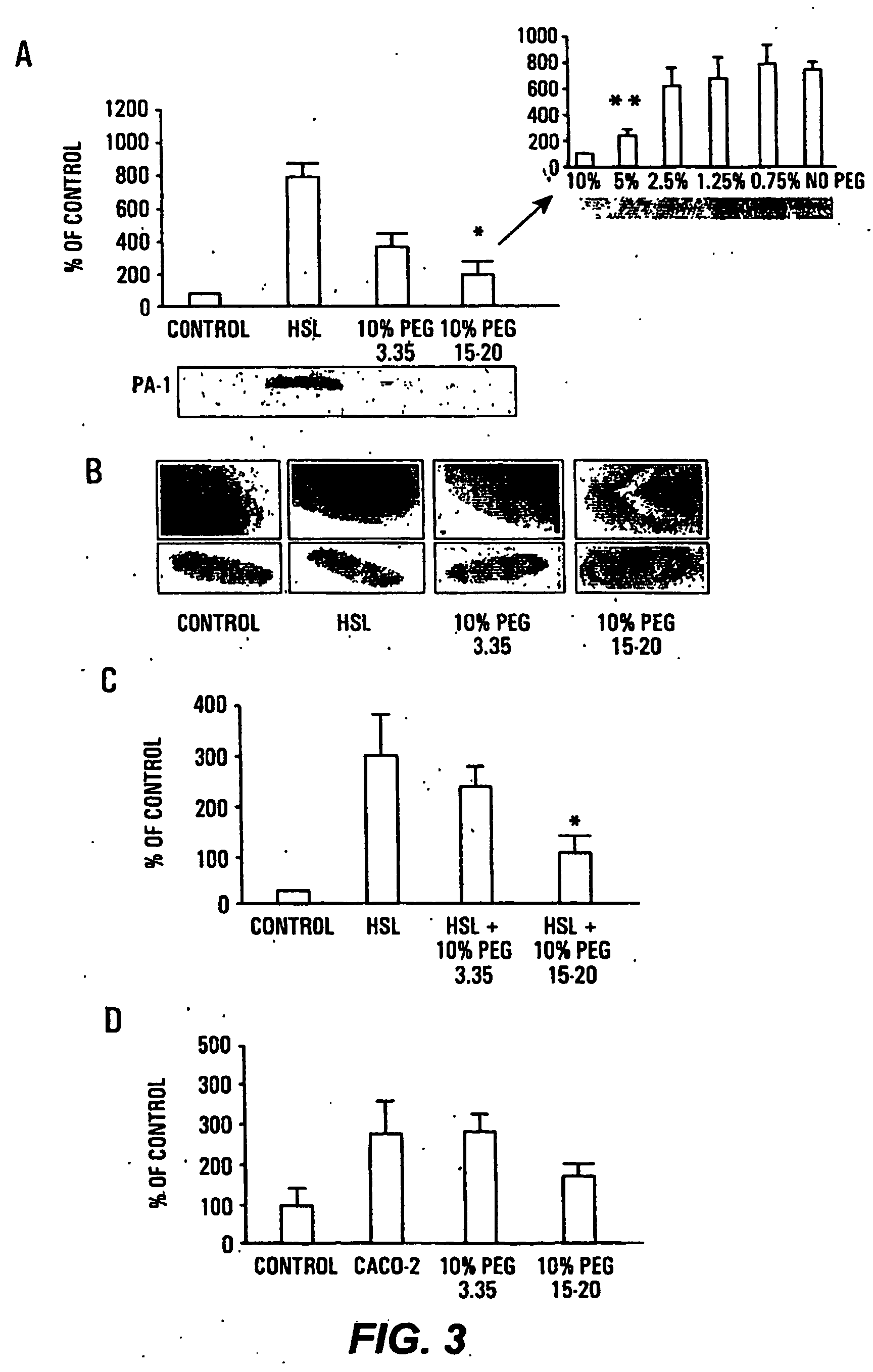
HMW PEG Inhibits Virulence Expression in Pathogens
[0077] The expression of the PA-I lectin / adhesin in P. aeruginosa PA27853 was increased in the cecum of mice following hepatectomy and played a key role in the lethal effect of P. aeruginosa in the mouse intestine. PA-I functions as a significant virulence determinant in the mouse intestine by facilitating the adherence of PA27853 to the epithelium as well as by creating a significant barrier defect to the cytotoxins, exotoxin A and elastase. PA-I expression in P. aeruginosa is regulated by the transcriptional regulator RhIR and its cognate activator C4-HSL. Expression. of PA-I in PA27853 was not only increased by exposure to C4-HSL, but also by contact with Caco-2 cells, Caco-2 cell membrane preparations, and supernatants from Caco-2 cell cultures.
[0078] Northern hybridization was used to analyze the expression of PA-I at the transcriptional level. Total RNA of P. aeruginosa was isolated by the modified three-detergent method. Pro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com