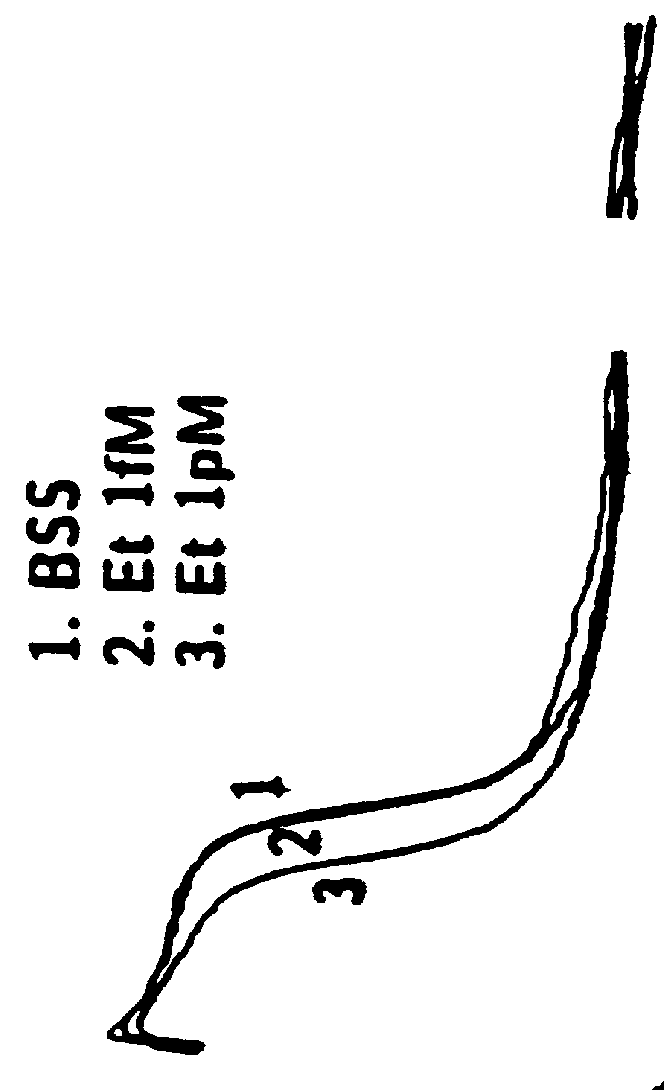
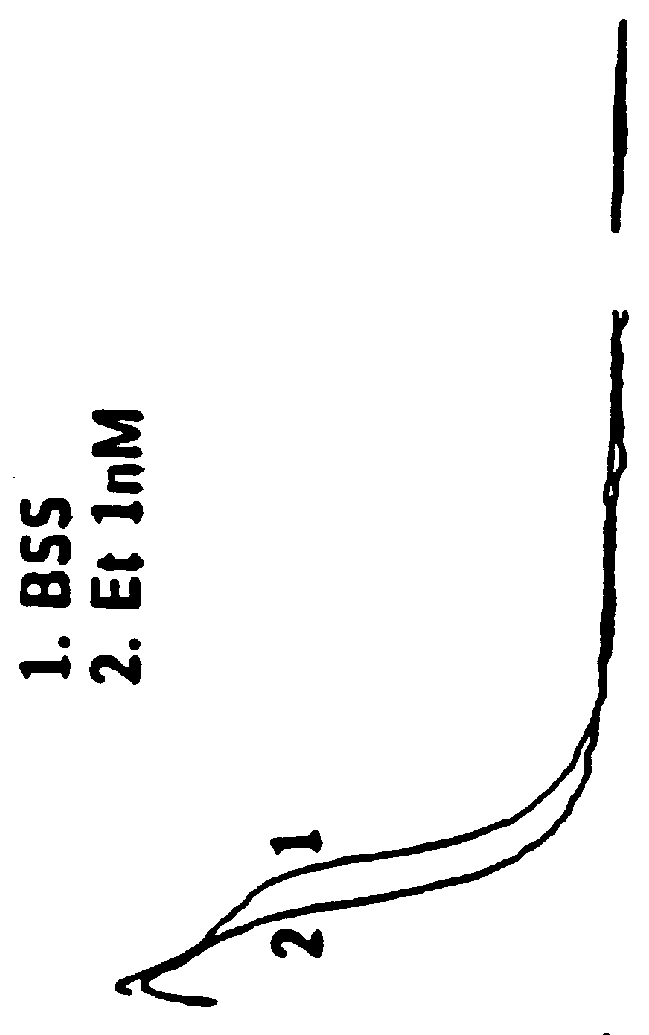
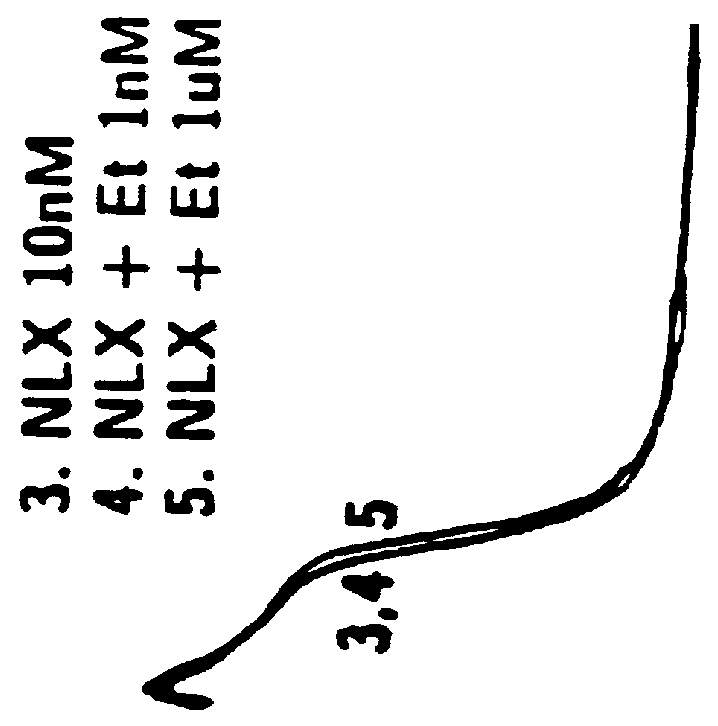
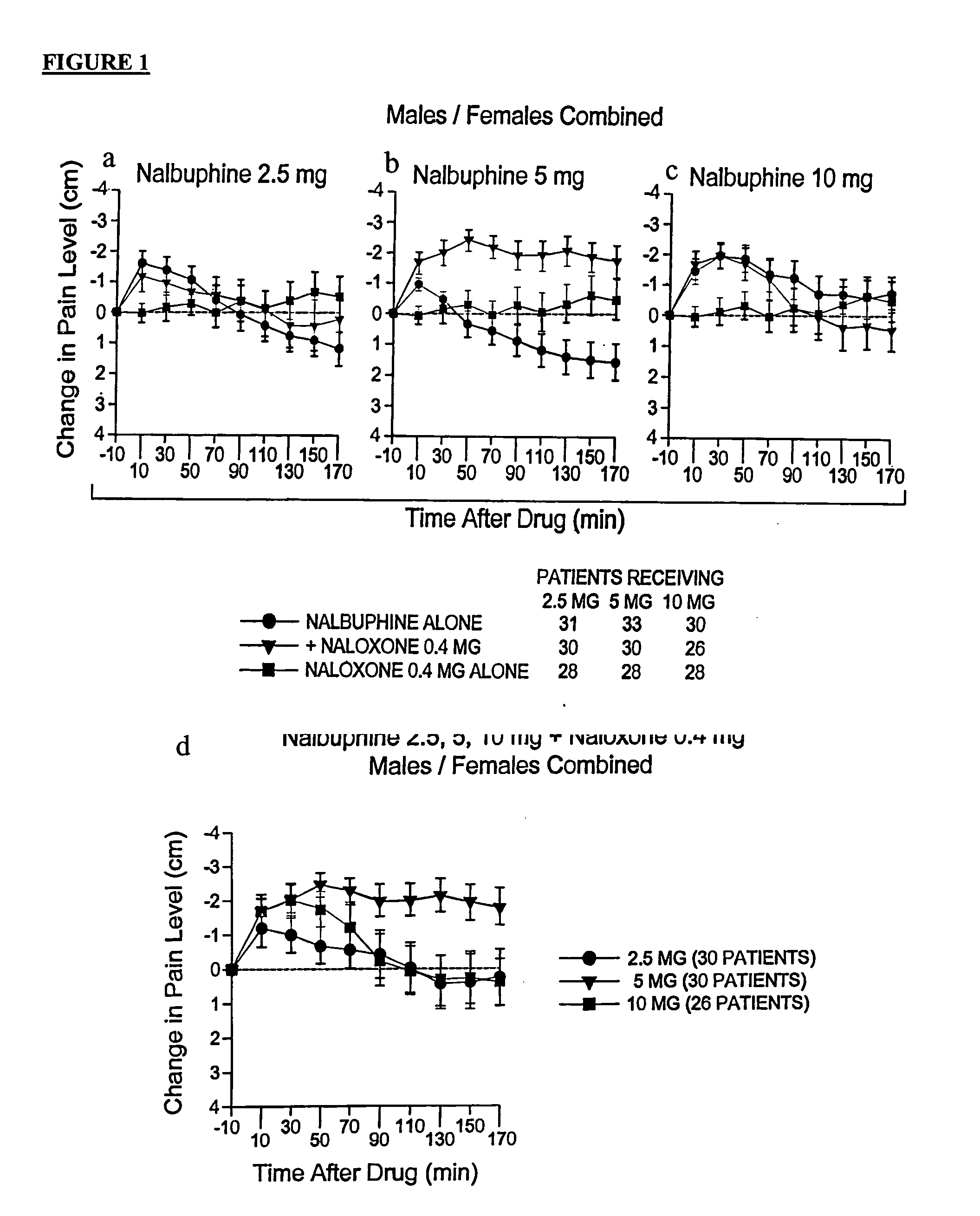
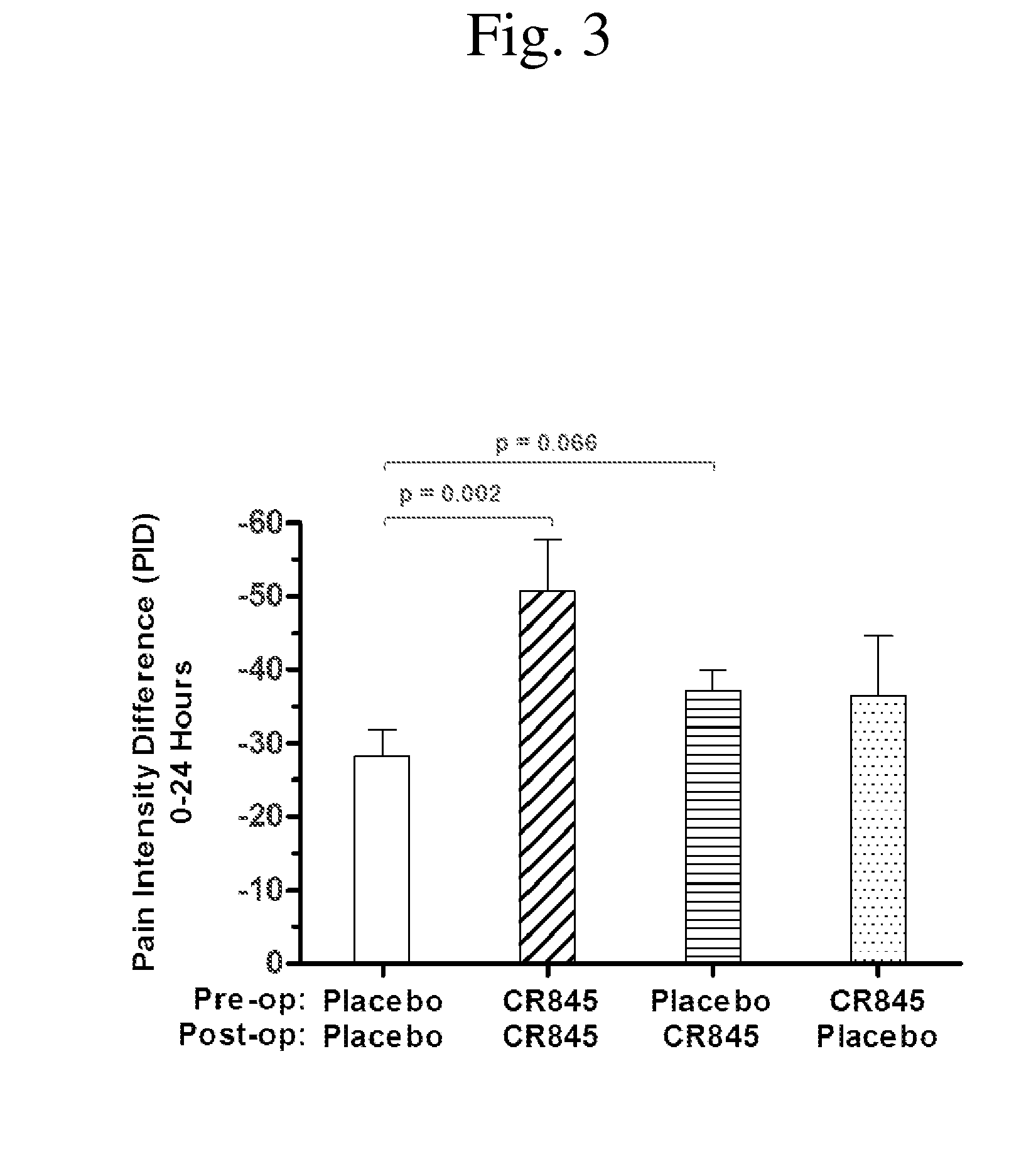
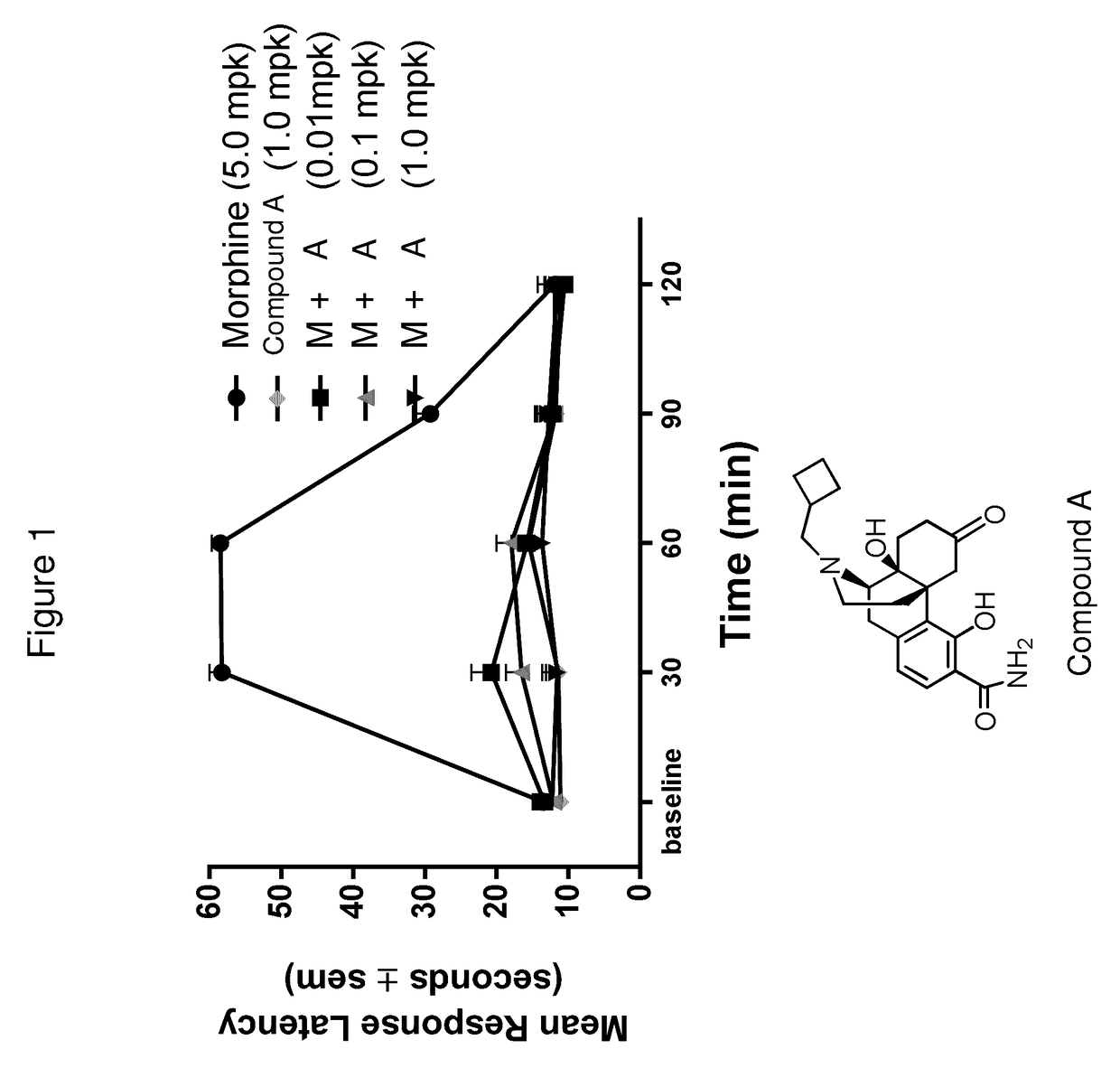
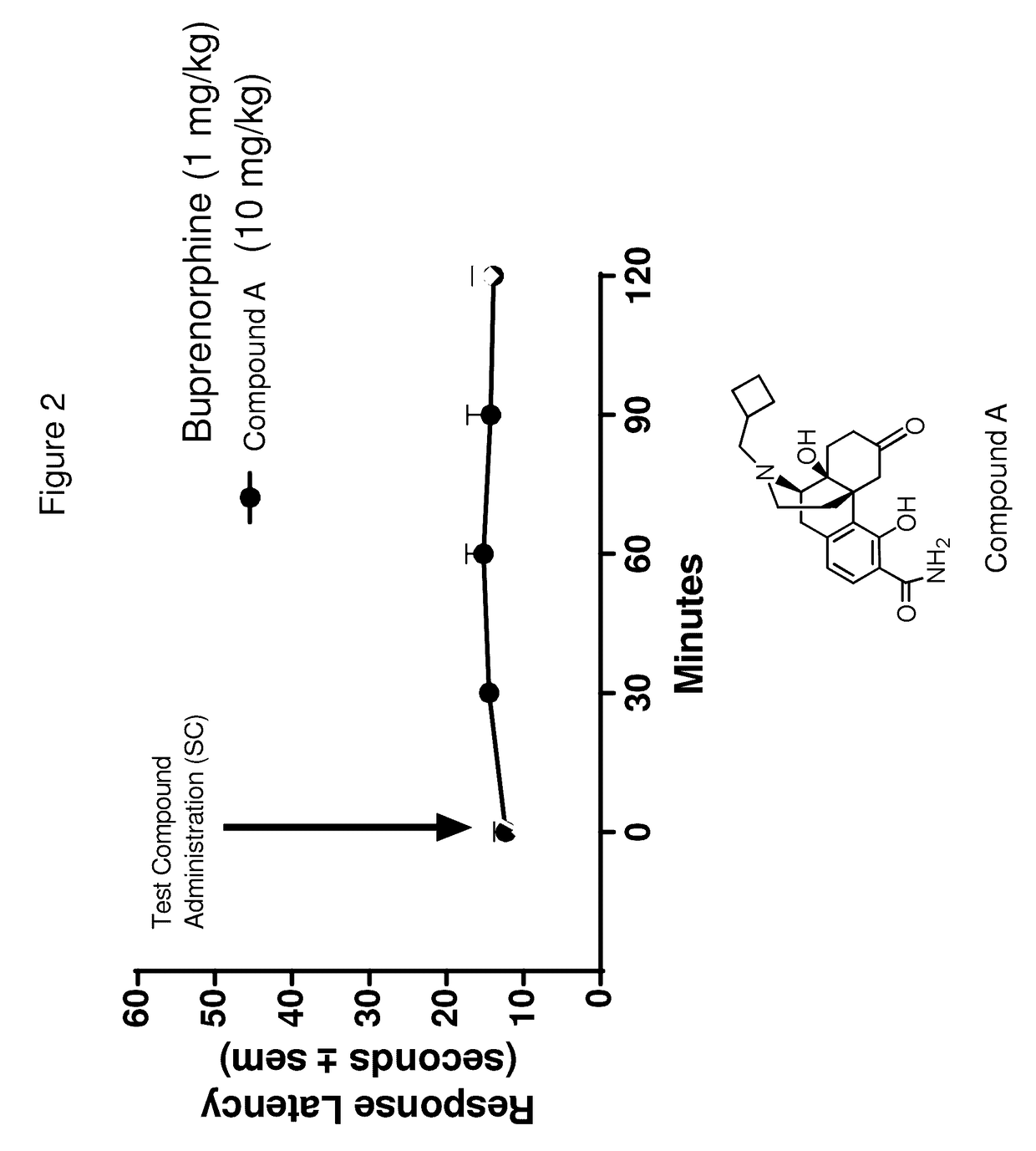
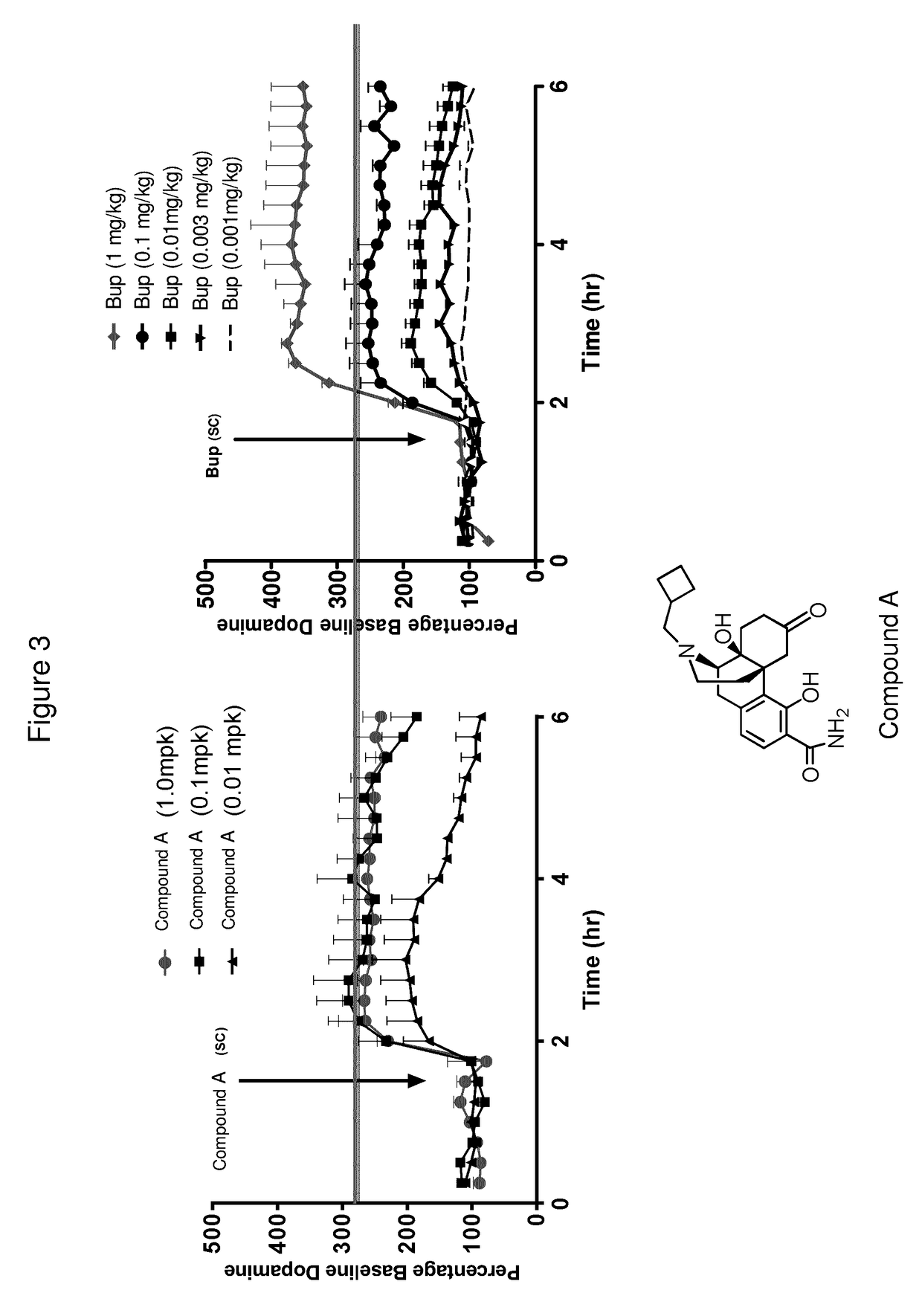
Patents
Literature
152 results about "Opioid Receptor Agonist" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
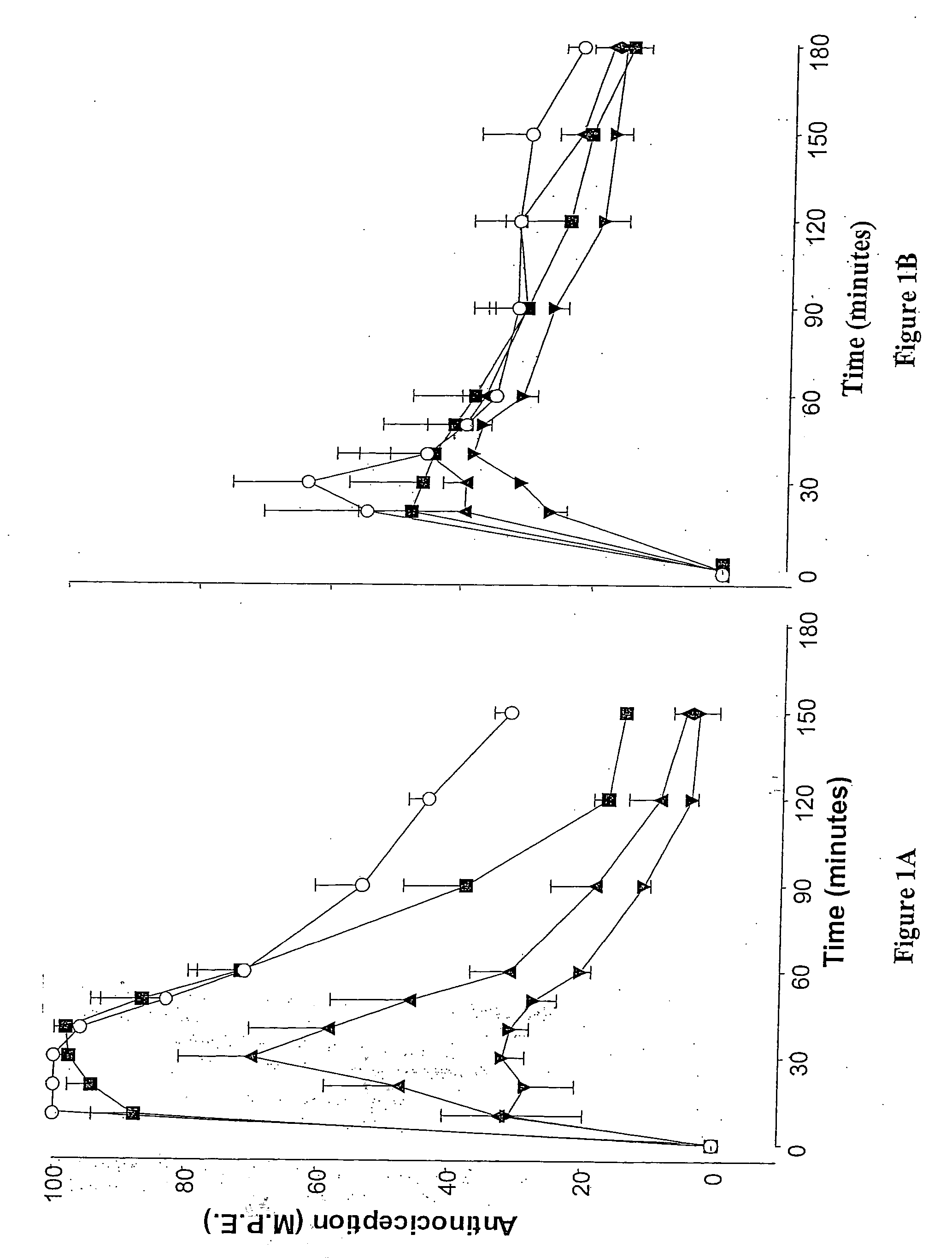
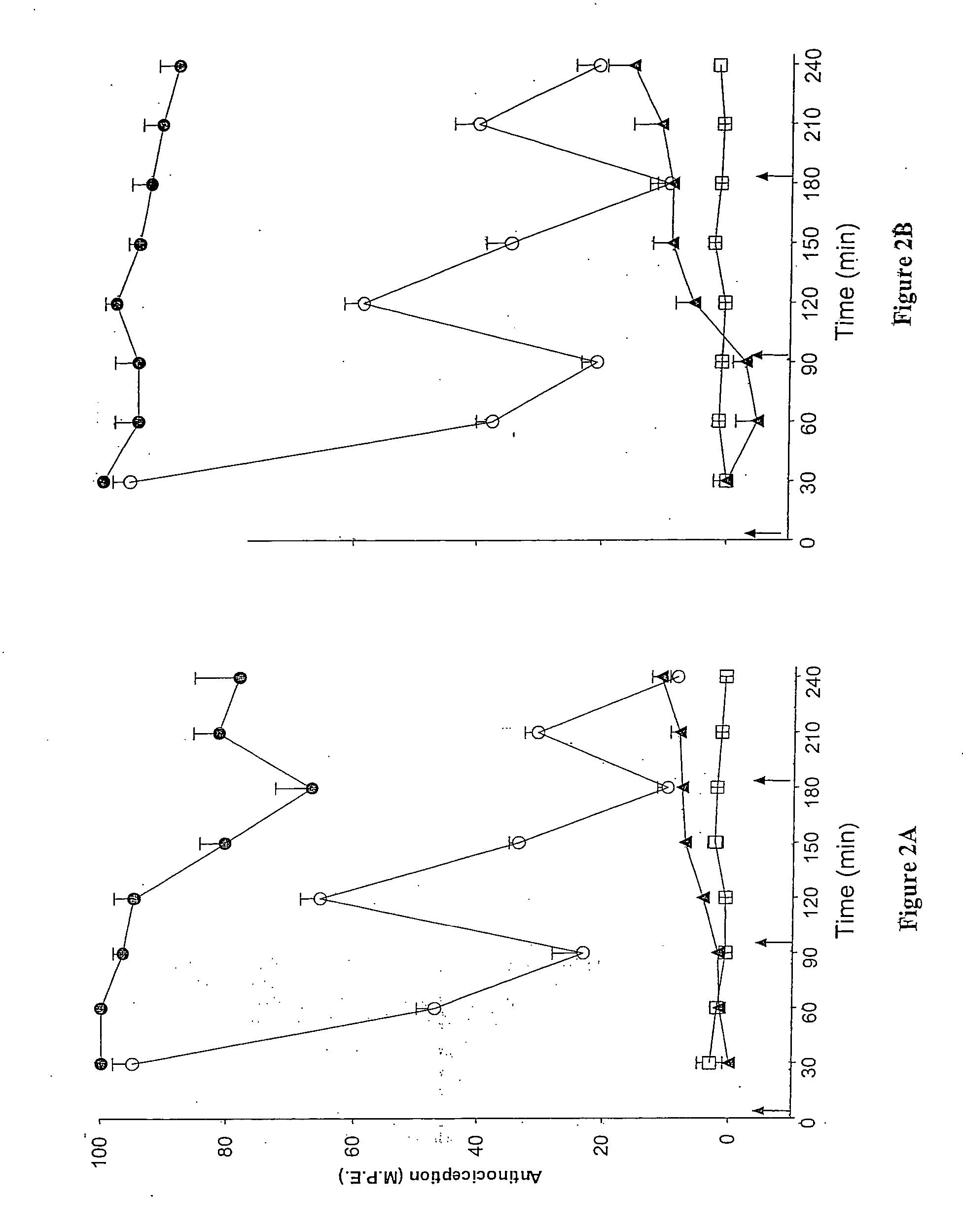
Method of simultaneously enhancing analgesic potency and attenuating dependence liability caused by exogenous and endogenous opioid agonists
InactiveUSRE36547E1Enhance analgesic potencyDecrease dependence liabilityCompound screeningBiocideEndogenous OpiatesNervous system
This invention relates to a method of selectively enhancing the analgesic potency of morphine and other clinically used bimodally-acting opioid agonists and simultaneously attenuating development of physical dependence, tolerance and other undesirable side effects caused by the chronic administration of said bimodally-acting opioid agonists comprising the co-administration of a bimodally-acting opioid agonist which activates both inhibitory and excitatory opioid receptor-mediated functions of neurons in the nociceptive (pain) pathways of the nervous system and an opioid receptor antagonist which selectively inactivates excitatory opioid receptor-mediated side effects. This invention also relates to a method of using excitatory opioid receptor antagonists alone to block the undesirable excitatory side effects of endogenous bimodally-acting opioid agonists which may be markedly elevated during chronic pain. This invention further relates to a method of long-term treatment of previously detoxified opiate, cocaine and alcohol addicts utilizing said excitatory opioid receptor antagonists, either alone or in combination with low-dose methadone, to prevent protracted physical dependence, and to compositions comprising an excitatory opioid receptor antagonist of the invention and a bimodally-acting opioid agonist.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
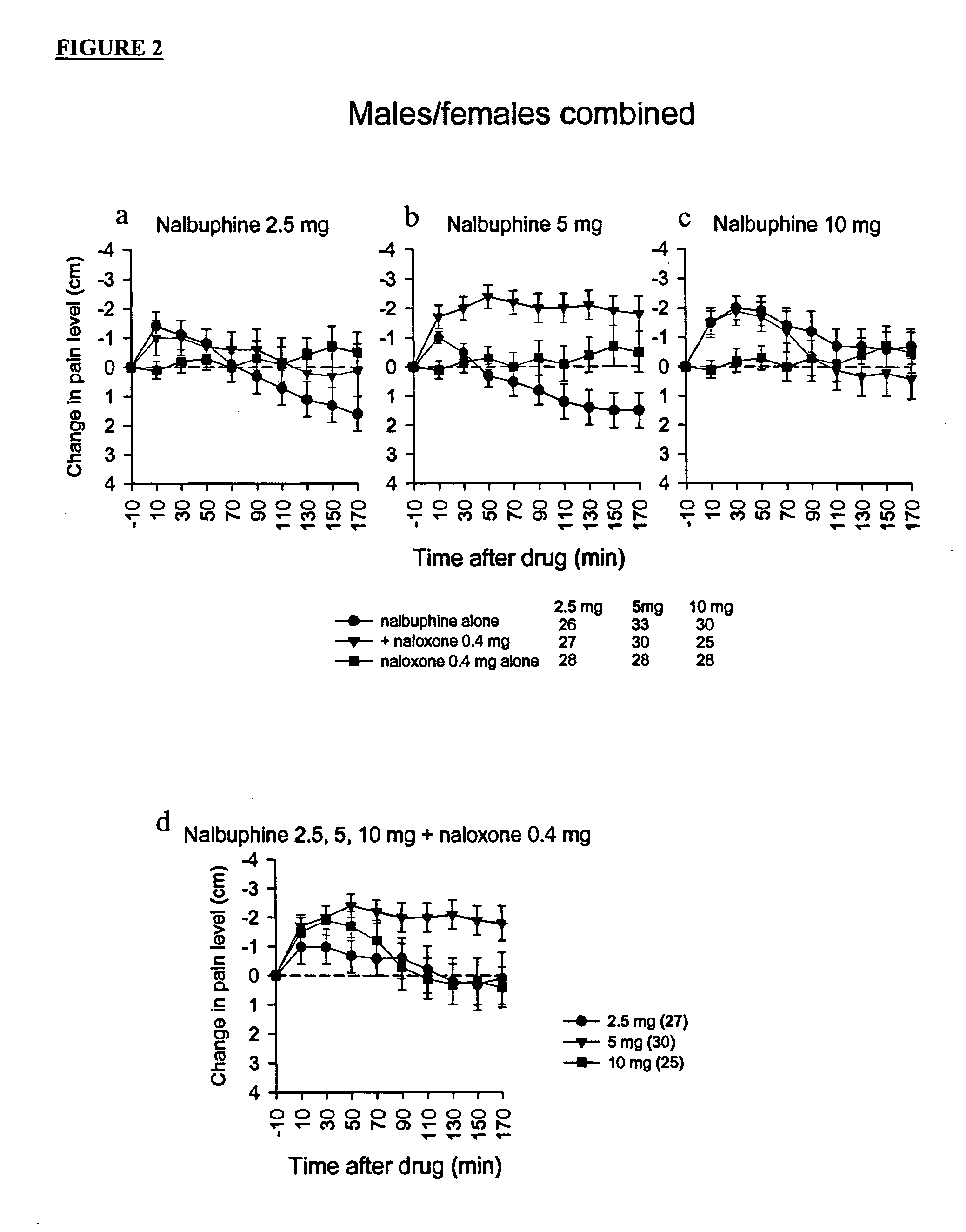
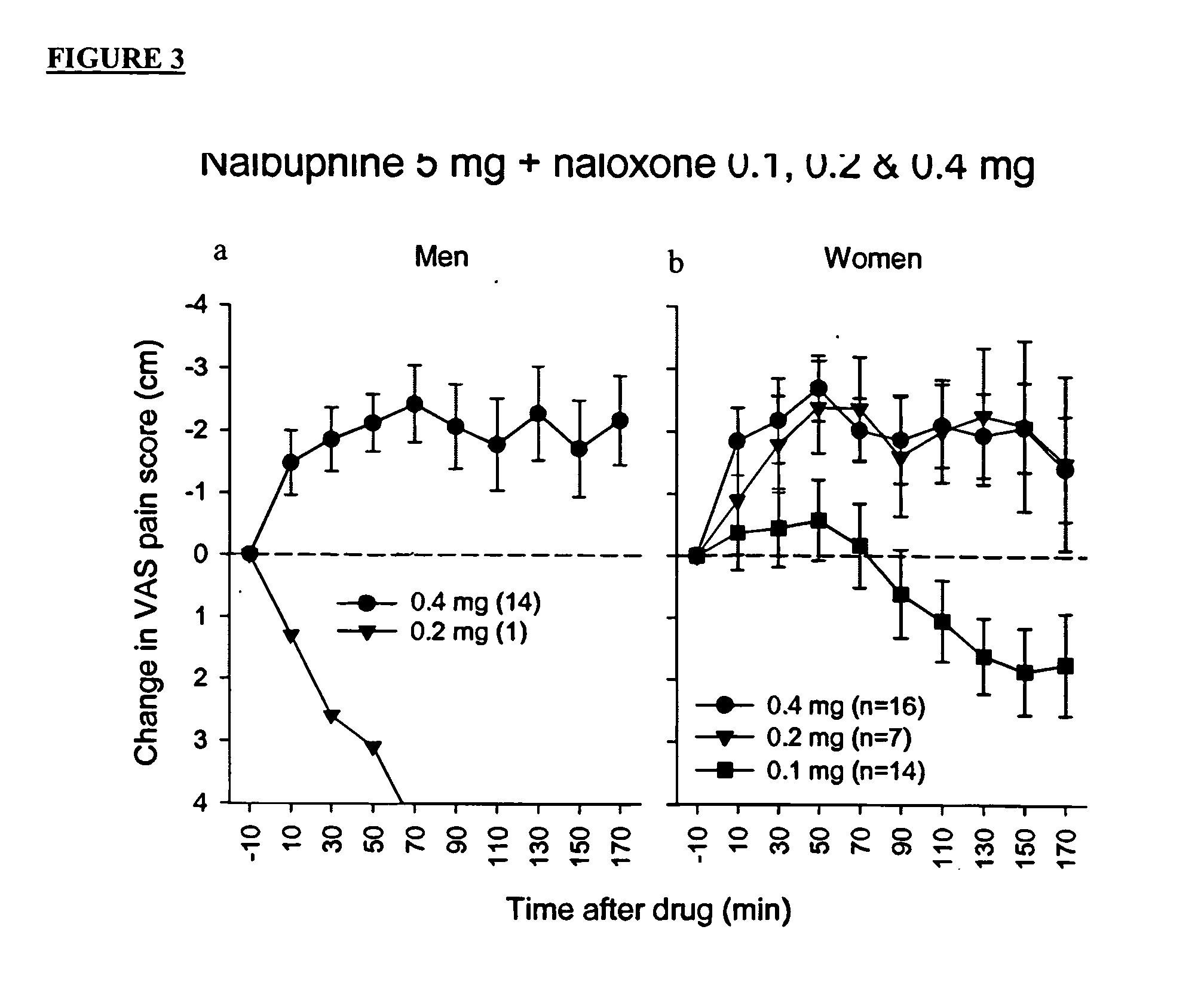
Treatment of pain with combinations of nalbuphine and other kappa-opioid receptor agonists and opioid receptor antagonists
InactiveUS20040180916A1Enhances nalbuphine analgesiaMinimize ToxicityBiocideNervous disorderOpioid antagonistPentazocine
Methods and compositions for treating, managing or ameliorating pain in a subject (preferably, a mammal, and more preferably, a human) comprising administration of a centrally acting (i.e., crosses the blood brain barrier) agonist of a kappa-opioid receptor and a centrally acting opioid antagonist such that the analgesia achieved by this administration is greater than with administration of either the kappa-opioid receptor agonist or the opioid antagonist alone. Preferably the kappa-opioid receptor is nalbuphine or a salt or prodrug of nalbuphine and the opioid antagonist is naloxone or a salt or prodrug of naloxone. Preferred methods of administration include mucosal (e.g. intranasal or pulmonary) and intravenous. Other kappa-opioid receptors include pentazocine and butorphanol.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and therapies for potentiating a therapeutic action of an opioid receptor agonist and inhibiting and/or reversing tolerance to opioid receptor agonists
Combination therapies of an opioid receptor agonist and an alpha-2 receptor antagonist in an amount effective to potentiate, but not antagonize, a therapeutic effect of the opioid receptor agonist are provided. Also provided are methods for use of these combination therapies in potentiating the therapeutic effects of opioid receptor agonists, inhibiting development of acute and / or chronic tolerance to opioid receptor agonists and treating conditions treatable by opioid receptor agonist therapy in a subject. In addition, a method for reversing opioid receptor agonist tolerance and / or restoring therapeutic effect of an opioid receptor agonist in a subject via administration of an alpha-2 receptor antagonist in an amount effective to potentiate, but not antagonize, the therapeutic effect of the opioid receptor agonist is provided.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON
Ischemic preconditioning
InactiveUS6103722AInduce effectAbolished hypotensionBiocideOrganic chemistryCardioprotectionHead injury sequelae
Methods and pharmaceutical compositions of matter are disclosed and claimed relating to cardioprotective effect mediated by delta ( delta ) opioid receptor agonists or more specifically delta-1 ( delta 1)-opioid receptor agonists. Further, methods drawn to reducing ischemic damage to organs and tissues having delta ( delta ) opioid receptor agonists or more specifically delta-1 ( delta 1)-opioid receptors are disclosed and claimed. Specifically, methods and pharmaceutical compositions of matter are taught as a means of providing cardioprotective treatment through the administration of delta ( delta ) opioid receptor agonists or more specifically delta-1 ( delta 1)-opioid receptor agonists, such as TAN67(-). Said methods and pharmaceutical compositions are envisioned as a means of reducing myocardial infarction arising from the onset and sequelae of myocardial ischemia.
Owner:THE MEDICAL COLLEGE OF WISCONSIN INC
Medicinal uses of mu-opioid receptor agonists
ActiveUS7498297B2Reduce intensityControl rateAntipyreticAnalgesicsDiseaseMu-Opioid Receptor Agonists
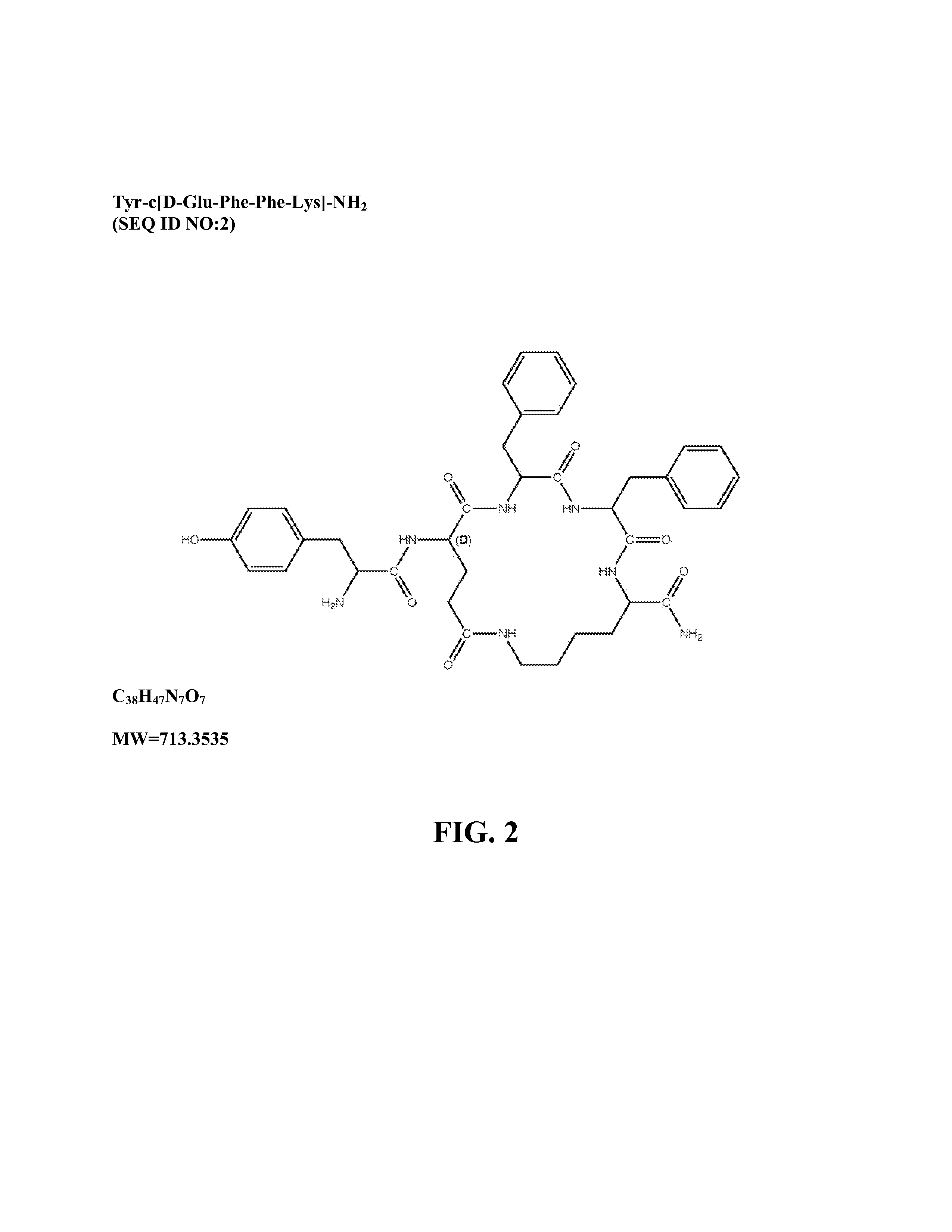
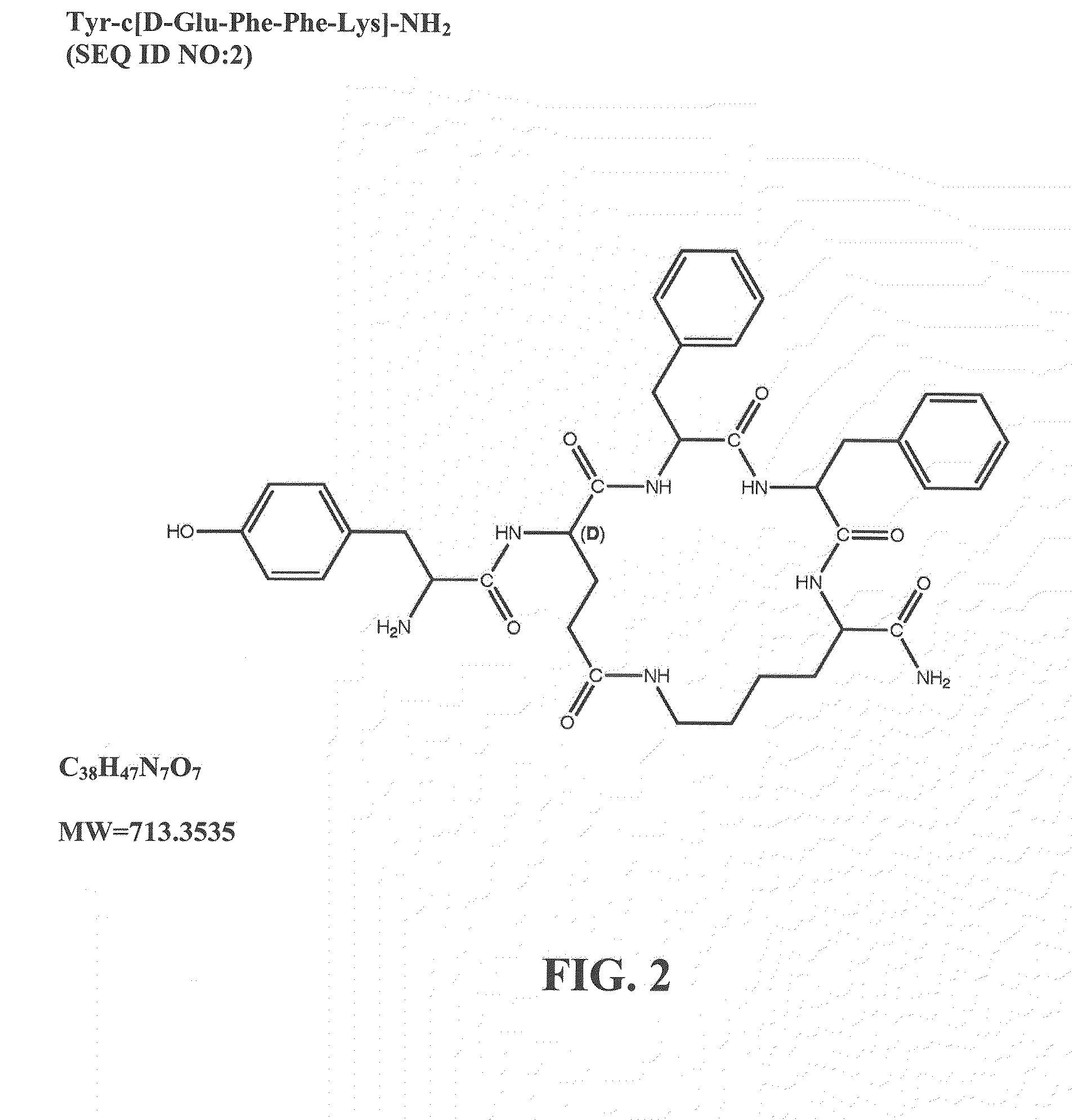
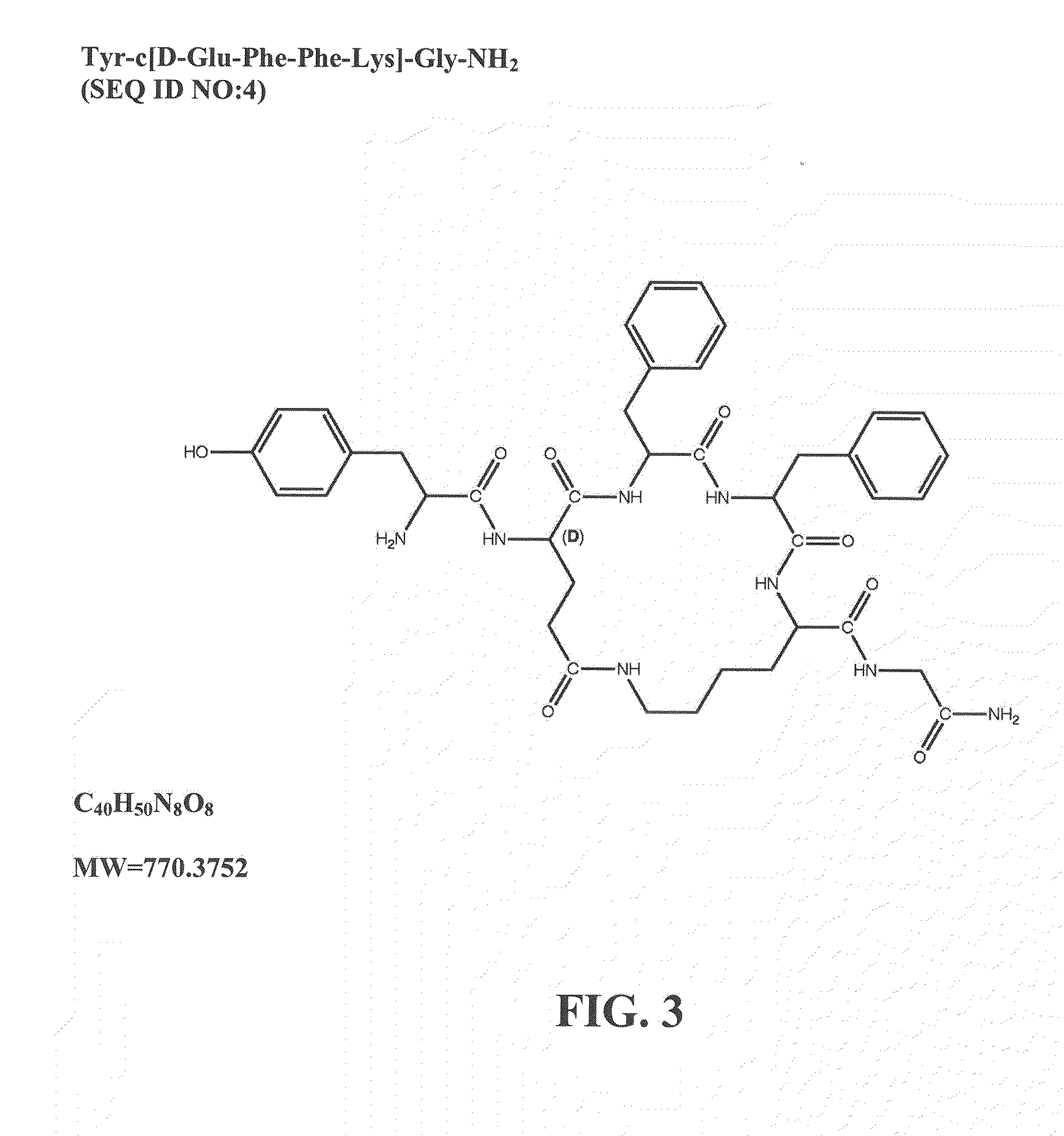
The present invention provides methods for stimulating a mu-opioid receptor agonist peptide in a mammal in need thereof. The methods comprise administering to the mammal an effective amount of a selective mu-opioid receptor agonist peptide that comprises at least two α-amino acid residues. At least one of the amino acid residues has a positive charge. The amino acid residue in the first position is a tyrosine or tyrosine derivative. The amino acid in the second position is a D-α-amino acid. The present invention also provides methods of treating a mammal suffering from conditions or diseases by administering to the mammal an effective amount of the peptides.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Opioid agonist antagonist combinations
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
Opioid agonist in a fast dispersing dosage form
InactiveUS7090866B2Act quicklyMinimizing side-effectsBiocidePowder deliveryPremedicationTranquilizing Agents
This invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for oral administration comprising a carrier and, as active ingredient, an opioid (μ receptor) agonist, such as fentanyl, or a salt thereof, characterized in that the composition is in the form of a fast-dispersing dosage form designed to release the active ingredient rapidly in the oral cavity. A process for preparing such a composition and the use of such a composition as an analgesic, for the treatment of chronic pain and / or breakthrough pain, as an anesthetic premedication, for the induction of anesthesia, as a sedative and / or for the treatment of anxiety are also provided.
Owner:CATALENT USA WOODSTOCK INC +3
Medicinal Uses of Mu-Opioid Receptor Agonists
InactiveUS20070027070A1Reduce intensityControl rateOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMu-Opioid Receptor AgonistsMedicine
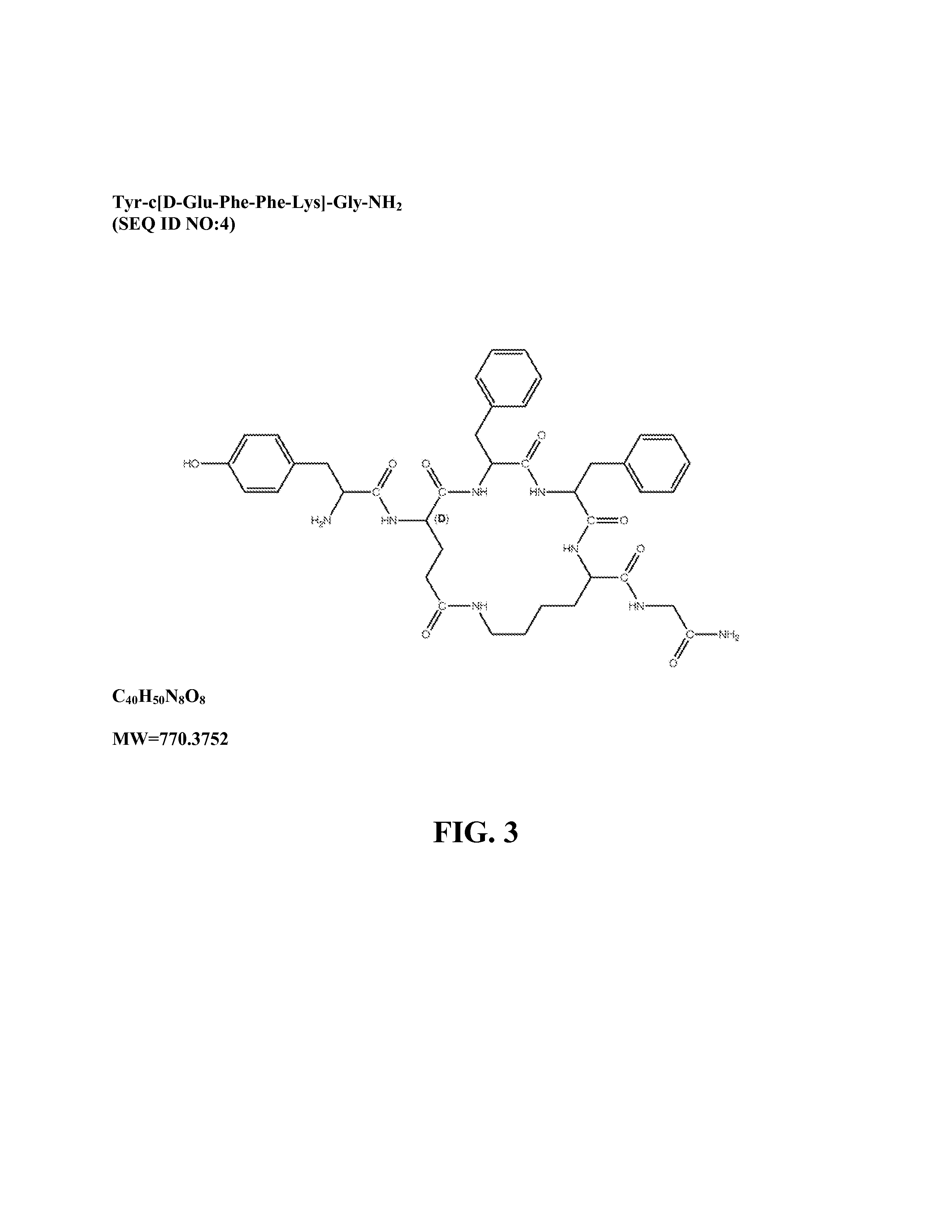
The present invention provides methods for stimulating mu-opioid receptors with agonist peptides in a mammal in need thereof. The methods comprise administering to the mammal an effective amount of a selective mu-opioid receptor agonist peptide that comprises at least two α-amino acid residues. At least one of the amino acid residues has a positive charge. The amino acid residue in the first position is a tyrosine or tyrosine derivative. The amino acid in the second position is a D-α-amino acid. The present invention also provides methods of treating a mammal suffering from conditions or diseases by administering to the mammal an effective amount of the peptides.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Oligomer-opioid agonist conjugates
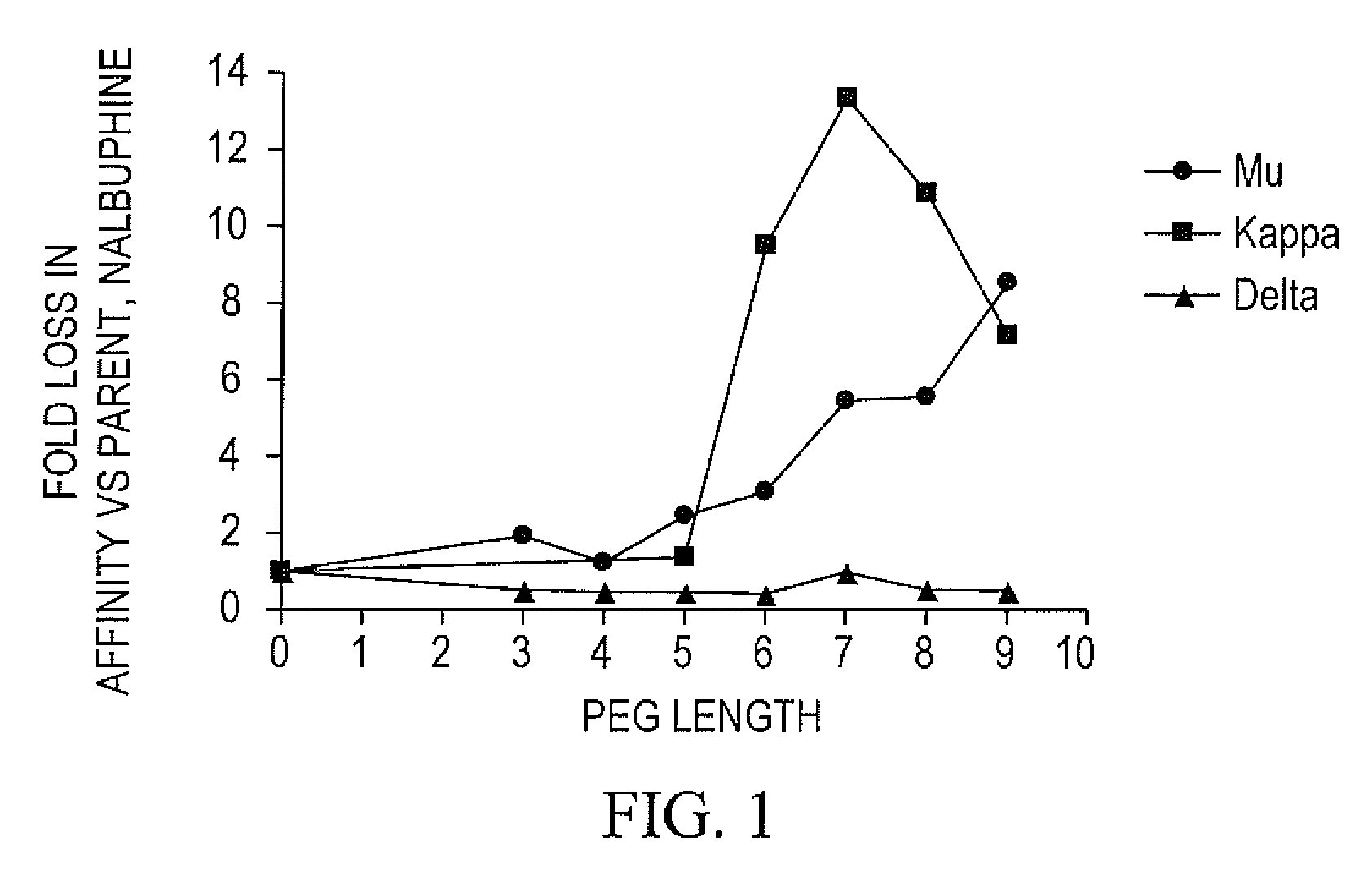
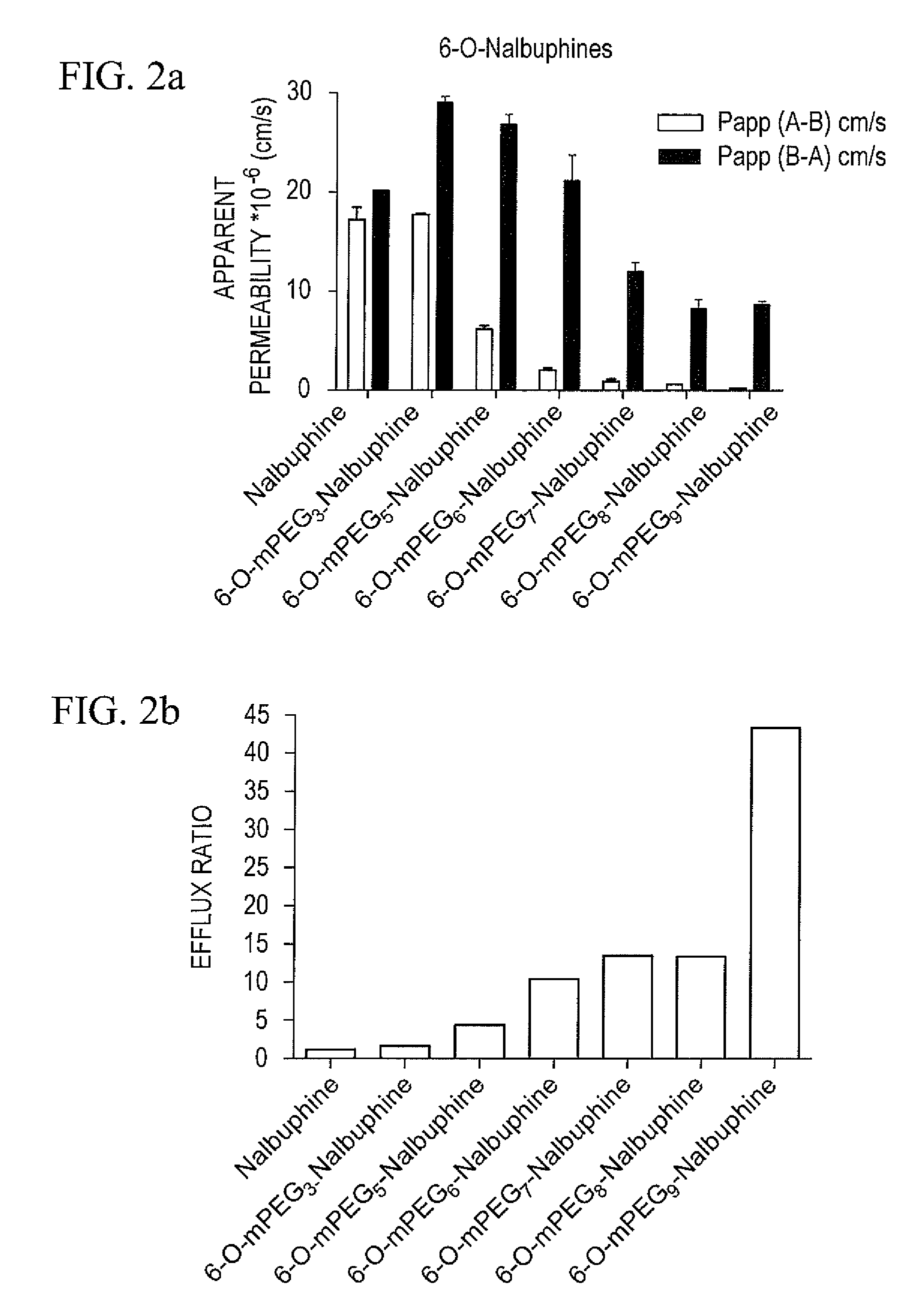
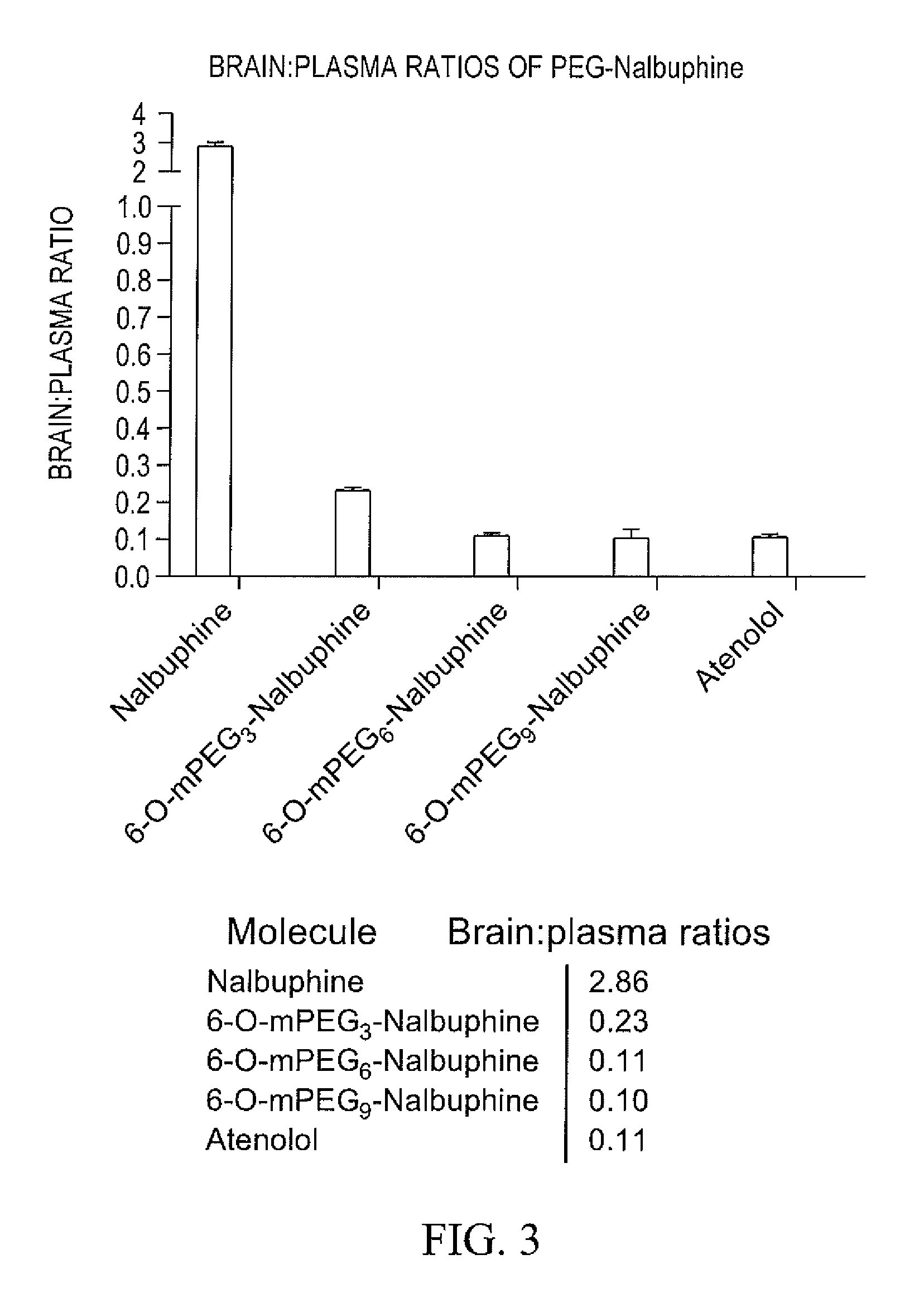
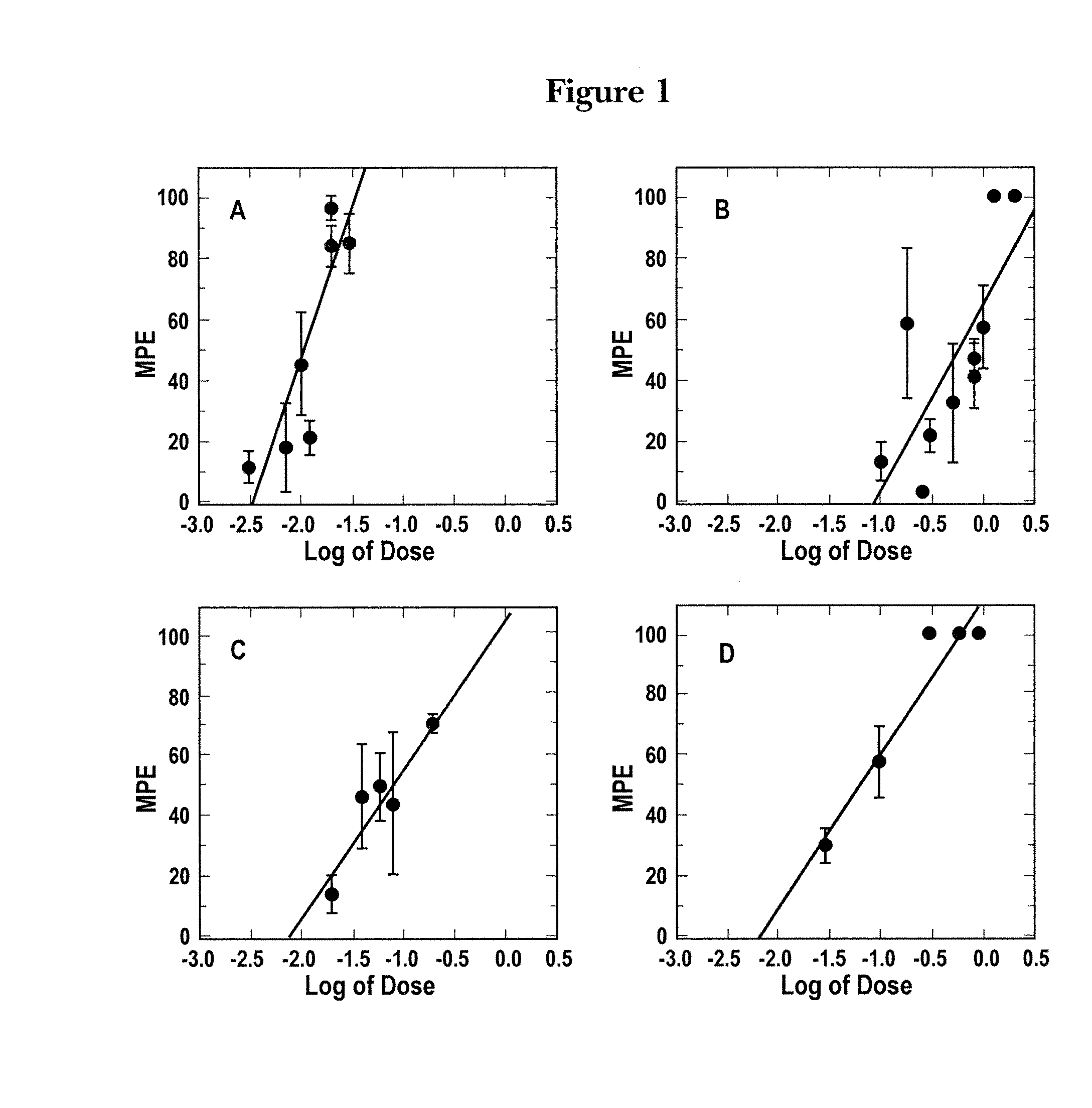
The invention provides compounds that are chemically modified by covalent attachment of a water-soluble oligomer. A compound of the invention, when administered by any of a number of administration routes, exhibits characteristics that are different from those of the compound not attached to the water-soluble oligomer.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods of Reducing Side Effects of Analgesics
InactiveUS20100227876A1Decreased gastrointestinal motilityReduce resistanceBiocideAnimal repellantsMu-Opioid Receptor AgonistsSide effect
The invention provides for compositions and methods of reducing pain in a subject by administering a combination of mu-opioid receptor agonist, kappa1-opioid receptor agonist and a nonselective opioid receptor antagonist in amounts effective to reduce pain and ameliorate an adverse side effect of treatment combining opioid-receptor agonists. The invention also provides for methods of enhancing an analgesic effect of treatment with an opioid-receptor agonist in a subject suffering from pain while reducing an adverse side effect of the treatment. The invention also provides for methods of reducing the hyperalgesic effect of treatment with an opioid-receptor agonist in a subject suffering from pain while reducing an adverse side effect of the treatment. The invention further provides for methods of promoting the additive analgesia of pain treatment with an opioid-receptor agonist in a subject in need while reducing an adverse side effect of the treatment.
Owner:RECHFENSEN
Pharmaceutical Composition Comprising Opioid Agonist And Sequestered Antagonist
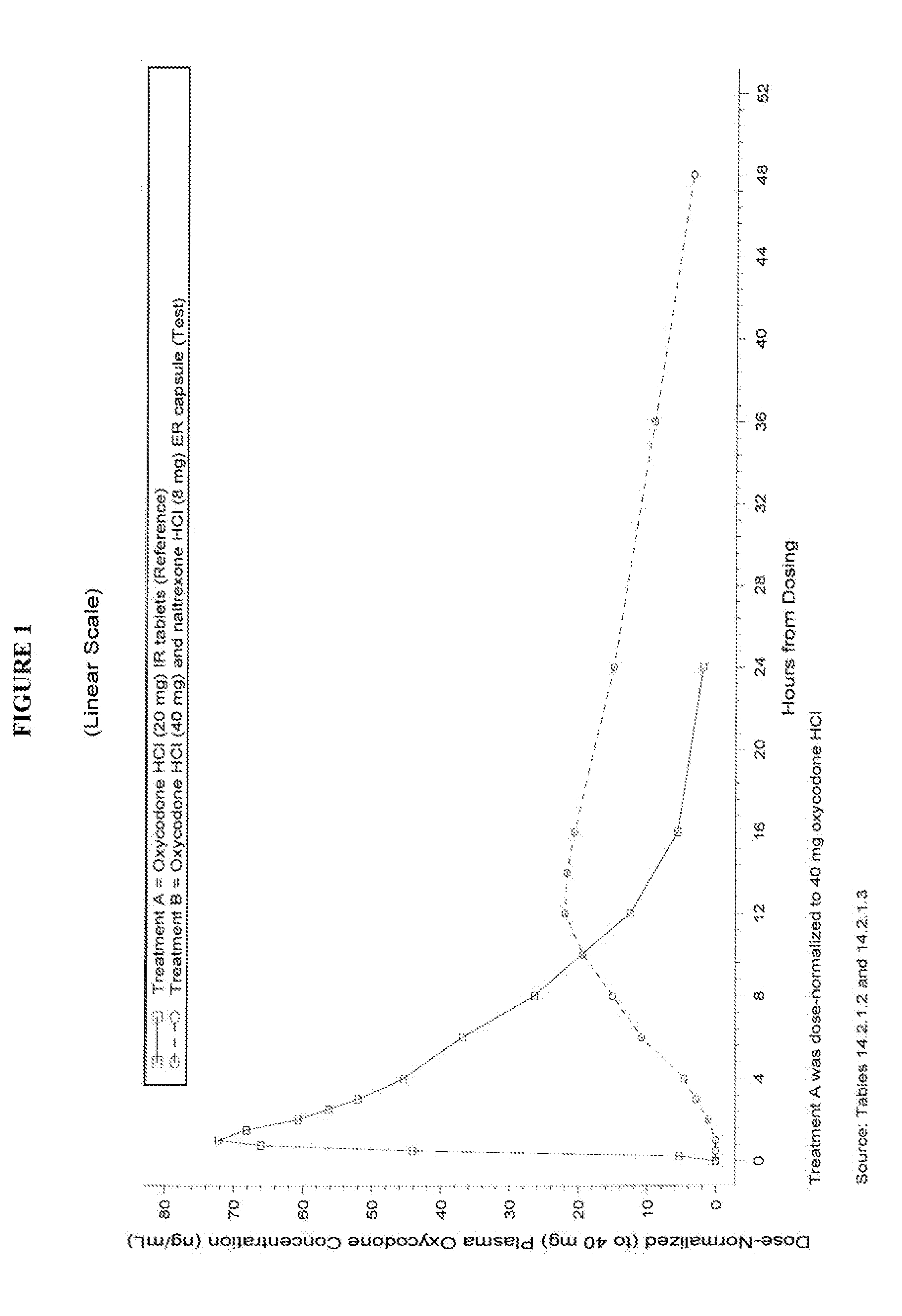
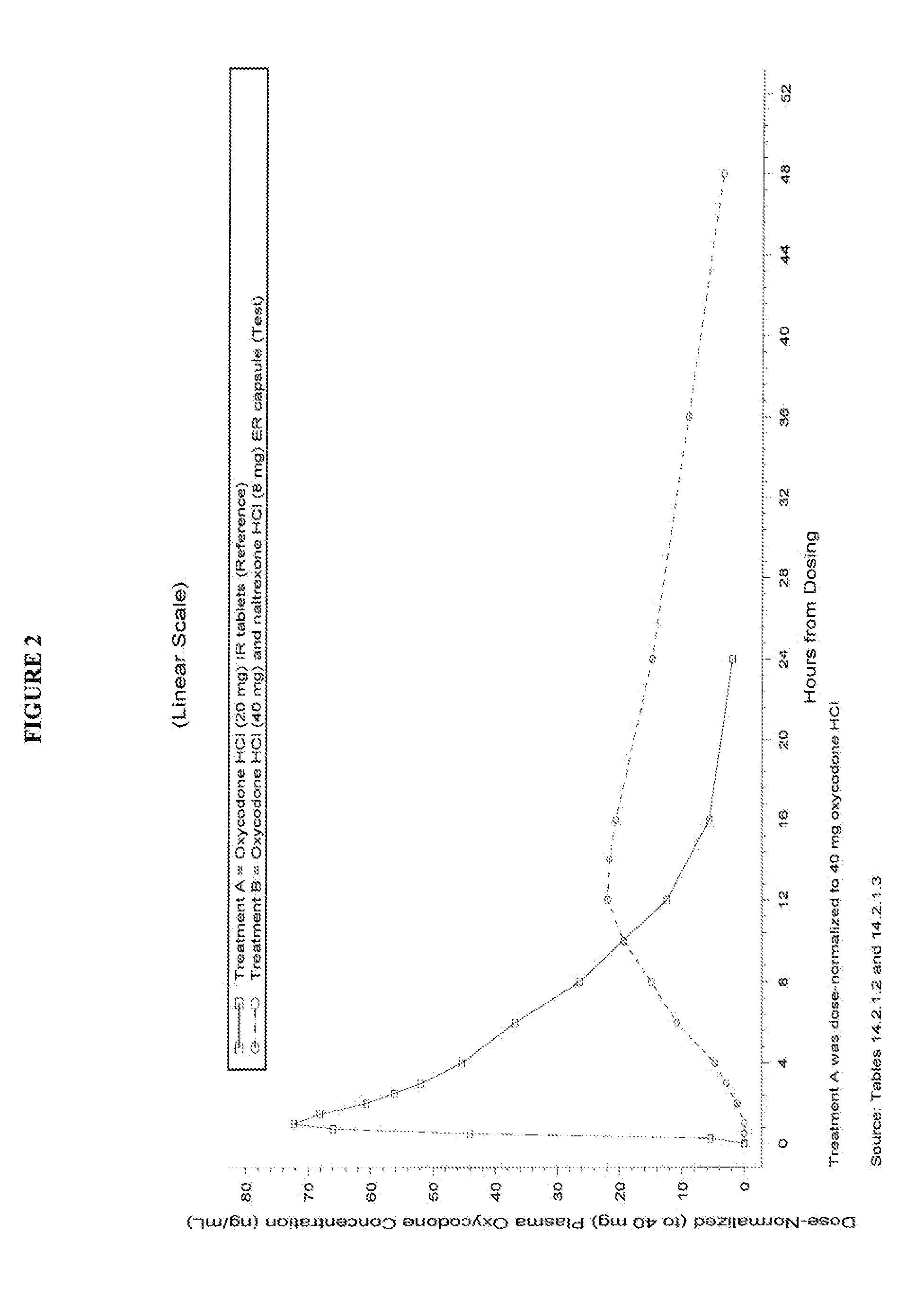
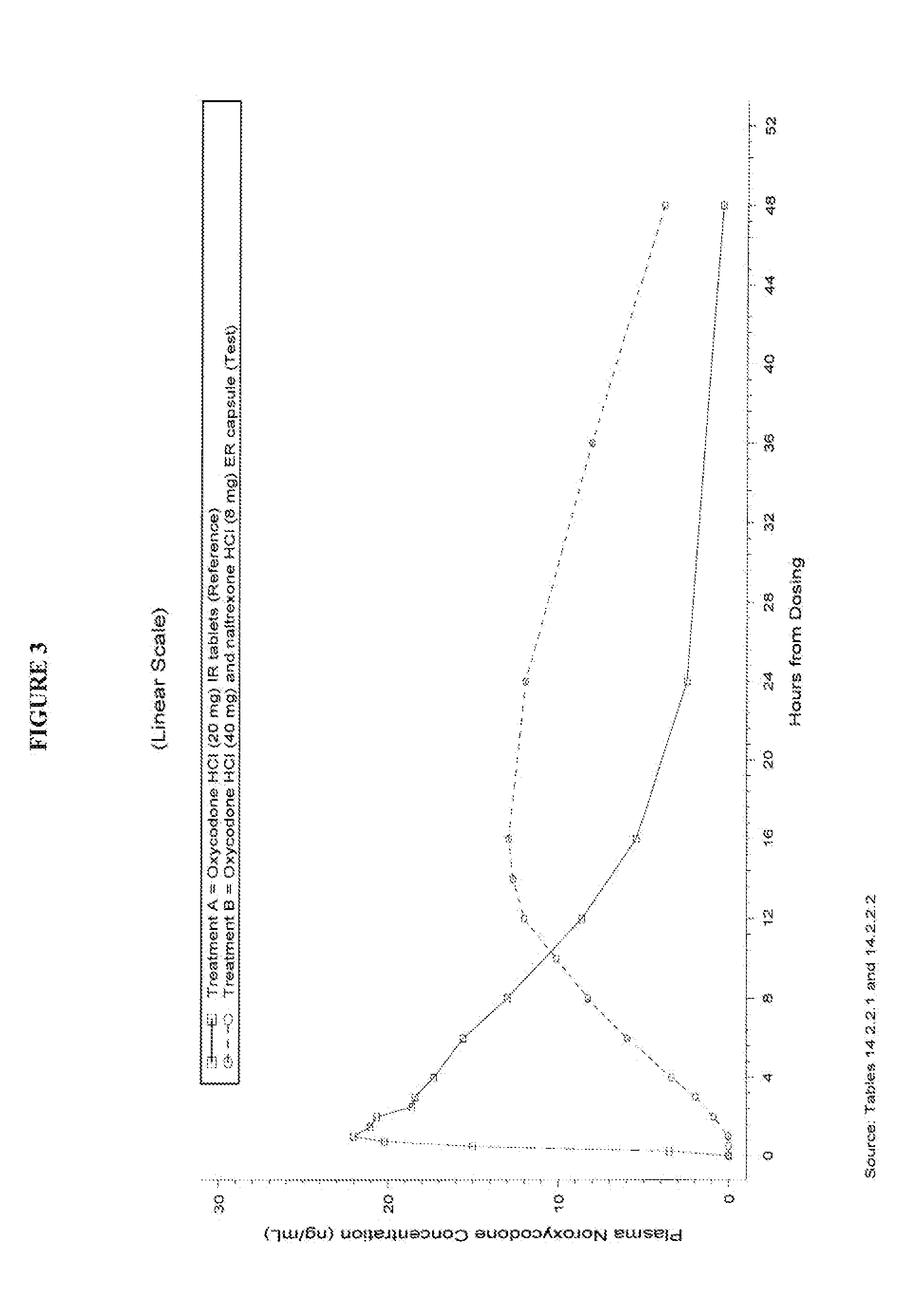
This invention pertains to pharmaceutical composition comprising a plurality of multi-layered beads having an oxycodone layer and a sequestering subunit comprising a naltrexone and a blocking agent, in particular pharmaceutical compositions comprising a higher level of naltrexone, and related compositions and methods of use, such as in the prevention of abuse of a therapeutic agent. The compositions of the present invention also have a long Tmax for oxycodone release and a flatter release profile of oxycodone over time.
Owner:WILSON EDWARD S
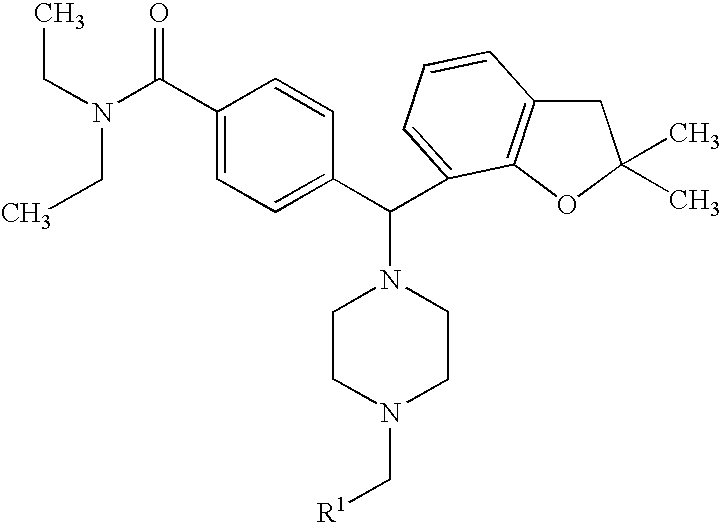
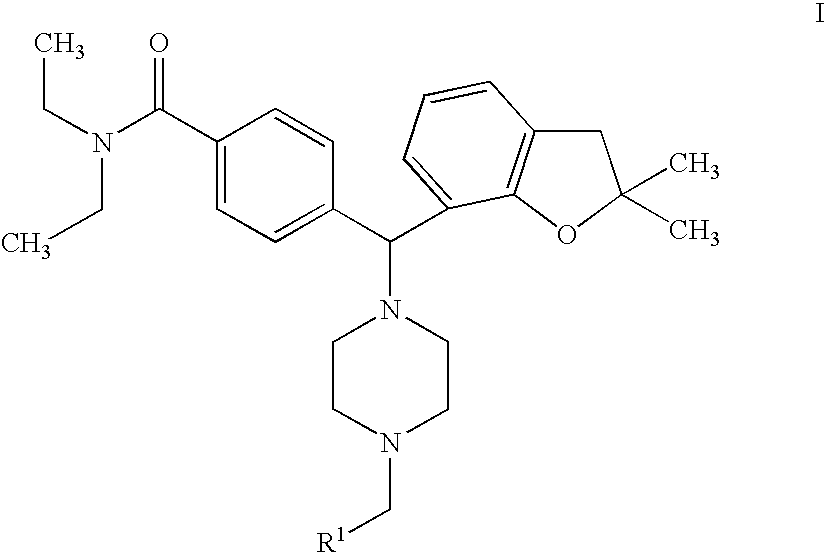
Piperazinomethylbenzamides as delta-opioid receptor agonists
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
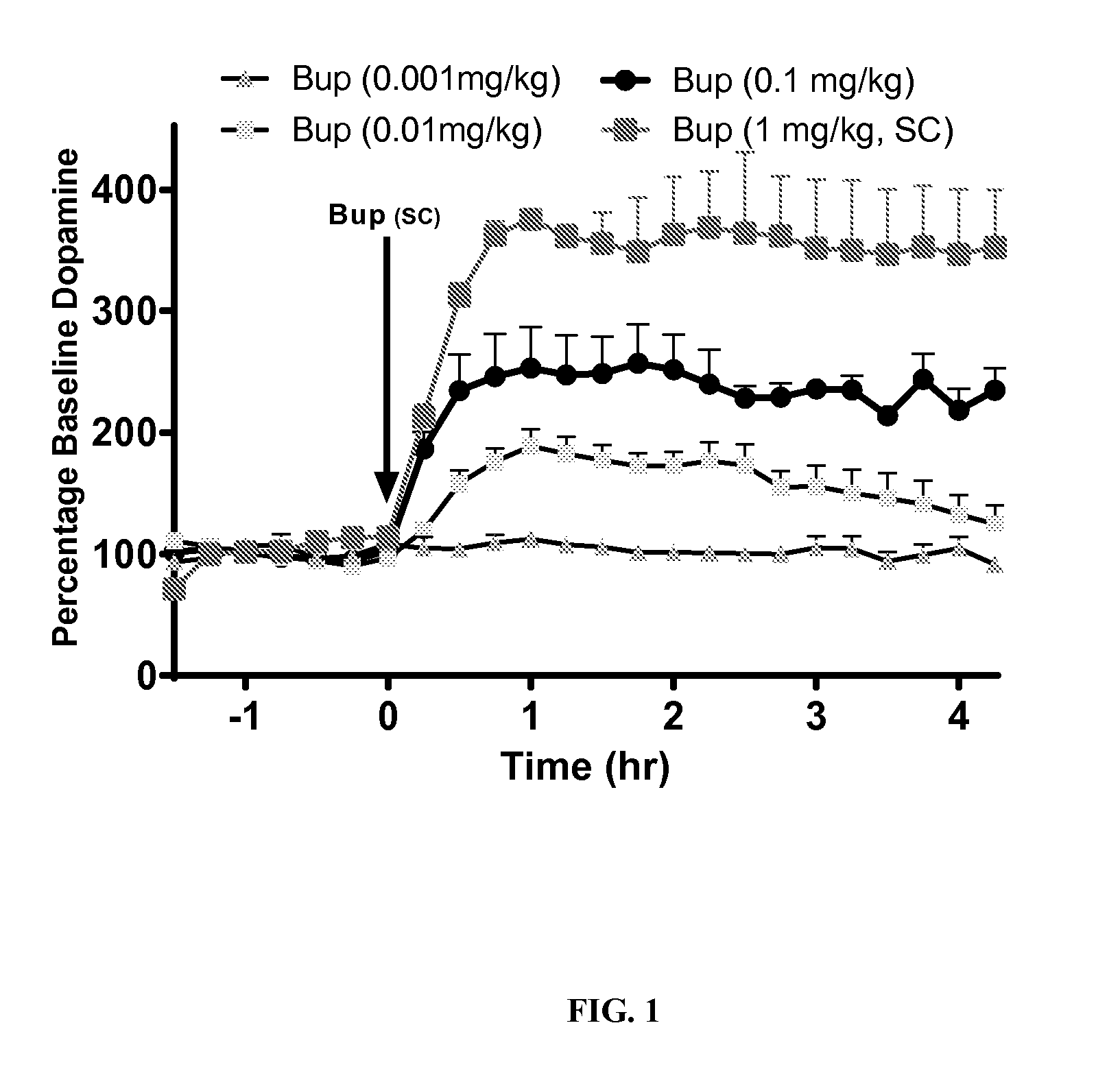
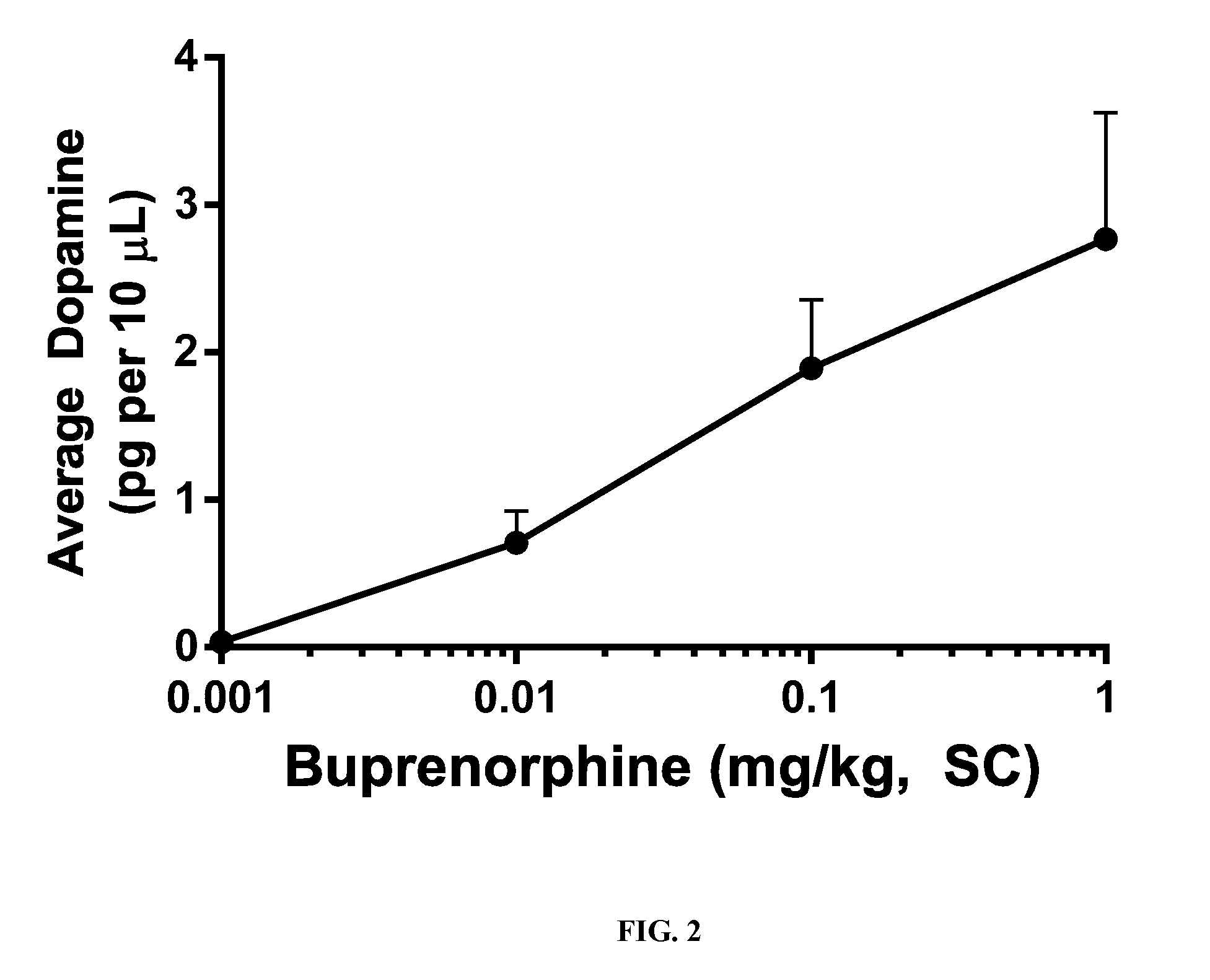
Composition Comprising a Therapeutic Agent and a Respiratory Stimulant and Methods for the Use Thereof
The present disclosure provides a safe method for anesthesia or the treatment of pain by safely administering an amount of active agent to a patient while reducing the incidence or severity of suppressed respiration. The present disclosure provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutic agent and a chemoreceptor respiratory stimulant. In one aspect, the compositions oppose effects of respiratory suppressants by combining a chemoreceptor respiratory stimulant with an opioid receptor agonist or other respiratory-depressing drug. The combination of the two chemical agents, that is, the therapeutic agent and the respiratory stimulant, may be herein described as the “drugs.” The present compositions may be used to treat acute and chronic pain, sleep apnea, and other conditions, leaving only non-lethal side effects.
Owner:HSU JOHN
Cardioprotective delta opioid receptor agonists and methods of using same
The present invention relates to compositions and methods of treatment for cardioprotection through the use of non-peptidic delta opioid receptor agonist compound(s) that mediate cardioprotective effects of ischemic preconditioning. The compounds are used to reduce injury associated with ischemia and reperfusion of cardiac tissue. Further, the compounds may be used in solutions preserving the viability of an isolated organ.
Owner:DMK PHARM CORP +1
Methods for Treating Depressive Symptoms
The present application relates methods for treating a depressive symptom comprising administering an effective amount of a μ opioid receptor agonist or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof to a subject in need thereof. Non-limiting examples of such agonist include the compounds of Formulas I, II, III, and IV, as well as the compounds of Table A.
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
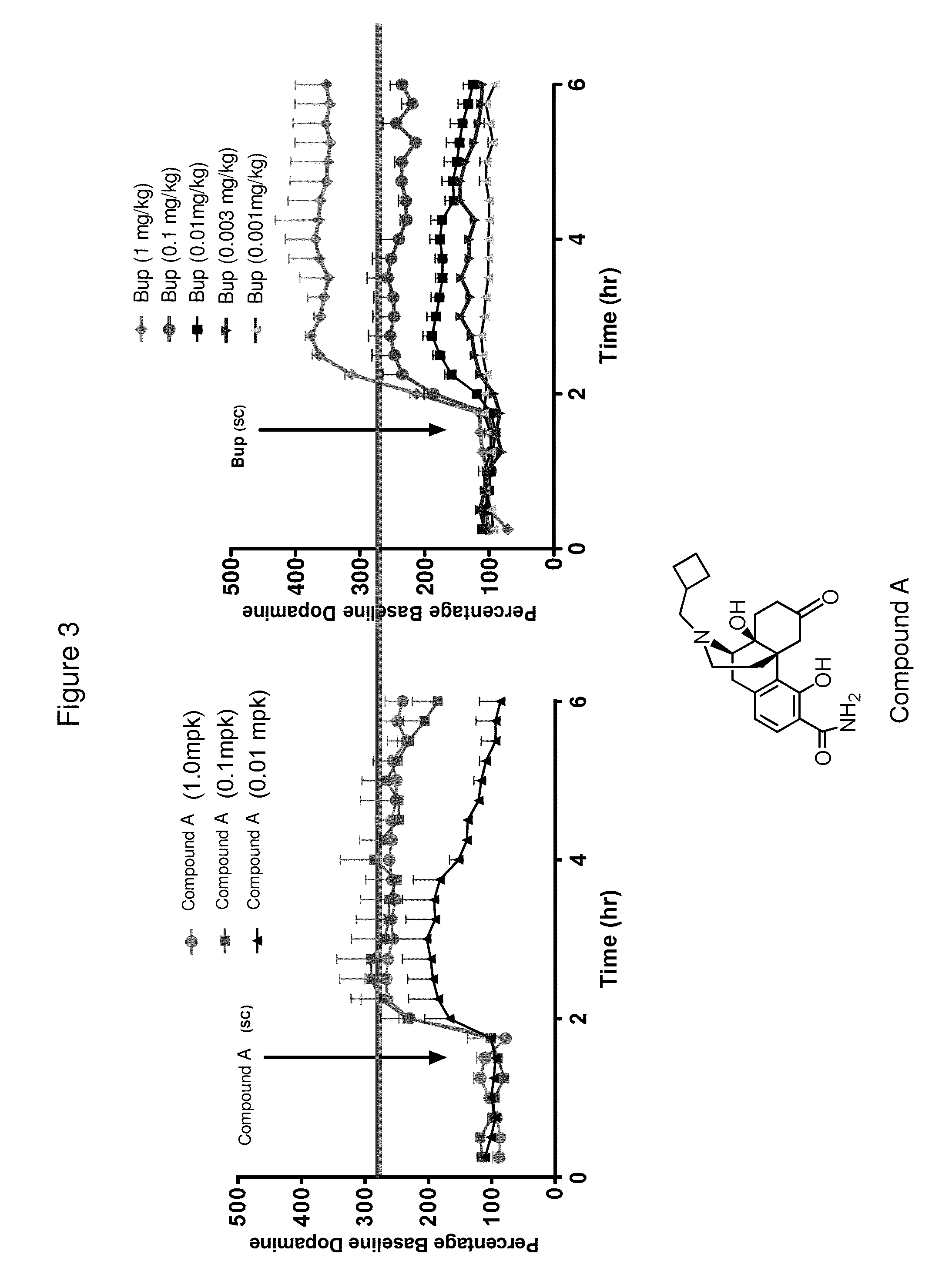
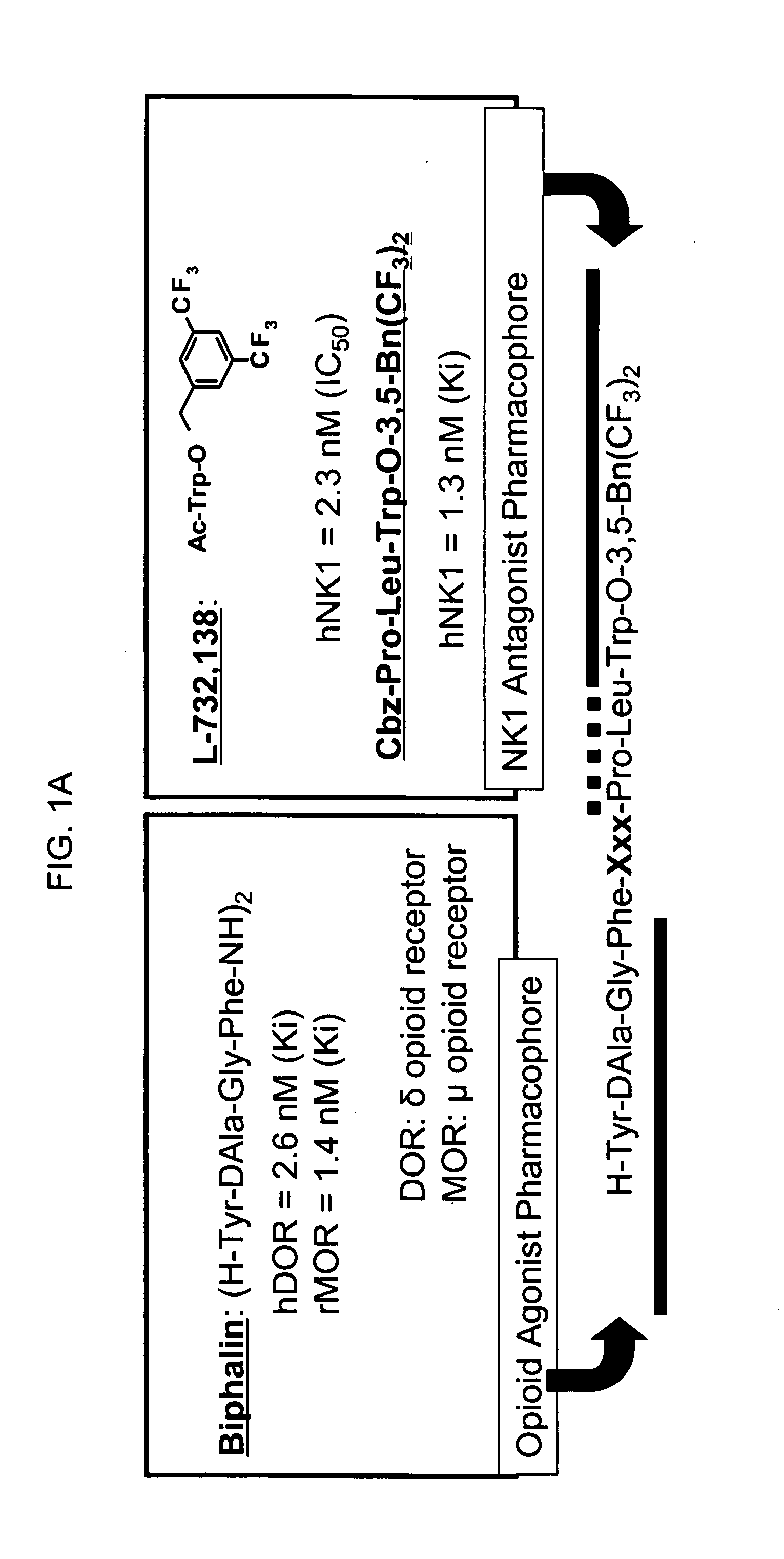
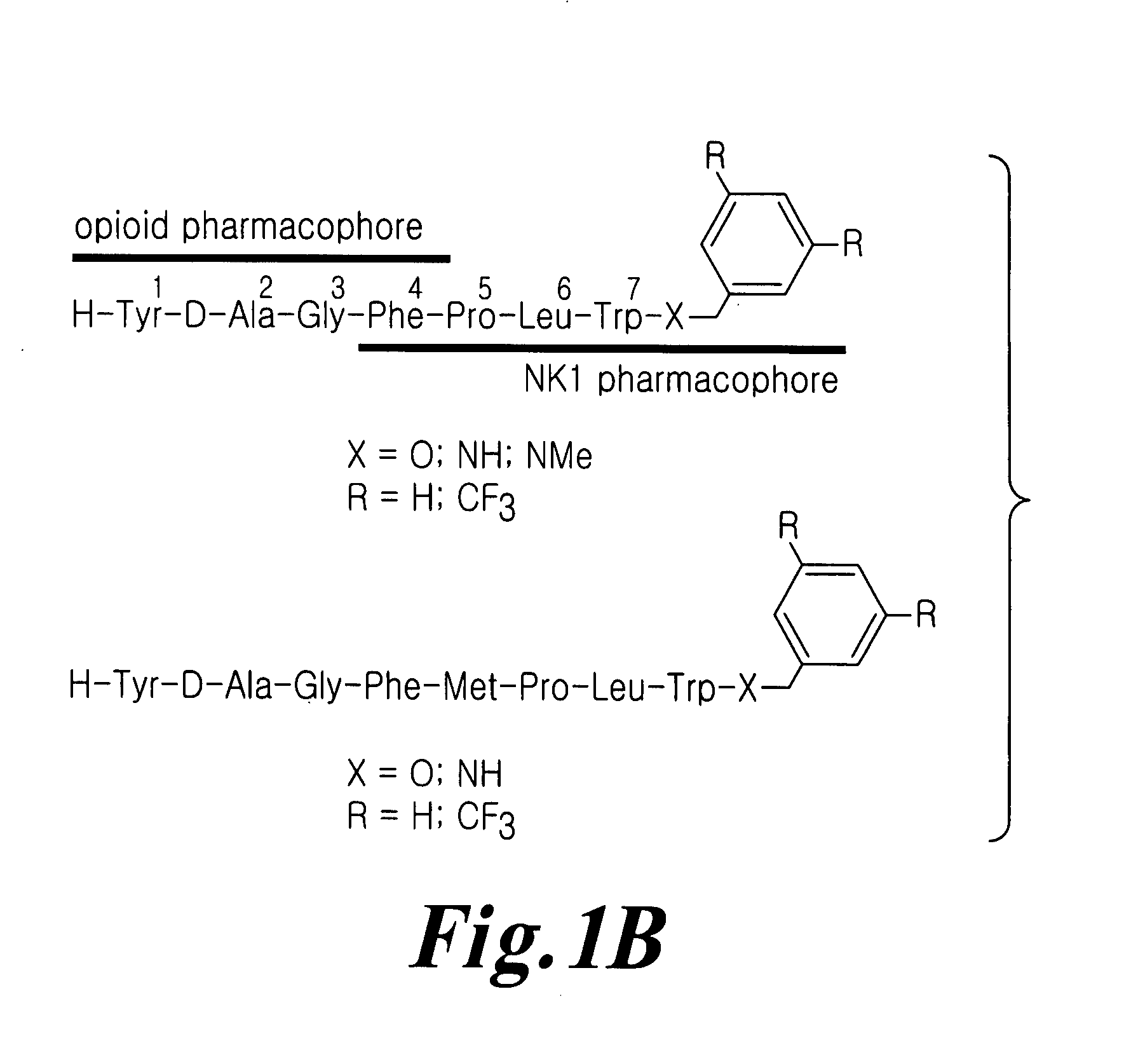
Bifunctional analgesic compounds for opioid receptor agonists and neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists
InactiveUS20080039404A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNeurokinin-1 Receptor AntagonistsC-terminus
The present invention provides a novel chimeric compound comprising an agonist opioid receptor binding moiety at its N-terminus and an antagonist neurokinin-1 (NK1) receptor binding moiety at its C-terminus for producing analgesia, a pharmaceutical composition comprising the chimeric compound, a method of making the compound, and a method of treating pain using the novel chimeric compounds.
Owner:UNIV ARIZONA
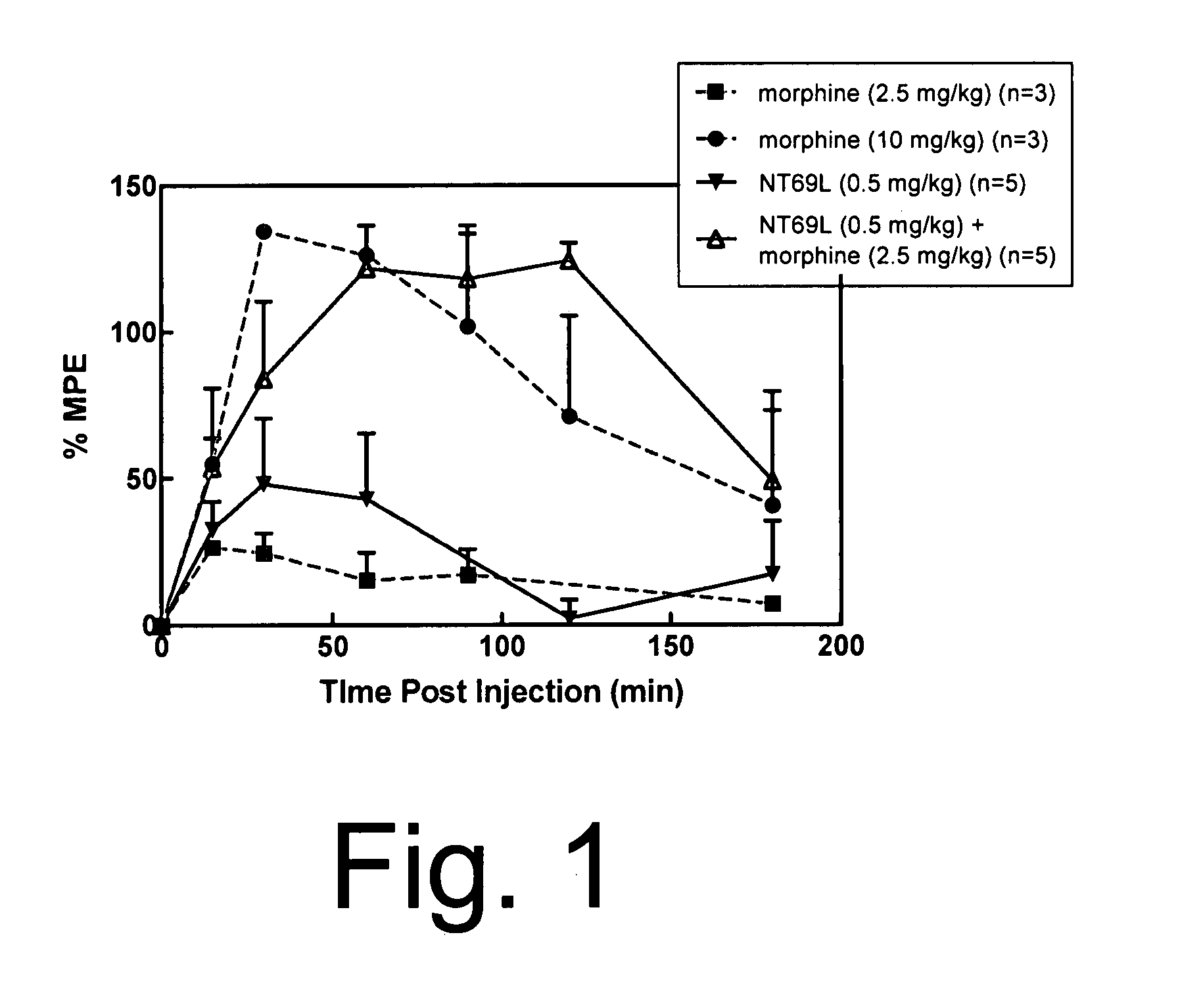
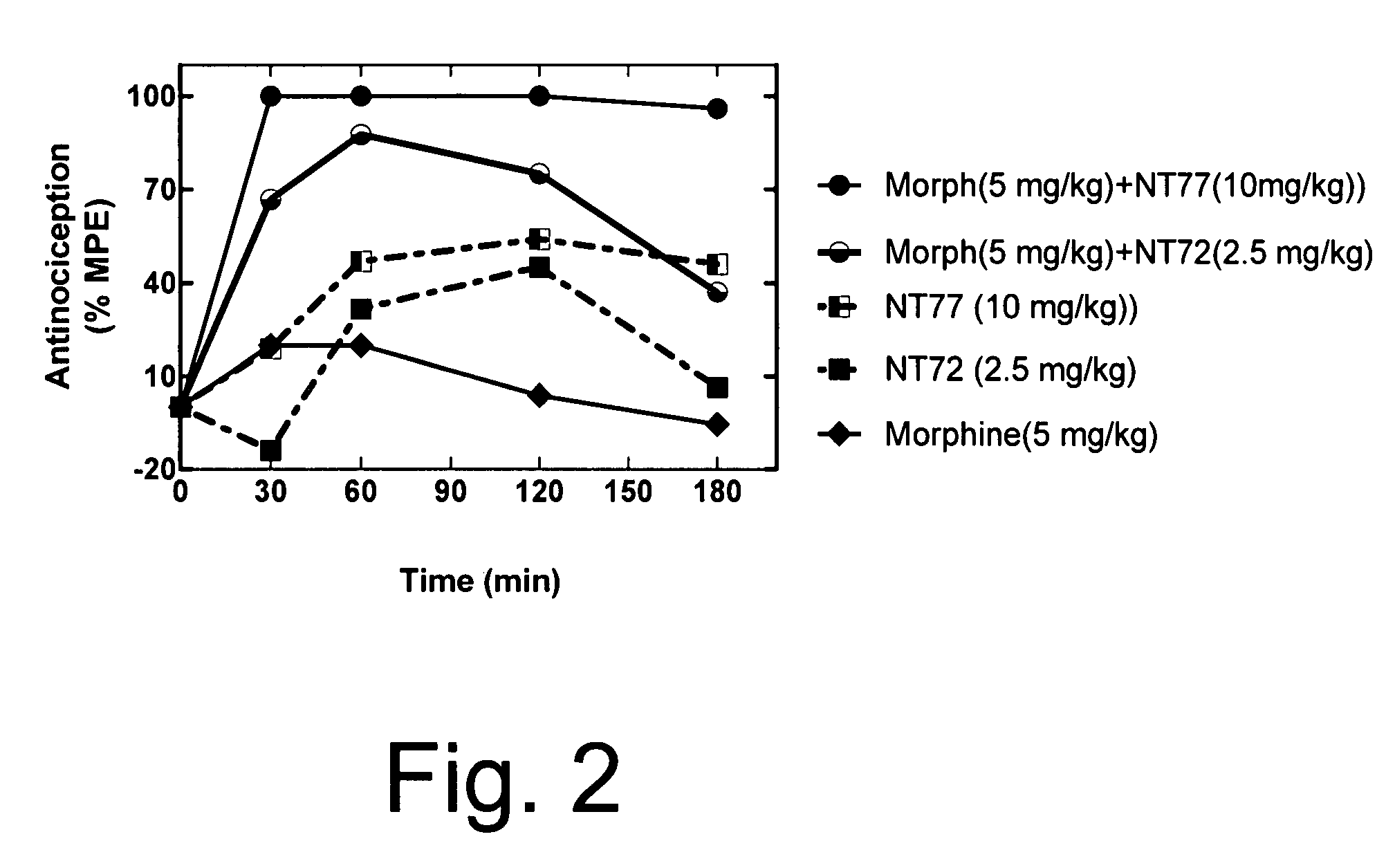
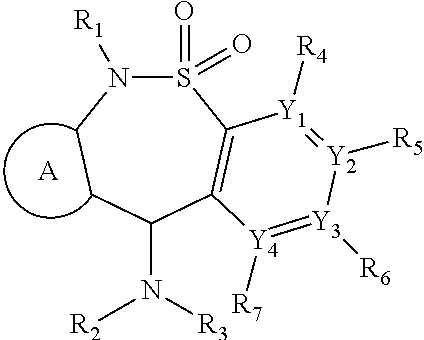
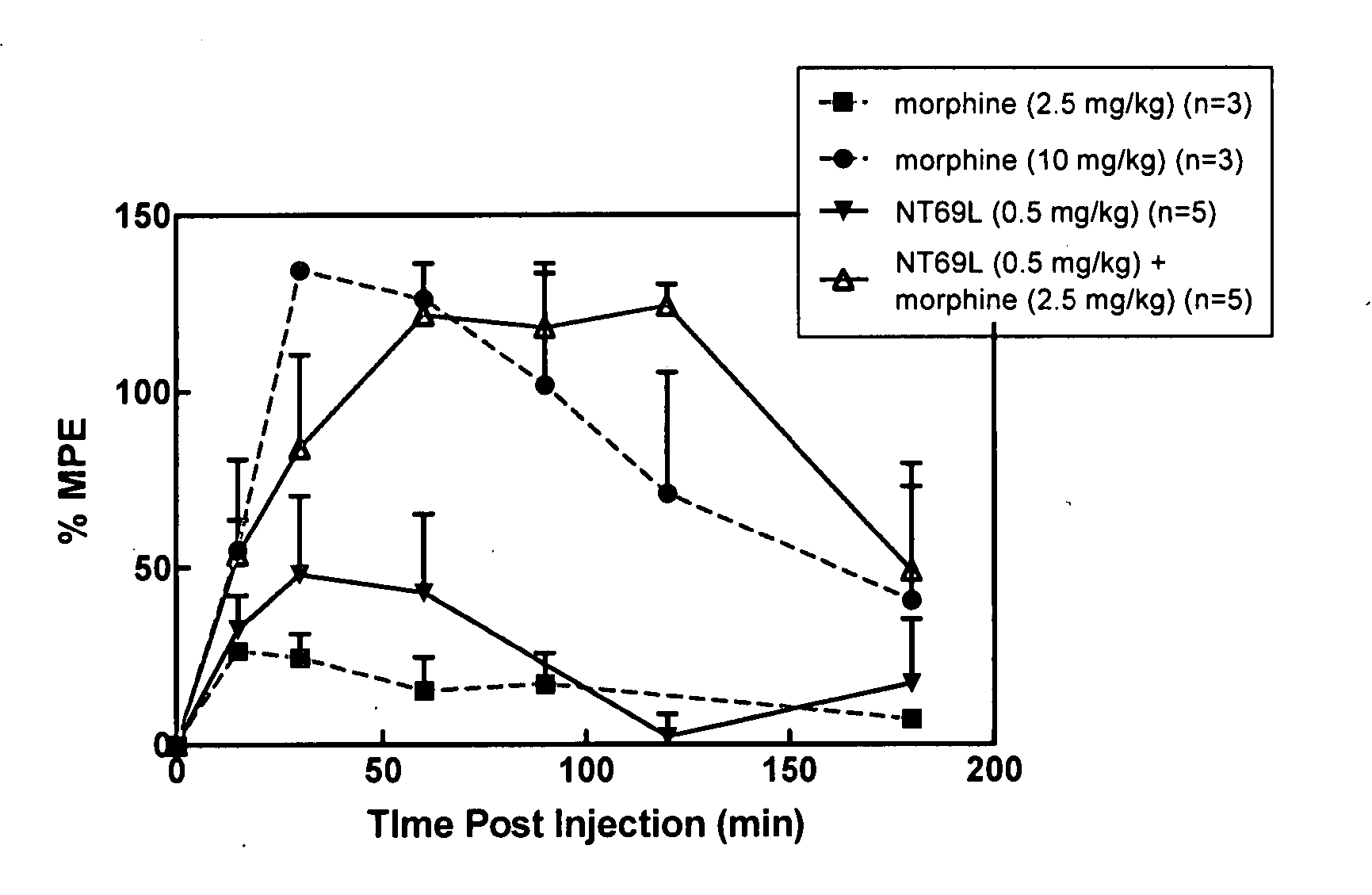
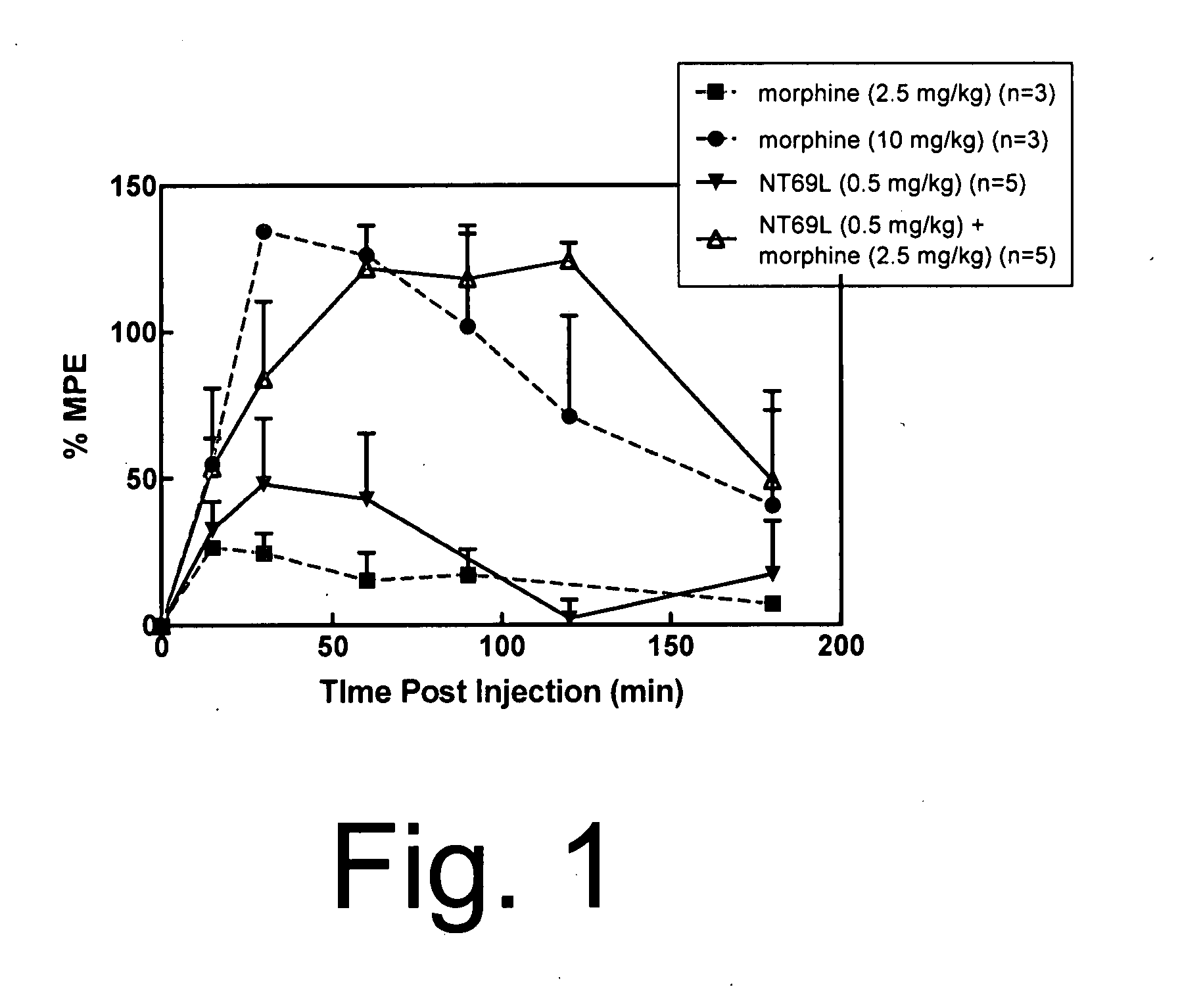
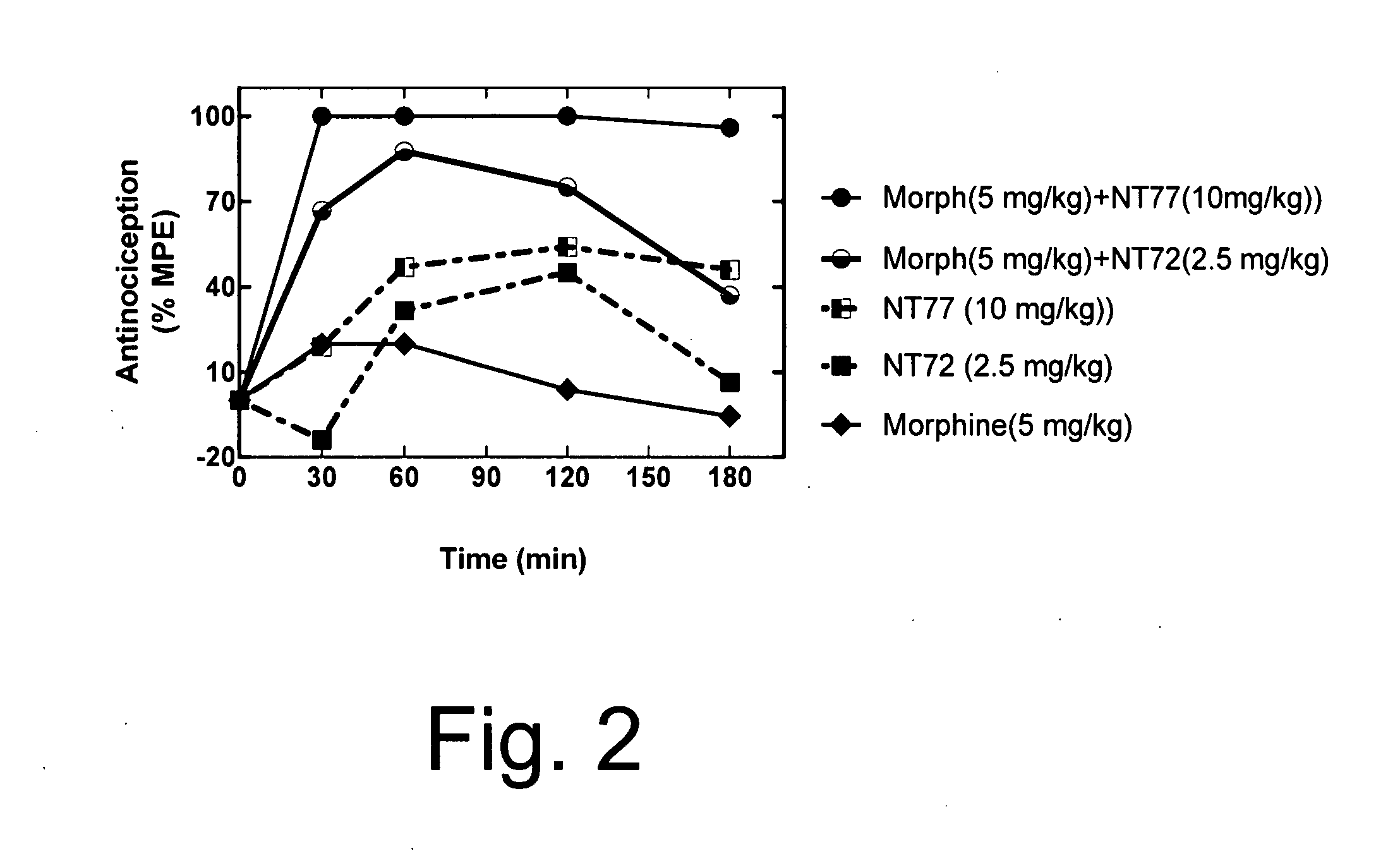
Neurotensin receptor agonists and opioid receptor agonists
InactiveUS7671025B2Low profileReduce constipationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderPharmacologyNeurotensin receptor
This document provides methods and materials for treating pain. For example, this document provides methods that involve administering a neurotensin receptor (NTR) agonist and an opioid receptor agonist to a mammal (e.g., a human). Compositions containing an NTR agonist in combination with an opioid receptor agonist also are provided.
Owner:SARENTIS THERAPEUTICS +1
Peripheral kappa receptor agonists for reducing pain and inflammation
InactiveUS20150150935A1Reducing patient needReducing kappa opioid receptor-associated inflammationBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseFactor ii
A method of treating of a mammalian subject suffering from an inflammatory disease or condition by administering a peripherally-restricted kappa opioid receptor agonist for reducing the inflammation is provided. The peripherally-restricted kappa opioid receptor agonist can include a peptide and the peptide can include D-amino acids. Administration of peripherally-restricted kappa opioid receptor agonists results in lowering of serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and elevation of levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines.
Owner:CARA THERAPEUTICS
Methods for treating depressive symptoms
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
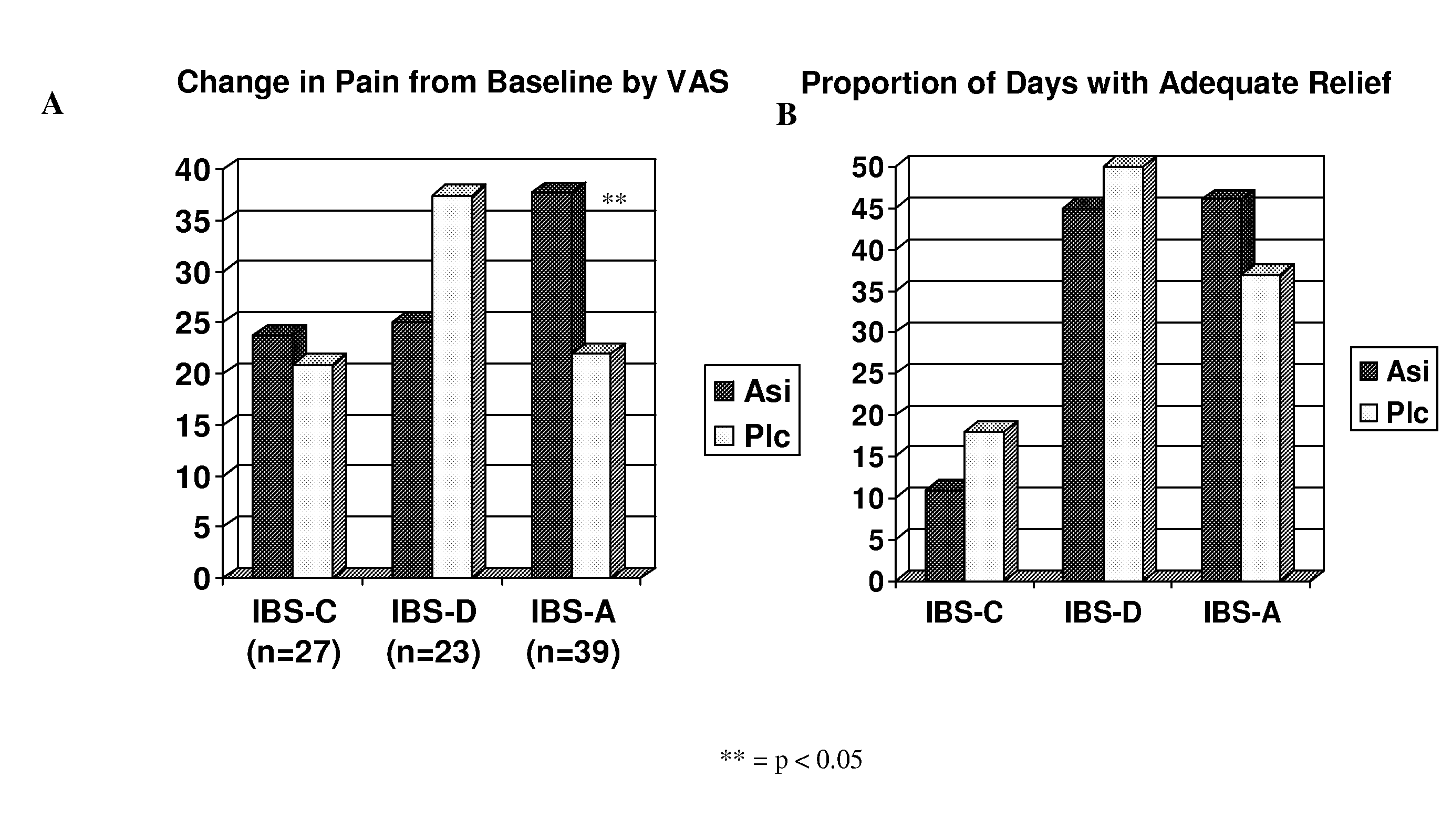
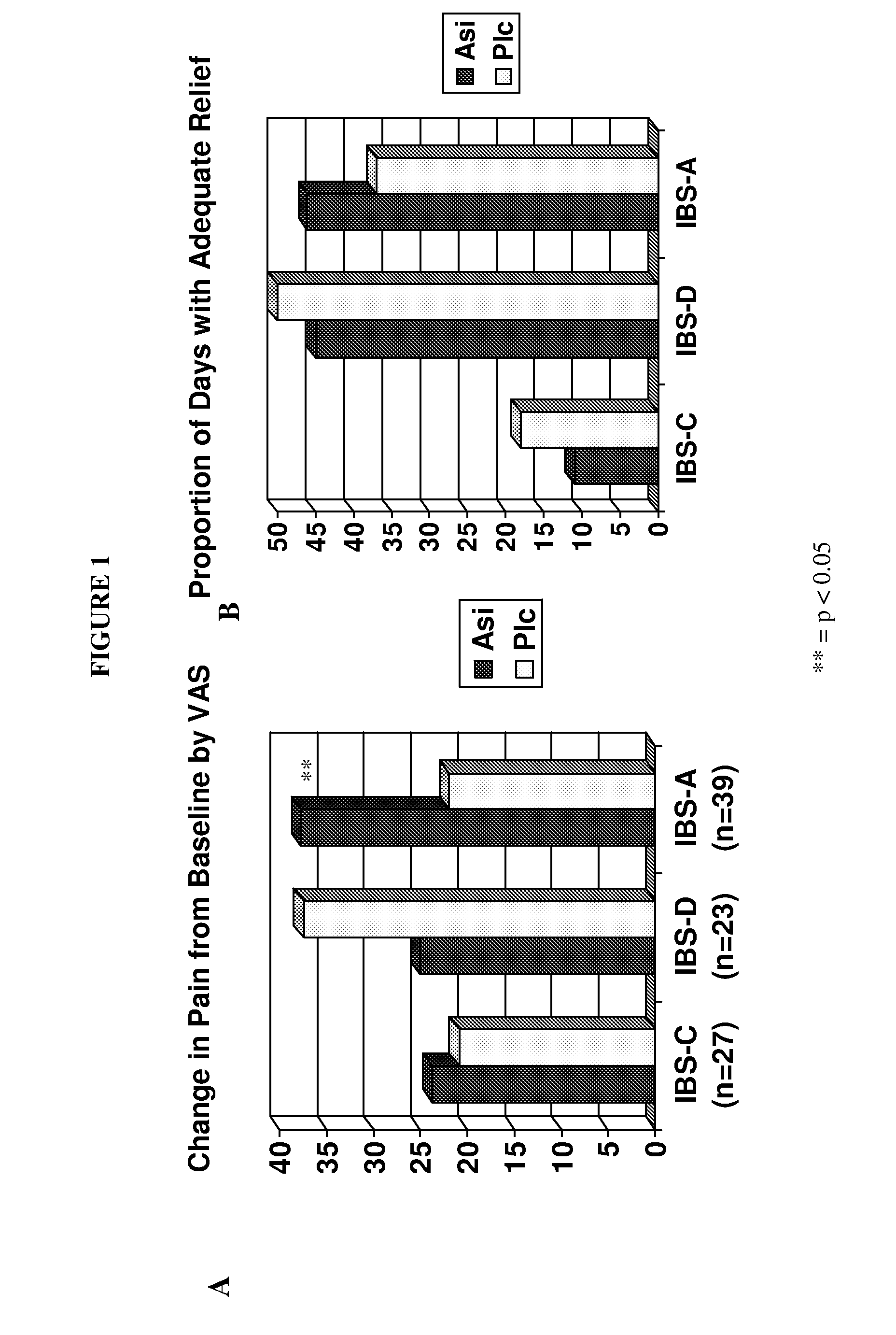
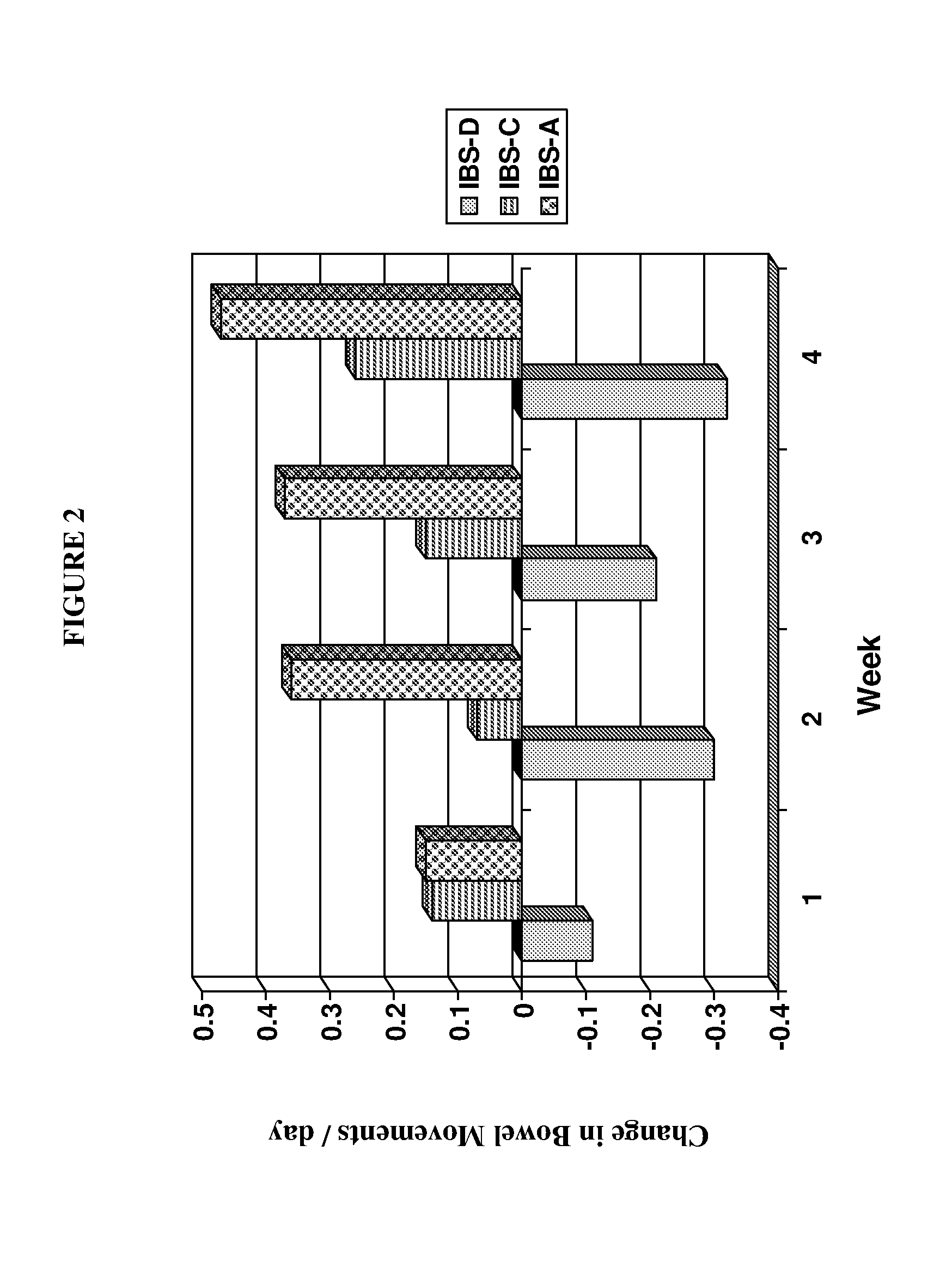
Kappa-opiate agonists for the treatment of diarrhea-predominant and alternating irritable bowel syndrome
InactiveUS20080242720A1Ameliorates painAmeliorates discomfortBiocideNervous disorderOPIATE AGONISTSDiarrhea
The present invention concerns methods useful in treating one or more subtypes of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), or useful in treating diarrhea. The invention relates to the use of peripherally selective kappa-opiate agonists, especially N-methyl-N-[(1S)-1-phenyl-2-((3S)-3-hydroxypyrrolidin-1-yl)ethyl]-2,2-diphenylacetamide and / or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof for treating a subject having diarrhea-predominant IBS (IBS-D) or IBS with alternating diarrhea and constipation (IBS-A), or a subject having diarrhea.
Owner:TIOGA PHARMA INC
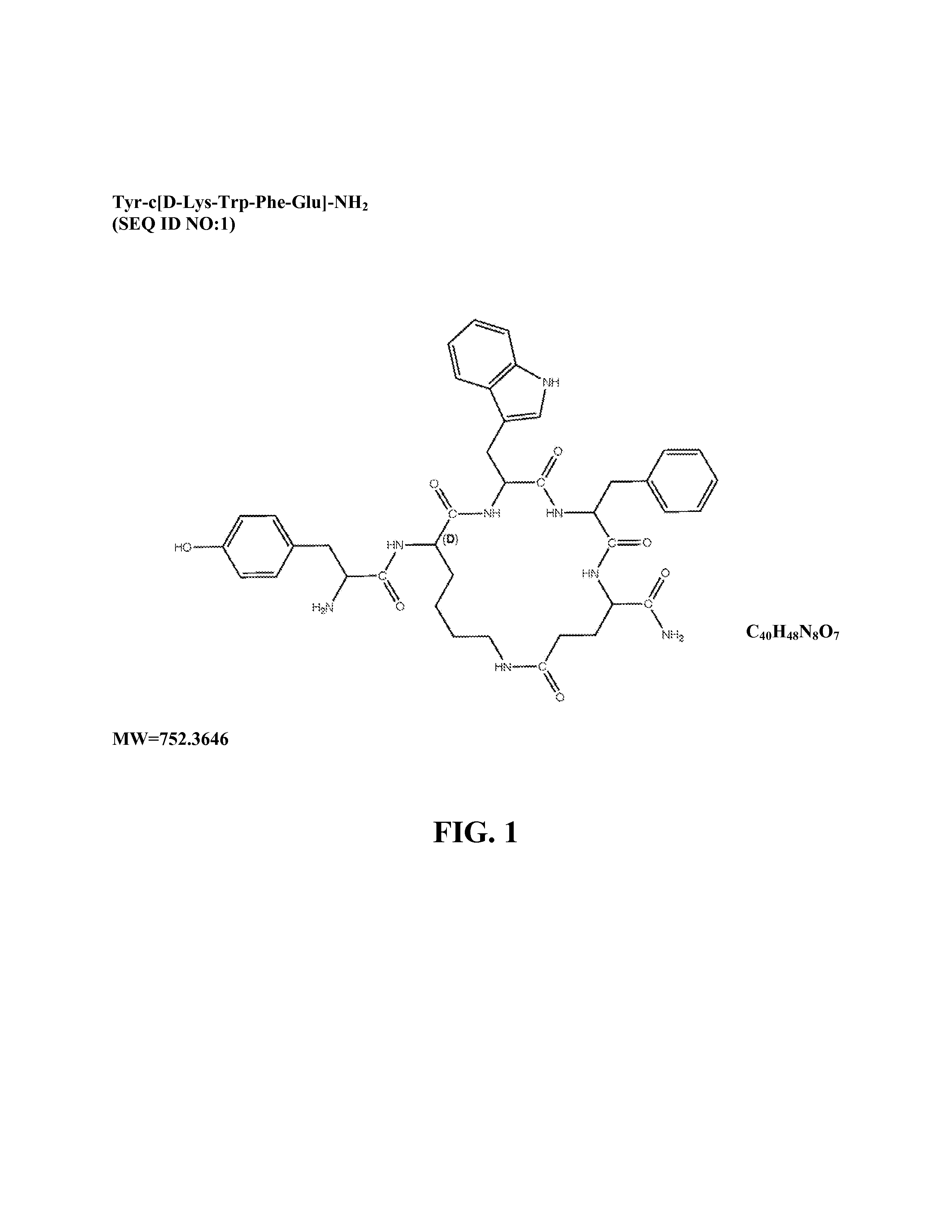
Mu opioid receptor agonist analogs of the endomorphins
InactiveUS20130178427A1Better therapeutic ratioImprove solubilityCompound screeningNervous disorderSolubilitySide effect
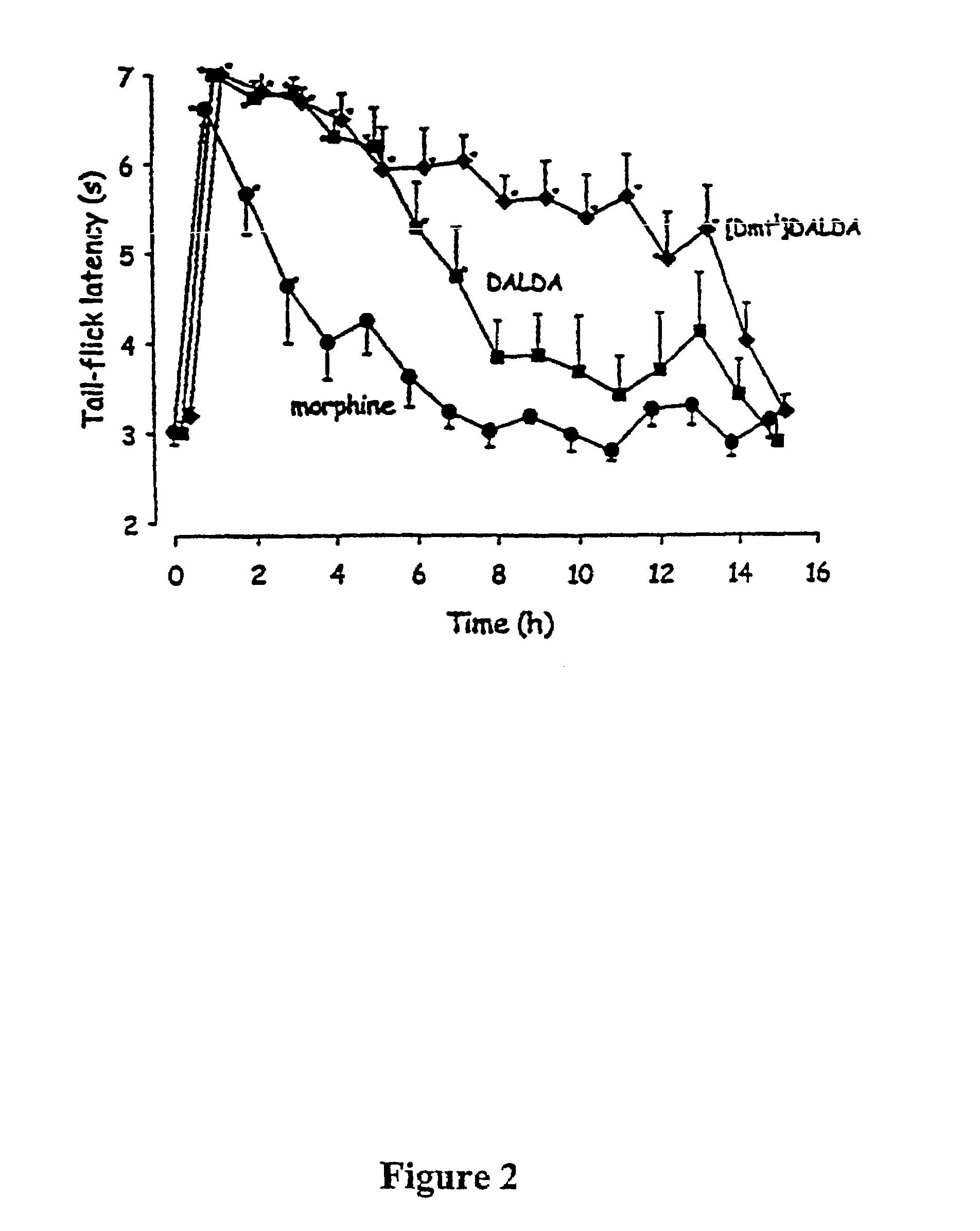
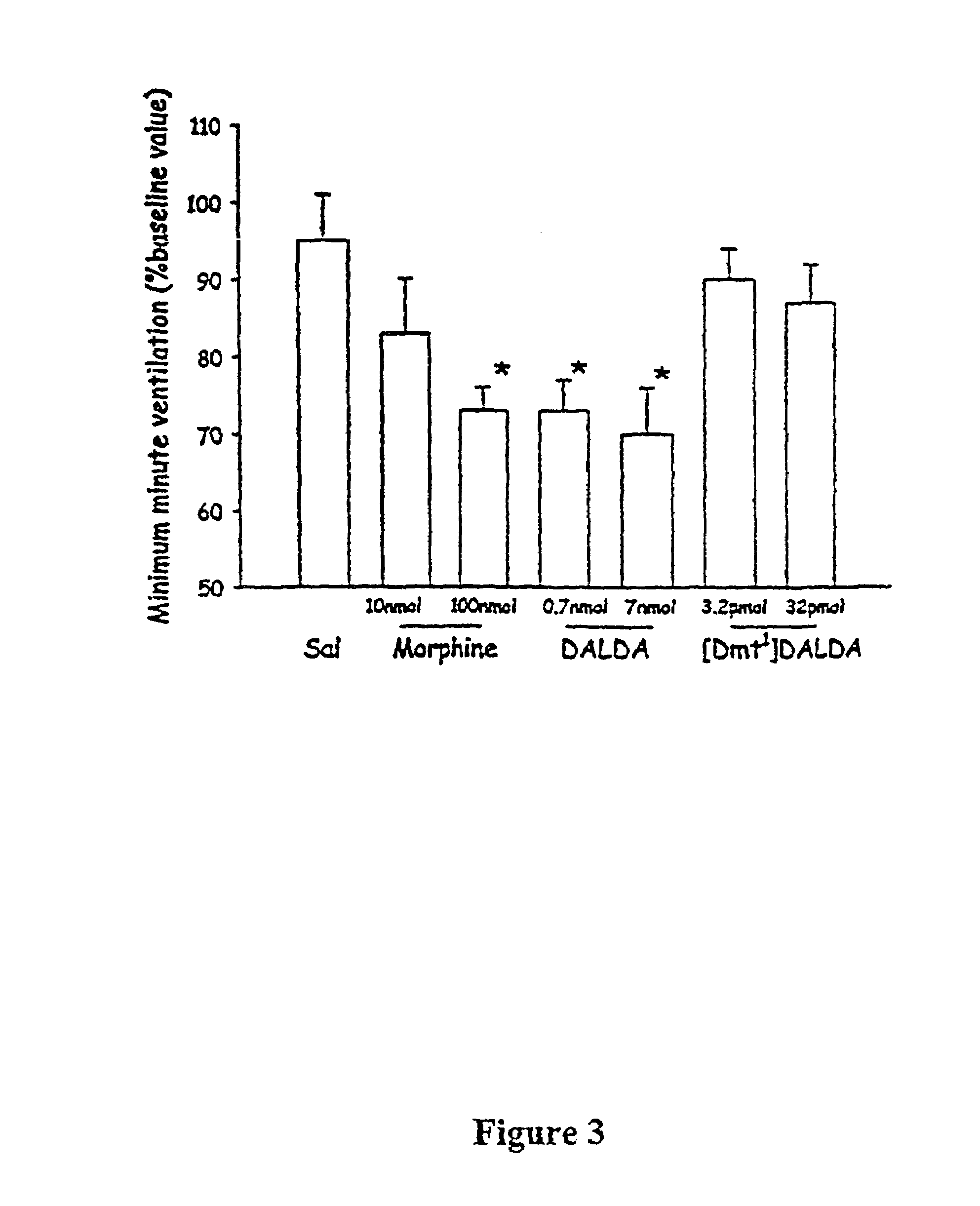
The invention relates to cyclic peptide agonists that bind to the mu (morphine) opioid receptor and their use in the treatment of acute and / or chronic pain. Embodiments of the invention are directed to cyclic pentapeptide and hexapeptide analogs of endomorphin that have (i) a carboxy-terminal extension with an amidated hydrophilic amino acid and (ii) a substitution in amino acid position 2, and a 2′,6′-dimethyltyrosine (Dmt) residue in place of the N-terminal tyrosine residue a position 1. These peptide analogs exhibit increased solubility compared to similar tetrapeptide analogs while maintaining favorable or improved therapeutic ratios of analgesia to side effects.
Owner:THE ADMINISTRATORS OF THE TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND +1
Opioid receptor agonist compounds and their use in treatment of pain
Structurally novel opioid receptor agonists are provided, and the use of these agonists in treatment of chronic and / or acute pain.
Owner:RES TRIANGLE INST
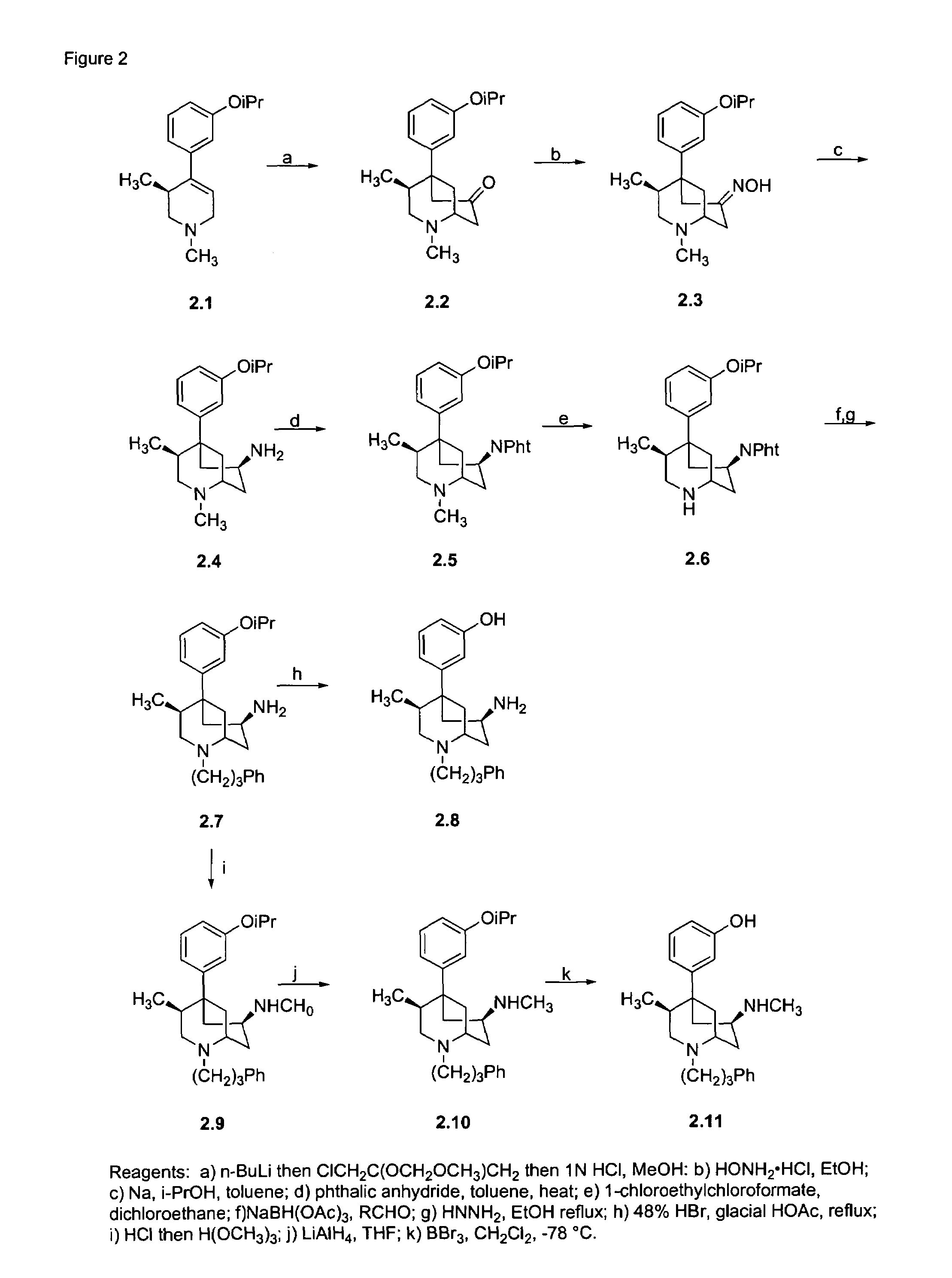
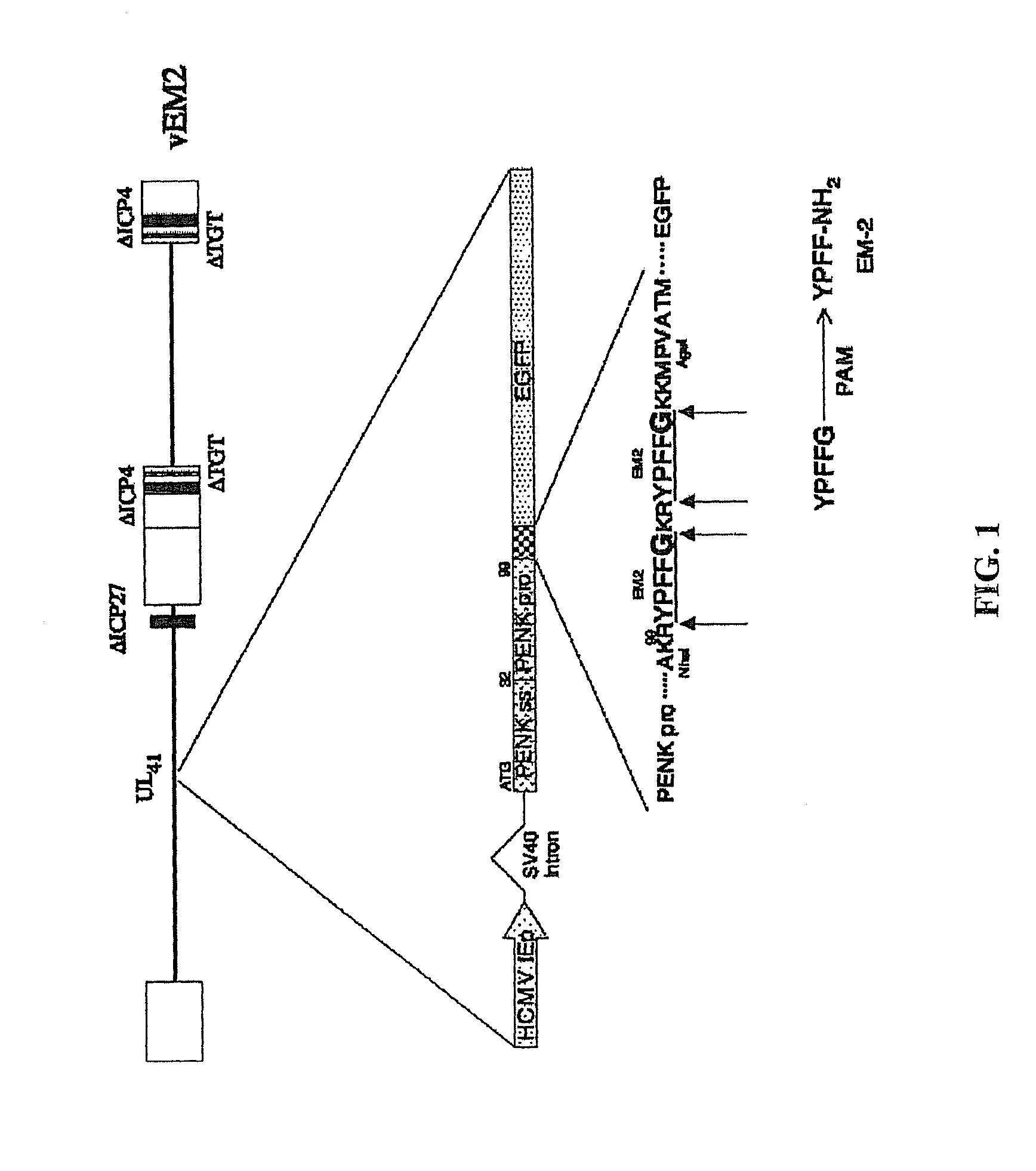
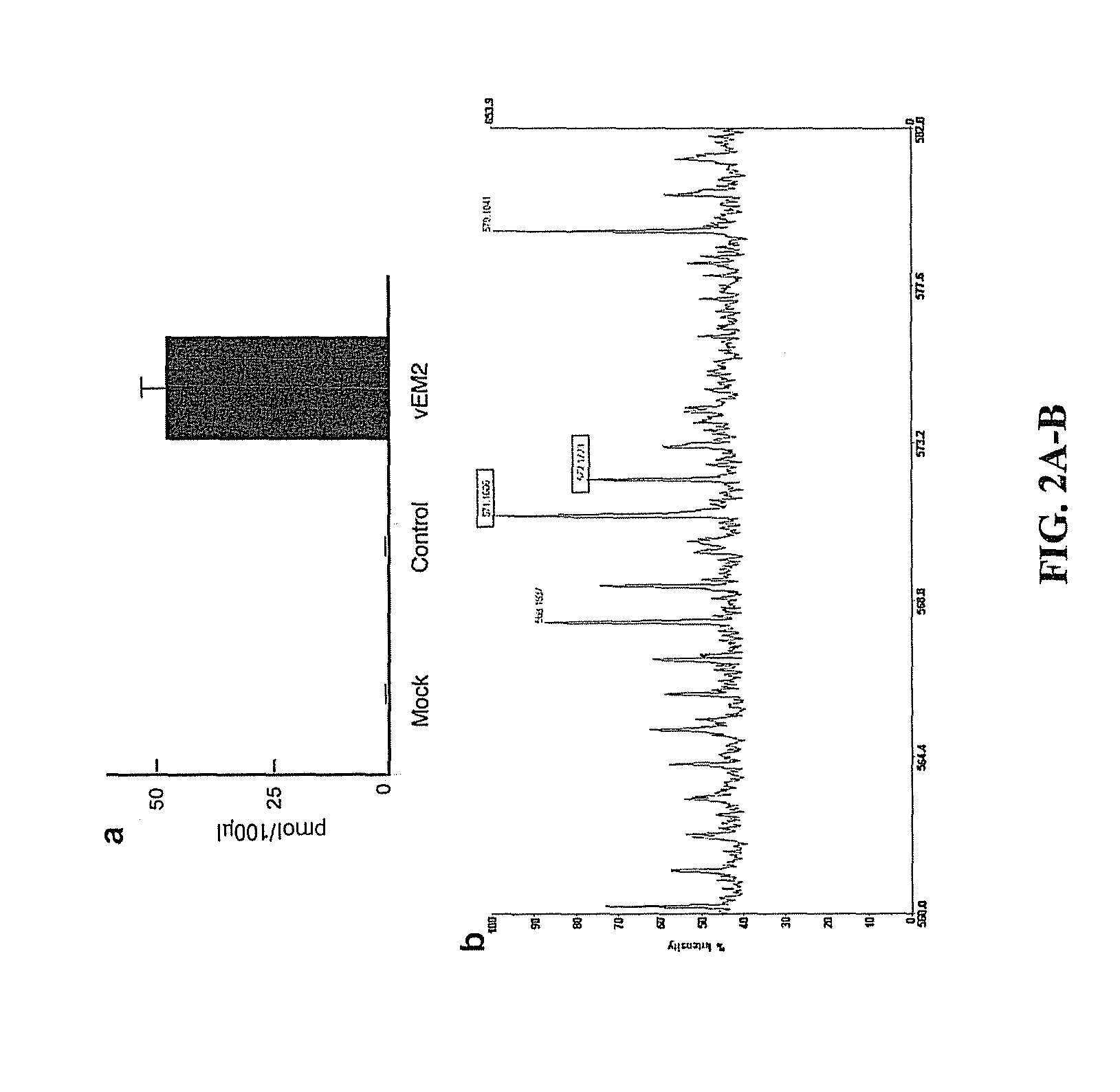
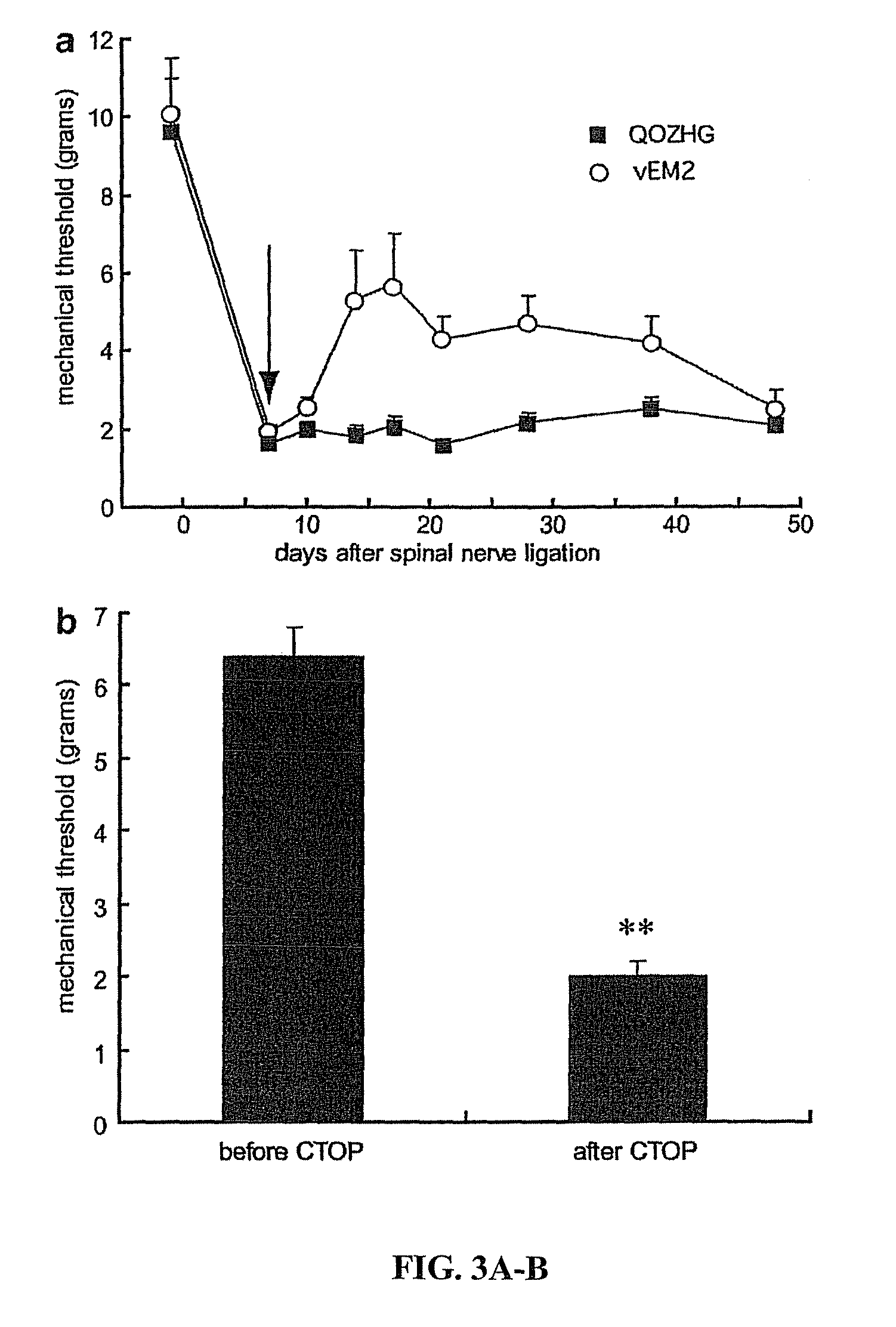
Method of amidated peptide biosynthesis and delivery in vivo: endomorphin-2 for pain therapy
The invention provides an expression cassette comprising a DNA sequence encoding amino acids 1-99 of human preproenkephalin, a DNA sequence encoding a precursor of a carboxy-amidated peptide flanked by dibasic cleavage sites and optionally a DNA sequence encoding a marker protein (such as Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP)) all in operable linkage and under control of a promoter. Where the encoded precursor of a carboxy-amidated peptide is an agonist for an opioid receptor, the invention further provides a method of treating neuropathic pain by administering the gene transfer vector comprising such an expression cassette to a patient. The invention also provides a method for detecting a peptide having a desired effect comprising introducing a library of DNA sequences encoding one or more precursors of carboxy-amidated peptides into host cells; expressing the carboxy-amidated peptides encoded in the library to provide expression products; and screening from the polypeptide expression products for the desired effect.
Owner:WOLFE DARREN P +2
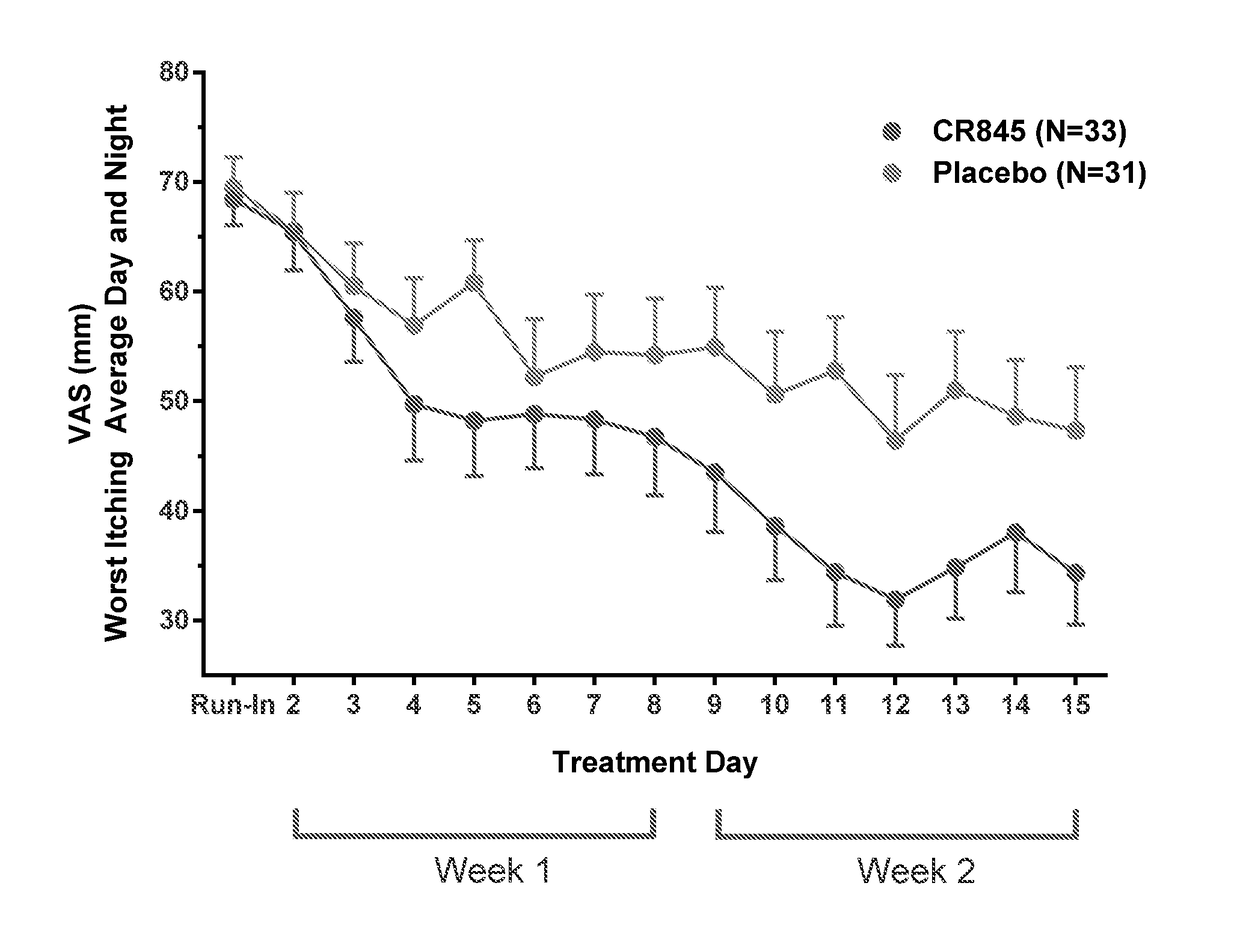
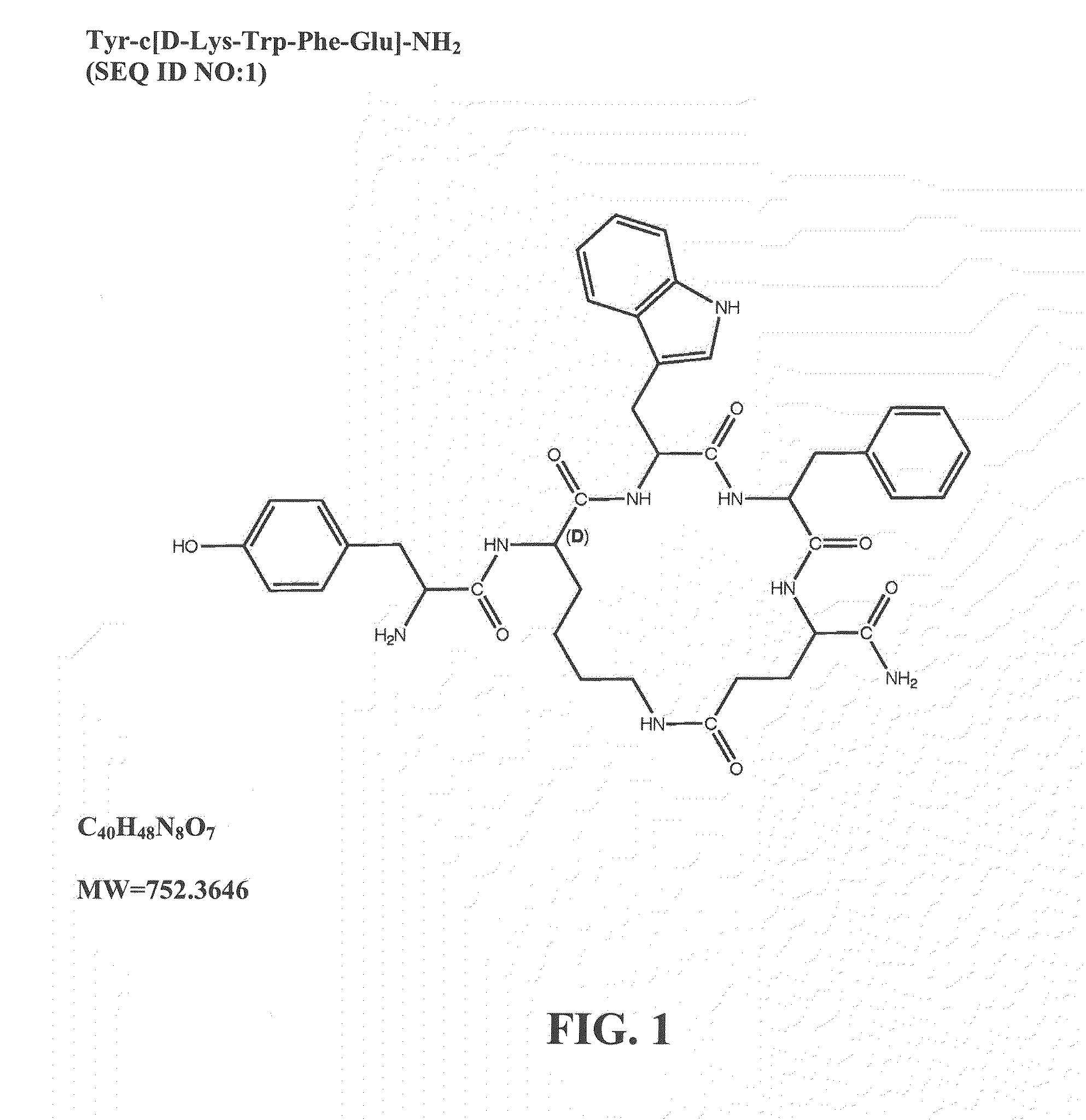
Peripheral kappa opioid receptor agonists for uremic pruritus in dialysis patients
InactiveUS20180078605A1Reduce adverse symptomsOrganic active ingredientsTetrapeptide ingredientsQuality of lifeMood Alteration
The invention provides a method of prevention, inhibition or treatment of uremic pruritus in a dialysis patient by administering an effective amount of a kappa opioid receptor agonist. Also provided is a method of inhibition or treatment of adverse symptoms associated with dialysis affecting the quality of life of dialysis patient, the method includes administering an effective amount of a kappa opioid receptor agonist. The adverse symptoms associated with dialysis addressable by the methods of the invention include uremic pruritus, sleep disruption, depression and other mood alterations.
Owner:CARA THERAPEUTICS
Mu opioid receptor agonist analogs of the endomorphins
ActiveUS20120322740A1Improve solubilityBetter therapeutic ratioCompound screeningNervous disorderSide effectMorphine
The invention relates to cyclic peptide agonists that bind to the mu (morphine) opioid receptor and their use in the treatment of acute and / or chronic pain. Embodiments of the invention are directed to cyclic pentapeptide and hexapeptide analogs of endomorphin that have (i) a carboxy-terminal extension with an amidated hydrophilic amino acid and (ii) a substitution in amino acid position 2. These peptide analogs exhibit decreased tolerance relative to morphine, increased solubility compared to similar tetrapeptide analogs, while maintaining favorable or improved therapeutic ratios of analgesia to side effects.
Owner:THE ADMINISTRATORS OF THE TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND +1
Application of beta-protein inhibitor in preparation of medicament for treating genetic correlated disease
InactiveCN1970074AImprove the level ofDoes not affect activityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseMedicine
The invention discloses a beta-inhibiting protein, nucleonic sequence and application of composition with nucleonic sequence to treat relative disease with histone acetylated reduction level, which also relates to the application of delta opitum receptor stimulating agent or k opitum receptor exciting agent to treat relative disease with histone acetylated reduction level. The invention provides a drug sieving method from candidate material to treat relative disease with histone acetylated reduction level.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Propellane compounds, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101402636ANo side effectsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderPropellaneSubstance abuse
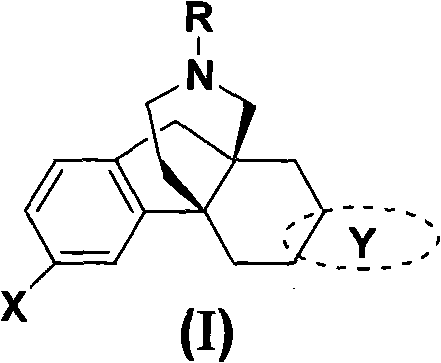
The invention discloses propellane compounds, a preparation method and application thereof, in particular aromatic or fat thick heterocyclic propellane compounds, a preparation method thereof and applications for treating drug abuse as an opioid receptor excitant or an antagonist and for using as a novel analgesic agent and so on. The structures of the compounds are shown in a general formula (I).
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
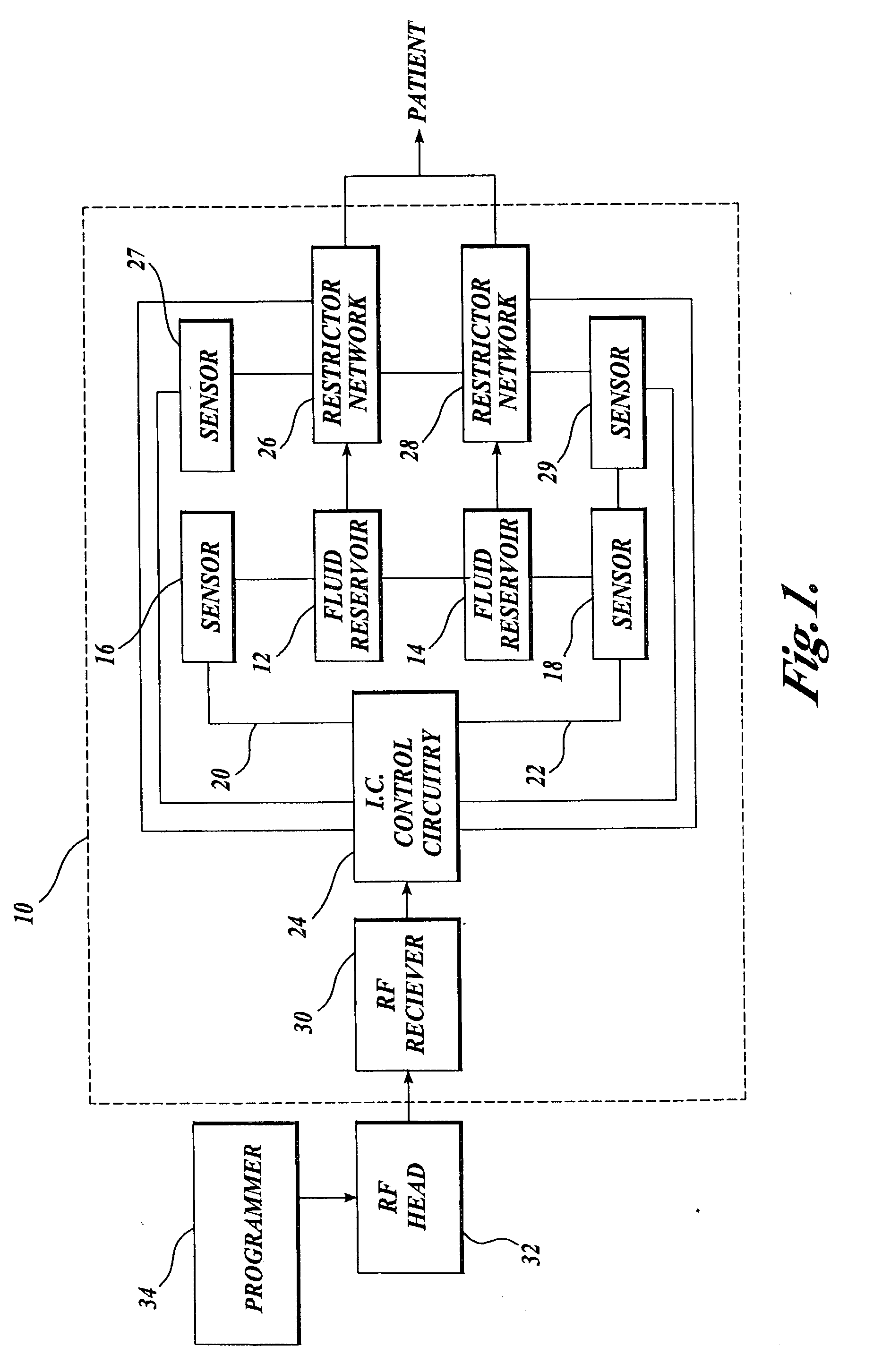
Rotational intrathecal analgesia
ActiveUS20030040486A1Reduce systemic side effectsMinimizing systemic side effectBiocideNervous disorderActive agentDrug administration
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Class of mu-opioid receptor agonists
ActiveUS10183919B2Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderMu-Opioid Receptor AgonistsStereochemistry
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Neurotensin receptor agonists and opioid receptor agonists
InactiveUS20080096823A1Enhance pharmacological effectsMinimize side effectsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDocument preparationPharmacology
This document provides methods and materials for treating pain. For example, this document provides methods that involve administering a neurotensin receptor (NTR) agonist and an opioid receptor agonist to a mammal (e.g., a human). Compositions containing an NTR agonist in combination with an opioid receptor agonist also are provided.
Owner:SARENTIS THERAPEUTICS +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com