Patents
Literature
229results about "Supine patient support/bases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
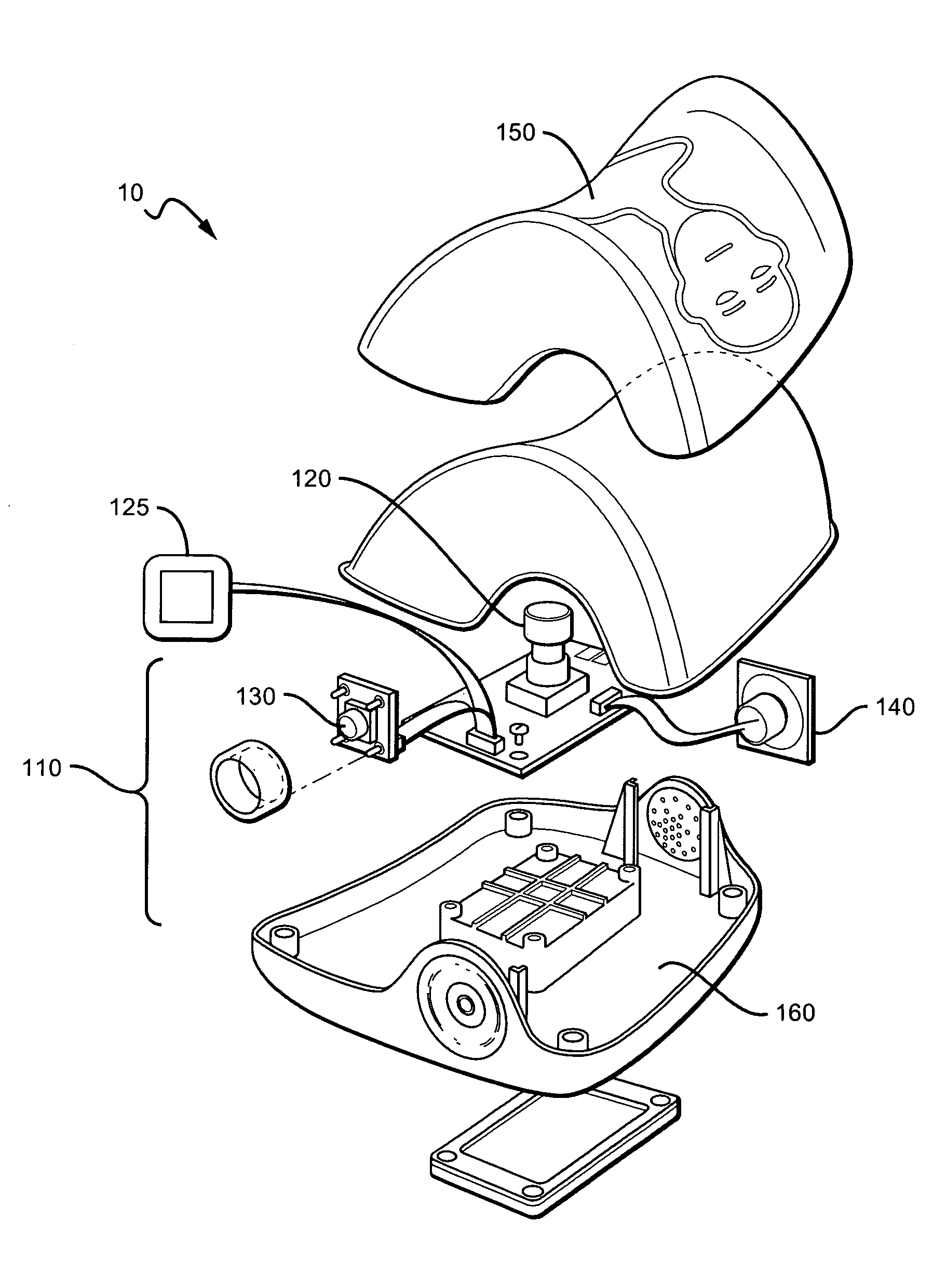
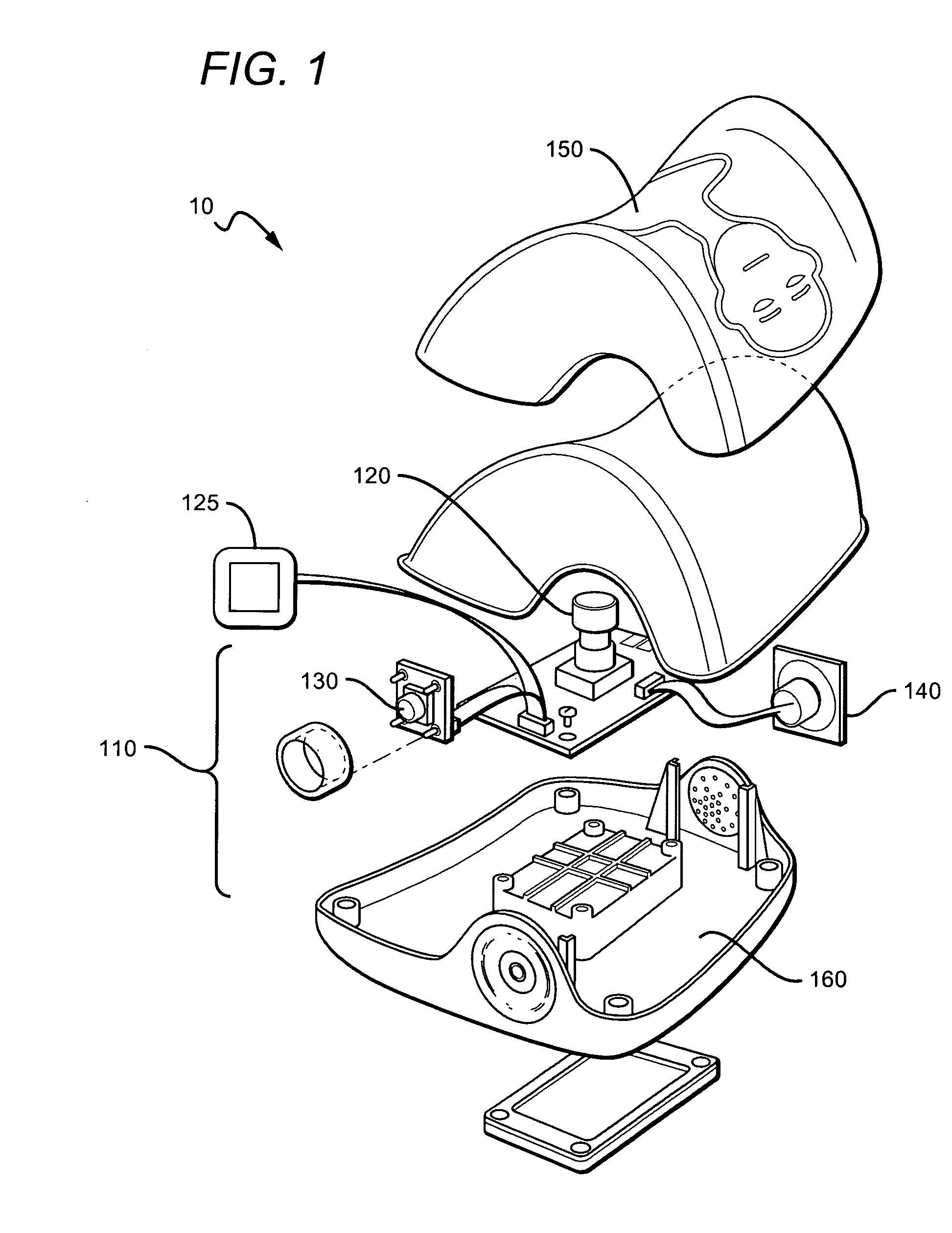
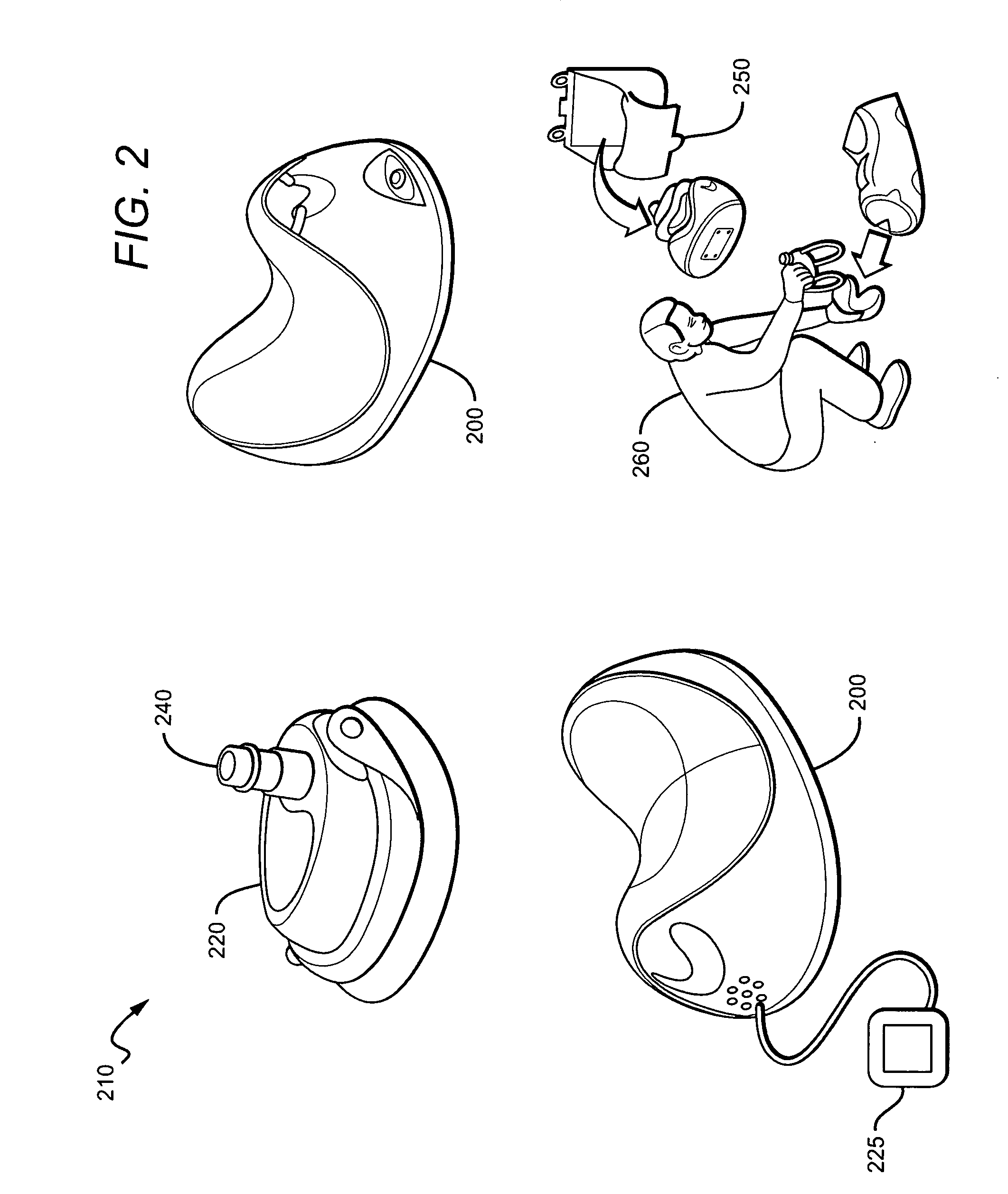
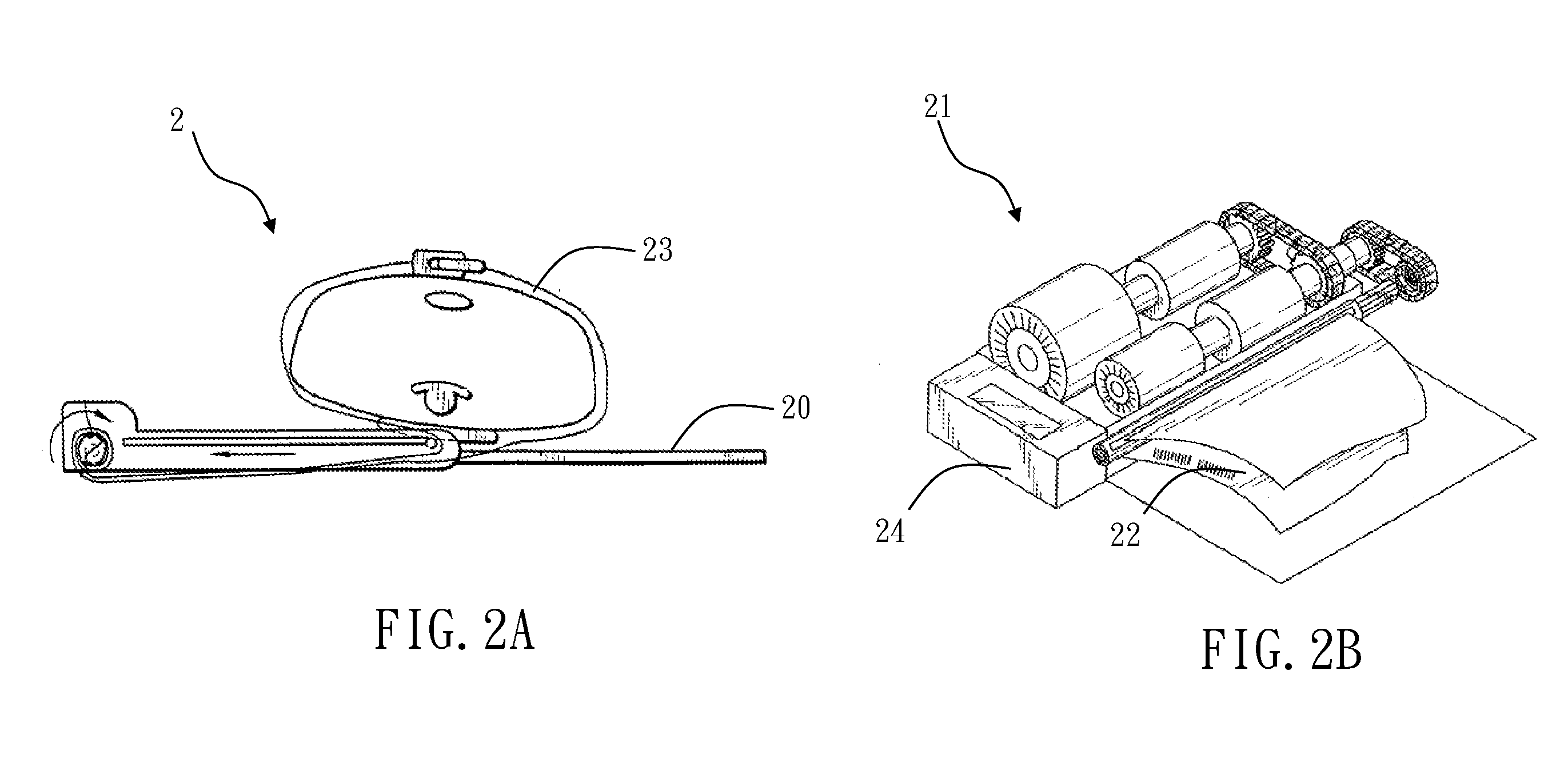
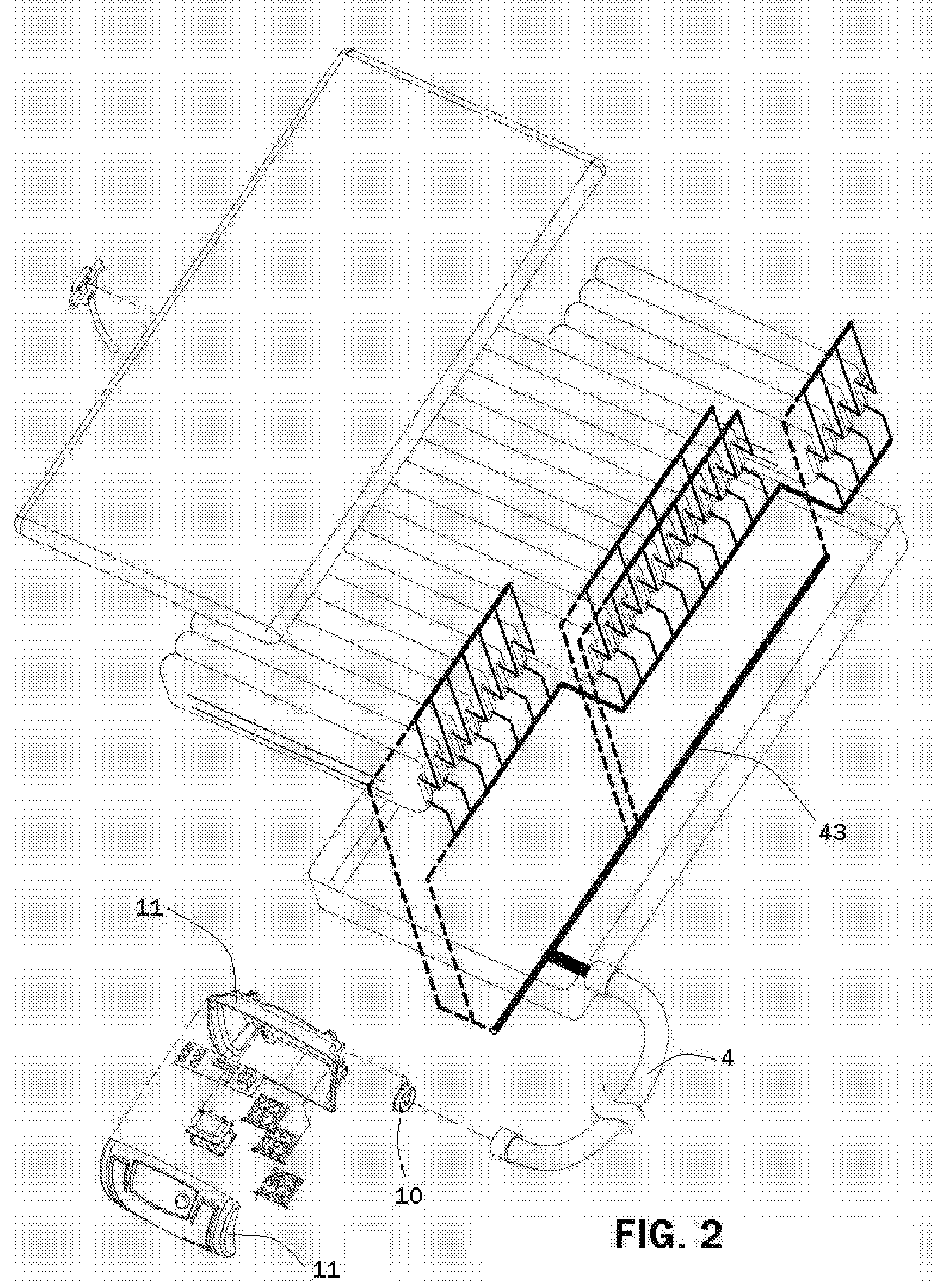
CPR system with feed back instruction
CPR systems that provide guidance to a CPR provider are presented. Contemplated CPR systems include sensors that collect a victim's biometric data during CPR. The data is processed by an electronic assembly which provides feedback to the CPR provider. The electronic assembly can be packaged within a cranio-cervical extension device having language independent instructions encoded on a surface of the device.
Owner:CPAIR
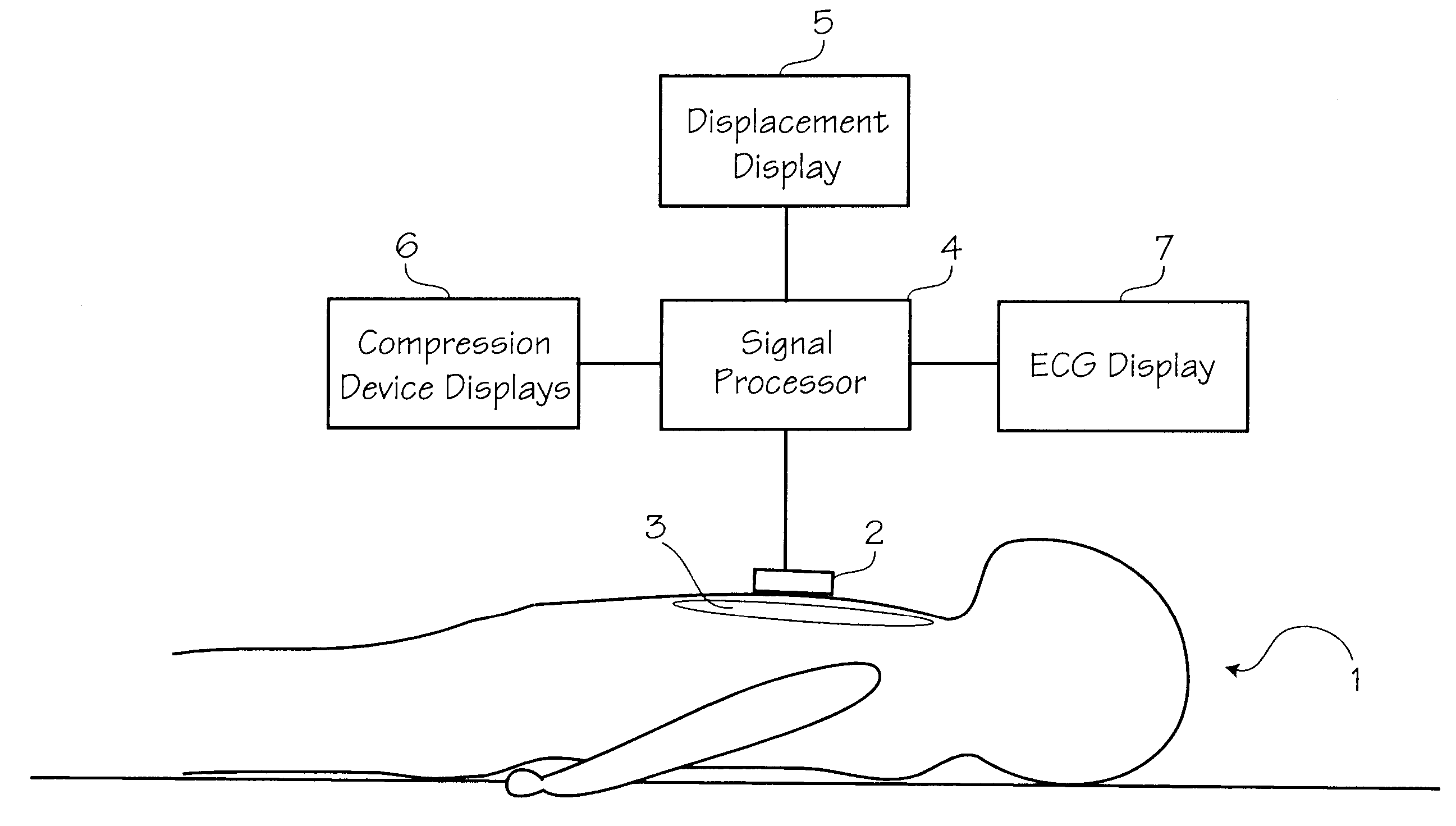
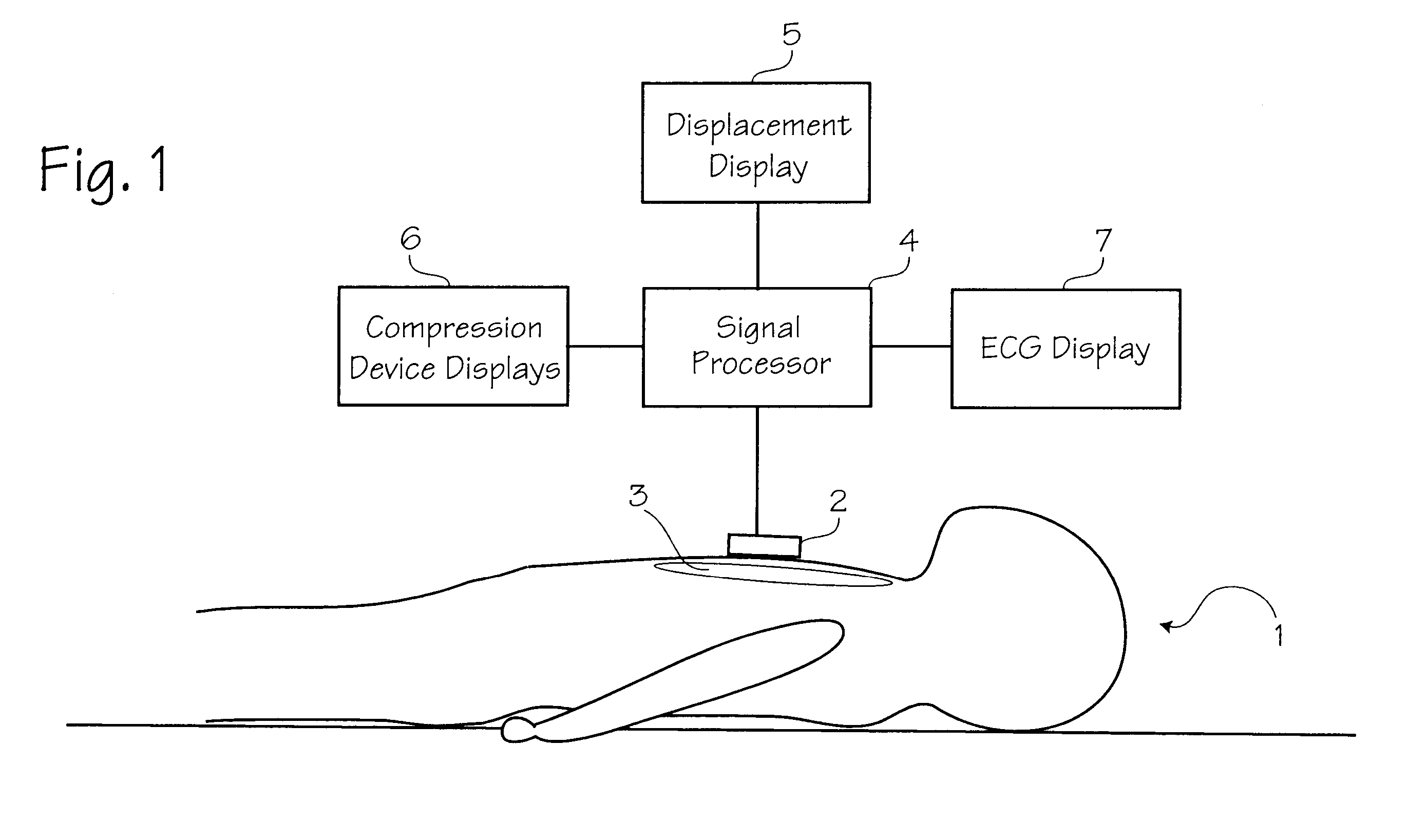
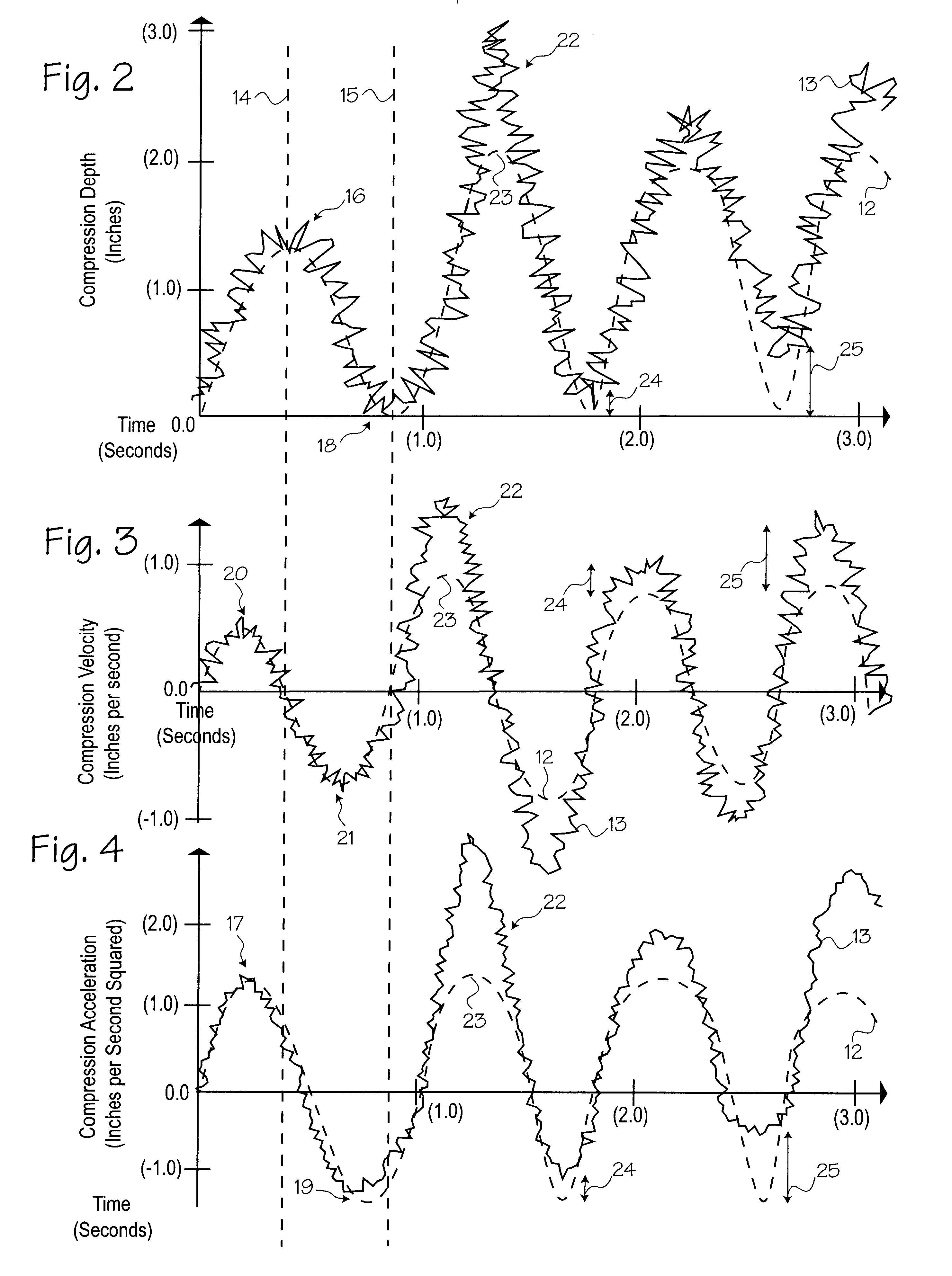
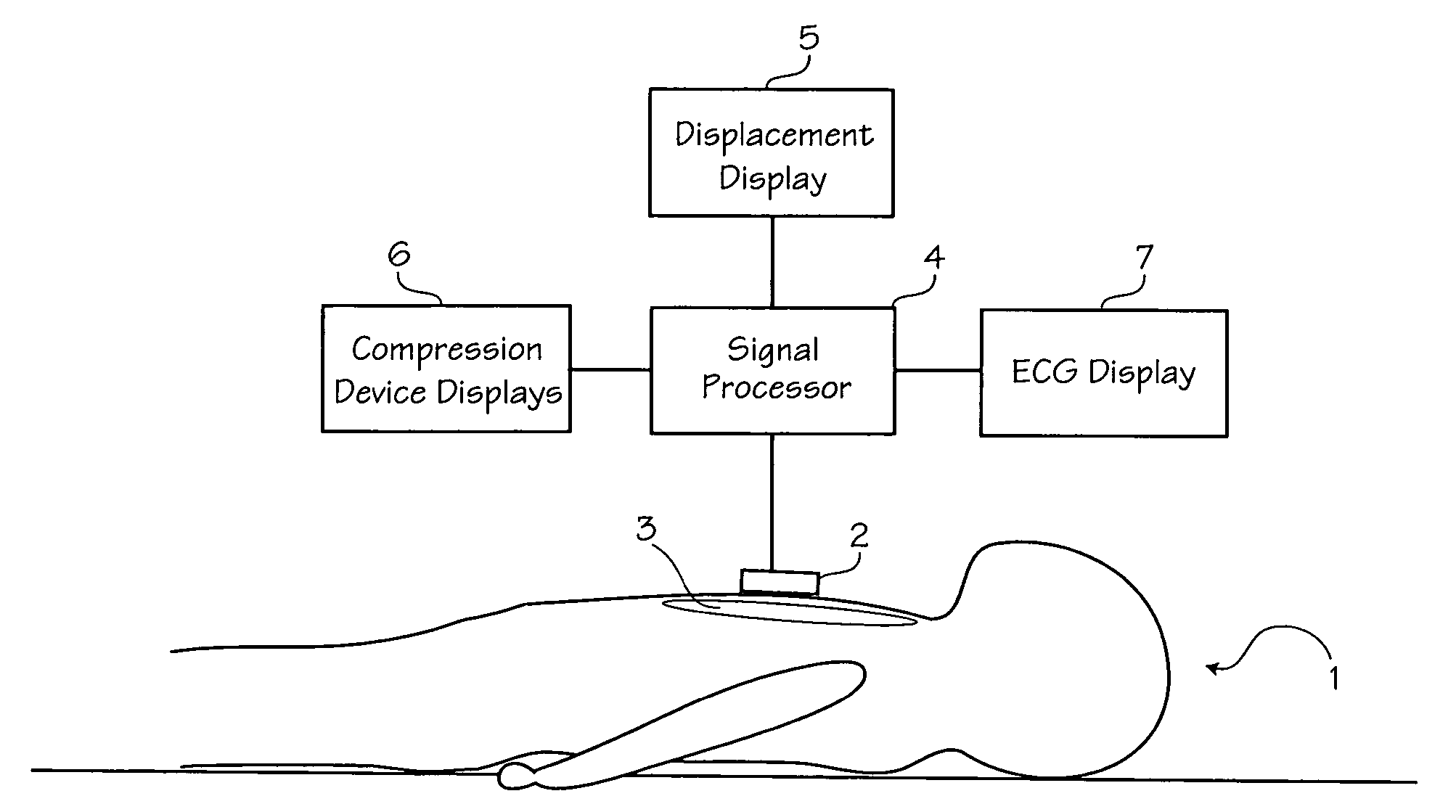
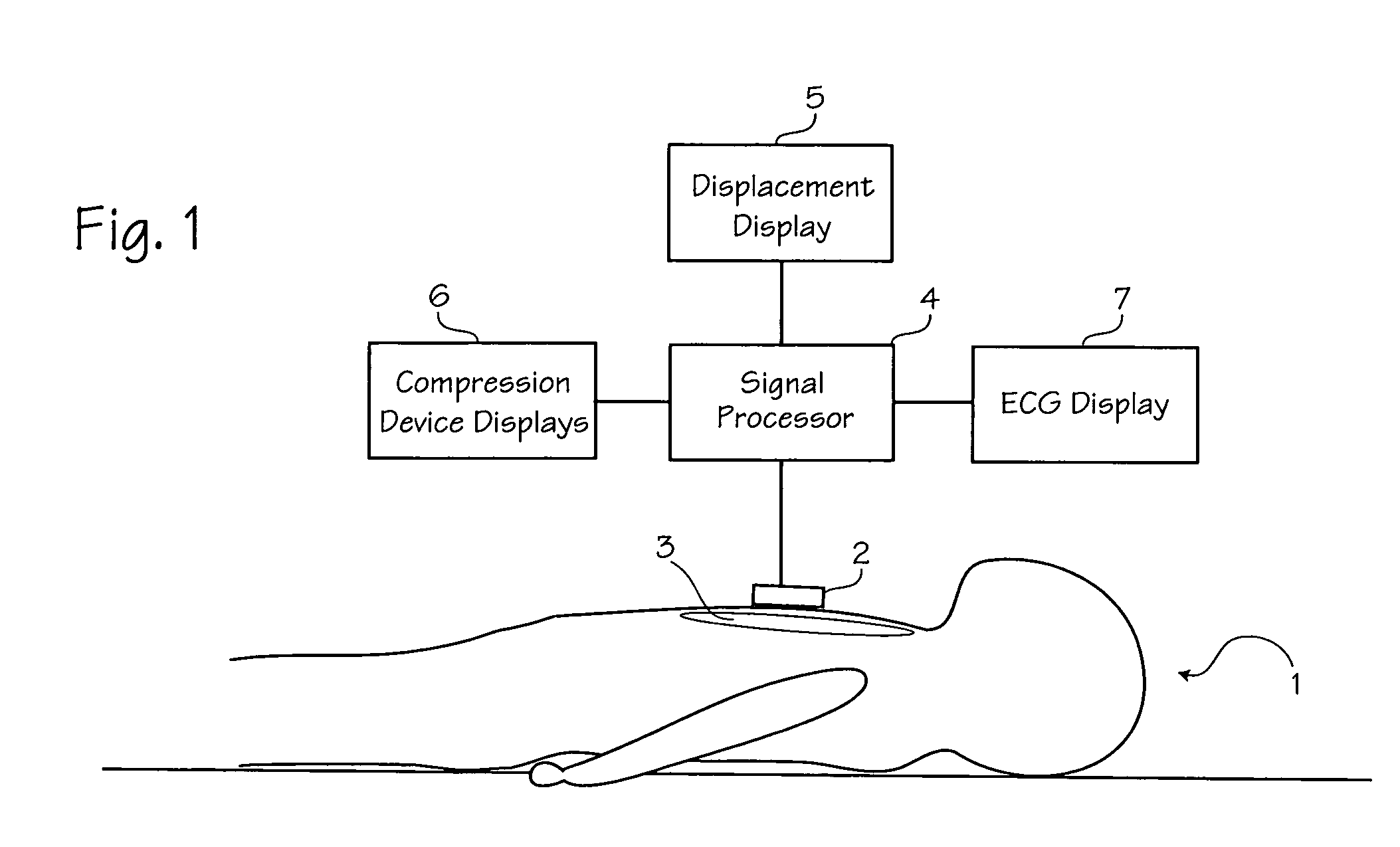
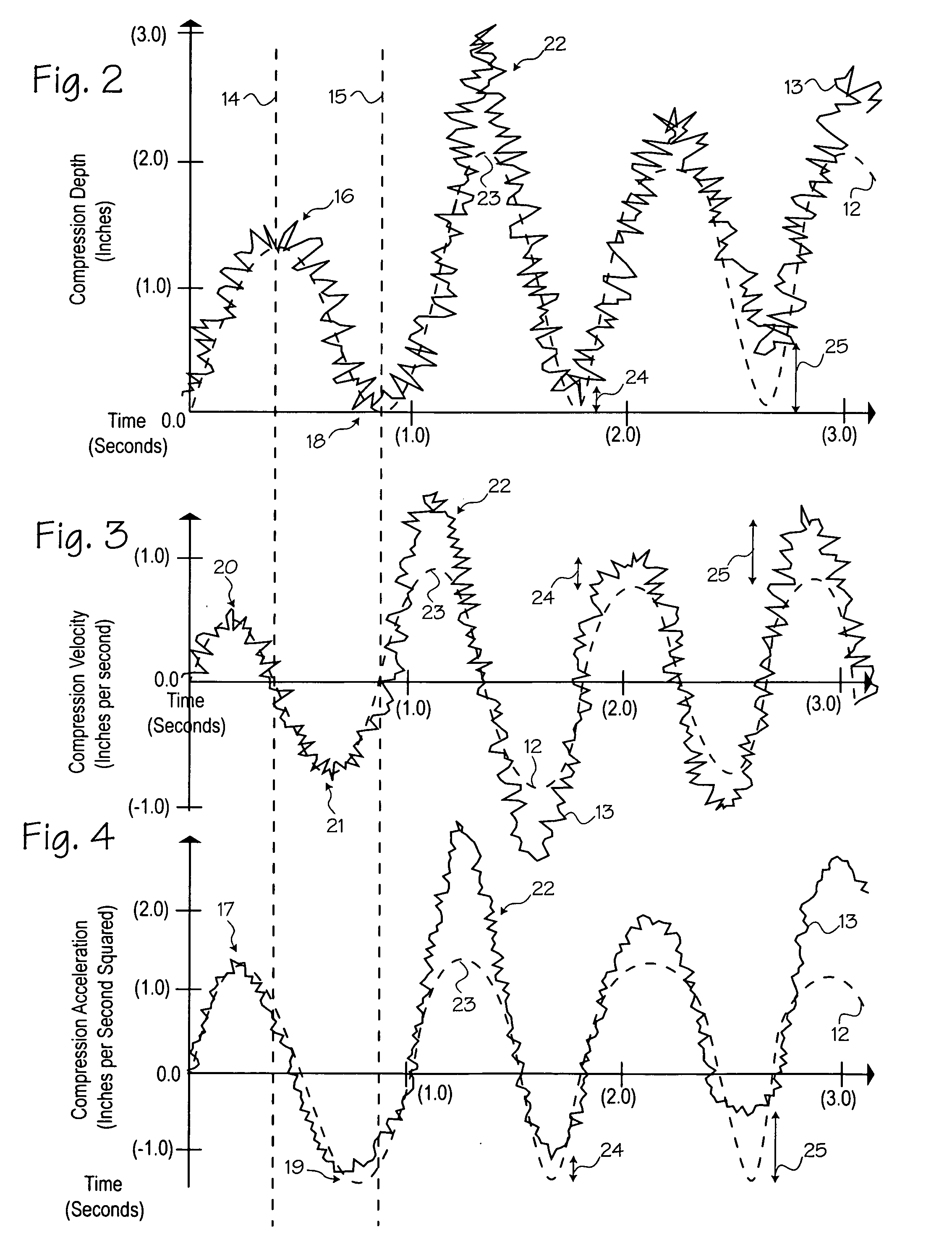
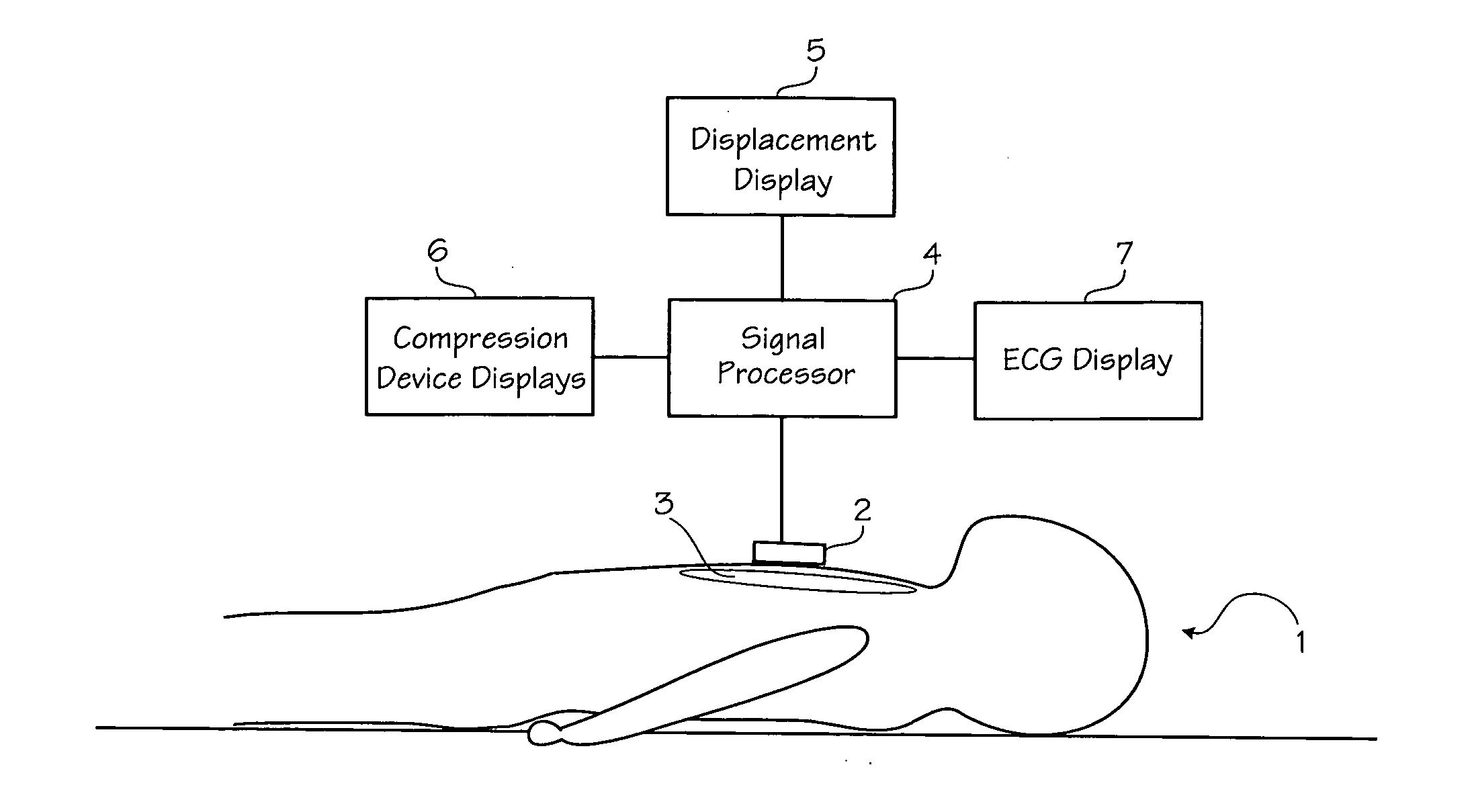
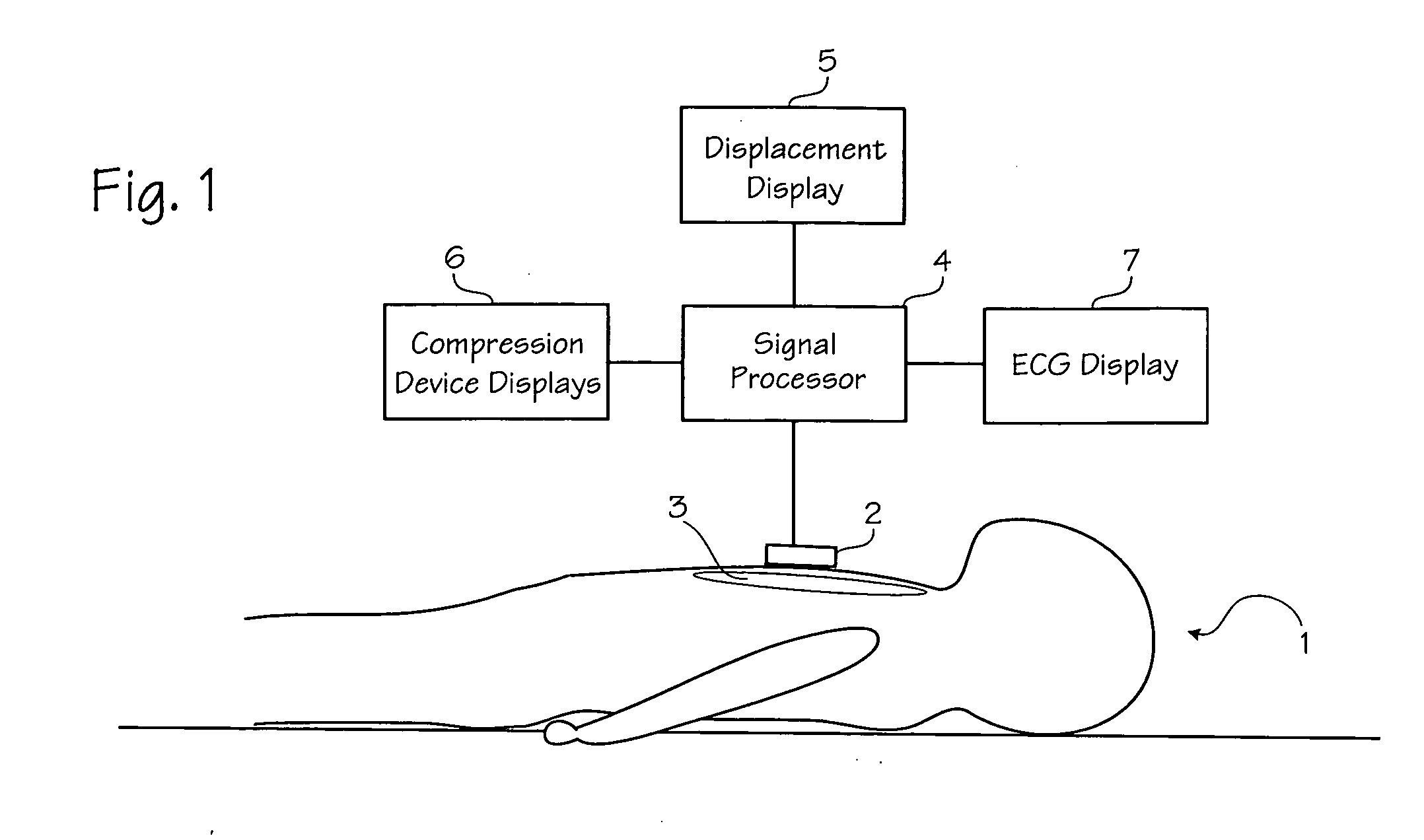
Method of determining depth of compressions during cardio-pulmonary resuscitation
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
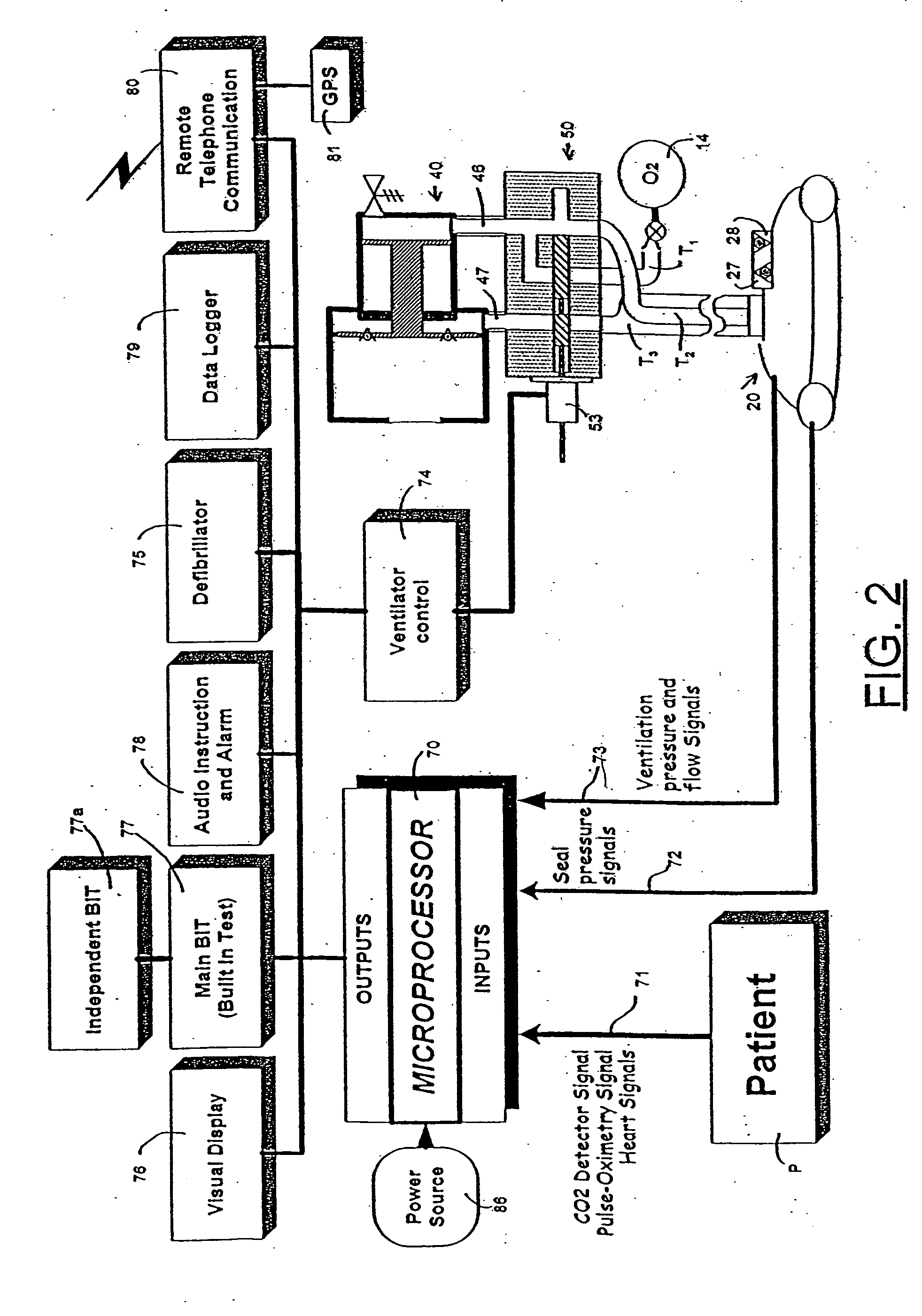
Emergency medical kit, respiratory pump, and face mask particularly useful therein
InactiveUS20050085799A1Efficient driveWide degree of automatic controlRespiratorsElectrocardiographyEmergency medicineNon invasive
An emergency medical kit for use, particularly by a non-professional, to render emergency medical treatment to a patient, includes: a pressurized-oxygen container within a housing; a face mask within the housing for application to the face of a patient requiring cardiopulmonary resuscitation; and a respiratory pump within the housing connected to the pressurized-oxygen container so as to be driven thereby to supply oxygen to the mask for inhalation by the patient, and to discharge the exhalations of the patient via the face mask to the atmosphere. The face mask includes an inflatable seal around its circumference engageable with the face of the patient receiving the mask for sealing the interior of the mask; a pressure sensor sensing the pressure in the inflatable seal; and an indicator for indicating whether the face mask is properly applied to the face of the patient. The kit further includes a neck rest having straps for attaching the face mask thereto in contact with the patient's face when the patient's head is placed on the head rest. According to a most essential aspect of the invention there is provided an emergency, fully automatic kit, based on non-invasive means for performing all stages of the “chain of survival” (including: external defibrillation, ventilation and automatic chest compression) by a single operator.
Owner:LURIA ODED +1
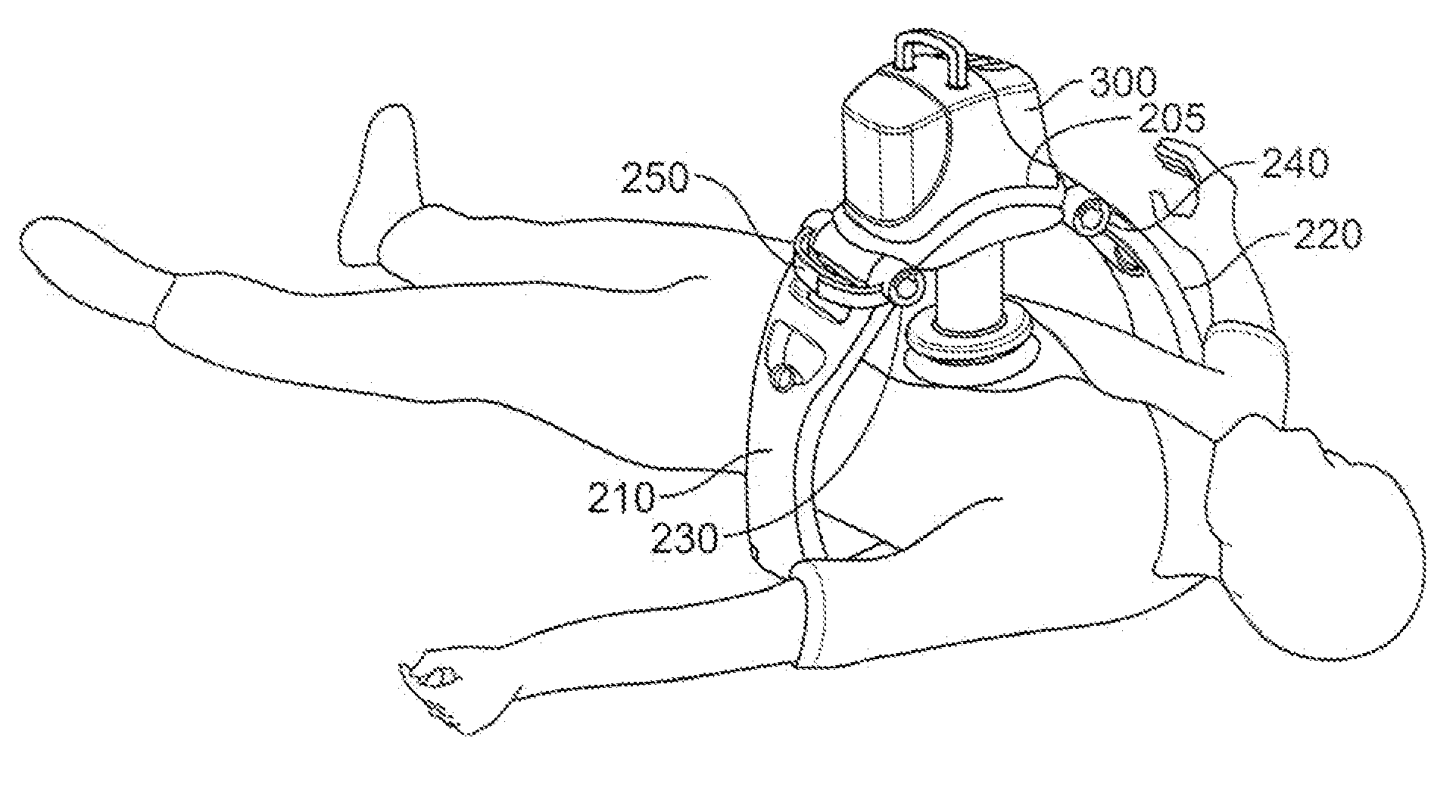
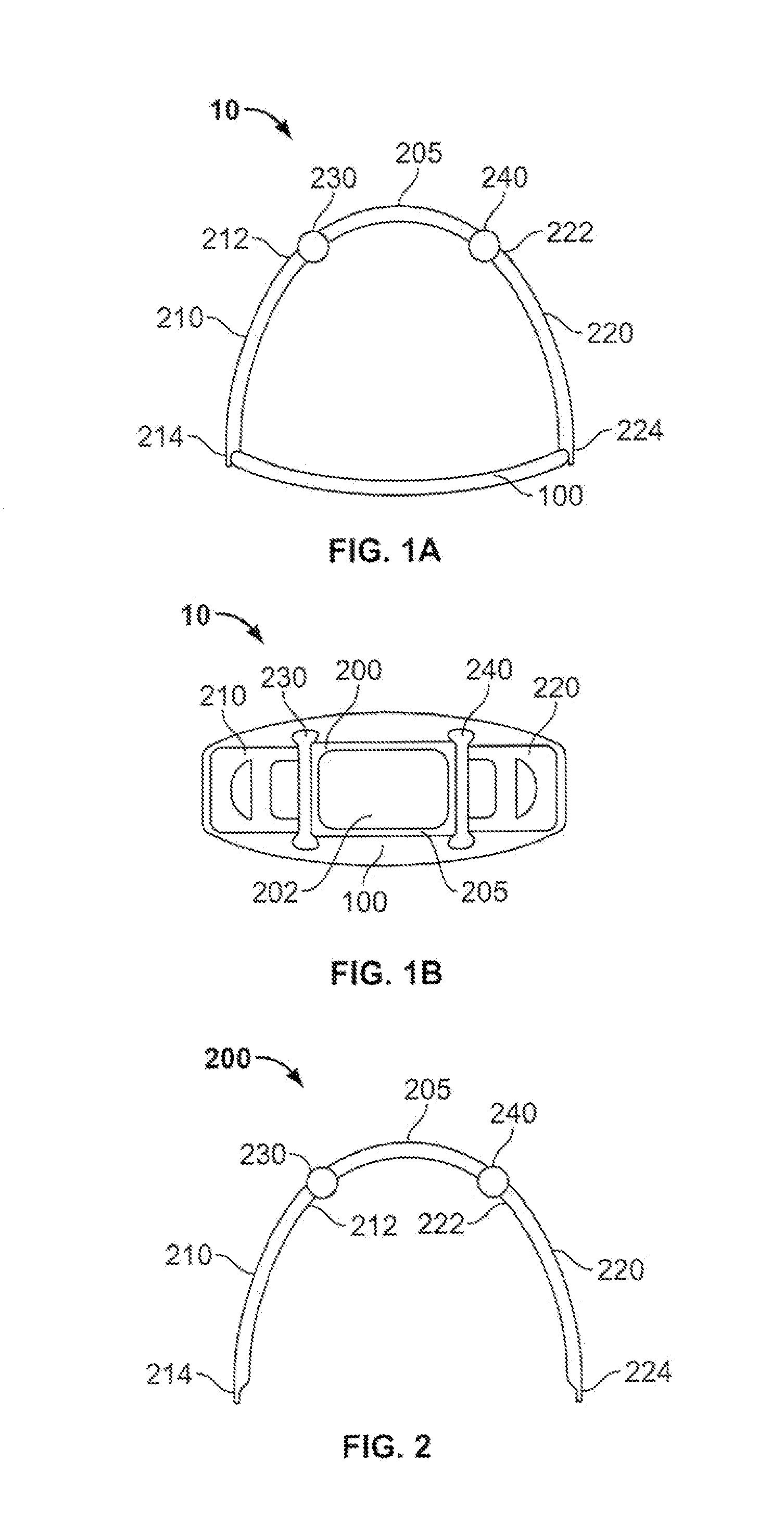
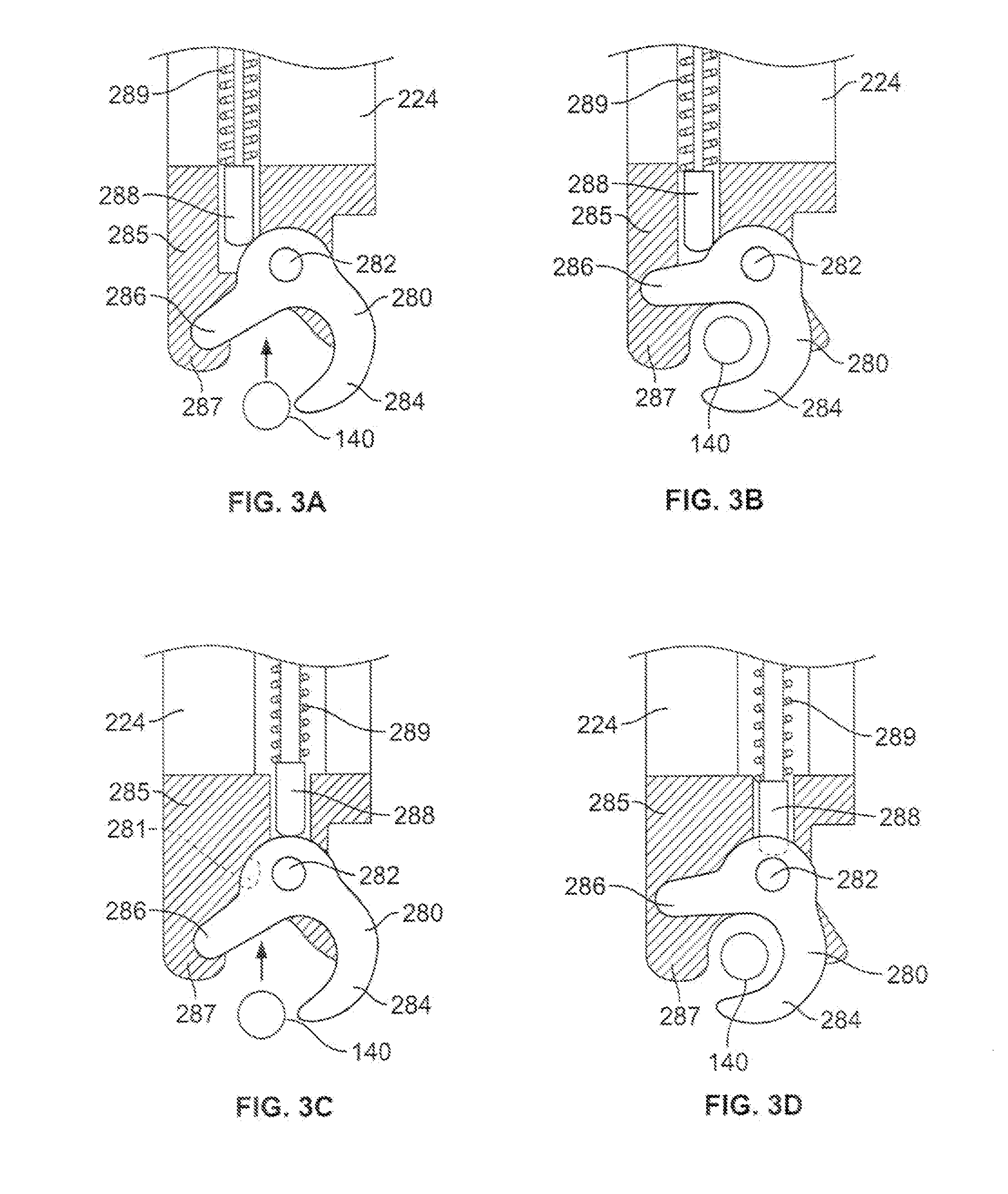
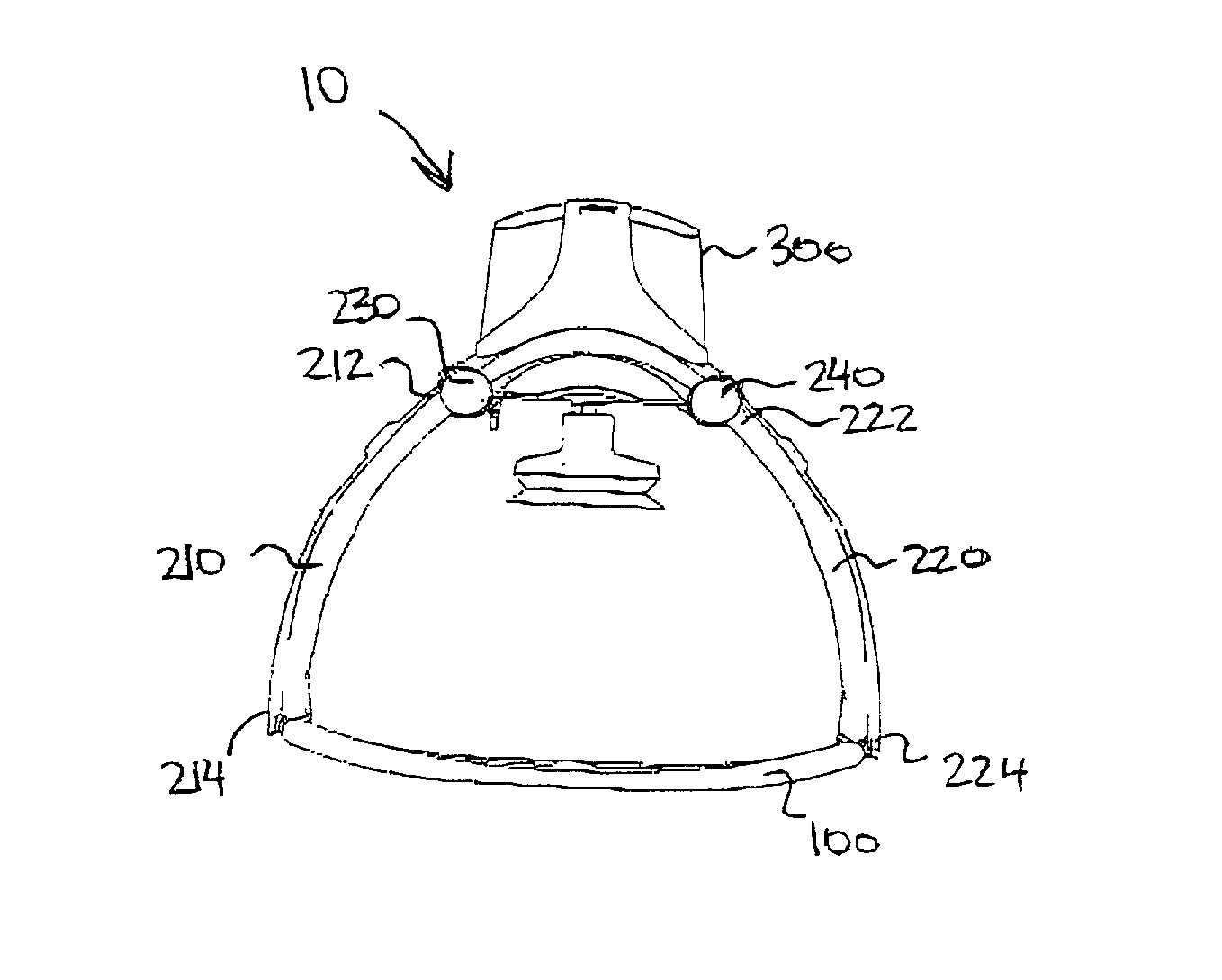
Rigid support structure on two legs for CPR
InactiveUS7569021B2Simple and accurate and effective cardiopulmonary resuscitationImprove accuracyElectrotherapyVibration massageMedicineCardiopulmonary resuscitation
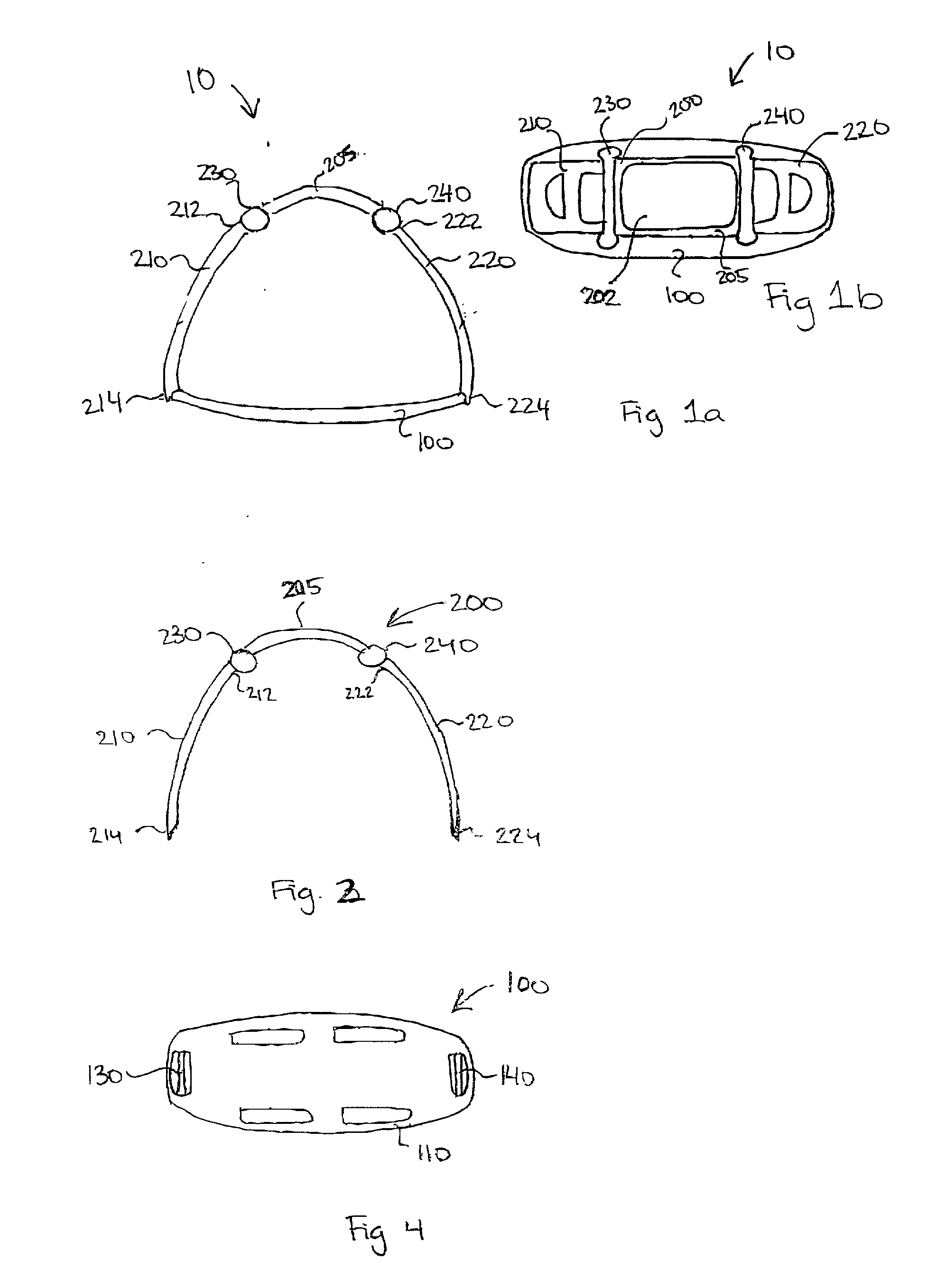
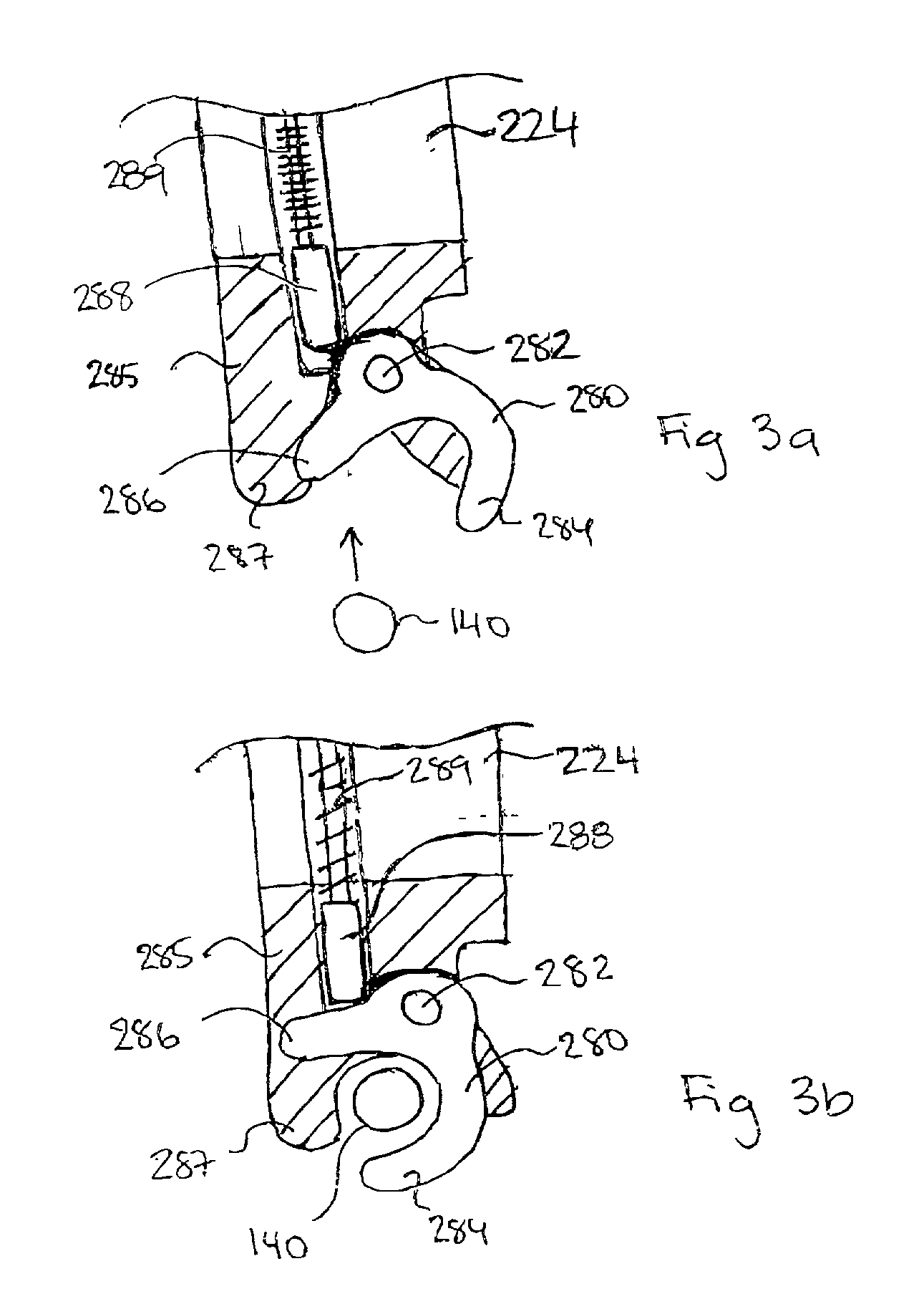
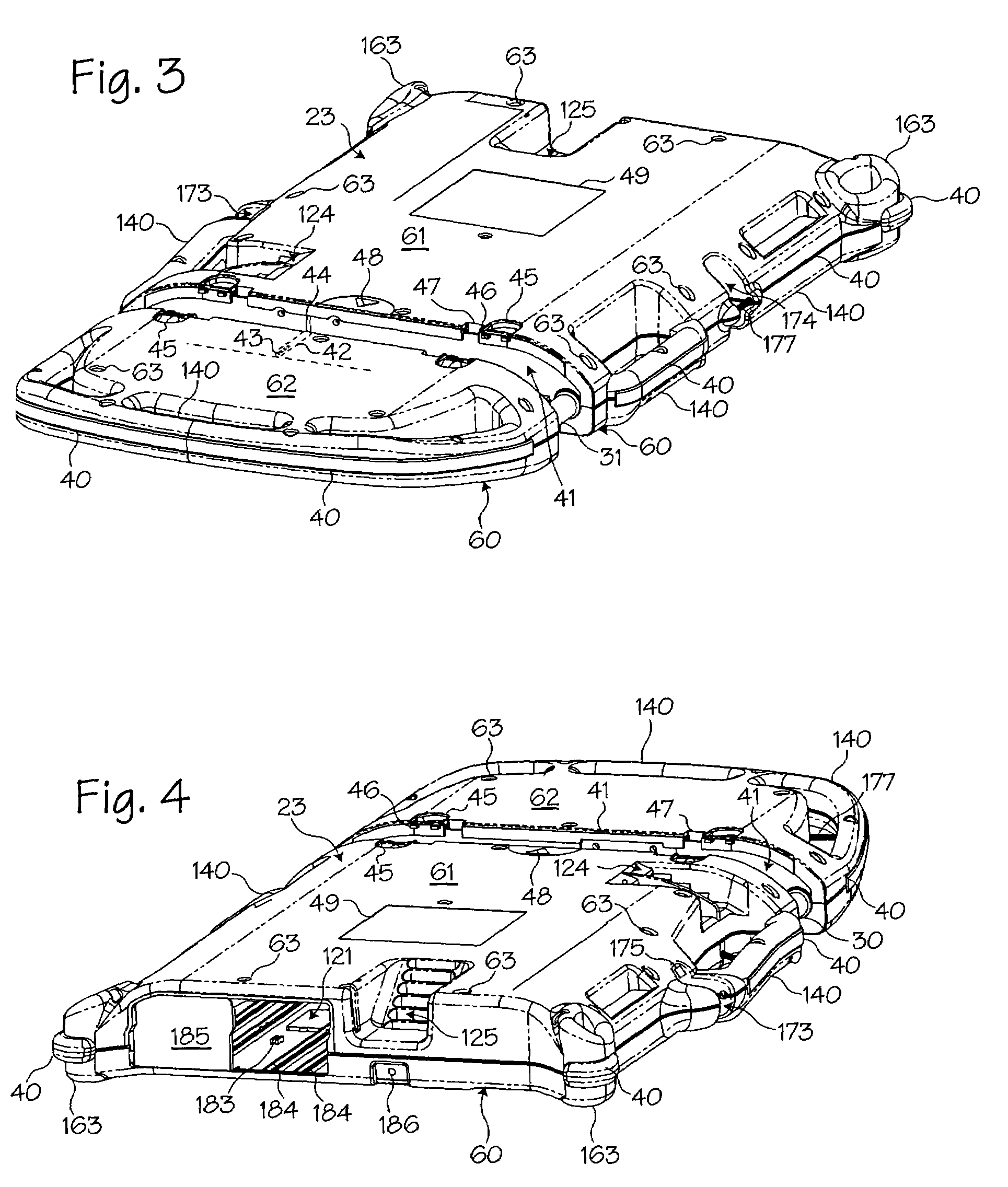
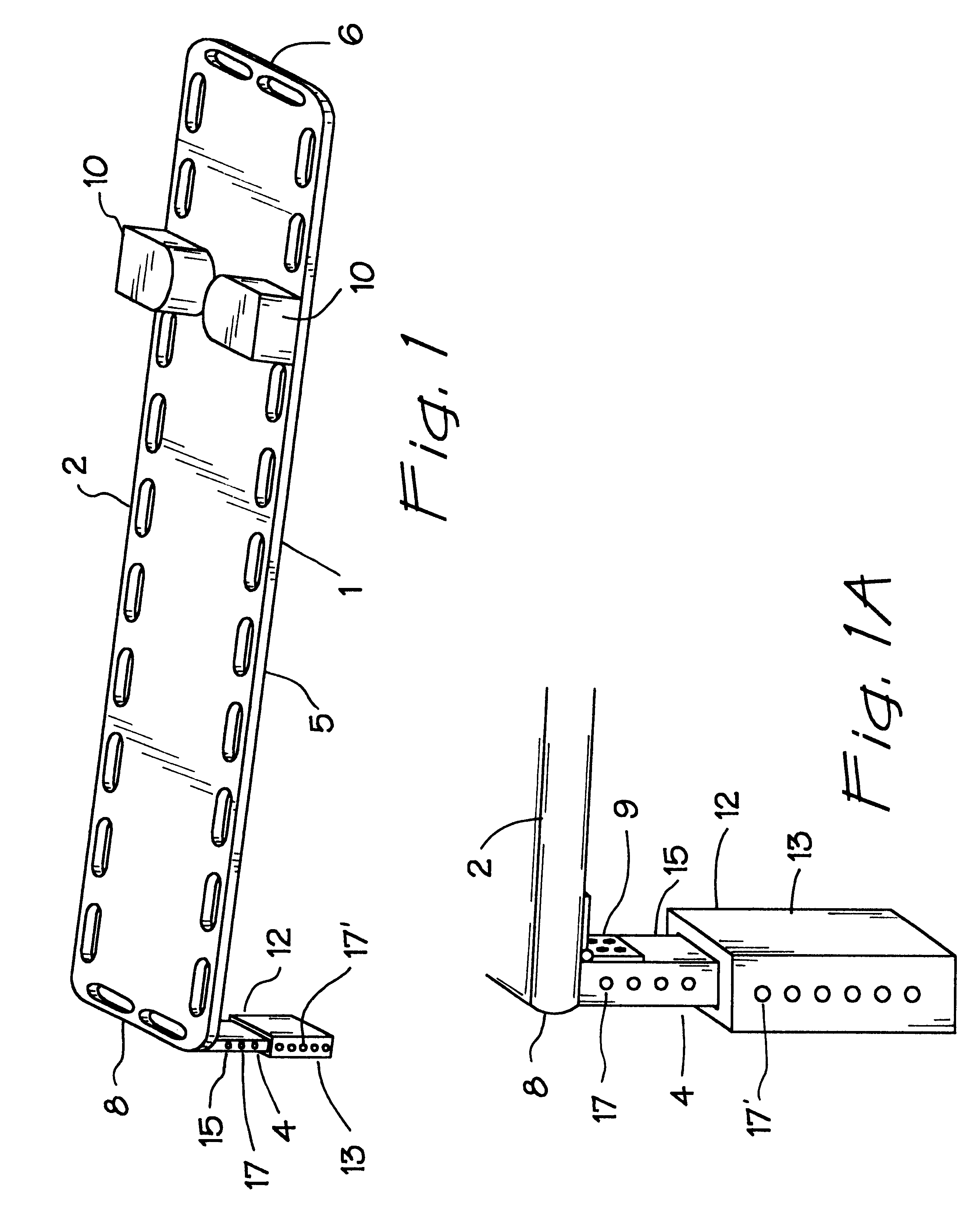
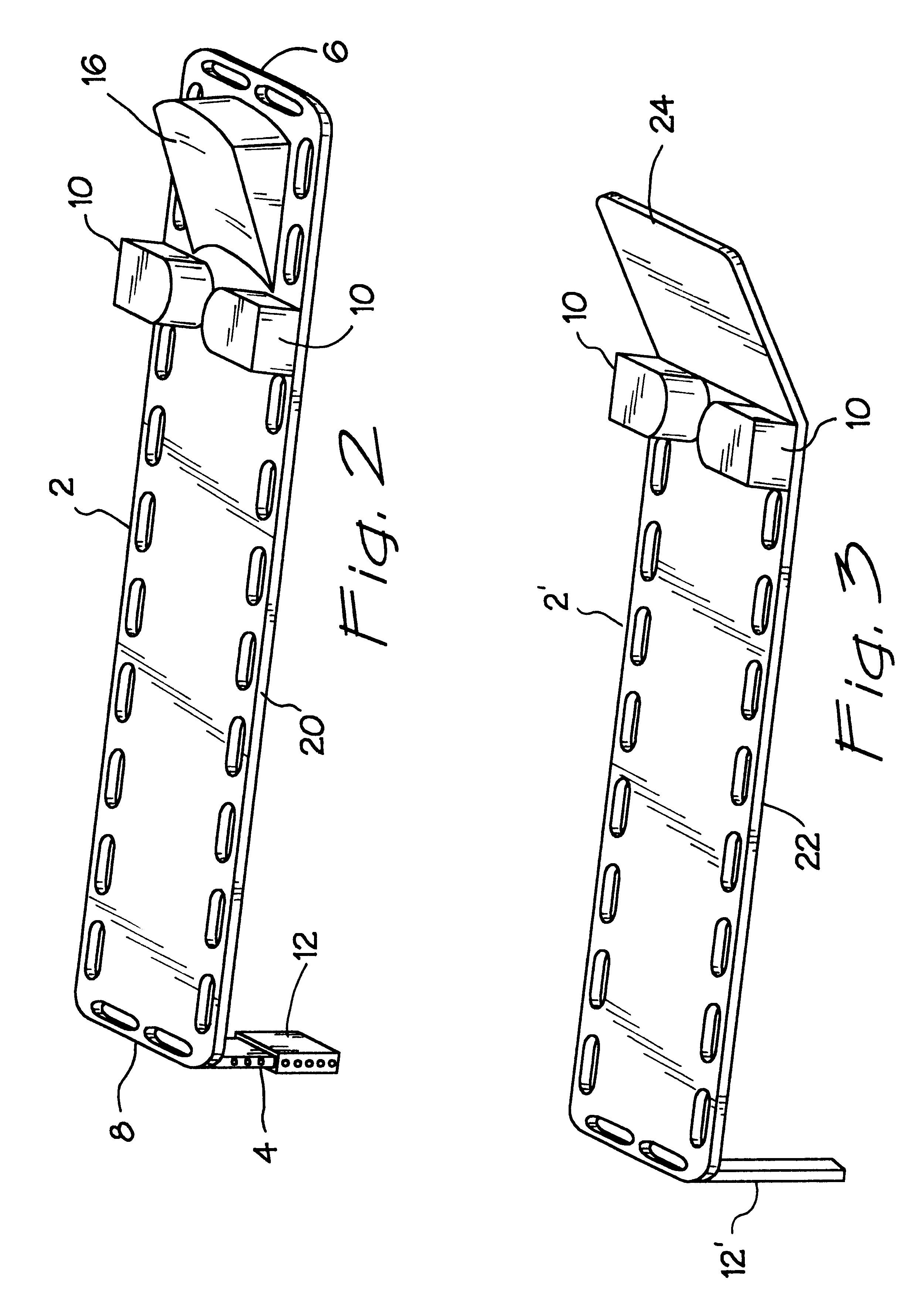
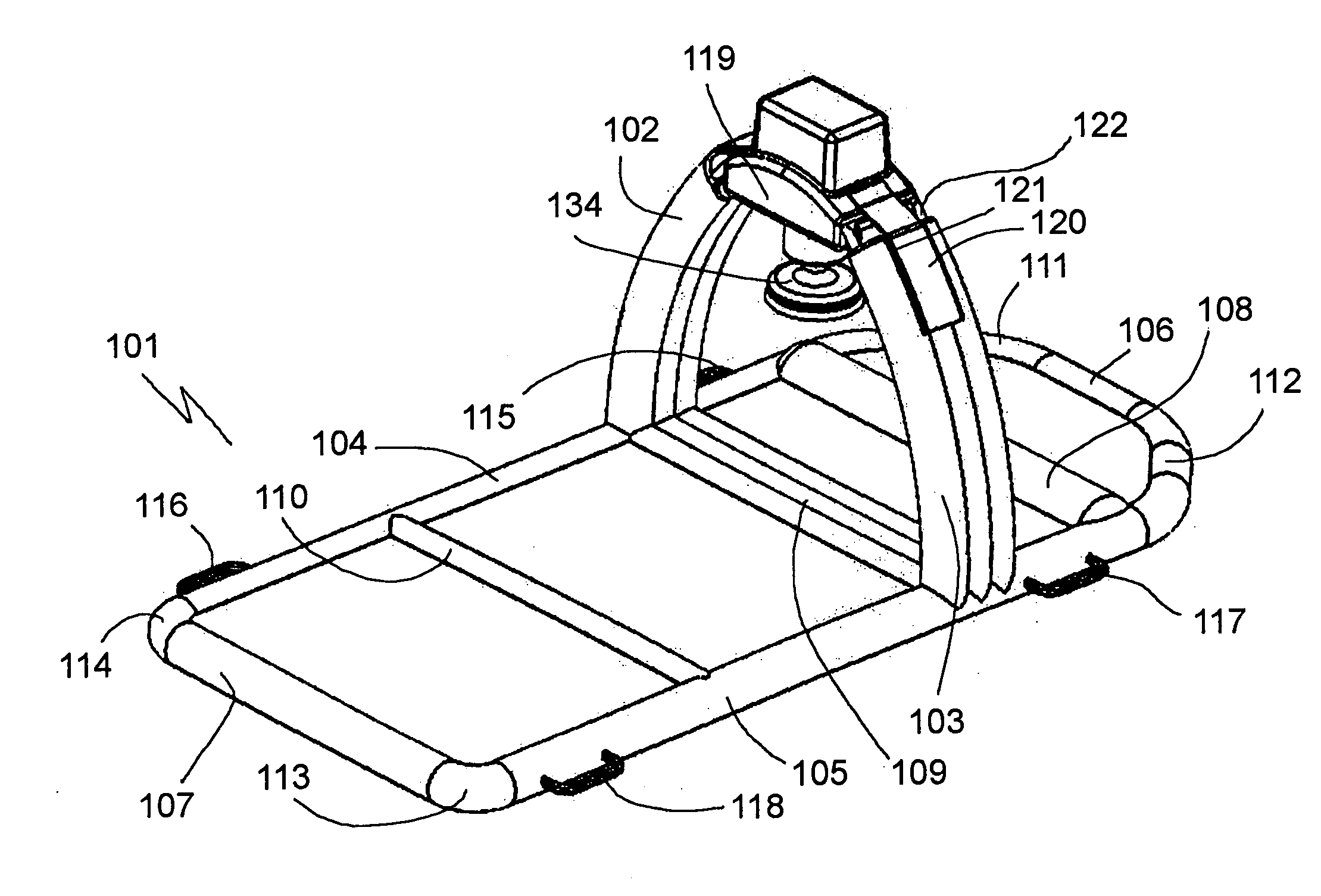
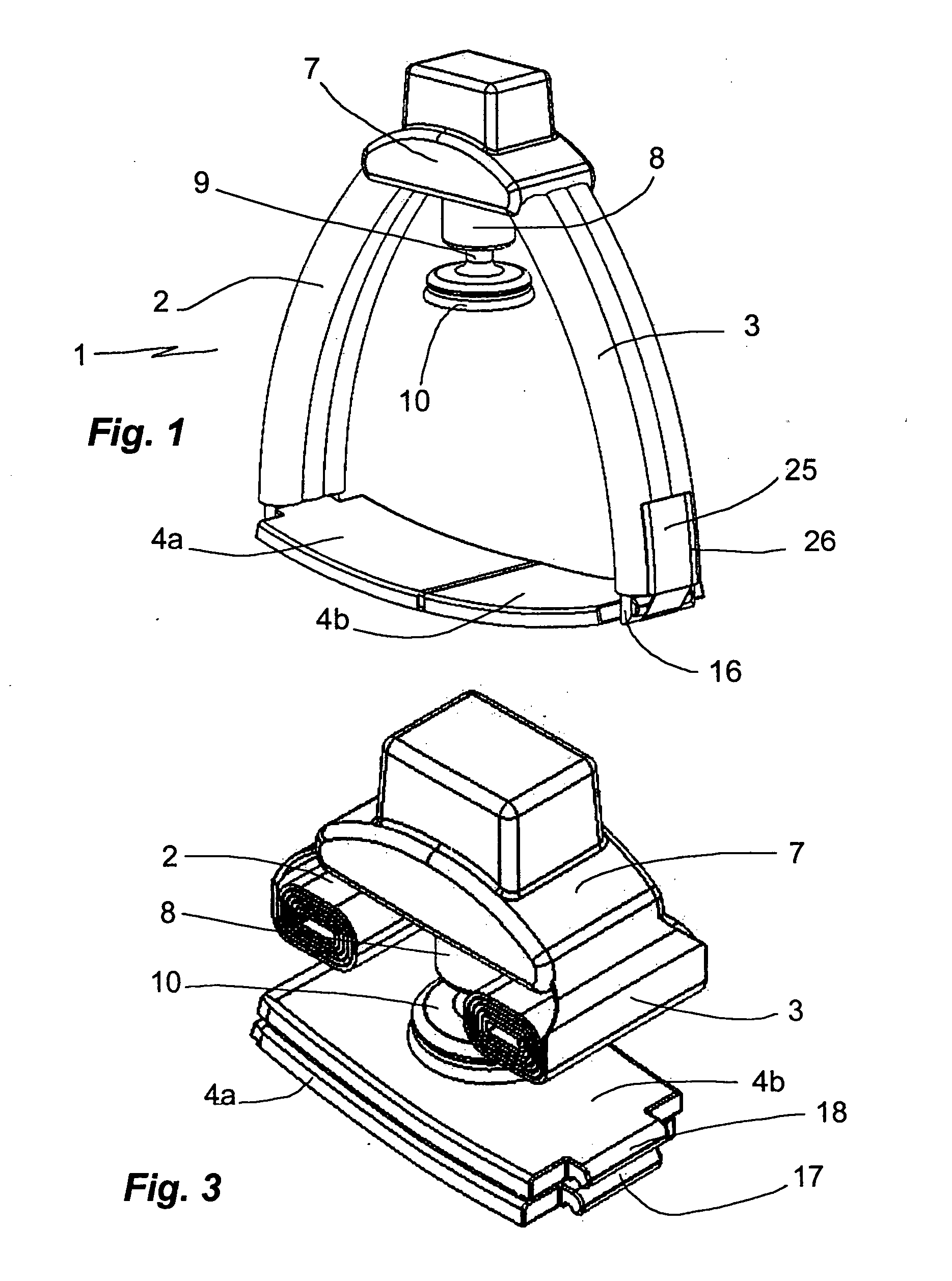
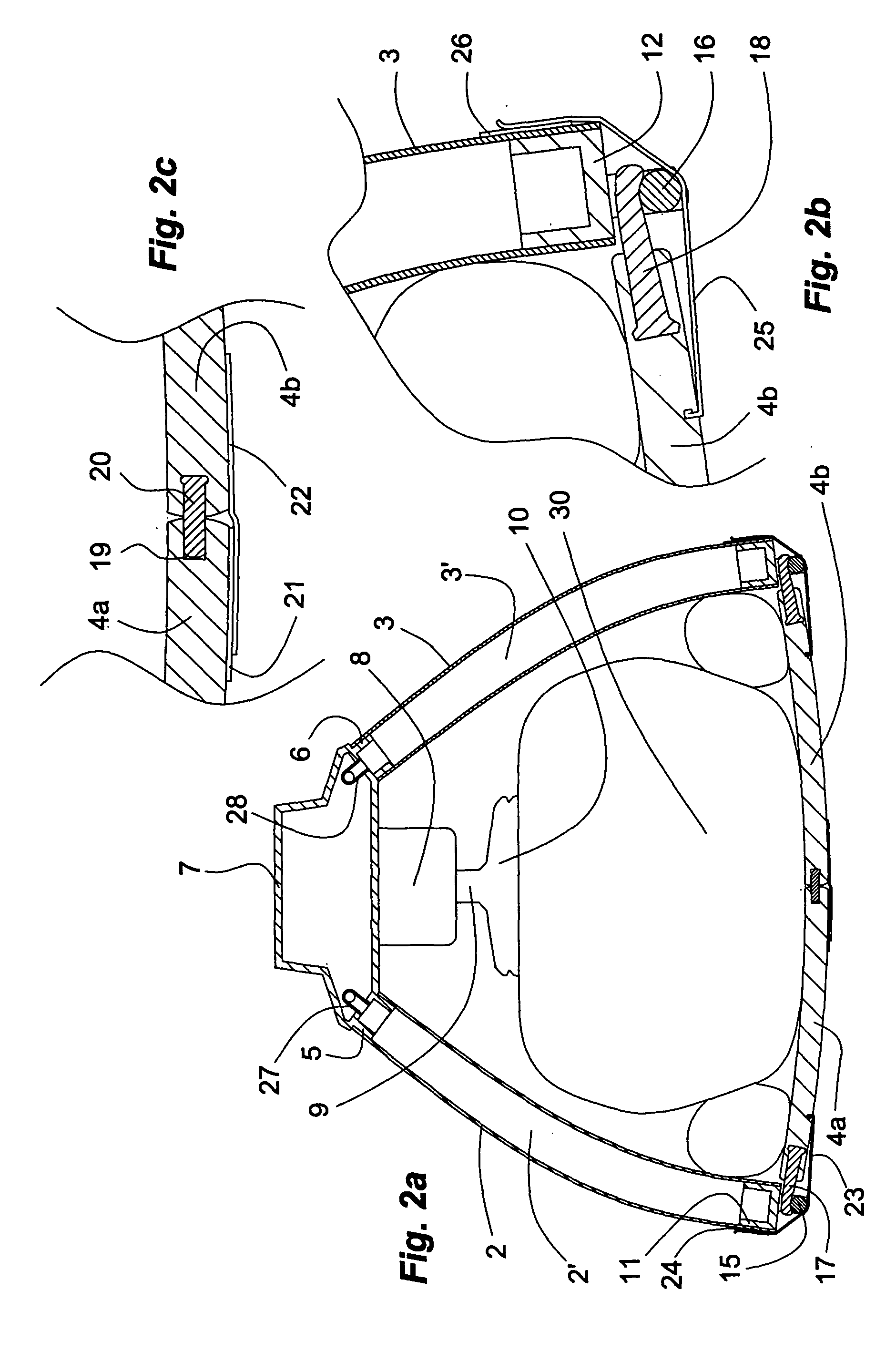
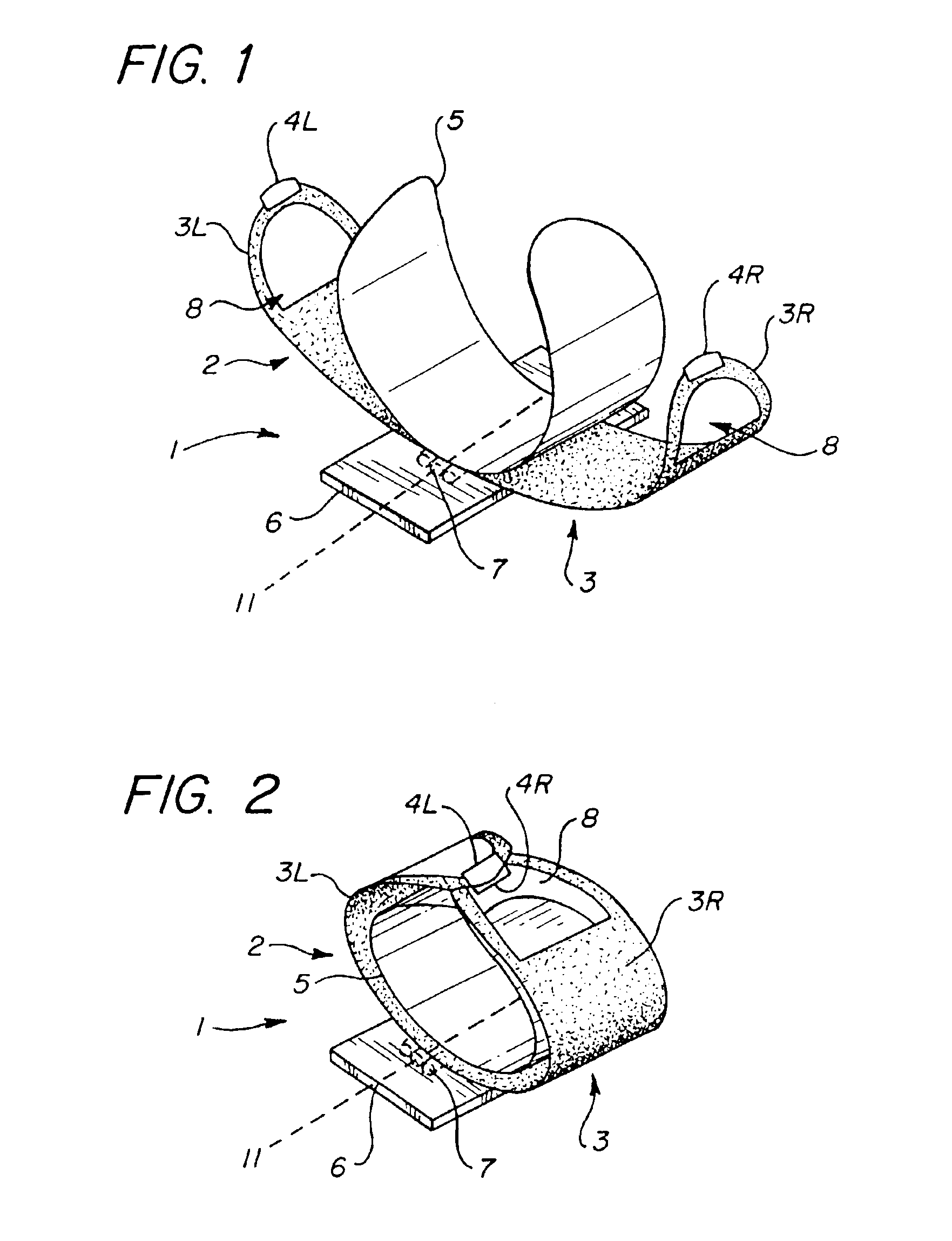
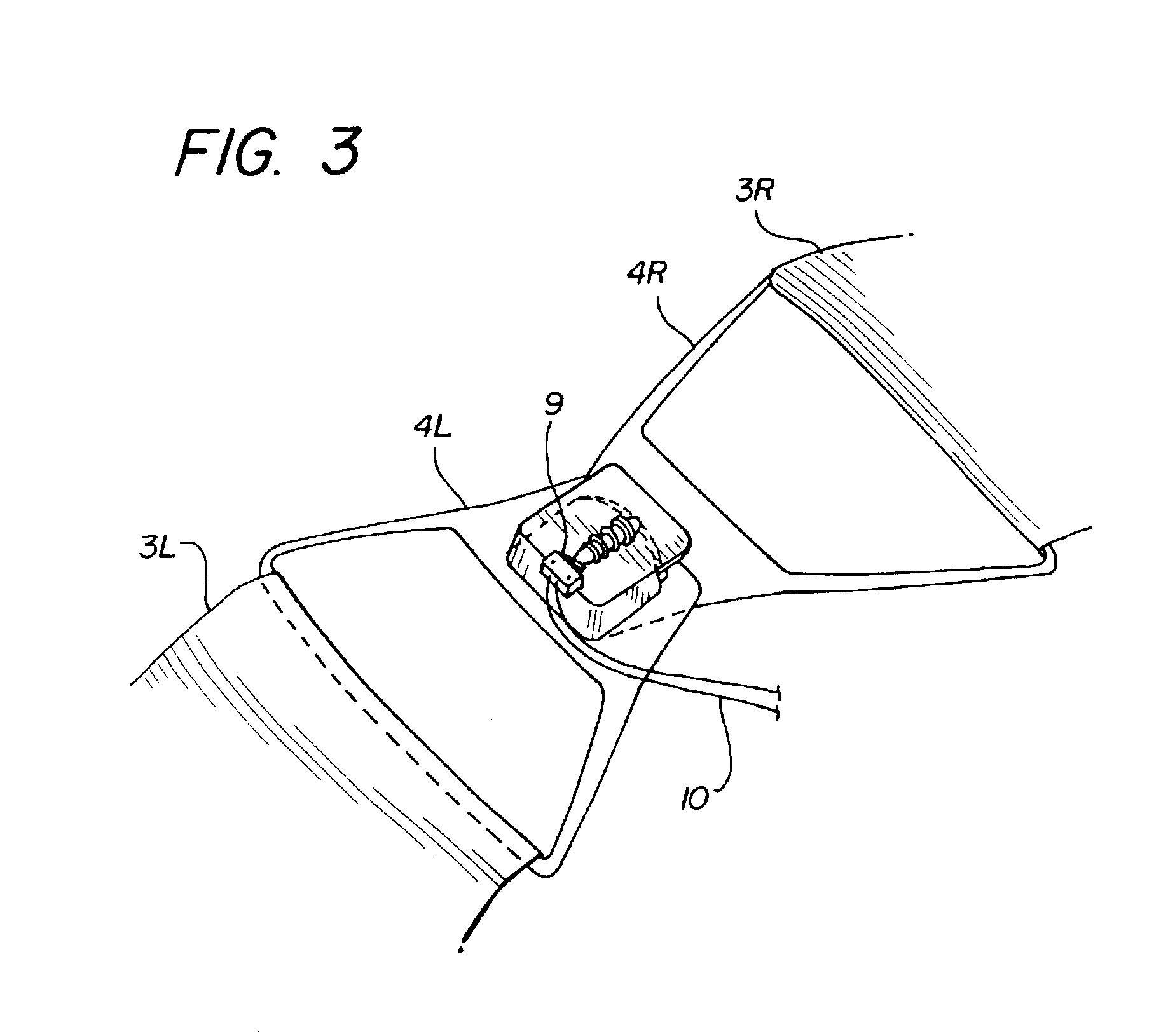
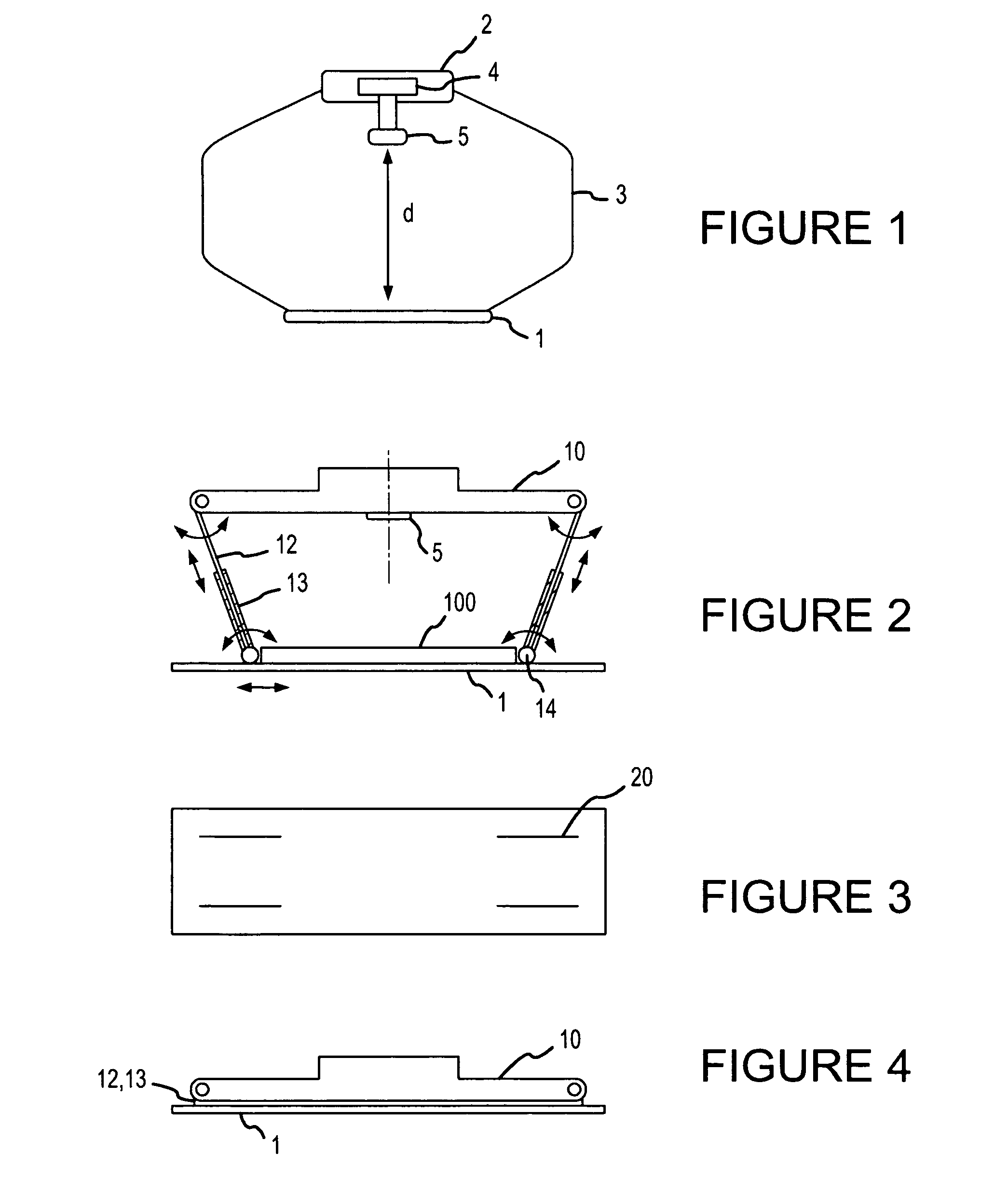
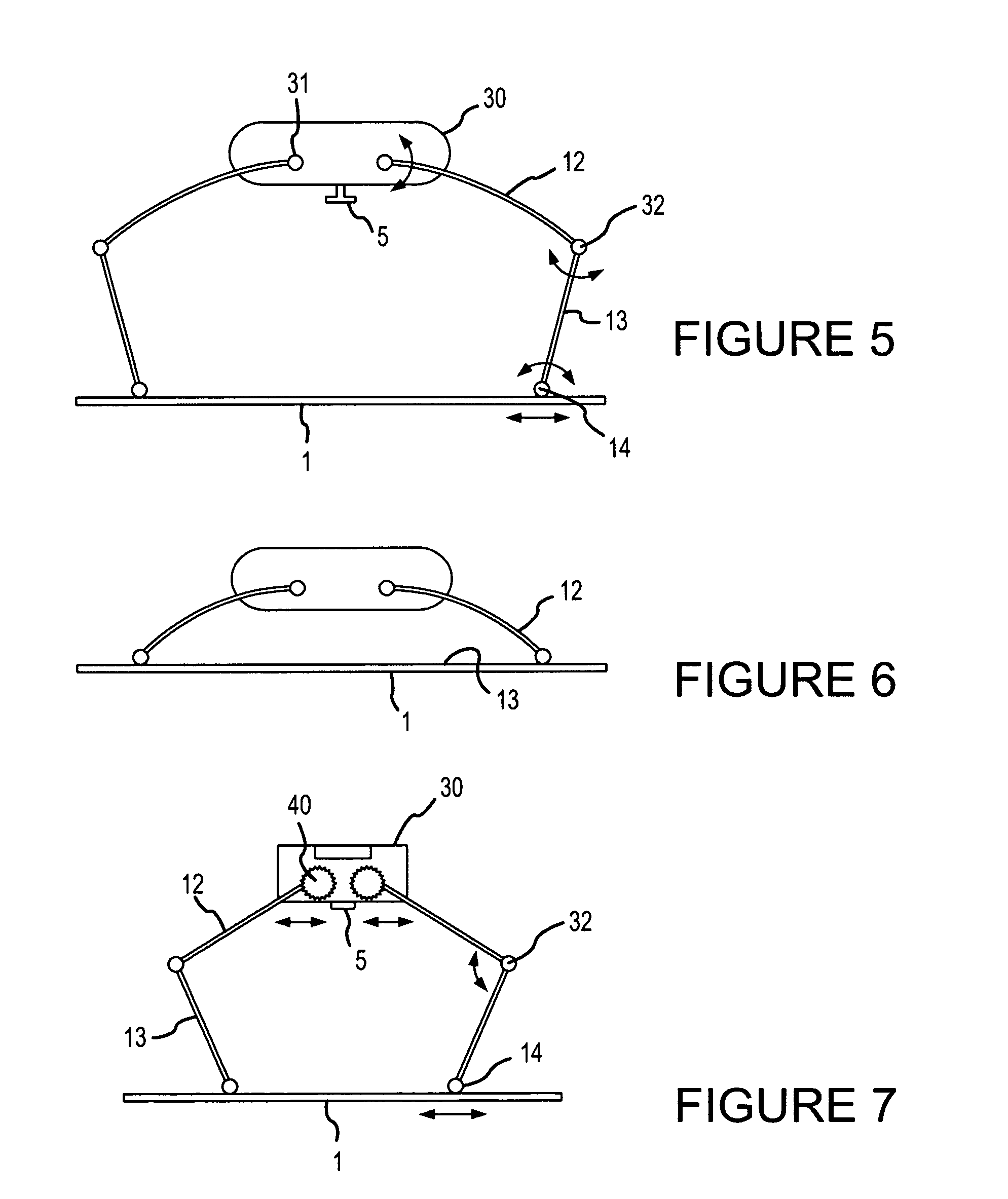
The present invention relates generally to a support structure for fixating a patient to a treatment unit, and especially to a support structure for fixating the patient to a cardiopulmonary resuscitation unit. An embodiment of the support structure (10) comprises a back plate (100) for positioning behind said patient's back posterior to said patient's heart and a front part (200) for positioning around said patient's chest anterior to said patient's heart. Further, the front part (200) can comprise two legs (210, 220), each leg (210, 220) having a first end (212, 222) pivotably connected to at least one hinge (230, 240) and a second end (214, 224) removably attachable to said back plate (100). Said front part (200) can further be devised for comprising a compression / decompression unit (300) arranged to automatically compress or decompress said patient's chest when said front part (200) is attached to said back plate (100).
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
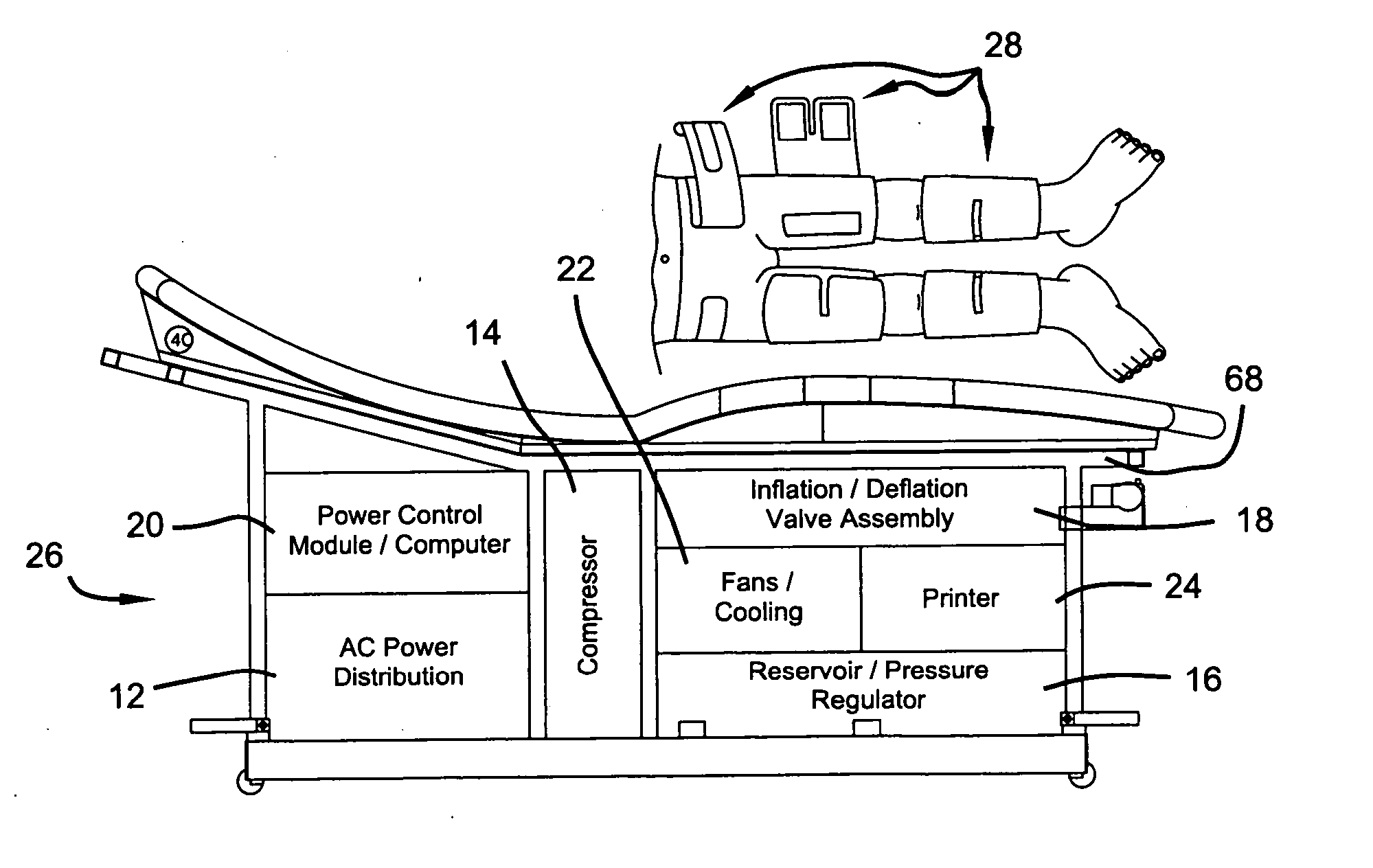
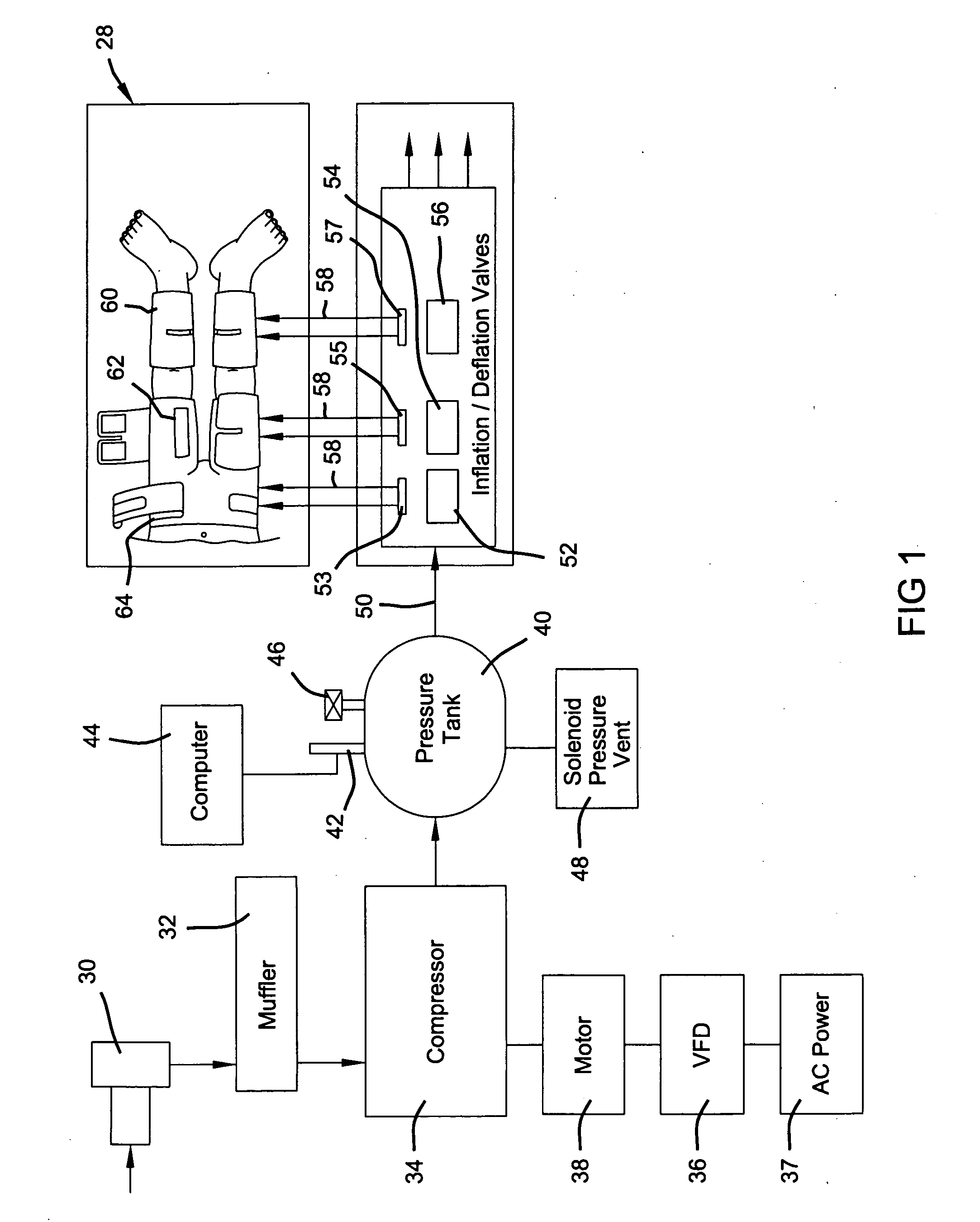
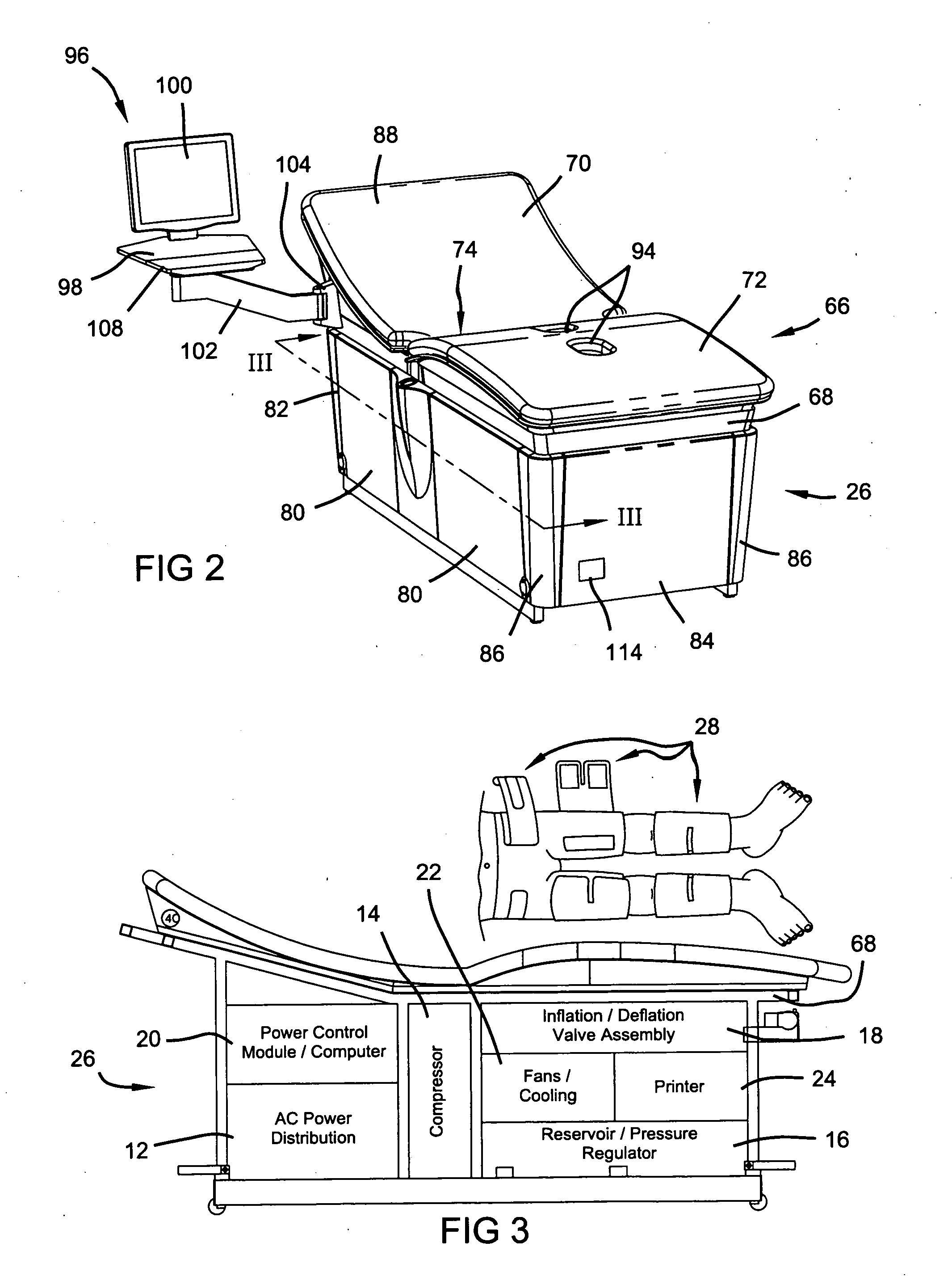
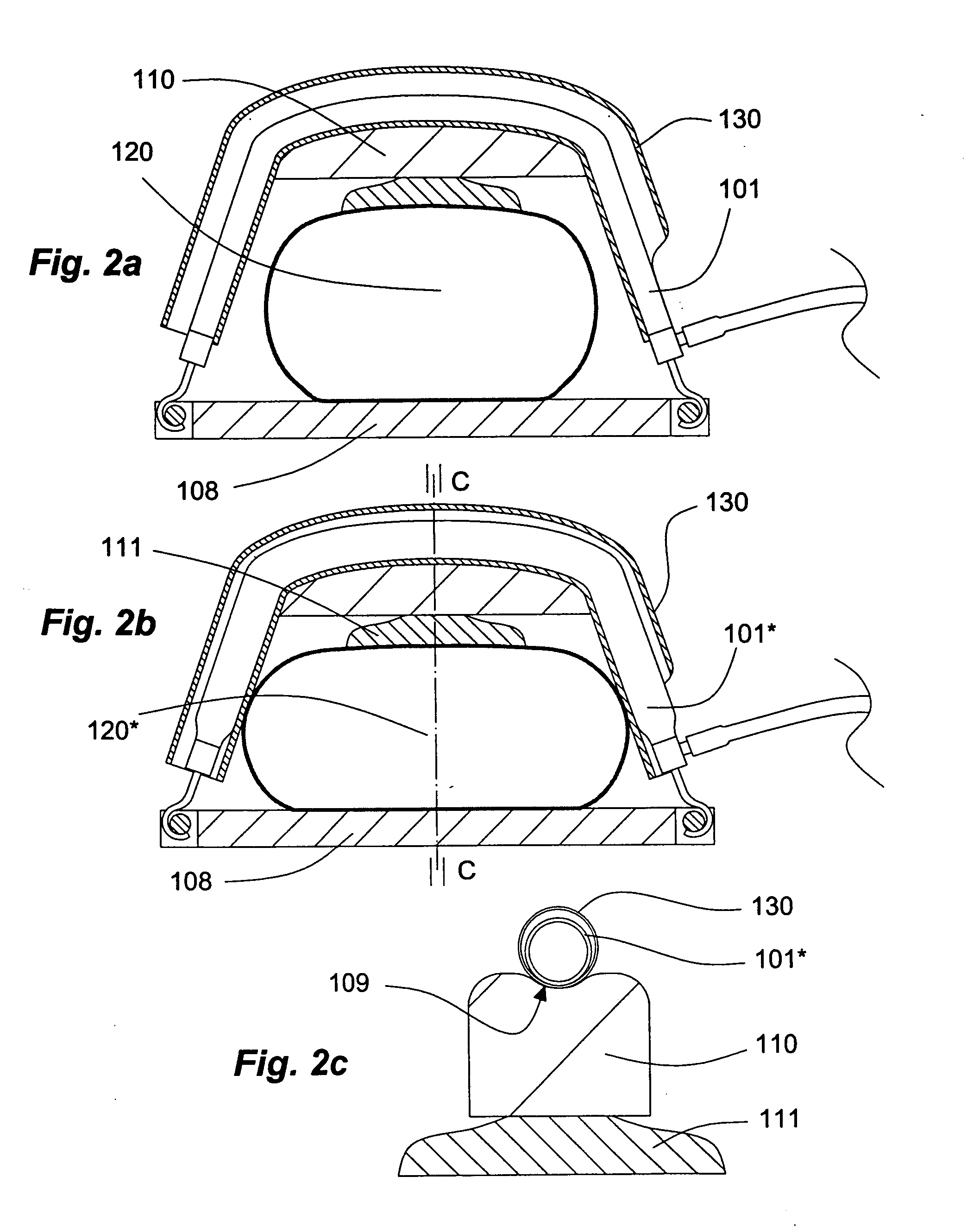
External counterpulsation device having a curvilinear bed
InactiveUS20060058717A1Augmented diastolic central aortic pressureIncreased venous returnPneumatic massageDiagnosticsCompressed fluidComputer module
A unitary external counterpulsation apparatus includes a curvilinear bed supported by a frame housing and fluid distribution assembly and control module. The bed includes a concave upper portion, a convex lower portion, and a saddle point therebetween. The fluid distribution assembly interconnects a plurality of inflatable devices adapted to be received about the lower extremities of a patient and a compressed fluid source. The control module controls distribution of compressed fluid from the source to the inflatable devices. Variable flow-rate valves optimize distribution of the compressed fluid.
Owner:HUI JOHN C K +3
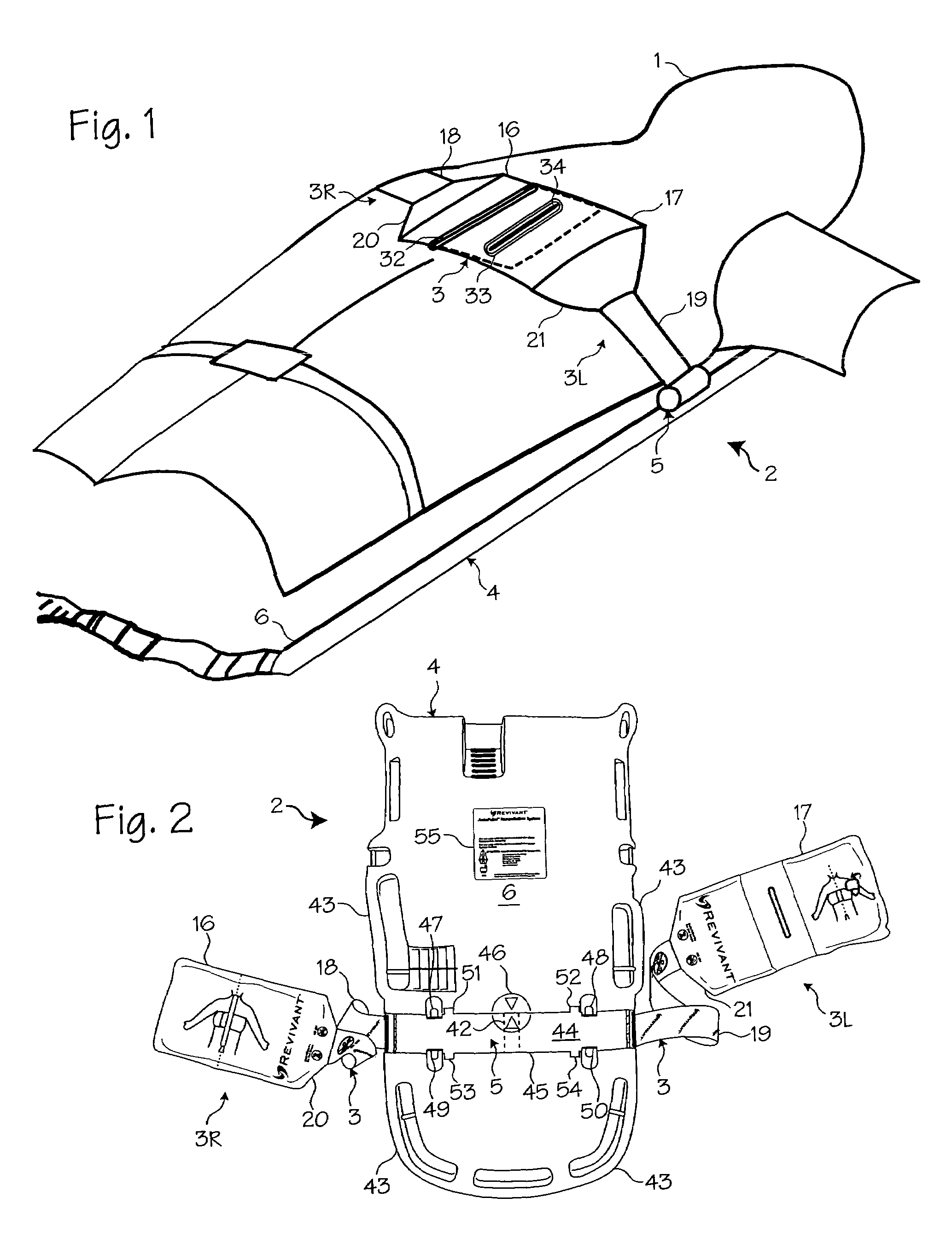
Support structure
InactiveUS20030181834A1Improve accuracySimple and accurate and effective cardiopulmonary resuscitationElectrotherapyVibration massagePhysical therapyCardiopulmonary resuscitation
The present invention relates generally to a support structure for fixating a patient to a treatment unit, and especially to a support structure for fixating the patient to a cardiopulmonary resuscitation unit. An embodiment of the support structure (10) comprises a back plate (100) for positioning behind said patient's back posterior to said patient's heart and a front part (200) for positioning around said patient's chest anterior to said patient's heart. Further, the front part (200) can comprise two legs (210, 220), each leg (210, 220) having a first end (212, 222) pivotably connected to at least one hinge (230, 240) and a second end (214, 224) removably attachable to said back plate (100). Said front part (200) can further be devised for comprising a compression / decompression unit (300) arranged to automatically compress or decompress said patient's chest when said front part (200) is attached to said back plate (100).
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
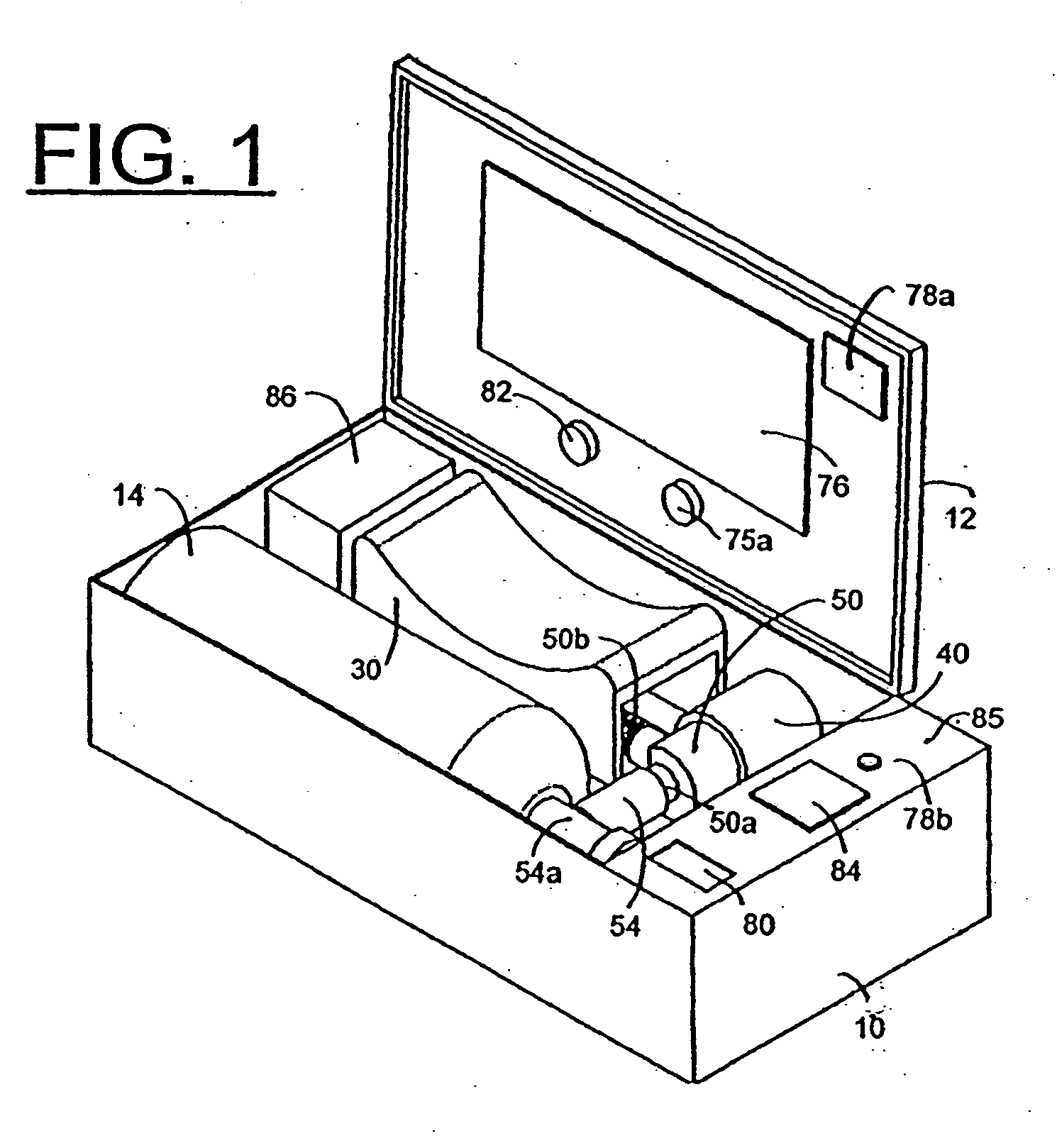
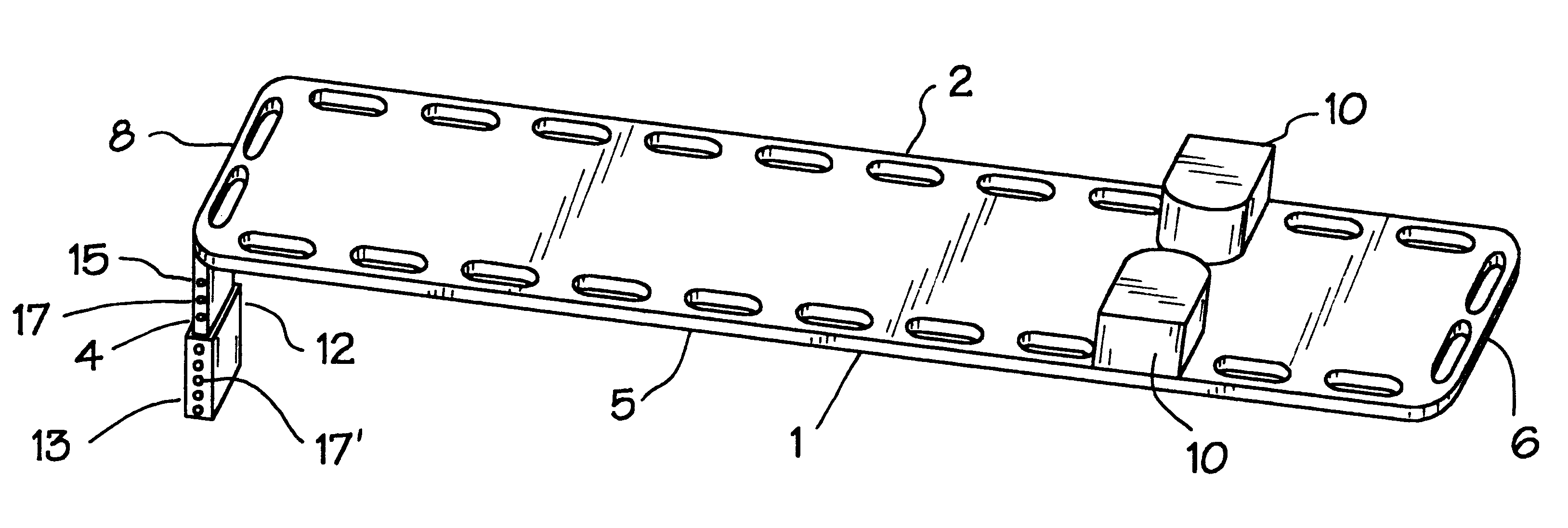
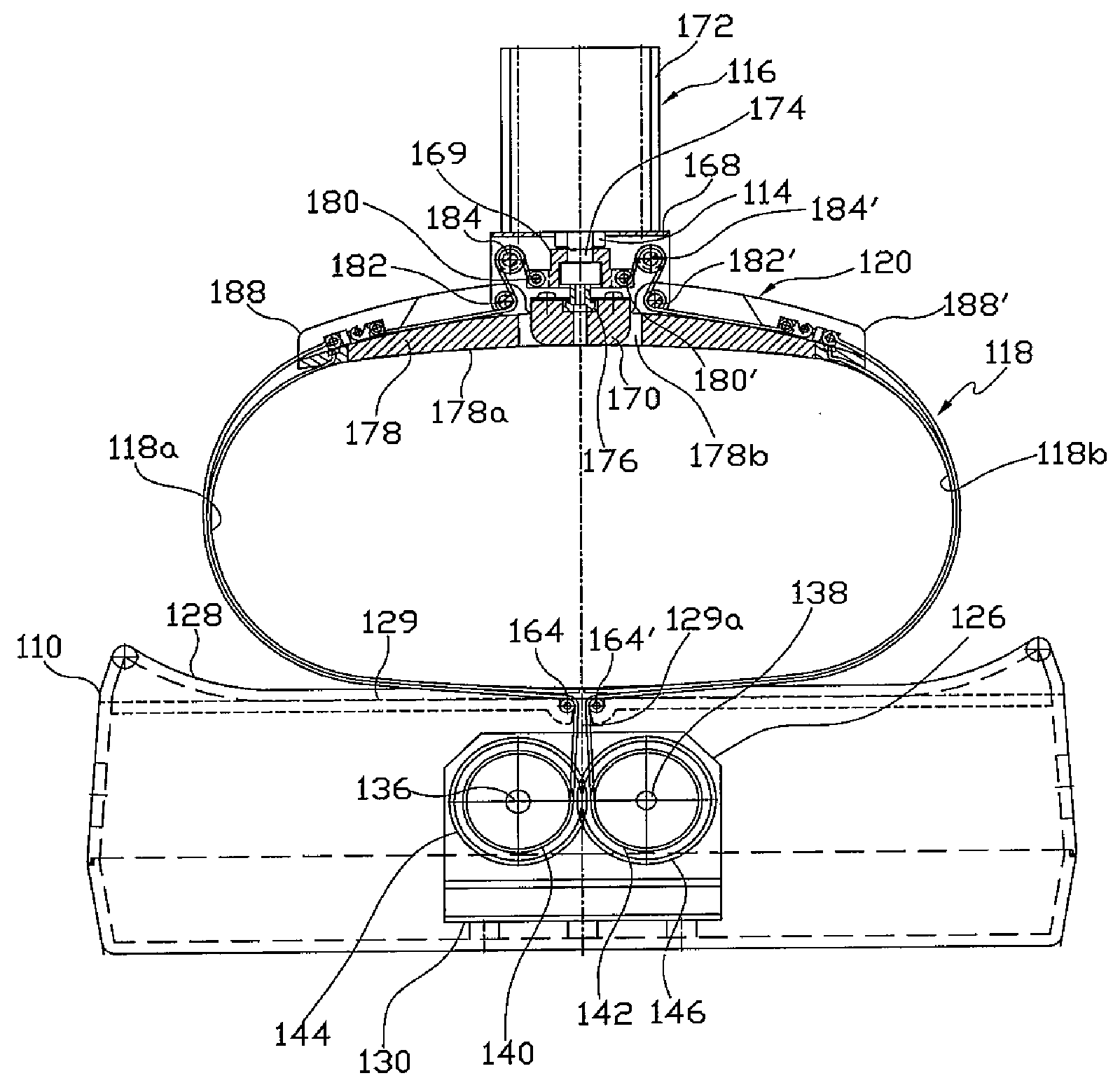
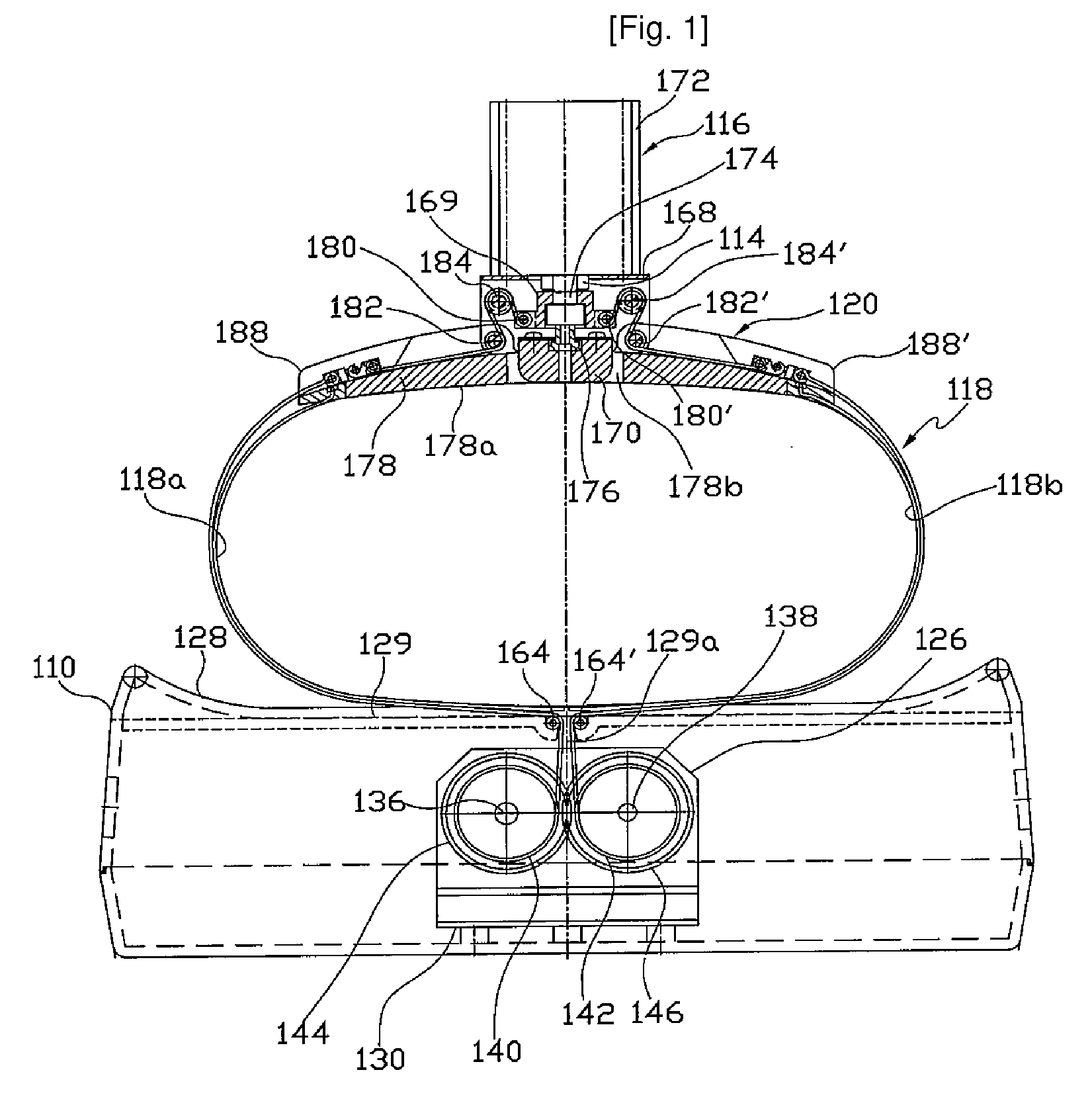
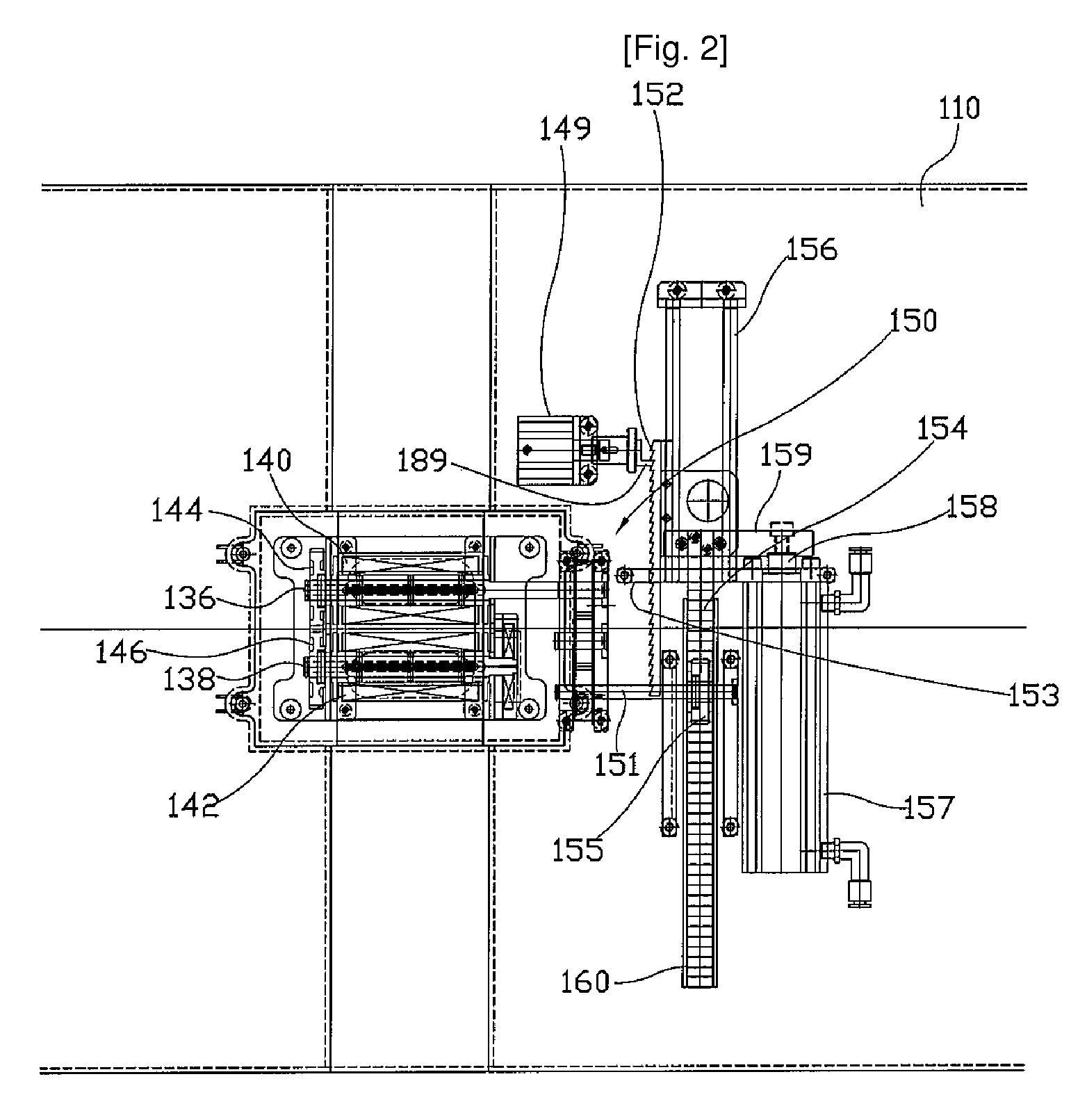
Lightweight electro-mechanical chest compression device
ActiveUS7347832B2Easy to changeLightweight materialElectrotherapySurgeryControl systemCompression device
A lightweight electro-mechanical chest compression device. The device is provided with a motor, a brake, a drive spool, a control system, and a metal channel beam to brace the device and guide a compression belt. The belt is provided in a belt cartridge that attaches to the channel beam. In use, the belt is secured around the patient and to the drive spool. The motor tightens the belt by turning the drive spool. The electro-mechanical chest compression device weighs less than 30 pounds when fully assembled with its power source.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
CPR compression device and method
InactiveUS6939314B2Easy to compressMaximize effectivenessRespiratorsMassage combsCompression devicePiston
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Devices for determining depth of chest compressions during CPR
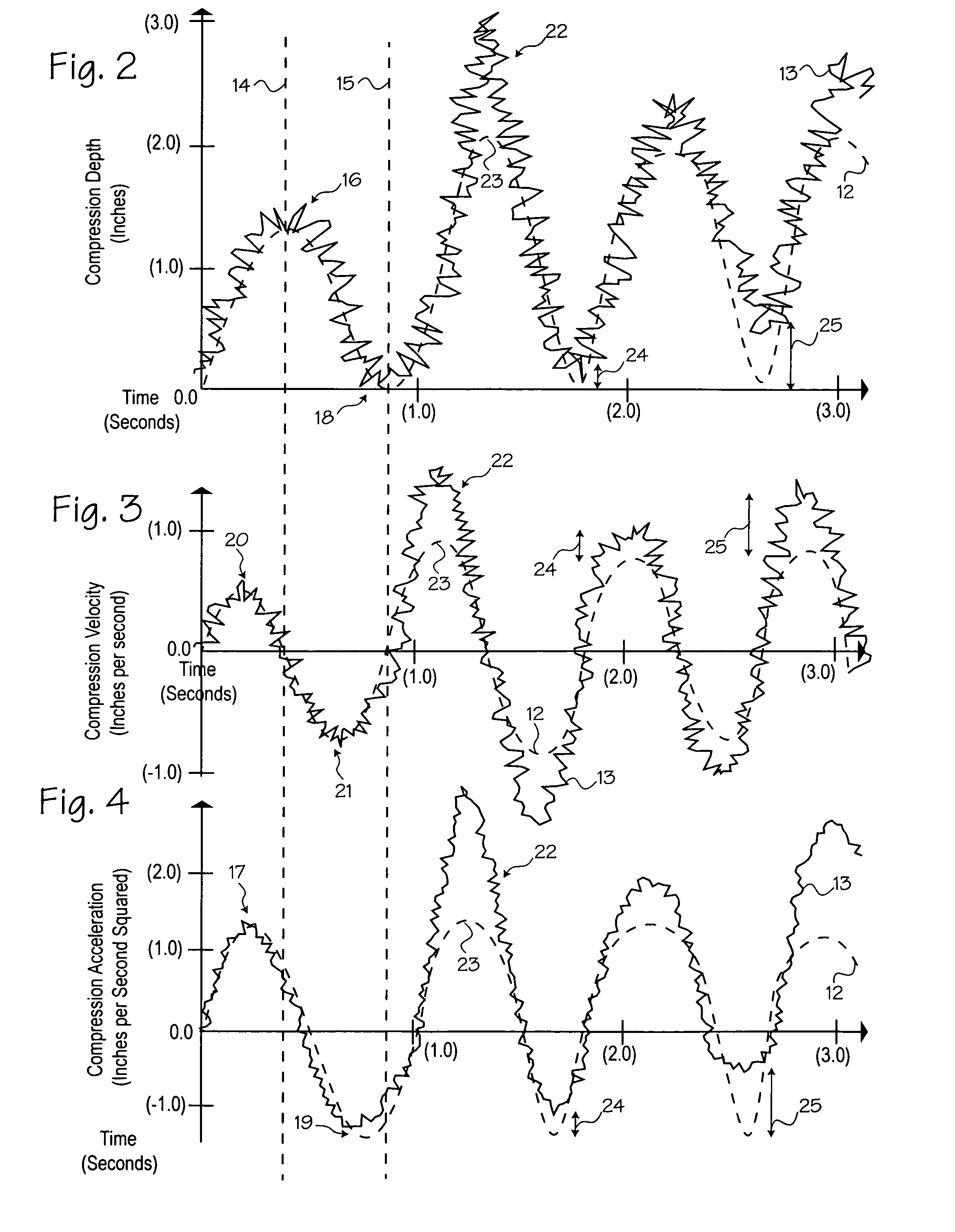
A method of processing a raw acceleration signal, measured by an accelerometer-based compression monitor, to produce an accurate and precise estimated actual depth of chest compressions. The raw acceleration signal is filtered during integration and then a moving average of past starting points estimates the actual current starting point. An estimated actual peak of the compression is then determined in a similar fashion. The estimated actual starting point is subtracted from the estimated actual peak to calculate the estimated actual depth of chest compressions. In addition, one or more reference sensors (such as an ECG noise sensor) may be used to help establish the starting points of compressions. The reference sensors may be used, either alone or in combination with other signal processing techniques, to enhance the accuracy and precision of the estimated actual depth of compressions.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
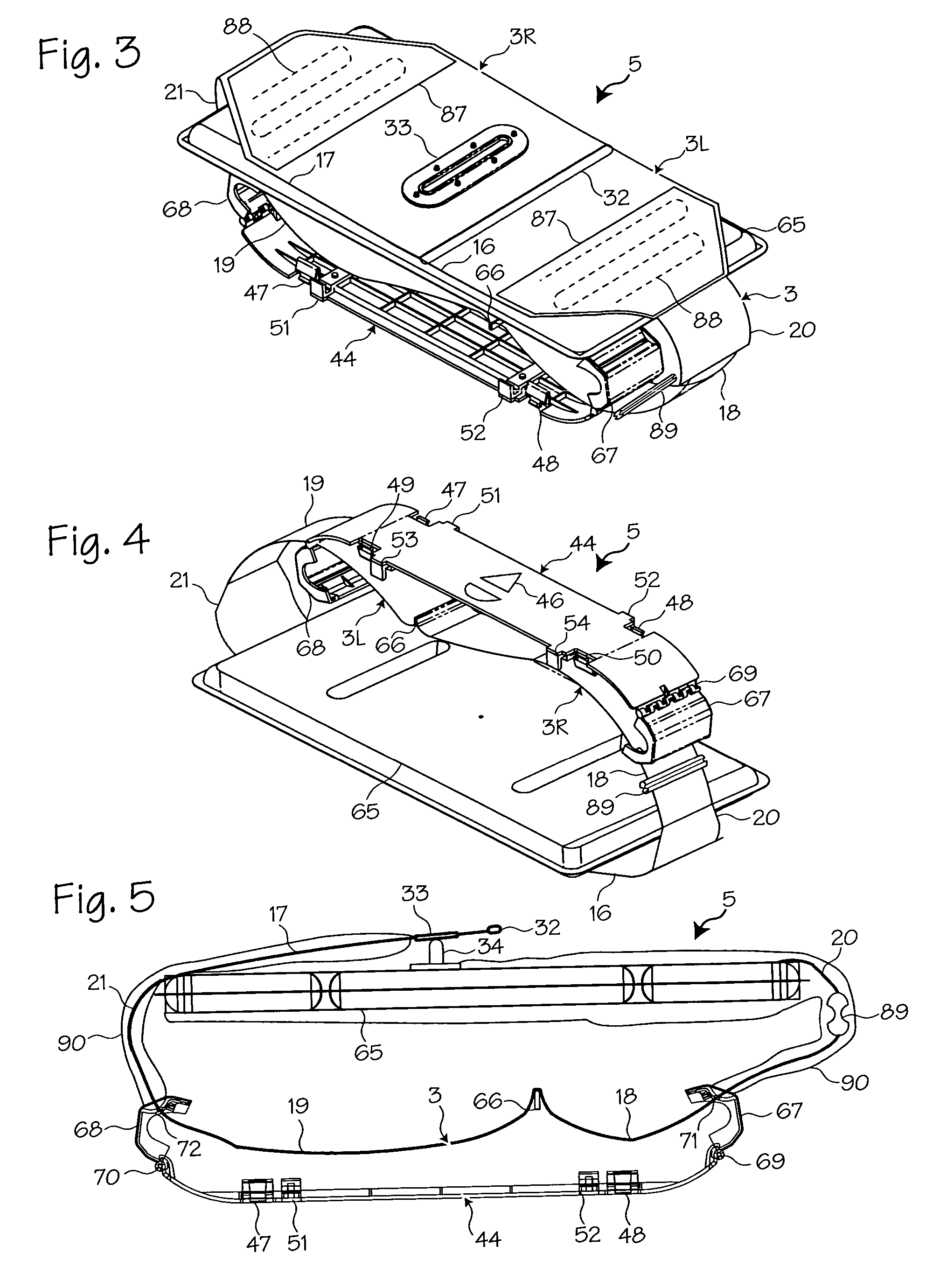
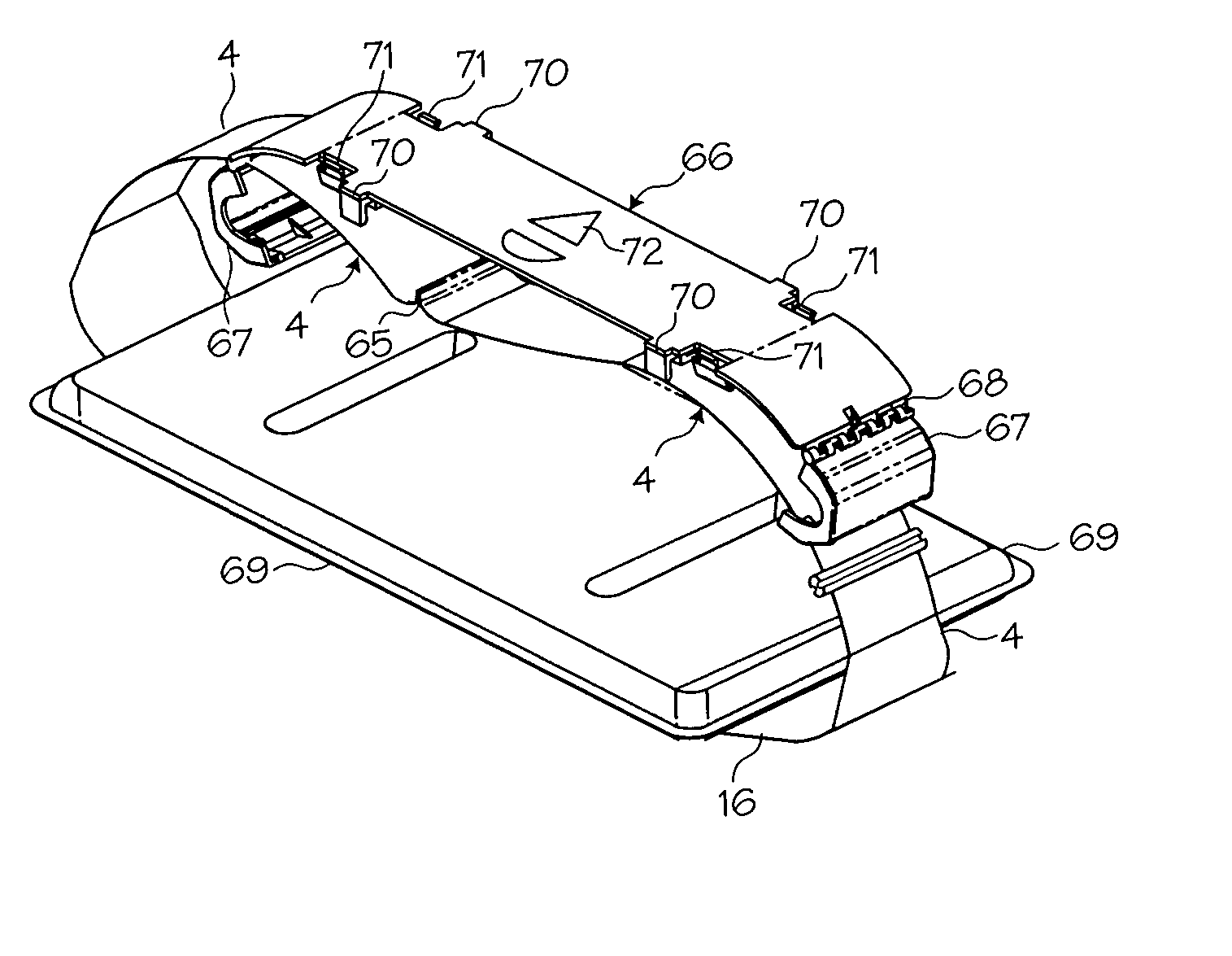
Methods and devices for attaching a belt cartridge to a chest compression device
Devices and methods for attaching a belt cartridge to a belt drive platform. A spline attached to the belt is inserted into a slot in the drive spool of the belt drive platform. The cover plate of the belt cartridge fits into a channel beam in the housing of the belt drive platform, thereby securing the cartridge to the housing. Belt guards, for protecting the cartridge, belt drive platform, patient and rescuer, are rotatably attached to the cover plate and are secured around spindles disposed on the sides of the housing.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
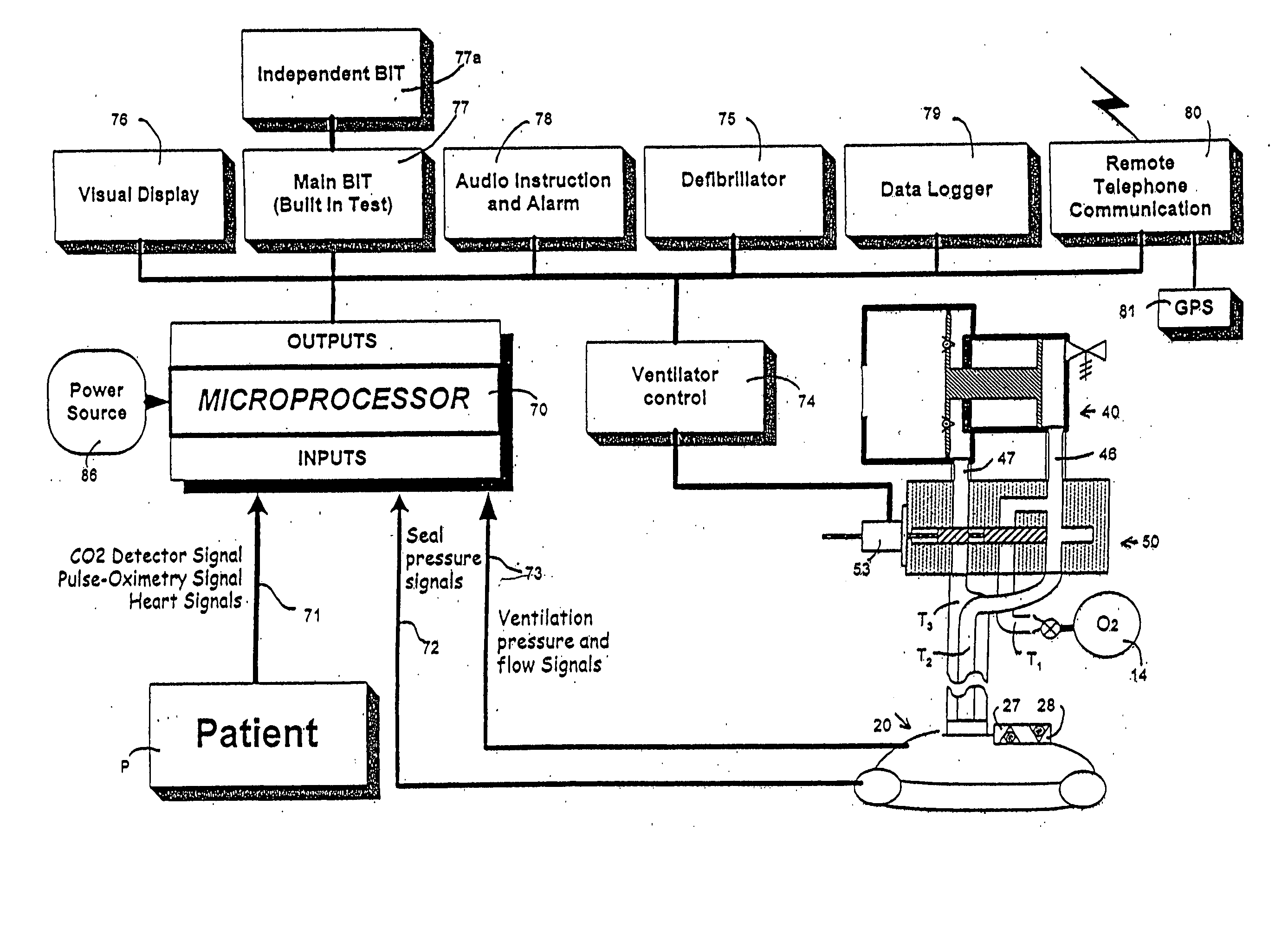
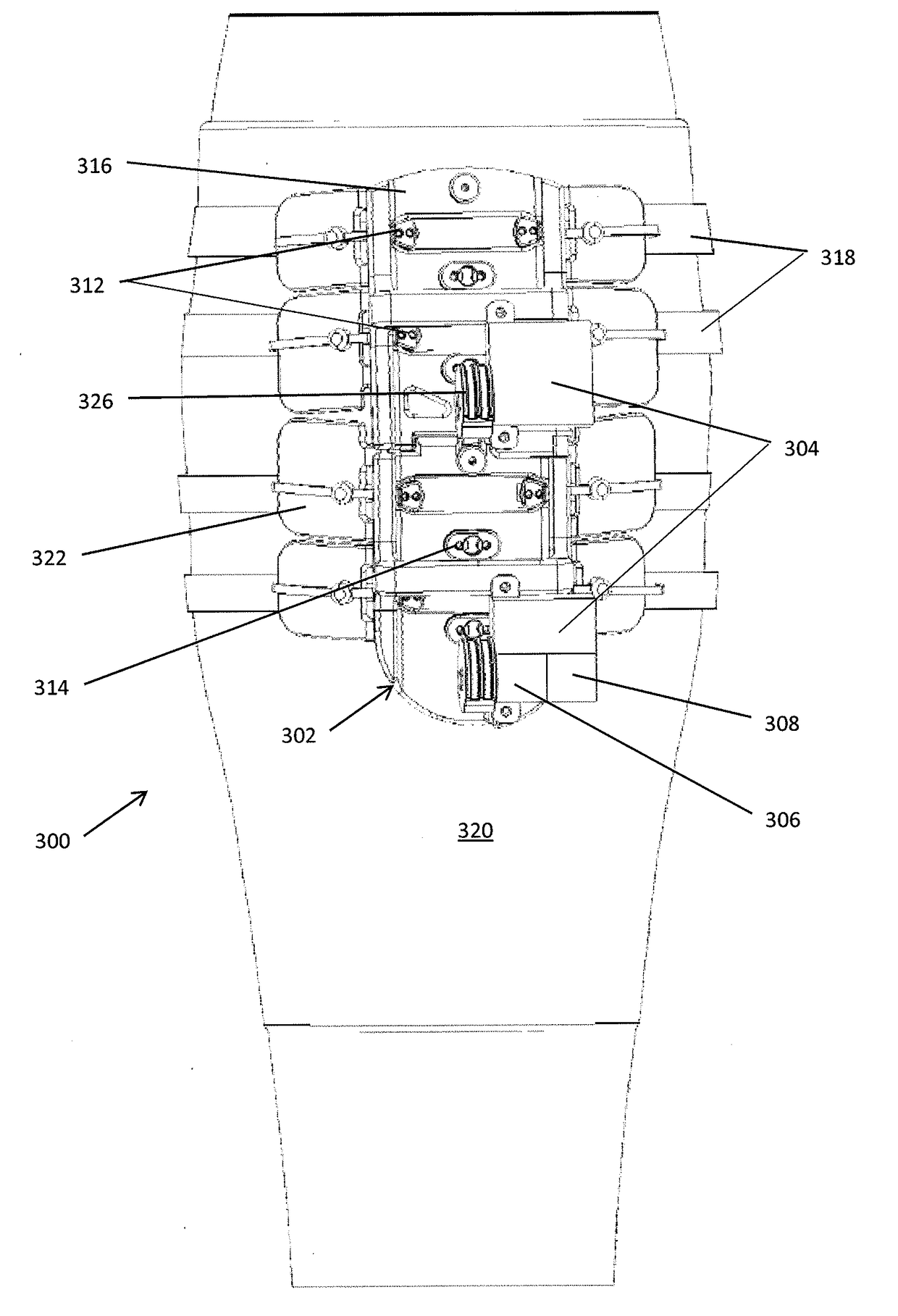
Cooperating defibrillators and external chest compression devices
ActiveUS7308304B2Optimize timingEffectiveness of chest compression could be monitoredRespiratorsDiagnosticsElectricityComputer module
Devices, methods, and software implementing those methods for providing communicating external chest compression (ECC) devices and defibrillation (DF) devices, where the ECC and DF devices can be physically separate from each other. Both ECC and DF devices are able to operate autonomously, yet able to communicate with and cooperate with another device when present. Some ECC and DF devices are adapted to be physically and / or electrically coupled to each other. One ECC device includes a backboard, a chest compression member, a communication module, controller, and at least one sensor, electrode lead or electrode. One DF device includes a defibrillator module, a controller, and a communication module that can communicate with the ECC communication module. The communicating ECC and DF devices may deliver ECC, pacing, defibrillation, ventilation, and cooling therapies, and may deliver instructions to human assistants, in a coordinated and cooperative fashion.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
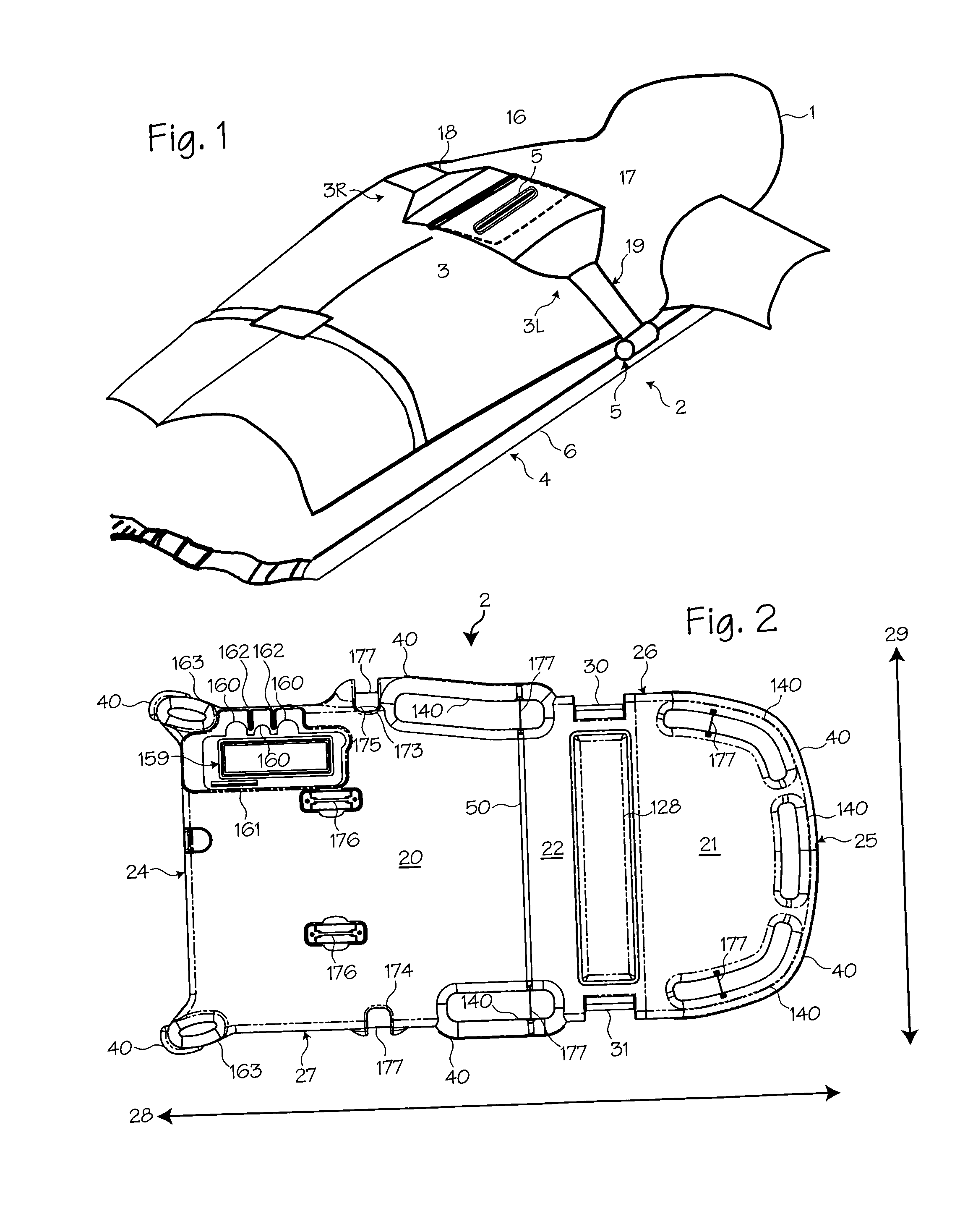
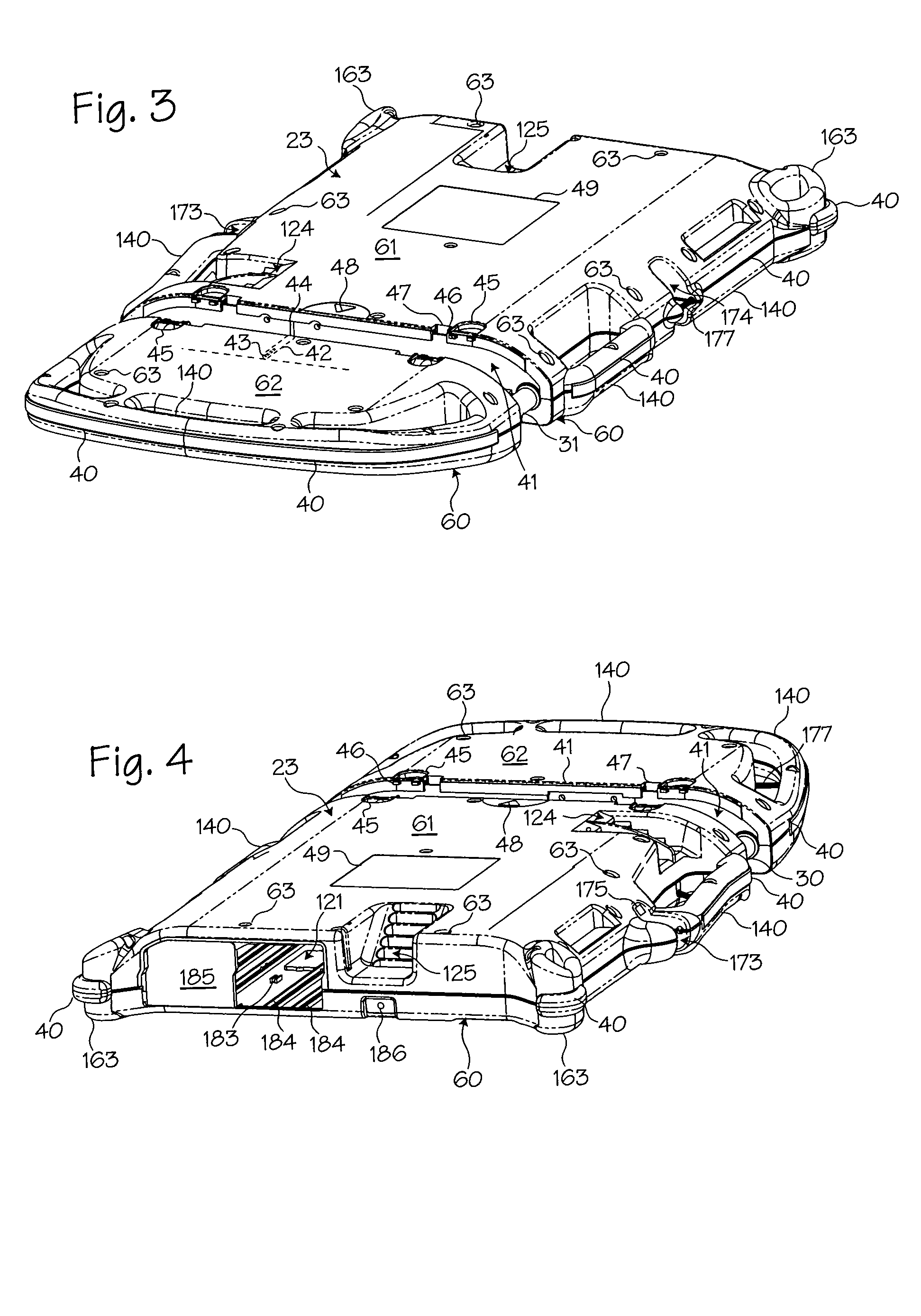
Compression belt system for use with chest compression devices
A compression belt cartridge for use with chest compression devices. The compression belt cartridge has a double-oar shaped belt and a cover plate through which the belt is threaded. The cover plate is provided with hooks and snap latches that fit into a belt drive platform. The cover plate is sized and dimensioned to fit within only selected platforms. The belt attaches to the means for tightening the belt via a spline attached to the belt. The means for tightening a belt then repetitively tightens the belt, thereby accomplishing chest compressions.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Method of estimating the actual ECG of a patient during CPR
A method of processing a raw acceleration signal, measured by an accelerometer-based compression monitor, to produce an accurate and precise estimated actual depth of chest compressions. The raw acceleration signal is filtered during integration and then a moving average of past starting points estimates the actual current starting point. An estimated actual peak of the compression is then determined in a similar fashion. The estimated actual starting point is subtracted from the estimated actual peak to calculate the estimated actual depth of chest compressions. In addition, one or more reference sensors (such as an ECG noise sensor) may be used to help establish the starting points of compressions. The reference sensors may be used, either alone or in combination with other signal processing techniques, to enhance the accuracy and precision of the estimated actual depth of compressions.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
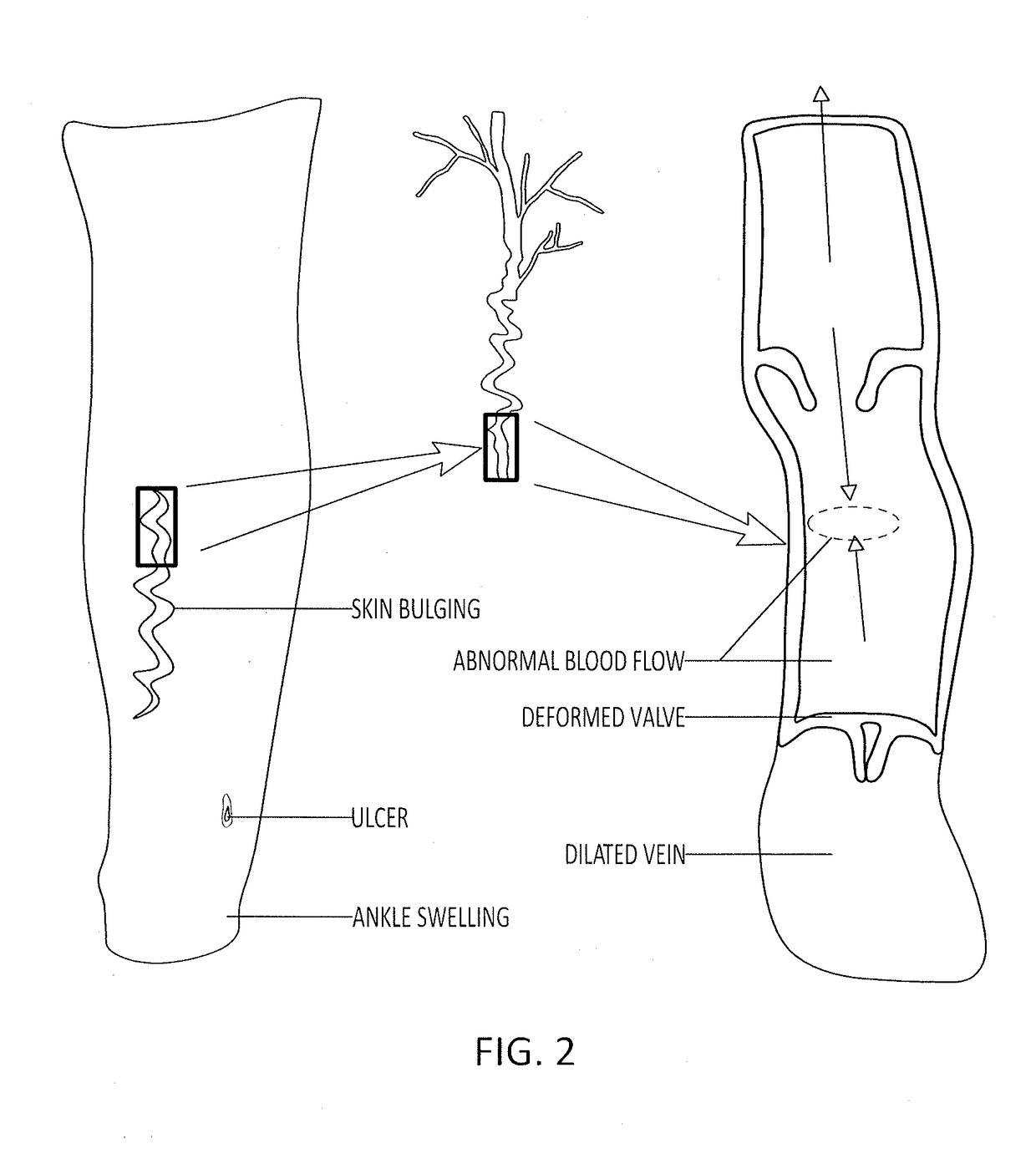
Tiltable backboard for cardiopulmonary resuscitation
InactiveUS6371119B1The process is simple and fastPromoting venous blood returnElectrotherapyOperating chairsVeinCardiorespiratory arrest
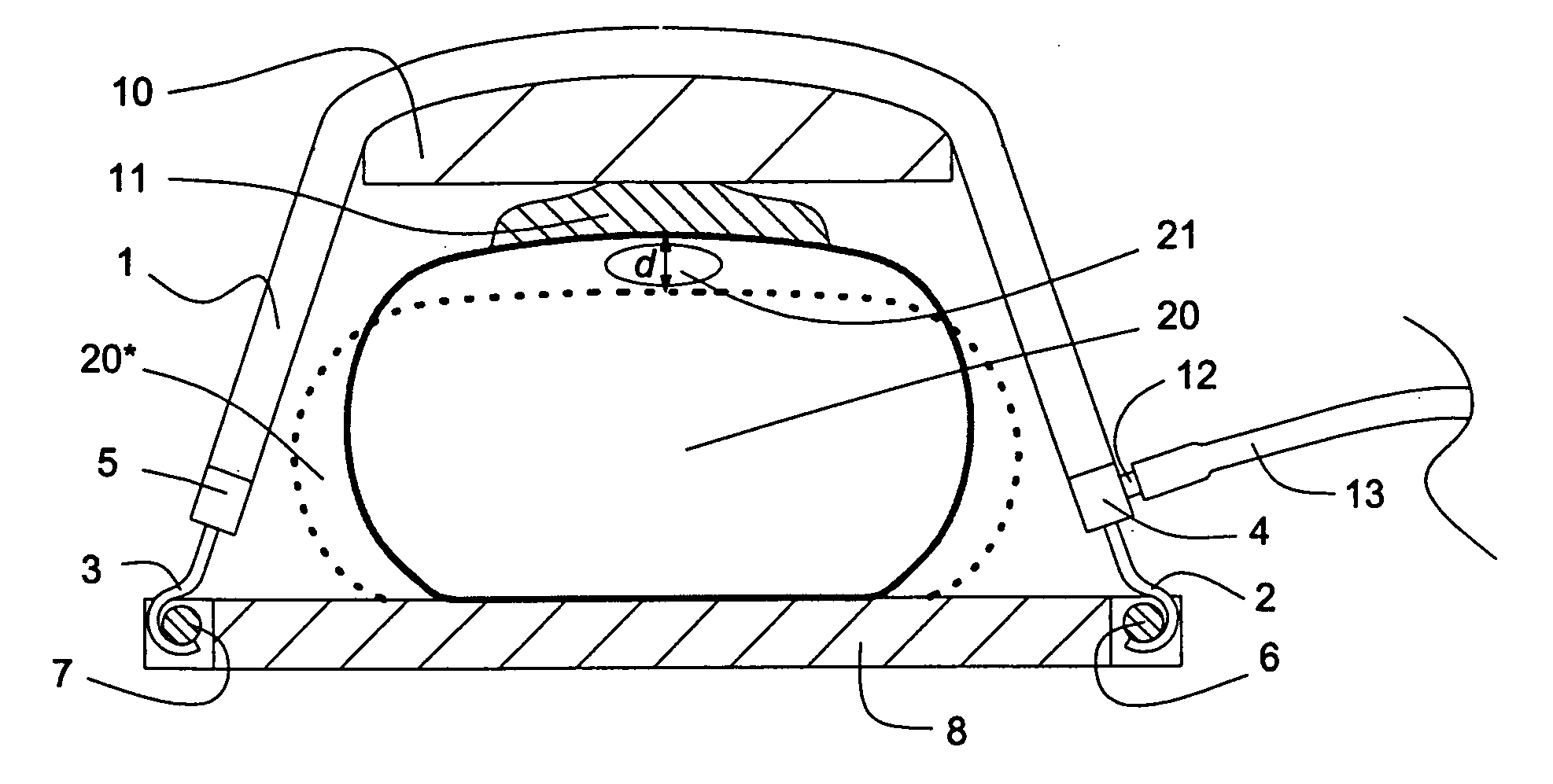
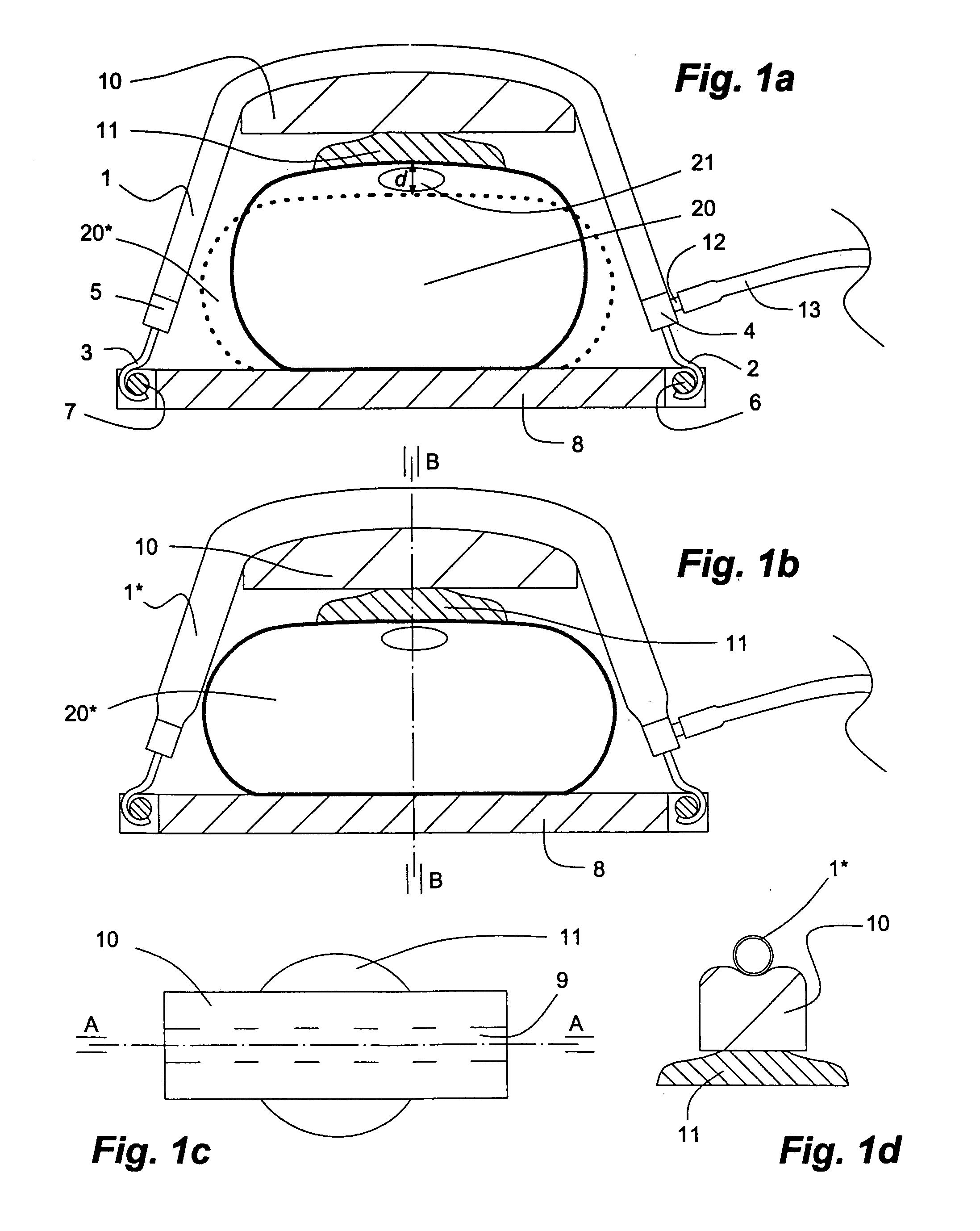
An apparatus and method to be used in CPR to promote diastolic filling of the heart in cardiac arrest situations during external or internal cardiac compression. A rigid backboard provided with a tilting apparatus to incline the backboard to a desired degree. The backboard can be also provided with a tiltable segment for forward head flexion. The body of a patient victim of cardiac arrest is placed supine over the rigid backboard and the backboard is tilted by actuation of the tilting apparatus to a desired angle thus positioning the patient with feet up and chest down, so that the lower extremities are higher than the abdomen and tilted down toward the abdomen, and the abdomen higher than the chest and tilted down toward the chest. Likewise, being the head flexed forward in respect to the remainder of the body, the head is positioned higher than the heart, and tilted down toward the heart. As a result of such a positioning, the blood in the venous system of the lower extremities, of the abdomen and head will be draining down toward the heart by gravity improving diastolic filling and ultimately will improve cardiac output with internal or external cardiac compressions being carried out with the patient maintained in such position.
Owner:ZADINI FILIBERTO P +1
Gas-driven chest compression apparatus
InactiveUS20100004572A1Improve returnSimple drive controlElectrotherapyIron-lungsEmergency medicineCPR - Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
A gas-driven chest compression apparatus for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) comprises a flexible pneumatic actuator, capable of axial contraction when fed with a pressurized driving gas, and means for controlling the contraction thereof. Also disclosed are methods of providing chest compressions to a patient by means of a CPR apparatus comprising actuator(s) of this kind, and a corresponding use of the actuator.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
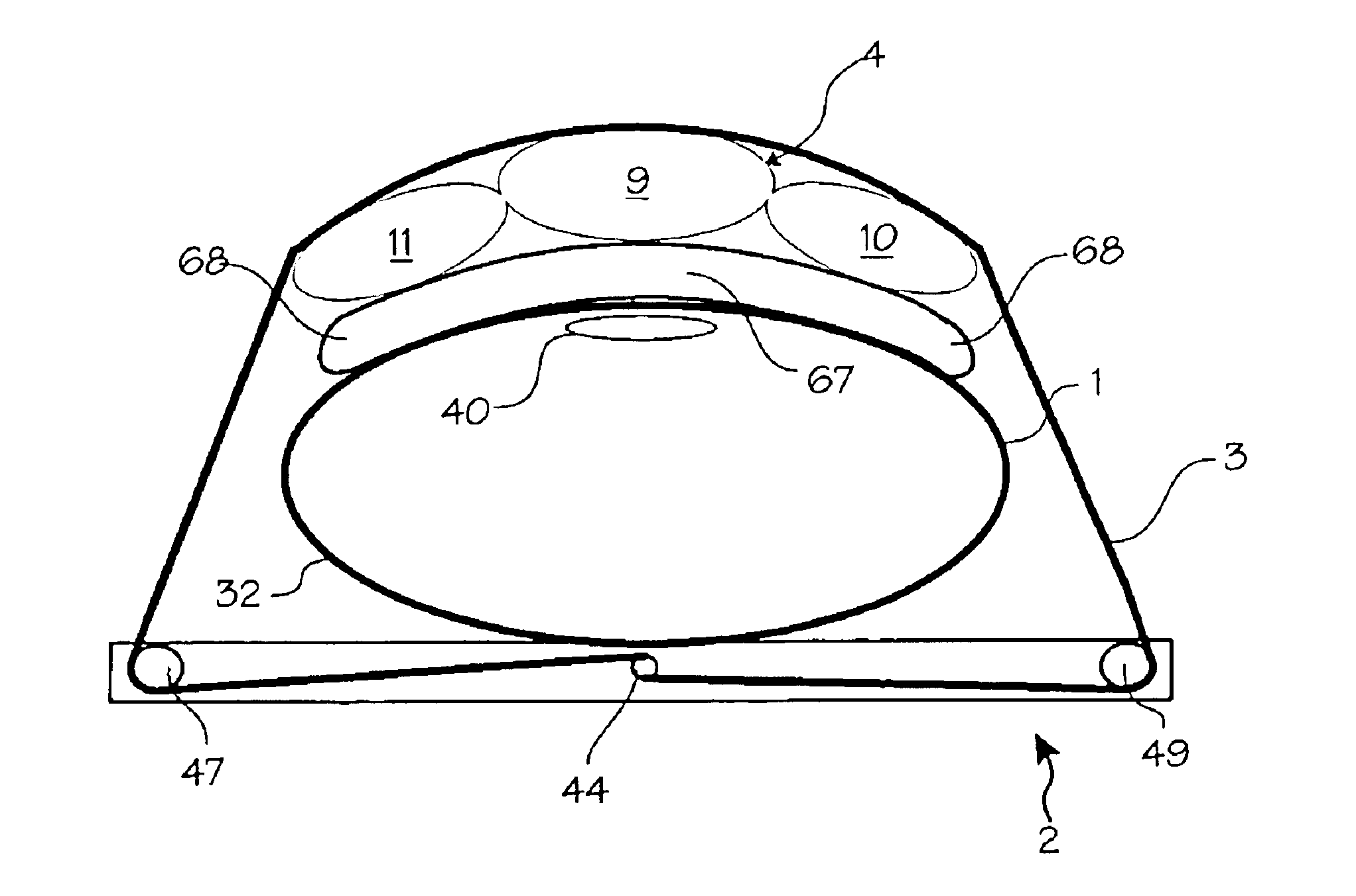
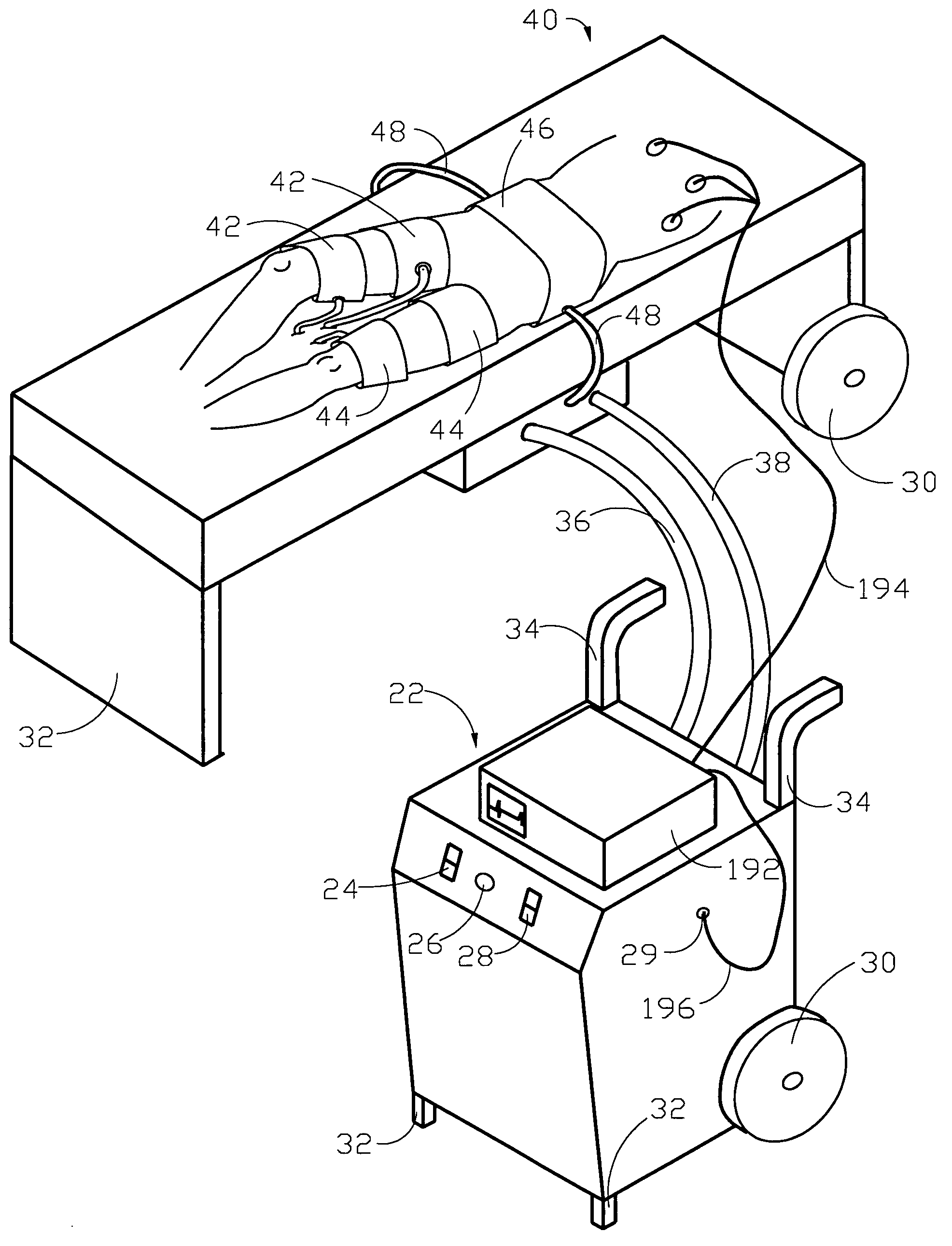
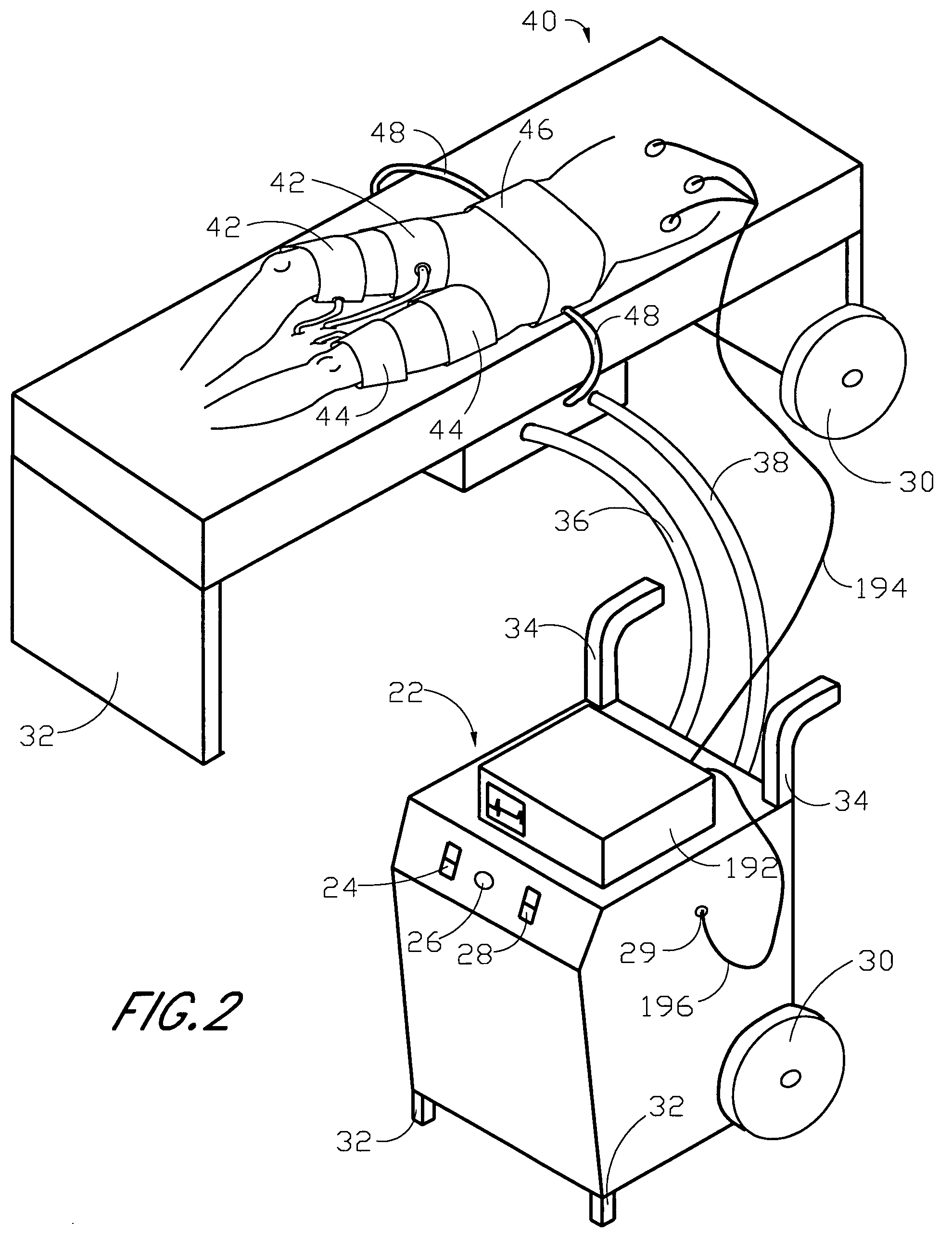
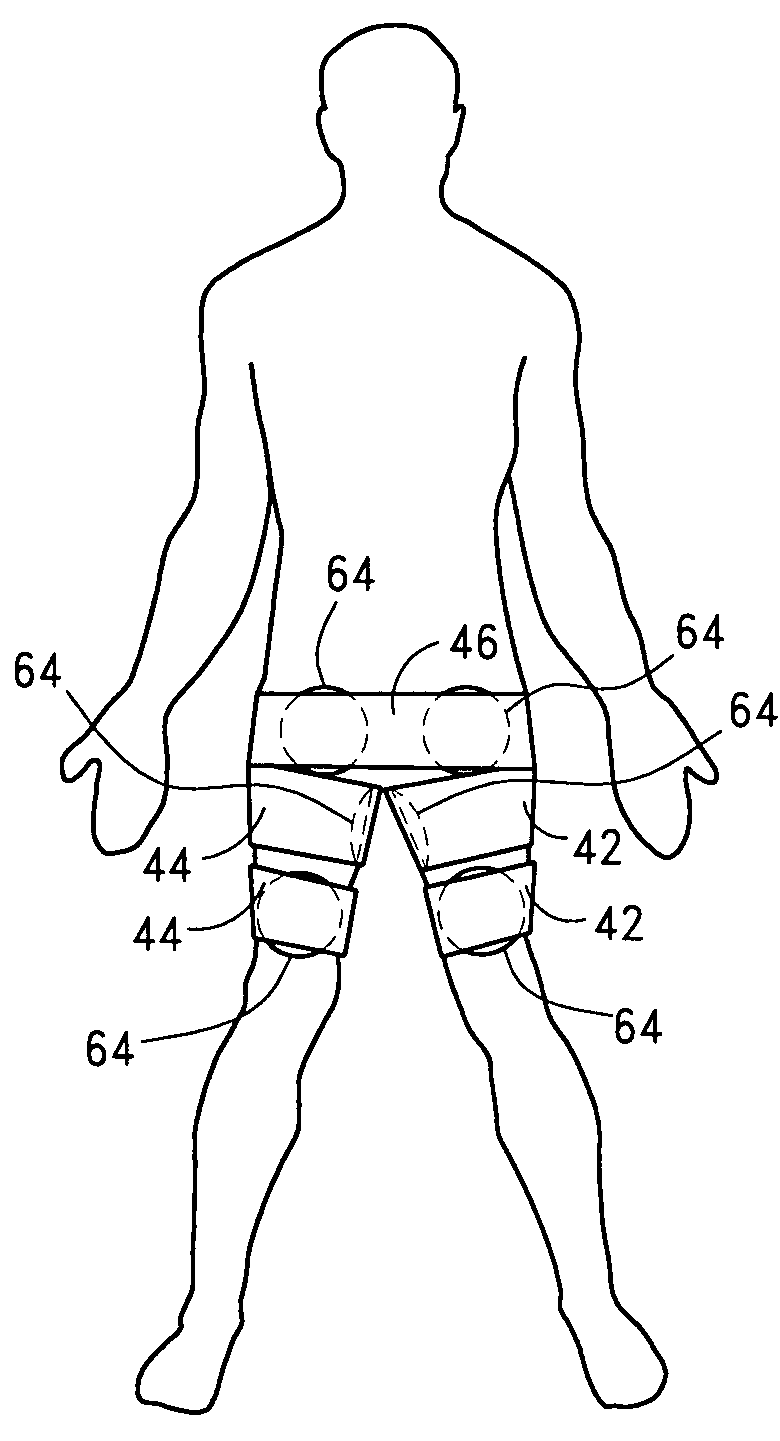
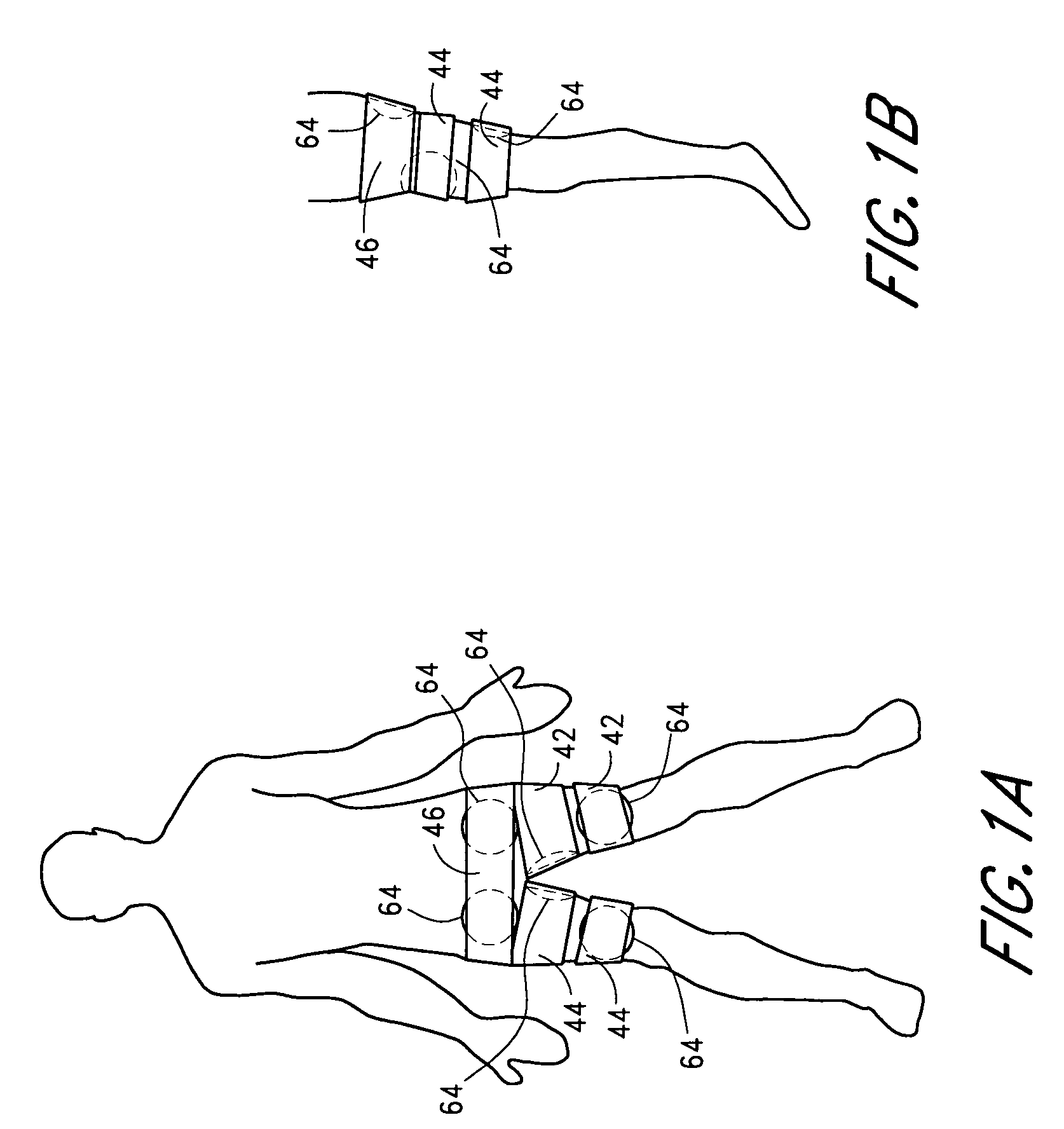
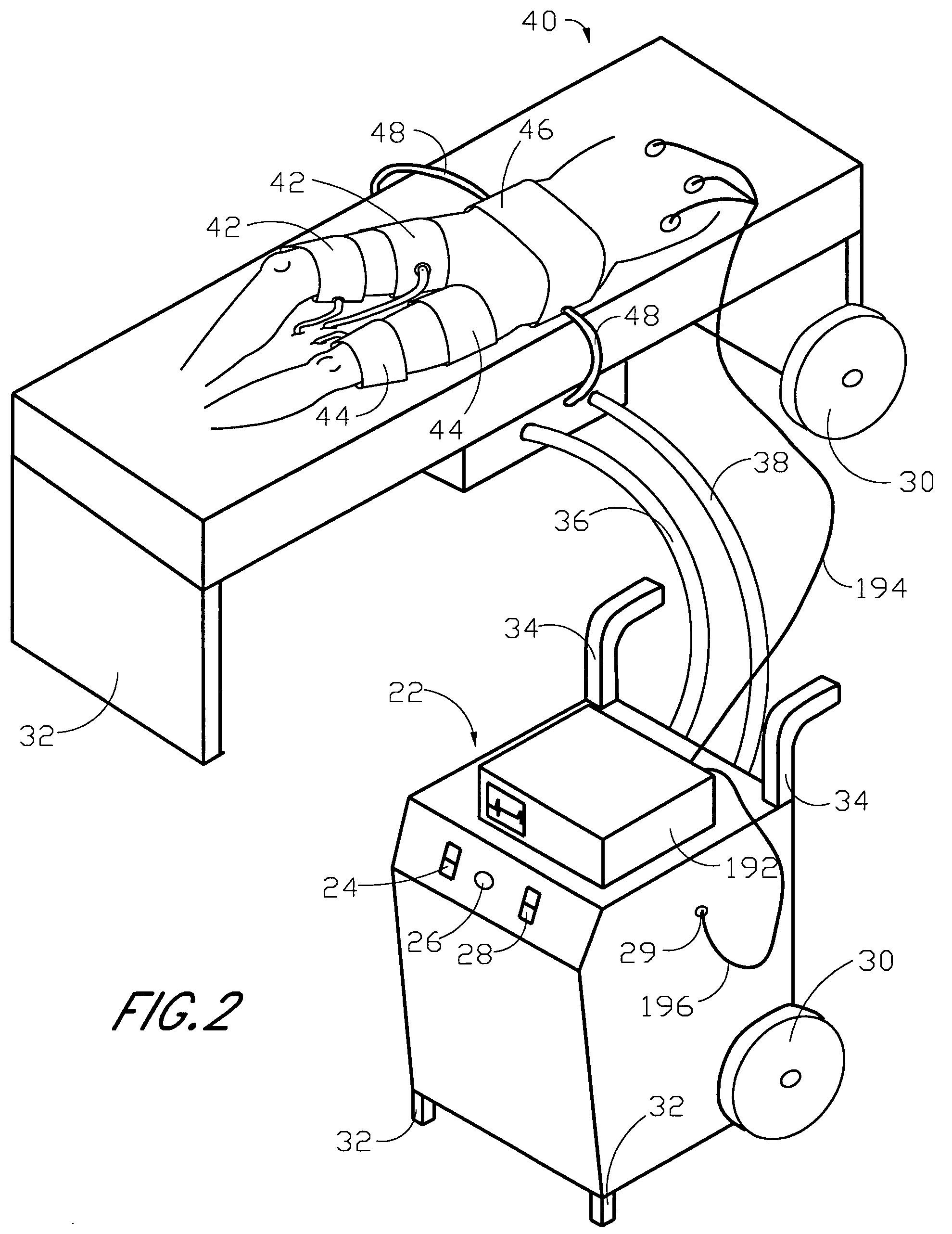
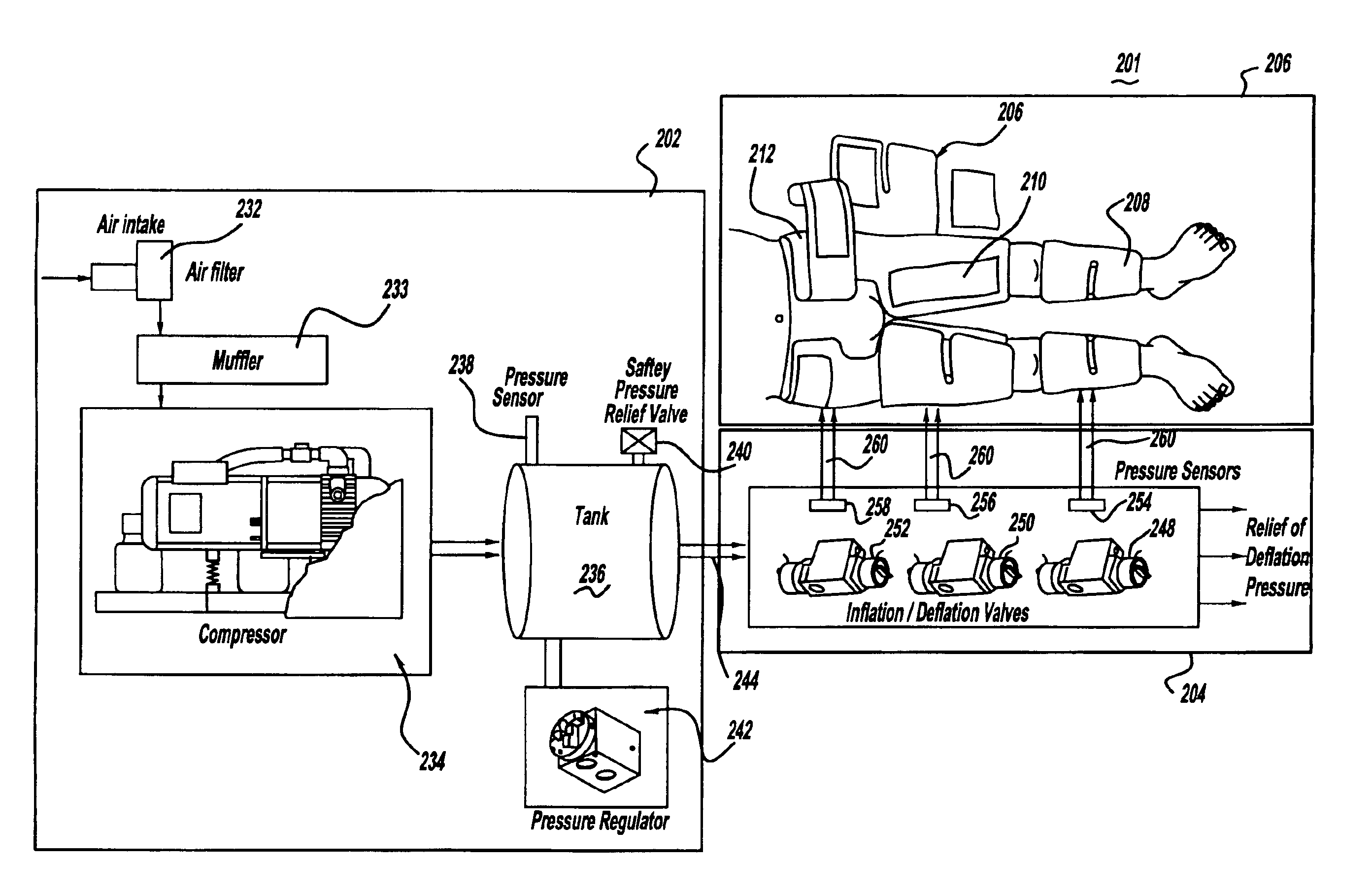
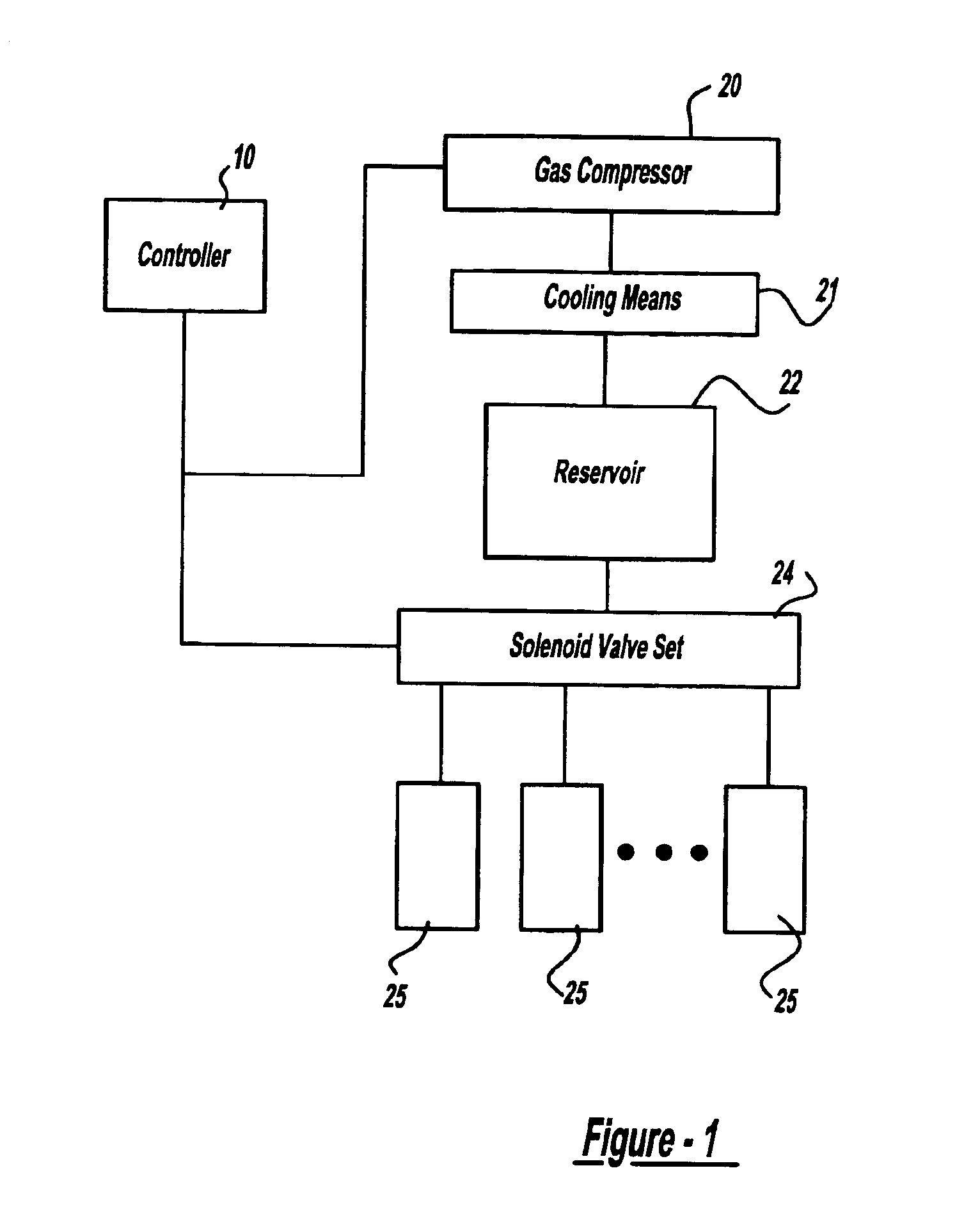
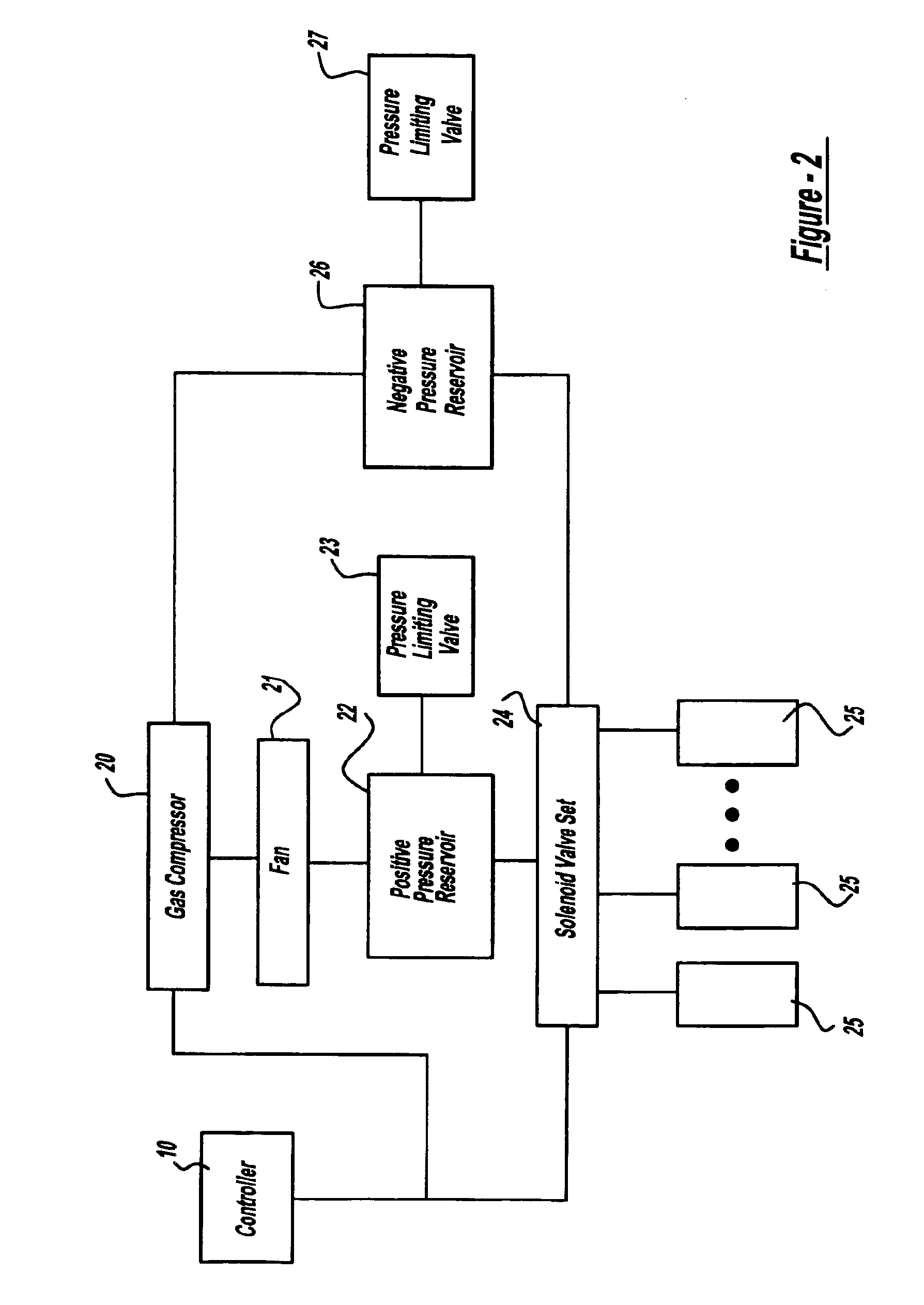
High-efficiency external counterpulsation apparatus and method for performing the same
The embodiments of the invention generally provide an external counterpulsation apparatus having an efficient cuff and bladder system. The embodiments generally allow effective treatment at lower pressures and a reduced total body surface area being compressed. An accurate and reliable combination of automatic and preset timing for inflation and deflation of the bladder system is used to simplify use of the apparatus.
Owner:PICKETT DAVID ANTHONY +1
High-efficiency external counterpulsation apparatus and method for performing the same
An external counterpulsation apparatus has an efficient cuff and bladder system. Embodiments of this system generally allow effective treatment at lower pressures and a reduced total body surface area being compressed. An accurate and reliable combination of automatic and preset timing for inflation and deflation of the bladder system is used to simplify use of the apparatus.
Owner:PICKETT DAVID ANTHONY +1
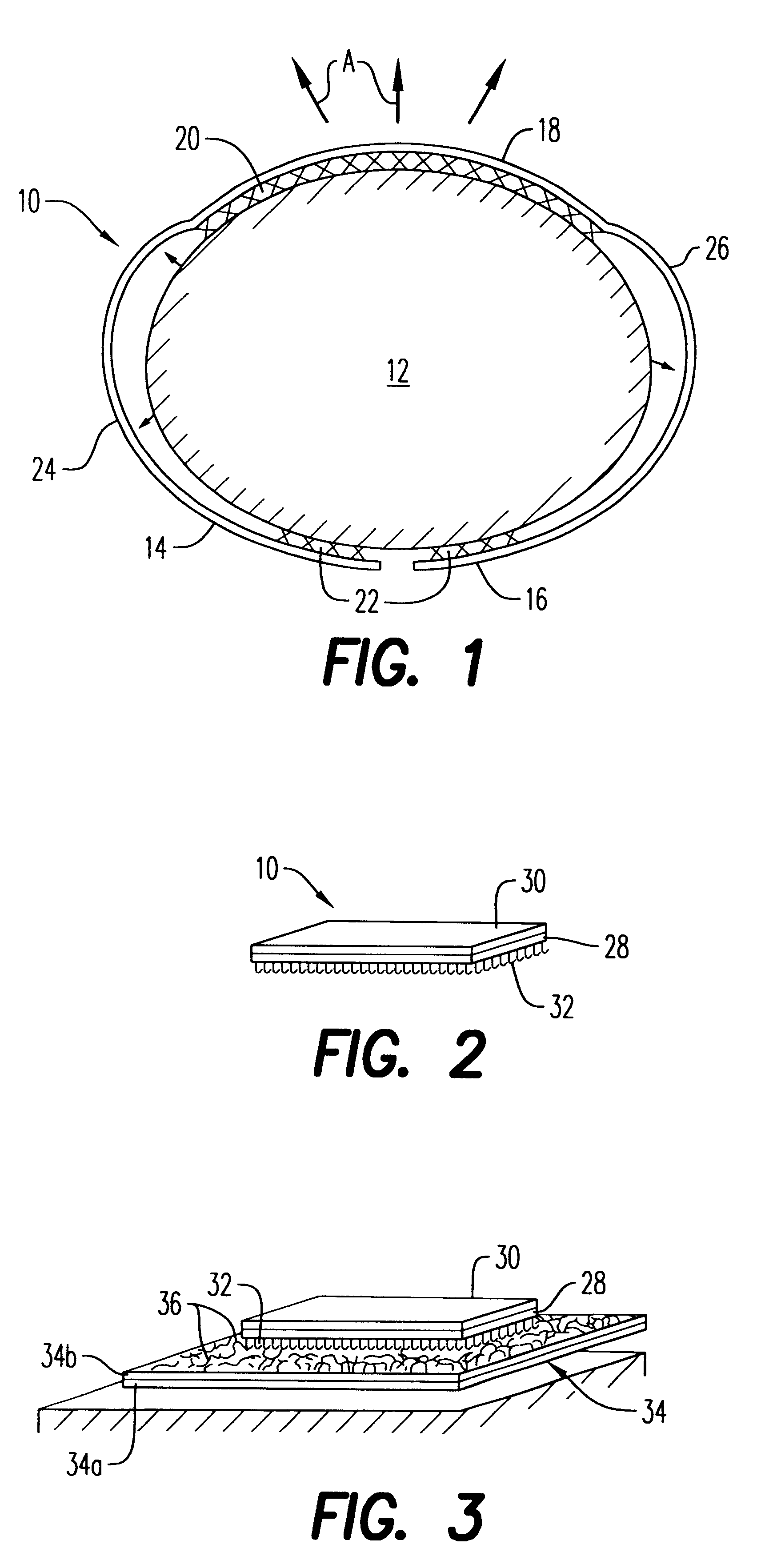
Chest brace and method of using same
A chest brace and method of using same that prevents the chest wall from buckling inwards during patient breathing by providing a distending force on the patient's thorax. The chest brace also restores the normal anterior-to-posterior chest dimensions by providing a distending force in this direction. The chest brace includes an anterior member adapted to overly a patient's chest. An adhesive mechanism secures the anterior member to a surface of such a patient. A support structure is coupled to the anterior member such that, in use, the support structure imparts a force on the anterior member in a manner so as to distend a thorax of such a patient.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
Adaptive compression therapy systems and methods
InactiveUS20170312161A1Physical therapies and activitiesBlood stagnation preventionAdaptive compressionCompression therapy
Systems, devices and methods for providing active and / or passive compression therapy to a body part can include a compression device worn over a compression stocking. The compression device can have a pulley based drive train that is driven by a motor to tighten and loosen compression elements, such as compression straps, in a precise, rapid, and balanced manner. Sensors can be used in the compression device and / or compression stockings to provide feedback to modulate the compression treatment parameters.
Owner:RADIAL MEDICAL INC
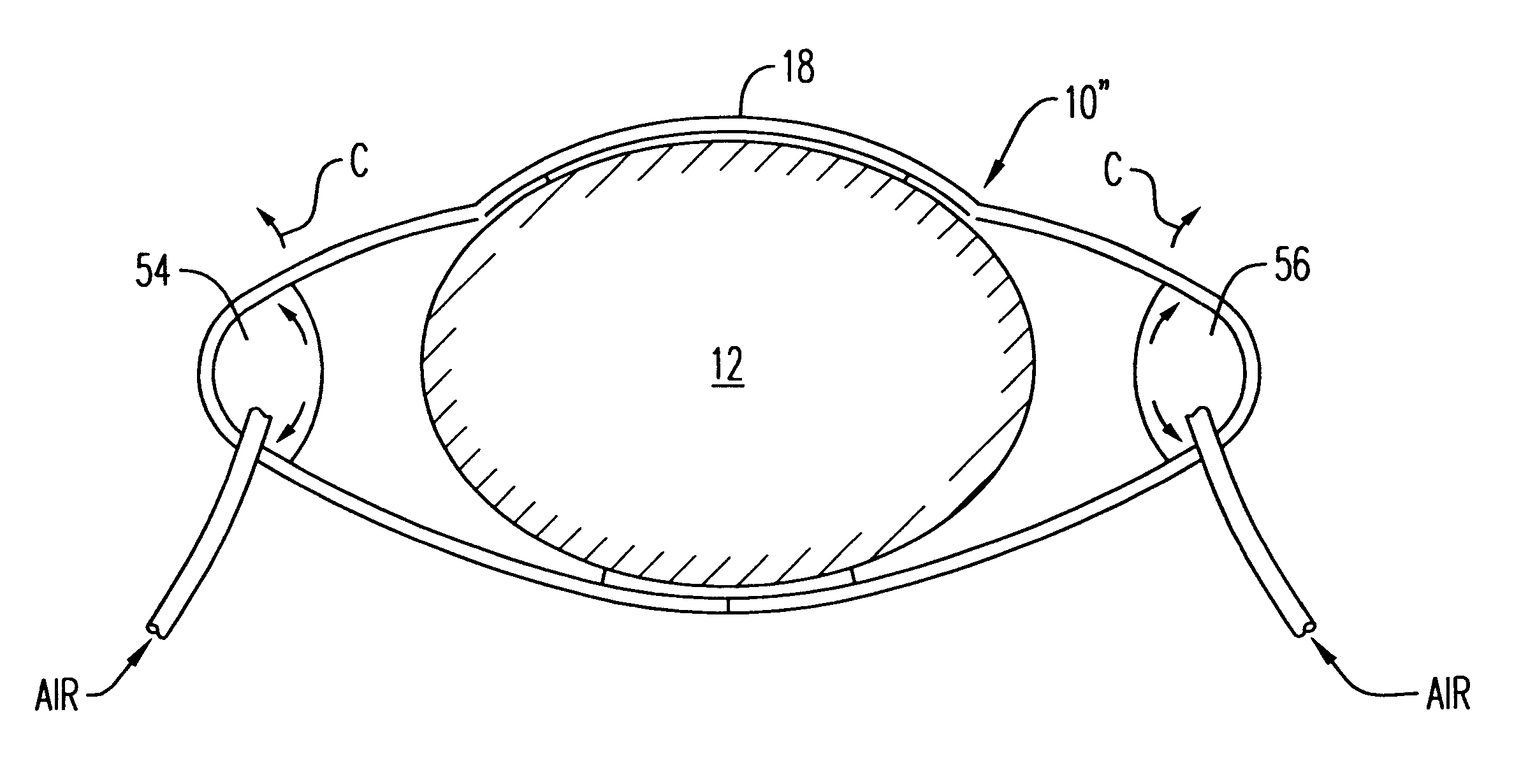
High efficiency external counterpulsation apparatus and method for controlling same
InactiveUS6962599B2Improve Utilization and EfficiencyIncrease loopElectrotherapyPneumatic massageCompressed fluidRoom temperature
The present invention provides a high efficiency external counterpulsation apparatus having accurate and reliable timing of inflation and deflation and reduced temperature of the pressurized gas, such that the gas flow temperature of the inflatable devices is near to room temperature, as well as faster and more responsive inflation / deflation equipment. The external counterpulsation apparatus includes a plurality of inflatable devices received about the lower extremities of the patient, a source of compressed fluid in communication with said plurality of inflatable devices, and a fluid distribution assembly interconnecting said source of compressed fluid and said inflatable devices. The fluid distribution assembly includes a selectively operable inflation / deflation valve interconnected between each of said inflatable devices and said source of compressed fluid. The fluid distribution assembly separately operates each inflation / deflation valve to sequentially inflate and deflate each inflatable devices.
Owner:VASOMEDICAL
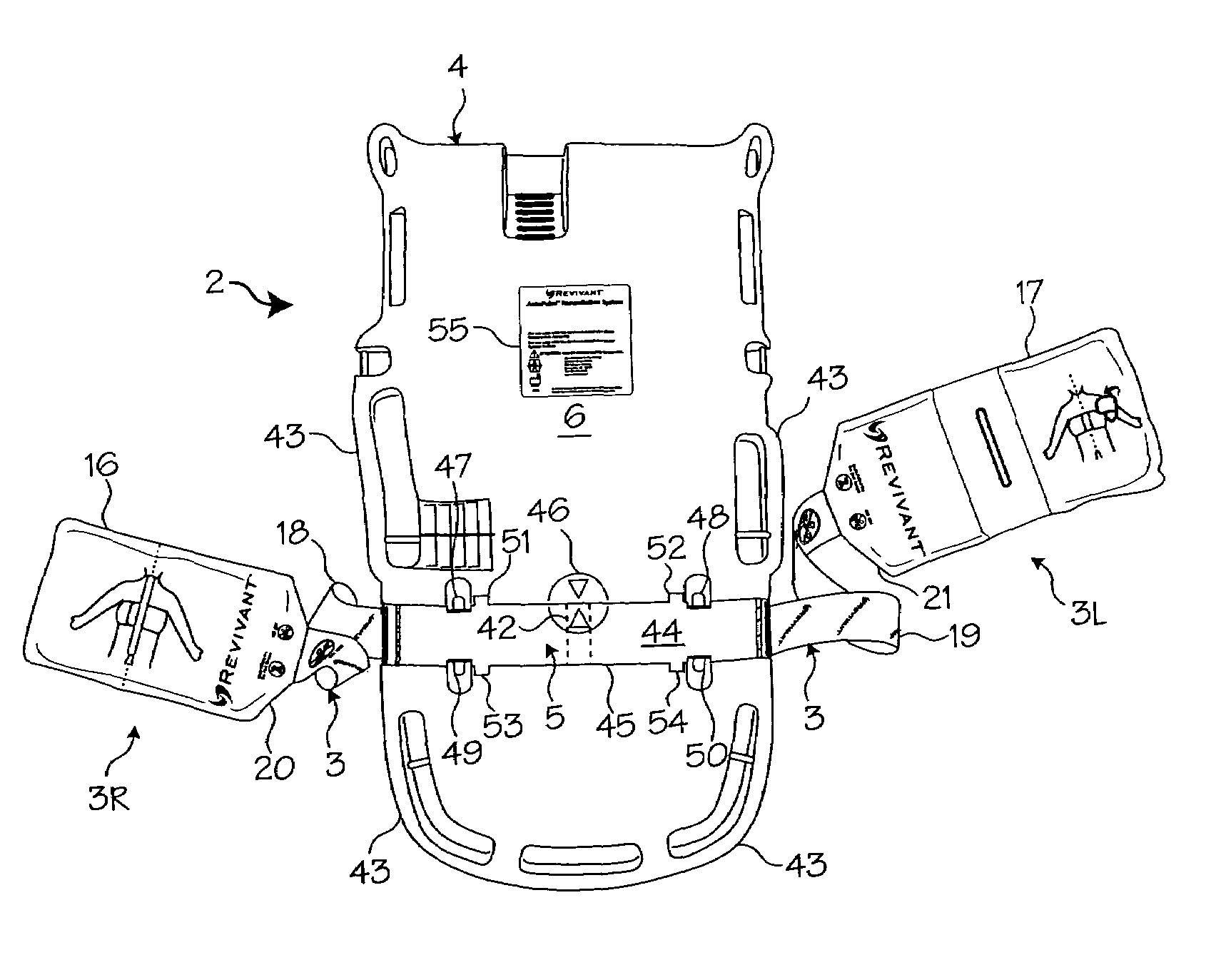
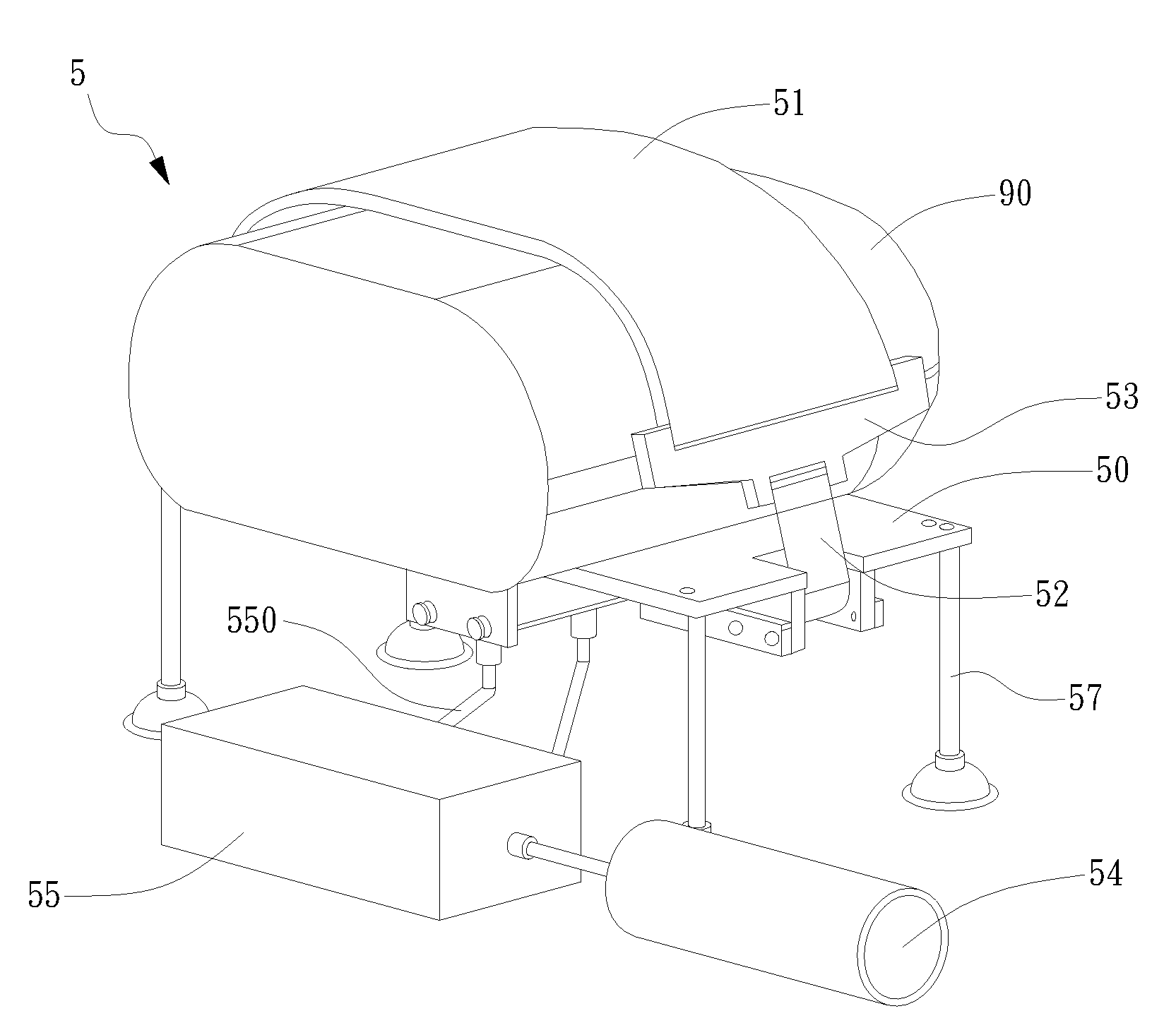
Support for a cpr apparatus
InactiveUS20100063425A1Easily attached to each otherEasily to dismountedElectrotherapyIron-lungsEngineeringCardiopulmonary resuscitation kit
Owner:JOLIFE AB
CPR chest compression device
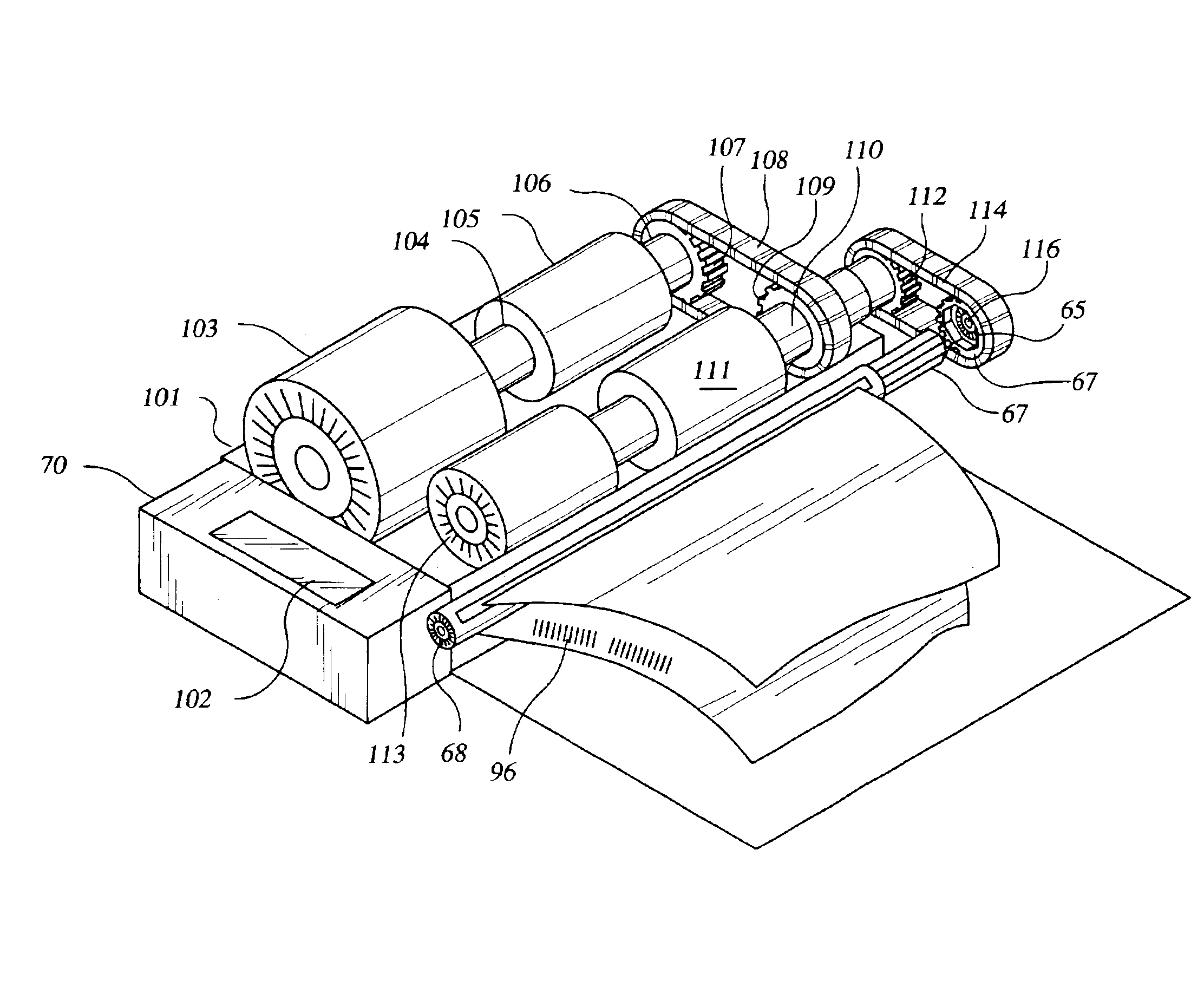
A resuscitation device for automatic compression of a victim's chest using a compression belt which exerts force evenly over the entire thoracic cavity. The belt is constricted and relaxed through a motorized spool assembly that repeatedly tightens the belt and relaxes the belt to provide repeated and rapid chest compression.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
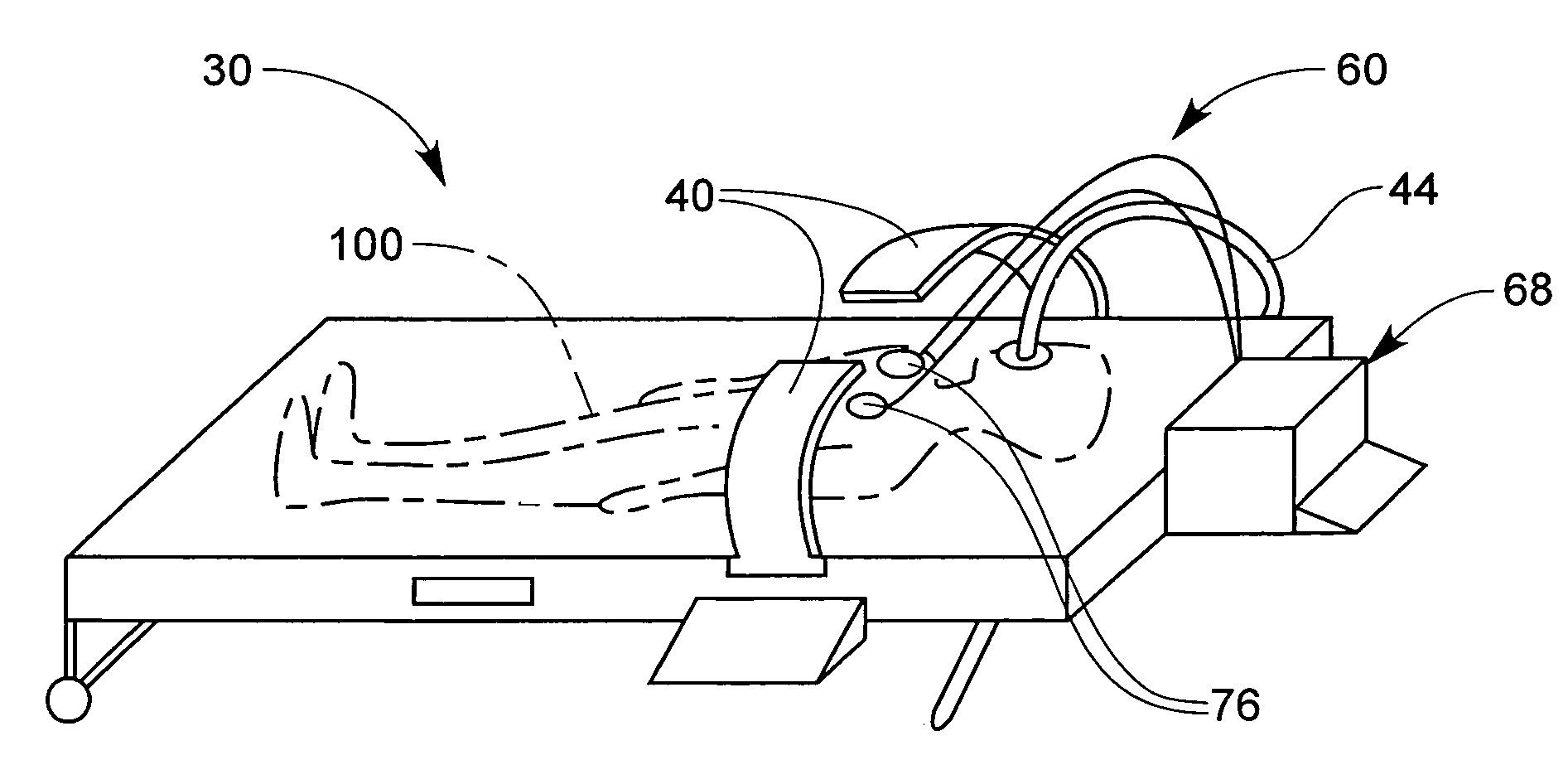
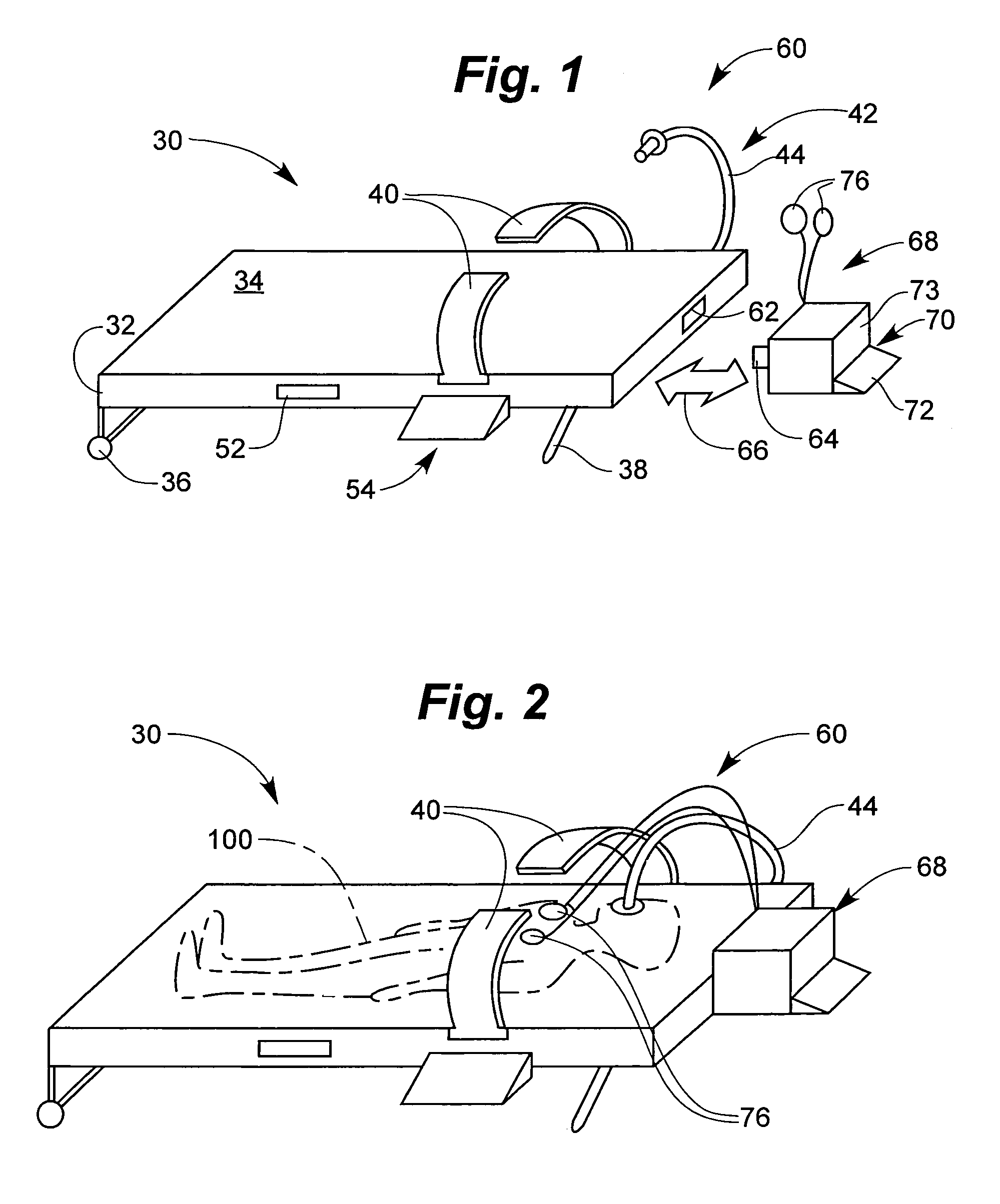
Backboard For an Automated CPR System
ActiveUS20120042881A1Easy to operateElectrotherapyRestraining devicesEngineeringCardiopulmonary resuscitation
A backboard for an automated cardio pulmonary resuscitation system, said backboard comprising a board element, the board element defining a plane and having a top edge, a bottom edge a first side edge and a second side edge; a set of connectors adapted for connection of the backboard to an automated cardio pulmonary resuscitation unit, said connectors being provided at said side edges; and at least one set of stabilizing elements extending away from an edge and transversely to said plane.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Resuscitation device and method
A resuscitation device for automatic compression of victim's chest using a compression belt which exerts force evenly over the entire thoracic cavity. The belt is constricted and relaxed through a motorized spool assembly which repeatedly tightens the belt and relaxes the belt to provide repeated and rapid chest compression. An assembly includes various resuscitation devices including chest compression devices, defibrillation devices, and airway management devices, along with communications devices and senses with initiate communications with emergency medical personnel automatically upon use of the device.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Chest Compression Belt with Belt Position Monitoring System
An automated chest compression device for performing CPR, with distance sensors disposed on a compressing mechanism and on a structure fixed relative to the CPR patient, for determining inferior / superior movement of the compressing mechanism over the course of multiple compressions.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
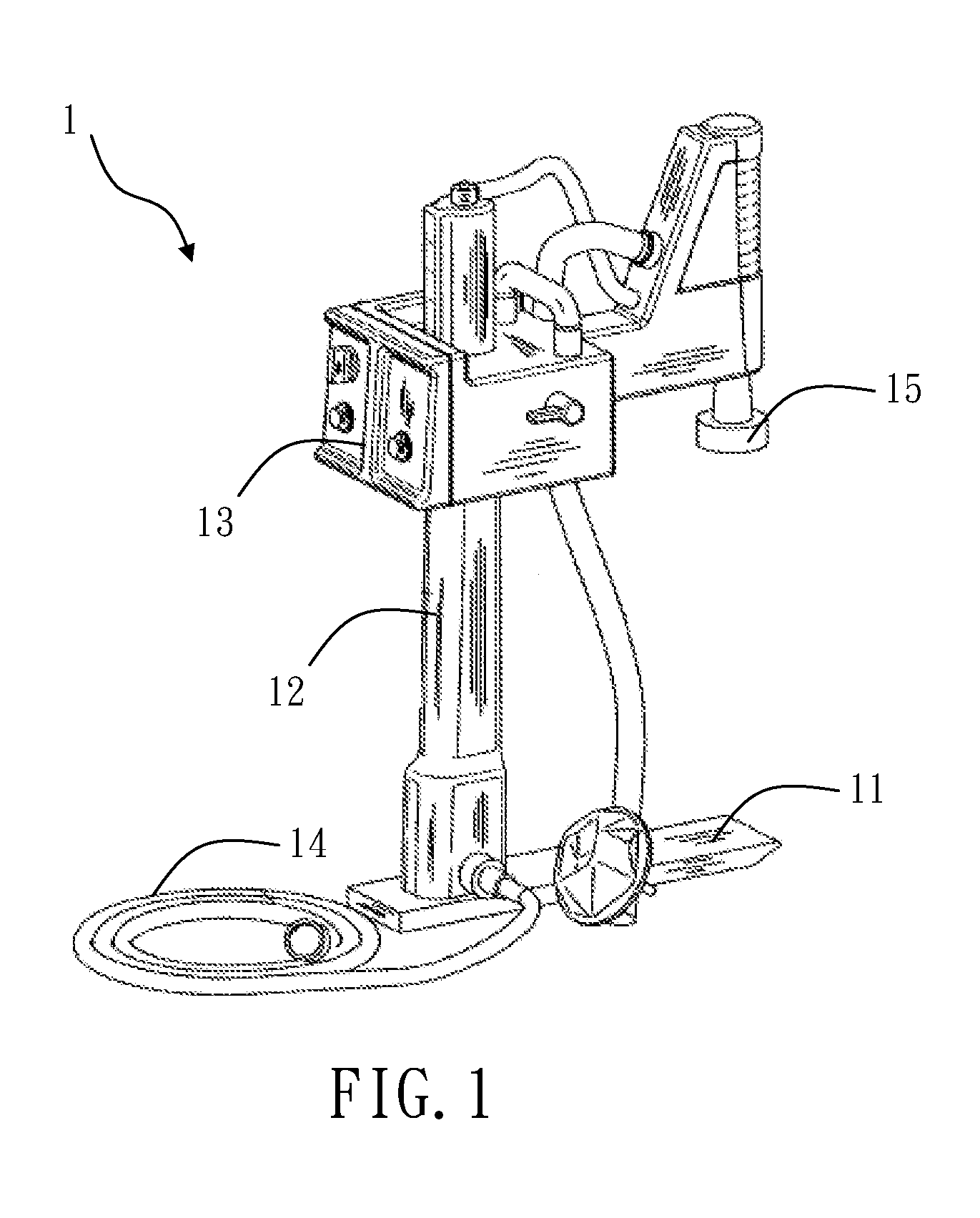
Support for chest compression system
A support for a chest compression system includes a back plate, a front part having a seat for a compression member of a chest compression system, and a side part connecting the back plate to the front part. The side part is adapted to provide adjustable spacing between the seat and the back plate to accommodate patients having different chest heights to allow the support to be snugly placed around the chest of a patient.
Owner:LAERDAL MEDICAL AS
Apparatus of cardiopulmonary resuscitator
ActiveUS20080146975A1Simplify mechanical designSimple designElectrotherapyIron-lungsElectricityReciprocating motion
The present invention discloses an apparatus of cardiopulmonary resuscitator that is operated through a driving mechanism controlled and driven by air power. The driving mechanism functions to actuate a belt adapted to extend around the chest of a patient to generate reciprocating movement of pressing and releasing so as to achieve a purpose of cardiopulmonary resuscitation for recovering heartbeat and breathing of the patent. By means of the disclosure of the present invention, the apparatus of cardiopulmonary resuscitator is capable of being operated in any kinds of occasions without worrying about lack of power electricity. Meanwhile, the driving mechanism can provide higher reliability and lower cost through the mechanism design that is more simplified than the design of electrical control element used in the conventional apparatus.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST +1
Mattress System
InactiveUS20140283308A1Simple structureEffective pressure rangeElectrotherapyStuffed mattressesTherapeutic effectEngineering
A mattress system devised to achieve a function of automatic detection, mainly including a mattress having a simple structure; a control unit equipped with a unique user interface for caregivers to simultaneously adjust three major functions, namely, therapy mode, therapy intensity and comfort level; and a connection pipe for supplying air and power. The system is further provided with a built-in auto-setting function to sense the body characteristics of the patient lying on the mattress and determine an effective supporting pressure range for the patient. By detecting a pressure difference representing the body characteristics of the patient lying on the mattress and comparing with the data stored in a built-in database, the system can always provide the patient with not only a well-proved therapeutic effect through the auto-setting function, but also an adjustable comfort level on the patient's request through the user interface.
Owner:SHL GRP AB
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation unit control apparatus
InactiveUS20090187123A1Easy constructionControl pressureRespiratorsElectrotherapyControl signalEmergency medicine
The present invention relates to a controller for a cardiopulmonary resuscitation apparatus. Automation and precise control can be realized in the cardiopulmonary resuscitation apparatus by using a driving unit involving in constricting the chest band of the cardiopulmonary resuscitation apparatus, locking, and pressing the chest by air pressure, and a control unit controlling the driving unit according to a control signal. Further, air pressure used in driving the cardiopulmonary resuscitation apparatus is controlled so as to be also supplied to a line of artificial respiration, such that a simple construction of the cardiopulmonary resuscitation apparatus and automation of artificial respiration are obtained. Thanks to the present invention, the operator does not have to care about the operation of the cardiopulmonary resuscitation apparatus while performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation, which allows the operator pay more attention to taking care of a patient.
Owner:HUMED +1
Lightweight electro-mechanical chest compression device
ActiveUS20050080364A1Easy to changeLightweight materialElectrotherapySurgeryControl systemCompression device
A lightweight electro-mechanical chest compression device. The device is provided with a motor, a brake, a drive spool, a control system, and a metal channel beam to brace the device and guide a compression belt. The belt is provided in a belt cartridge that attaches to the channel beam. In use, the belt is secured around the patient and to the drive spool. The motor tightens the belt by turning the drive spool. The electro-mechanical chest compression device weighs less than 30 pounds when fully assembled with its power source.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com