Patents
Literature
96results about How to "Simple drive control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
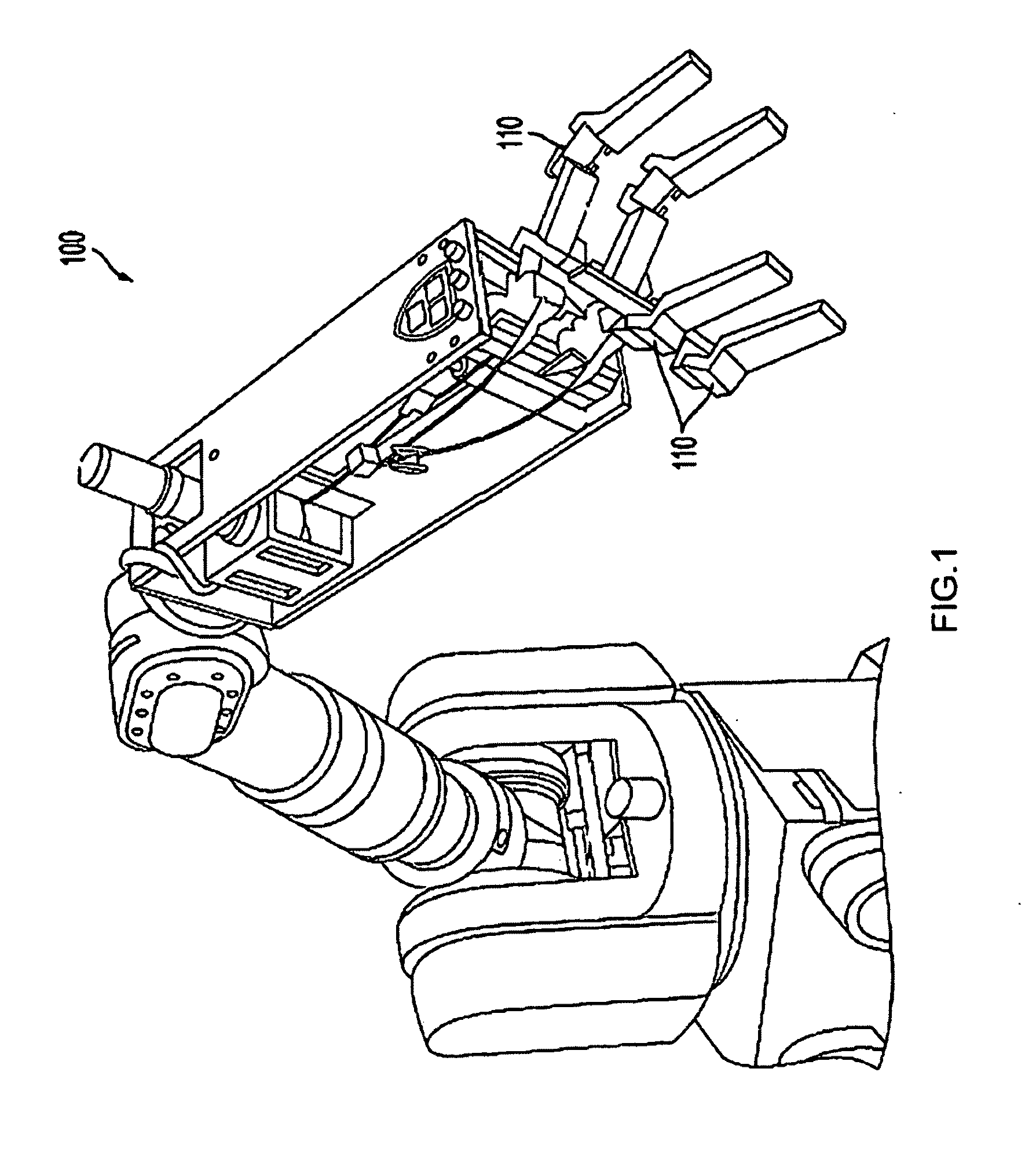
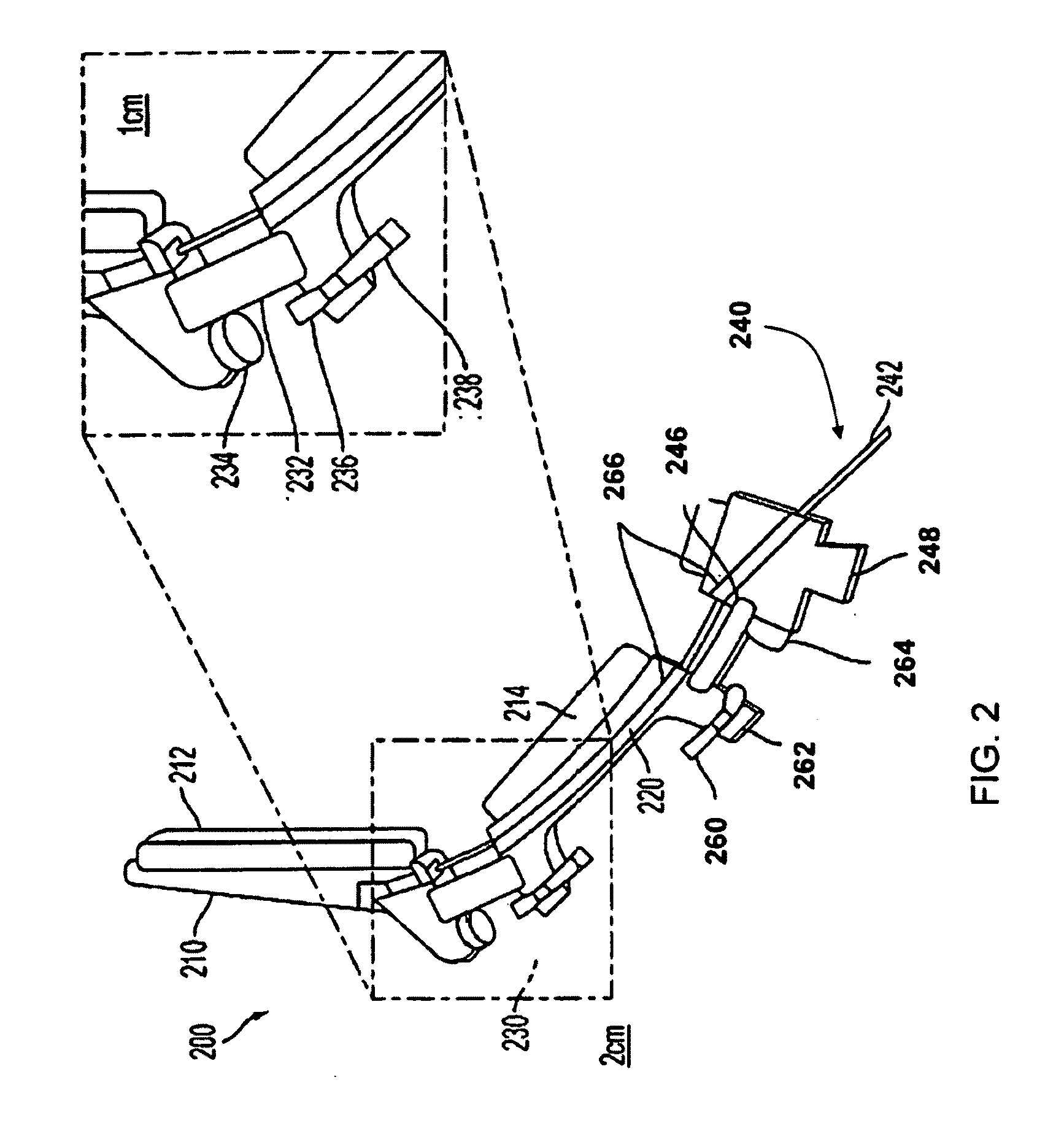
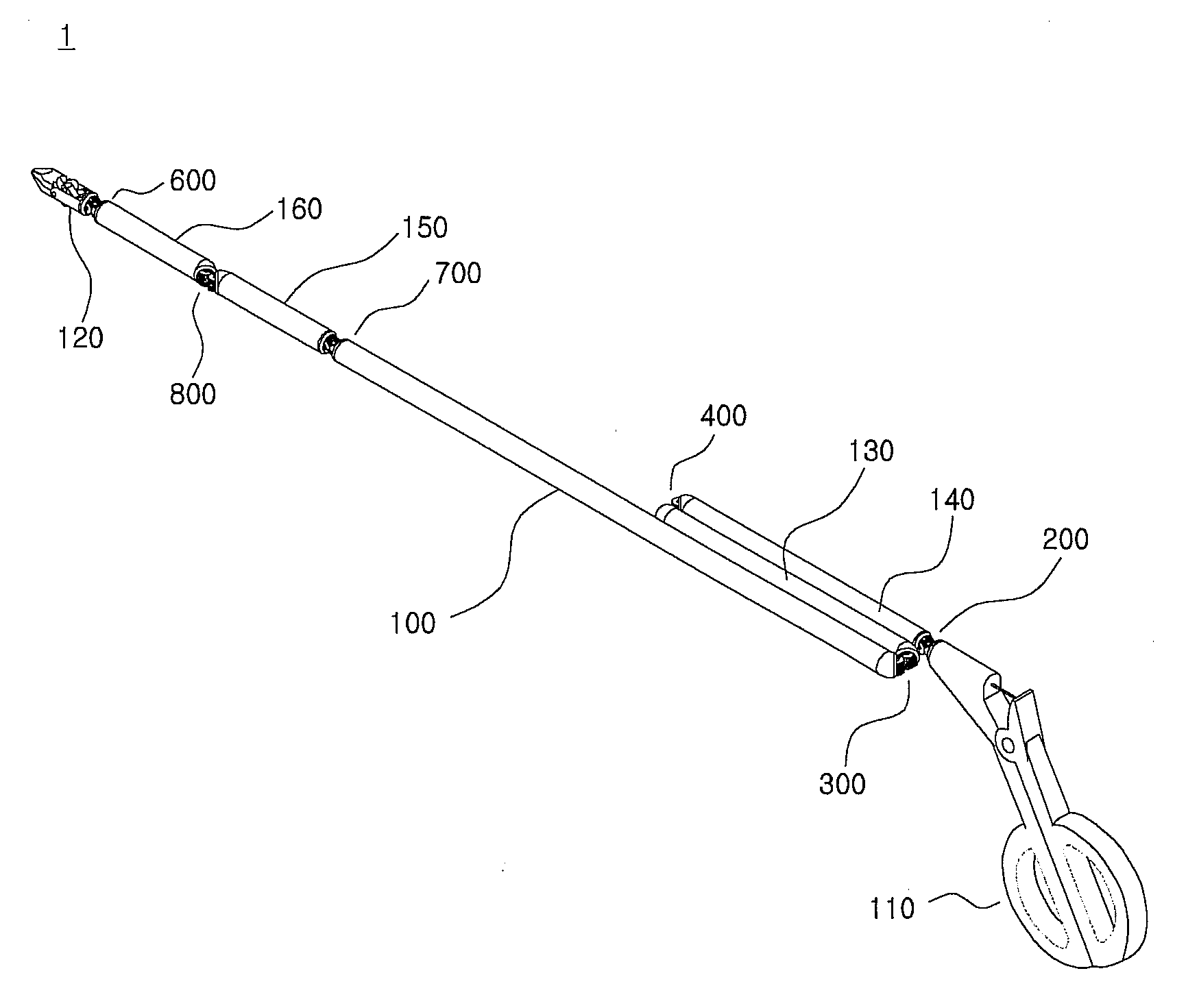
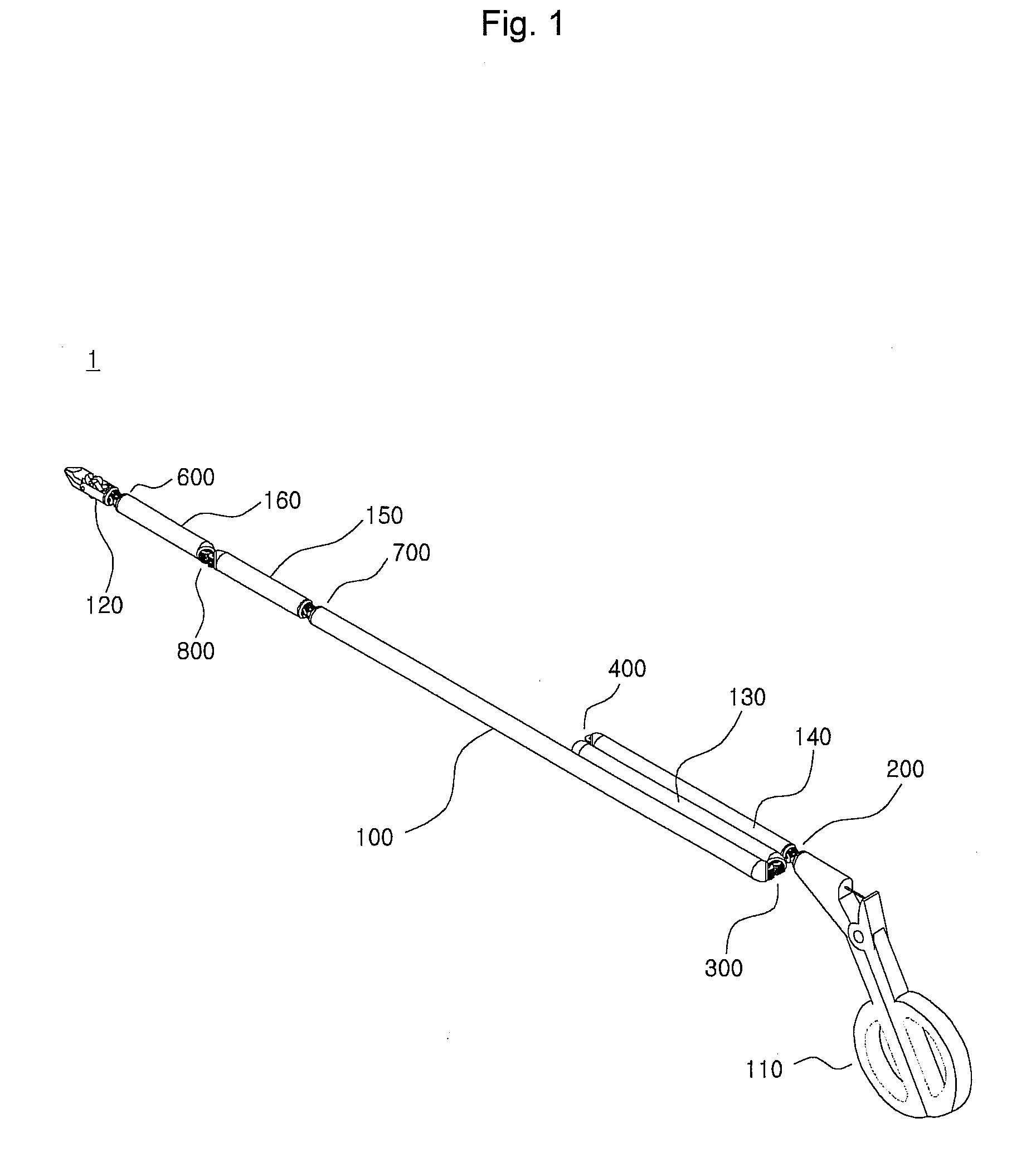
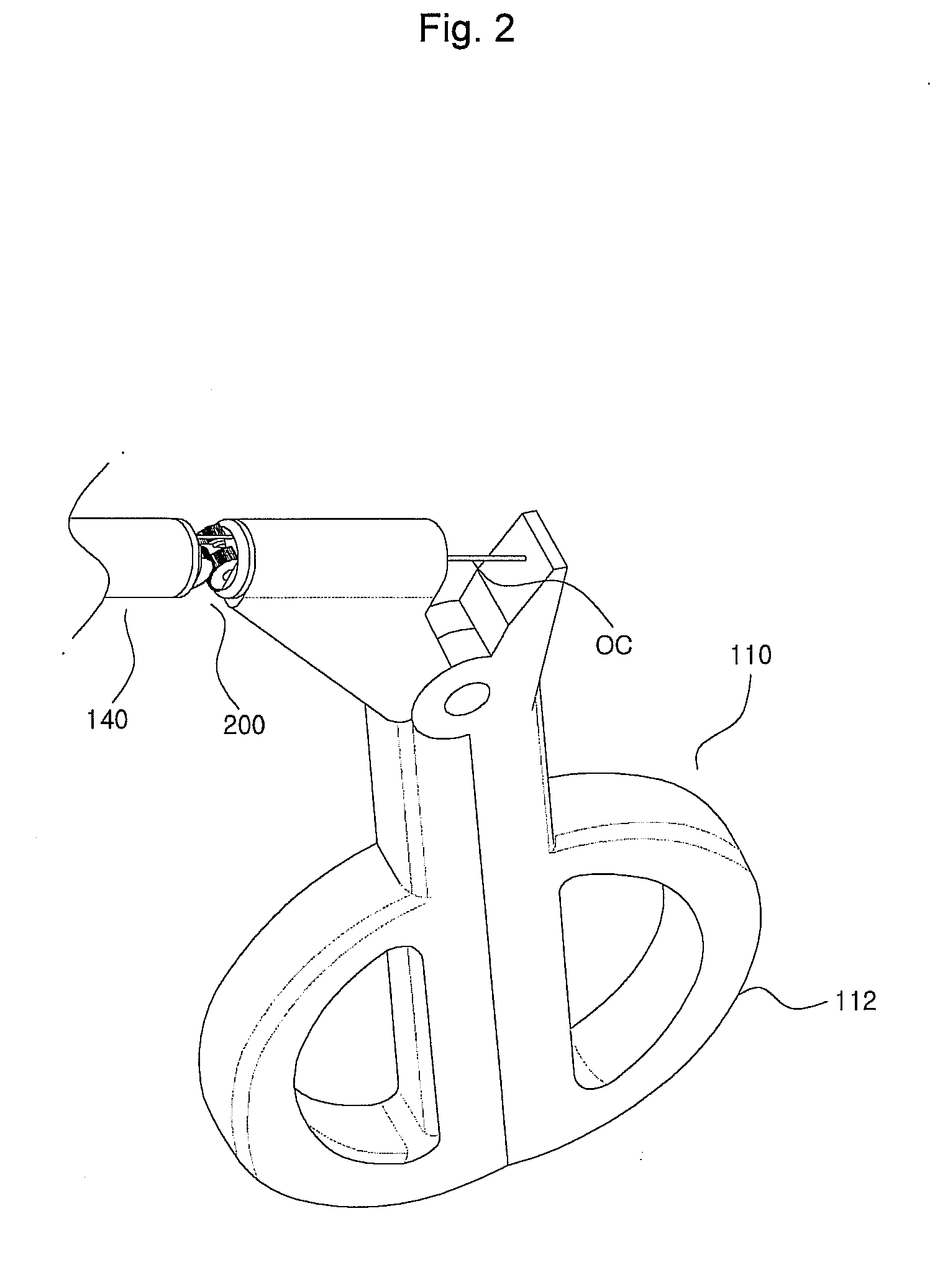
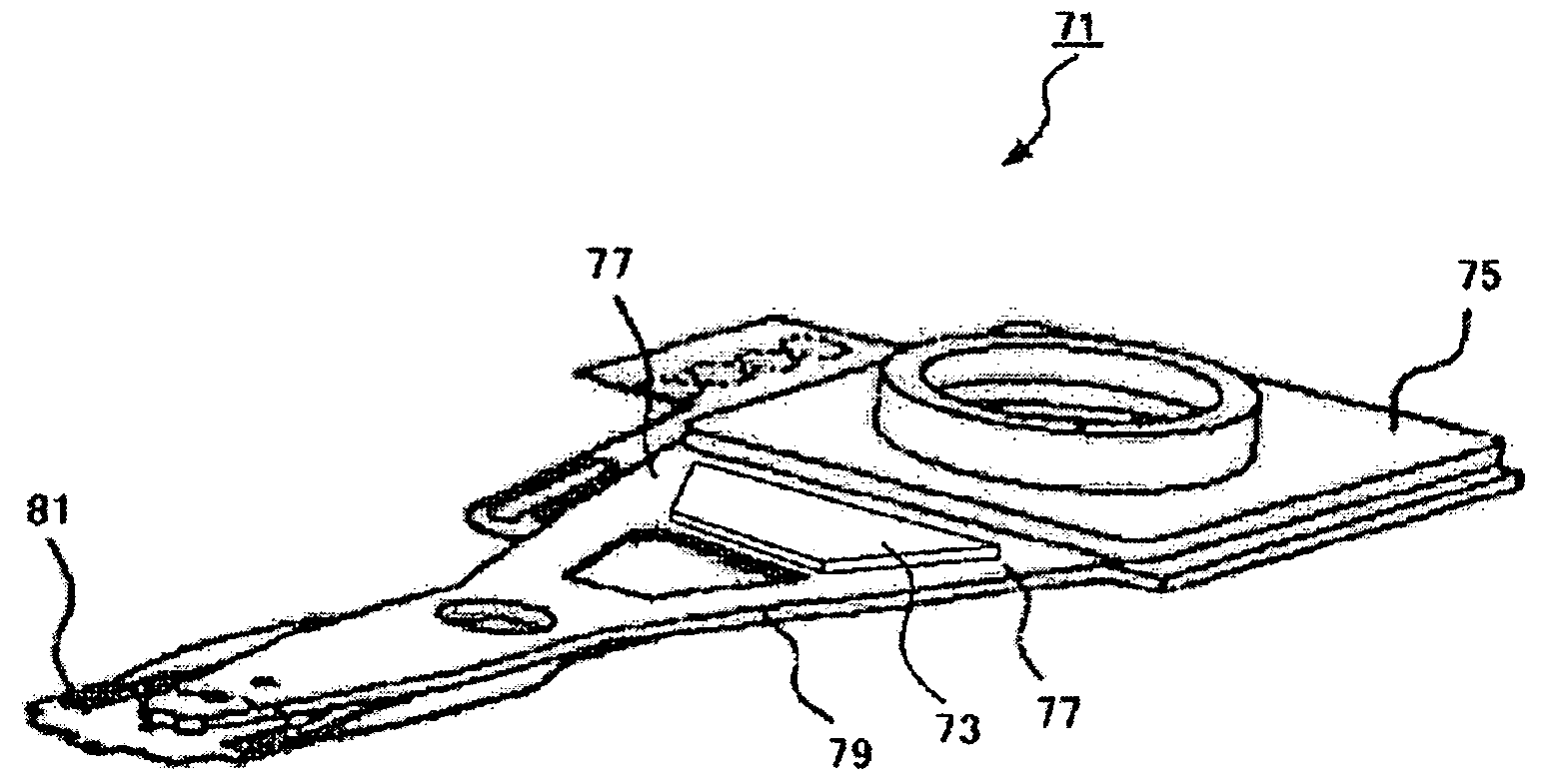
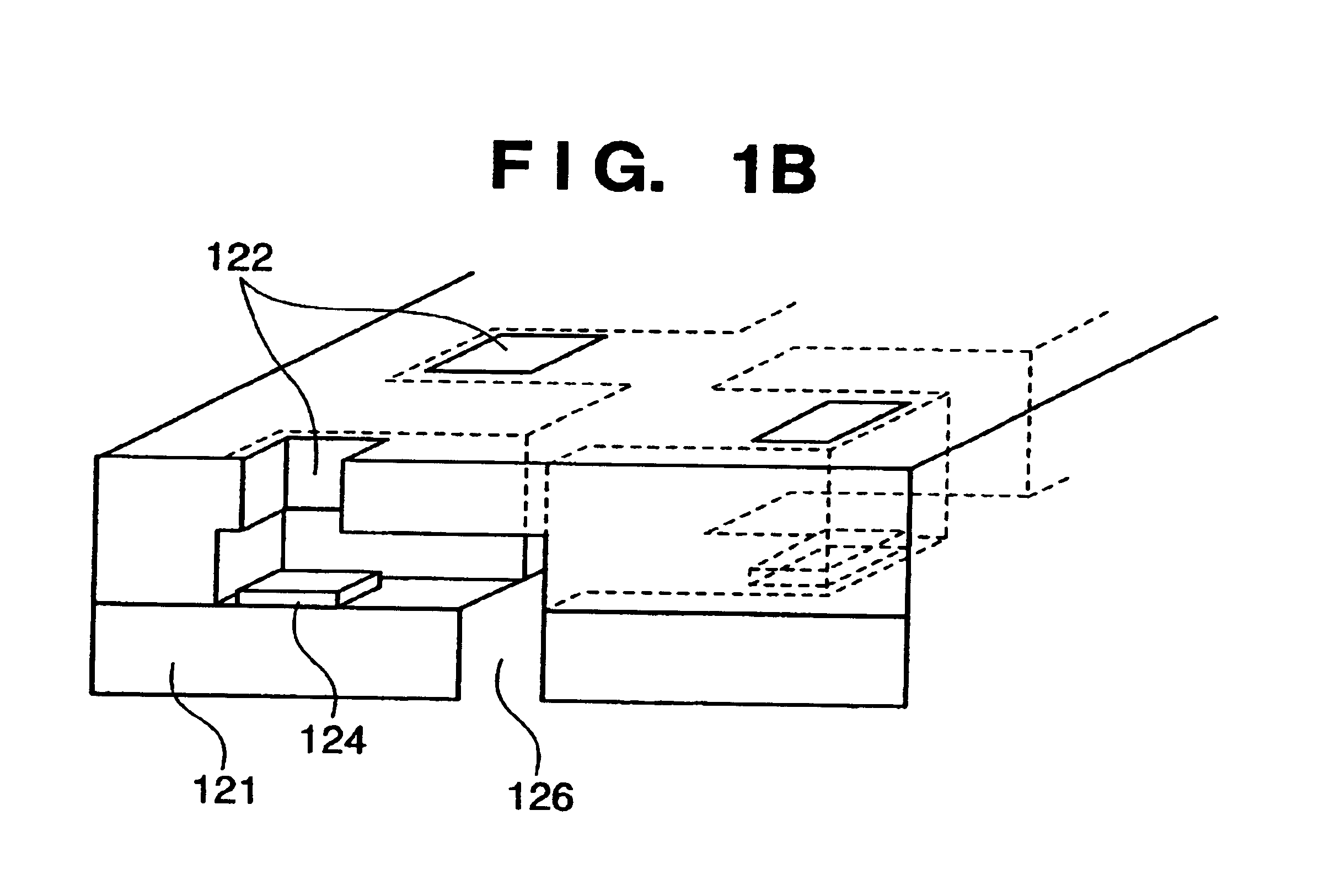
Tool for minimally invasive surgery and method for using the same
InactiveUS20110172648A1Simple drive controlEasy accessDiagnosticsSurgical needlesLess invasive surgeryActuator
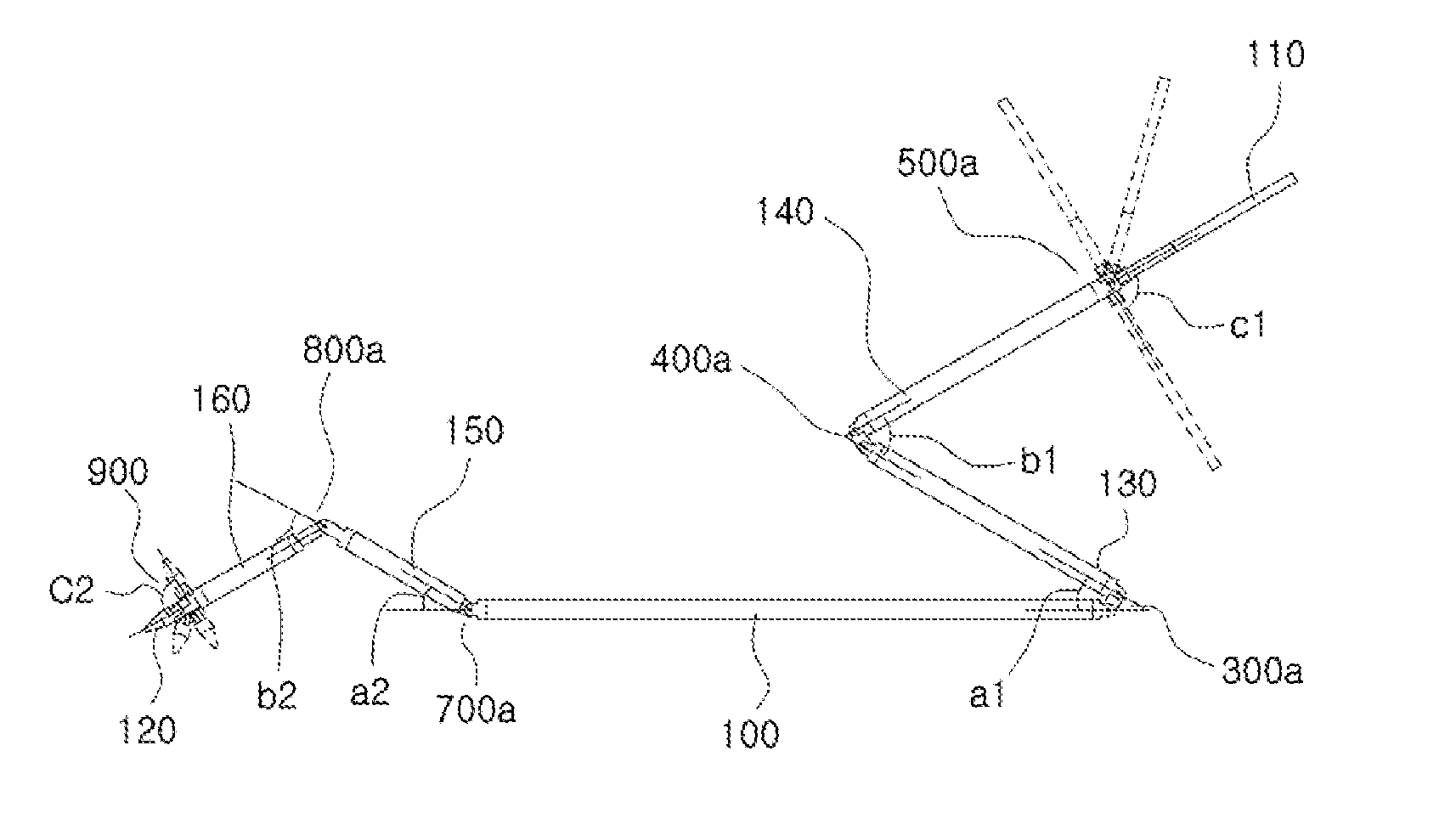
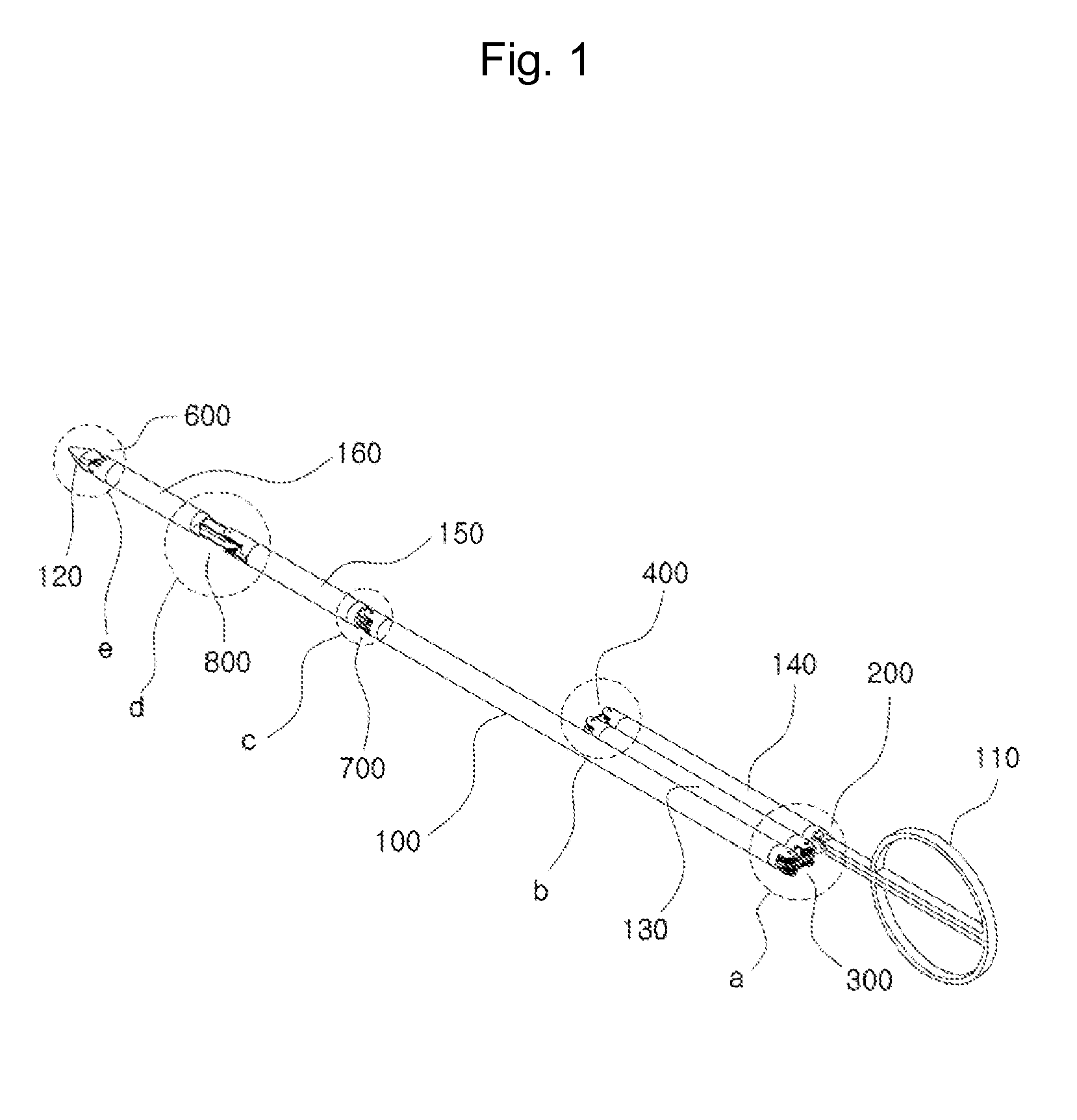
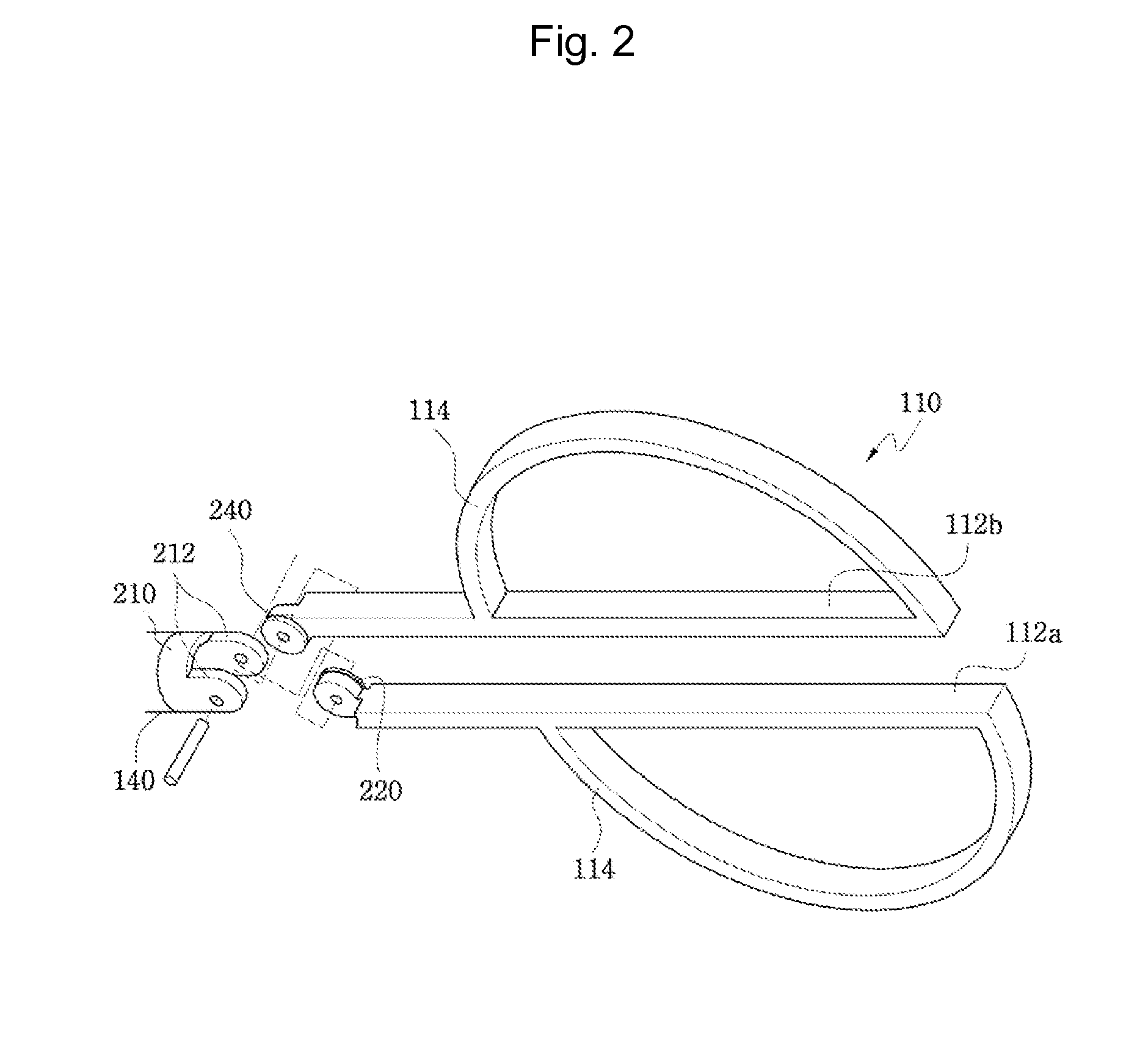
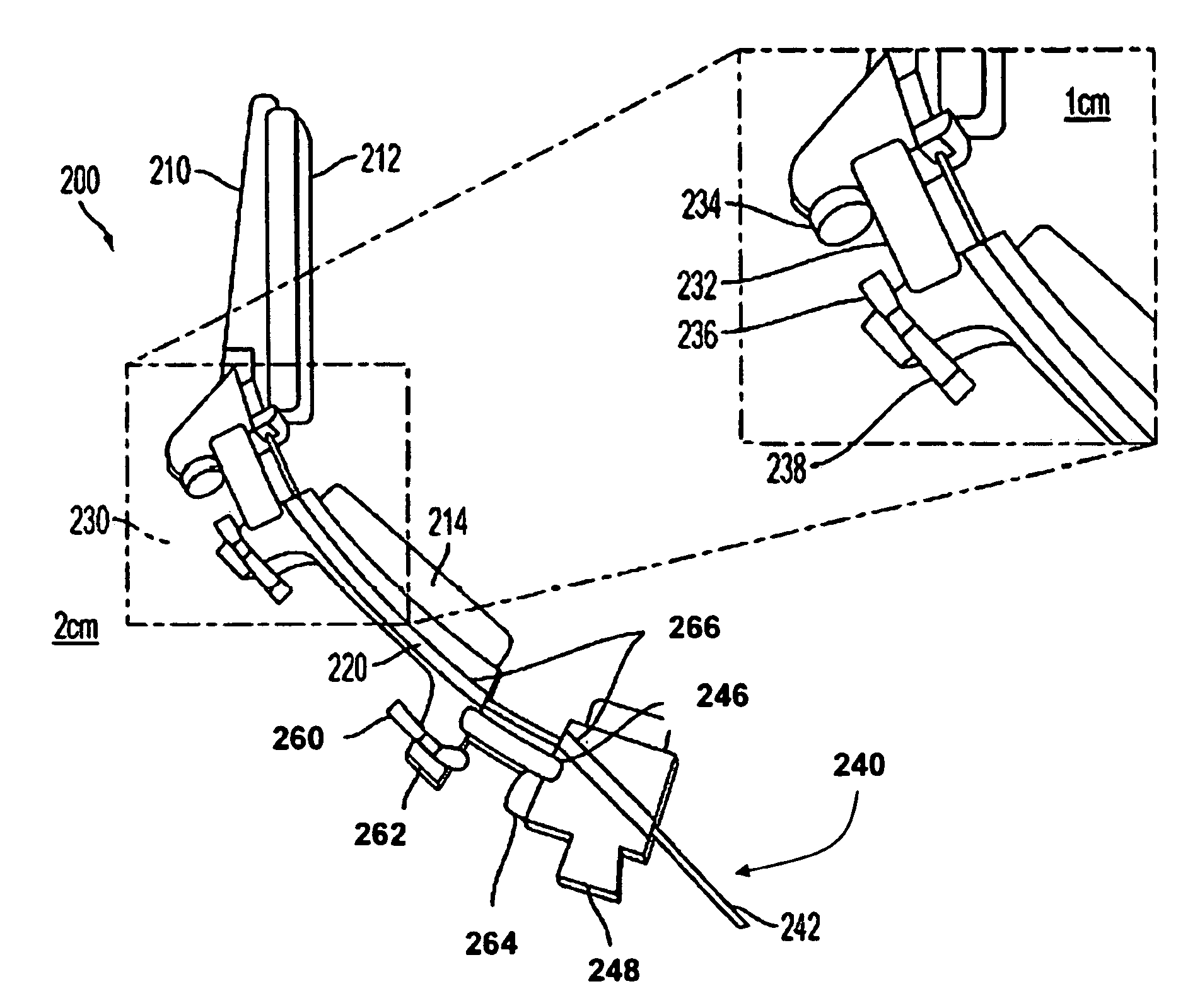
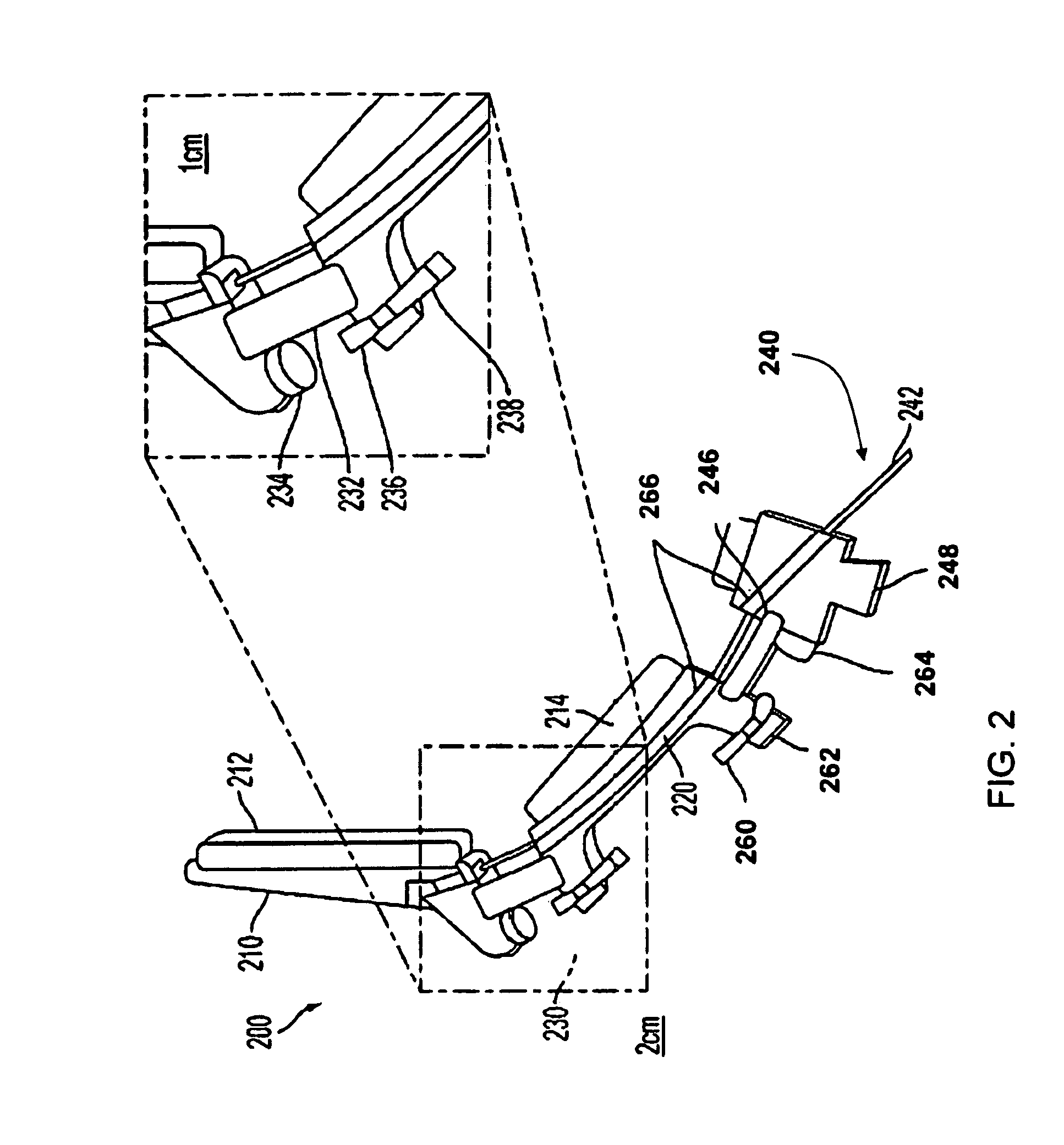
The present invention relates to an easy-to-control tool for minimally invasive surgery and a method for using the same. In accordance with an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a tool for minimally invasive surgery and a method for using the same comprising, a main shaft, a first control shaft and a second control shaft positioned in sequence from one end of the main shaft, a first actuating shaft and a second actuating shaft positioned in sequence from the other end of the main shaft, an adjustment handle positioned around one end of the second control shaft, an end effector positioned around one end of the second actuating shaft, a pitch control part positioned around one position of the positions between the main shaft and the first control shaft, between the first control shaft and the second control shaft, and between the second control shaft and the adjustment handle, for transferring a motion of the adjustment handle in a pitch direction to the end effector, a first yaw control part and a second yaw control part positioned around the other positions of the positions between the main shaft and the first control shaft, between the first control shaft and the second control shaft, and between the second control shaft and the adjustment handle, respectively, for transferring a motion of the adjustment handle in a yaw direction to the end effector, a pitch actuating part positioned around one position of the positions between the main shaft and the first actuating shaft, between the first actuating shaft and the second actuating shaft, and between the second actuating shaft and the end effector, a first yaw actuating part and a second yaw actuating part positioned around the other positions of the positions between the main shaft and the first actuating shaft, between the first actuating shaft and the second actuating shaft, and between the second actuating shaft and the end effector, respectively, a first pitch cable and a second pitch cable for transferring motions from the pitch control part, the first yaw control part, and the second yaw control part to the pitch actuating part, the first yaw actuating part, and the second yaw actuating part, respectively, and a yaw cable for transferring a motion from the first yaw control part to the first yaw actuating part with the first pitch cable and the second pitch cable.
Owner:JEONG CHANG WOOK
Robust Compliant Adaptive Grasper and Method of Manufacturing Same
ActiveUS20090302626A1Not interfere with and reduce complianceIncrease heightProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsElastomerHuman environment
A mechanical grasping system that is both simple to fabricate and operate and robust. A multi-fingered hand may be driven by a single actuator, yet can grasp objects spanning a wide range of size, shape, and mass. The hand may be constructed using polymer-based Shape Deposition Manufacturing, with joints formed by elastomeric flexures and actuator and sensor components embedded in tough rigid polymers. The passively compliant, adaptive hand has superior robustness properties, able to withstand large impacts without damage and capable of grasping objects in the presence of large positioning errors, appropriate for use in unstructured and / or human environments.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
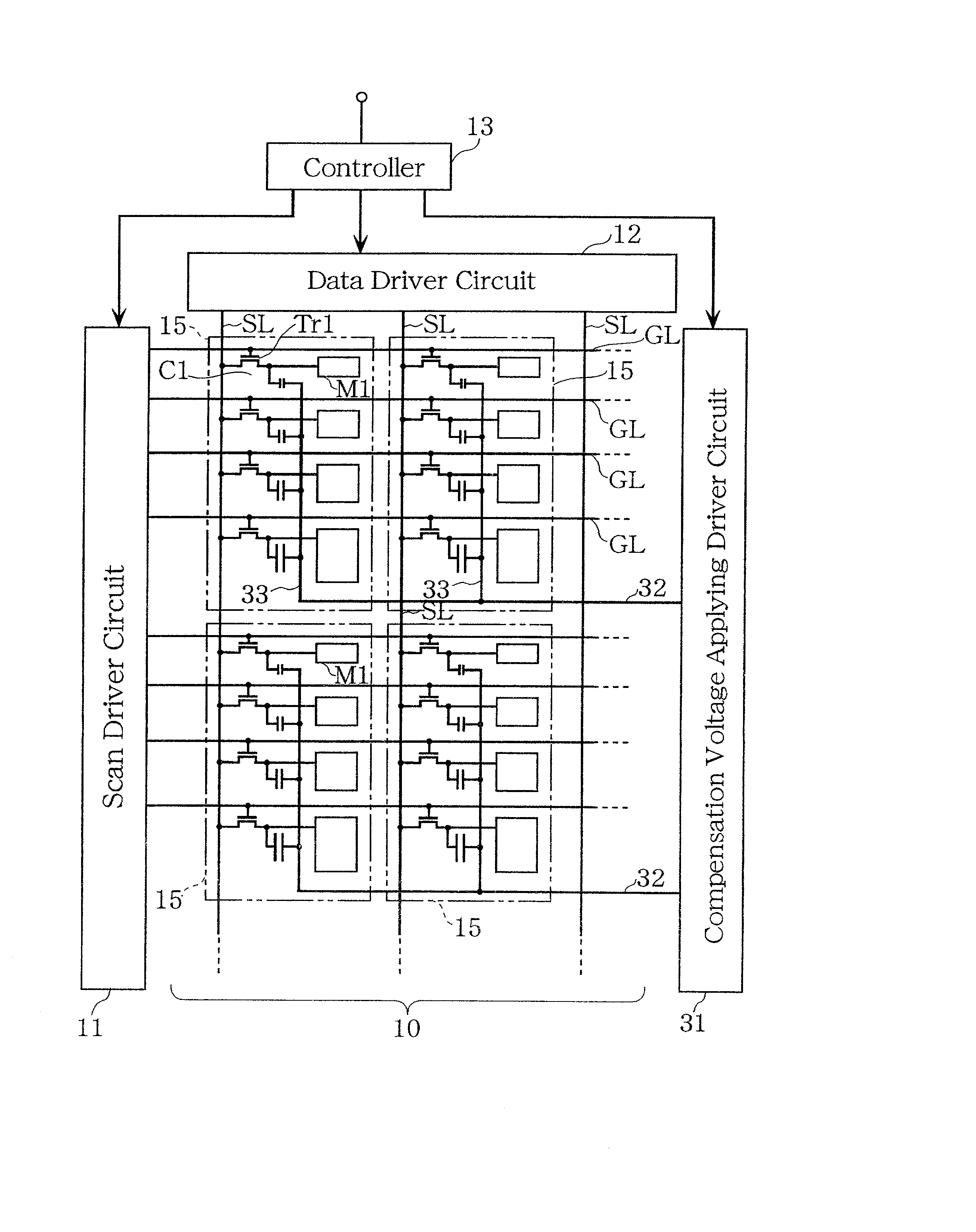
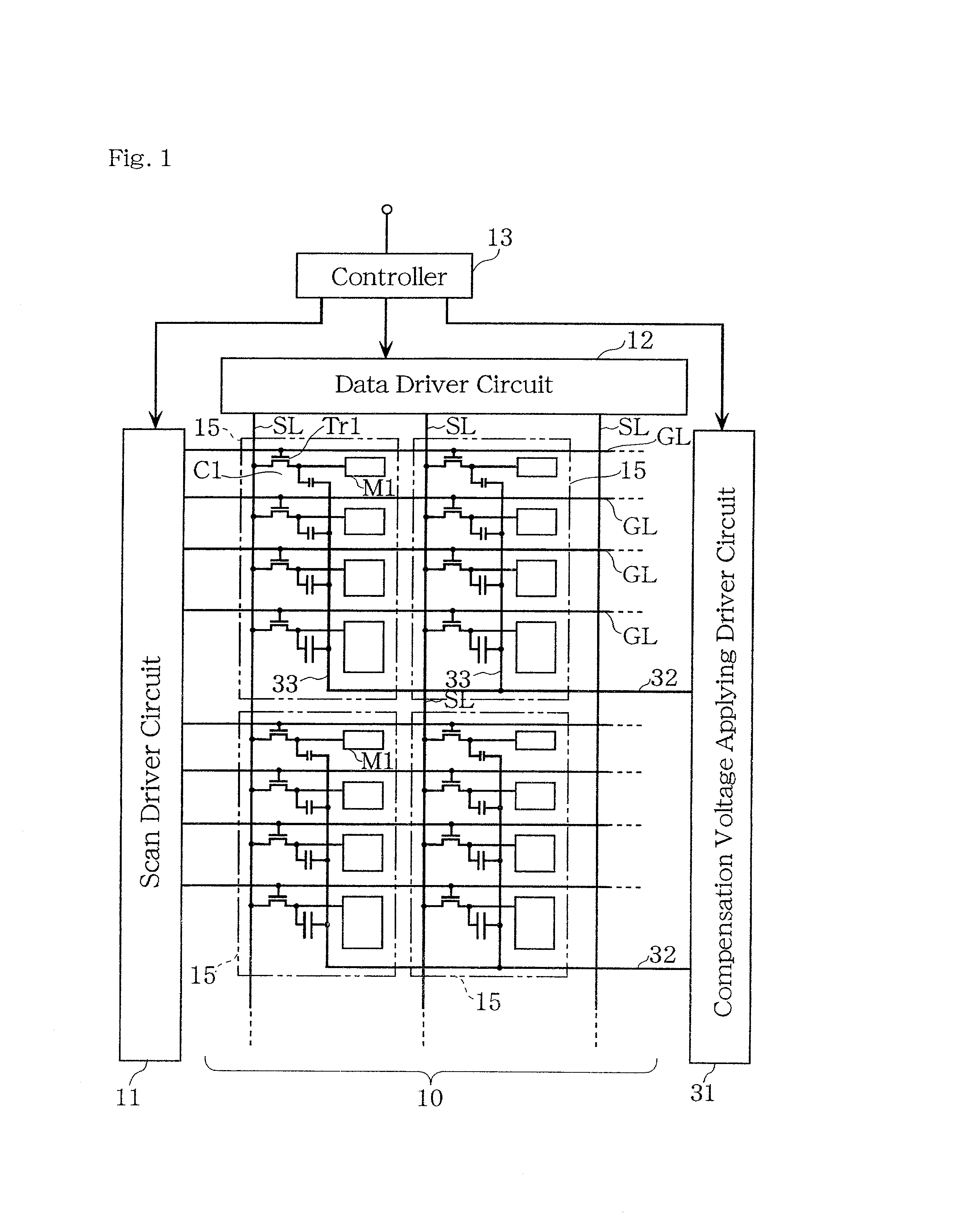
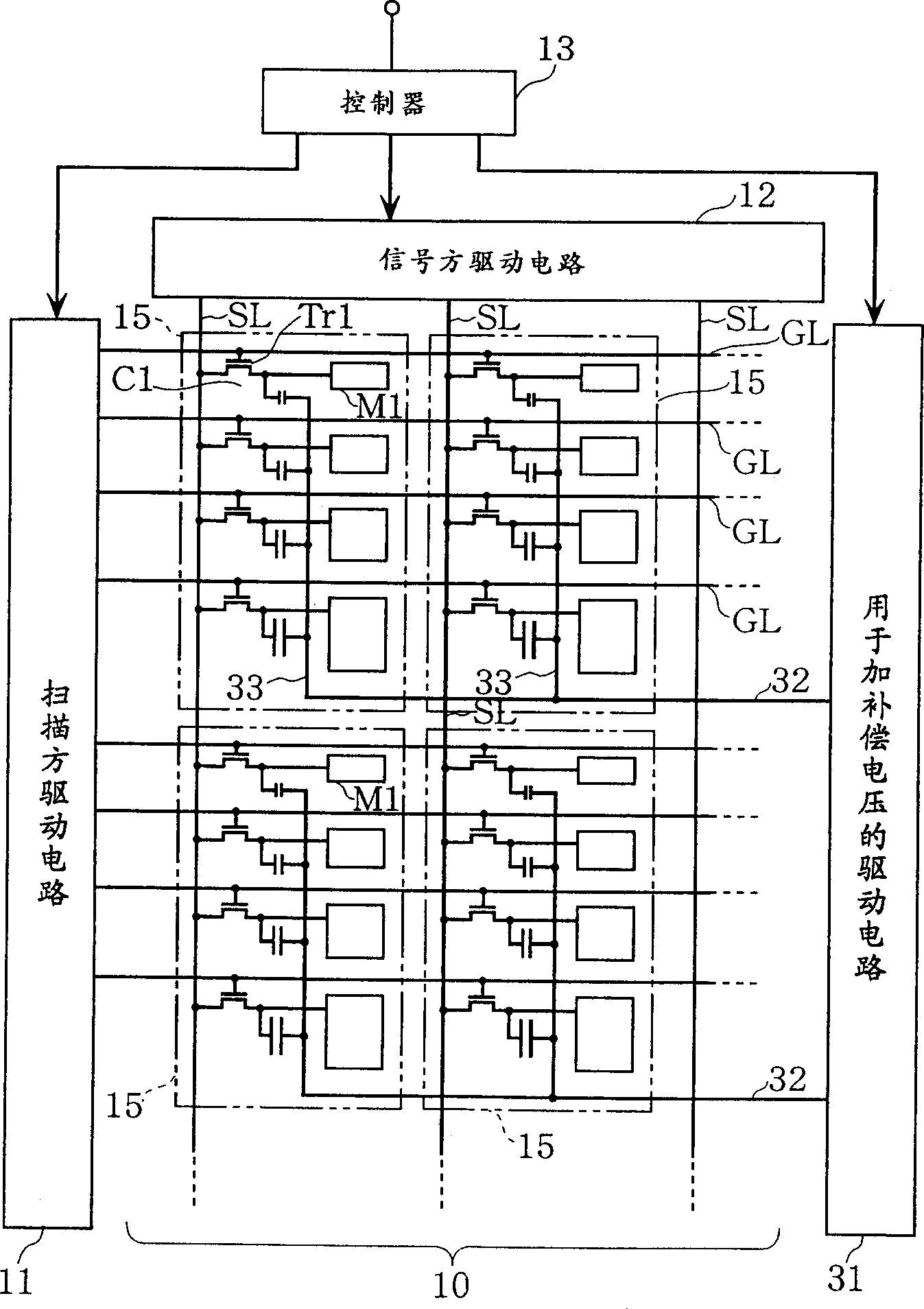
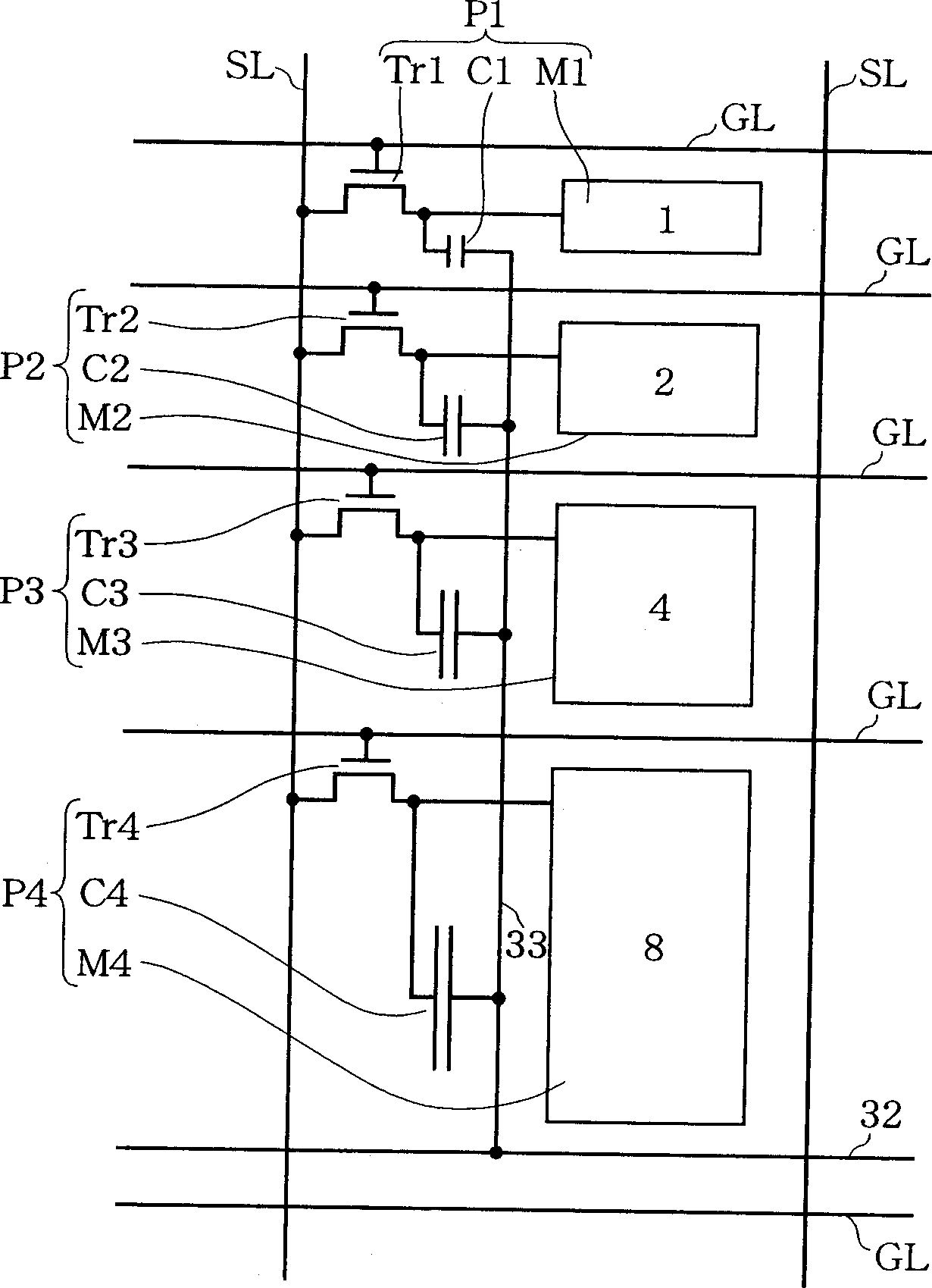
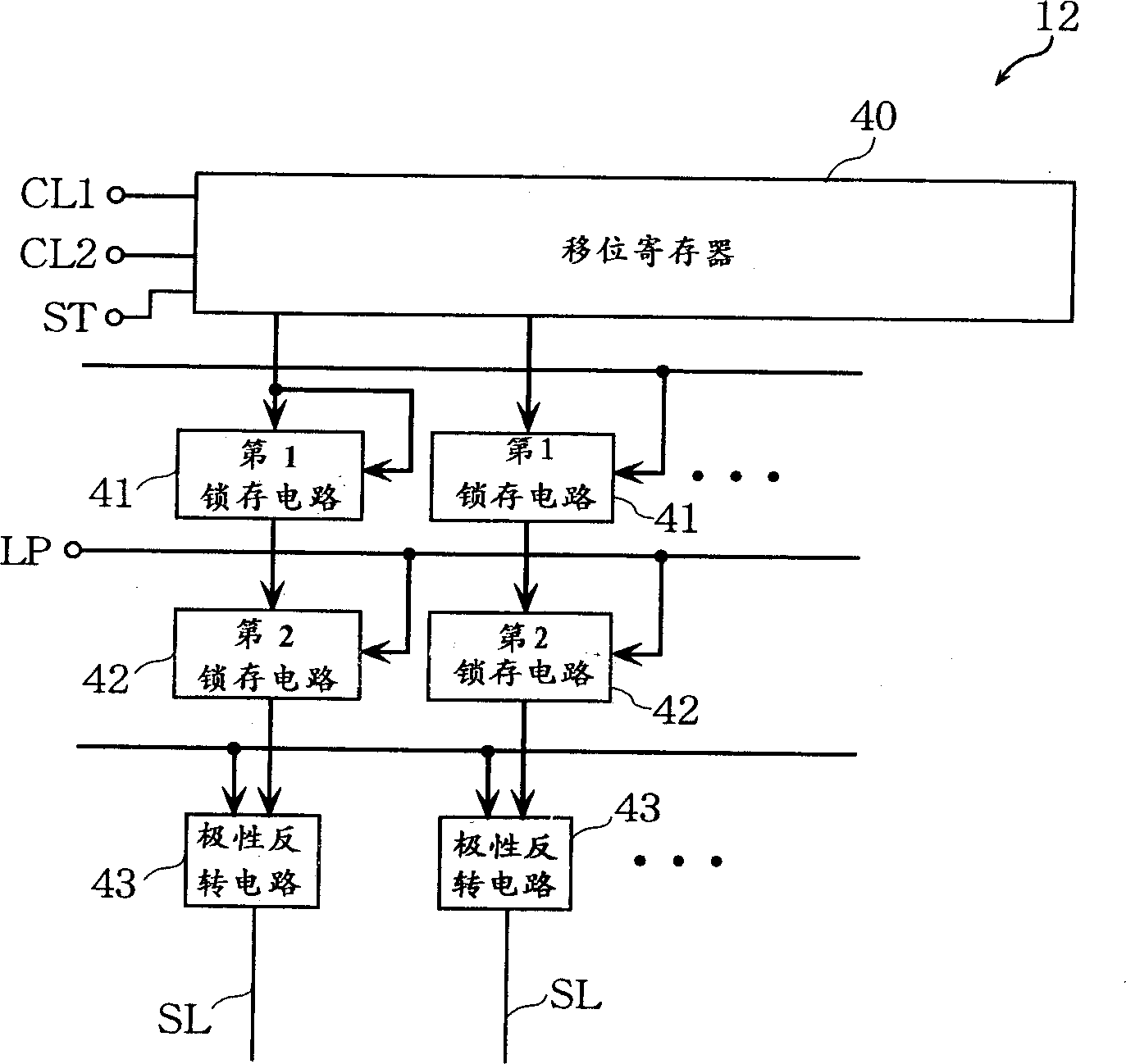
Liquid crystal display device, electroluminescent display device, method of driving the devices, and method of evaluating subpixel arrangement patterns
InactiveUS7084848B2Reduce power consumptionImprove image qualityStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesCapacitanceActive-matrix liquid-crystal display
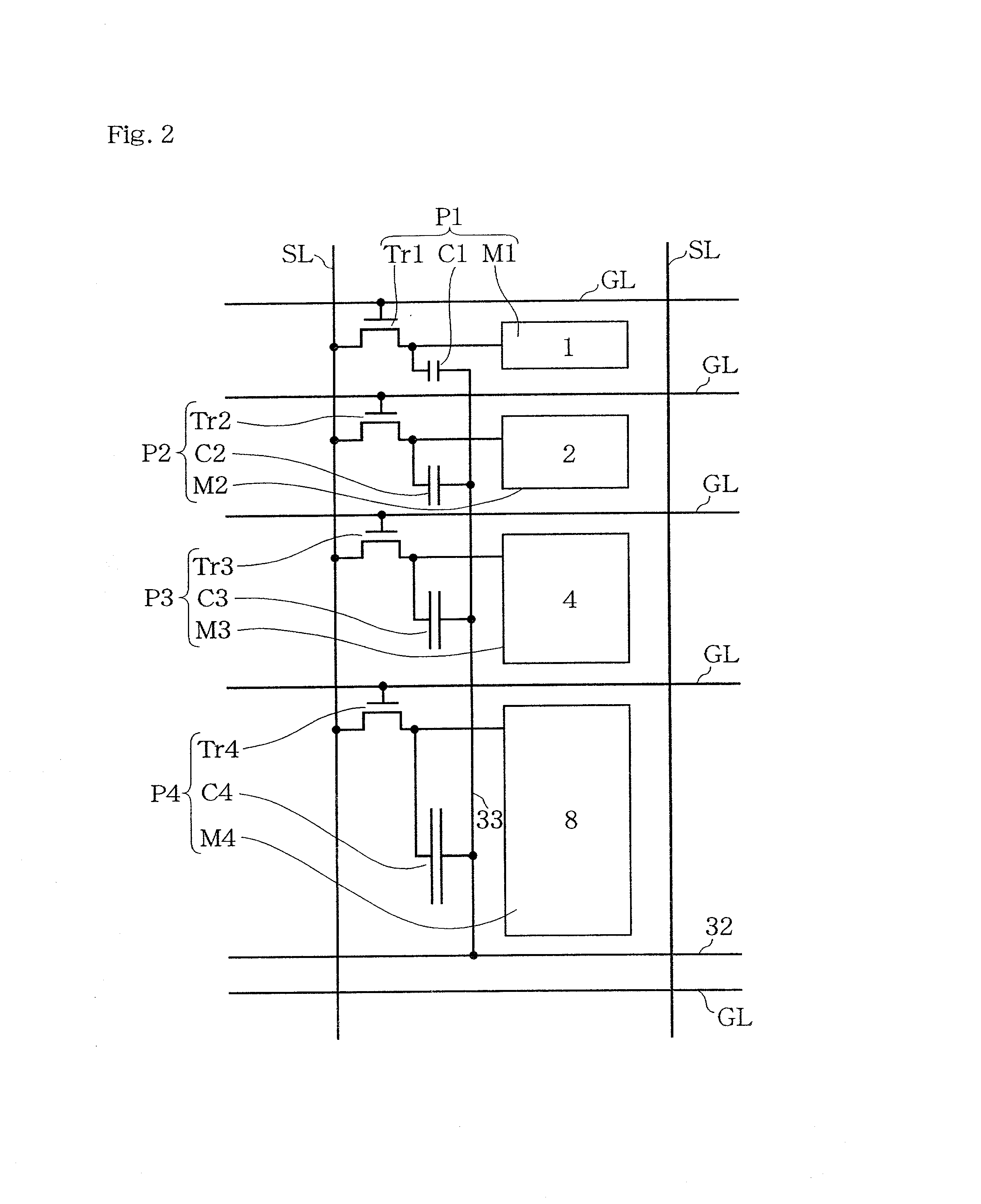
An active matrix liquid crystal display device has a plurality of unit pixels being arranged in a matrix configuration, each unit pixel being divided into a plurality of subpixels. Each of the subpixels has a subpixel electrode, a pixel transistor connected to the subpixel electrode, and a voltage controlling capacitor connected to the subpixel electrode. A voltage controlling capacitor line for supplying a compensation voltage signal is connected to the voltage controlling capacitor so that after the writing to the subpixel has been completed, the potential of the compensation voltage signal is varied to modulate the potential of the subpixel electrode to be a predetermined voltage, using the voltage controlling capacitor. Such combining of spatial dithering attained by a pixel-dividing technique and a capacitively-coupled driving method eliminates the need for digital-to-analog converter circuits, attains gray scale display based on a digital image signal, and achieves a reduction in power consumption.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY CENT INC
Robust compliant adaptive grasper and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS8231158B2Not interfere with and reduce complianceReduce the possibility of damageProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsDegrees of freedomEngineering
A multi-fingered underactuated mechanical grasping system driven by a single actuator, yet can grasp objects spanning a wide range of size, shape, and mass. A member for moving a link relative to a base acts in parallel to a direction of compliance of a joint between the link and the base. The joint has a plurality of degrees of freedom. The number of members for moving links in the grasping system is less than the number of degrees of freedom in the grasping system.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Gas-driven chest compression apparatus
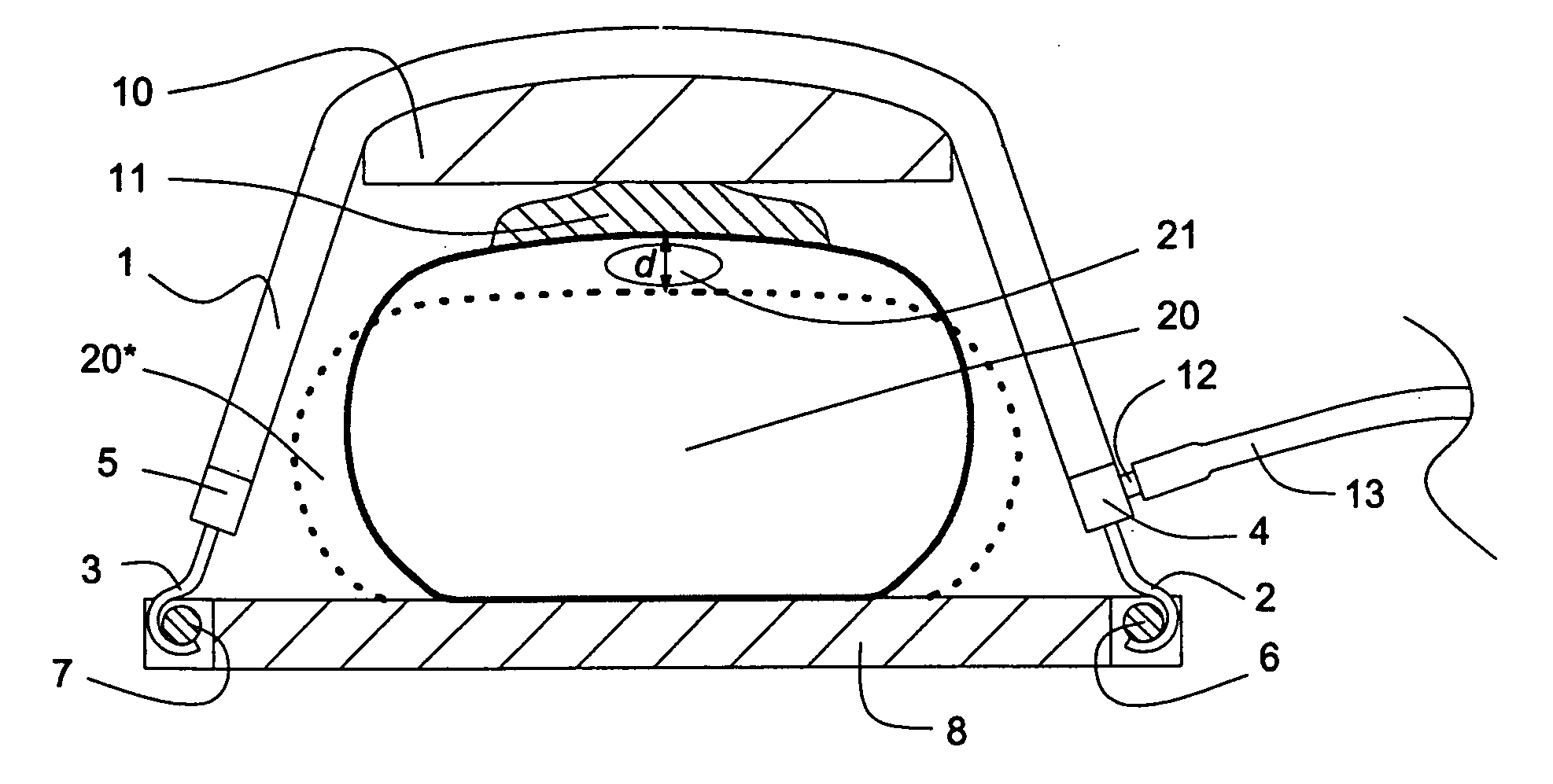
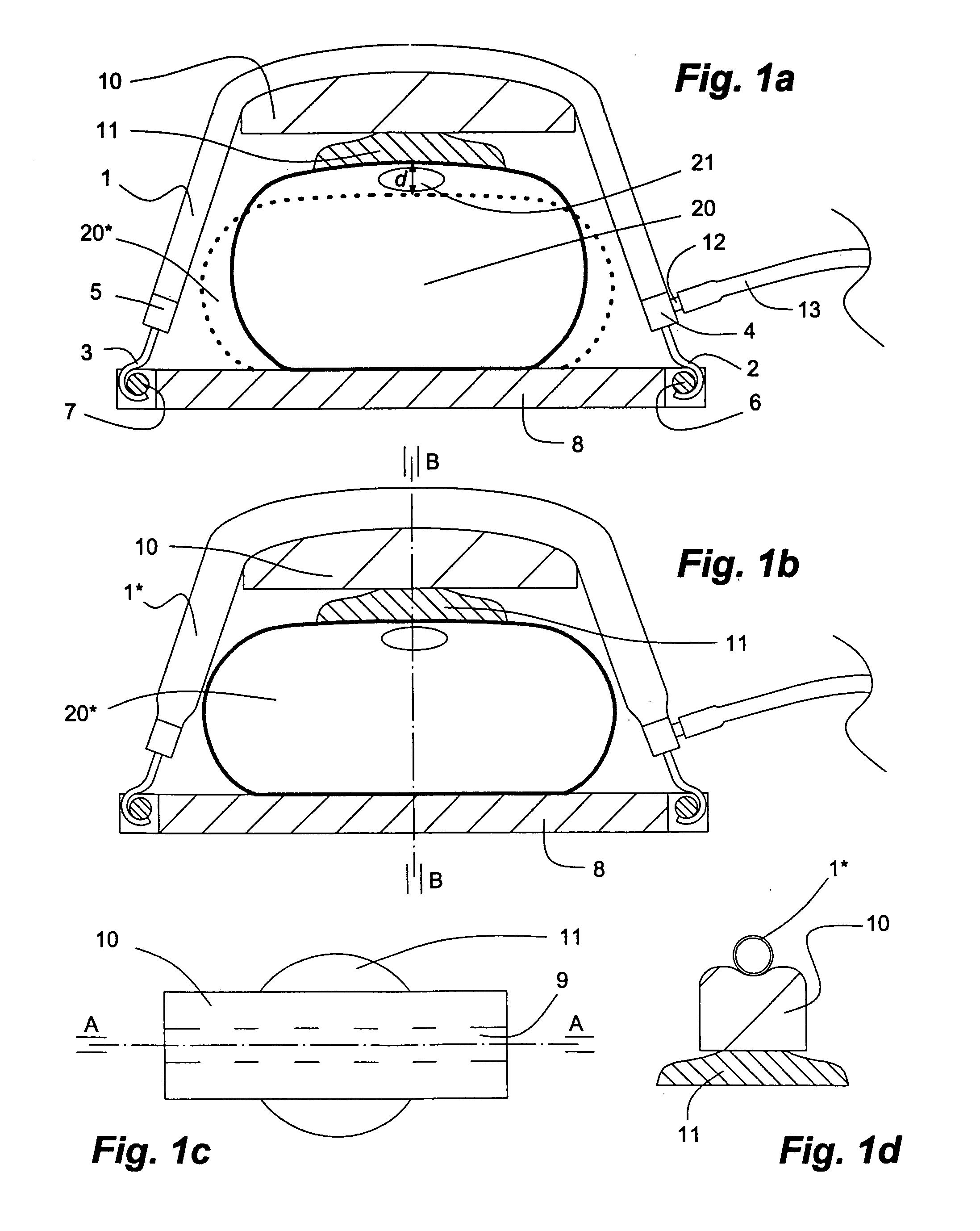
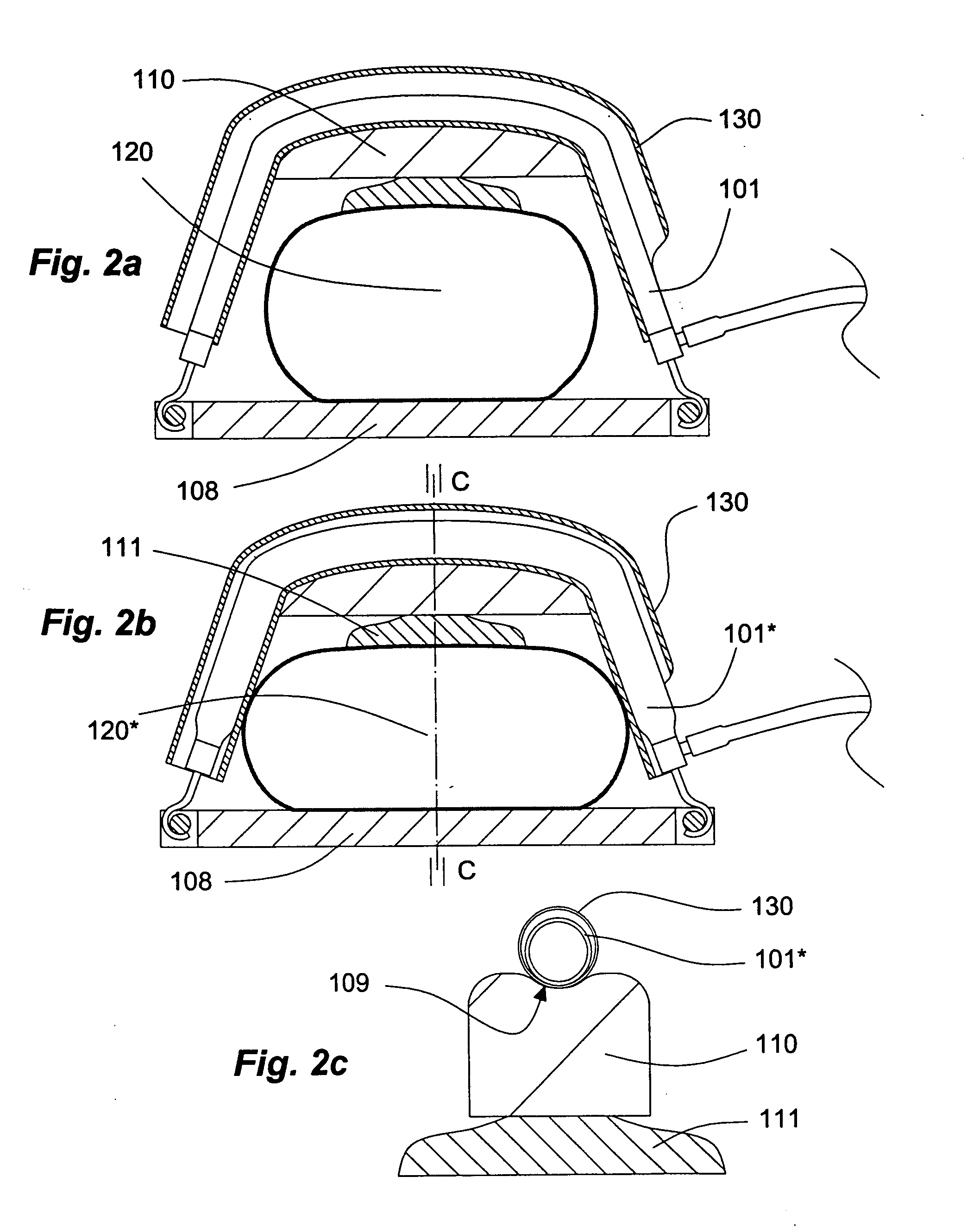
InactiveUS20100004572A1Improve returnSimple drive controlElectrotherapyIron-lungsEmergency medicineCPR - Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
A gas-driven chest compression apparatus for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) comprises a flexible pneumatic actuator, capable of axial contraction when fed with a pressurized driving gas, and means for controlling the contraction thereof. Also disclosed are methods of providing chest compressions to a patient by means of a CPR apparatus comprising actuator(s) of this kind, and a corresponding use of the actuator.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
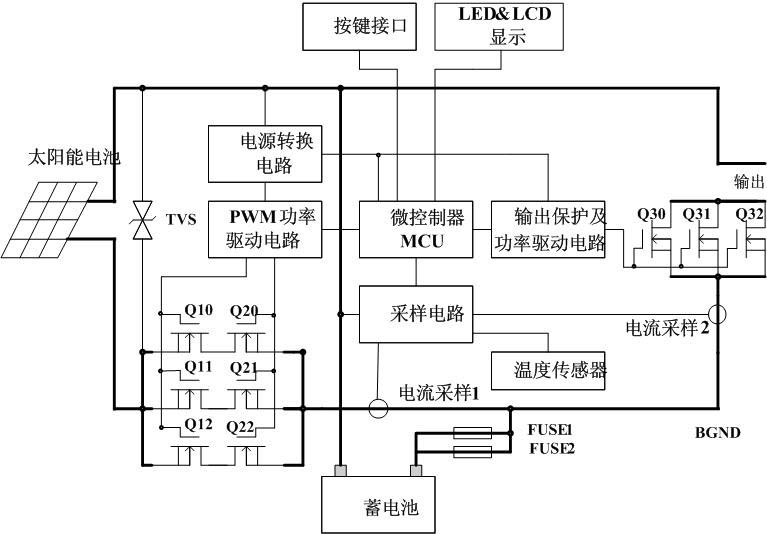
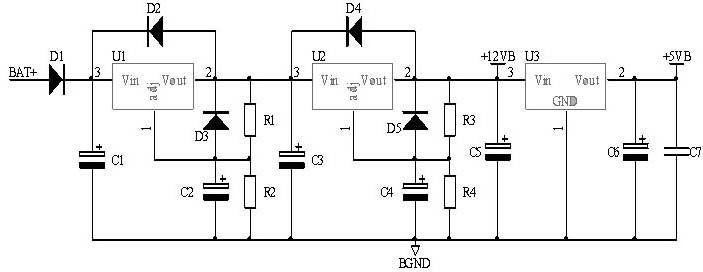
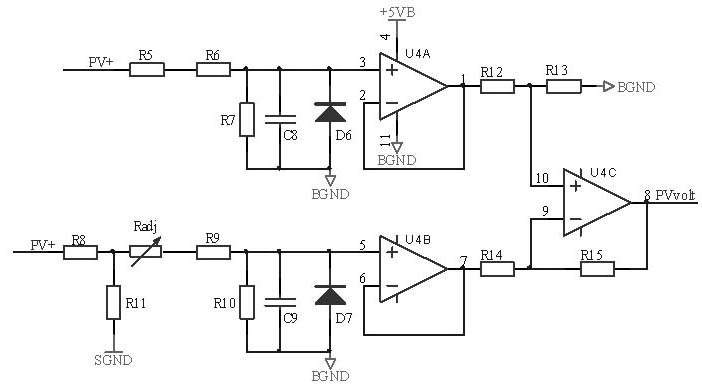
Solar charging control circuit
ActiveCN102035238ASimple structureSimple drive controlBatteries circuit arrangementsPhotovoltaicsMicrocontrollerElectrical battery
The invention discloses a solar charging control circuit, which is used for controlling a solar cell to charge a storage battery and supply power to a load. The solar charging control circuit comprises a power switching circuit, a sampling circuit, a microcontroller, a pulse width modulation (PWM) power driving circuit, an output protection and power driving circuit, a charging loop and a load loop. The circuit overcomes the defects existing in the conventional solar charging controller and meets the requirements of application of large and medium-sized solar photovoltaic power stations according to characteristics and charging and discharging characteristics of a lead acid storage battery and power output characteristic of the solar cell; and the solar charging control circuit has the advantages of high capacity and efficiency, low cost, longer service life, more accurate battery management and more intelligent system.
Owner:EAST GRP CO LTD
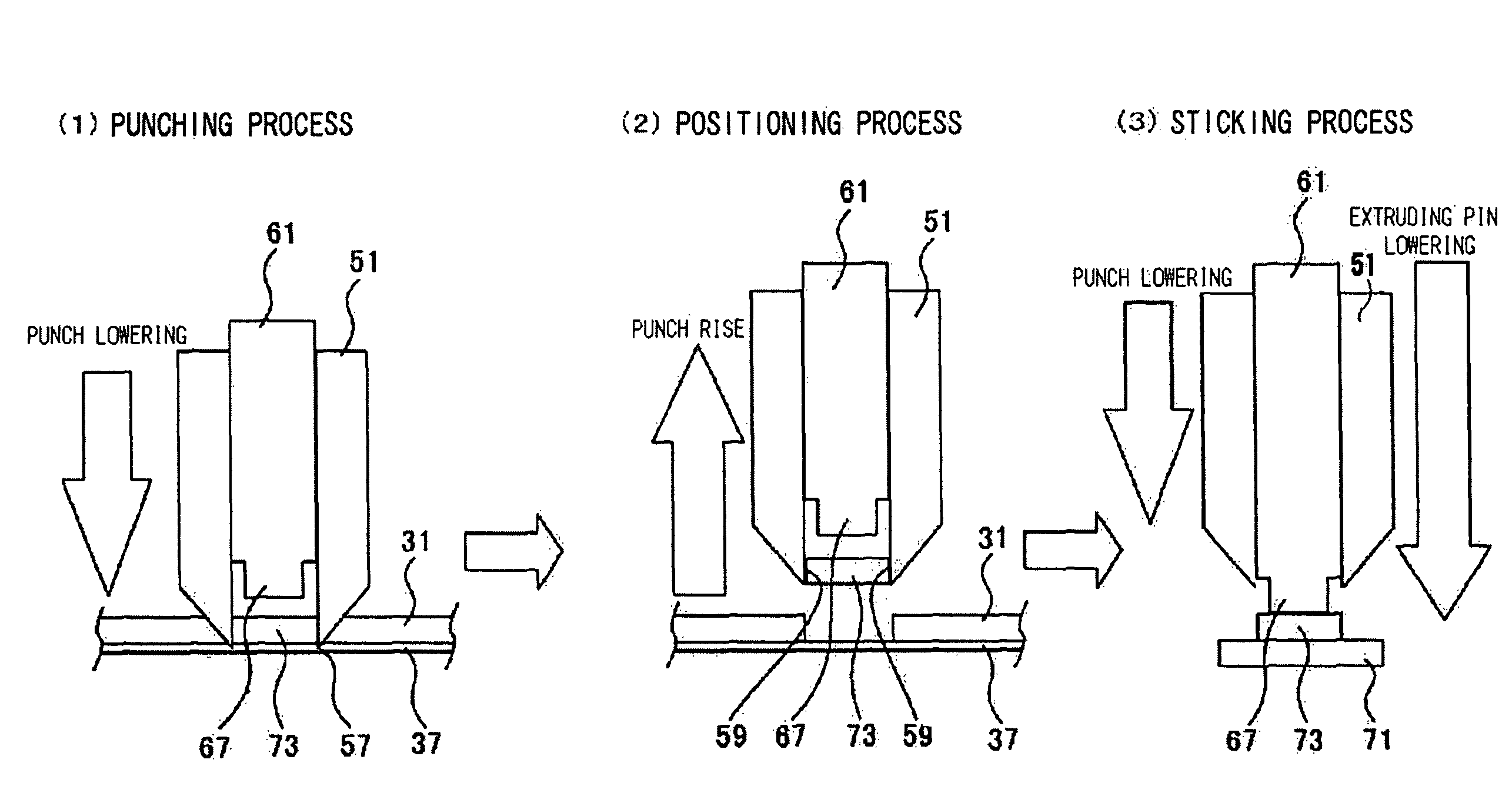
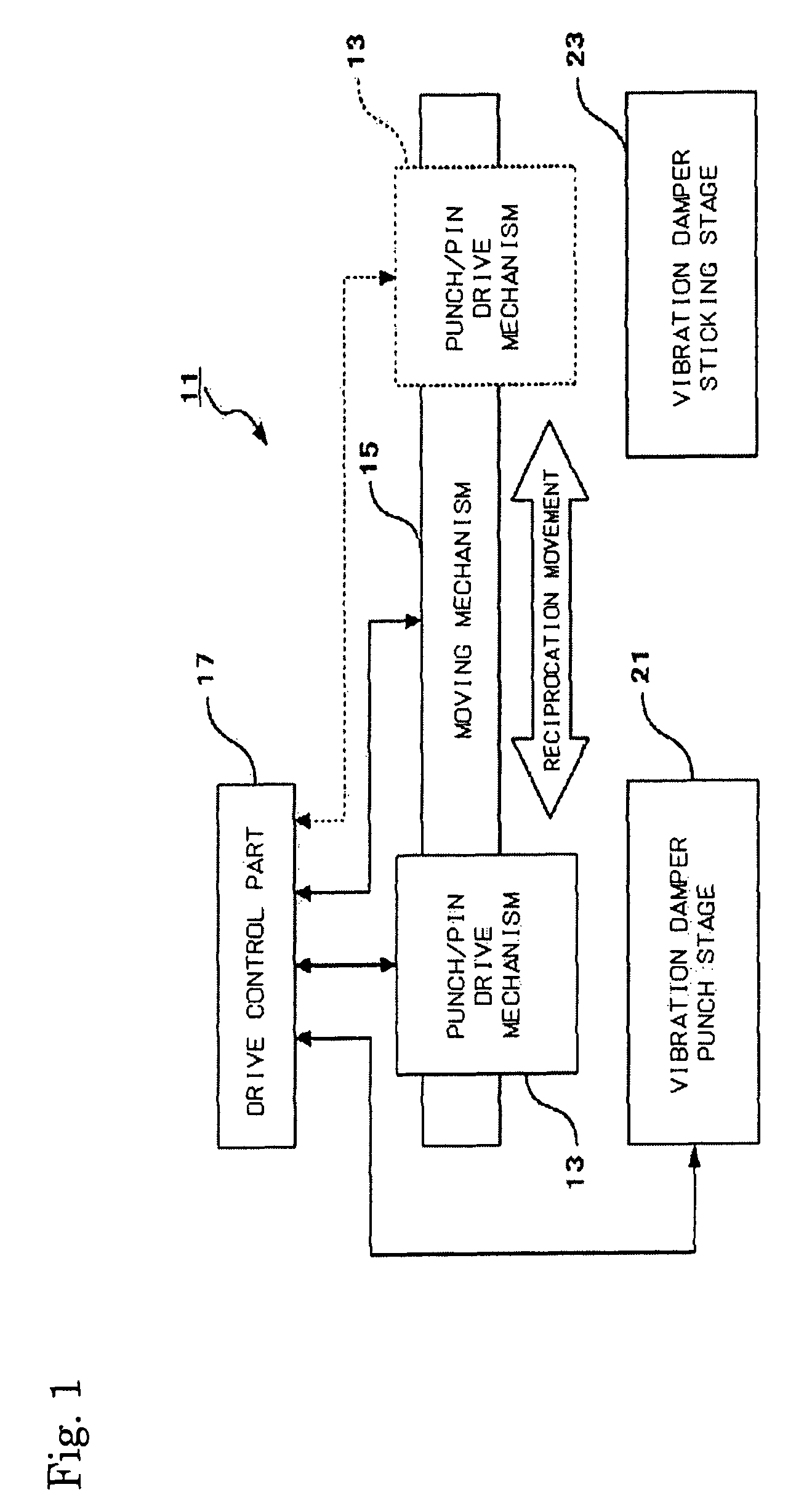
Method for manufacturing a head suspension
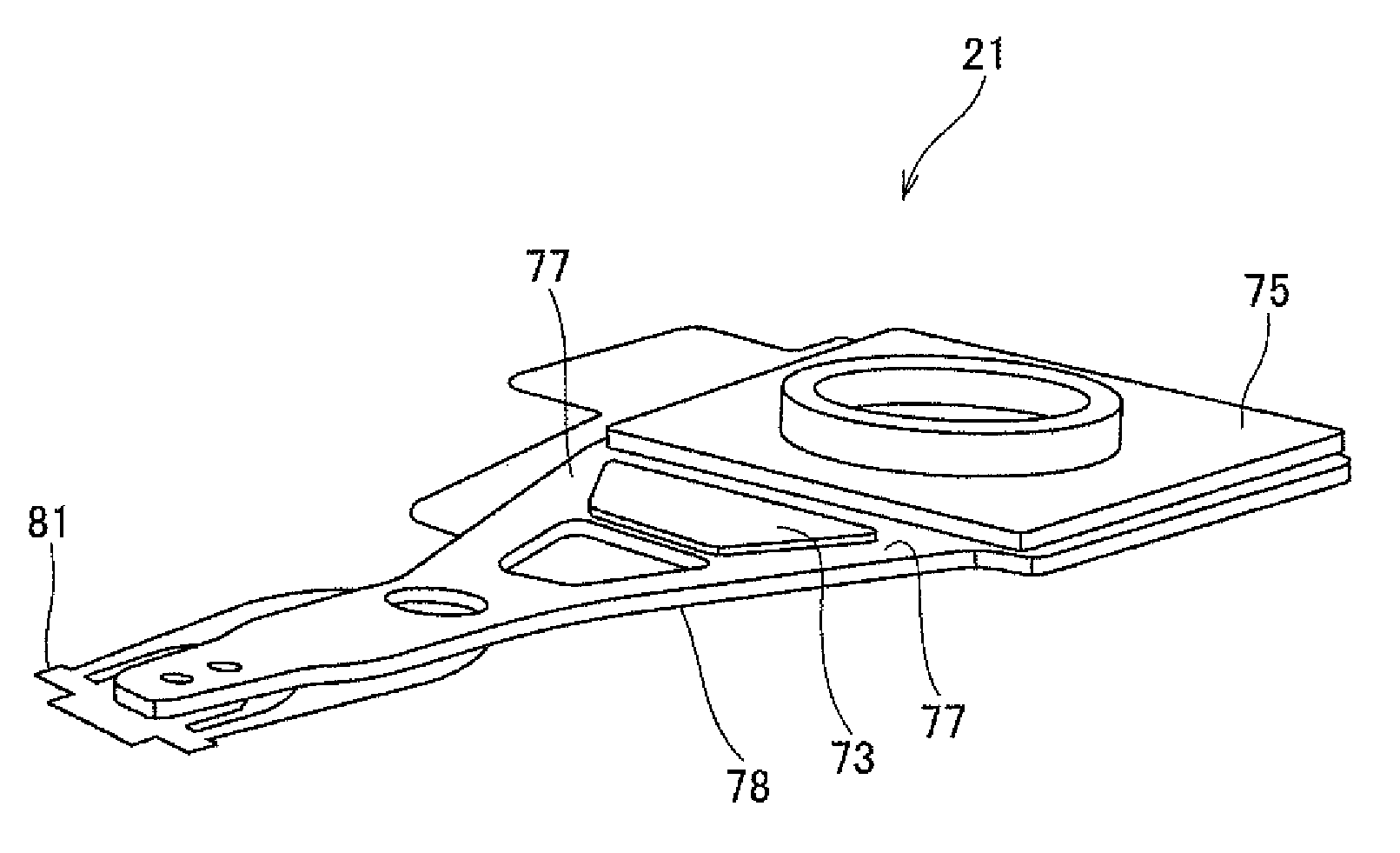
ActiveUS8151440B2Dispersion suppressionImprove productivityElectrical transducersRecord information storageProduction rateVibration control
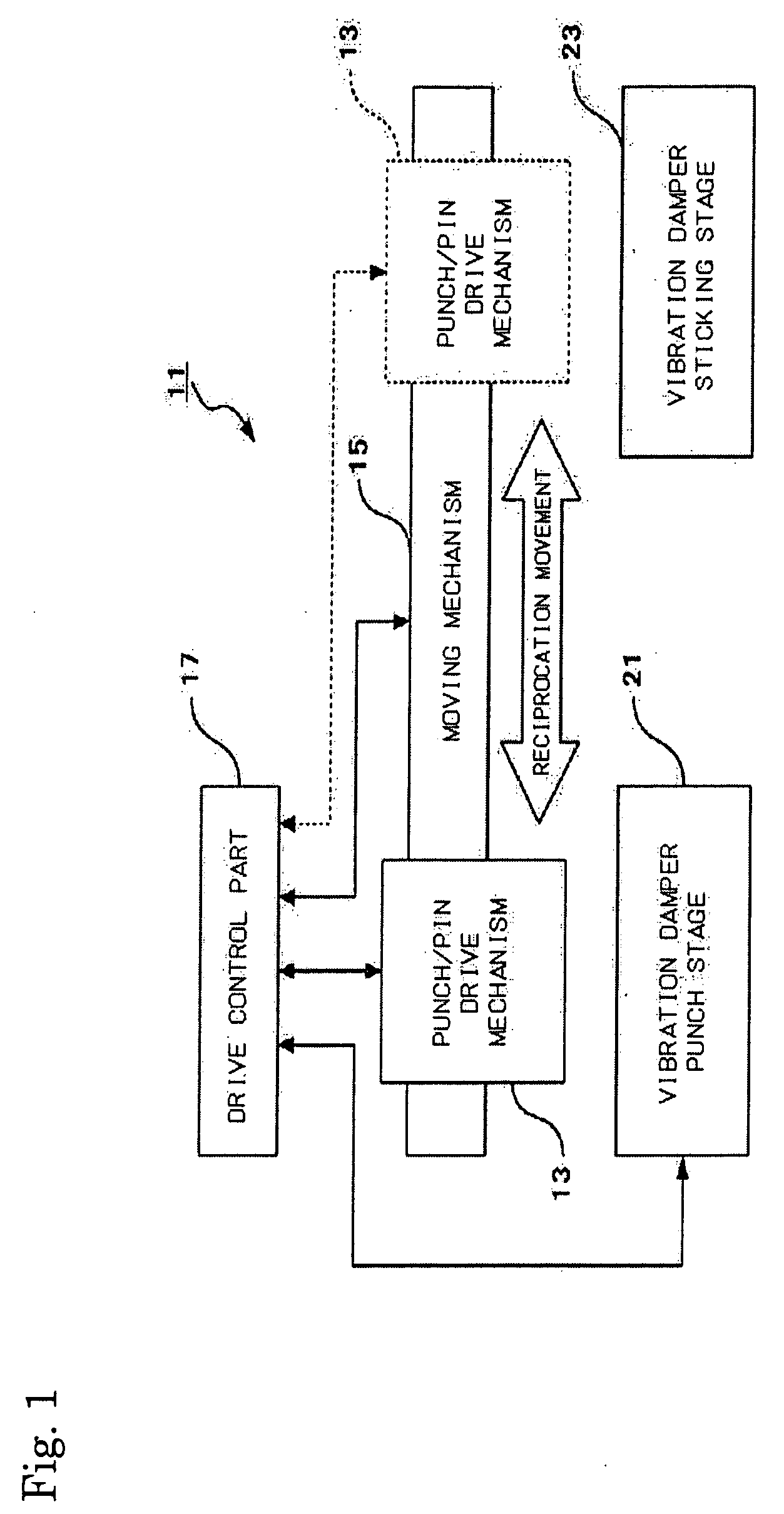
A method for manufacturing a head suspension is capable of suppressing the dispersion in the vibration control effect of a head suspension and improve productivity, the manufacturing method includes a step of punching, by use of a hollow punch having a tooth portion at a distal end thereof, a vibration damper piece out from a base material having a vibration damper provided detachably on a liner through an attaching surface, to hold the vibration damper piece on a hollow internal surface of the punch, a step of positioning the punch holding the vibration damper piece on an objective portion of a semi-finished head suspension, and a step of attaching, by use of an extruding implement, the vibration damper piece on the objective portion with the attaching surface through extruding the vibration damper piece from the punch.
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
Display device and driving method thereof, and display pattern evaluation for sub-element of picture
InactiveCN1351323AReduce consumptionSmall footprintStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesCapacitanceDisplay device
An active matrix liquid crystal display device has a plurality of unit pixels being arranged in a matrix configuration, each unit pixel being divided into a plurality of subpixels. Each of the subpixels has a subpixel electrode, a pixel transistor connected to the subpixel electrode, and a voltage controlling capacitor connected to the subpixel electrode. A voltage controlling capacitor line for supplying a compensation voltage signal is connected to the voltage controlling capacitor so that after the writing to the subpixel has been completed, the potential of the compensation voltage signal is varied to modulate the potential of the subpixel electrode to be a predetermined voltage. Such method eliminates the need for digital-to-analog converter circuits, attains gray scale display based on a digital image signal, and achieves a reduction in power consumption.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY CENTRAL CO LTD
Tool for minimally invasive surgery and method for using the same
The present invention relates to an easy-to-control tool for minimally invasive surgery and a method for using the same. In accordance with an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a tool for minimally invasive surgery and a method for using the same comprising, a main shaft, a first control shaft and a second control shaft positioned in sequence from one end of the main shaft, a first actuating shaft and a second actuating shaft positioned in sequence from the other end of the main shaft, an adjustment handle positioned around one end of the second control shaft, an end effector positioned around one end of the second actuating shaft, a pitch control part positioned around one position of the positions between the main shaft and the first control shaft, between the first control shaft and the second control shaft, and between the second control shaft and the adjustment handle, for transferring a motion of the adjustment handle in a pitch direction to the end effector, a first yaw control part and a second yaw control part positioned around the other positions of the positions between the main shaft and the first control shaft, between the first control shaft and the second control shaft, and between the second control shaft and the adjustment handle, respectively, for transferring a motion of the adjustment handle in a yaw direction to the end effector, a pitch actuating part positioned around one position of the positions between the main shaft and the first actuating shaft, between the first actuating shaft and the second actuating shaft, and between the second actuating shaft and the end effector, a first yaw actuating part and a second yaw actuating part positioned around the other positions of the positions between the main shaft and the first actuating shaft, between the first actuating shaft and the second actuating shaft, and between the second actuating shaft and the end effector, respectively, and a pitch cable, a first yaw cable, and a second yaw cable for transferring motions from the pitch control part, the first yaw control part, and the second yaw control part to the pitch actuating part, the first yaw actuating part, and the second yaw actuating part.
Owner:JEONG CHANG WOOK
Method, apparatus and jig for manufacturing head suspension, and head suspension
ActiveUS20090183359A1Dispersion suppressionImprove productivityElectrical transducersRecord information storageProduction rateVibration control
A method for manufacturing a head suspension is capable of suppressing the dispersion in the vibration control effect of a head suspension and improve productivity, the manufacturing method includes a step of punching, by use of a hollow punch having a tooth portion at a distal end thereof, a vibration damper piece out from a base material having a vibration damper provided detachably on a liner through an attaching surface, to hold the vibration damper piece on a hollow internal surface of the punch, a step of positioning the punch holding the vibration damper piece on an objective portion of a semi-finished head suspension, and a step of attaching, by use of an extruding implement, the vibration damper piece on the objective portion with the attaching surface through extruding the vibration damper piece from the punch.
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
Inkjet printhead, driving method of inkjet printhead, and substrate for inkjet printhead
InactiveUS6966629B2Simple structureSimple drive controlOther printing apparatusElectrical and Electronics engineeringInkjet printing
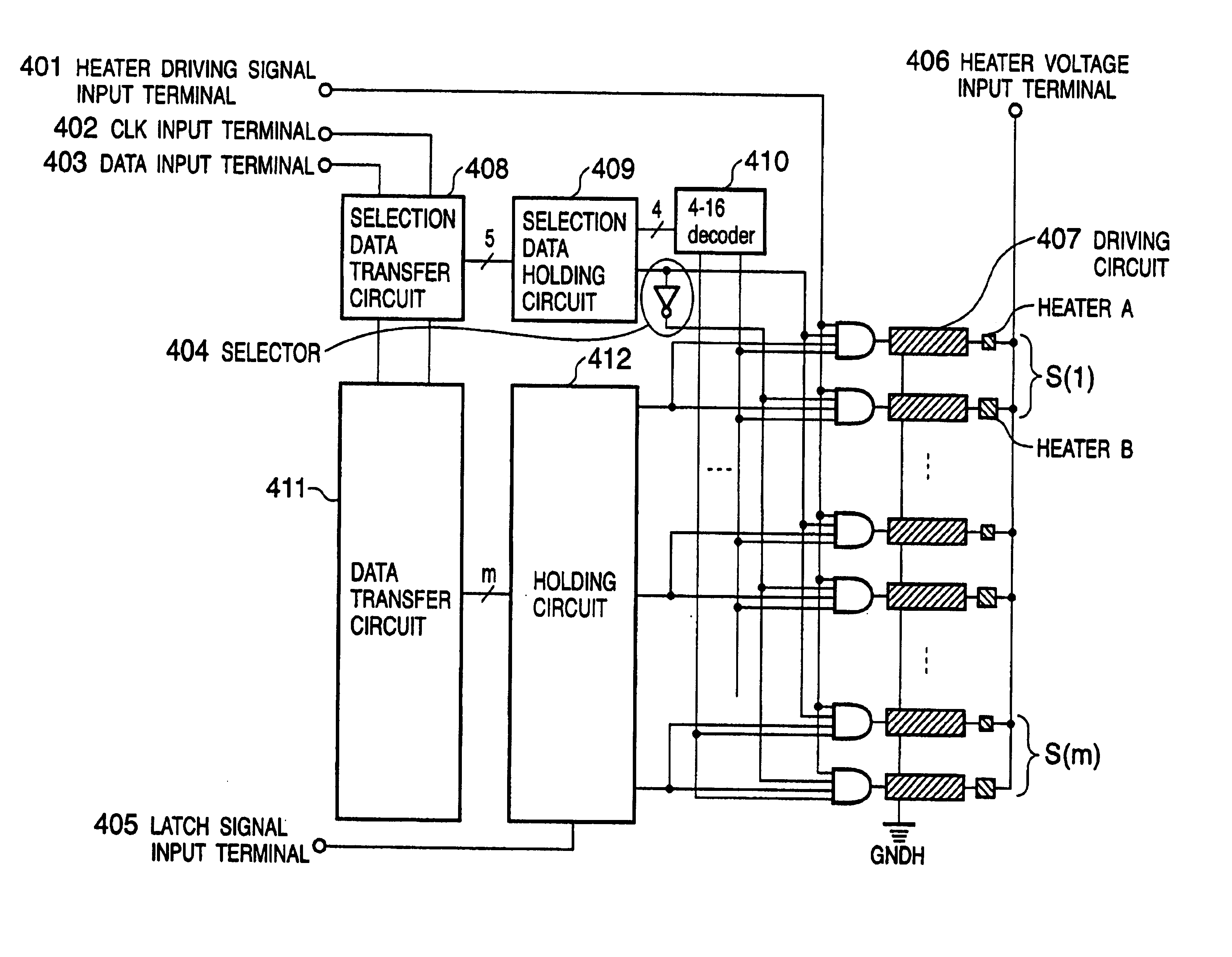
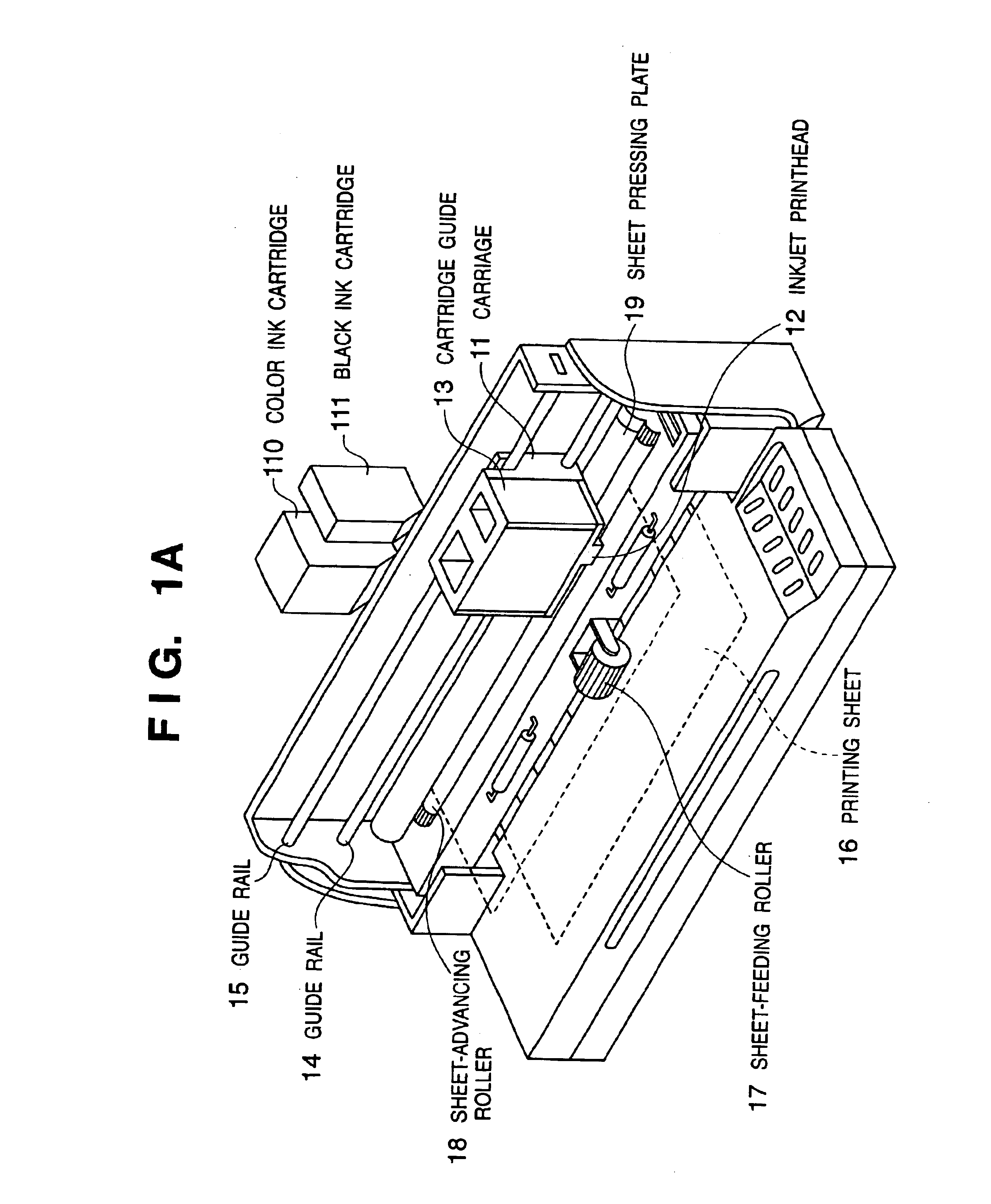
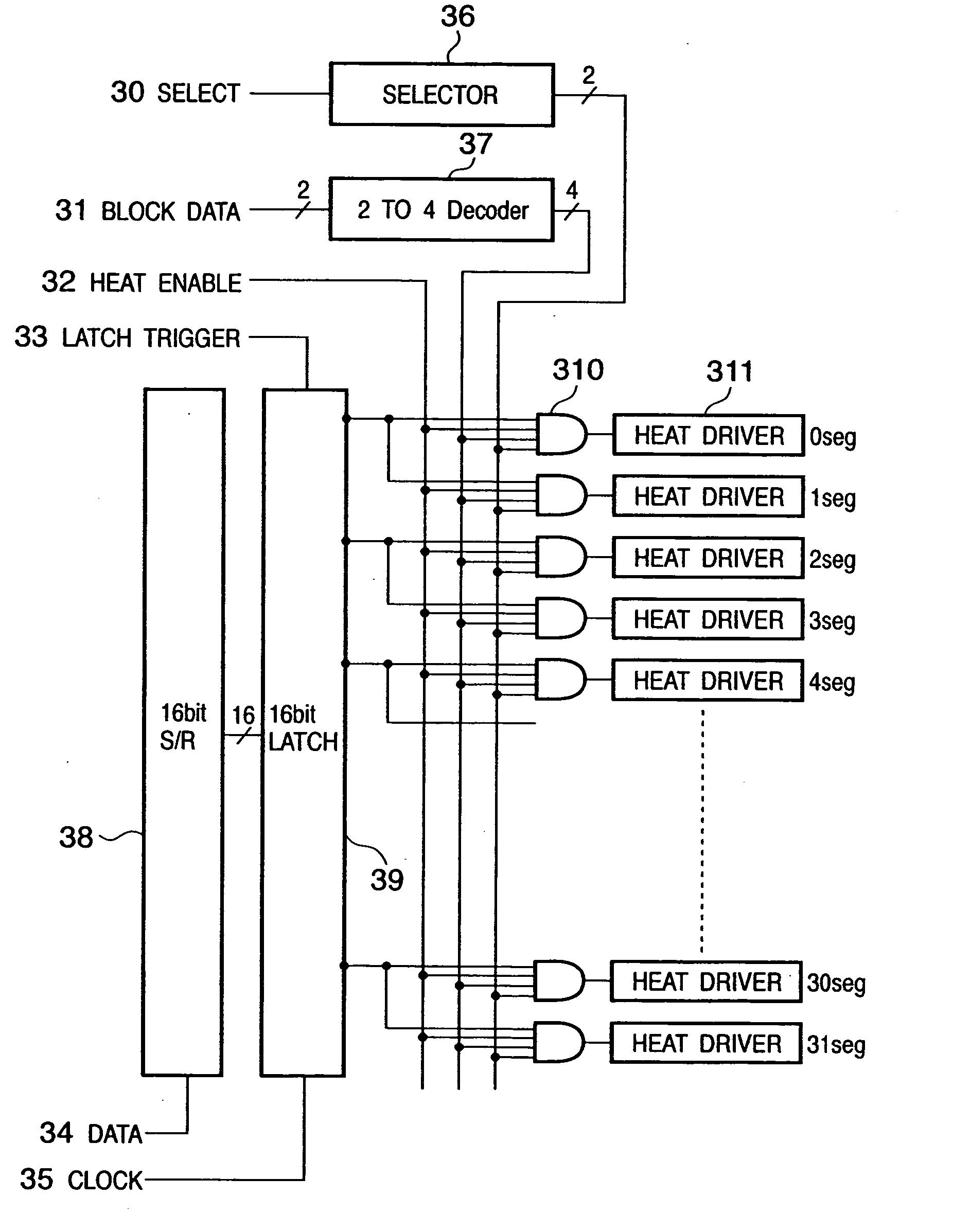
To drive an inkjet printhead having an array of printing elements, where the first and second printing elements which discharge relatively different amounts of ink are arranged on the same array in a predetermined direction, print data for the first or second printing element is serially inputted, the inputted print data is sequentially stored, the stored print data is latched, a selection signal indicative of which of the first or second printing element is to be driven is inputted, a driving signal indicative of a driving period is inputted, and respective printing elements are driven in accordance with the latched print data, the selection signal, and the driving signal. Accordingly, it is possible to reduce the cost of the printhead having plural types of printing elements, which discharge relatively different amounts of ink, and possible to easily control driving of the printhead.
Owner:CANON KK
Multi-degree-of-freedom micromanipulator driven by multi-polarization mode piezoelectric actuator
InactiveCN102497129ARealize three-dimensional translationRealize high-precision micro-movementPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCantilevered beamPiezoelectric actuators
The invention discloses a multi-degree-of-freedom micromanipulator which is driven by a multi-polarization mode piezoelectric actuator. The micromanipulator comprises a substrate, a nested x and y axis translation micromotion mechanism, a Z axis translation micromotion mechanism, a Z axis turning micromotion mechanism and an end executive mechanism, wherein three-dimensional translation is realized by using a piezoelectric pile actuator with a piezoelectric strain constant d33 driving a flexure hinge; Z axis turning is realized by using a piezoelectric turning actuator with a piezoelectric strain constant d15 driving a reverse arm; and the end executive mechanism is a micro clamp holder consisting of a piezoelectric double-chip cantilever beam based on a piezoelectric strain constant d31 or a micro injection probe. High accurate micromotions such as the three-dimensional translation, turning around with a Z axis and swing around with an X axis are realized by the drive of the piezoelectric actuator in different polarization modes, and operations such as clamping, transport, probing, injection and the like are realized by different end executive arms. The micromanipulator has the advantages of freedom decoupling, compact structure, flexible operation, convenient control, high motion precision and the like, and the micromanipulator can be applied in the fields of biomedicine, micro electro mechanical engineering and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method, apparatus and jig for manufacturing head suspension, and head suspension
ActiveUS20130055561A1Dispersion suppressionImprove productivityRecord information storageMounting of arm assembliesProduction rateVibration control
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
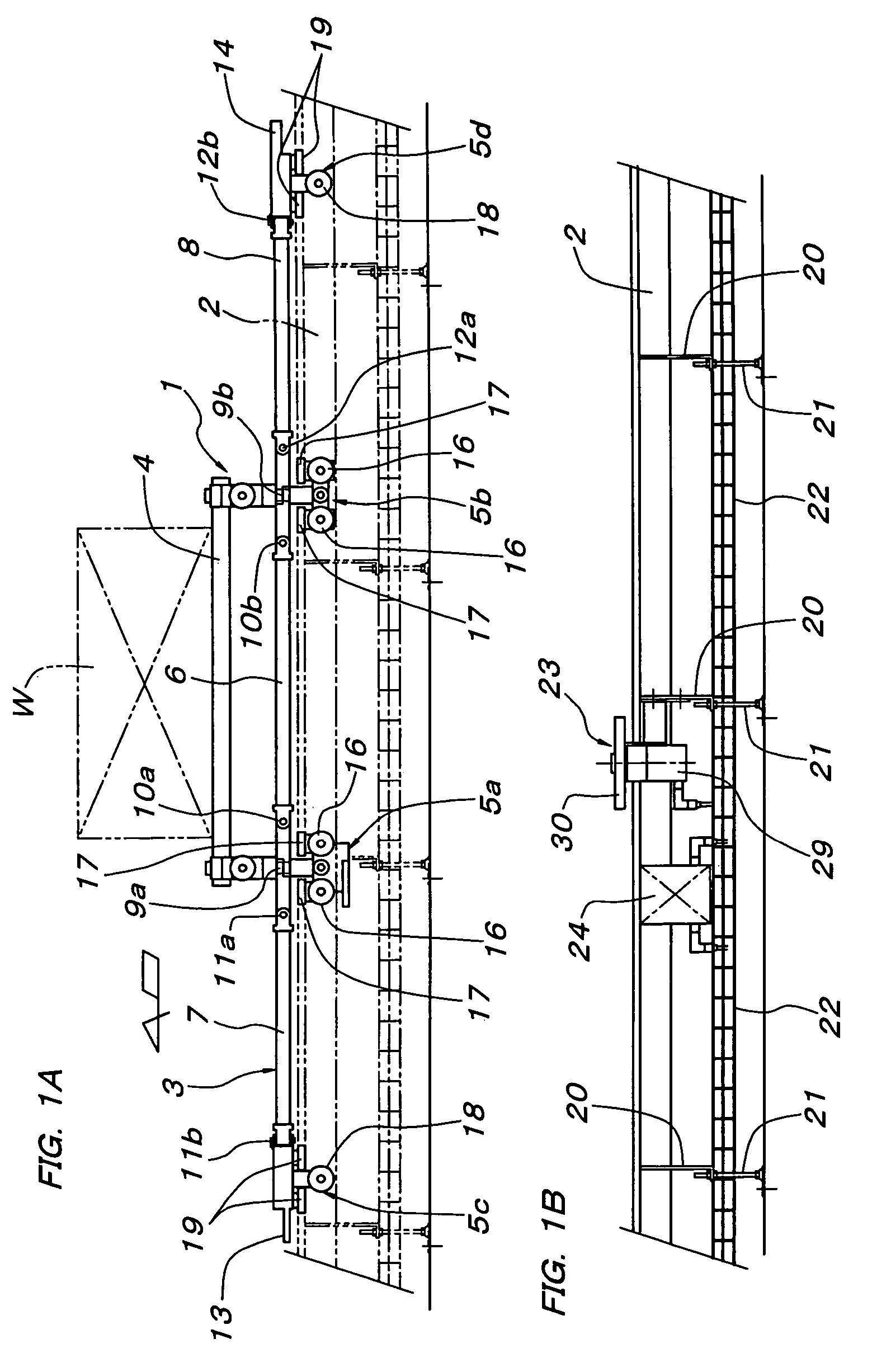
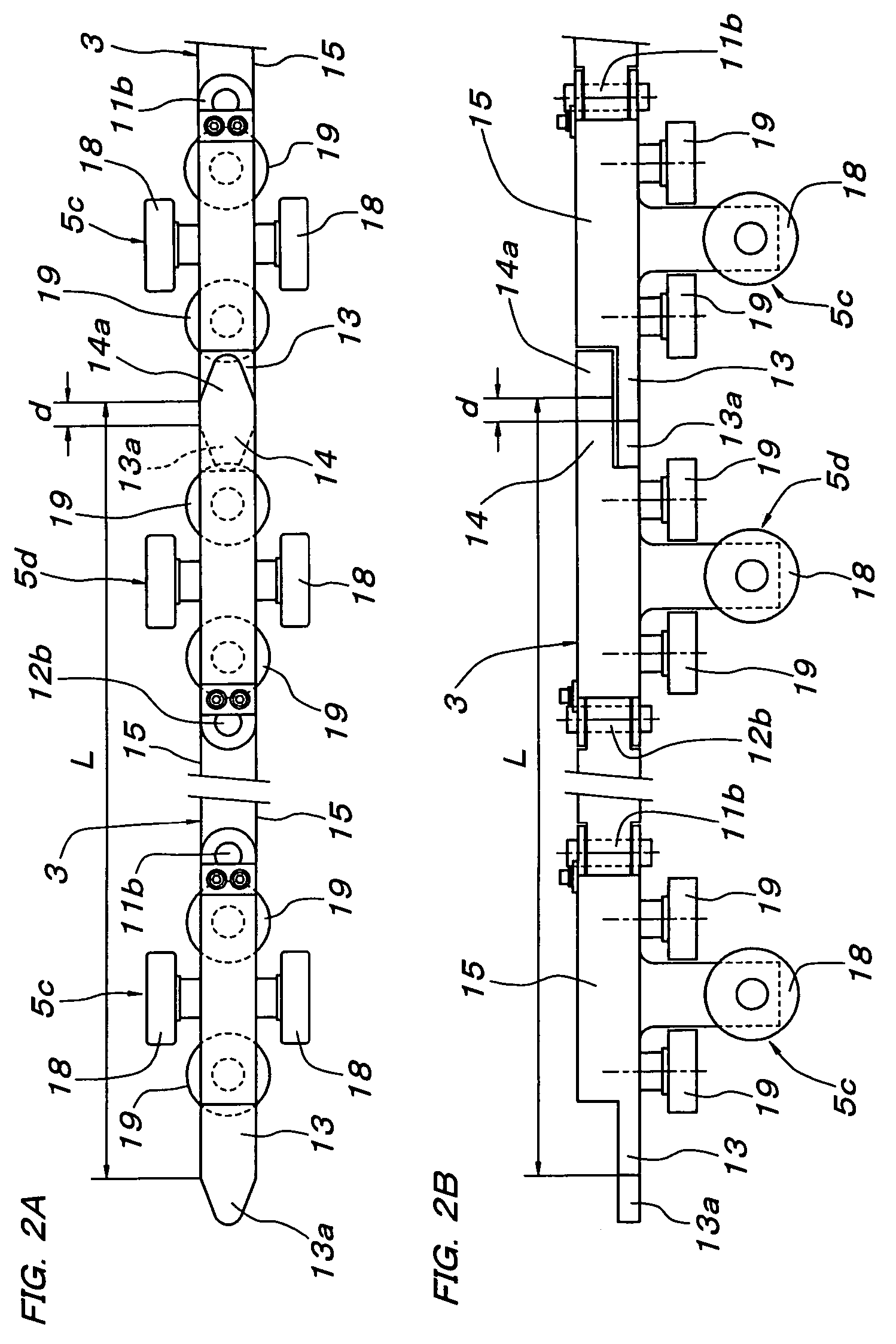
Friction drive conveyor
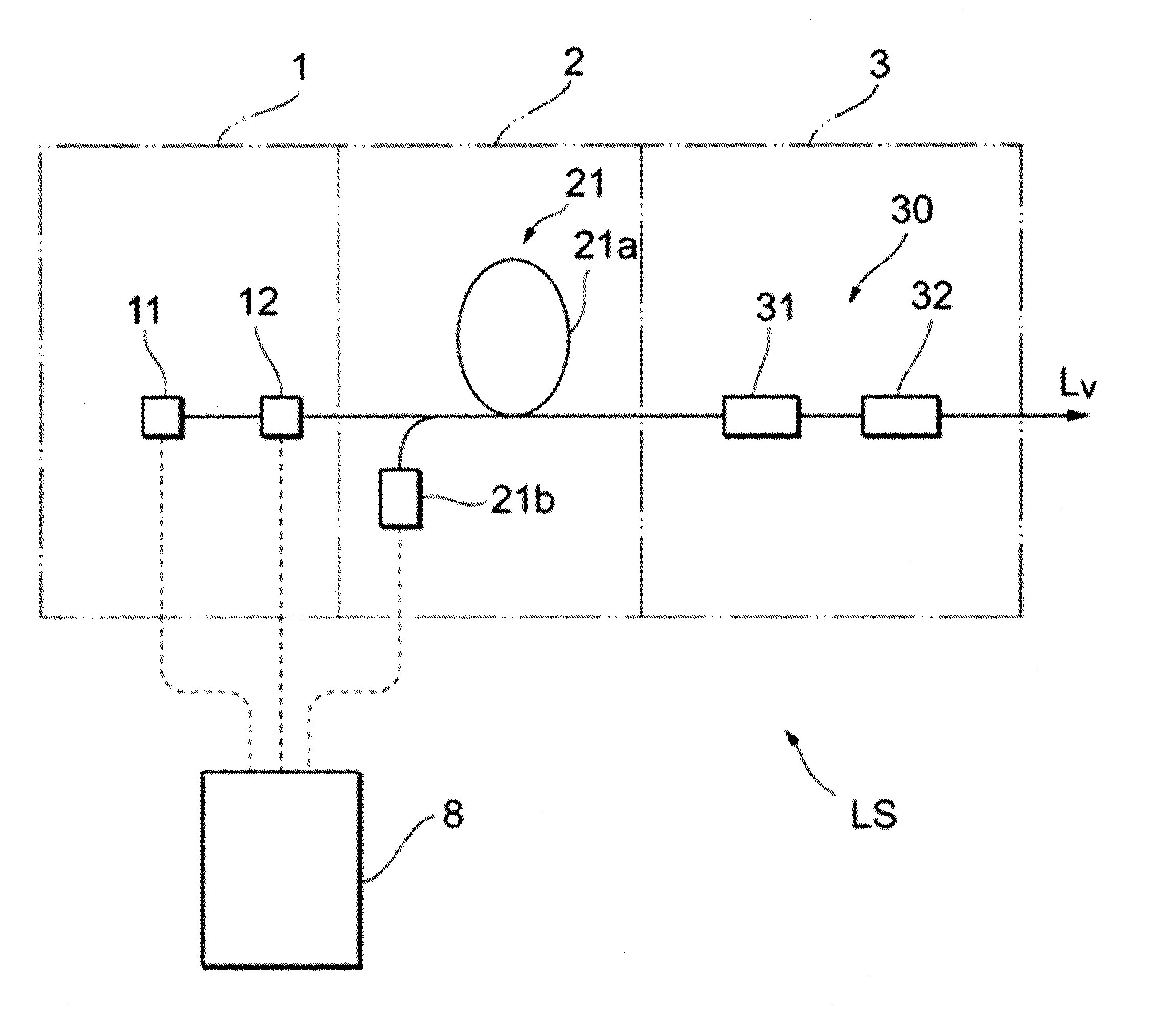
ActiveUS7127997B2Easily and efficiently carry-outSimple structureRailway componentsTramway railsEngineeringFriction drive
The present invention relates to a friction drive conveyor including carriers 1, which can be propelled along a track by frictional wheels 30 fitted along the track. Each frictional wheel 30 can be driven by a brakeless motor 29. A sensor 32 senses whether each frictional wheel 30 is in contact with any one frictional surface 15 of the carriers 1. The track includes a section along which the frictional wheels 30 are supported at regular intervals equal to or slightly shorter than the total length L of the frictional surfaces 15 on each side of each carrier 1. On the basis of a signal output from each sensor 32, a controller 24 so controls the associated brakeless motor 29 as to start rotating the associated frictional wheel 30 in contact with any one frictional surface 15 when the forward next wheel 30 gets free of the frictional surfaces 15, and as to stop driving the frictional wheel 30 having got free of the frictional surfaces 15.
Owner:DAIFUKU CO LTD
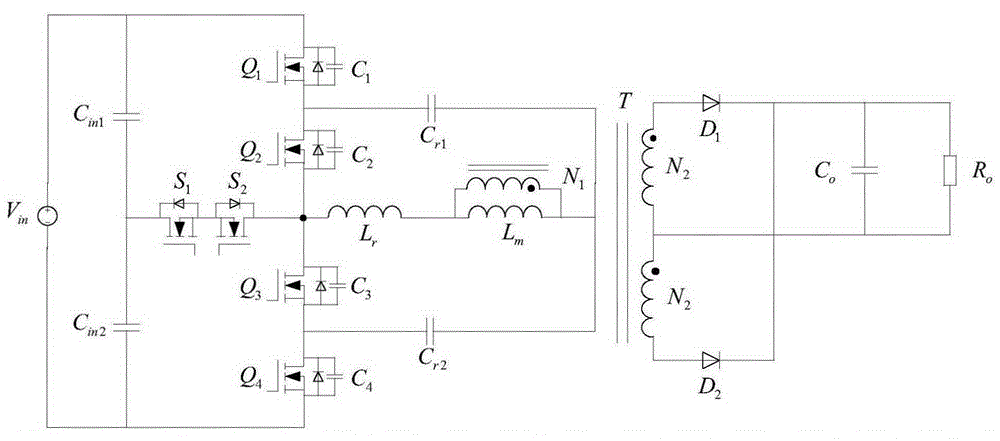
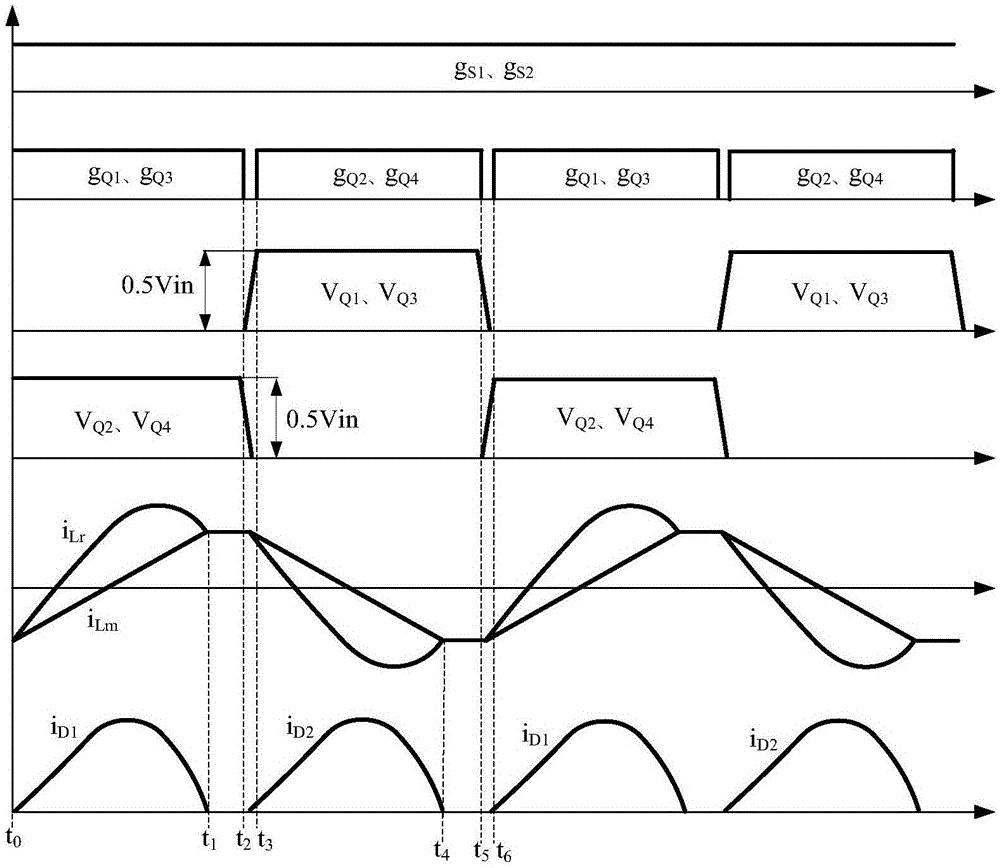
Wide input range three-level LLC resonant converter and level switching control method
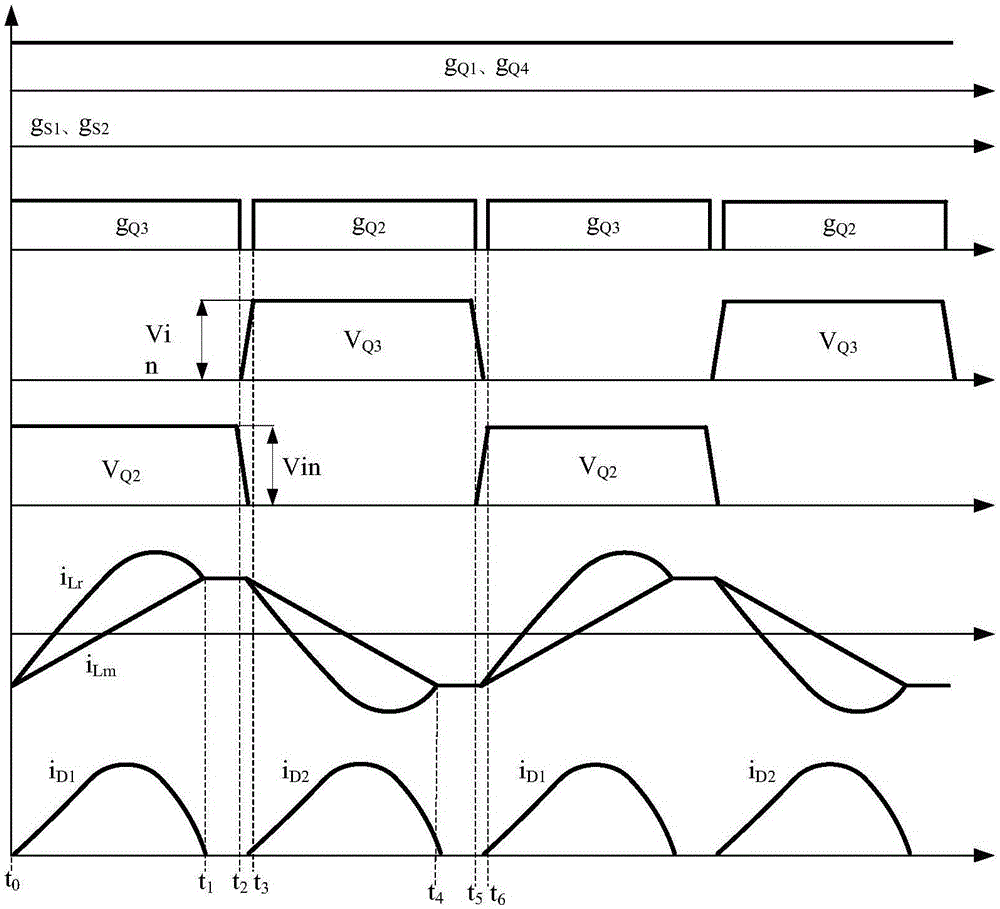
InactiveCN105119496AHigh gainSimple topologyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationThree levelFull bridge
The invention discloses a wide input range three-level LLC resonant converter and a level switching control method, and belongs to the technical field of electric power electronic transformation. The inverter is mainly formed by electrically connecting an input direct current voltage source Vin, bus dividing capacitors Cin1 and Cin2, two-way switch tubes S1 and S2, full-bridge switch tubes Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4, resonant capacitors Cr1 and Cr2, a resonant inductor Lr, a magnetic inductor Lm, a transformer T, rectifier diodes D1 and D2, an output filter capacitor Co and a load Ro. When the inverter works in a three-level mode, the switch tubes S1 and S2 are closed, the switch tubes Q1 and Q3 are simultaneously turned on / off, the switch tubes Q2 and Q4 are simultaneously turned on / off, the switch tubes Q2 and Q4 are complementary to the switch tubes Q1 and Q3, and a duty ratio is fixed as 0.5. When the inverter works in a two-level mode, the switch tubes S1 and S2 are disconnected, the switch tube Q1 and the switch tube Q4 are closed, the switch tube Q2 and the switch tube Q3 are turned on in a complementary way, and the duty ratio is fixed as 0.5. The wide input range three-level LLC resonant converter has the advantages of wide input voltage range, simple circuit topological structure, simple driving control and the like.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
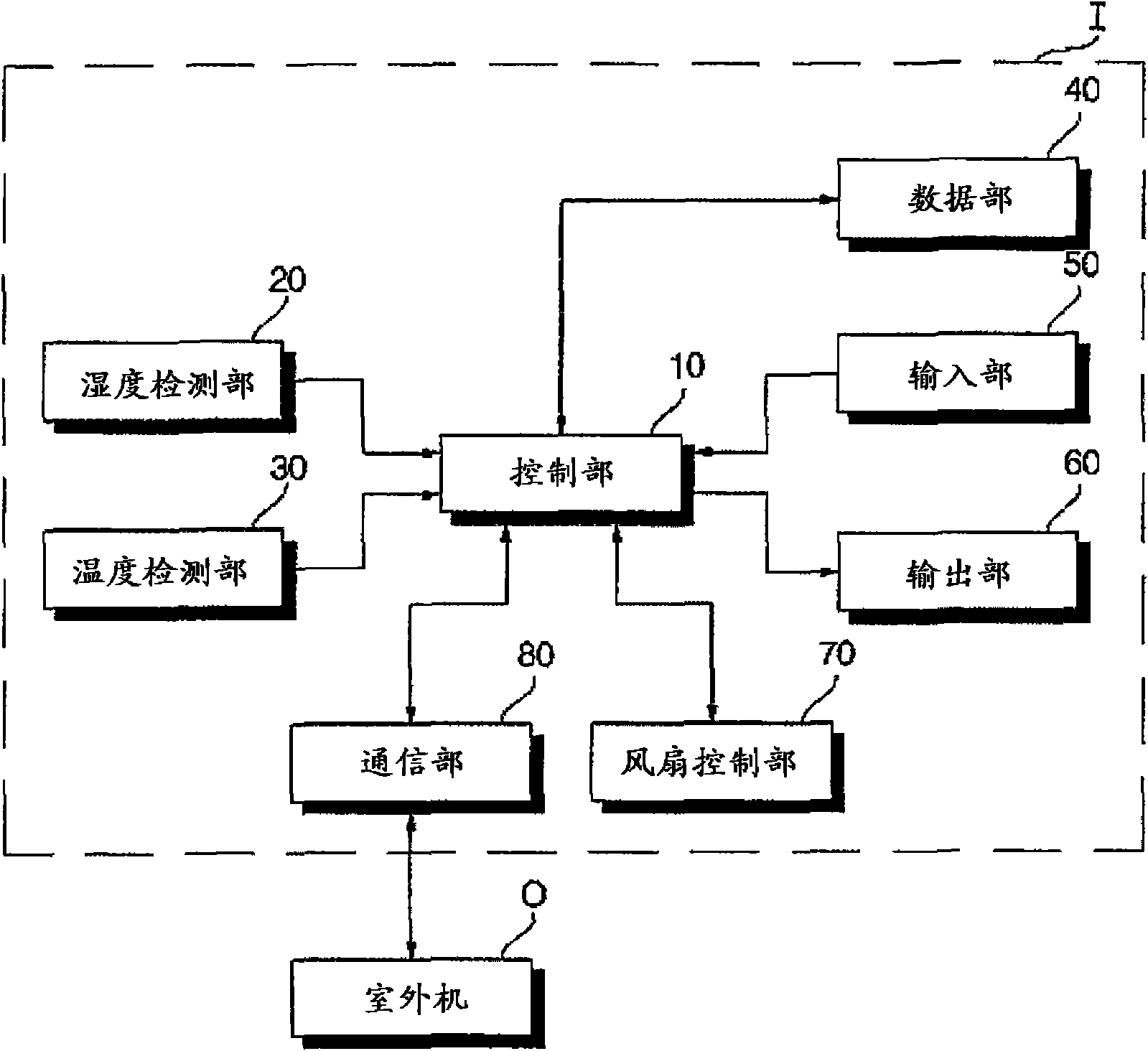
Dehumidifying operation method of air conditioner
InactiveCN101576305AEasy to adjustSimple drive controlMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsEngineeringHumidity
The invention relates to dehumidifying operation method of an air conditioner. During dehumidifying operation, a weighed value driven by a compressor is endowed according to indoor load and drive of the compressor is controlled. The compressor executes action and stops action repeatedly so as to control humidity effectively. In addition, during dehumidifying operation, a limit temperature is set and the air conditioner is operated or stopped according to indoor temperature so as to control humidity effectively to prevent over-low indoor temperature. Therefore, the invention provides comfortable environment with effect of improving degree of satisfaction.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
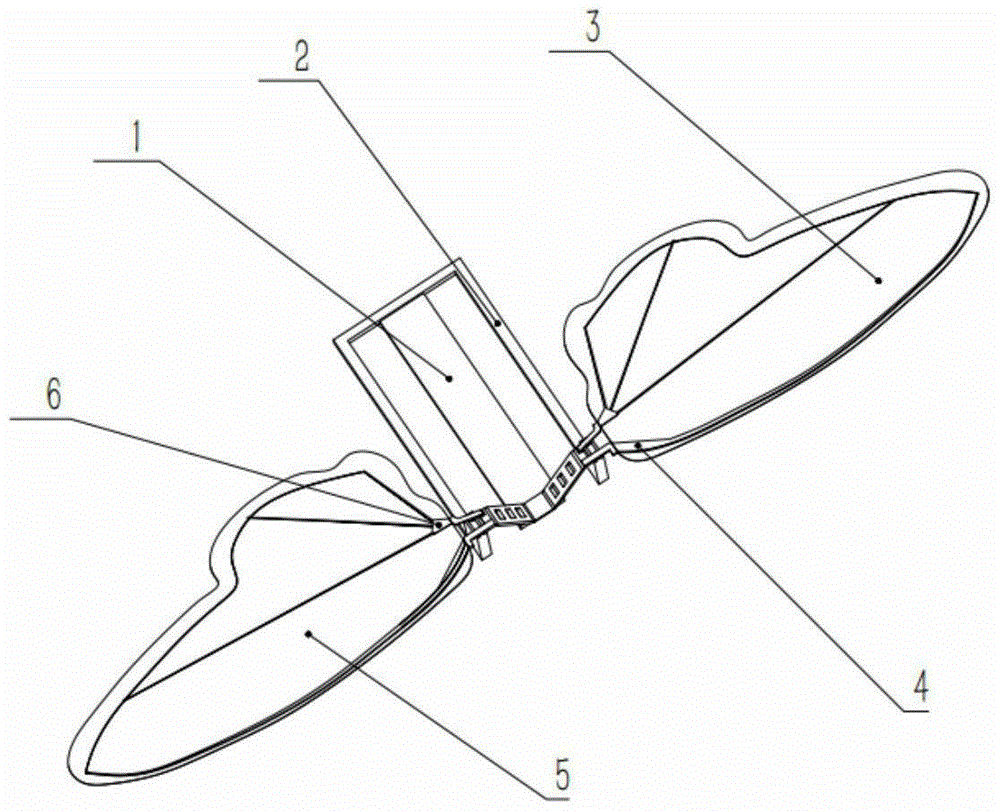
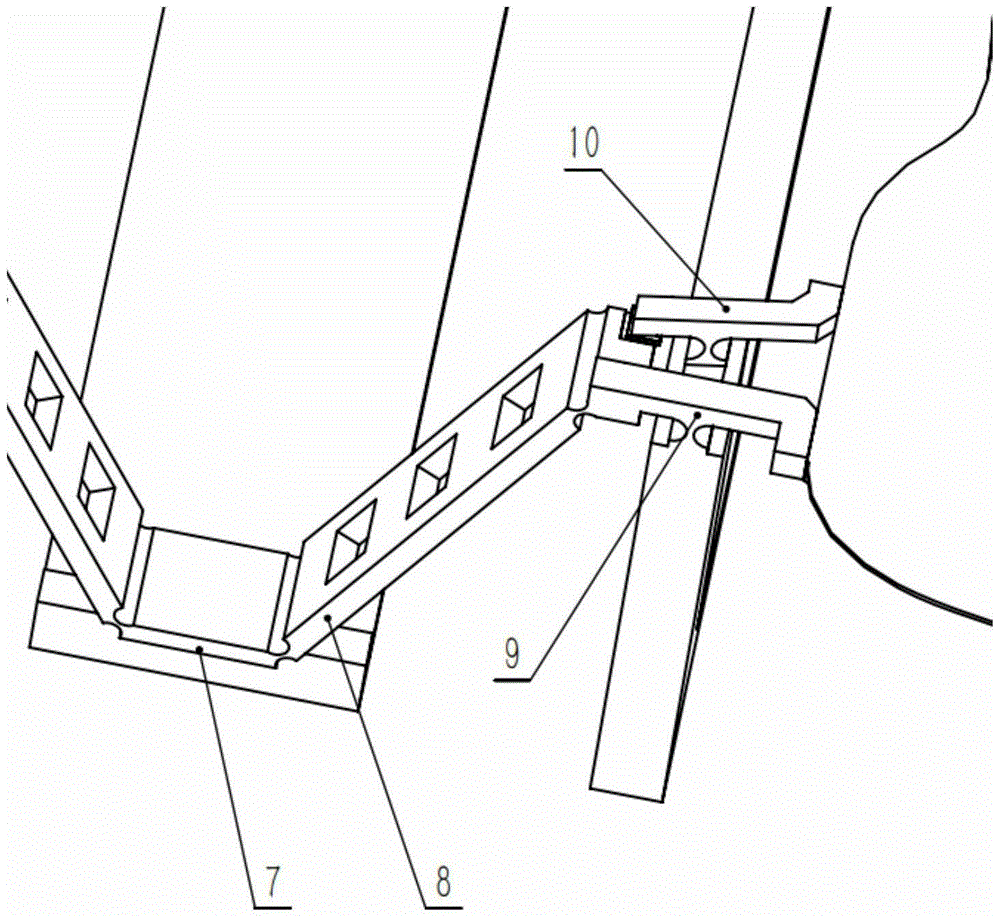
Flexible deformed wing
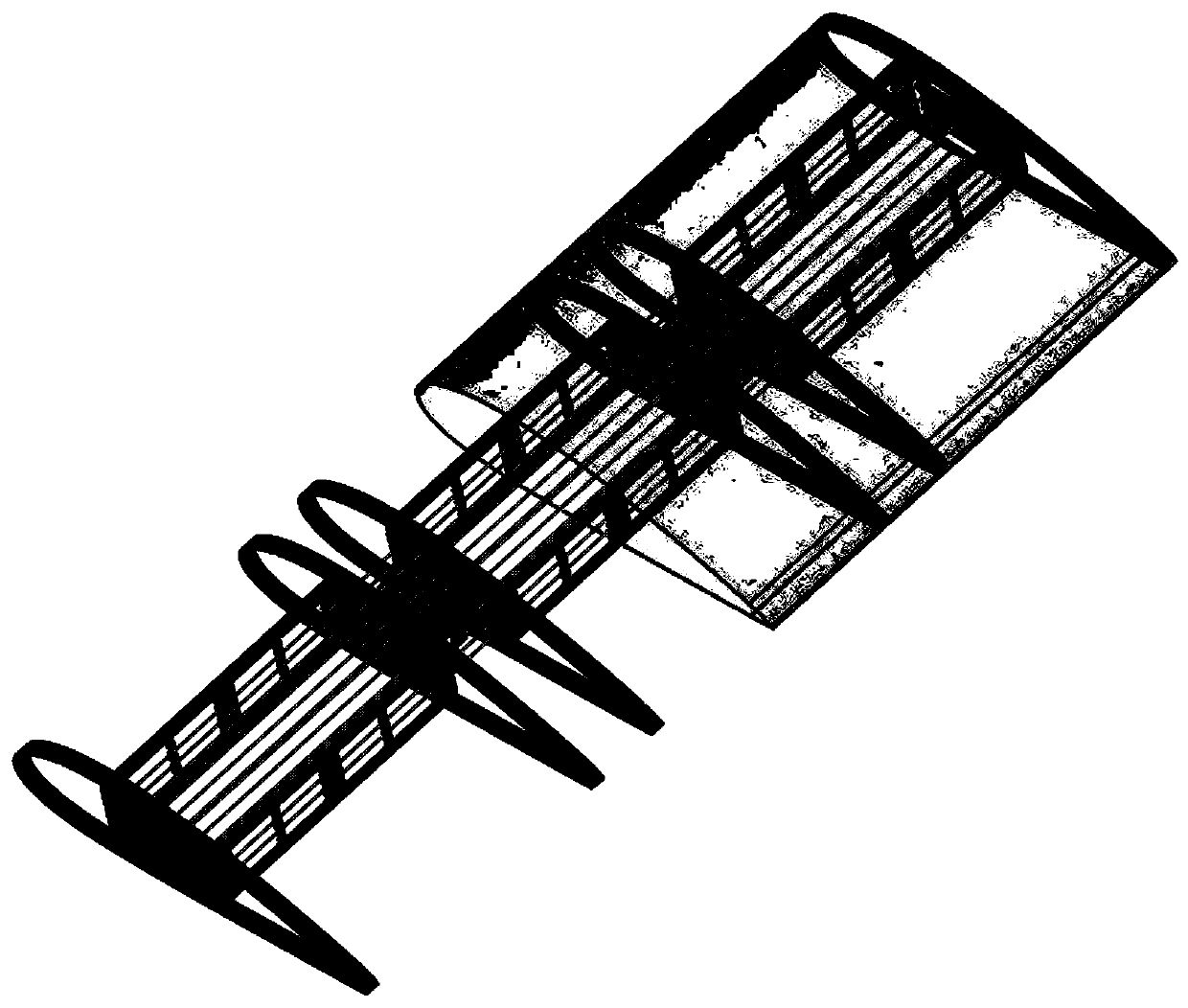
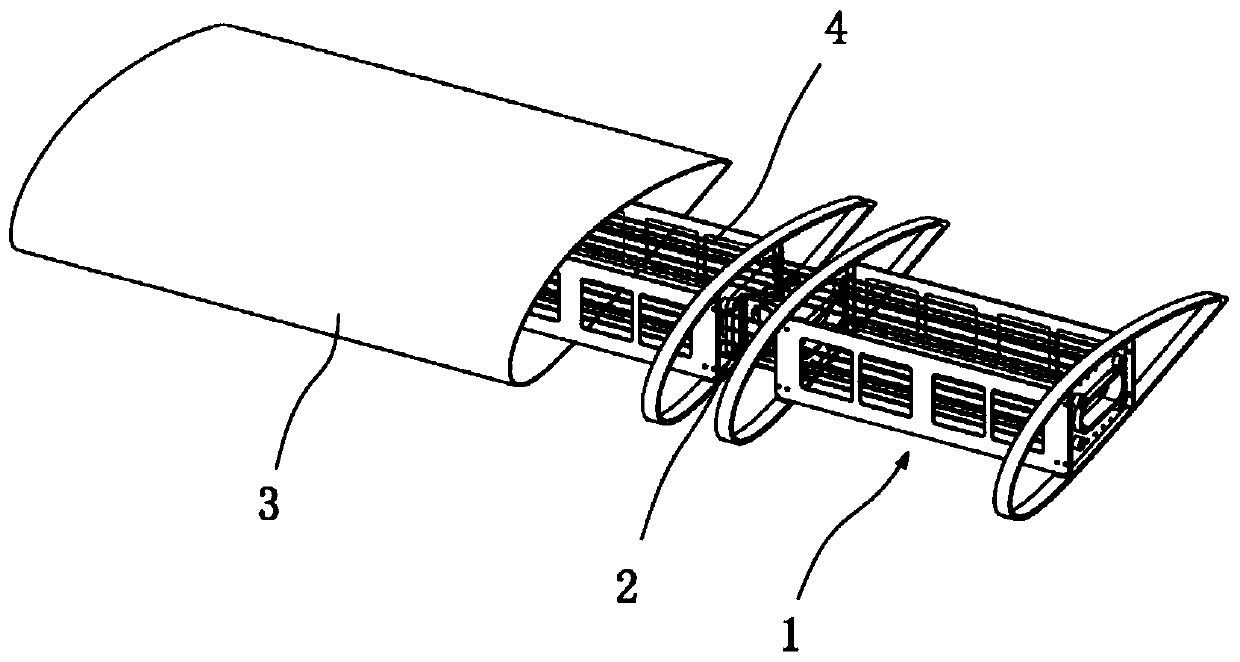
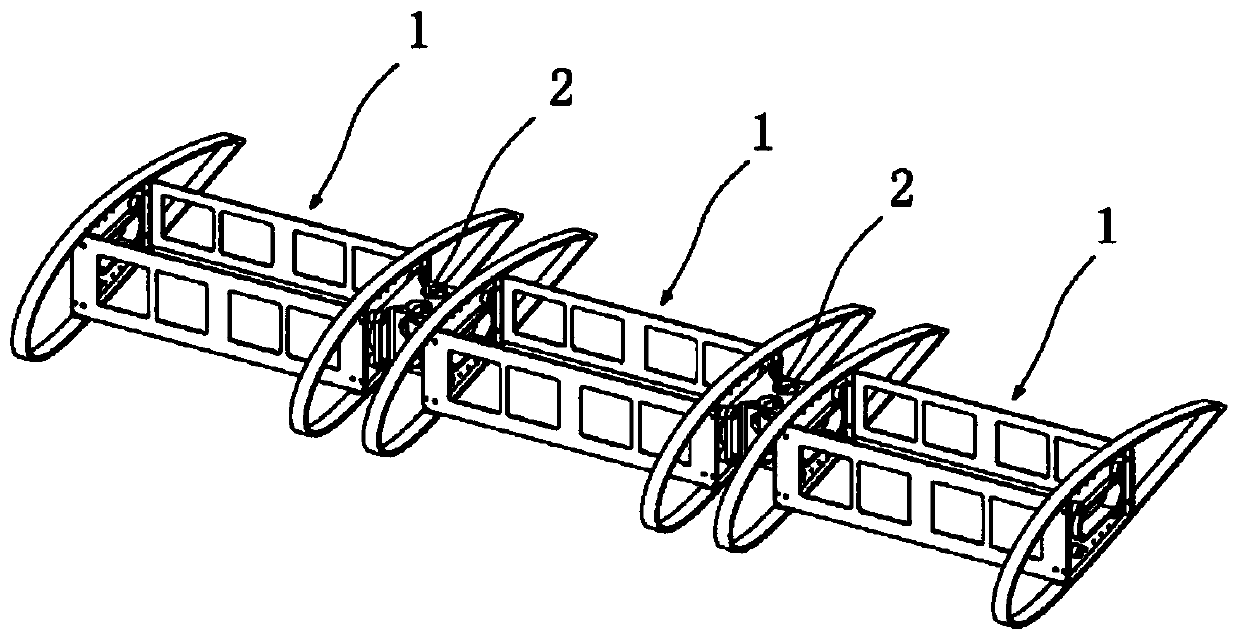
ActiveCN110053760AEasy to liftImprove mobilityWing adjustmentsUltimate tensile strengthAerospace engineering
The invention provides a flexible deformed wing. The flexible deformed wing comprises a plurality of wing box modules, flexible hinges, a skin and a drive module, wherein the wing box modules which are connected with one another form a prefabricated wing-shaped structure body, the outer edge of the prefabricated wing-shaped structure body is covered with the skin, and the drive module is used forcontrolling the spanwise bending degree and the sweep angle of the wing box modules. Each wing box module comprises two ribs and two wing spars, wherein the two ribs are oppositely arranged in the length direction of the prefabricated wing-shaped structure body, the two wing spars are oppositely arranged in the width direction of the prefabricated wing-shaped structure body, and the two wing sparsare connected with each other through the two ribs to form a wing box; and each flexible hinge has a bending rotation axis and a sweep angle rotation axis which are perpendicular to each other, and the drive module controls the wing box modules to separately change the spanwise bending degree and the sweep angle around the bending rotation axes and the sweep angle rotation axes. The spanwise bending degree and the sweep angle of the wing can be continuously and smoothly changed, and the flexible deformed wing has the advantages of high structural strength, light weight and the like.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
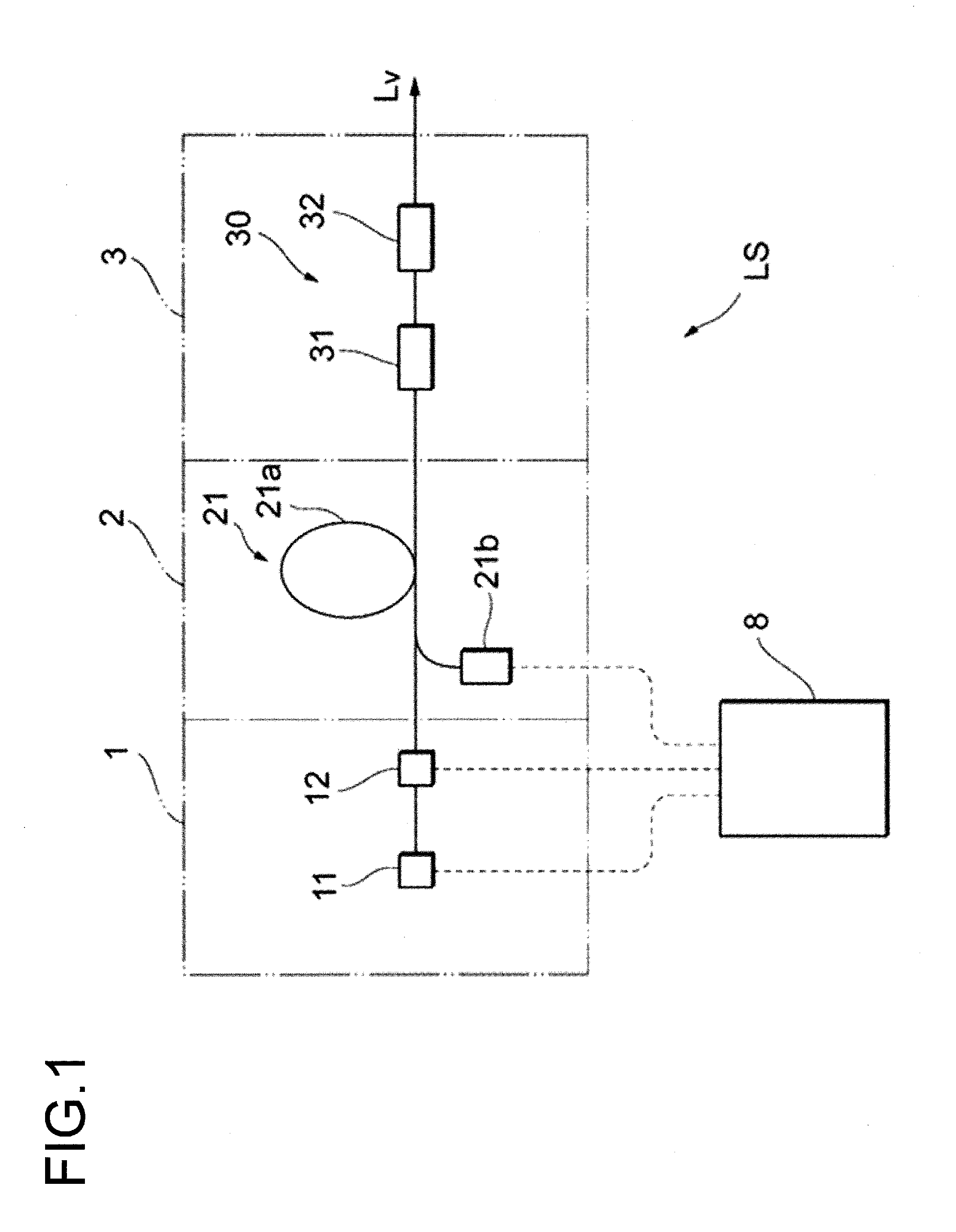
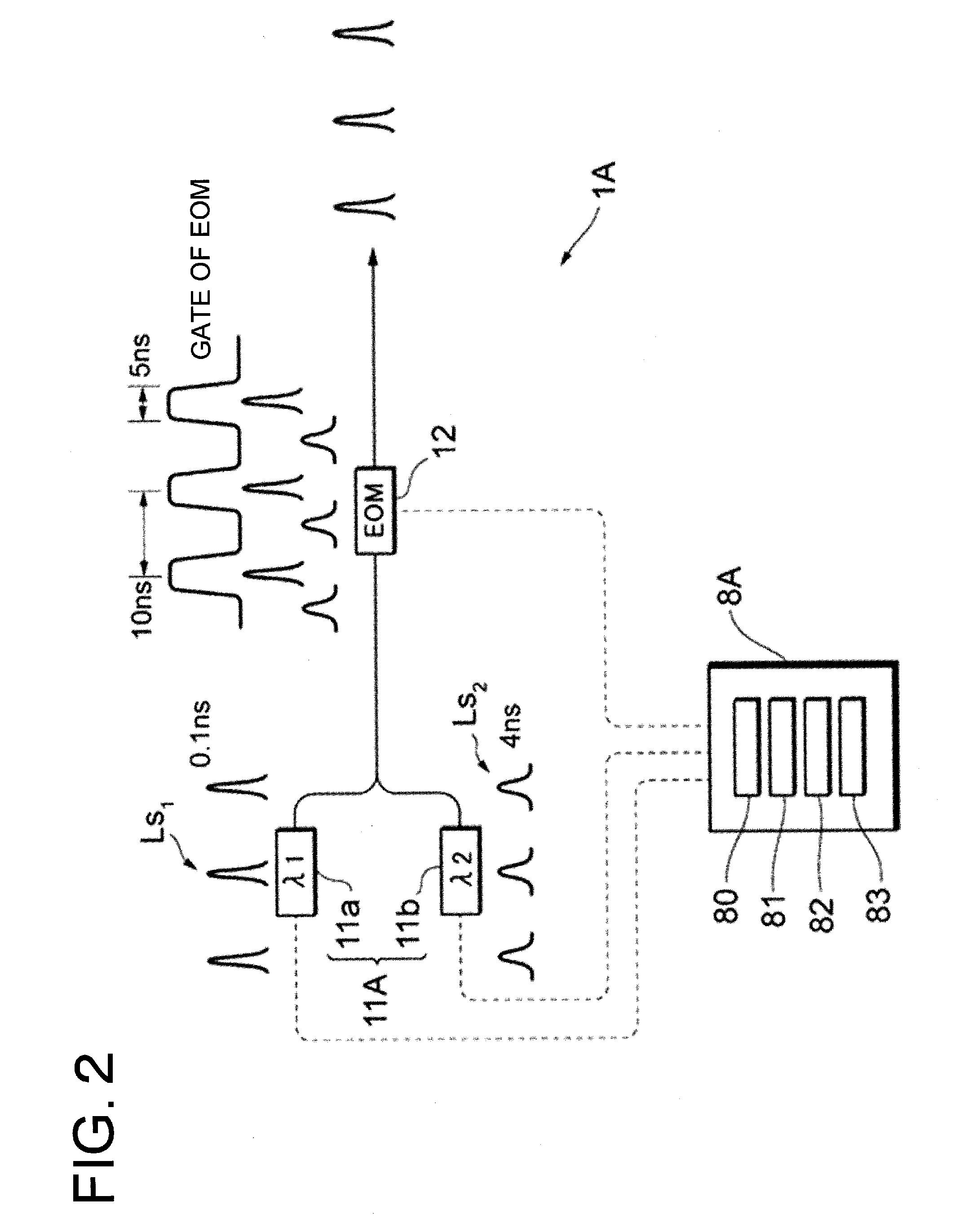
Laser device, and exposure device and inspection device provided with the laser device
ActiveUS20160240993A1Improve wavelength conversion efficiencyWavelength conversion efficiency is very lowActive medium materialPhotomechanical exposure apparatusAudio power amplifierTransmittance
A laser device includes: a laser light source which generates a laser light in a pulse waveform of preset predetermined frequency; intensity modulator which is driven with a transmittance waveform wherein transmittance changes at either the predetermined frequency or an integer-multiple frequency thereof and which extracts and outputs the laser light which is outputted from the laser light source; control unit which controls an operation of the intensity modulator; an amplifier which amplifies the laser light which is outputted from the intensity modulator; and a wavelength conversion optical element which converts a wavelength of the laser light which is amplified by the amplifier, wherein the control unit changes relative timing of the transmittance waveform with respect to the pulse waveform, thereby changing the pulse waveform of the laser light which is emitted from the intensity modulator, to output a pulse light of predetermined waveform from the wavelength conversion optical element.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Flapping-wing micro air vehicle based on fan driving
The invention discloses a flapping-wing micro air vehicle based on fan driving. The flapping-wing micro air vehicle is characterized in that a fan driver is combined with hinged connecting rod mechanisms, is arranged in the hinged connecting rod mechanisms and is fixedly connected with the inner-side end surfaces of the hinged connecting rod mechanisms; the hinged connecting rod mechanisms at two sides are symmetrically arranged; a driving connecting rod is fixed on the free end of the fan driver, and a pushing rod is connected with the driving connecting rod; one end of a control rod is connected with the pushing rod, the other end of the control rod is fixedly connected with the front edges of wings, and the control rod is connected with the hinged connecting rod mechanisms at the side surfaces of the fan driver; a torsion control rod is connected with the hinged connecting rod mechanisms at the side surfaces of the fan driver; one end of the torsion control rod is in contact with a wear-resistant cushion block stuck at the end part of the pushing rod, and the other end of the torsion control rod is connected with the rear edges of the wings; and the up-down vibration of the fan driving mechanism is transferred and amplified under a loading alternating voltage, and the wings are driven by the action of flexible hinges to realize up-down flapping and torsion. The flapping-wing micro air vehicle disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the structure is simple, the processing is convenient and the driving control is simple.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Disc type transverse flux permanent magnet brushless motor and method
ActiveCN110620449AIncreased torque densityShorten the axial lengthMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsTransverse fluxBrushless motors
The invention provides a disc type transverse flux permanent magnet brushless motor and a method. The motor comprises two stator discs and a rotor disc, wherein the two stator discs are symmetricallydistributed on two sides of the rotor disc, the rotor disc is connected with a rotating shaft, two groups of permanent magnets distributed along the circumference are distributed on the rotor disc andare respectively called as an inner permanent magnet group and an outer permanent magnet group along the radial direction, each group comprises a plurality of permanent magnets with N poles and S poles arranged in a staggered manner along the circumferential direction, polarities of the upper and lower permanent magnets in the radial direction are opposite, each stator disc is composed of a plurality of stator iron cores which are uniformly distributed along the circumferential direction, each stator iron core comprises a C-shaped iron core pole body, a fan-shaped iron core pole shoe and an armature winding which is wound on a C-shaped iron core arm. The motor is advantaged in that industrial robot servo PMSM types are expanded, motor torque density is improved, the axial length of the motor is reduced, the motor can be flexibly applied to more occasions, the weight of a motor rotor part is greatly reduced, the rotational inertia of the motor is reduced, and a torque inertia ratio ofthe motor is improved.
Owner:山东艾克索仑电气有限公司
Electric vehicle driving and charging integrated circuit and torque elimination control method thereof
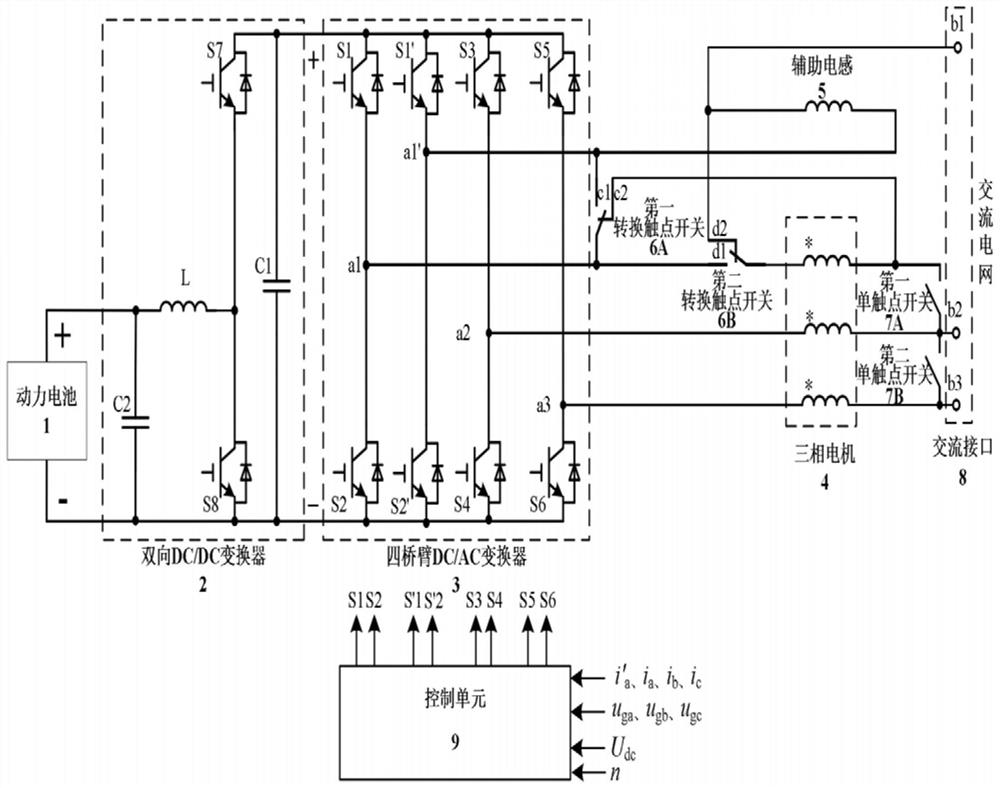
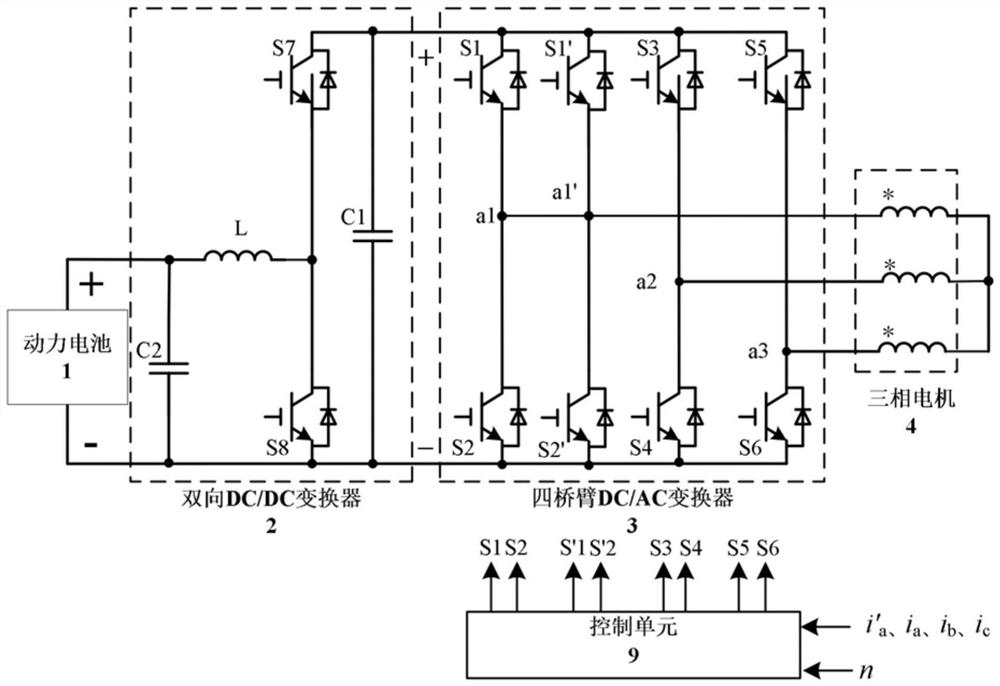
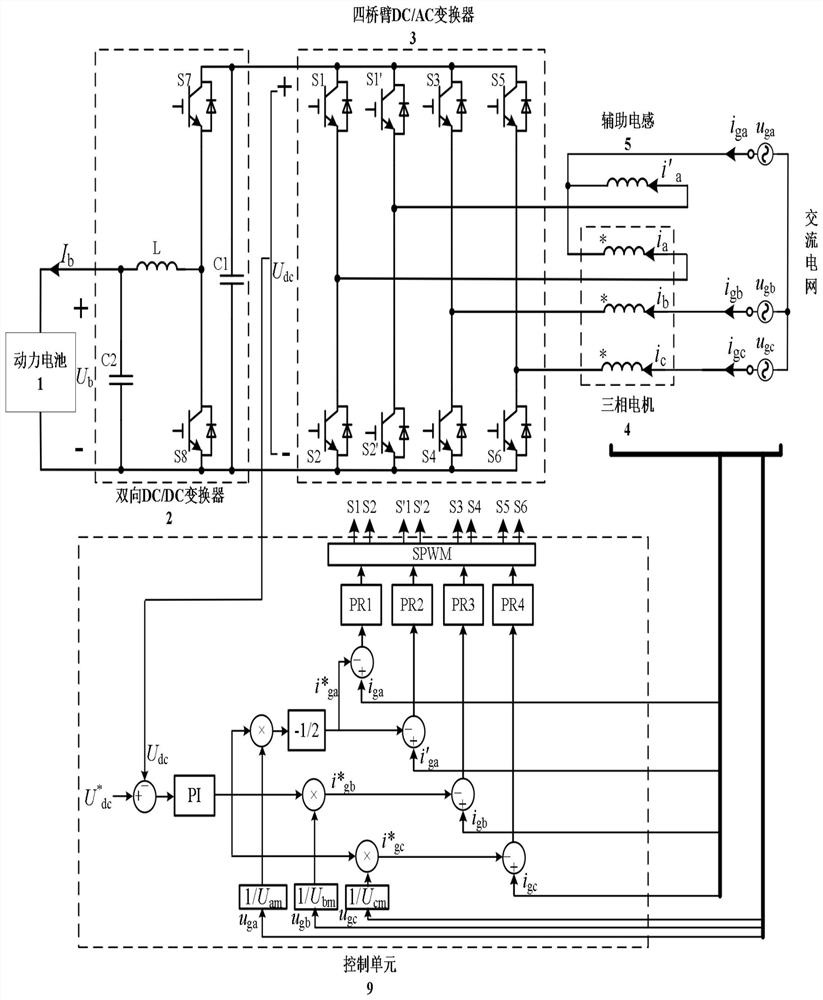
ActiveCN112787390ASimple controlImprove power densityElectronic commutation motor controlBatteries circuit arrangementsAutomotive engineeringThree-phase electric power
The invention discloses an electric vehicle driving and charging integrated circuit and a torque elimination control method thereof. The electric vehicle driving and charging integrated circuit comprises a power battery, a bidirectional DC / DC converter, a four-bridge arm DC / AC converter, a three-phase motor, an auxiliary inductor, a first conversion contact switch, a second conversion contact switch, a first single-contact switch, a second single-contact switch, an alternating current interface and a control unit. The circuit only adds one auxiliary inductor to realize three-phase input charging, and has the advantages of simple motor driving control, no need of redesign of the motor and high power density. The invention further provides a torque elimination control method of the circuit. Motor torque elimination during charging is achieved through bridge arm parallel control, the inductance value of an auxiliary inductor does not need to be designed to be consistent with the equivalent inductance of a motor stator winding, and the method has the advantage of being high in robustness.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Stator permanent magnet mixed stepping motor
InactiveCN103812241ASimple structureReduce manufacturing costMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic polesTorque density
The invention discloses a stator permanent magnet mixed stepping motor which comprises a stator portion and a rotor portion. The rotor portion comprises a rotor overlying core and a rotary shaft in the core. Same small teeth are evenly distributed on the outer periphery of the rotor overlaying core. The stator portion comprises a stator core, a stator winding and permanent magnets. Magnetic poles are distributed on the inner periphery of the stator core. Stator small teeth with tooth gaps same as those of the rotor small teeth are distributed on pole shoes of the magnetic poles, a coil is arranged on each magnetic pole body, the coils are connected in series or in parallel to form a multi-phase winding of a stator according to a certain rule, grooves are formed along the periphery evenly at the symmetrical positions of a stator core yoke portion, the permanent magnets are arranged in the grooves and distributed evenly, magnetizing is conducted in the tangential direction, and the magnetizing directions of two adjacent permanent magnets are opposite. The motor has the advantages of being simple in structure and process, low in cost and high in efficiency, power density and torque density. Meanwhile, a motor magnetic field is a two-dimensional field, and analyzing and designing are easy.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
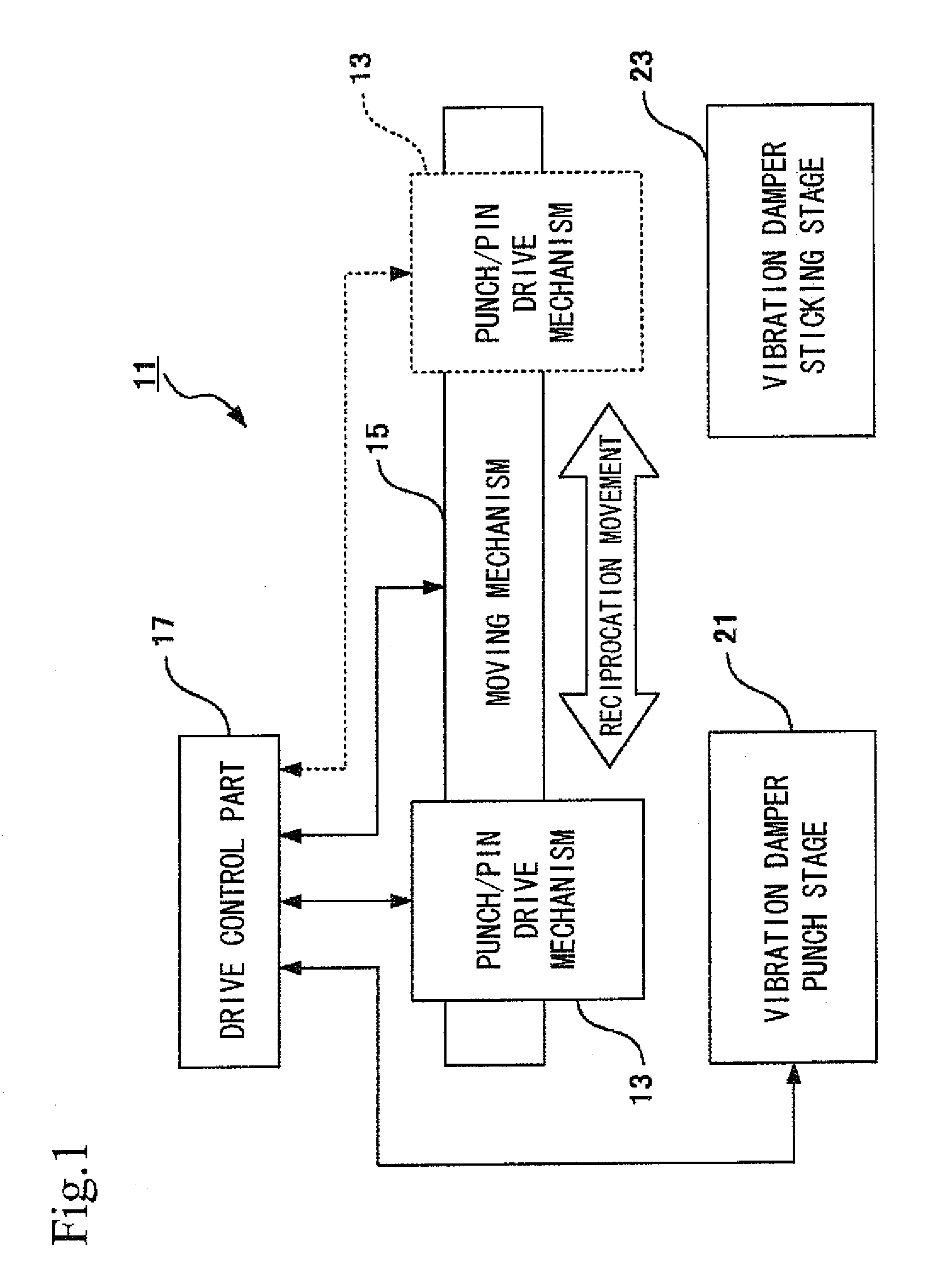
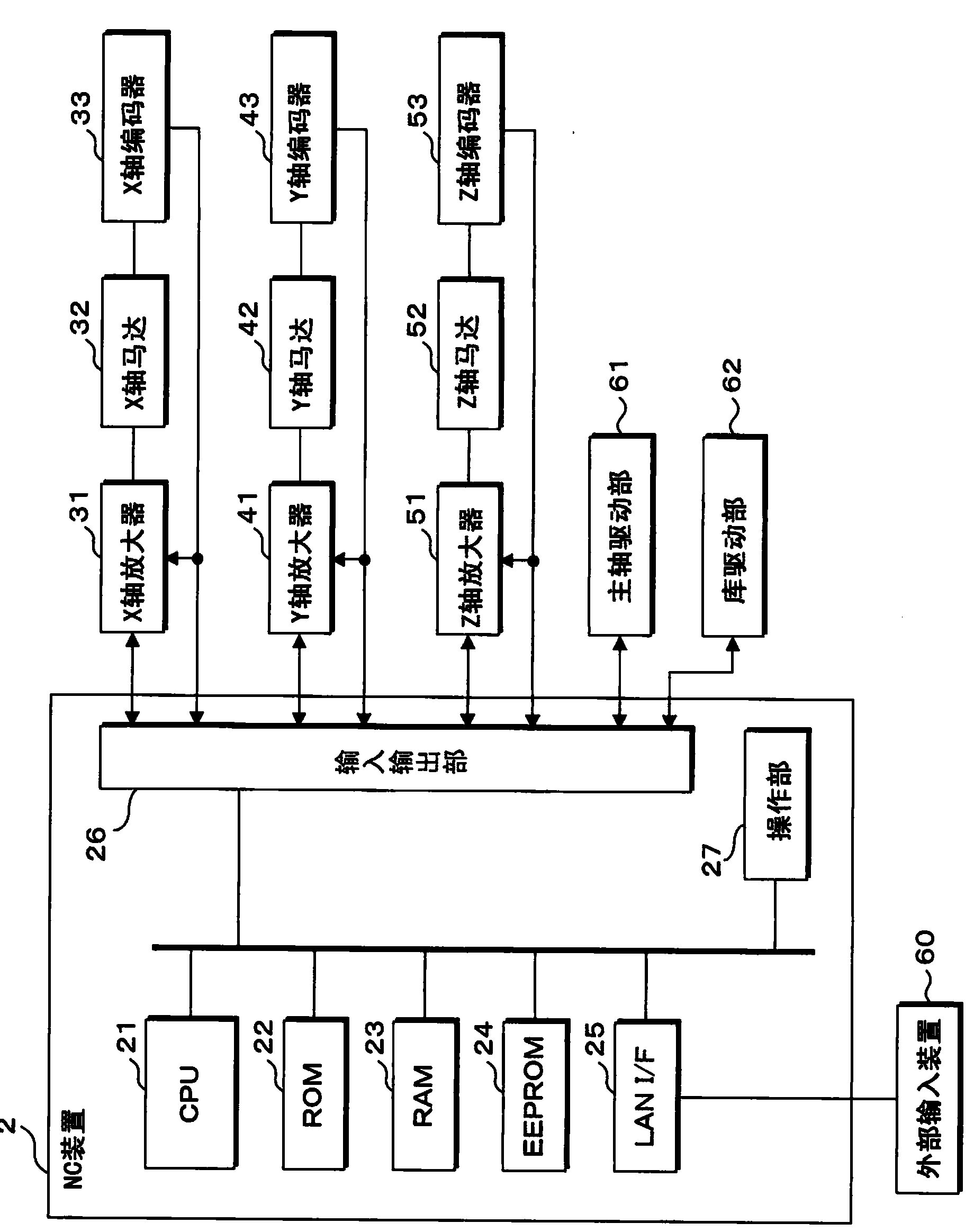
Numerical control device and driving control method
ActiveCN104070411AReduce vibrationSimple drive controlAutomatic control devicesFeeding apparatusEngineeringTime constant
The invention provides a numerical control device and a driving control method. The numerical control device performs controlling in an X-axis direction and a Y-axis direction which are crossed and utilizes motors respectively arranged on each axis for driving a worktable that supports a workpiece. A first wave filter sets a derivative of a frequency of a vibration generated in the X-axis direction to a time constant (T1). A second wave filter sets the derivative of a frequency of a vibration generated in the Y-axis direction to a time constant (T2). The numerical control device smoothes the speed instruction signal of a motor through the first wave filter and the second wave filter, thereby suppressing vibration of the worktable in the X-axis direction and the Y-axis direction.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
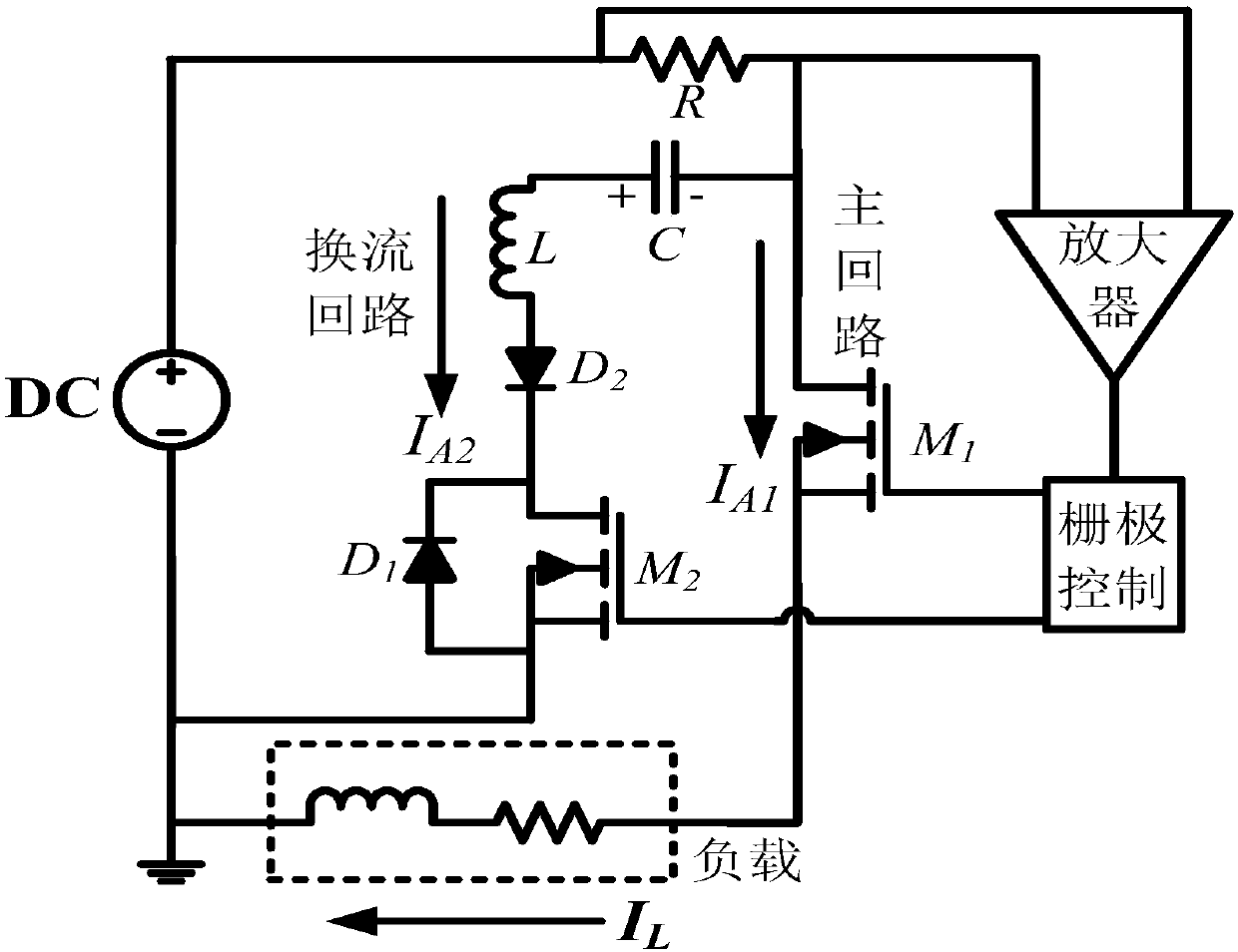
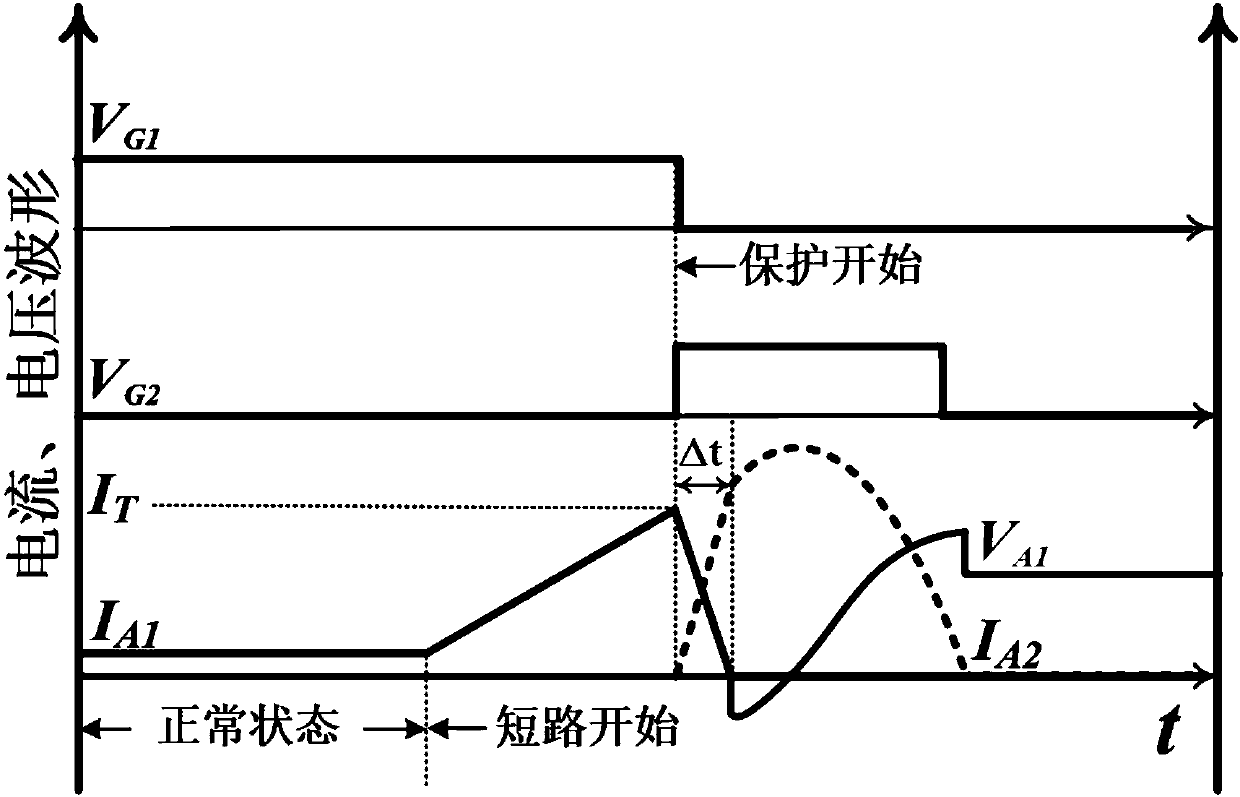
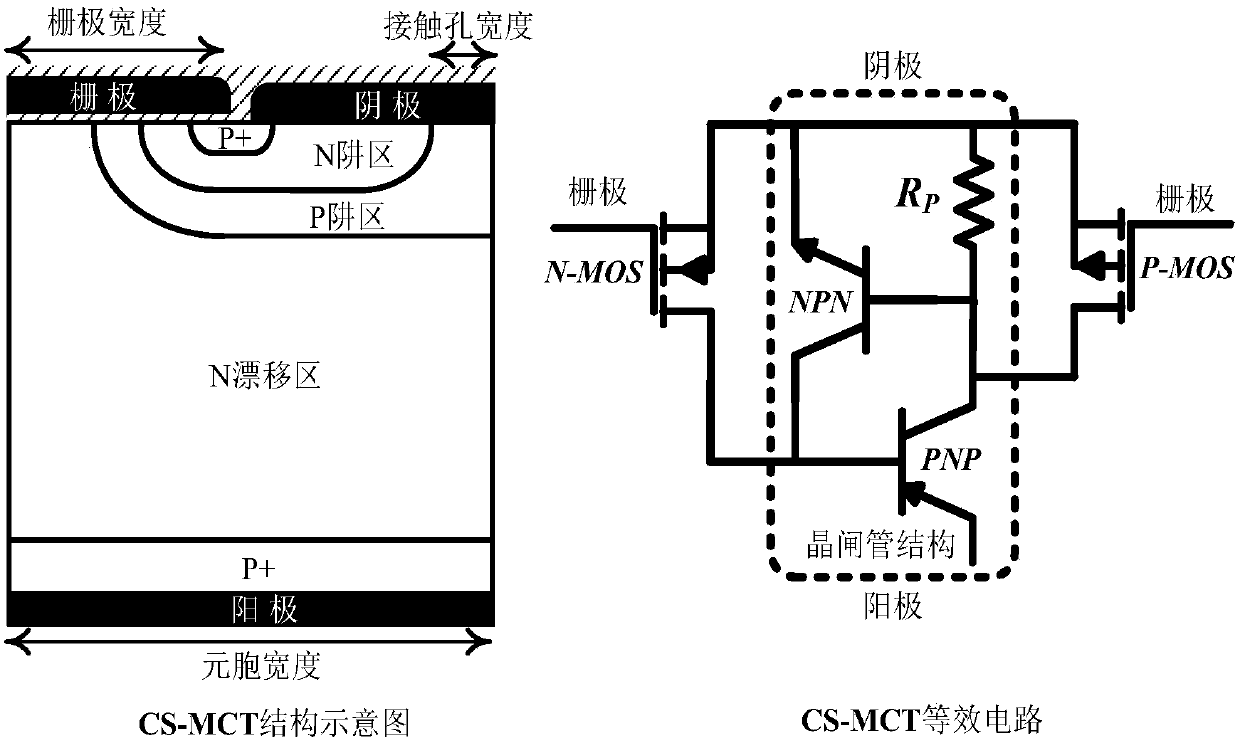
Cathode short MOS-controlled thyristor-based DC solid state circuit breaker
ActiveCN107592101AReduce conduction voltage dropLower on-resistanceElectronic switchingControl signalEngineering
The present invention belongs to the electronic technology field, in particular relates to a cathode short MOS-controlled thyristor-based DC solid state circuit breaker. The cathode short MOS-controlled thyristor-based DC solid state circuit breaker of the present invention mainly comprises a main loop composed of a DC power supply, a cathode short MOS-controlled thyristor (CS-MCT) (M1) and a load, a current commutation loop composed of the DC power supply, a capacitor C, an inductor L, a CS-MCT(M2) and diodes (D1 and D2), a current detection unit composed of a current sampling resistor R andan amplifier and a grid control unit, and is characterized by adopting the CS-MCT having the low conduction resistance and high di / dt capability as a switching tube, combining the current detection unit and the grid control unit to realize the short circuit current sampling and the control signal feedback, and utilizing the shunting action of the current commutation loop to interrupt a short circuit current rapidly. Compared with a conventional solid state circuit breaker, the CS-MCT-based DC solid state circuit breaker of the present invention has the advantages of being low in power consumption and fast in response speed.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Two-freedom-degree hybrid stepping motor for bionic eyeballs of robot
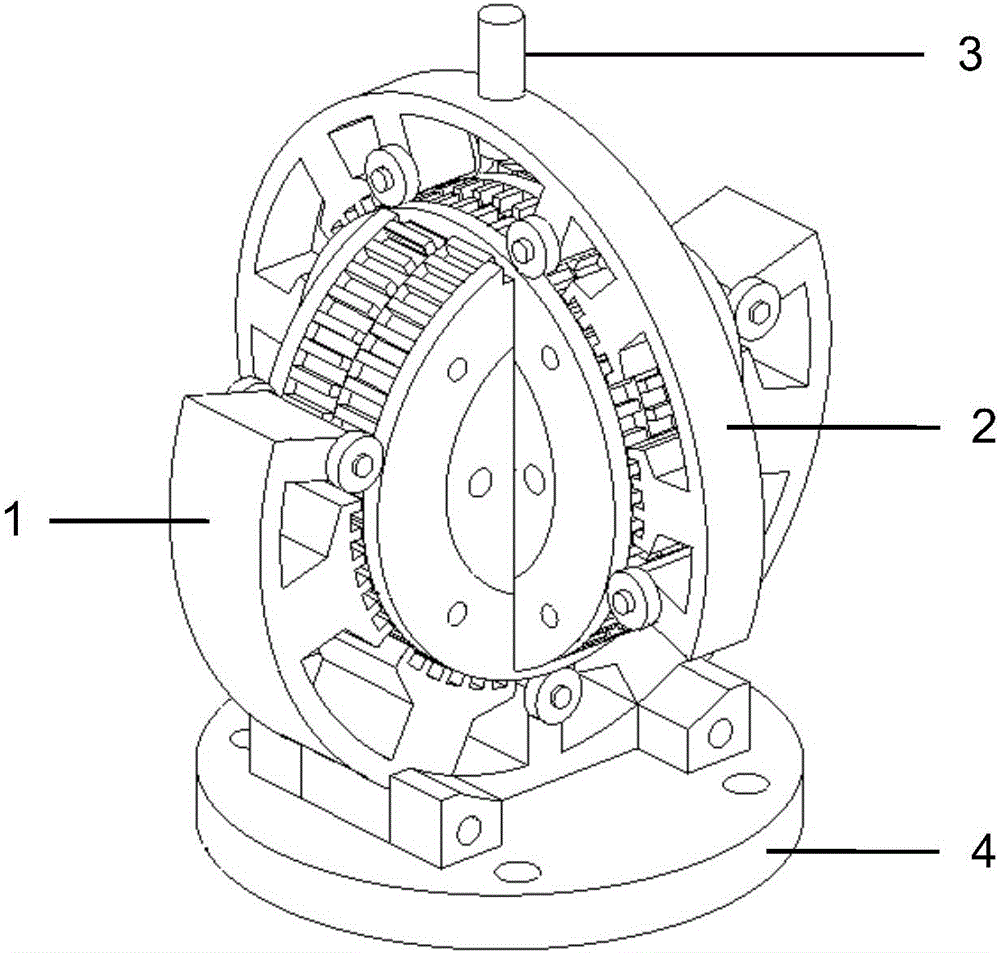
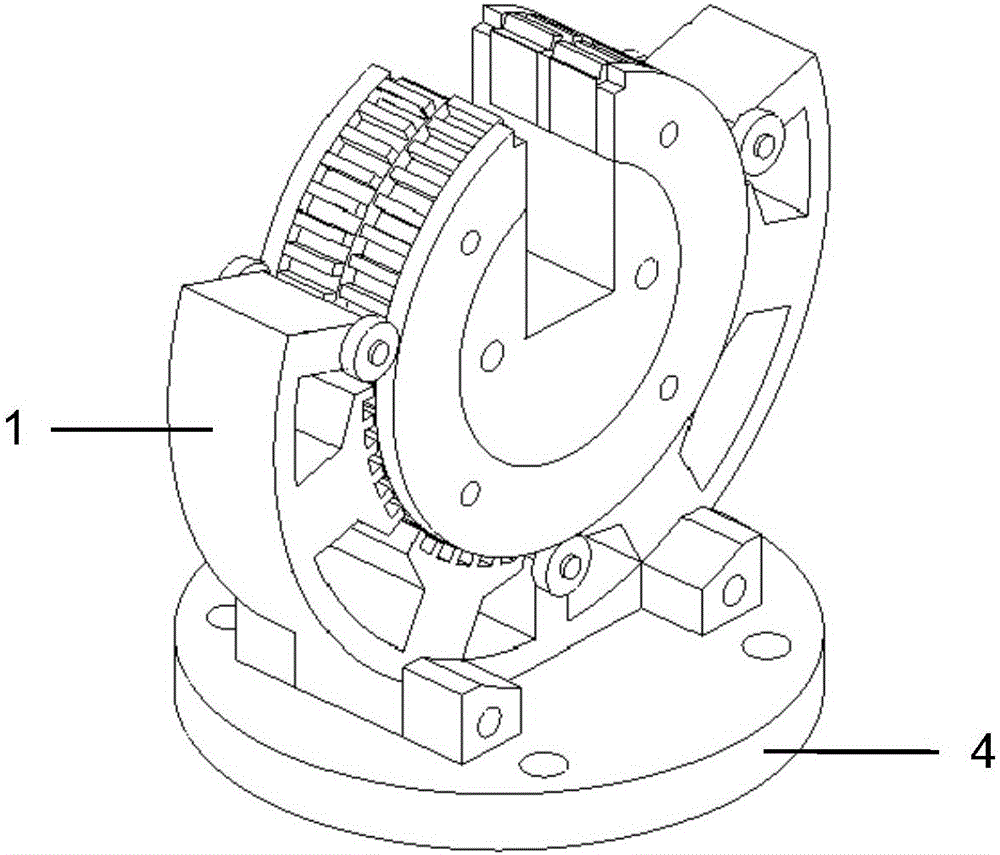
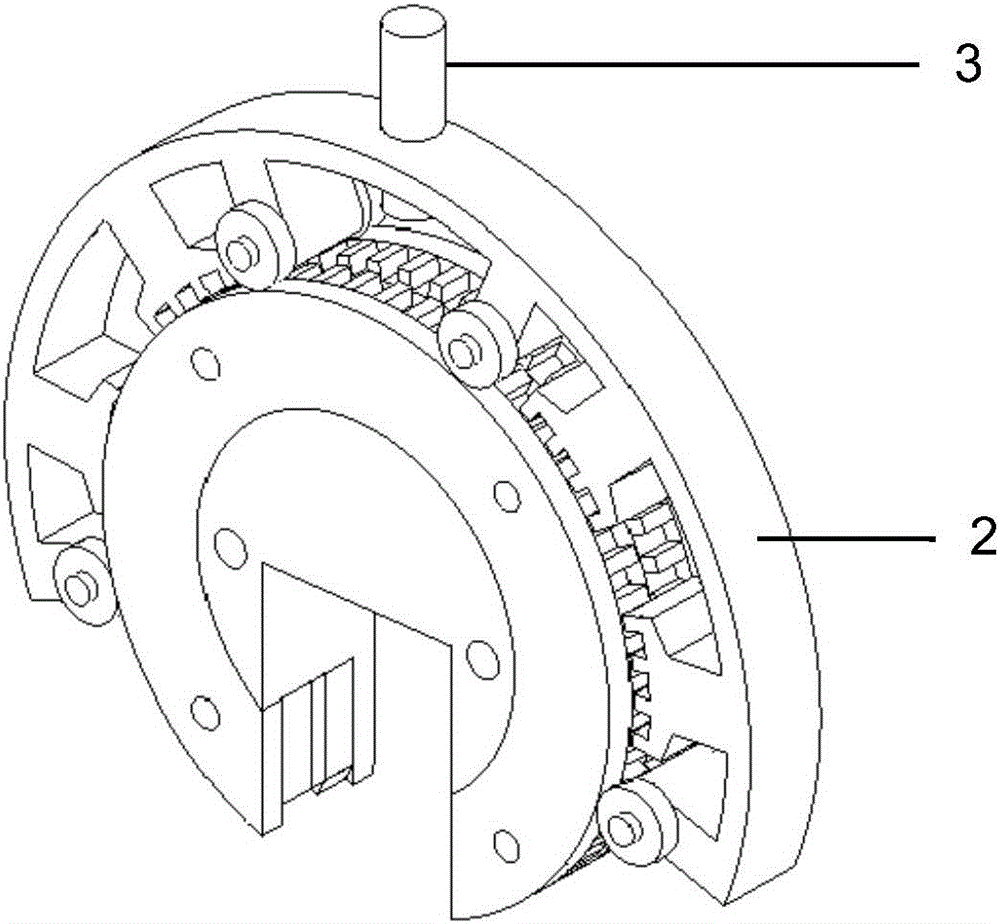
InactiveCN106451994AHighly integratedHigh material utilizationMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing technologyTwo degrees of freedom
The invention discloses a two-freedom-degree hybrid stepping motor for bionic eyeballs of a robot. The stepping motor comprises a first freedom degree motor, a second freedom degree motor and output shafts, wherein the first freedom degree motor is of a circular structure with a notch, the second freedom degree motor is of a circular structure with an opening, the notch is matched with the opening, and the planes of the two motors are perpendicularly orthogonal; the first freedom degree motor and the second freedom degree motor both comprise stators and rotors, the stators and the rotors can relatively move in the planes of the motors, and the two-freedom-degree movement of the output shaft of one freedom degree motor can be achieved through respective independent movement of the two freedom degree motors. The two-freedom-degree hybrid stepping motor has the advantages of being simple in structure and manufacture technology, convenient in analysis design, high in mechanical integration level, high in open-loop operation location accuracy, easy in performance experiment test and favorable for shortening the development period of products and improving the performance and the competitiveness of the products.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Bidirectional switch circuit and power converter having the same
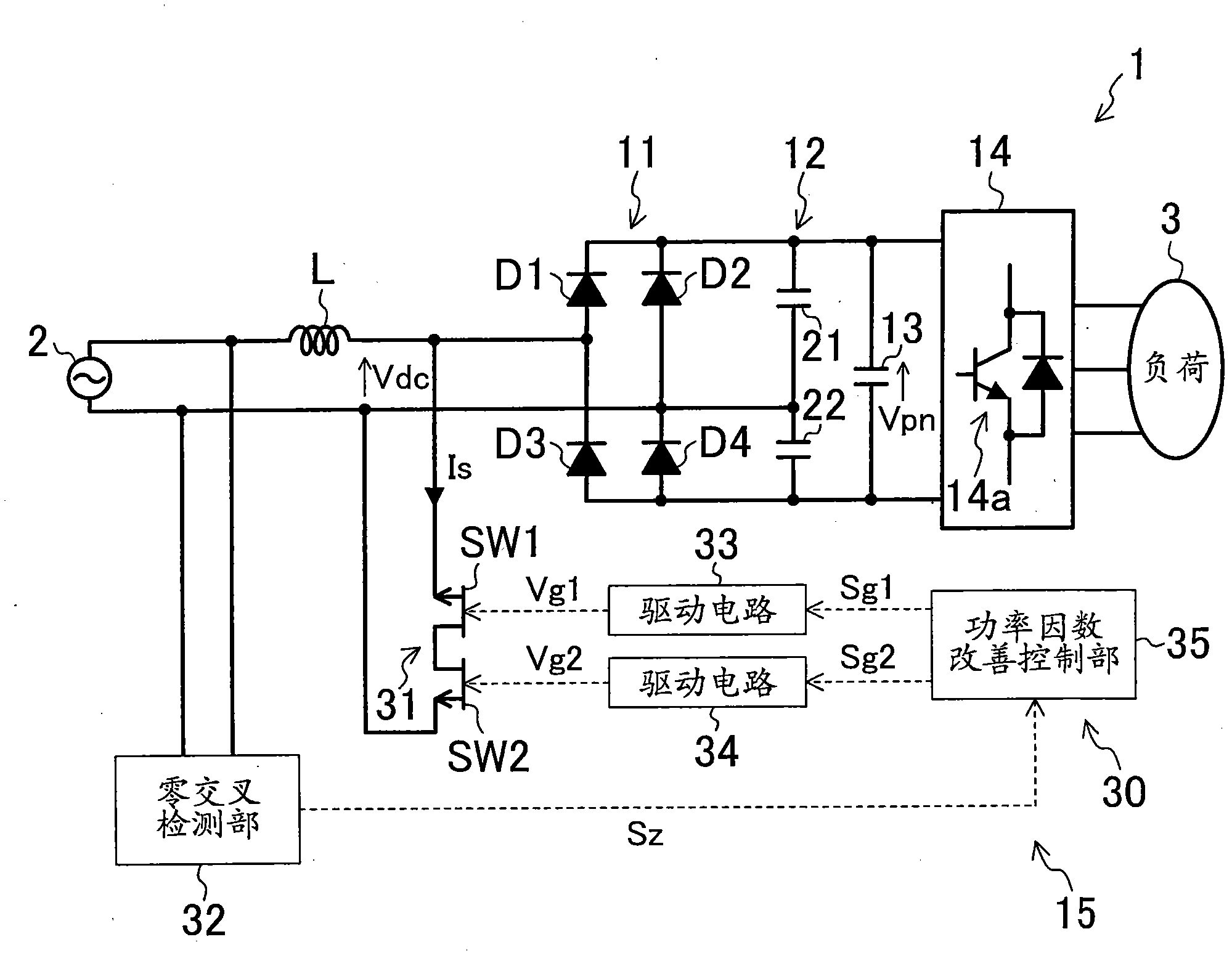
ActiveCN101999204AReduce the number of componentsPrevent delay and loss from increasingEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringVoltage
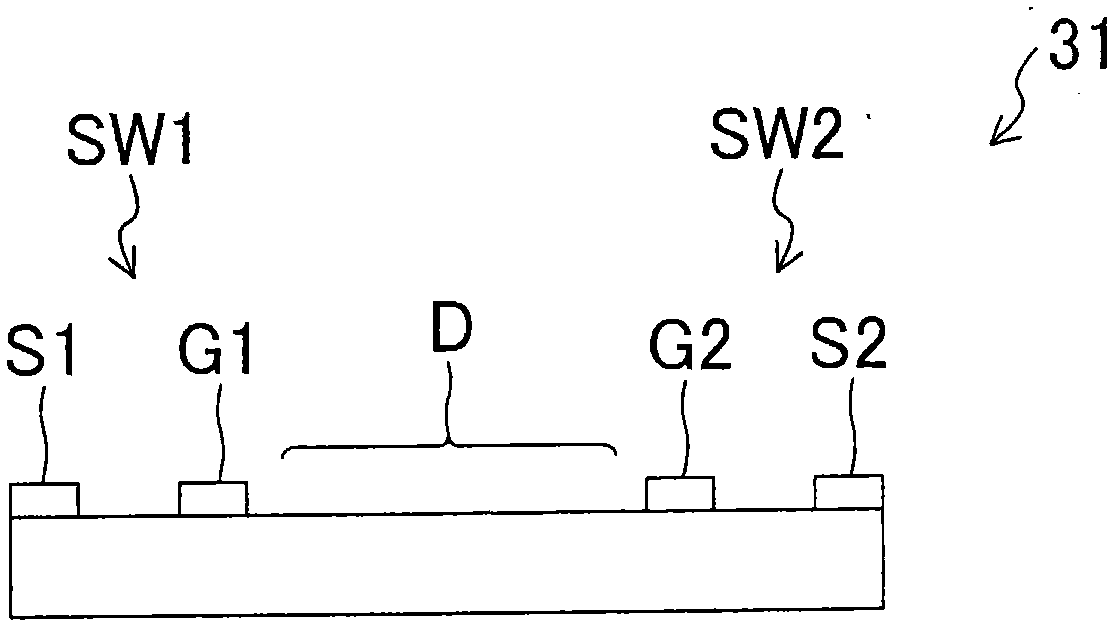
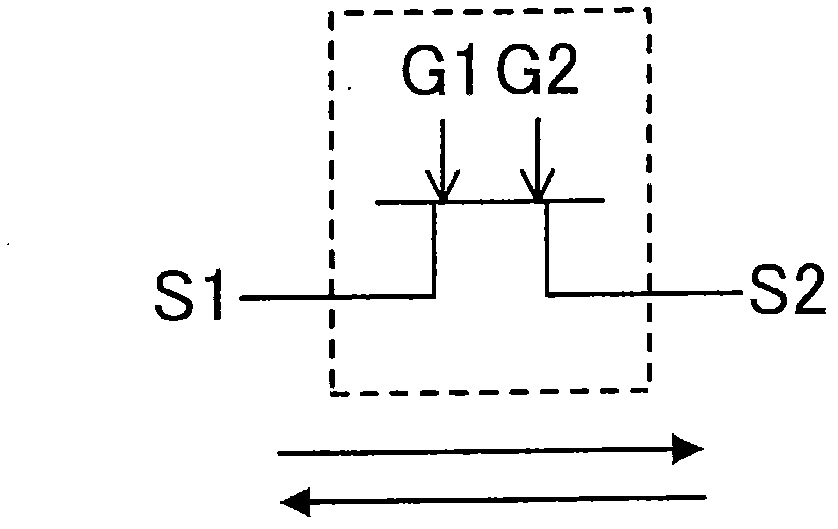
Provided is a bidirectional switch circuit wherein two switching elements are electrically connected in two directions. Out of the two switching elements (SW1, SW2) connected in series, the switching element (SW1) wherein a reverse direction voltage higher on the source (S1) side than that on the drain (D) side is applied, is configured such that a current can be carried from the source (S1) side to the drain (D) side, even in a state where ON drive signals are not inputted to a gate terminal (G1).
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Inkjet printhead, driving method of inkjet printhead, and substrate for inkjet printhead
InactiveUS20050190222A1Simple structureSimple drive controlOther printing apparatusEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
To drive an inkjet printhead having an array of printing elements, where the first and second printing elements which discharge relatively different amounts of ink are arranged on the same array in a predetermined direction, print data for the first or second printing element is serially inputted, the inputted print data is sequentially stored, the stored print data is latched, a selection signal indicative of which of the first or second printing element is to be driven is inputted, a driving signal indicative of a driving period is inputted, and respective printing elements are driven in accordance with the latched print data, the selection signal, and the driving signal. Accordingly, it is possible to reduce the cost of the printhead having plural types of printing elements, which discharge relatively different amounts of ink, and possible to easily control driving of the printhead.
Owner:CANON KK
Gas-driven chest compression apparatus
InactiveUS8657764B2Simple drive controlEasy to controlElectrotherapyIron-lungsEmergency medicineCardiopulmonary resuscitation
A gas-driven chest compression apparatus for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) comprises a flexible pneumatic actuator, capable of axial contraction when fed with a pressurized driving gas, and means for controlling the contraction thereof. Also disclosed are methods of providing chest compressions to a patient by means of a CPR apparatus comprising actuator(s) of this kind, and a corresponding use of the actuator.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
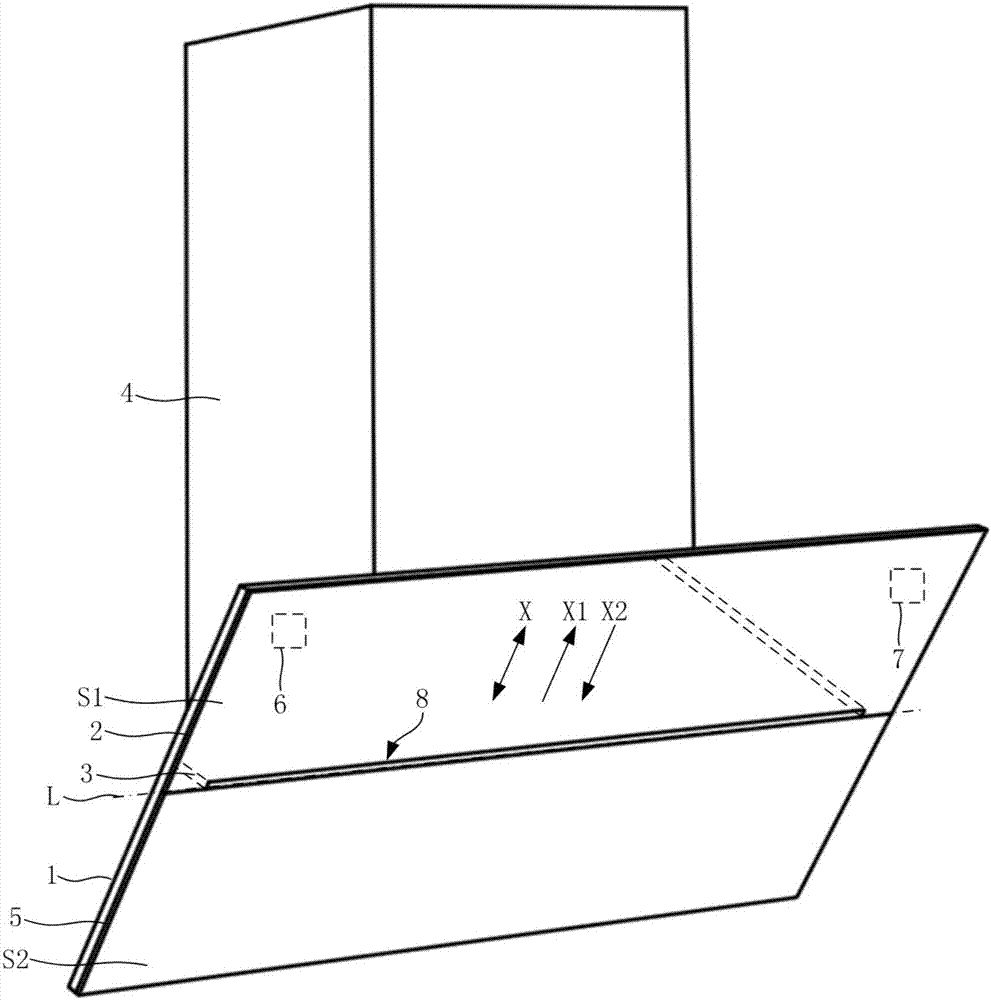
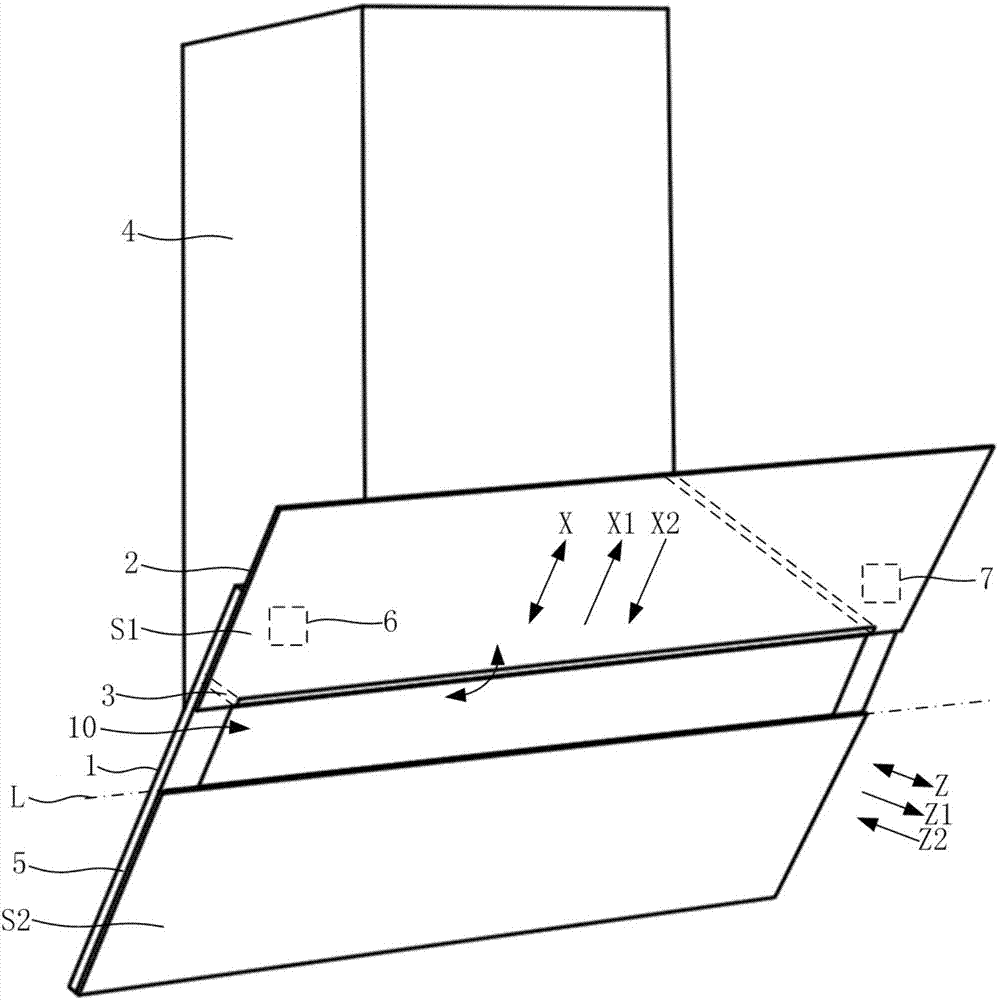
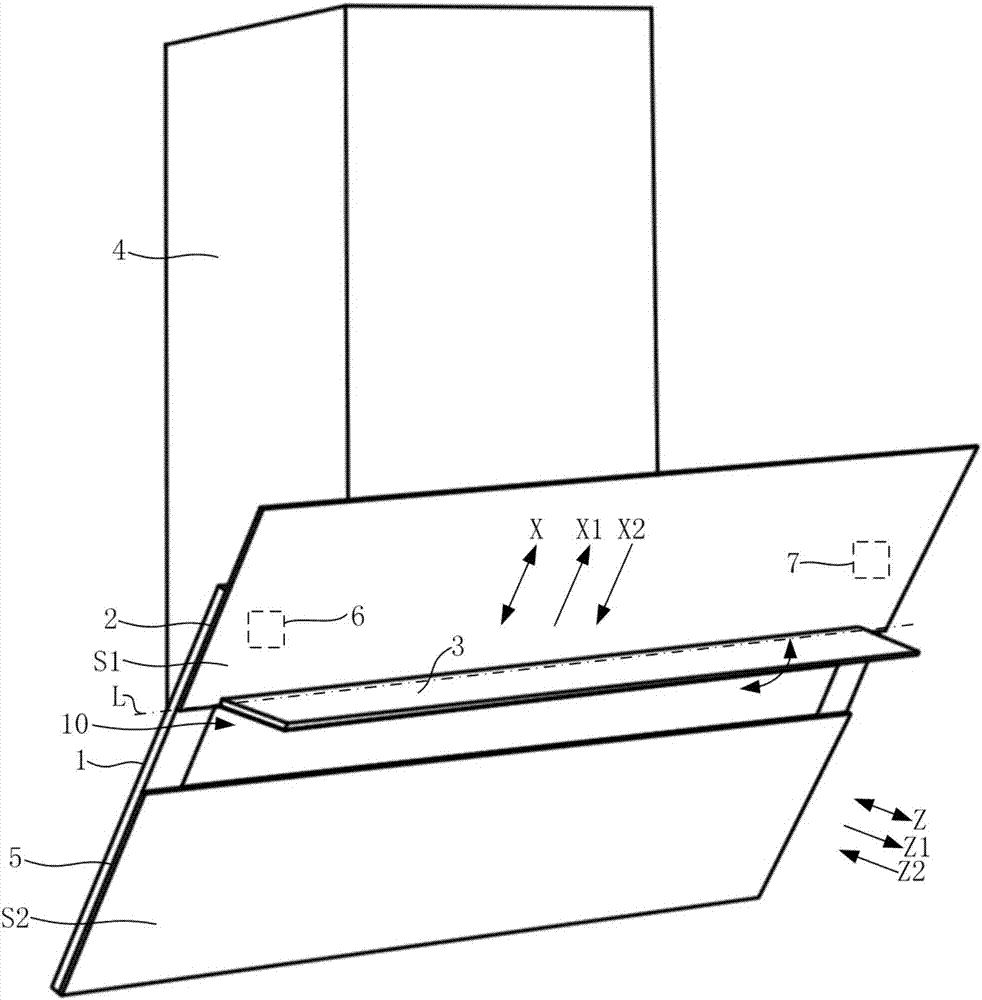
Side sucking type range hood and fume sucking control method thereof
ActiveCN107218632AImprove the smoke effectSimple drive controlDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringFront panel
The invention discloses a side sucking type range hood and a fume sucking control method thereof. The range hood comprises a fume collecting hood (1) and a front panel (2) movably mounted in front of the fume collecting hood (1); the fume collecting hood (1) is provided with a fume inlet (10), and the front panel (2) can move relative to the fume collecting hood (1) to be switched between an opening state and a closing state; the side sucking type range hood also comprises a movably arranged fume guiding plate (3) which can move to be in an extending state when the front panel (2) is in the opening state; and under the extending state, at least part of the fume guiding plate (3) forms a brim part in front of the front panel (2) to guide cooking fume into the fume inlet (10). Under the condition of larger cooking fume quantity, the fume guiding plate (3) is driven to move to be in the extending state to improve the fume collecting effect of the side sucking type range hood, therefore, the fume sucking effect of the side sucking type range hood is enhanced, and the purposes of timely sucking away the cooking fume and fast purifying a kitchen environment are achieved.
Owner:BSH ELECTRICAL APPLIANCES JIANGSU +1
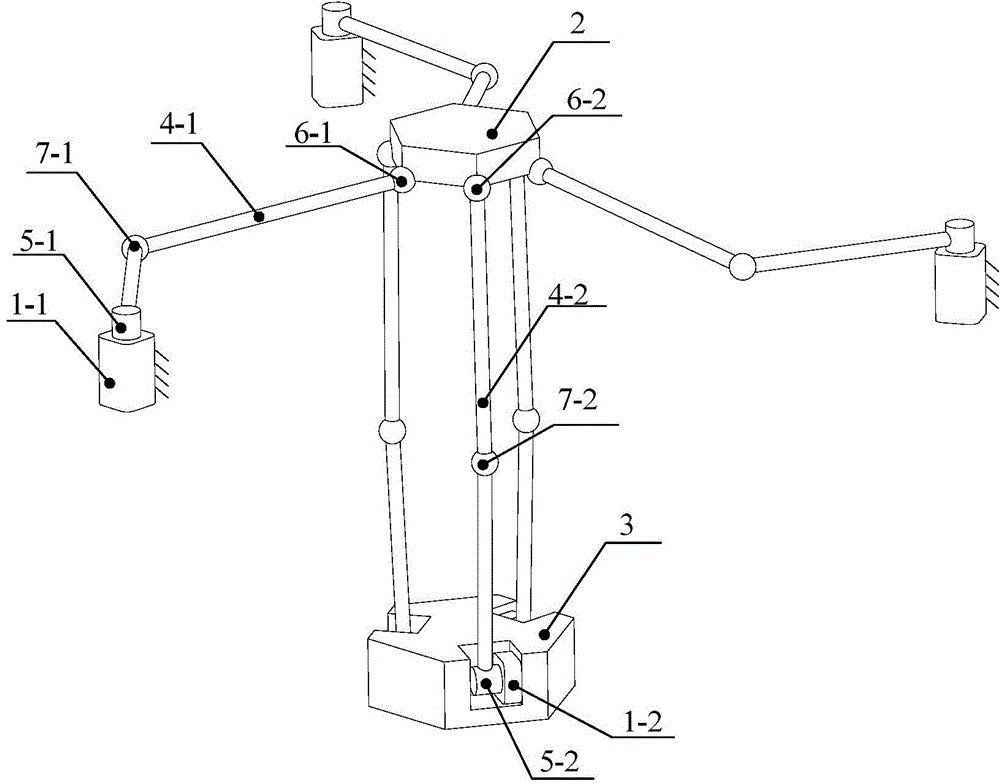
Six-freedom-degree parallel platform in driving orthogonal arrangement
ActiveCN104678885ALarge working spaceSimplify decoupled calculationsNumerical controlElectric machineryDrive motor
The invention discloses a six-freedom-degree parallel platform in driving orthogonal arrangement. The six-freedom-degree parallel platform comprises driving motors, a movable platform, a fixed base and connecting rod branch chains, wherein the driving motors are divided into two groups, each group of driving motors is respectively in center symmetrical distribution in the respective fixed plane, the axial lines of output shafts of the first group of driving motors are mutually parallel but not coplanar, the axial lines of output shafts of the second group of driving motors are positioned in the same plane, the axial lines of the output shafts of the two groups of driving motors are mutually orthogonal, the connecting rod branch chains are divided into two groups, and each group of connecting rod branch chains is respectively connected onto the movable platform in a center symmetrical way, but all of the connecting rod branch chains are not crossed in one point; each group of connecting rod branch chains is connected with the driving motors through rotating pairs, and is connected with the movable platform through a ball hinge or a hooke joint, each connecting rod branch chain consists of multiple sections of connecting rods, all sections of connecting rods are connected through the ball hinges or the hooke joints. The six-freedom-degree parallel platform has the advantages that the carrying capability is high, the decoupling calculation is simple, the work space is large, the system rigidity and the dynamic response features can be improved, a transmission system is simple, the driving control is easy, the manufacturing cost and the maintenance cost are low, and the system pollution is little.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com