Antibacterial peptide separated from cow blood and code sequence and application thereof
An antibacterial peptide and an isolated technology are applied in the field of antibacterial peptides and their coding sequences, which can solve the problems such as research reports on the isolation and identification of antibacterial peptides that have not yet been seen, and achieve safe accumulation of poisoning, no toxic side effects, convenient artificial synthesis, and simple structure. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1: Collection and processing of blood
[0029]After the slaughter of healthy dairy cows, collect their blood in a test tube containing heparin (15IU / ml) by aseptic method, place it in an ice bath, send it to the laboratory within 1 hour, and wash it with 0.9% sterile normal saline immediately red blood cells 3 times, and then lysed red blood cells with 0.83% ammonium chloride solution (volume ratio 3:1). After centrifuging at 700×g at 4° C. for 15 minutes to remove white blood cells, the solution containing the heme polypeptide was lyophilized and dissolved in 0.01% acetic acid.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2: the purification of antibacterial peptide
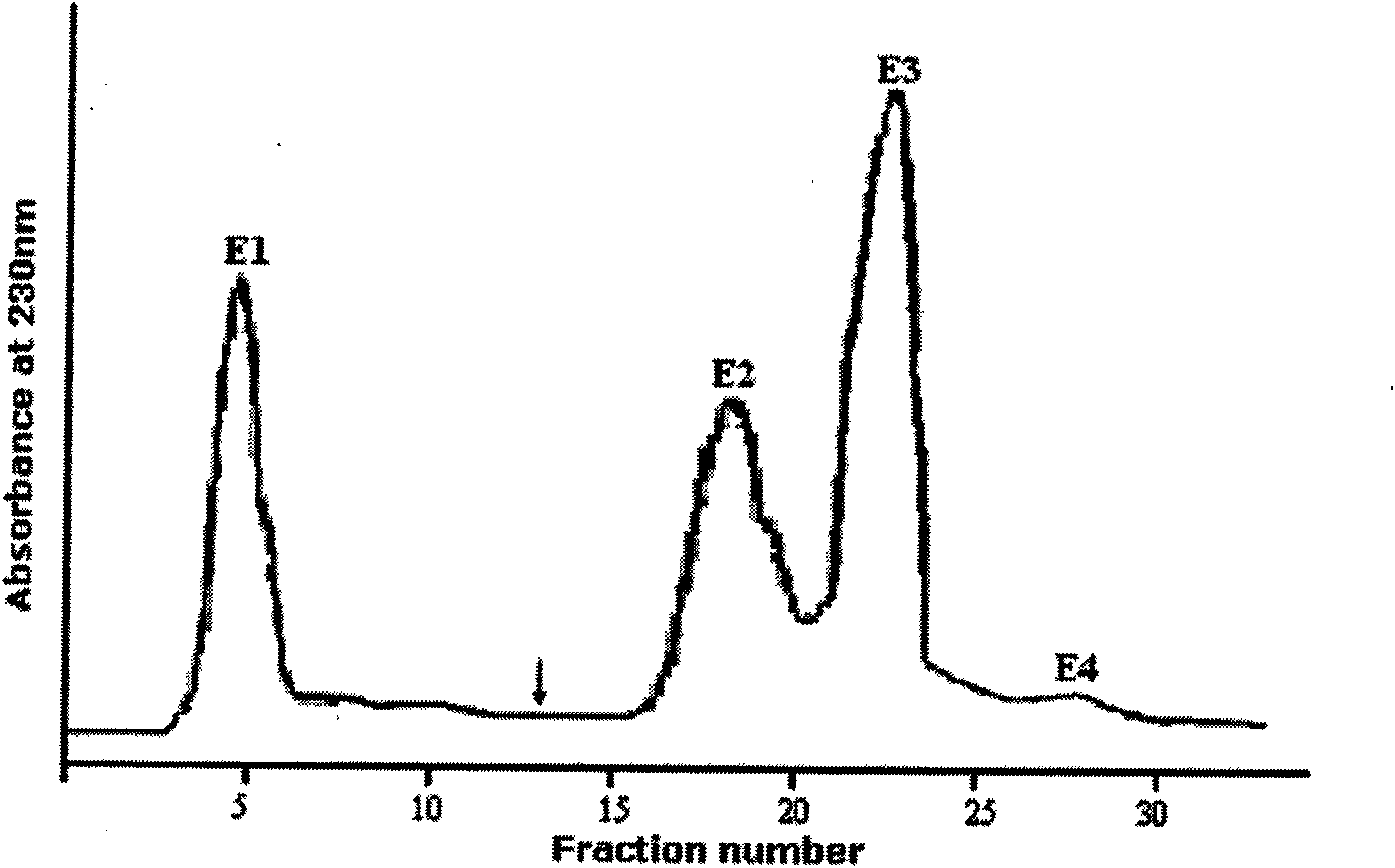
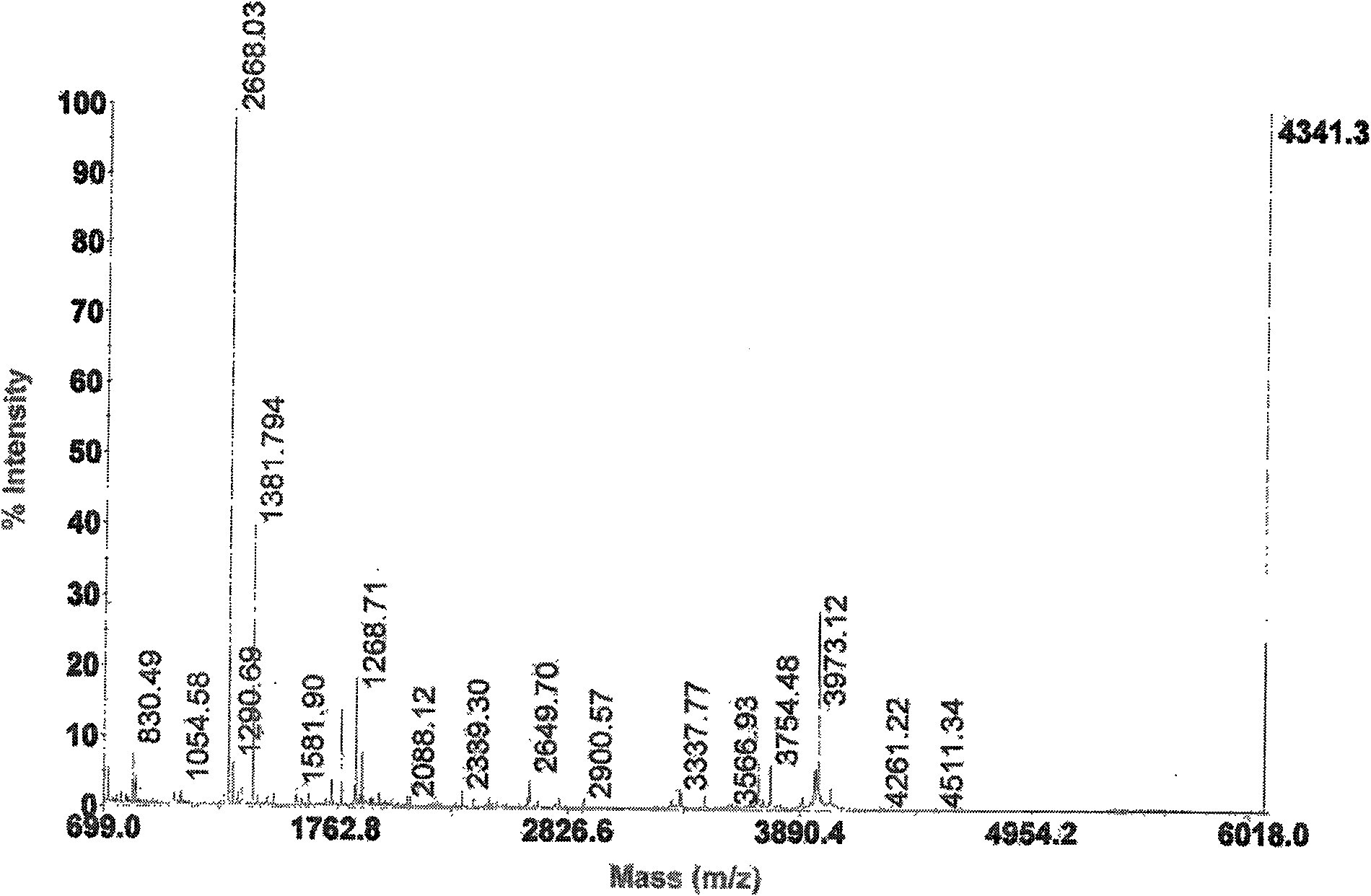
[0031] The antimicrobial peptides in the crude heme solution were separated by ion exchange column chromatography (reversible adsorption of cationic peptides and ion exchange columns immobilized by negative ions). Pass the crude sample through an ion exchange column. The cationic complex is bound to the anionic resin, the non-cationic molecules are washed away by 25mM ammonium acetate, and the cationic molecules are eluted by 10% acetic acid. The collected solution was poured into the column at a rate of 20 mL / h, and its absorbance was monitored at a wavelength of 230 nm with a double-beam UV-Vis spectrophotometer. The eluted peaks were collected (5 mL / peak), lyophilized, and resuspended with 0.01% acetic acid. After separation, there are 4 peaks in total, E1 is an anion peak, E2, E3 and E4 are cation peaks, see figure 1 , through antibacterial activity detection (the method of embodiment 3), find that peak li...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Embodiment 3: detection of antibacterial activity
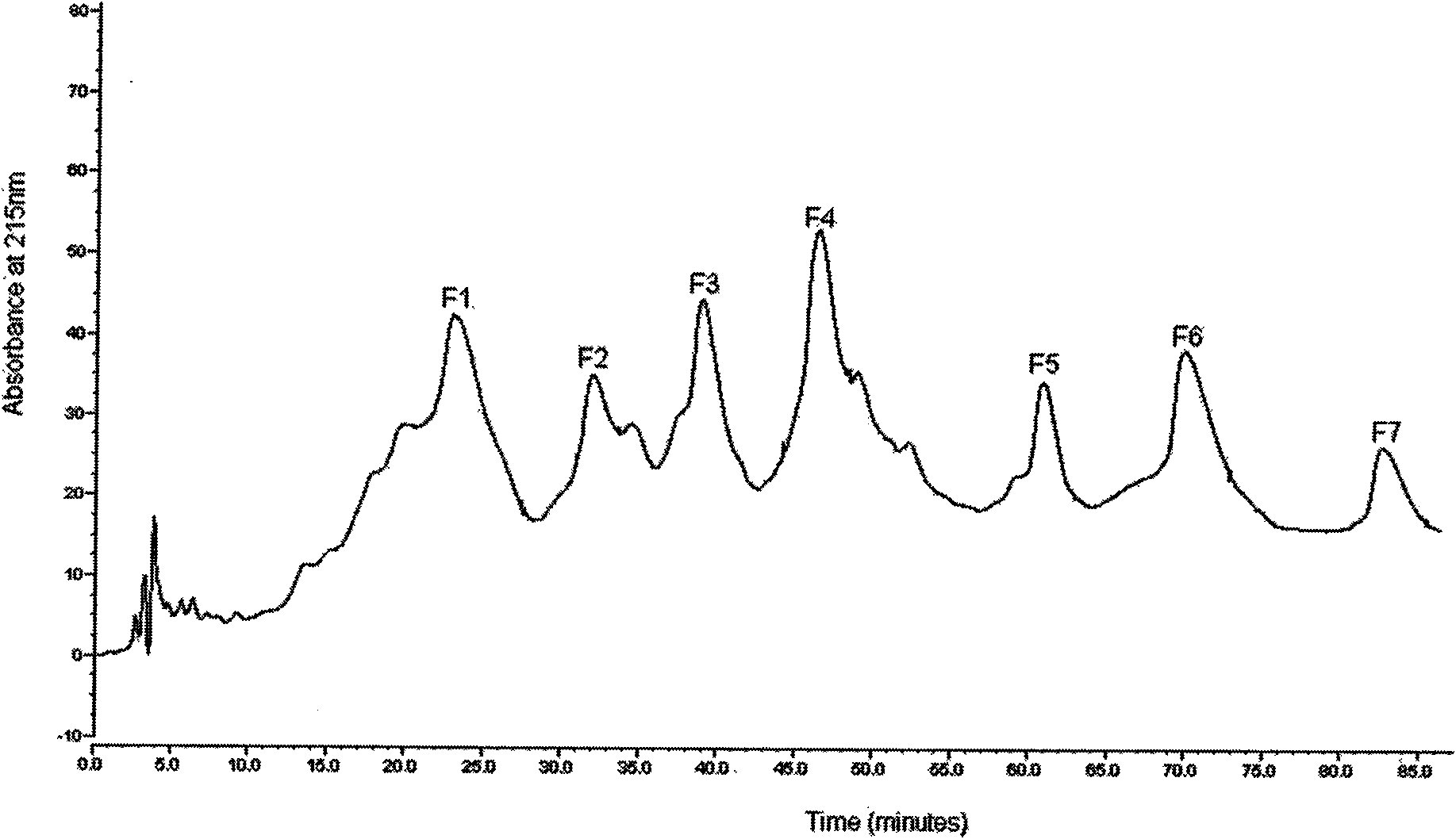
[0034] Antimicrobial activities of peptides separated by ion exchange and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (tested strains were Staphylococcus aureus NCTC 4163, Escherichia coli O111 and Candida albicans 3135A) were determined by plate diffusion method.
[0035] Spread the above-mentioned 3 kinds of tested microorganisms on the sterilized lower layer agar medium containing nutrients (10mL trypticase casein soybean broth (product of Cole-Parmer Company), 10g ultrapure agar (Sigma A-6013 ), 1L of distilled water, pH 7.4), punch holes with a hole diameter of about 2 mm, heat the alcohol lamp slightly to seal the back, add 5 μL of test samples with a concentration of 0.8 μg / ml to each well with a pipette, and Each plate includes positive and negative controls. Positive controls used common antibiotics: polymyxin B against gram-negative bacteria, nisin (nisin) against gram-positive bacteria, and nystat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com