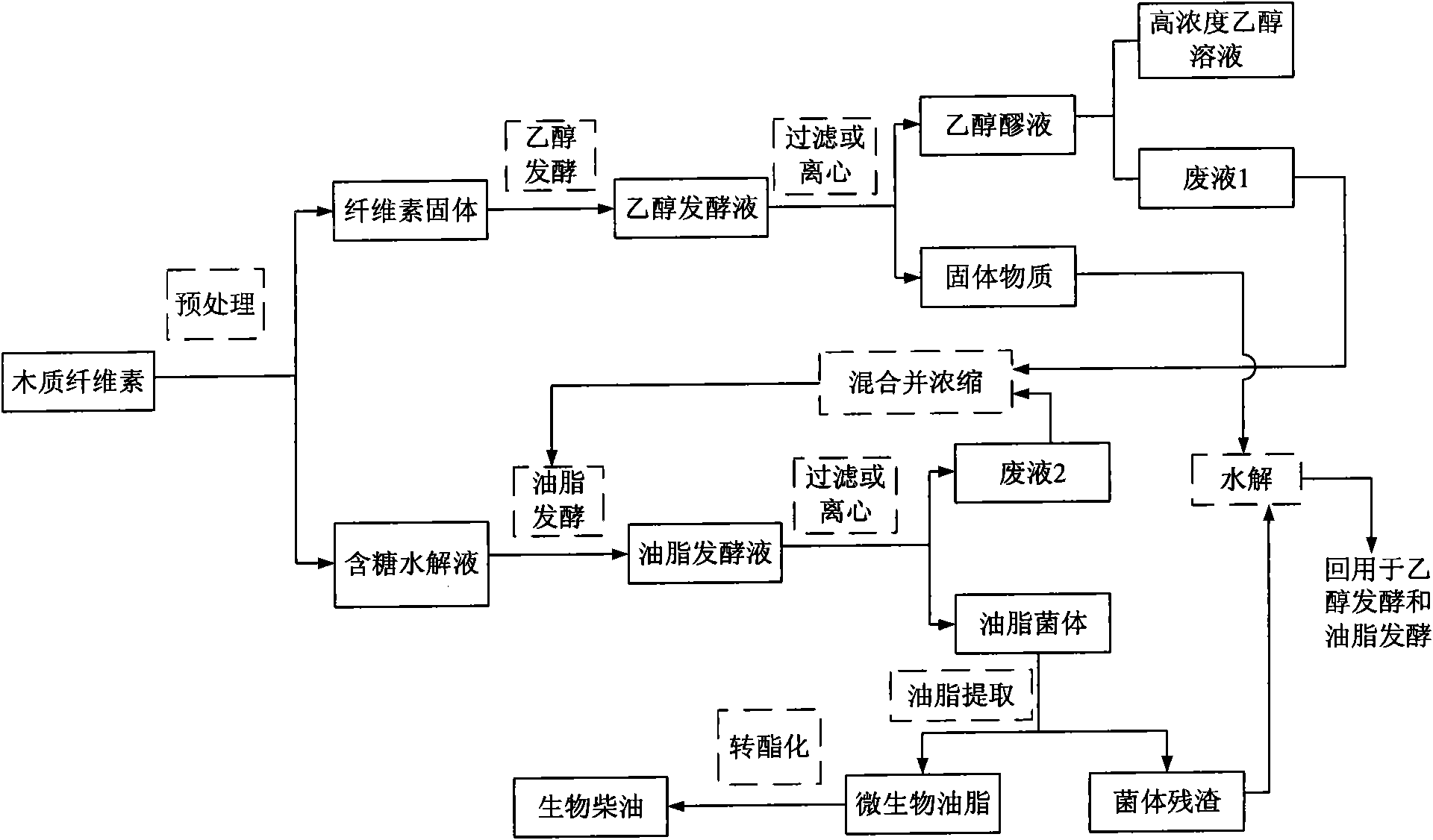
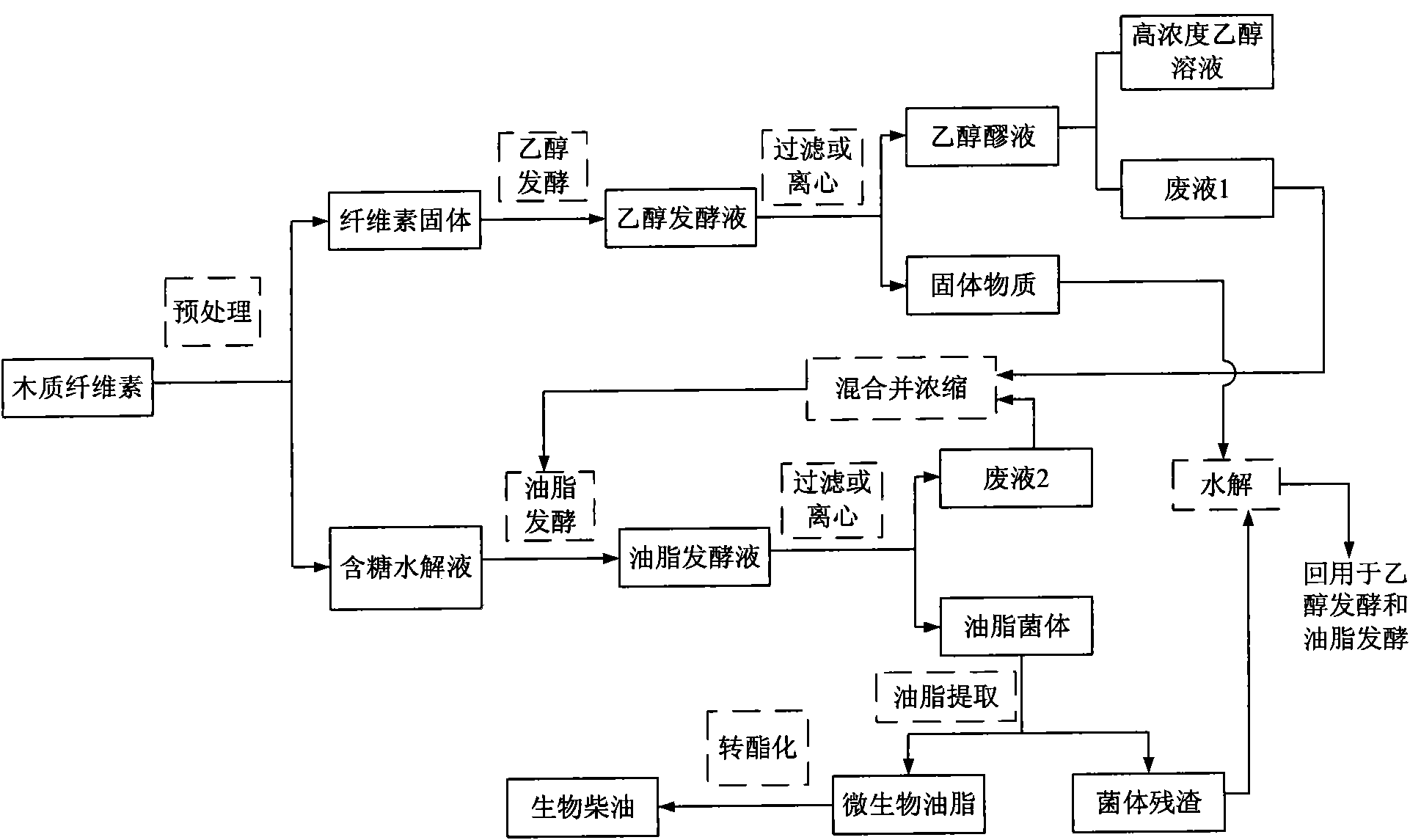
Method for joint production of ethanol and microbial lipid by using methyl cellulose as raw material
A microbial oil and lignocellulose technology, which is applied in the fields of biofuel, fuel, petroleum industry, etc., can solve the problems of difficult management, slow growth of woody oil plants, difficulty in large-scale development and utilization, etc., to reduce waste liquid discharge, The effect of low price and reduced cost of nitrogen source
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] The lignocellulosic raw material used is bagasse, and the place of origin is Nanning, Guangxi. With reference to "Pulp and Paper Analysis and Detection" (Shi Shulan, Pulp and Paper Analysis and Detection, Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2003.), the bagasse components are analyzed by relevant measurement methods, and the analysis results are: in this bagasse, The ash content is 1.38%, the hot water extract is 5.16%, the 1% NaOH extract is 34.20%, the benzene-alcohol extract is 3.17%, the cellulose content is 44.98%, and the cellulose content is 76.76%. The acid-insoluble lignin content is 18.45%, and the acid-soluble lignin content is 1.80%.
[0036] Bagasse and 1% sulfuric acid solution were mixed at a liquid-to-solid ratio of 10:1 and pretreated at 160°C for 0.5h. The pretreated cellulose solids were analyzed, and the contents of glucan, xylan and total lignin were 56.0%, 2.37% and 40.6%, respectively. The solid was added with 2g / L ammonium sulfate, 5g / L potassi...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The bagasse used is the same as in Example 1.
[0039] Bagasse and 1% sulfuric acid solution were mixed at a liquid-to-solid ratio of 10:1 and pretreated at 160°C for 0.5h. The liquid phase was collected, filtered briefly and then poured into a foam separation device. Air was introduced from the bottom at a ventilation rate of 10L gas / L liquid / h, and foam generation was observed. After half an hour, the aeration was stopped, and the non-foaming liquid (residual liquid) was collected and evaporated under reduced pressure. After being concentrated 10 times, the pH was adjusted to 2.0 with calcium hydroxide. After the solid matter was removed by filtration, 2% activated carbon based on the liquid weight was used for detoxification treatment at 80° C. for 30 minutes, and then filtered to obtain a clear liquid. After adjusting the pH to 6.0 with calcium hydroxide, filter again to obtain a sugar-containing hydrolyzate. Measured by high performance liquid chromatography wher...
Embodiment 3
[0041] After the waste liquid 1 in the embodiment 1 and the waste liquid 2 in the embodiment 2 were mixed, they were evaporated under reduced pressure, so that the xylose concentration therein reached 50 g / L. Ammonium sulfate, yeast powder, potassium dihydrogen phosphate and magnesium sulfate were added to concentrations of 0.1 g / L, 0.75 g / L, 0.4 g / L and 1.5 g / L, respectively. After stirring evenly, sterilize at 115°C for 15 minutes. Then oleaginous yeast (Rhodosporidium toruloides, Rhodosporidium toruloides AS 2.1389) was inoculated according to the inoculum amount of 10%, and cultured at 30° C. for 168 hours. The concentration of residual sugar in the fermentation broth was determined to be: xylose 10.1g / L, arabinose 5.25g / L, and the biomass of bacteria was 14.5g / L. The fermentation broth was centrifuged to obtain the bacteria, and the oil was extracted by the acid-heat method. The oil content in the bacteria was analyzed to be 51.2%, and the oil yield was 18.6g oil / 100g co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com